A relative flux sensor and a method of determining a ratio between maximum light intensities, a control device, a color tunable lamp, a luminaire and a computer program product
A luminous flux sensor and luminous flux technology, applied in lighting devices, electroluminescent light sources, light sources, etc., can solve problems such as expensive methods and systems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
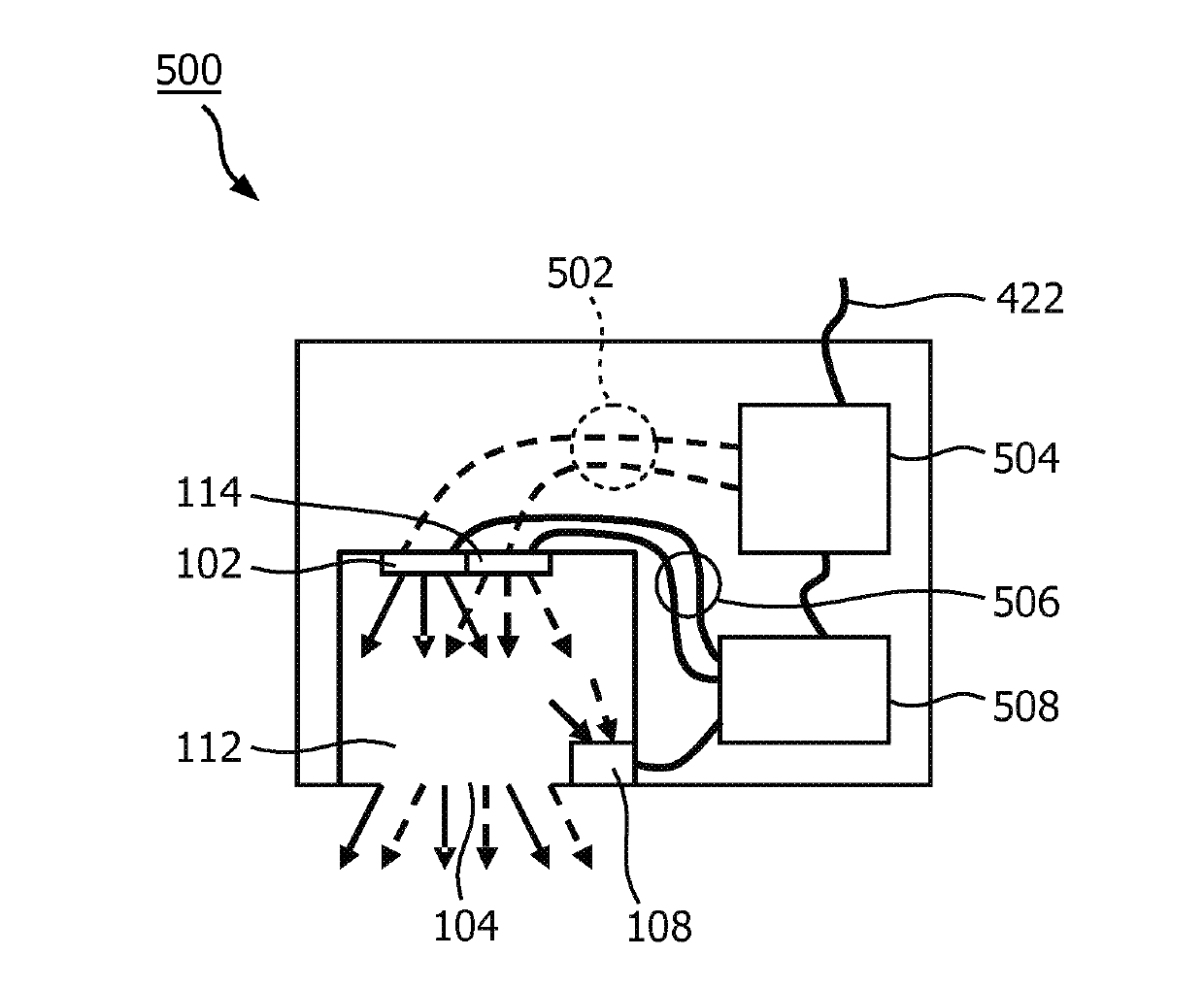
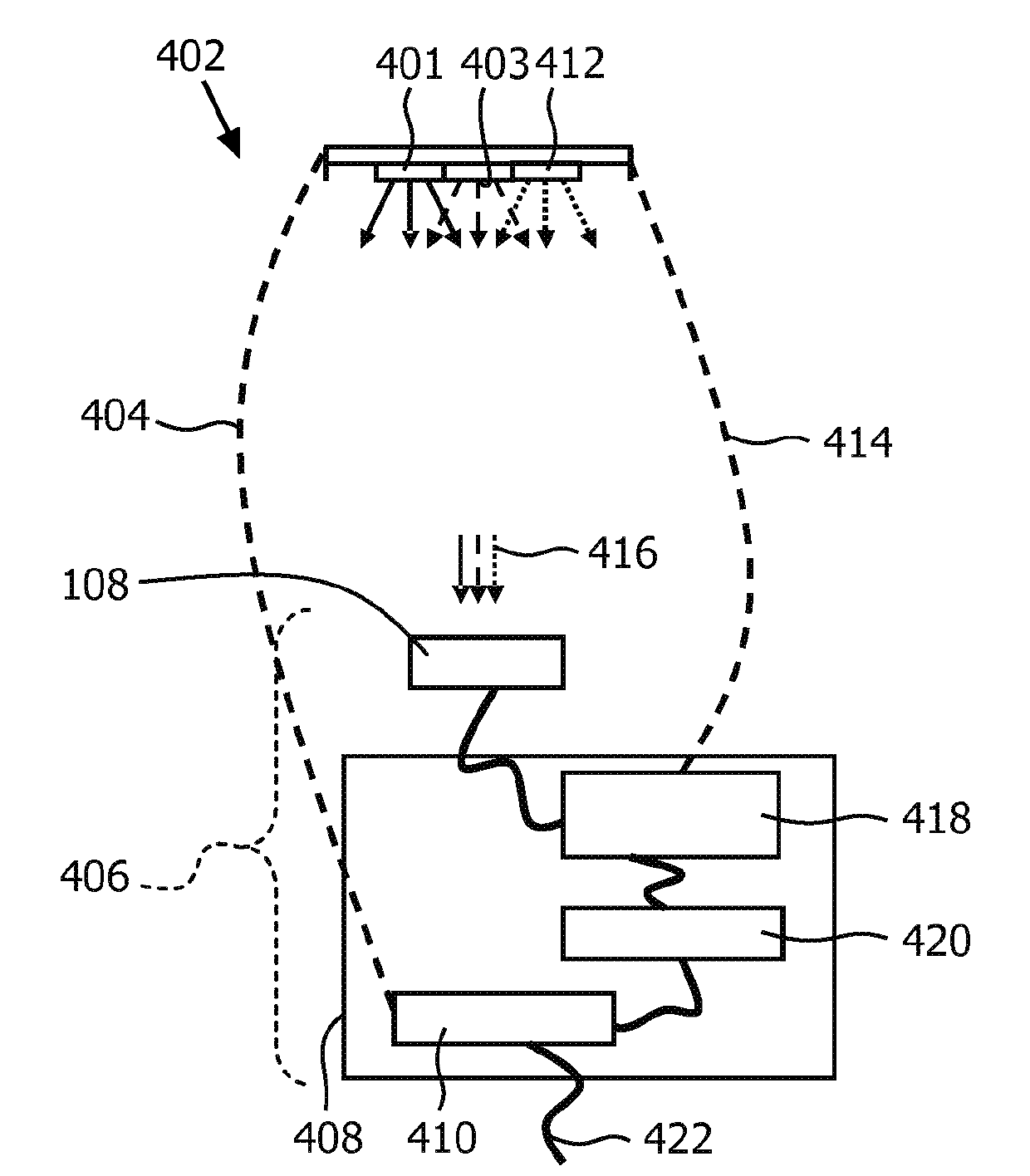
[0071] The first embodiment is shown in figure 1 . A light source 101 is shown comprising a first light emitting diode (LED) 102 and a second LED 114 . The first LED 102 emits light of a first color into the light mixing cavity 112 of the light source 101 . The second LED 114 emits light of a second color into the light mixing cavity 112 . The second color is different from the first color. The light mixing cavity 112 includes a light exit window 104 . Light that is a mixture of the first color and the second color is emitted through the light exit window 104 into the environment of the light source 101 .
[0072] A relative light flux sensor 122 is also shown. The relative light flux sensor 122 includes a light input 106 through which light can enter the relative light flux sensor 122 to impinge on the color point sensor 108 . Color point sensor 108 is coupled to sensor controller 118 of relative light flux sensor 122 . The sensor controller 118 is coupled to an output...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com