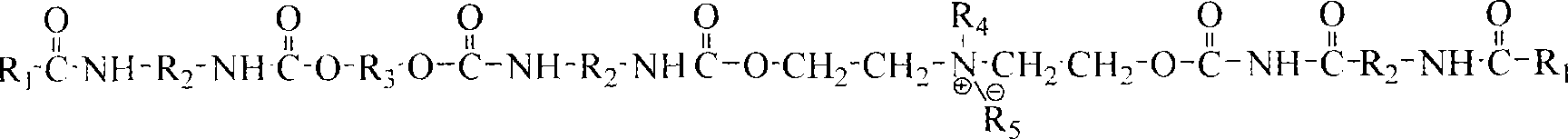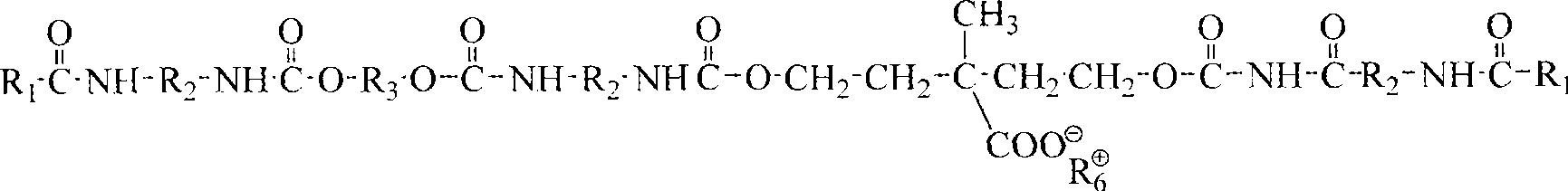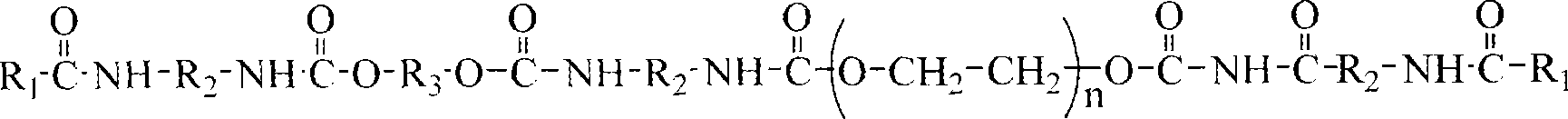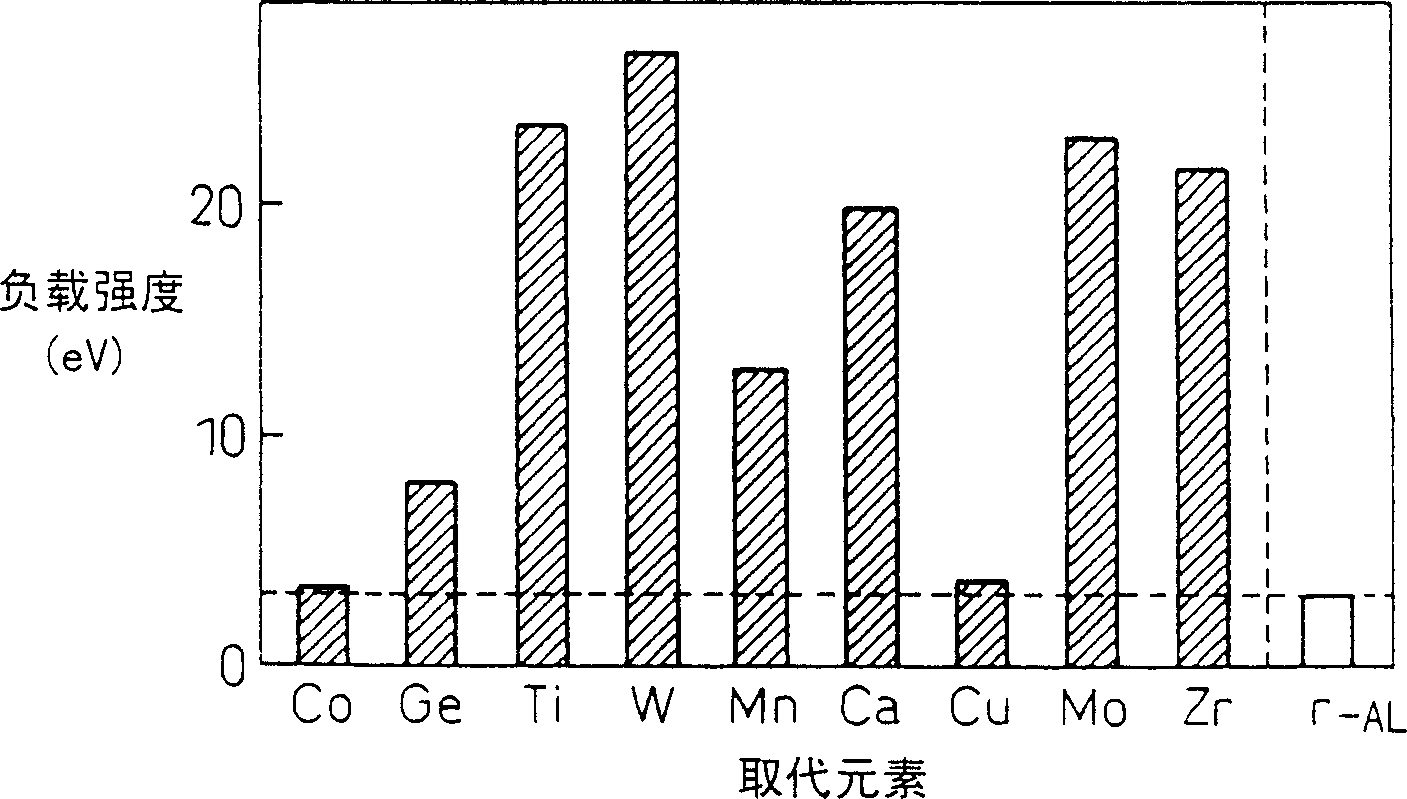Patents
Literature
57 results about "Functional Method" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An indirect treatment approach that involves finding the dynamic balance point and one of the following: applying an indirect guiding force, holding the position or adding compression to exaggerate position and allow for spontaneous readjustment. The osteopathic practitioner guides the manipulative procedure while the dysfunctional area is being palpated in order to obtain a continuous feedback of the physiologic response to induced motion. The osteopathic practitioner guides the dysfunctional part so as to create a decreasing sense of tissue resistance (increased compliance).
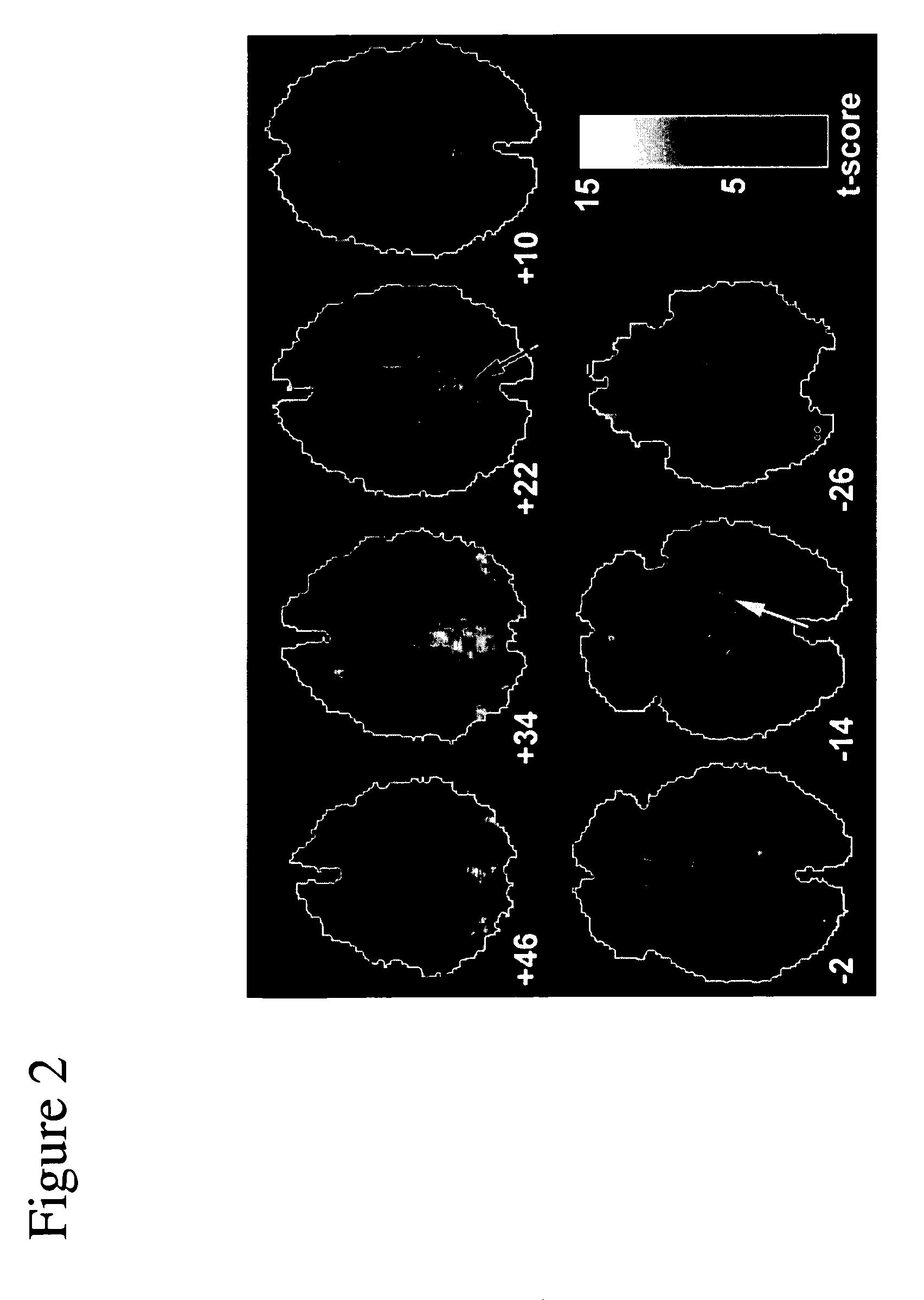
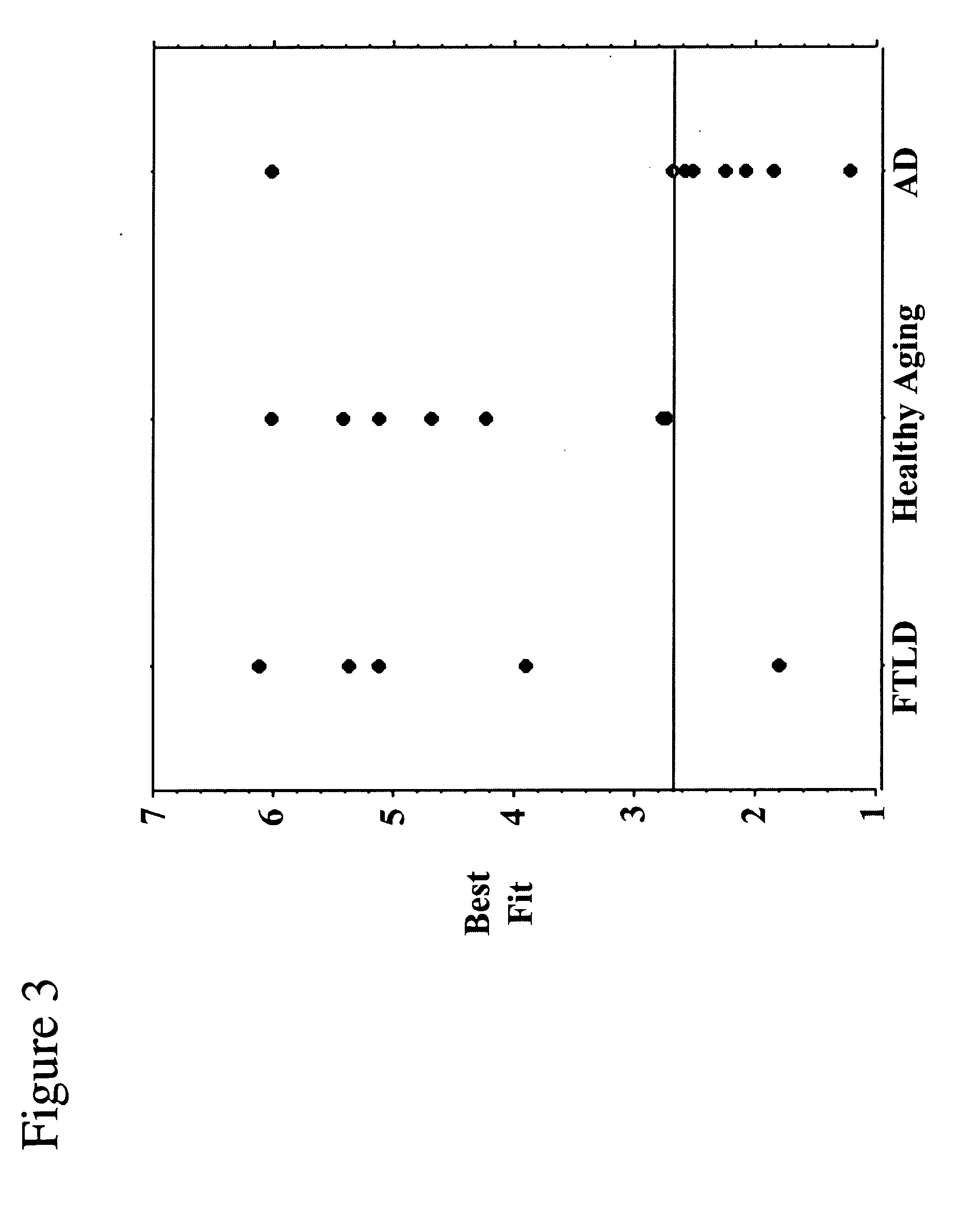
Evaluation of Alzheimer's disease using an independent component analysis of an individual's resting-state functional MRI
InactiveUS20050215884A1More automatedMore objectiveDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDiseaseFunctional methods
A clinically valuable method is provided for evaluating the onset or progression of Alzheimer's disease using a non-invasive biomarker obtained from an independent component analysis (ICA) of an individual's resting state functional MRI. The method is relatively more automated and objective than previous methods and exploits dysfunctional connectivity across an entire network of brain regions in Alzheimer's disease. It eliminates the need for investigator's intervention as much as possible and is more robust than structural and functional methods targeting the hippocampus.
Owner:GREICIUS MICHAEL D +2
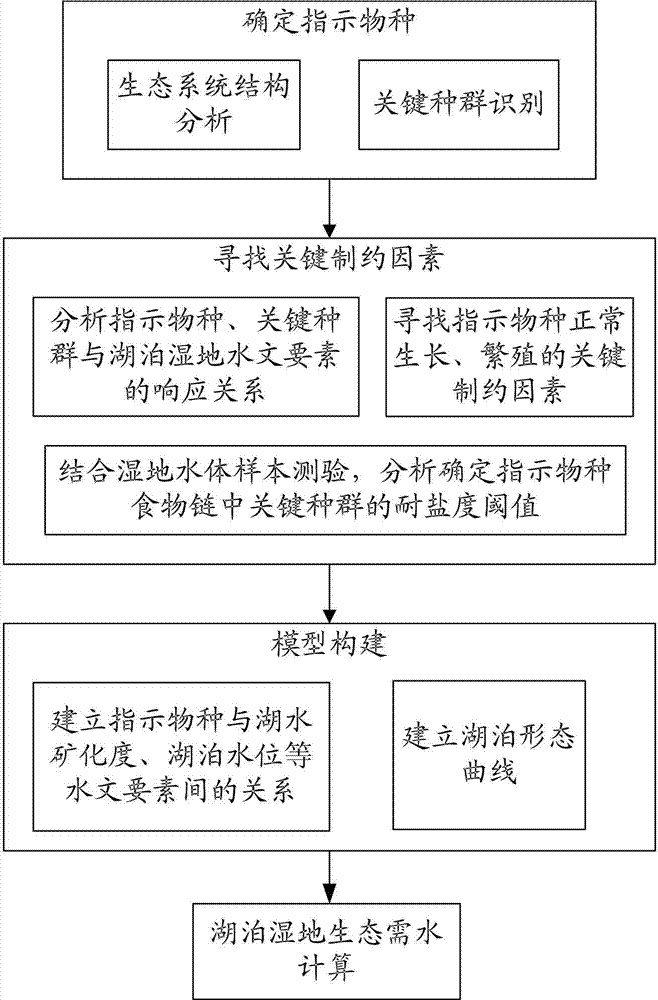
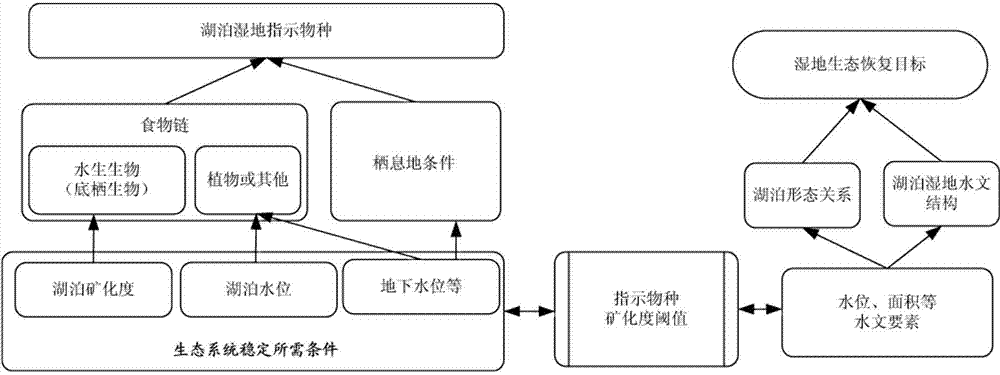
Quantitative calculation method for lake wetland ecological water requirement in arid region
The invention relates to a quantitative calculation method for lake wetland ecological water requirement in an arid region. The method includes determining indicator species, searching for key restraining factors, building a model and calculating the lake wetland ecological water requirement. Compared with a water quantity balancing method, a curve relevant method, a minimum water level method and the like in the prior art, the method achieves the effect that structure and stability of an ecological system in the arid region are comprehensively considered. Compared with a functional method, the method achieves the effect that hydrological condition required by the indicator species around the lake wetland for growth and propagation is considered and is suitable for the lake wetland in the arid region. The method can be directly used for determining an ecological restoring target of the lake wetland in the arid region, guiding the implementation of wetland ecological water supplementation measures and has an important theoretical and practical meaning for basin water resource planning and configuration.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
Waterborne ultraviolet-heat dual curing coating composite and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101418147AImprove adhesionHigh hardnessPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsFunctional methodsSpray coating
The invention provides a water-dilutable ultraviolet-thermal double curing coating composition and a preparation method thereof. The components of the double curing coating composition in percentage by weight are: 3.5 to 60 percent of water-dilutable urethane acrylate oligomer, 17 to 47 percent of water-dilutable polyurethane polylol, 20 to 49 percent of water-dilutable curing agent, 0.4 to 9 percent of light trigger and 0.4 to 1.6 percent of auxiliary agent. The preparation method for the double curing coating is simple and does not require complex equipment; and the working life of the coating is long and reaches as long as 9 hours; the coating obtained can be used for preparing a coating by the functional methods of spray coating, brush coating and roller coating; ultraviolet curing can be completed within a short period of time between 10 and 30 seconds, and thermal curing can be completed within a period of time between 1 and 3 minutes at a temperature of between 40 and 60 DEG C; a paint film obtained after double curing has good leveling property, flexibility, shock resistance and adhesion and high hardness; and the coating does not contain an organic solvent and a reactive diluent, and is an environment-friendly coating.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
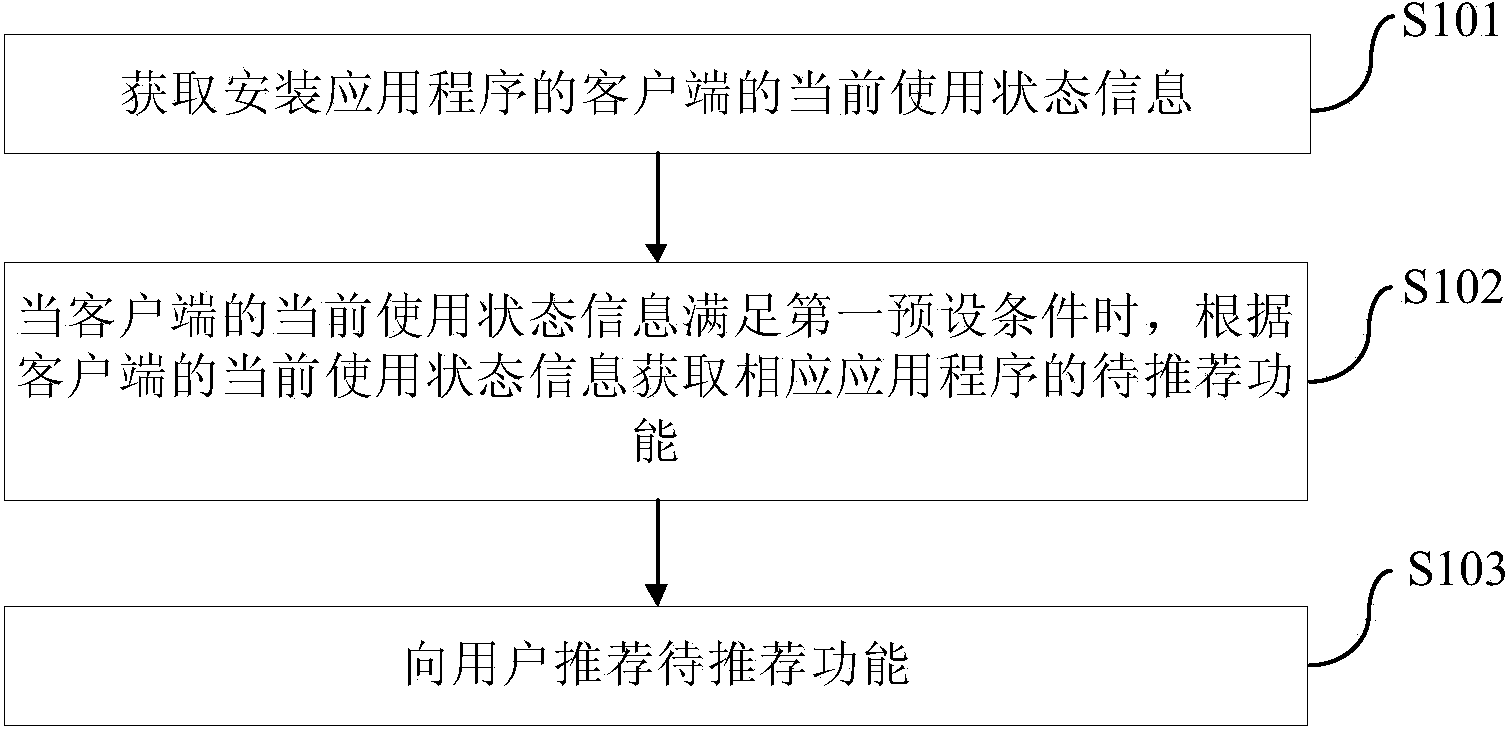
Functional guide method and device of application program and client terminal
InactiveCN103761104AMeet usage habitsImprove experienceSpecific program execution arrangementsRelevant informationClient-side
The invention provides a functional guide method and device of an application program and a client terminal. The method comprises the following steps of obtaining current use state information of a mobile terminal for mounting the application program; when the current use state information of the mobile terminal meets a first preset condition, obtaining a function to be recommended of the corresponding application program according to the current use state information of the mobile terminal; and recommending the function to be recommended to a user. The method can timely provide current required function guide for the user according to the relevant information of the client terminal, conform to user operation habits better and effectively improve user experience.
Owner:BEIJING CHEETAH MOBILE TECH CO LTD
Method for preparing counter electrode of dye-sensitized solar cell
InactiveCN101976608AImprove conductivityImprove thermal conductivityLight-sensitive devicesSolid-state devicesCarbon filmFunctional methods
The invention discloses a method for preparing a counter electrode of a dye-sensitized solar cell, which comprises the following steps of: 1) preparing water-soluble single-layer or multi-layer graphene from graphite through a chemical oxidation method, or preparing organically water-soluble single-layer or multi-layer graphene from the graphite through an organic functional method; 2) preparing the water-soluble or organically water-soluble single-layer or multi-layer graphene onto the surface of a glass substrate for molding, and airing to prepare a thin film of the single-layer or multi-layer graphene; and 3) reducing the glass substrate with the thin film of the single-layer or multi-layer graphene by using a reducing agent, or calcining under the protection of nitrogen or argon to obtain the counter electrode of the dye-sensitized solar cell, which is coated with the single-layer or multi-layer grapheme film on the surface of the glass substrate. Electrons generated by a dye-sensitized TiO2 thin-film electrode are transferred to electrolyte to finish a cycle, so the optical energy is converted into electric energy and the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the cell is improved.
Owner:IRICO
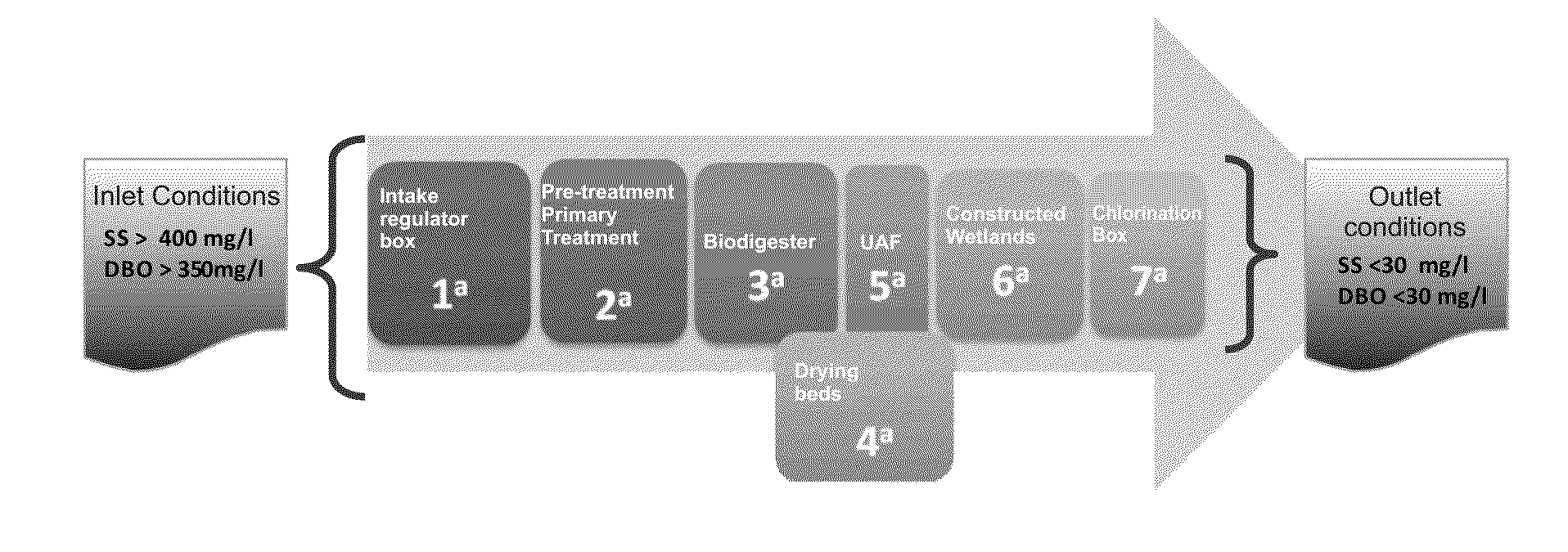
System and multi-functional method for treating wastewater
InactiveUS20160207808A1Liquid degasificationBiological treatment apparatusConstructed wetlandFunctional methods
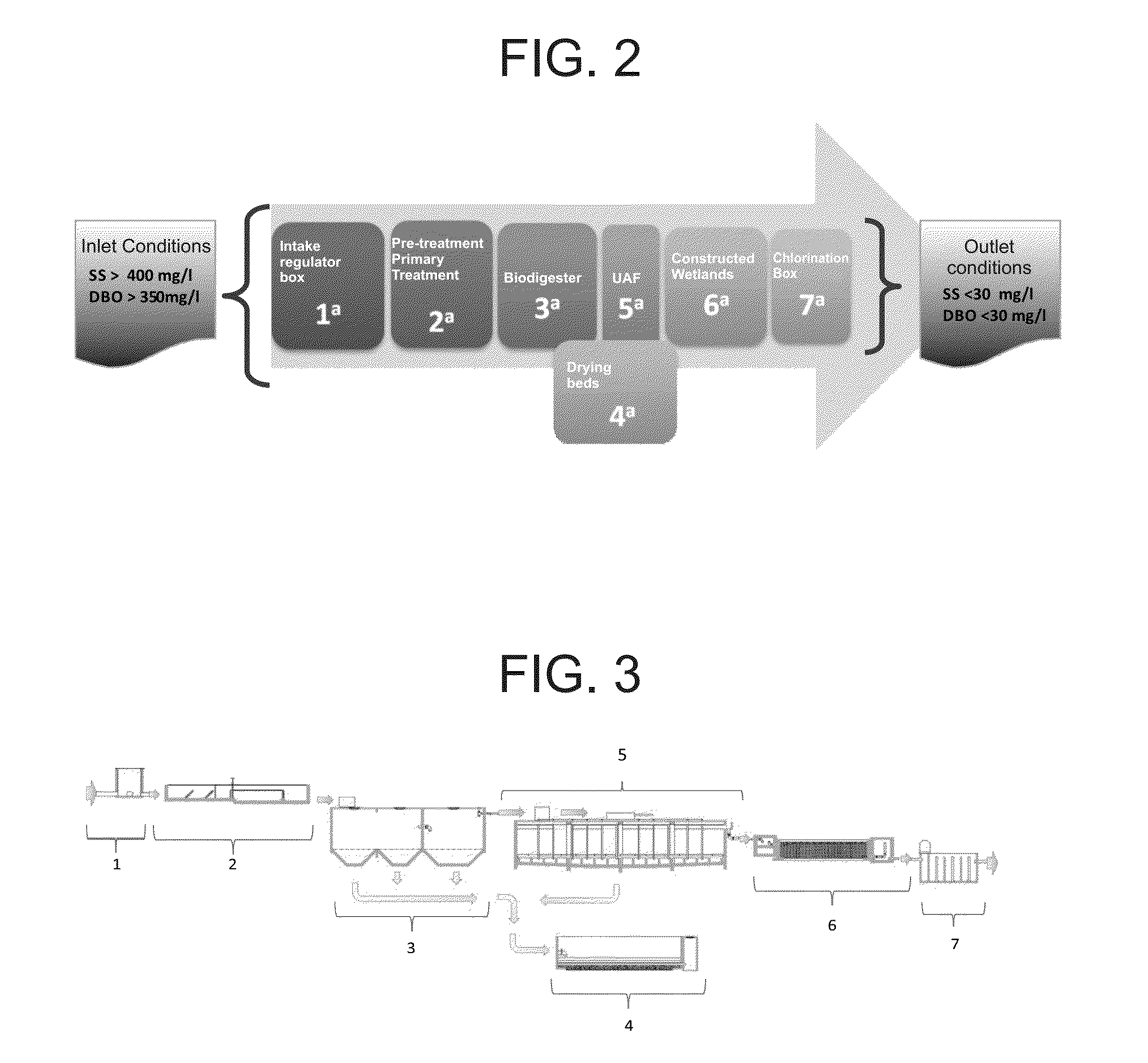
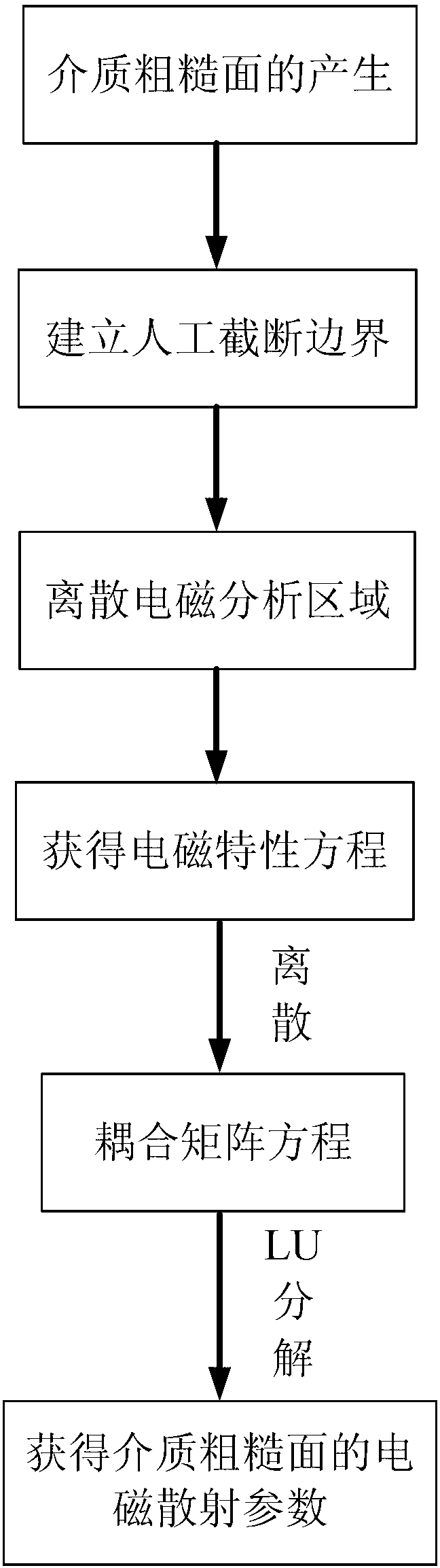
The invention relates to a municipal wastewater treatment system (STAR) for forming a wastewater treatment plant (PTAR), characterized by the functional and structural relationship between the components thereof. The invention comprises seven treatment stages in the STAR and the arrangement thereof, including: an intake regulator box having a discharge outlet; a pretreatment stage consisting of solid separation screens and grit channels; and anaerobic biodigester; an up-flow anaerobic filter; drying beds; subsurface flow constructed wetlands; and a chlorine contact channel. The STAR and PTAR according to the invention are suitable for use in a single home, as well as for use by communities of approximately 5,000 (thousand) inhabitants, and their capacity can be increased to the extent that new elements are provided at each of the different steps, simply by adding and adapting modules, without having to replace the already operating elements.
Owner:CASTELLANOS ROLD N MARCO ANTONIO
Medium rough surface finite element electromagnetic simulation method based on integral boundary
InactiveCN103279600AImprove accuracyAvoid incomplete absorptionSpecial data processing applicationsRough surfaceFunctional methods
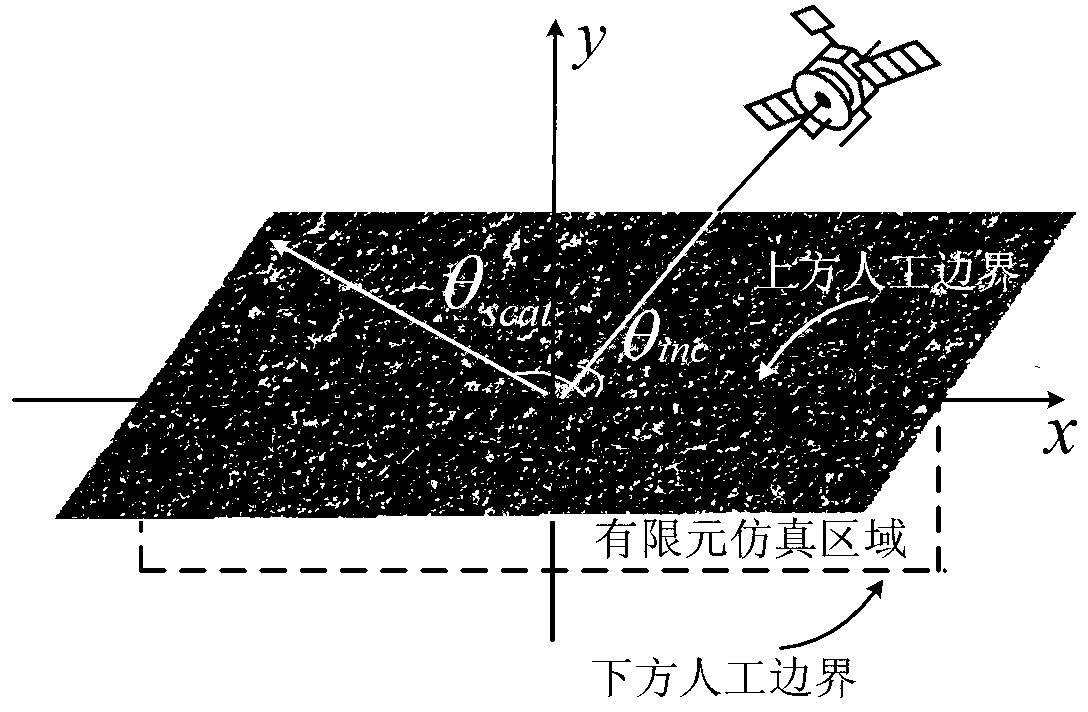
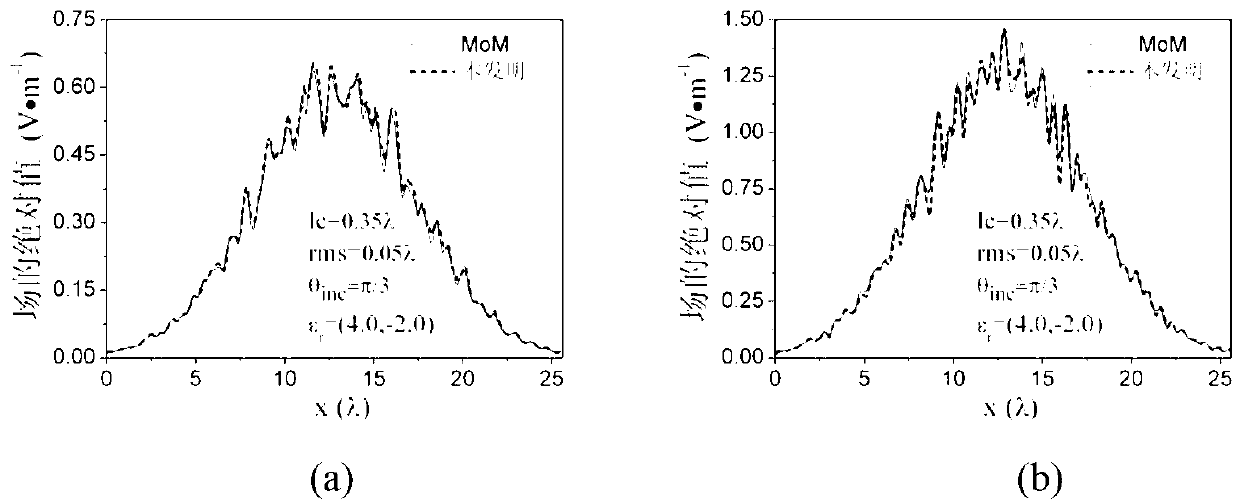
The invention discloses a medium rough surface finite element electromagnetic simulation method based on integral boundary. The medium rough surface finite element electromagnetic simulation method based on the integral boundary mainly solves the problem that similarity of inhomogeneous media and approximate absorbing boundary are difficult to solve by integral equation class methods. The medium rough surface finite element electromagnetic simulation method based on the integral boundary comprises the achieving steps of using a monte carlo method for obtaining a medium rough surface, carrying out truncation processing and scattering on the medium rough surface through an artificial boundary, acquiring a finite element equation of a simulation area according to a functional method inside the simulation area, using an integral equation method for obtaining integral boundary conditions outside the simulation area, forming an electromagnetic coupled equation through continuous conditions, and finally obtaining radar scattering parameters of the medium rough surface by solving an electromagnetic coupled matrix equation. Compared with the prior art, the medium rough surface finite element electromagnetic simulation method based on the integral boundary can be more easily used for simulating inhomogeneous medium electromagnetic problems than the integral equation class methods, can improve electromagnetic simulation precision compared with the approximate absorbing boundary, and can be used for acquiring the electromagnetic scattering parameters of medium rough surface unbounded area problems.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
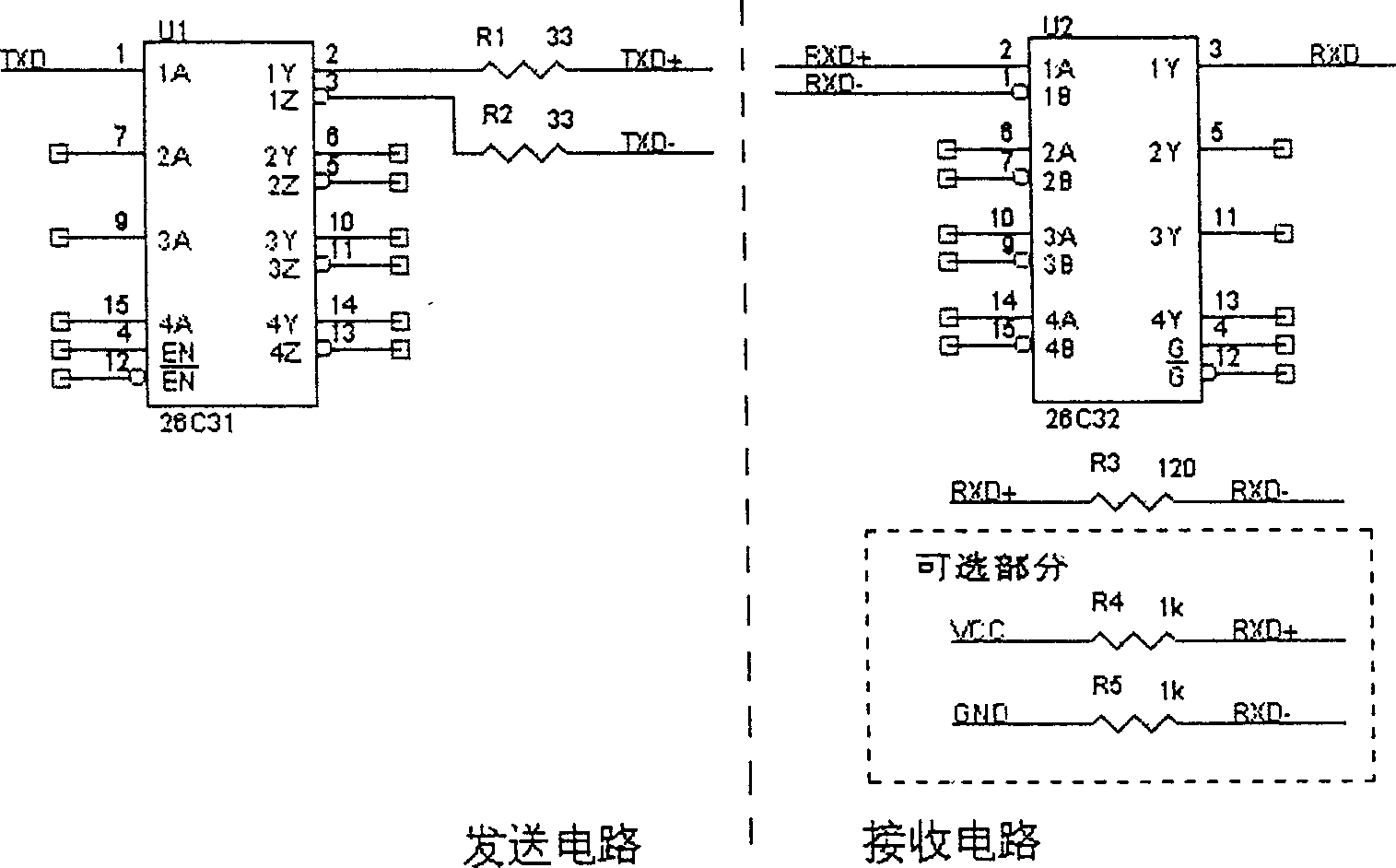
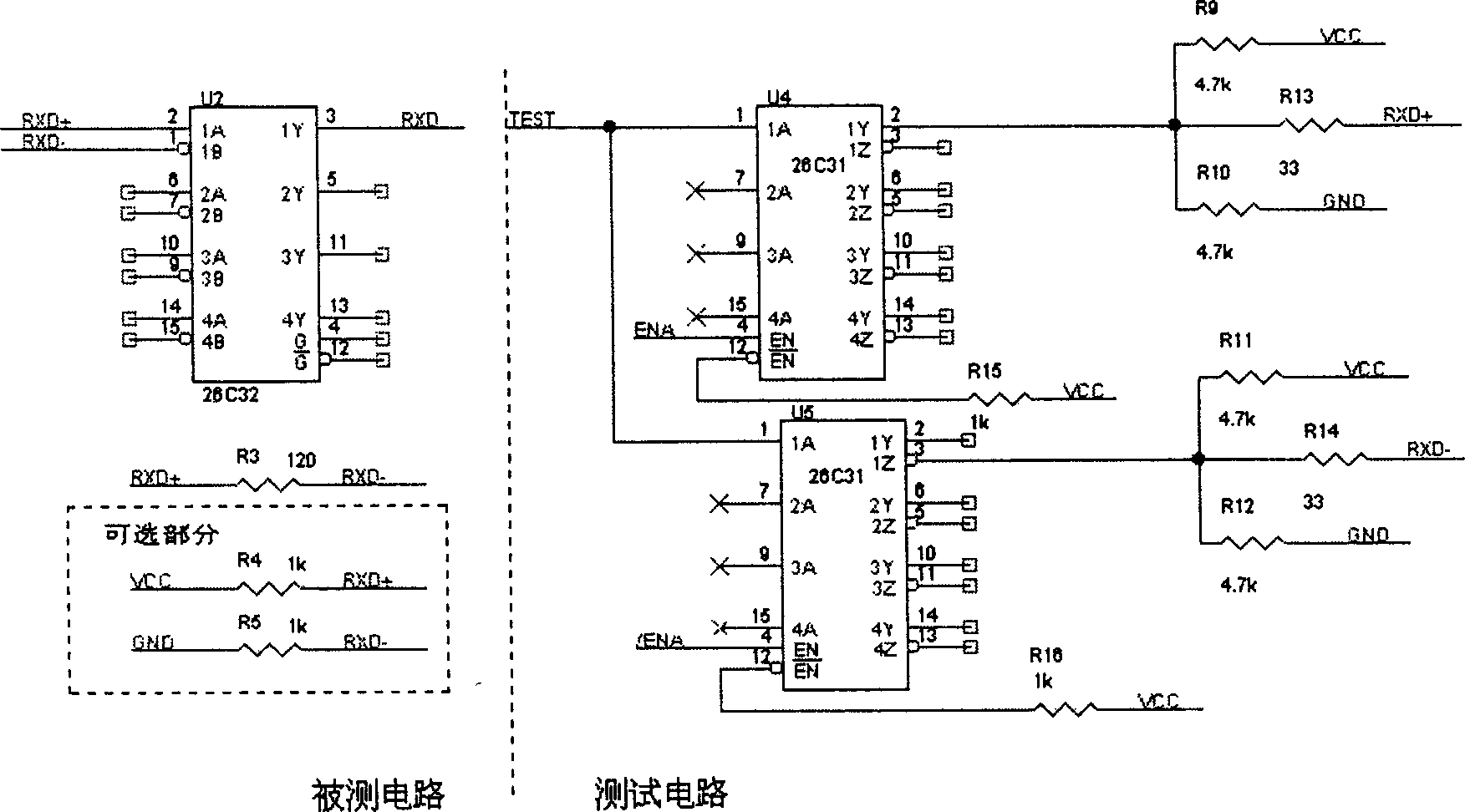
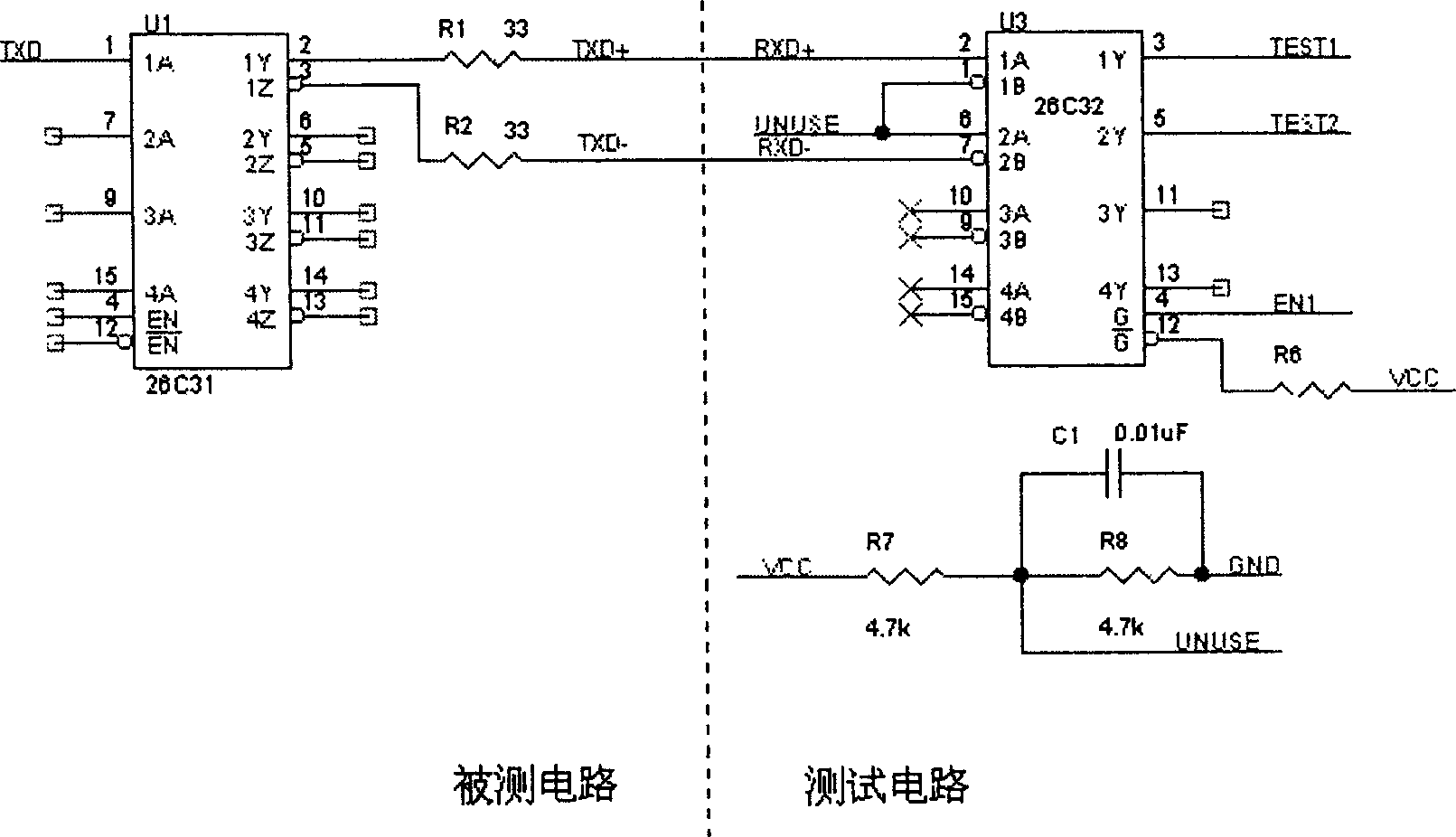
Functional test method for measuring fault at single end of difference serial circuit
InactiveCN1415971ALow costReduce volumeElectronic circuit testingFunctional testingFunctional testingDifferential signaling
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
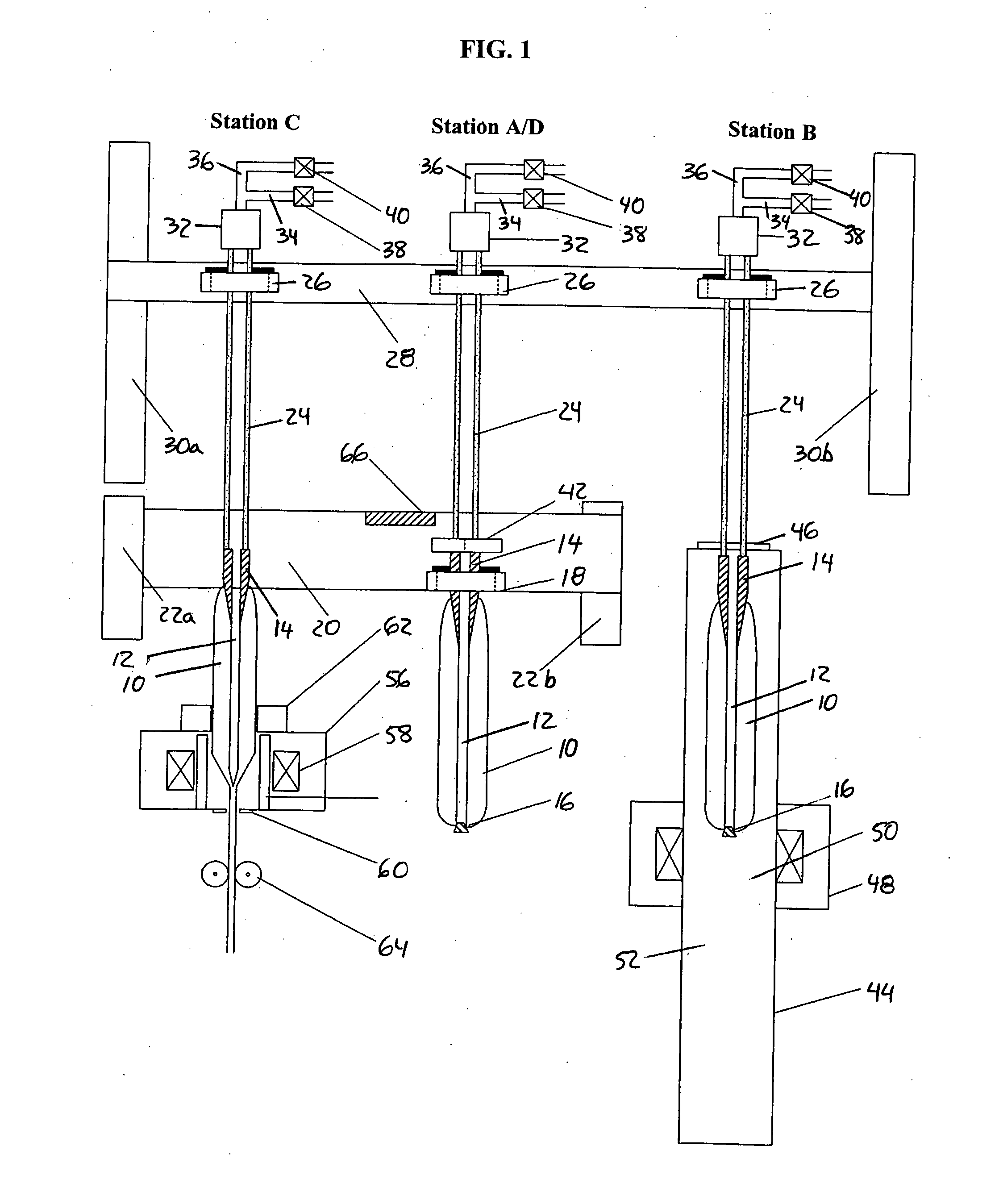
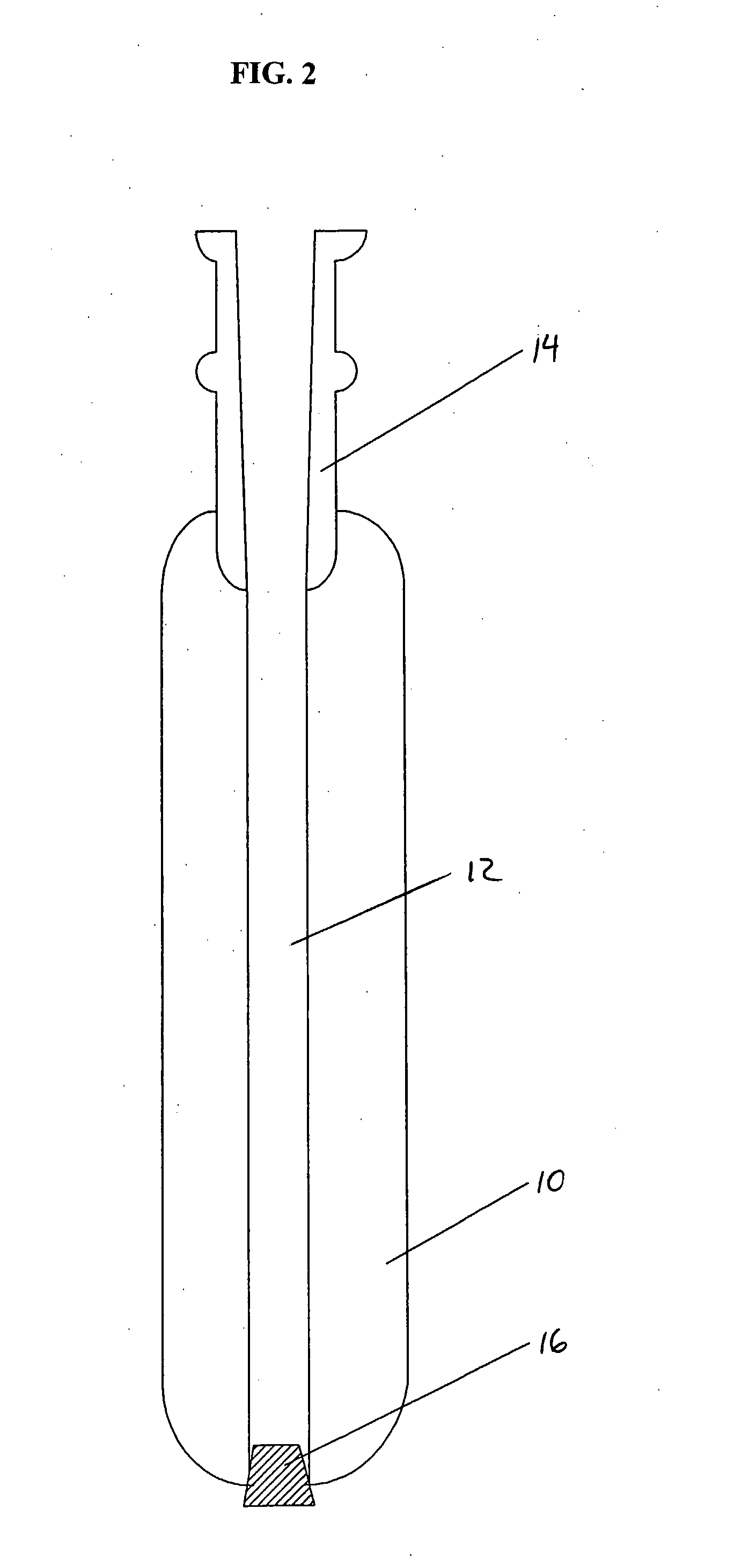
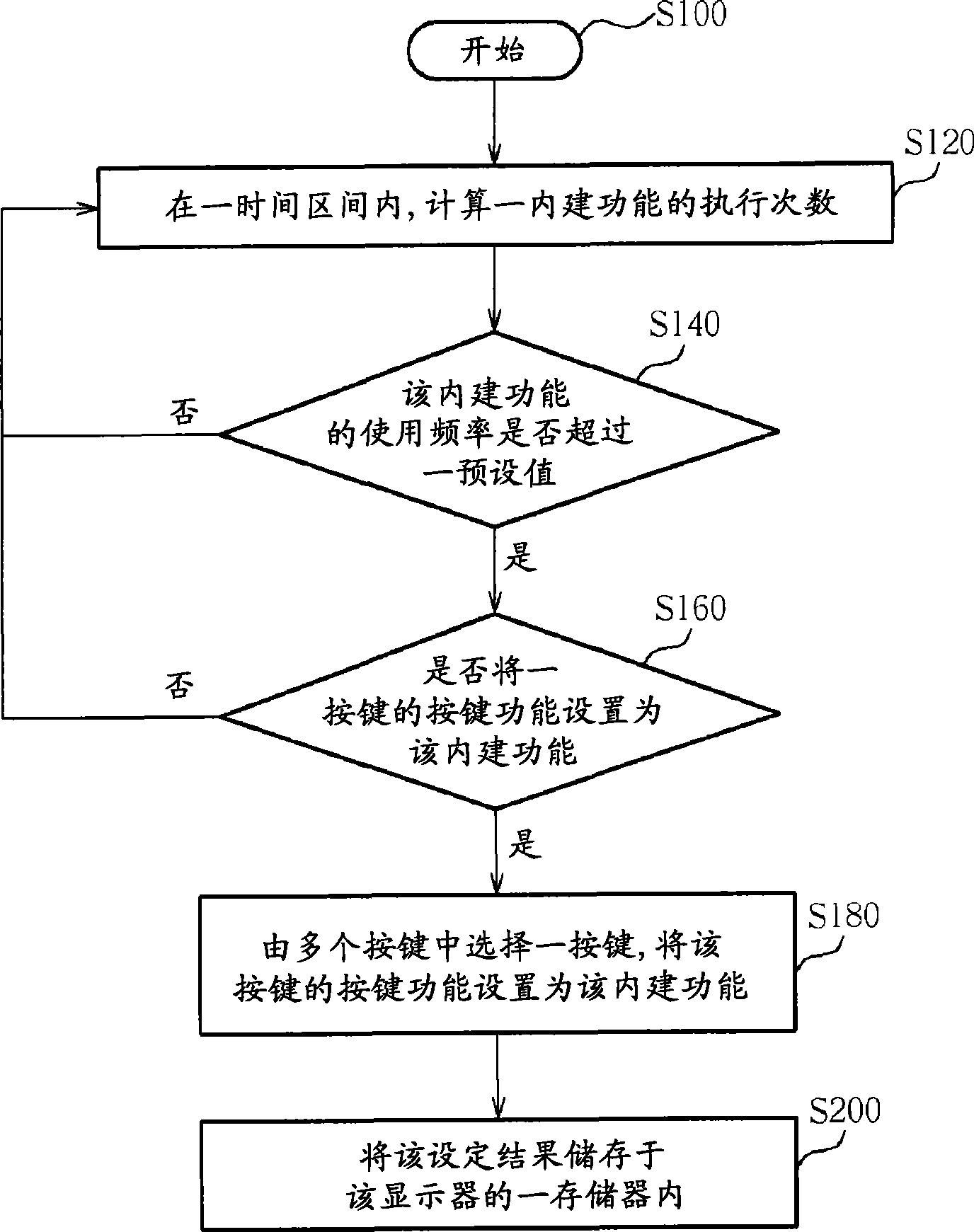
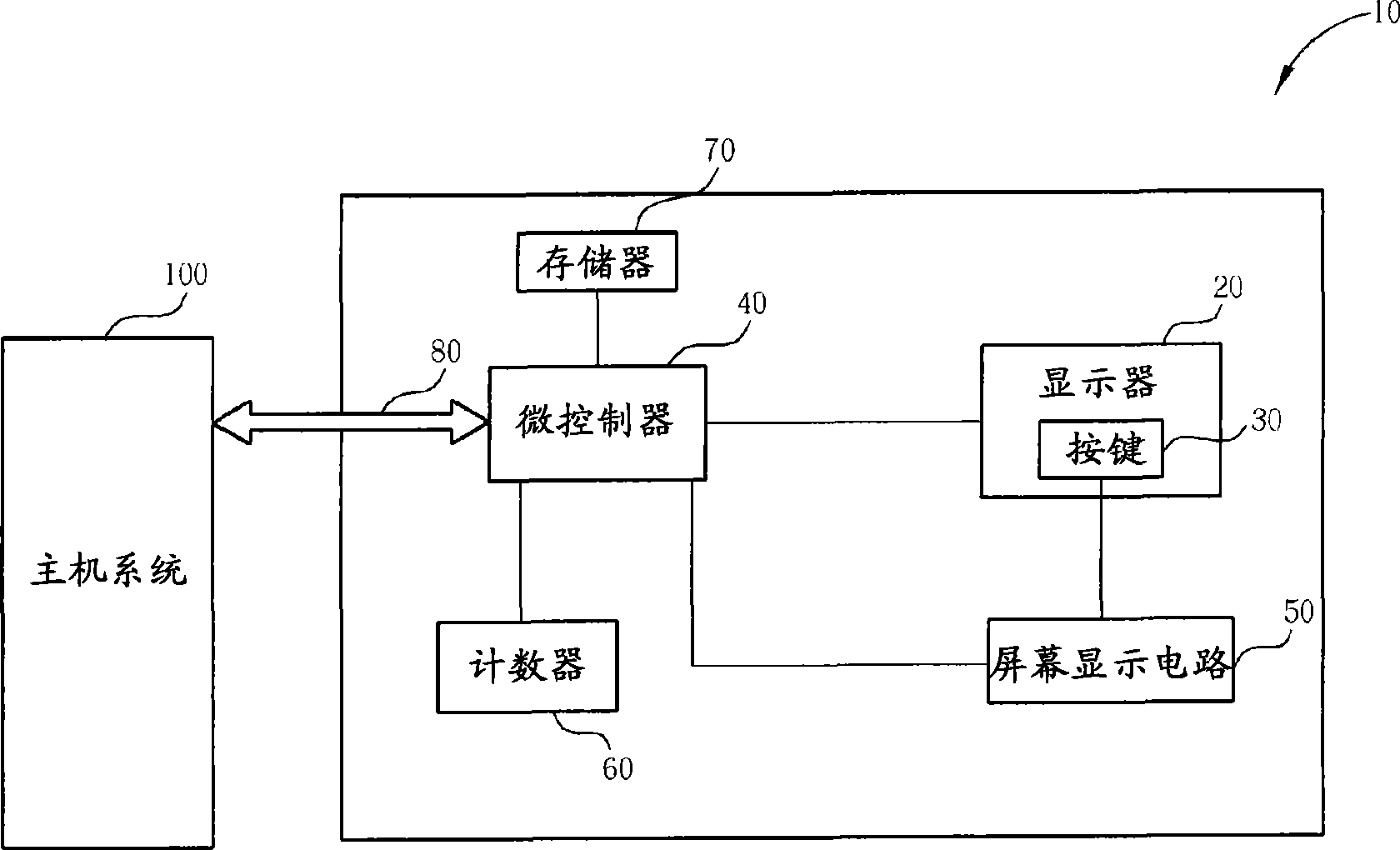
Method for setting push-button function of display and display system
The invention relates to a method for setting key functions of a display and a display system. The method uses a counter to calculate the executed times of a built-in function at a time interval, in the display provided with a plurality of built-in functions. When the executed times of the built-in function at the time interval exceed a default, the executing frequency of the built-in function is regarded to reach the set standard of a hot key. One of a plurality of keys in the display is selected, and the key function of the key is set to the built-in function reaching the set standard of the hot key, so as to customize the key function of the display.
Owner:QUISDA CORP
UI-based mobile end automated test method and system
InactiveCN109359052AImplement automated testingImprove test efficiencySoftware testing/debuggingTest efficiencyPresent method
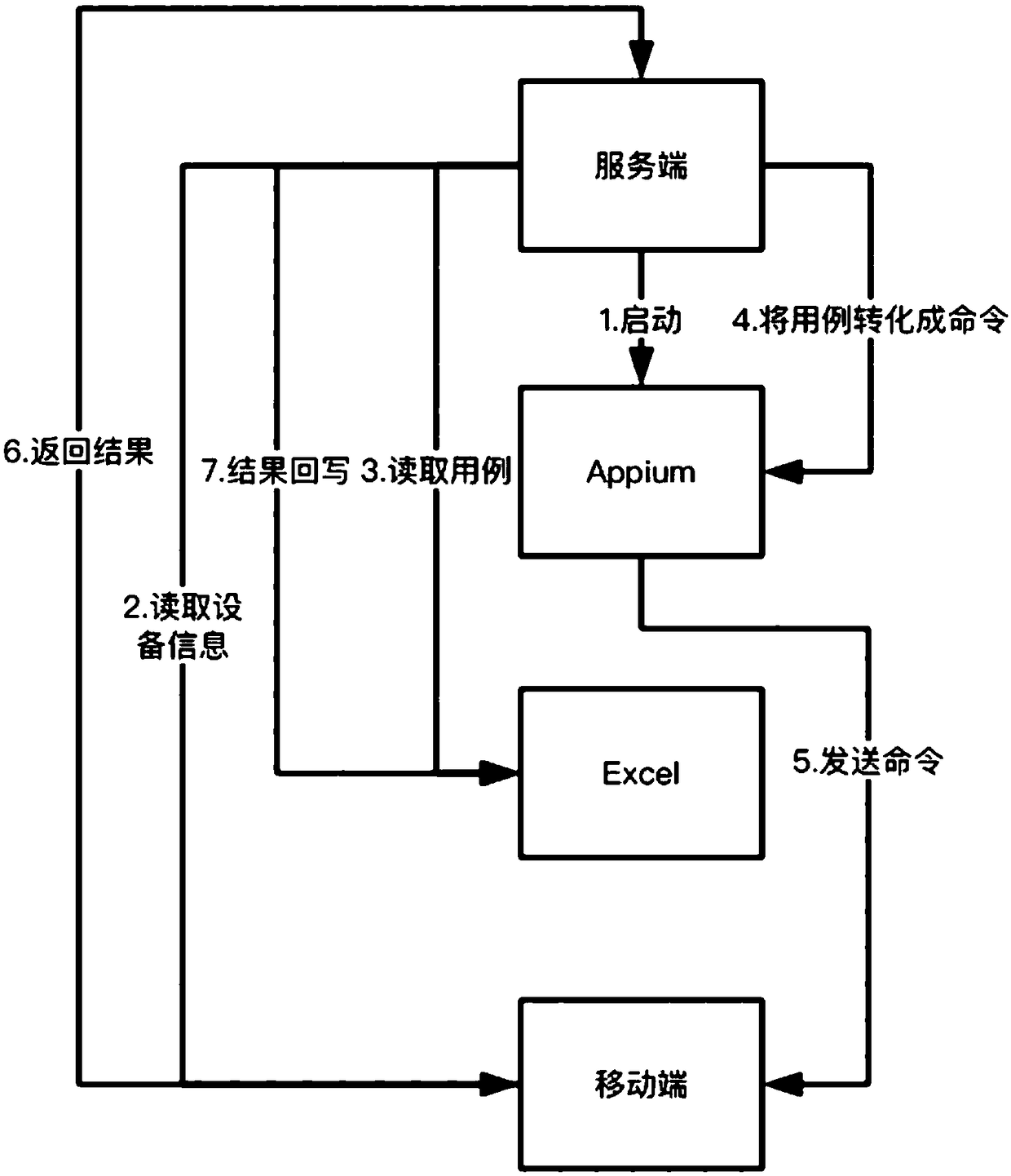
The invention provides a UI-based mobile end automated test method and system. The server adopts keyword driving logic to compile test cases. The server establishes a connection with the mobile terminal which needs to carry out UI test, the server reads the mobile terminal equipment information of the mobile terminal, the server reads the test case of the Excel form, and obtains each test operation keyword arranged according to the operation order, and corresponding operation object; Then, the server transforms the test cases into test commands, and sends the test commands and the configuration information determined in step 5 to the Appium module. The mobile terminal executes corresponding test commands and feeds back the test execution results to the server. The method and system have the advantages that the user only needs to input the test operation keyword and the operation object in the Excel form, and the corresponding method in the system can be called to realize the UI automation test of the mobile terminal through the whole functional method package, which has the advantages of high test efficiency.
Owner:BEIJING CHEZHIYING TECH CO LTD
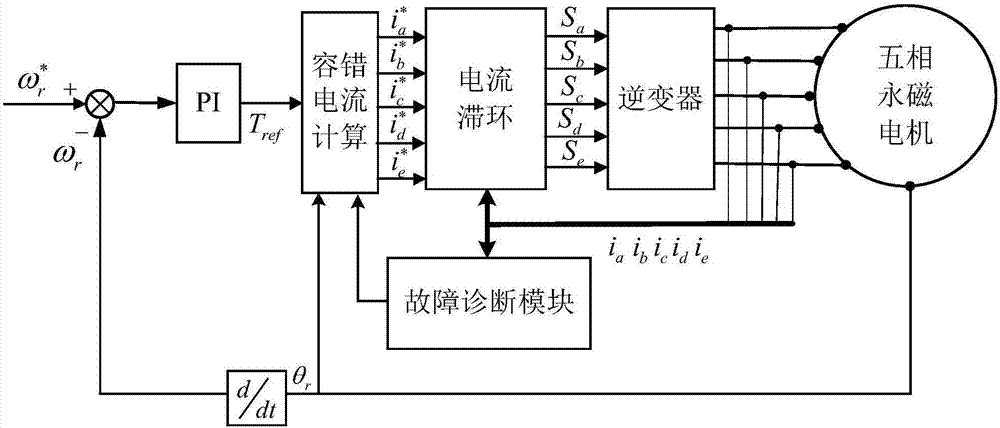
Torque ripple minimum fault-tolerant control method considering reluctance torque
ActiveCN107222138AEliminate torque rippleIncrease output torque capabilityTorque ripple controlAC motor controlHysteresisFunctional methods
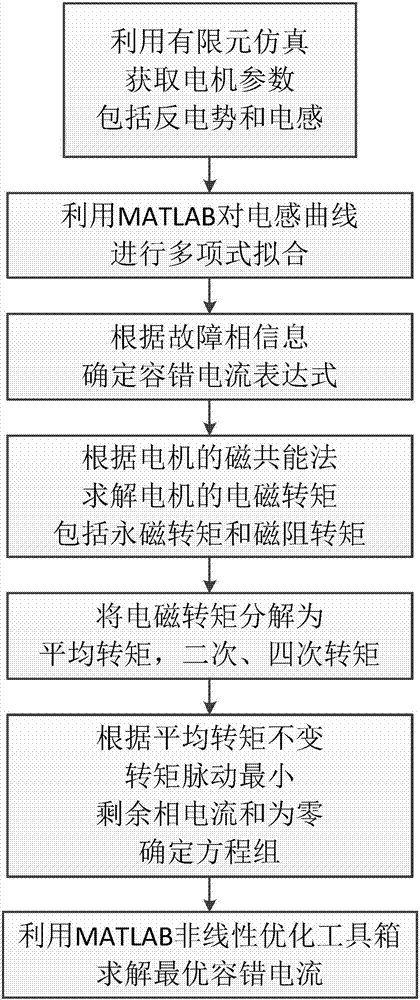
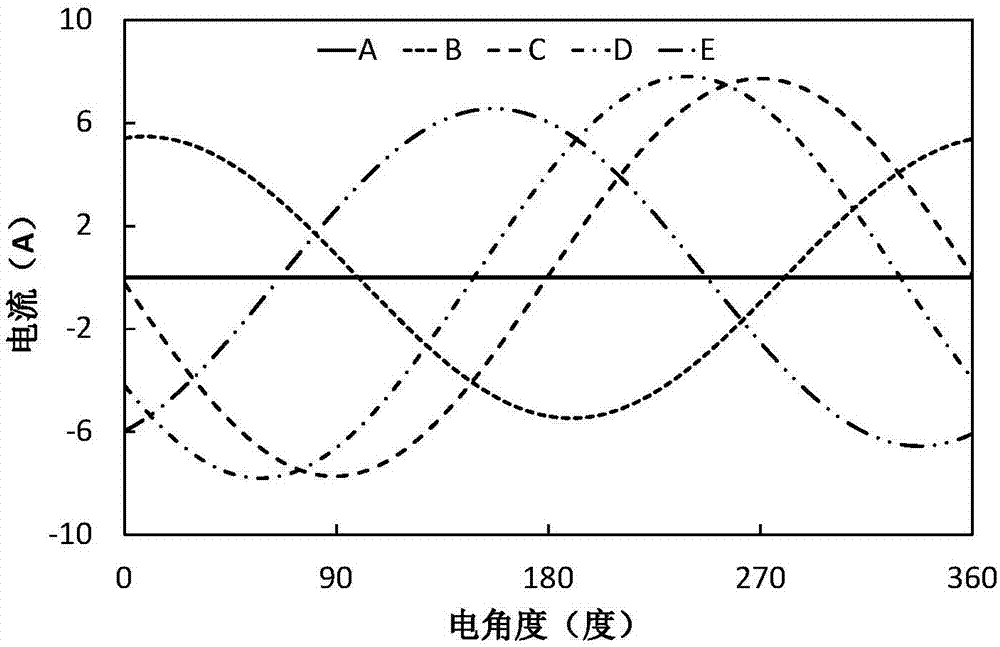
The invention discloses a torque ripple minimum fault-tolerant control method considering a reluctance torque. The torque ripple minimum fault-tolerant control method comprises the following steps of acquiring a motor parameter by finite element simulation software, wherein the motor parameter mainly comprises a no-load counter potential and an inductance waveform; performing polynomial fitting on the obtained inductance waveform by a matrix laboratory (MATLAB); determining an expression of a fault-tolerant current according to information of a fault phase; solving an electromagnetic torque of a motor according to a magnetic functional method of the motor and according to the obtained fault-tolerant current, inductance and the counter potential, wherein the electromagnetic torque comprises a permanent-magnet torque component and a reluctance torque component; decomposing the obtained electromagnetic torque into an average torque component, a secondary torque component and a quartic torque component; determining an equation set according to a principle that the average torque before and after a fault is not changed, the torque pulse is minimum and the sum of remaining normal phase currents is zero; and solving an optimal fault-tolerant current under the optimization condition of minimum quadratic sum of current amplitudes by an MATLAB non-linear optimization tool box. The torque pulse minimum fault-tolerant control containing the reluctance torque is achieved by a current hysteresis controller.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
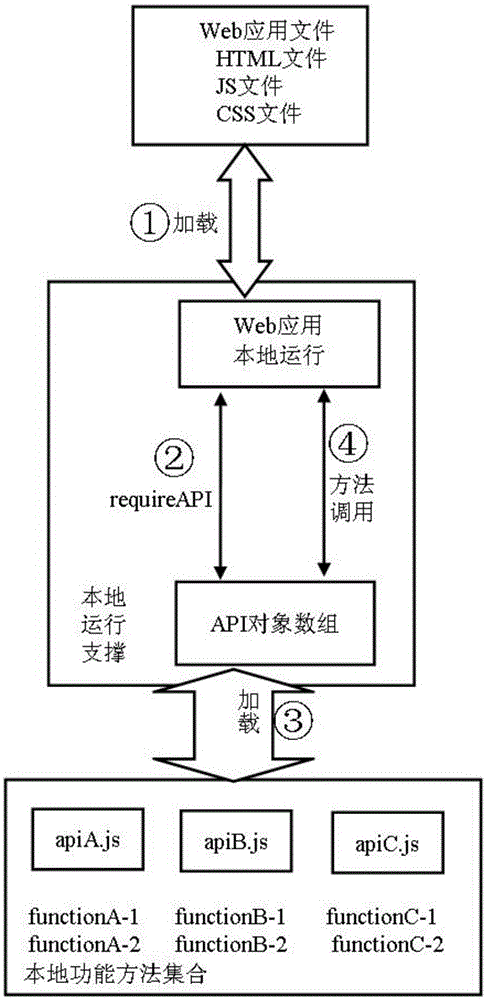
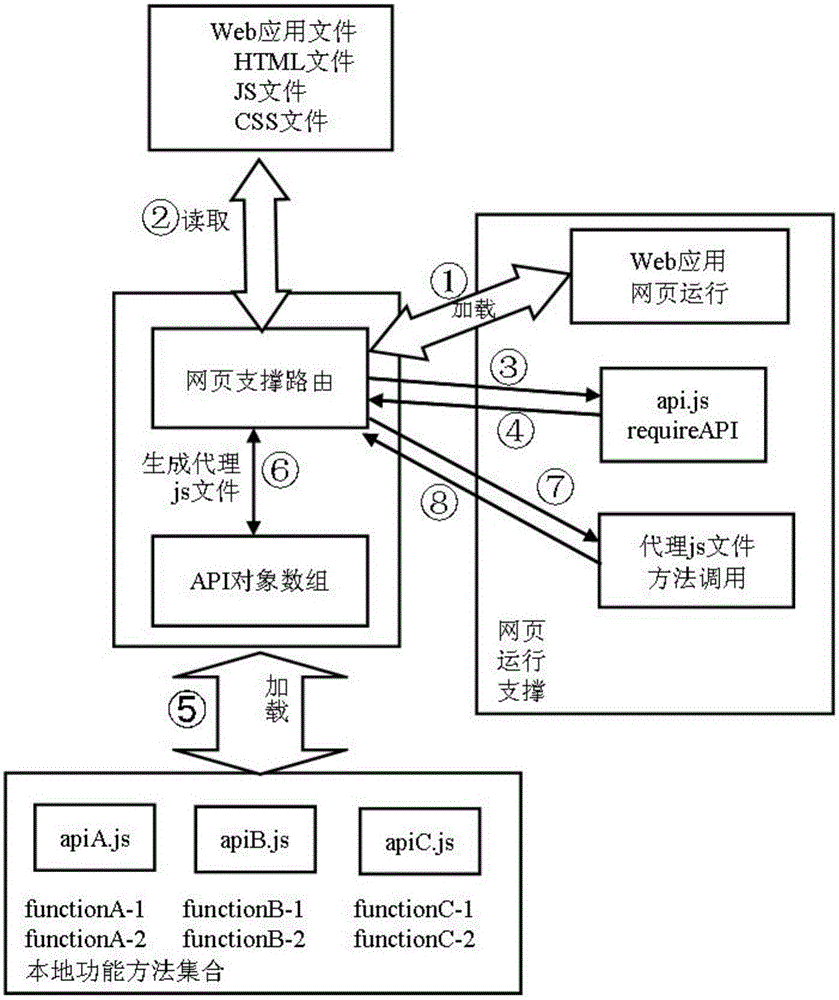
Cross device running Web application software implementation system and method
The present invention relates to a cross device running Web application software implementation system and a method thereof. In the system, a Web application basic implementation unit is responsible for basic implementation of Web application, calling of local functional method sets and establishment of a script file for realizing local functional methods; a Web application local running supporting unit is responsible for realizing the reference of an application file and the calling of the local functional methods when the Web application runs locally; and a Web application web page running supporting unit is responsible for realizing the reference of the application file and the calling of the local functional methods when the Web application runs on the web pages. Based on the method, a developer only needs to develop the Web application once to run the application by virtue of two access modes including a browser mode and a local start-up mode, namely, the application can be operated as the web page Web application and local Web application at the same time; and a variety of Web application access modes can be provided for users, and moreover, the users can be enabled to access the application and data of the users on more devices.
Owner:INST OF SOFTWARE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
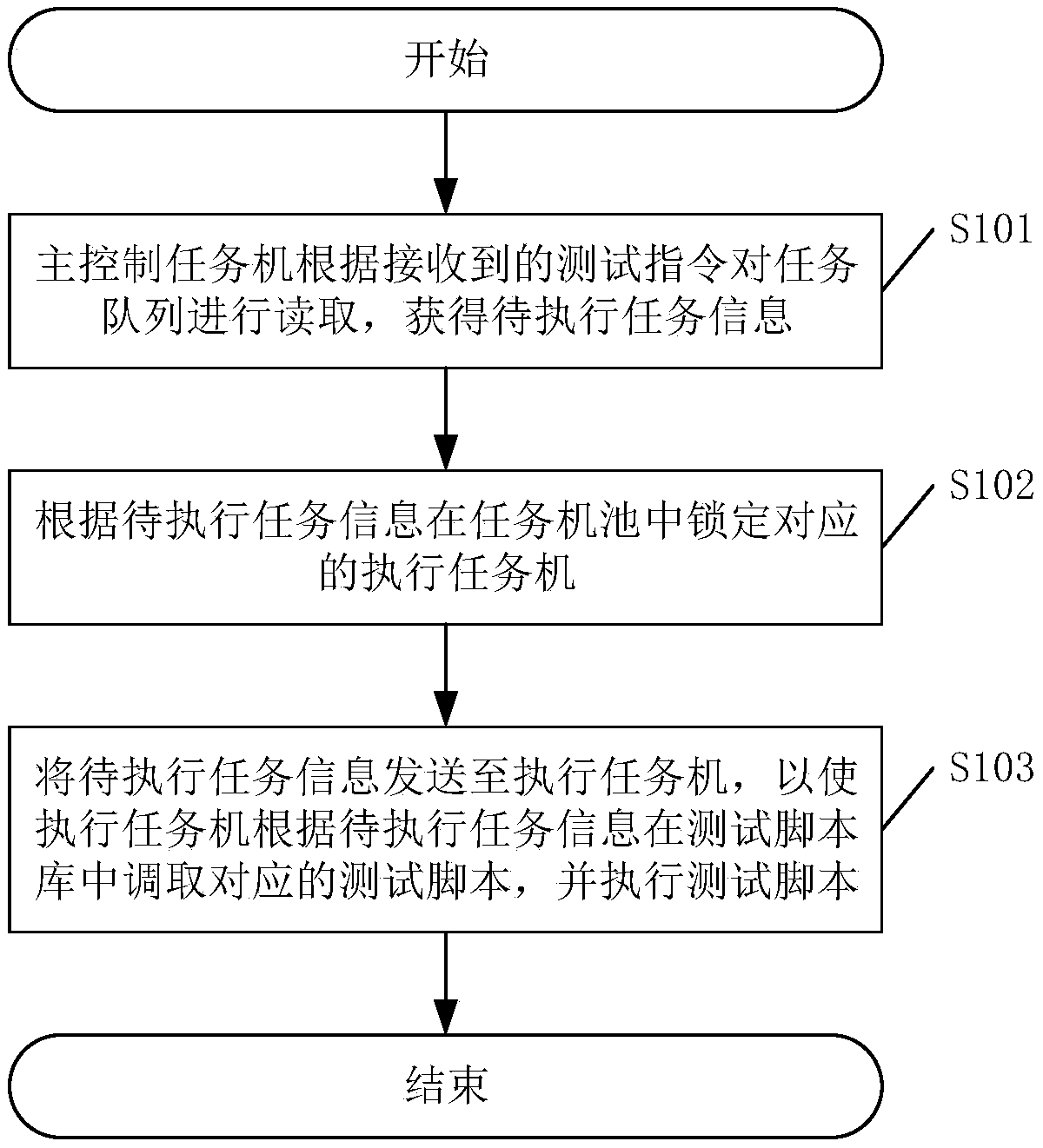
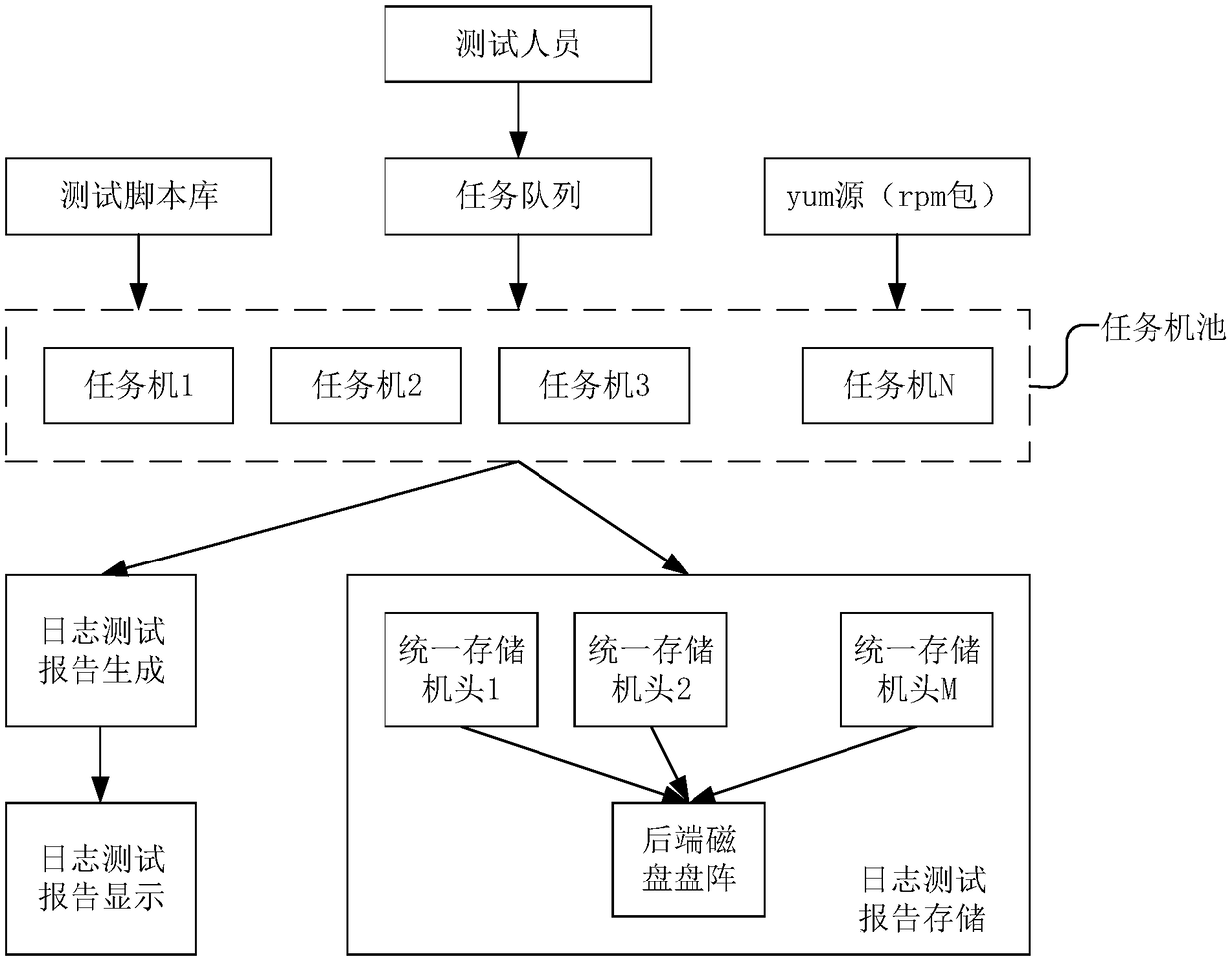
Functional test method, device and related equipment for storage system
InactiveCN109460333AReach full testShorten the timeDetecting faulty hardware by remote testFaulty hardware testing methodsTest scriptFunctional testing
The invention discloses a function test method of a storage system, which comprises the following steps: a main control task machine reads a task queue according to a received test instruction to obtain task information to be executed; Locking a corresponding executing task machine in a task machine pool according to the task information to be executed; Sending the to-be-executed task informationto the execution task machine, so that the execution task machine calls the corresponding test script in the test script library according to the to-be-executed task information, and executing the test script; The function test method can improve the efficiency of function test effectively, at the same time, achieve a comprehensive test of the storage system, and further ensure the normal operation of the system. The invention also discloses a function testing device of a storage system, a function testing system and a computer-readable storage medium, which also have the above-mentioned beneficial effects.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU YUNHAI INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Dynamic calibration method and device for thrust test of pulse detonation engine test bed
InactiveCN109060239AAccuracy not guaranteedForce/torque/work measurement apparatus calibration/testingPhase differenceFunctional methods
The invention provides a dynamic calibration method and a device for a thrust test of a pulse detonation engine test bed. The dynamic calibration method comprises the following steps of: applying a trapezoidal pulse force, which is similar to a thrust waveform of a pulse detonation engine, to a test system by using a vibration exciter; calibrating output of the test system by using impedance headoutput; when natural frequency of the test system is constant, driving the vibration exciter with different pulse frequencies, thereby obtaining output of the test system at different frequencies; obtaining amplitude ratios and phase differences at corresponding frequencies by using a transfer function and an autocorrelation functional method; and fitting and drawing an amplitude ratio and phase difference curve. According to the dynamic calibration method for the thrust test of the pulse detonation engine test bed, defects in dynamic calibration of a pulse detonation engine thrust testing system are remedied, system output obtained at certain test system natural frequencies and pulse detonation engine operating frequencies can be corrected according to the amplitude ratio and phase difference curve, and highly precise test results can be obtained.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
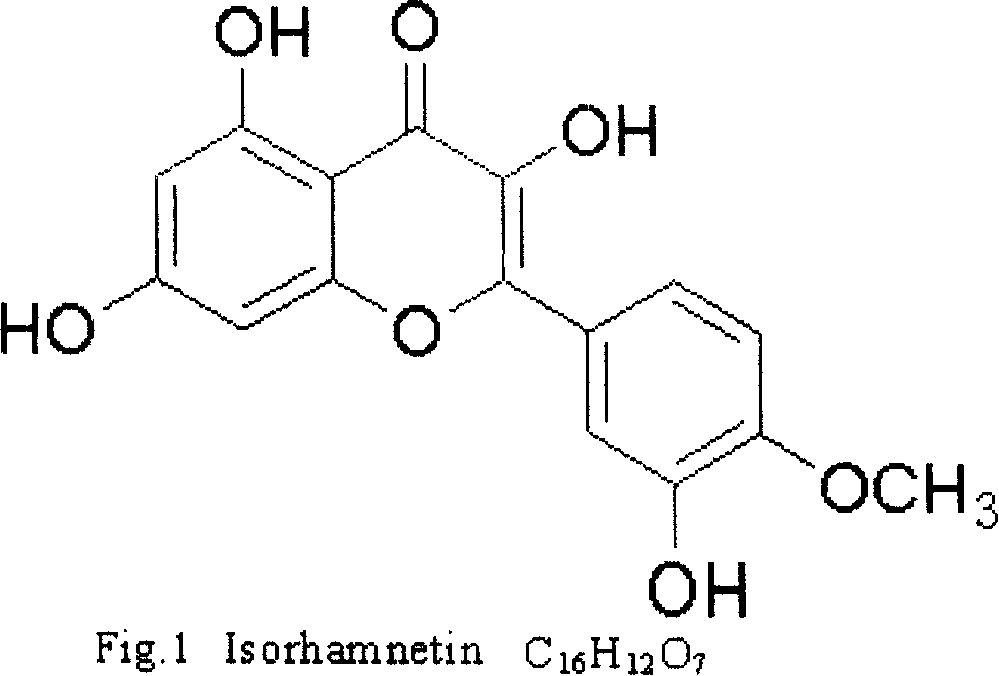
Method for abstracting active ingredient of Isorhamnetin in folium ginkgo with ultrasound wave
InactiveCN101153034AGood effectProtectiveOrganic chemistryGinkgophyta medical ingredientsFunctional methodsGinkgo biloba
The present invention relates to a novel extraction technology of effective components in Chinese medicine. Specifically, the present invention relates to a novel method of using ultrasound to extract an effective component isorhamnetin in ginkgo leaves. The method uses a design program of orthogonal experiment. Based on technical parameters of the generation method, ultrasonic intensity, functional duration, functional method, solvent type, temperature of the system, and the mixing method of ultrasound through screening and extraction process, the fresh ginkgo leaves can be prepared. The ginkgo leaves are dried at a temperature of 60 DEG C for 24 hours and crushed and screened (0.45 Mu m) to be a material. The ginkgo leaves are filled into ethanol solution of 45 percent in an ultrasonic extraction reactor; the material and solution are mixed according to a ratio (Kg: L) of 1 to from 17 to 19. The generation method of ultrasound comprises a simulated audible device of ultrasound and a radial cylindrical vibration transducer. The ultrasonic power is 100W, and the ultrasonic frequency is 28 kHz. In the extraction method, the ultrasound functions once with an interval of 3 minutes; the functional time of ultrasound is 3 minutes; the total extraction time is 36 minutes; the extraction temperature is 45 DEG C; the stirring method is an air-lift stirring way; the content of isorhamnetin in the extraction solution is analyzed by using high-efficiency liquid-phase chromatogram and the quantity is fixed in a standard-material external marking way. With the methods, the extraction rate of the effective component isorhamnetin in ginkgo leaves can reach 96.77 percent.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF TECH ZHEJIANG UNIV ZHEJIANG
Functional testing method and system for to-be-tested system
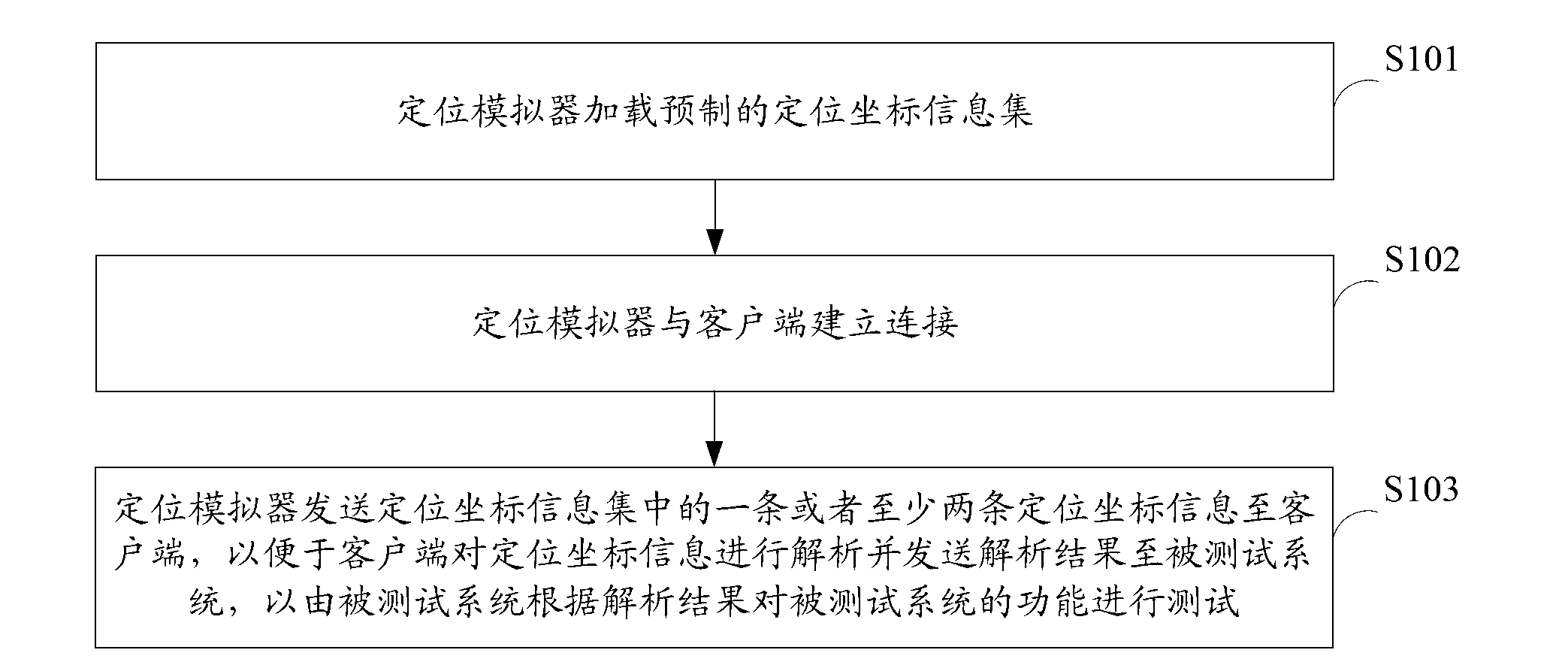
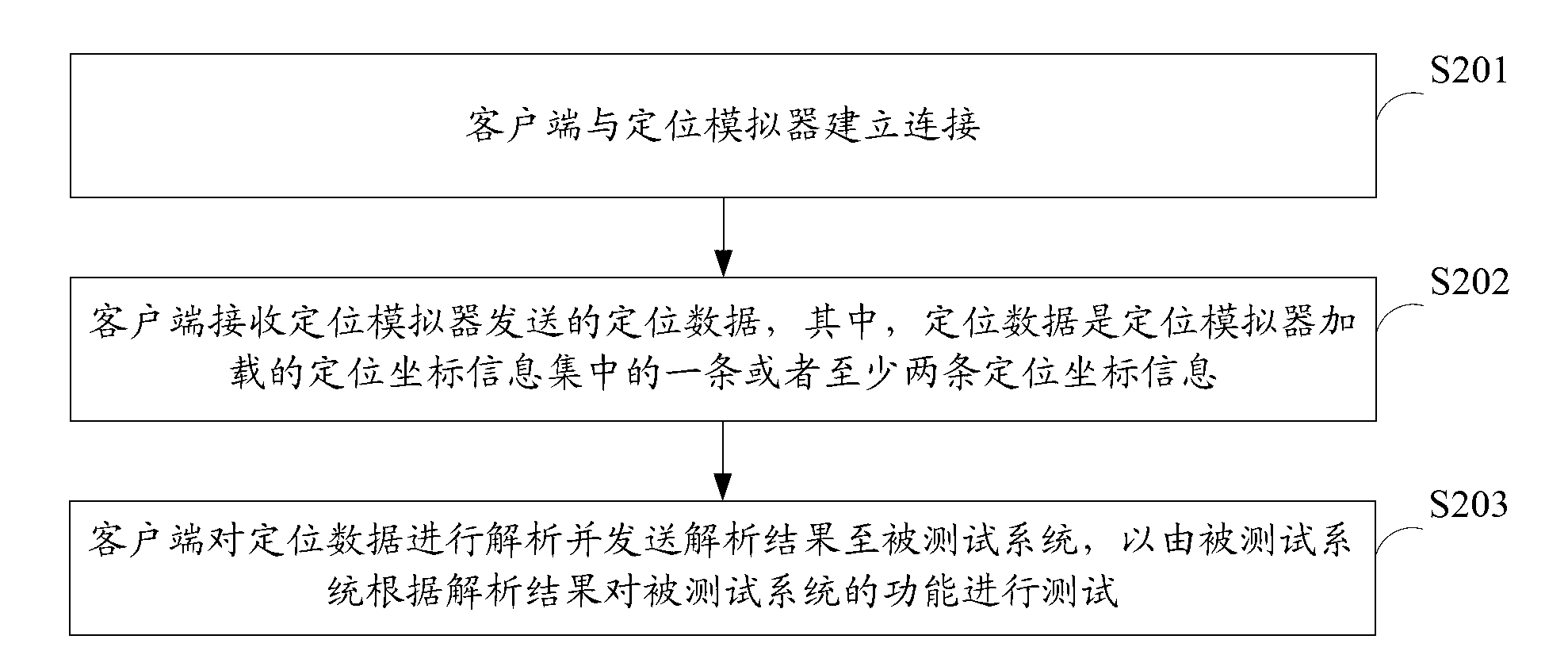
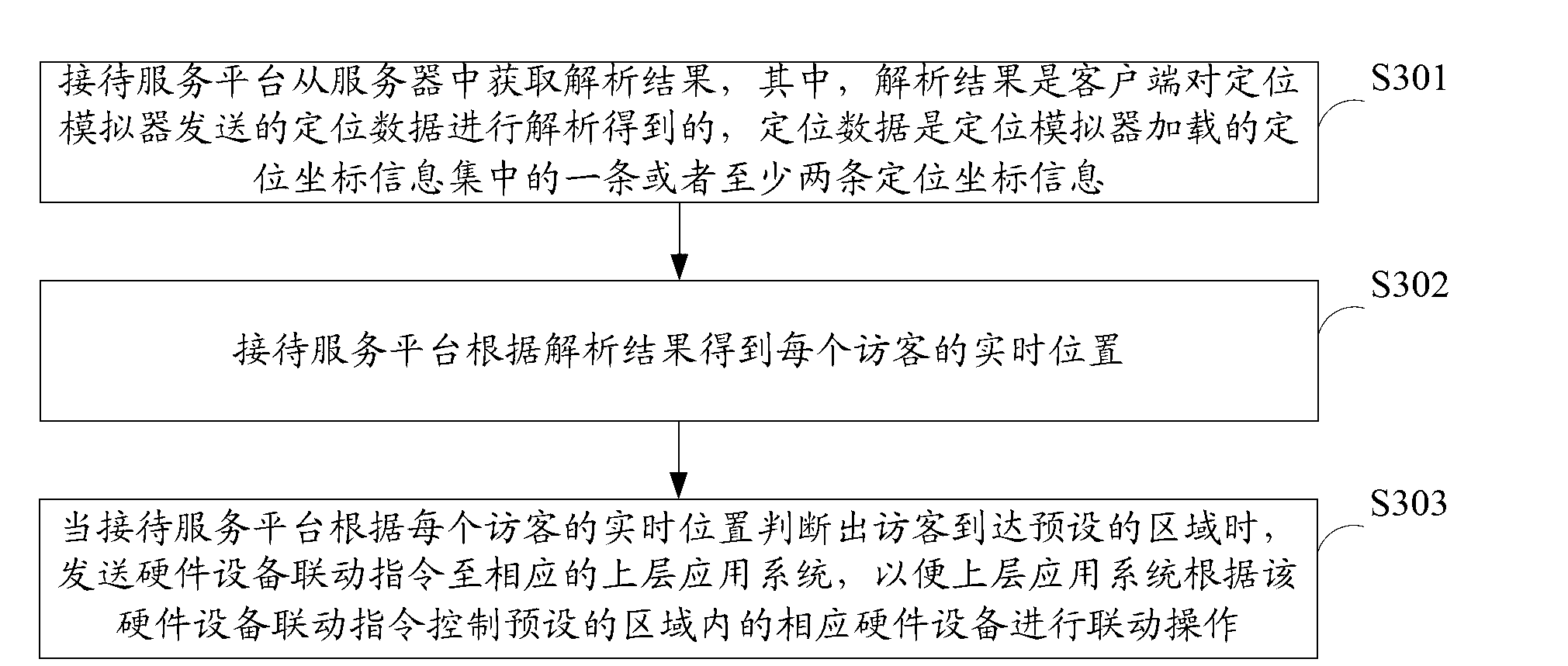
InactiveCN103324570AHigh precisionAvoid troubleSoftware testing/debuggingFunctional testingClient-side
The invention belongs to the technical field of testing and provides a functional testing method and a system for a to-be-tested system. The functional testing method for the to-be-tested system includes that a positioning simulator loads a preset positioning coordinate information set; connection between the positioning simulator and a client side is established; the positioning simulator sends one or at least two pieces of positioning coordinate information in the positioning coordinate information set to the client side; accordingly the client side is conveniently to analysis the positioning coordinate information and send an analytical result to the to-be-tested system and the to-be-tested system tests to-be-tested system functions according to the analytical result. According to the functional testing method and the system for the to-be-tested system, the positioning simulator loads the preset positioning coordinate information set, the preset positioning coordinate information set is a set of positioning coordinate data which are wrote through developers according to user requirements and are high in accuracy in comparison with positioning coordinate data which are collected through a real positioning device in real time.
Owner:ANKE SMART CITY TECH PRC
Dragon-shaped solar and air energy composite aircraft
InactiveCN107458596ASave spaceImprove driving convenienceEnergy efficient board measuresNetwork topologiesWind drivenFunctional methods
The invention discloses a dragon-shaped solar and air energy composite aircraft. The dragon-shaped solar and air energy composite aircraft is provided with an aircraft body, two flight devices are mounted on the aircraft body; aerofoils are respectively mounted at four corners of each of the flight devices through screws and nuts; a pulley is fixed at the bottom of each of the aerofoils through screws and nuts; wind-driven generators are respectively mounted at the two edges of each of the flight devices through screws and nuts; silicon battery panels are respectively arranged on the two sides of the front end of a chassis; an energy accumulator and a control processor are embedded in the chassis; the control processor is connected with the energy accumulator through a lead; the energy accumulator is connected with the wind-driven generators and the silicon battery panels through a lead; a waterproof thin film is attached onto the surface of the flight device. The dragon-shaped solar and air energy composite aircraft disclosed by the invention has the benefits that as the pulley is arranged at the bottom of each of the aerofoils, the space of the aircraft is effectively saved, and the driving convenience of the aircraft is improved; multiple functional methods can be increased through mounting the wind-driven generators and the silicon battery panels, so that the cruising ability of the aircraft is improved.
Owner:重庆华凤衣道文化创意有限公司
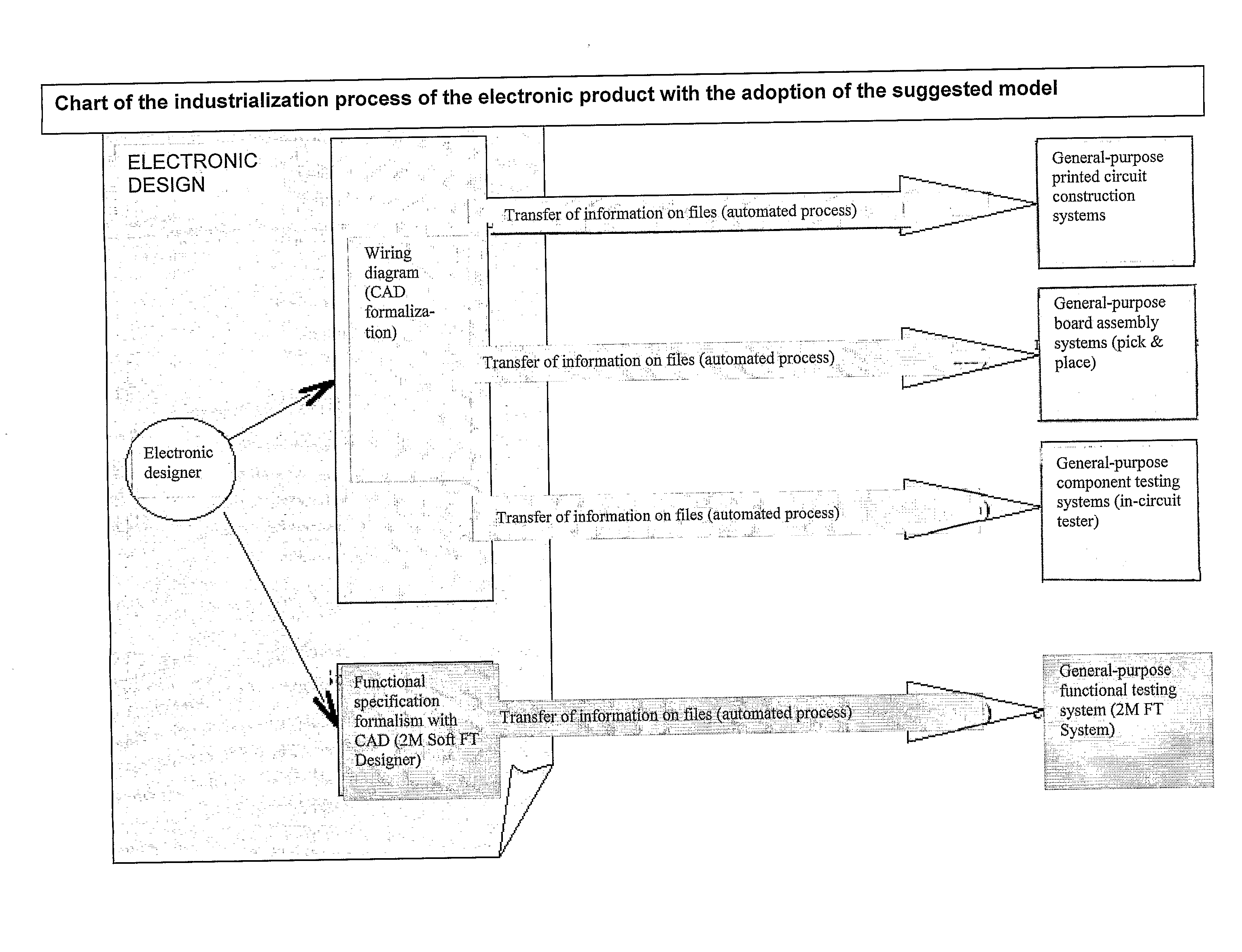
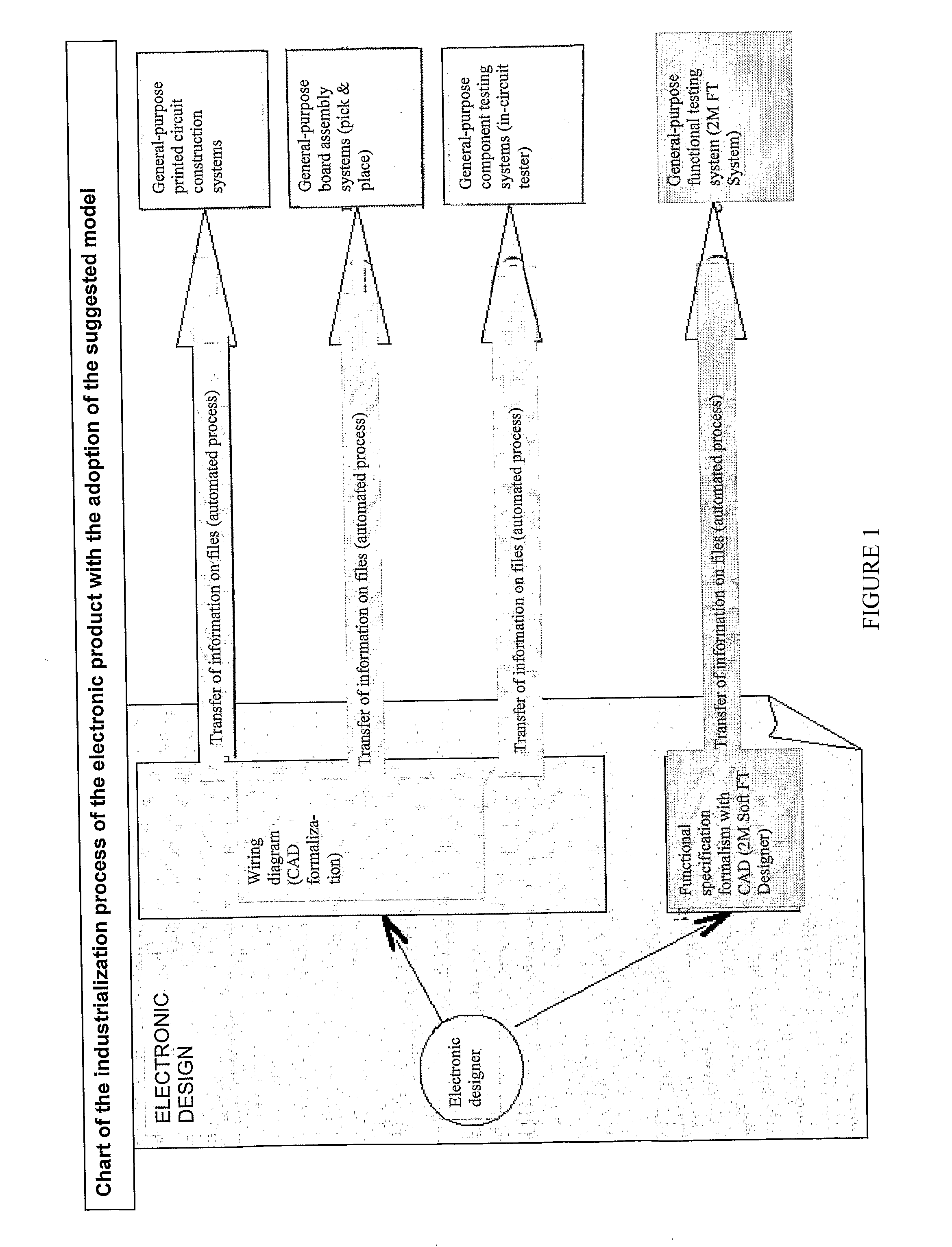
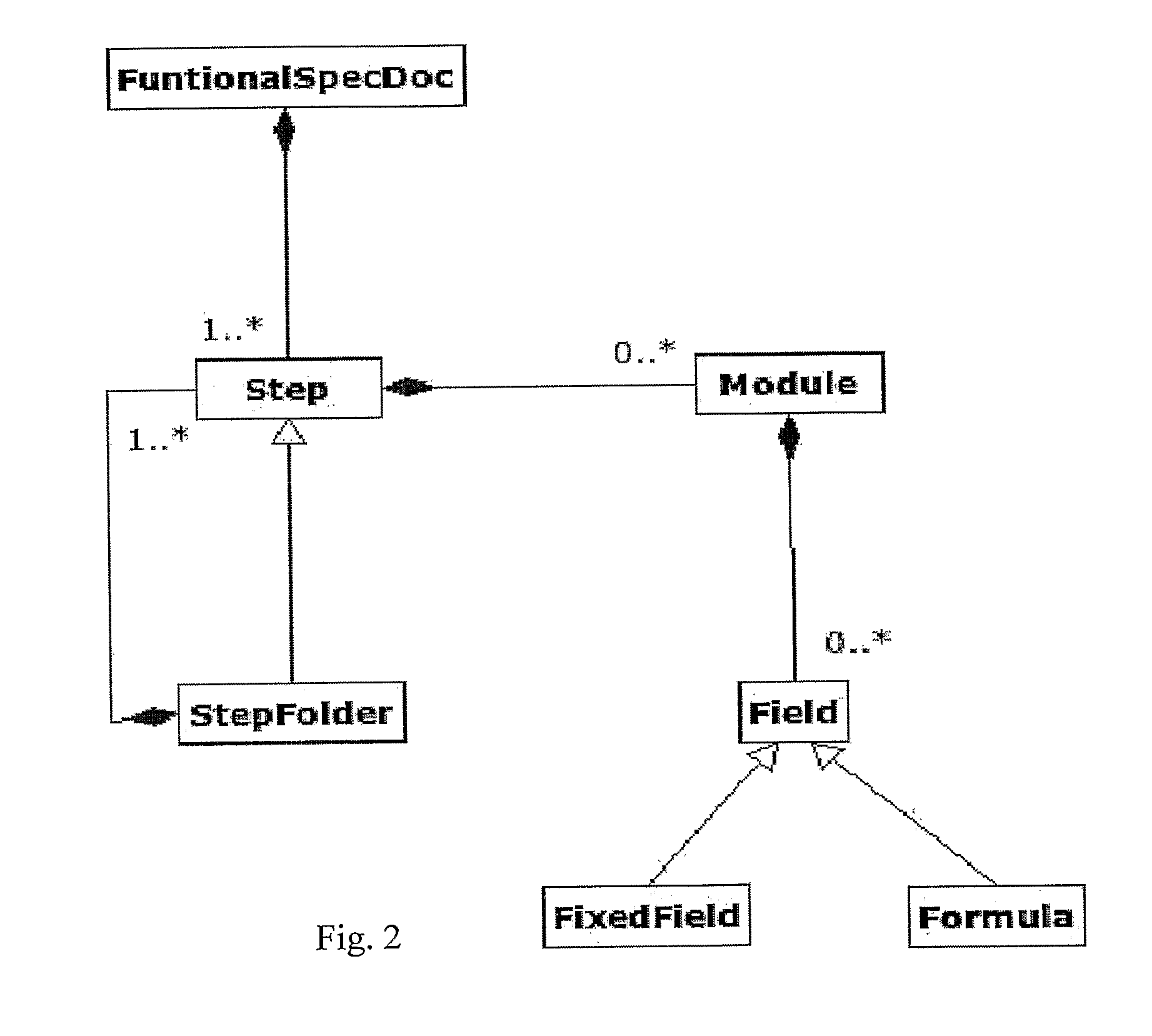
Functional testing method and device for an electronic product
InactiveUS20100274519A1Computer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsGeneral purposeProduct type
A functional testing method of electronic products includes writing a document defining a functional specification of a product by a structured document according to a recursive model of a functional specification, so that this is comprehensible by human and non-human interpreters, thus automating the setting up of a functional testing apparatus of electronic products. The functional testing apparatus is adapted to interpret the document, is general-purpose and includes an interface with corresponding drivers, replaceable in relation to the type of product subject to functional test.
Owner:CREA - COLLAUDI ELETTRONICI AUTOMATIZZATI
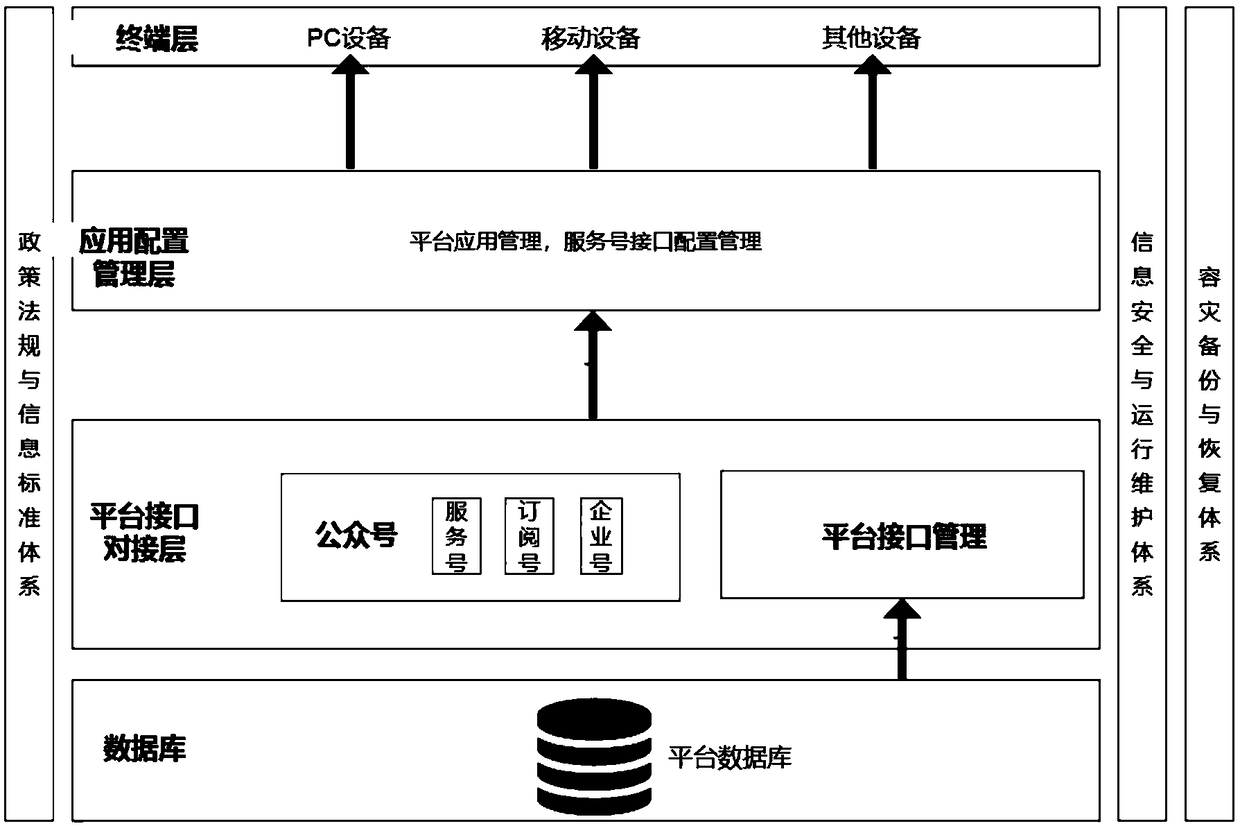
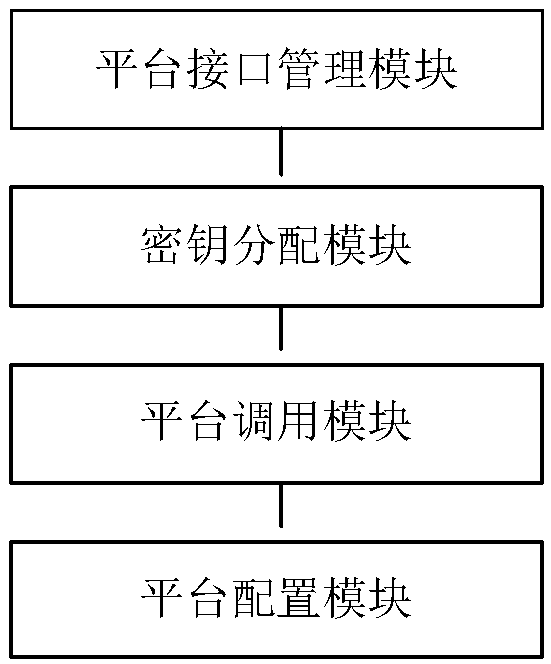
A service system for managing a WeChat enterprise number and a service number
InactiveCN109167683ASolve the conundrum of simultaneous managementEffective classificationData switching networksMultiple platformFunctional methods
The invention discloses a service system for managing a WeChat enterprise number and a service number, belonging to the technical field of the Internet. The service system comprises a database layer,a platform interface docking layer, an application configuration management layer and a terminal display layer. The database layer is provided with a platform database for storing the key data of various WeChat public numbers including enterprise numbers, service numbers and subscription numbers and the service data of platform configuration management. The interface docking layer performs dockingtest according to the Tencent api interface. On the basis of the original add a unified management of multiple platforms to achieve a management end, multiple WeChat public number management at the same time, the application configuration management through interface operations to invoke the docking layer of the functional methods to achieve the integration of multiple platforms. The terminal layer supports multi-terminal access at the same time. In order to get rid of the restriction of pc access and consider the working efficiency and convenience, the terminal layer integrates the mobile platform and supports all kinds of message alerts at the mobile terminal.
Owner:合肥智圣新创信息技术有限公司
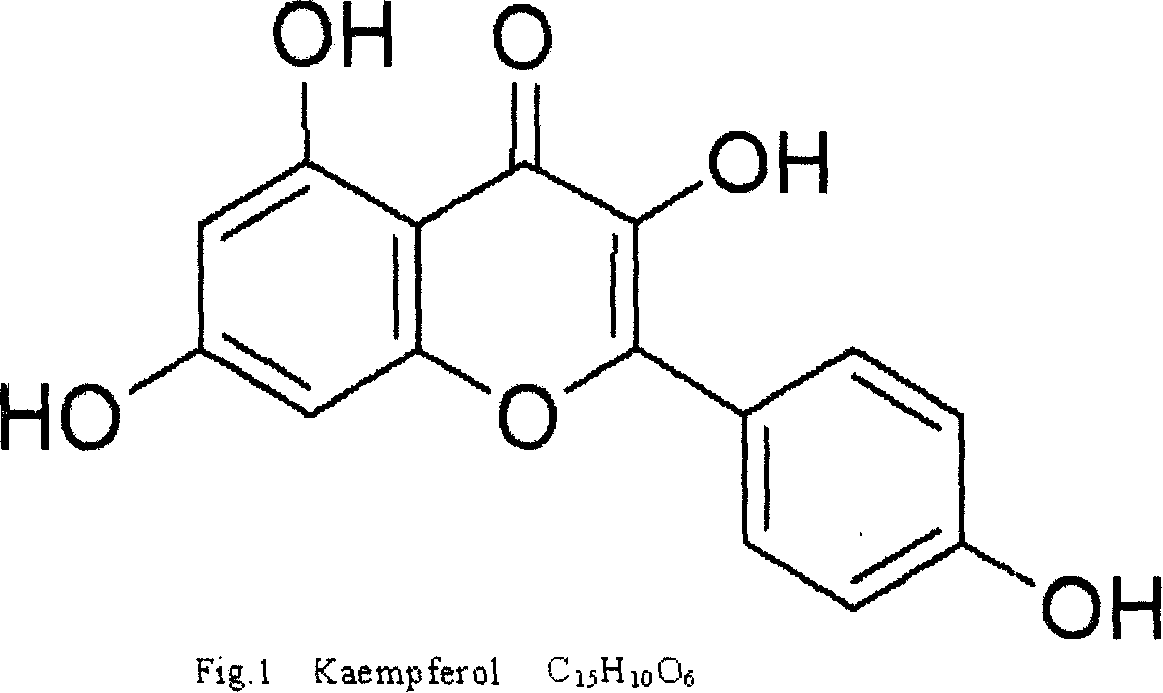
Method for abstracting active ingredient of kaempferol in folium ginkgo with ultrasound wave
InactiveCN101153033AProtectiveDoes not destroy biological activityOrganic chemistryGinkgophyta medical ingredientsFunctional methodsGinkgo biloba
The present invention relates to a novel extraction technology of effective components in Chinese medicine. Specifically, the present invention relates to a novel method of using ultrasound to extract an effective component kaempferol in ginkgo leaves. The method uses a design program of orthogonal experiment. Based on technical parameters of the generation method, ultrasonic intensity, functional duration, functional method, solvent type, temperature of the system, and the mixing method of ultrasound through screening and extraction process, the fresh ginkgo leaves can be prepared. The ginkgo leaves are dried at a temperature of 60 DEG C for 24 hours and crushed and screened (0.45 Mu m) to be a material. The ginkgo leaves are filled into ethanol solution of 45 percent in an ultrasonic extraction reactor; the material and solution are mixed according to a ratio (Kg: L) of 1 to 15. The generation method of ultrasound comprises a simulated audible device of ultrasound and a radial cylindrical vibration transducer. The ultrasonic power is 100W, and the ultrasonic frequency is 35 kHz. In the extraction method, the ultrasound functions once with an interval of 2 minutes; the functional time of ultrasound is 5 minutes; the total extraction time is 28 minutes; the extraction temperature is 35 DEG C; the stirring method is an air-lift stirring way; the content of kaempferol in the extraction solution is analyzed by using high-efficiency liquid-phase chromatogram. With the methods, the extraction rate of the effective component kaempferol in ginkgo leaves can reach 97.35 percent.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF TECH ZHEJIANG UNIV ZHEJIANG
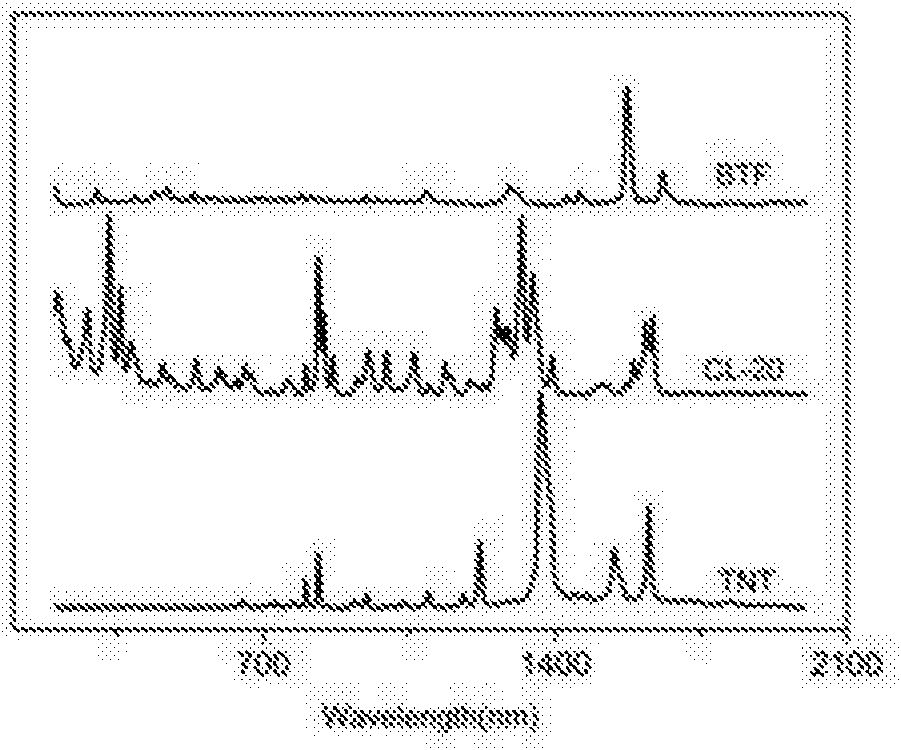
Identification method of eutectic structure of explosive
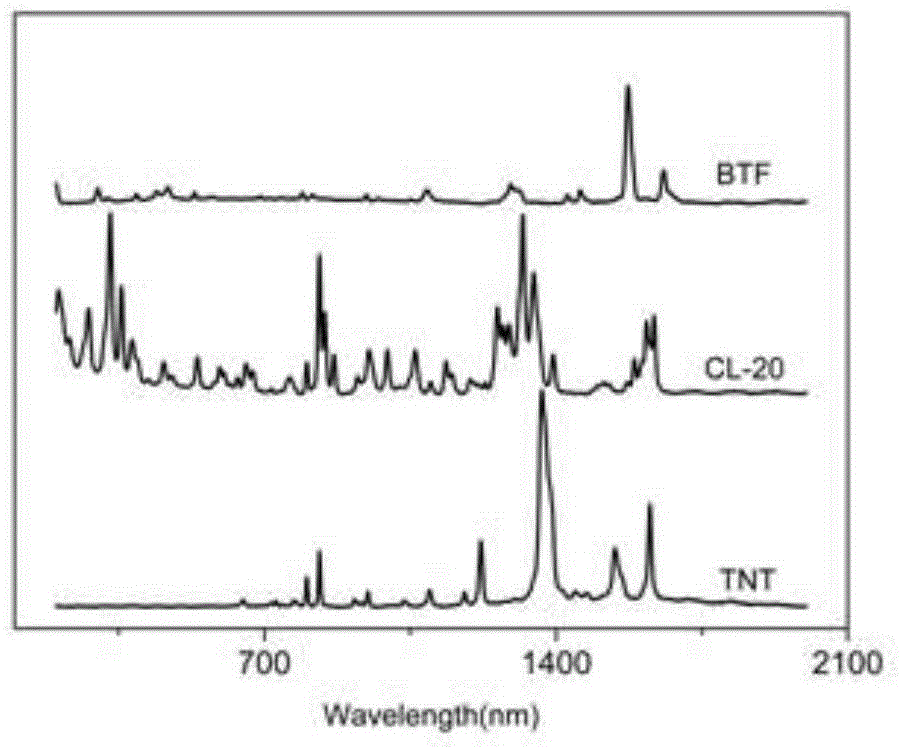
ActiveCN105300957ARealize analysis and identificationQuick analysisRaman scatteringSingle substanceFunctional methods
The invention discloses an identification method of a eutectic structure of explosive. The identification method comprises the following steps: firstly determining Raman spectra of a eutectic explosive sample and single-substance explosive samples to obtain corresponding fingerprint spectrum characteristic peaks; adopting a B3LYP mixing functional method, and calculating vibration frequencies of explosive molecules respectively by using a DFT (Density Functional Theory); then identifying the fingerprint spectrum characteristic peaks of the explosive molecules and attributing a vibration mode; and finally, comparing the Raman spectra of the eutectic explosive sample and the two single-substance explosive samples, attributing the vibration mode of the eutectic explosive sample according to vibration peak displacement of the fingerprint spectrum characteristic peaks of the two single-substance explosive samples, and analyzing the forming reasons of the eutectic structure through Raman characteristic displacement. According to the identification method, the eutectic structure of the explosive is rapidly analyzed and identified by simply mixing the single-substance explosive and the single-substance explosive mixed two by two, and taking the single-substance explosive to react two by two to form the inconsistent eutectic Raman spectra and generate different Raman peak position changes.
Owner:INST OF CHEM MATERIAL CHINA ACADEMY OF ENG PHYSICS
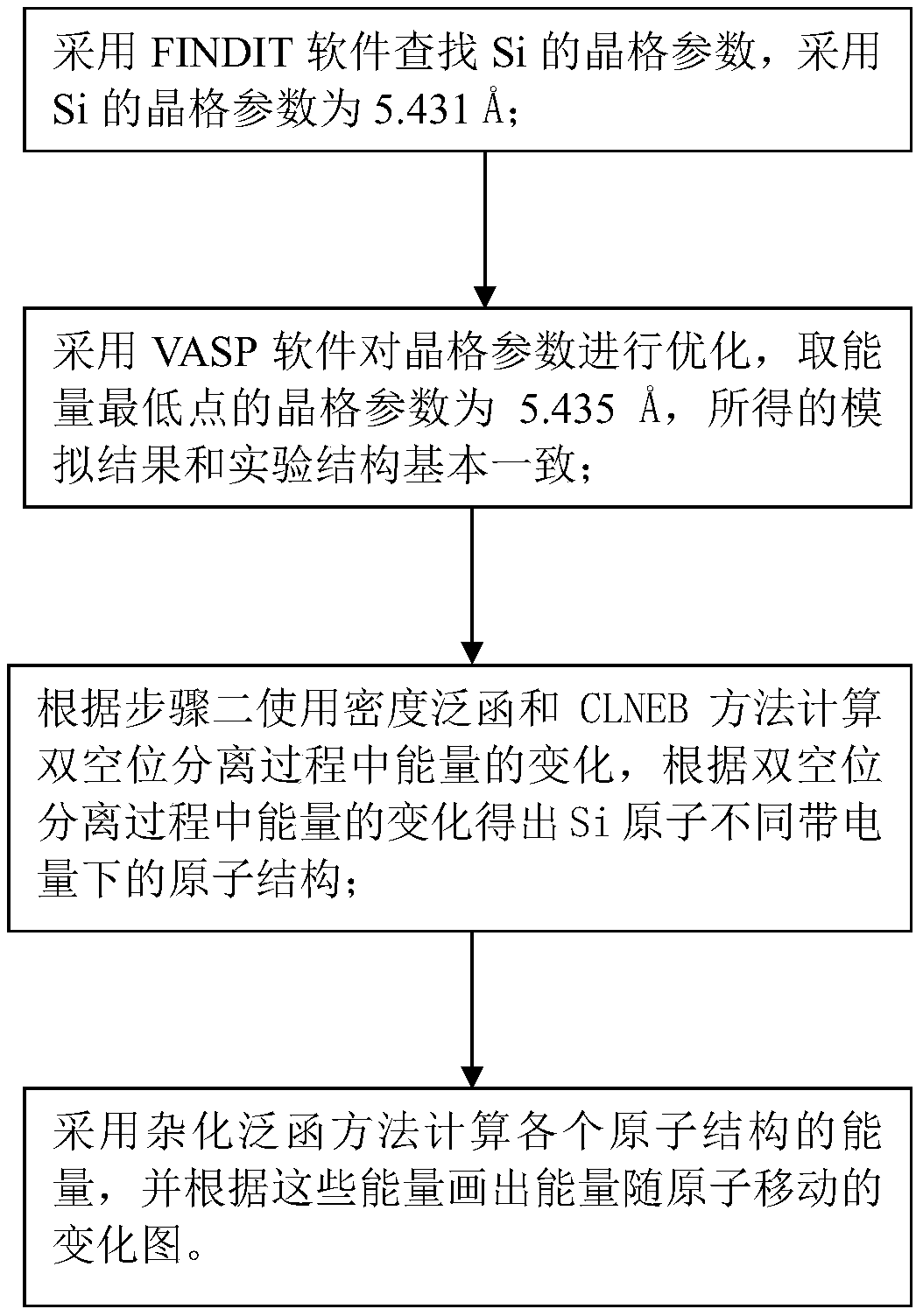
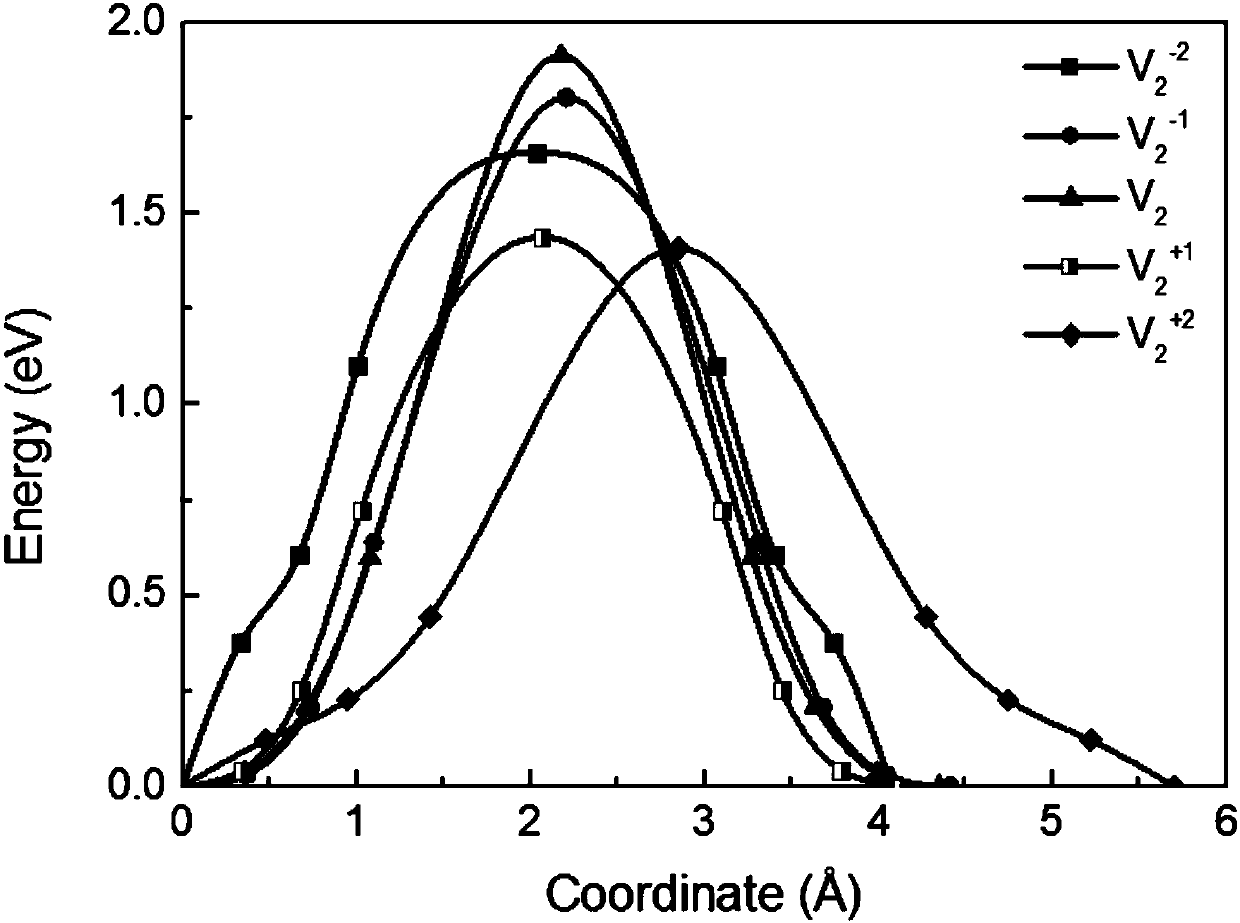
Density functional and hybrid functional-based method for calculating defect motion of Si
ActiveCN108345767AEnergy preciseImprove calculation accuracyMolecular entity identificationSpecial data processing applicationsFunctional methodsDensity based
The invention discloses a density functional and hybrid functional-based method for calculating a defect motion of Si, relates to a method for calculating the defect motion of the Si, and aims to solve the problem of low accuracy of obtaining defect motion energy of the Si by adopting a density functional method at present. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a lattice parameter of the Si;obtaining a lattice parameter of an energy minimum point of the Si; according to the lattice parameters and the band-gap width, obtaining a simulative result consistent with an experimental result; calculating energy change in a bivacancy separation process by using density functional and CLNEB methods, obtaining atomic structures of Si atoms under different electrified capacity, and calculatingthe energy change in the bivacancy separation process by adopting a hybrid functional method according to the structures. The method is used in the field of Si defect motion calculation.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
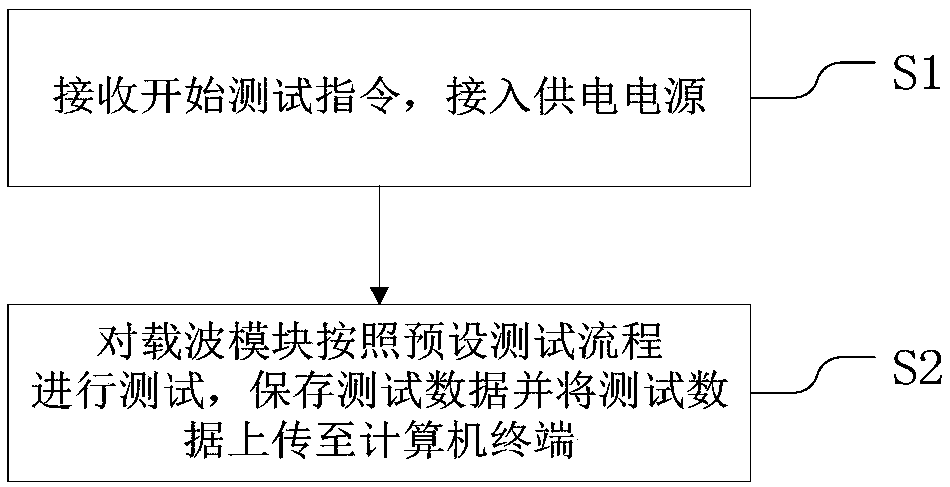
Functional test method and system for power line carrier module
ActiveCN107659336AThe testing process is simpleAdd test functionPower distribution line transmissionLine-transmission monitoring/testingFunctional testingTest flow
The invention relates to the field of carrier meter reading system detection, provides a functional test method for a power line carrier module, and aims to solve the problems that a functional test method of the carrier module is complicated and the test function is single. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the steps: S1, receiving a test starting instruction, and connecting to a power supply; and S2, test the carrier module according to a preset test flow, saving test data and uploading the test data to a computer terminal. Through the functional test method for a broadband carrier module disclosed by the invention, performance detection of the carrier module can be completed by one click; operation is convenient and easy; and the test function is complete.
Owner:宁波德晶元科技有限公司
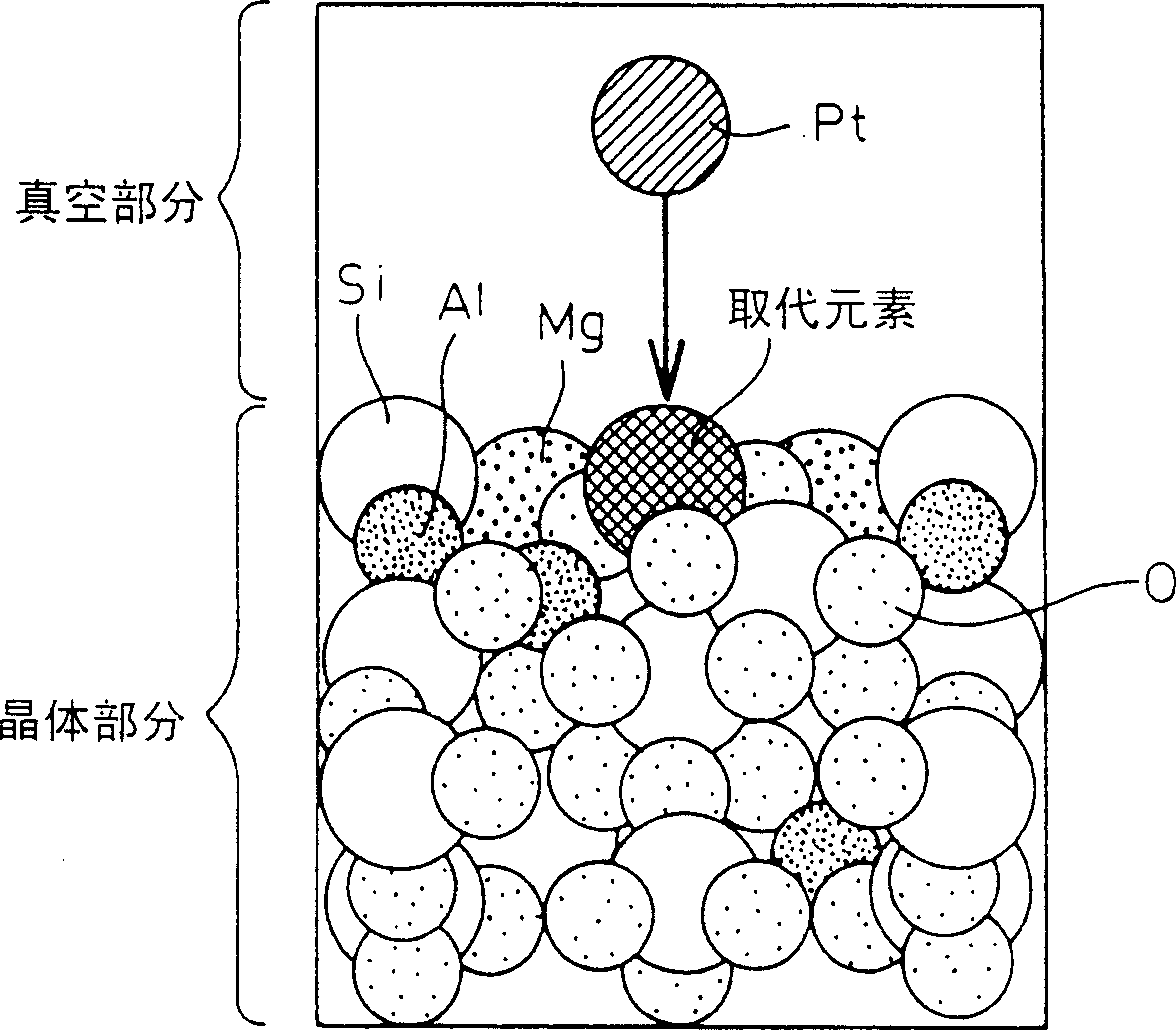
Catalyst
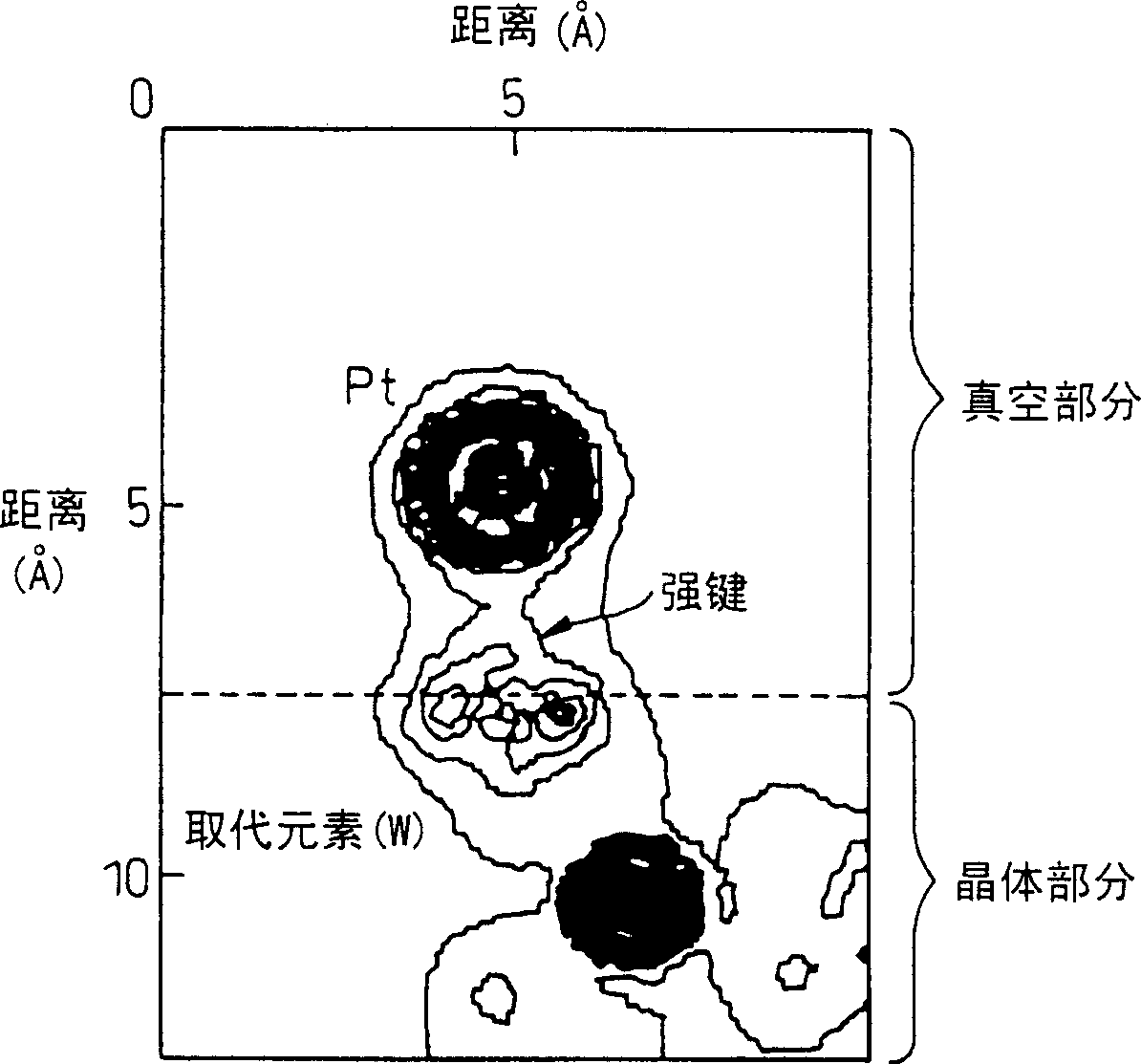
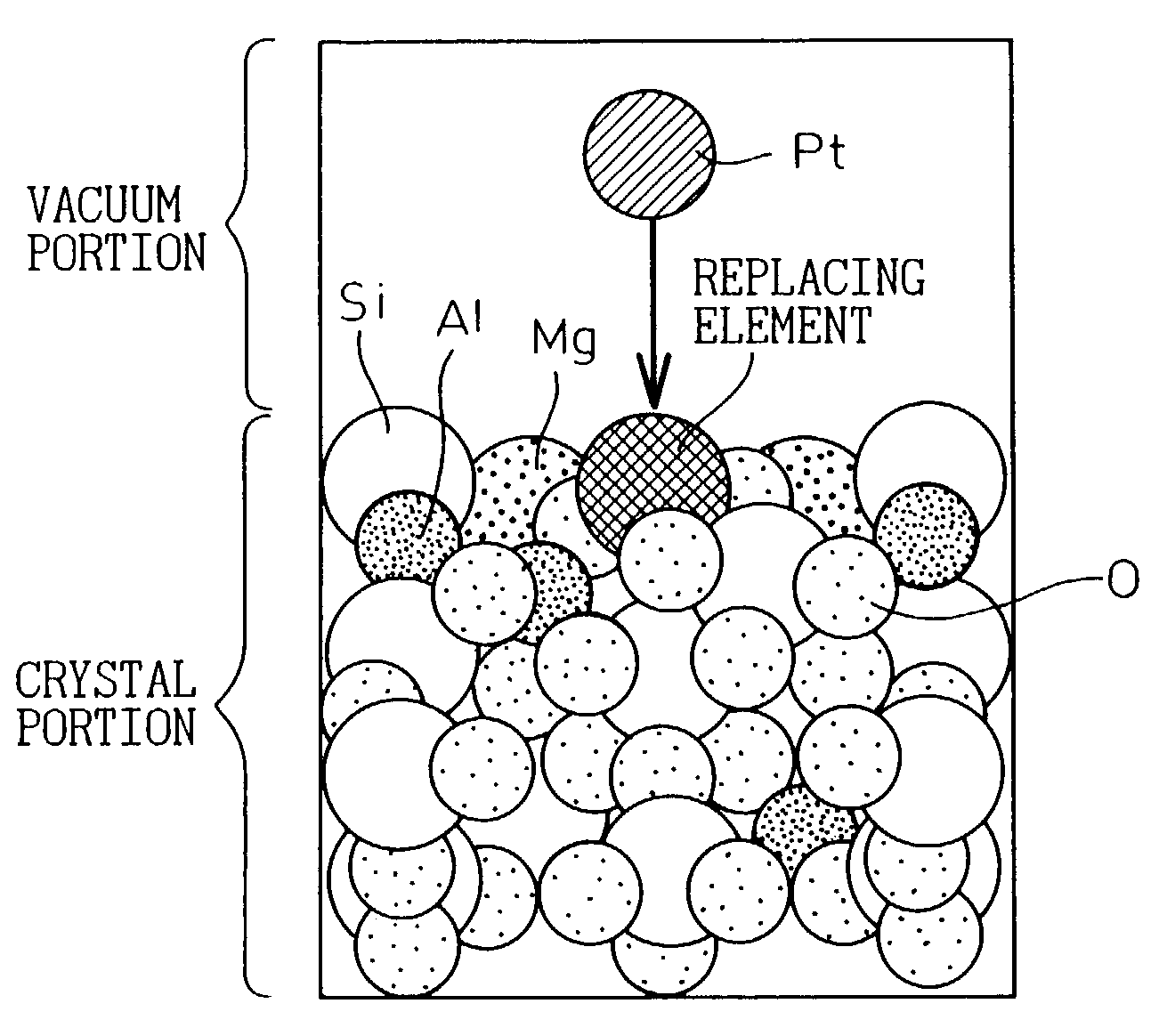
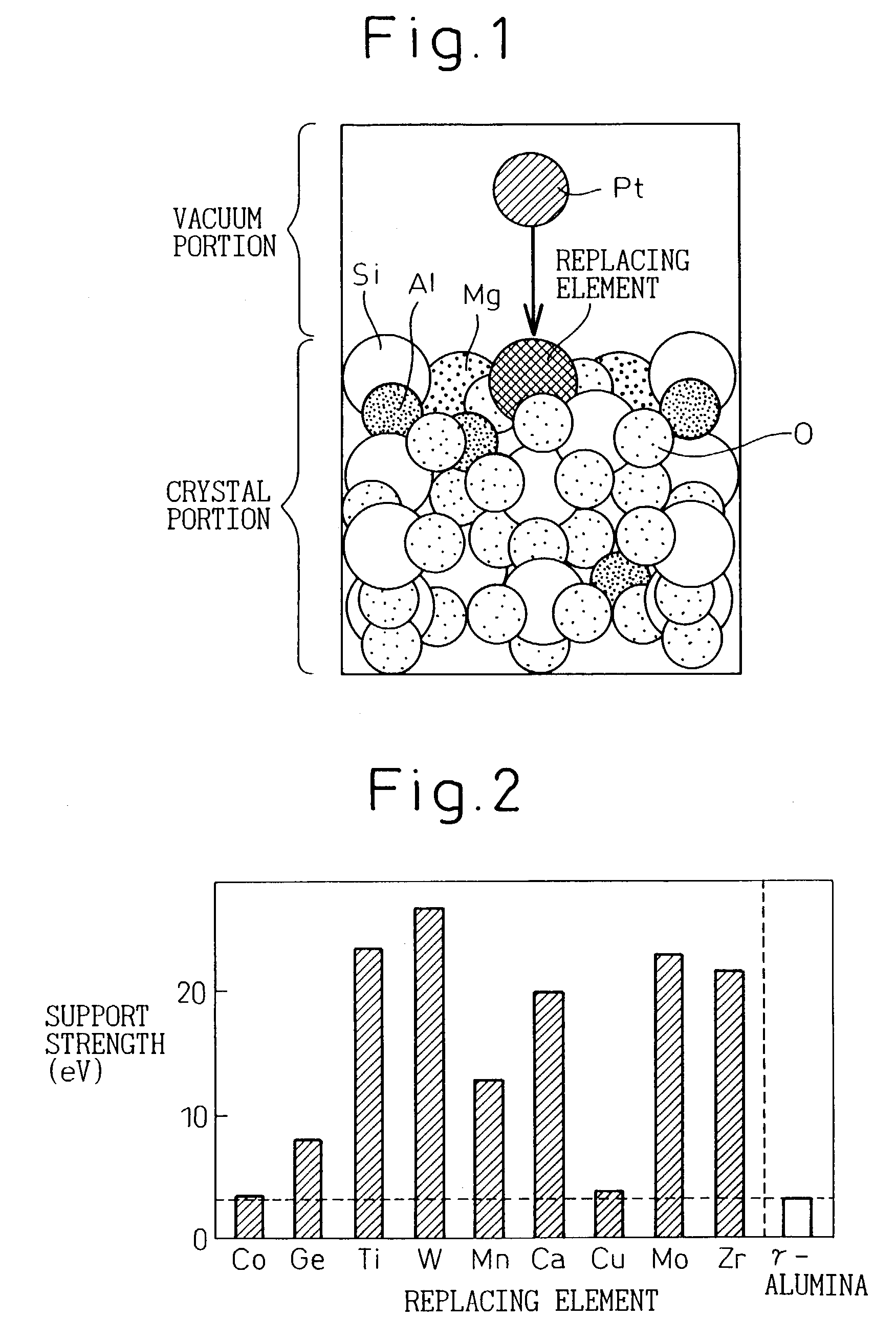
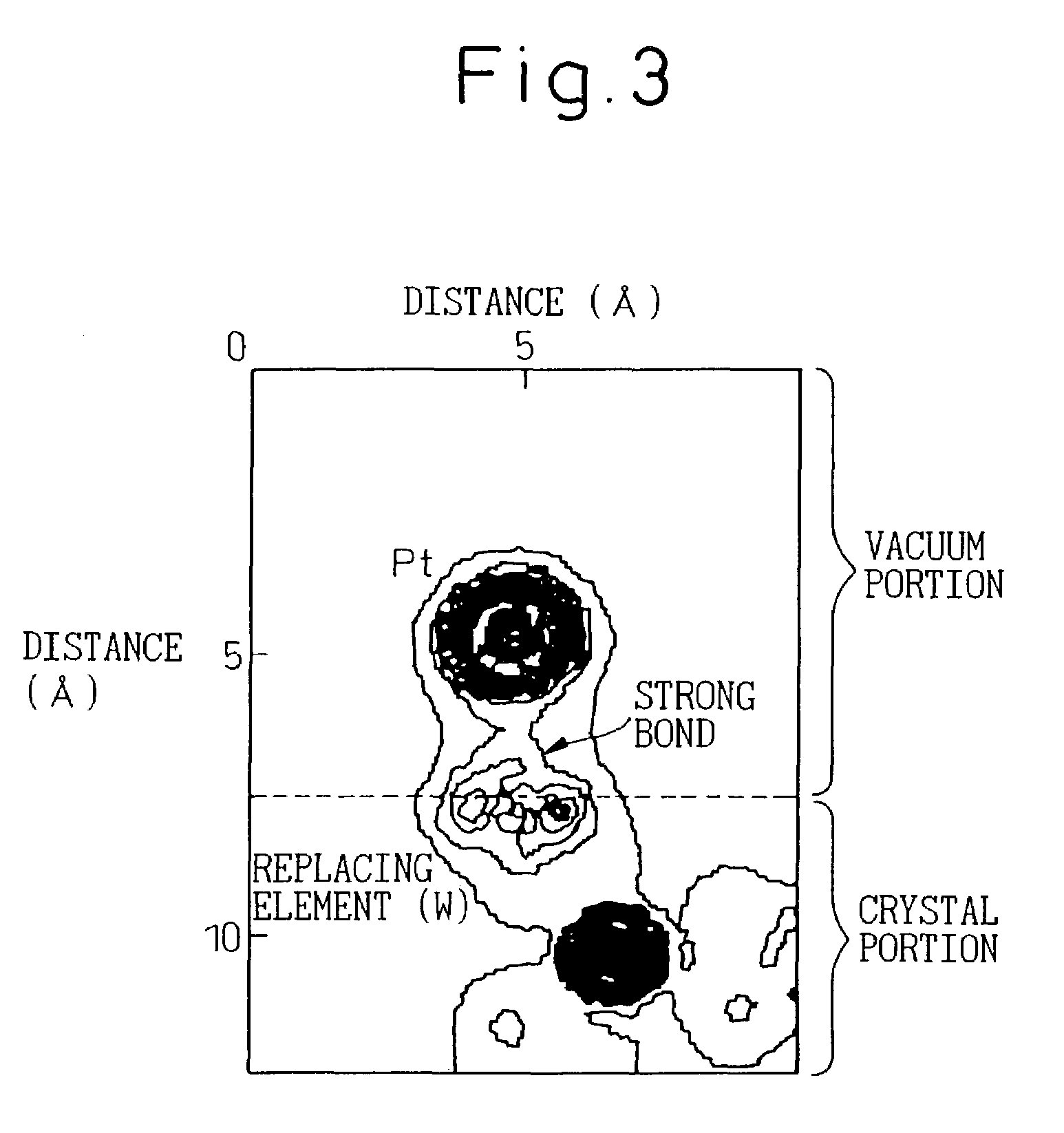
This invention aims at providing a catalyst body exhibiting a lower degradation of a catalyst due to thermal durability and capable of keeping higher catalyst performance for a long time. A catalyst component such as Pt is directly supported by Zr, W, etc, replacing elements inside a support such as Al of cordierite to provide a catalyst body without forming a coating layer. A combination of the catalyst component and the element inside the support is selected so that support strength is greater than 5 eV by simulation using a density functional method. Coarsening of catalyst particles can be suppressed and a high-performance catalyst body excellent in thermal durability can be obtained.
Owner:DENSO CORP
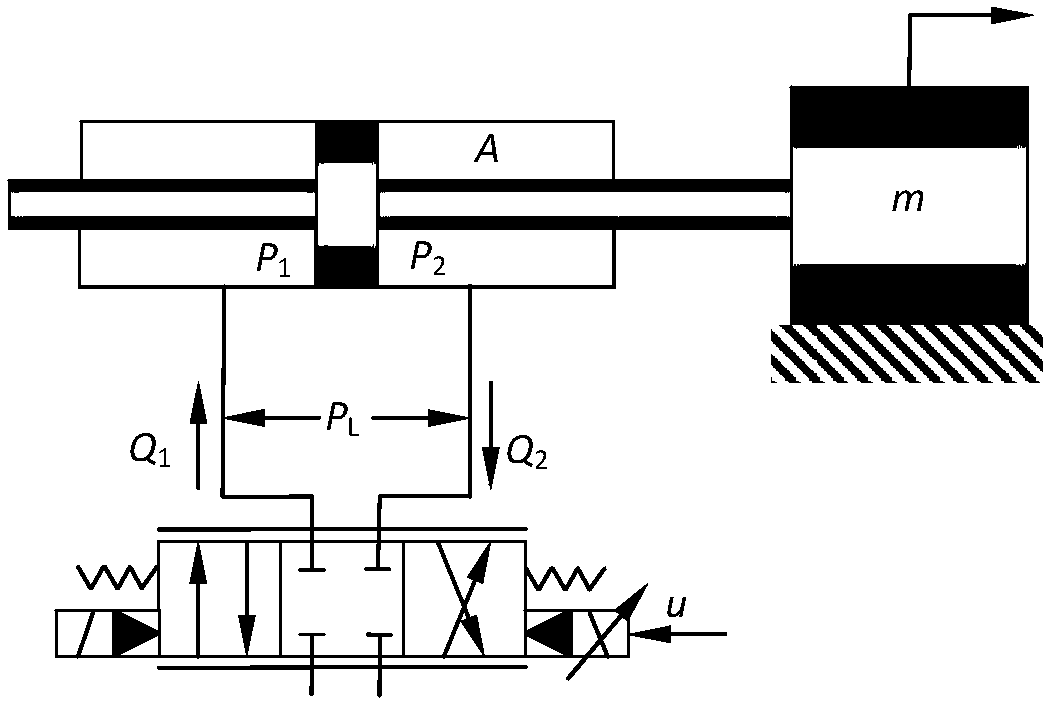
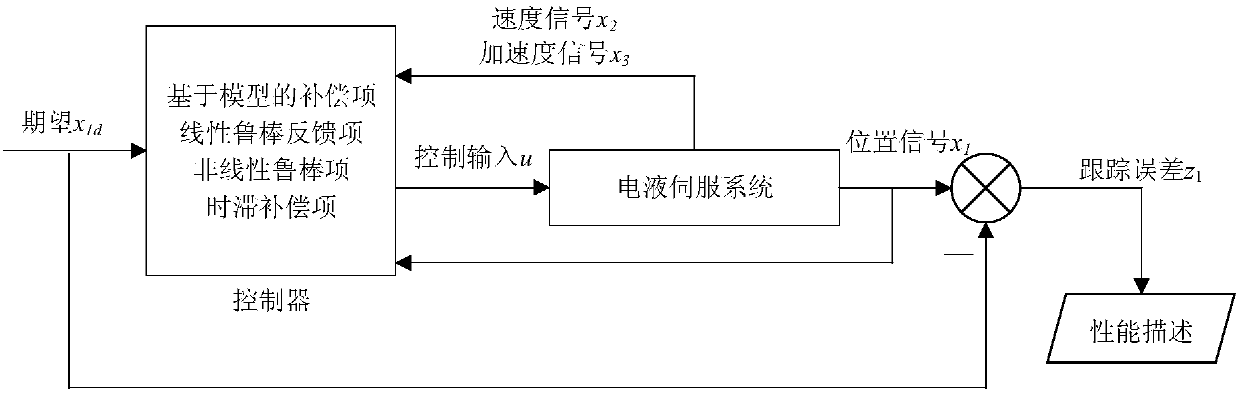
Electro-hydraulic servo system position tracking control method considering input delay constraints
ActiveCN108345268ASolve the problem of input delay constraints affecting system performanceGood high-precision position tracking performanceProgramme controlComputer controlLyapunov stabilityMathematical model
The invention discloses an electro-hydraulic servo system position tracking control method considering input delay constraints. The method comprises steps: a mathematical model for the electro-hydraulic servo system is built; a controller considering input delay constraints is designed; and a Lyapunov stability theory is applied to stability proving, the bounded and stable position tracking performance of the system is obtained, and a result of all signals of the system to be bounded is obtained. Through introducing an input delay compensation signal in the controller, an open-loop error system without input delay is thus acquired, and in combination of a Lyapunov-krasovskii functional method, influenced brought by delay are eliminated. The problem that input delay constraints in the actual electro-hydraulic servo system influence the system performance can be effectively solved, and better high-precision position tracking performance can be acquired.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Catalyst body
InactiveUS7129193B2Stable supportEasy to degradeExhaust apparatusDispersed particle separationCatalyst degradationHeat resistance
This invention aims at providing a catalyst body exhibiting a lower degradation of a catalyst due to thermal durability and capable of keeping higher catalyst performance for a long time. A catalyst component such as Pt is directly supported by Zr, W, etc, replacing elements inside a support such as Al of cordierite to provide a catalyst body without forming a coating layer. A combination of the catalyst component and the element inside the support is selected so that support strength is greater than 5 eV by simulation using a density functional method. Coarsening of catalyst particles can be suppressed and a high-performance catalyst body excellent in thermal durability can be obtained.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Thermal activation delayed fluorescence probe for detecting hydrogen peroxide
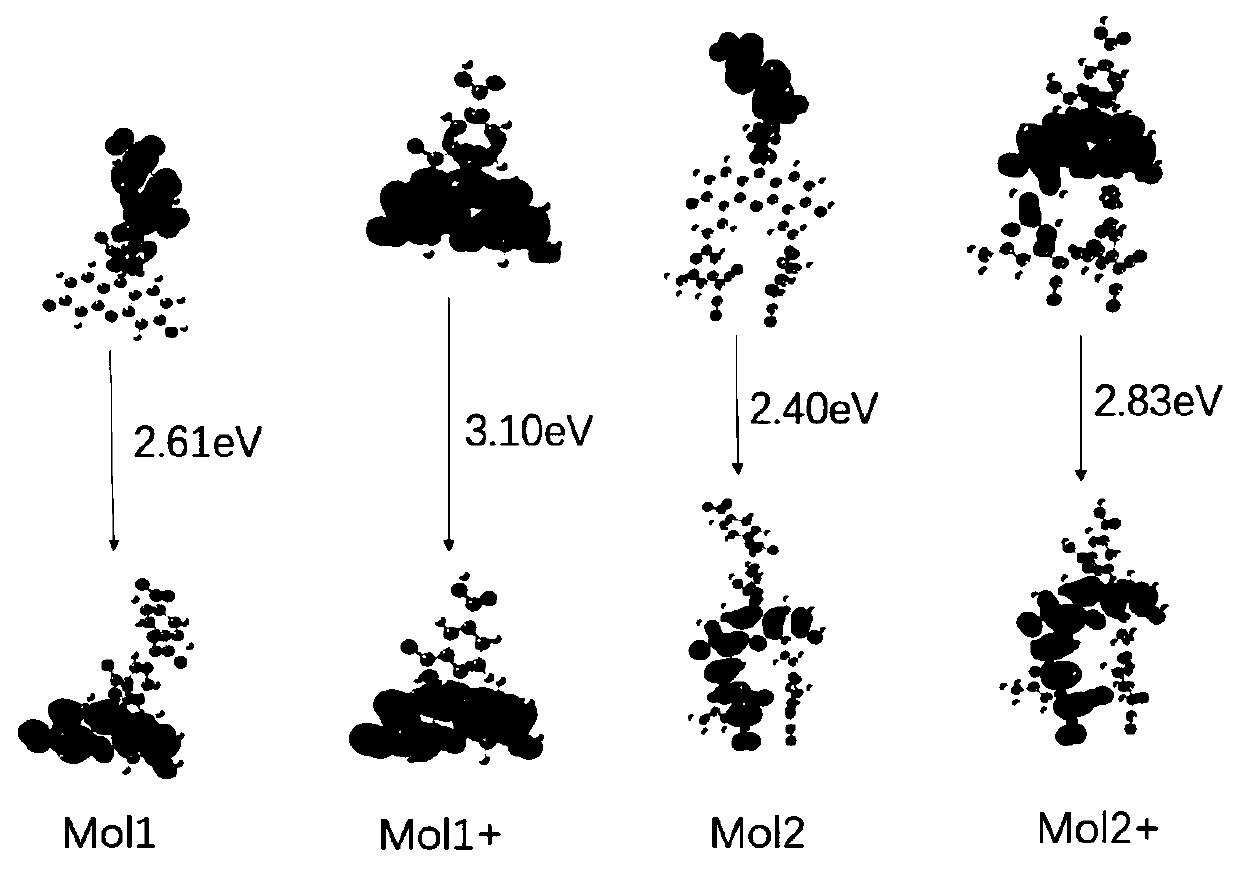
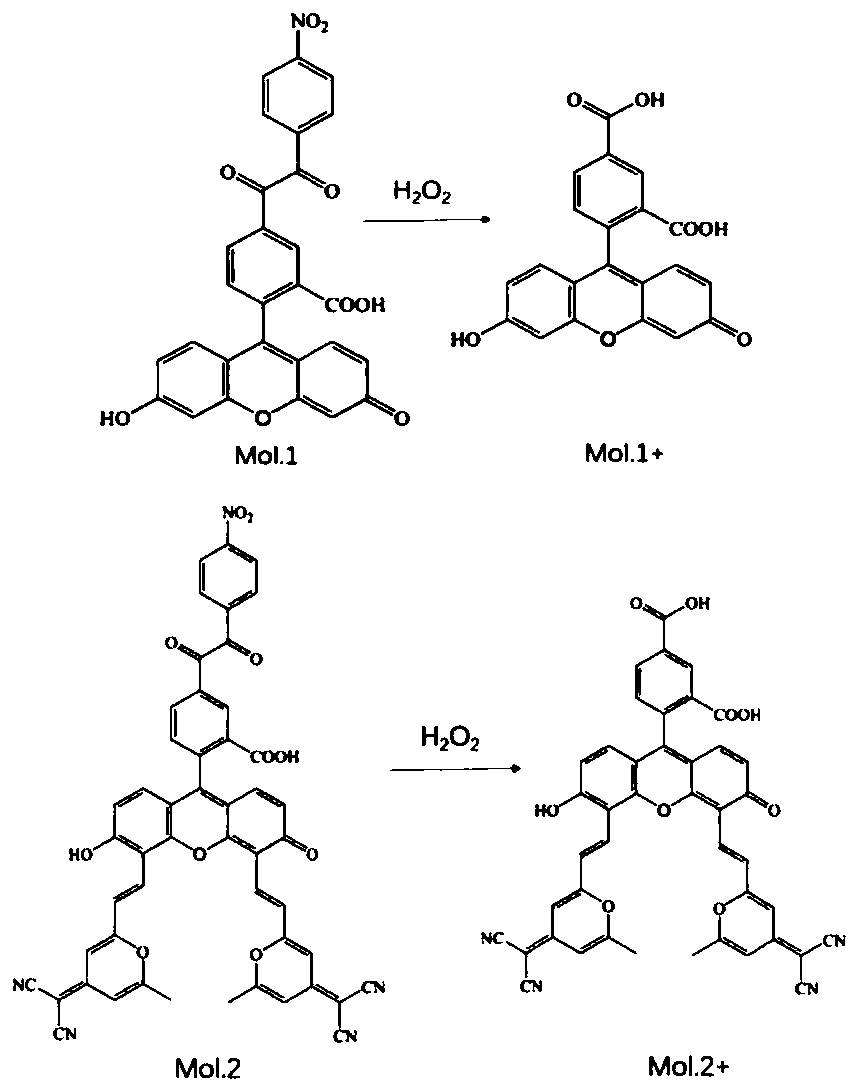
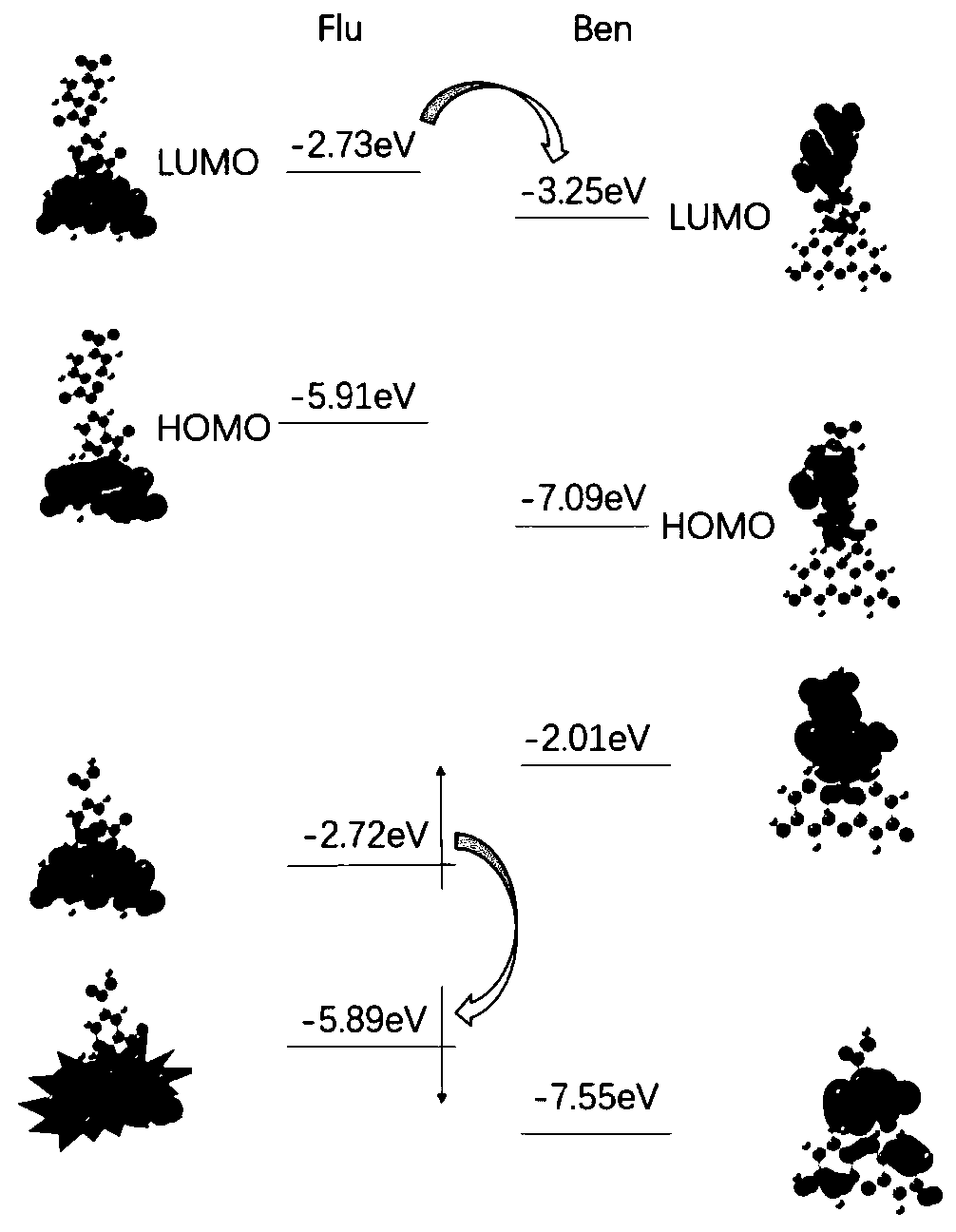
InactiveCN109970726ADelayed fluorescence effectObvious red shiftOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFunctional methodsSide chain
The invention relates to a thermal activation delayed fluorescence probe for detecting hydrogen peroxide. Optical properties of two fluorescent probe molecules Mol 1 and Mol 2 used for detecting hydrogen peroxide are calculated based on the time-dependent density functional theory, and response mechanisms of the two fluorescent probe molecules are explained. The result shows that compared with theexperimental probe molecule Mol 1, the Mol 2 has the characteristics that the absorption peak and the emission peak are obviously subjected to red shift due to the fact that a metal-free side chain is added, and a better fluorescence probe property is exhibited. In addition, through analysis of molecular orbital distribution and charge transfer difference graphs, the photoinduced electron transfer mechanism of the probe is explained. According to the invention, the S-T energy gap of the two probes is calculated through an optimal functional method, the results shows that the energy gap of thedesigned molecule Mol 2 is 0.31 eV, and the Mol 2 is a probe molecule with a delayed fluorescence effect.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
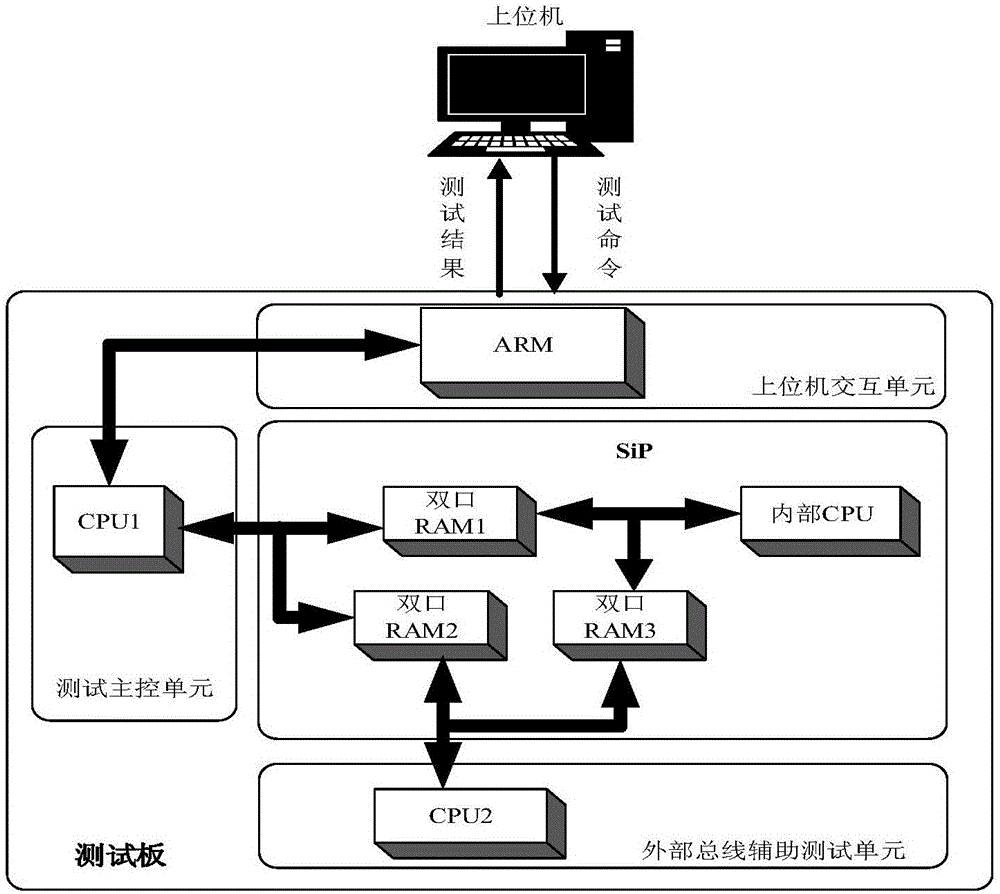
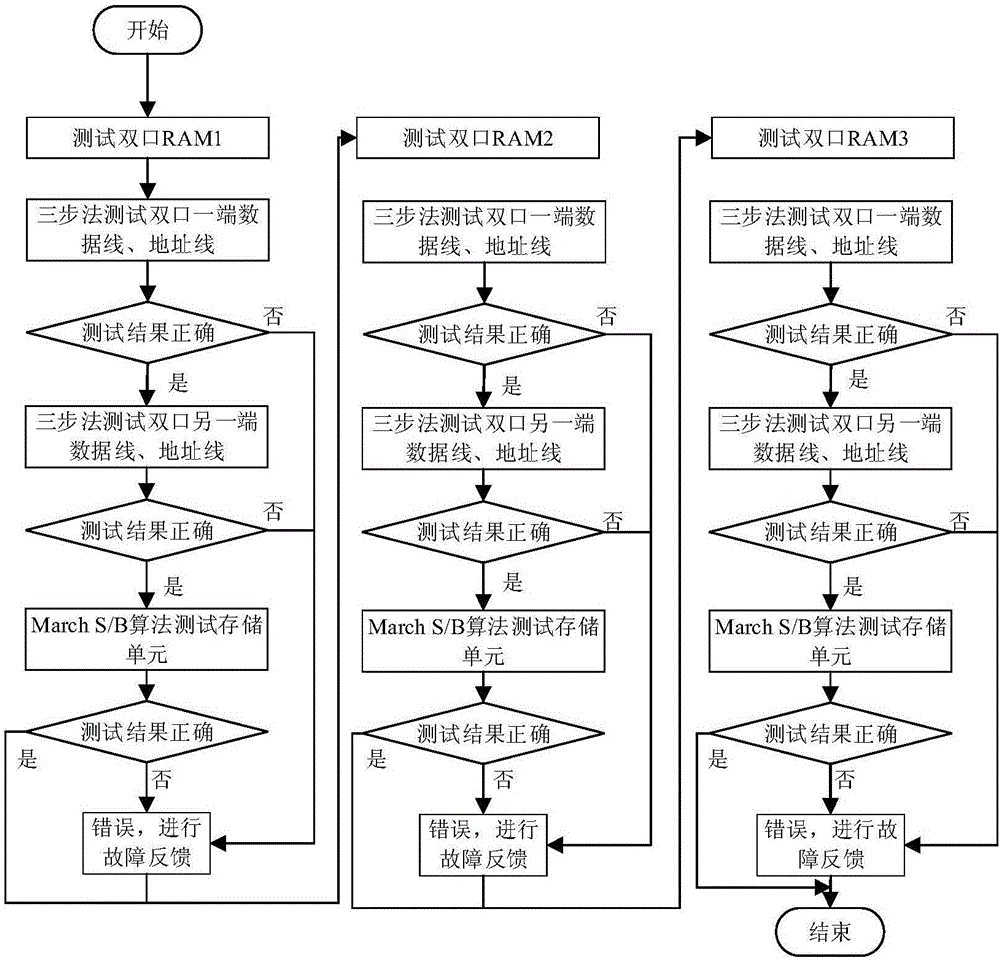
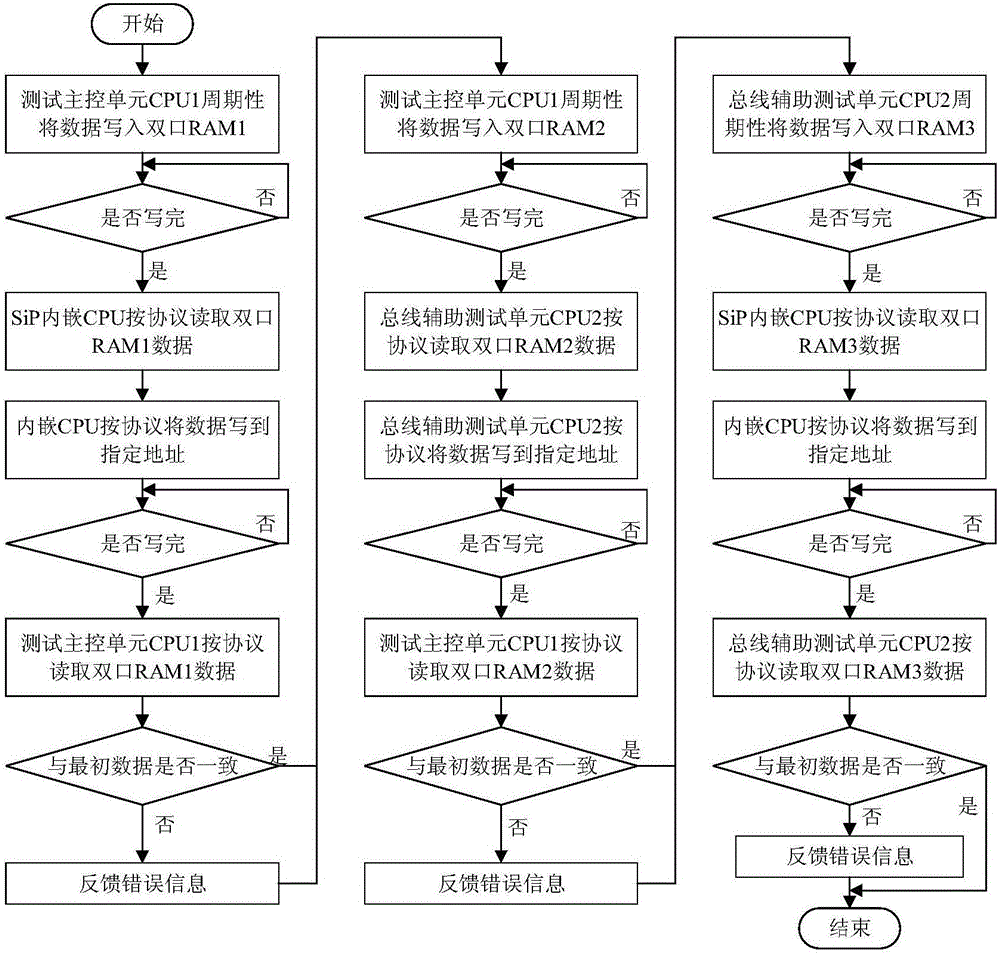
Functional test method for SiP (system in package) embedded memory
InactiveCN106646191AImprove reliabilityImprove fault coverageElectronic circuit testingTest efficiencyFault coverage
The present invention belongs to the SiP testing technical field and relates to a functional test method for a SiP (system in package) embedded memory. According to the functional test method of the invention, a functional test and structural test-combined ideal is adopted to carry outer a detailed function test on SiP, and therefore, on the one hand, a fault coverage rate can be increased, the reliability of SiP application can be improved, and on the other hand, test efficiency can be improved to a certain extent.
Owner:TIANJIN JINHANG COMP TECH RES INST
Identification method of eutectic structure of explosive
InactiveCN107589102ARealize analysis and identificationQuick analysisRaman scatteringSingle substanceFunctional methods
The invention discloses an identification method of a eutectic structure of explosive. The identification method comprises the following steps: firstly determining Raman spectra of a eutectic explosive sample and single-substance explosive samples to obtain corresponding fingerprint spectrum characteristic peaks; adopting a B3LYP mixing functional method, and calculating vibration frequencies of explosive molecules respectively by using a DFT (Density Functional Theory); then identifying the fingerprint spectrum characteristic peaks of the explosive molecules and attributing a vibration mode;and finally, comparing the Raman spectra of the eutectic explosive sample and the two single-substance explosive samples, attributing the vibration mode of the eutectic explosive sample according to vibration peak displacement of the fingerprint spectrum characteristic peaks of the two single-substance explosive samples, and analyzing the forming reasons of the eutectic structure through Raman characteristic displacement. According to the identification method, the eutectic structure of the explosive is rapidly analyzed and identified by simply mixing the single-substance explosive and the single-substance explosive mixed two by two, and taking the single-substance explosive to react two by two to form the inconsistent eutectic Raman spectra and generate different Raman peak position changes.
Owner:徐文敏
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com