Patents
Literature
949results about "Mechanical oscillations control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
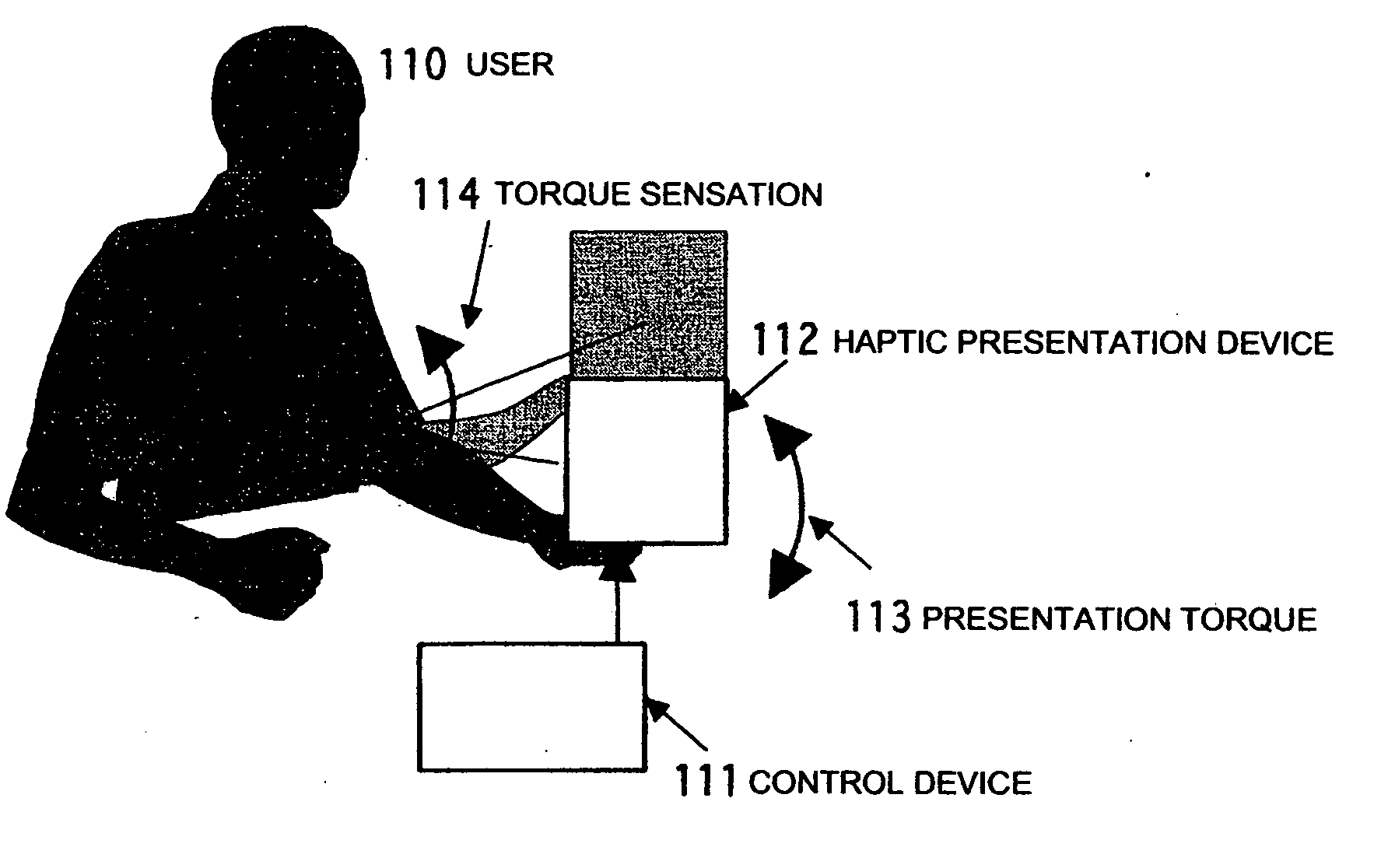
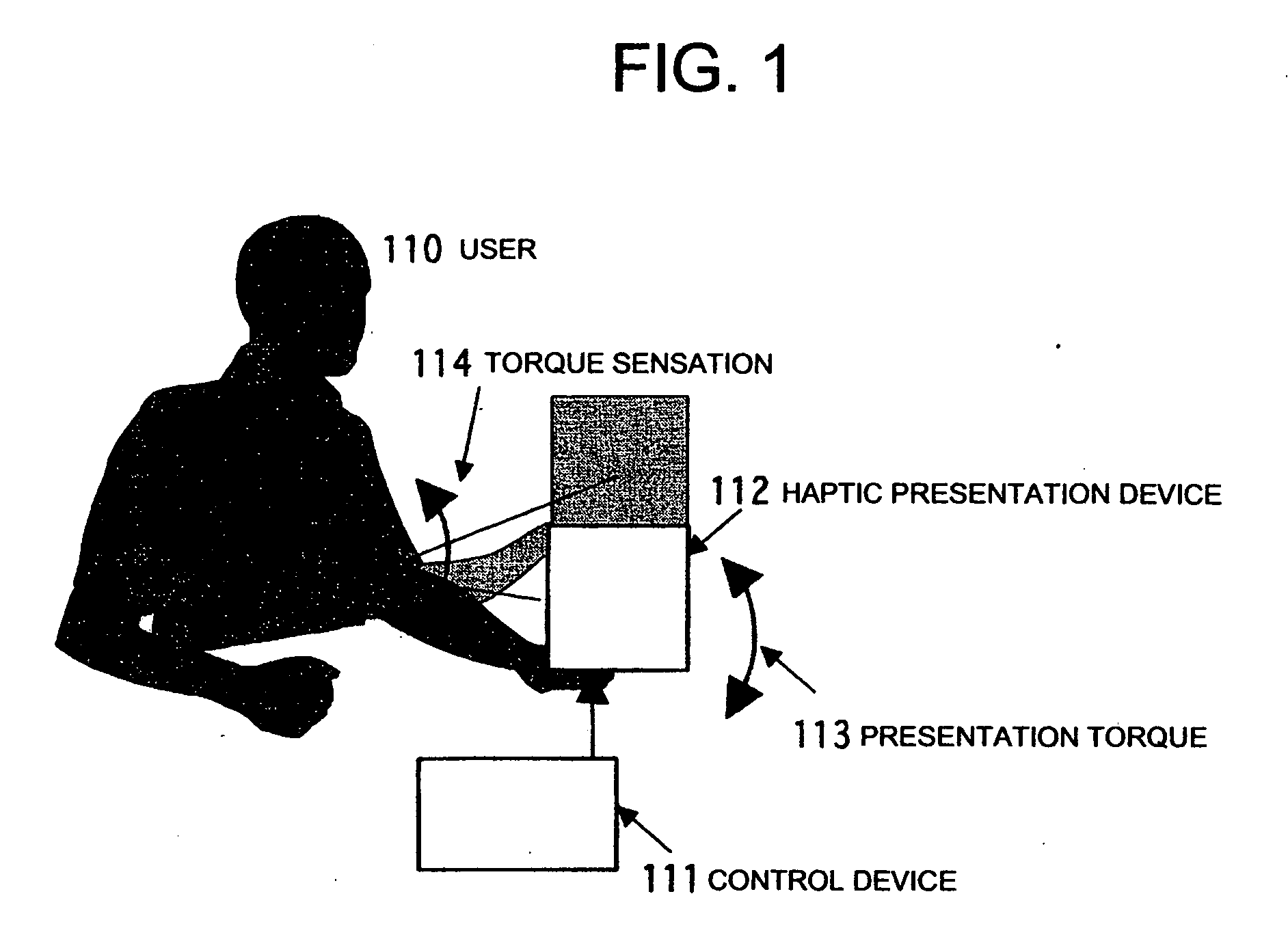
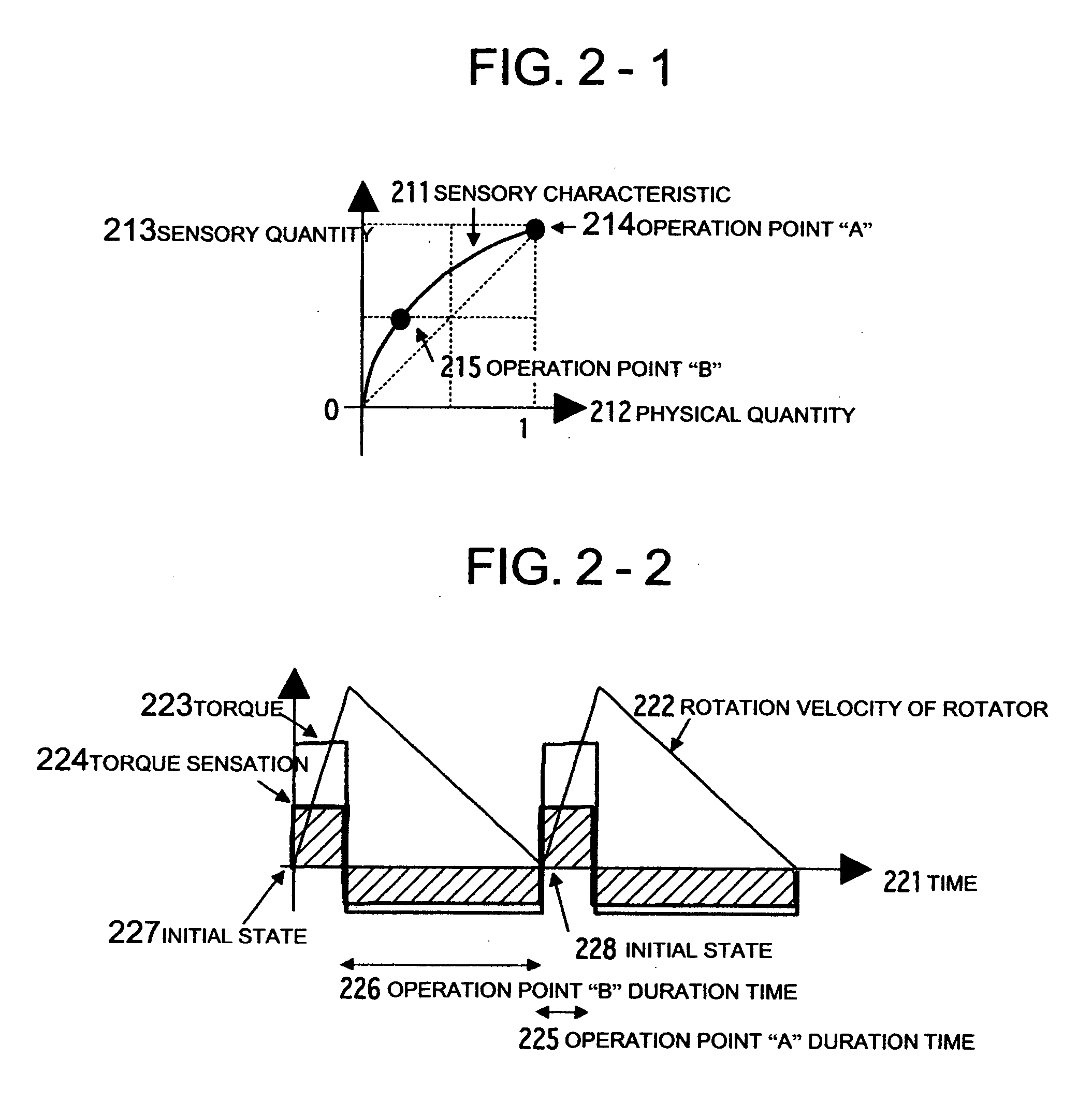
Tactile force sense information display system and method
InactiveUS20070091063A1Efficiently presentedInformation can be presentedInput/output for user-computer interactionMechanical oscillations controlHuman bodyInformation display systems
A system and a method are realized in which in a conventional non-grounding man-machine interface having no reaction base on the human body and for giving the existence of a virtual object and the impact force of a collision to a person, a haptic sensation of a torque, a force and the like can be continuously presented in the same direction, which can not be presented by only the physical characteristic of a haptic sensation presentation device. In a haptic presentation device 112, the rotation velocity of at least one rotator in the haptic presentation device 112 is controlled by a control device 111, and a vibration, a force or a torque as the physical characteristic is controlled, so that the user 110 is made to conceive various haptic information of the vibration, force, torque or the like. The haptic information presentation system uses a human sensory characteristic or illusion to suitably control the physical quantity, and causes the person to feel a force which can not exist physically, or a haptic sensory physical characteristic.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
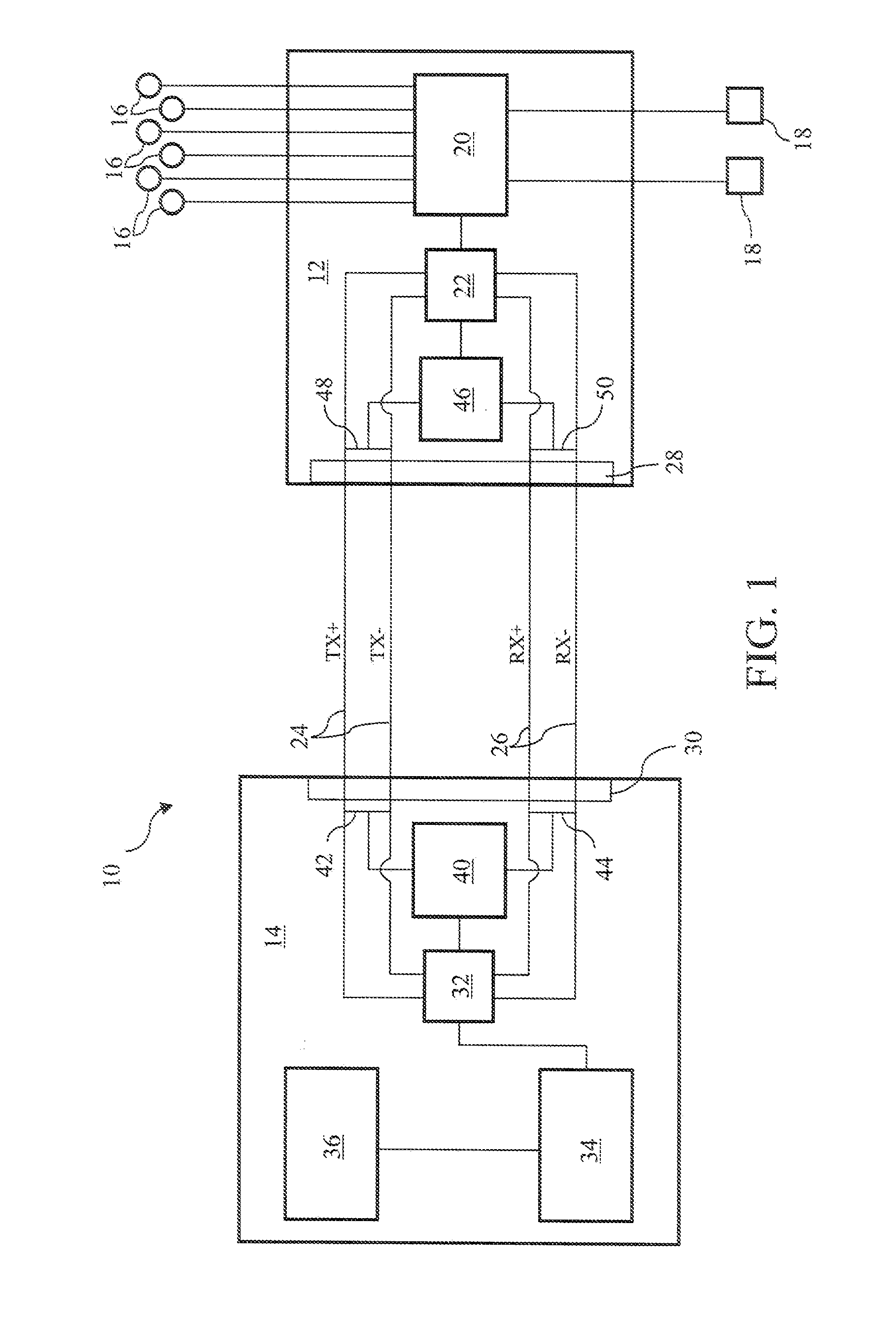
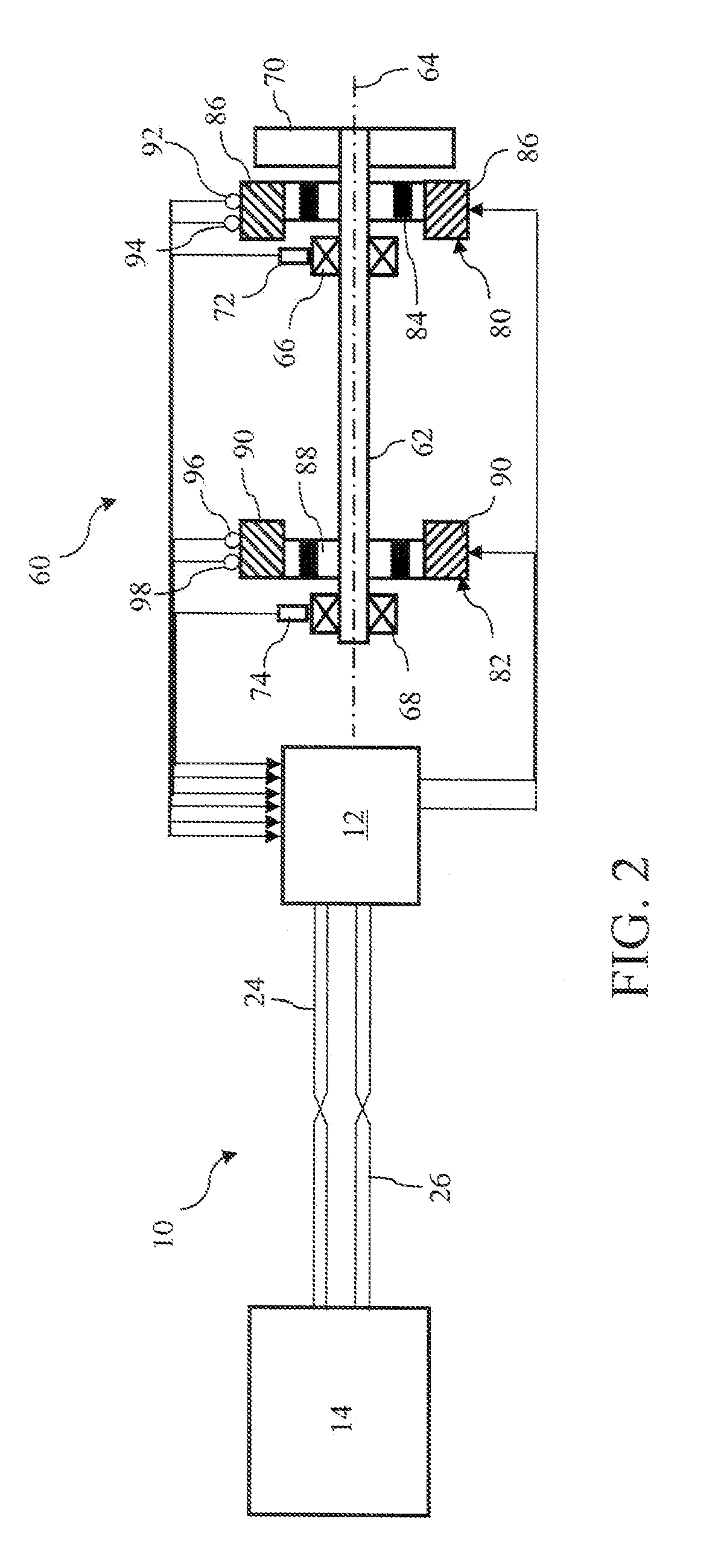
Motion control system with digital processing link
InactiveUS20110208361A1Evenly spreading energy contentReduce generationProgramme controlSampled-variable control systemsVibration controlControl signal
A digital processing link for a vibration control system collects sensor signals at a transfer station and combines the sensor signals into a collective signal that is transmitted under a digital communications protocol to a base station. The sensor signals are separated at the base station and individually processed to produce one or more output control signals to actuators for counteracting the measured vibration.
Owner:LORD CORP
Synchronized array of vibration actuators in a network topology
ActiveUS20150081110A1Sampled-variable control systemsMechanical oscillations controlDiagnostic Radiology ModalityControl vector
The disclosure relates to a Synchronized Array of Vibration Actuators in a Network Topology providing synchronized arrays of low-cost, readily available vibration actuators to emulate superlative single actuators and bring together sets of these emulated high-performance actuators to create a broad range of desired control effects. Such actuator arrays may operate in both spatial and temporal modes, creating haptic effects that relate to the user via their position and orientation in space. The spatial mode may create h-pulses or the amplitude of a vibrational effect may change based on position of the device. The temporal mode may create vibrational effects that interact with the user to create an awareness of time. Additionally modes include performance, bandwidth, magnitude and reliability modes. The different control modalities may be combined together into a single vector control space, which spans the haptic capabilities of sets and / or subsets of actuators.
Owner:COACTIVE DRIVE CORP
Position control method and robot
ActiveUS20110004343A1Simple configurationQuick controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorTemperatue controlPosition controlRobot
A position control method for controlling a position of a movable portion, includes: performing control of allowing the movable portion to approach a predetermined position by moving the movable portion; and performing control of moving the movable portion to the predetermined position by moving the movable portion and detecting a relative position of the movable portion with respect to the predetermined position by using an imaging unit.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
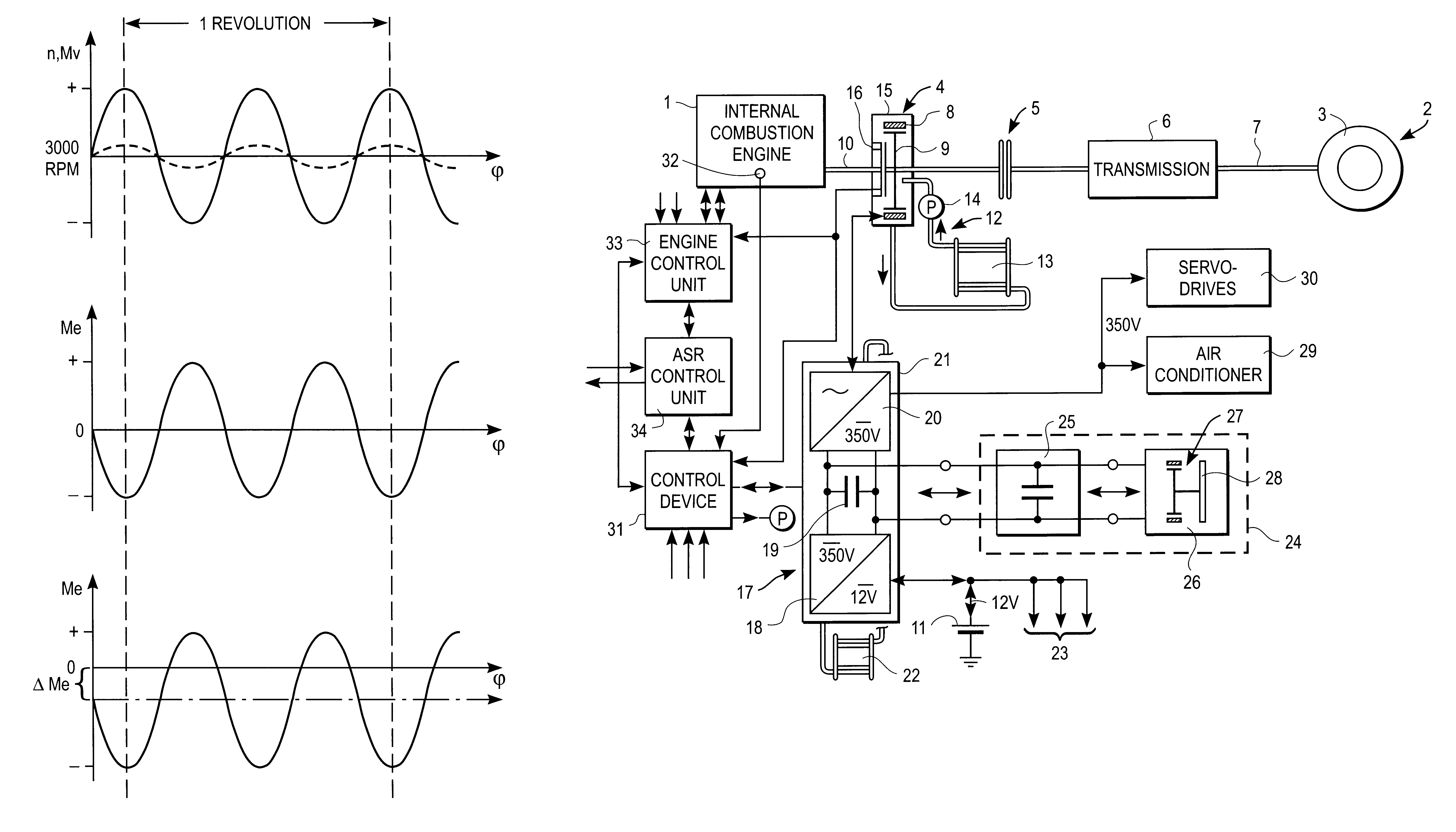
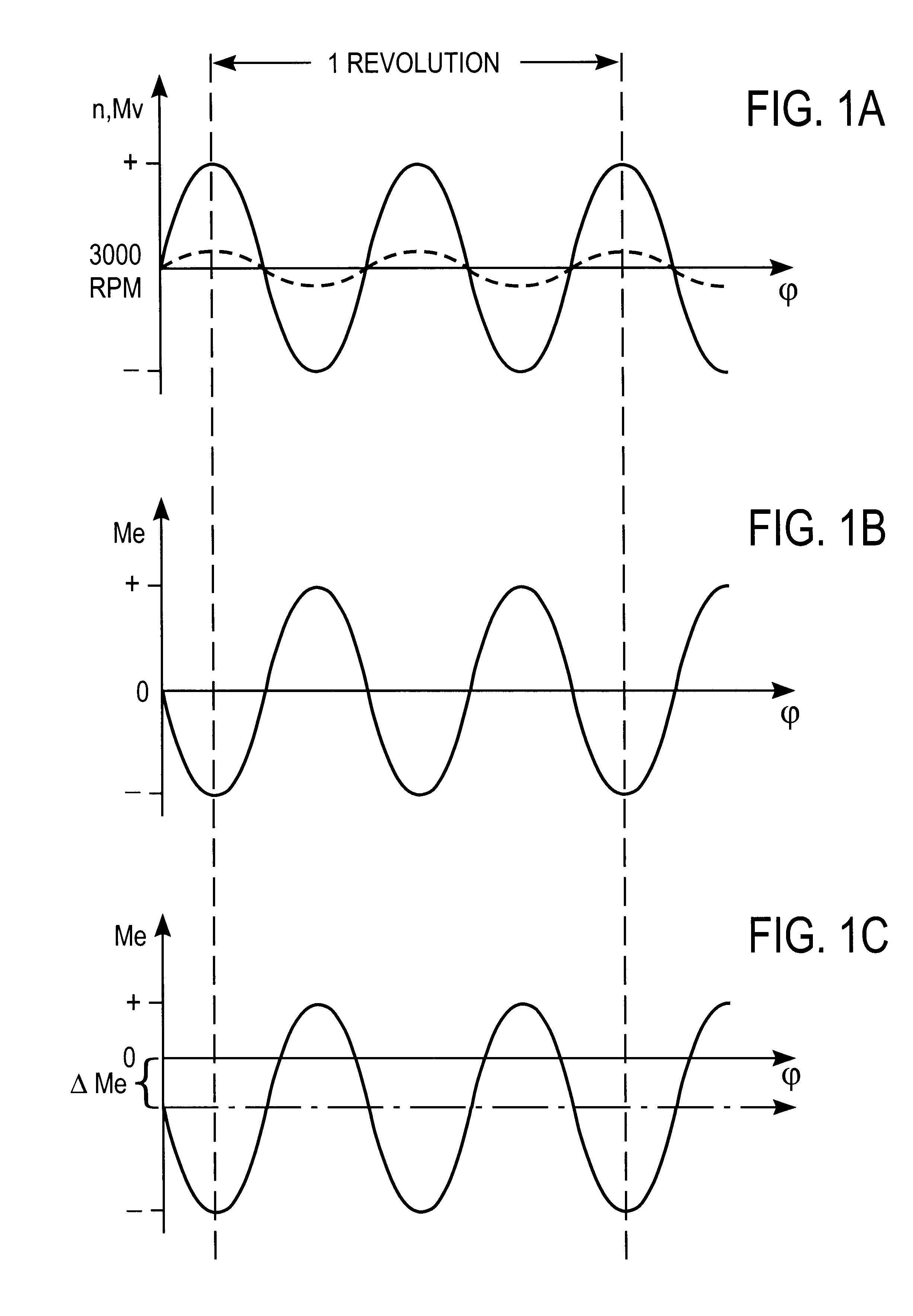
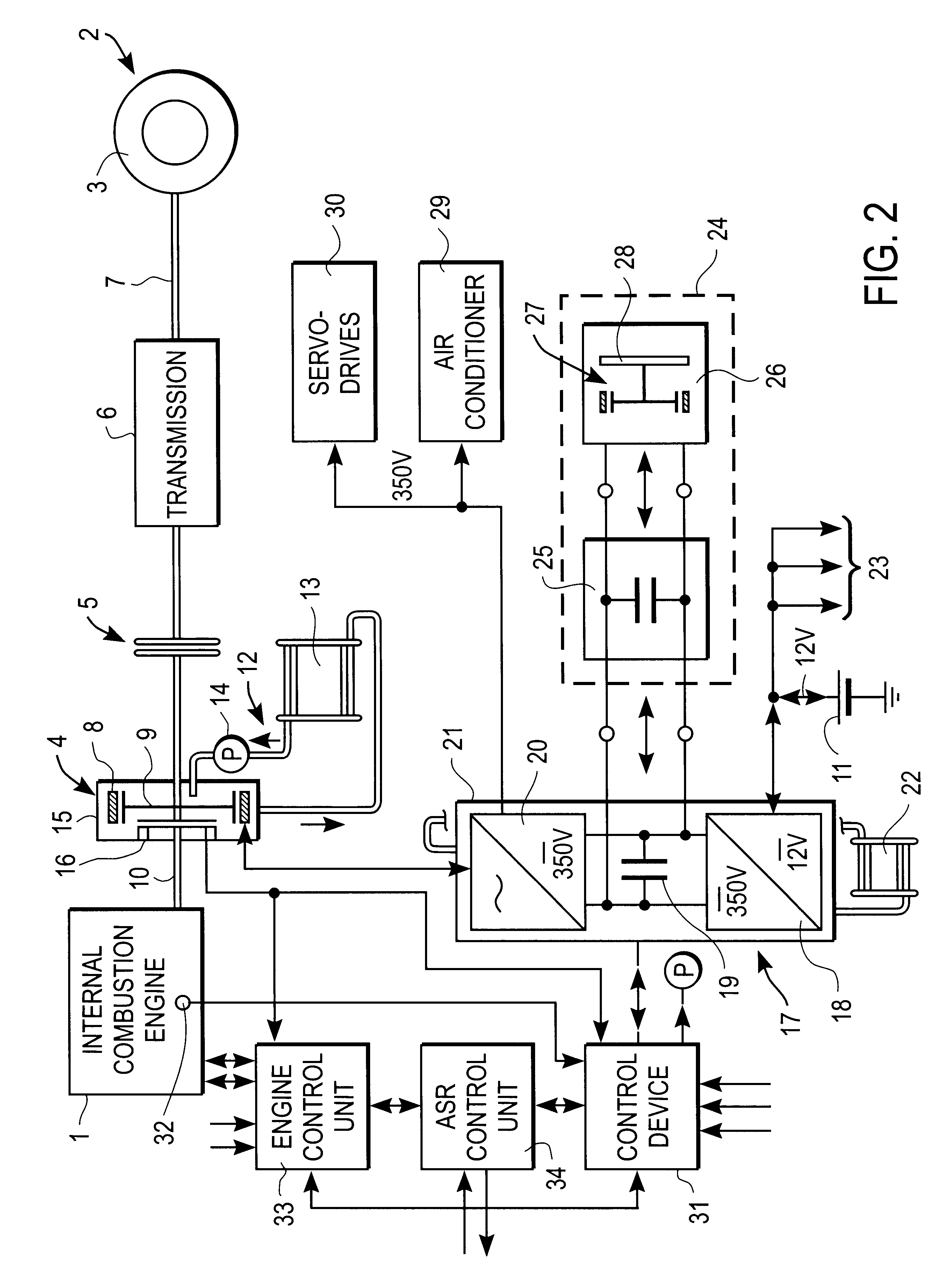
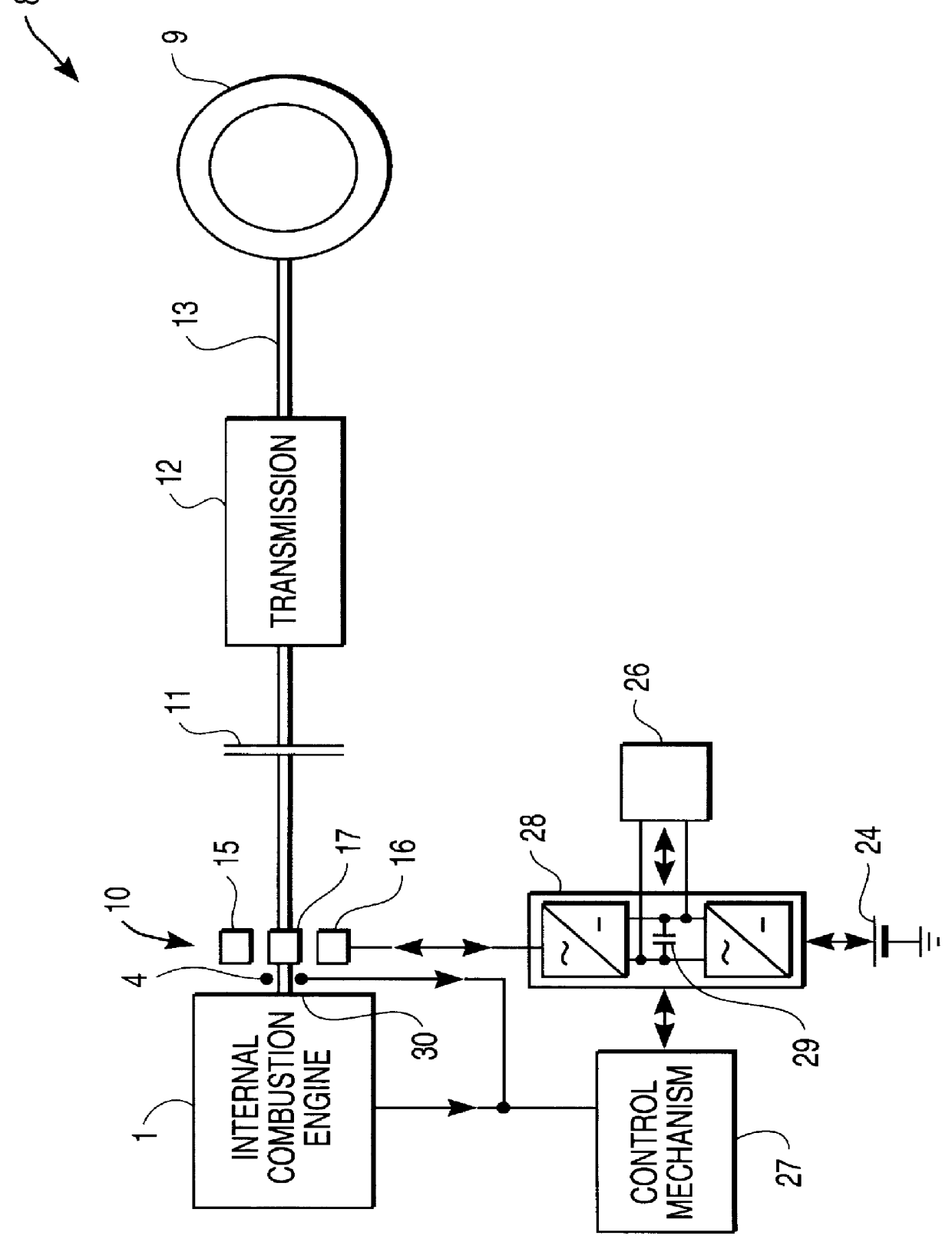
System for actively reducing rotational nonuniformity of a shaft, in particular, the drive shaft of an internal combustion engine, and method for this
InactiveUS6405701B1Rotating vibration suppressionDC motor speed/torque controlExternal combustion engineDrive shaft
The invention concerns a system for active reduction of rotational nonuniformities of a shaft, especially the drive shaft (10) of an internal combustion engine or a shaft that is coupled or can be coupled to it, with at least one electric machine (4), which is coupled or can be coupled to the shaft, wherein the electric machine (4) is controlled such that it generates a rapidly varying torque, to reduce the rotational nonuniformities, and it superimposes on this torque a positive or negative torque in order to further achieve a driving action or braking or generator type action. The invention is also oriented to a corresponding method for active reduction of rotational nonuniformities.
Owner:CONTINENTAL ISAD ELECTRONICS SYST GMBH & CO KG
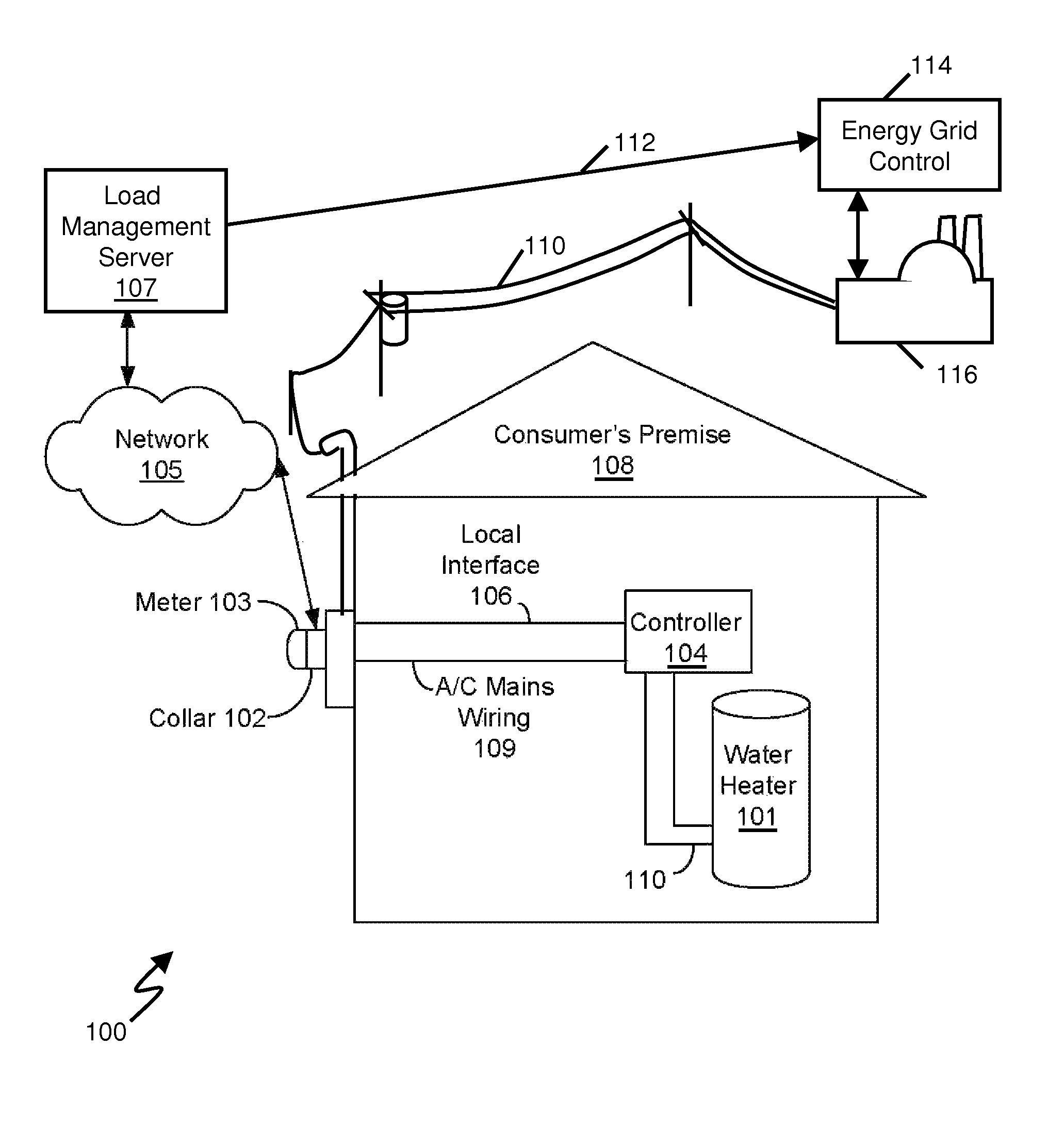
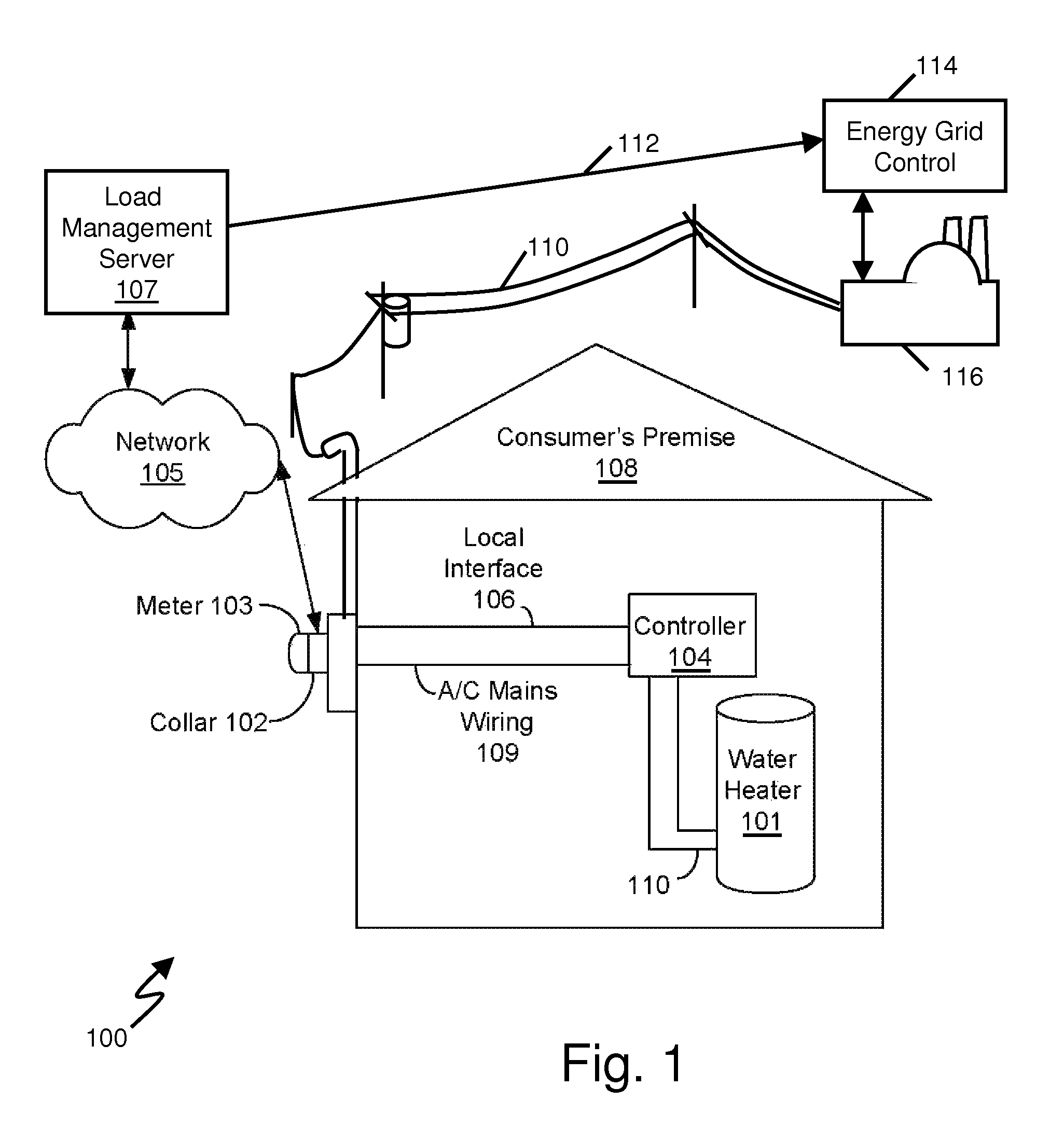
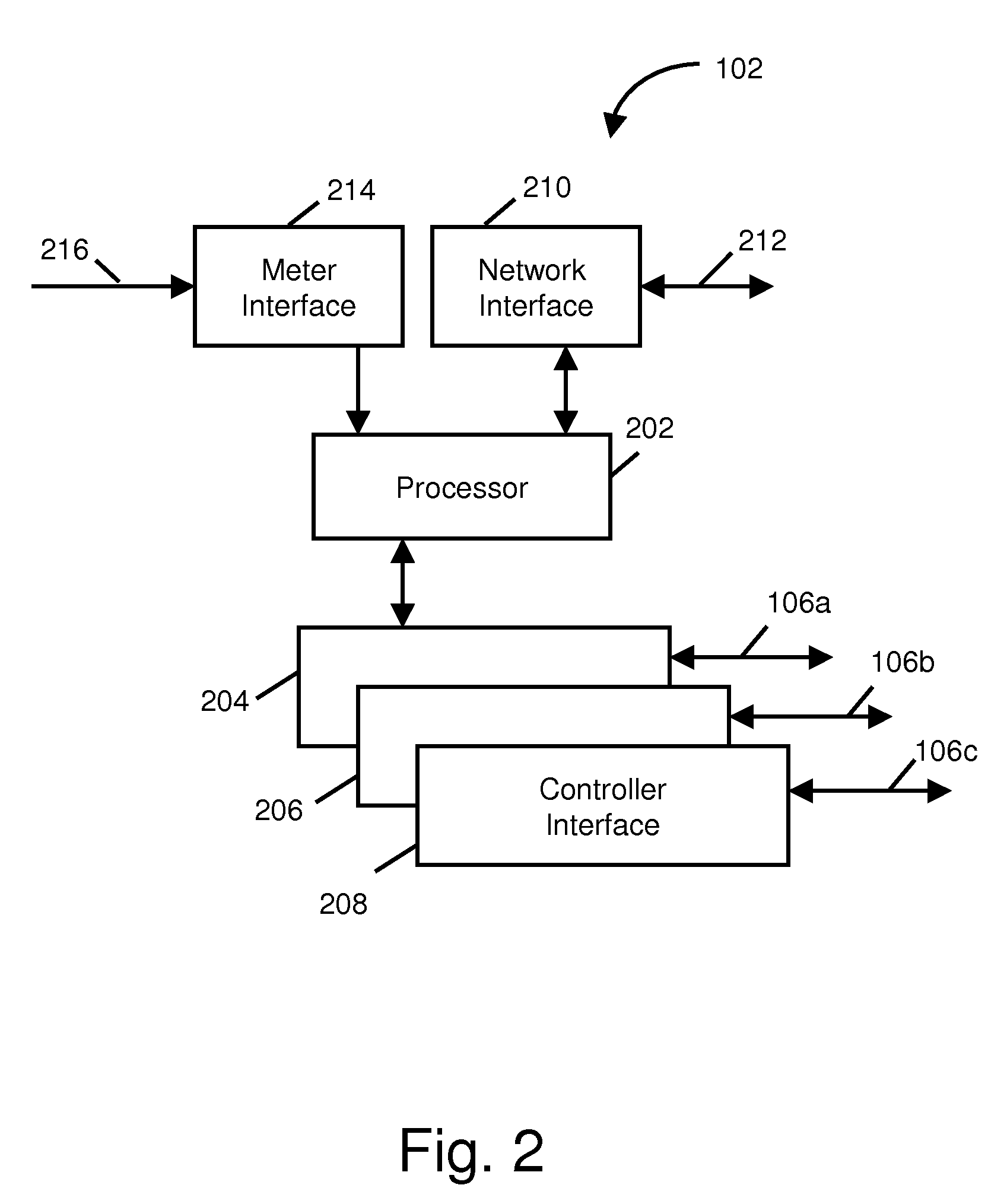
Water heater demand side management system
A system for shifting energy demand from on-peak time windows to off-peak time windows by using hot water heater load shifting, while providing the end user with the level of service (i.e., availability of hot water) according to the user's customary use described by service quality criteria. The shift is accomplished by a controller located at the end user establishment and in communication with a central control server. The controller monitors local water heater upper and / or lower temperature and controls upper and / or lower water heater heating elements in accordance with a demand shift process commanded by the central control server. The controller may determine usage and remaining capacity for reporting back to the central control server. A volumetric capacity and usage determination is disclosed. The control server may select water heaters according to use patterns and / or measured capacity. One embodiment is adapted for use with existing water heaters without disrupting safety features of the existing water heater.
Owner:CARINA TECH +1
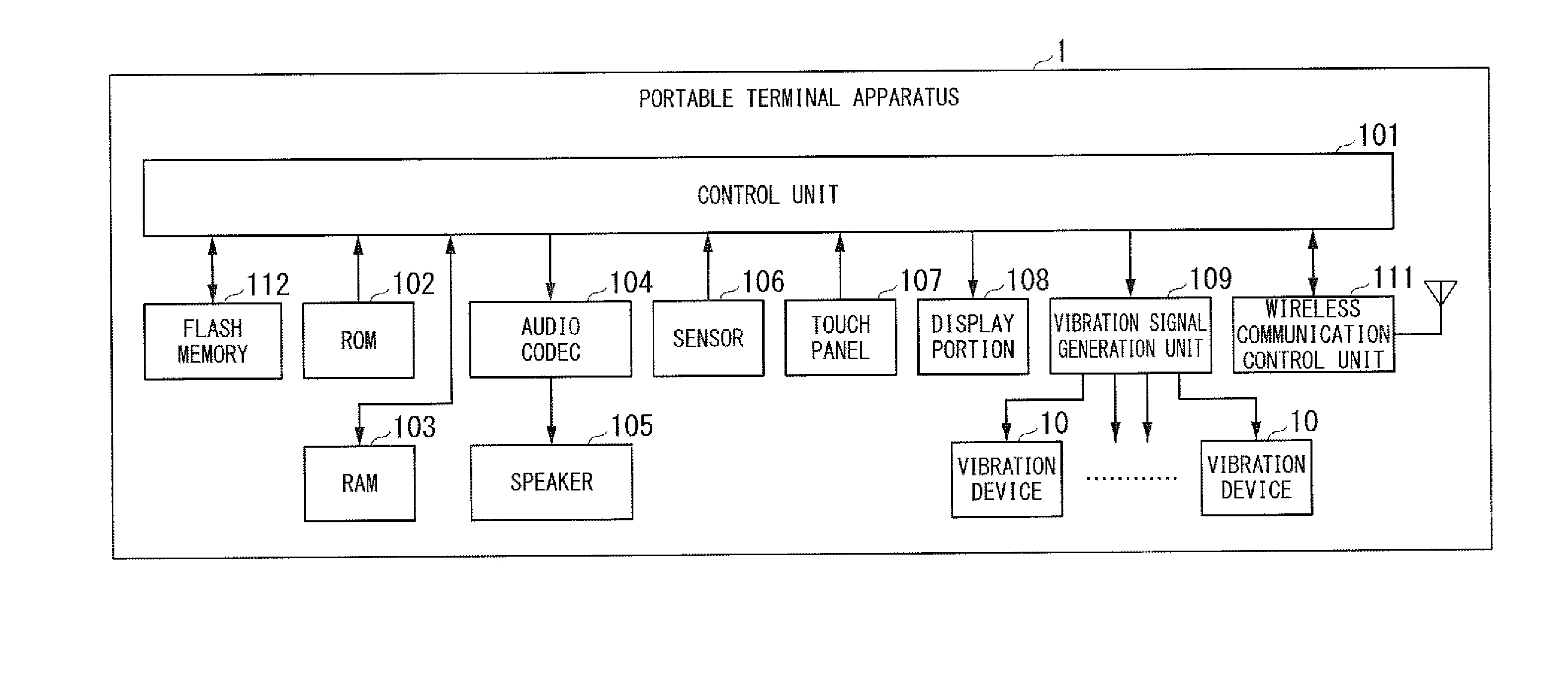
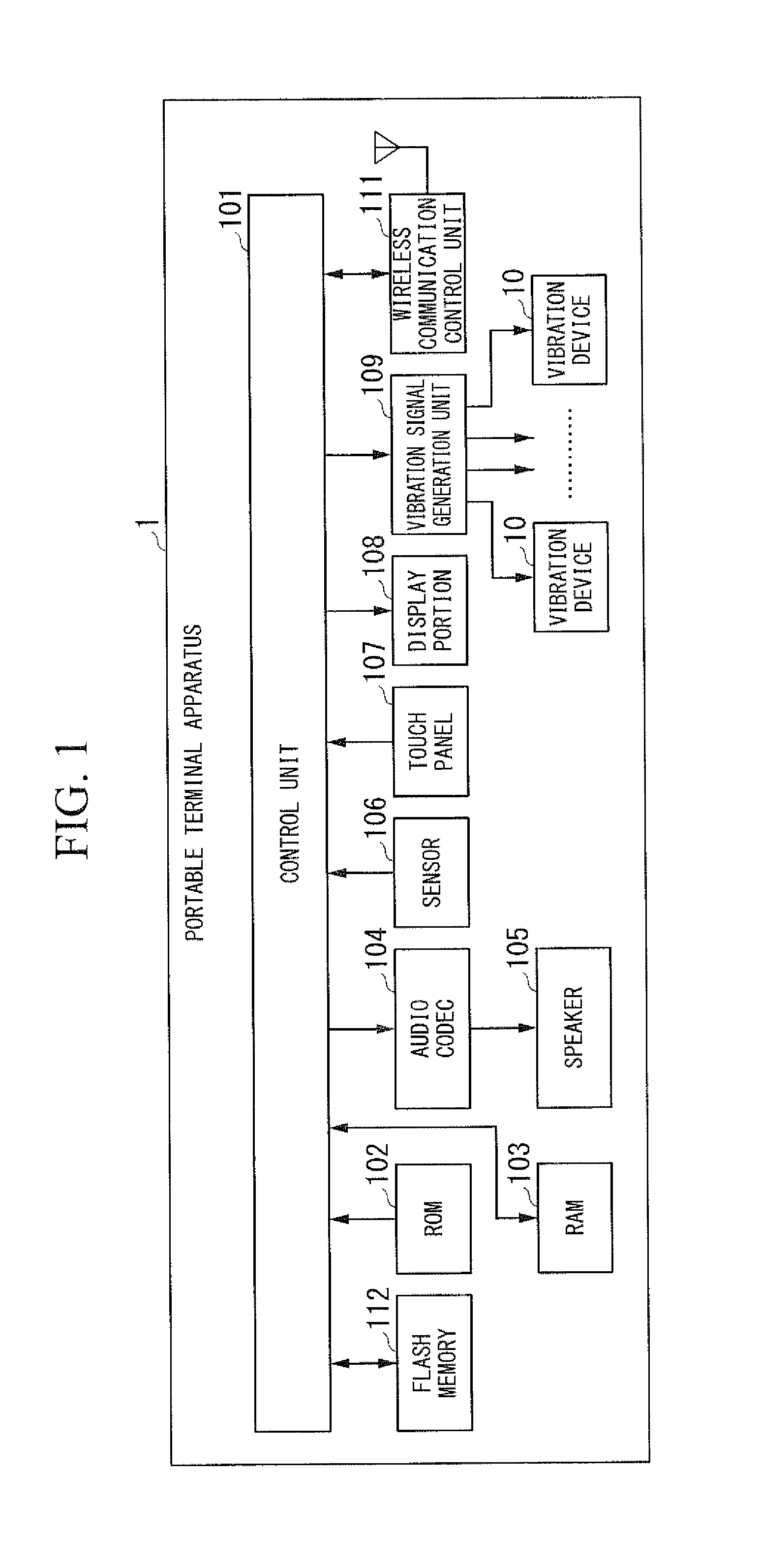
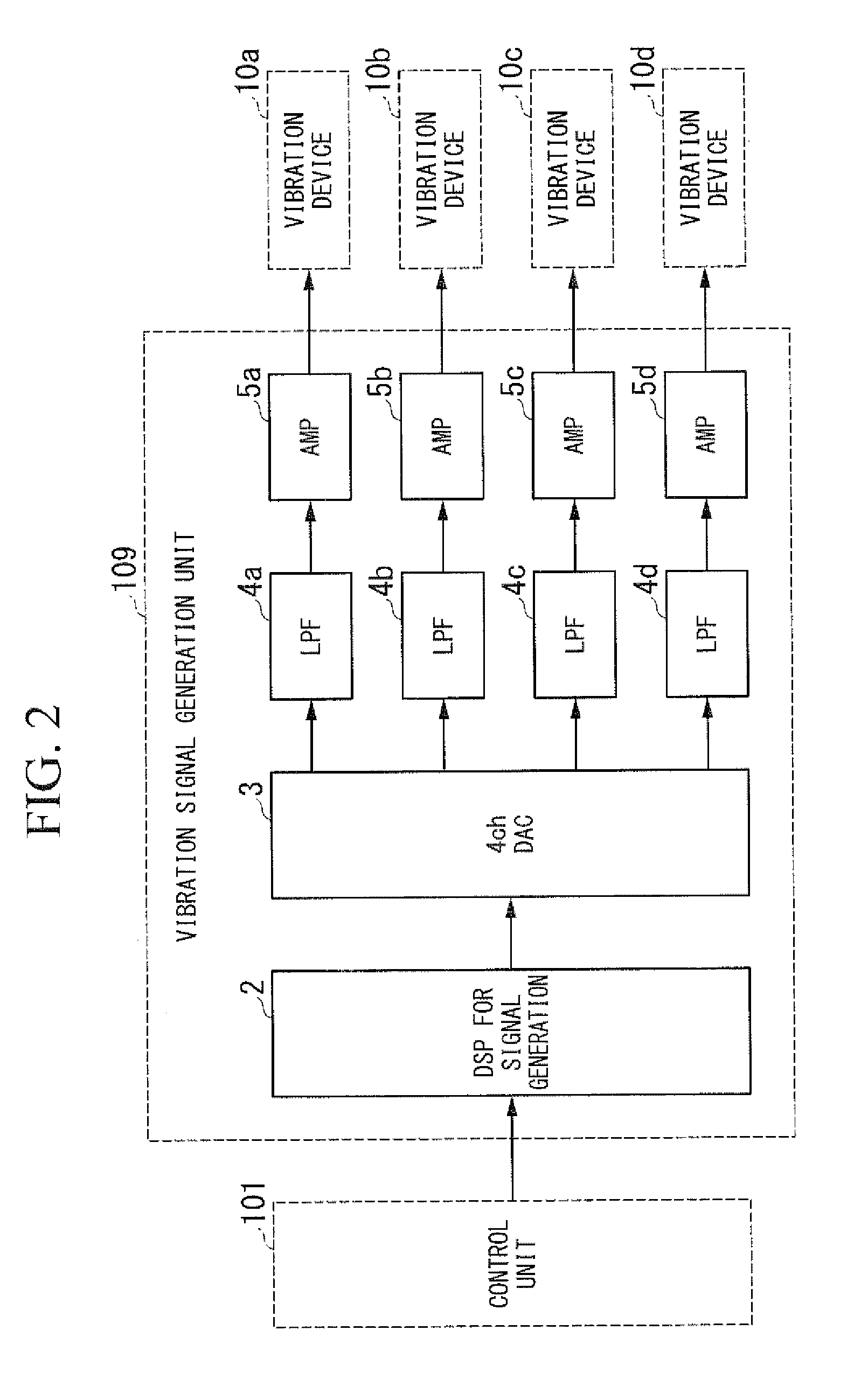
Electronic apparatus and vibrating method
InactiveUS20130261811A1Sampled-variable control systemsMechanical oscillations controlTerminal equipmentComputer terminal
A portable terminal apparatus (electronic apparatus) includes a plurality of vibration devices, disposed at different positions, which generate vibrations, and a control unit that independently controls frequencies or strengths of the vibrations generated by the plurality of vibration devices for each of the vibration devices.
Owner:NIKON CORP
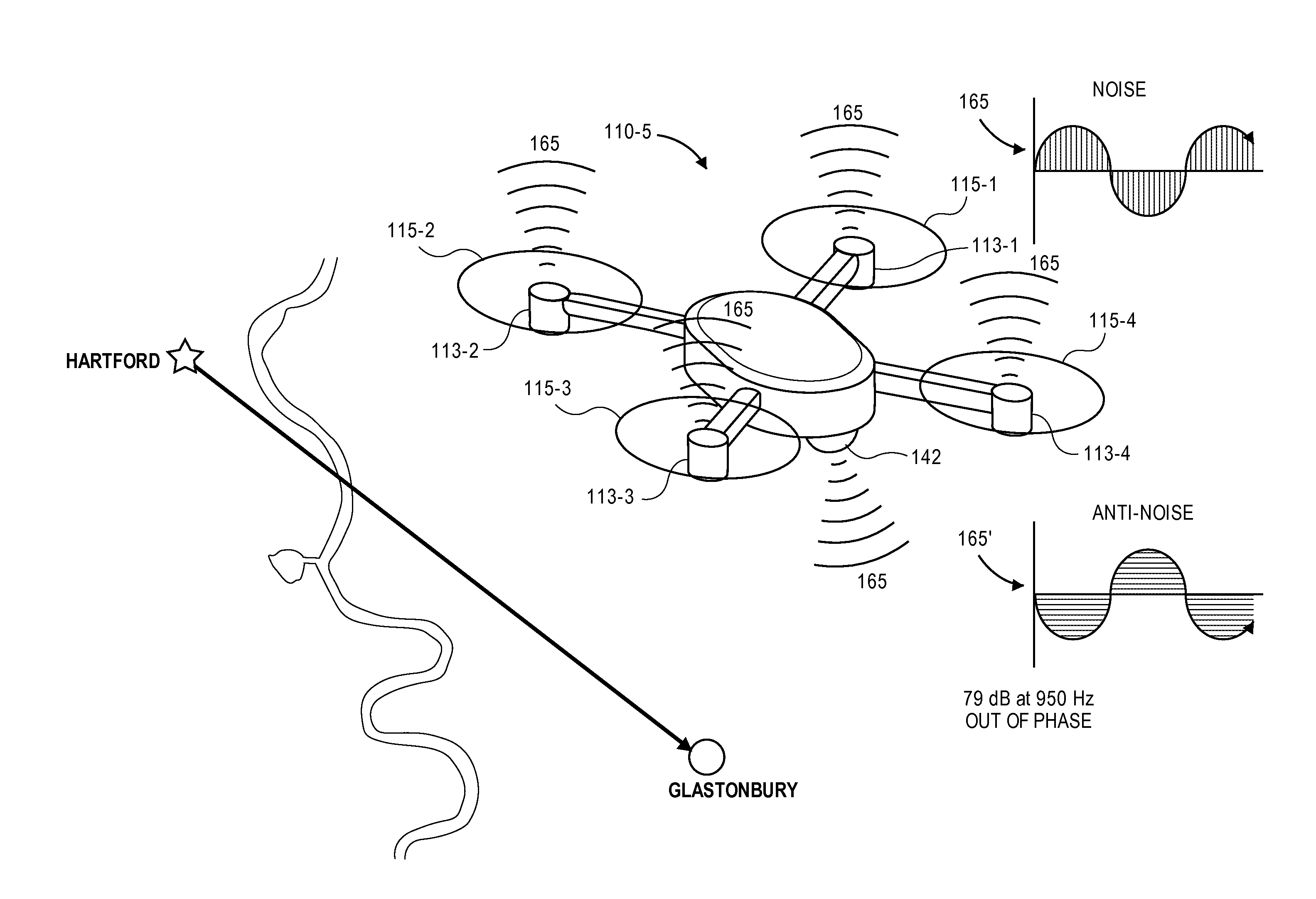
Active airborne noise abatement
ActiveUS9442496B1Mechanical oscillations controlEnergy saving arrangementsSound pressureComputer science
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
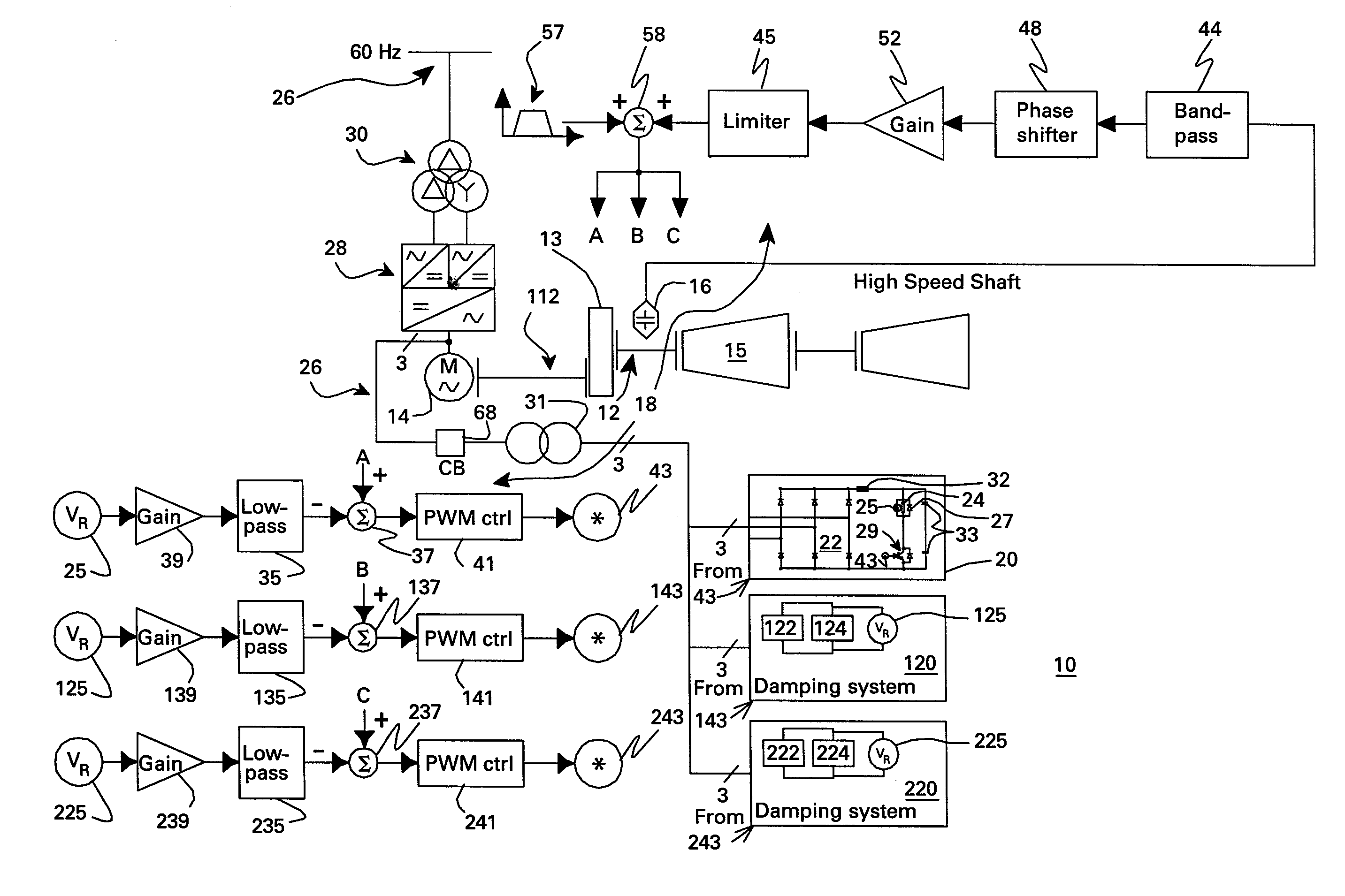
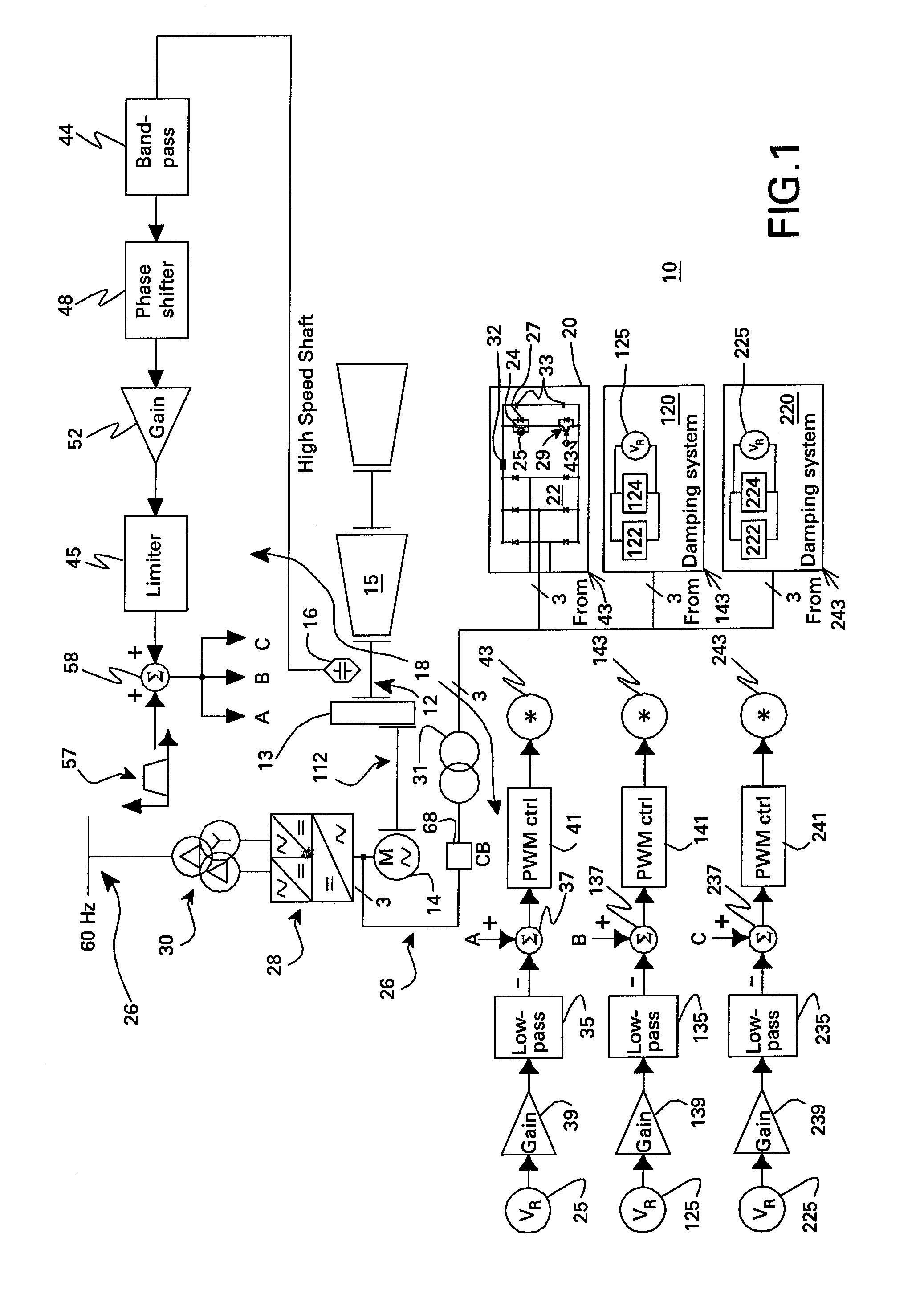
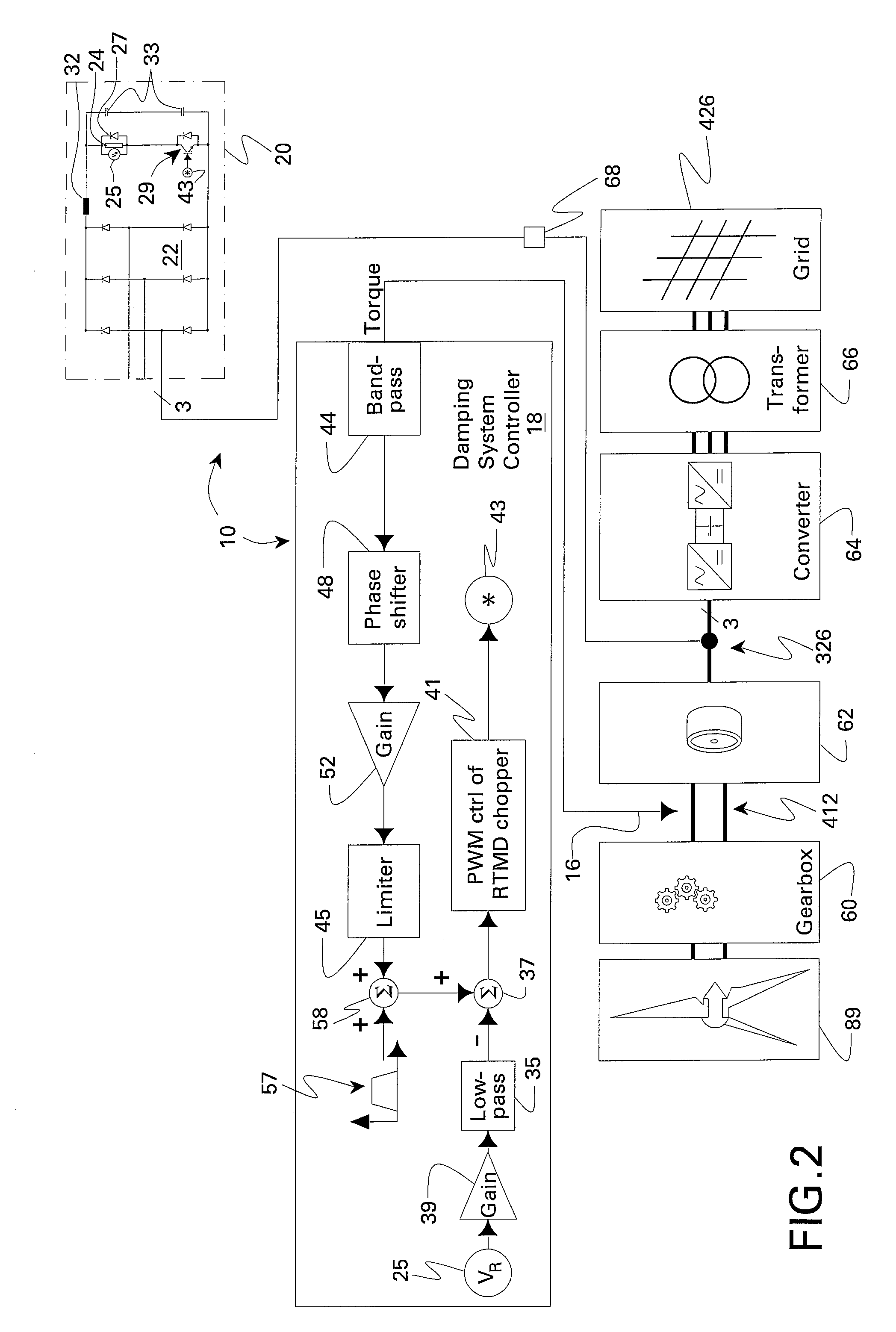
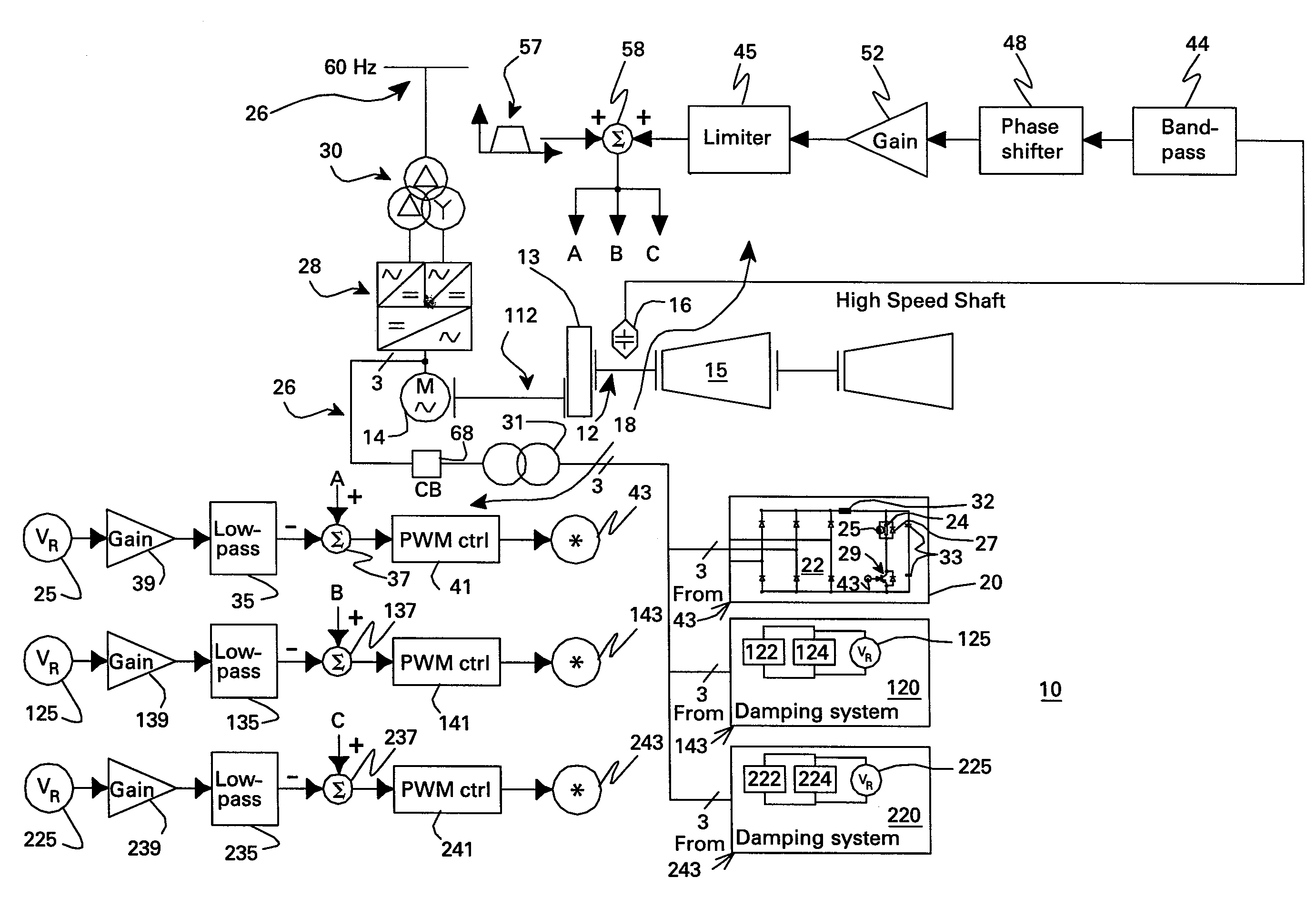
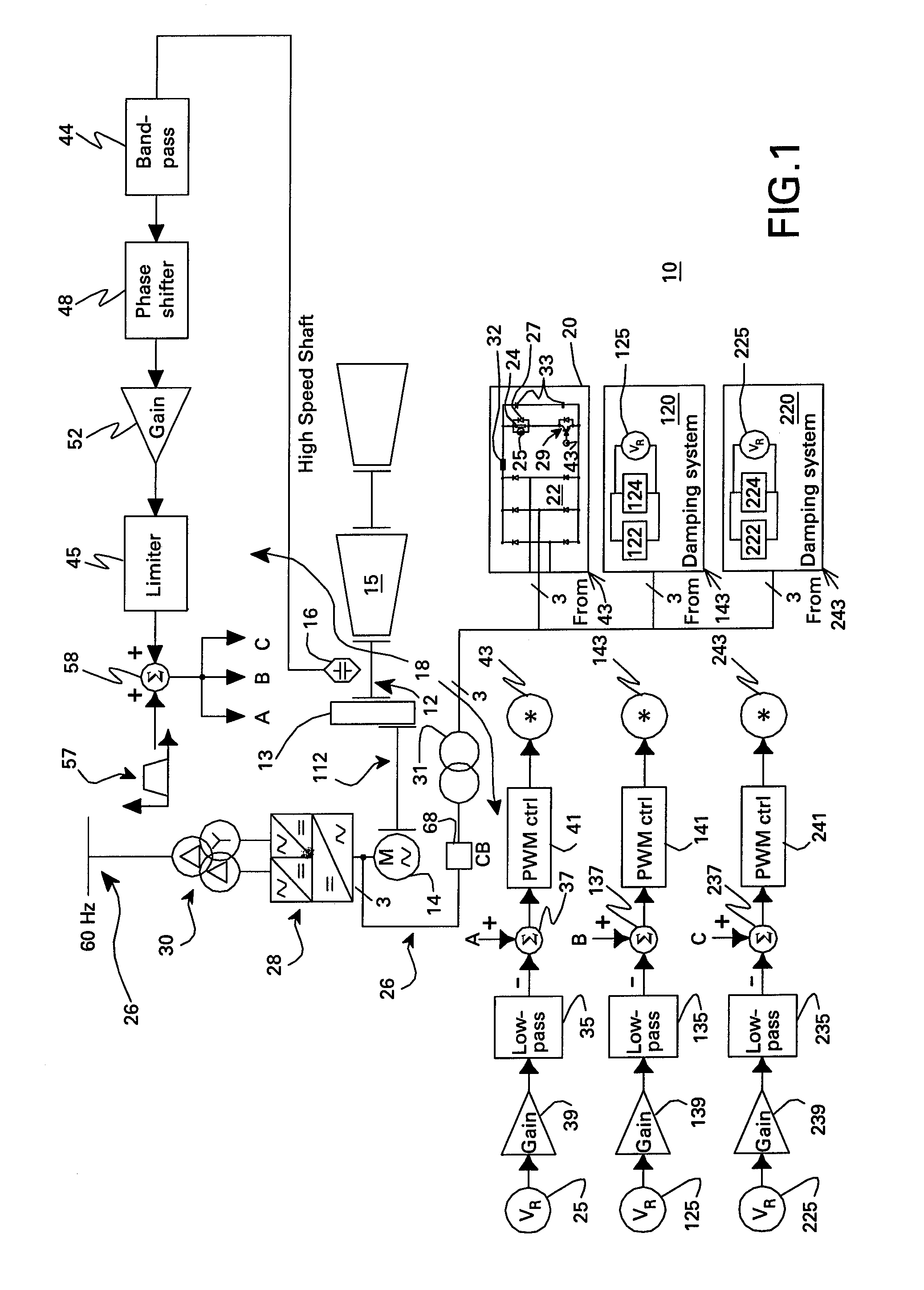
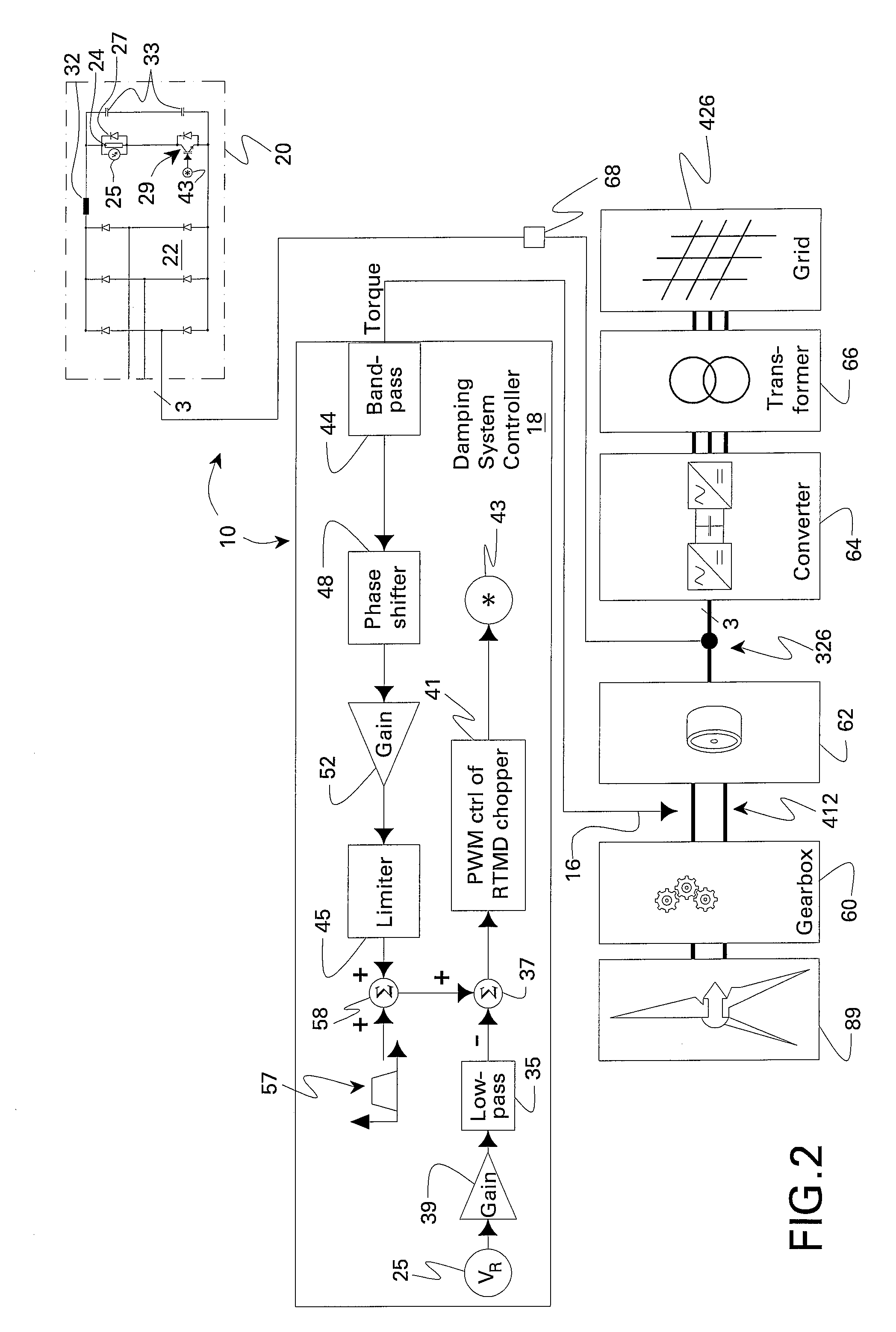
Resistive torsional mode damping system and method
InactiveUS20070279012A1Emergency protective circuit arrangementsDynamo-electric converter controlPower ratingTorsional vibration
A resistive torsional mode damping system for a shaft of a machine includes: a sensor configured for sensing a signal representative of torque on the shaft; a controller configured for using the sensed signal for detecting a presence of a torsional vibration on the shaft corresponding to a natural frequency of the shaft and for generating control signals for damping the torsional vibration; and a damper including a damping converter and resistor coupled to a DC output of the damping converter, the damping converter being coupled to the machine through a power bus and having a power rating on the order of less than or equal to about five percent of a nominal power of the machine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
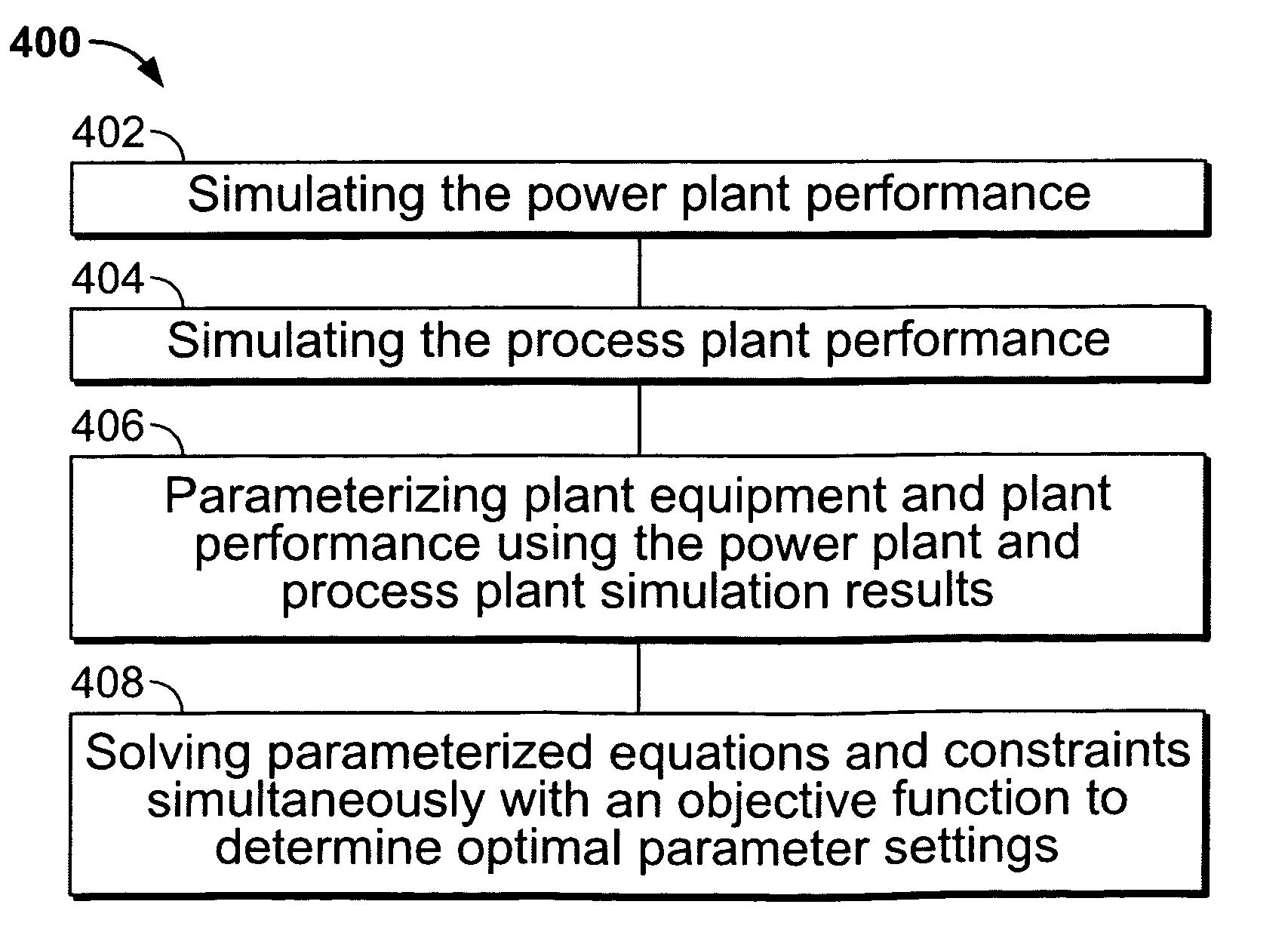
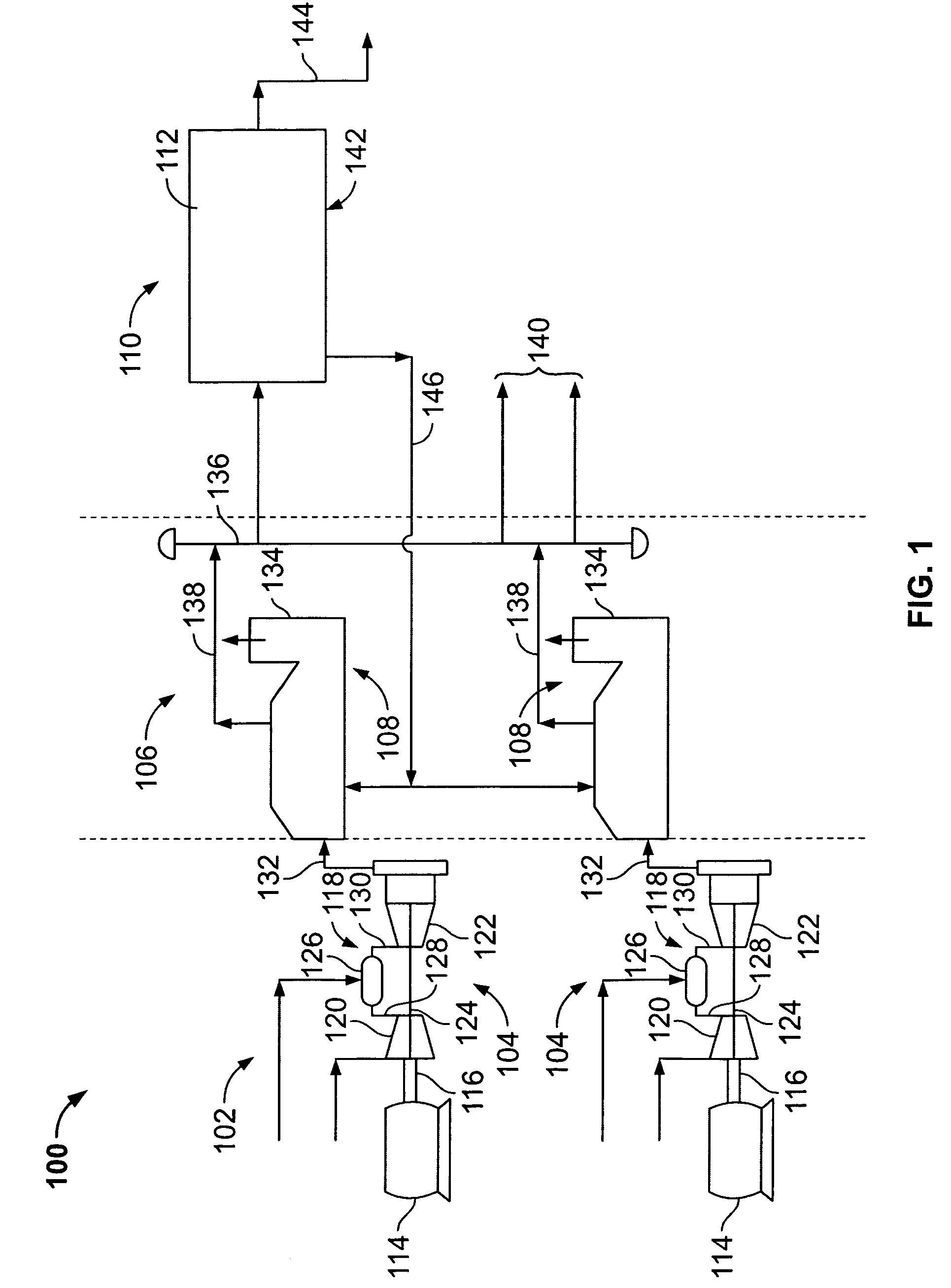
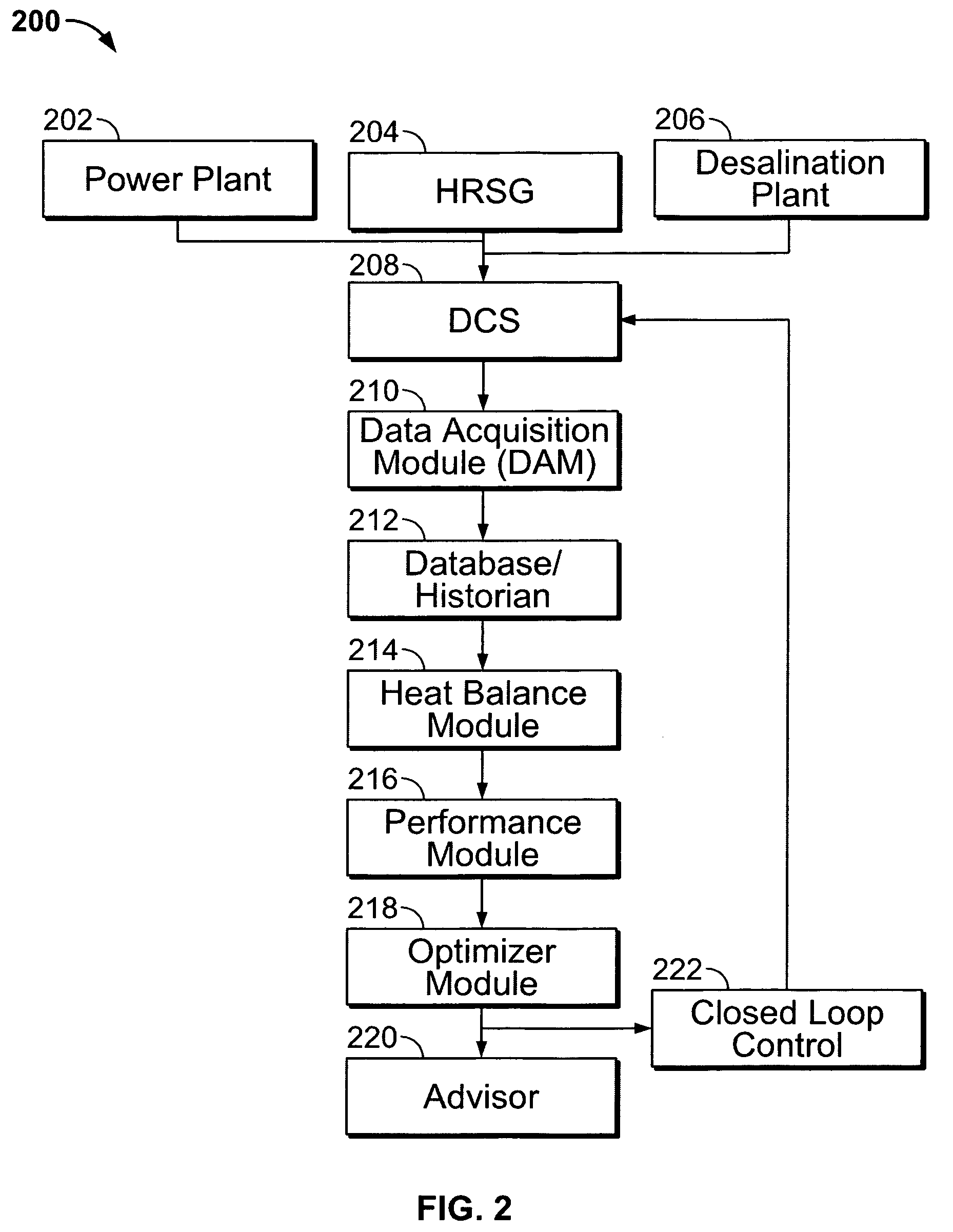
Methods and apparatus for optimizing combined cycle/combined process facilities
InactiveUS7356383B2Improve efficiencyLevel controlAnalogue computers for nuclear physicsPower stationProcess engineering
Methods and systems for operating combined cycle electrical generating plants is provided. The method includes simulating the electrical power plant performance, simulating the steam utilizing process plant performance, parameterizing plant equipment and plant performance using the power plant and process plant simulation results, and solving parameterized simultaneous equations and constraints with an objective function to determine parameter settings that facilitate enhancing an efficiency of the combined cycle electrical generating / steam-utilizing process plant.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
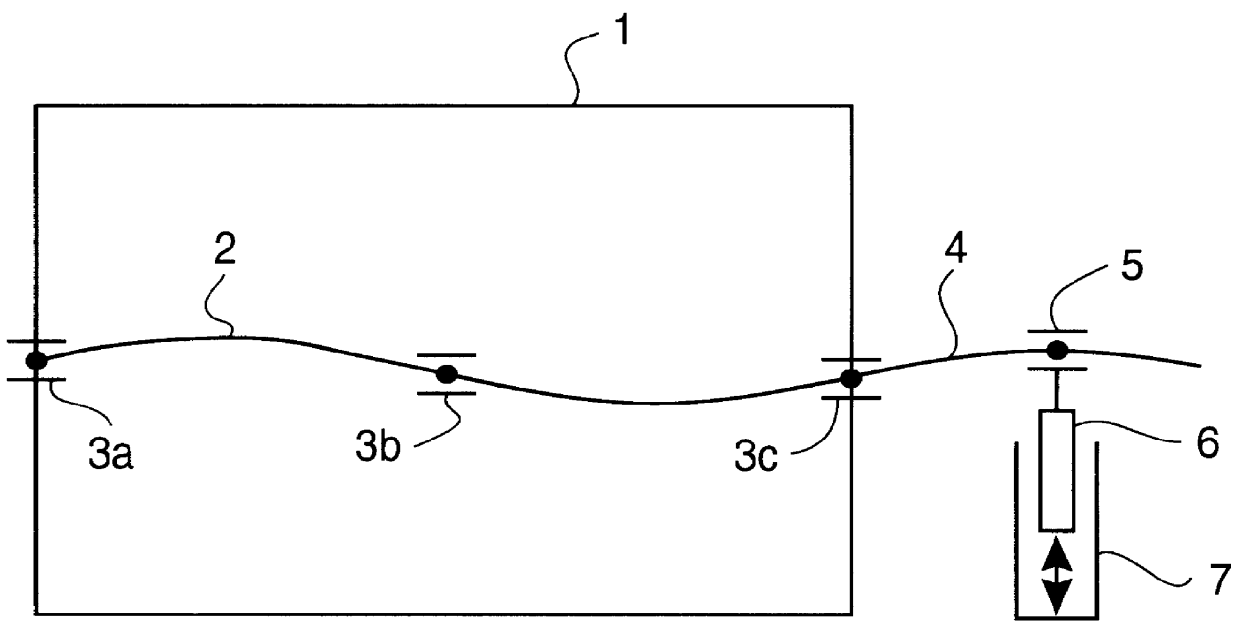
System for actively reducing radial vibrations in a rotating shaft, and method of operating the system to achieve this
InactiveUS6138629AReduce vibrationReduce unevennessRotating vibration suppressionBraking element arrangementsDrive shaftEngineering
PCT No. PCT / DE96 / 01665 Sec. 371 Date Jul. 23, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jul. 23, 1998 PCT Filed Aug. 31, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 08477 PCT Pub. Date Mar. 6, 1997The invention concerns a system for active reduction of radial vibrations of a rotating shaft (4), especially the drive shaft of an internal combustion engine (1), with at least one active electromagnetic device (7; 10; 15, 16), which is configured and controlled such that it applies radial forces to the shaft (4), which counteract the radial vibrations of the shaft (4).
Owner:CONTINENTAL ISAD ELECTRONICS SYST GMBH & CO KG
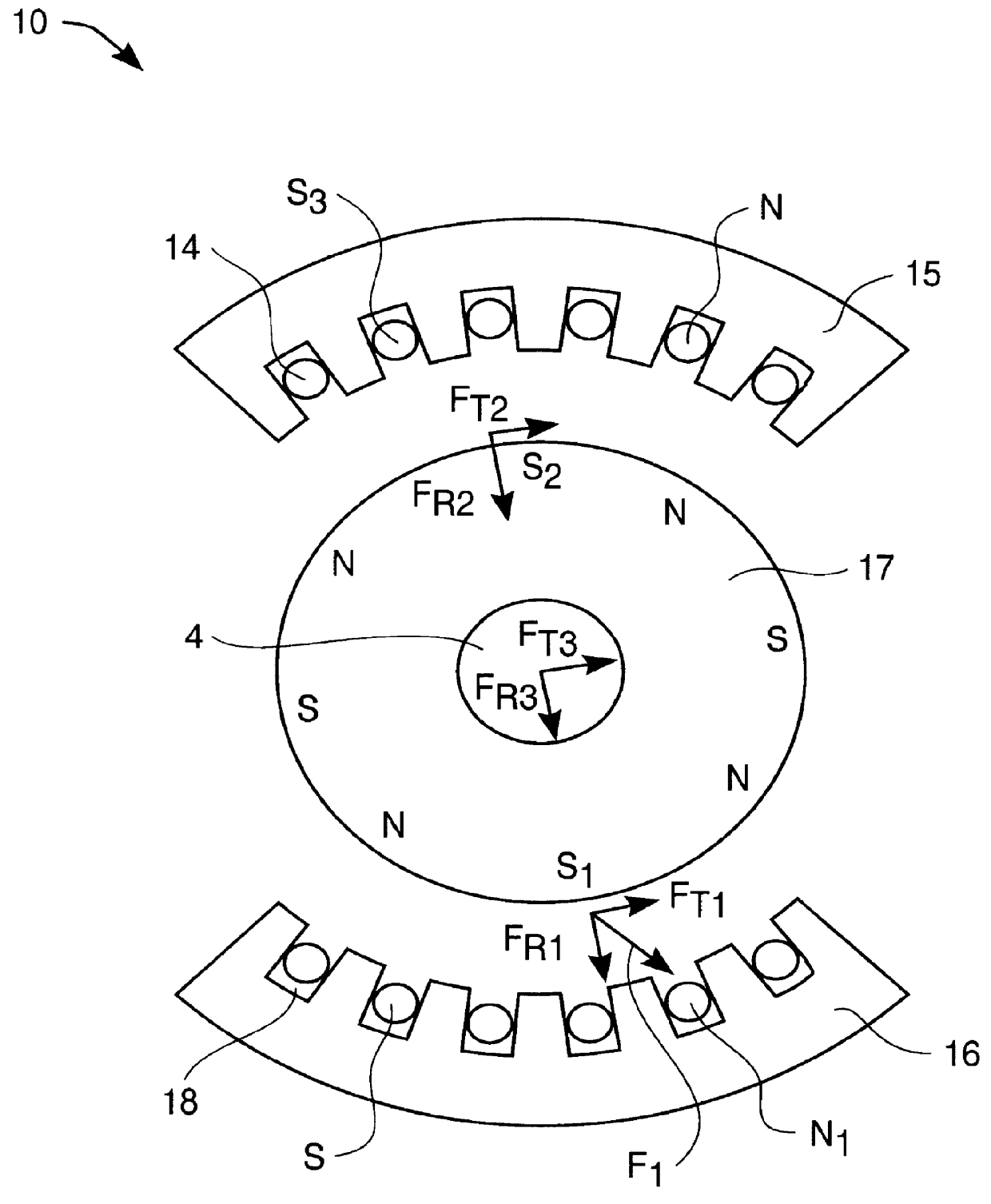
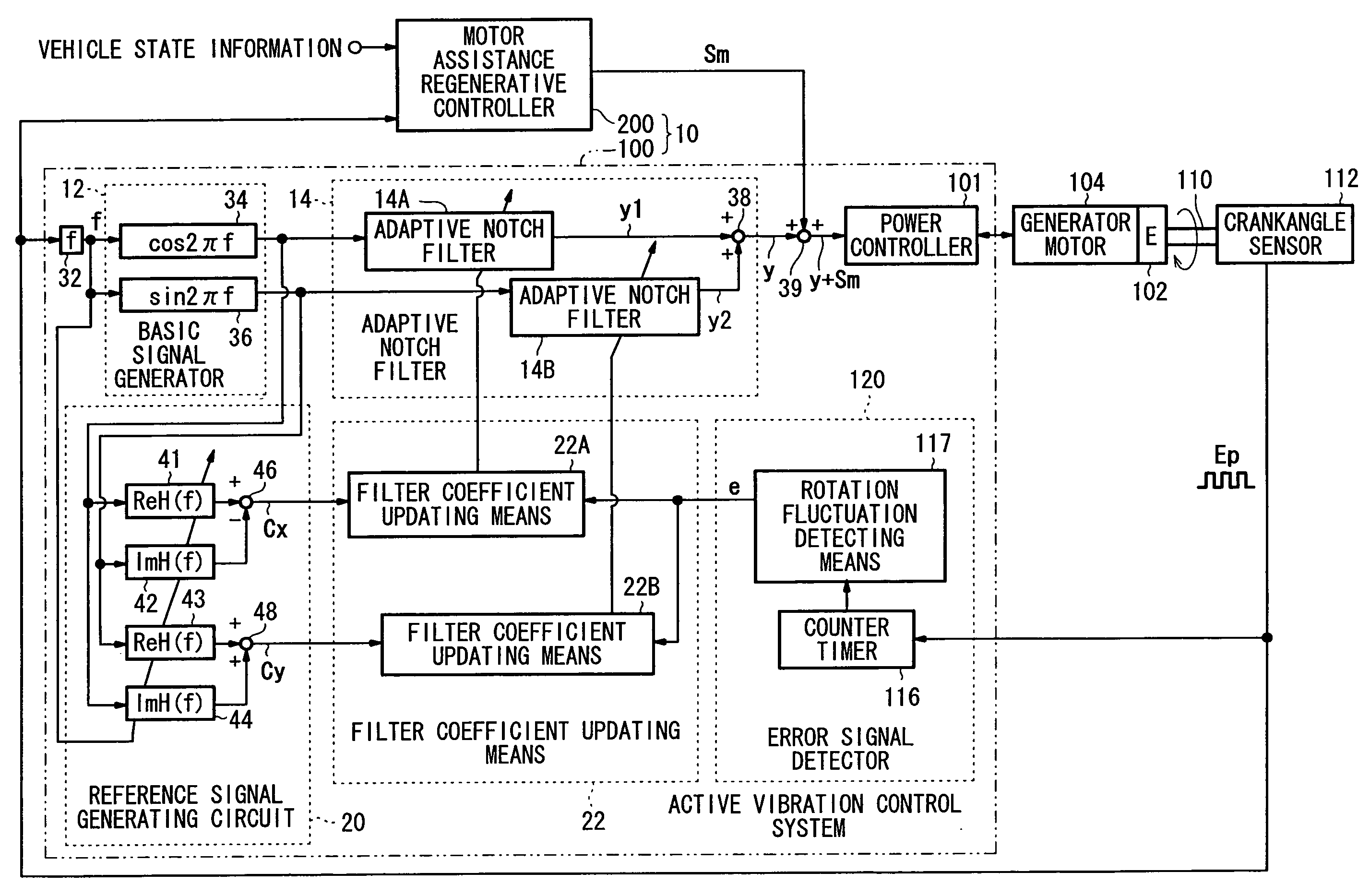
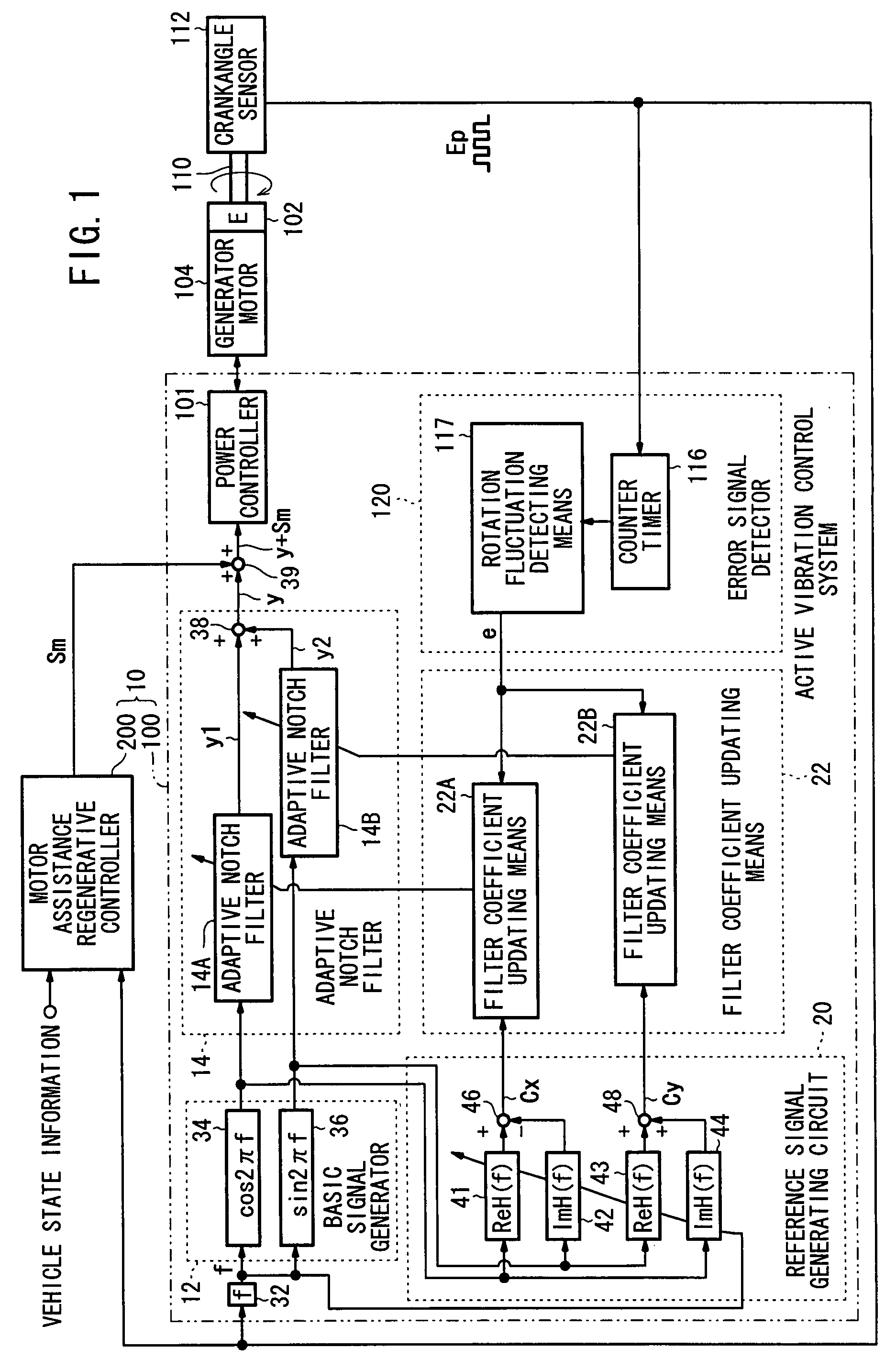
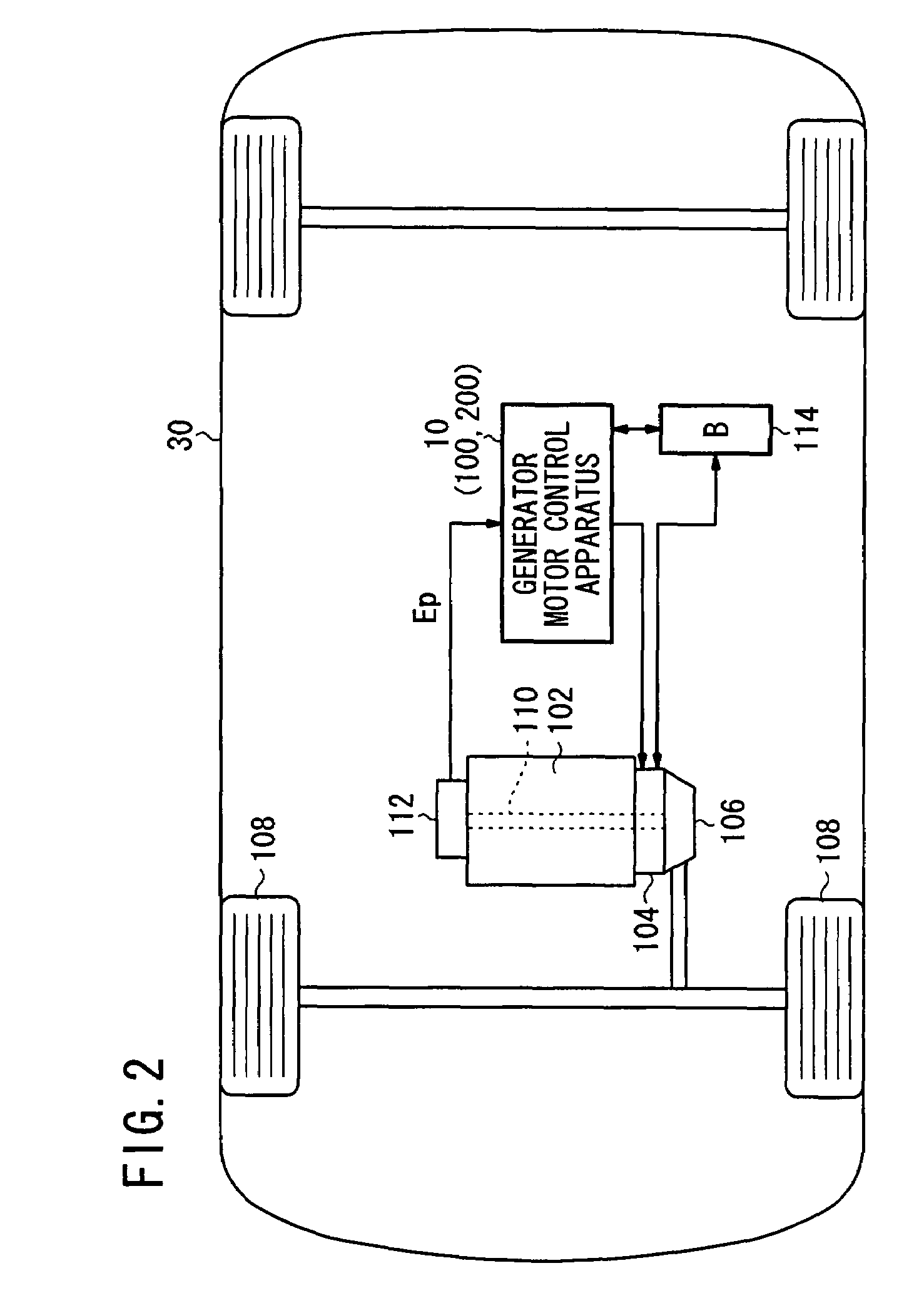
Active vibration control system for hybrid vehicle
ActiveUS7633257B2Suppresses torque fluctuationsRapid responseHybrid vehiclesMechanical oscillations controlAdaptive filterControl signal
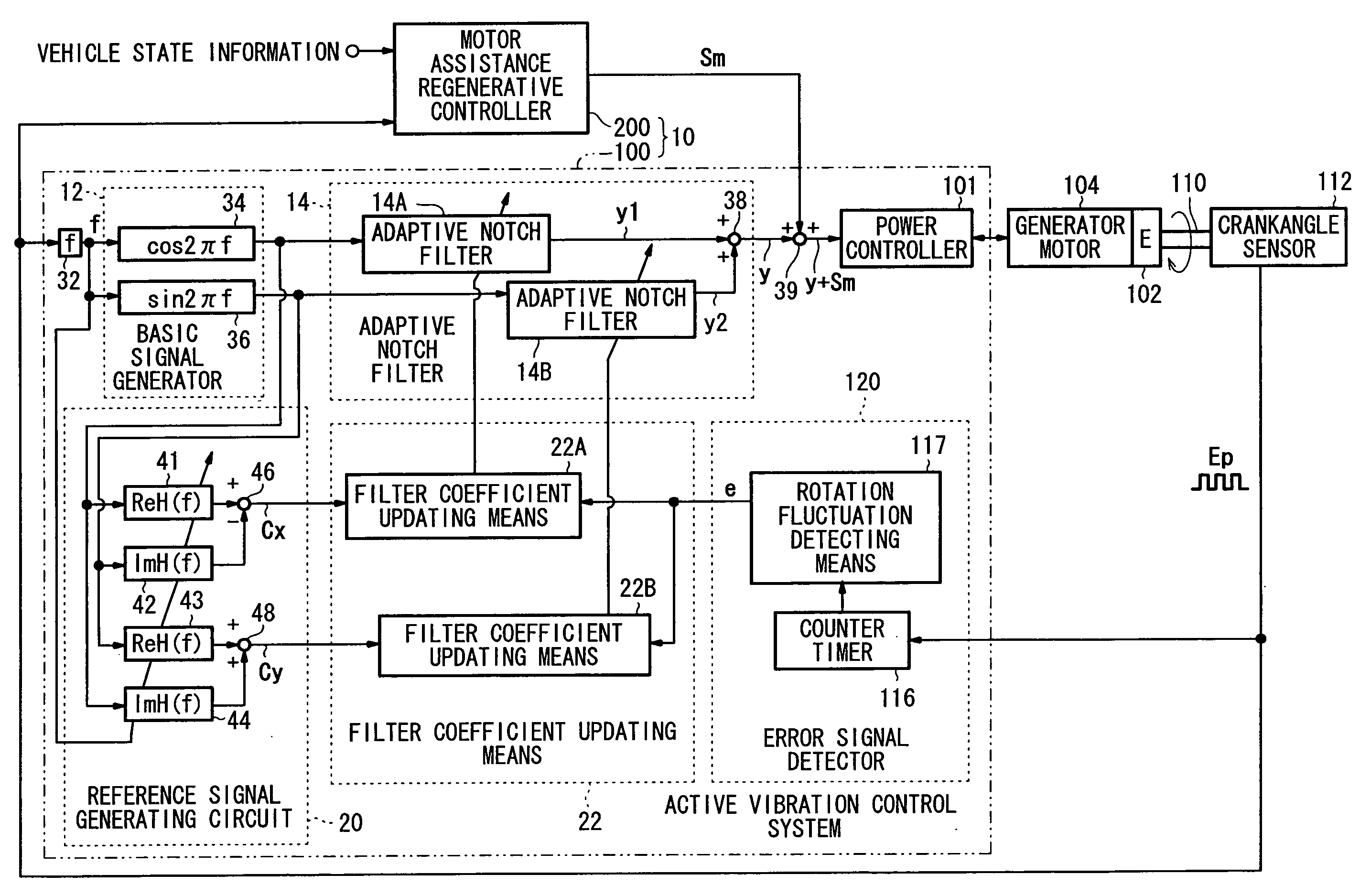
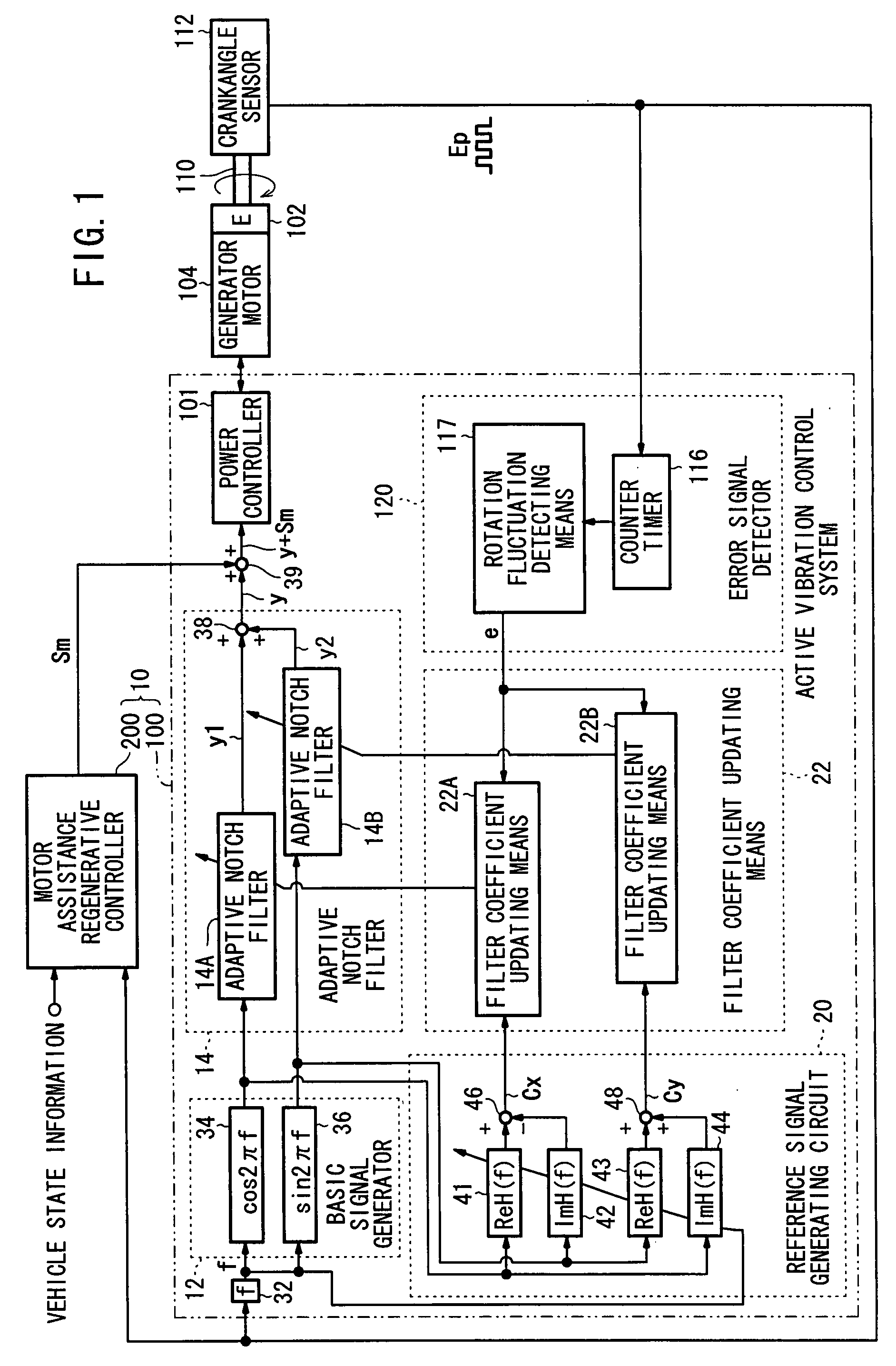
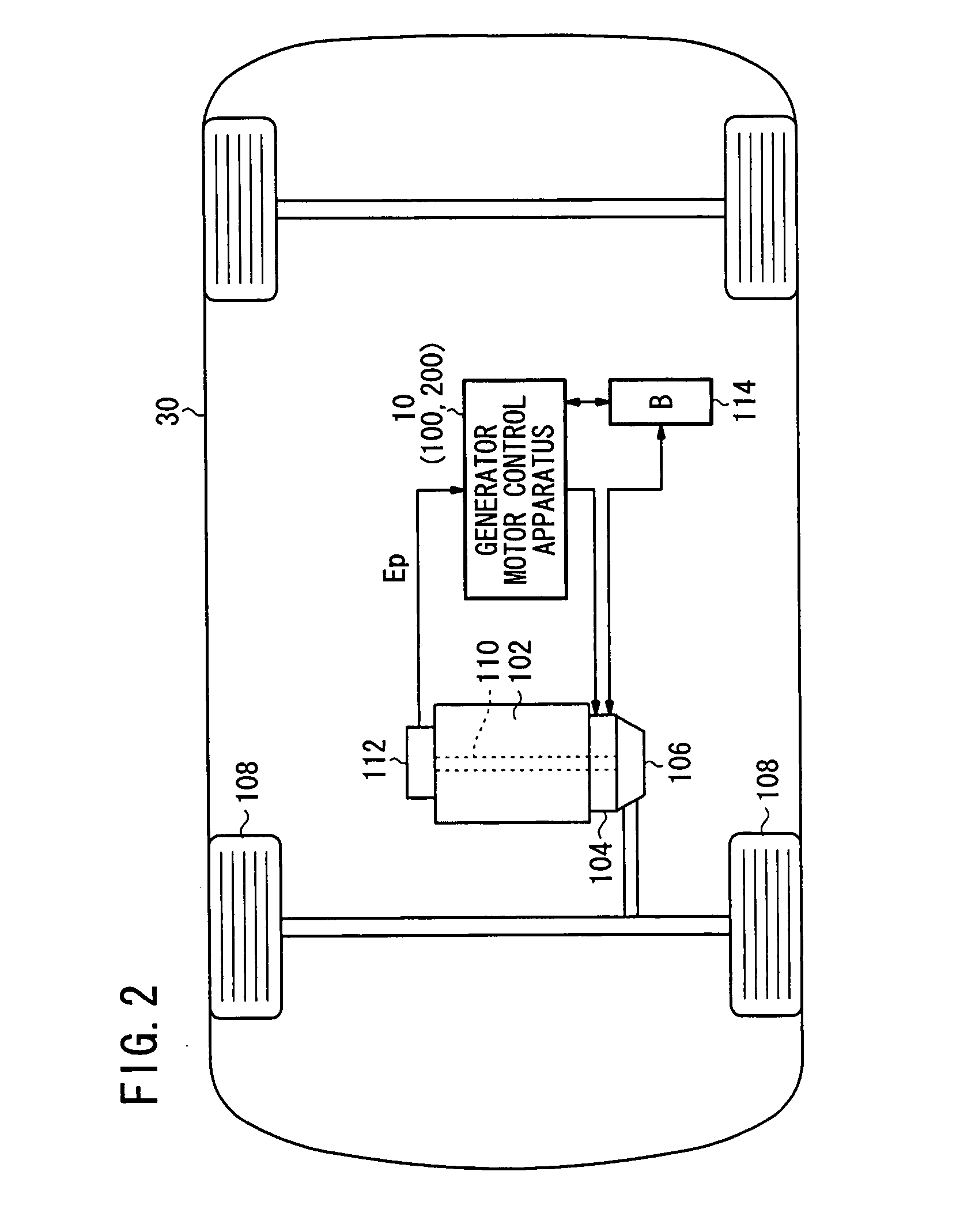
In a motor-assisted hybrid vehicle, an active vibration control system suppresses torque fluctuations of an engine without detriment to the response of a static torque. An adaptive notch filter outputs a control signal depending on a harmonic basic signal generated by a basic signal generator from a rotational frequency of a crankshaft. A combiner combines the control signal with a drive signal for the generator motor and supplies the combined signal through a power controller to the generator motor. The basic signal is supplied to corrective filters having the transfer function of the generator motor to output a reference signal. The filter coefficient of an adaptive notch filter is successively updated so that an error signal representative of a rotational speed fluctuation of the crankshaft will be minimized.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Resistive torsional mode damping system and method
InactiveUS7423411B2Emergency protective circuit arrangementsDynamo-electric converter controlElectrical resistance and conductanceControl signal
A resistive torsional mode damping system for a shaft of a machine includes: a sensor configured for sensing a signal representative of torque on the shaft; a controller configured for using the sensed signal for detecting a presence of a torsional vibration on the shaft corresponding to a natural frequency of the shaft and for generating control signals for damping the torsional vibration; and a damper including a damping converter and resistor coupled to a DC output of the damping converter, the damping converter being coupled to the machine through a power bus and having a power rating on the order of less than or equal to about five percent of a nominal power of the machine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
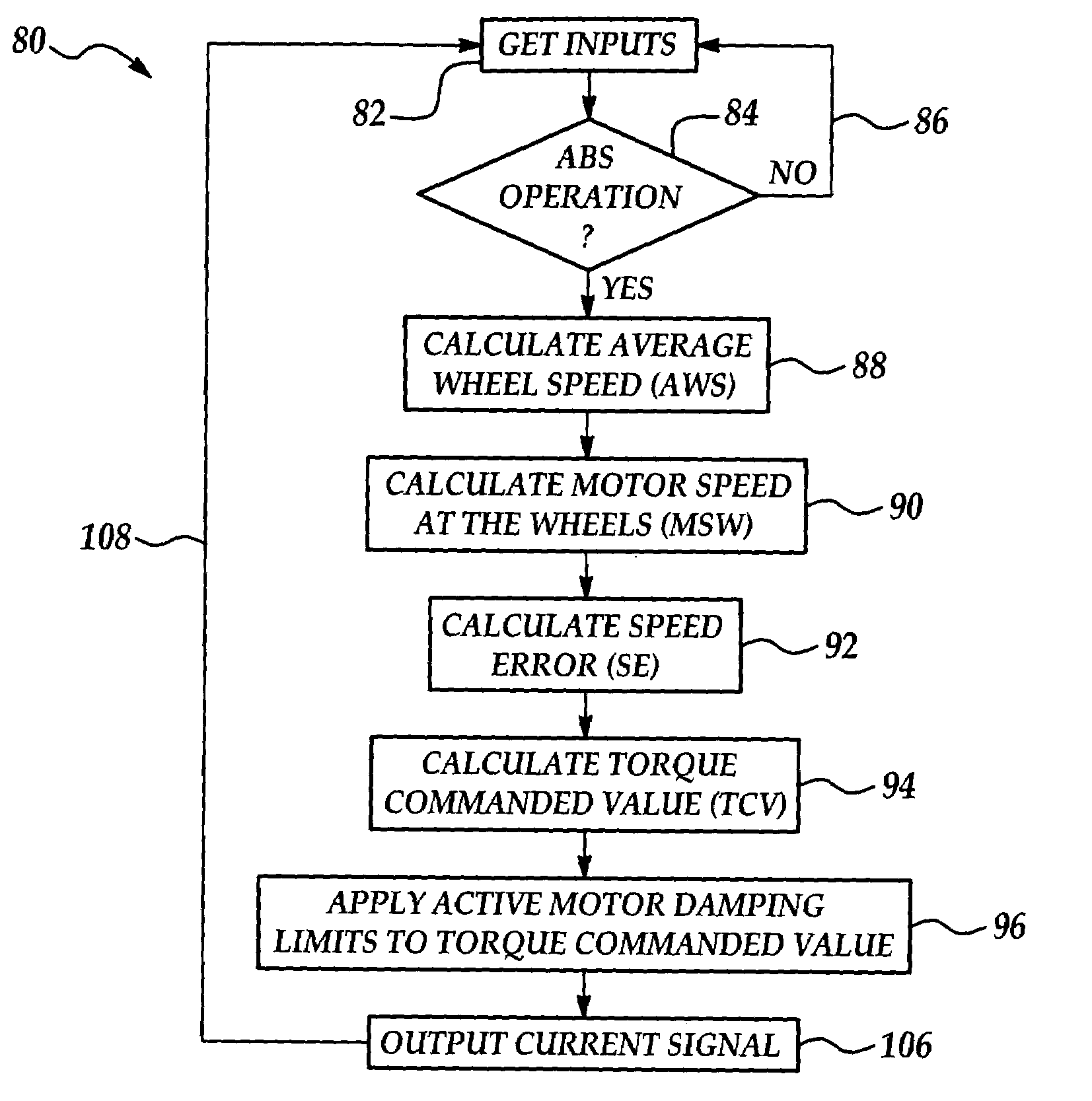
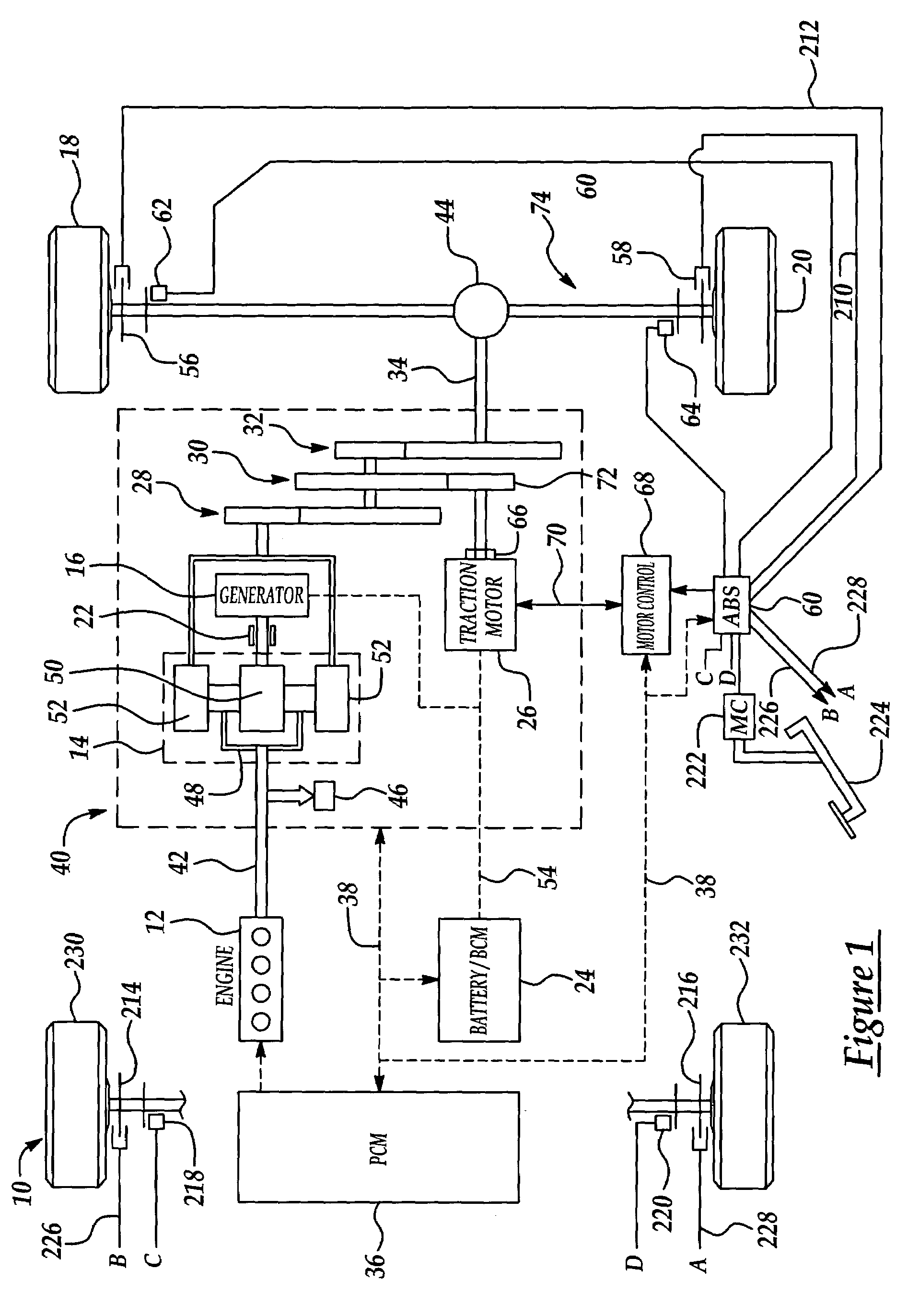
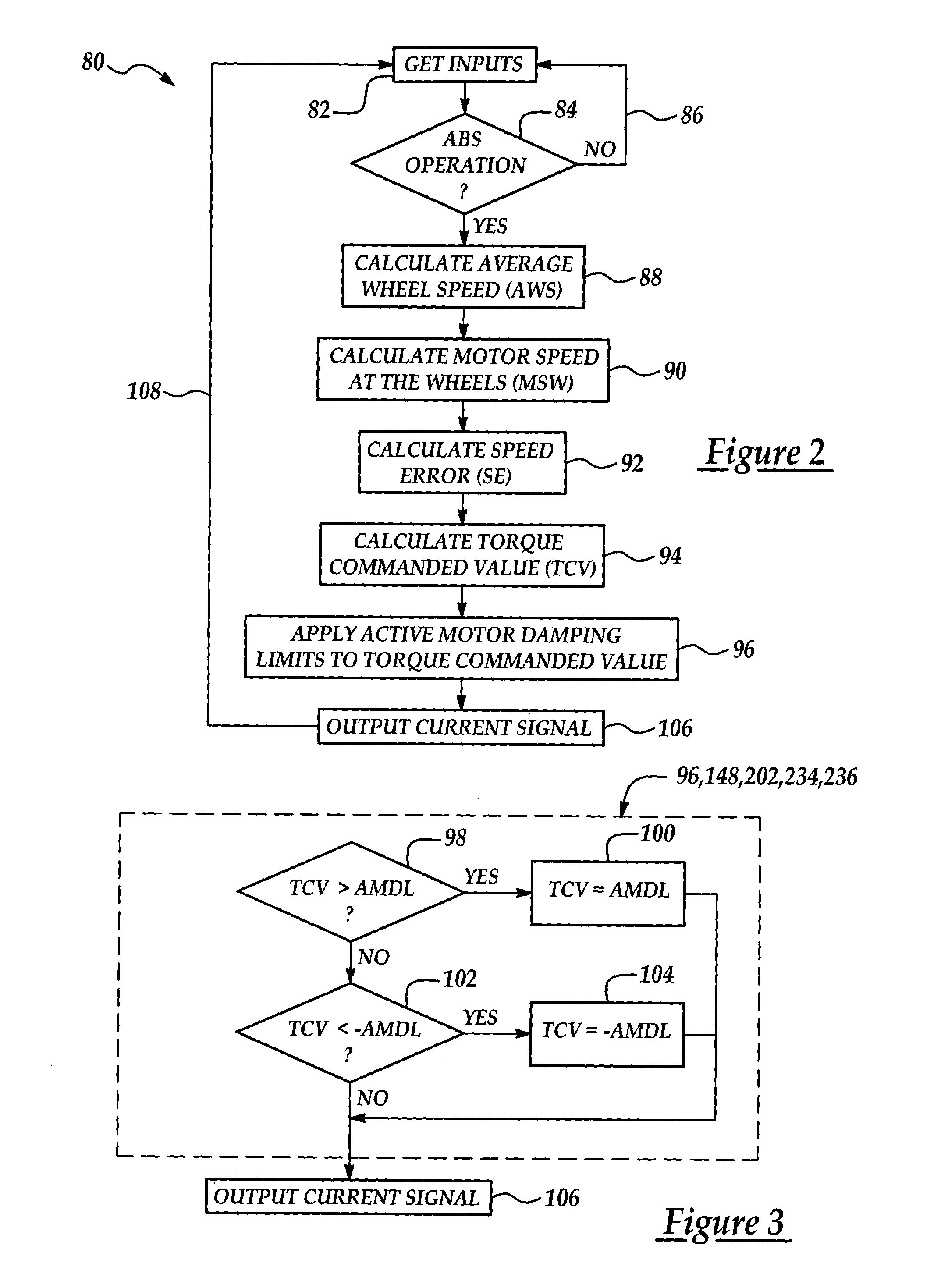
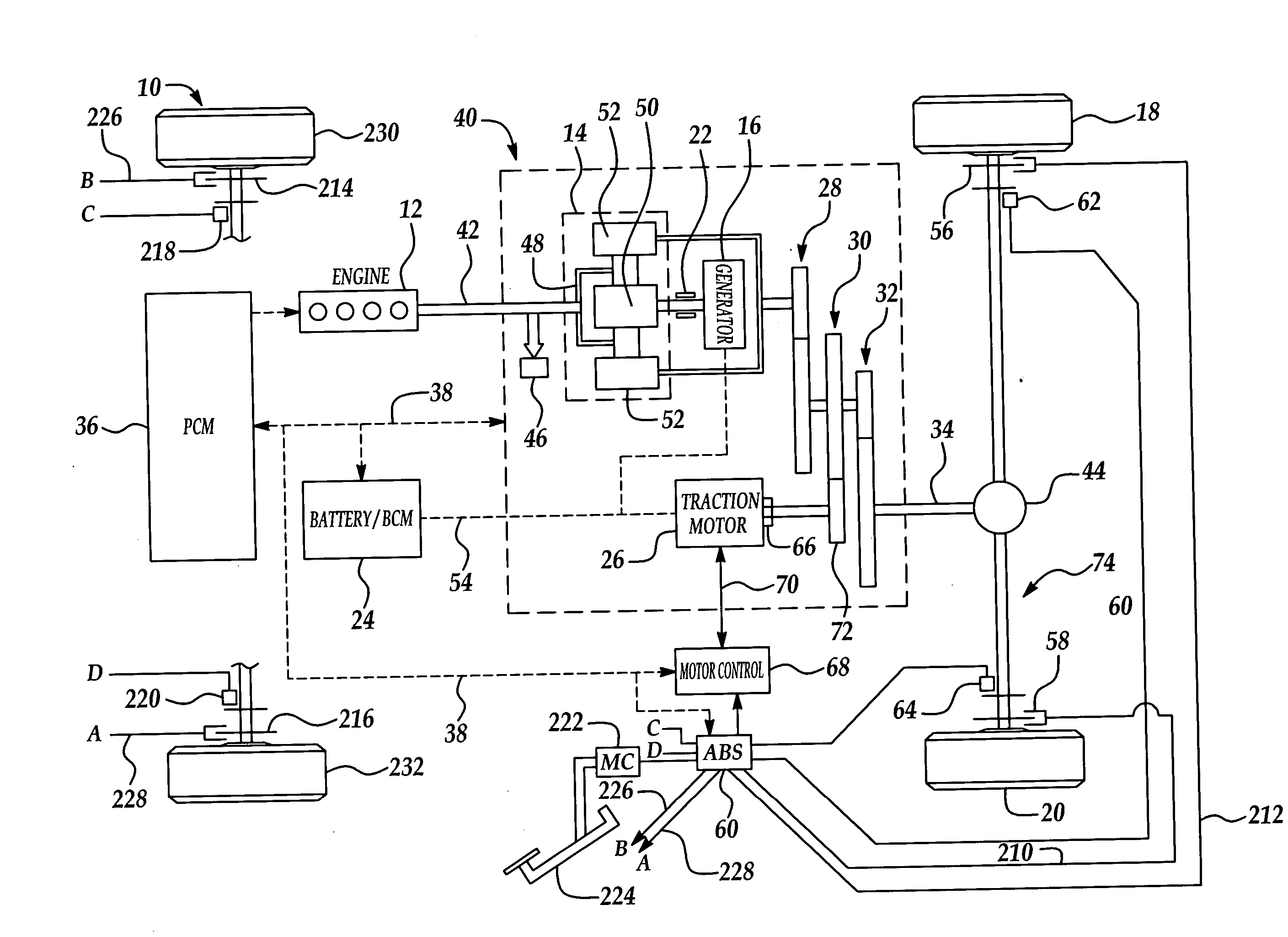
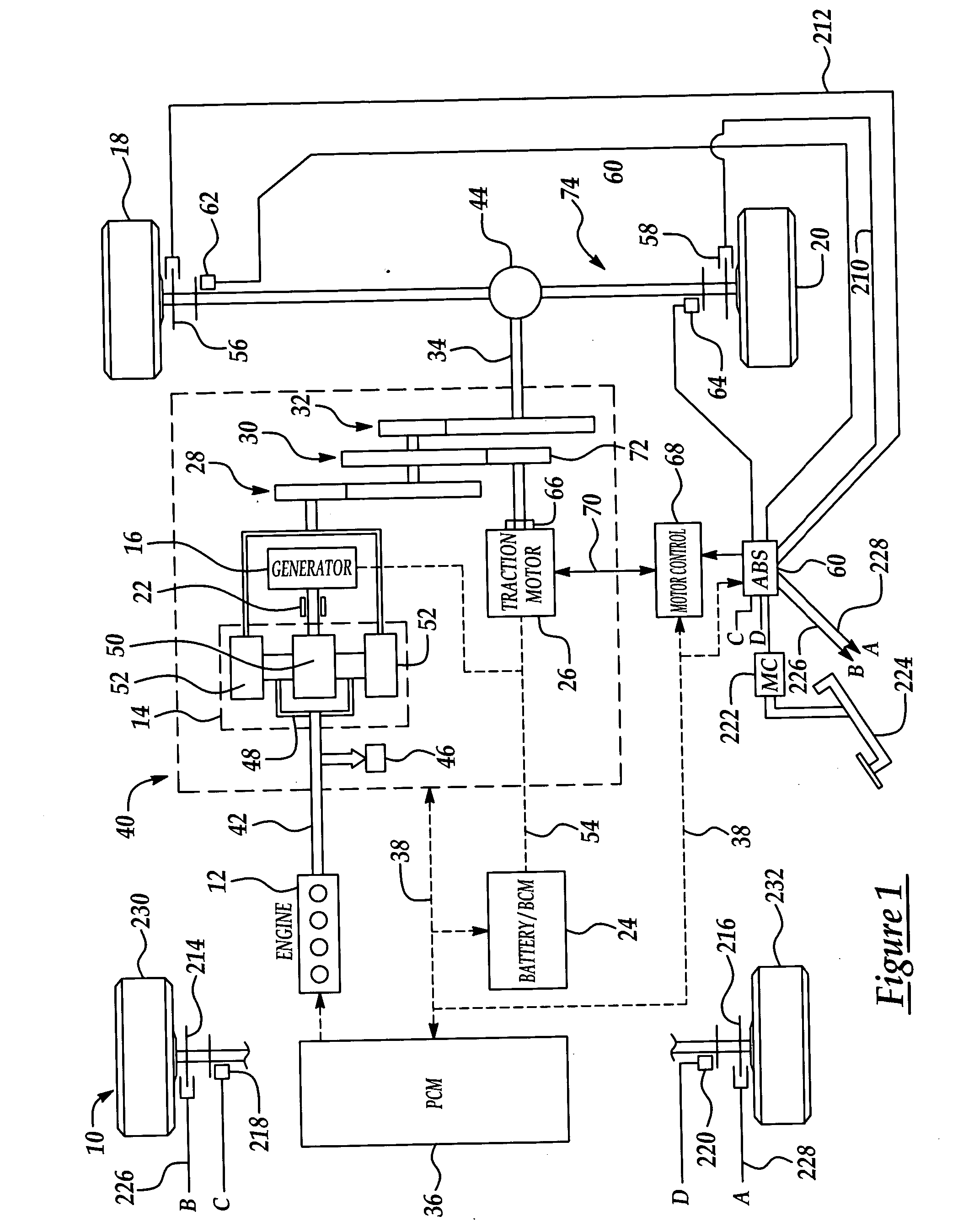
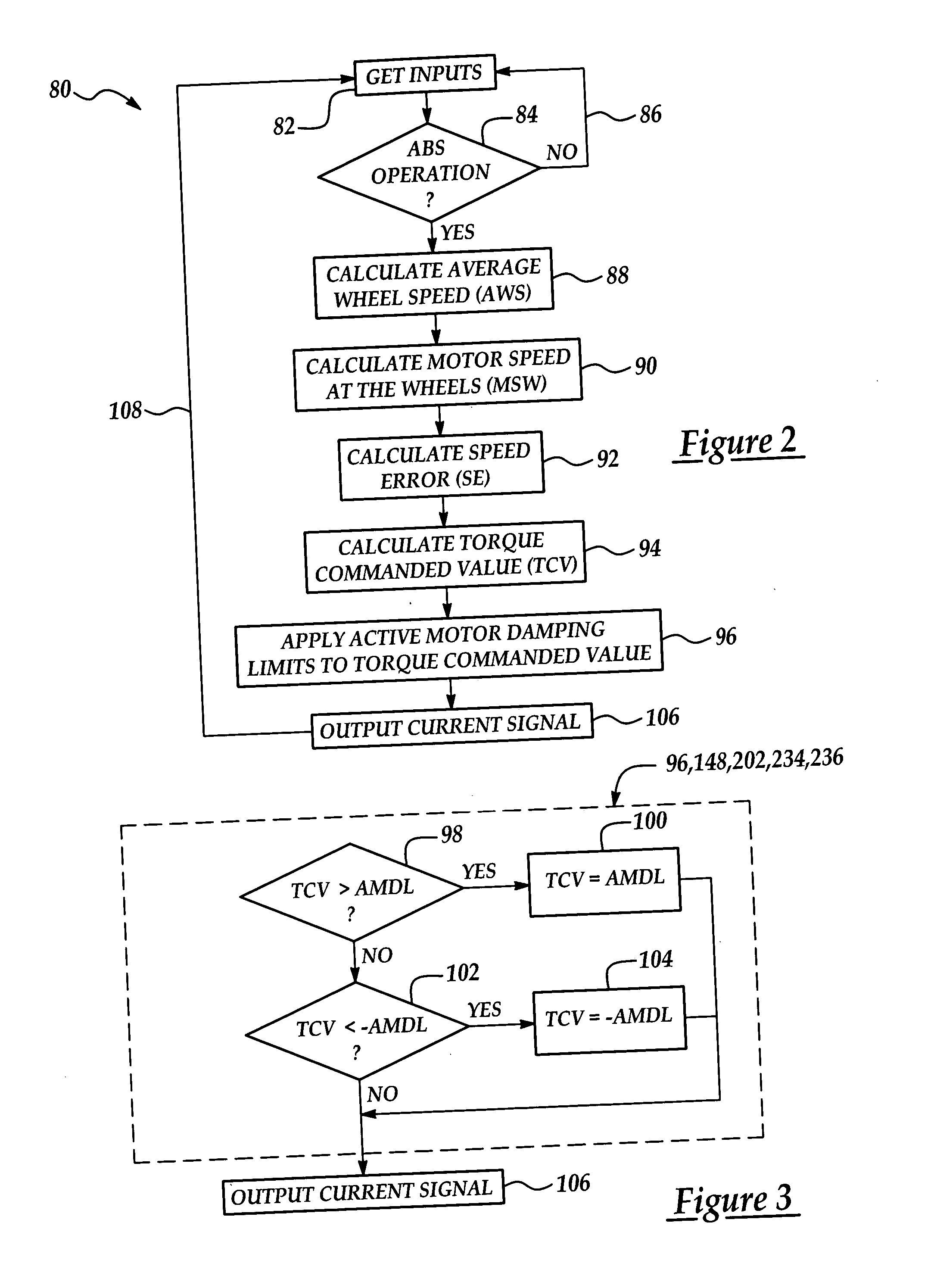
Active motor damping to mitigate electric vehicle driveline oscillations
ActiveUS7024290B2Reduce oscillationOscillation suppressionDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesMotor speedDrive wheel
A system and method for actively damping driveline oscillations in a motor vehicle having a traction motor to drive a vehicle's drive wheels and an antilock brake system (ABS). A traction motor controller controls a torque output signal of the motor to effectively to dampen driveline oscillations during an ABS operation. A proportional, a proportional derivative, or a derivative controller may be used to generate the torque output signal based on at least one of motor speed, an average of the drive wheel speeds, a difference in the two speeds, a motor angular acceleration, an average wheel angular acceleration, and a difference in the angular accelerations. Motor speed signals and average drive wheel speed signals may be filtered to eliminate high frequency components of each speed signal. Additionally, amplitude of the torque output signal may be limited within a positive upper and a negative lower active motor damping limit.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
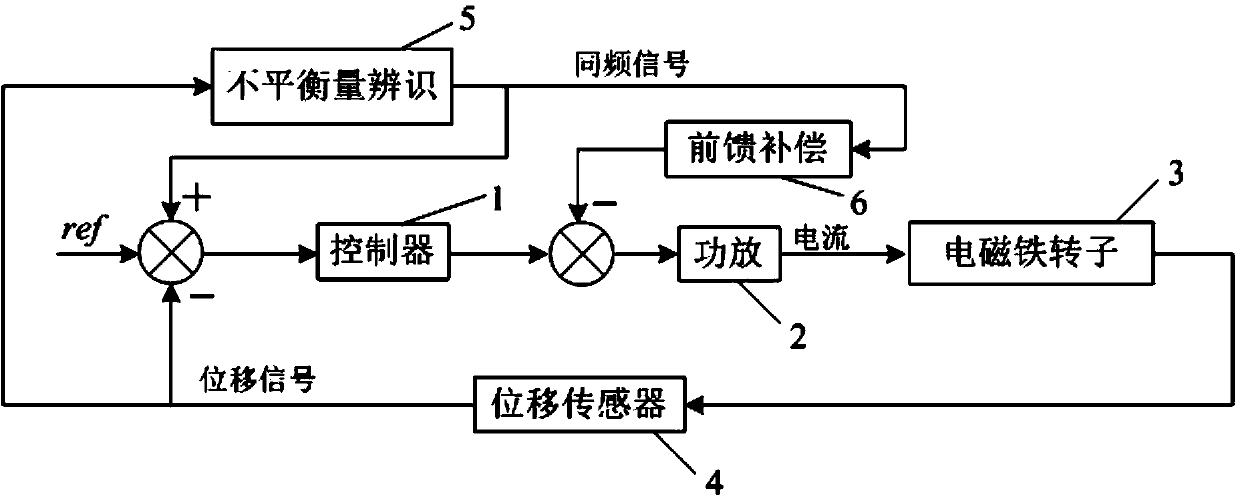
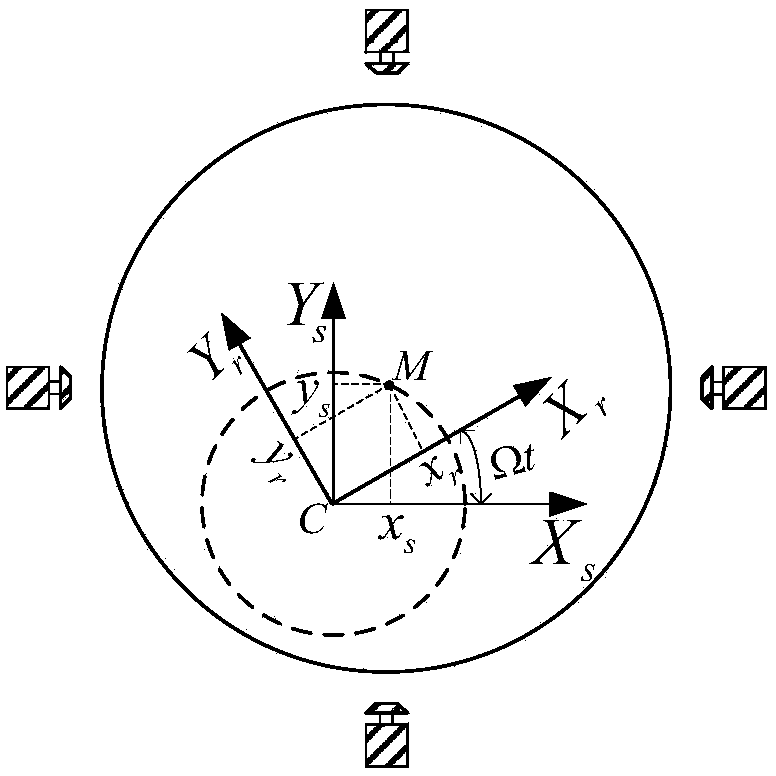
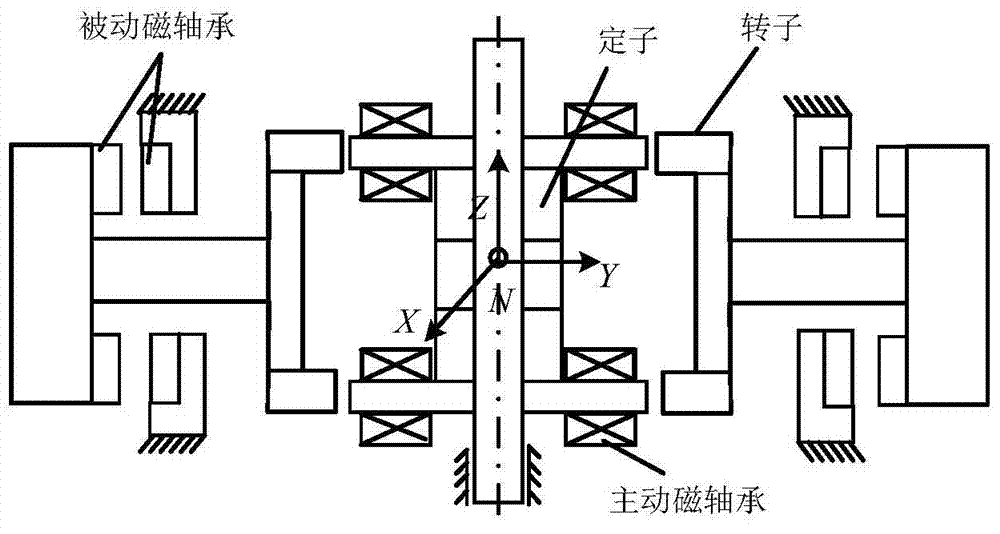
Unbalance identification and vibration suppression control system for magnetic suspension rotating machinery
ActiveCN103425051AHigh compensation accuracyOvercoming Compensation Attenuation ProblemsMechanical oscillations controlAdaptive controlMagnetic bearingStabilization control
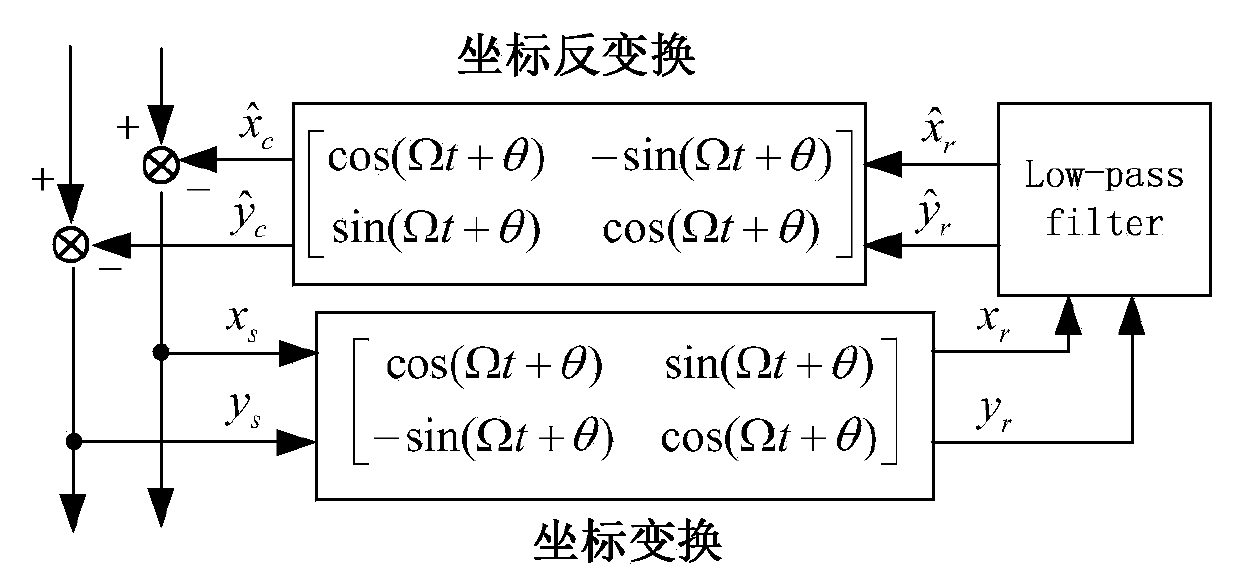
An unbalance identification and vibration suppression control system for a magnetic suspension rotating machinery comprises an unbalance identification module, an unbalanced force compensation module, a magnetic bearing power amplifier, an electromagnet rotor and a displacement sensor. Based on stable control of a magnetic suspension rotor, the unbalance of a magnetic bearing is identified in an online manner by a novel wave trap based on coordinate transformation, on one hand, the identification amount is used for compensating common-frequency current stiffness force, on the other hand, proper common-frequency current stiffness force is generated according to the identification amount to compensate common-frequency displacement stiffness force, and the influence of the low-pass characteristic of the power amplifier on compensation precision of the common-frequency displacement stiffness force is eliminated by leading a simplified inverse model of the magnetic bearing power amplifier into a feed-forward channel. When the magnetic suspension rotor rotates at a high speed, common-frequency bearing force is greatly reduced, and unbalanced vibration of the magnetic suspension rotor is remarkably suppressed. The unbalance identification and vibration suppression control system is simple, convenient, easy and particularly suitable for an actual high-speed magnetic suspension rotor system.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
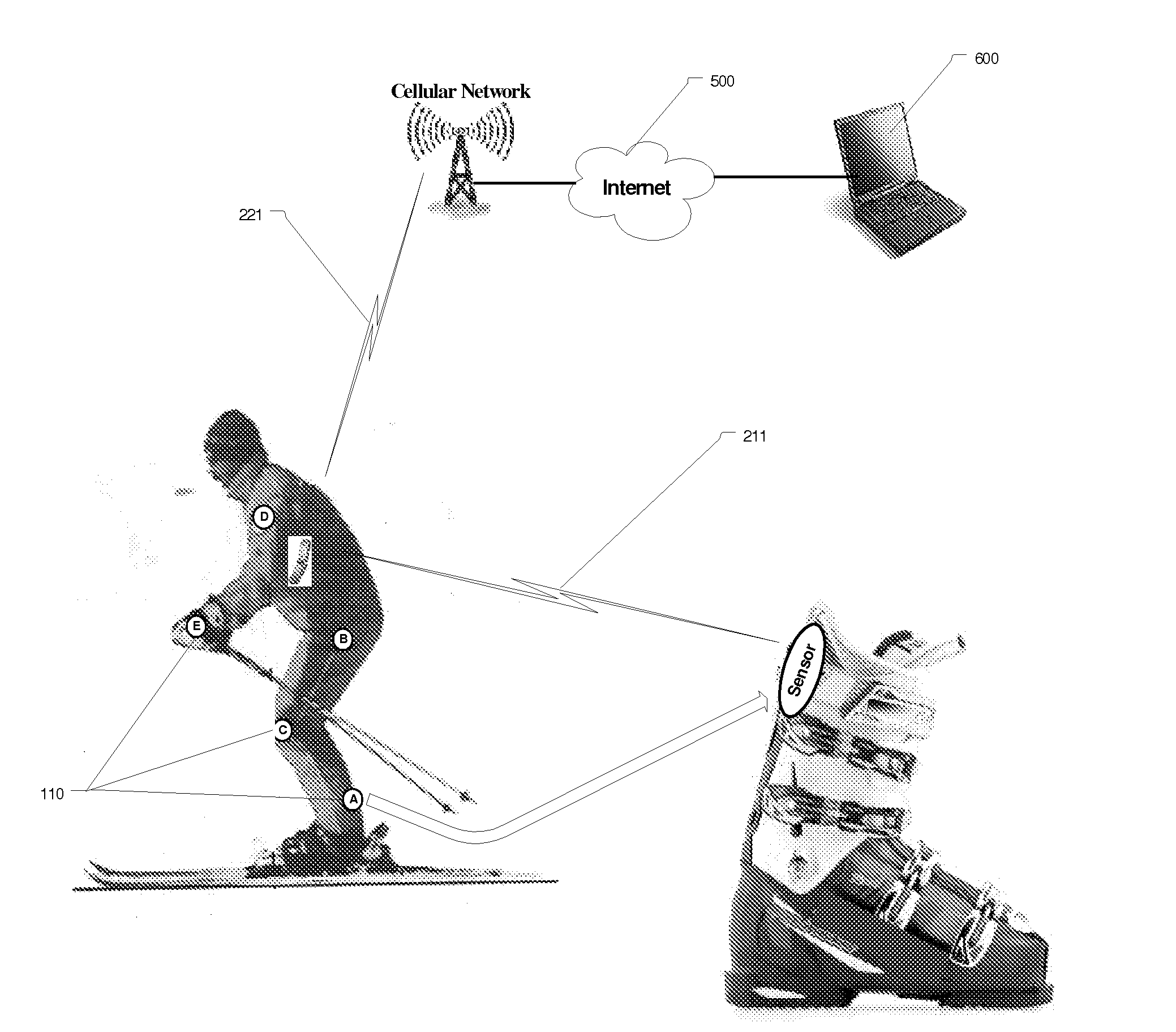
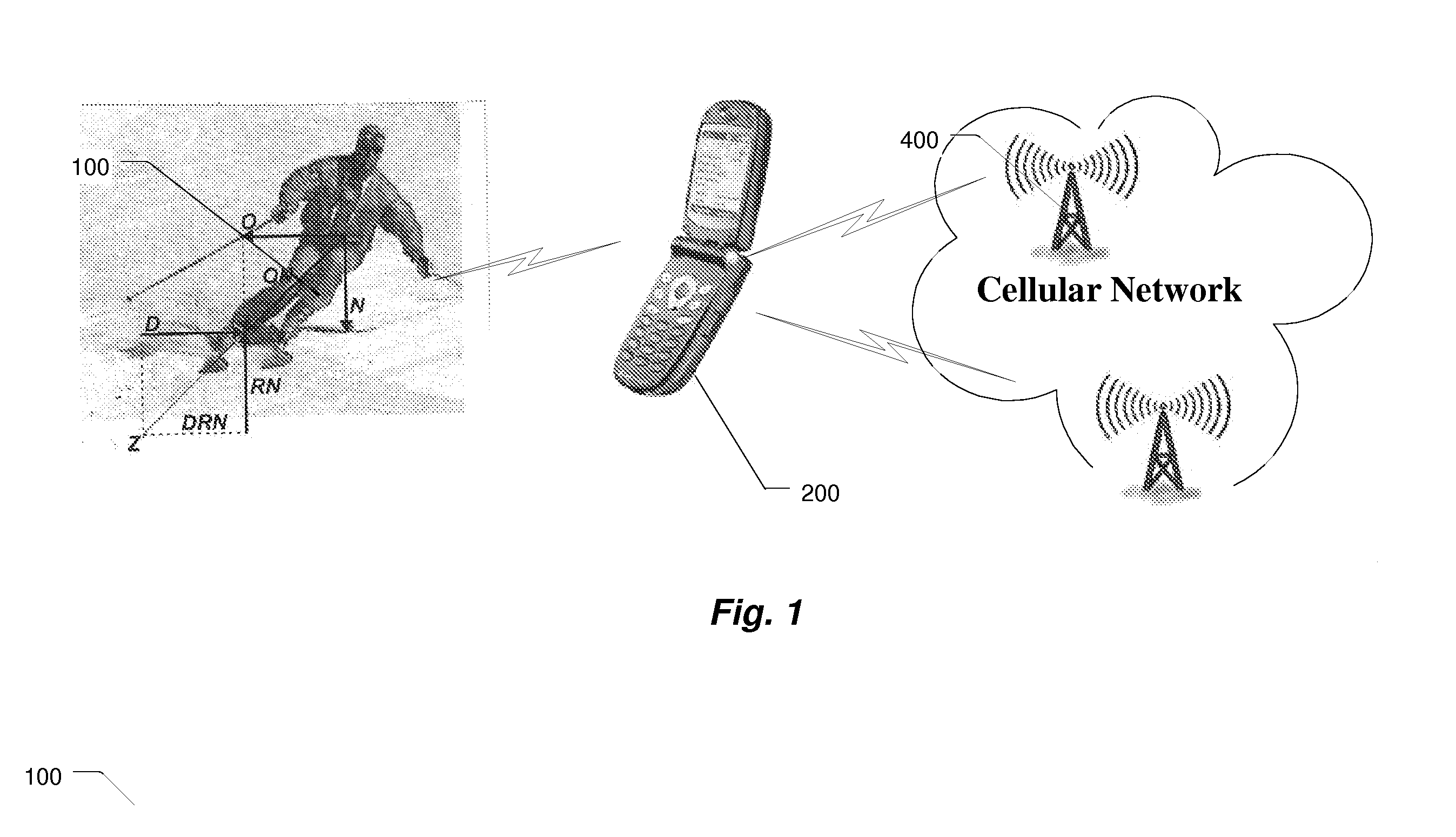
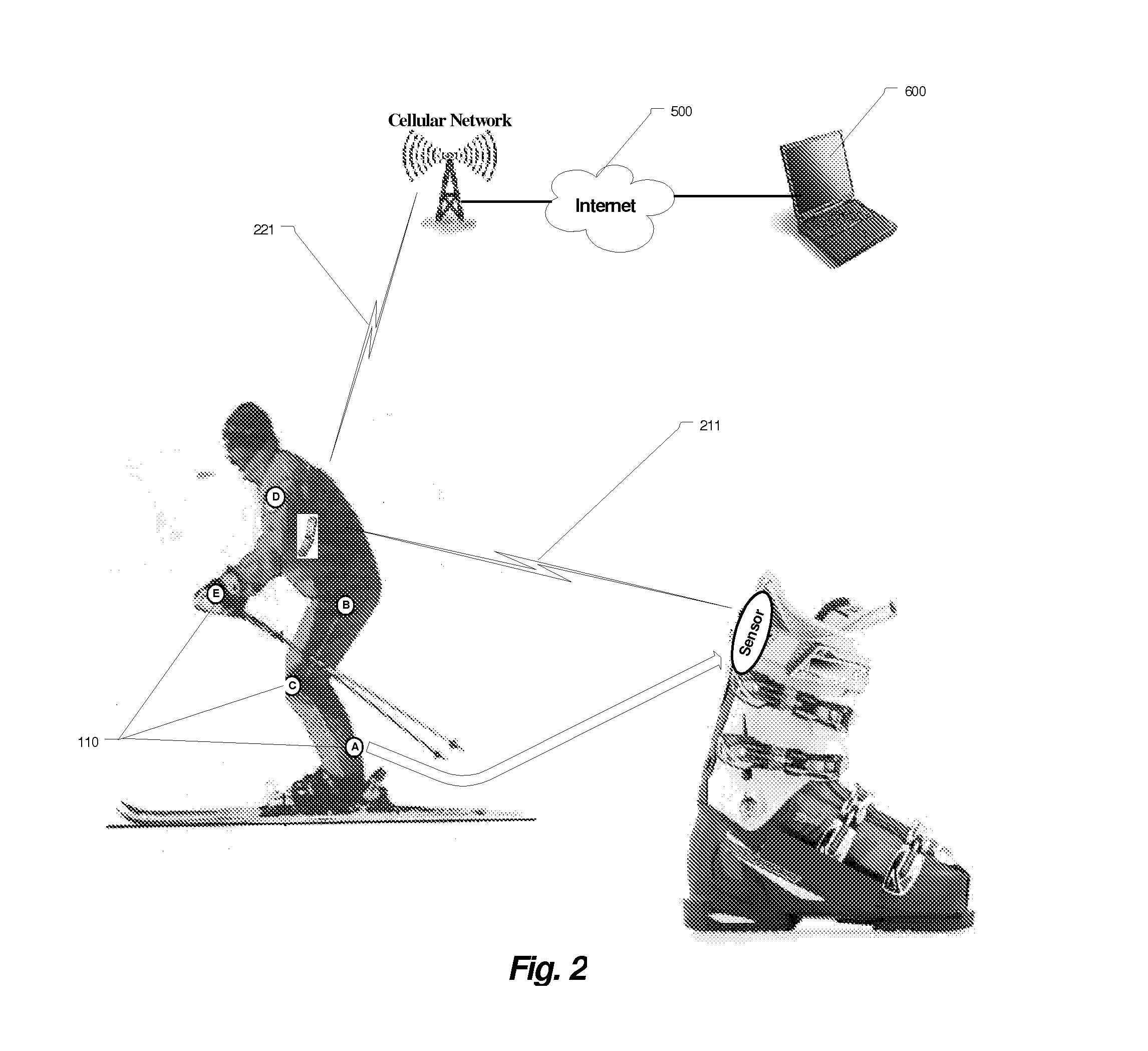
Wireless System for Monitoring and Analysis of Skiing
ActiveUS20110131012A1Improve protectionAcceleration measurementFluid speed measurementRemote analysisEngineering
This invention allows for remote monitoring of the skier / skiing performance. The system consists of a various MEMS sensors embedded in skier clothing and equipment. These sensors measure instantaneous changes in acceleration in x / y / z axis and changes in earth magnetic field—relative to the skier position, to provide six degree of freedom in calculation of skier position as well as moments applied to the ski edge and forces experiences by the skier body. These sensors communicate with the monitoring application residing in the user wireless terminal (call phone) over the PAN wireless network. The instantaneous measurements are analyzed either locally or remotely and when the system is configured in an active mode, a corrective response to the MEMS actuators embedded in the ski or ski bindings may be send does changing the parameters of the run or provide enhanced safety.
Owner:MOTION METRICS LTD
Active motor damping to mitigate electric vehicle driveline oscillations
ActiveUS20060025905A1Component can be removedReduce oscillationDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesMotor speedDrive wheel
A system and method for actively damping driveline oscillations in a motor vehicle having a traction motor to drive a vehicle's drive wheels and an antilock brake system (ABS). A traction motor controller controls a torque output signal of the motor to effectively to dampen driveline oscillations during an ABS operation. A proportional, a proportional derivative, or a derivative controller may be used to generate the torque output signal based on at least one of motor speed, an average of the drive wheel speeds, a difference in the two speeds, a motor angular acceleration, an average wheel angular acceleration, and a difference in the angular accelerations. Motor speed signals and average drive wheel speed signals may be filtered to eliminate high frequency components of each speed signal. Additionally, amplitude of the torque output signal may be limited within a positive upper and a negative lower active motor damping limit.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
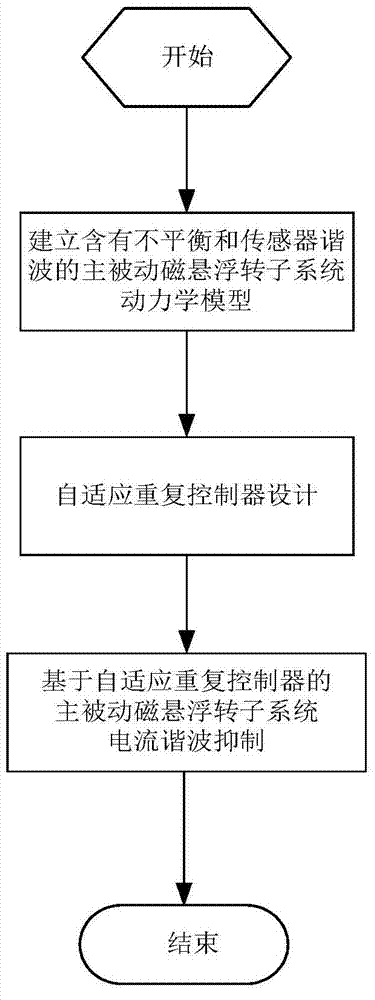
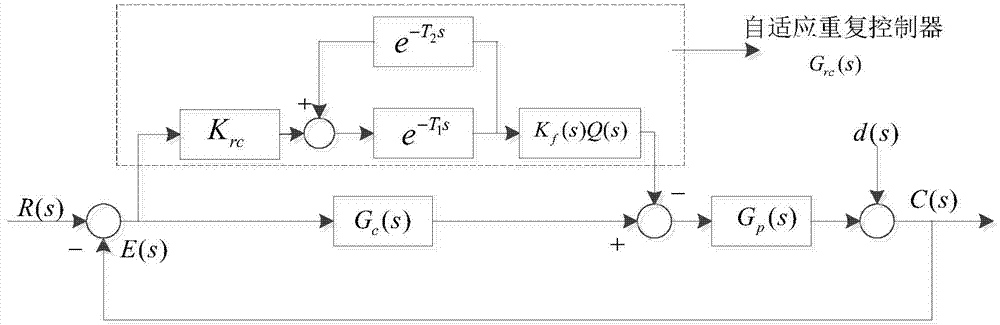
Current harmonic suppression method for magnetic suspension rotor system based on self-adaptive repetitive controller
ActiveCN104503238ASuppress harmonic currentFast convergenceMechanical oscillations controlAdaptive controlSelf adaptiveEngineering
The invention relates to a harmonic current suppression method for a magnetic suspension rotor system based on a self-adaptive repetitive controller. The harmonic current suppression method comprises the following steps: firstly establishing dynamical models for the active-passive magnetic suspension rotor system containing unbalance and sensor harmonic waves, secondly designing the self-adaptive repetitive controller, and giving out the harmonic current suppression method according to the characteristics of the active-passive magnetic suspension rotor system. The method is suitable for harmonic current suppression of an active magnetic bearing coil of the active-passive magnetic suspension rotor under the condition that unbalance mass and the sensor harmonic waves exist, and is high in precision and high in rate of convergence.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
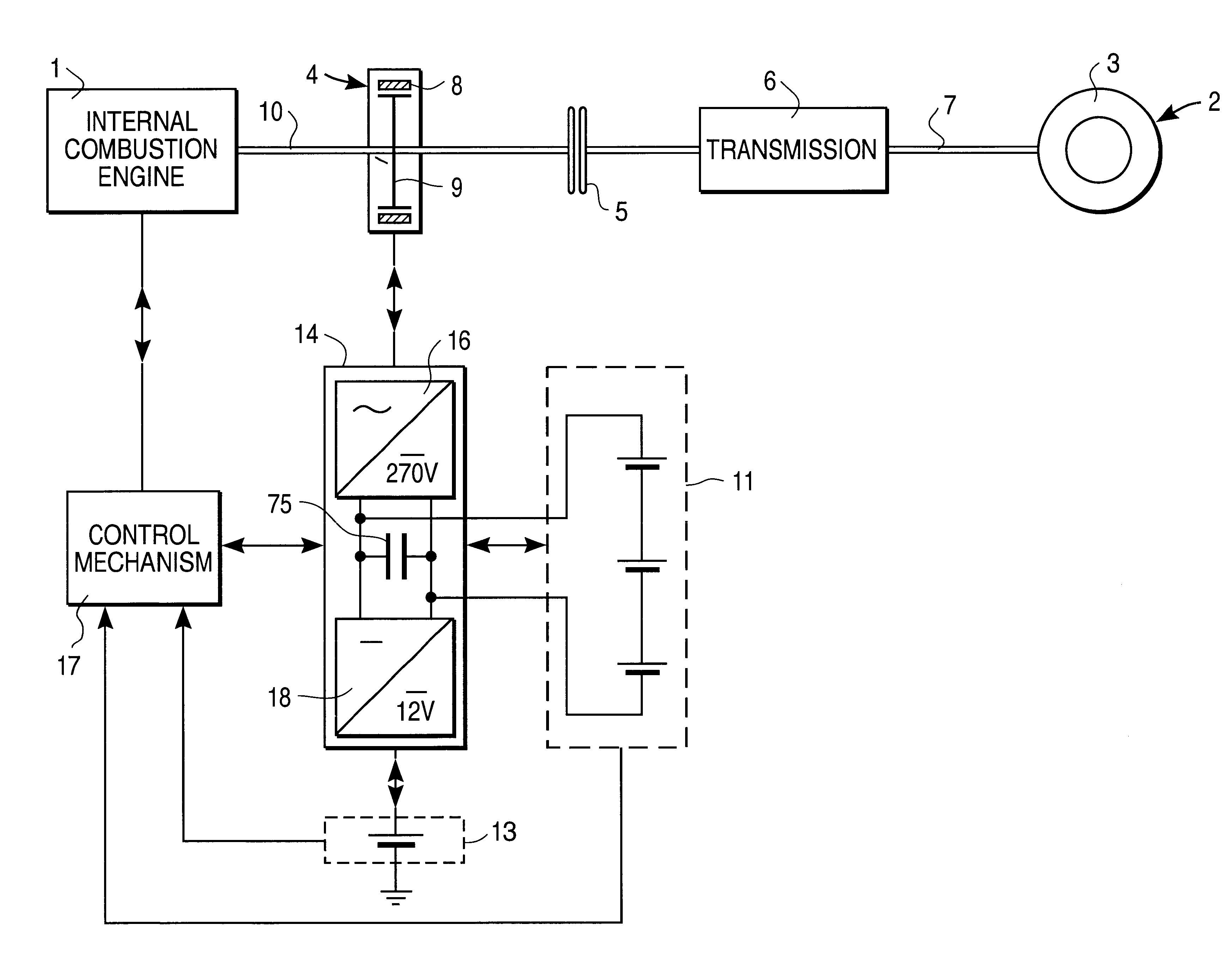
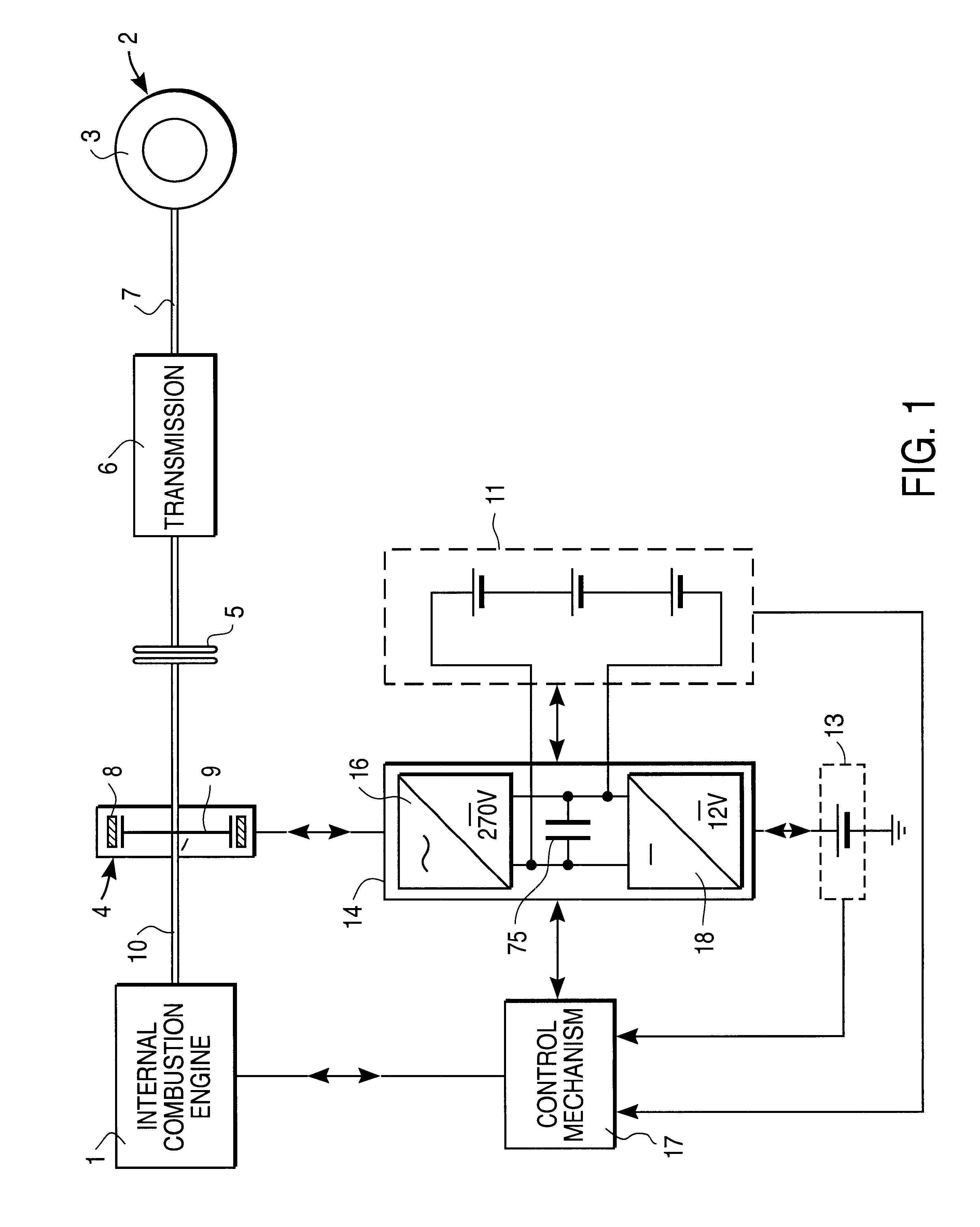
Drive system with drive-motor, electric machine and battery
InactiveUS6281646B1Low efficiencyImprove efficiencyRotating vibration suppressionBraking element arrangementsElectrical batteryElectric machine
The invention concerns a drive system with a drive motor (1), especially the internal combustion engine of a motor vehicle, an electric machine (4), which provides additional driving action, and at least one short-duty battery (11), which furnishes at least some of the energy required during the driving action of the electric machine (4).
Owner:GRUNDL ANDREAS +2
Apparatus and Method for Monitoring A Device Having A Movable Part
ActiveUS20170315516A1Accurate decisionEfficient use ofVibration measurement in solidsMachine part testingOne-class classificationEigen frequency
An apparatus for monitoring of a device including a moveable part, especially a rotating device, wherein the apparatus includes a control module which receives a measured vibration signal of the device provided by a sensor connected to the device, provides a spectrum of the measured vibration signal, pre-processes the spectrum to determine base frequencies and side frequencies, where the base frequencies are frequencies having peak powers corresponding to eigen frequencies of the device or faulty frequencies and the side frequencies correspond to other frequencies, where the control module additionally processes the base and side frequencies by applying separately a one-class classification on the base and side frequencies, combines the results of the one-class classifications to obtain a classification signal representing a confidence level, and outputs a decision support signal based on the classification signal, where the decision support signal indicates an error status of the monitored device.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
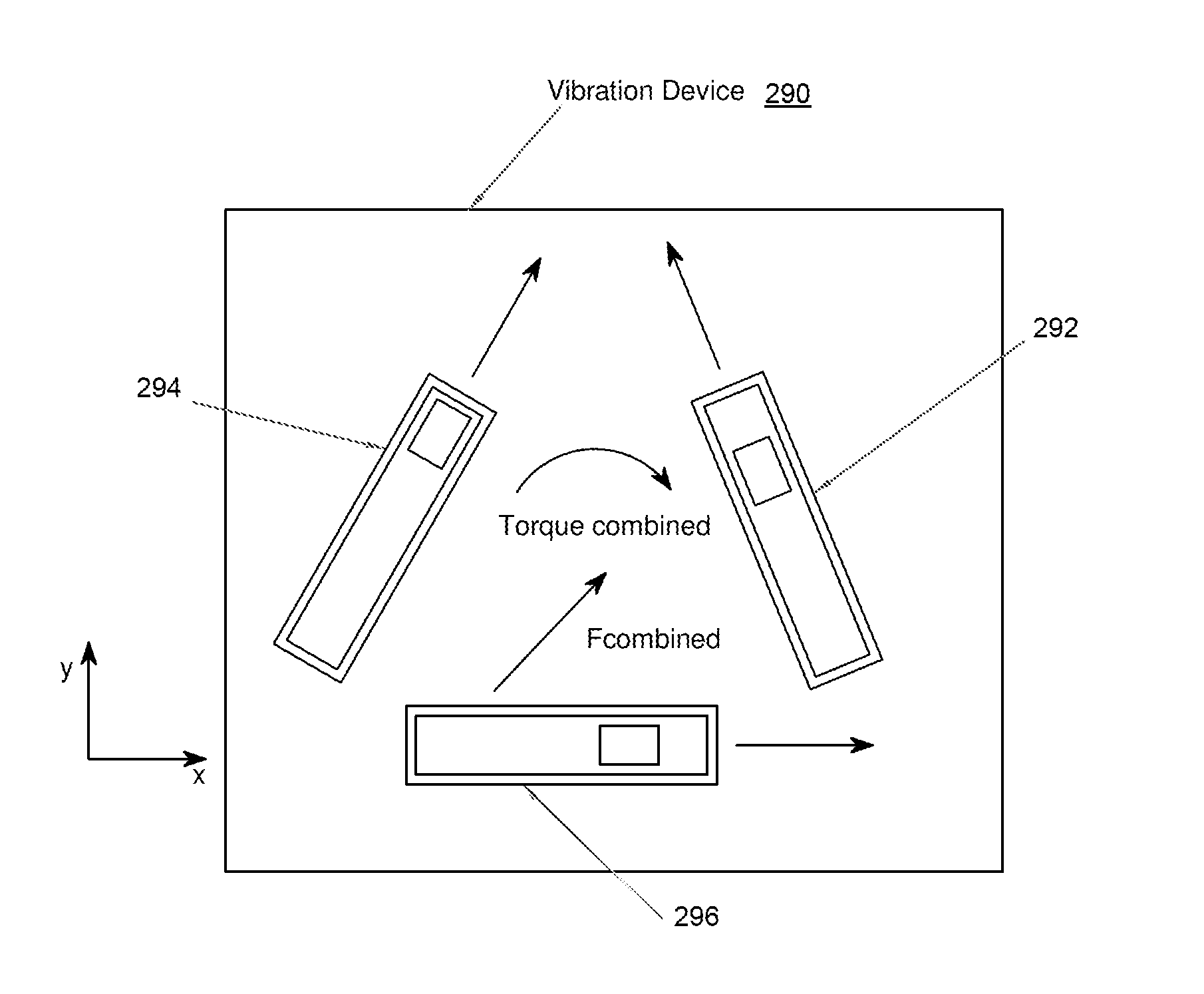
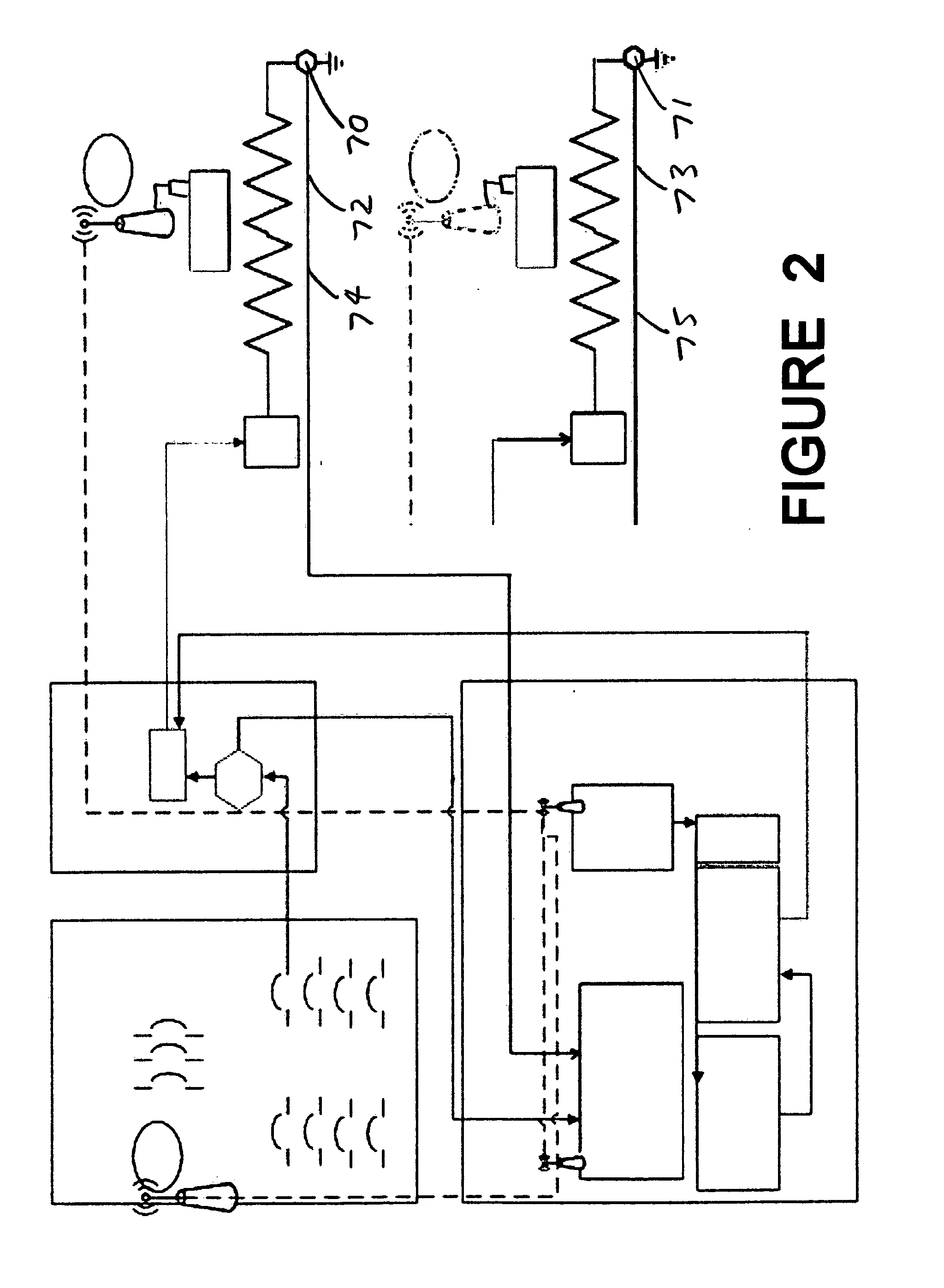
Helicopter multi-frequency vibration active control method
InactiveCN105843270AReduce order requirementsAvoiding Frequency Modulation ProblemsMechanical oscillations controlEngineeringActuator
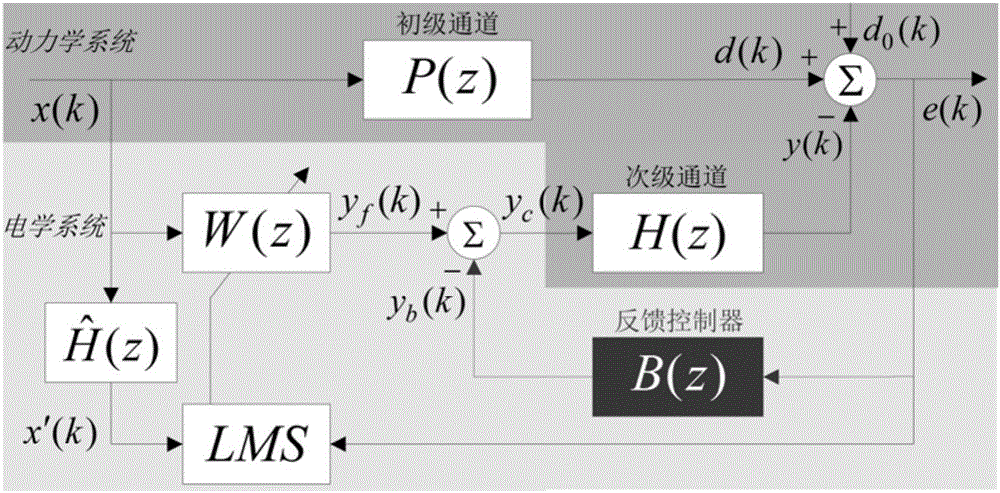
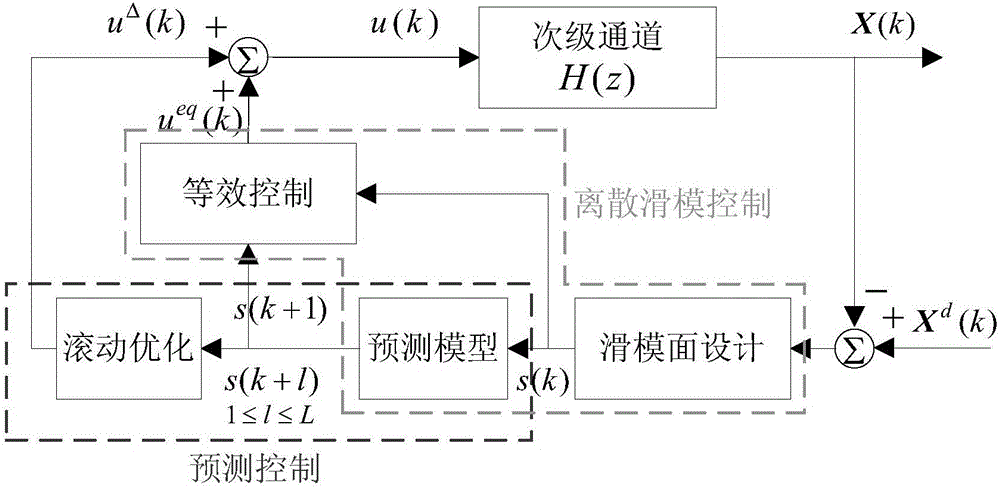
The invention discloses a method for actively controlling multi-frequency vibration of a helicopter, including system identification, collecting the control voltage of the actuator and the acceleration response at the controlled point, using the recursive least squares algorithm for system identification, and finally obtaining the discrete state space of the secondary channel Equation; feedback controller design, using the secondary channel discrete state space equation obtained in step 1 to carry out discrete predictive sliding mode feedback controller design; reference signal and error signal acquisition, according to the helicopter rotor characteristics and speed characteristics, extract the rotor excitation frequency, synthesize reference signal, and collect the vibration response error signal at the controlled point; the feedforward-feedback hybrid control algorithm iterates, and uses the reference signal and error signal obtained in step 3 to iterate the feedforward controller and the feedback controller to obtain the feedforward-feedback Feedback the mixed control voltage signal; output the control quantity; use the mixed control voltage obtained in step 4 as the input signal at the next moment, drive the actuator to produce the required response, and return to step 3.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Damping apparatus for reducing vibration of automobile body
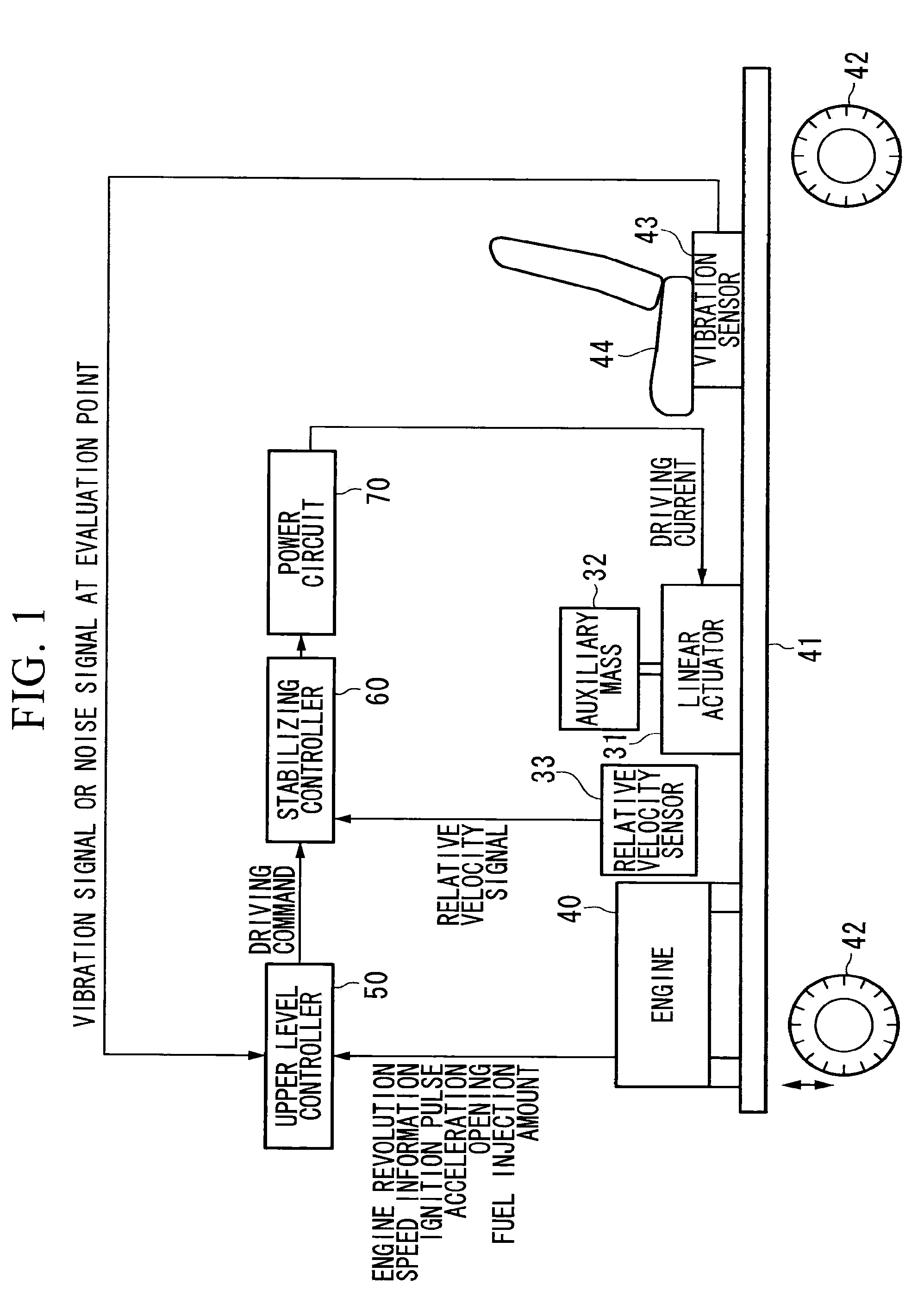
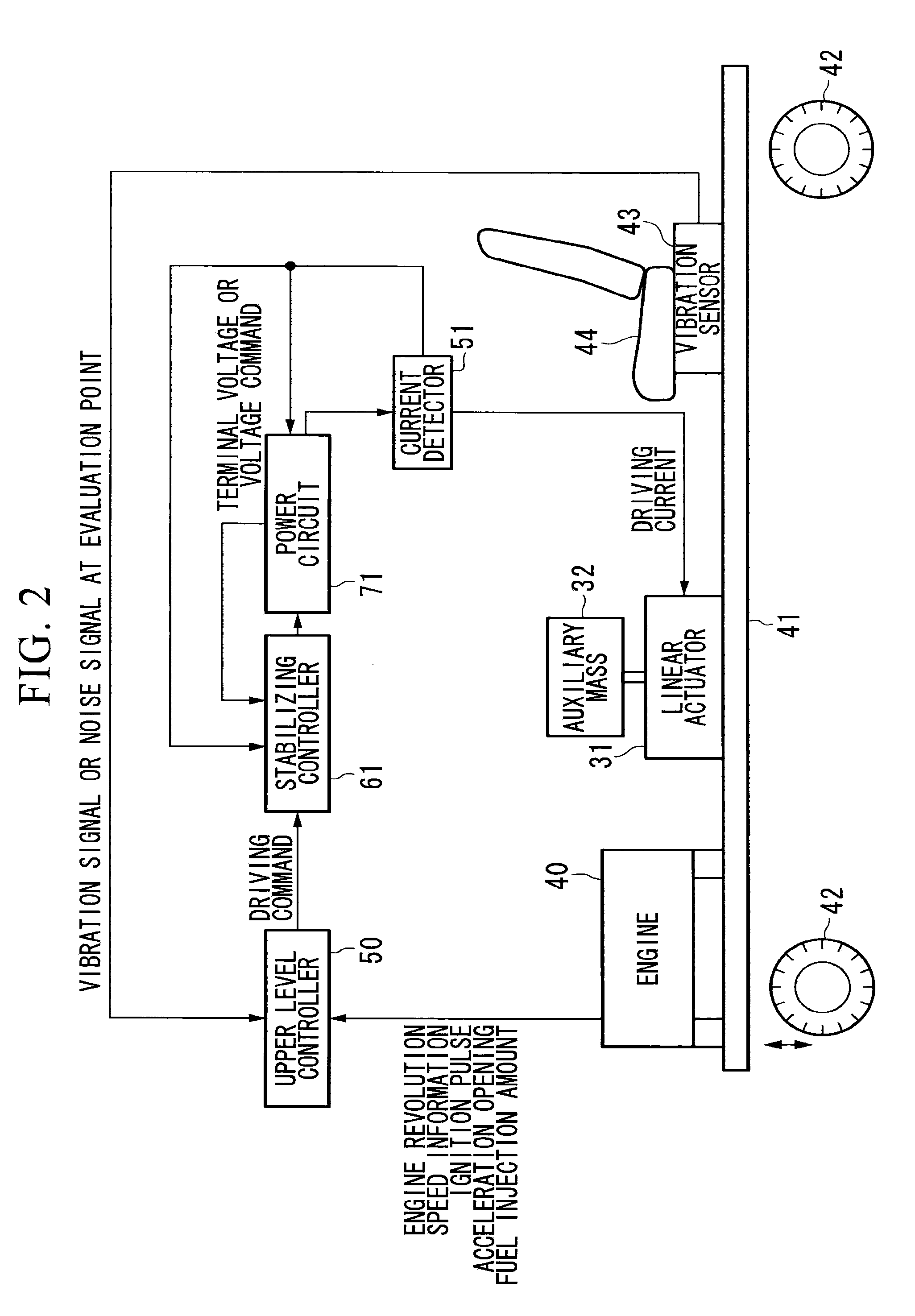
ActiveUS20100204881A1High damping characteristicsReduce apparent natural frequencyPortable framesVehicle body stabilisationRelative displacementTerminal voltage
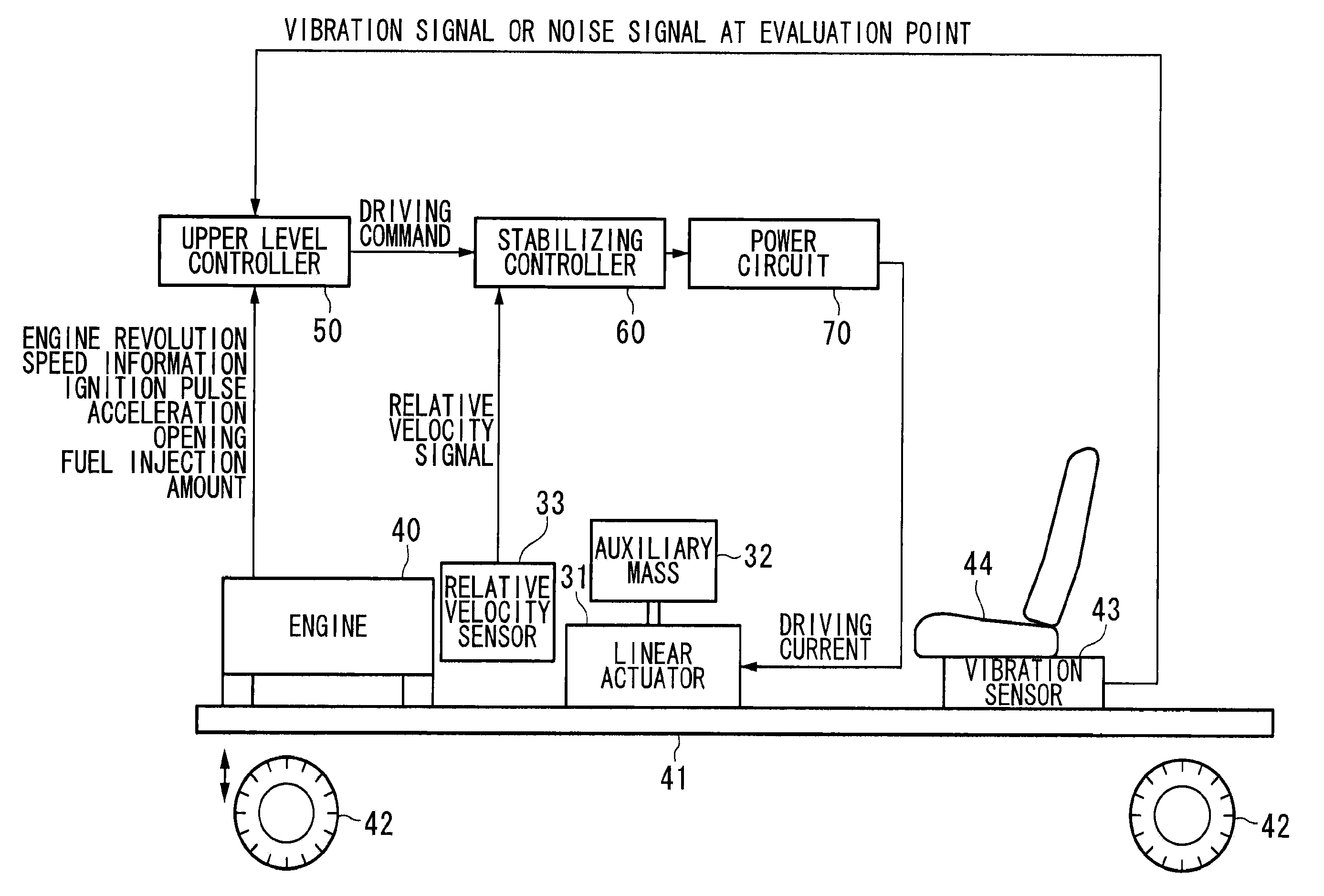
A damping apparatus for an automobile is provided, capable of ensuring a high level of reliability while obtaining excellent damping effect with simple configuration. The damping apparatus for an automobile that reduces vibrations of an automobile body may include an actuator that is attached to the automobile body and drives an auxiliary mass; a current detector that detects a current flowing through an armature of the actuator; a section that detects a terminal voltage applied to the actuator; a calculation circuit that calculates an induced voltage of the actuator, and further calculates at least one of the relative velocity, relative displacement, and relative acceleration of the actuator, based on a current detected by the current detector and the terminal voltage; and a control circuit that drive-controls the actuator based on at least one of the relative velocity, relative displacement, and relative acceleration of the actuator calculated by the calculation circuit.
Owner:SHINKO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Cabinet cooling
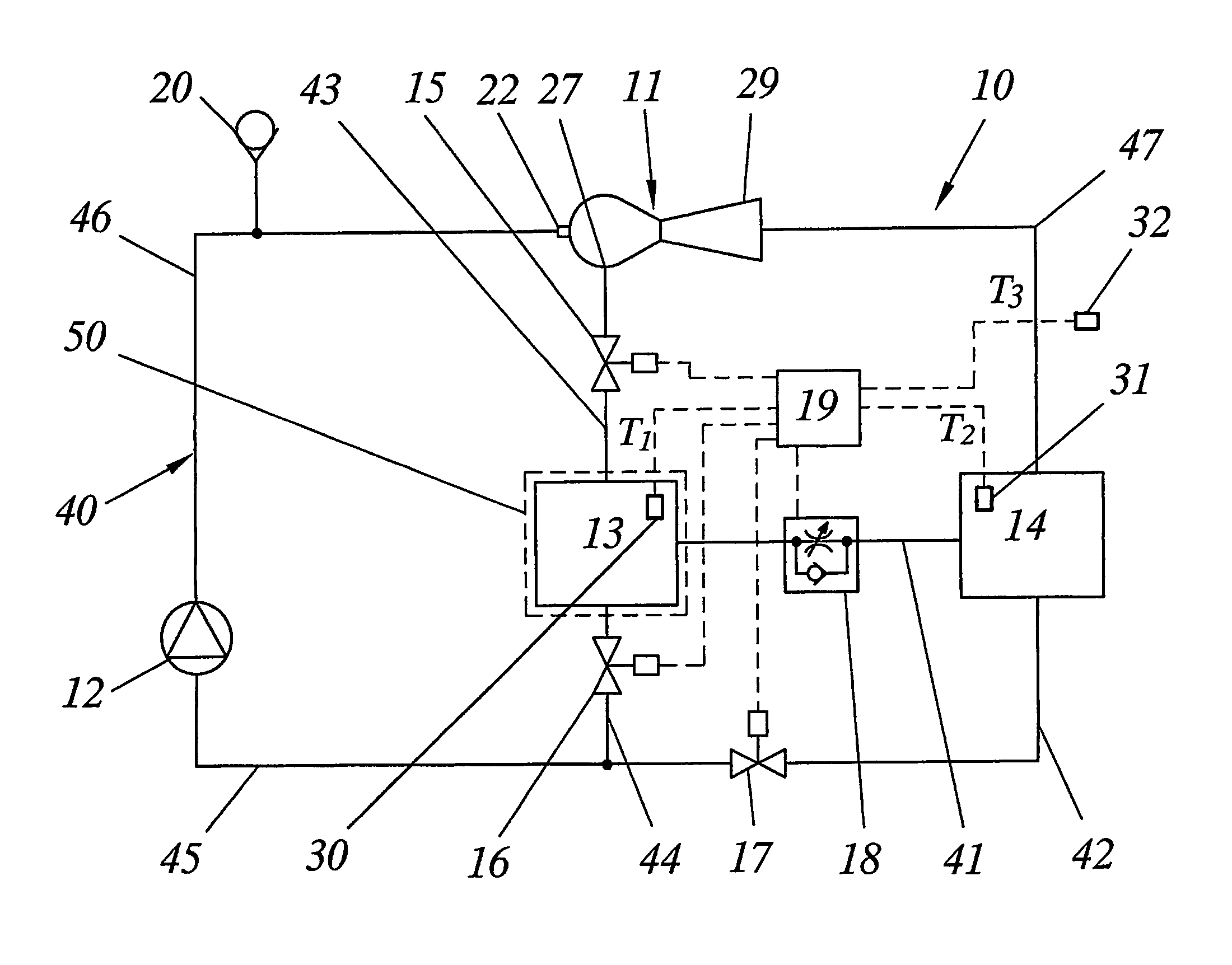
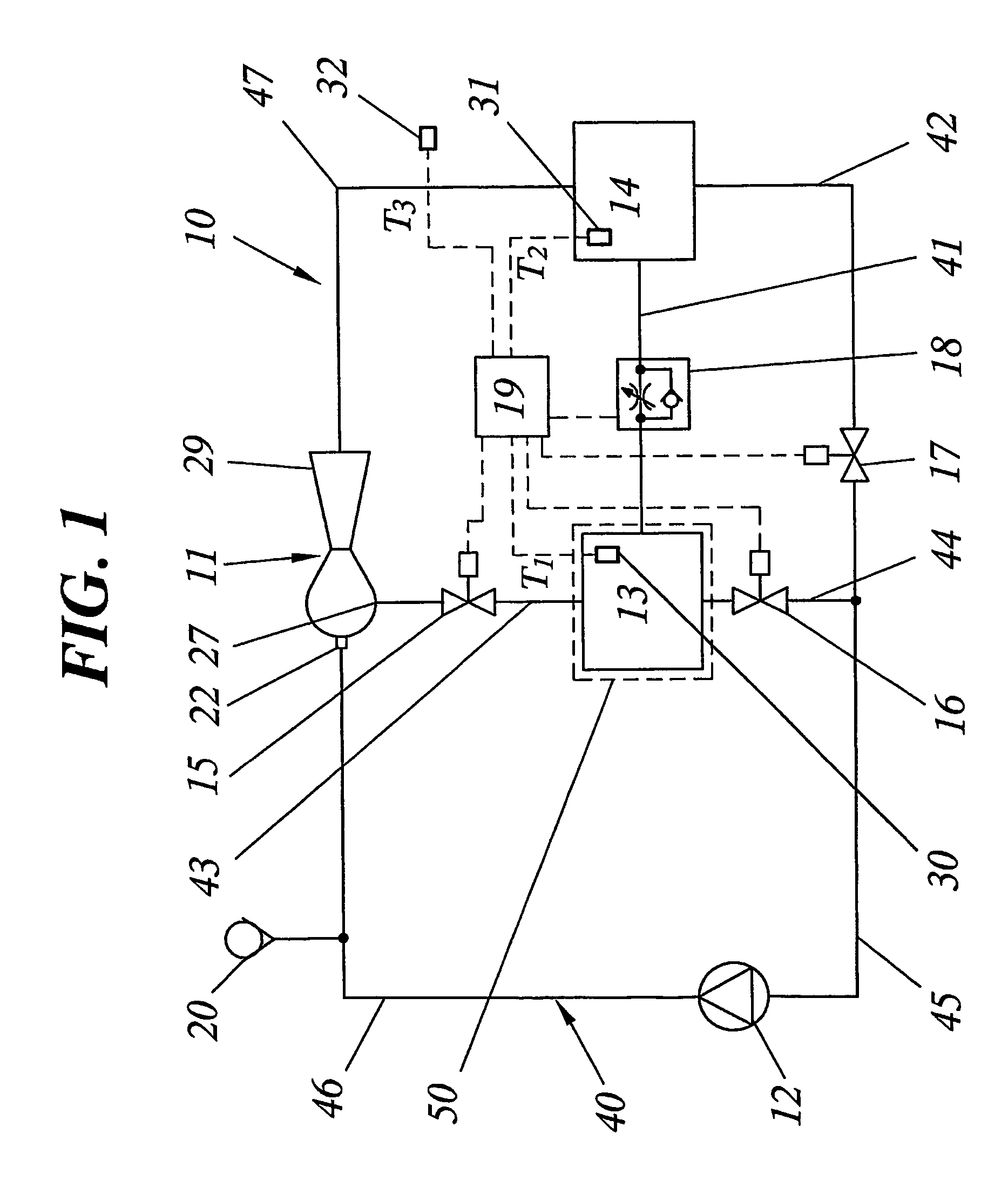
InactiveUS7061763B2Dissipating electronic componentsIncrease heat loadMechanical oscillations controlDomestic cooling apparatusElectronics coolingControl system
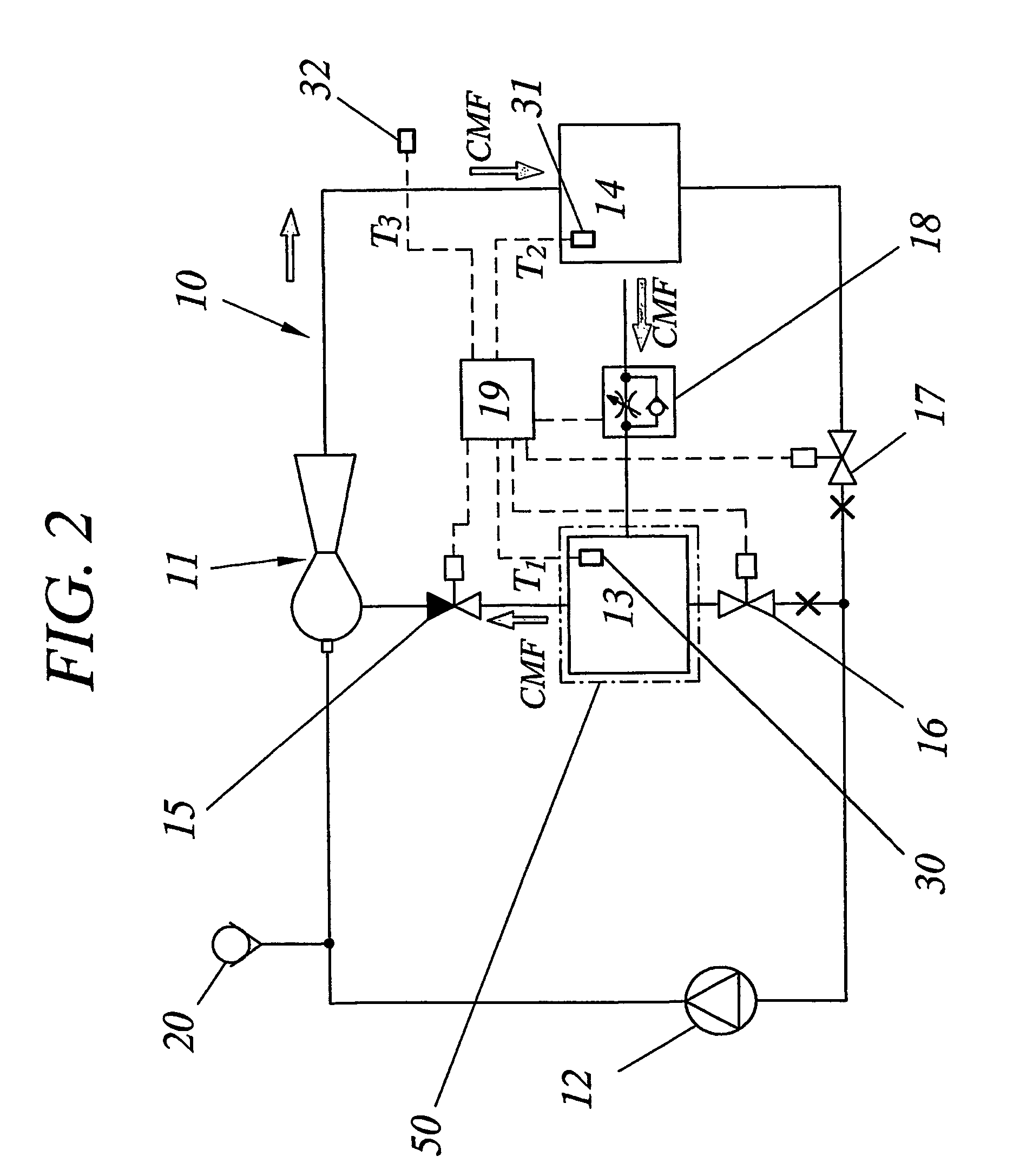
A novel electronics cooling method and system is disclosed. A very flexible and efficient operation of an electronics cooling system (10) is achieved by controlling circulation of a cooling medium in a closed system (40) containing an evaporator (13), a condenser (14), an ejector (11) and control valves (15–18). Specifically, the system is continuously allowed to operate in the most appropriate mode by controlling the valves (15–18) of the system (10) based on detected heat load and / or detected heat transfer conditions. By automatically adapting the mode of operation of the system based on the actual prevailing conditions, a unique flexibility is obtained with regard to the cooling mode in which the system will be operated. This means that the cooling capacity will be constantly optimized and that the investment cost as well as the cost for operating the system will be reduced compared to known systems having equal maximum cooling capacity.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Active vibration control system for hybrid vehicle
ActiveUS20070222407A1Suppresses torque fluctuationsReduce vibrationHybrid vehiclesMechanical oscillations controlAdaptive filterControl signal
In a motor-assisted hybrid vehicle, an active vibration control system suppresses torque fluctuations of an engine without detriment to the response of a static torque. An adaptive notch filter outputs a control signal depending on a harmonic basic signal generated by a basic signal generator from a rotational frequency of a crankshaft. A combiner combines the control signal with a drive signal for the generator motor and supplies the combined signal through a power controller to the generator motor. The basic signal is supplied to corrective filters having the transfer function of the generator motor to output a reference signal. The filter coefficient of an adaptive notch filter is successively updated so that an error signal representative of a rotational speed fluctuation of the crankshaft will be minimized.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
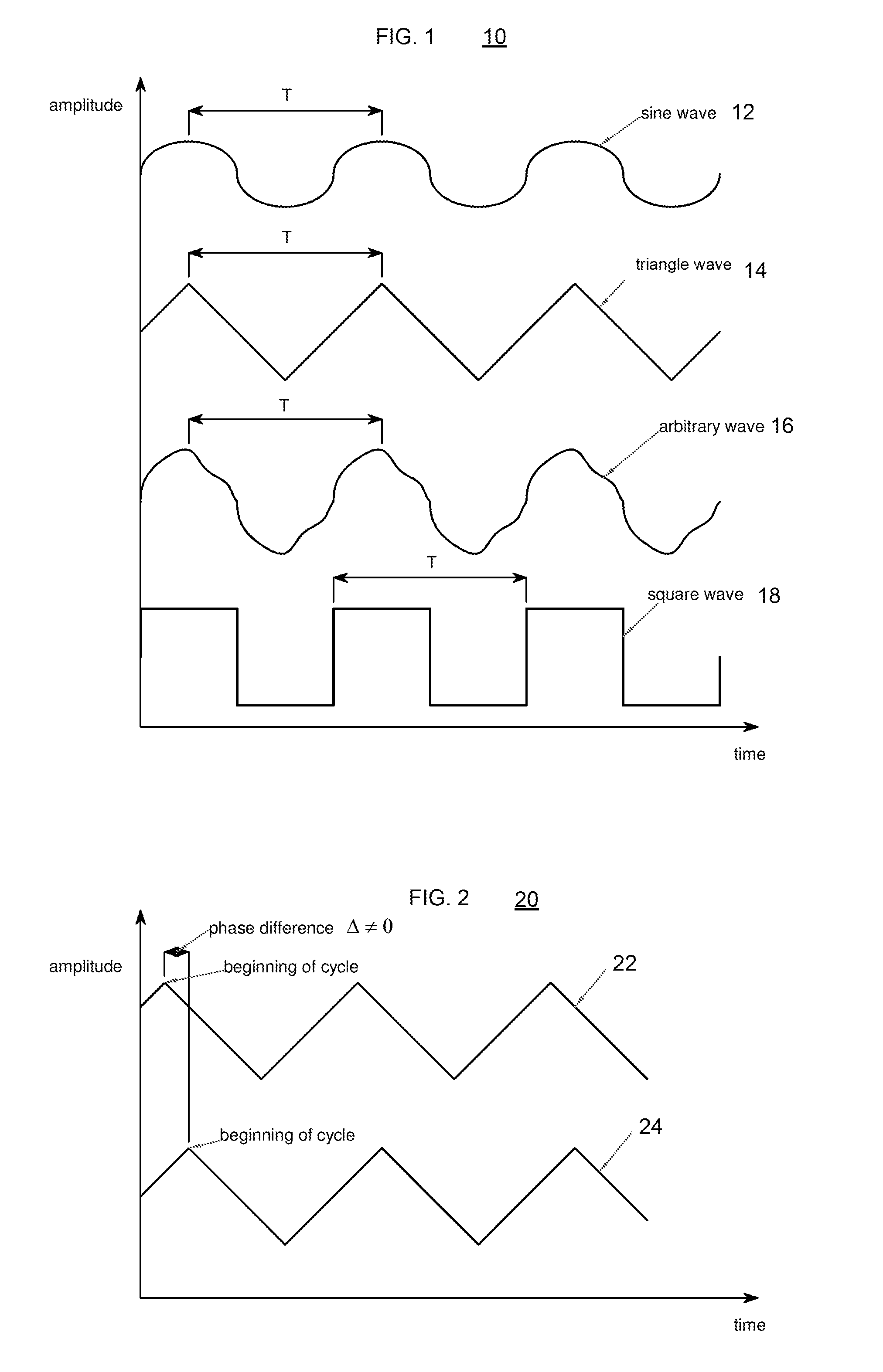
Flexible contilever plate vibration control set and control method based on acceleration sensor
InactiveCN101261523ABandwidthLight in massMechanical oscillations controlSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementElectricityAccelerometer
The invention discloses a flexible cantilever plate vibration control device on the basis of accelerometers and a control method. The device is symmetrically affixed with a plurality of piezoelectric ceramic sheets on the front and back surfaces of a fixed end of the flexible plate, the polarities of the two surfaces of a plurality of piezoelectric ceramic sheets are reverse, then a plurality of piezoelectric ceramic sheets are connected in parallel to compose a bending mode piezoelectric driver; the two surfaces of the longitudinal middle part of a free end of the flexible plate are anti-symmetrically affixed with a plurality of piezoelectric ceramic sheets, the polarities of the two surfaces of the piezoelectric ceramic sheets are same, then the piezoelectric ceramic sheets are connected in parallel to compose a torsional mode driver, an accelerometer A and an accelerometer B are respectively arranged at the two side angle positions of the free end of the flexible plate; the device has small weight and less wiring, which only needs the two accelerometers to be used as the sensors of the flexible cantilever plate. The method utilizes the optimized configuration of the two accelerometers and the piezoelectric driver to realize the decoupling on the detection and the driving control of the bending mode and the torsional mode of the flexible cantilever plate, thus realizing the purpose of active inhibition of multi-bending and multi-torsinal mode vibration of the flexible plate.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Collision energy-absorbing device
InactiveUS7070217B2Mechanical oscillations controlMicrobiological testing/measurementMobile vehicleVehicle frame
A collision energy-absorbing device includes a body member connected between the frame assembly of a motor vehicle and a bumper beam. The body member collapses as the bumper beam and the frame assembly are moved relatively toward one another during a vehicle collision. The body member has a first telescoping portion and a second telescoping portion that are connected by a connecting portion. The telescoping portions have different cross-sectional dimensions to enable the telescoping portions to move one within the other into collapsing telescoping relation as the body member collapses with the connecting portion being deformed and received between the telescoping portions. One or more protrusions extending from one of the telescoping portions interfere with relative movement of the other of the telescoping portions to retard movement of the telescoping portions into telescoping relation.
Owner:MAGNA INTERNATIONAL INC
Wireless electric heat trace and vibration control and monitoring system
InactiveUS20110163082A1Quick fixReduce distanceTemperature control using digital meansMechanical oscillations controlCurrent transducerVibration control
A monitoring system for monitoring the temperature and vibration of equipment, comprising a central digital computer, a MESH communication network, wherein the network feeds signals to the central digital computer, a plurality of heating elements for heating the equipment, temperature / vibration sensors adapted to measure the temperature of the equipment, wherein each sensor is adapted to provide a signal representing the temperature / vibration of the piece of equipment to which the sensor is associated, to the network, wherein each temperature / vibration sensor can also be used to control the electric heaters, a temperature sensor that monitors the ambient temperature of the facility, and current transducers associated with the heaters, to monitor the energy use and current loss of the heaters, wherein the central computer uses the data it receives from the other elements of the monitoring system to determine when the equipment is not at the correct temperature / vibration and diagnoses the reason why.
Owner:BRACE INTEGRATED SERVICES INC
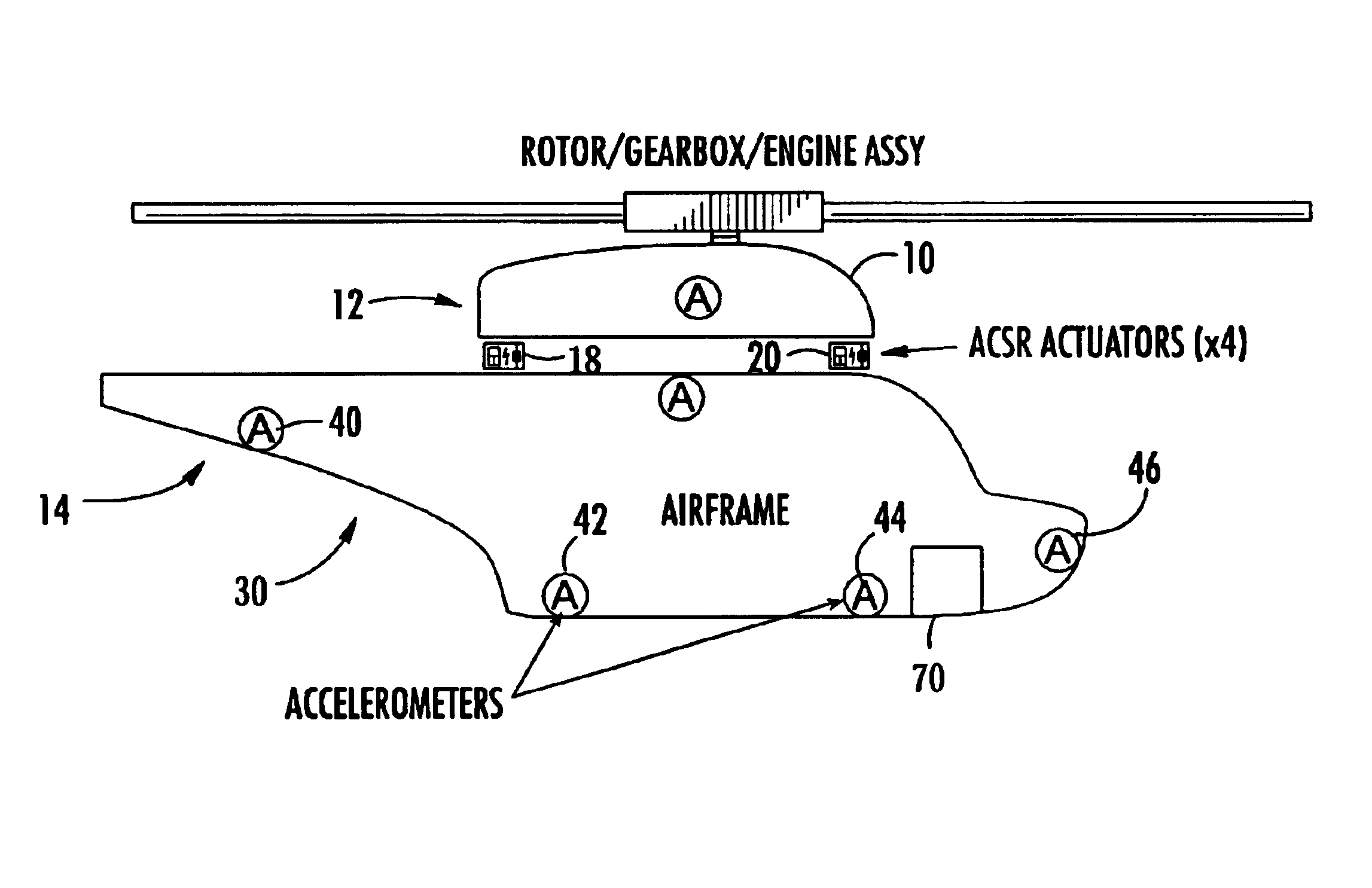
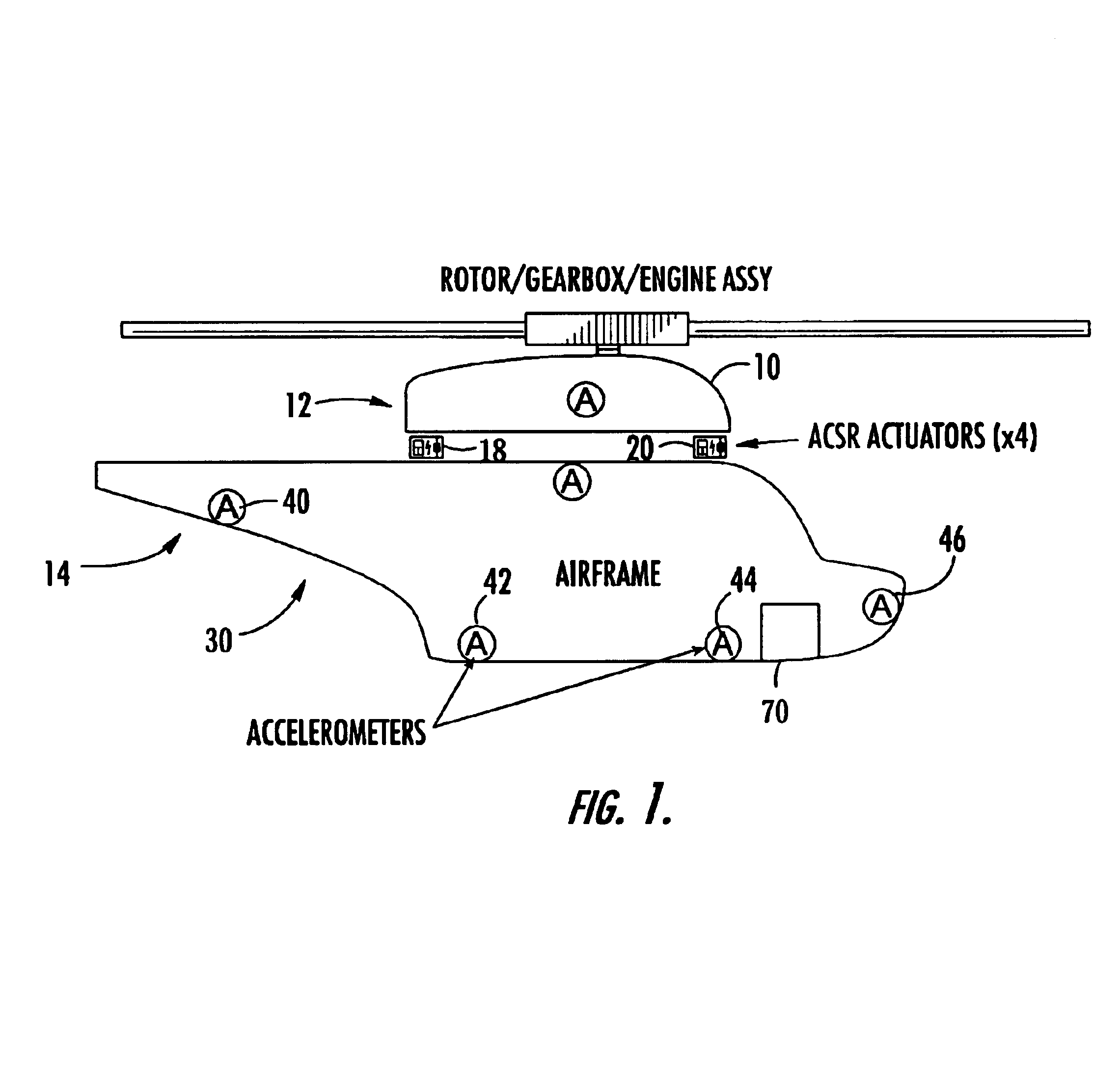
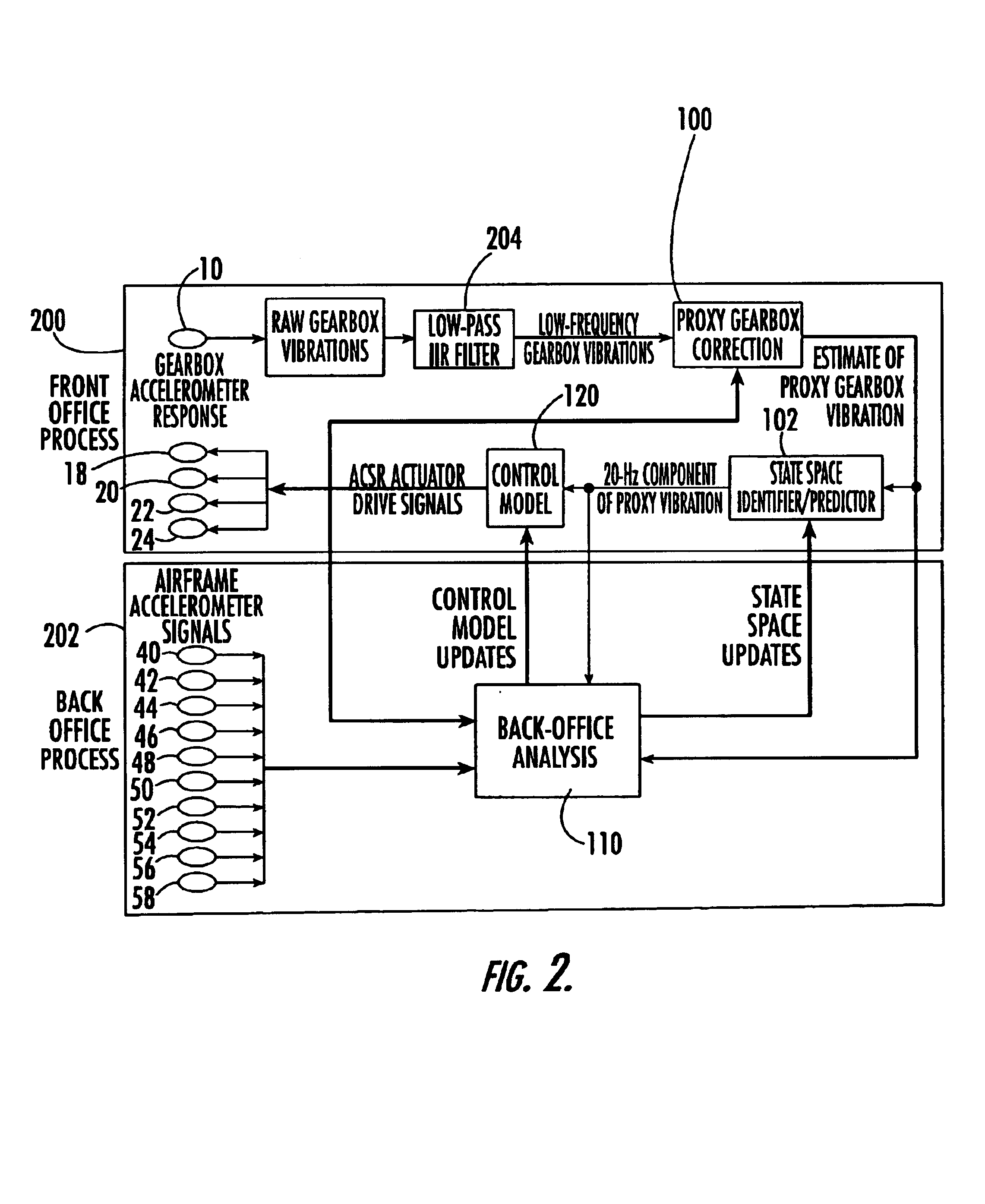
Active vibration control system
InactiveUS7017857B2Control vibrationEasy to controlPropellersMechanical oscillations controlControl systemChaotic systems
An active vibration control system including a sensor responsive to a source of vibration and which provides an output signal representative of the vibrations; at least one actuator positioned to impart canceling vibrations to the source of vibrations based on an input signal; a correction subsystem responsive to the actuator for estimating the sensor output in the absence of the canceling vibrations and which outputs a corrected output signal representative only of the vibrations emanating from the source; and a state space predictor responsive to the corrected output signal for determining the input signal to the actuator based on variations in the corrected output signal to better control vibrations especially in chaotic systems.
Owner:FOSTER-MILLER
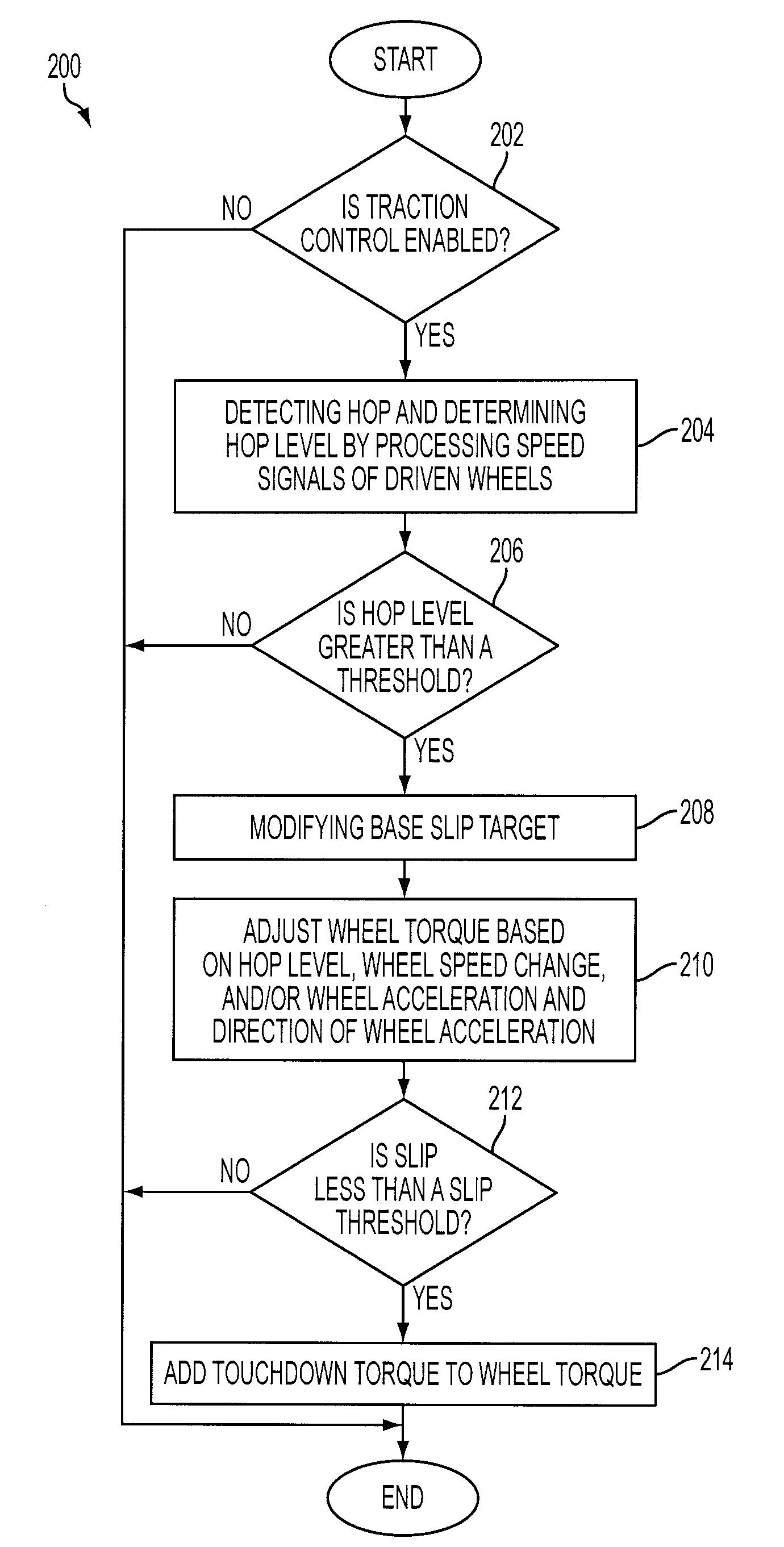
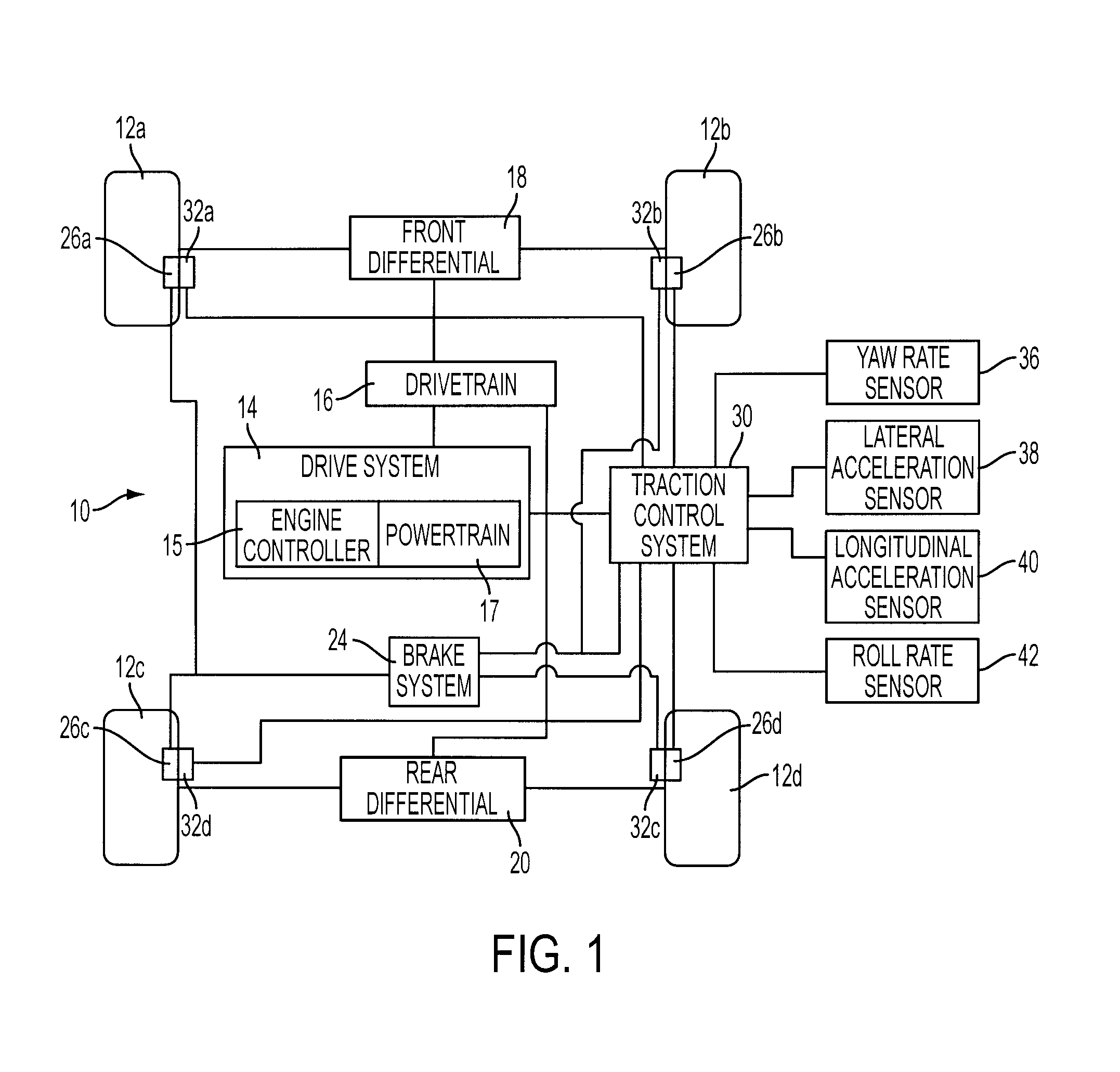
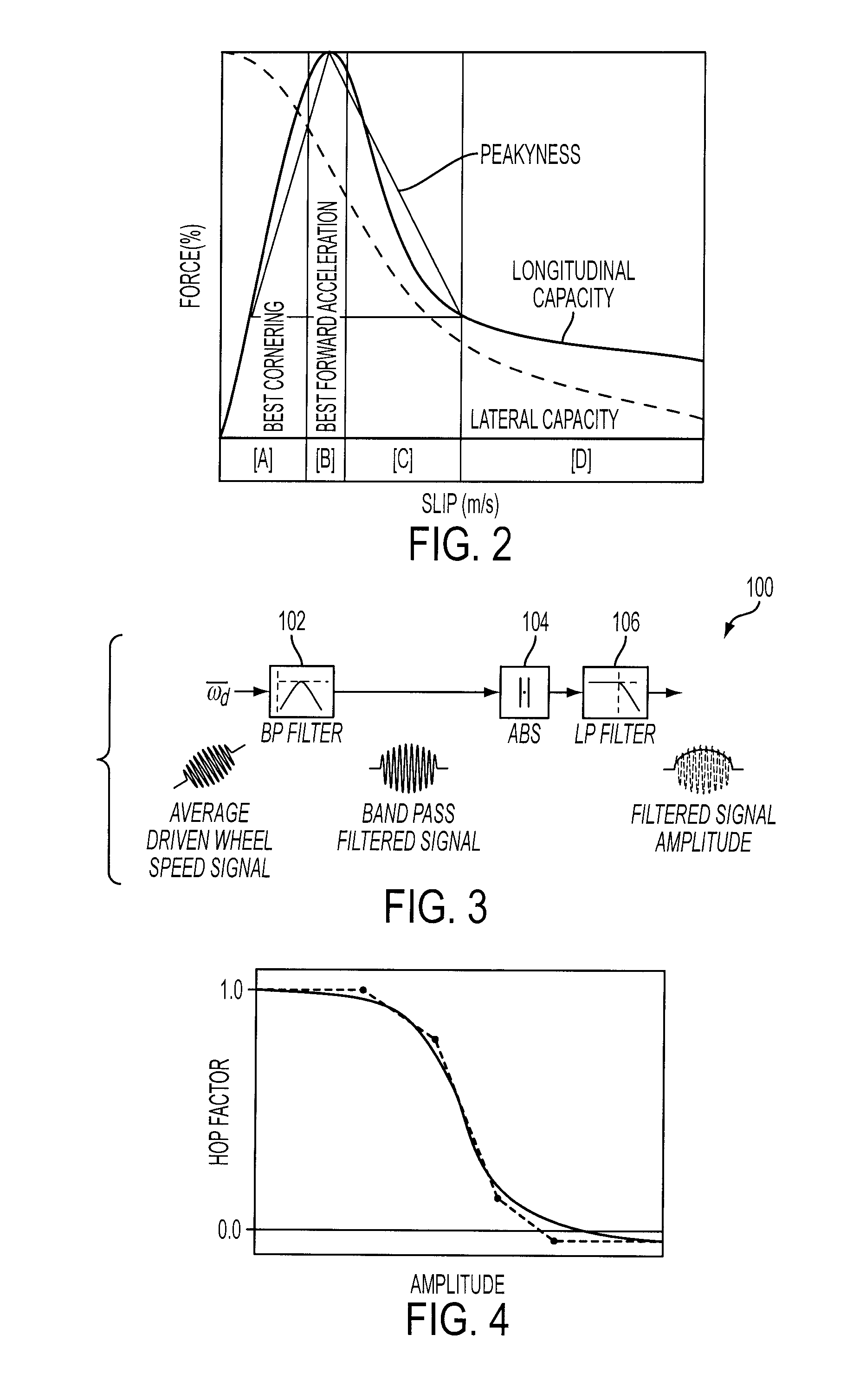
Detection and Control of Power Induced Hop During Traction Control in a Vehicle
ActiveUS20090107747A1Reduce torque adjustmentReduce vibrationMechanical power/torque controlMechanical oscillations controlDrive wheelBand-pass filter
A method for controlling a powertrain of a vehicle with wheels during a traction control event is provided. The method comprises adjusting wheel torque in response to an amplitude of a band-pass filtered driven wheel speed and a direction of acceleration of driven wheels.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
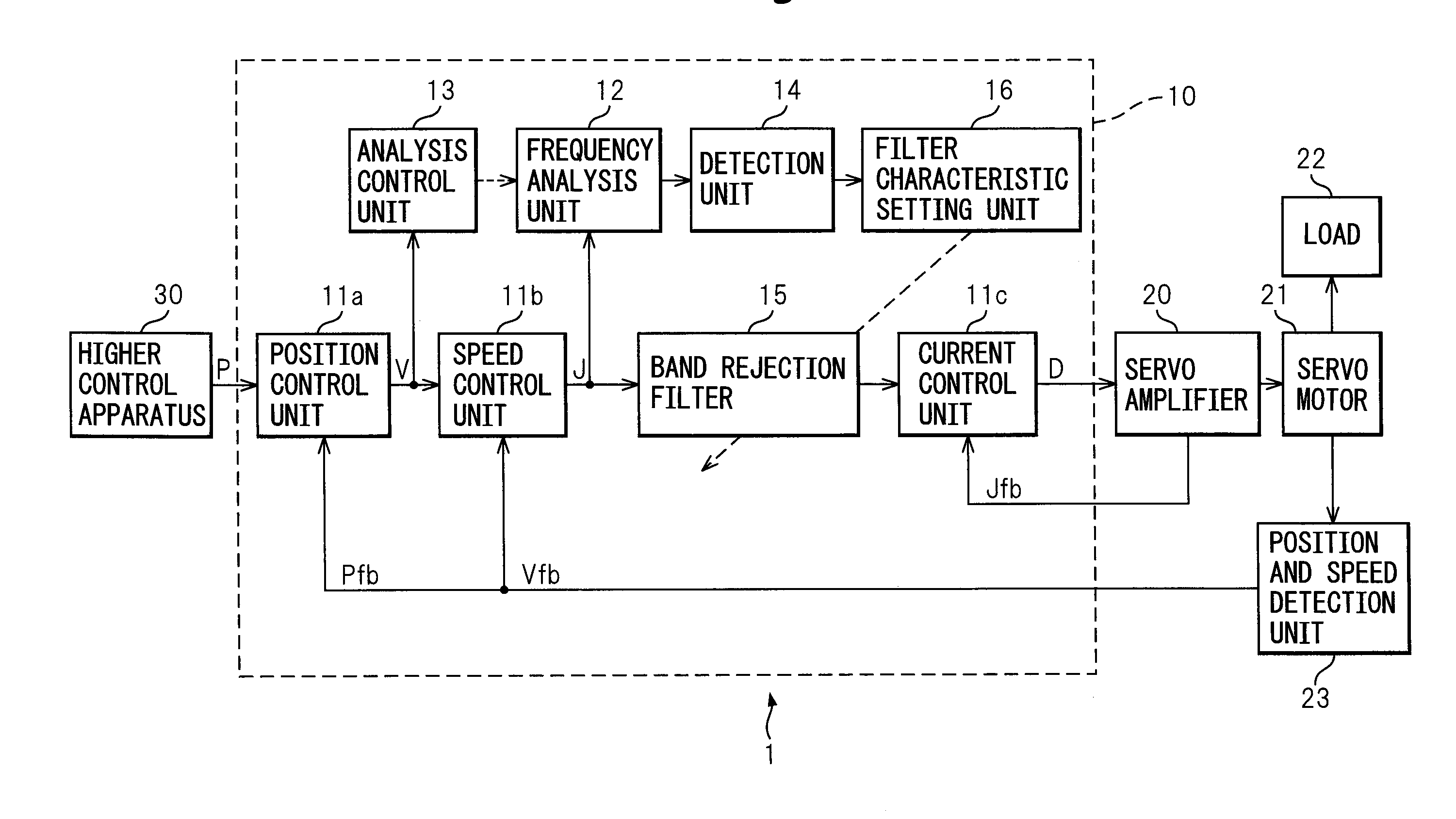
Control apparatus
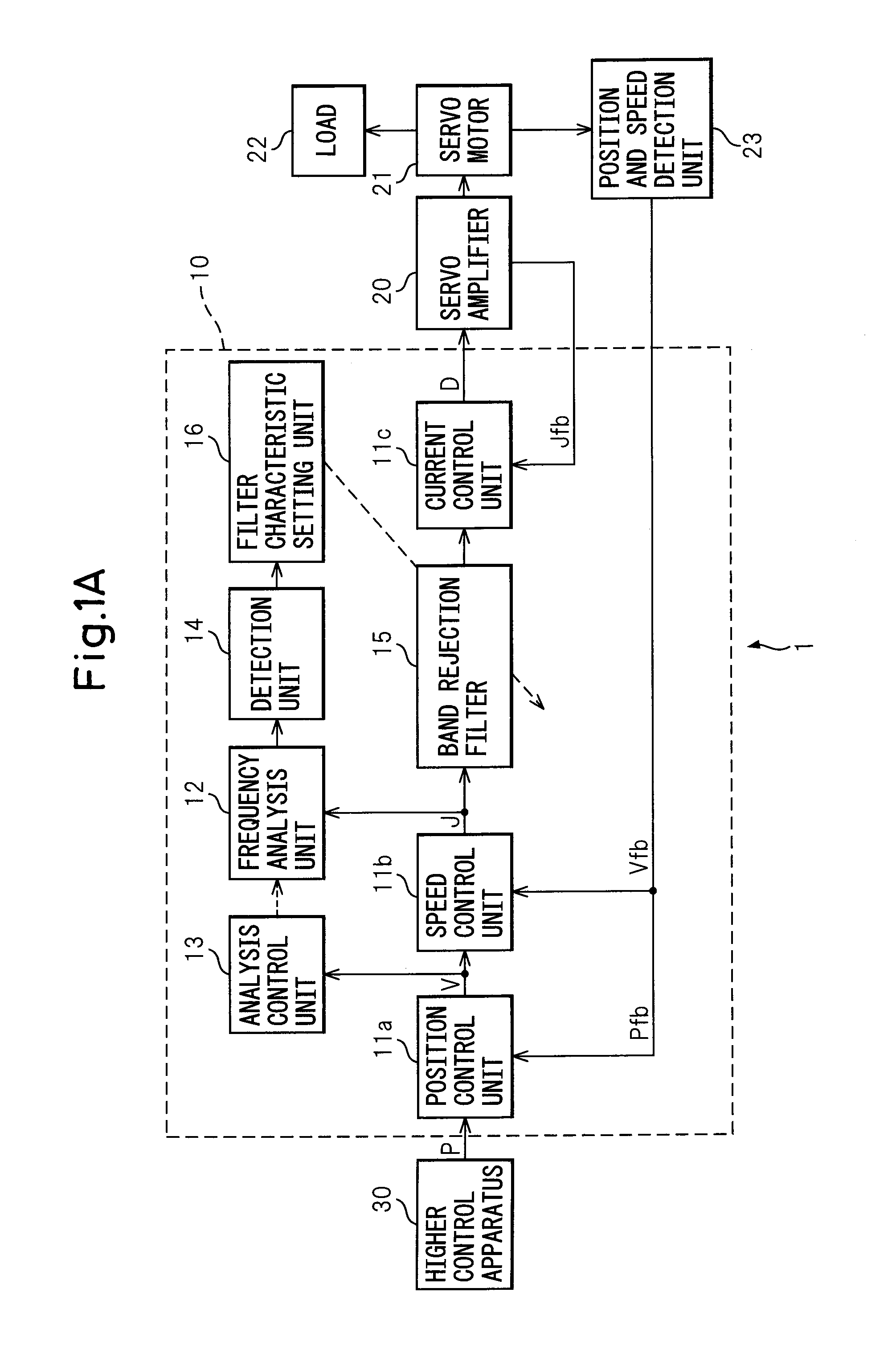
ActiveUS20090009128A1Accurate detectionReducing natural vibrationMechanical oscillations controlElectric motor controlControl signalBand-stop filter
A control apparatus of the present invention comprising a control unit outputting a control signal controlling a servo motor and suppressing natural vibration of a controlled object including a motor and a machine driven by the motor while controlling the controlled object, comprising a frequency analysis unit analyzing a frequency component included in a torque command, an analysis control unit controlling the start or stopping of the frequency analysis unit, a detection unit detecting a natural frequency of the controlled object from an analysis result of the frequency analysis unit, a-band rejection filter receiving as input the torque command, stripping the command of the natural frequency component, and outputting the resultant command to the motor through a current control unit and servo amplifier, and a filter characteristic setting unit setting the frequency to be stripped at the filter based on the natural frequency detected by the detection unit.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com