Patents
Literature
137results about "Field acceleration method control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
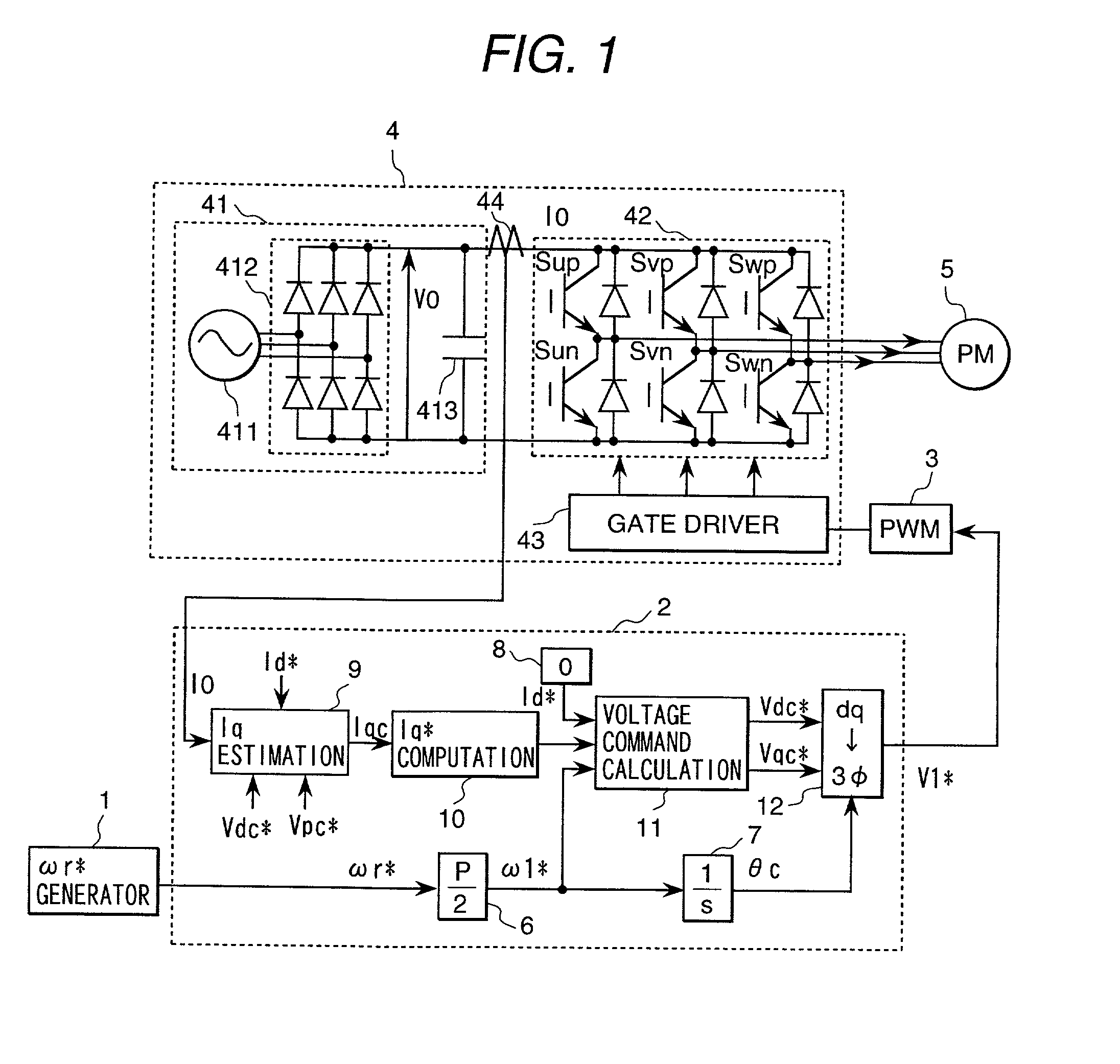
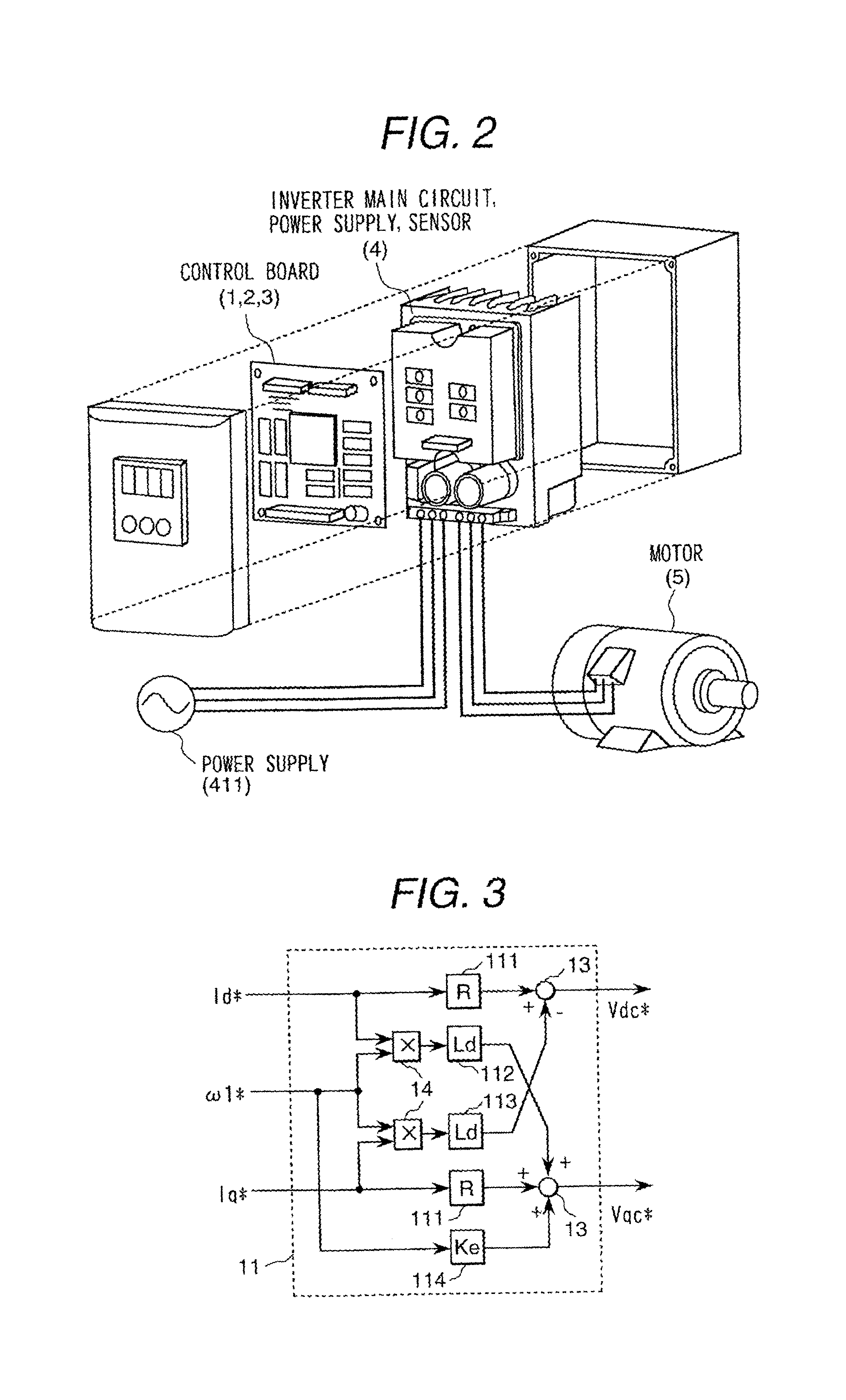
Method and apparatus for motor control
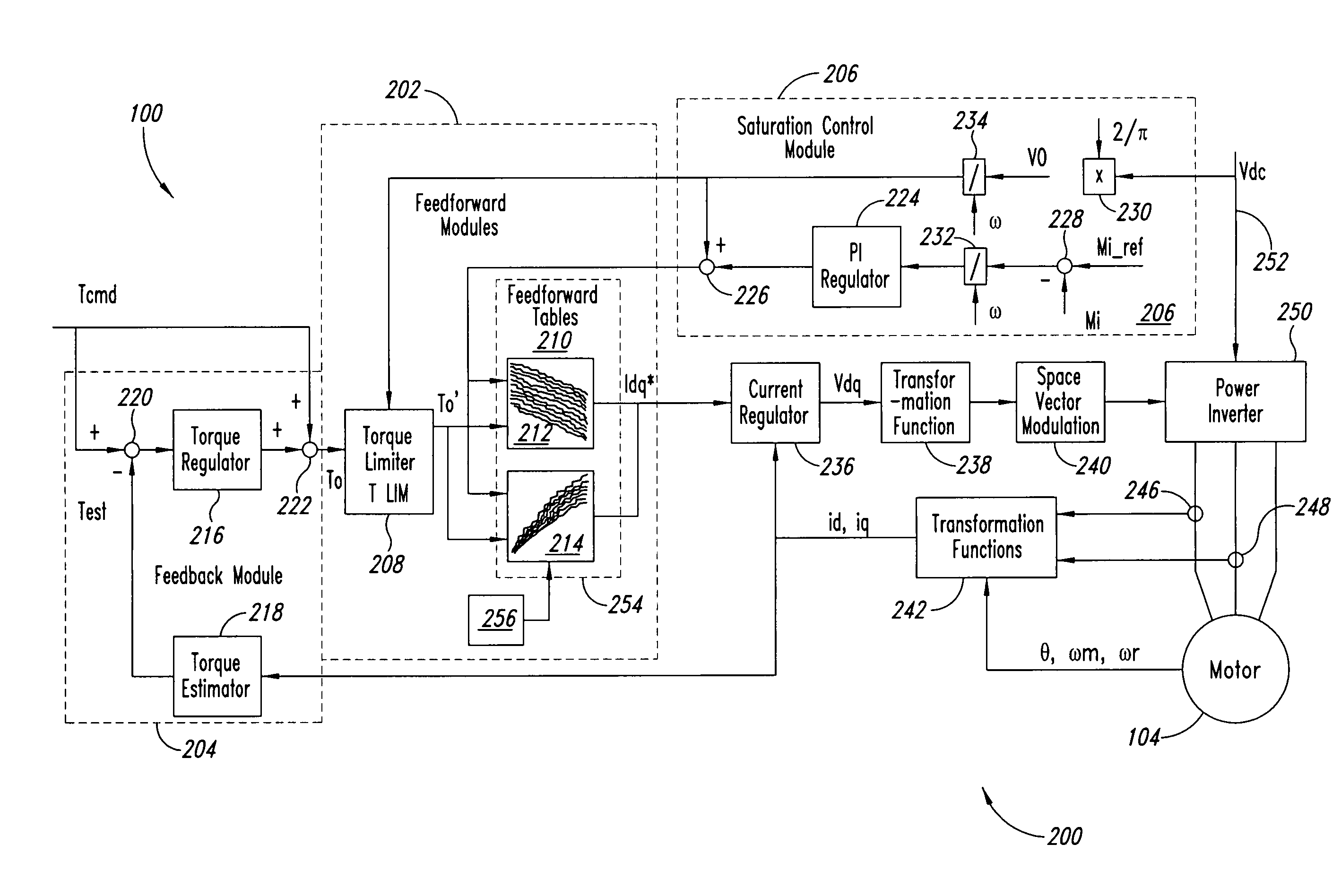
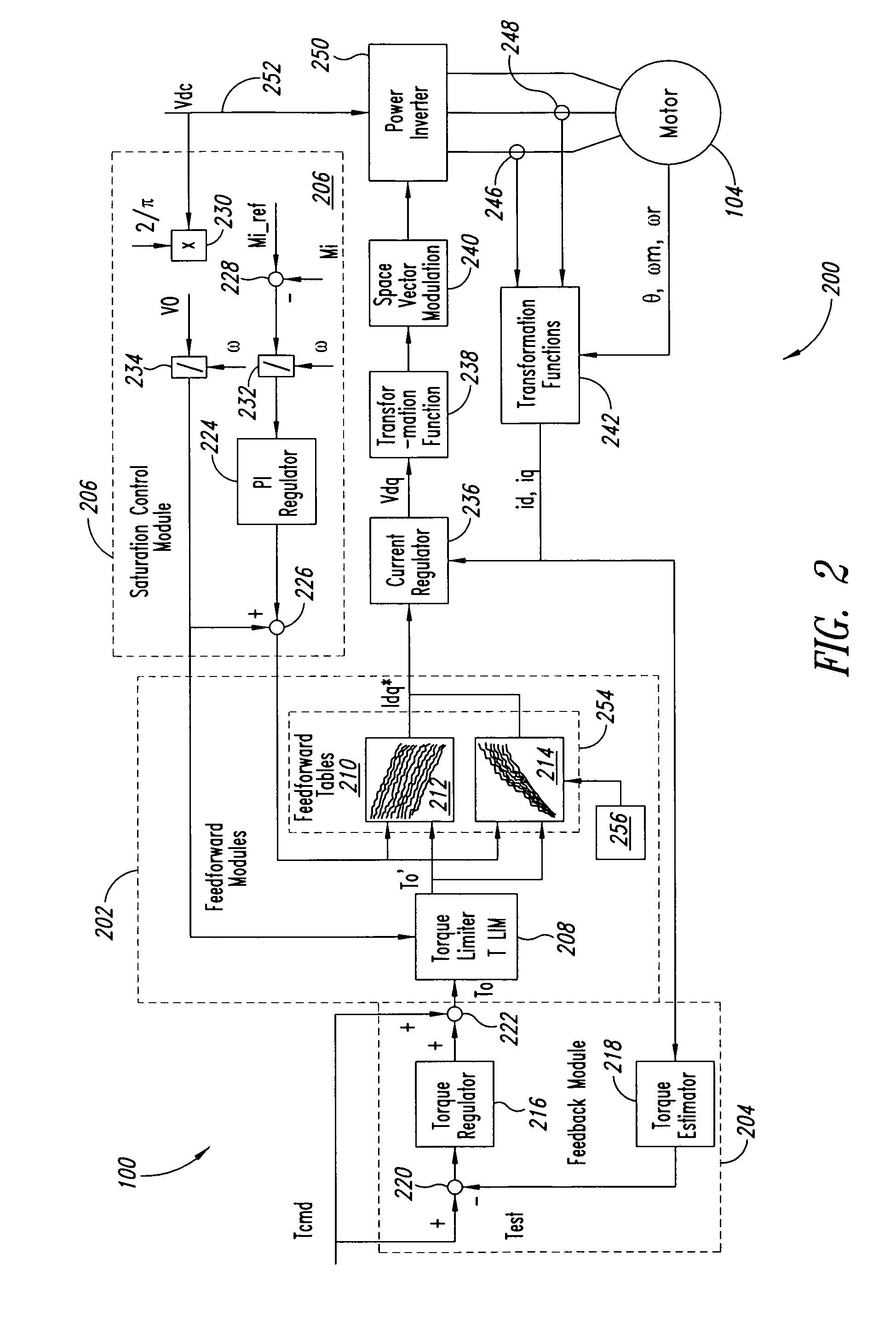
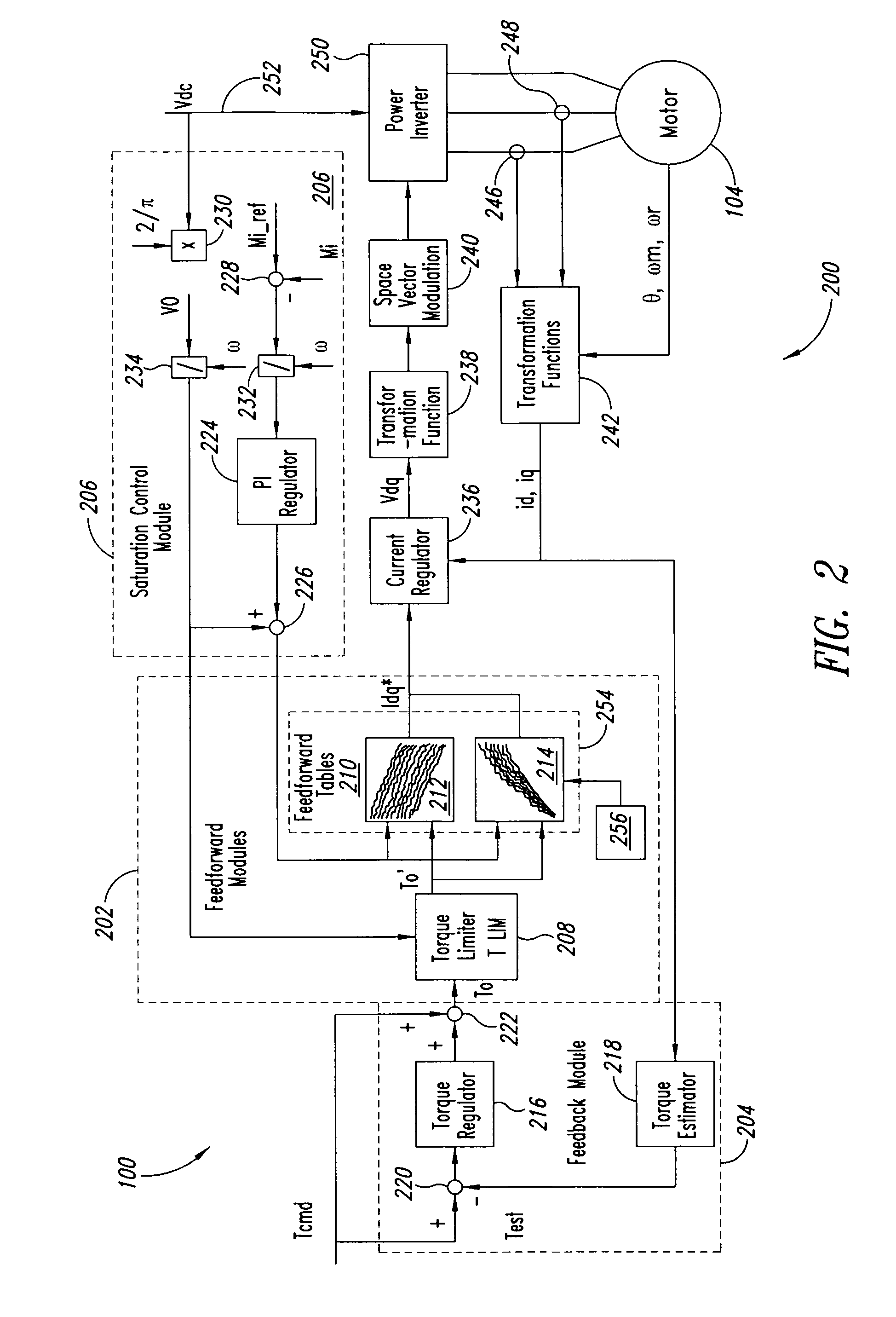
A system and method for controlling a permanent magnet motor are disclosed. Briefly described, one embodiment receives a torque command and a flux command; receives information corresponding to a direct current (DC) bus voltage and a motor speed; computationally determines feedforward direct-axis current information and feedforward quadrature-axis current information from a plurality of parameters associated with the permanent magnet motor; determines a current signal (idq*) based upon at least the requested torque command, the flux command, the DC bus voltage, the motor speed, the feedforward direct-axis current information, and the feedforward quadrature-axis current information; and controls a power inverter that converts DC power into alternating current (AC) power that is supplied to the permanent magnet motor, such that the permanent magnet motor is operated in accordance with the determined idq*.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE SYST INC
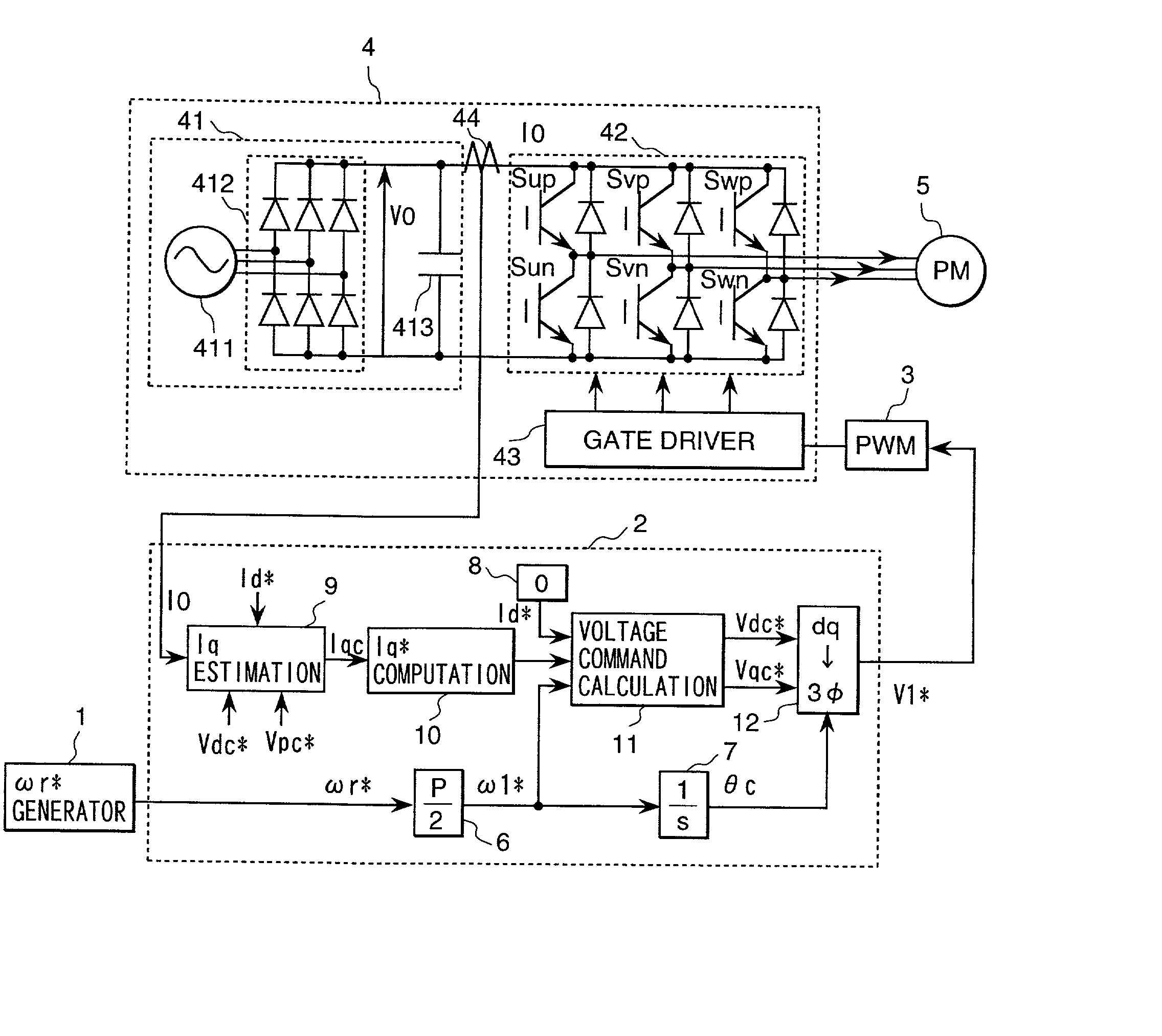
Sensorless control system for synchronous motor
InactiveUS20030030404A1DC motor speed/torque controlSynchronous motors startersSynchronous motorDc current
A synchronous motor drive system in accordance with the present invention detects a DC current of an inverter which drives a synchronous motor, and based on the magnitude of the current, estimates torque current components that flow through the motor, and then based on the estimated value, determines the voltage which is applied to the motor, and finally estimates and computes the magnetic pole axis located inside the motor using the estimated value of the torque current.
Owner:HITACHI JOHNSON CONTROLS AIR CONDITIONING INC
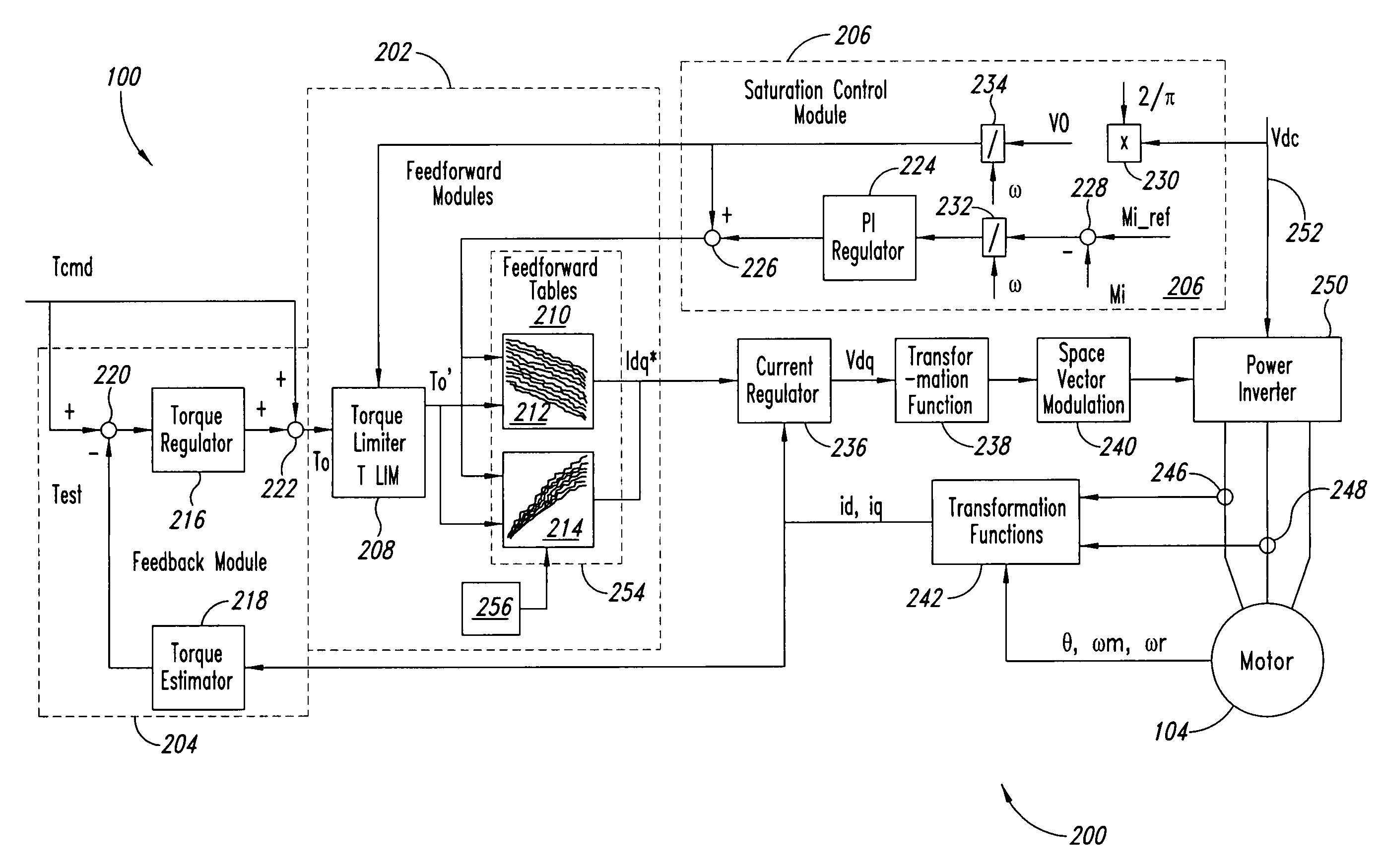
Method and apparatus for motor control
InactiveUS20080116842A1Electronic commutation motor controlSpeed controllerMotor speedPower inverter
A system and method for controlling a permanent magnet motor are disclosed. Briefly described, one embodiment receives a torque command and a flux command; receives information corresponding to a direct current (DC) bus voltage and a motor speed; computationally determines feedforward direct-axis current information and feedforward quadrature-axis current information from a plurality of parameters associated with the permanent magnet motor; determines a current signal (idq*) based upon at least the requested torque command, the flux command, the DC bus voltage, the motor speed, the feedforward direct-axis current information, and the feedforward quadrature-axis current information; and controls a power inverter that converts DC power into alternating current (AC) power that is supplied to the permanent magnet motor, such that the permanent magnet motor is operated in accordance with the determined idq*.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE SYST INC
Sensorless control system for synchronous motor
InactiveUS6690137B2DC motor speed/torque controlSynchronous motors startersSynchronous motorControl system
A synchronous motor drive system in accordance with the present invention detects a DC current of an inverter which drives a synchronous motor, and based on the magnitude of the current, estimates torque current components that flow through the motor, and then based on the estimated value, determines the voltage which is applied to the motor, and finally estimates and computes the magnetic pole axis located inside the motor using the estimated value of the torque current.
Owner:HITACHI JOHNSON CONTROLS AIR CONDITIONING INC
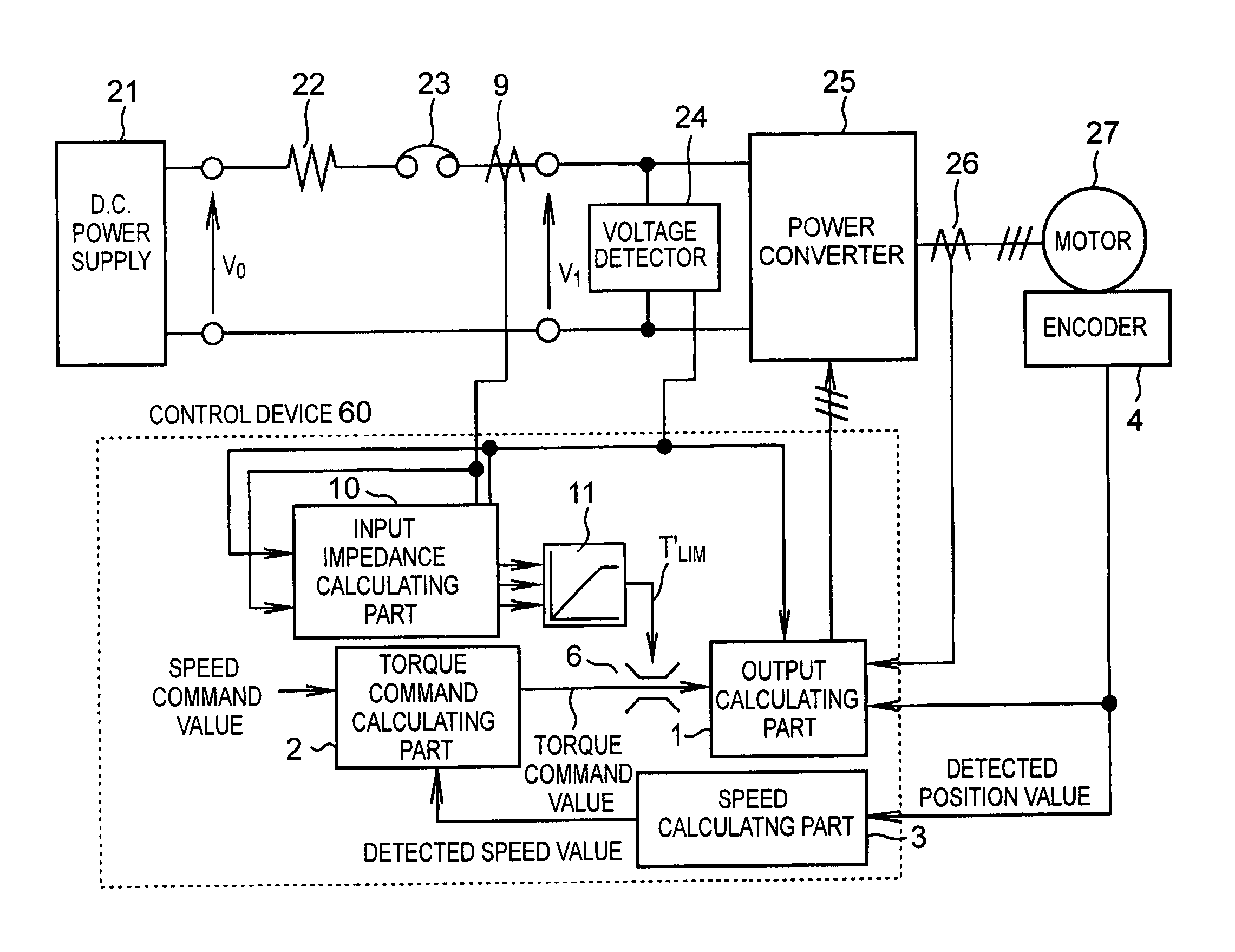
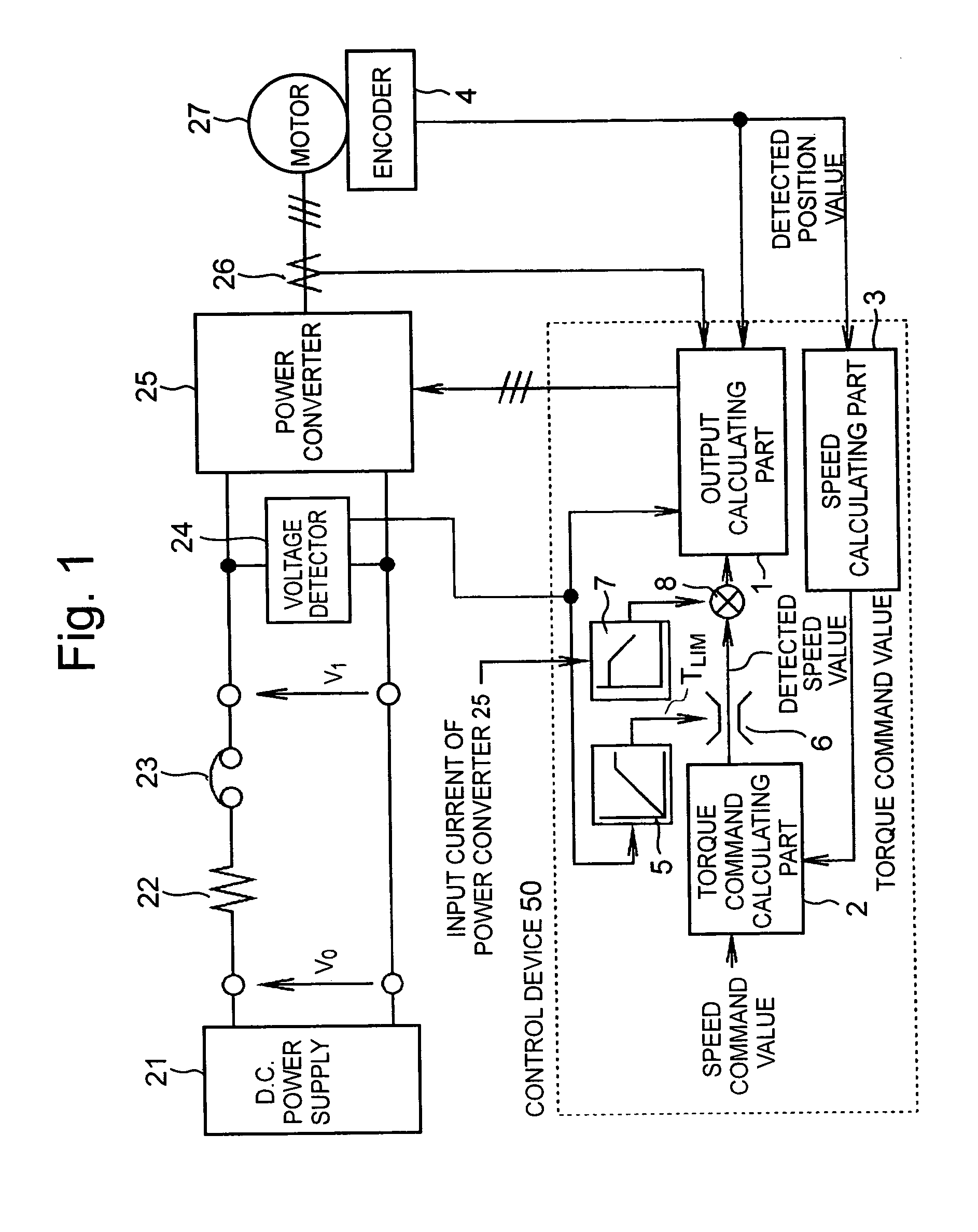
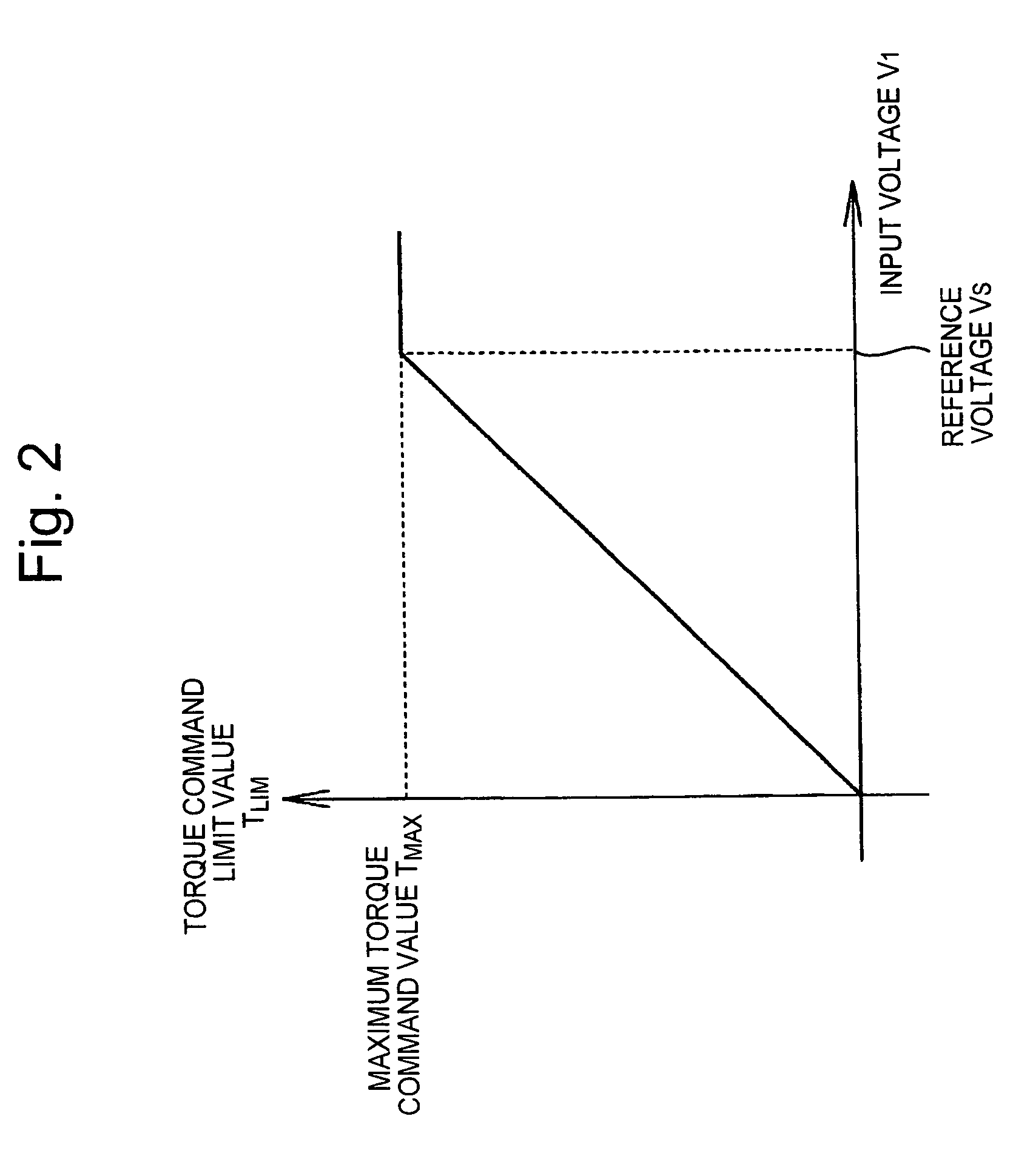
Method and system for controlling motor torque
ActiveUS20050077853A1Single motor speed/torque controlField acceleration method controlControl systemInput impedance
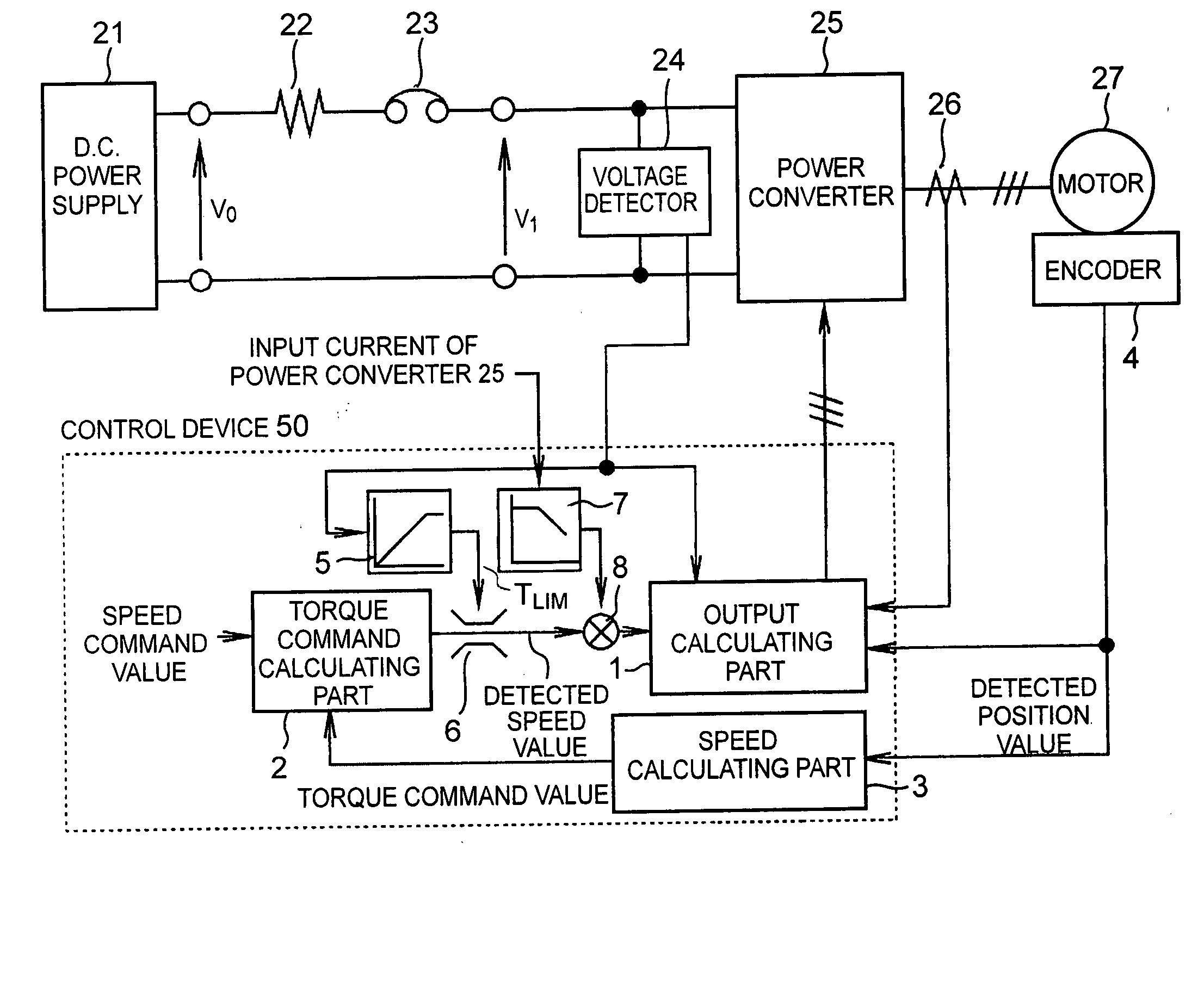
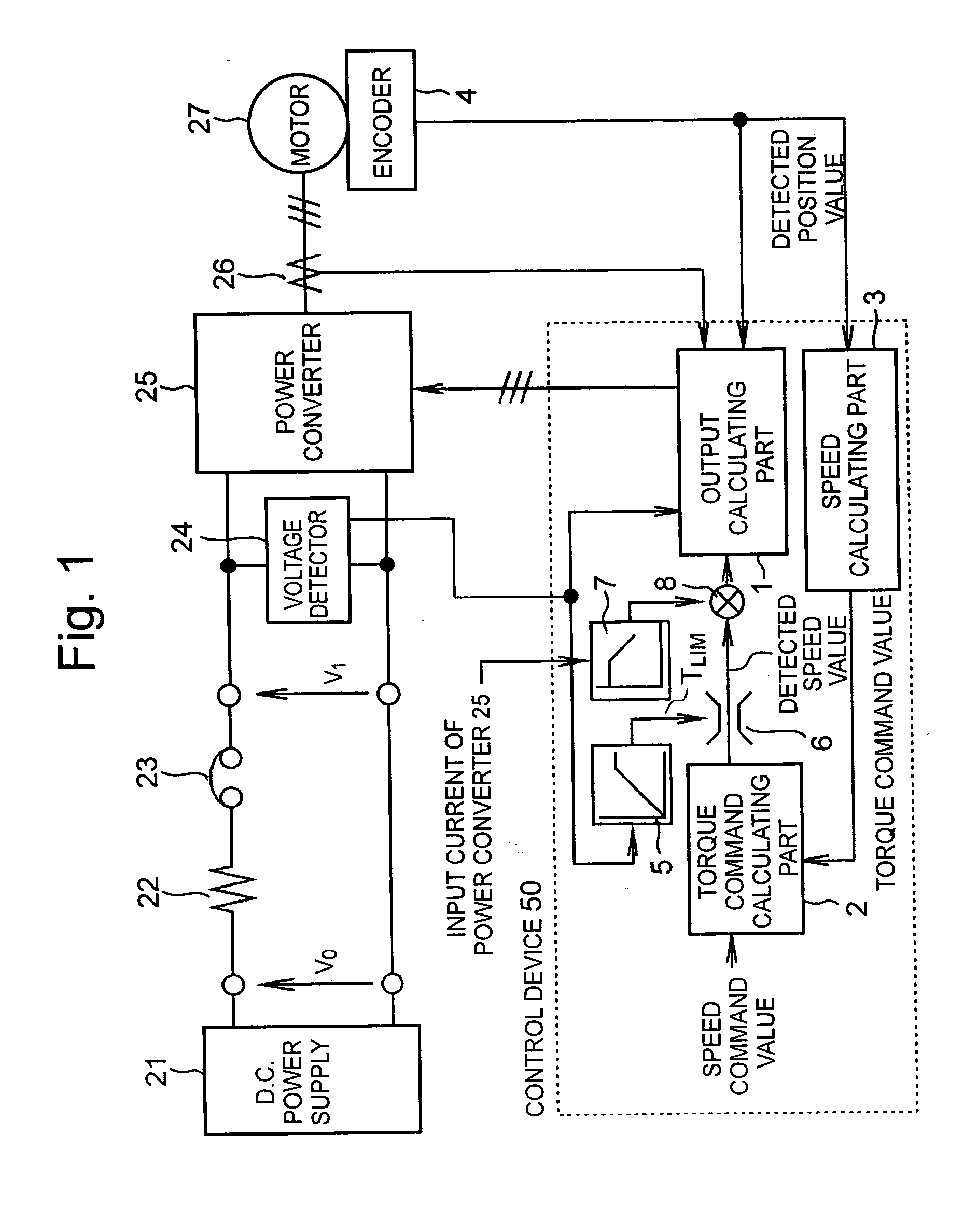
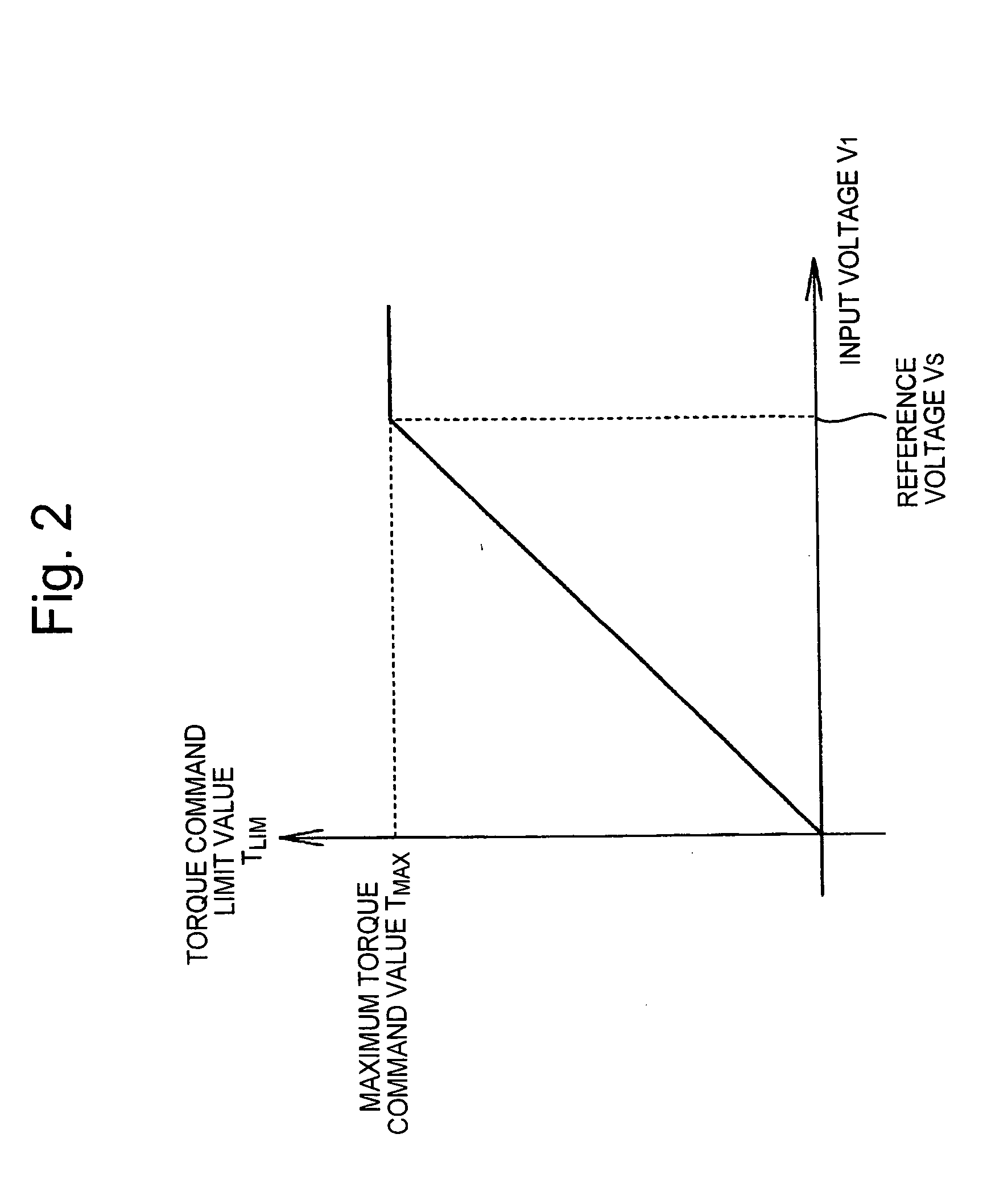
A method and system for controlling motor torque provides improved responsiveness and reliability in motor control applications. The motor control system includes a power converter, a voltage detector for detecting the converter input voltage and a control circuit for controlling the converter. The control circuit includes a torque command limit value generator and a torque command limiter for limiting a torque command value. The system may also include a torque command coefficient generator for generating a coefficient corresponding to an input current of the power converter, and a multiplier for calculating a final torque command value for the motor by multiplying together the torque command value and the torque command coefficient. The torque command limit and coefficient values may be determined from the converter input voltage, calculated or detected converter input current and calculated input impedance between a power supply and the converter.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
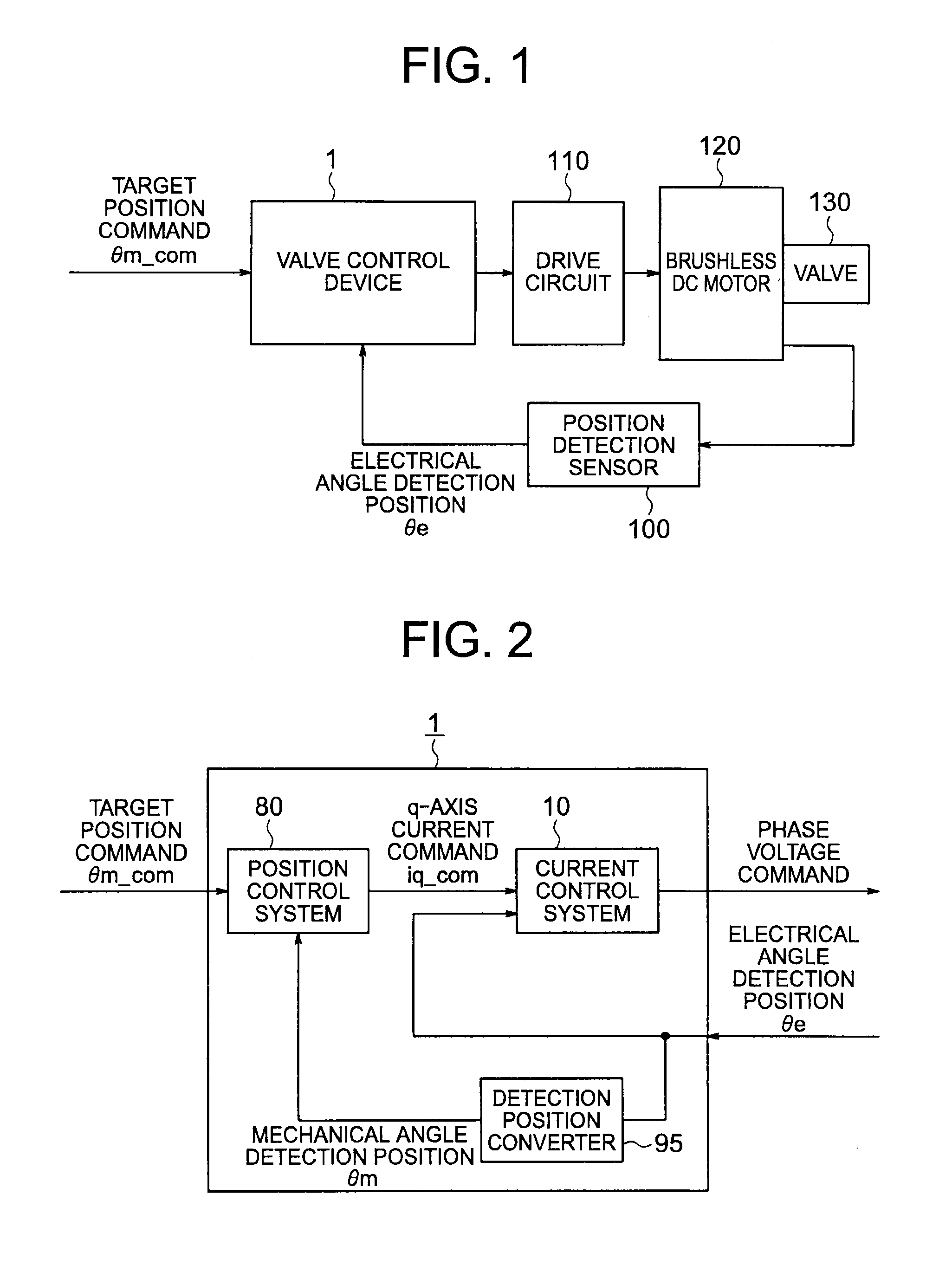
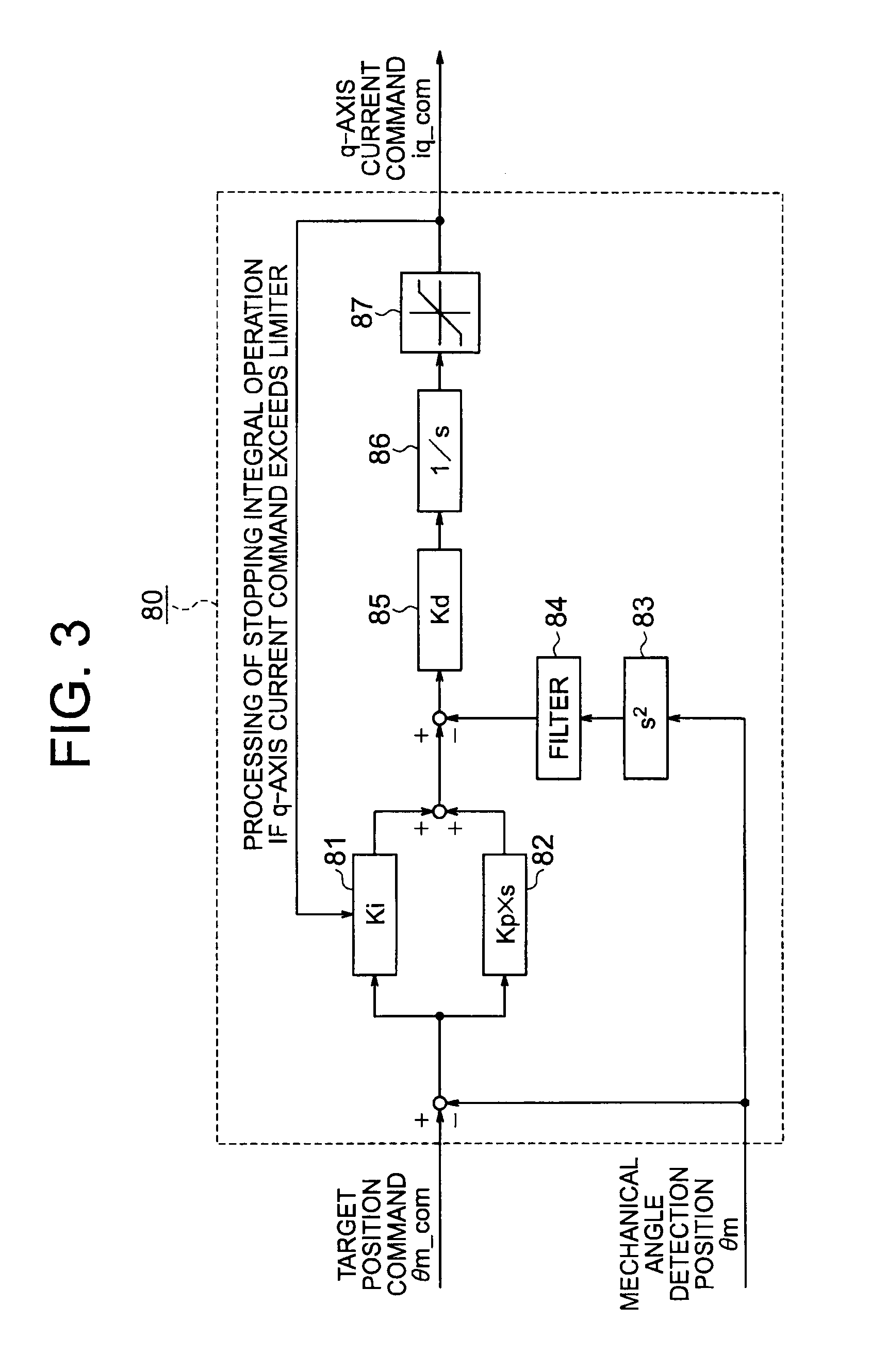
Valve control device
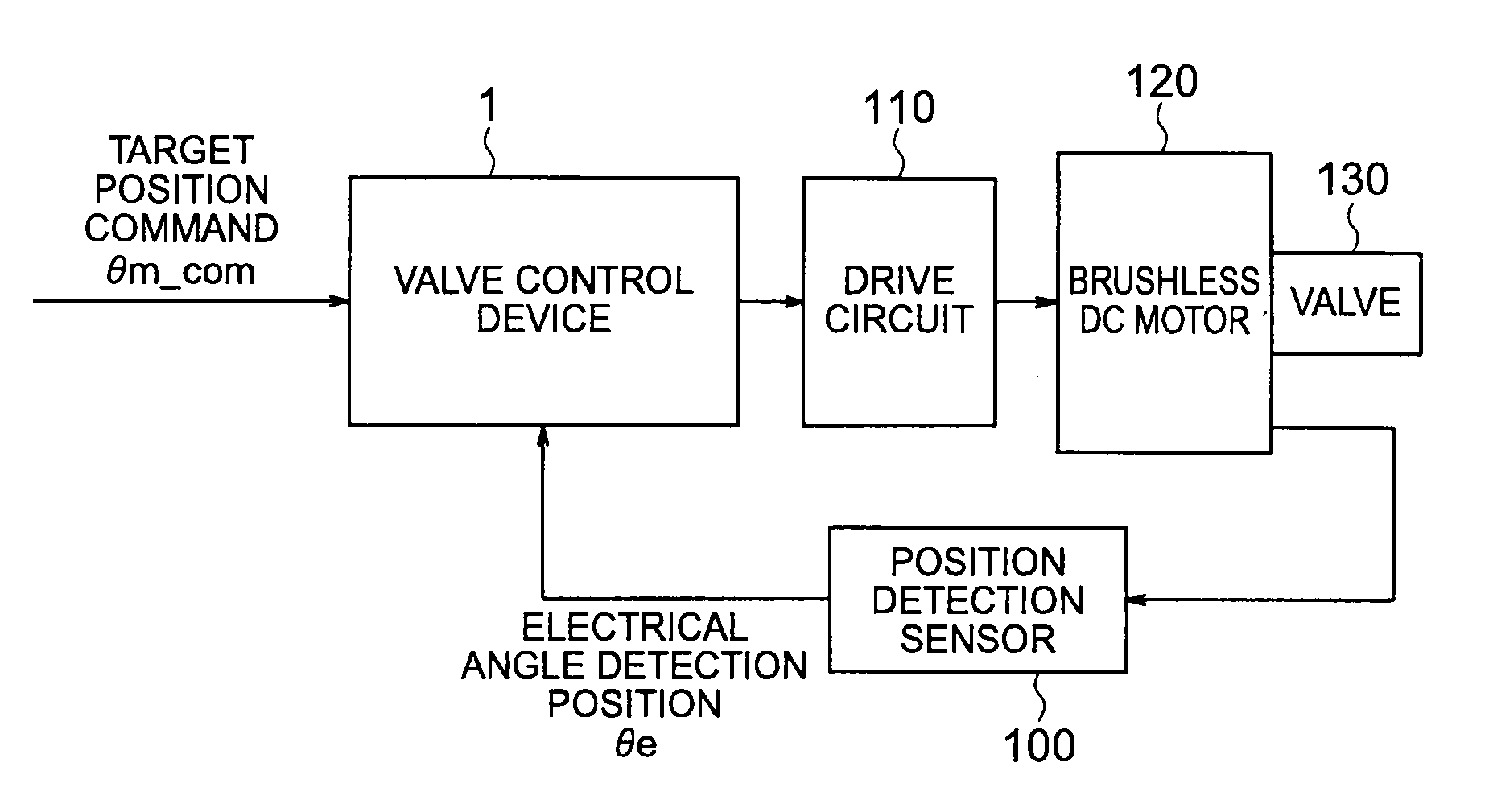
ActiveUS20110273127A1Generate efficientlyShorten speedTorque ripple controlElectrical controlCurrent sensorPosition bias
In opening / closing control for the valve mechanism to which the return torque is applied in an opening direction or a closing direction of the valve, provided are a position control system for outputting a q-axis current command based on a position deviation between a target position command directed to the brushless DC motor and the coarse present position of the motor obtained by using the position detection sensor of a pulse output type, and a current control system in which a virtual current feedback is built for outputting a phase voltage command without a current sensor based on the q-axis current command and the coarse present position of the motor obtained by using the position detection sensor of the pulse output type.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
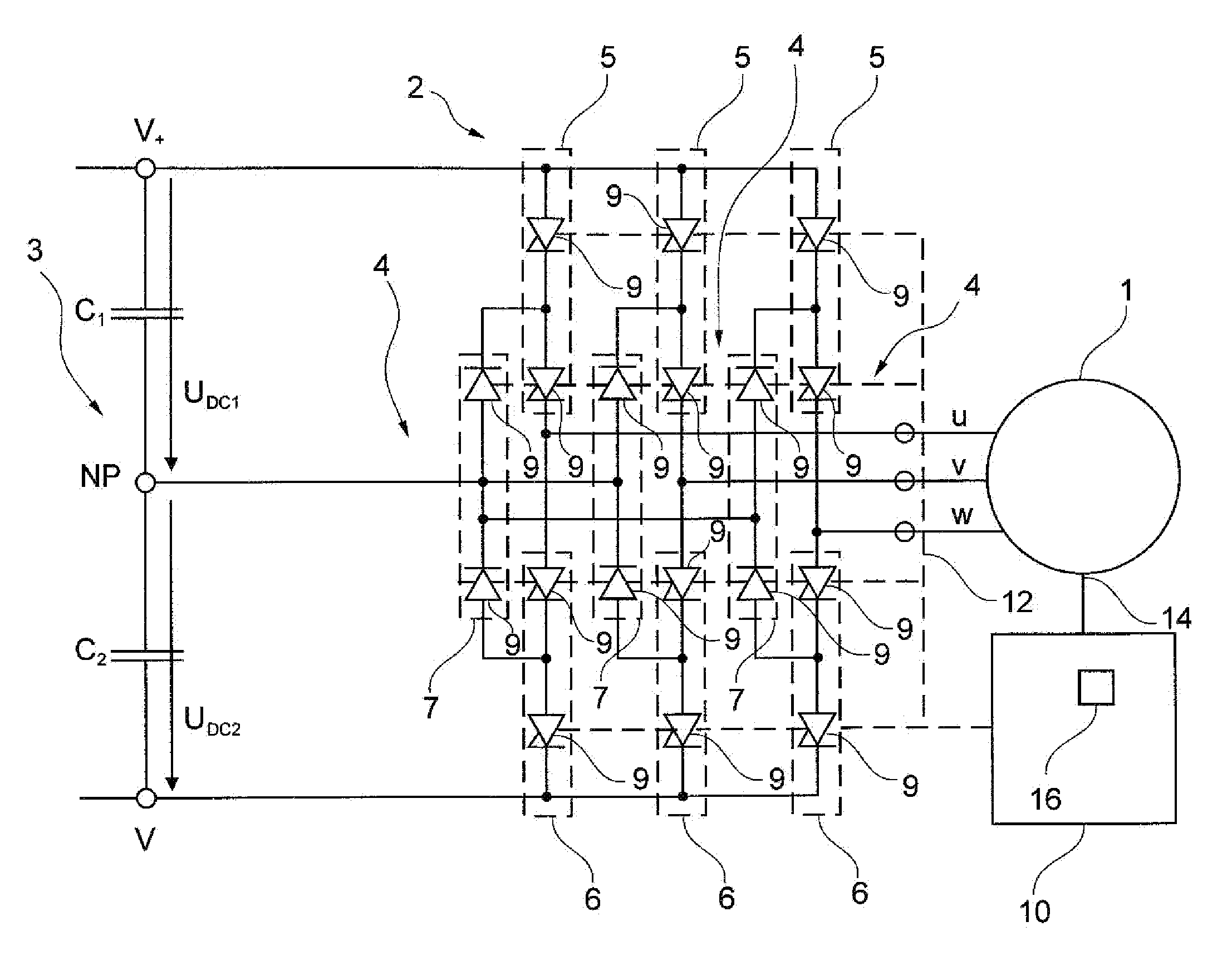
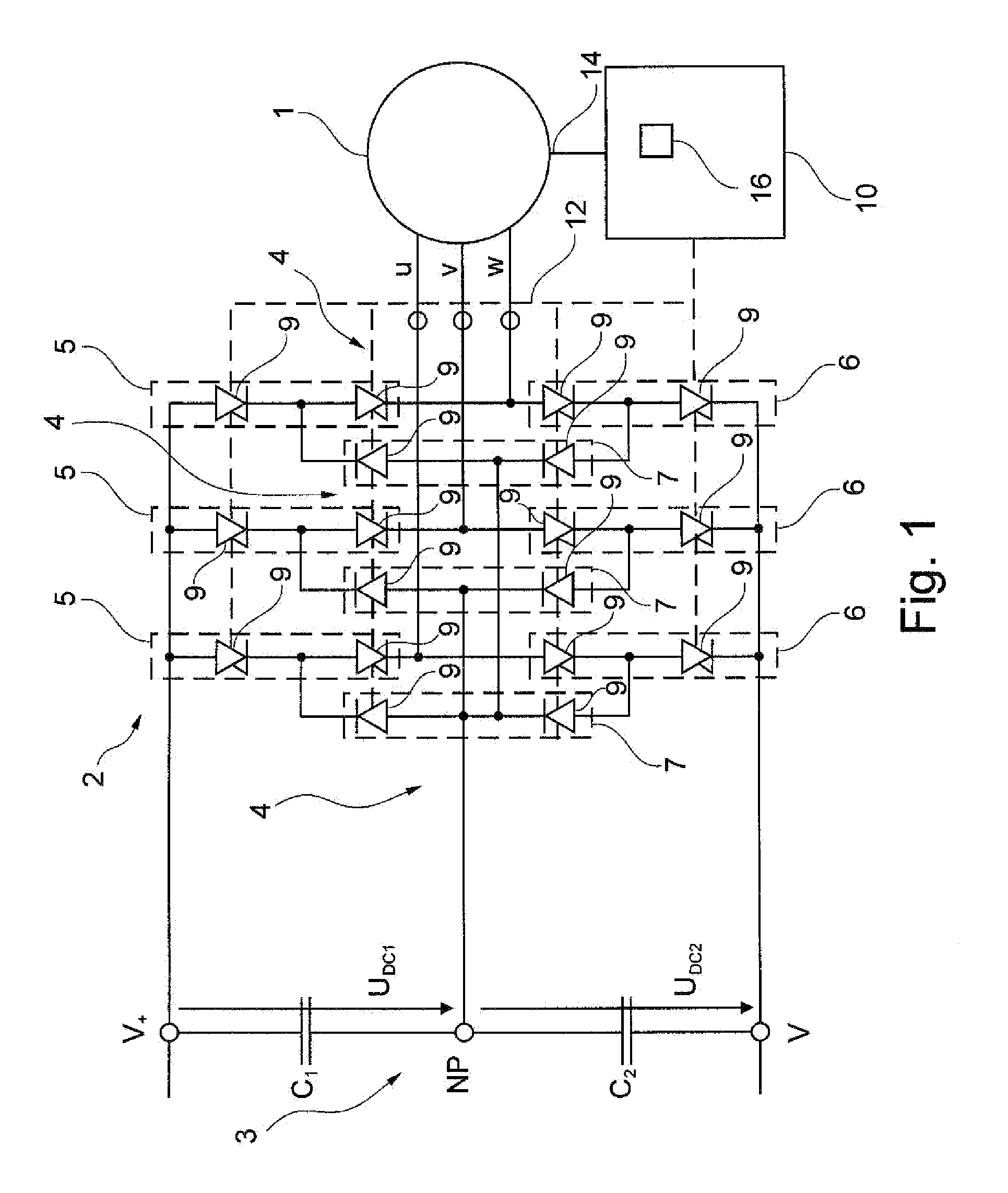
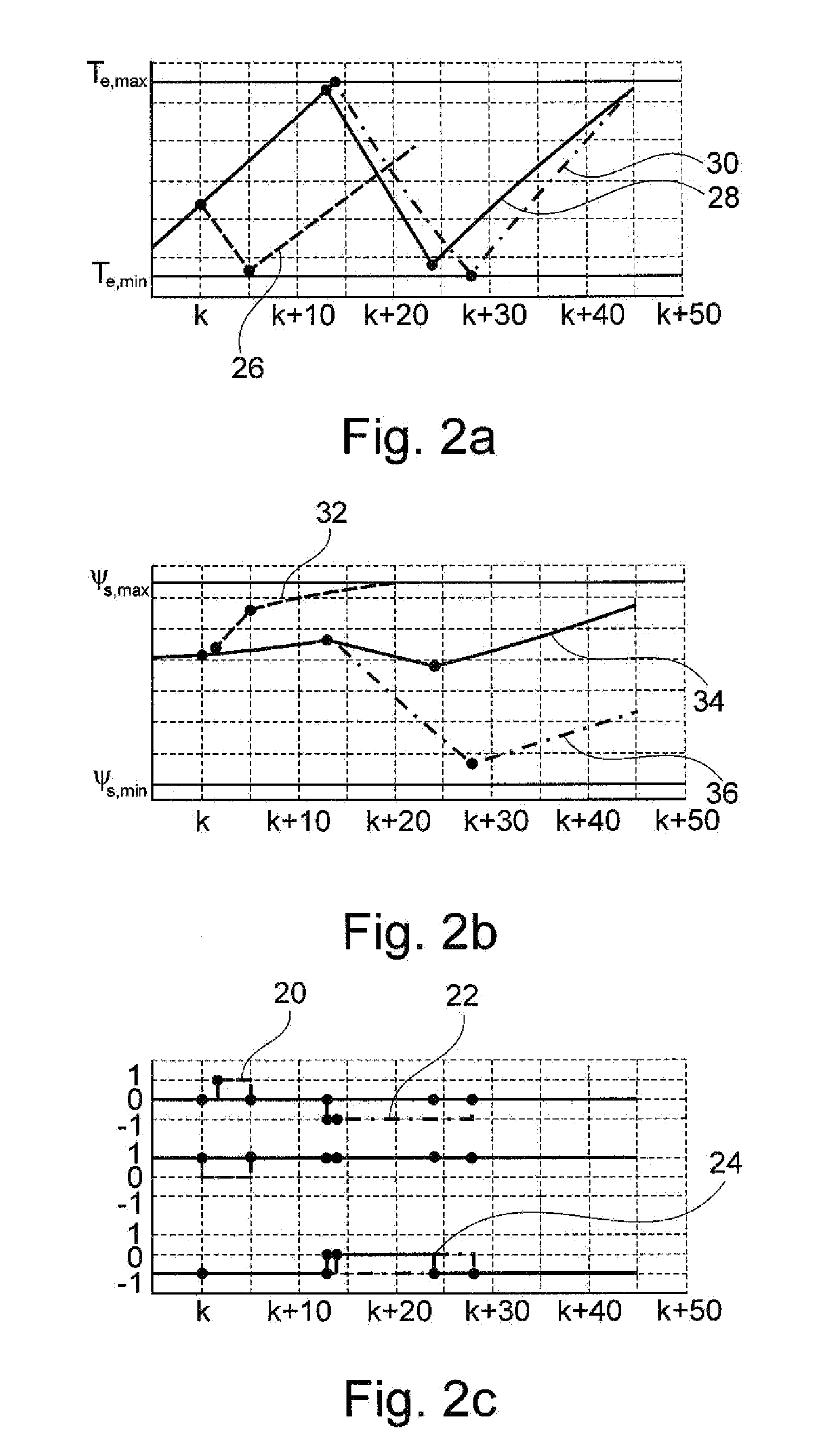
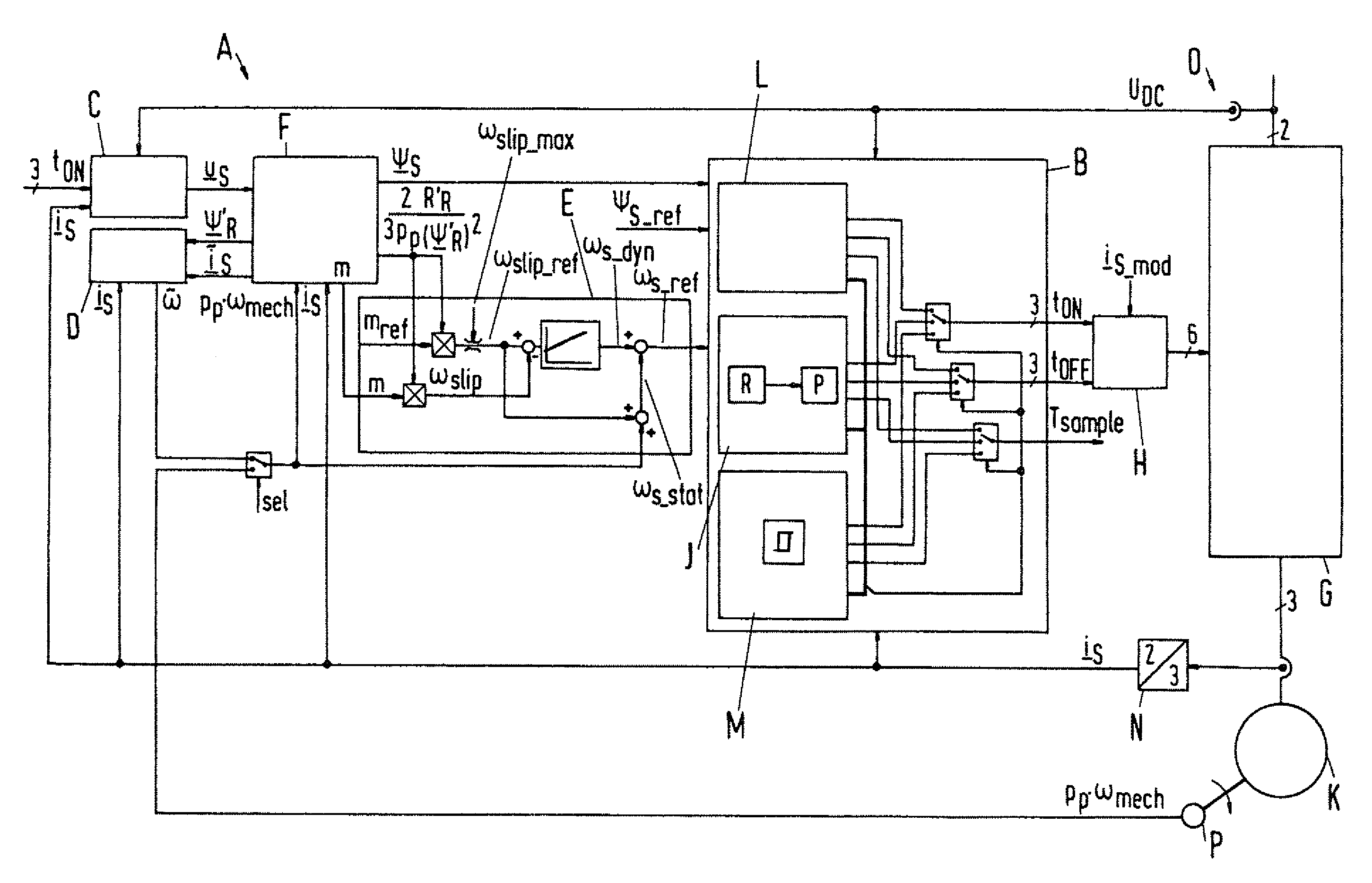
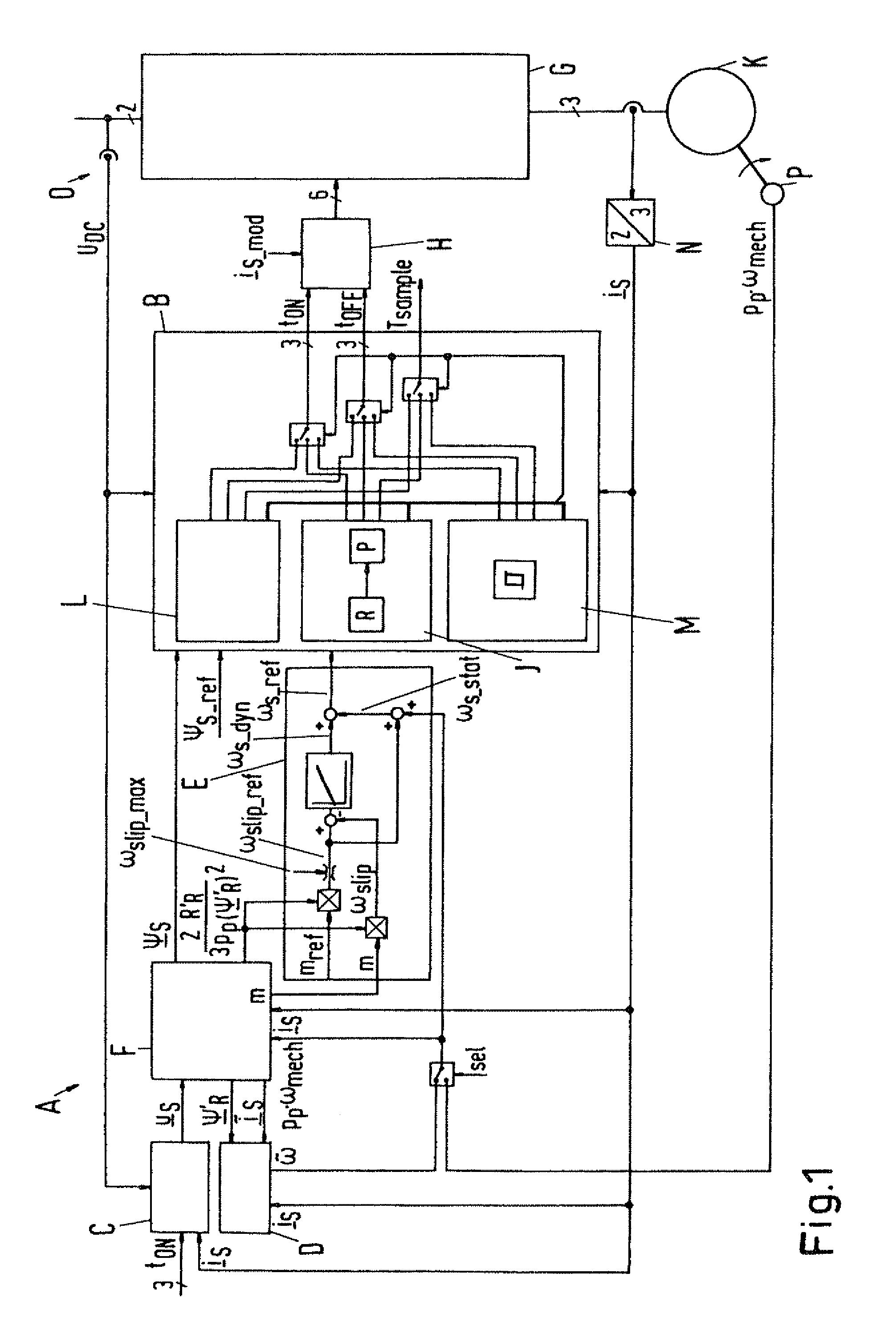
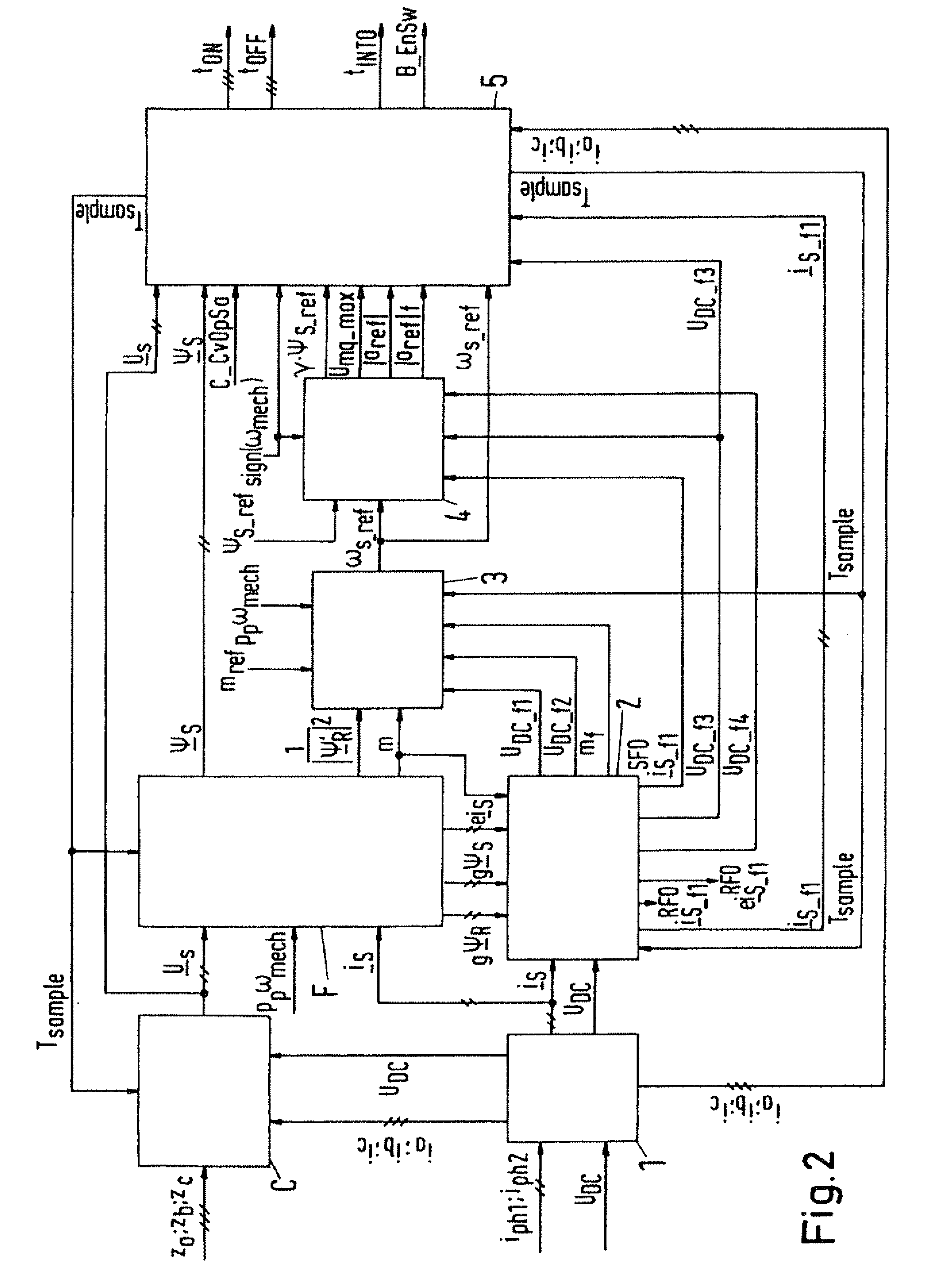
Method for controlled application of a stator current set point value and of a torque set point value for a converter-fed rotating-field machine
InactiveUS7746039B2Avoid disadvantagesBroaden the fieldElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsElectric machineMagnetic poles
Owner:SIEMENS AG
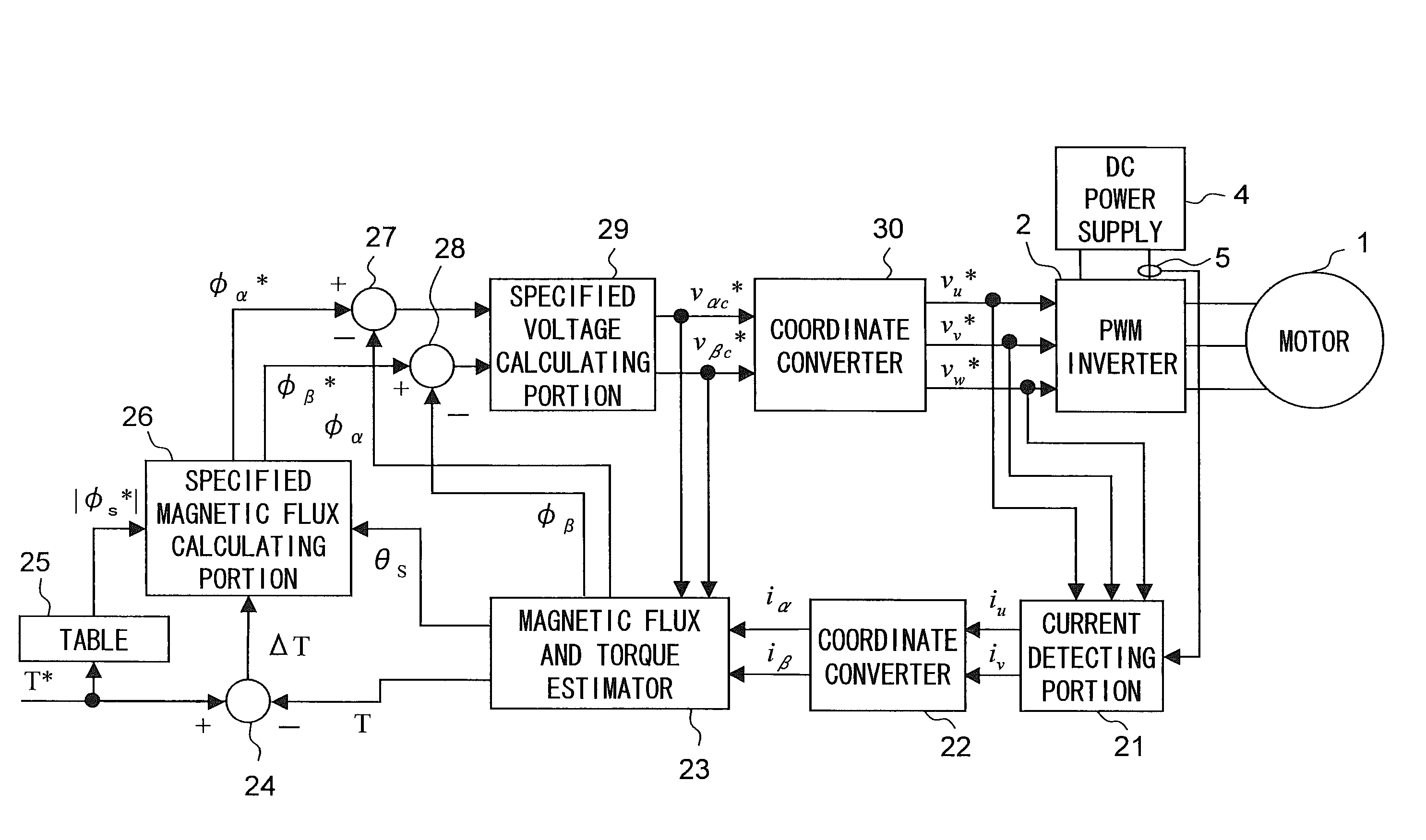
Motor control device
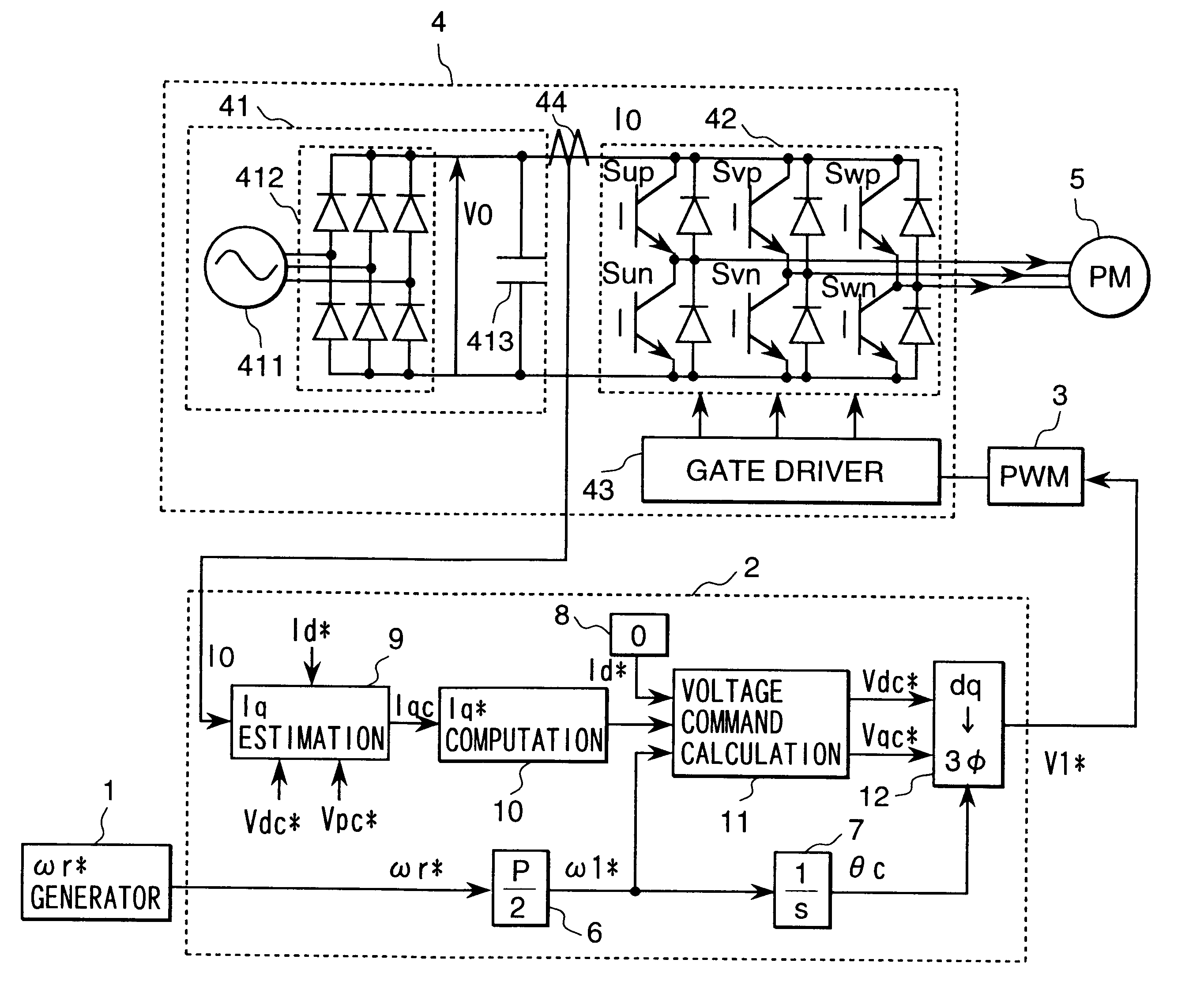
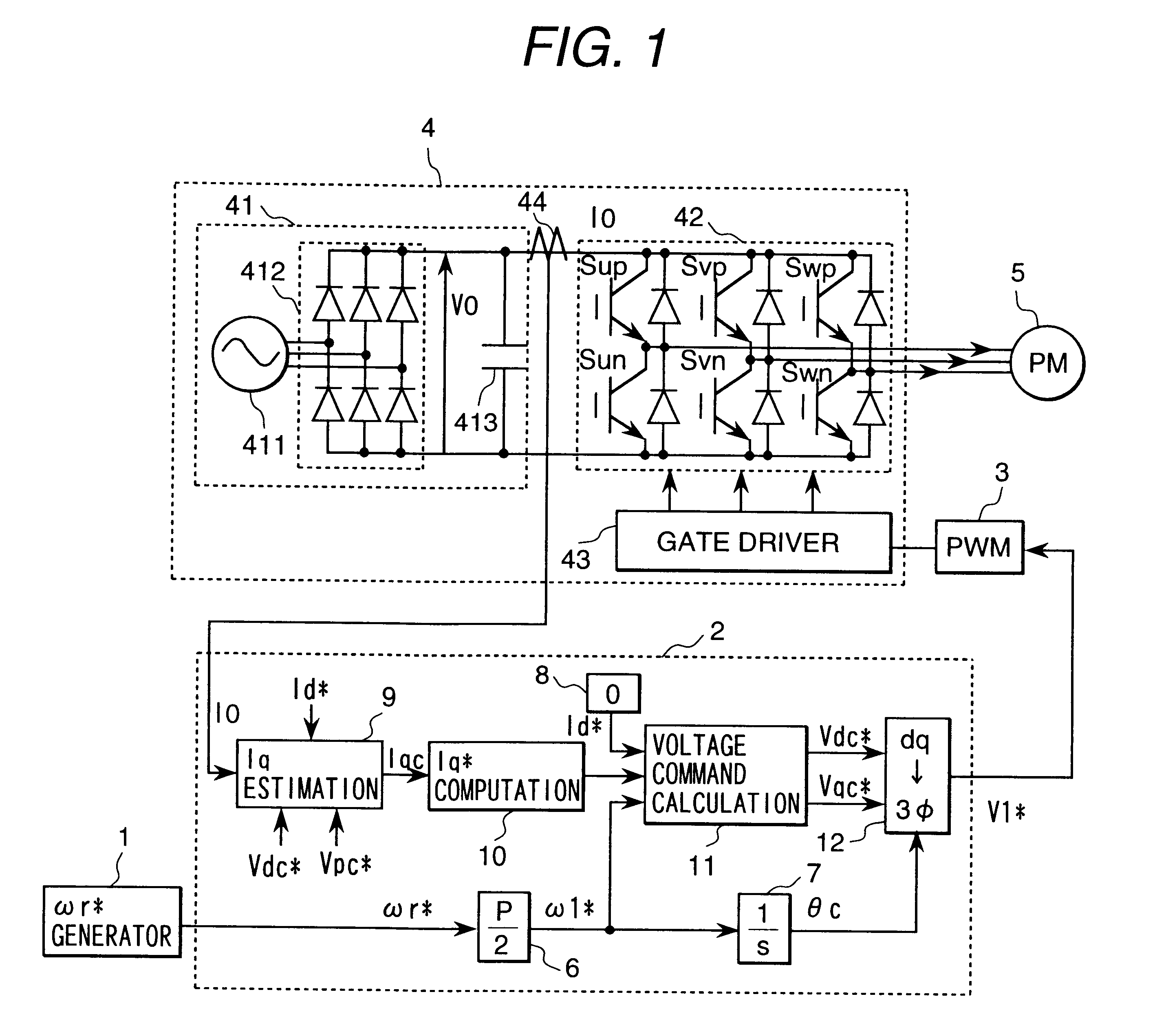
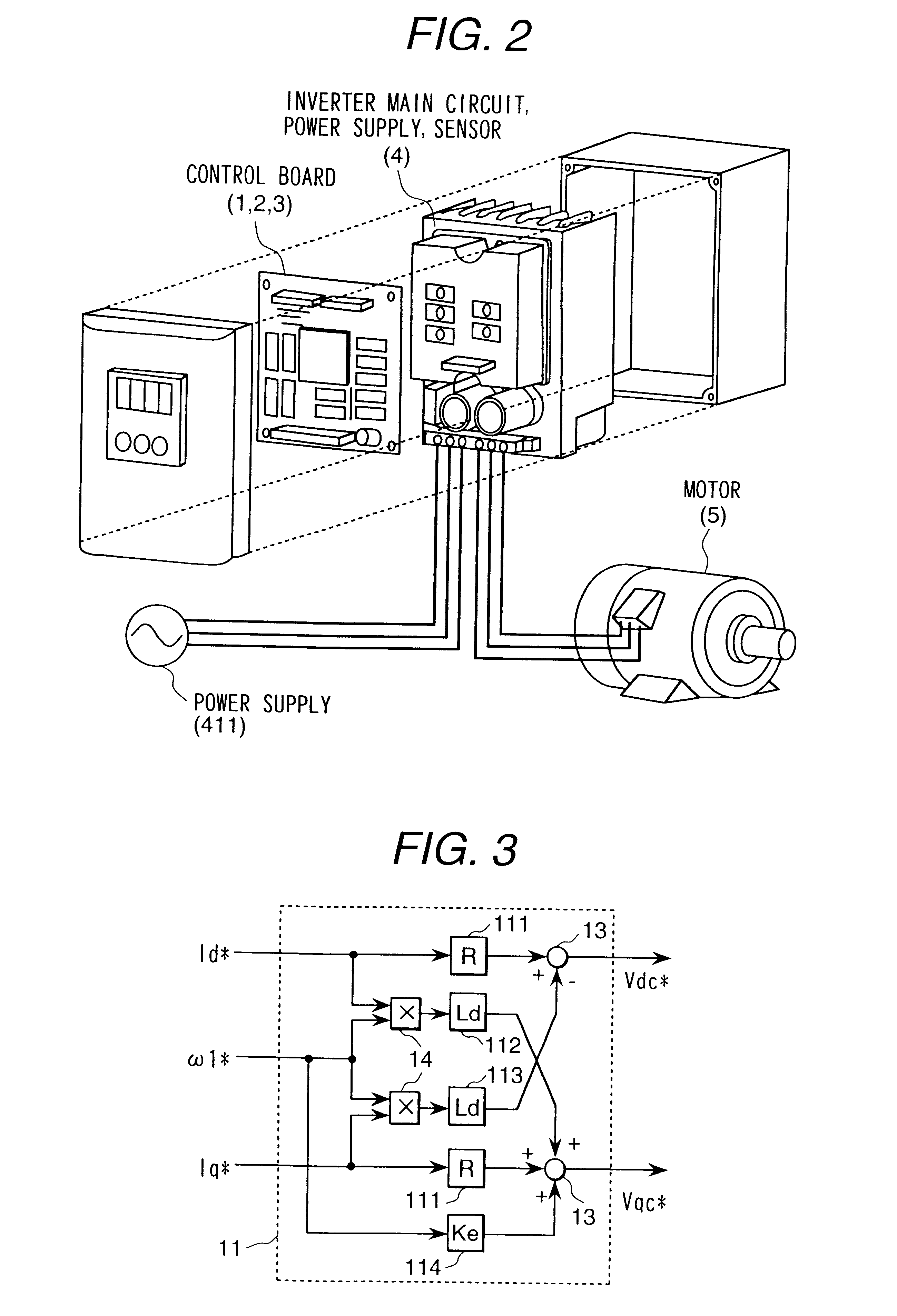
A motor control device includes a motor current detector for detecting motor current flowing in a three-phase motor based on current flowing between an inverter driving the motor and a DC power supply, a specified voltage vector generating portion for generating a specified voltage vector indicating a voltage vector to which an applied voltage to the motor should follow based on a magnetic flux linkage of an armature winding of the motor, a specified voltage vector correcting portion for correcting the generated specified voltage vector, and a magnetic flux estimating portion for estimating the magnetic flux linkage based on the motor current and the specified voltage vector after the correction. The motor control device controls the motor via the inverter in accordance with the specified voltage vector after the correction.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
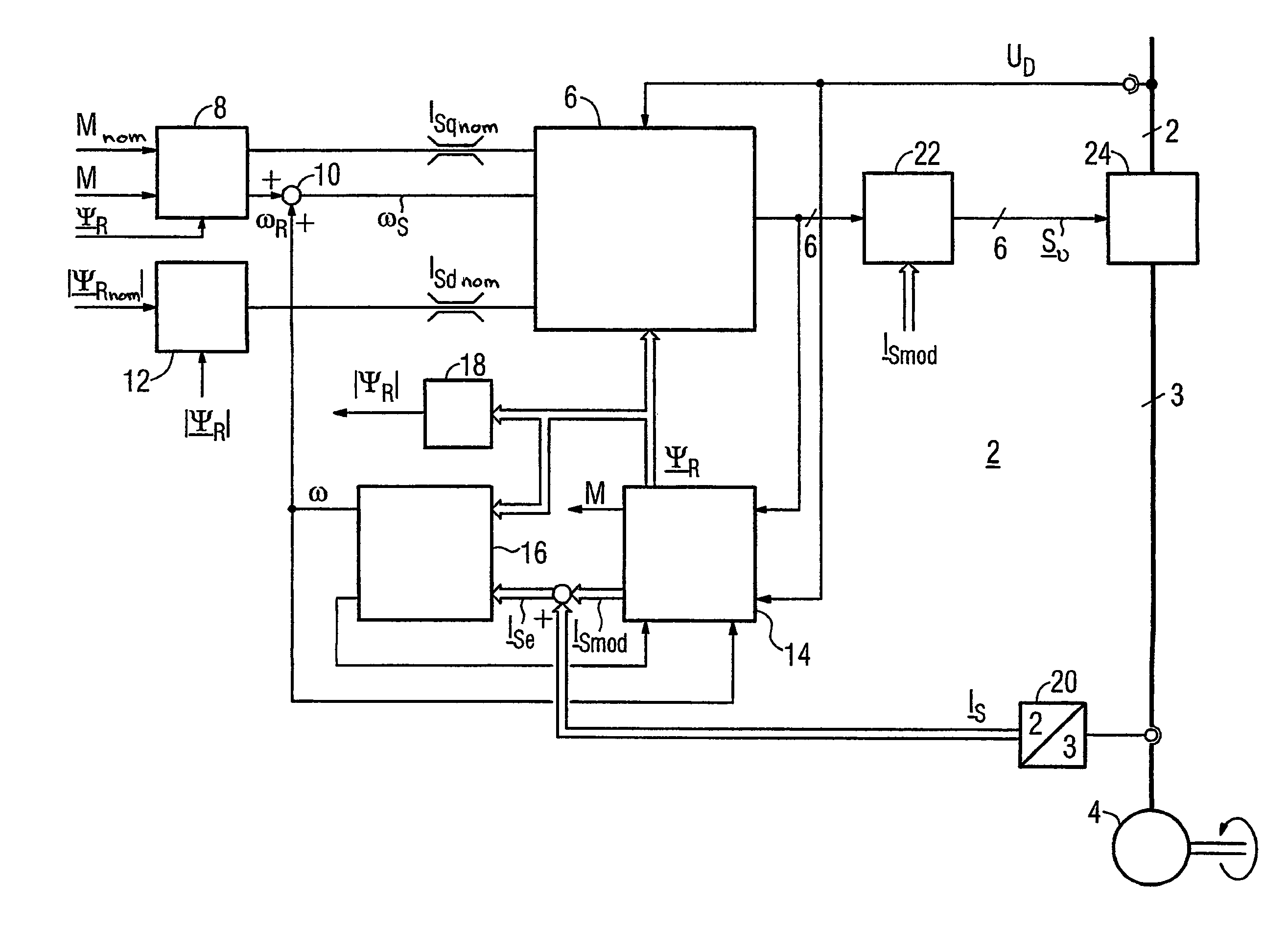
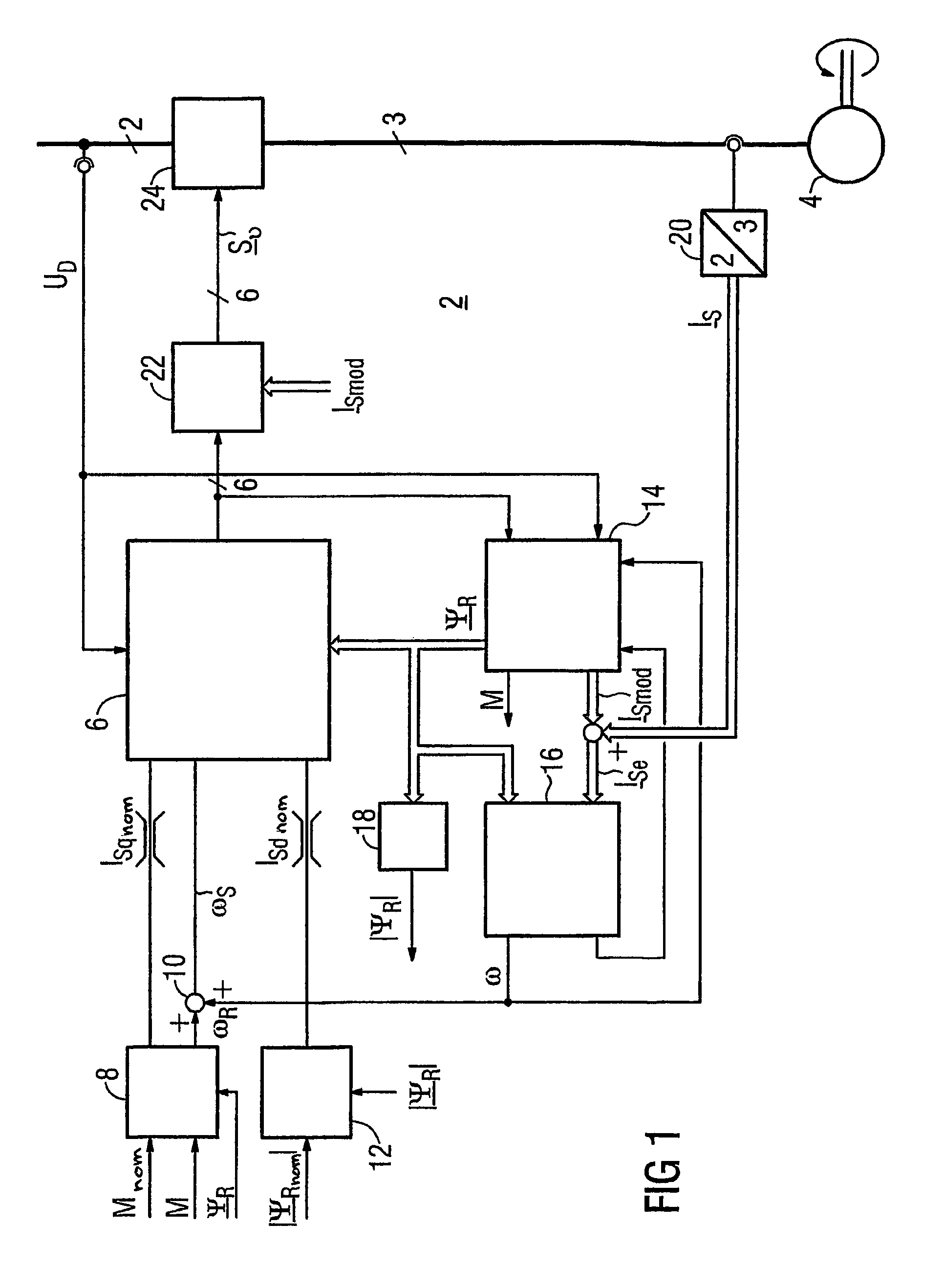
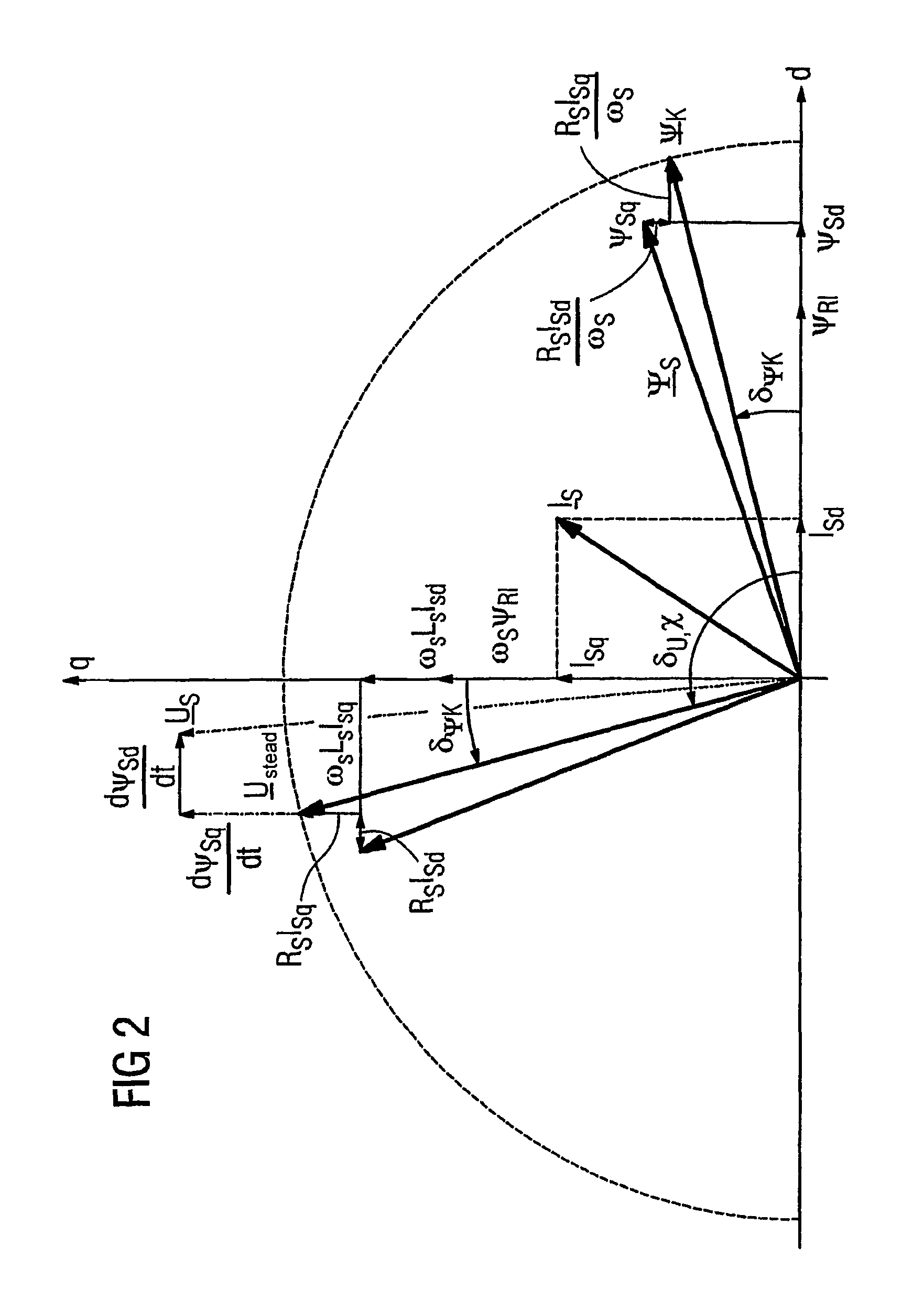
Method for Controlled Application of a Stator Current Set Point Value and of a Torque Set Point Value for a Converter-Fed Rotating-Field Machine
InactiveUS20080136380A1Avoid disadvantagesBroaden the fieldElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsElectric machineMagnetic poles
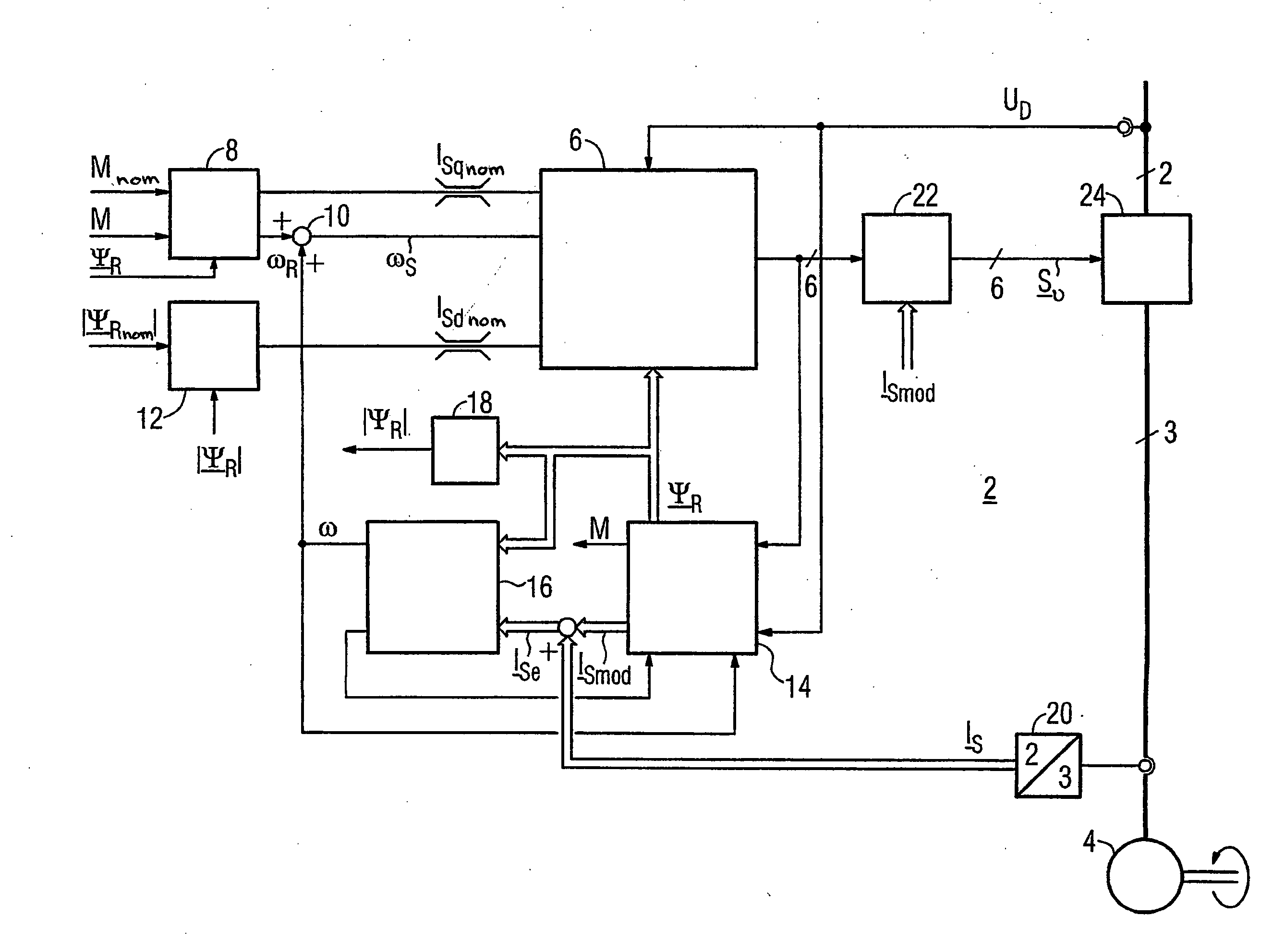
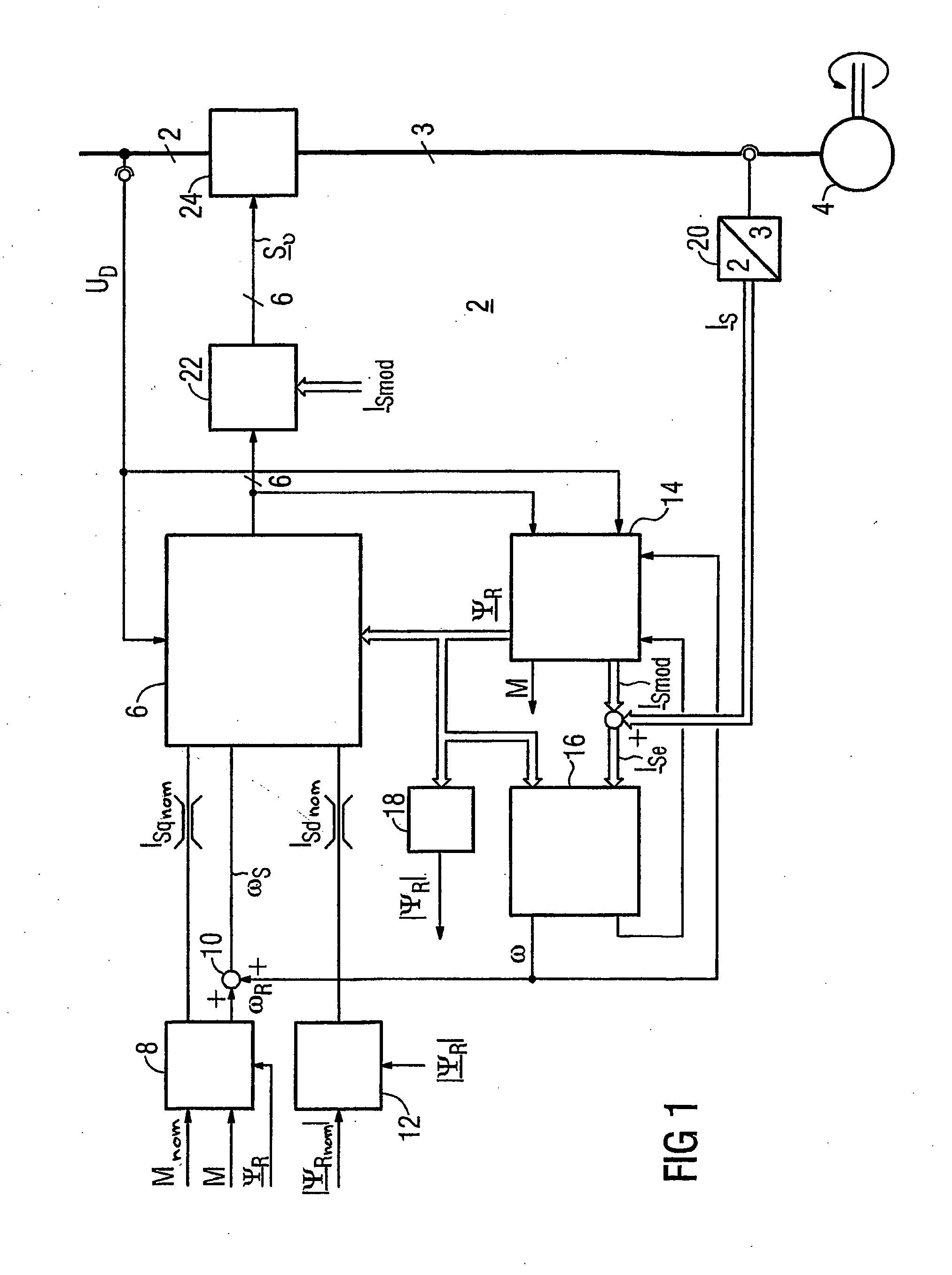
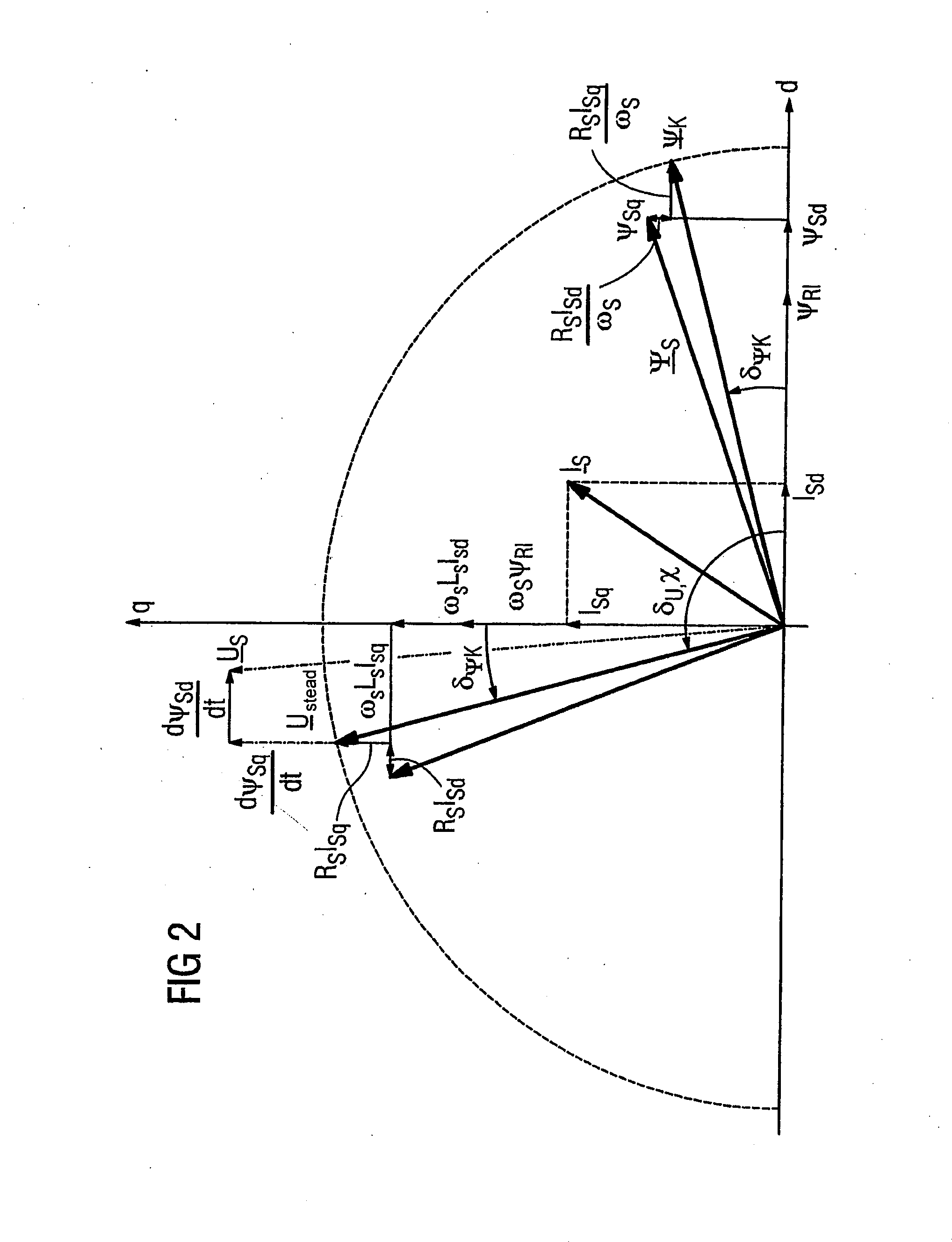
The invention relates to a method for the controlled application of a stator-current target value (ISnom) and a torque target value (Mnom) for a polyphase machine (4) that is supplied by an electronic power converter. According to the invention: current components (ISdnom, ISqnom) in a co-ordinate system (d, q) with a fixed rotor flux or rotating magnetic pole are calculated in accordance with a torque target value and in asynchronous machines in accordance with a rotor-flux target value (ΨRnom), a calculated rotor-flux actual value (Ψ<SB>R< / SB>) or a rotating magnetic-pole flux; a stator-circuit frequency (ω<SB>S< / SB>) is determined; a terminal-flux target value (ΨKnom) is calculated in accordance with the values (ISnom, ISqnom, Ψ<SB>R< / SB>, ω<SB>S< / SB>) by means of the machine parameters (L, R<SB>S< / SB>), said terminal-flux target value being subsequently projected onto a flux-course curve, selected from stored, off-line optimised flux-course curves. This permits the state of the stator current (I<SB>S< / SB>) to be regulated in relation to the rotor flux (Ψ<SB>R< / SB>) or rotating magnetic-pole flux by means of momentary values, facilitating a stationary and dynamic precise control of motor currents (I1,I2,I3) and thus the torques (M) of a polyphase machine (4).
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Torque control method for electro-magnetic doubly salient motors
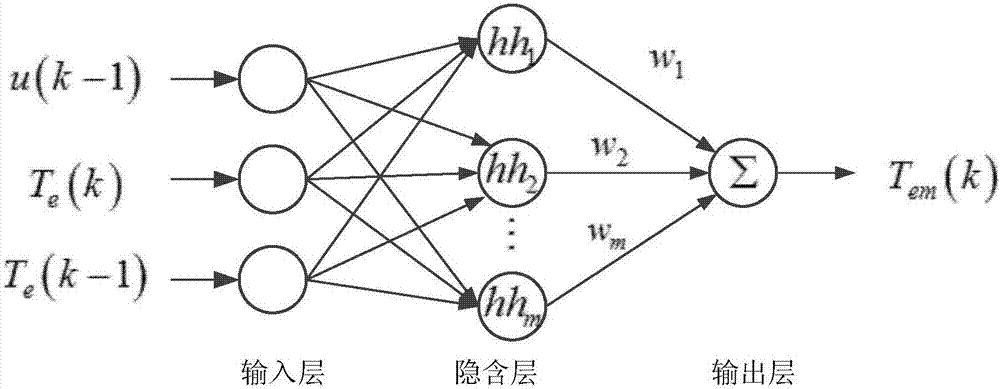
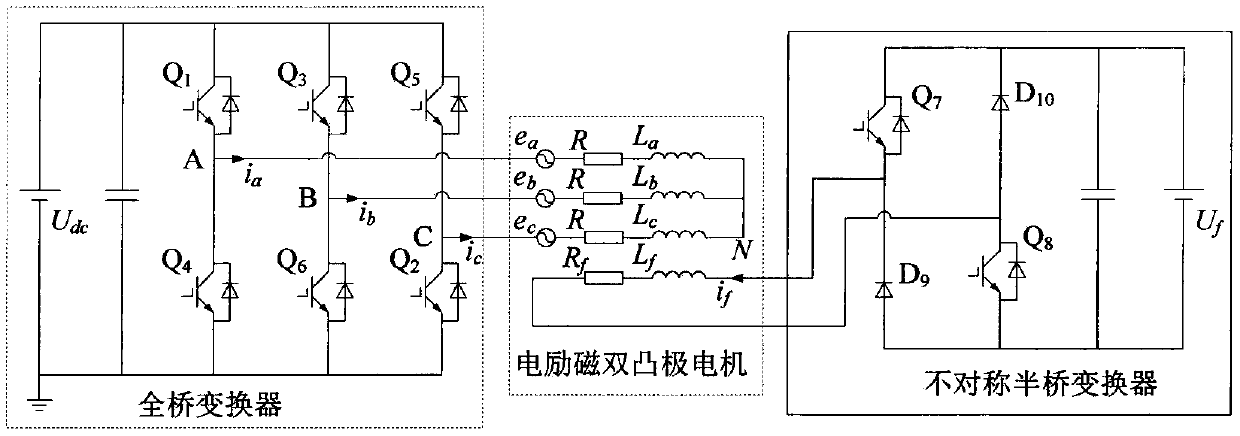
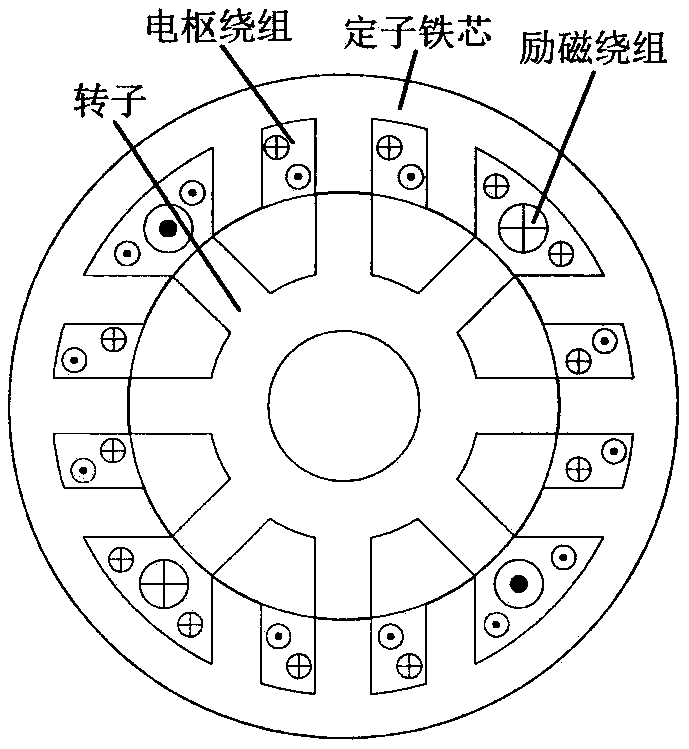
ActiveCN109450330ASuppression of torque rippleField acceleration method controlDirect torque controlMagnetic reluctanceTorque observer
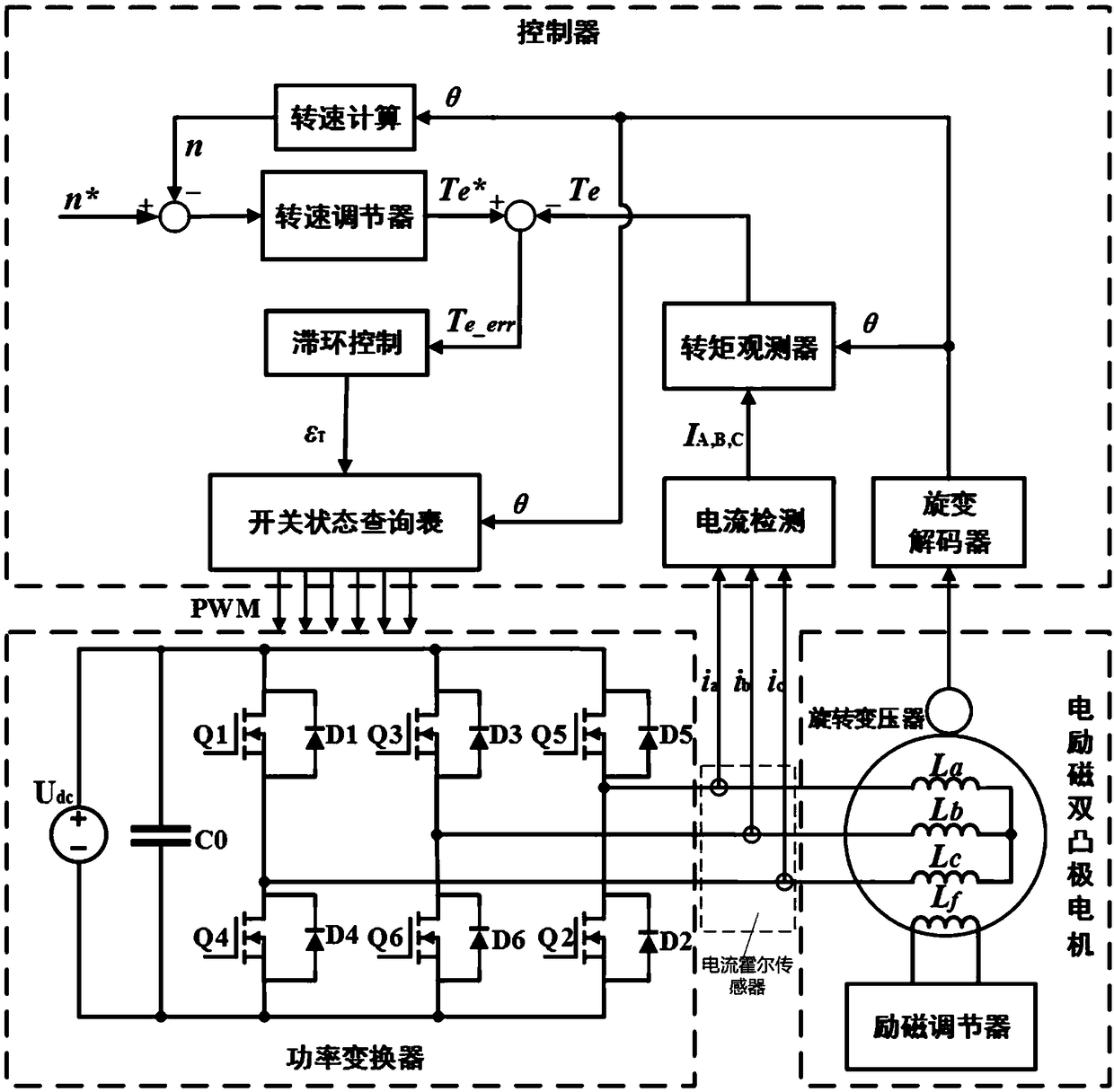
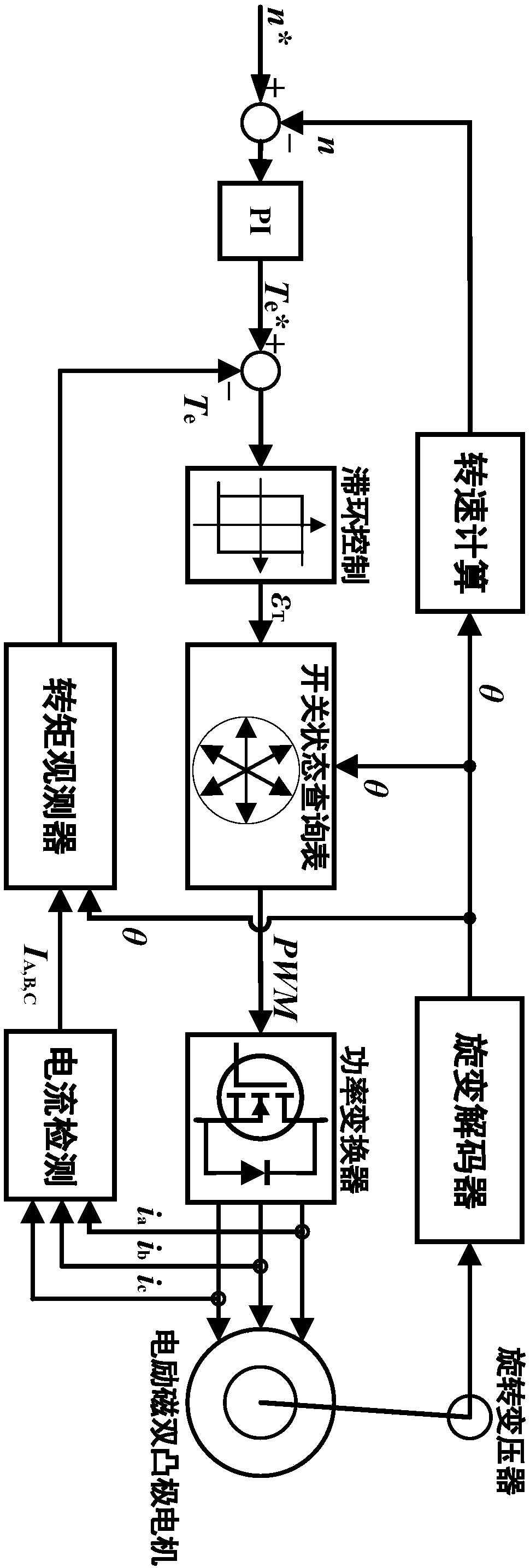
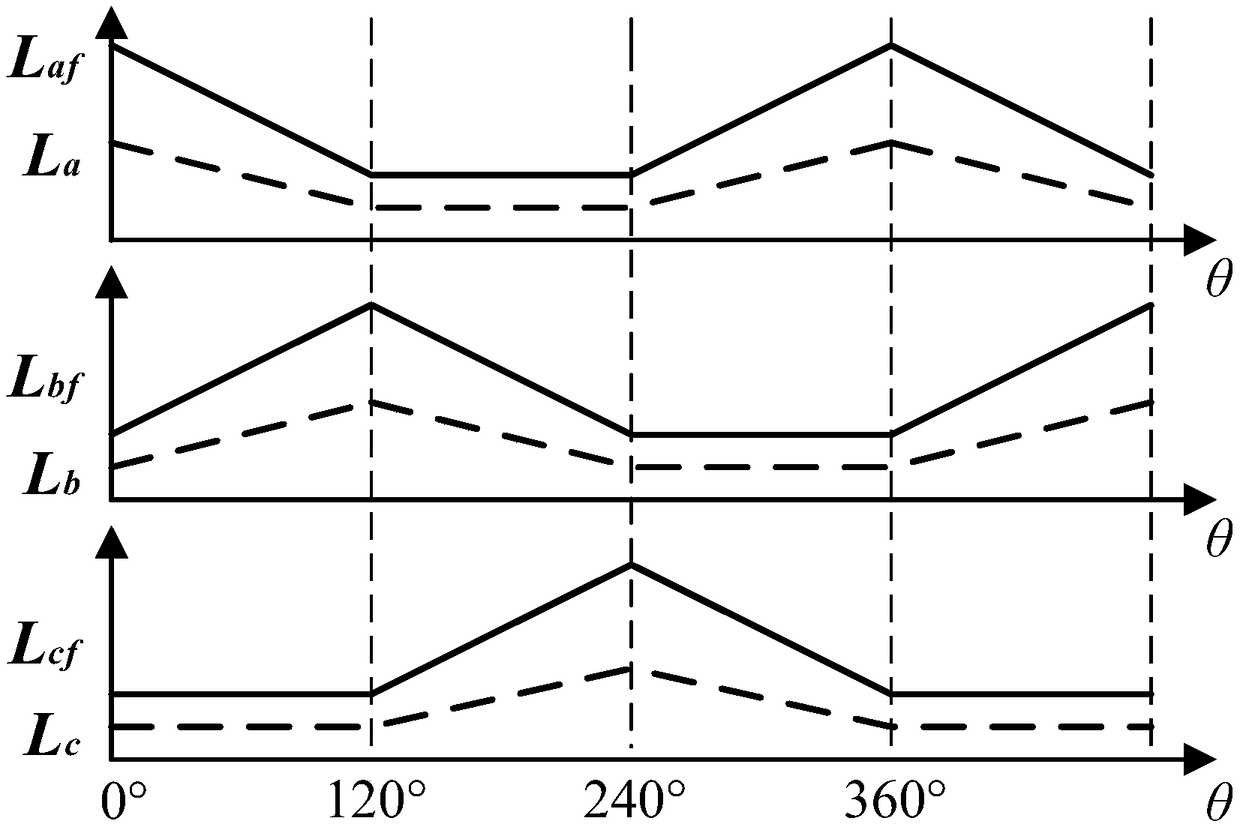
Embodiments of the invention disclose a torque control method for electro-magnetic doubly salient motors, relate to the technical field of variable magnetic reluctance type motor control, and aim at inhibiting torque pulsation and enhancing the torque performance of electro-magnetic doubly salient motors. According to the control method, a rotation speed and torque double loop locked control structure is adopted, the rotation speed and torque are used as controlled volumes, and the controlled volumes are driving signals of a power converter. The control principle is described as follows: the output of a rotation speed outer ring serves as a given value of the torque; a torque observer outputs a corresponding torque value according to an acquired three-phase current signal and an acquired rotor position signal to serve as a feedback value of the torque; and the given value and feedback value of the torque undergo hysteresis control and switching state query table to output correspondingpower converter driving signals. The method is suitable for the torque performance optimization of electro-magnetic doubly salient motors.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
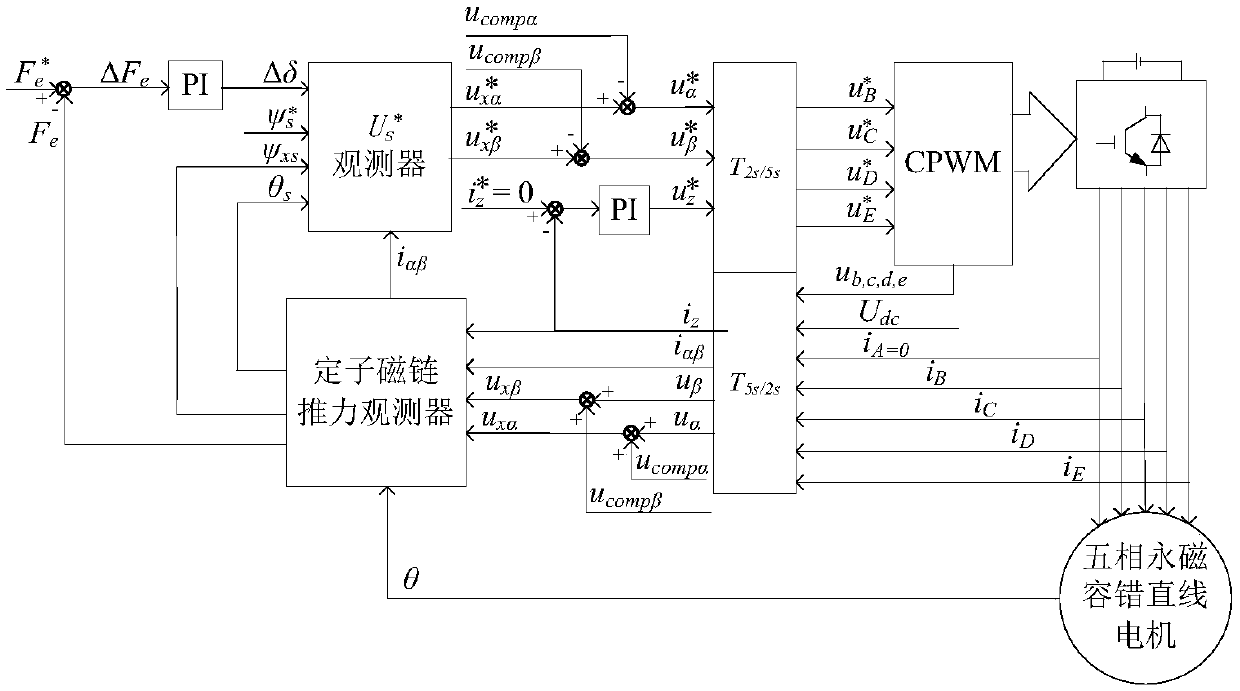
One-phase open-circuit fault-tolerant direct thrust control method for five-phase permanent magnet linear motor
InactiveCN108306571AIncreased complexitySave memory resourcesElectric motor controlVector control systemsPhase currentsModulation function
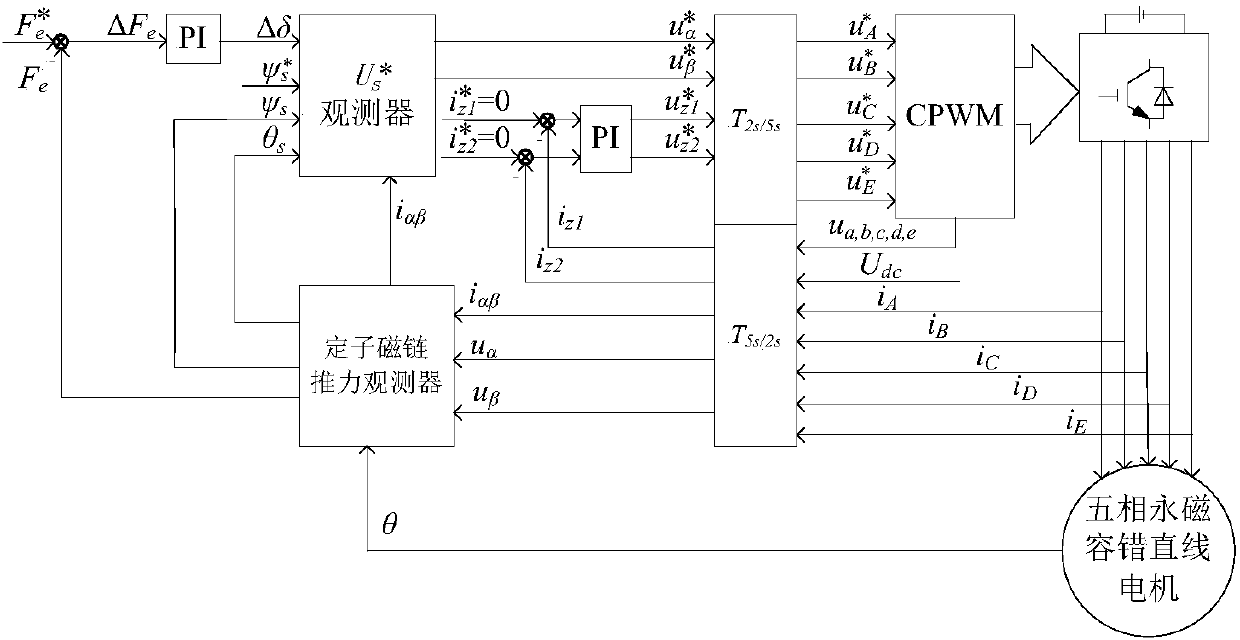
The invention discloses a one-phase open-circuit fault-tolerant direct thrust control method for a five-phase permanent magnet linear motor. Firstly, a Clark transform matrix and an inverse matrix thereof are derived based on fault-tolerant phase current. On the above basis, a stator flux linkage on alpha-beta is derived, a stator virtual flux linkage is defined according to the requirements of acircular stator flux linkage trajectory, and thus the voltage compensation on alpha-beta is derived. The stator actual voltage on the alpha-beta is derived by a modulation function of a voltage sourceinverter, and voltage is combined with voltage compensation and stator current, and a stator virtual flux linkage and thrust are observed by a stator flux observer and a thrust observer. Then statorvirtual target votlage is calculated according to given thrust, a given stator flux linkage amplitude and the observed stator virtual flux linkage and thrust. Finally, the stator actual voltage is calculated by the voltage and the voltage compensation, and the motor is controlled by the voltage by the voltage source inverter. According to the method, a thrust fluctuation caused by a motor failureis suppressed, and more importantly, the dynamic performance and steady state performance are consistent with that in a normal condition.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
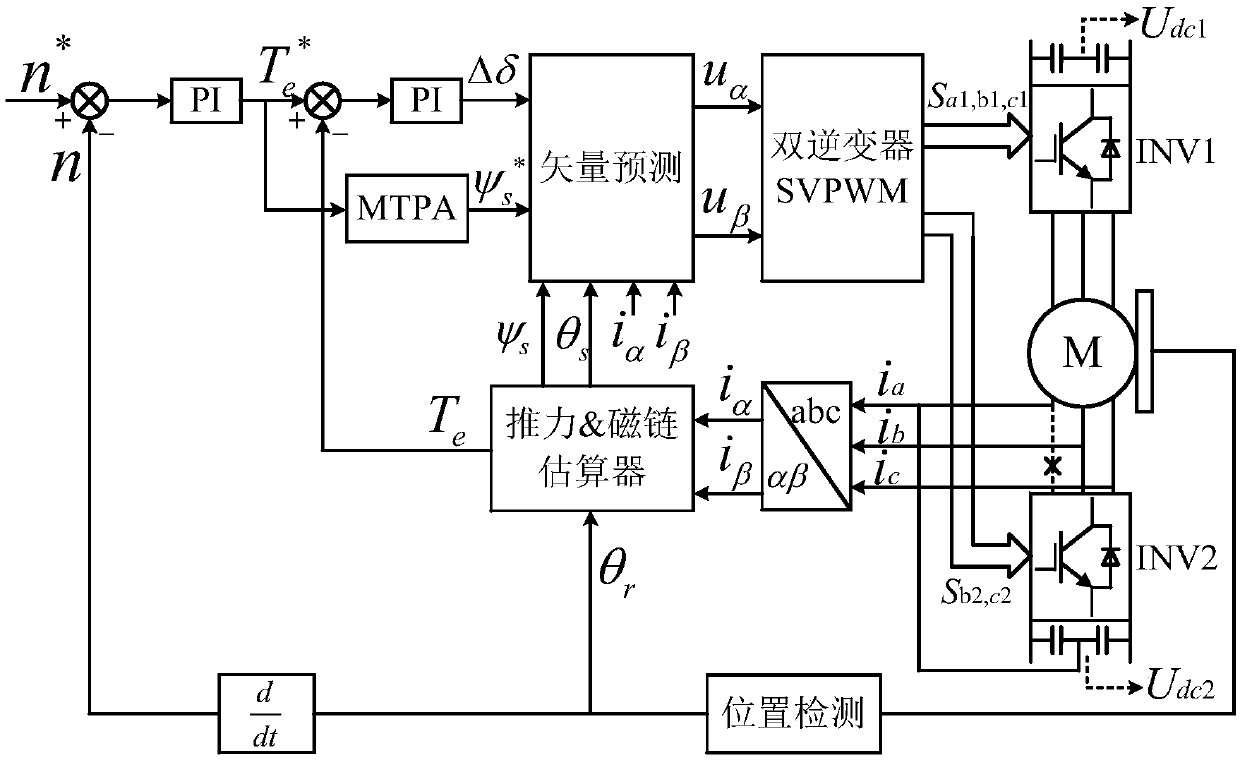
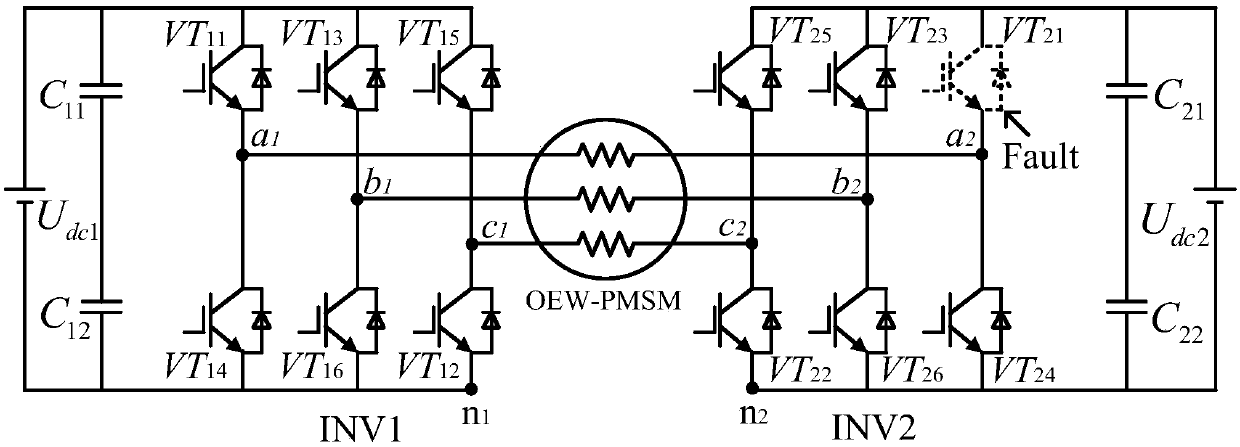
Permanent-magnet synchronous-motor open-winding fault-tolerant direct torque control method based on improved SVPWM
ActiveCN108418502AGuaranteed voltage utilizationGuaranteed uptimeElectric motor controlField acceleration method controlVoltage vectorControl signal
The invention discloses a permanent-magnet synchronous-motor open-winding fault-tolerant direct torque control method based on improved SVPWM. The method comprises the following steps of when an inverter switch tube has an open circuit fault, cutting off connection between a motor port and the fault inverter switch tube, connecting the motor port to a power supply midpoint, and using the remainingswitch tube to carry out fault-tolerant reconstruction on a system topology; through a PI controller, outputting a given torque; using a ''current method'' to estimate a stator flux linkage; and through the difference value of the given torque and an estimated torque, acquiring the variable quantity d delta of a load angle, using a maximum torque current ratio control method to give a reference stator flux linkage, and based on that, calculating a given reference voltage vector. Through the remaining switch tube, improved spatial voltage vector pulse width modulation reconstruction is performed. A double-inverter PWM control signal with a fixed switch frequency is output to an inverter. Under the open circuit fault of the switch tube, the safe and stable operation of a system under the fault is guaranteed, and the system has a good stable state and dynamic performance.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
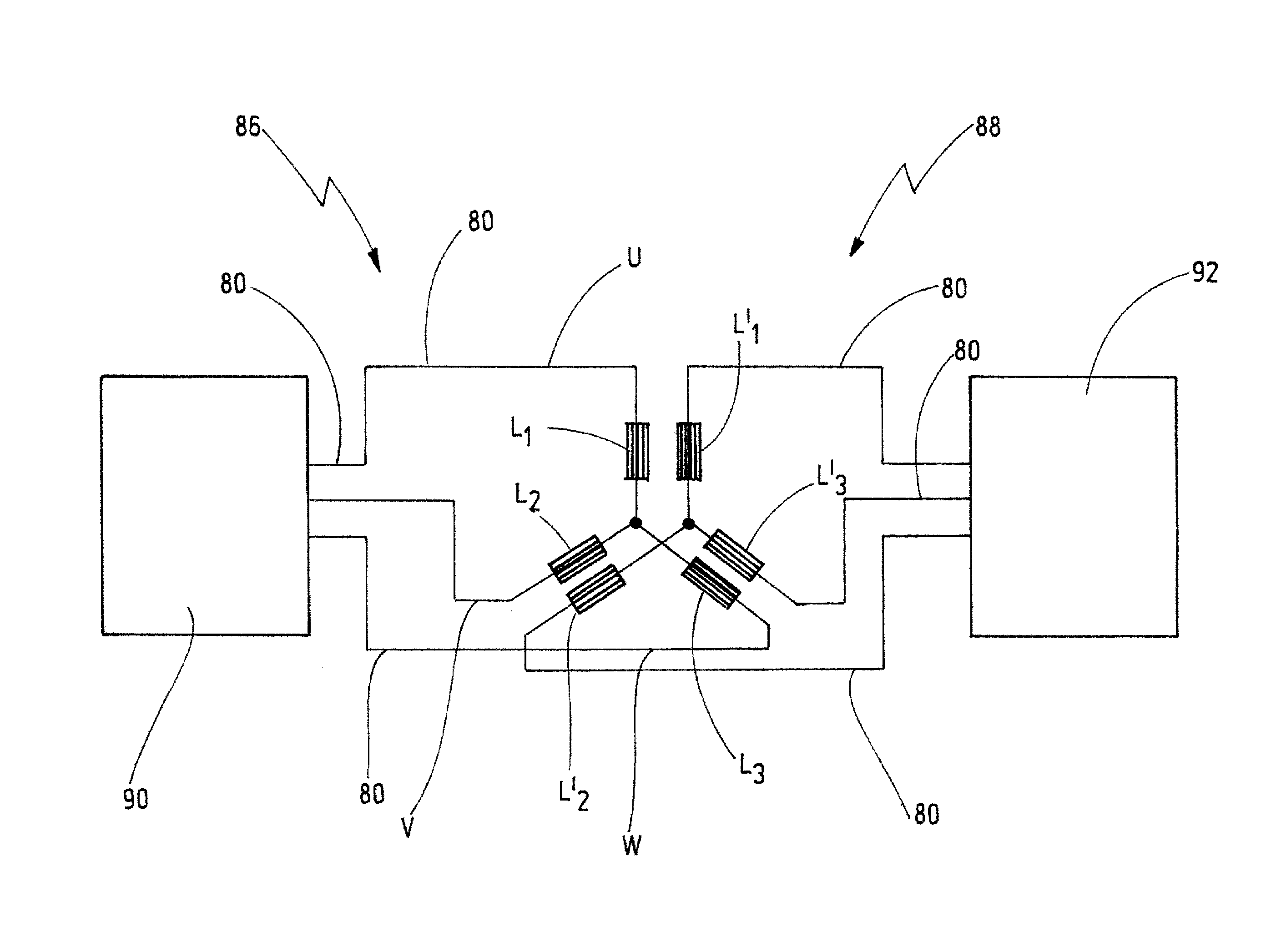
Open-loop and/or closed-loop control system of a 3-phase power converter for the operation of an asynchronous machine
InactiveUS8129936B2Maximum possible structural uniformityImprove structural stabilitySingle-phase induction motor startersMotor/generator/converter stoppersLoop controlClosed loop
An open-loop and / or closed-loop control device for operating an asynchronous machine which is fed by a 3-phase power converter. The open-loop and / or closed-loop control structure has a stator flux controller and a pulse pattern generator for generating pulse signals based on mean values. An output of the stator flux controller is connected to an input of the pulse pattern generator, with the result that the pulse pattern generator can generate the pulse signals as a function of a manipulated variable which is generated by the stator flux controller. The stator flux controller is configured so as to generate the manipulated variable as a function of a desired value of the stator flux of the asynchronous machine and as a function of a desired value of the torque of the asynchronous machine. The stator flux controller has a dead-beat control response.
Owner:BOMBARDIER TRANSPORTATION GMBH
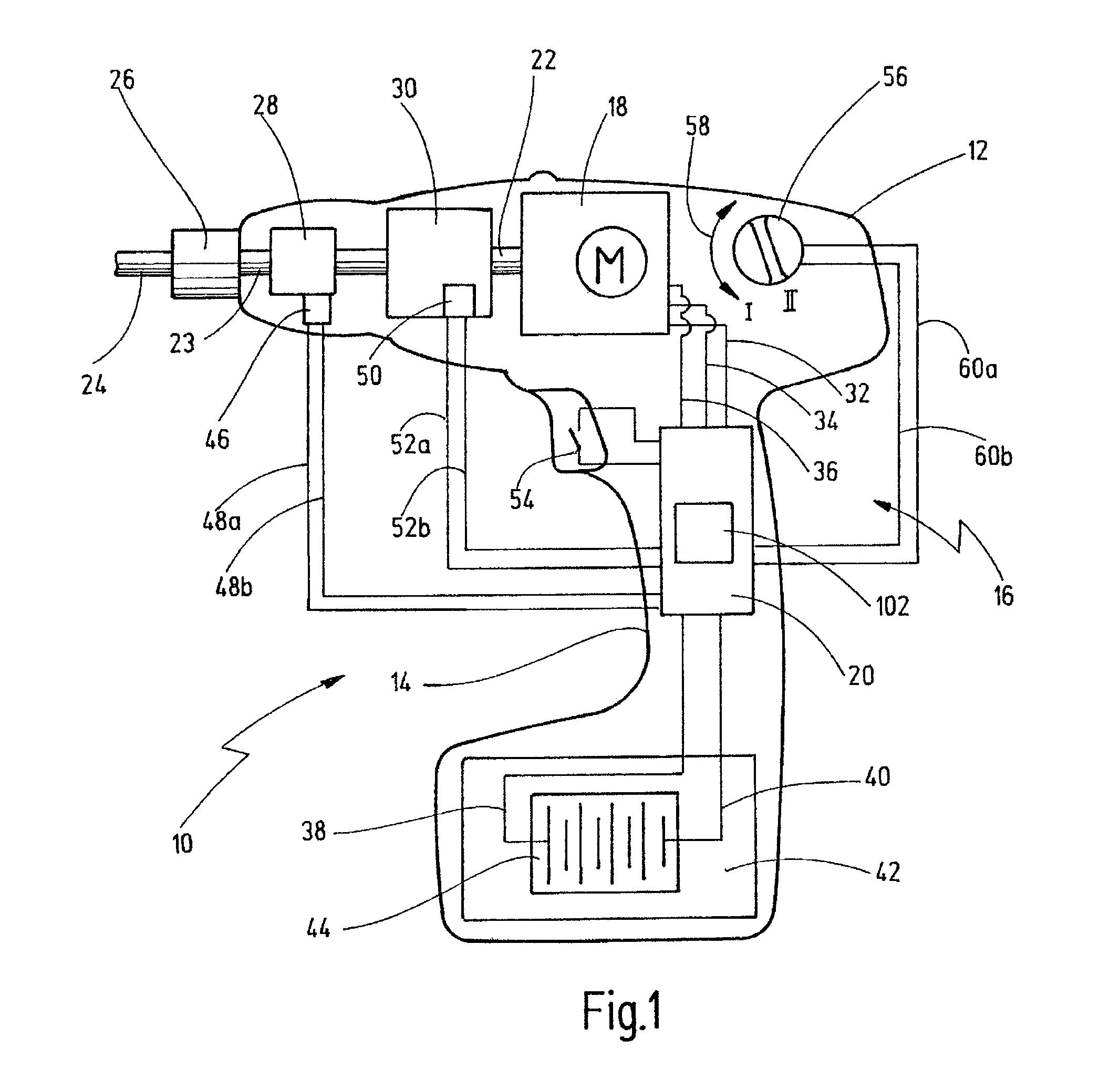
Electric Drive
InactiveUS20140009101A1Easy to useIncrease output torqueElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersElectricityElectric drive
An electric drive is disclosed, in particular for a power tool, including a rotor, a stator, and a first coil arrangement, which is designed to drive the rotor by a first rotating field, and including a first motor control arrangement, which is designed to supply the first coil arrangement with electric current in order to generate a first rotating field. The stator has a second coil arrangement for generating a second rotating field. The second coil arrangement can be actuated and energized separately from the first coil arrangement so as to actuate the second coil arrangement in an arbitrary commutation sequence.
Owner:C & E FEIN
Stator flux linkage calculation method based on vector transformation and signal filtering
ActiveCN105846748AFast dynamic responseFast convergenceField acceleration method controlDirect torque controlLow-pass filterBand-pass filter
The invention discloses a stator flux linkage calculation method based on vector transformation and signal filtering. An alternating current motor stator flux linkage voltage model is used to carry out amplitude and phase transformation on an input back electromotive force vector to directly acquire an original stator flux linkage vector. Through signal filtering and compensation, an anticipant stator flux linkage is acquired. Vector transformation schemes based on a programmable low pass filter (LPF) and a band pass filter (BPF) are respectively designed. According to the principle that calculation flux linkage amplitude is converged to a given flux linkage value as soon as possible, an optimized function is acquired. LPF and BPF advantages are combined to acquire the flux linkage calculation method of the optimal performance. Furthermore, a BPF algorithm is decomposed, so that the structure of the optimized flux linkage algorithm is simplified. The calculation quantity is reduced, and system resources are saved. According to the invention, the algorithm has little dependence on motor parameters, and has the advantages of wide application range and high portability; and the calculated flux linkage has the advantages of small distortion and high accuracy.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Fault-tolerant direct torque control method of series motor driving system having input lack of phase
ActiveCN106487308ARealize decoupling controlIncrease load capacityElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsPower inverterMotor drive
The invention relates to a fault-tolerant direct torque control method of a series motor driving system having an input lack of a phase. The fault-tolerant direct torque control method is particularly applied to a six-phase permanent-magnet synchronous motor of which power is supplied by a single inverter and which is connected in series with a three-phase permanent-magnet synchronous motor driving system, and aims to achieve decoupling control on instantaneous electromagnetic torques of two motors by using remaining five-phase inversion bridge when an input end of the dual-motor series driving system is lack of a phase, so that the reliability of the series driving system is improved.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
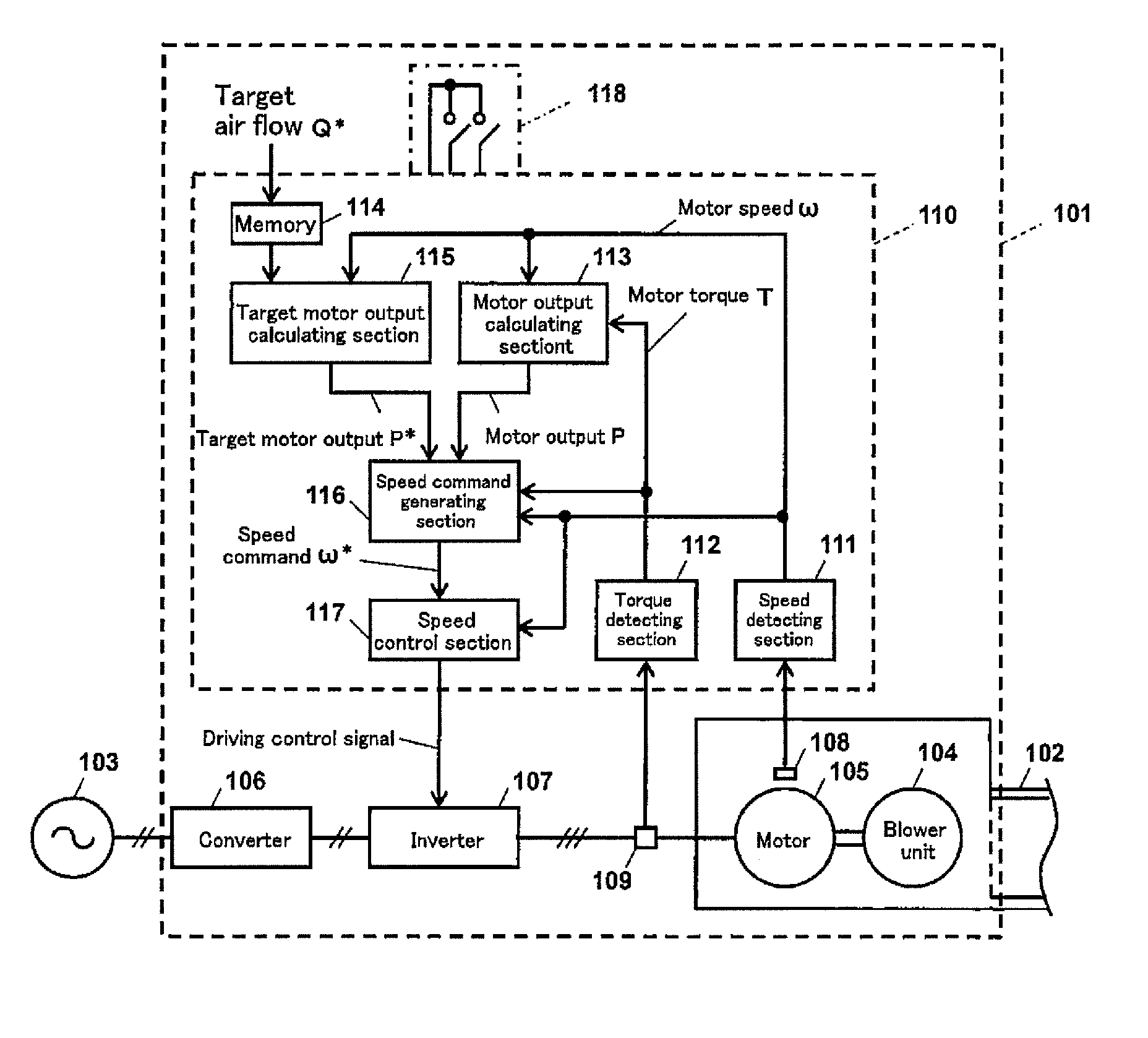
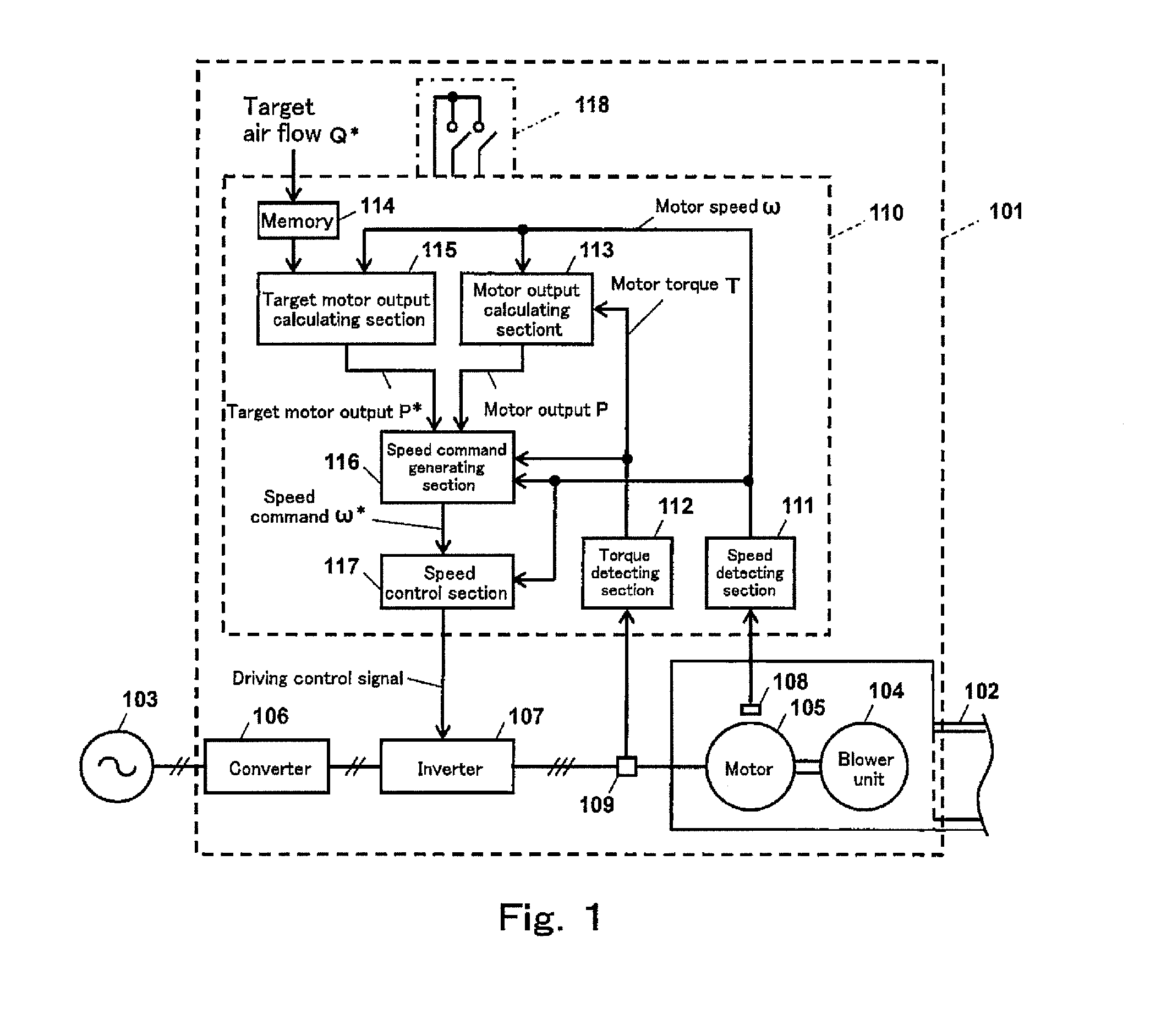
Motor control device, motor control method, and blower apparatus
ActiveUS20150233380A1Few experiment stepImprove accuracyElectric motor controlField acceleration method controlMotor speedMotor control
A motor control device which controls a motor for driving a blower unit, comprises: a target motor output calculating section which calculates a target motor output which causes an air flow of air supplied from the blower unit to coincide with a target air flow; and an operation command generating section which obtains the motor output of the motor, and generates a command for controlling a physical amount of the motor such that the motor output coincides with the target motor output based on a result of comparison between the motor output and the target motor output; and the target motor output calculating section is configured to calculate the target motor output as a product of a polynomial of variables derived by dividing the target air flow by the motor speed, and a cube of the motor speed.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Direct power and stator flux vector control of a generator for wind energy conversion system
ActiveUS20130009611A1Effective controlConvenient and efficient controlElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsWind energy conversionVariable speed wind turbine
A method for controlling a variable speed wind turbine generator is disclosed. The generator is connected to a power converter comprising switches. The generator comprises a stator and a set of terminals connected to the stator and to the switches of the power converter. The method comprises: determining a stator flux reference value corresponding to a generator power of a desired magnitude, determining an estimated stator flux value corresponding to an actual generator power, determining a difference between the determined stator flux reference value and the estimated stator flux value, and operating said switches in correspondence to the determined stator flux reference value and the estimated stator flux value to adapt at least one stator electrical quantity to obtain said desired generator power magnitude.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Wide speed regulation range and low torque ripple suppression method of brushless direct current motor
InactiveCN108574429ASuppression of torque rippleDirect torque control structure is simpleTorque ripple controlElectric motor controlPhase currentsControl manner
The invention relates to the wide speed regulation range and low torque ripple suppression method of a brushless direct current motor. A rotating-speed and torque double-closed-loop control mode is adopted. At a non-commutation moment, torque control is performed. At a commutation moment, overlapping commutation is performed and a current prediction module is added to carry out duty ratio calculation. When a Hall position signal jump sign commutation begins, a turn-off phase current decreases to zero and sign commutation is ended. At this time, an overlapping commutation method is adopted; andin order to reflect the current of a non-commutation phase on a direct current bus during a delayed turn-off period, the measure of using turn-off phase and non-commutation phase synchronization PWMmodulation to open phase constant open is adopted during a commutation period. Simultaneously, a non-commutation phase current value and a motor rotation speed at a current moment which is a k momentare sampled, according to the operation state of the motor at the current moment which is the k moment, a three-phase winding opposite electromotive force is acquired, a current prediction control module is used to calculate a prediction control law D so as to control inversion circuit output, and the torque ripple suppression of the brushless direct current motor under a wide speed regulation range is realized.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
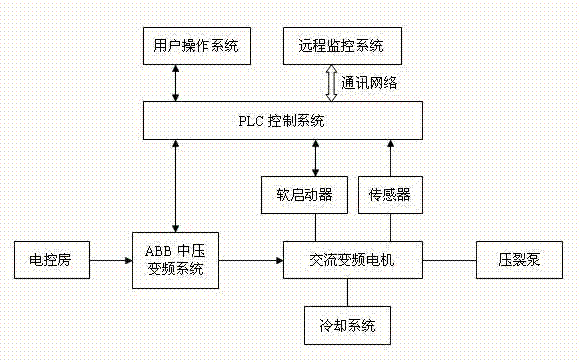
Medium-voltage frequency conversion system used for shale gas extraction
InactiveCN103095209AImprove work efficiencyReduce volumeField acceleration method controlDirect torque controlElectric machineFrequency conversion
The invention discloses a medium-voltage frequency conversion system used for shale gas extraction. The medium-voltage frequency conversion system comprises an electric control chamber, an ABB medium-voltage frequency conversion system, a motor system, a programmable logic controller (PLC) control system, a fracturing pump, a user operating system and a remote monitoring system. The motor system comprises an alternate current frequency conversion motor, a soft starter, a sensor and a cooling system. The soft starter, the sensor and the cooling system are respectively connected with the alternate current frequency conversion motor. Voltage output of the electric control chamber is connected with the ABB medium-voltage frequency conversion system, output of the medium-voltage frequency conversion system is connected with the alternate current frequency conversion motor, the alternate current frequency conversion motor directly drives the fracturing pump, data output of the sensor is connected with the PLC control system, and the PLC control system is also respectively connected with the ABB medium-voltage frequency conversion system, the soft starter and the user operating system. According to the medium-voltage frequency conversion system, the motor directly drives the fracturing pump to replace a traditional mechanical transmission line, work efficiency of a unit is improved, the size and the weight of the unit are reduced, and manufacturing cost is reduced.
Owner:SICHUAN HONGHUA ELECTRIC
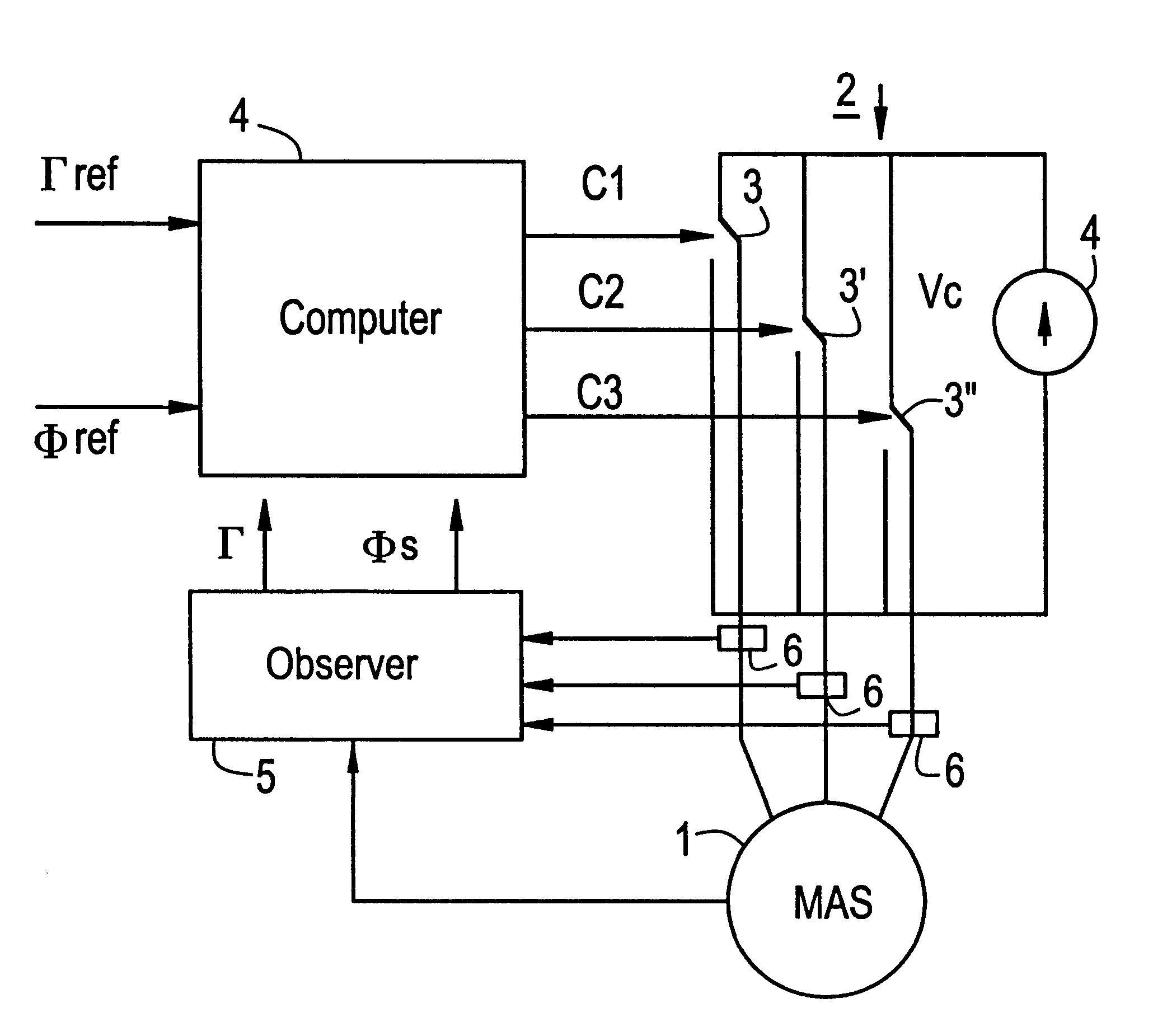
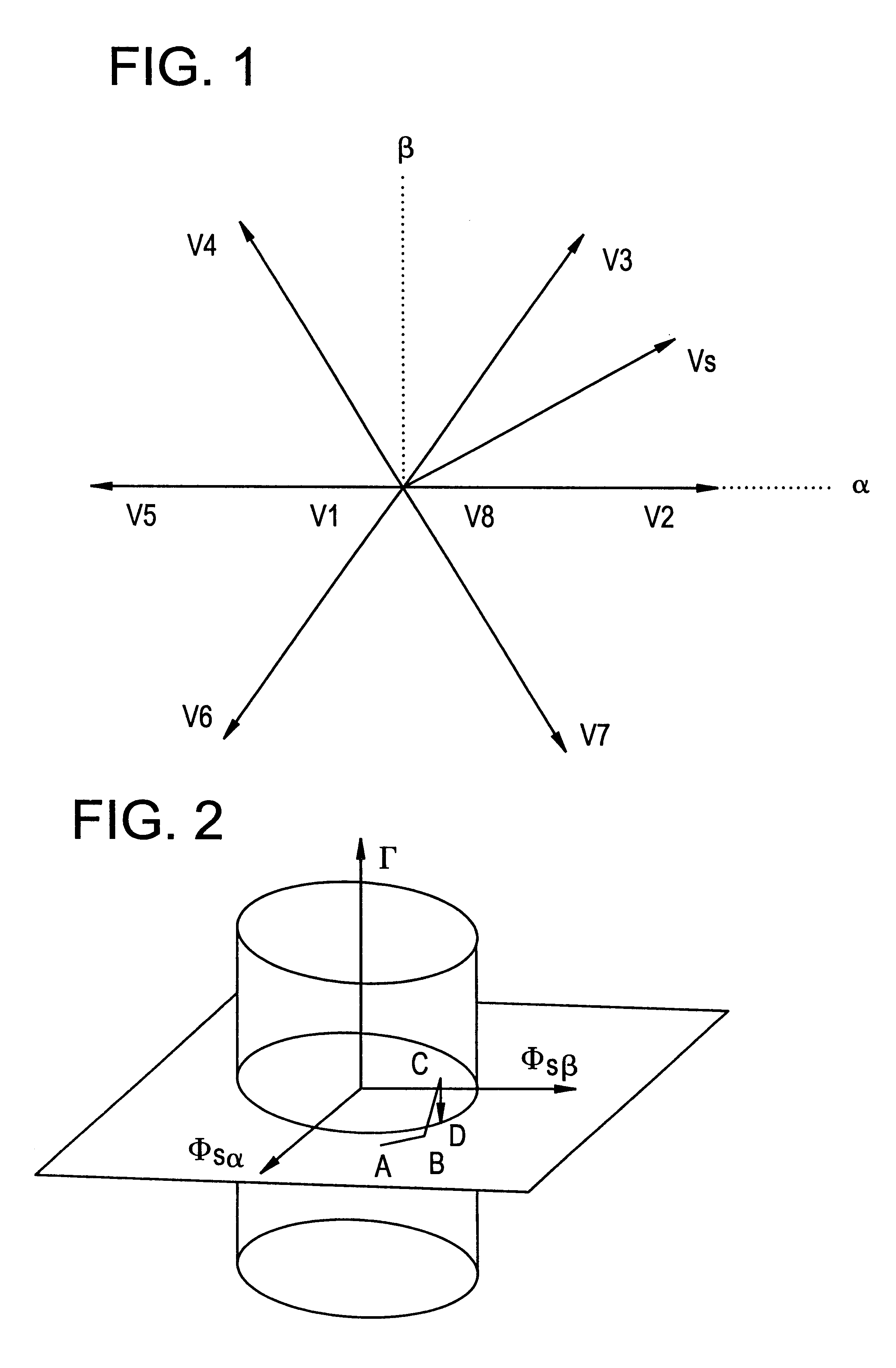
Method of controlling a rotary electrical machine, a servo-control system for implementing the method, and a rotary machine fitted with such a system
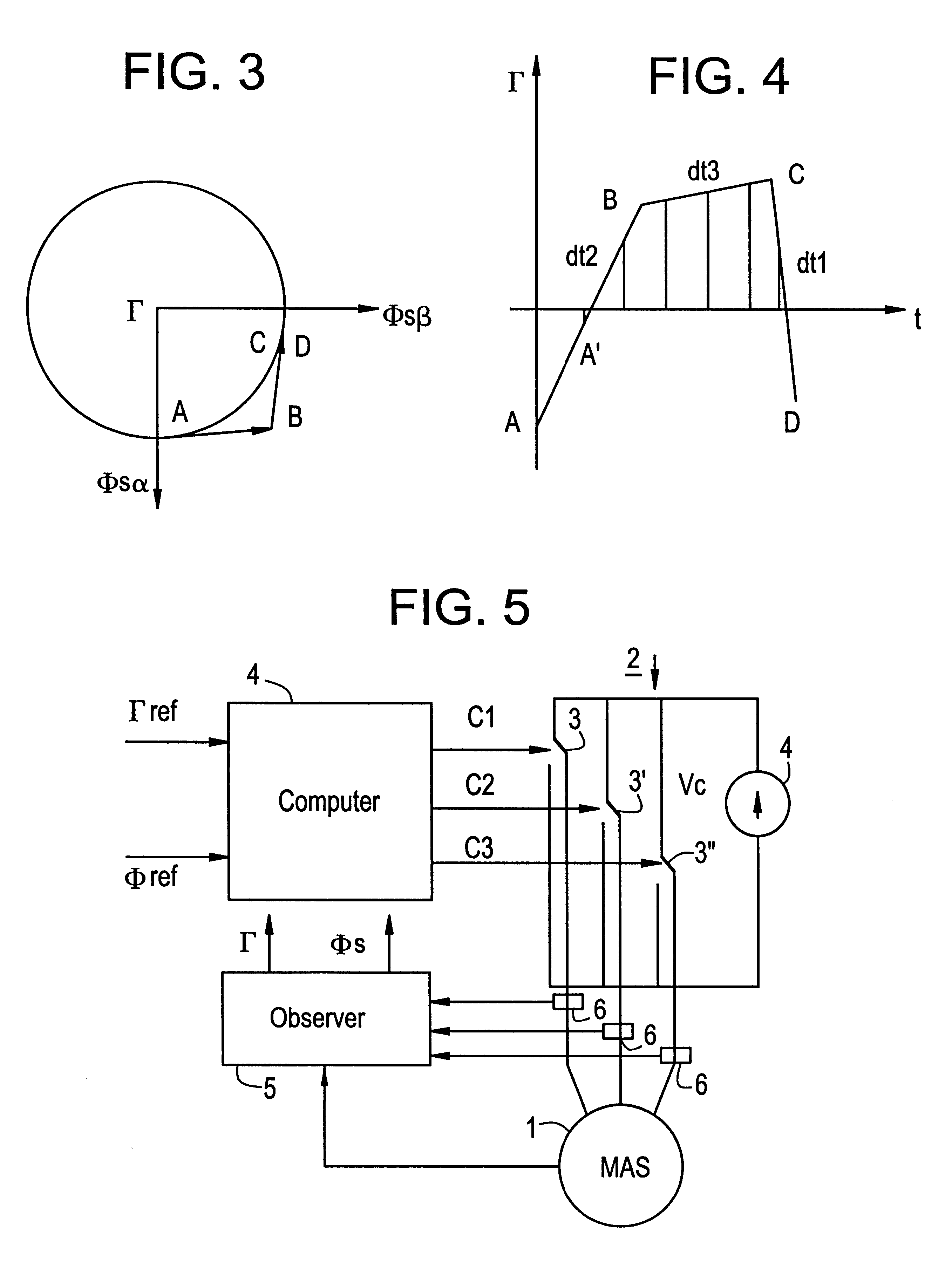
InactiveUS6198248B1Minimizing torque impulseDC motor speed/torque controlElectric motor controlElectric machineControl theory
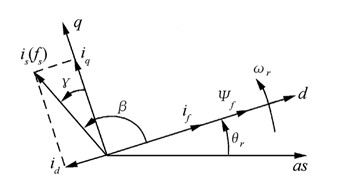
A method of controlling the torque of a rotary machine powered by means of an inverter and servo-controlled by a system having sensors, an observer, and a computer which delivers controls to the switches of the inverter on the basis of values supplied to the observer by the sensors, in the form of sequences of three vectors to bring the torque Γ and the stator flux ΦS of the machine towards reference values for Γref and ΦSref. The measurement sampling period is selected to be equal to the sequence period DTML which corresponds to half the switching period of the inverter. The characteristics of the vectors for each sequence are obtained by solving the following system of equations:in which dΓ / dta and dΓ / dtp are variations over time in torque respectively when an active vector Va or a passive vector Vp is applied, Γn being the present torque, and ta and tp are the respective times during which the vectors are applied.
Owner:ALSTOM ENTREPRISE
Method and system for controlling motor torque
ActiveUS7042181B2Single motor speed/torque controlField acceleration method controlControl systemInput impedance
A method and system for controlling motor torque provides improved responsiveness and reliability in motor control applications. The motor control system includes a power converter, a voltage detector for detecting the converter input voltage and a control circuit for controlling the converter. The control circuit includes a torque command limit value generator and a torque command limiter for limiting a torque command value. The system may also include a torque command coefficient generator for generating a coefficient corresponding to an input current of the power converter, and a multiplier for calculating a final torque command value for the motor by multiplying together the torque command value and the torque command coefficient. The torque command limit and coefficient values may be determined from the converter input voltage, calculated or detected converter input current and calculated input impedance between a power supply and the converter.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method for controlling doubly-fed machine
ActiveUS7023160B2Guaranteed uptimeGenerator control circuitsSynchronous motors startersEngineeringDoubly fed machine
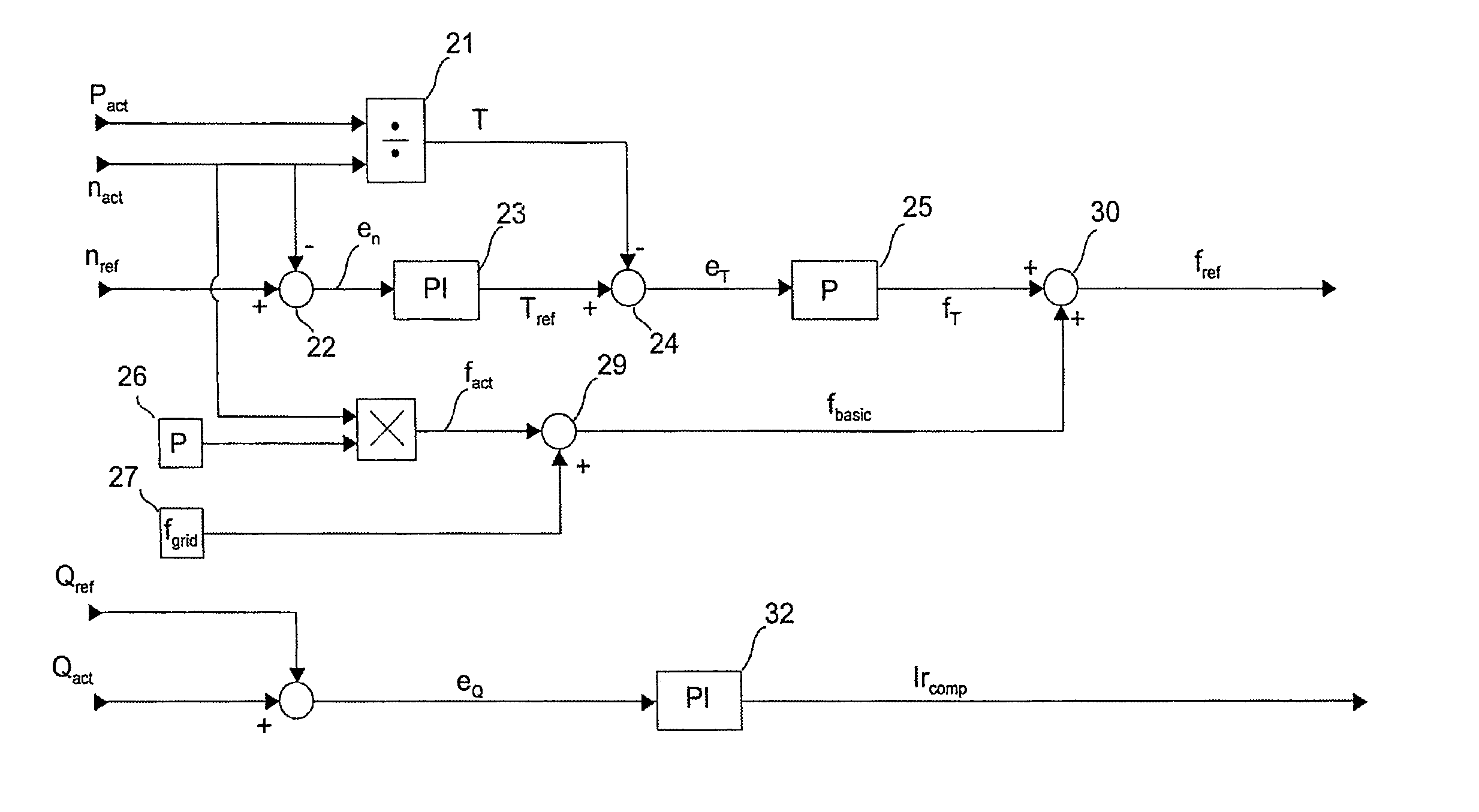
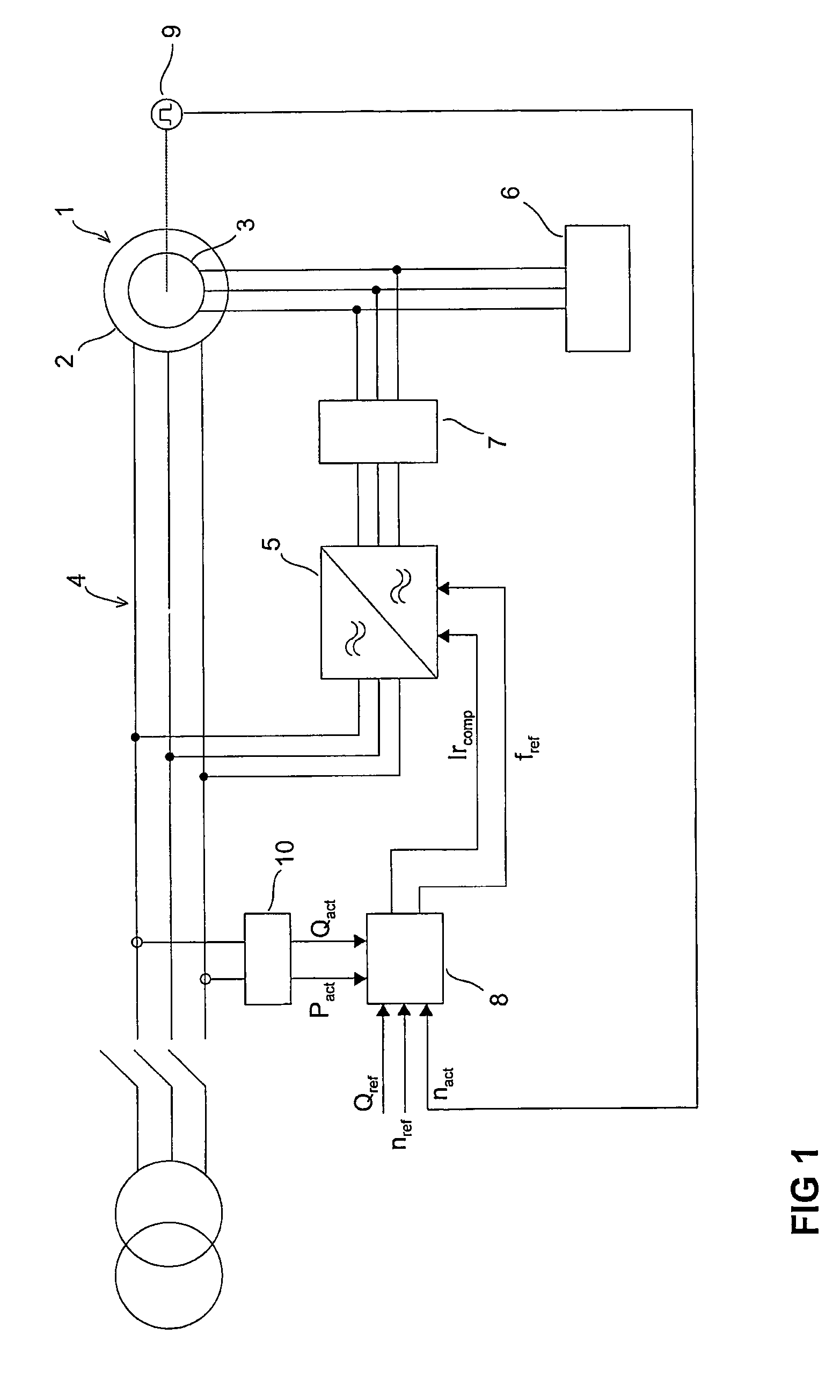
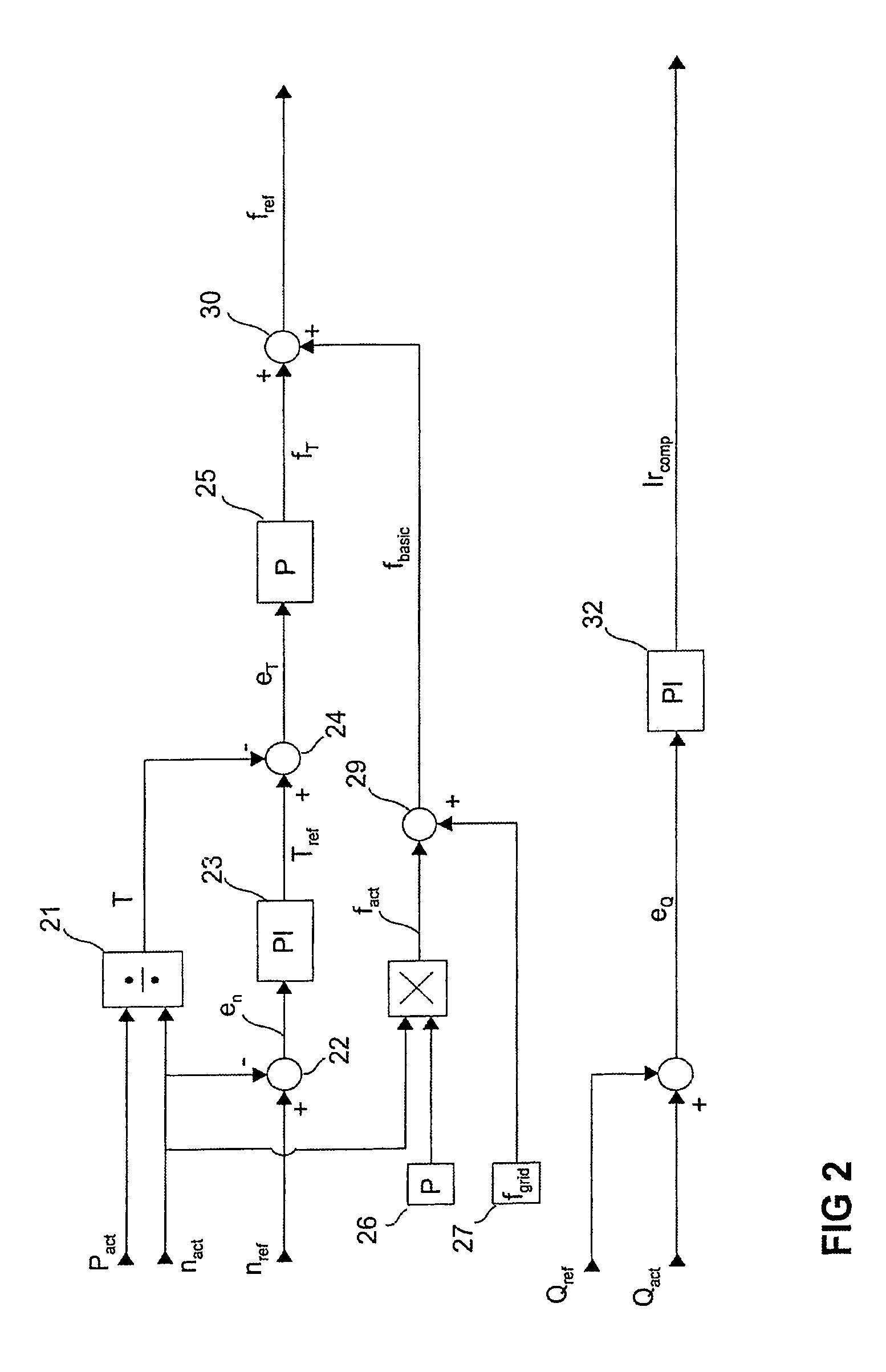
A method for operating a doubly-fed machine by determining its rotational speed (nact), forming a rotational speed reference (nref), measuring network voltage and current, and calculating network active power (Pact) and reactive power (Qact). Thereafter, calculating shaft torque (T) based on active power (Pact) and rotating speed (nact), forming a frequency reference (Fref) for the inverter based on machine rotating speed (nact), rotating speed reference (nref), shaft torque (T), and the known pole pair number and network frequency, forming a reactive power reference (Qref) for the machine. Forming an Ir compensation reference (IRref) for the inverter on the basis of the reactive reference (Qref) and the reactive power (Qact), and controlling the inverter to produce rotor voltage based on frequency reference (Fref) and the IR compensation reference
Owner:ABB OY
Model prediction-direct torque control method for permanent magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN109391202ASuppress interferenceAvoid upper and lower limit pulsationElectric motor controlField acceleration method controlMulti inputHysteresis
A model prediction-direct torque control method for a permanent magnet synchronous motor belongs to the technical field of control. The object of the invention is to complete the accurate estimation of torque and flux linkage in a system by using a reduced-order observer, and then to design the model prediction-direct torque control method for a permanent magnet synchronous motor of a hub motor drive system controller through a model prediction control algorithm. The steps include: selecting motor torque and flux linkage as state variables, selecting an objective function enabling the minimumerror between a predicted value and an expected value of torque and flux linkage, and obtaining three-phase voltage for controlling the motor to finish control over the PMSM. The model prediction control algorithm applied by the invention can effectively deal with the multi-input multi-output and multi-constraint optimization control problems, replaces a hysteresis loop comparator and a switch selection module of conventional direct torque control, avoids the upper and lower limit pulsation of the hysteresis loop and unnecessary switching losses, and effectively suppresses the torque pulsationof the drive motor.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Fuzzy fractional order PID switched reluctance motor torque control method and system
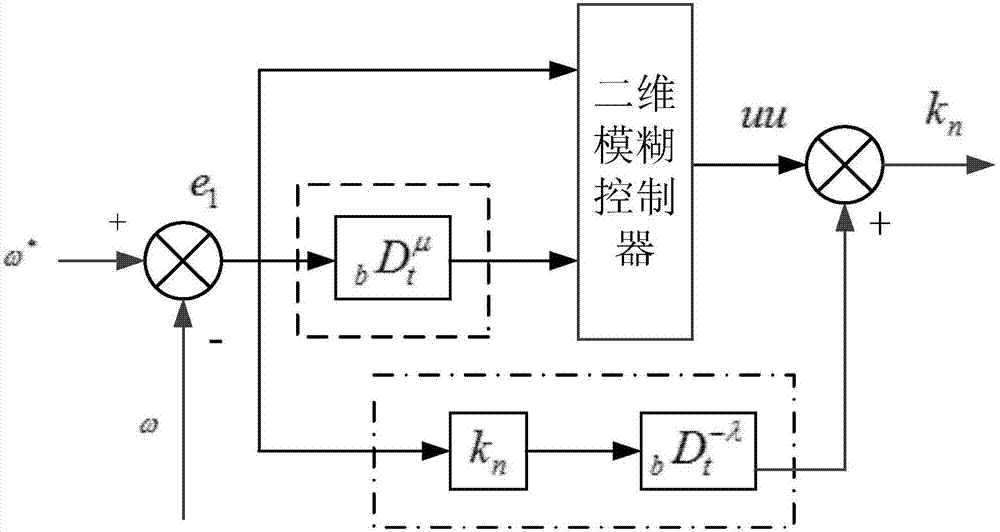
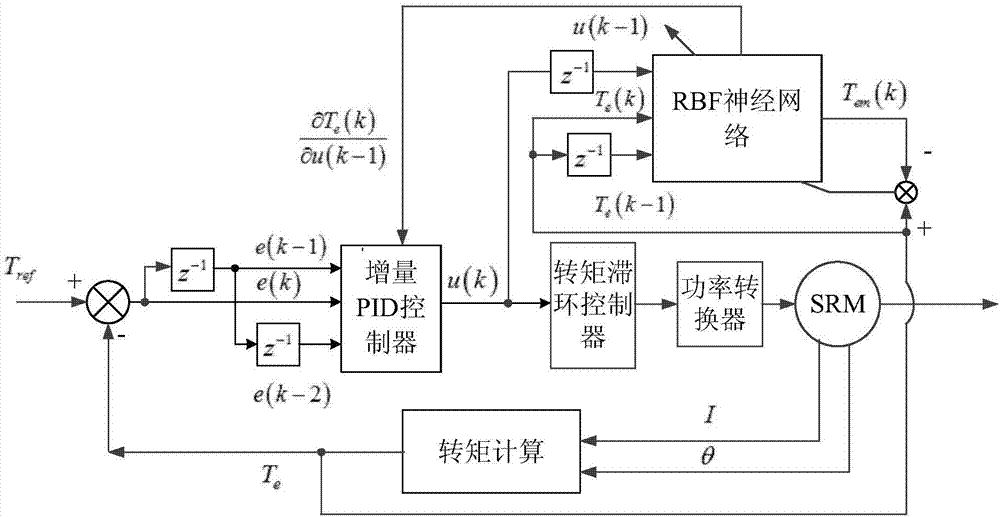
ActiveCN107171612ASolve the disadvantages of being susceptible to high-frequency interferenceHigh steady state accuracyElectric motor controlField acceleration method controlProportional integral differentialControl engineering
The present invention discloses a fuzzy fractional order PID (Proportional Integral Differential) switched reluctance motor torque control method and system. A fuzzy fractional order PID controller is arranged at an outer ring, fractional differential and fractional integration are introduced in a two-dimensional fuzzy controller; and the fractional integration is employed to solve the defect that first-order pure differential is easy to be interfered by high frequency and improve the stable state precision of the system. A PID torque controller arranged at an inner ring comprises an increment PID controller, an inner ring torque hysteresis controller and a RBF (Radio Basis Function) neural network; the parameters of the increment PID controller are obtained through modeling of the RBF neural network; the modeling of the RBF neural network is and learned and completed through the difference of the output of the RBF neural network and the torque of an SRM (Switched Reluctance Motor); and the output of the increment PID controller is taken as the input signals of the inner ring toque hysteresis controller. The fuzzy fractional order PID controller arranged at the outer ring and the PID torque controller arranged at the inner ring are mutually cooperated to directly control the torque of the SRM so as to effectively reduce the torque pulsation, and the dynamic performance is good, the adaptability is high, and the realization is easy.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Control method for reducing torque ripple of doubly salient electro-magnetic motor
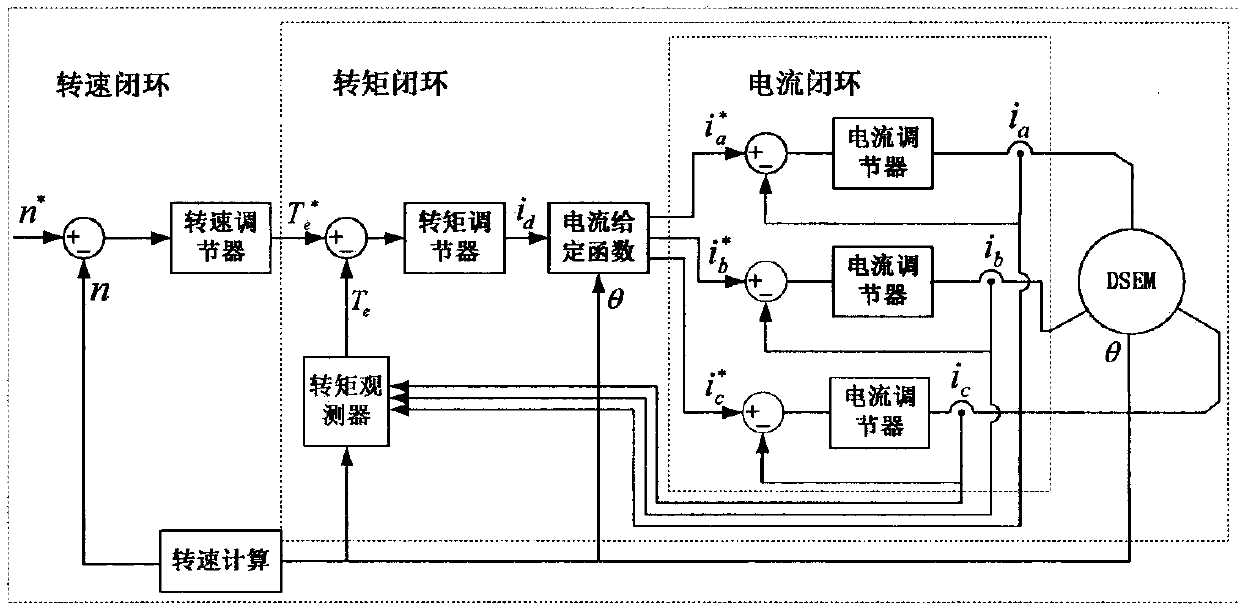
ActiveCN110829939AAchieve direct controlReduce torque rippleField acceleration method controlDirect torque controlLoop controlElectric machine
The invention discloses a control method for reducing torque ripple of a doubly salient electro-magnetic motor, and belongs to the technical field of motor control. With torque ripple minimization being taken as a target, and based on a current given function designed according to the torque generation principle and mutual inductance characteristics of the doubly salient electro-magnetic motor, the method can calculate a current given value required by each phase according to the output of a torque regulator and the position of a rotor at the moment. The output of the current given function serves as set values of three-phase current respectively, so that the problem that the three-phase current is given by the same current and cannot be controlled at the same time when the three phases are conducted at the same time in the phase change stage since the doubly salient electro-magnetic motor adopts traditional torque current closed-loop control is solved; and torque is generated by fullyutilizing mutual inductance change of the three phases, so that the torque generation efficiency of three-phase current is improved while torque pulsation is reduced. The method is suitable for optimizing the torque performance of the electro-magnetic doubly salient motor, and the efficiency of the doubly salient electro-magnetic motor during electric operation is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Intelligent reconstruction flexible motor driven controller
ActiveCN102497151AOvercome the shortcomings that robustness cannot meet the requirementsElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsDigital signal processingMotor drive
The invention discloses an intelligent reconstruction flexible motor driven controller which comprises a digital signal processing module, a CPLD module, an intelligent power module, a sensor module and a host computer. The invention is characterized in that: output current of the digital signal processing module outputs a PWM wave through the CPLD module; output of the CPLD module is connected with the intelligent power module through base electrode driving; the sensor module acquires feedback current, load torque and moment of inertia of a target motor and outputs the feedback current, the load torque and the moment of inertia to the digital signal processing module; the digital signal processing module is connected with the host computer through a communication line; the host computer receives the feedback current, the load torque and the moment of inertia of the digital signal processing module, employs a flexible control method, and sends a corresponding control strategy to the digital signal processing module. According to a driver, the corresponding control strategy is adjusted according to the change of load, and control precision and system stability are raised.
Owner:溧阳常大技术转移中心有限公司
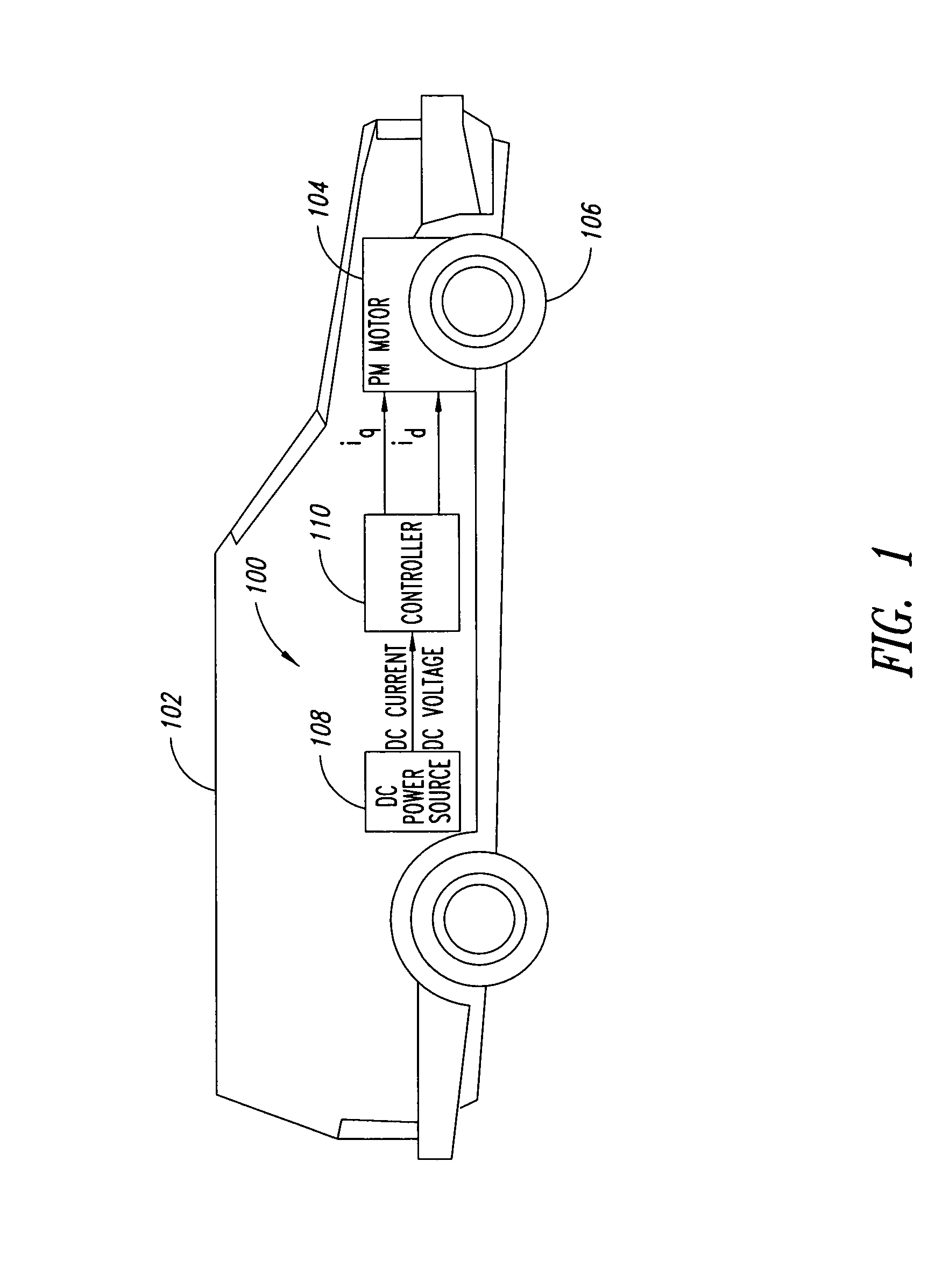
Electric motor torque control
ActiveUS20140070738A1Hybrid vehiclesSynchronous motors startersPermanent magnet synchronous motorEngineering
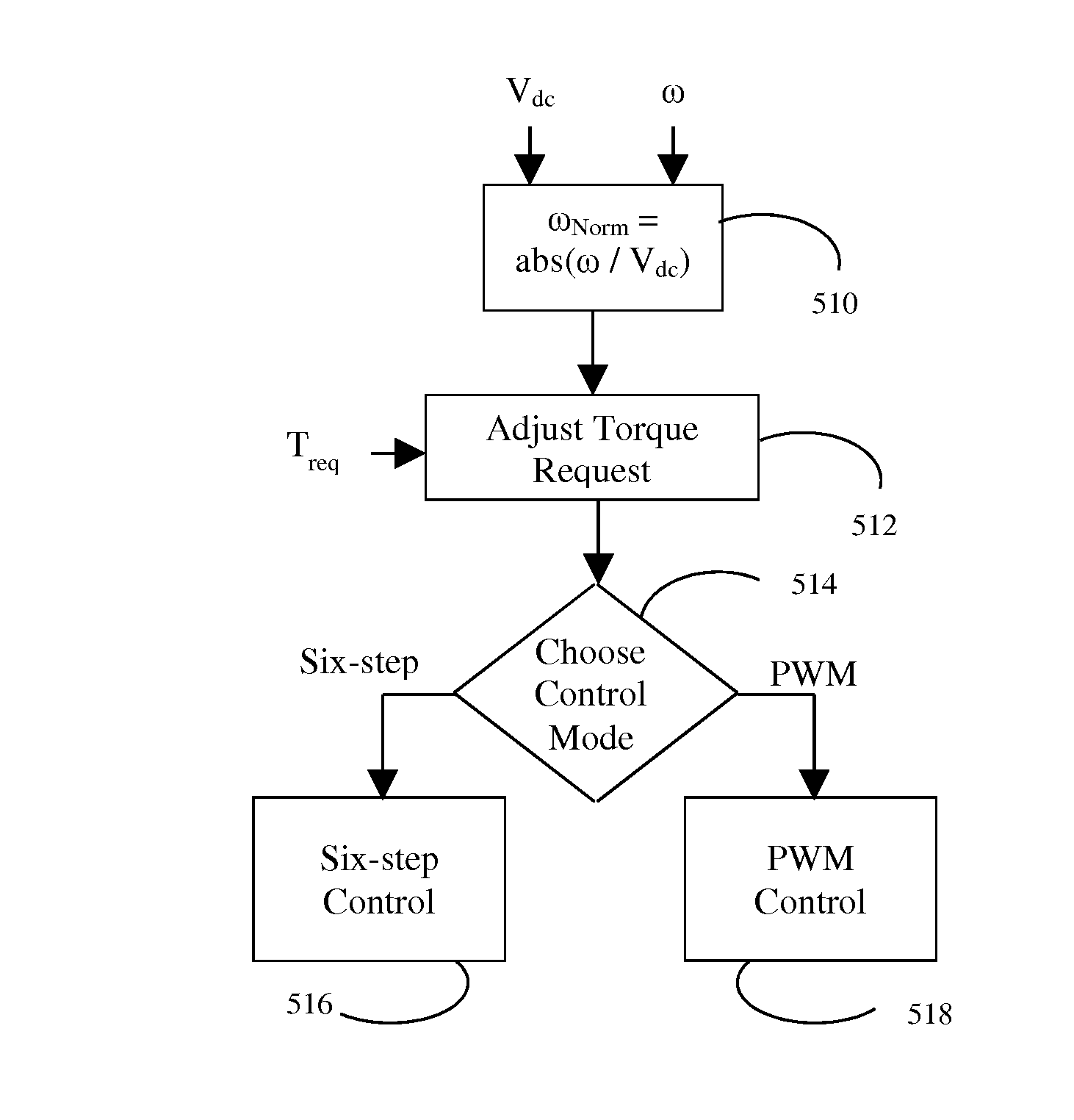
A vehicle includes one or more inverter-fed electric machines such as permanent magnet synchronous motors. In response to a torque request, a controller issues commands to an inverter calculated to cause the motor to produce the requested torque. A method of operating the inverter may determine the commands based on the ratio of rotor speed to inverter input voltage, reducing the approximation error associated with multi-dimensional lookup tables. When the speed and voltage vary while maintaining a constant ratio and constant torque request, the issued commands produce a winding current in the electrical machine with constant direct and quadrature components.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Motor control device
ActiveCN101507097AAvoid damageIncrease credibilityTorque ripple controlElectric motor controlCapacitanceLoad torque
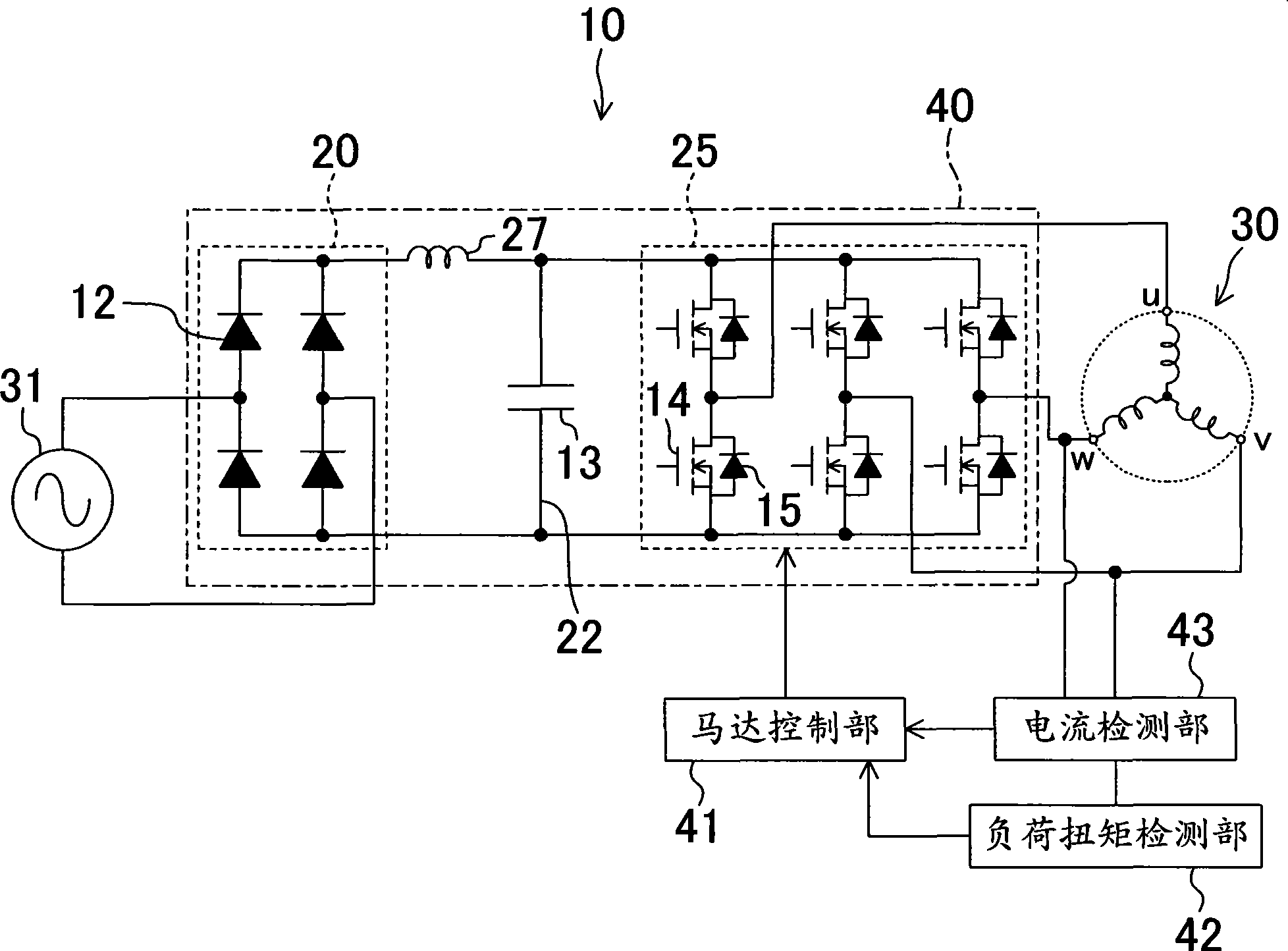
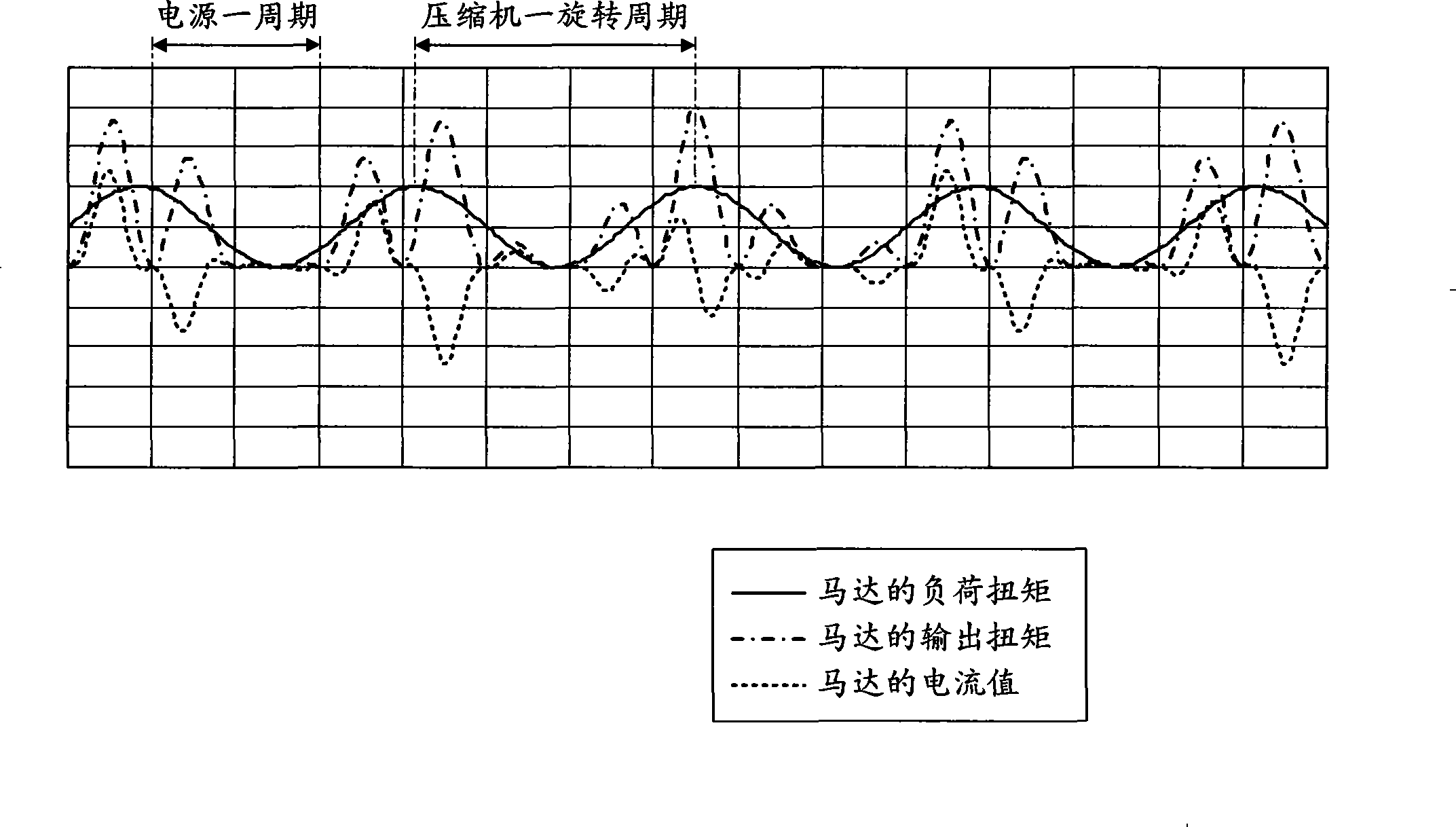
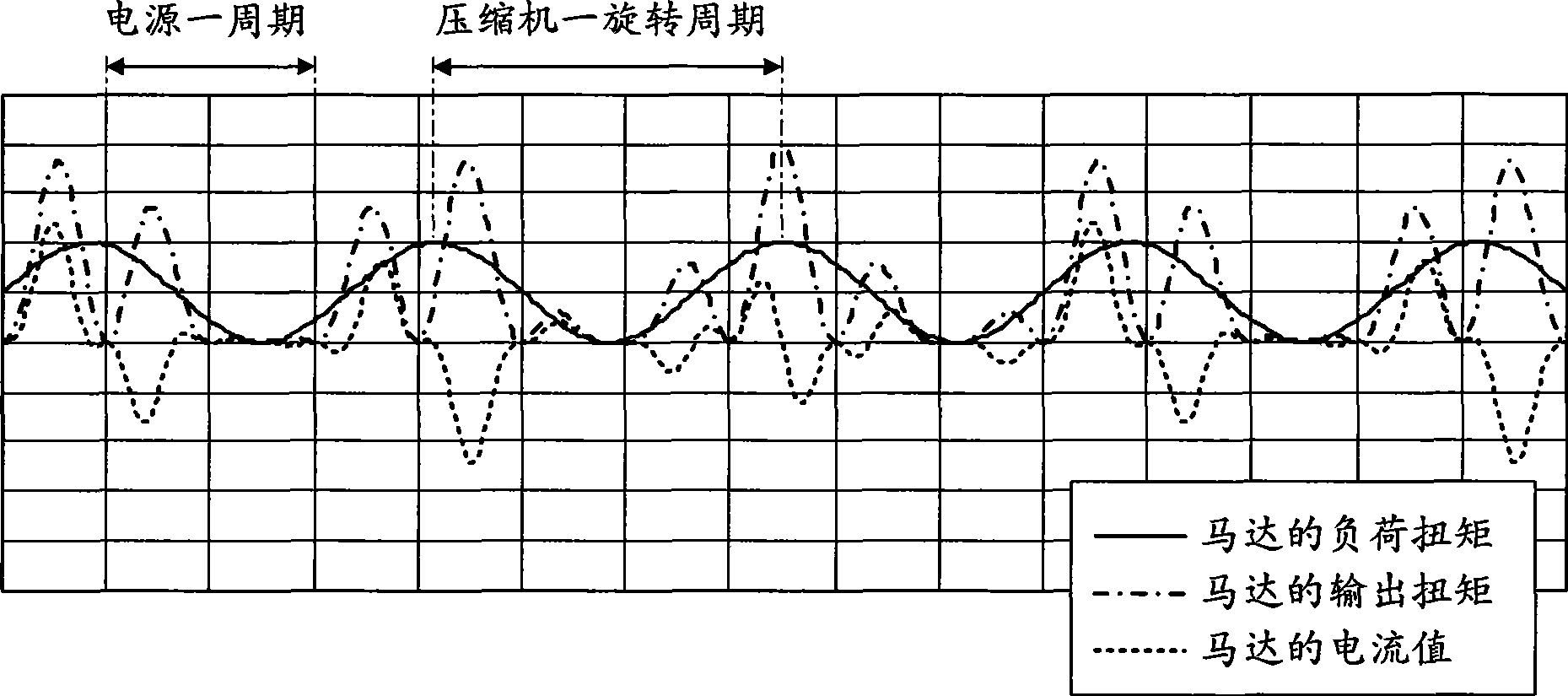
A motor control device (10) includes: a power conversion unit (40) having a rectification circuit (20) for rectifying AC voltage from an AC power supply (31), a capacitor circuit (22) for receiving an output from the rectification circuit (20) and outputting a pulsating rectified voltage from both ends of the capacitor (13), and an inverter circuit (25) for receiving the rectified voltage and outputting AC current to a motor (30); and a motor control unit (41) for controlling the inverter circuit (25) so as to control the motor (30). The motor control unit (41) performs torque control operation to vary the output torque of the motor (30) inaccordance with the load torque of the motor (30).
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com