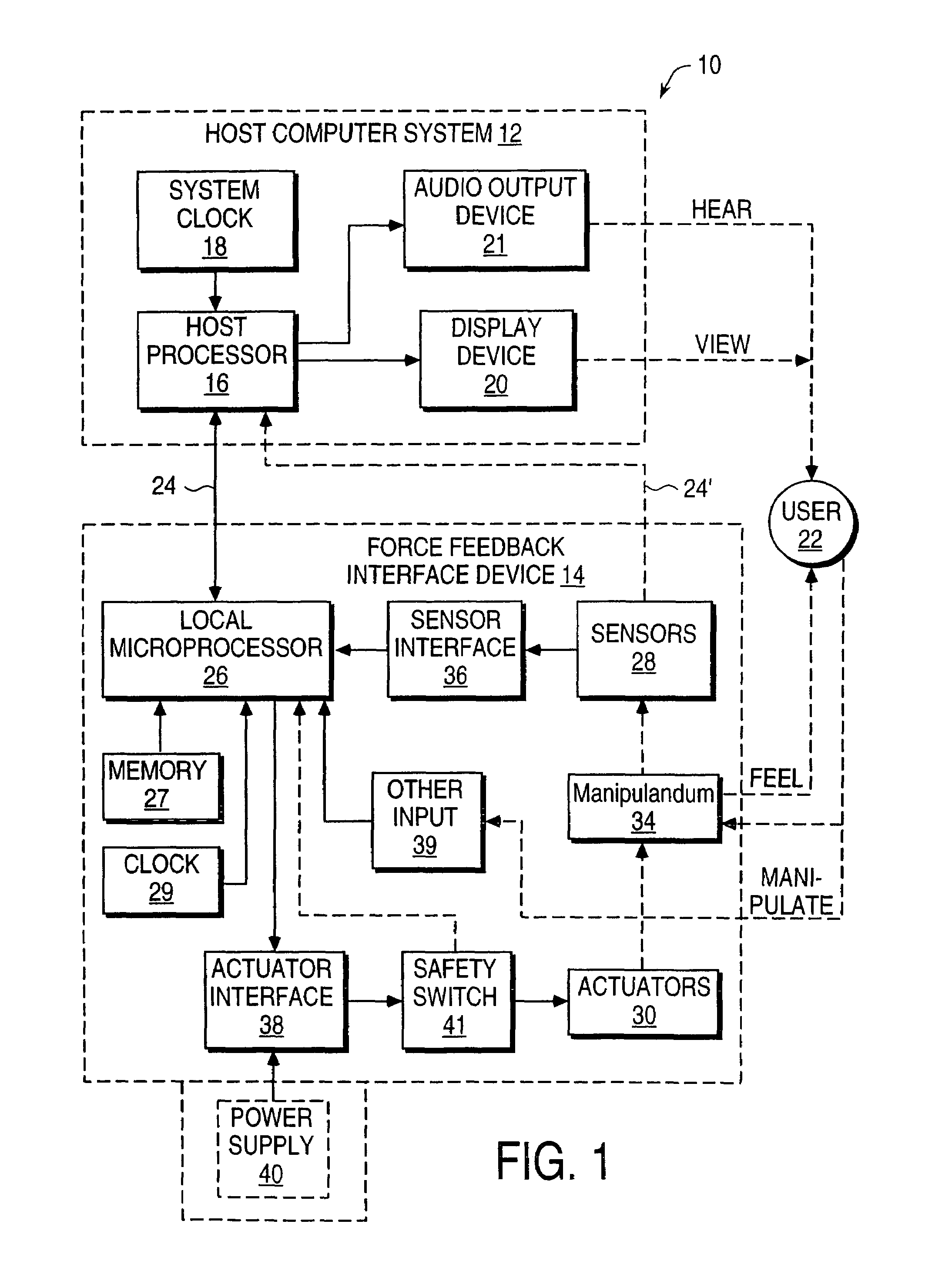
Patents
Literature
517 results about "Haptic sensation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Haptic sensation - a sensation localized on the skin. cutaneous sensation, skin sensation. tactile sensation, tactual sensation, touch sensation, feeling, touch - the sensation produced by pressure receptors in the skin; "she likes the touch of silk on her skin"; "the surface had a greasy feeling".
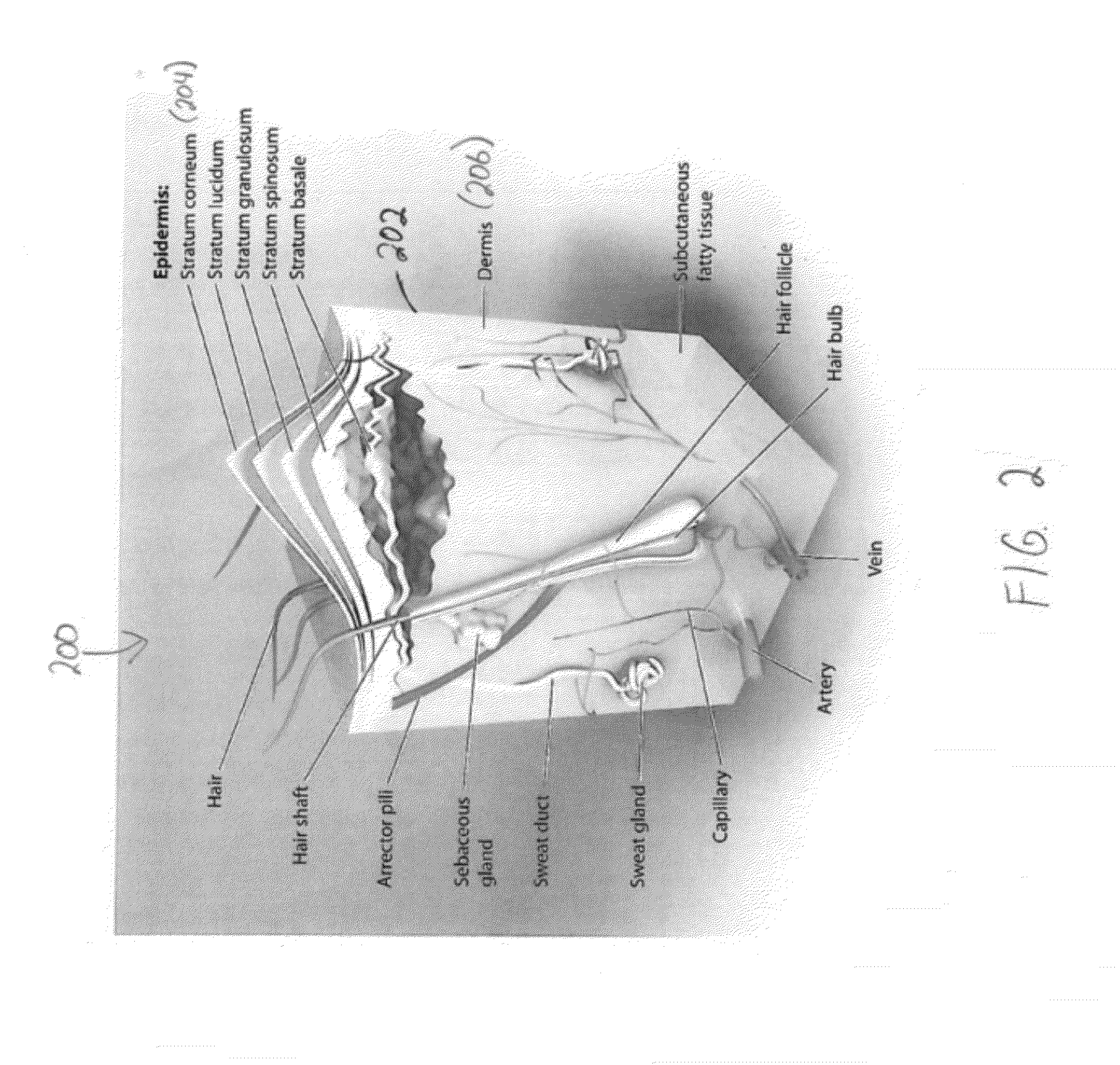
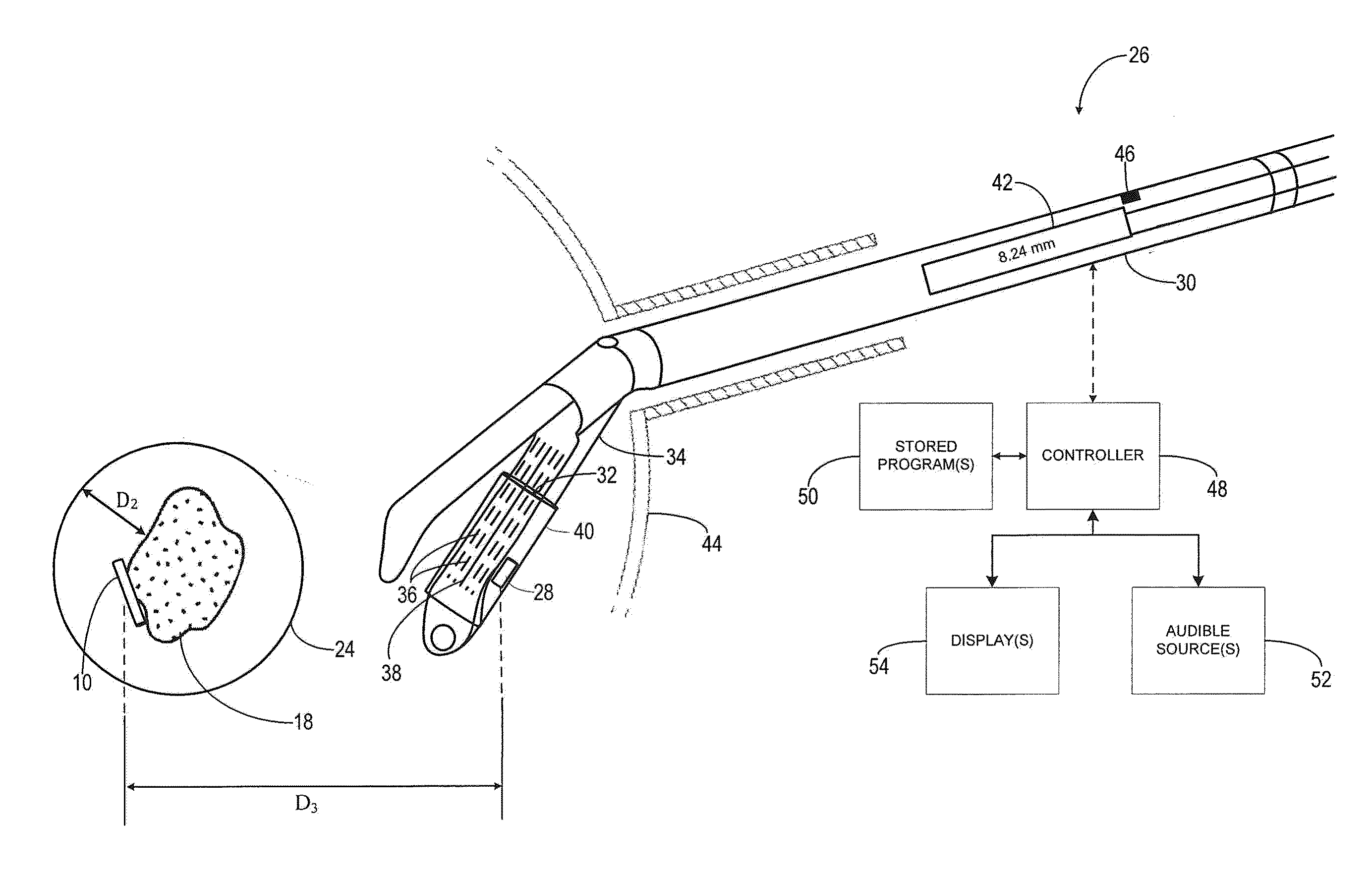
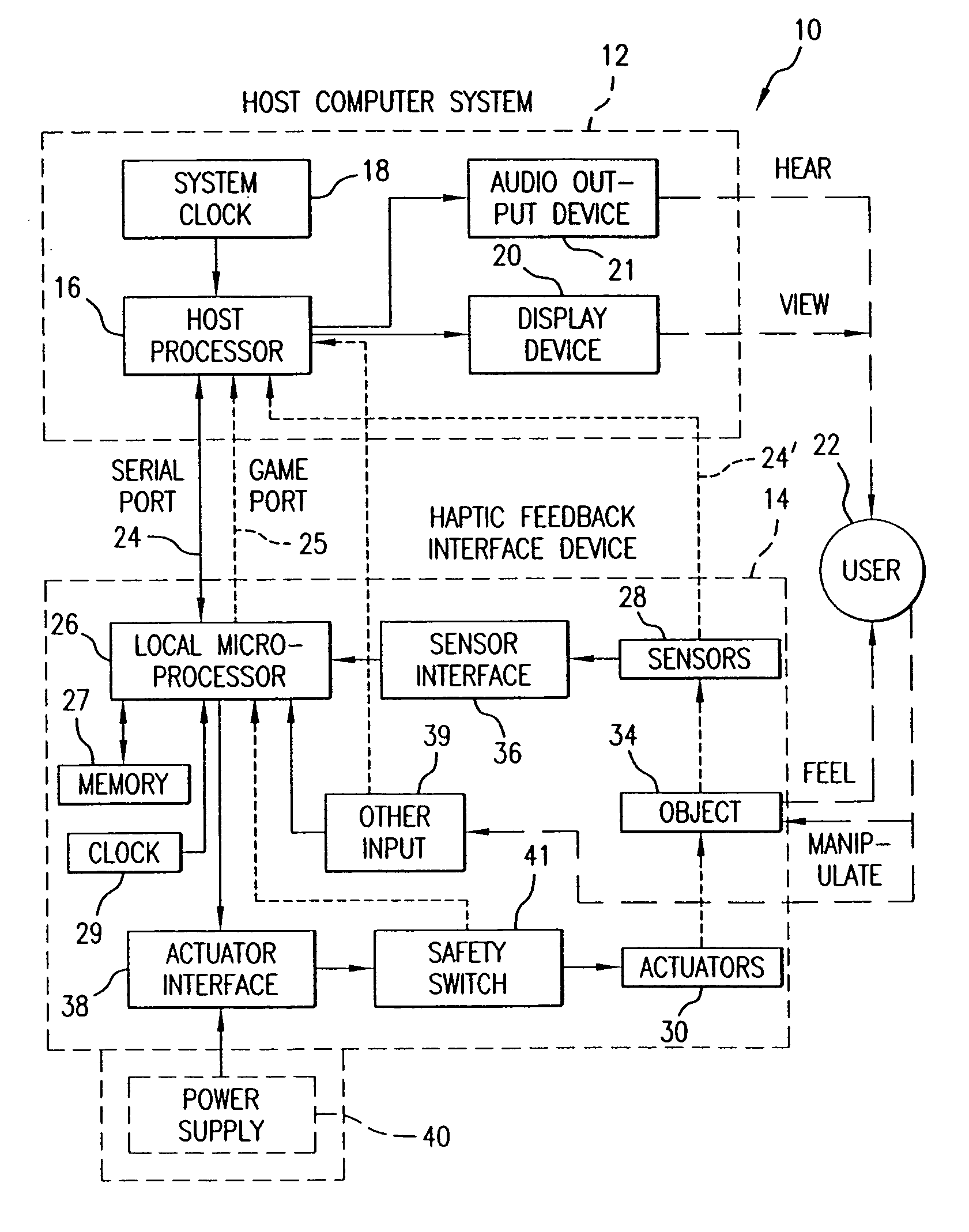
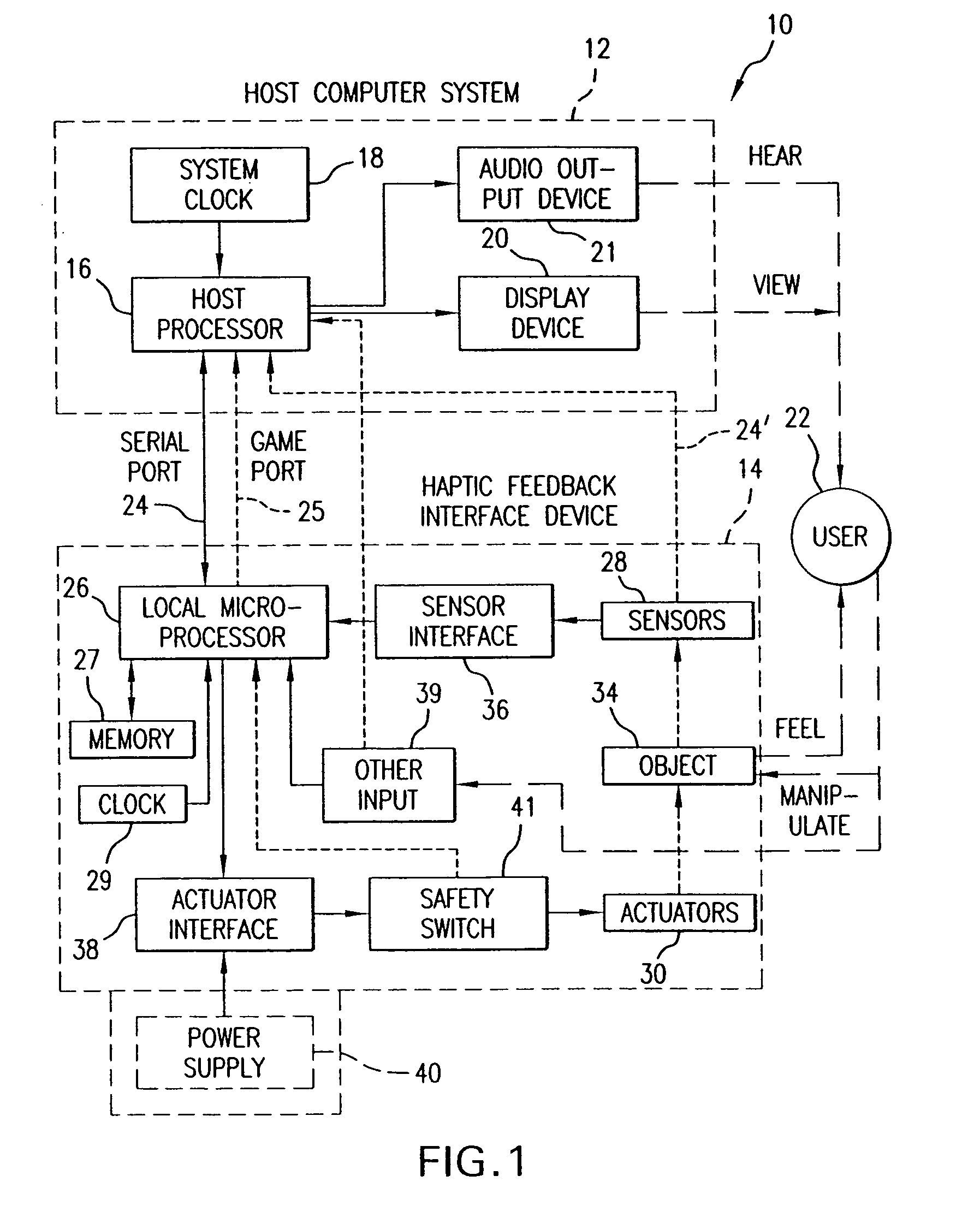
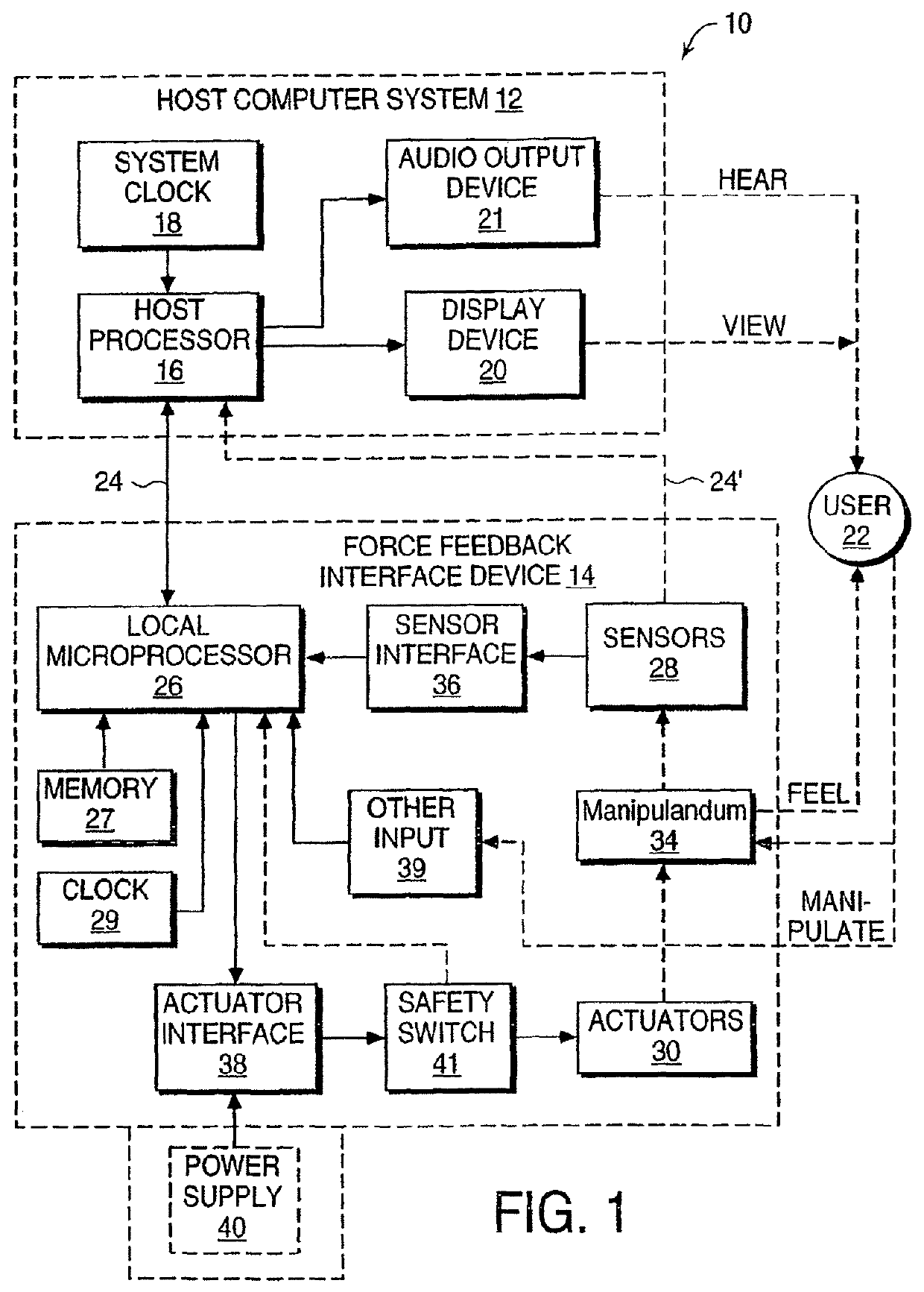
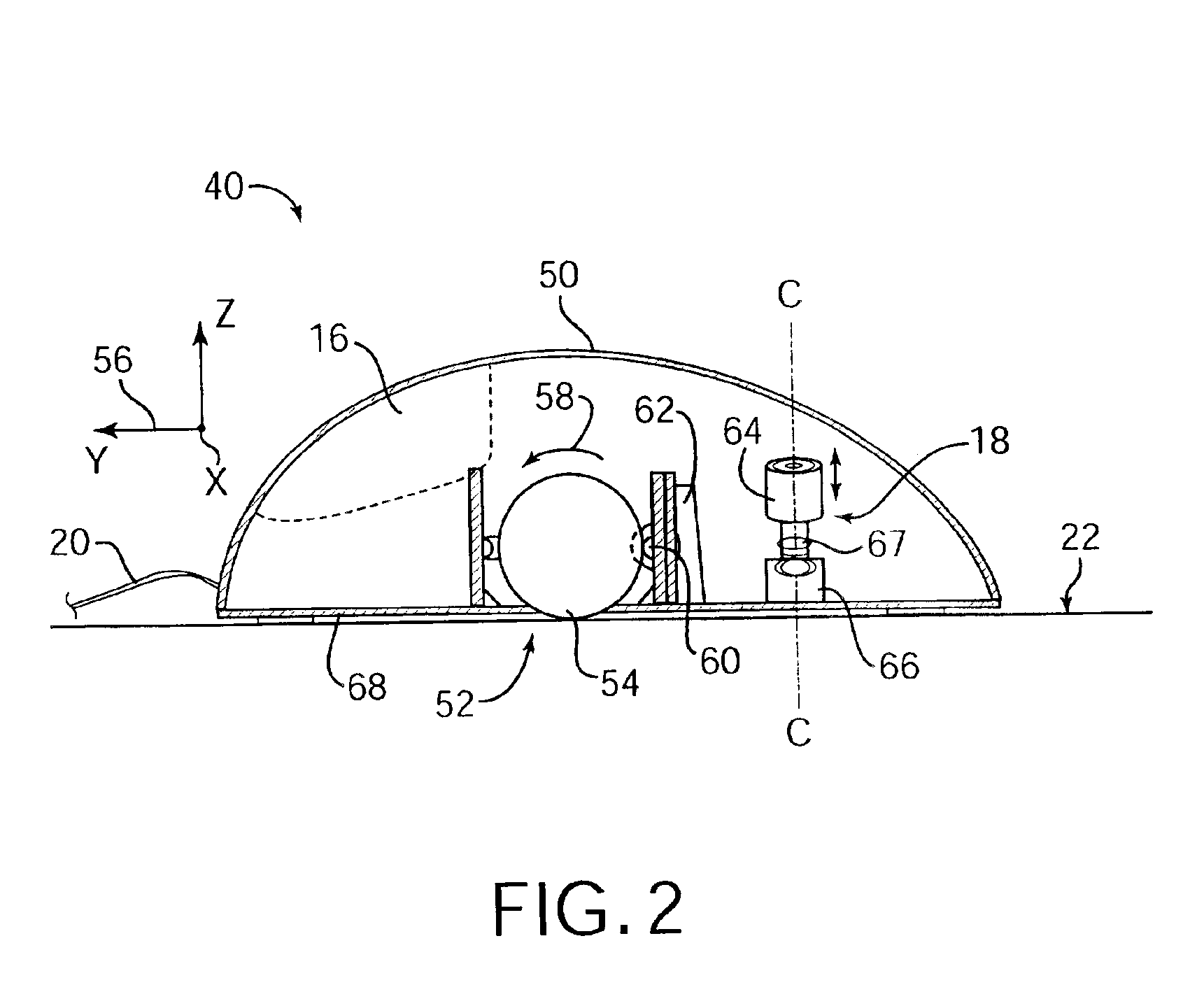
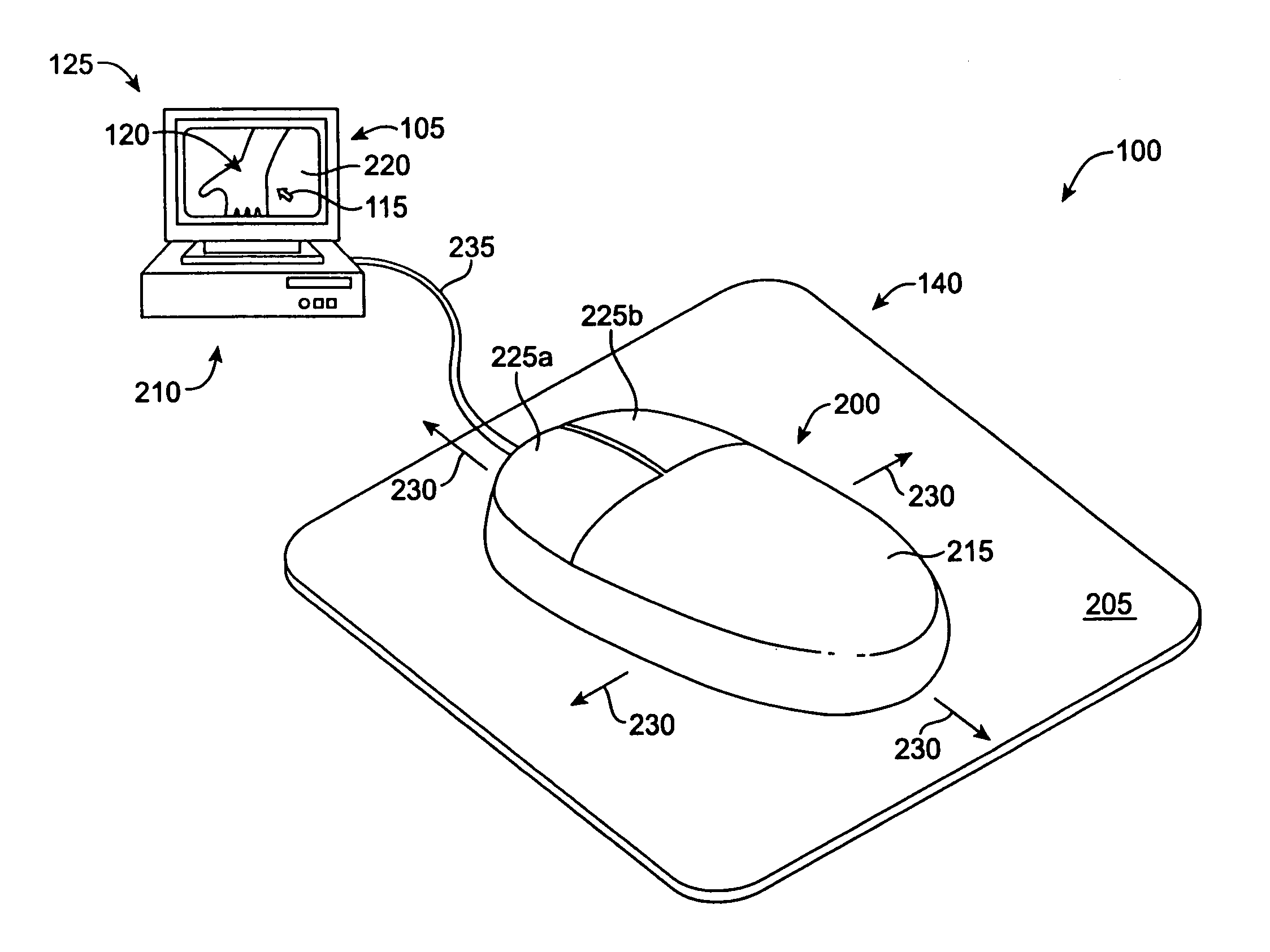
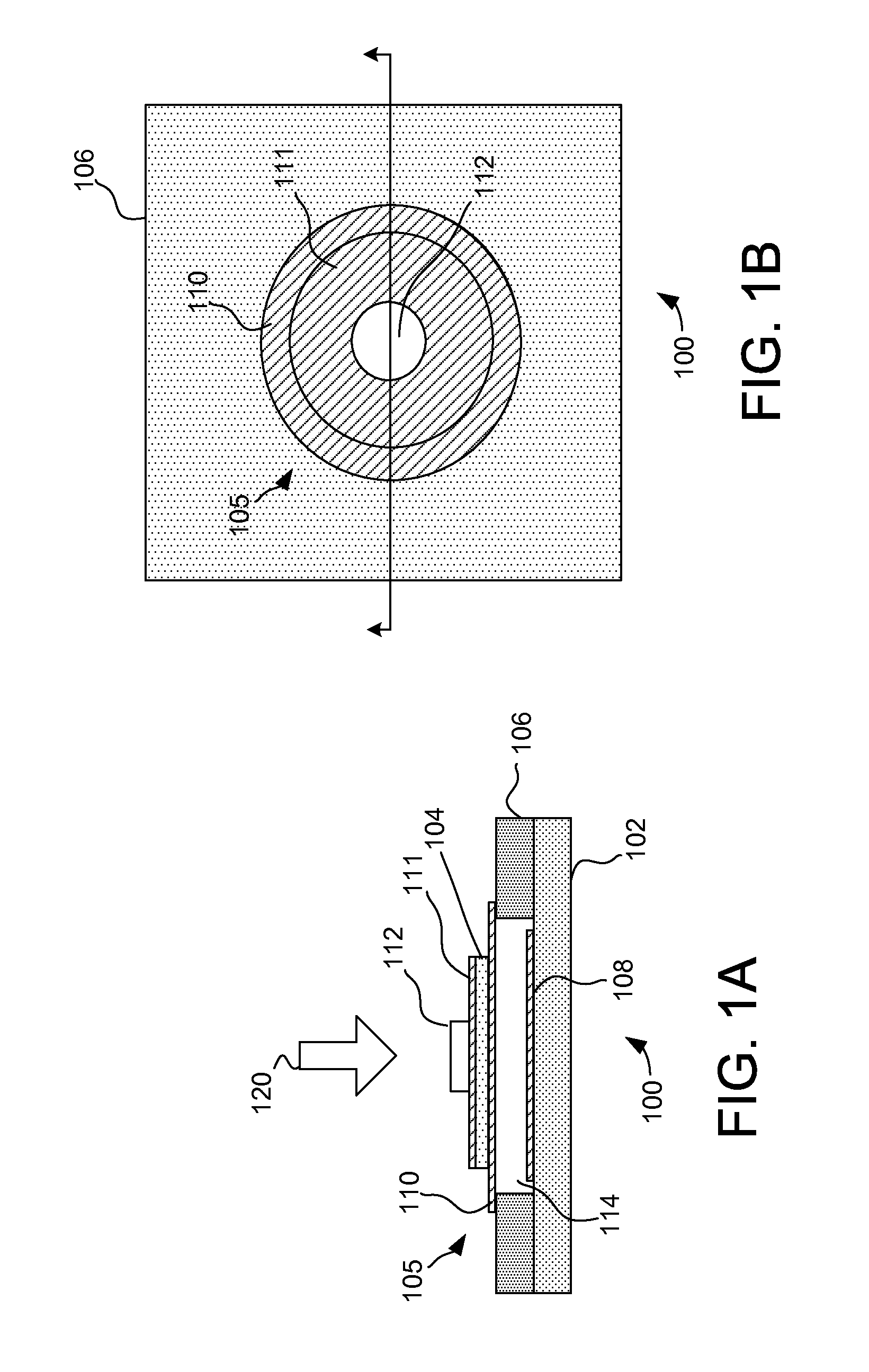
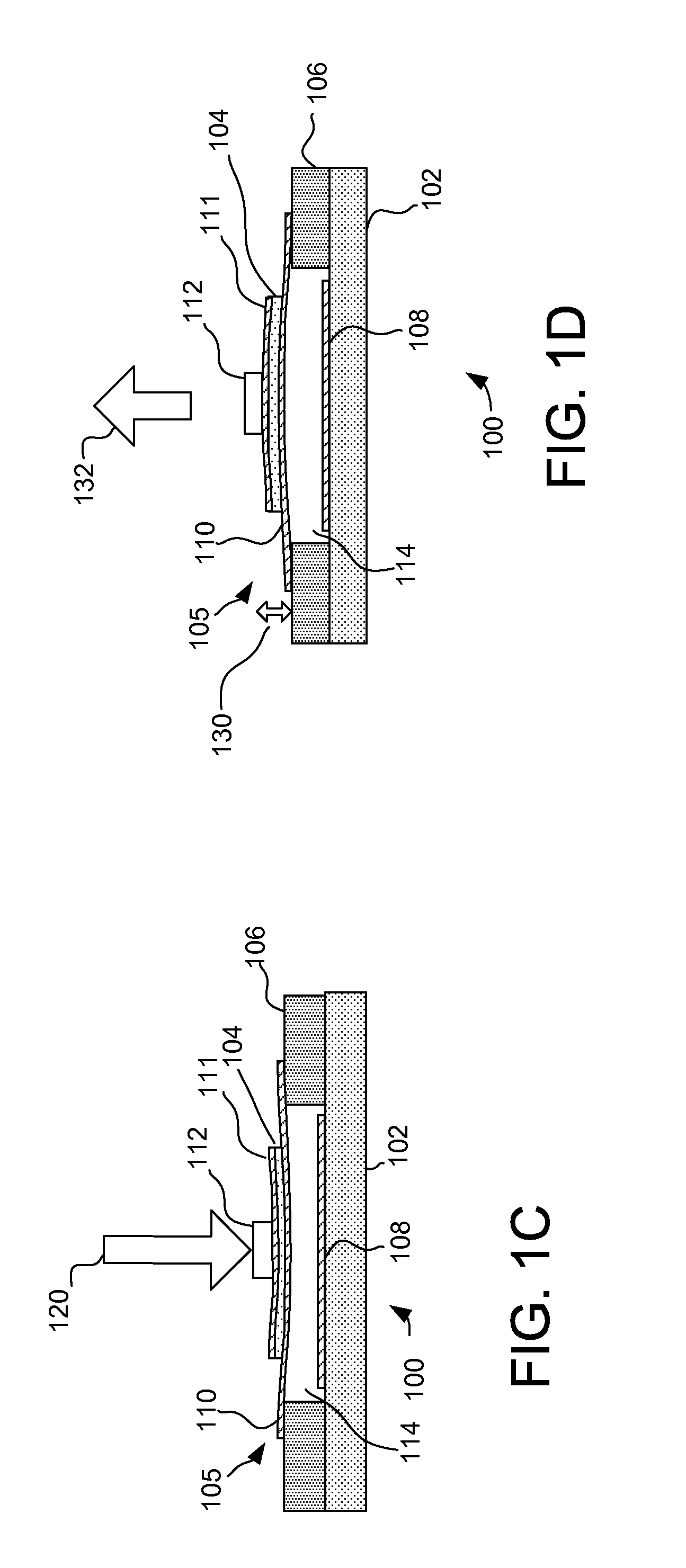
System and method for a tissue resection margin measurement device
ActiveUS20160192960A1Minimally invasiveCompensation for deformationMedical imagingSurgical needlesMeasurement deviceVisual perception
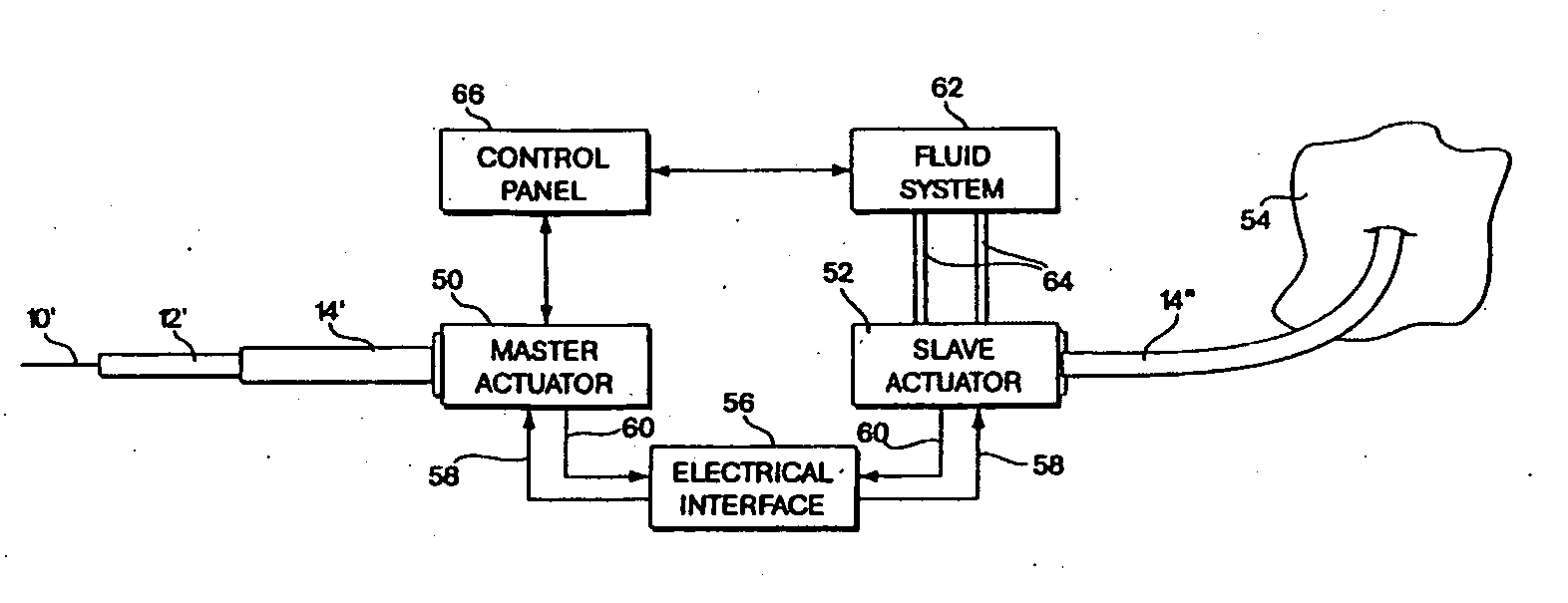
Embodiments of the invention provide a system and method for resecting a tissue mass. The system for resecting a tissue mass includes a surgical instrument and a first sensor for measuring a signal corresponding to the position and orientation of the tissue mass. The first sensor is dimensioned to fit insider or next to the tissue mass. The system also includes a second sensor attached to the surgical instrument configured to measure the position and orientation of the surgical instrument. The second sensor is configured to receive the signal from the first sensor. A controller is in communication with the first sensor and / or the second sensor, and the controller executes a stored program to calculate a distance between the first sensor and the second sensor. Accordingly, visual, auditory, haptic or other feedback is provided to the clinician to guide the surgical instrument to the surgical margin.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
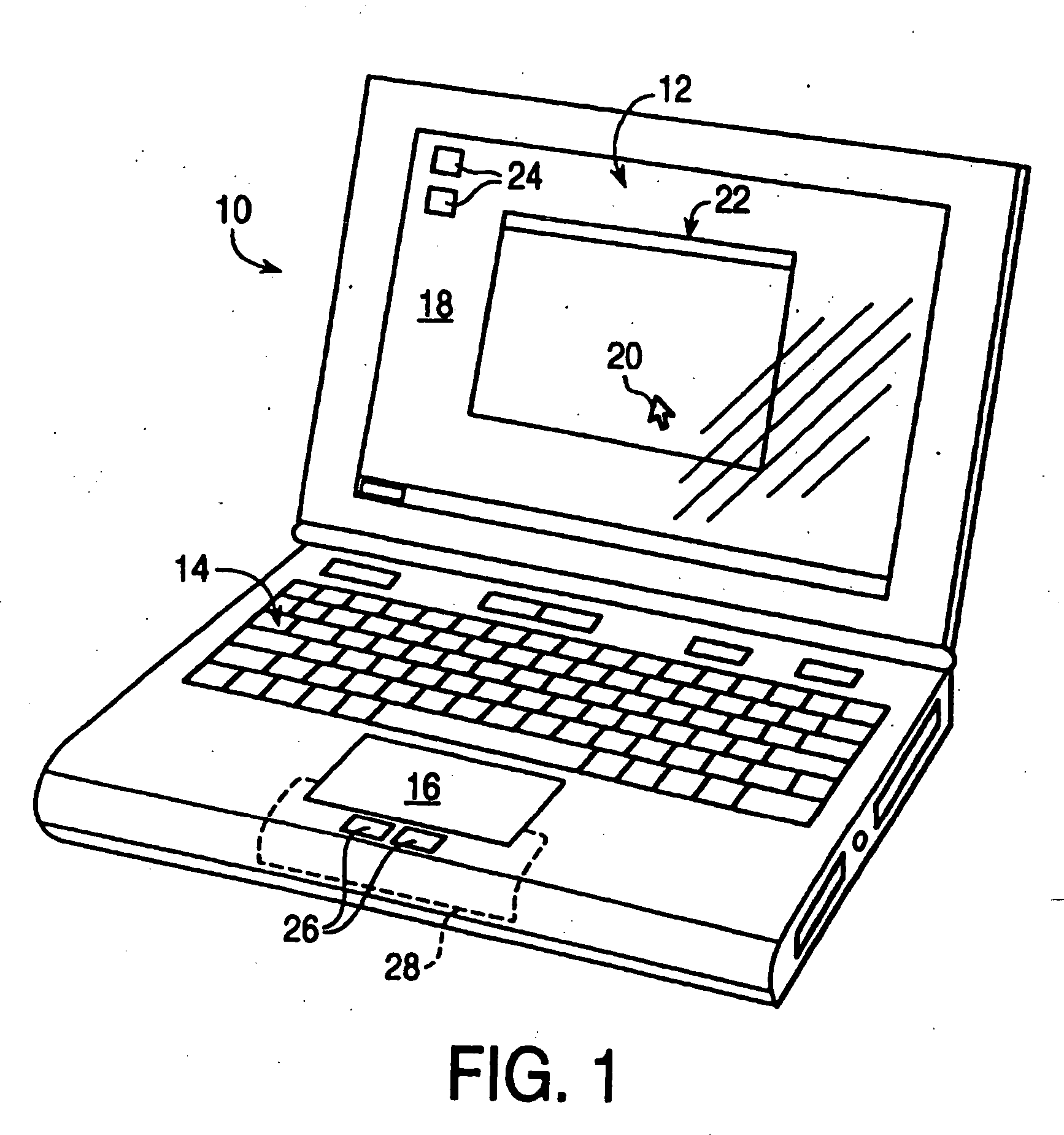
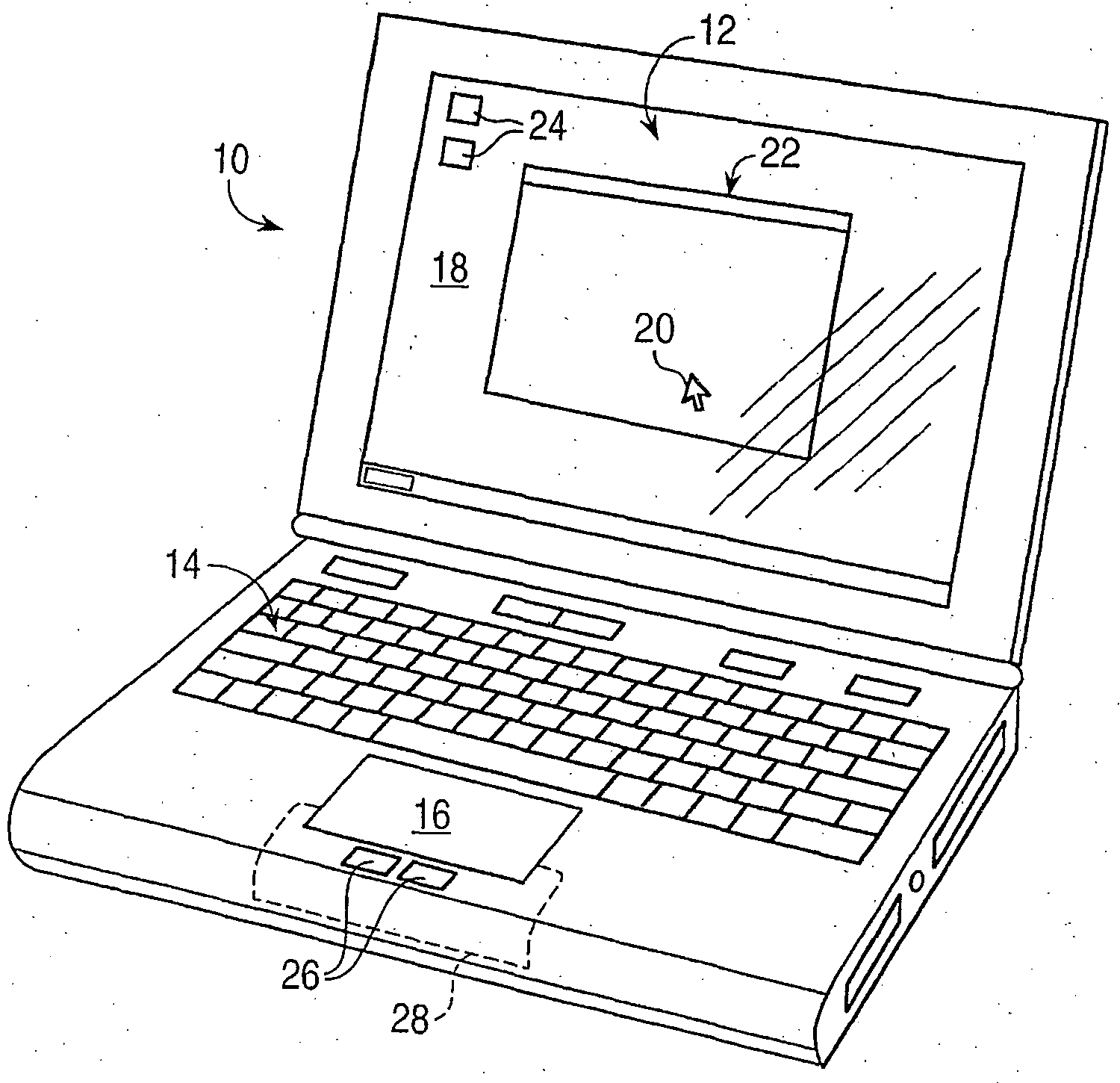
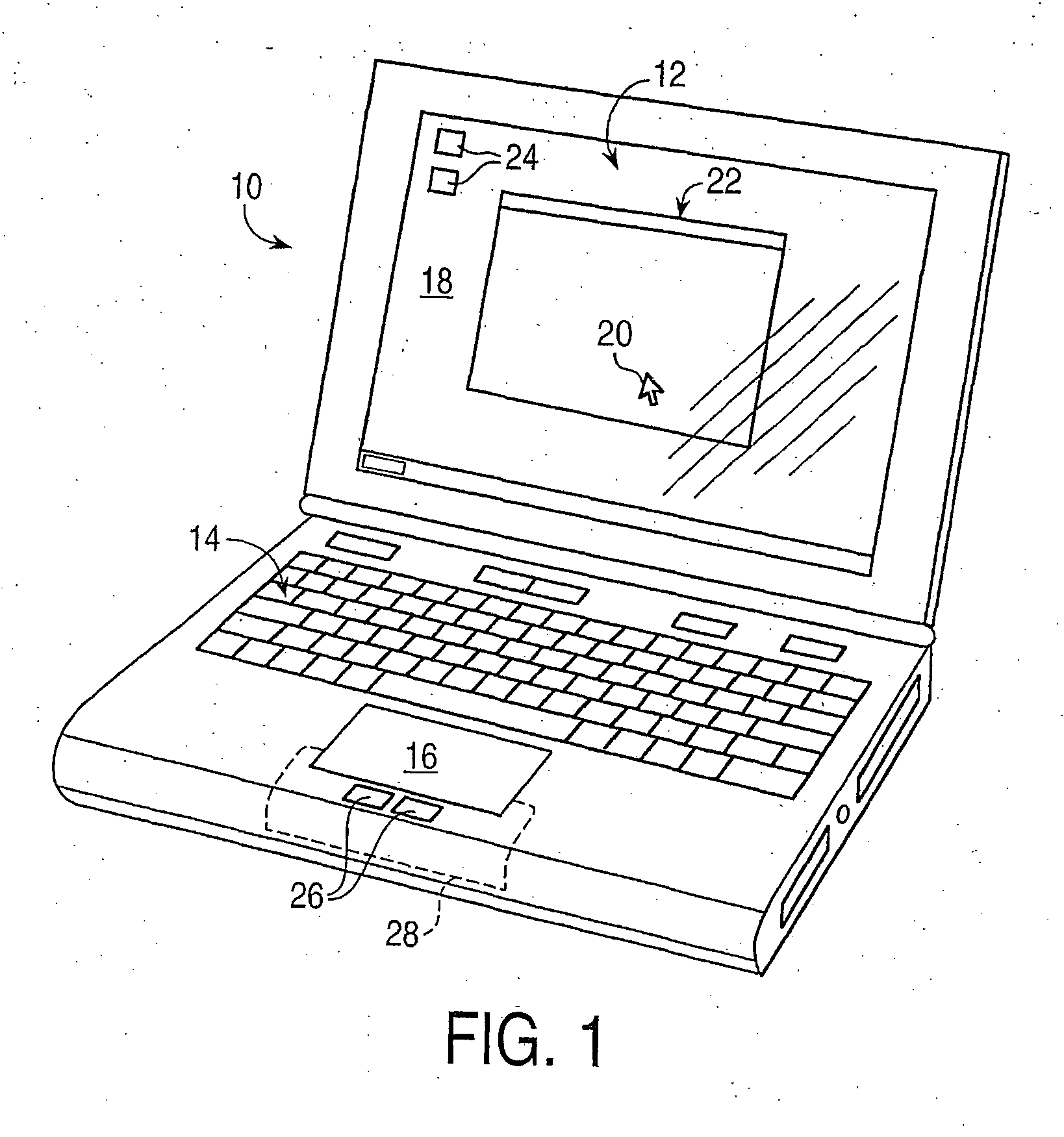
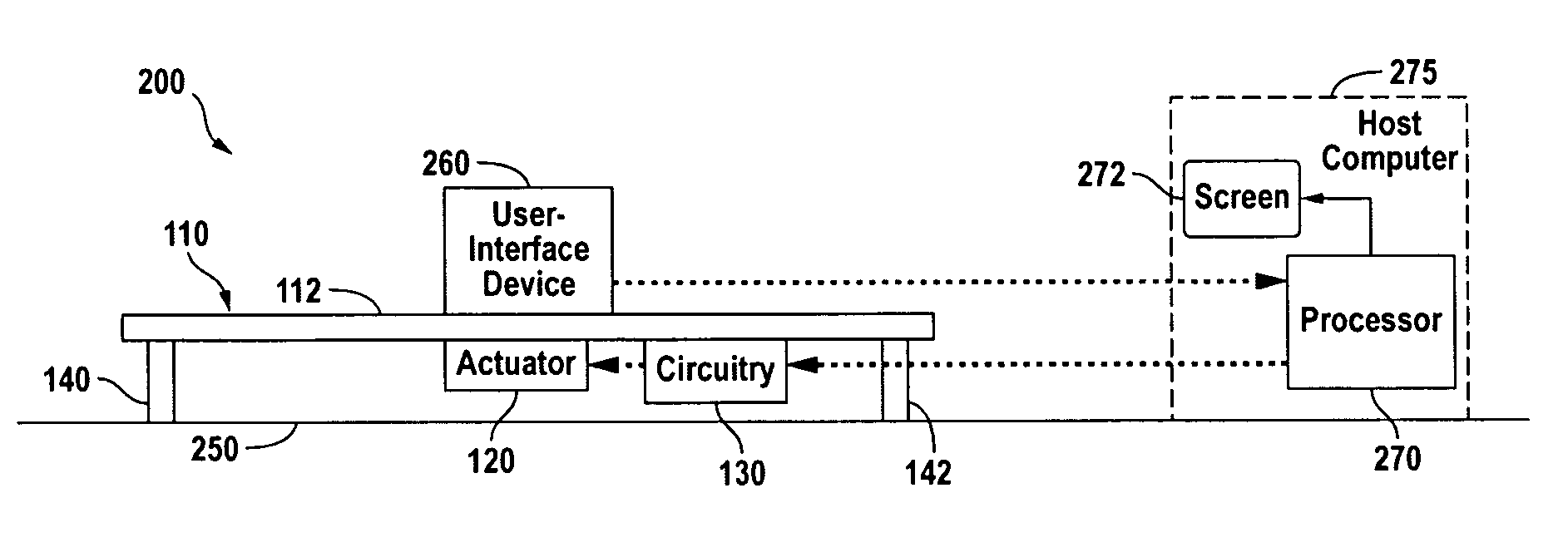
Haptic feedback for button and scrolling action simulation in touch input devices
ActiveUS20060119586A1Enhanced interactionEnhance manipulationCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsActuator
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Haptic metering for minimally invasive medical procedures
InactiveUS20070103437A1Need be addressDiagnosticsSurgical needlesHaptic sensationTwo degrees of freedom
A method of providing spatially metered haptic sensations to a user includes detecting motion of a surgical instrument within two degrees of freedom; repeatedly determining whether the surgical instrument has moved by an incremental distance in a particular direction with respect to some portion of a patient's body; and imparting a discrete haptic sensation upon a user each time it is determined that the surgical instrument has moved by the incremental distance in a particular direction.
Owner:OUTLAND RES
Haptic feedback for button and scrolling action simulation in touch input devices
ActiveUS20060109256A1Enhanced interactionEnhance manipulationCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsActuator
A planar touch control is used to provide input to a computer and haptic feedback is provided thereto. A touch control includes a touch input device with a planar touch surface that inputs a position signal to a processor associated with the computer based on a location of user implemented contact on the touch surface. The computer can position or modify a cursor or image in a displayed graphical environment based at least in part on the position signal, or perform a different function. At least one actuator is also coupled to the touch input device and outputs a force to provide a haptic sensation to the user via the touch surface.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
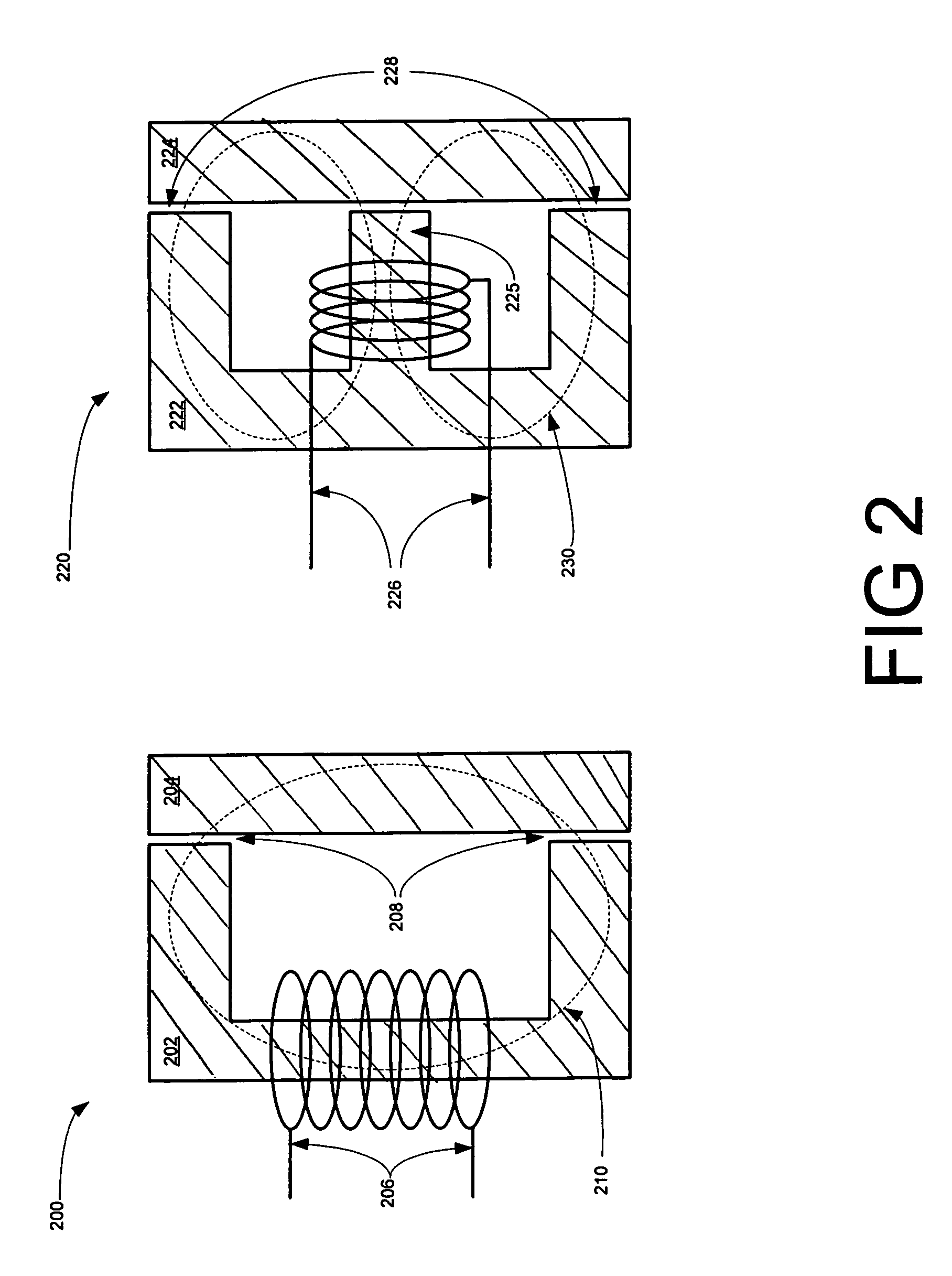
Haptic input devices
InactiveUS20050017947A1Enhanced interactionEnhance manipulationInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsPiezoelectric actuators
A haptic feedback touch control used to provide input to a computer. A touch input device includes a planar touch surface that provides position information to a computer based on a location of user contact. The computer can position a cursor in a displayed graphical environment based at least in part on the position information, or perform a different function. At least one actuator is also coupled to the touch input device and outputs a force to provide a haptic sensation to the user. The actuator can move the touchpad laterally, or a separate surface member can be actuated. A flat E-core actuator, piezoelectric actuator, or other types of actuators can be used to provide forces. The touch input device can include multiple different regions to control different computer functions.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
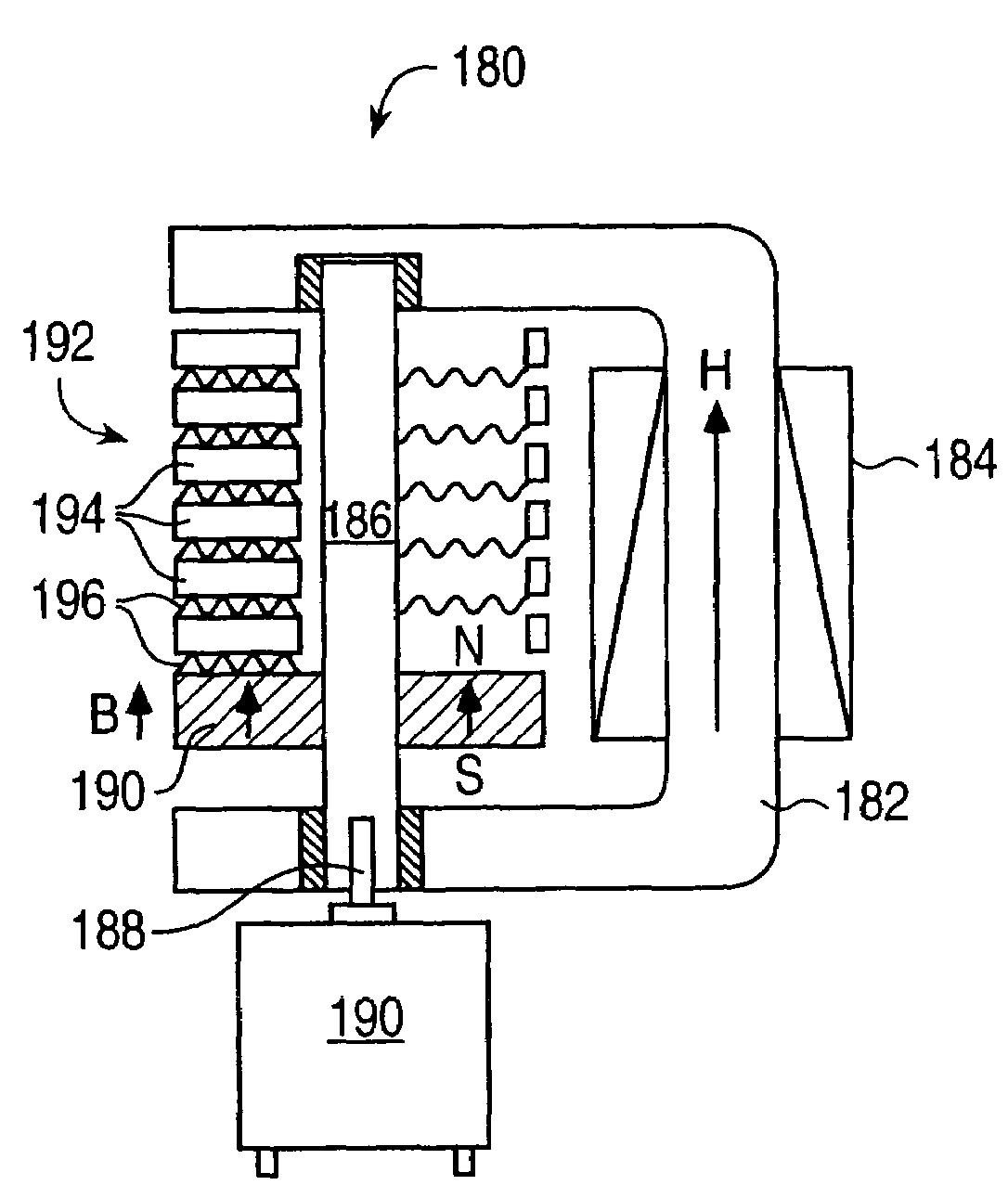
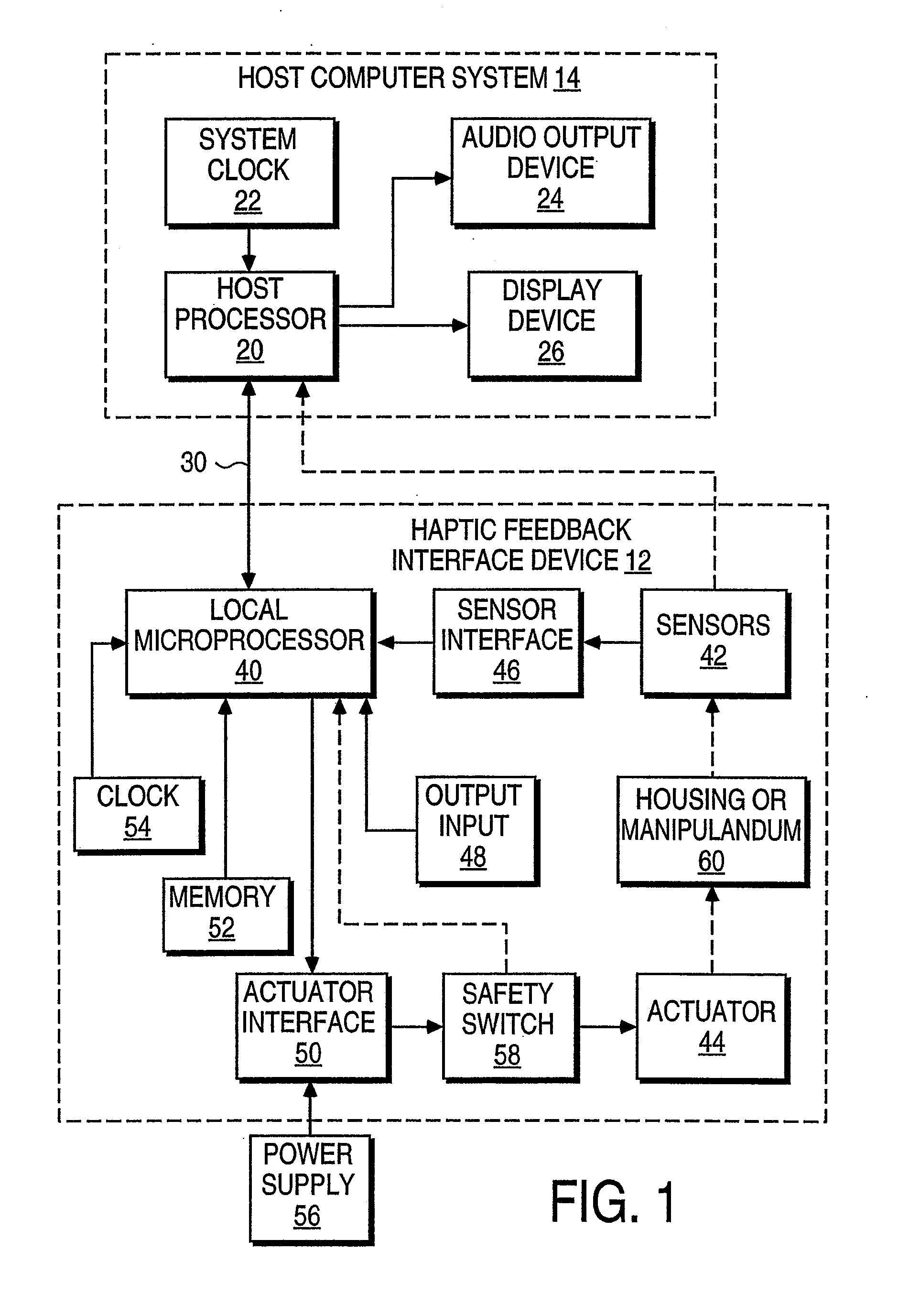
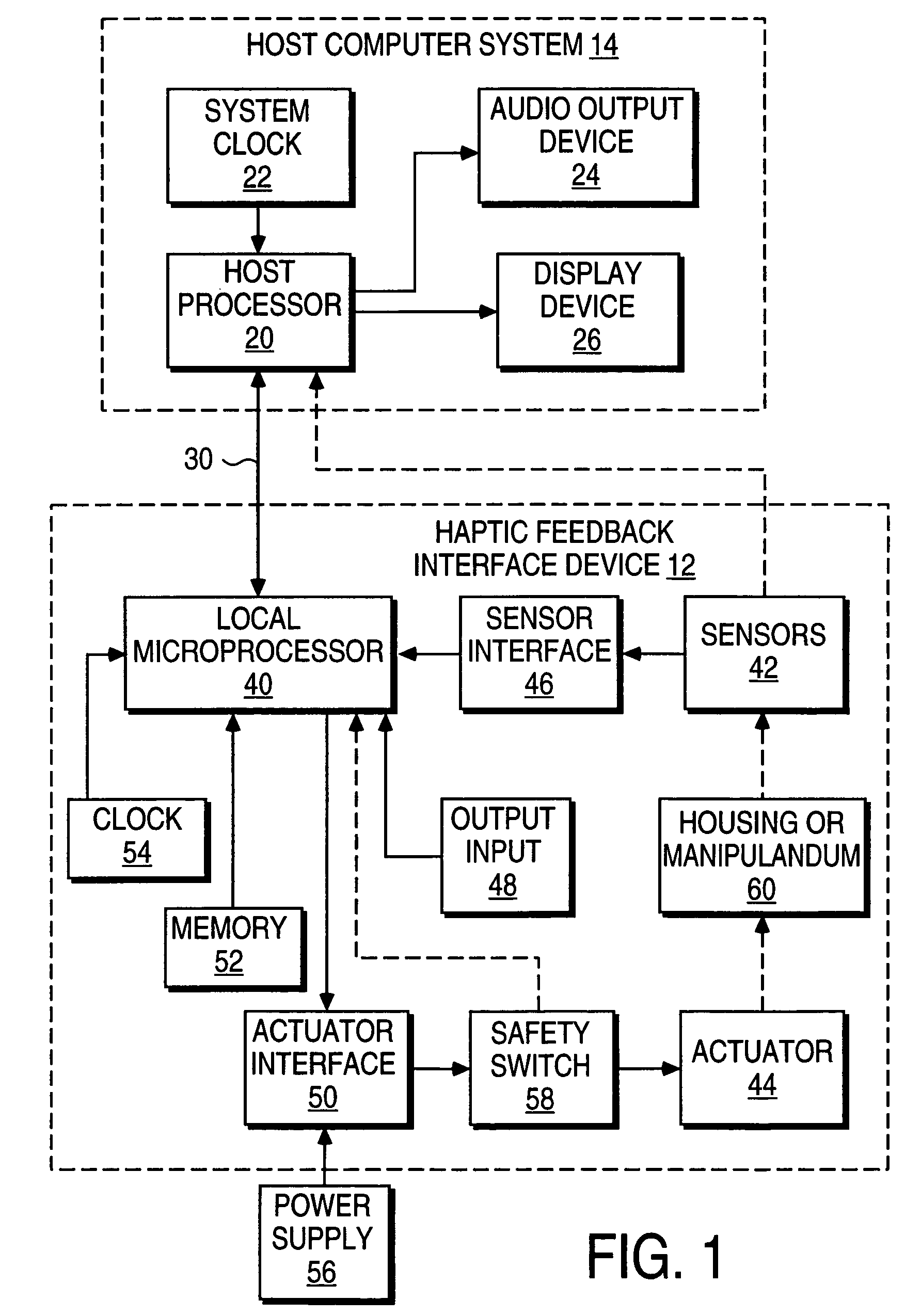
Haptic devices using electroactive polymers
ActiveUS7196688B2Low costEfficiently provideInput/output for user-computer interactionManual control with multiple controlled membersActive polymerHaptic sensing
Haptic feedback interface devices using electroactive polymer (EAP) actuators to provide haptic sensations and / or sensing capabilities. A haptic feedback interface device is in communication with a host computer and includes a sensor device that detects the manipulation of the interface device by the user and an electroactive polymer actuator responsive to input signals and operative to output a force to the user caused by motion of the actuator. The output force provides a haptic sensation to the user. Various embodiments of interface devices employing EAP actuators are described, including embodiments providing direct forces, inertial forces, and braking forces.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
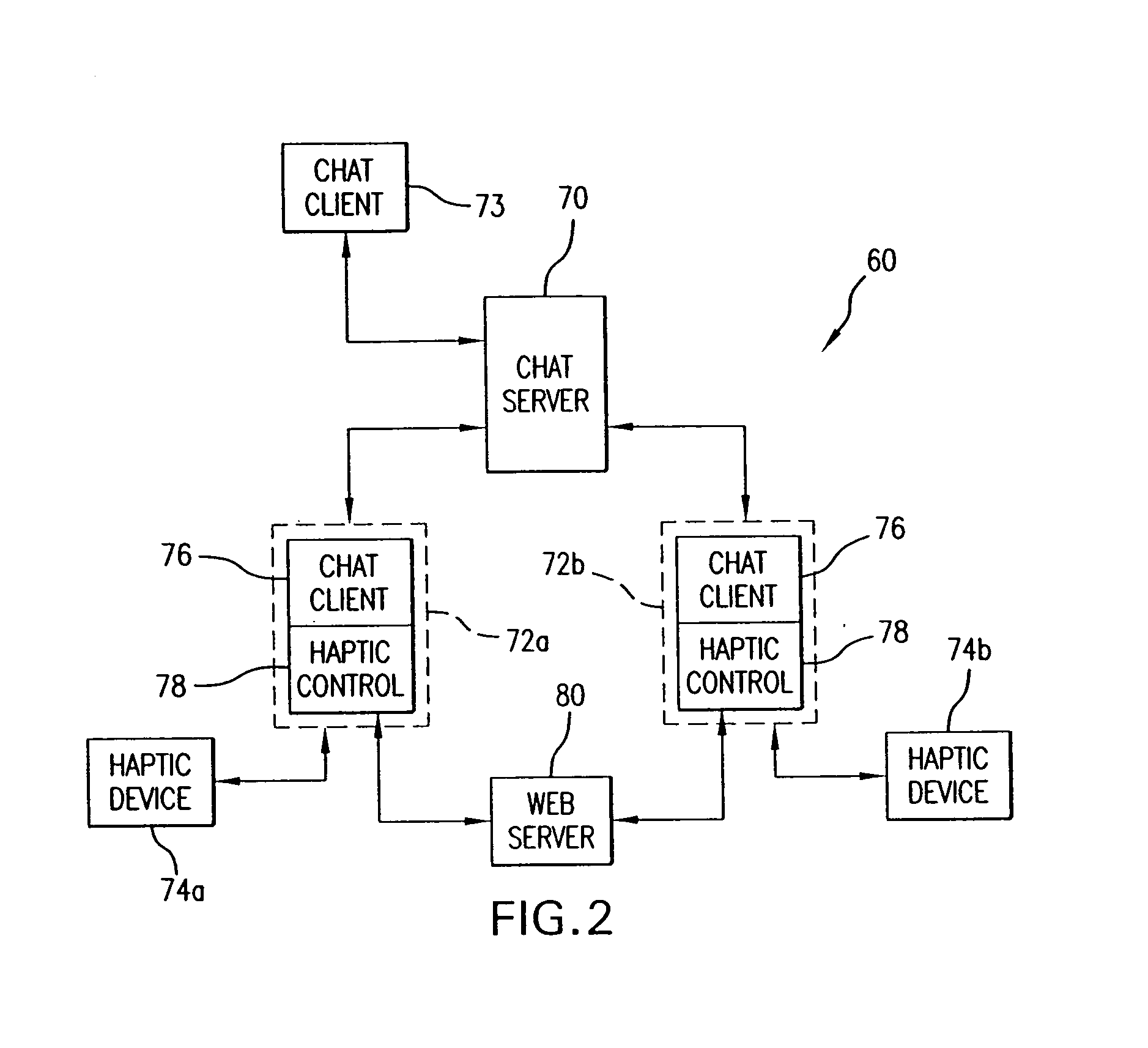
Chat interface with haptic feedback functionality
InactiveUS7159008B1Enhancements to chat messagesInput/output for user-computer interactionMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork connectionDisplay device
A chat interface allowing a user to exchange haptic chat messages with other users in a chat session over a computer network. A chat interface can be displayed by a local computer and receives input data from a user of the local computer, such as text characters or speech input. The input data provides an outgoing chat message that can include sent force information. The outgoing chat message is sent to a remote computer that is connected to the local host computer via a computer network. The remote computer can display a chat interface and output a haptic sensation to a user of the remote computer based at least in part on the force information in the outgoing chat message. An incoming message from the remote computer can also be received at the chat interface, which may also include received force information. The incoming chat message is displayed on a display device to the user of the local computer. A haptic sensation can be output to the user of the local computer using a haptic device coupled to the local computer, where the haptic sensation is based at least in part on the received force information received from the remote computer.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Vibrotactile haptic feedback devices
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
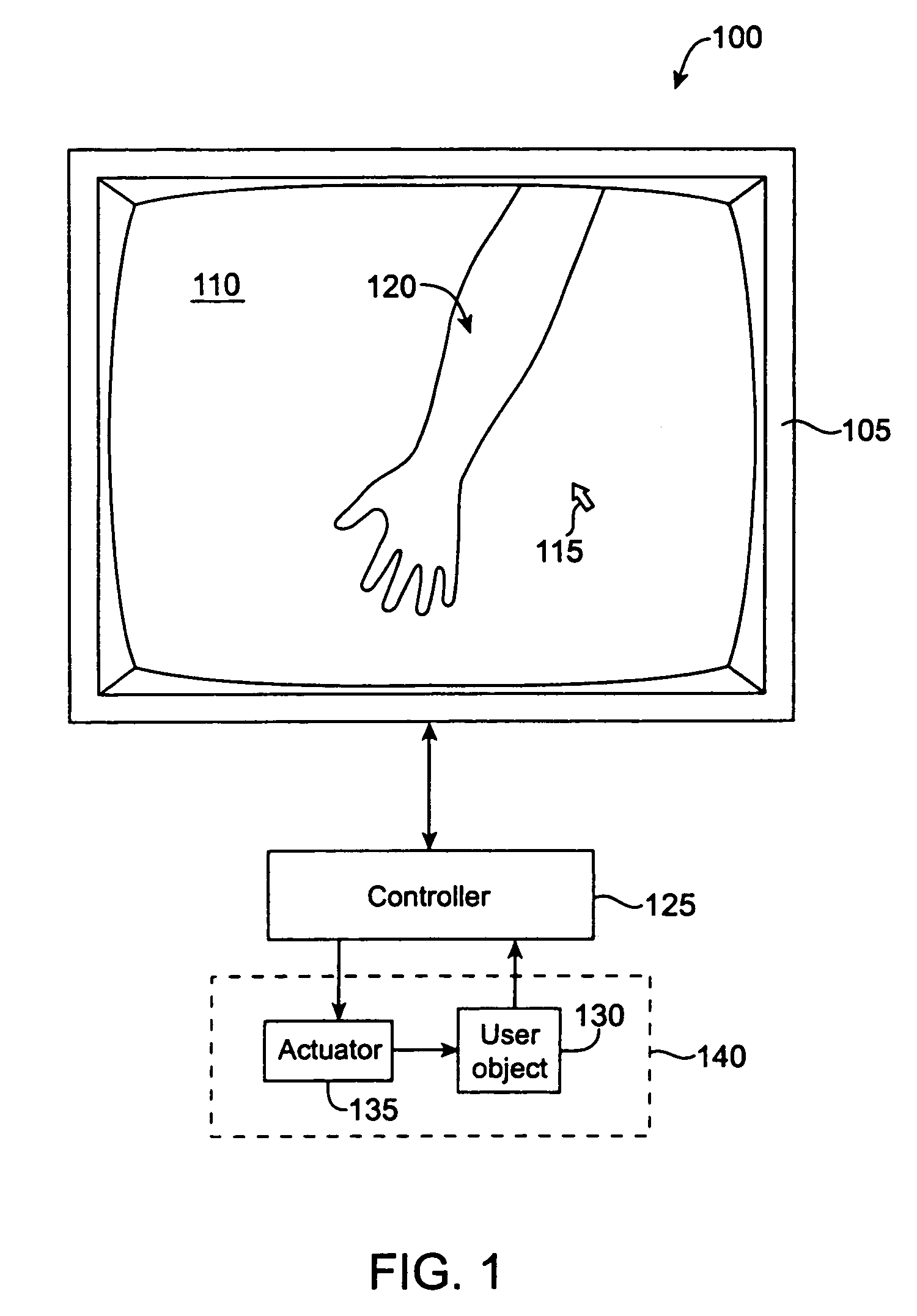
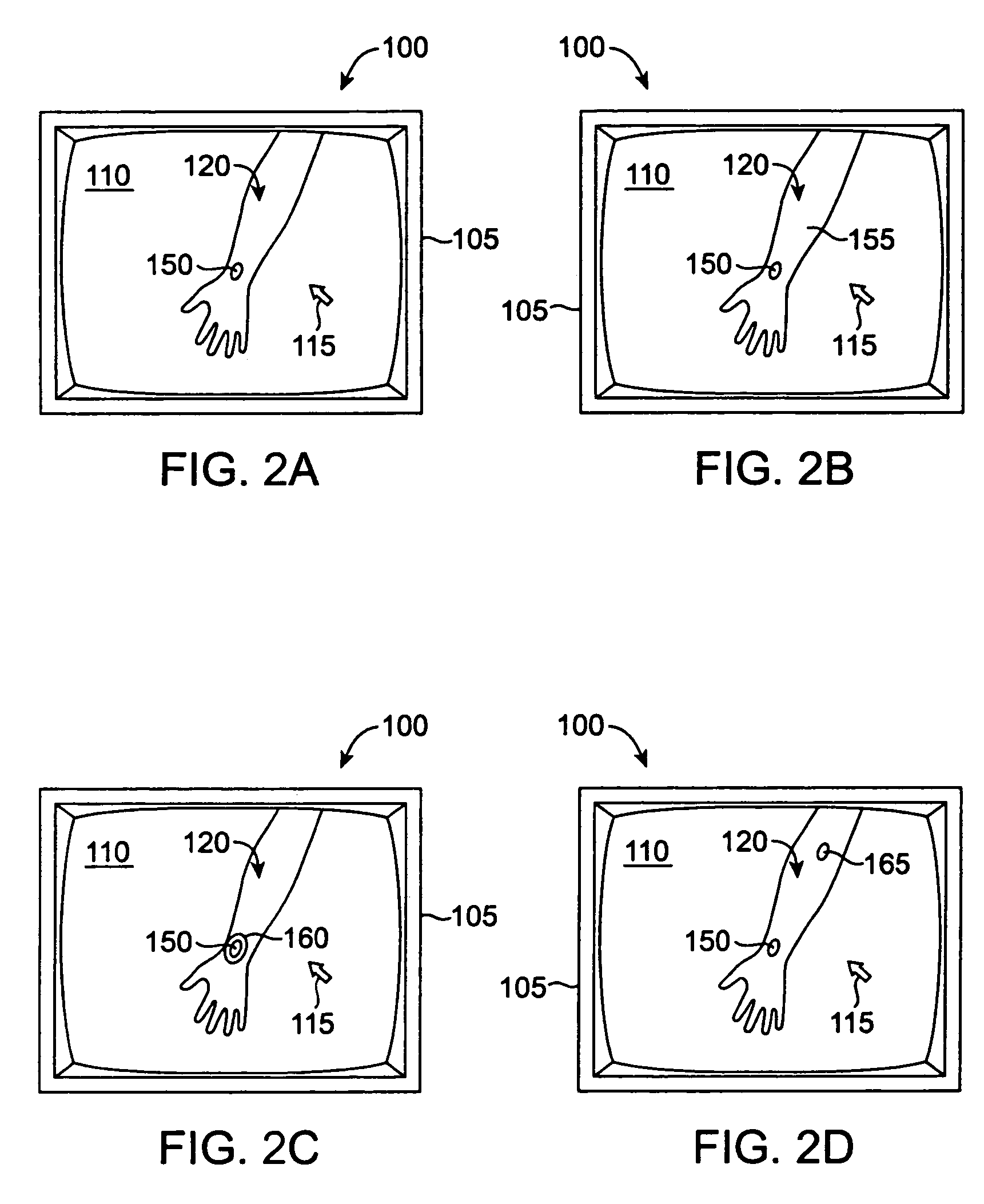
Haptic sensations for tactile feedback interface devices
InactiveUS6906697B2Long durationLow magnitudeInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsHaptic sensing
Haptic sensations for tactile feedback computer interface devices. In one method, a tactile sensation is output during the interaction of a cursor and a graphical object, the tactile sensation being based on a periodic waveform and having a frequency correlated with a size of the graphical object interacted with the cursor. Another method includes receiving an indication of a position of a cursor, causing the cursor to snap to a graphical object, such as a line, when the cursor is within a predetermined distance so that the cursor can be moved along or within the graphical object, and enabling the output of a vibration sensation while the cursor is moved along or within the object. In another method, a tactile sensation includes a pop sensation that is a short, high magnitude sensation, and then a ringing sensation during or immediately after the output of the pop sensation and which can fade in magnitude over time.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
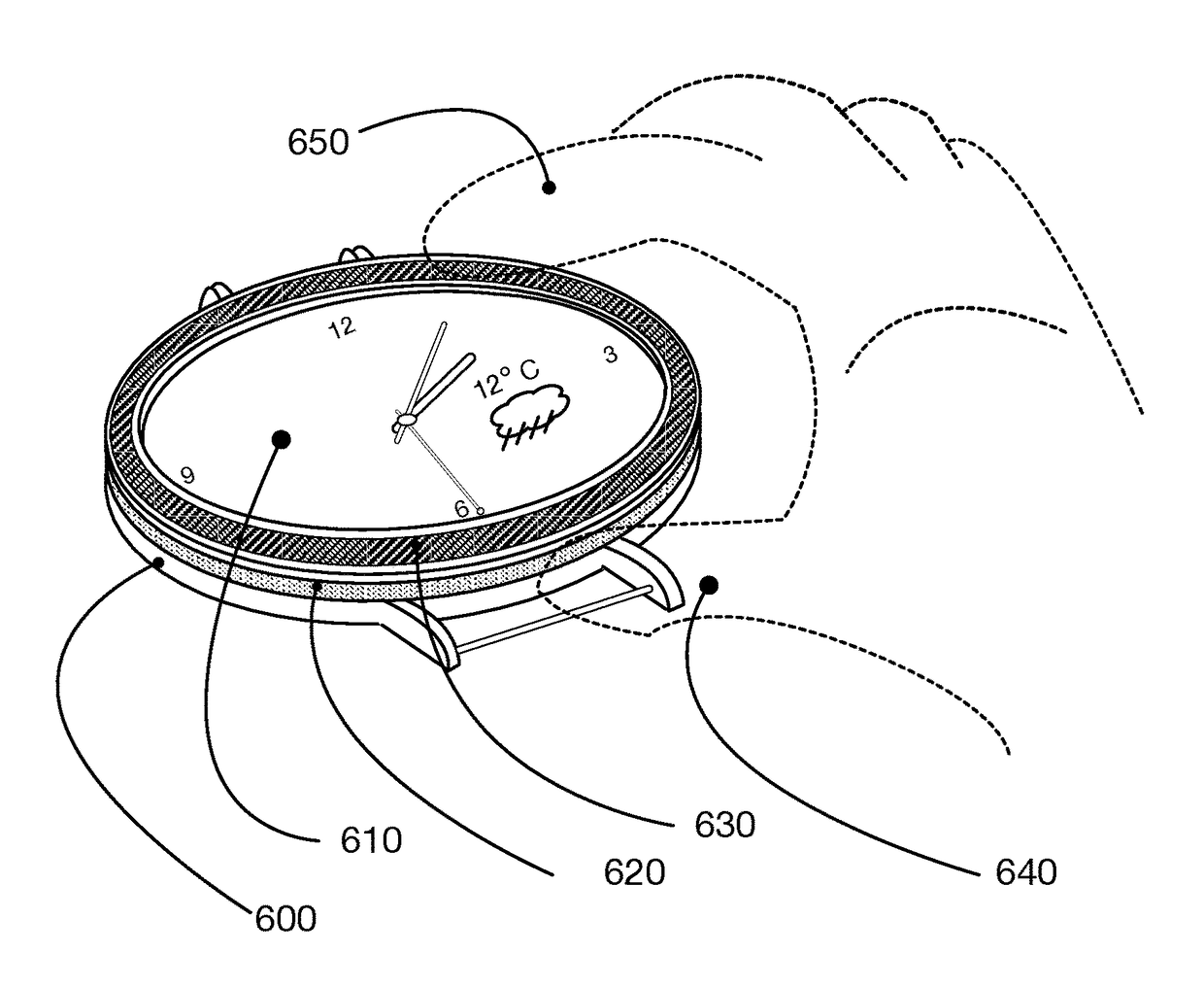
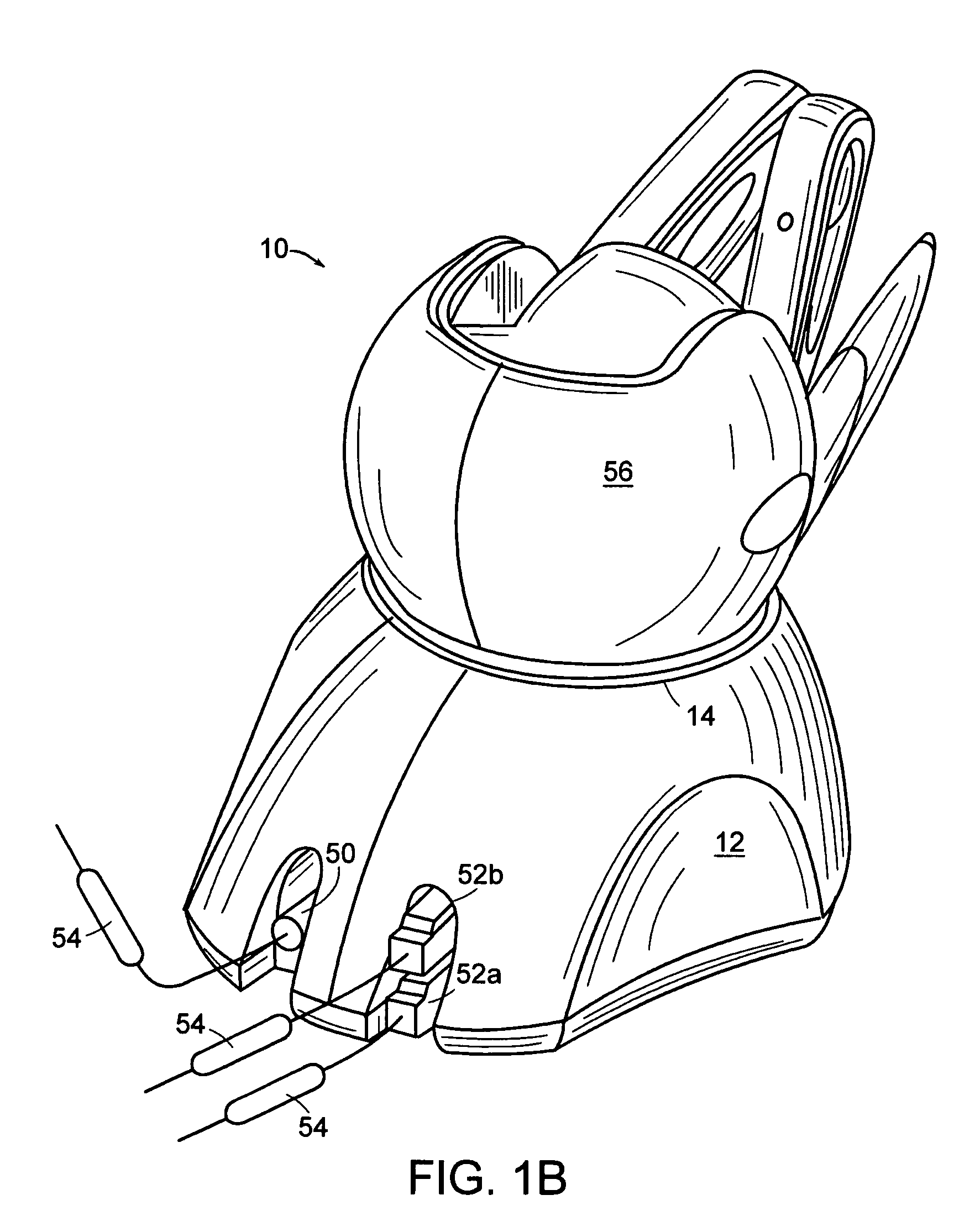
A wearable smart watch with a control-ring and a user feedback mechanism
ActiveUS20180052428A1Improve efficiency and effectivenessImproving efficiency and effectivenessVisual indicationElectric windingEngineeringUser feedback
Owner:ABRAMOV ANDREY
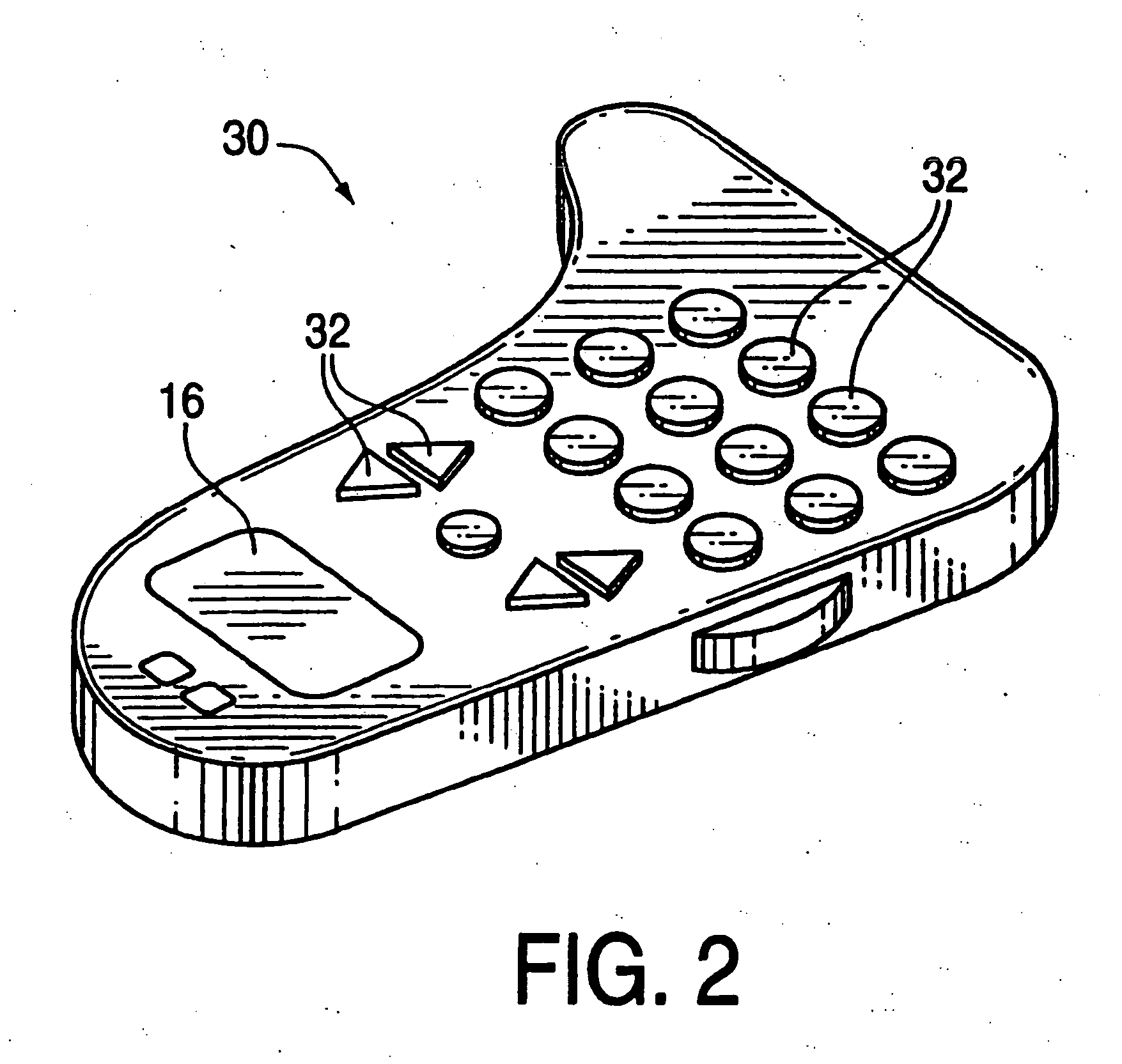
Haptic pads for use with user-interface devices
InactiveUS7336266B2Input/output for user-computer interactionTransmission systemsTactile deviceHaptic sensation
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
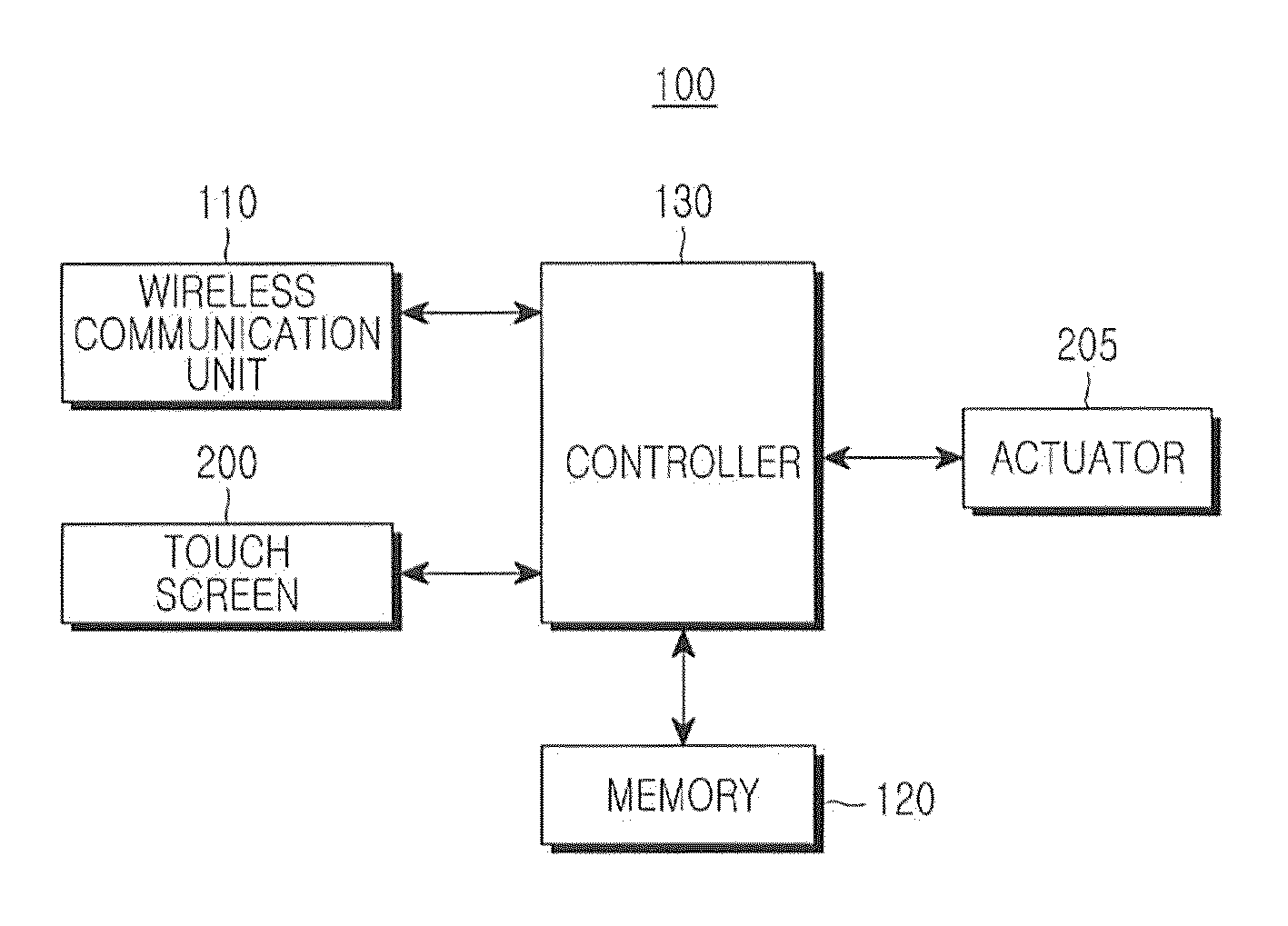
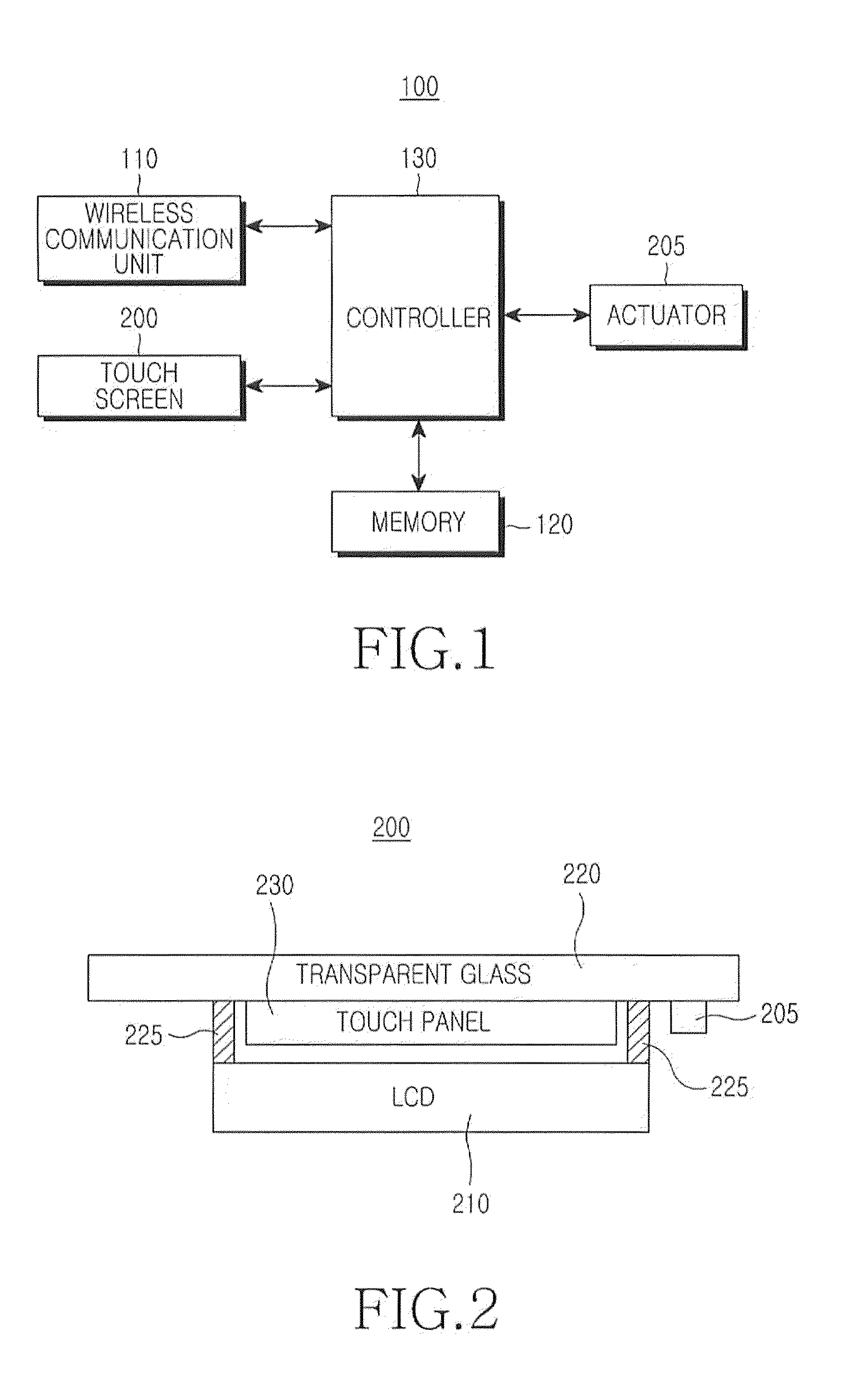
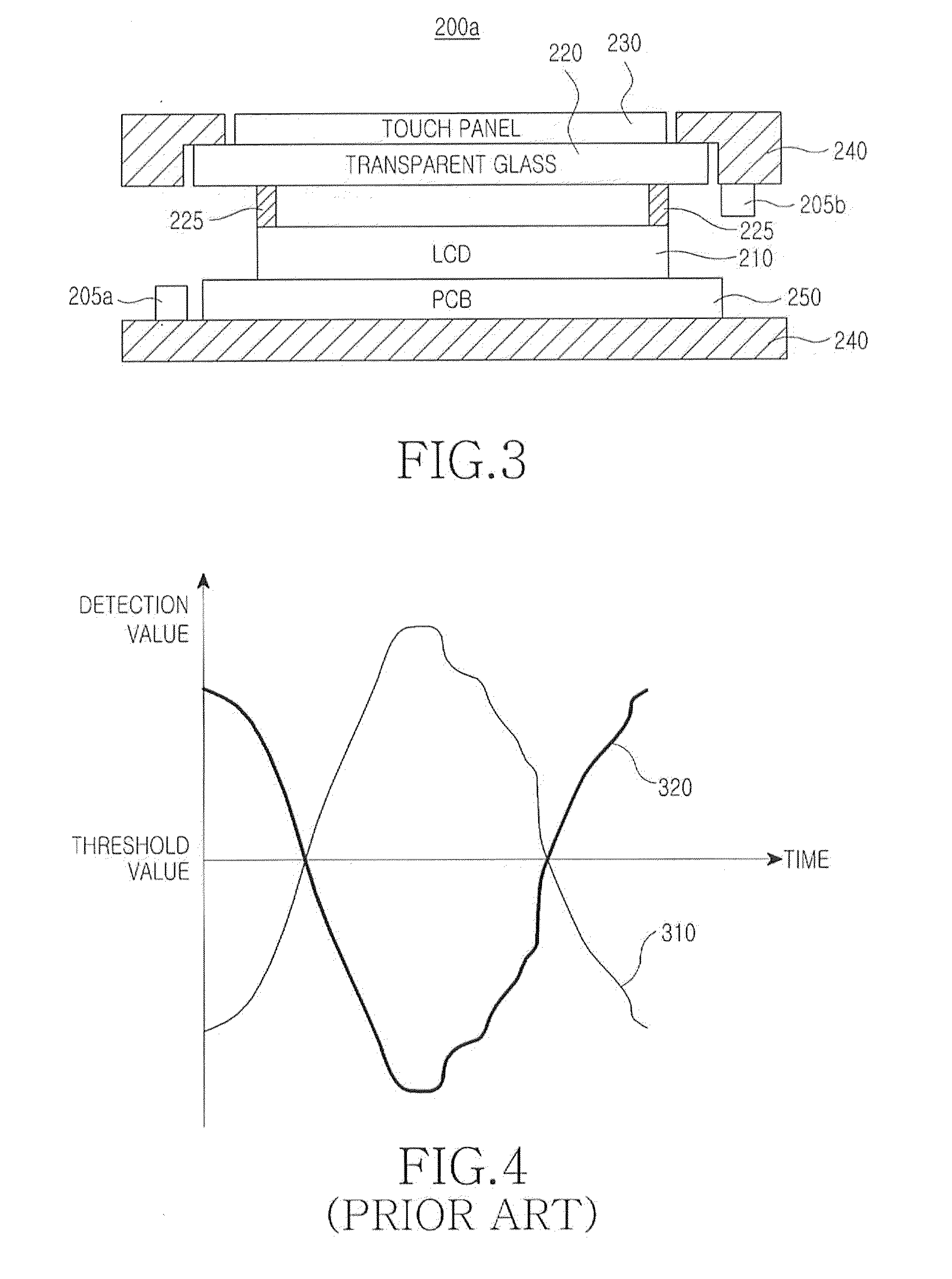
Method for providing haptic feedback in a touch screen
Disclosed is a method for providing a haptic feedback in a touch screen, which includes displaying a plurality of soft buttons on a touch screen; applying a first pattern vibration to the touch screen if a pressing detection value for a corresponding soft button according to contact of a user input means reaches a predetermined first threshold value; and applying a second pattern vibration to the touch screen if a pressing detection value for the corresponding soft button reaches a predetermined second threshold value, the second pattern vibration being different from the first pattern vibration, the second threshold value being different from the first threshold value.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for providing haptic effects to a touch panel
ActiveUS7825903B2Promote sportsTransmission systemsCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay deviceTouchpad
A method and apparatus for generating haptic effects for a touch panel or other interface device employs a touch-sensitive panel, a display and an actuator. The actuator includes a first structural element and a second structural element, a biasing element and two magnetic devices. The first magnetic device is configured to be carried by the first structural element and the second magnetic device is configured to be carried by the second structural element. The first structural element is coupled to a touch-sensitive panel and the second structural element may be coupled to the display or to a relatively fixed item. The biasing element couples the first and second structural elements together and deforms to facilitate a movement between the first and second structural elements. The actuator provides haptic effects by facilitating relative movement between the first and second structural elements.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
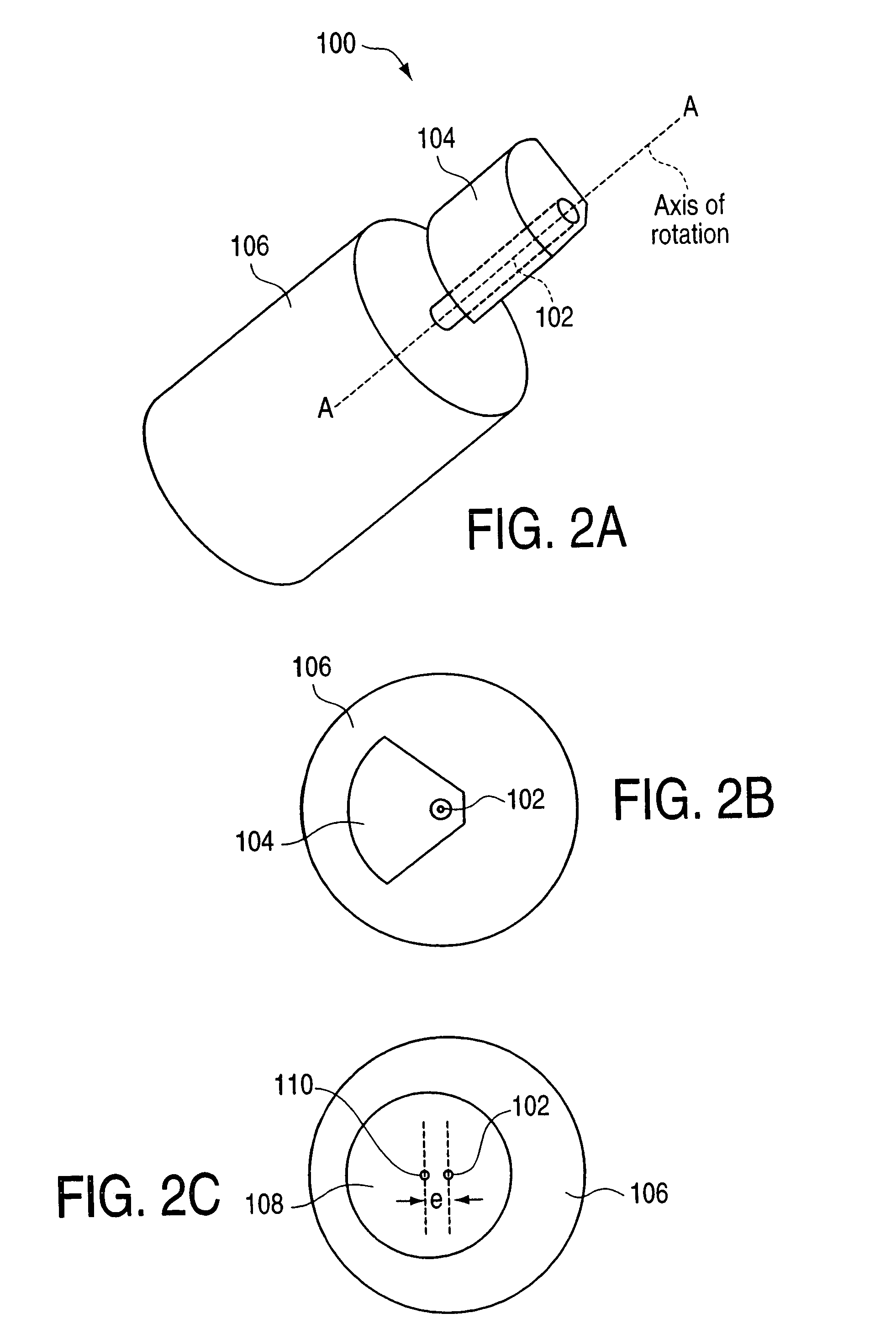
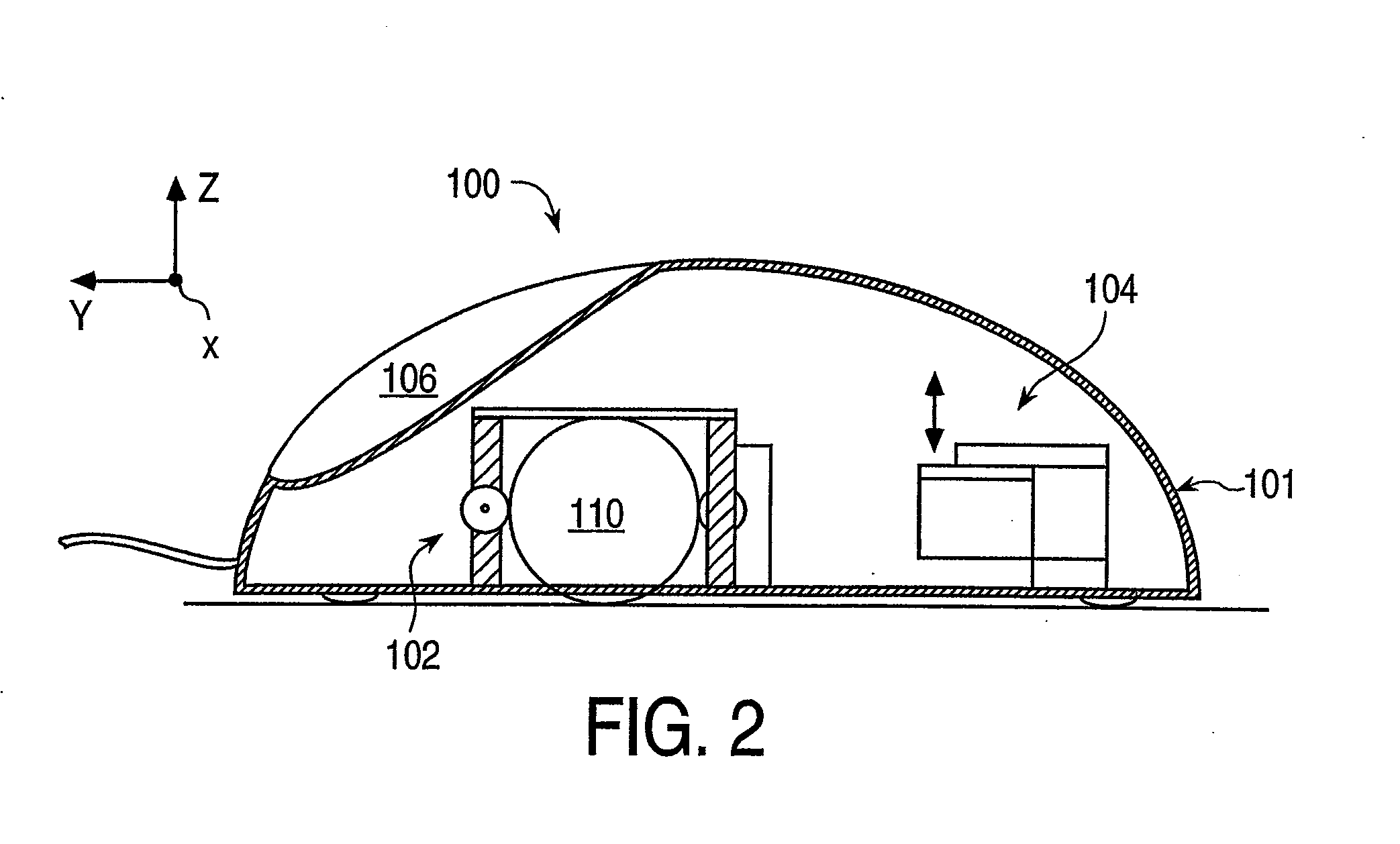
Vibrotactile haptic feedback devices
InactiveUS7561142B2Easy to useInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsCouplingRemote control
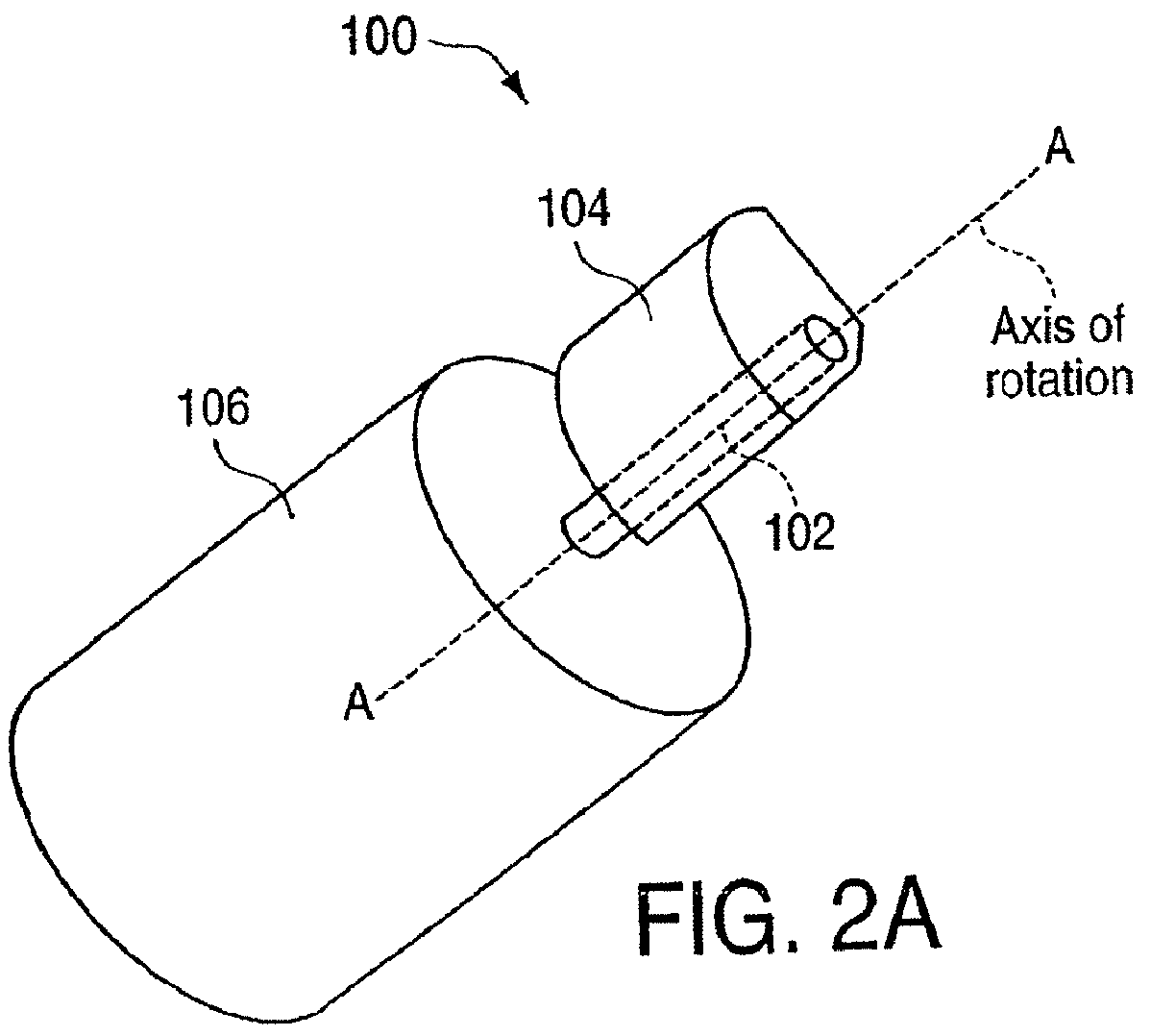
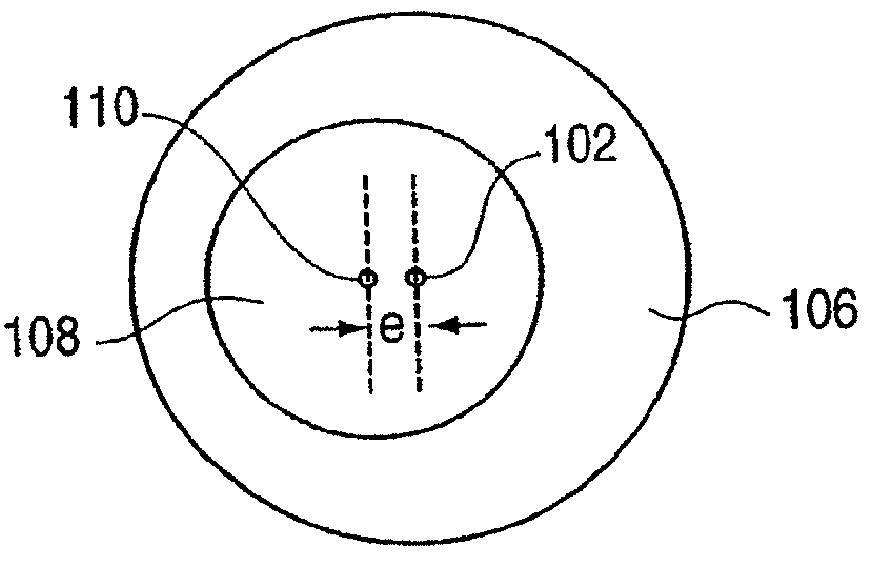
Method and apparatus for controlling magnitude and frequency of vibrotactile sensations for haptic feedback devices. A haptic feedback device, such as a gamepad controller, mouse, remote control, etc., includes a housing, an actuator coupled to the housing, and a mass. In some embodiments, the mass can be oscillated by the actuator and a coupling between the actuator and the mass or between the mass and the housing has a variable compliance. Varying the compliance allows vibrotactile sensations having different magnitudes for a given drive signal to be output. In other embodiments, the actuator is a rotary actuator and the mass is an eccentric mass rotatable by the actuator about an axis of rotation. The eccentric mass has an eccentricity that can be varied relative to the axis of rotation while the mass is rotating. Varying the eccentricity allows vibrotactile sensations having different magnitudes for a given drive signal.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Touch interface device having an electrostatic multitouch surface and method for controlling the device
ActiveUS20120287068A1Large forceInput/output processes for data processingElectrical polarityEngineering
A touch interface device includes a touch surface, a first electrode, and a second electrode. The first electrode is coupled with the touch surface. The first electrode also configured to receive a first haptic actuation electric potential. The second electrode is coupled with the touch surface. The second electrode also is configured to receive a different, second haptic actuation electric potential having an opposite polarity than the first haptic actuation potential. The first and second electrodes generate an electrostatic force that is imparted on one or more appendages of an operator that touches the touch surface above both the first electrode and the second electrode in order to generate a haptic effect.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
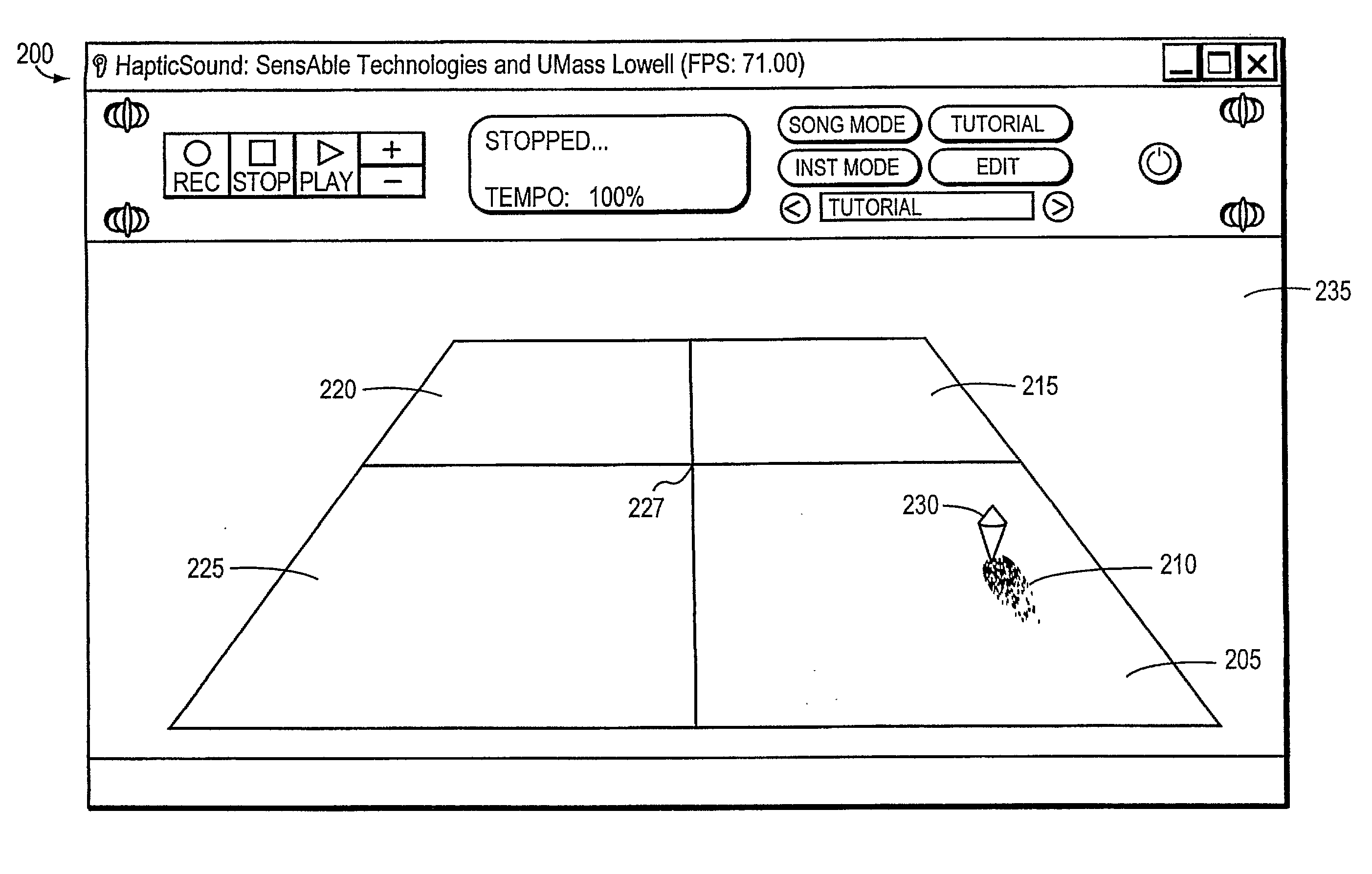
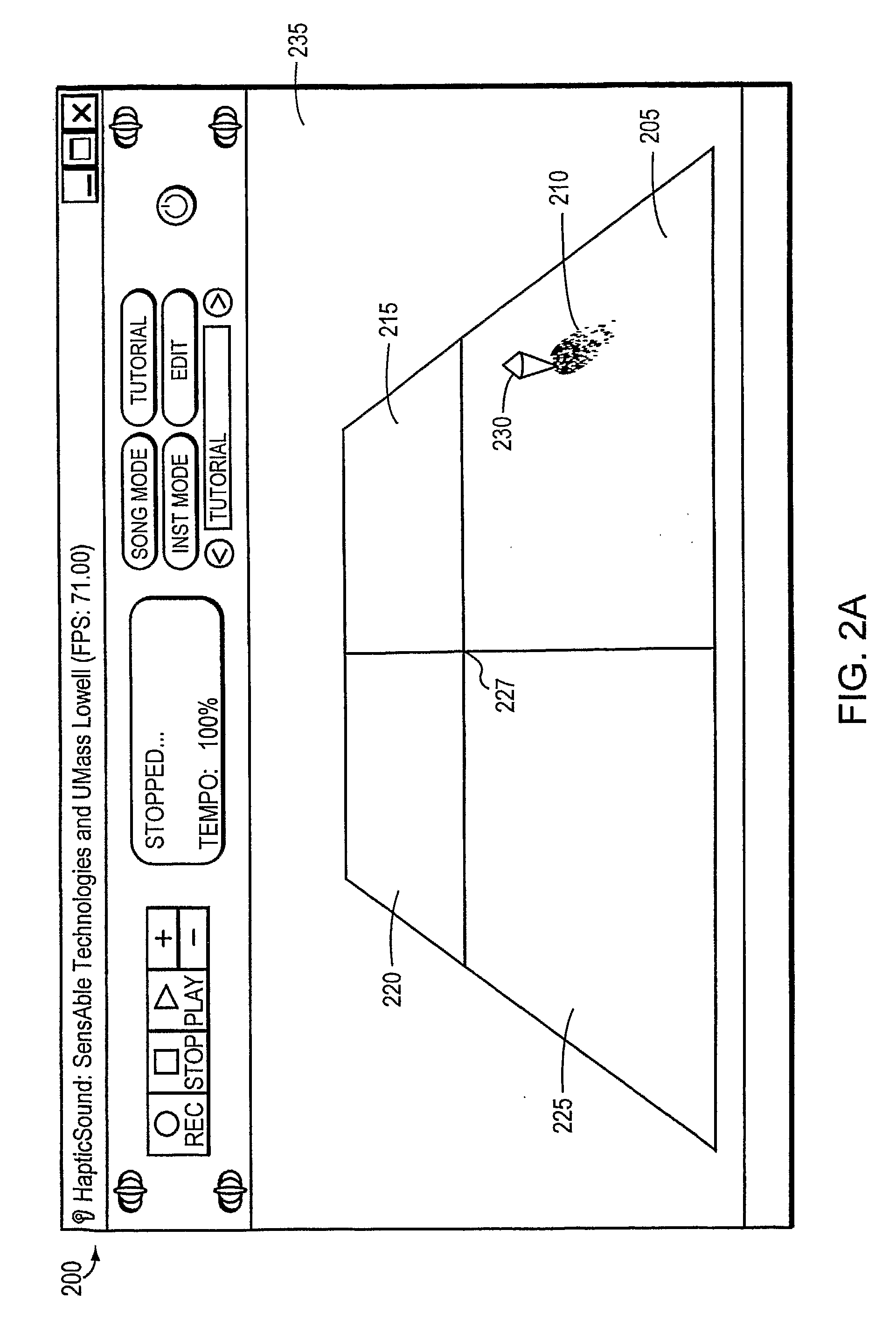
Virtual musical interface in a haptic virtual environment
InactiveUS20110191674A1Facilitates learning and production and other type of interactionInput/output for user-computer interactionElectrophonic musical instrumentsHuman–computer interactionVisual perception
Owner:SENSABLE TECH
Tactile force sense information display system and method
InactiveUS20070091063A1Efficiently presentedInformation can be presentedInput/output for user-computer interactionMechanical oscillations controlHuman bodyInformation display systems
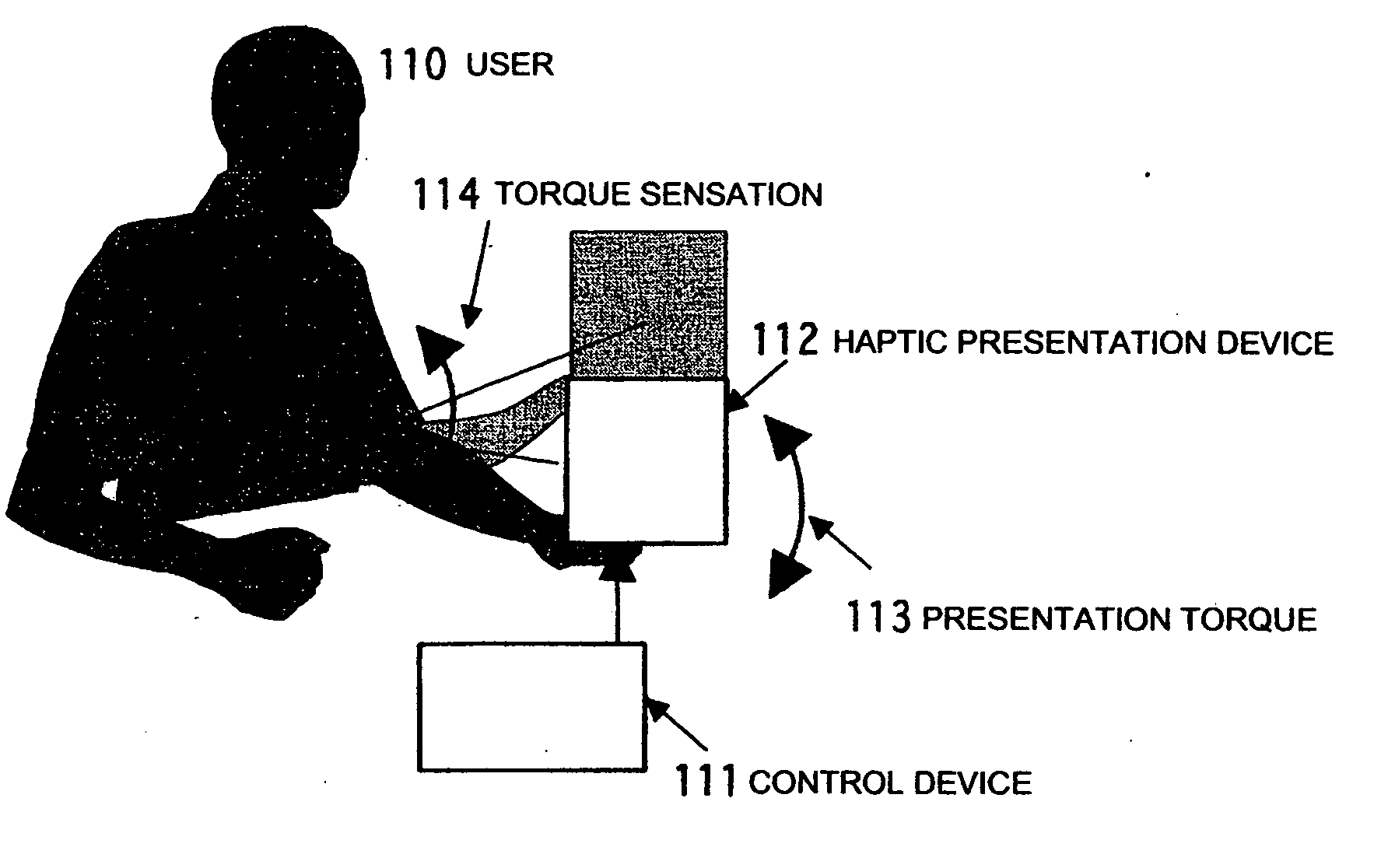
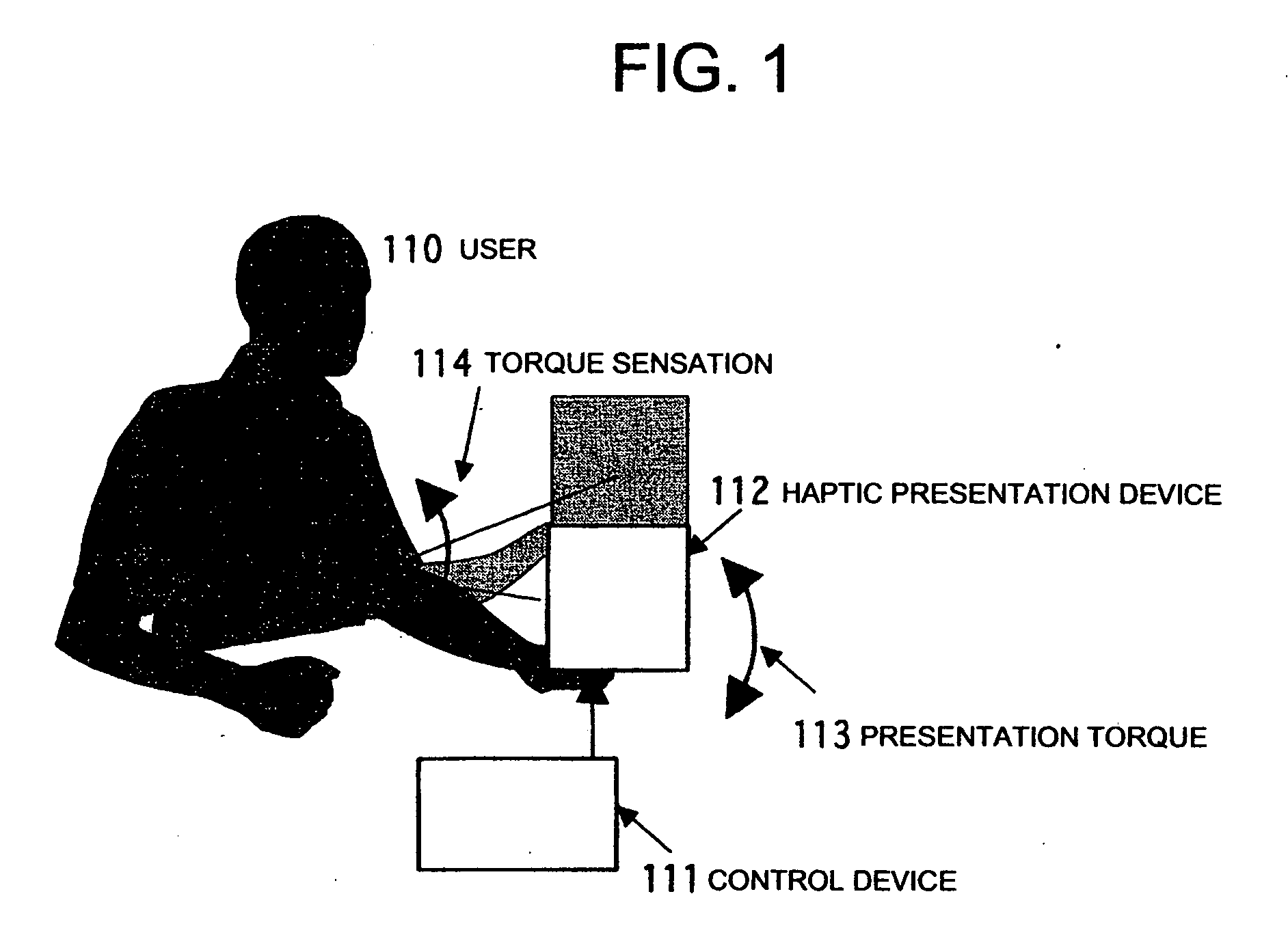
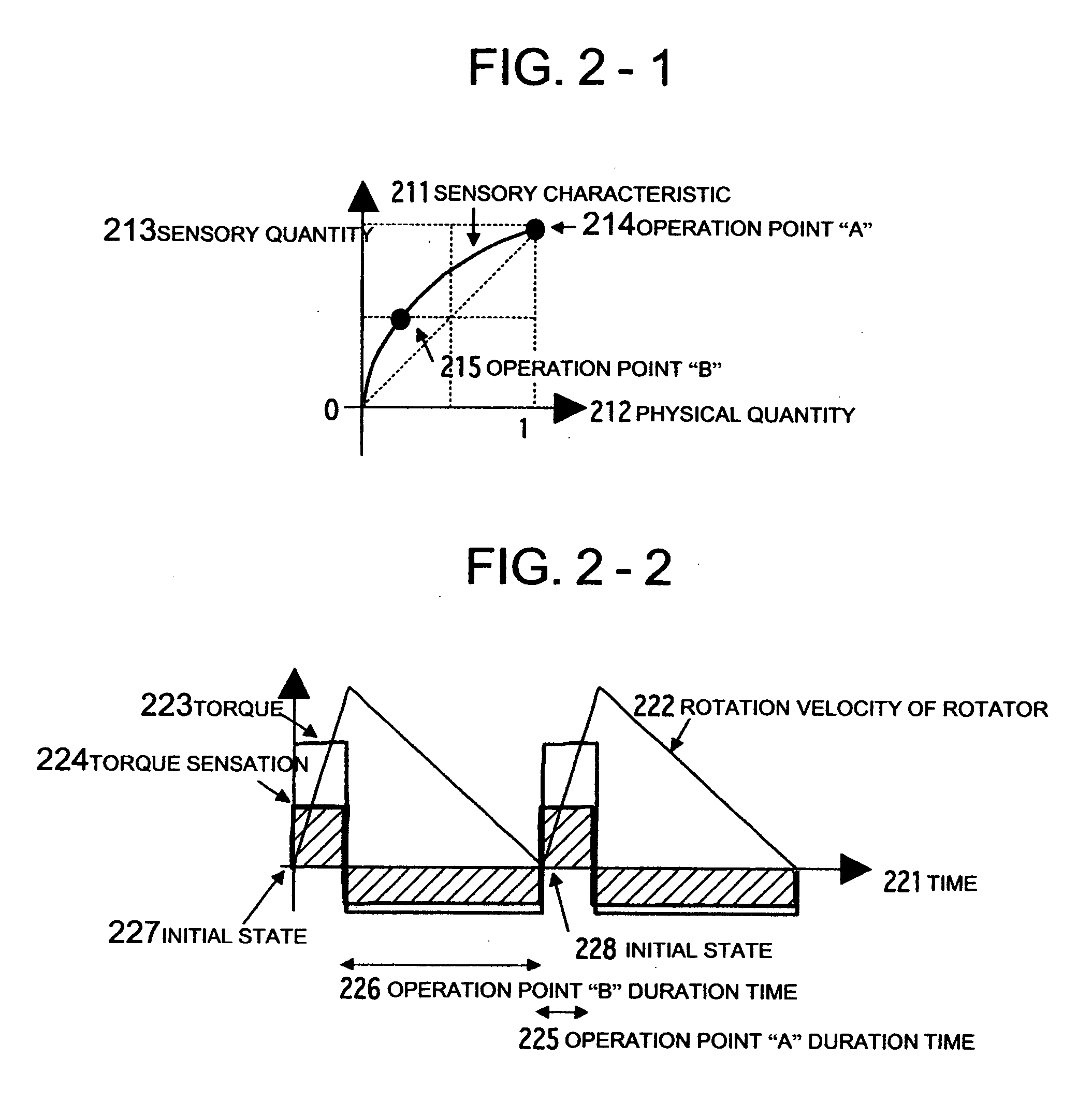
A system and a method are realized in which in a conventional non-grounding man-machine interface having no reaction base on the human body and for giving the existence of a virtual object and the impact force of a collision to a person, a haptic sensation of a torque, a force and the like can be continuously presented in the same direction, which can not be presented by only the physical characteristic of a haptic sensation presentation device. In a haptic presentation device 112, the rotation velocity of at least one rotator in the haptic presentation device 112 is controlled by a control device 111, and a vibration, a force or a torque as the physical characteristic is controlled, so that the user 110 is made to conceive various haptic information of the vibration, force, torque or the like. The haptic information presentation system uses a human sensory characteristic or illusion to suitably control the physical quantity, and causes the person to feel a force which can not exist physically, or a haptic sensory physical characteristic.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
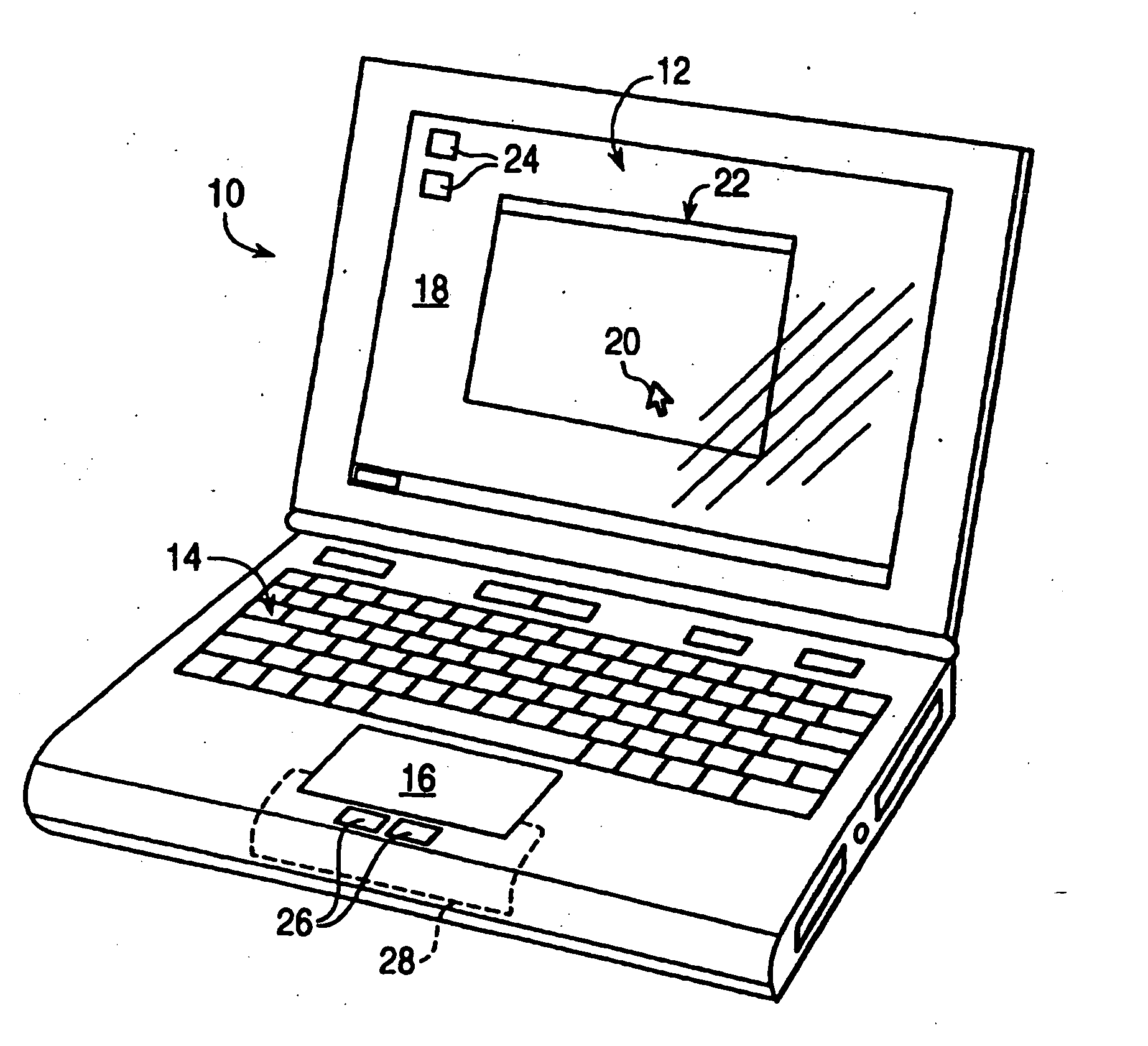
Tactile Enhancement For Input Devices
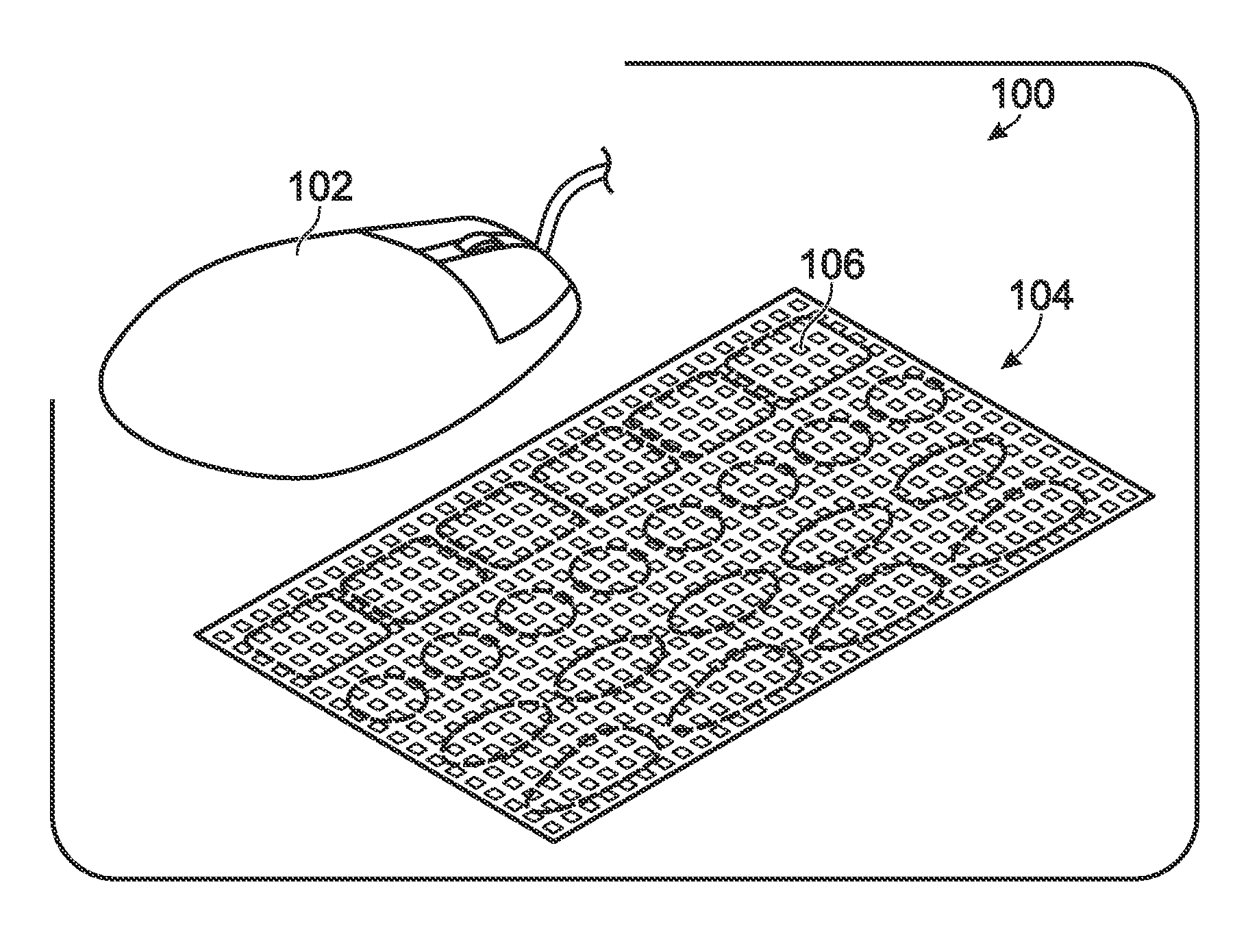
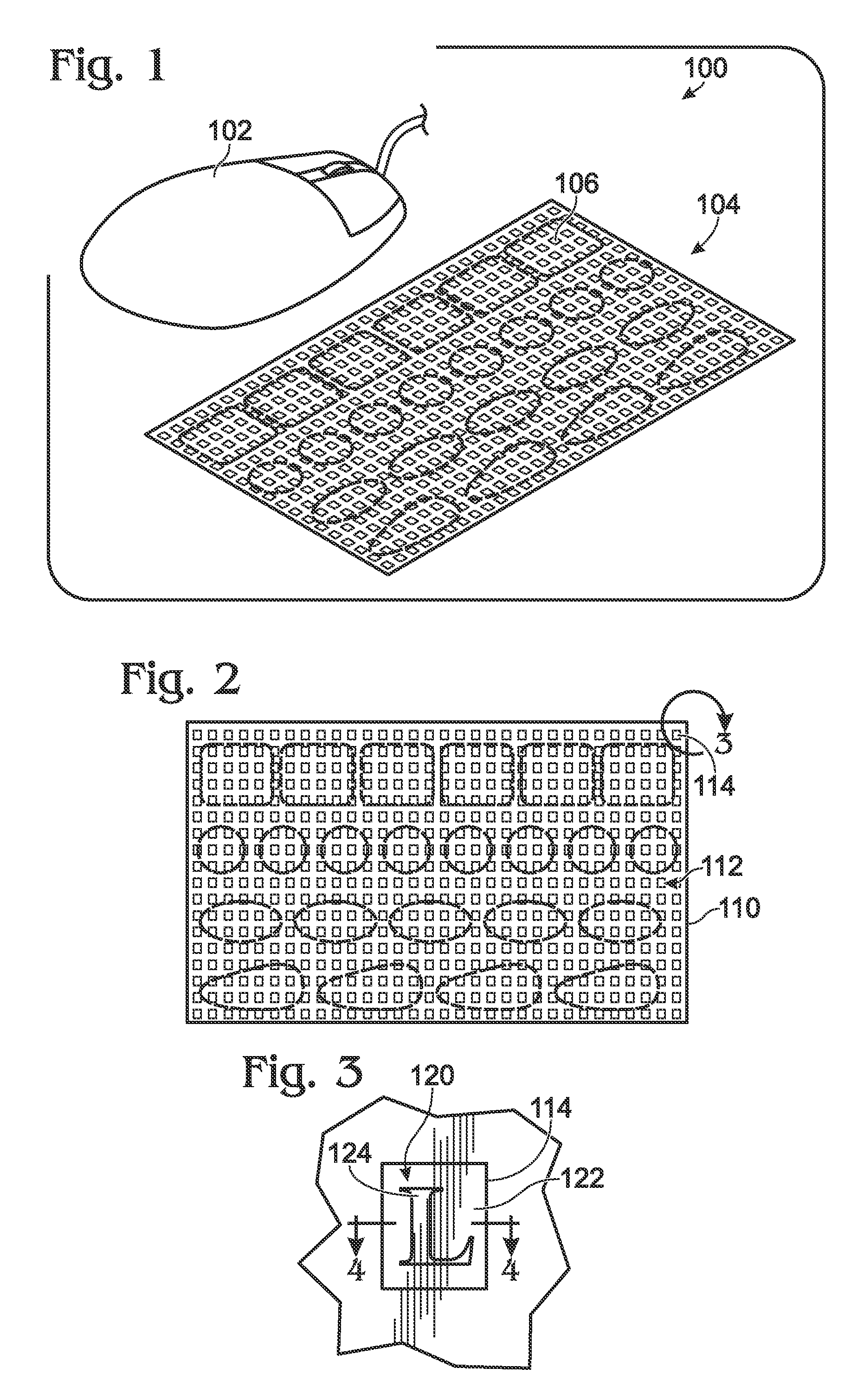
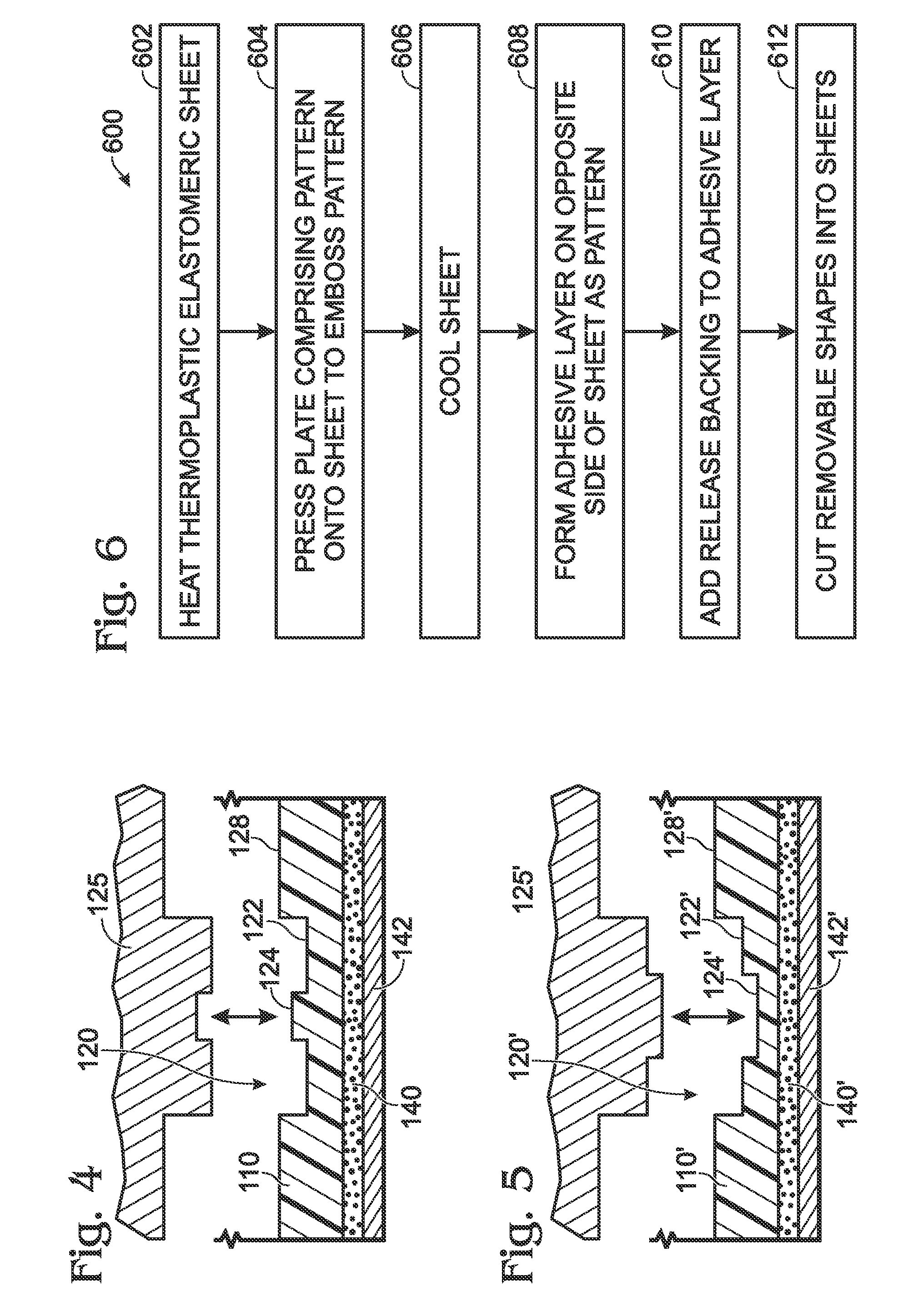
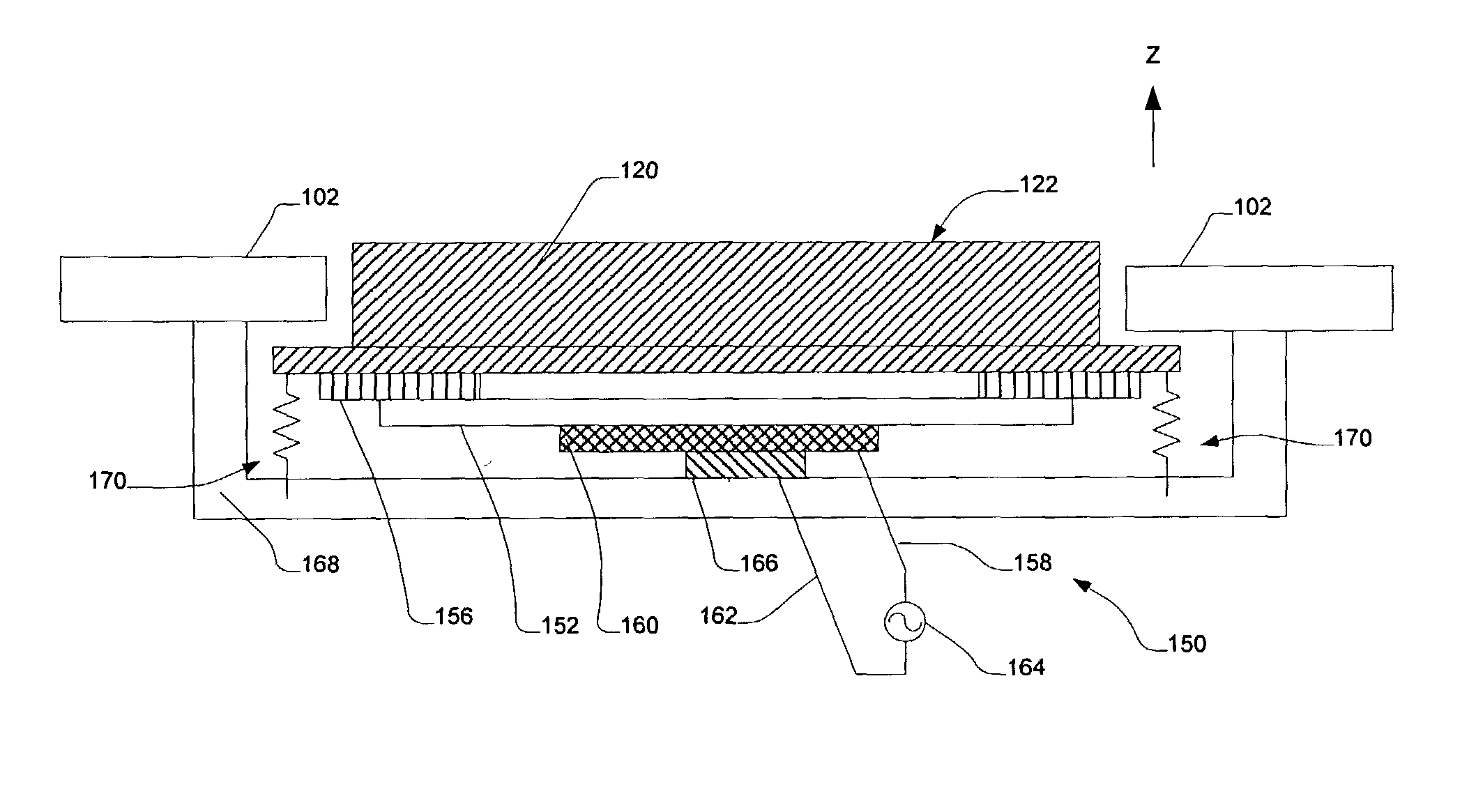
InactiveUS20100038821A1Well formedLayered productsCeramic shaping apparatusThermoplastic elastomerEngineering
Embodiments related to the tactile enhancement of a computer input device are disclosed herein. In one disclosed embodiment, a method of making removable tactile-enhancing grips for a computer input device is disclosed. The method comprises heating a thermoplastic elastomeric sheet to a temperature at which the thermoplastic elastomeric sheet is capable of receiving and retaining an imprinted feature, pressing onto the thermoplastic elastomeric sheet a plate comprising a pattern, thereby embossing the pattern onto the thermoplastic elastomeric sheet, and cooling the thermoplastic elastomeric sheet to a temperature at which the pattern is retained in the thermoplastic elastomeric sheet. An adhesive layer is then formed on an opposite side of the thermoplastic elastomeric sheet as the pattern.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method of using tactile feedback to deliver silent status information to a user of an electronic device
ActiveUS7567232B2Input/output for user-computer interactionContact surface shape/structureHaptic sensationHuman–computer interaction
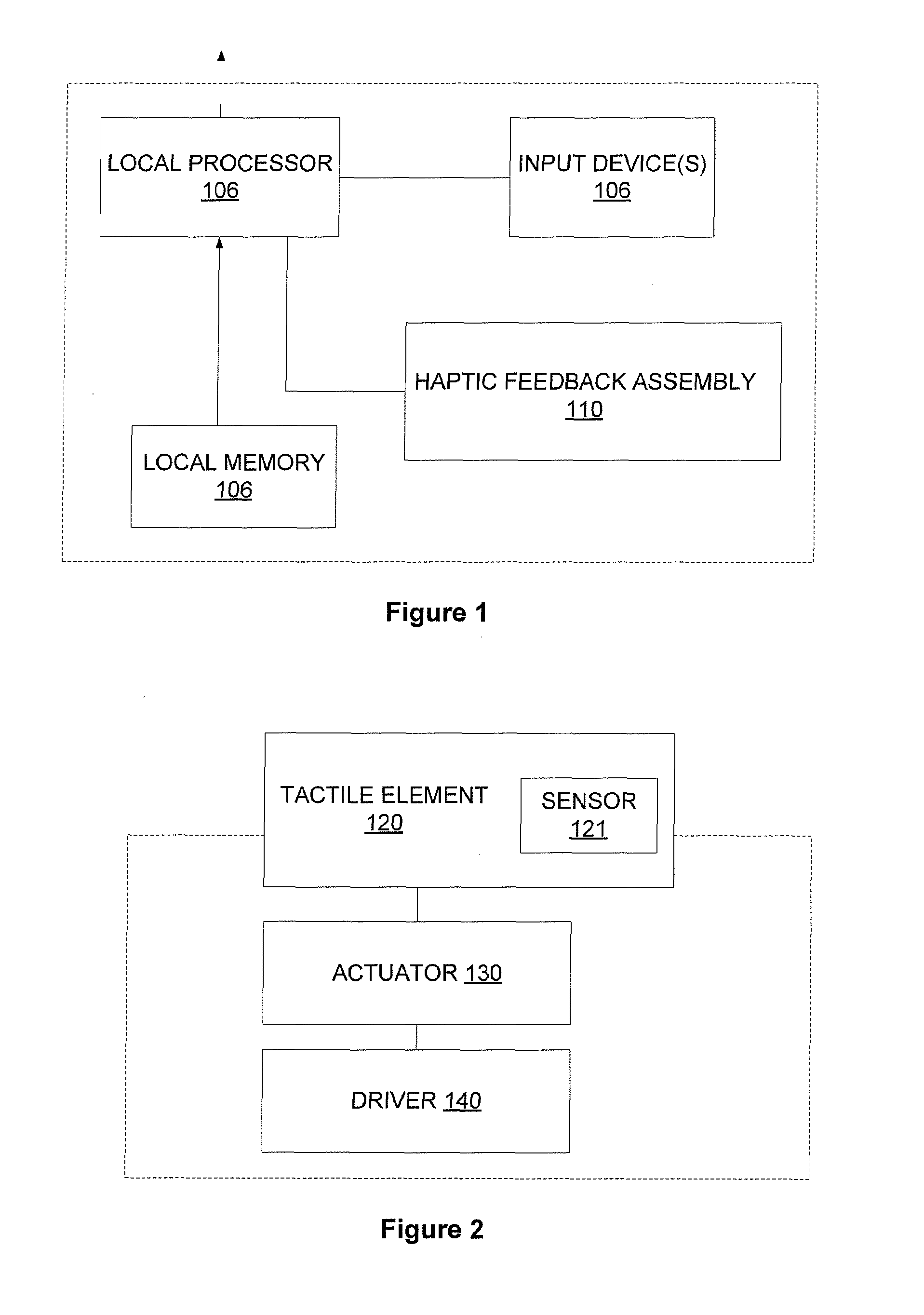
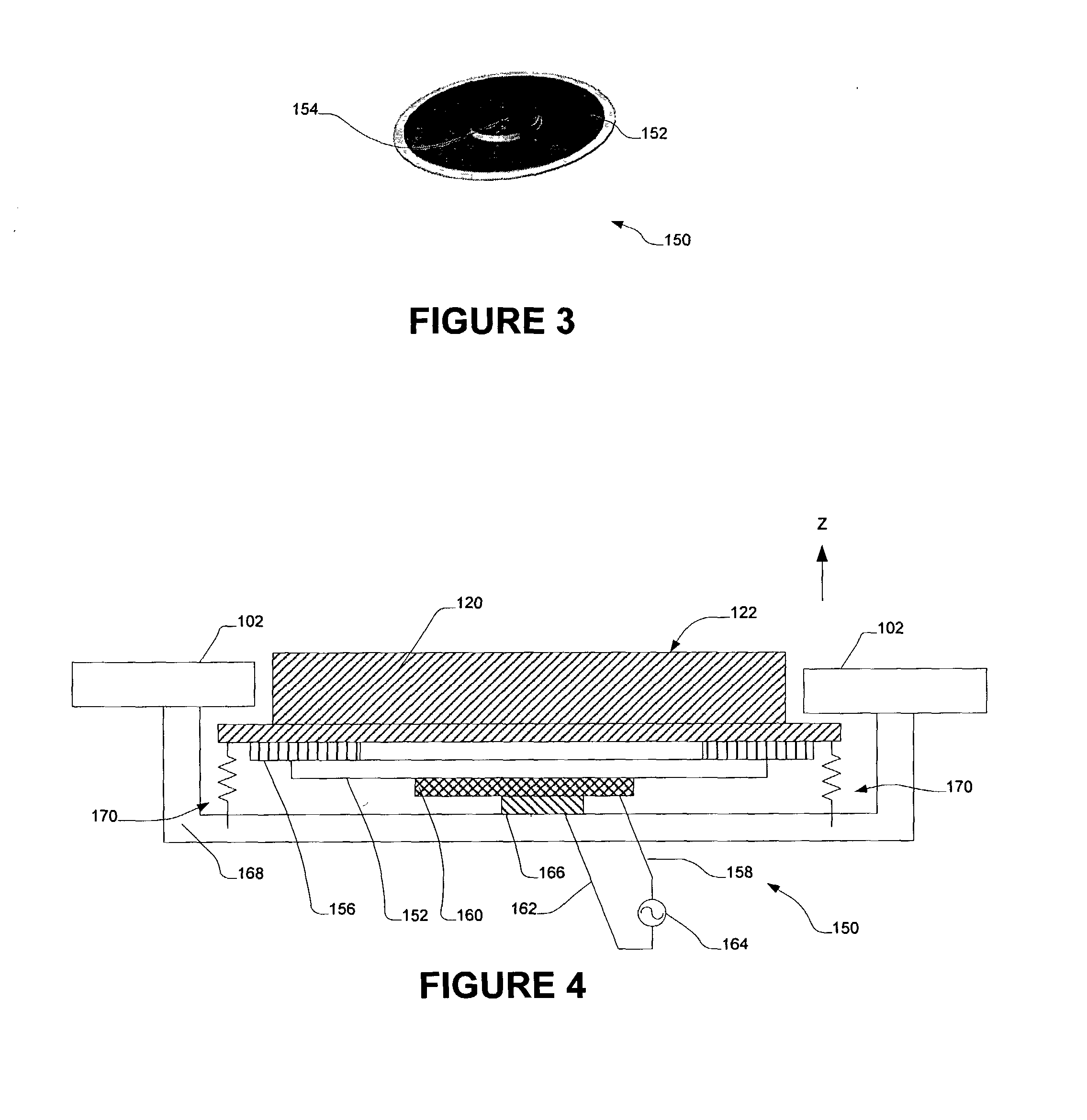
Embodiments of the present invention use haptic feedback to deliver status information to users in environments and situations where sight and / or sound is too overt from a privacy perspective. In one embodiment, localized haptic sensations can be delivered to a user through a tactile element that is positioned on a region of a housing of the electronic device that is engaged by a user.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Tactile driver feedback regarding the operational readiness of a vehicle
InactiveUS20110187521A1Increase rangeLot of attentionVehicle seatsRailway vehiclesDriver/operatorHaptic sensation
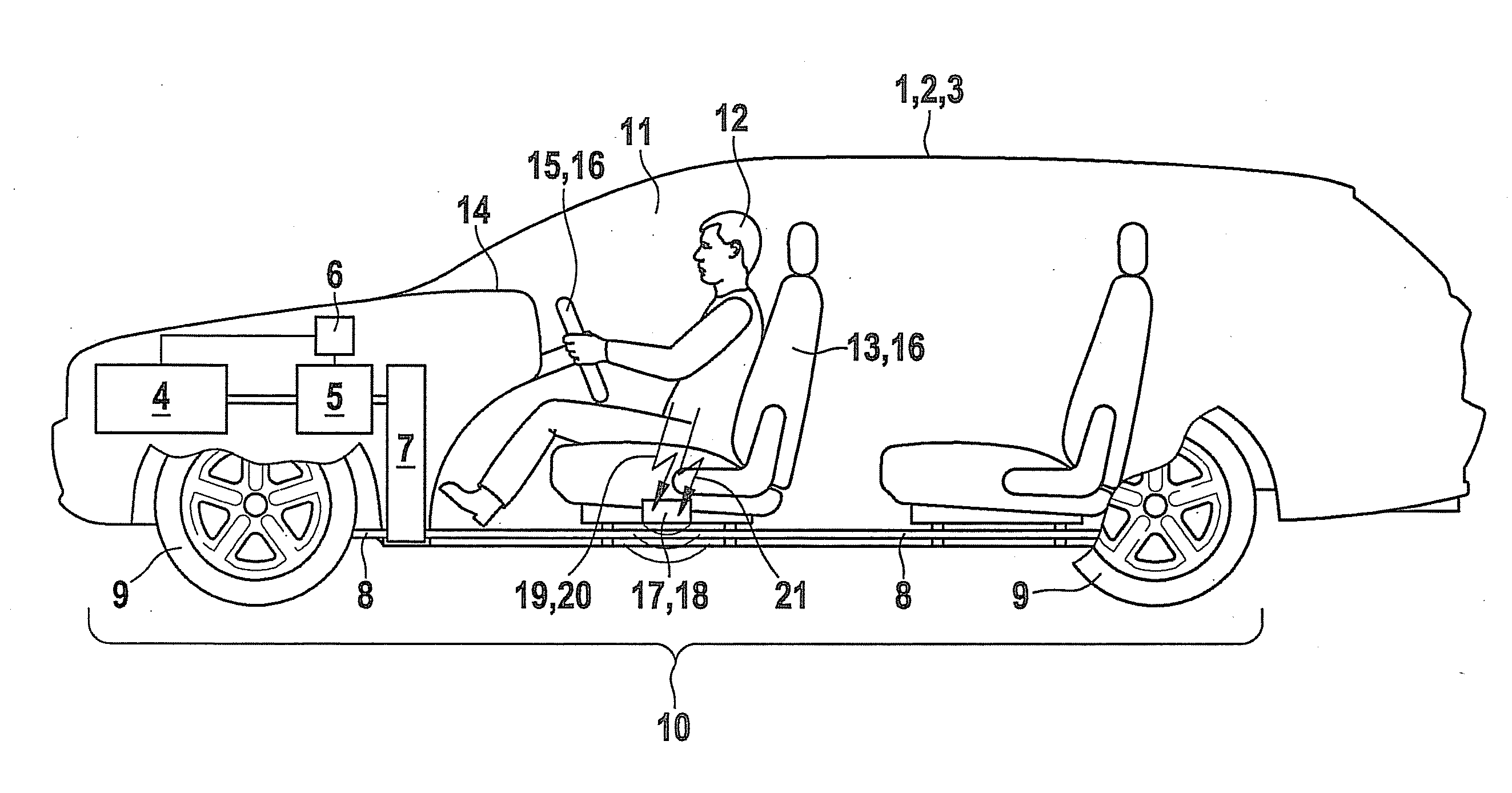
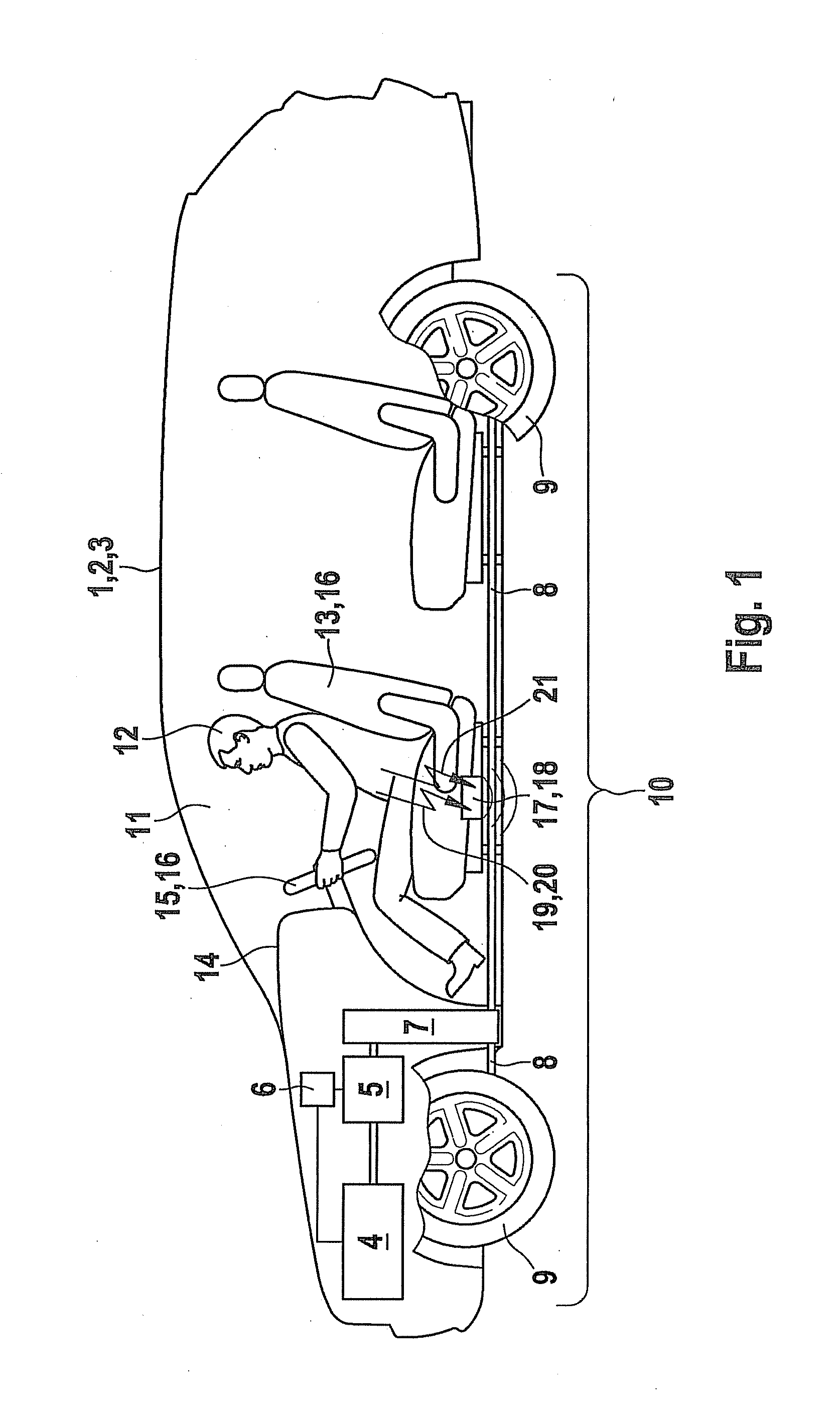
A method is described for generating a tactile driver feedback regarding the operational readiness of a vehicle, in particular a hybrid vehicle, the feedback being generated as a function of the state of a drive train of the vehicle.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
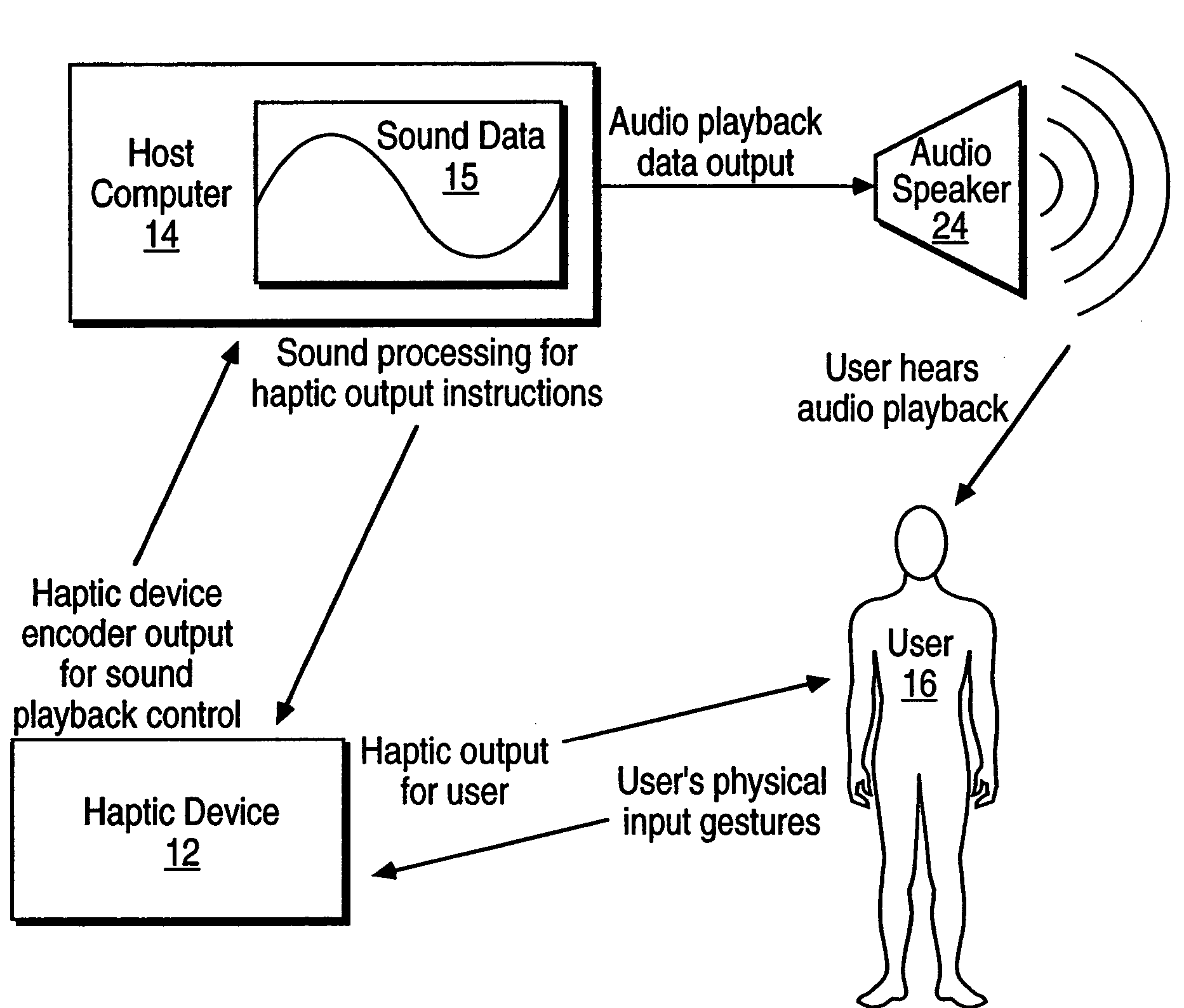
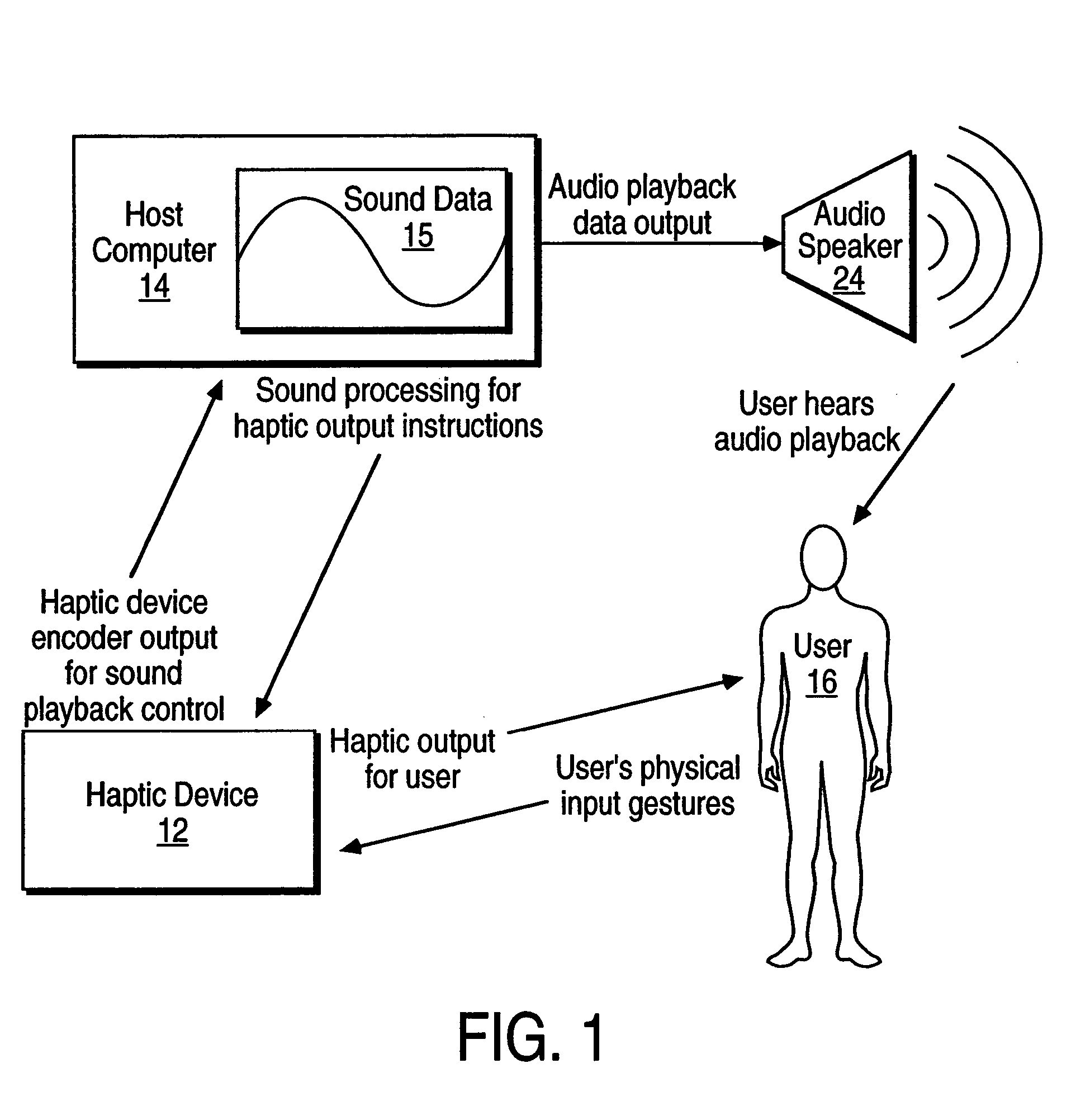
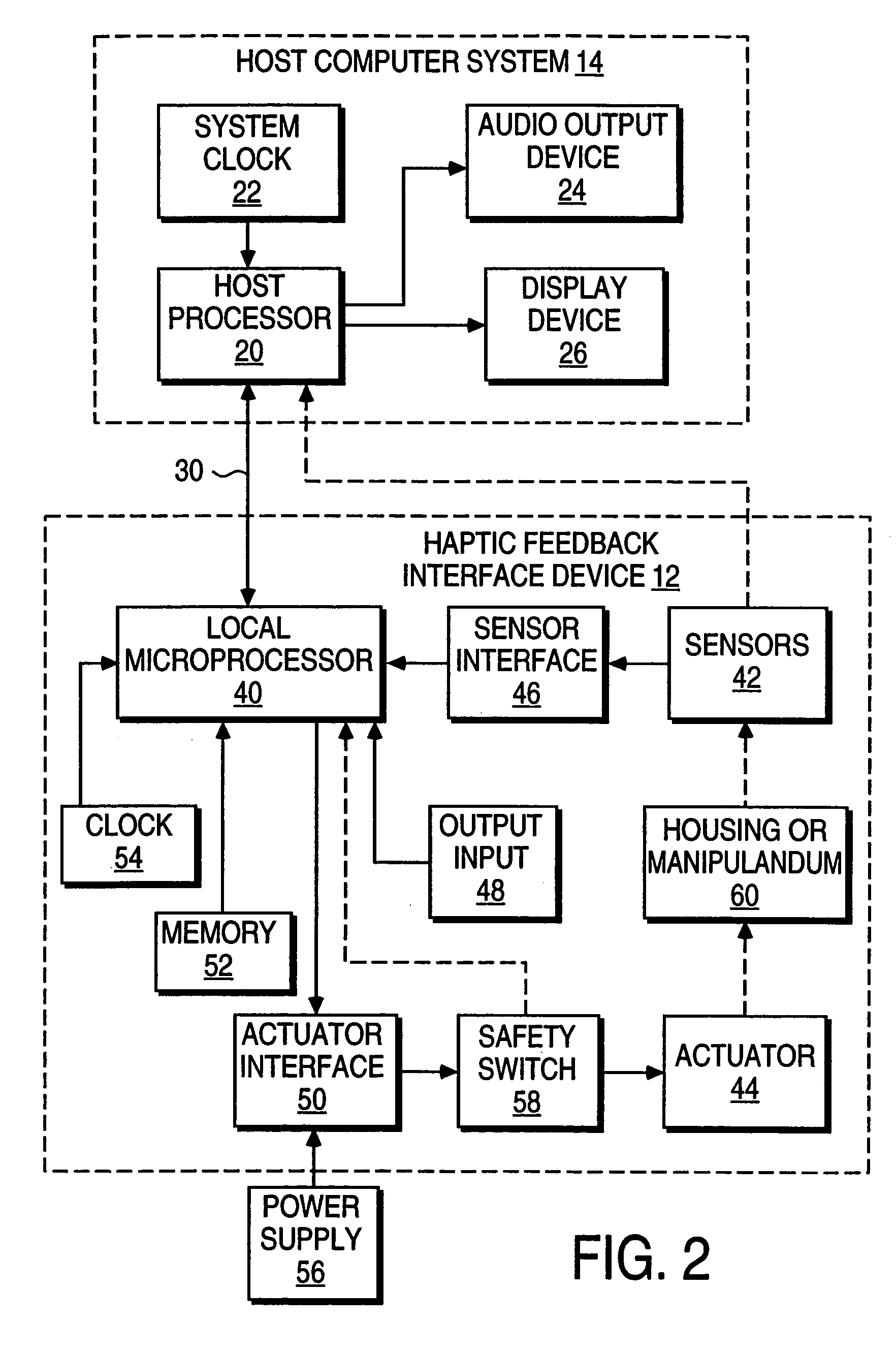
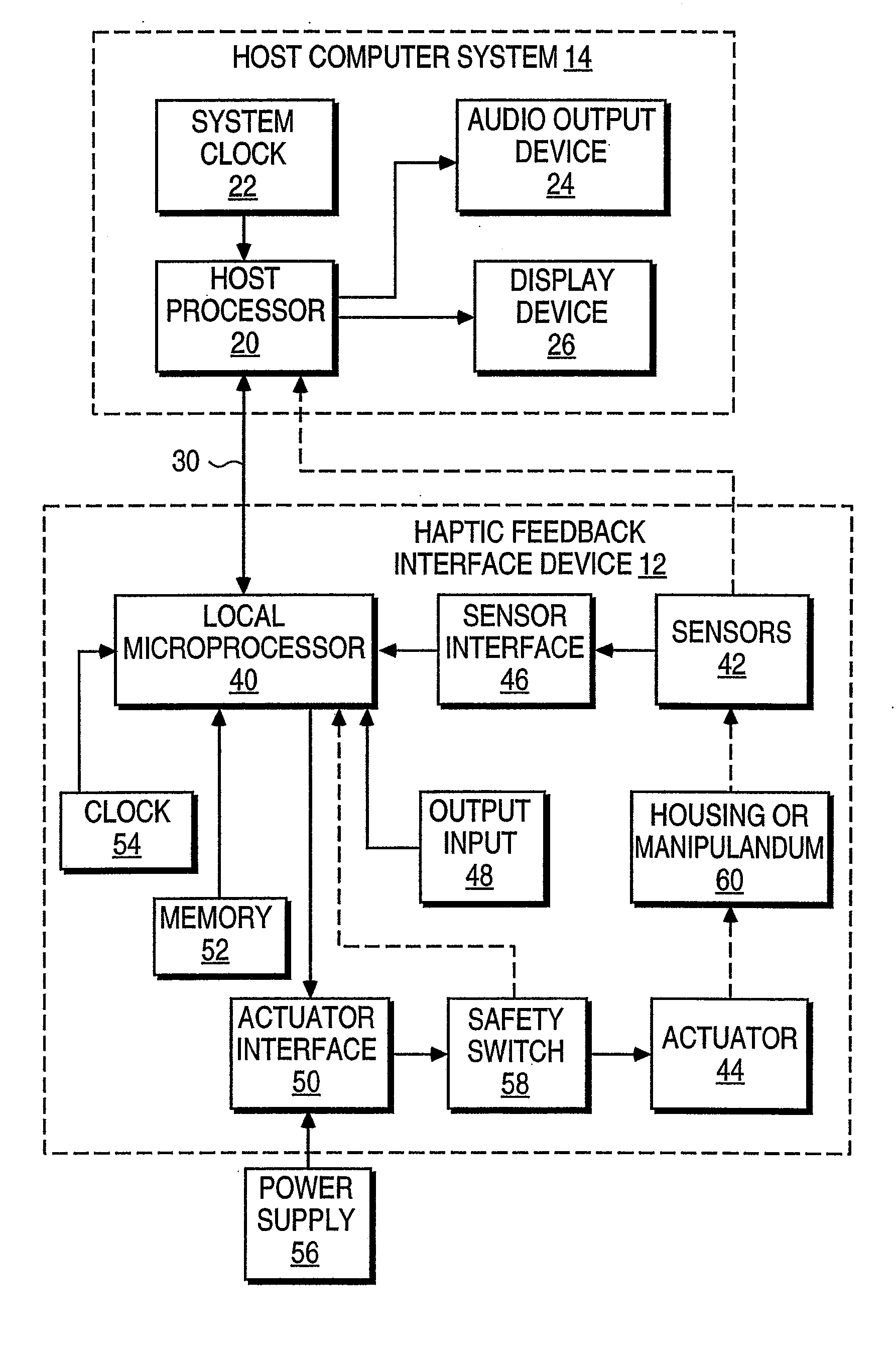
Sound data output and manipulation using haptic feedback
InactiveUS7208671B2Precise and Efficient ControlBetter informedInput/output for user-computer interactionElectrophonic musical instrumentsUser inputHaptic sensation
Sound data output and manipulation with haptic feedback. Haptic sensations are associated with sound data to assist in navigating through and editing the sound data. The sound data is loaded into computer memory and played such that sound is output from an audio device. The sound playing is controlled by user input for navigation through the sound data. Haptic commands are generated based on the sound data and are used to output haptic sensations to the user by a haptic feedback device manipulated by the user. The haptic sensations correspond to one or more characteristics of the sound data to assist the user in discerning features of the sound data during the navigation through and editing of the sound data.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
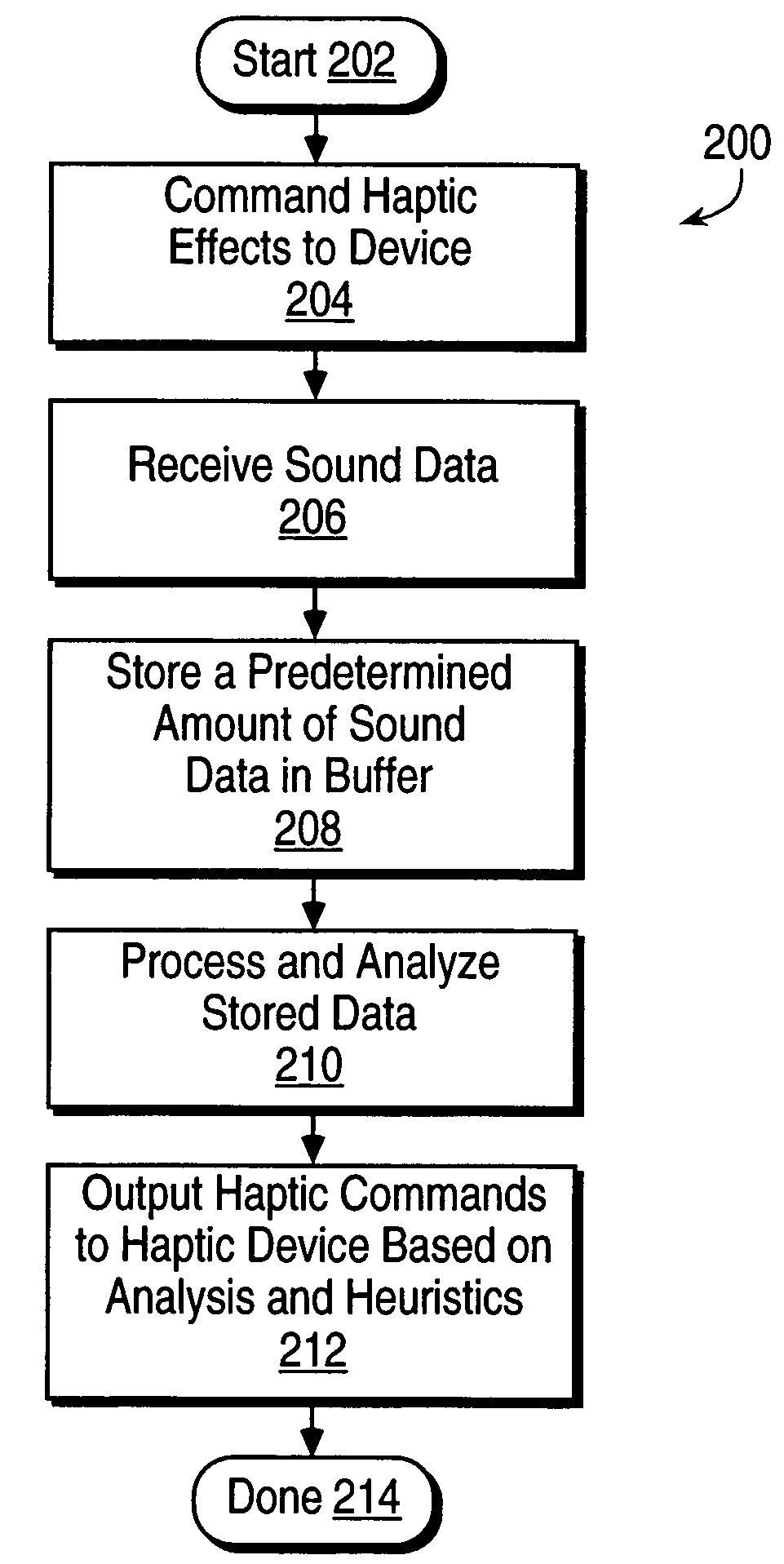
Haptic Feedback Sensations Based on Audio Output From Computer Devices
InactiveUS20100066512A1Improve user experienceInput/output for user-computer interactionRepeater circuitsHeuristicHaptic sensation
Triggering haptic sensations based on sound output from a computer device. A portion of sound data is stored that is output to a user as audio from an application program running on a computer. The portion of sound data is analyzed using intelligent heuristics to extract at least one sound feature from the sound data. The execution of at least one haptic effect is triggered based on the sound feature, where the haptic effect is commanded to the haptic feedback device approximately correlated to the output of the portion of sound to the user as audio. The haptic effect causes a haptic sensation to be output to the user. Different haptic effects can be associated with different sound features, frequency ranges, amplitudes, etc.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
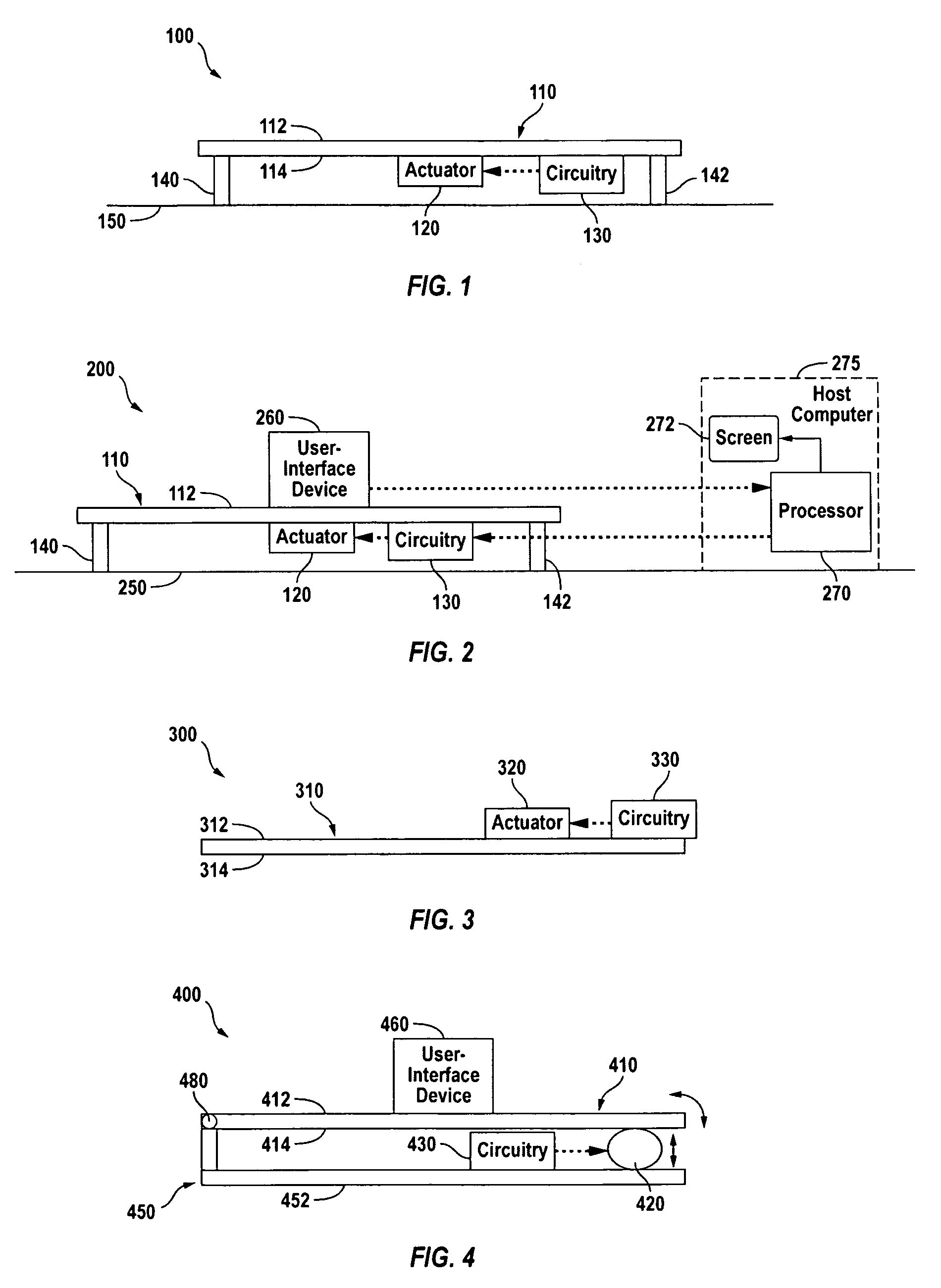
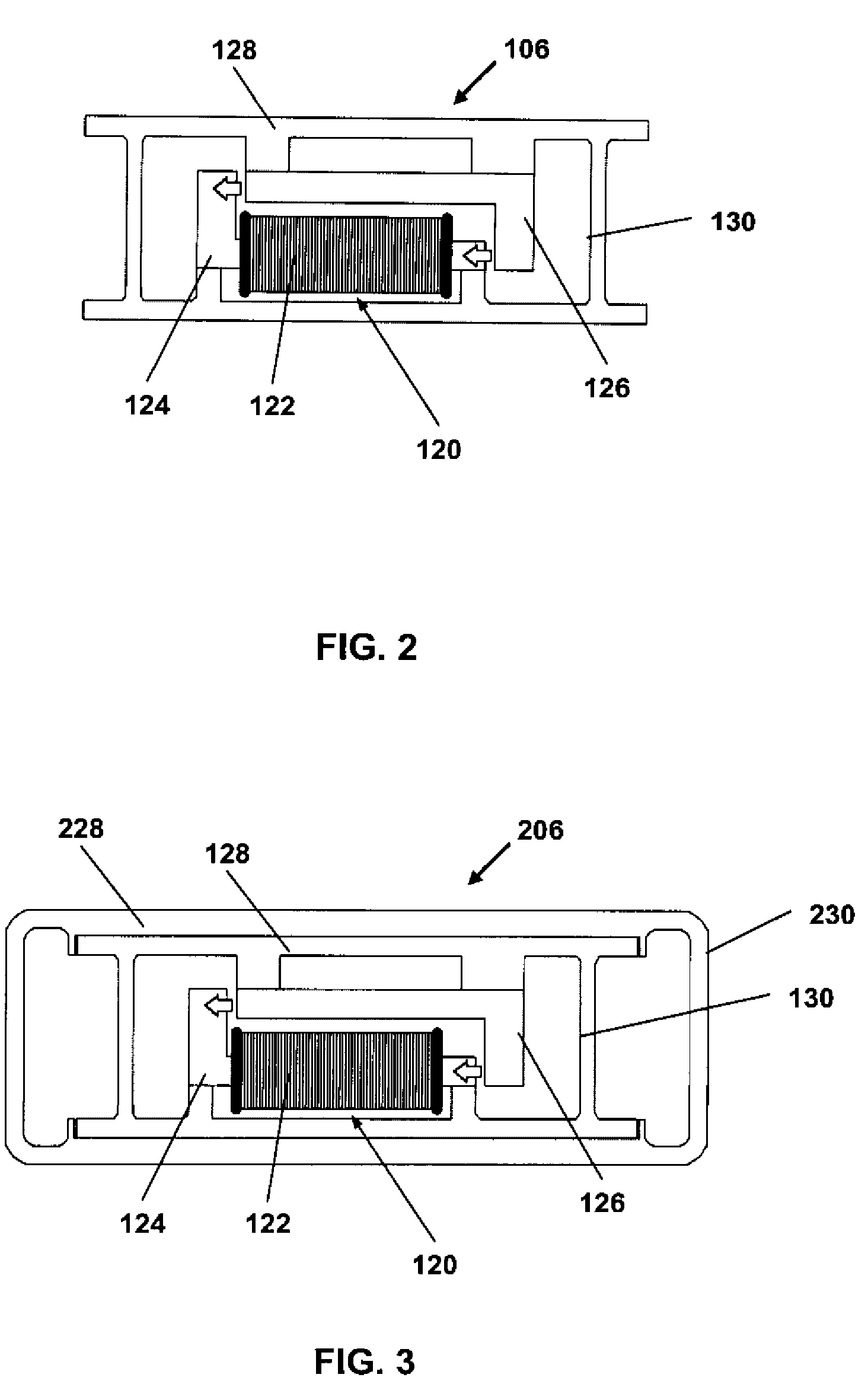
Haptic actuator assembly and method of manufacturing a haptic actuator assembly
InactiveUS20090174672A1Easy to manufactureLow costRepeater circuitsInput/output processes for data processingActuatorHaptic sensation
A haptic actuator assembly and a method of manufacturing a haptic actuator assembly. The haptic actuator assembly includes a rail of predetermined length and a haptic actuator coupled to the rail, wherein the rail is coupled to another device to provide haptic feedback. The method of manufacturing a haptic actuator assembly includes the steps of providing a rail and coupling a haptic actuator to the rail.
Owner:METHODE ELETRONICS INC
Haptic feedback sensations based on audio output from computer devices
InactiveUS7623114B2Improve user experienceInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsHeuristicHaptic sensation
Triggering haptic sensations based on sound output from a computer device. A portion of sound data is stored that is output to a user as audio from an application program running on a computer. The portion of sound data is analyzed using intelligent heuristics to extract at least one sound feature from the sound data. The execution of at least one haptic effect is triggered based on the sound feature, where the haptic effect is commanded to the haptic feedback device approximately correlated to the output of the portion of sound to the user as audio. The haptic effect causes a haptic sensation to be output to the user. Different haptic effects can be associated with different sound features, frequency ranges, amplitudes, etc.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Haptic interface for palpation simulation
InactiveUS7307619B2Easy to carrySimulate the realInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsPalpation
A palpation simulator comprises an interface for interfacing a user with a computer running a palpation simulation. The computer generates a graphical environment comprising a cursor and a graphical representation of at least a portion of a living body. In one version, a method comprises providing an object in communication with the computer, controlling the cursor in relation to manipulation of at least a portion of the object by the user, and outputting a haptic sensation to the user when the cursor interacts with a region within the graphical representation to provide the user with haptic feedback related to a simulated palpation of the region.
Owner:IMMERSION MEDICAL
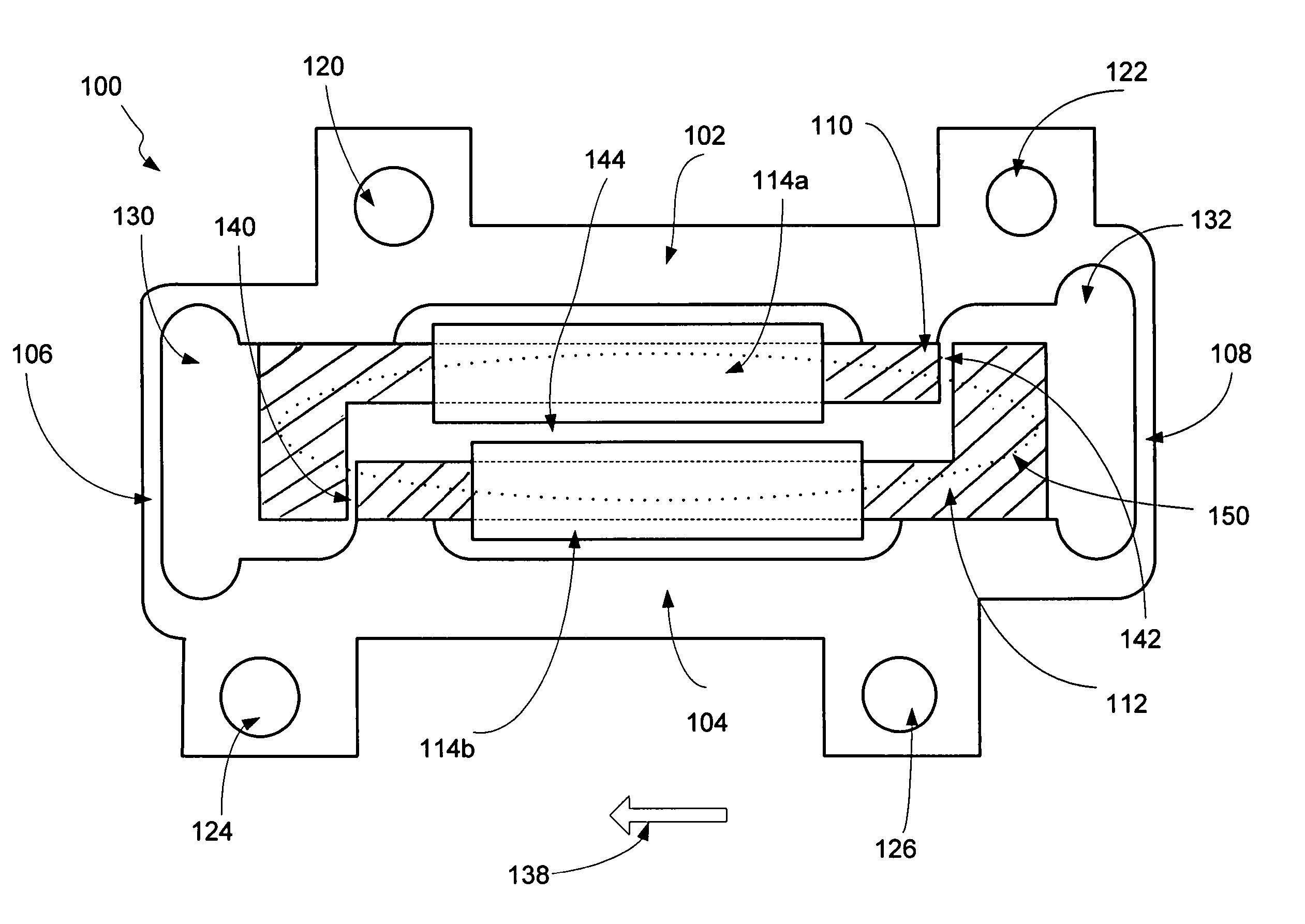
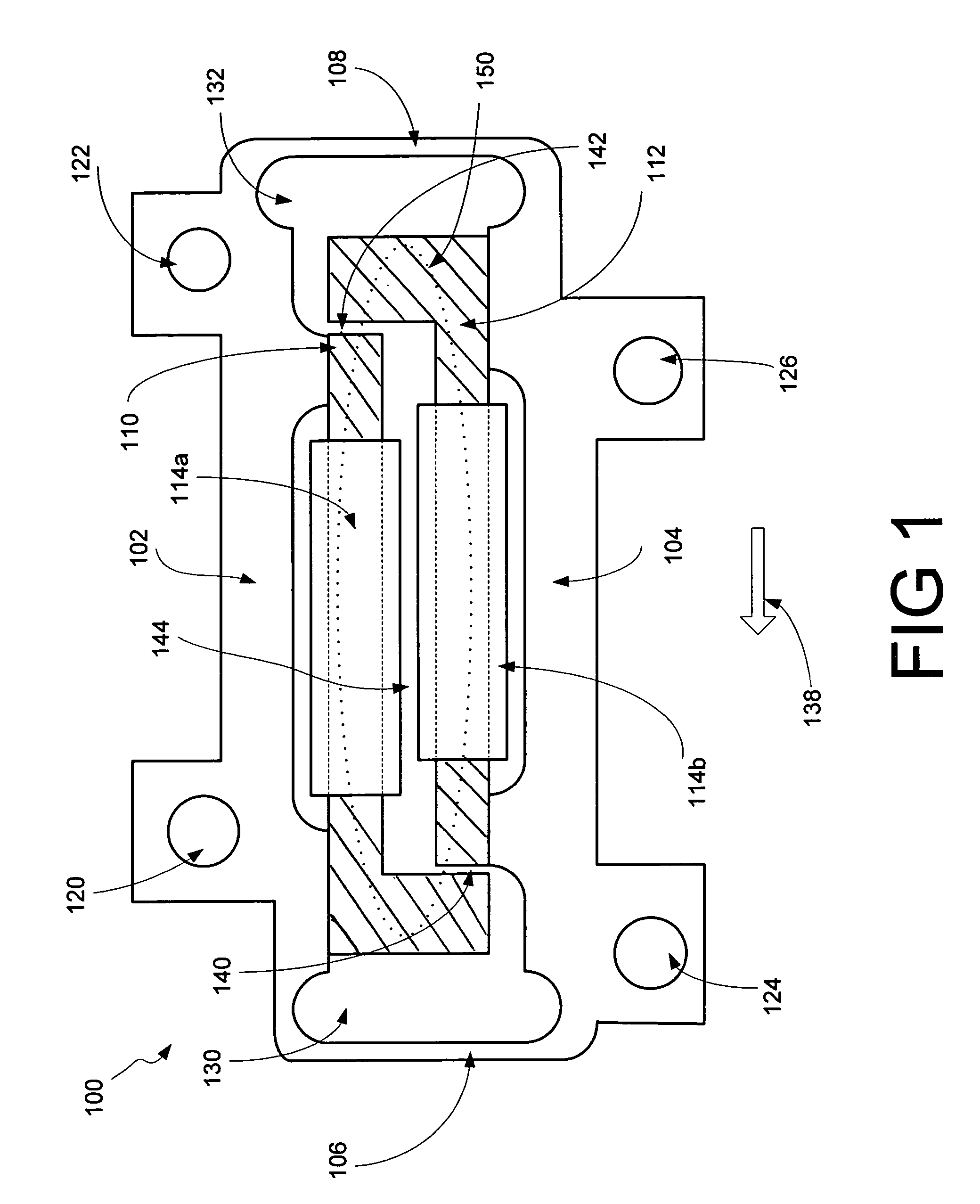
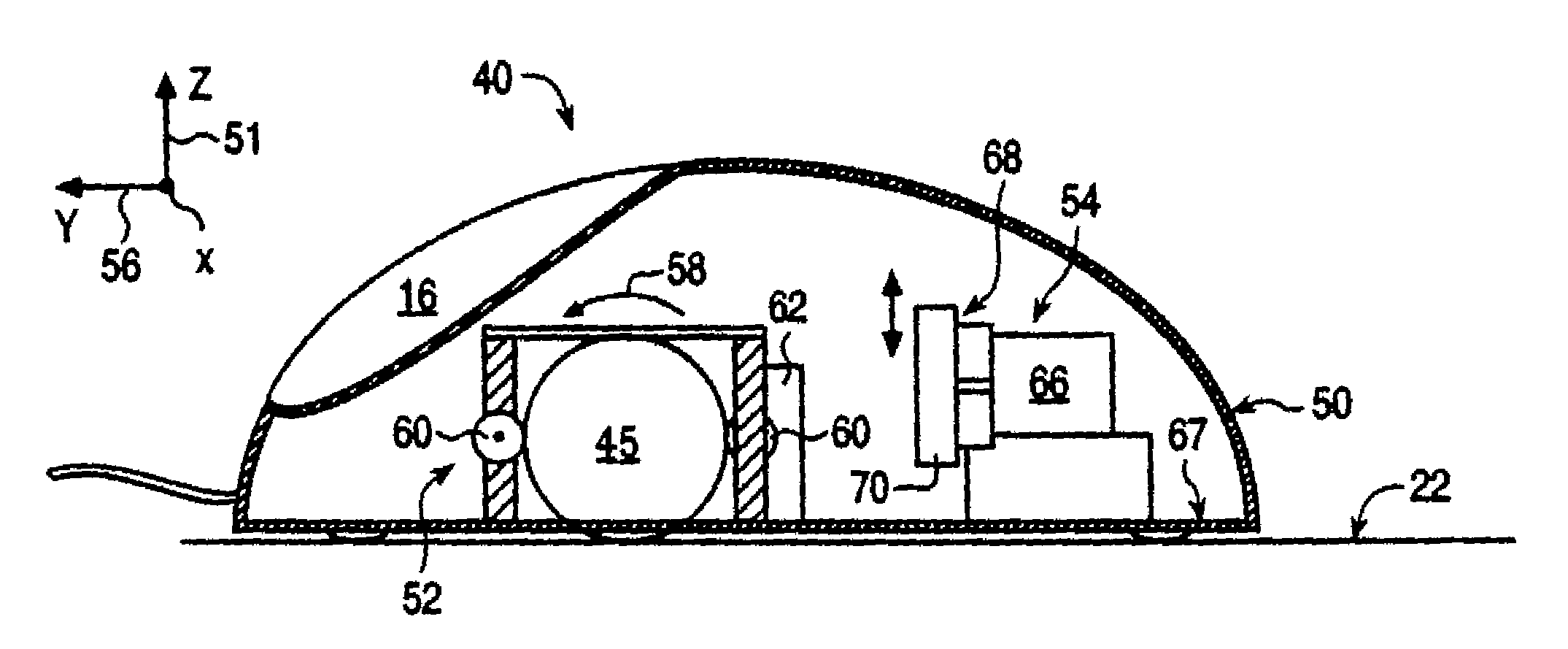
Haptic interface device and actuator assembly providing linear haptic sensations
InactiveUS7432910B2Low-cost forceLow costInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsLinear motionInertial mass
An interface device and method providing haptic sensations to a user. A user physically contacts a housing of the interface device, and a sensor device detects the manipulation of the interface device by the user. An actuator assembly includes an actuator that provides output forces to the user as haptic sensations. In one embodiment, the actuator outputs a rotary force, and a flexure coupled to the actuator moves an inertial mass and / or a contact member. The flexure can be a unitary member that includes flex joints allowing a portion of the flexure to be linearly moved. The flexure can converts rotary force output by the actuator to linear motion, where the linear motion causes a force that is transmitted to the user. In another embodiment, the actuator outputs a force, and a mechanism coupling the actuator to the device housing uses the force to move the actuator with respect to the device housing. The actuator acts as an inertial mass when in motion to provide an inertial force that can be transmitted to the user. The mechanism can be a flexure including at least one flex joint or a mechanism with bearings.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Force reflecting haptic interface
ActiveUS20050093821A1Input/output for user-computer interactionDigital data processing detailsDocking stationControl system
A multi-function force reflecting haptic interface including various sub-assemblies is disclosed. The sub-assemblies include multiple function user interfaces, a user interface docking station for setting the interface to a home position, temperature monitoring and control systems, and various kinematic cable drive systems.
Owner:3D SYST INC
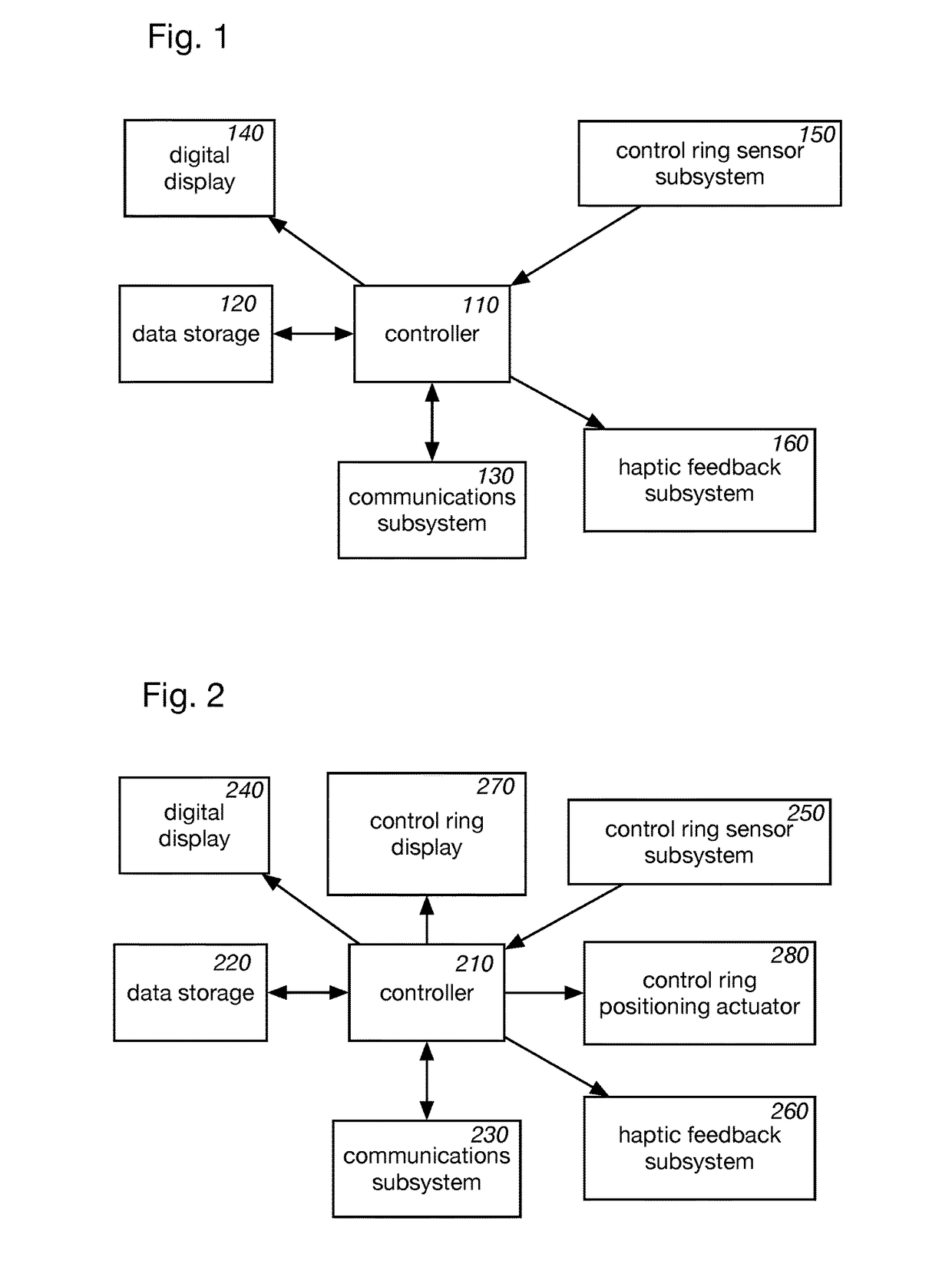
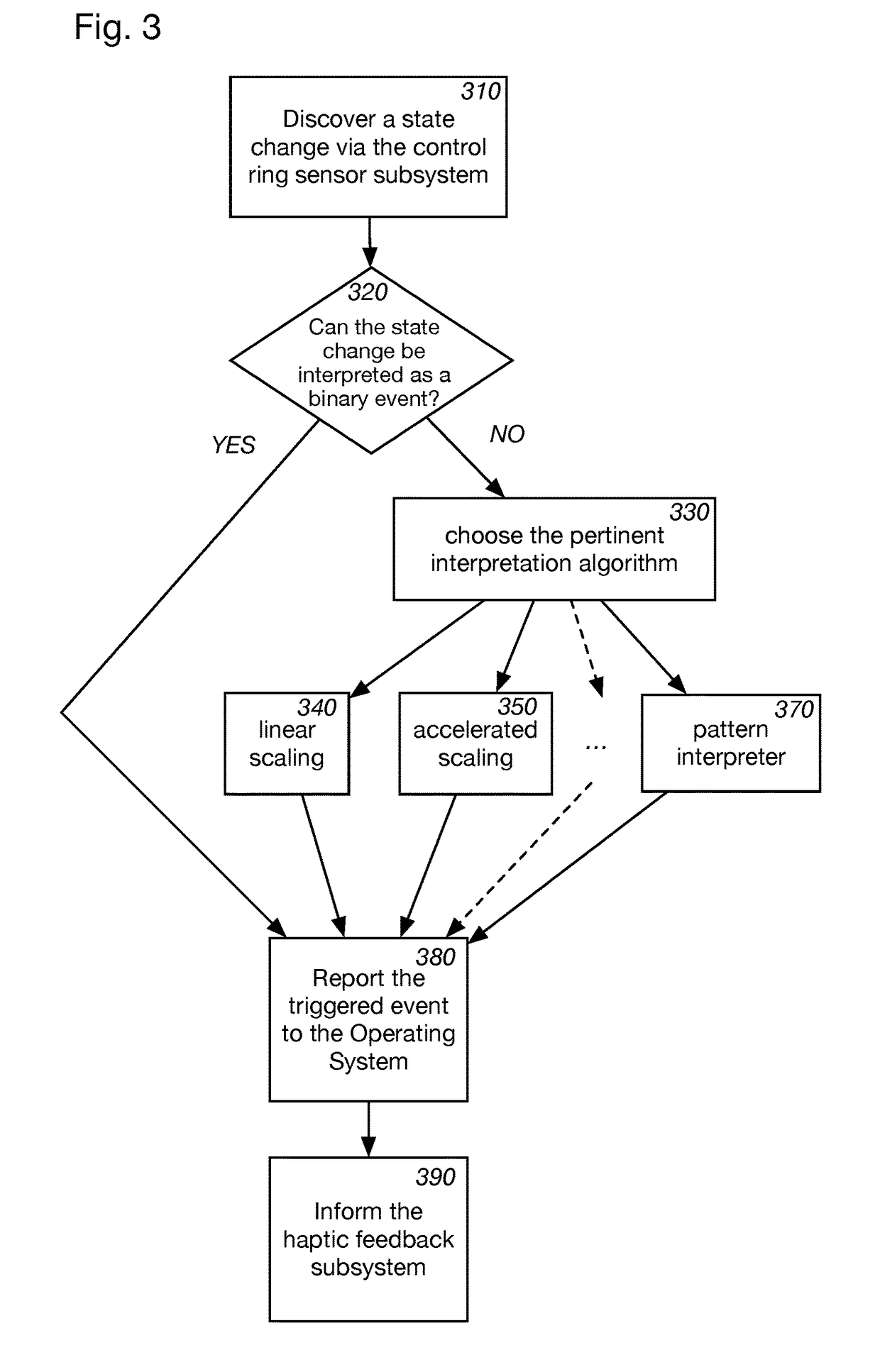
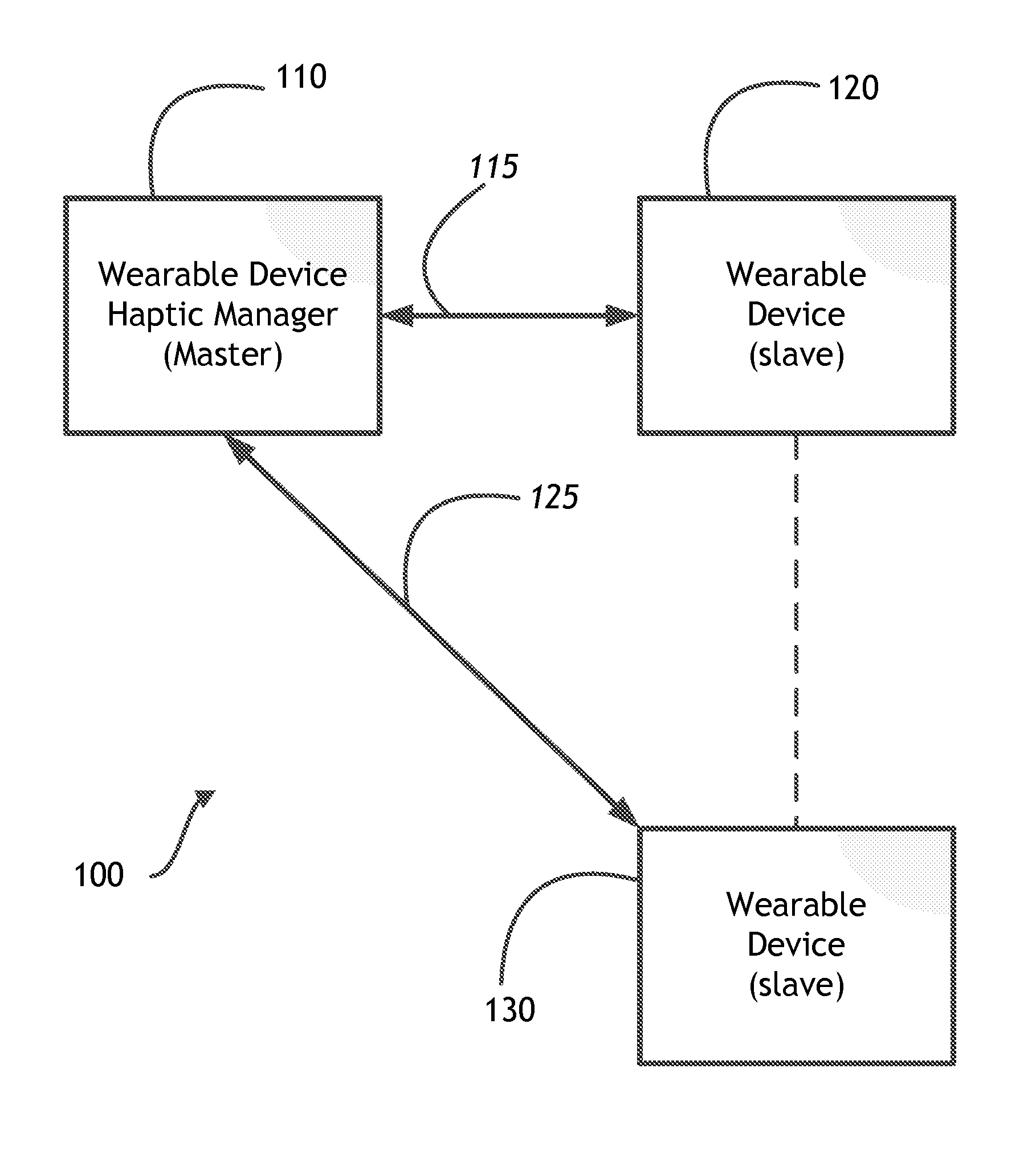
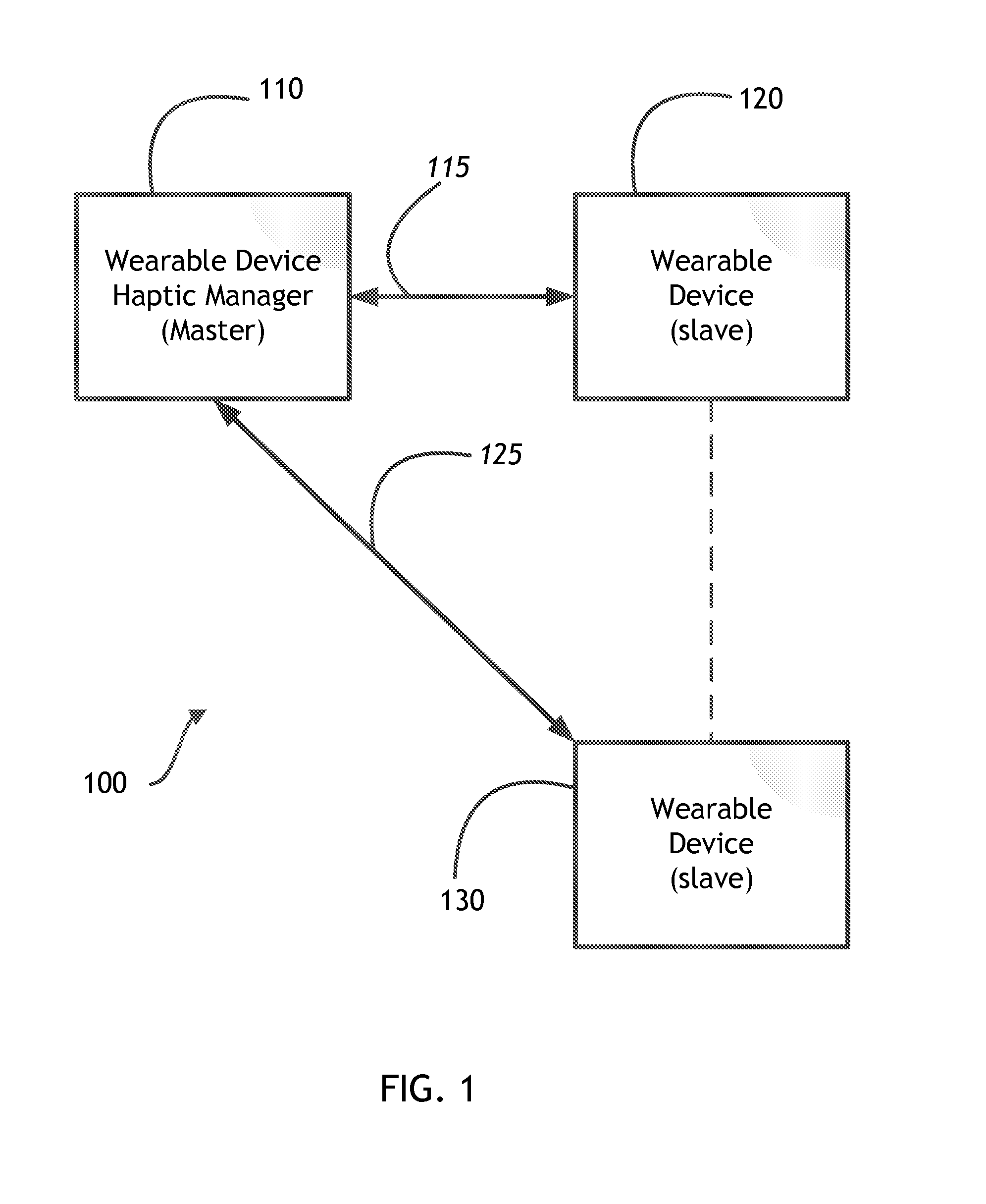
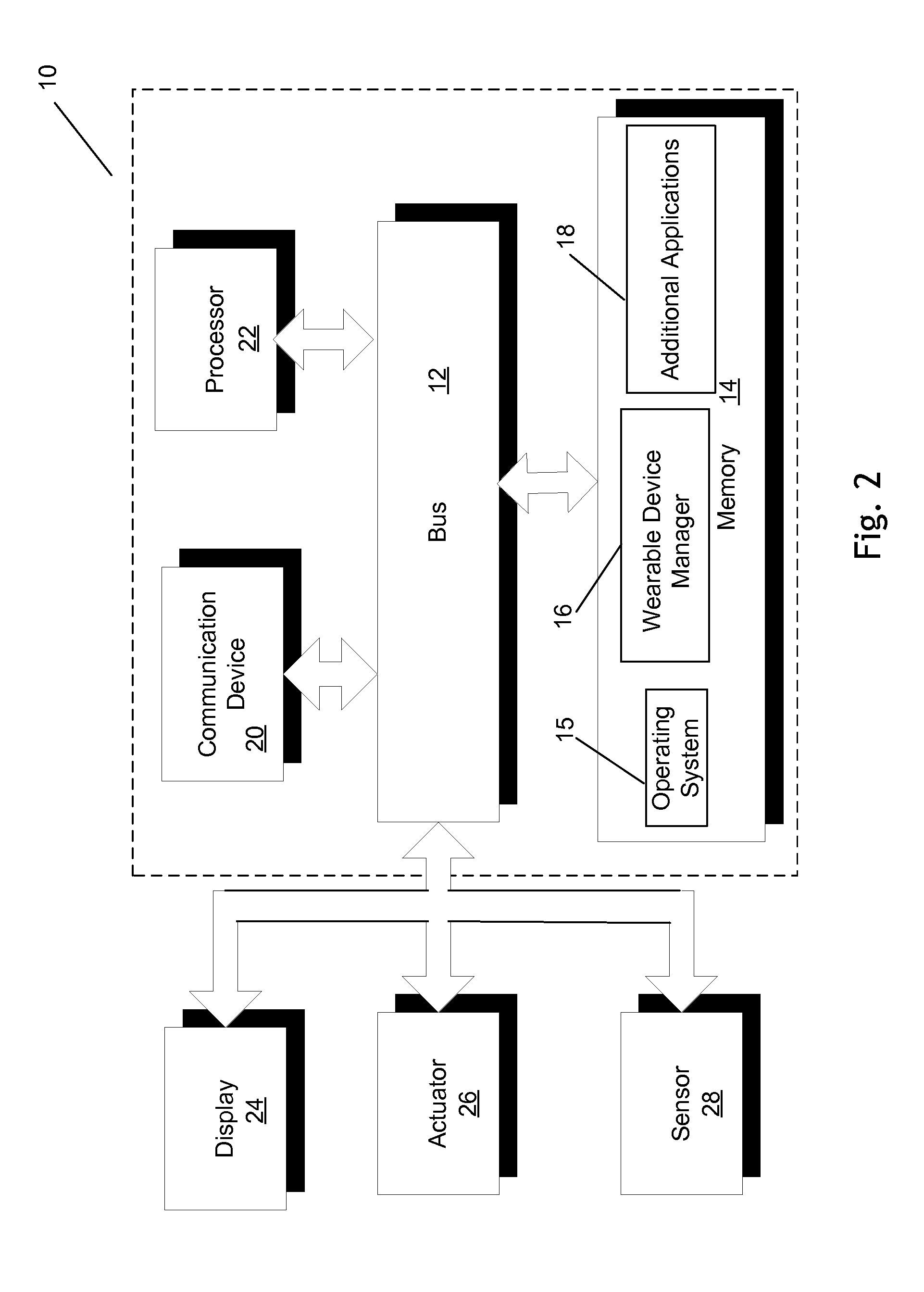
Wearable device manager
A system for managing a plurality of wearable devices on a user receives information to be conveyed using haptic effects and determines an intent of the information. The system then determines, for each of the plurality of wearable haptic devices, a location of the wearable haptic device on the user and a haptic capability. The system then maps the information as a haptic effect to one or more of the wearable haptic devices based at least on the determined locations on the user and the haptic capabilities.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
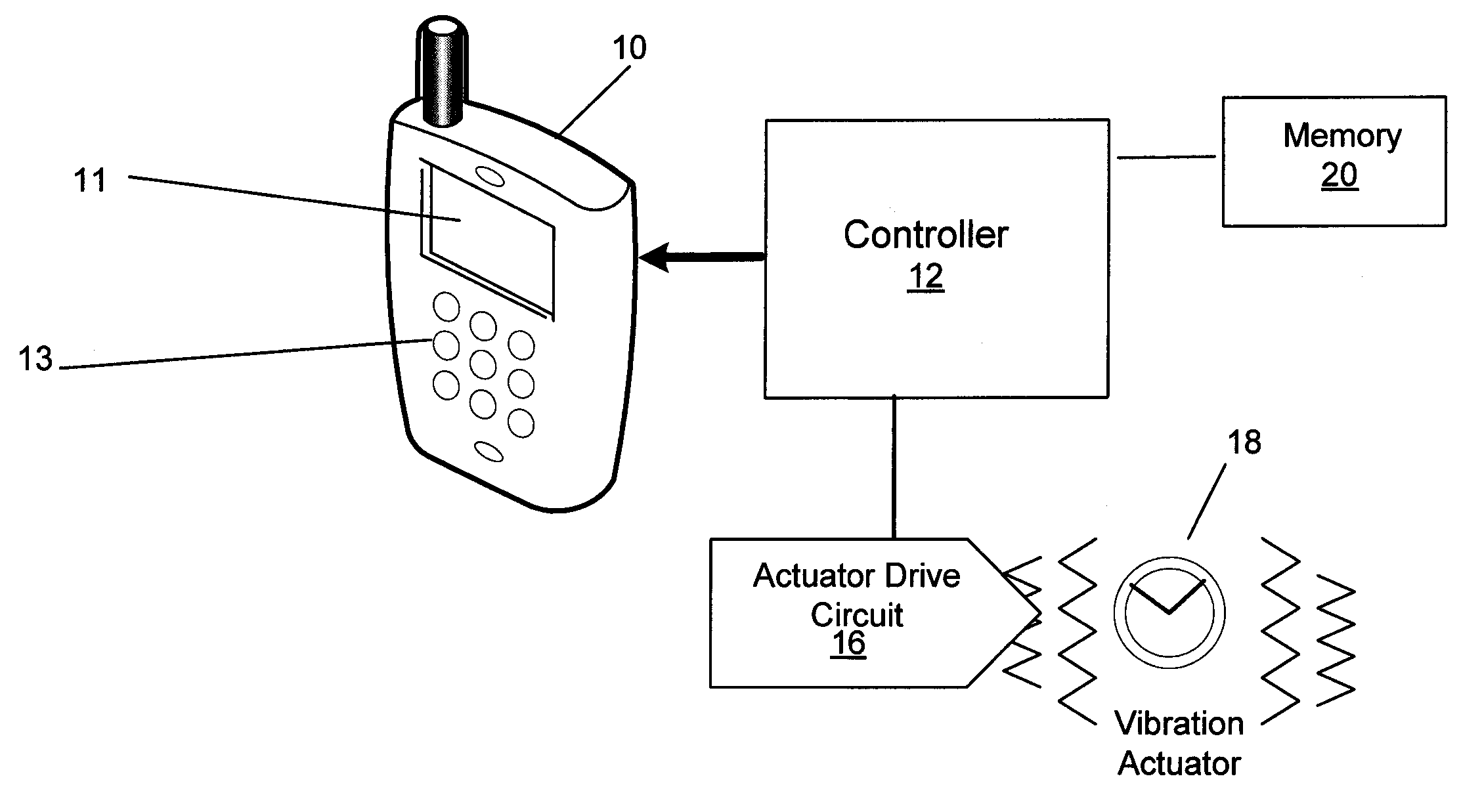
Haptic Feedback System with Stored Effects
ActiveUS20080198139A1Processing power requiredPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCurrent supply arrangementsEngineeringHaptic sensation
A haptic feedback system that includes a controller, a memory coupled to the controller, an actuator drive circuit coupled to the controller, and an actuator coupled to the actuator drive circuit. The memory stores at least one haptic effect that is executed by the controller in order to create a haptic effect.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Input device with force sensing and haptic response
ActiveUS20120274599A1Improve device performanceFacilitates force determinationInput/output processes for data processingCapacitanceEngineering
Devices and methods are provided that facilitate improved input device performance. The devices and methods utilize a first electrode disposed on a first substrate, a second electrode coupled to a first side of a piezoelectric material and a third electrode coupled to a second side of the piezoelectric material. The second electrode and the third electrode are configured to facilitate actuation of the piezoelectric material, while the first electrode and the second electrode define at least part of a variable capacitance that facilitates force determination. A spacing element is coupled to the first substrate and defines a spacing between the first electrode and the second electrode. A transmission element is coupled to the third electrode and configured such that a force biasing the transmission element causes the second electrode to deflect relative to the first electrode, thus changing the variable capacitance.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com