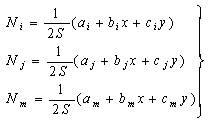Patents
Literature
644 results about "Finite element grid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
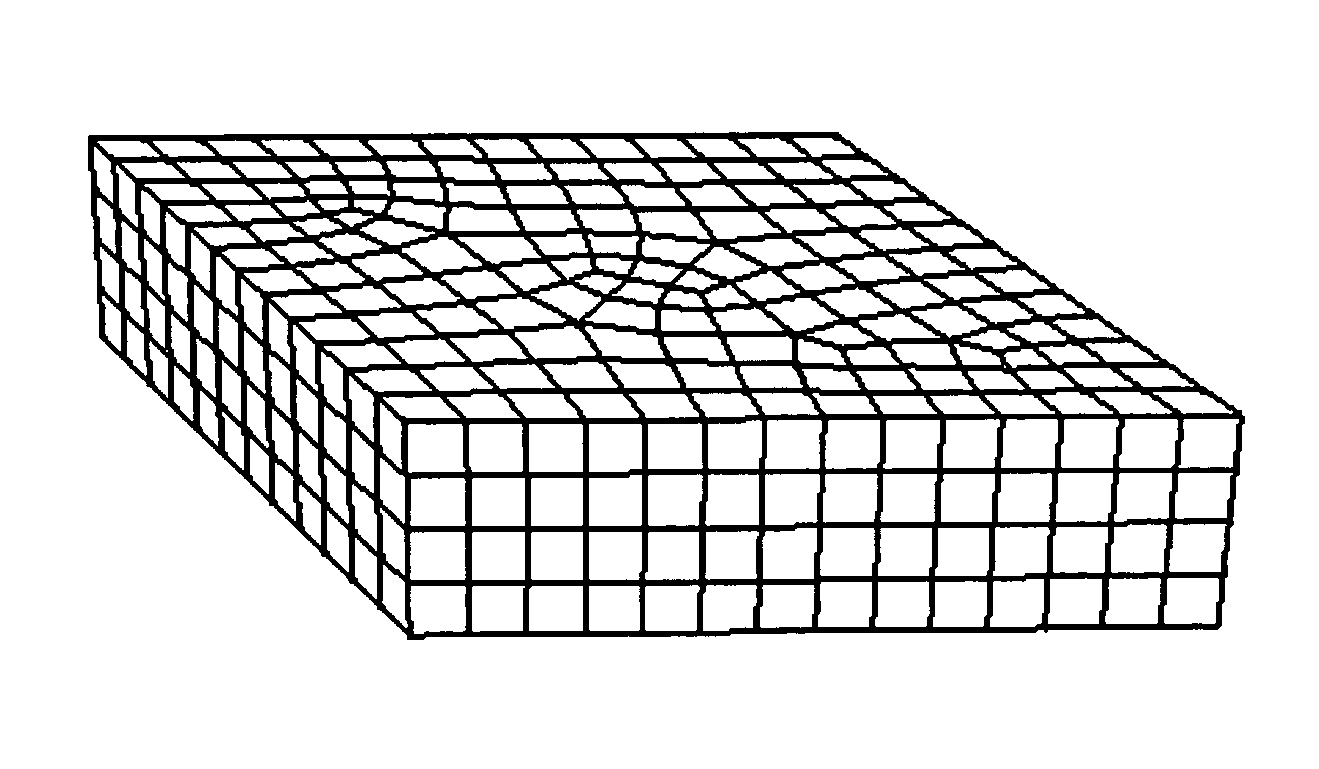
Three-dimensional entity model surface finite element mesh automatic generation method
ActiveCN102306396AQuality improvementGuaranteed convergenceSpecial data processing applications3D modellingNODALDensity distribution
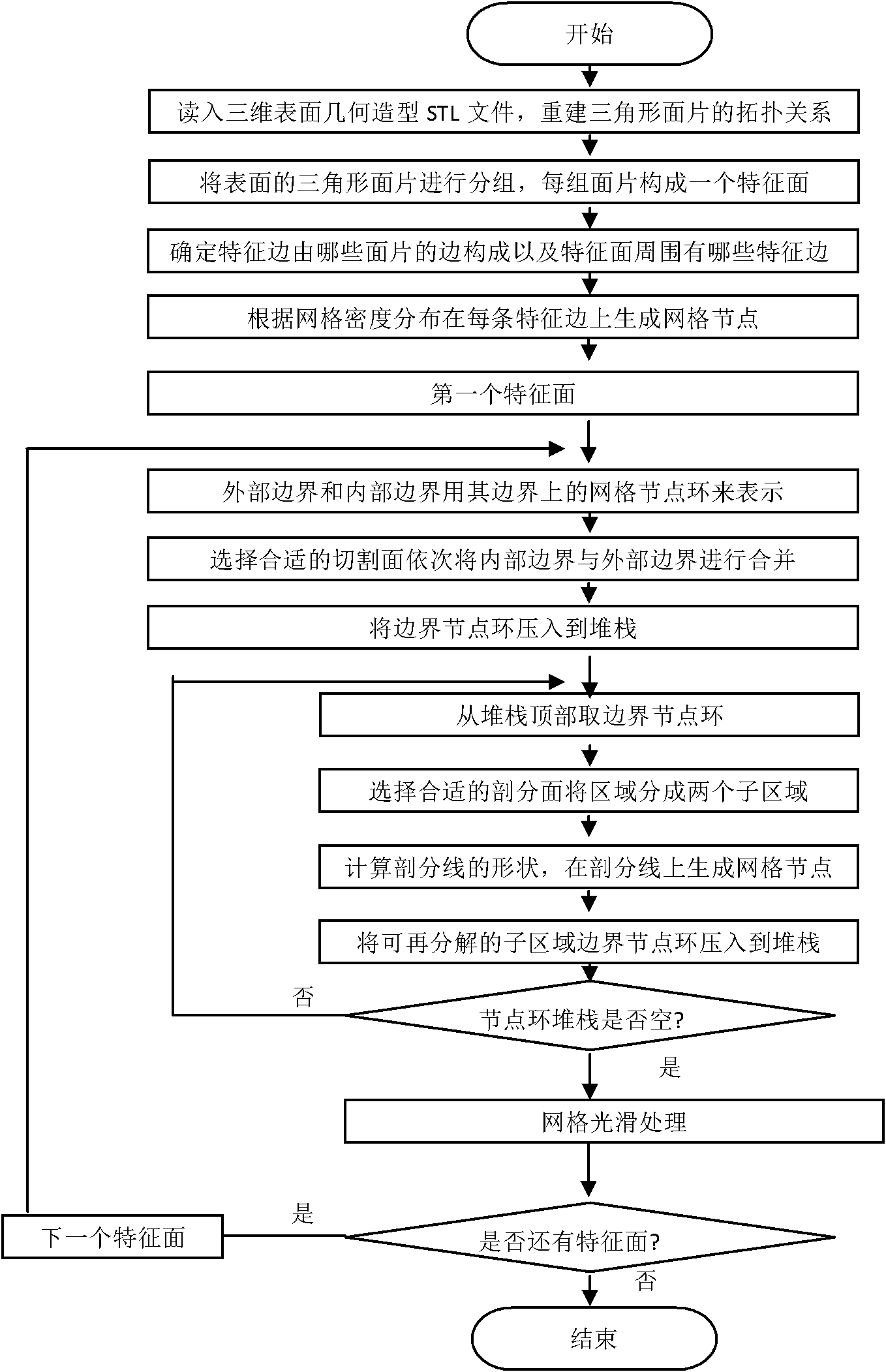
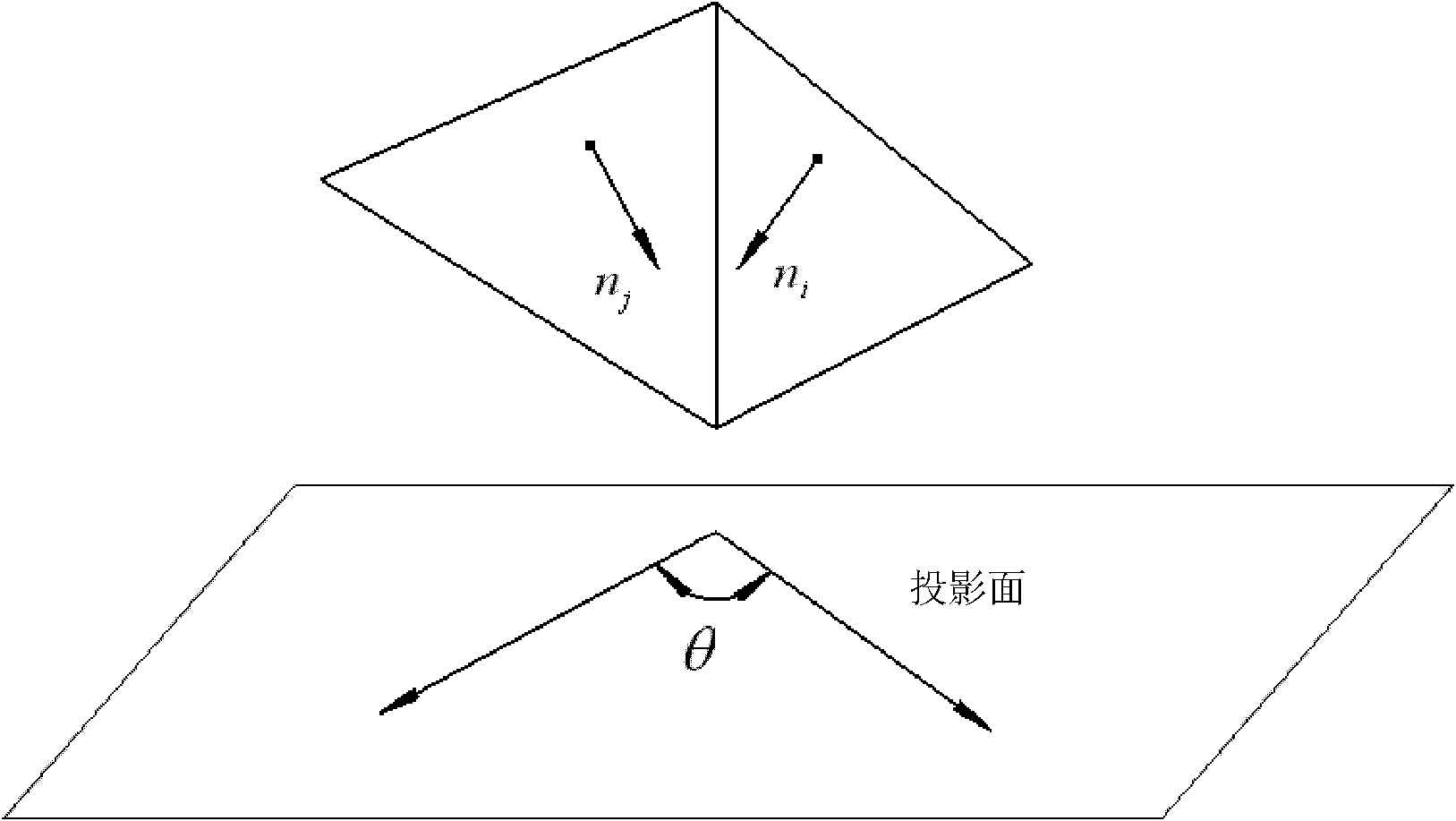
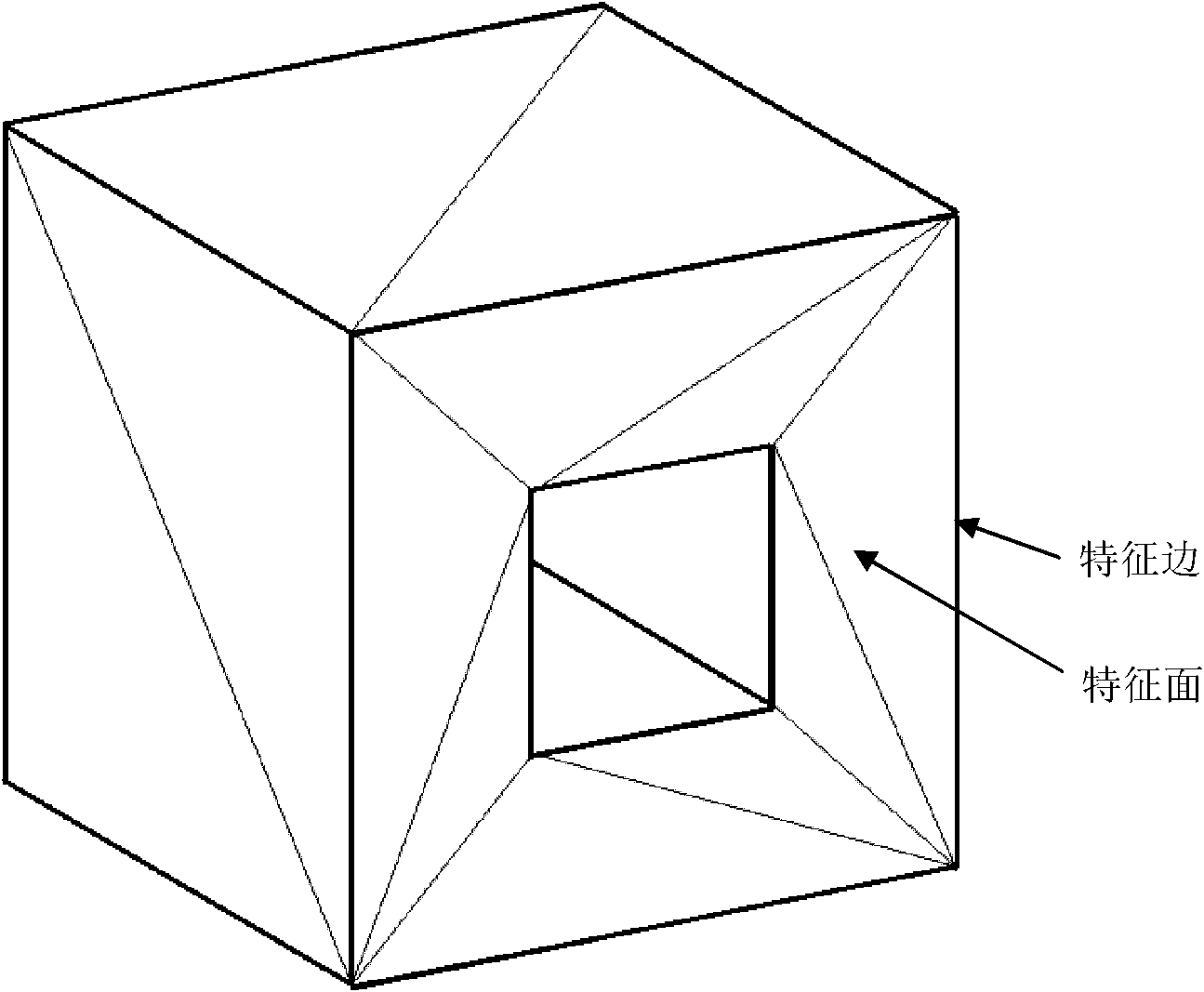
The invention relates to a three-dimensional entity model surface finite element mesh automatic generation method which has the characteristics of good dimension control performance of mesh quality, density and dimension, good convergence in a dividing process, high calculation efficiency, stability and reliability. The method comprises the following steps: (1.1) establishing a three-dimensional geometrical model, reading an STL neutral file of a model surface, and reconstructing a topology relation of triangle patches; (1.2) according to a relation between a triangle patch and an adjacent patch, grouping surface triangle patches, wherein each group of triangle patches is a characteristic face; (1.3) determining boundaries of each characteristic face, and determining characteristic edges on each characteristic face boundary; (1.4) according to mesh density distribution, generating mesh nodes on each characteristic edge, and expressing boundaries of the characteristic face with mesh node rings on the boundaries; (1.5) selecting a cut surface and an optimal dissection surface, and generating mesh nodes on cut lines and dissection lines; (1.6) generating a surface mesh on each characteristic face, and carrying out smoothing process.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Subsurface flow simulating and predictive analysis method
InactiveCN102156779AFull disclosureAccurately revealSpecial data processing applications3D modellingDesign softwareMesh grid
The invention relates to a subsurface flow simulating and predictive analysis method which comprises the following steps of: dynamically observing and collecting groundwater date of a mining area, integrating the groundwater data into a graphic workstation by utilizing a data engine, automatically establishing a finite element mesh model of the dynamic water level of each water layer, and determining parameter partitions and corresponding parameter values so as to realize the dynamic analog of water level of the water layer and the simulation of groundwater migration; and carrying out the simulation of a groundwater seepage field and the dynamic and real-time simulation of aquifer in designed software and hardware environments, and carrying out interactive analysis, prediction and evaluation on various models in the VR environment and the WEB environment by using tools such as interactive operation, information inquiry, and the like. The method can provide the scientific basis of reasonably developing and utilizing water resources for the future development and the evolution tendency of groundwater resources, and achieves low overall cost, easy popularization and use as well as flexible and reliable operation.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF PETROCHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY +1
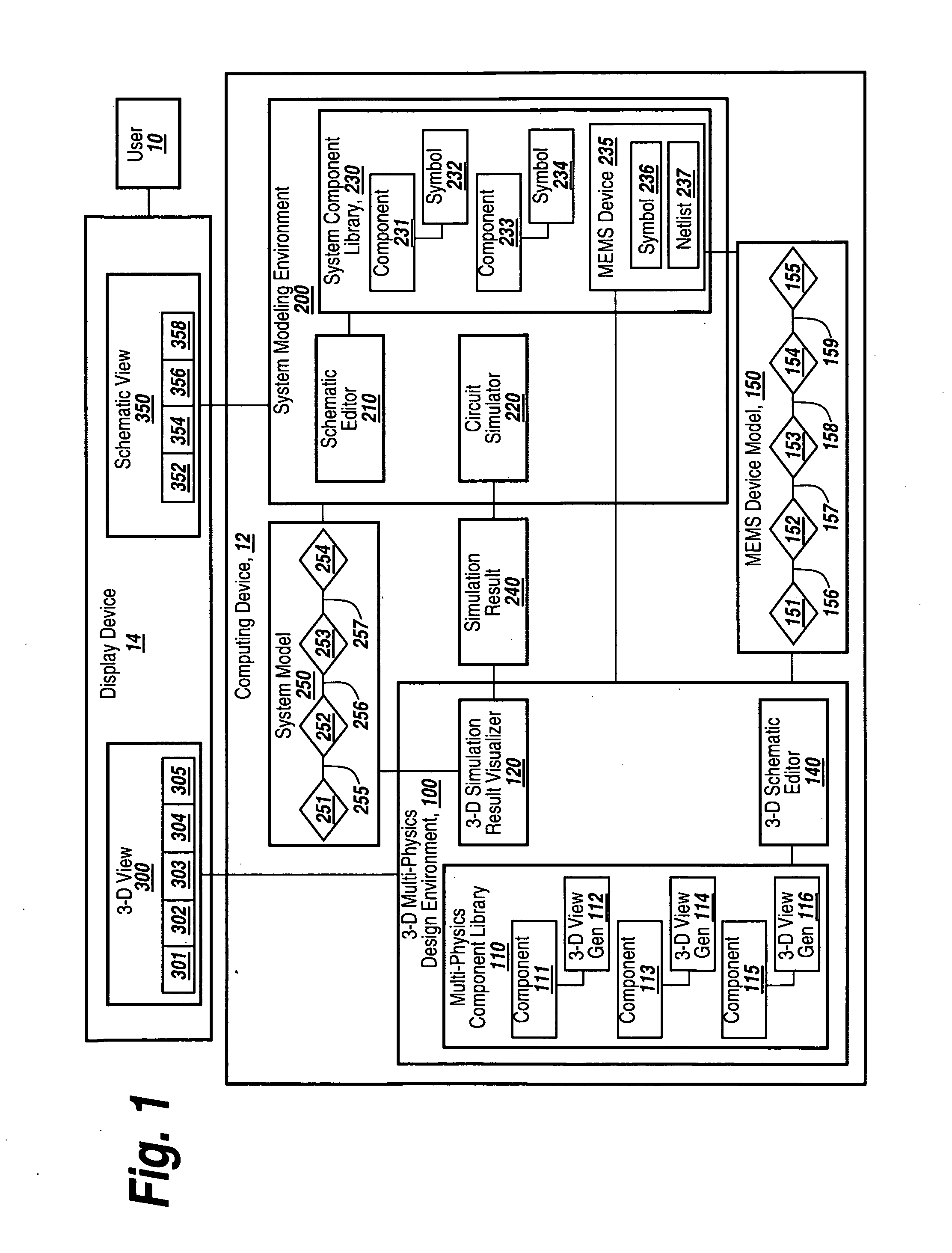
System and method for three-dimensional schematic capture and result visualization of multi-physics system models
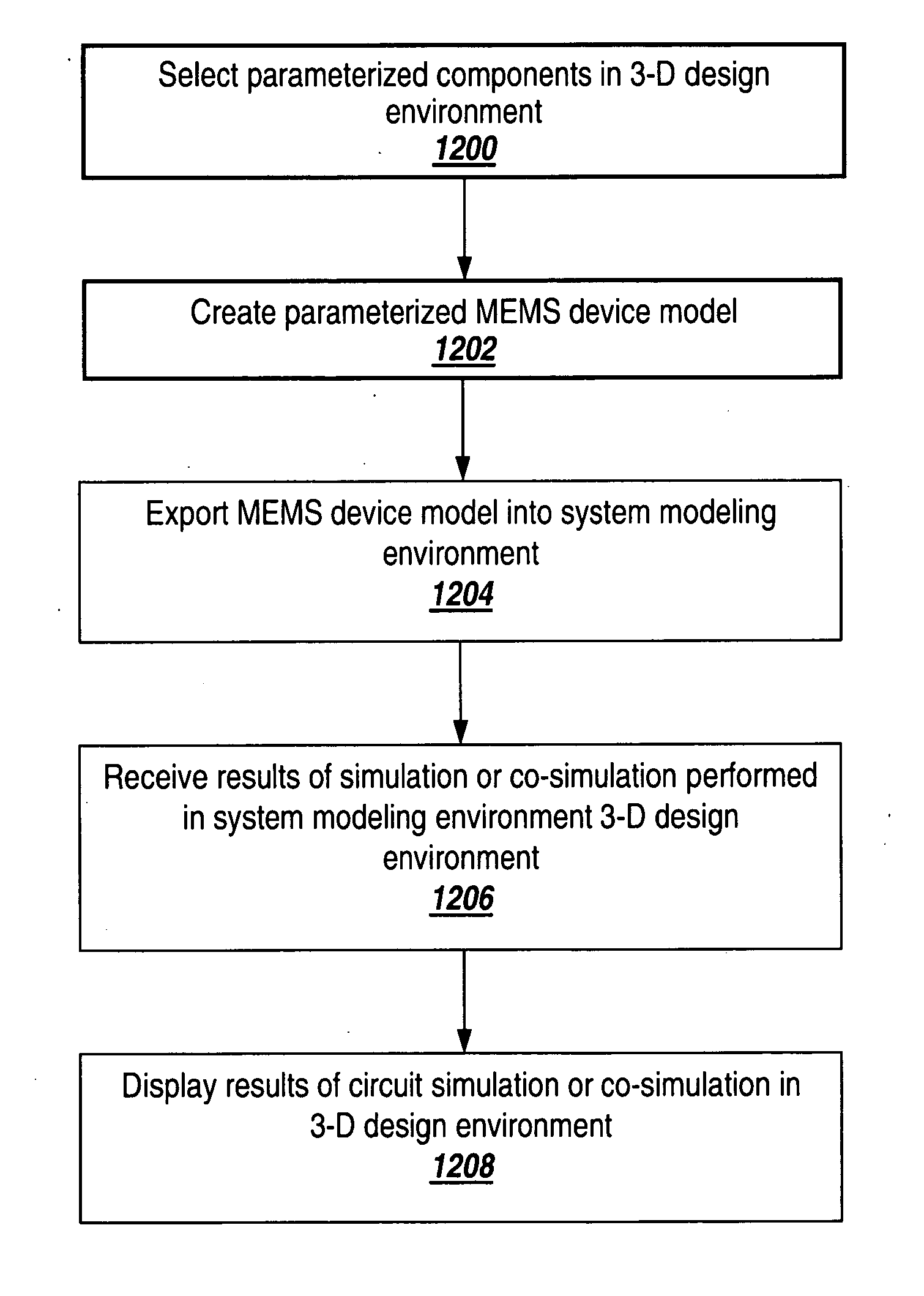
A 3-D multi-physics design environment (“3-D design environment”) for designing and simulating multi-physics devices such as MEMS devices is discussed. The 3-D design environment is programmatically integrated with a system modeling environment that is suitable for system-level design and simulation of analog-signal ICs, mixed-signal ICs and multi-physics systems. A parameterized MEMS device model is created in a 3-D graphical view in the 3-D design environment using parameterized model components that are each associated with an underlying behavioral model. After the MEMS device model is completed, it may be exported to a system modeling environment without subjecting the model to preliminary finite element meshing.
Owner:COVENTOR
Quick feedback analyzing system in tunnel constructing process
InactiveCN102155231AOvercoming the blindness of pre-designDynamic information construction improvementMining devicesTunnelsEngineeringAlgorithm optimization
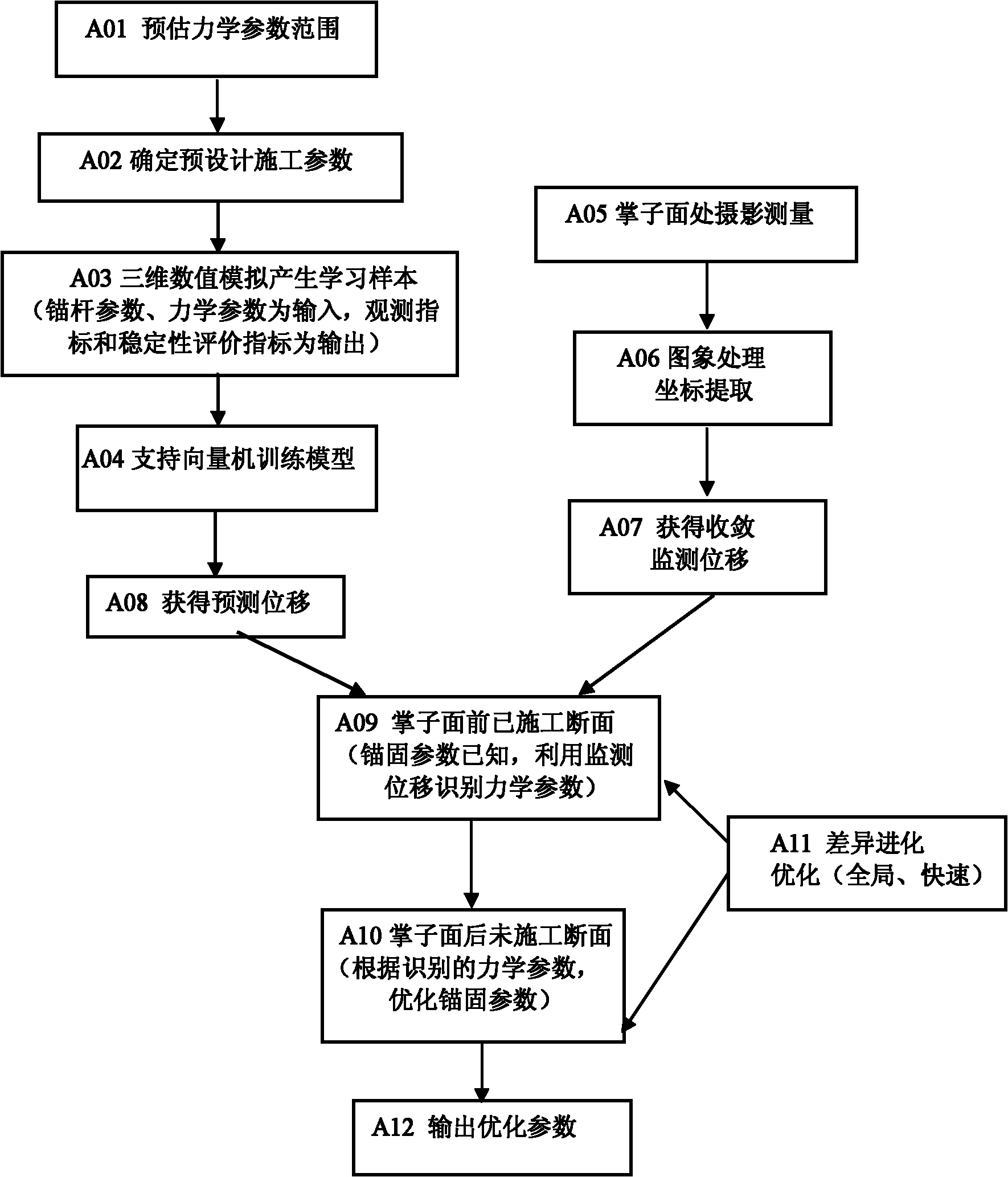
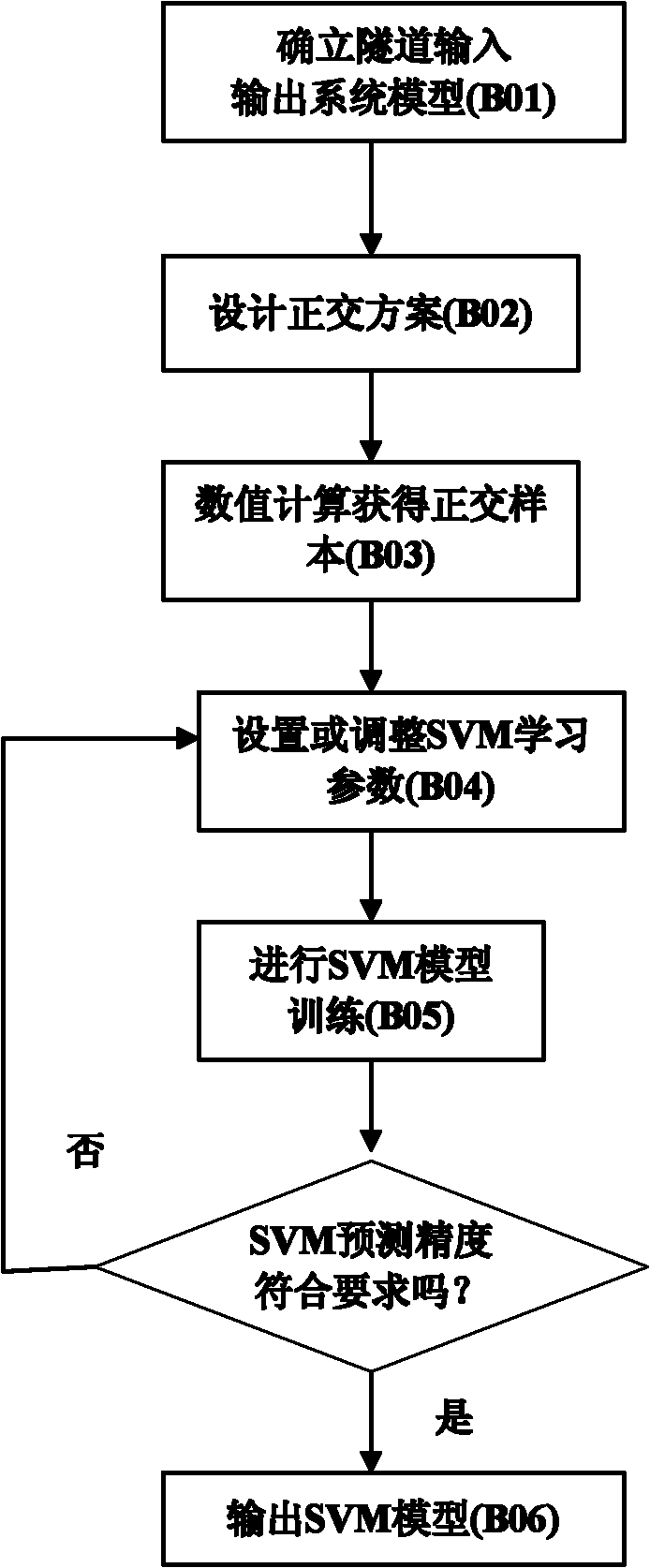
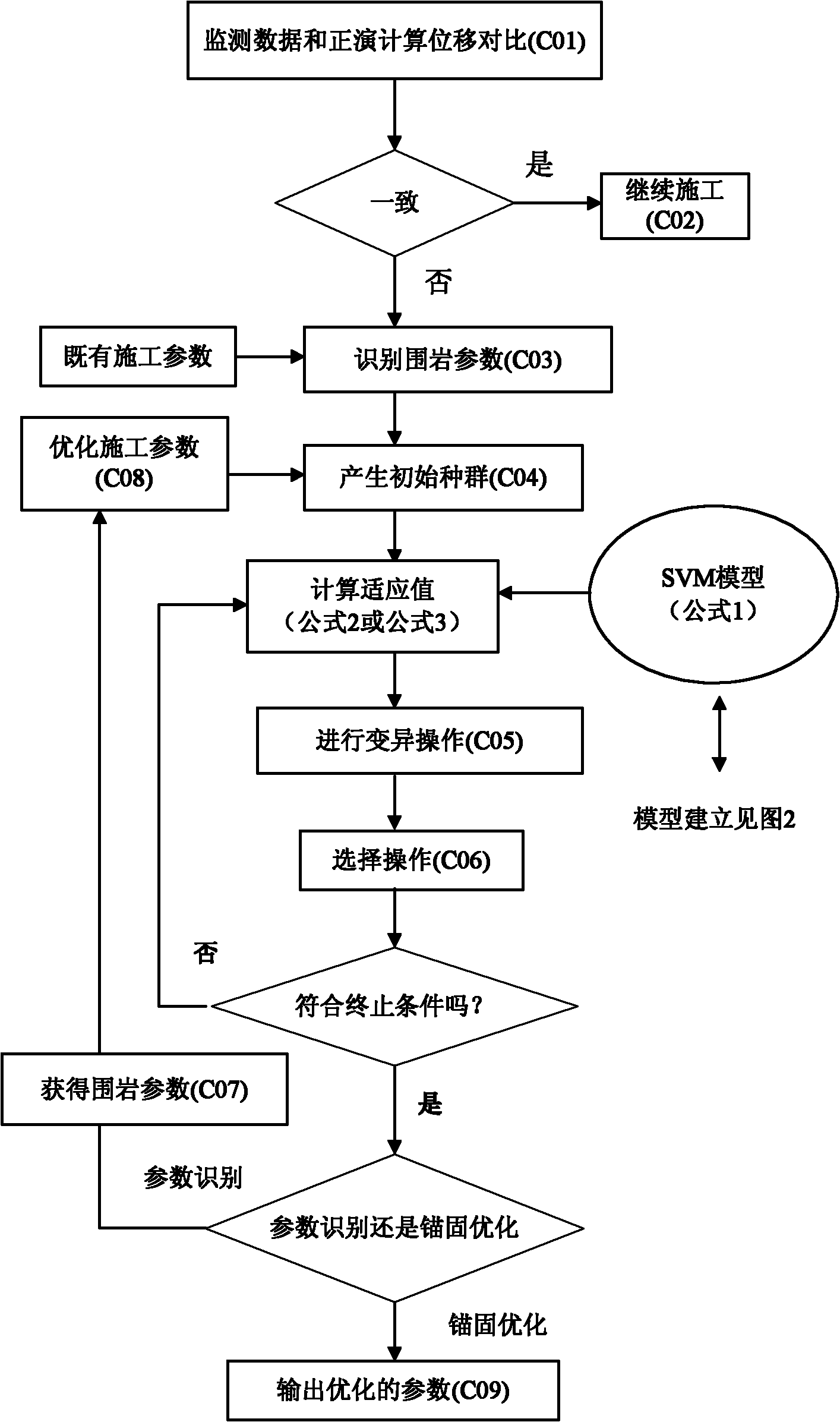
The invention discloses a quick feedback analyzing system in a tunnel constructing process. The system adopts a scheme: understanding currently adopted designing construction parameters; establishing a tunnel excavation three-dimensional finite element numerical grid calculation model; acquiring surrounding rock layering and convergent displacement monitoring information after a tunnel is excavated; establishing a non-linear support vector machine model; fixing an anchoring parameter according to the actual construction parameter, and optimally identifying rock mechanic parameters by adoptinga differential optimization algorithm; optimizing the construction parameter of an anchoring scheme by adopting a differential evolution algorithm; and optimizing the rock mechanic parameters by calling the differential evolution and optimization algorithms to further solve the construction parameter of the anchoring scheme, and outputting the construction parameter of the optimized anchoring scheme as a construction scheme through a computer display screen to guide the constructors to construct. The quick feedback analyzing system ensures that the monitoring information is used for optimizing the anchoring parameter while being used for identifying the surrounding rock parameters, so that the dynamic information construction is improved to a level of quantitative analysis.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
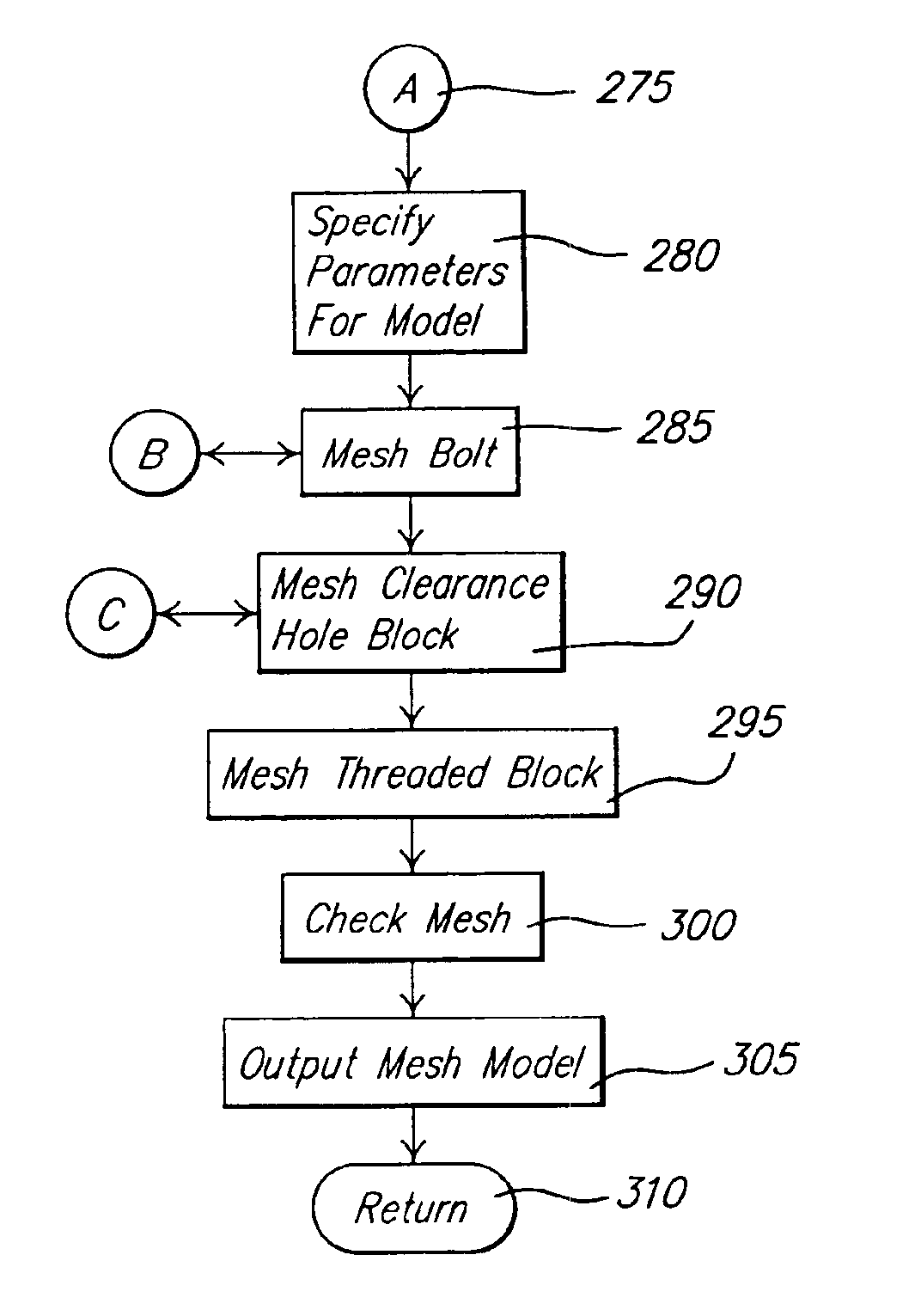
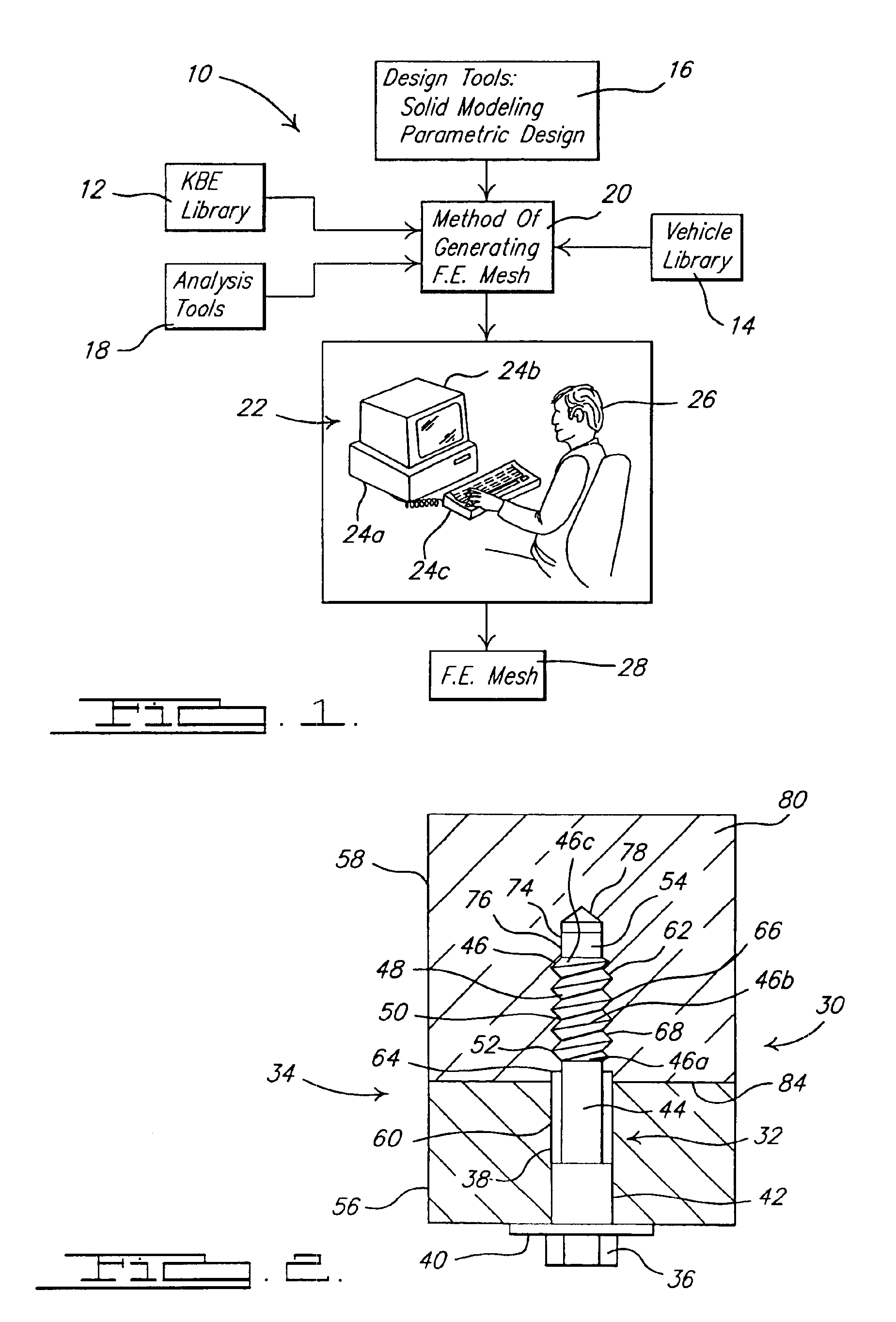
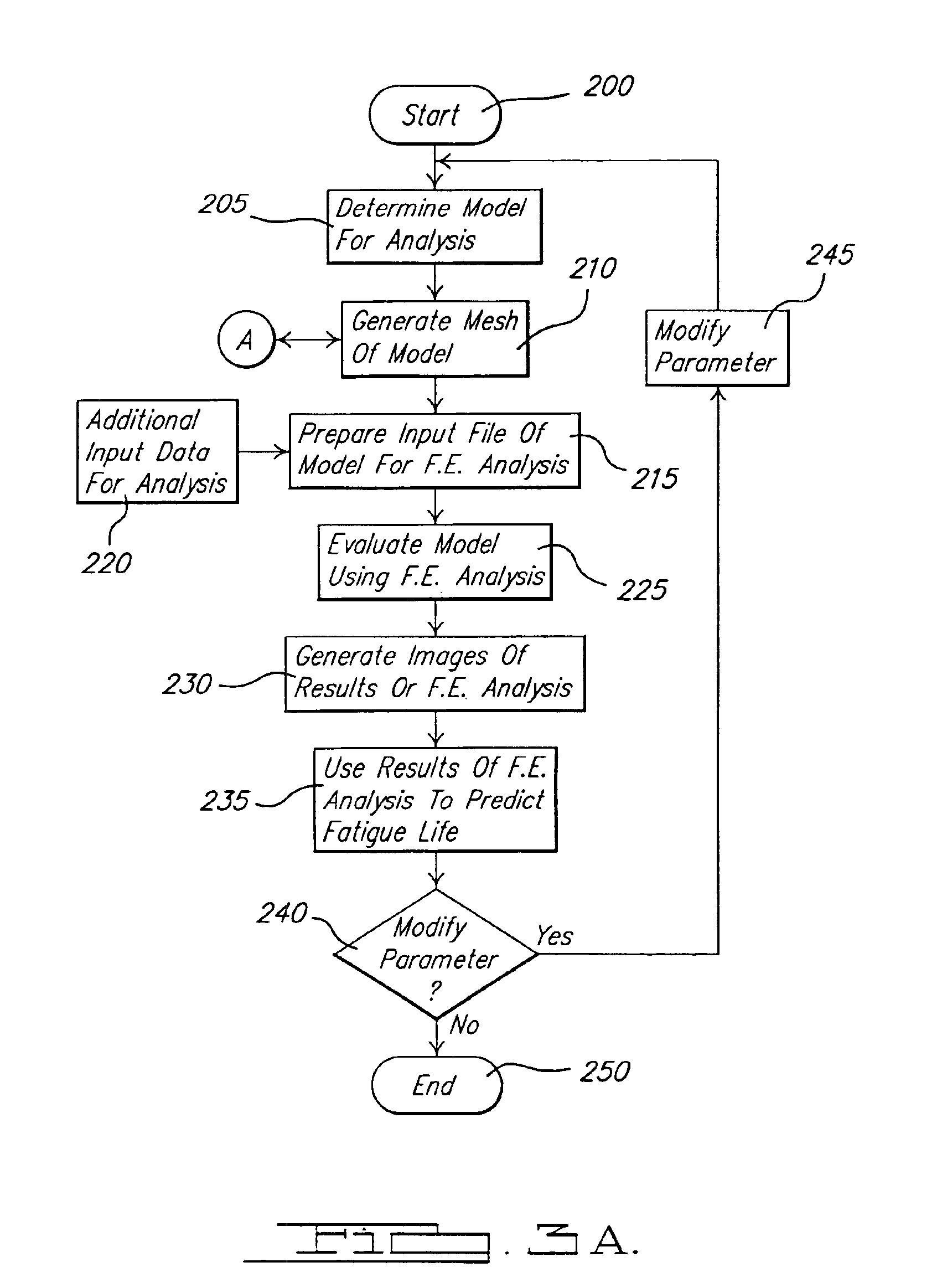
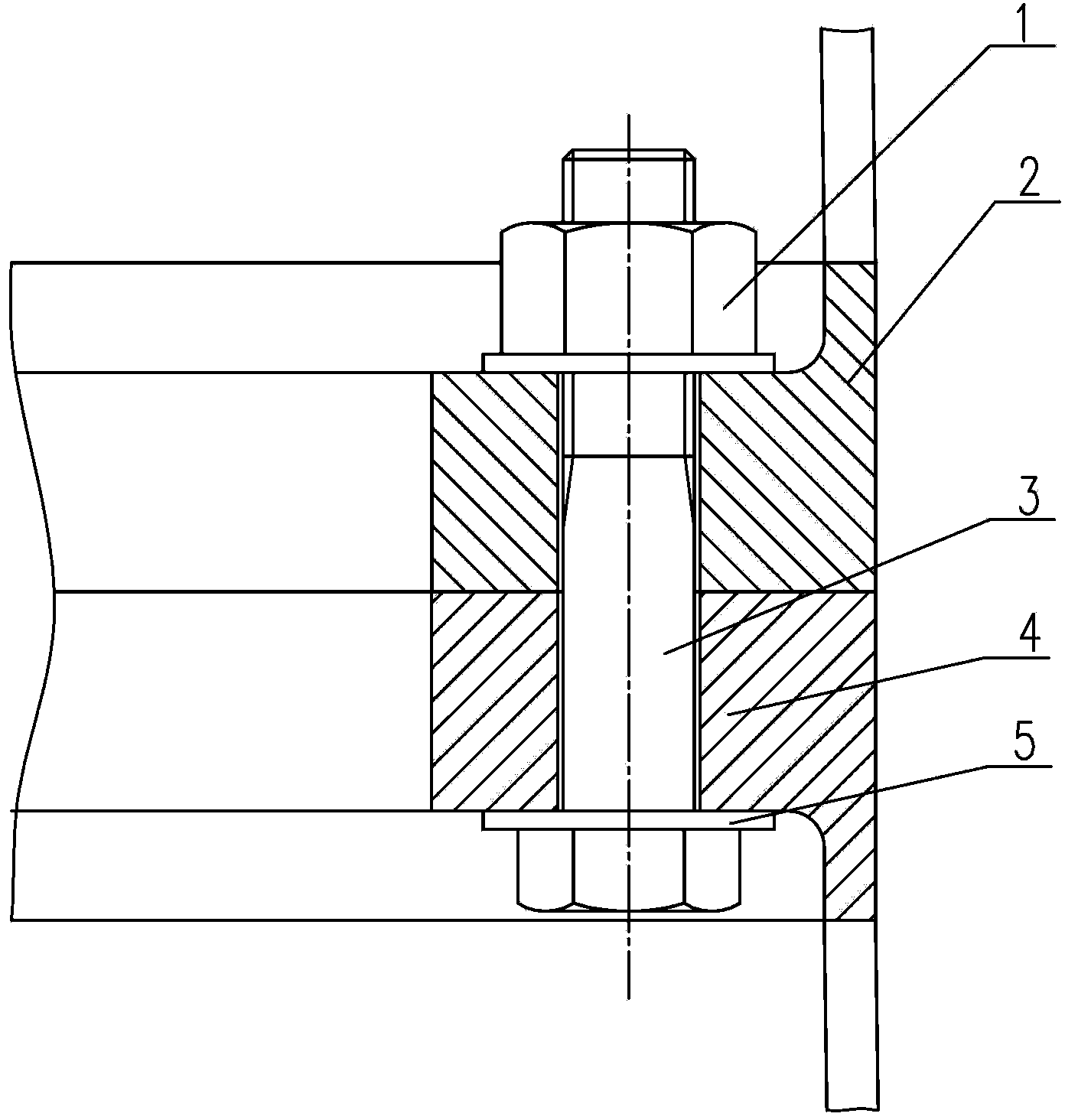
System and method of generating a finite element mesh for a threaded fastener and joining structure assembly
InactiveUS6904395B1Quality improvementShorten design timeGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationElement analysisComputerized system
A system and method of generating a finite element mesh for a threaded fastener and joining structure assembly includes a computer system for generating a mesh model of the threaded fastener and joining structure assembly by creating nodes and elements for each non-threaded portion of the threaded fastener and joining structure assembly using cylindrical coordinates and creating nodes and elements for each threaded portion of the threaded fastener and joining structure assembly using helical coordinates. The system and method also includes a user evaluating the mesh model of the threaded fastener and joining structure assembly using finite element analysis and evaluating a result of the finite element analysis using a visualization software program and a computer system. The system and method further includes a user predicting a stress of the threaded fastener and joining structure assembly from the evaluation of the result of the finite element analysis.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
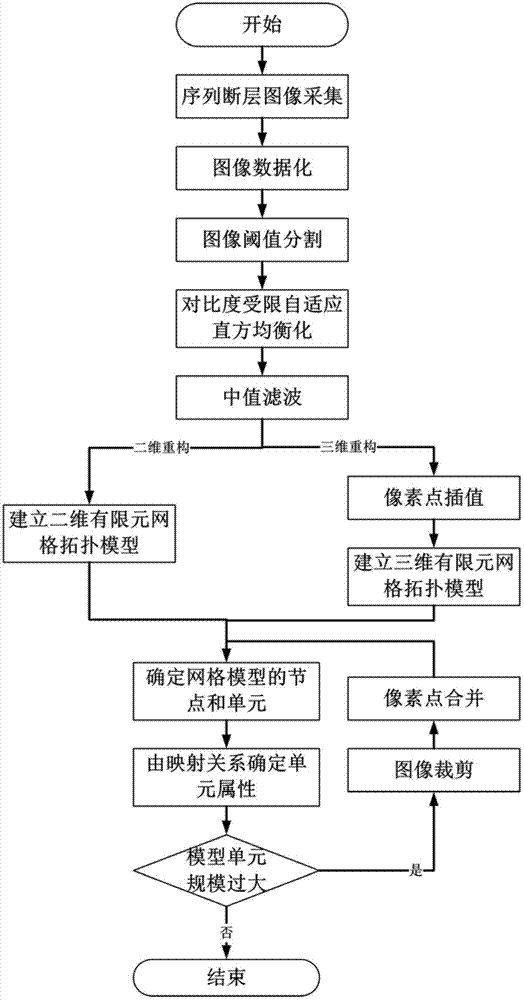
Method for accurately reconstructing dissimilar material microcosmic finite element grid model on basis of CT (computed tomography) images
ActiveCN102768699AReduce the impactHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsComputed tomographyElement analysis
The invention provides a method for accurately reconstructing a microcosmic finite element grid model of a dissimilar material on the basis of CT (computed tomography) images. According to the method, sequence CT images are acquired through industrial CT, and micro-structural information in the CT images is mapped onto the reconstructed finite element grid model on basis of digitization and threshold segmentation, so that any detailed structural information in the dissimilar material can be represented in the reconstructed model. The method improves the reconstruction accuracy by means of contrast-limited adaptive histogram equalization, median filtering and pixel interpolation, and improves the reconstruction efficiency through image cut and pixel combination. With the method, rectangular (two-dimensional) and cuboid (three-dimensional) unit grid models with higher finite element analysis accuracy are directly reconstructed, error accumulation during reconstruction, grid partition and other links of the existing geometric reconstruction method is avoided, and reconstruction accuracy and efficiency are improved. The method can be widely applied to fields such as performance prediction and optimization design of dissimilar materials.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for solving finite element models using time slabbing
InactiveUS7006951B2Reduce memory usageGeometric CADComputation using non-denominational number representationElement modelEngineering
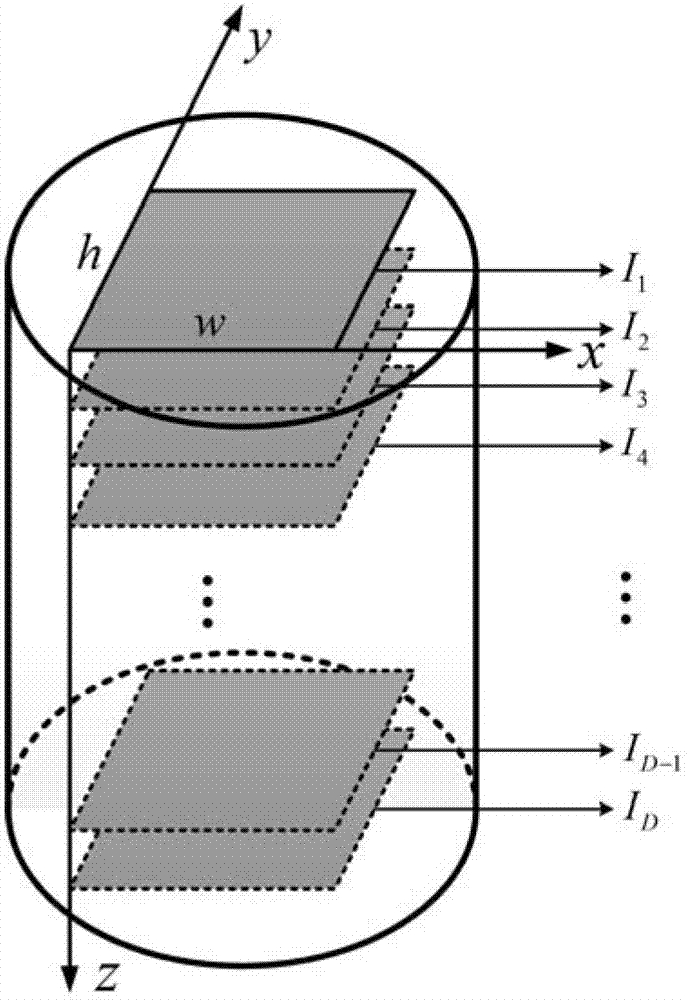
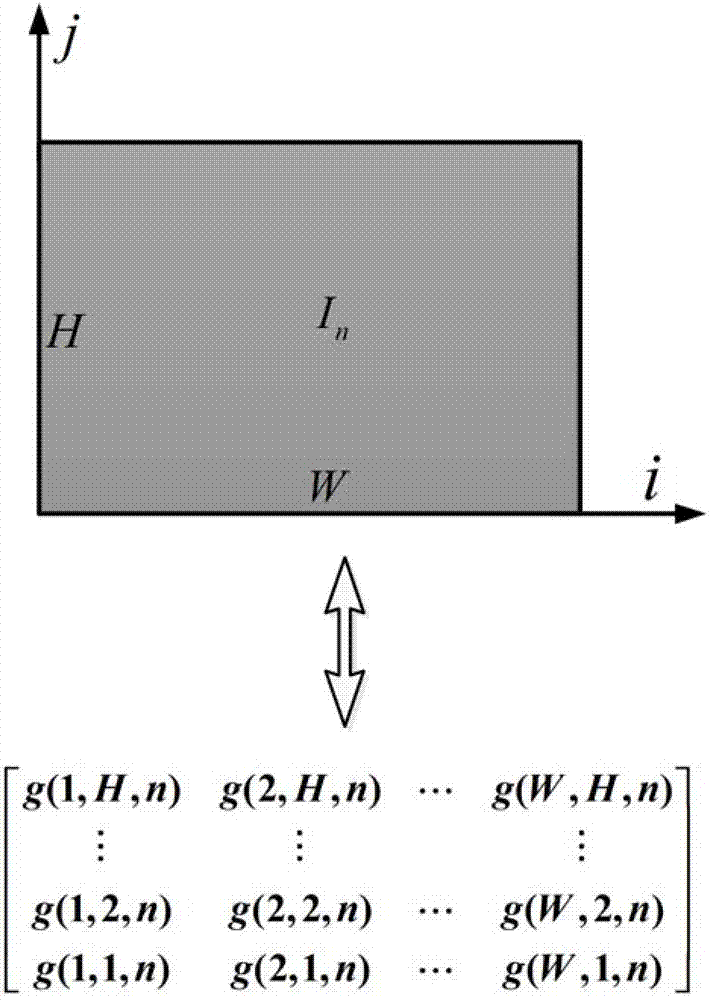
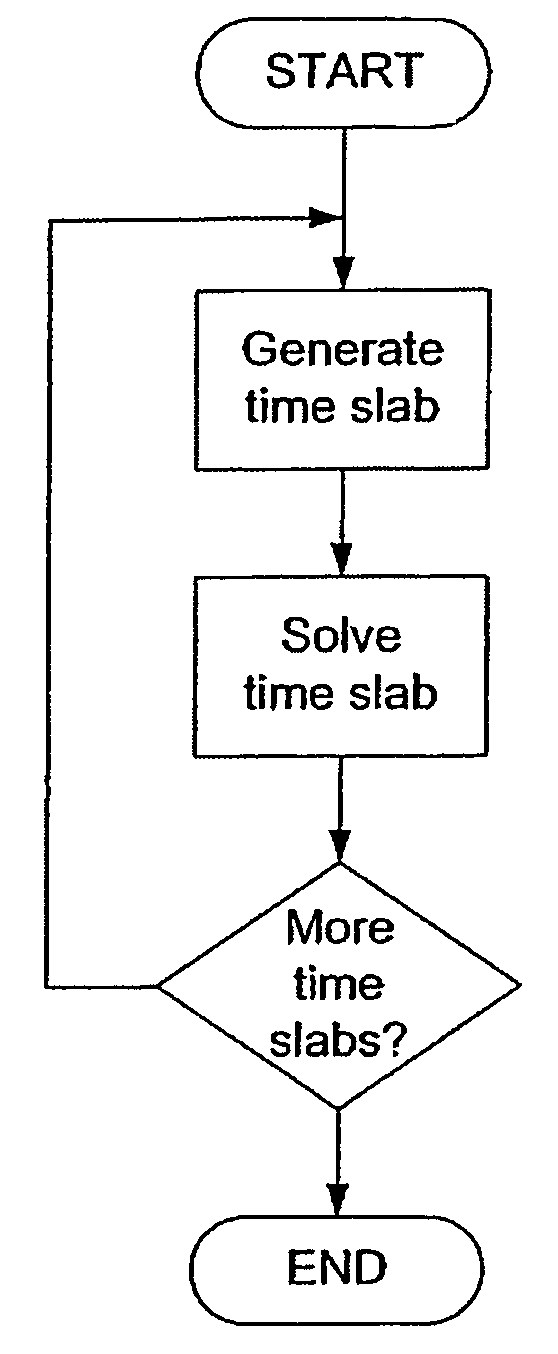
A method for solving finite element problems in n+1 dimensions by iteratively extruding an n-dimensional finite element mesh in an n+1th dimension to form “slabs” which can be more easily solved within the entire n+1-dimensional problem. In a preferred embodiment, a three-dimensional unstructured finite element mesh representing a physical system is extruded in the time dimension. The four-dimensional prisms formed by the extrusion are divided into simplices, forming the four-dimensional finite element mesh of an individual time slab. Time slabs corresponding to a series of time intervals are sequentially generated and solved. In a preferred embodiment, only a few time slabs are stored in working memory at a time so that a reduced amount of memory (in comparison to conventional methods of solving comparable problems) is required.
Owner:LANDMARK GRAPHICS CORP
Method and system for solving finite element models using multi-phase physics
InactiveUS7027964B2Satisfactory propertyGeometric CADComputation using non-denominational number representationElement modelWeight coefficient
Systems and methods for solving finite element models, wherein the matrix that governs the solution is modified by adjusting the weighting coefficients of the matrix so that the elements which lie on the diagonal of the matrix are non-negative and the elements which are off the diagonal are non-positive. In one embodiment, a system is discretized on a finite element mesh with the contribution of each node to the discretization being weighted based upon the direction of fluid flow across each element. The nodes which are upstream from the other nodes of the respective elements are weighted more heavily to cause the resulting matrix to be substantially diagonal. This matrix is solved using traditional techniques.
Owner:LANDMARK GRAPHICS CORP
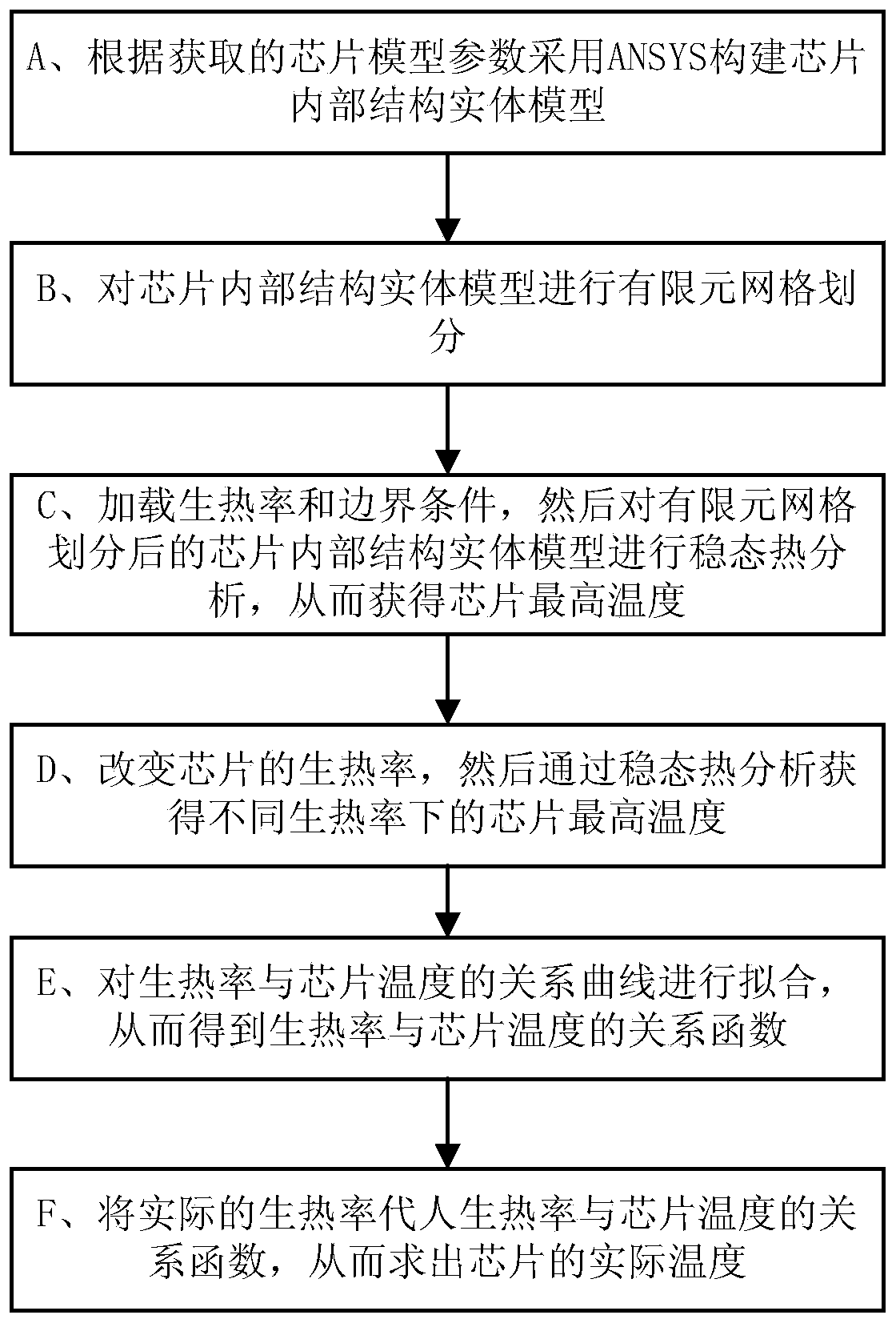
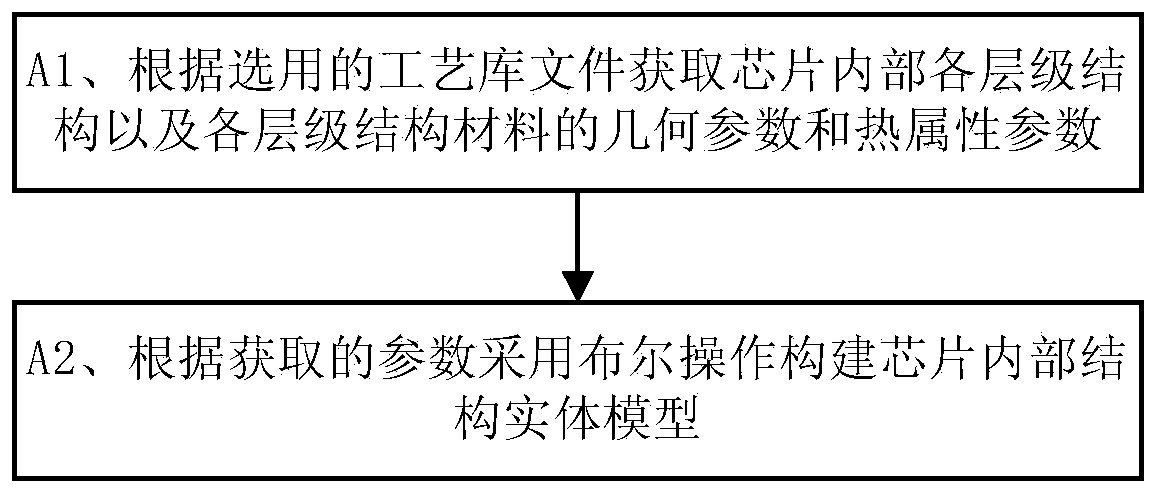
Chip temperature predicating method based on ANSYS finite element heat analysis
ActiveCN104182568ALow costEasy to operateSpecial data processing applicationsGeneration rateHeat analysis
The invention discloses a chip temperature predicating method based on ANSYS finite element heat analysis. The chip temperature predicating method comprise steps as follows: a chip interior structure solid model is established by ANSYS according to acquired chip model parameters; the chip interior structure solid model is subjected to finite element mesh generation; the heat generation rate and the boundary conditions are loaded, then, the chip interior structure solid model after finite element mesh generation is subjected to steady-state heat analysis, and the maximum temperature of a chip is obtained; the heat generation rate of the chip is changed, and the maximum temperature of the chip under different heat generation rates is acquired through steady-state heat analysis; the relation curve of the heat generation rate and the chip temperature is fitted, and a relation function of the heat generation rate and the chip temperature is obtained; and the actual heat generation rate is substituted into the relation function of the heat generation rate and the chip temperature, and the actual temperature of the chip is obtained. According to the method, the temperature predication is placed at the physical design stage of the chip, the cost is reduced and the operation is simple and convenient; and the method can be widely applied to the technical field of semiconductors.
Owner:SYSU CMU SHUNDE INT JOINT RES INST +1
Optimum design method of non-bearing frame structure of light vehicle
InactiveCN104112050AIncreased bending stiffnessIncrease stiffnessSpecial data processing applicationsVehicle frameData file
The invention provides an optimum design method of a non-bearing frame structure of a light vehicle. The optimum design method comprises the steps of establishing a three-dimensional geometrical model of the original frame structure of the light vehicle by use of SolidWorks software and outputting the model in the IGES (Initial Graphics Exchange Specification) data file format, thereby obtaining the IGES model of the frame structure, next, reading the IGES model of the frame structure in Hypermesh software, performing geometrical processing and dividing finite element meshes by use of the Hypermesh software, and performing topological optimization on the cross beam structure of the frame by use of the structure optimization function of the Hypermesh software without changing the structural forms of the longitudinal beam and the attached seats of the frame, thereby realizing the optimum design of the arrangement position and the structural form of the cross beam structure. The optimum design method of the non-bearing frame structure of the light vehicle is capable of improving the bending rigidity and torsional rigidity of the frame of the light vehicle and the inherent frequency of the frame structure without increasing the weight of the frame structure, thereby ensuring that the frame has relatively high overall rigidity and improving the reliability, security, operation stability and vibration property of the vehicle.
Owner:ACADEMY OF ARMORED FORCES ENG PLA
Fluorescent molecule tomography rebuilding method based on linear relationship
A tomography reconstruction method of fluorescence molecules based on a linearity relation belongs to the technical field of the image reconstruction in biomedicine. The reconstruction method is characterized in that the method sequentially comprises the following steps: 1. the outside surface outline is obtained by picture processing and numerical fitting based on the map data of a mouse used in experiment; 2. the outside surface outline is led into a finite element software package for meshing; 3. every excitation light source, and finite element grid nodes which are corresponding to corresponding fluorescence monitoring points are found; 4. aiming at one given excitation light source sk, a linear relation matrix Wsk between fluorescence intensity which is detected from surface and unknown fluorescent probe distribution is established; 5. aiming at all excitation light sources, a general linear relation matrix is generated; 6. after the linear relation is obtained, a algebra reconstruction method is used for iterating the fluorescent probe distribution which approaches the reality. The method is characterized in that non-uniform optical parameters can be handled and the precise linear relation between the fluorescence intensity which is detected from surface and the unknown fluorescent probe distribution is rapidly established.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Calculating method of ultimate strength checking of connection of flange and bolt
InactiveCN103353907AWide applicabilitySimple calculationSpecial data processing applicationsStress conditionsFinite element analysis software
The invention provides a calculating method of ultimate strength checking of connection of a flange and a bolt. The method comprises the following steps: sampling a finite element analysis software as a platform to conduct modeling, conducting mesh generation with a finite element, setting load of a connection structure and boundary conditions, and conducting calculation to obtain the stress condition of the bolt, wherein the setting of the load of the connection structure and the boundary conditions is particularly as follows: the relation between an upper flange and a lower flange is the standard friction contact relation in a model; a high strength gasket and a bolt nut, and a high strength gasket and a bolt screw cap are connected by adopting a conode way; the high strength gasket and the upper flange, and the high strength gasket and the lower flange are connected by adopting a binding contact manner; the structural node space coordinates system of a tower cylinder restraining the bottom end of the lower flange is the degree of freedom in three directions of X, Y, and Z; a node is built in the center of the upper flange, and is connected with the top end of a tower cylinder model by multipoint restriction of a beam element, and an ultimate working condition load is applied in the center of the upper flange; each connection bolt applies bolt pretension force. The bolt stress intensity and danger positions calculated by the method are higher in accuracy.
Owner:CHINA CREATIVE WIND ENERGY +3
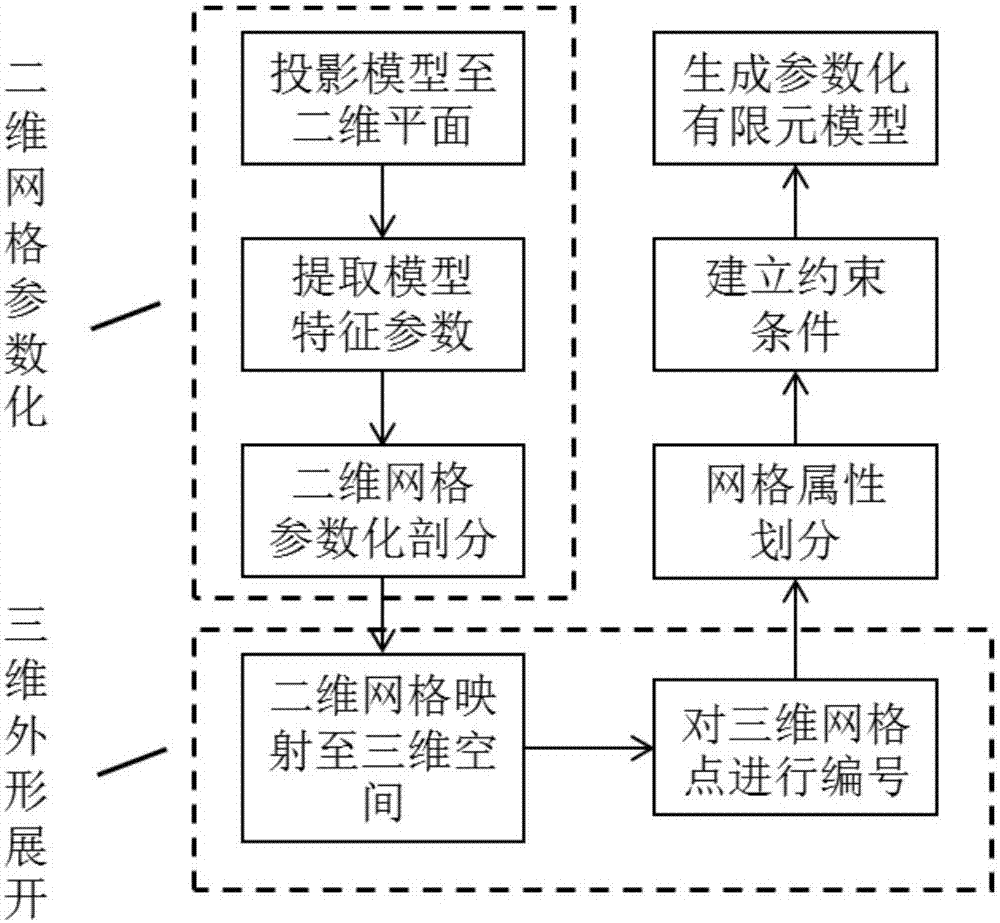
Structural finite-element parametric modeling method applicable to grating-configuration rudder surface
The invention discloses a structural finite-element parametric modeling method applicable to a grating-configuration rudder surface. According to the method, a mapping transformation method based on a finite element model and a parametric approach to achieving conversion from two-dimensional mesh parameterization division to three-dimensional appearance expansion are adopted. The method includes the steps of specifically conducting two-dimensional plane projection on the grating-configuration rudder surface, extracting characteristic parameters, and conducting two-dimensional parameterization division; building a mapping relation between a two-dimensional finite element mesh and a three-dimensional finite element mesh, designing a numbering rule for finite element mesh points, and achieving conversion from the two-dimensional mesh to the three-dimensional appearance expansion; by means of a high-level computer language program, implementing the structural finite-element parametric modeling procedures for the grating-configuration rudder surface. By using the method, in a conceptual design phase or a preliminary design phase, the structural modeling efficiency can be greatly increased, the costs of time and manpower are low, parameters of self-compiled programs can be adjusted quickly, analysis applicability is high, the obtained model is applicable to analytical calculation of structural vibration, structural dynamics and the like, and the method is applicable to grating-configuration rudder surfaces and grating-configuration airfoils.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
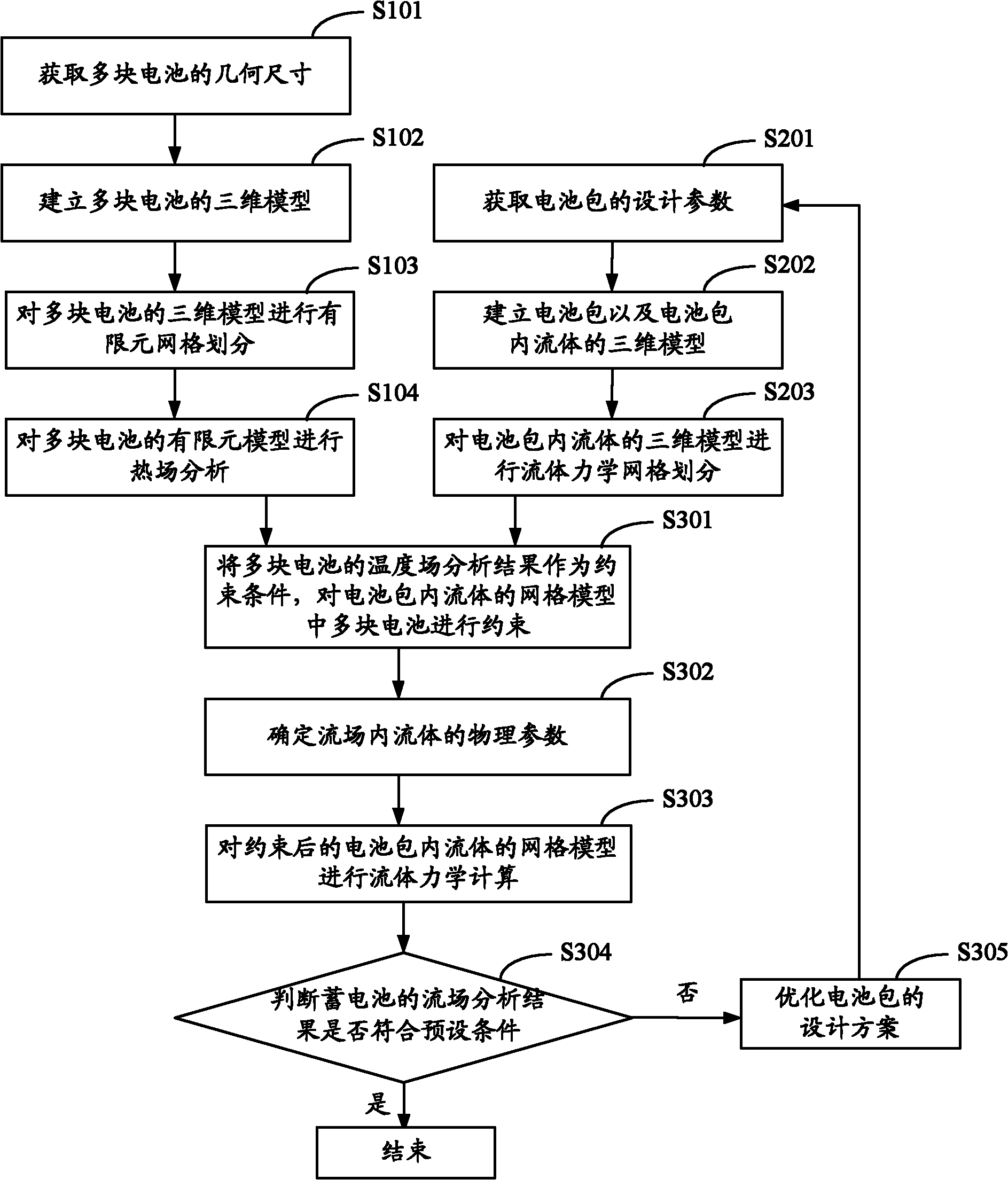
Finite element method-based storage battery thermal management analysis and optimization method
InactiveCN102034006AGreat adaptabilityGreat ability to solveSpecial data processing applicationsExtended finite element methodField analysis
The invention discloses a finite element method-based storage battery thermal management analysis and optimization method. The finite element method-based storage battery thermal management analysis and optimization method comprises the following steps of: acquiring parameters of a plurality of batteries and a battery pack respectively and establishing three-dimensional models of the plurality of batteries and the battery pack; performing the meshing of a definite element on the three-dimensional models of the plurality of batteries and then performing thermal field analysis after the meshing to acquire temperature field analytical results of the plurality of batteries; performing fluid mechanics meshing on the three-dimensional models of fluid in the battery pack and then after the meshing, using temperature field analytical results of the plurality of batteries as constraint conditions of the plurality of batteries in the fluid grid models in the battery pack; performing fluid mechanics calculation on the constrained grid models to acquire flow field analytical results of the storage batteries; judging whether the flow field analytical results accord with preset conditions or not; and if the flow field analytical results do not accord with the preset conditions, optimizing the design scheme of the battery pack and establishing the models again. The finite element method-based storage battery thermal management analysis and optimization method is not limited to mathematic analysis capacity, has higher adaptability and solving capacity, does not need entity models, is economic and quick in the analytical process, and has higher degree of freedom and flexibility.
Owner:上海奕洁汽车科技有限公司
Modeling method of plate rolling in online control model
InactiveCN101604144ACalculation speedEasy to controlRoll mill control devicesMetal rolling arrangementsModel methodEngineering
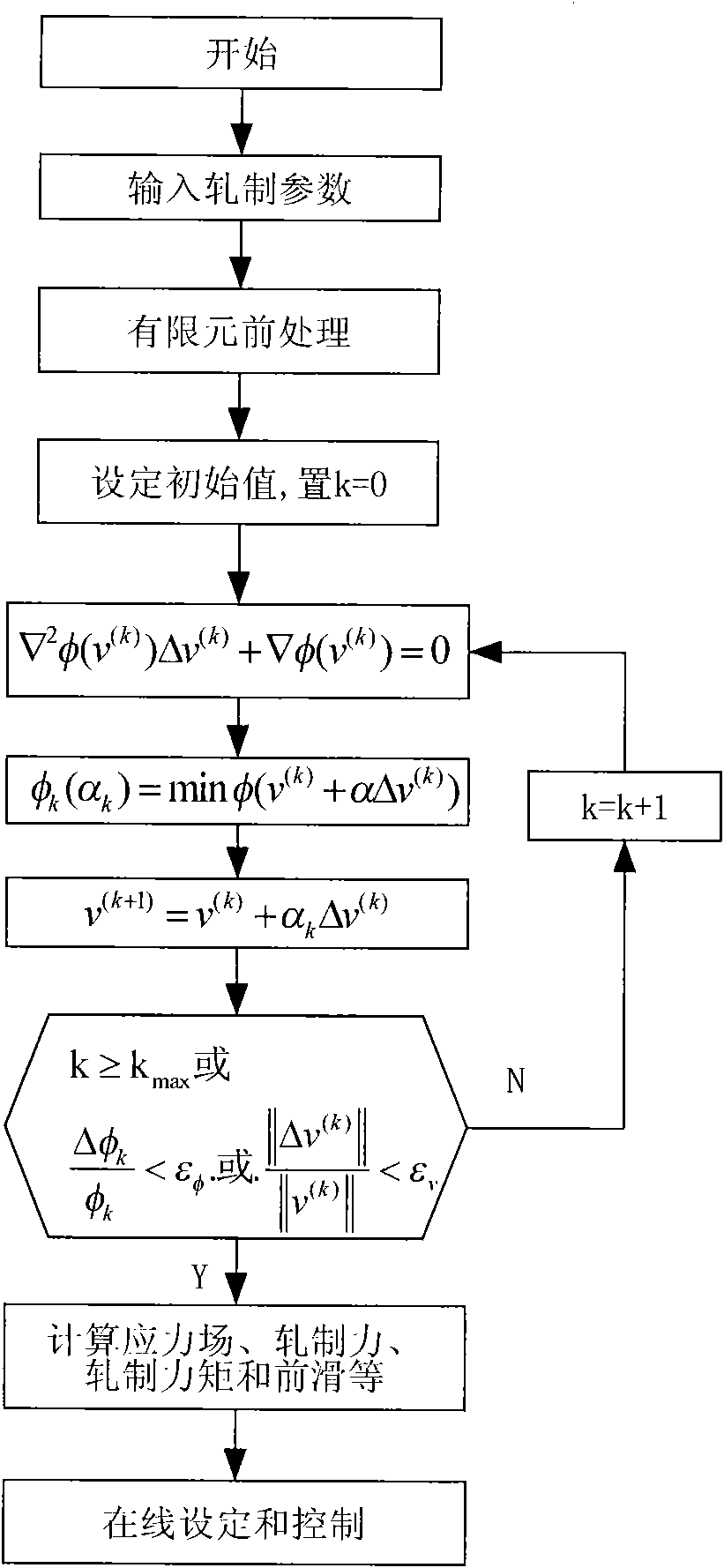
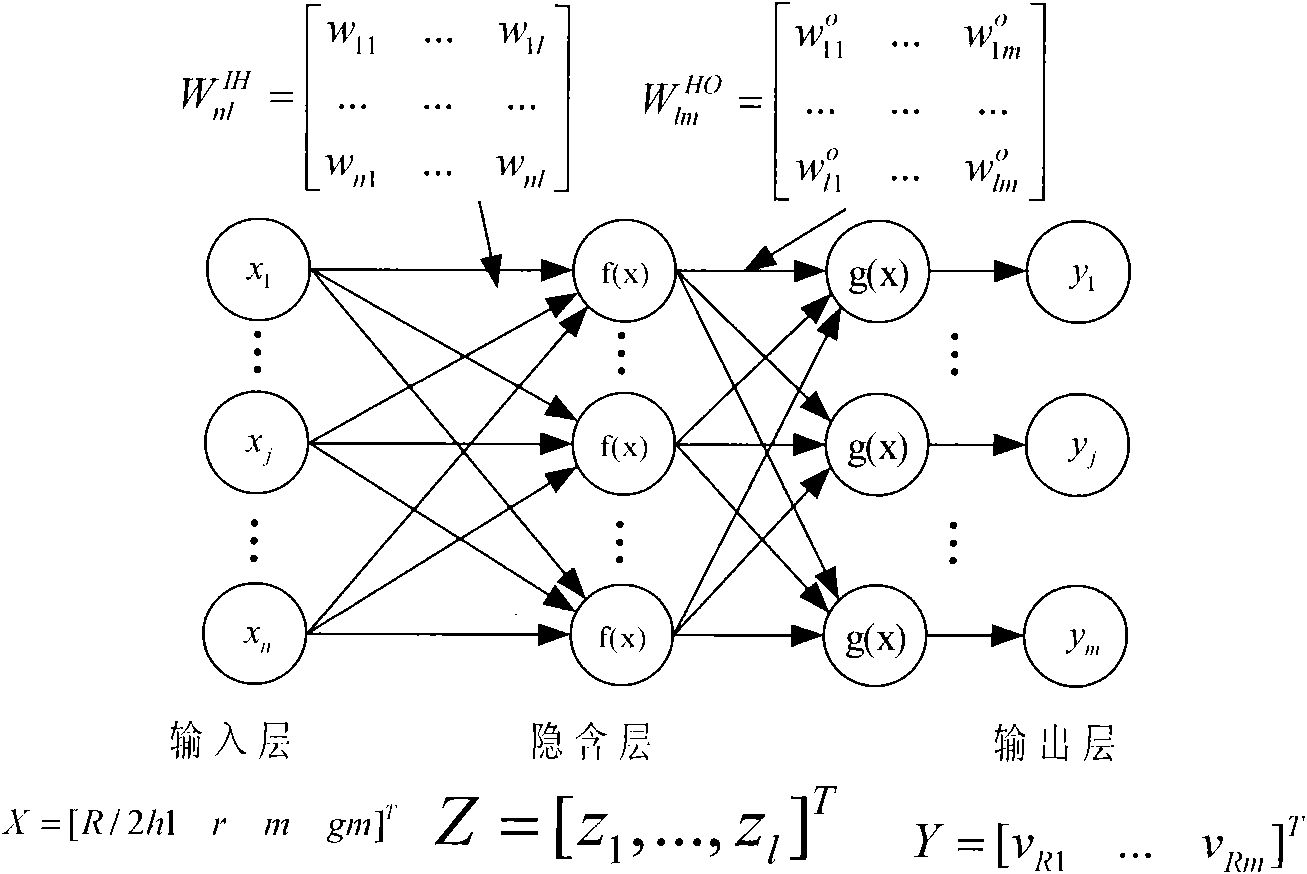
The invention relates to a modeling method of plate rolling in an online control model, which carries out the modeling by a rigid-plastic finite element method. The modeling method comprises the following steps: taking a central line of a plate as an x shaft and the thickness direction of the plate as a y shaft to build a two-dimension plane strain rolling model; inputting rolling conditions and parameters; dividing finite element grids in a rolling deformation region at the lower side of the rolling contact region by adopting a quadratic element and carrying out finite element pretreatment; setting the initial speed field of the finite element; building a rigid-plastic finite element energy functional by taking the initial speed field as an initial value, iterating and solving a minimum value point of the energy functional by adopting the damping Newton method, and obtaining the actual speed field; calculating the strain field and the strain field according to the actual speed field, further calculating online control parameters of the rolling force, the rolling torque and the forward slip value, and obtaining the plate rolling model. The invention improves the calculation speed of the finite element, realizes the online rapid calculation and control of the rigid-plastic finite element of the plate rolling and has strong antijamming capacity and good stability.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
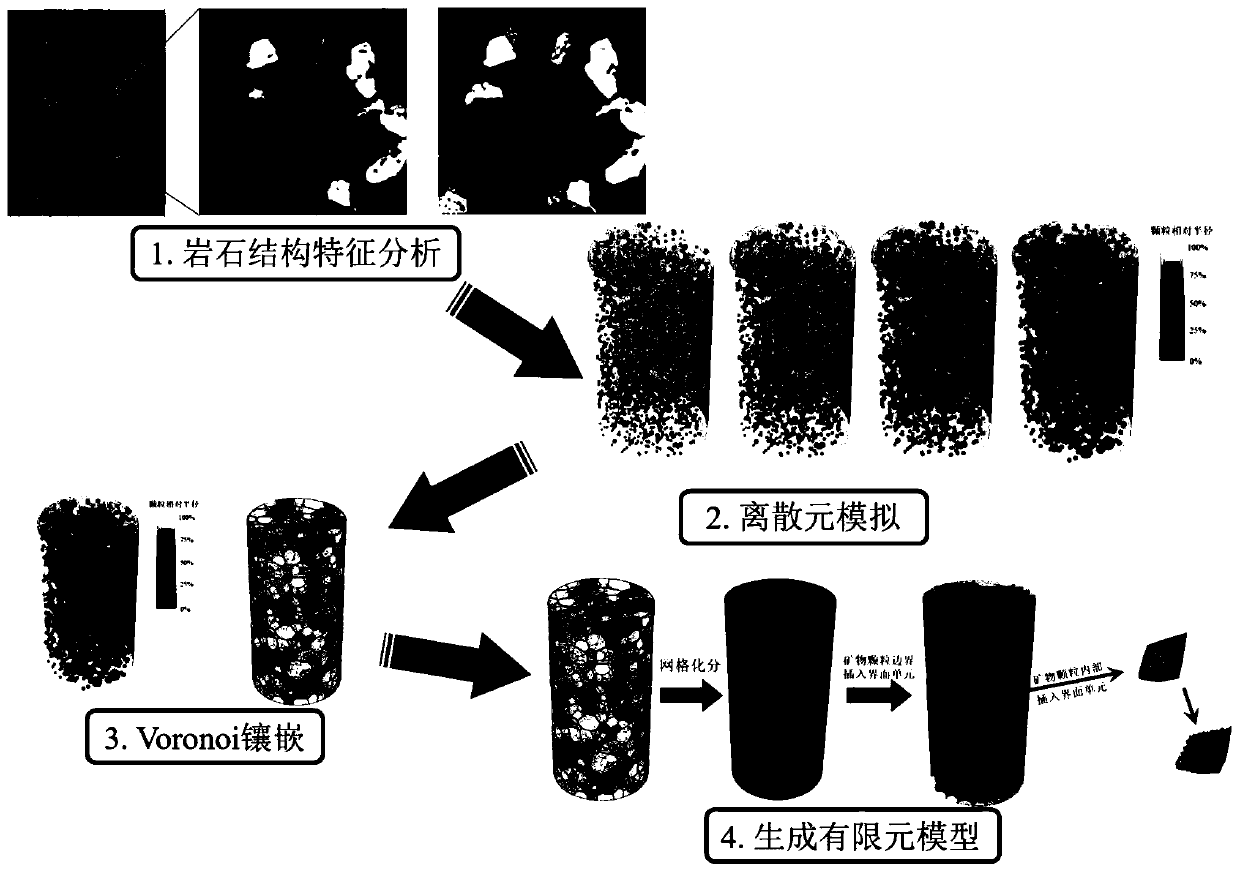
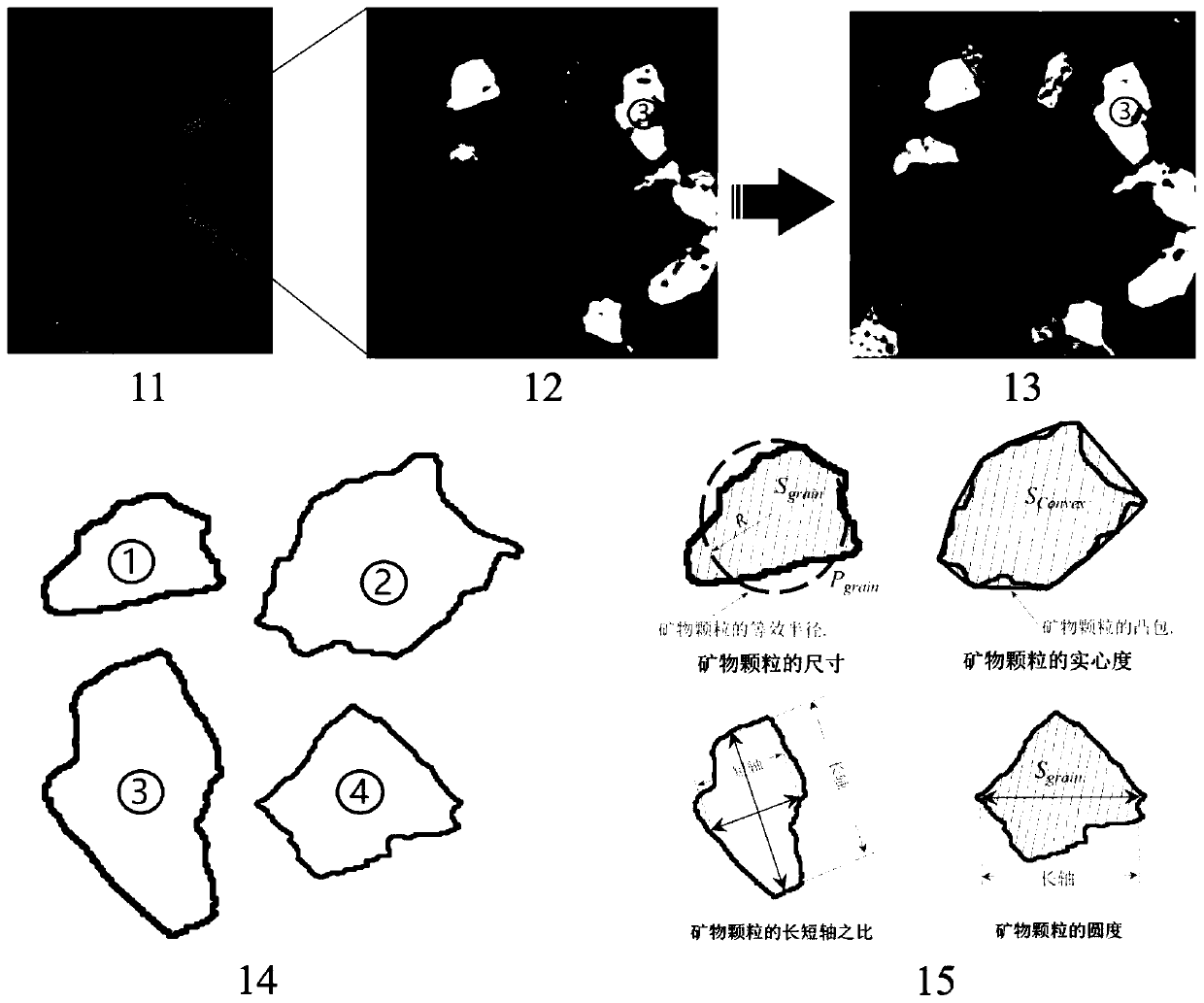
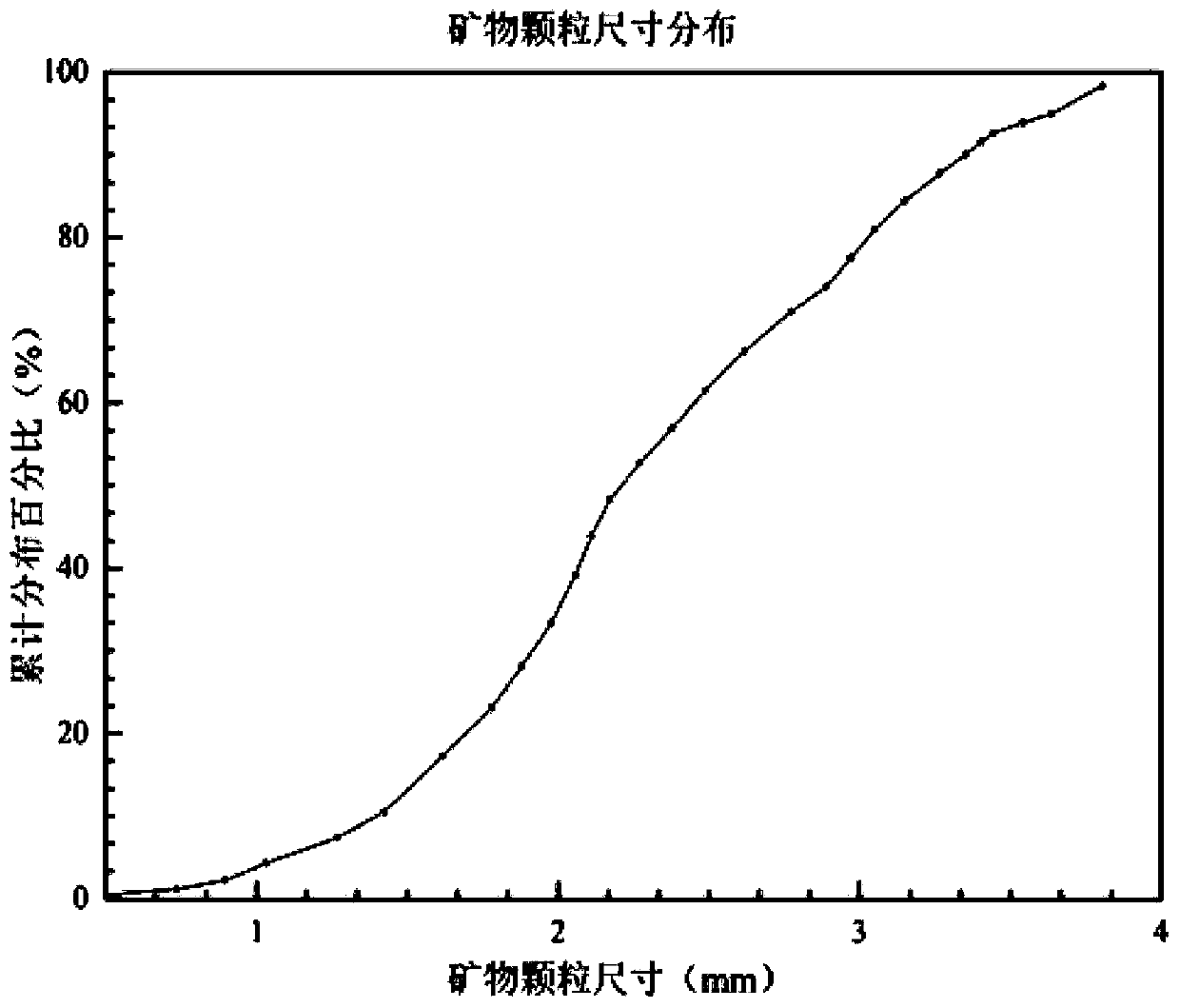
Microscomic numerical model generation method considering rock structure characteristics and mineral composition
ActiveCN110069844ASimulation is accurateImprove computing efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsFree interfaceMineral particles
The invention discloses a microscomic numerical model generation method considering rock structure characteristics and mineral composition. Microscopic structure characteristics and mineral composition of rock can be considered, a microscopic numerical model reflecting the rock structure characteristics and the mineral composition is established, and rock mechanics numerical simulation can be carried out more truly. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out rock structure characteristic analysis on a rock sample to obtain the size, form, mineral type and other information of mineral particles; simplifying the mineral particles with irregular shapes into balls with reduced sizes, and rearranging the particles by adopting a particle size expansion method, and obtaining a compact structure; secondly, extracting information such as spatial positions and sizes of particles, and performing Voronoi graph-based spatial region division on the particle assembly; and finally, performing finite element mesh division on the obtained Voronoi polycrystal structure, and inserting thickness-free interface units into mineral particle boundaries and the interiors of particles to generate a finite element numerical model capable of reflecting a rock structure and a lithofacies structure.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
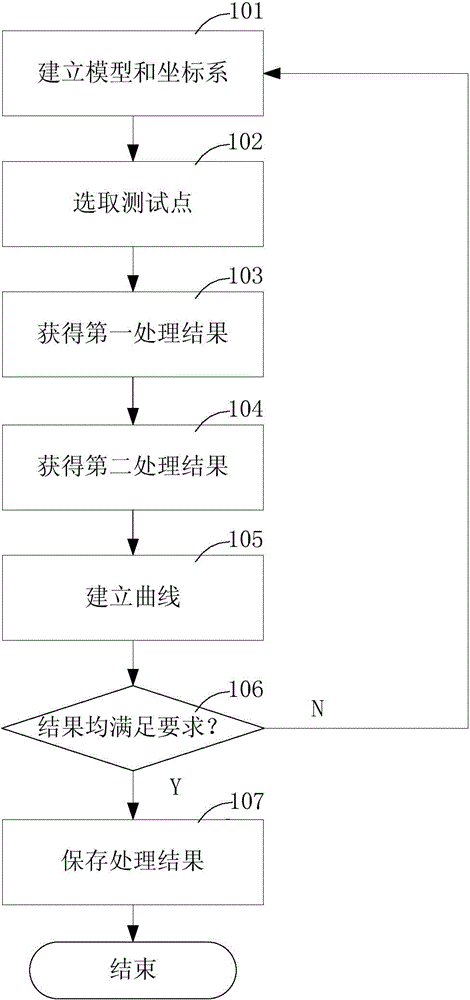
CAE (computer aided engineering)-based car body rigidity analysis method
InactiveCN104573174AReduce workloadThe result is accurateSpecial data processing applicationsReturn-to-zeroWorkload
The invention relates to the technical field of computer aided engineering (CAE), in particular to a CAE (computer aided engineering)-based car body rigidity analysis method used for analyzing the bending rigidity and the torsional rigidity of a front longitudinal beam, a threshold and a rear longitudinal beam of the car body. The CAE-based car body rigidity analysis method comprises the following steps: establishing a finite element mesh model of the car body and a coordinate system; carrying out a simulation test by applying load and constraints; obtaining a processing result, and generating a curve; then, judging whether the processing result meets requirements; if the processing result meets the requirements, storing the processing result, and otherwise, establishing a finite element mesh model of the car body again to conveniently carry out a simulation test. In the method, the displacement and the torsion angle of a node are analyzed by the finite element mesh model of the car body to carry out rigidity analysis instead of calculating by selecting the node by experience, and therefore the result is more accurate; an analysis result is automatically obtained, the workload of engineers is lightened, and project development time is saved; the result can be returned to zero to make the result to be normalized, the result has high compatibility, and comparison and analysis can be conveniently carried out.
Owner:BRILLIANCE AUTO
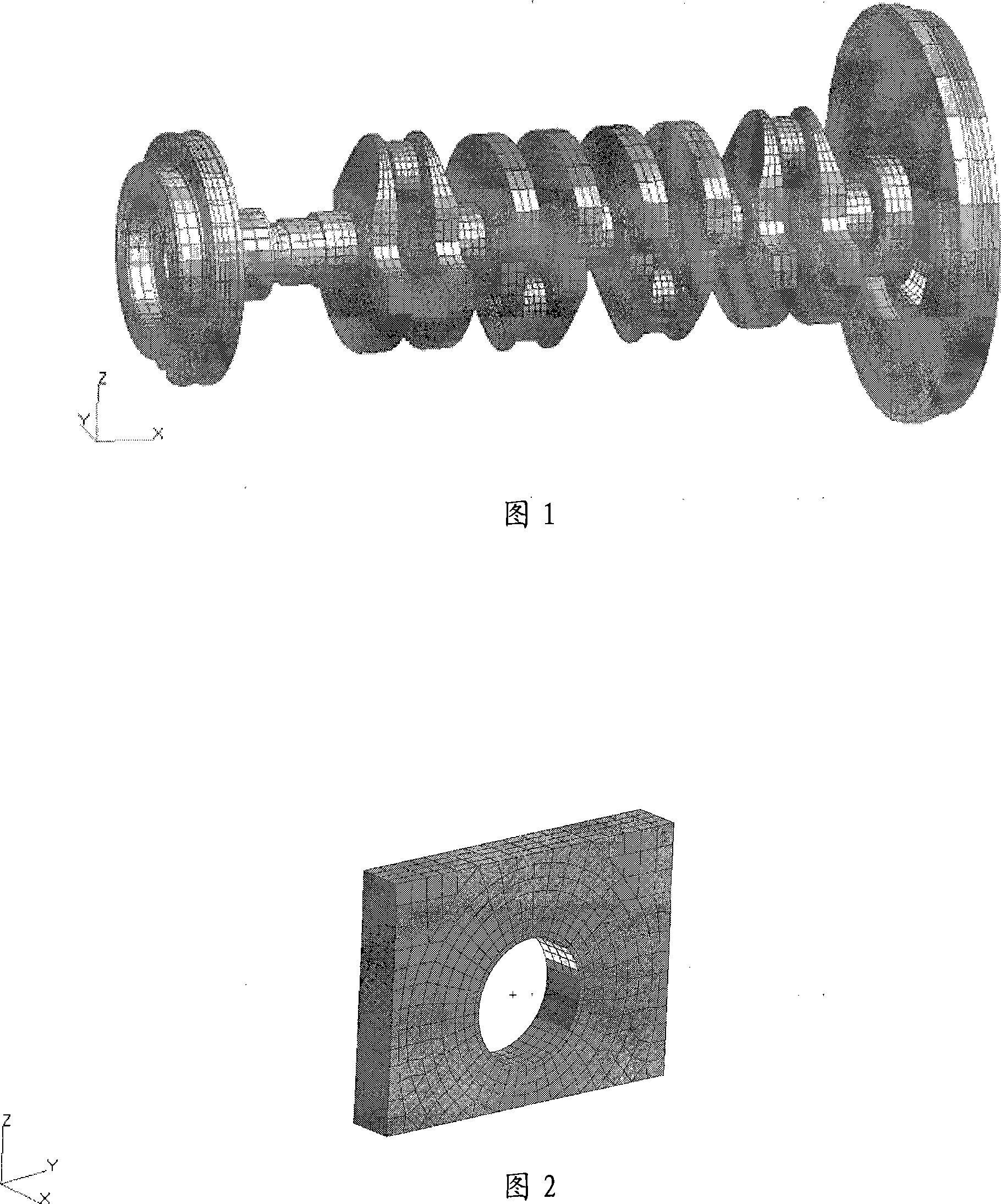
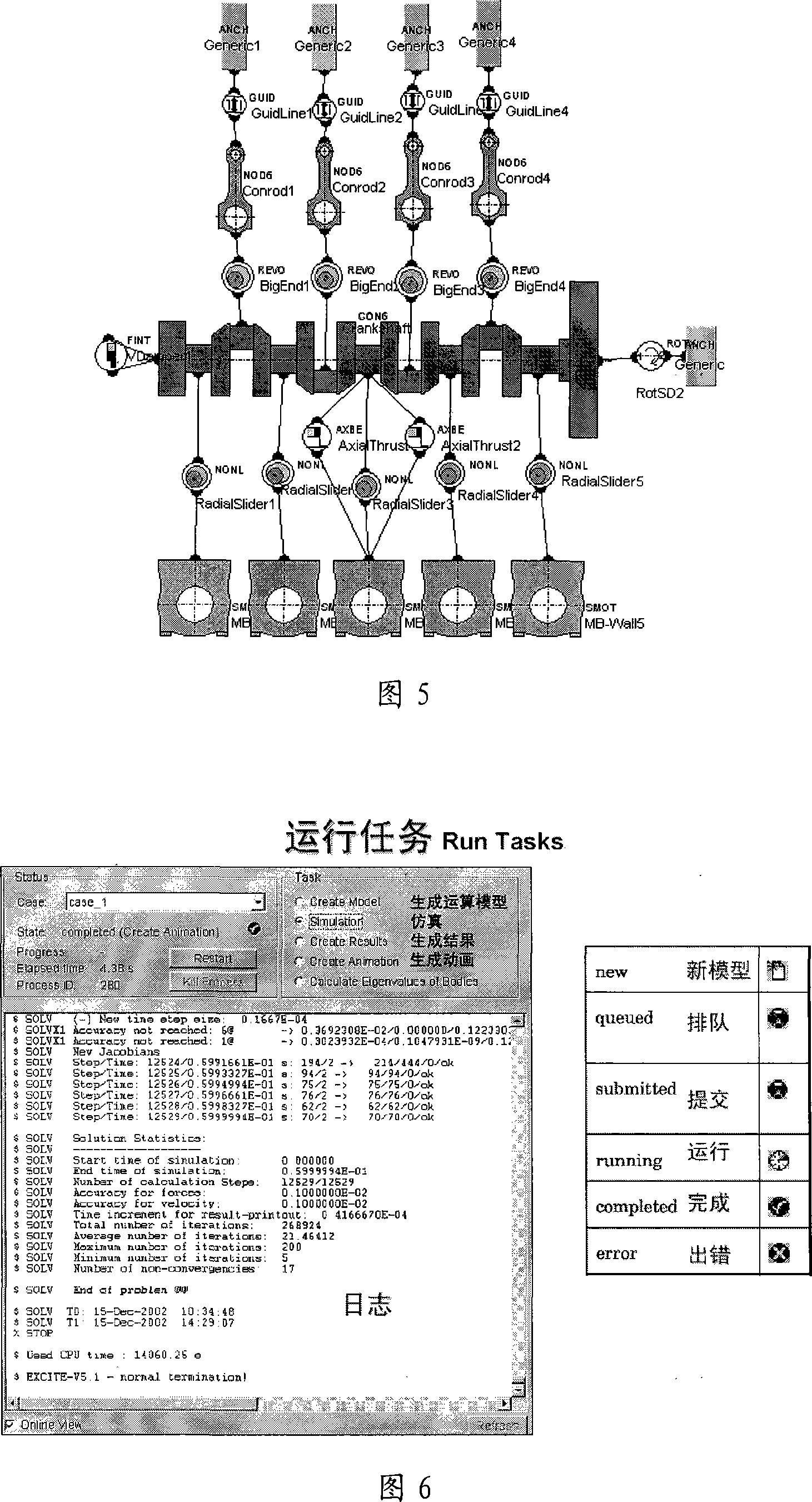
Engine crankshaft dynamic analysis method
The invention discloses an analysis method of motor crank dynamics, which includes that: in Hypermesh software, a crank system is divided by finite element mesh generation into a crank, a flywheel, a belt pulley, a timing gear and a main bearing seat etc.; use Nastran software to execute the reduction solving of a finite element substructure; in EXCITE software, construct a model of the crank system dynamics, and exert the corresponding boundary condition on elements to implement simulation calculation; use the Nastran software to implement restoration solving of dynamic stress on the crank, perform post-processing and execute fatigue analysis on dangerous points; reasonably evaluate the crank system according to the results, and if the structure is not reasonable, the structure optimization is still needed. The method uses EXCITE calculation technique to execute dynamics analysis on the motor crank, obtains the strength and the fatigue parameters of the motor crank, and further evaluates the structure parameters of the crank and the related parts of the motor reasonably, therefore, making the improvement thereof.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
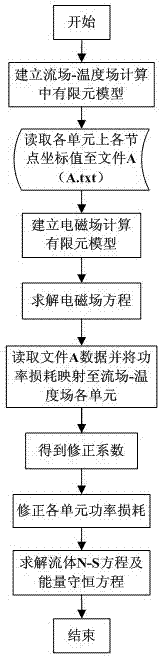
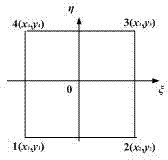
Irregular mesh mapping method used in electromagnetic field-flow field-temperature field coupling calculation
ActiveCN103617367ASolve the accuracy problemSolve needsSpecial data processing applicationsTypes of meshResearch Object
An irregular mesh mapping method used in electromagnetic field-flow field-temperature field coupling calculation comprises the following steps of 1 establishing a flow field-temperature field calculation model; 2 reading node coordinate values of discrete units of the model; 3 re-establishing a geometric model of a research object in the electromagnetic field calculation, performing model discrete to form a triangular finite element mesh and performing electromagnetic field value calculation; 4 mapping power consumption onto units in a temperature field; 5 obtaining a mapping correction factor; using power consumption densities of the units as loads to be loaded into the temperature field for solution and calculation, and obtaining a temperature result; accordingly obtaining the power consumptions of the units in the temperature field. By adopting the irregular mesh mapping method used in the electromagnetic field-flow field-temperature field coupling calculation, data transfer of different types of meshes can be adopted in different physical fields, the mesh number is greatly decreased, and the calculation time and the calculation accuracy are shortened and improved.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Reconstruction of parameterization model of quadrilateral finite element grid model
InactiveCN105787226AHigh expressionReduce in quantityDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNODALReconstruction algorithm
The invention provides a parameterization reconstruction algorithm of a quadrilateral finite element grid model. By taking a quadrilateral grid model obtained by finite element analysis software as the basis, a unit number and a node coordinate of the quadrilateral grid model are used as input information for reconstructing a topological relation between quadrilateral grid units; merging operation including unit grid standard merging, block domain self-adaptive merging and the like are carried out according to obtained topological information, so that the quantity of block domains is reduced and merged sub-domains are obtained; characteristic points on boundaries of the sub-domains obtained by merging are remained and are connected to form a certain quantity of quadrilateral final sub-domains; and finally, a body parameterization model is obtained by carrying out construction, adjustment and optimization of a body parameter model according to the boundaries of the obtained final sub-domains. The algorithm can be used for carrying out parameterization reconstruction on the quadrilateral grid model of structures including a porous plate and the like, and the obtained body parameterization model is applicable to isogeometric analysis; and the algorithm has the advantages of simplicity in expression, whole-domain smoothing and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Numerical simulation technology for hollow section porthole die extrusion welding process
InactiveCN101604350AEnable continuous simulationExtrusion diesSpecial data processing applicationsData fileEngineering
The invention discloses numerical simulation technology for a hollow section porthole die extrusion welding process, which belongs to the technical field of metal extrusion. The technology comprises the steps of: adopting finite element software Deform-3D to simulate a porthole die extrusion process; adopting a finite element fractional step method for calculation; transforming a three-dimensional solid model of finite element meshes into a three-dimensional surface model taking small triangular patches as basic description units, namely an STL (Stereolithography) model in the finite element software Deform-3D when the volume of penetration areas of mesh units of a welding surface is equal to that of unfilled areas of the welding surface; repairing triangular patch meshes, which are penetrated with each other, of the welding surface in the STL model to ensure that original penetration areas and the unfilled areas reform the three-dimensional surface model consisting of triangular patch units; adopting a 3X fraction method to import the repaired STL model into the finite element software Deform-3D; and adding nodal data of original units into the model to generate a new data file, and finishing simulation analysis of a porthole die extrusion welding stage and the overall process of the extrusion.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Building method for laser welding heat source model
ActiveCN103049623AEfficiency is obviousImprove efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsCouplingOpen source
The invention relates to a building method for a welding heat source model, in particular to a building method for a laser welding heat source model. The method solves the problem in laser welding simulation of large-scale complex construction members that laser heat source achieving difficulty is large, and calculating efficiency is low. The method includes: step 1, building a three-dimensional finite element grid model; step 2, building a Gaussian heat source mode of a heat source surface; step 3, expanding welding energy along the laser welding pool depth direction; and step 4, solving a governing equation based on finite element software and conducting heat-machine coupling calculation, namely building of the laser welding heat source model is finished. The building method is applied to the field of welding.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
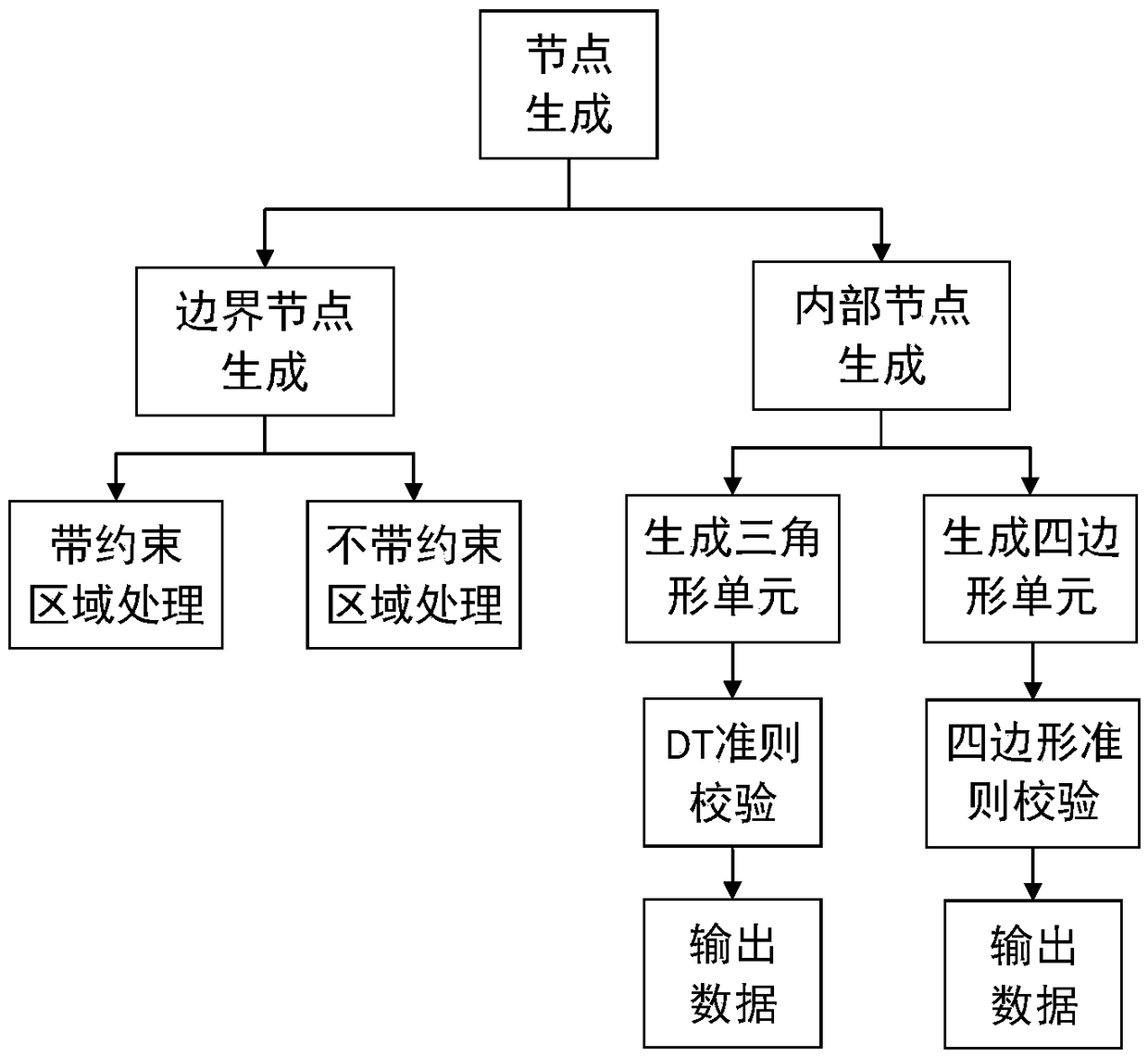
Method for creating three-dimensional finite element mesh
ActiveCN1991846AQuality improvementShorten the timeSpecial data processing applicationsCalculation errorComputer image
The invention belongs to fields of computer image processing; a method of generating three-dimensional finite element grid is disclosed that includes steps as following: 101. Two-dimension surface grid is divided on surface of the three-dimensional model of object noumenon; 102. The noumenon basic grid which encompasses the three-dimensional model is generated by the noumenon basic grid built by projection borderline; 103. The Two-dimension surface grid is inserted into the back of the noumenon basic grid, eliminating the noumenon grid which is out of the noumenon surface grid; the noumenon three-dimensional grid needed is obtained. Because said technical project is adopted, the Two-dimension surface grid and the noumenon basic grid are obtained easily, for adopting the penetration algorithm, the time of generating final noumenon grid is decreased than traditional approach, quantity of work in several months can be accomplished within several days even several hours. At the same time, because the three-dimensional noumenon grid generated is hexahedron grid, the quantity of grid id higher, the calculation error can be improved greatly.
Owner:靖江德方科技服务有限公司
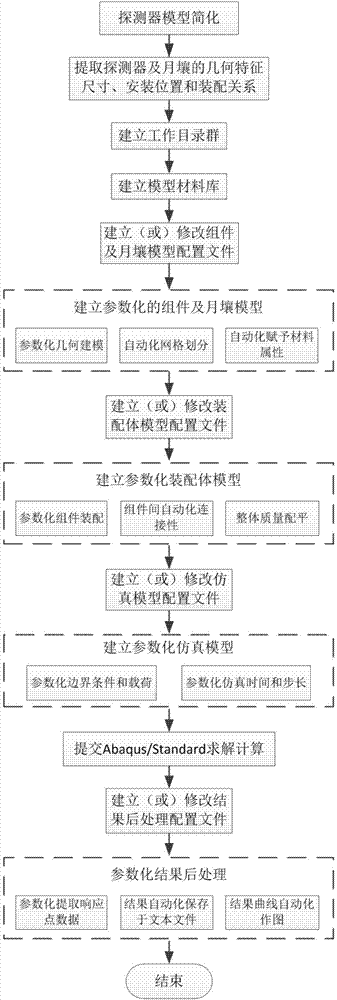
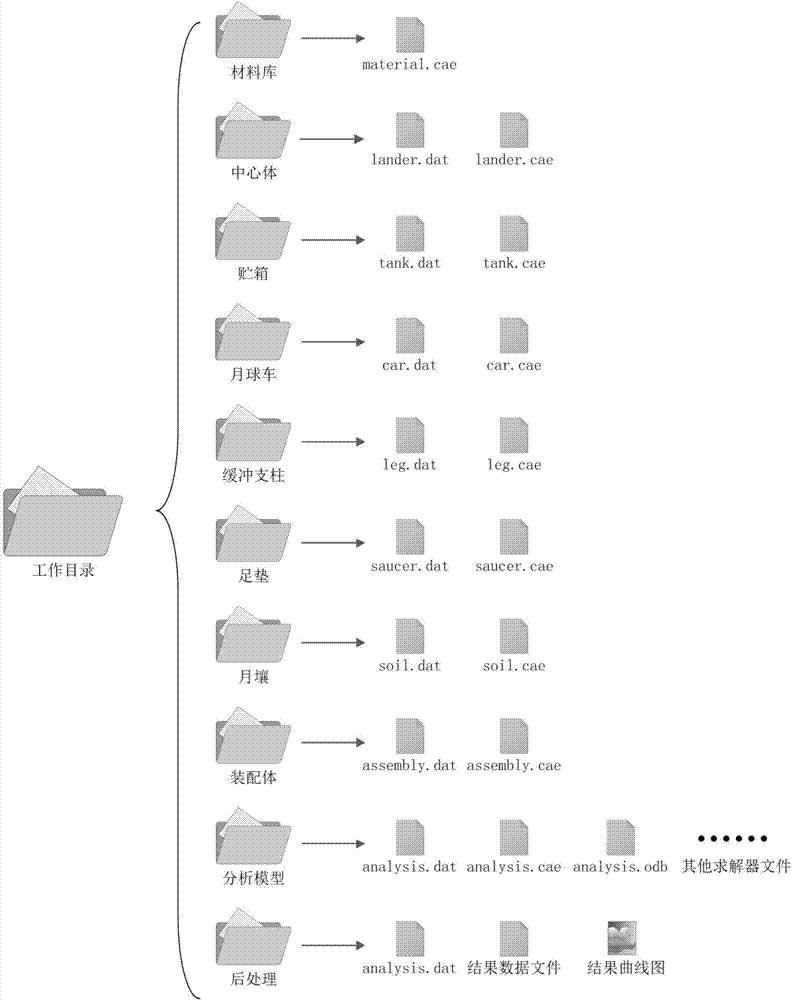
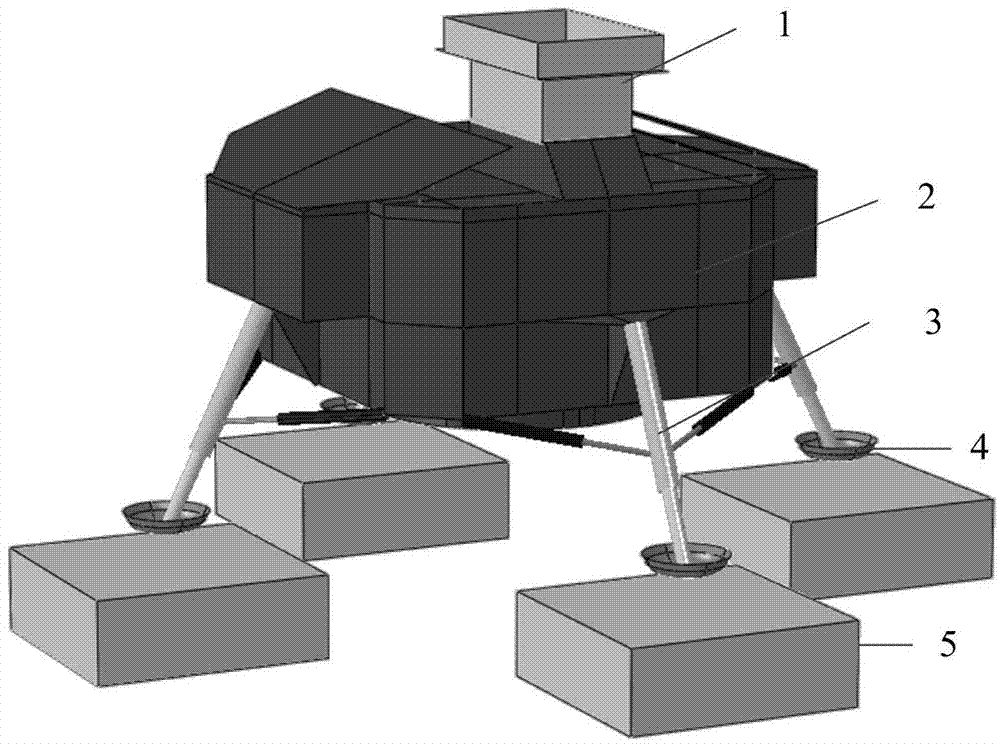
Parameterization simulation method of lunar probe soft landing dynamics
InactiveCN103678824AAutomate the creationSimple designSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelDeep space exploration
The invention relates to a parameterization simulation method of lunar probe soft landing dynamics, and belongs to the technical field of deep space exploration. The method integrates finite element modeling, solving calculating and result post-processing, finite element models of all components (including a center body, a fuel storage box, a lunar rover, buffering pillars and a foot pad) of a probe can be generated, and assembly, working condition setting, solving calculating and result extracting can be finished automatically. By means of the method, automatic establishing of a parameterization model of the lunar probe soft landing dynamics is realized, re-handling brought to designing personnel by re-meshing and component connection relationship re-setting which are caused by the fact that a certain characteristic is changed in the finite element modeling process of the lunar probe is avoided, and the problem of designing efficiency in the dynamics analysis of the lunar probe soft landing process in the prior art is solved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
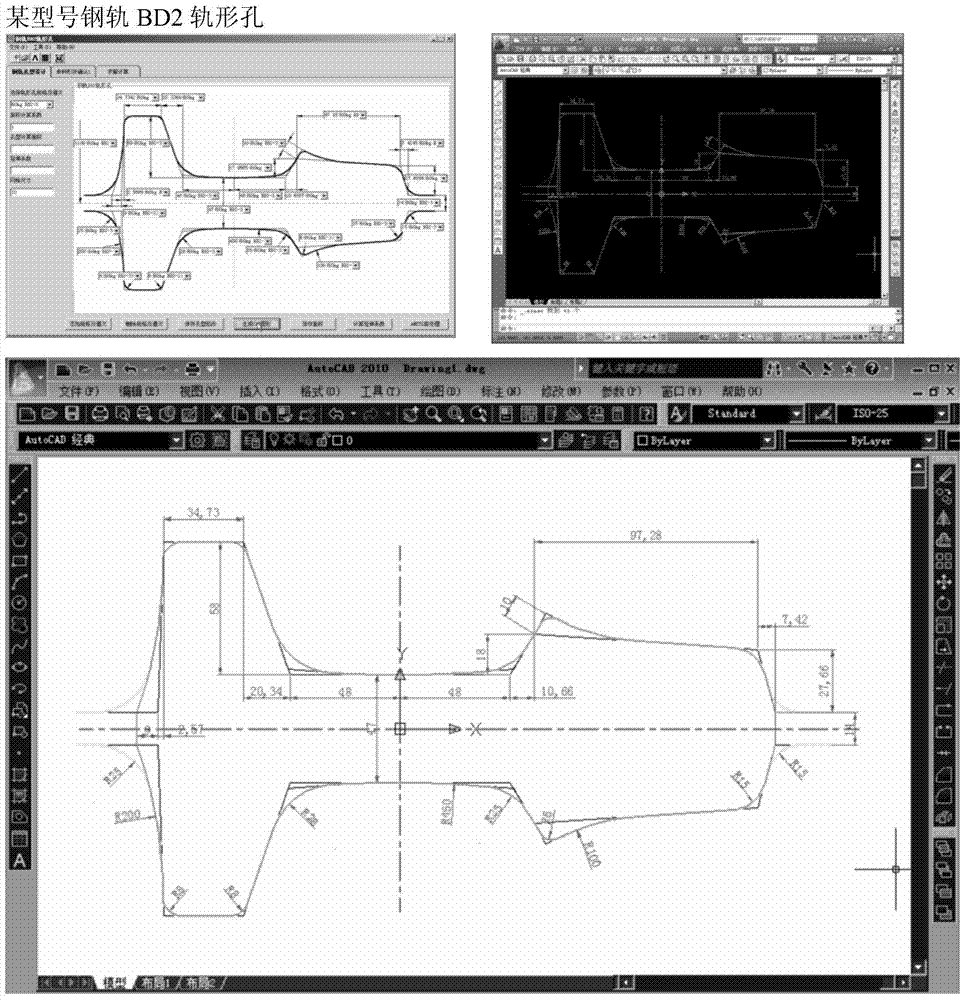
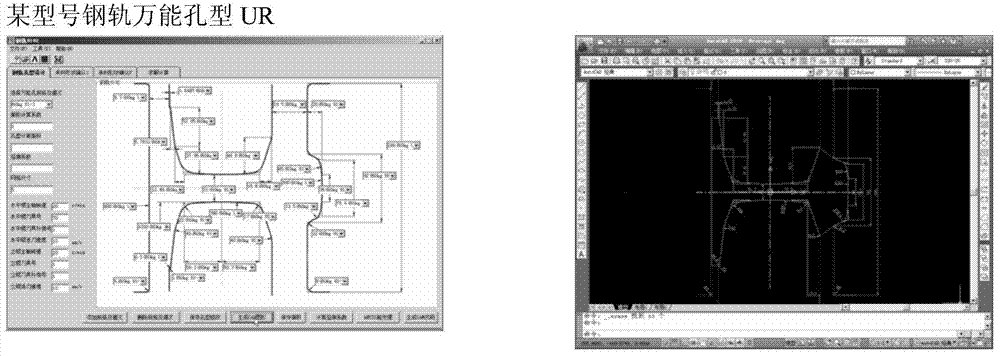
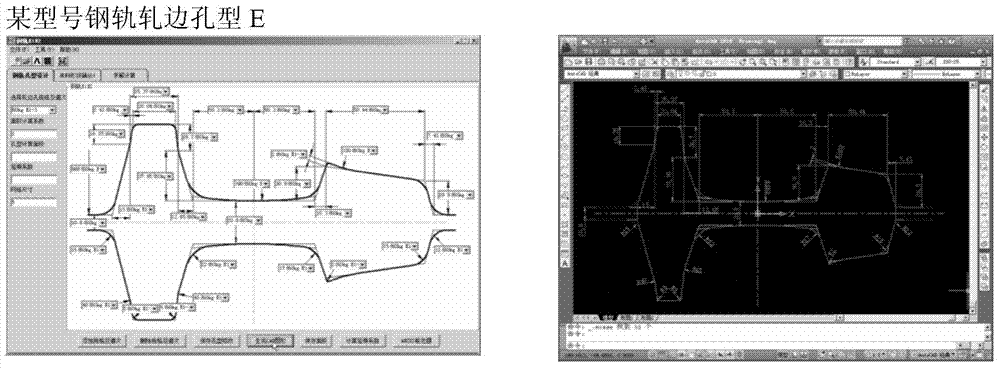
Simulation design method for rolling hole patterns of steel rail
ActiveCN104217063AQuick divisionNo background sub-network requiredSpecial data processing applicationsComputer aided educationManufacturing technology
The invention discloses a simulation design method for rolling hole patterns of a steel rail, and belongs to the technical field of design and manufacturing of steel rail rolling equipment. The simulation design method for the rolling hole patterns of the steel rail, provided by the invention, is convenient to operate, high in automation degree and capable of improving the simulation analysis accuracy and avoiding errors. The method comprises the following steps: developing a set of simulation design software comprising a CAD (Computer Aided Design) hole pattern design module, a CAE (Computer Aided Education) hole pattern optimization module and a CAM (Computer Aided Manufacturing) hole pattern processing code generation module, and calling corresponding database information through the modules respectively; designing the rolling hole patterns of all rolling passes of the steel rail, dividing finite element grids for the rolling hole patterns with different specifications, establishing and correcting a related boundary condition model, and generating CAM codes of the rolling hole patterns of rollers corresponding to all the rolling passes. Due to the fact that the design and optimization of the rolling hole patterns of the steel rail and the generation of CAM processing codes are completed through the software respectively, the operation is simplified, the efficiency is improved, and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:PANGANG GRP PANZHIHUA STEEL & VANADIUM
Measurement method of virtual hepatic vein pressure gradient
The invention belongs to the field of early-stage non-invasive diagnosis and relates to a measurement method of a virtual hepatic vein pressure gradient. The measurement method of the virtual hepatic vein pressure gradient comprises the following steps: carrying out three-dimensional modeling on a hepatic vein-portal vein system; dividing a mathematical model by a finite element mesh; and calculating the virtual hepatic vein pressure gradient (vHVPG) by fluid mechanical emulation. The three-dimensional modeling of the vein-portal vein system, the finite element mesh division and the fluid mechanical emulation calculation are optimized and completed, and a vHVPG detection novel technology with better diagnosis advantages is constructed and identified; and a non-invasive manner which is safe and novel and can accurately measure is provided for the early-stage non-invasive diagnosis of patients with portal hypertension.
Owner:NANFANG HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
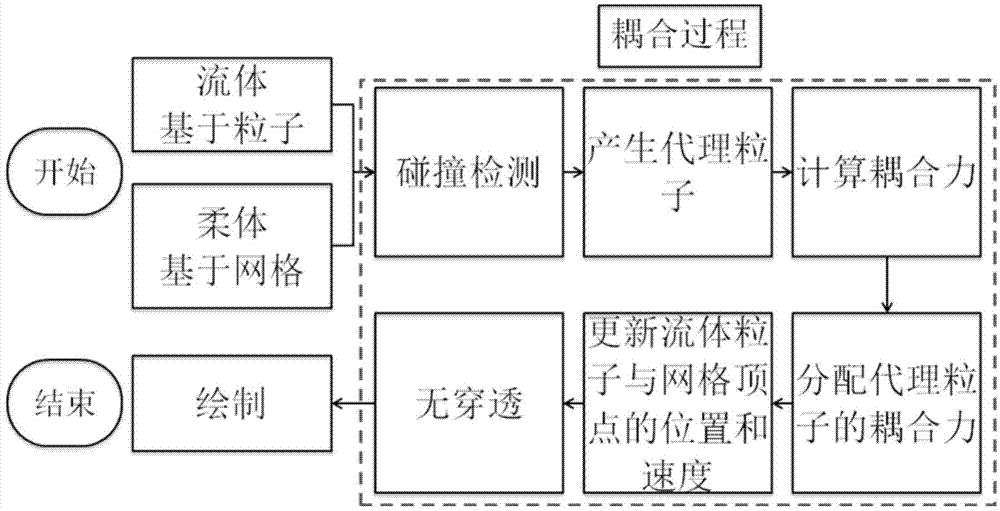
Fluid-solid coupling method based on smoothed-particle hydrodynamics (SPH) and nonlinear finite elements
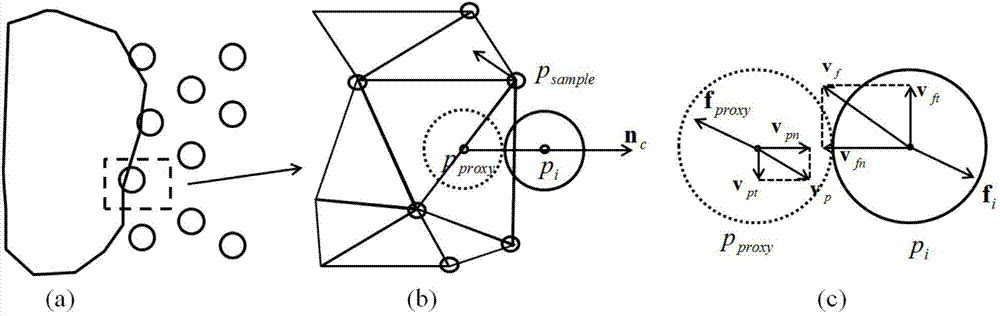
InactiveCN103699715ASolve problems that are difficult to directly coupleEasy to implement in parallelSpecial data processing applicationsSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsElement model
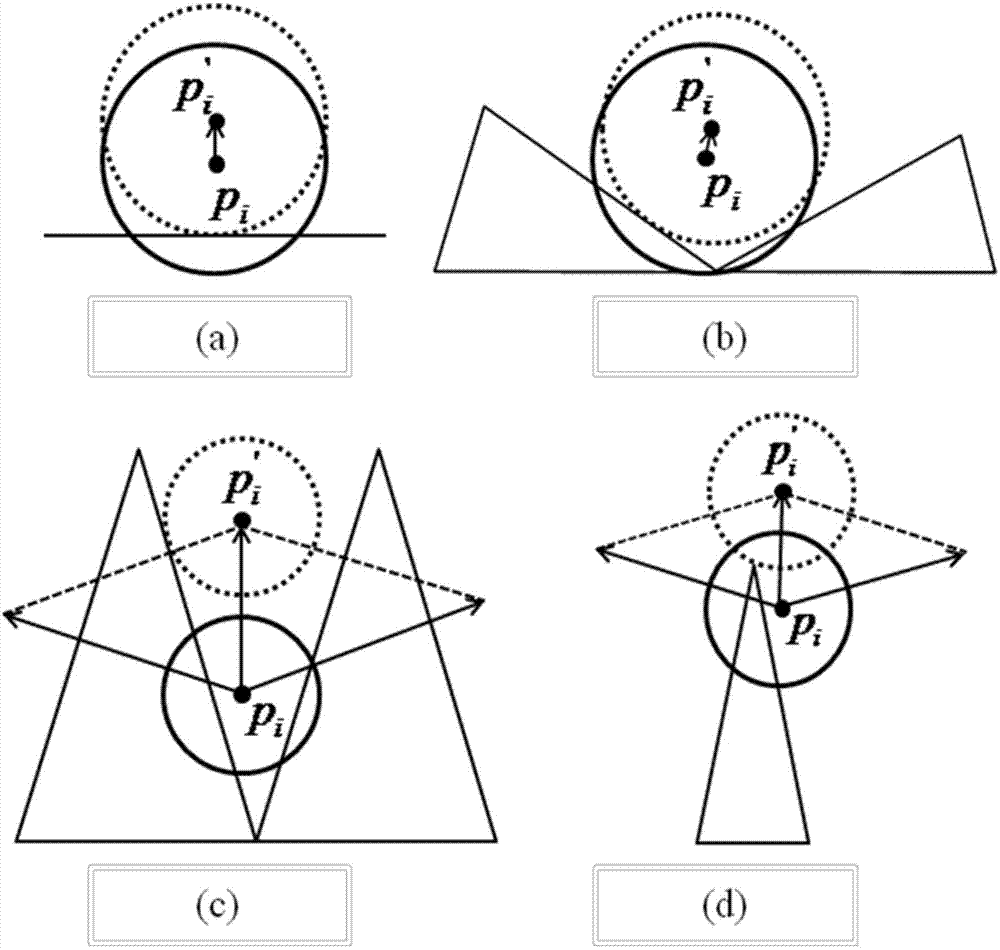
The invention provides a fluid-solid coupling method based on smoothed-particle hydrodynamics (SPH) and nonlinear finite elements. The method comprises the following six steps: at a collision detection stage, detecting collision information of fluid particles with a finite element network; at an agent particle generation stage, generating collision agent particles presenting a finite element model according to the collision information for processing the collision between a fluid and a solid; at a coupling force calculation stage, calculating force generated by collision between agent particles and fluid particles according to the position and speed relations of the agent particles and the fluid particles; at a coupling force allocation stage, controlling the position relation of the agent particles and the finite element model and allocating the coupling force to a finite element stress model; at a position and speed updating stage, driving the position and speed update of the finite element model and a fluid particle model according to the calculated coupling force; at a non-penetration modification stage, modifying penetration fluid particles according to an updated position.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
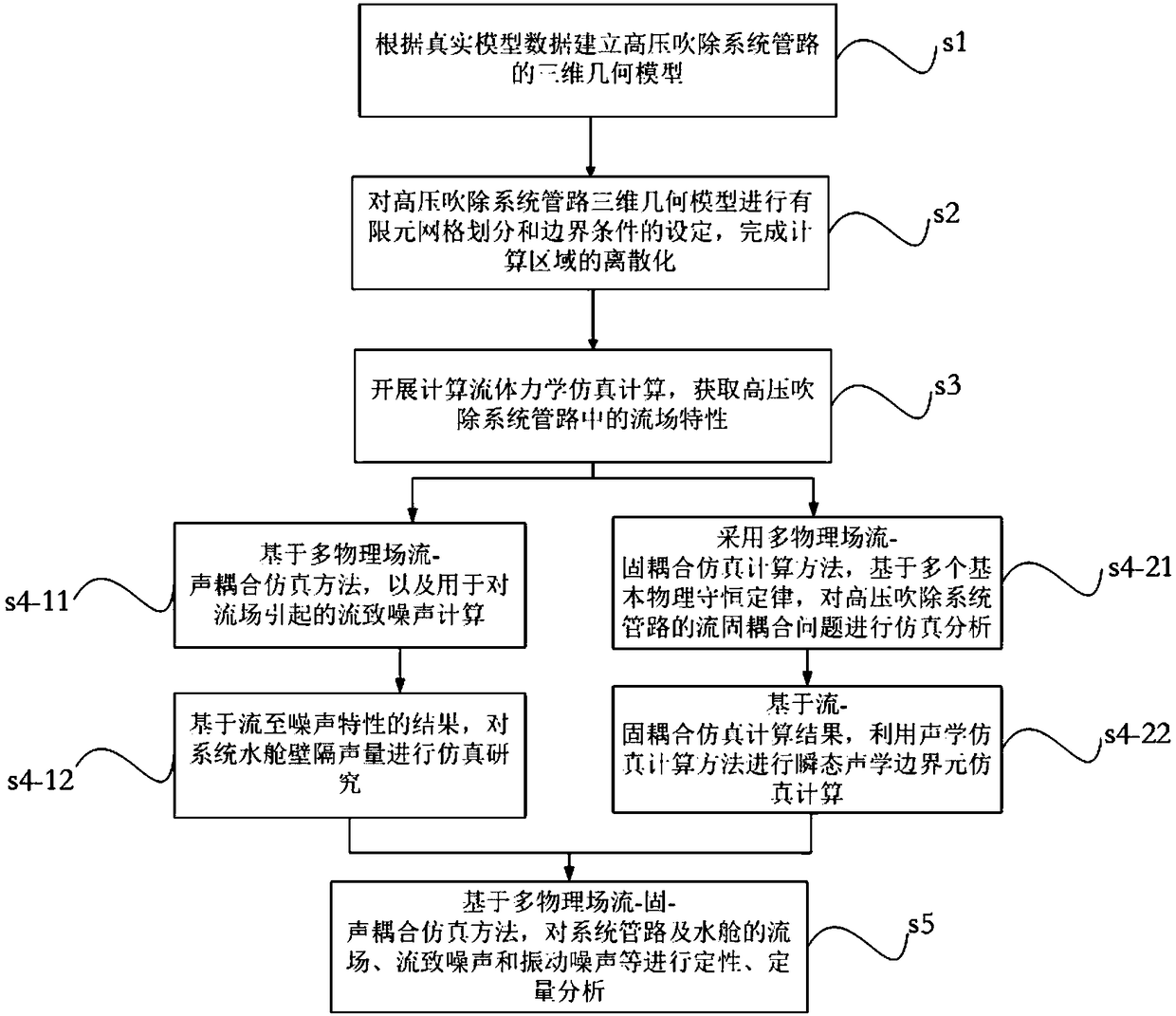
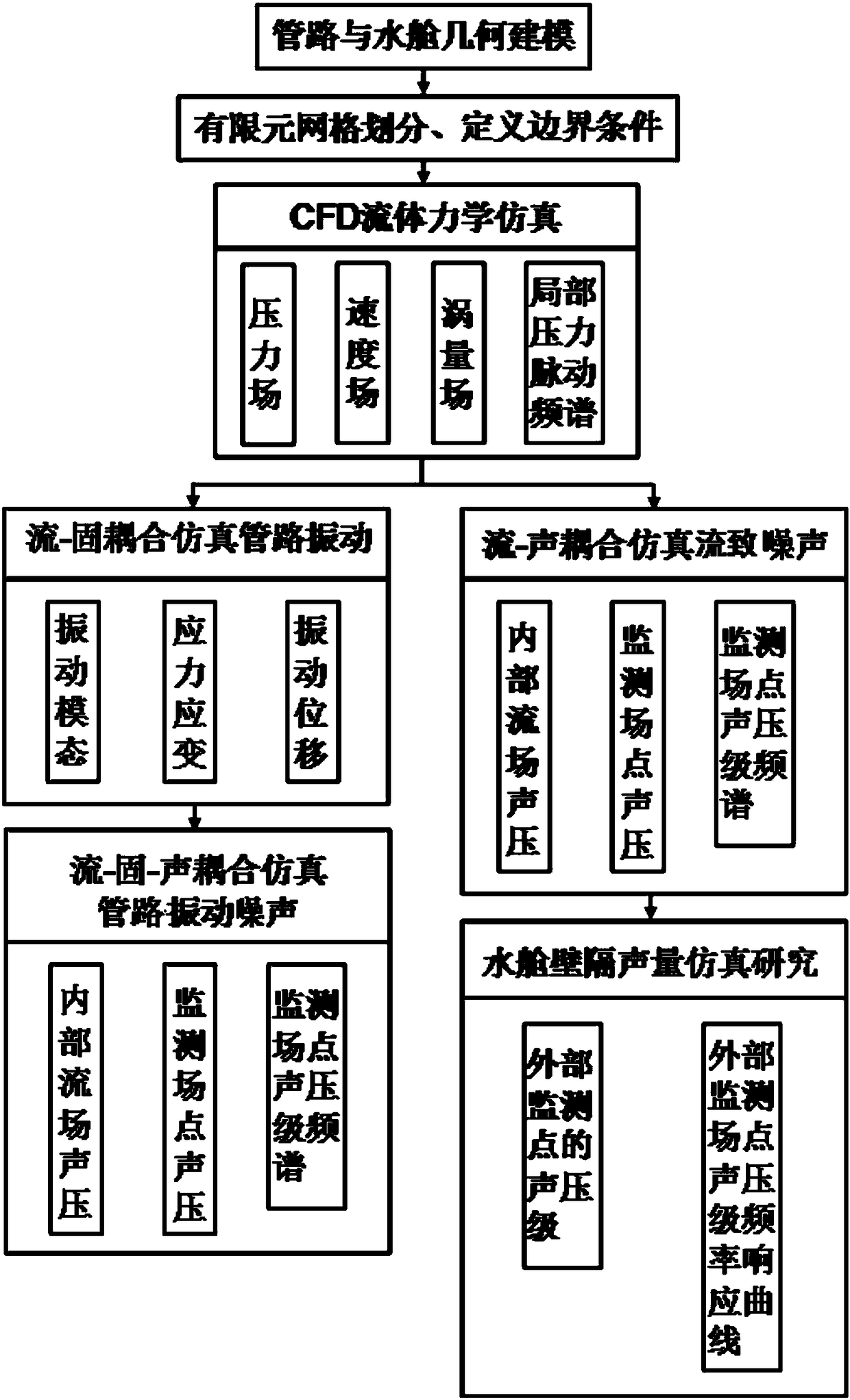
Multi-physical field coupling simulation method and system for submarine high-pressure blow-off pipeline system
InactiveCN108416127AImprove security and concealmentImprove noise characteristicsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMultiphysics couplingPhysical field
The invention discloses a multi-physical field coupling simulation method and a multi-physical field coupling simulation system for a submarine high-pressure blow-off pipeline system. The method comprises the steps of establishing a three-dimensional geometrical model of a high-pressure blow-off system pipeline; performing finite element mesh division and boundary condition setting on the three-dimensional geometrical model of the high pressure blow-off system pipeline; performing fluid mechanic simulation calculation to obtain flow field characteristics in the high-pressure blow-off system pipeline and flow-induced noise characteristics in the blow-off system; performing simulation analysis on a fluid-solid coupling problem of the high-pressure blow-off system pipeline based on a multi-physical field fluid-solid coupling simulation calculation method; performing transient acoustic boundary element simulation calculation by use of an acoustic simulation calculation method based on a fluid-solid coupling simulation calculation result; and performing qualitative and quantitative analysis on flow field noises, flow-induced noises and vibration noises of the system pipeline and a watertank based on the multi-physical field fluid-solid-sound coupling simulation method. Through the multi-physical field coupling simulation means, the invention provides a noise prediction system for the submarine high-pressure blow-off pipeline system.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
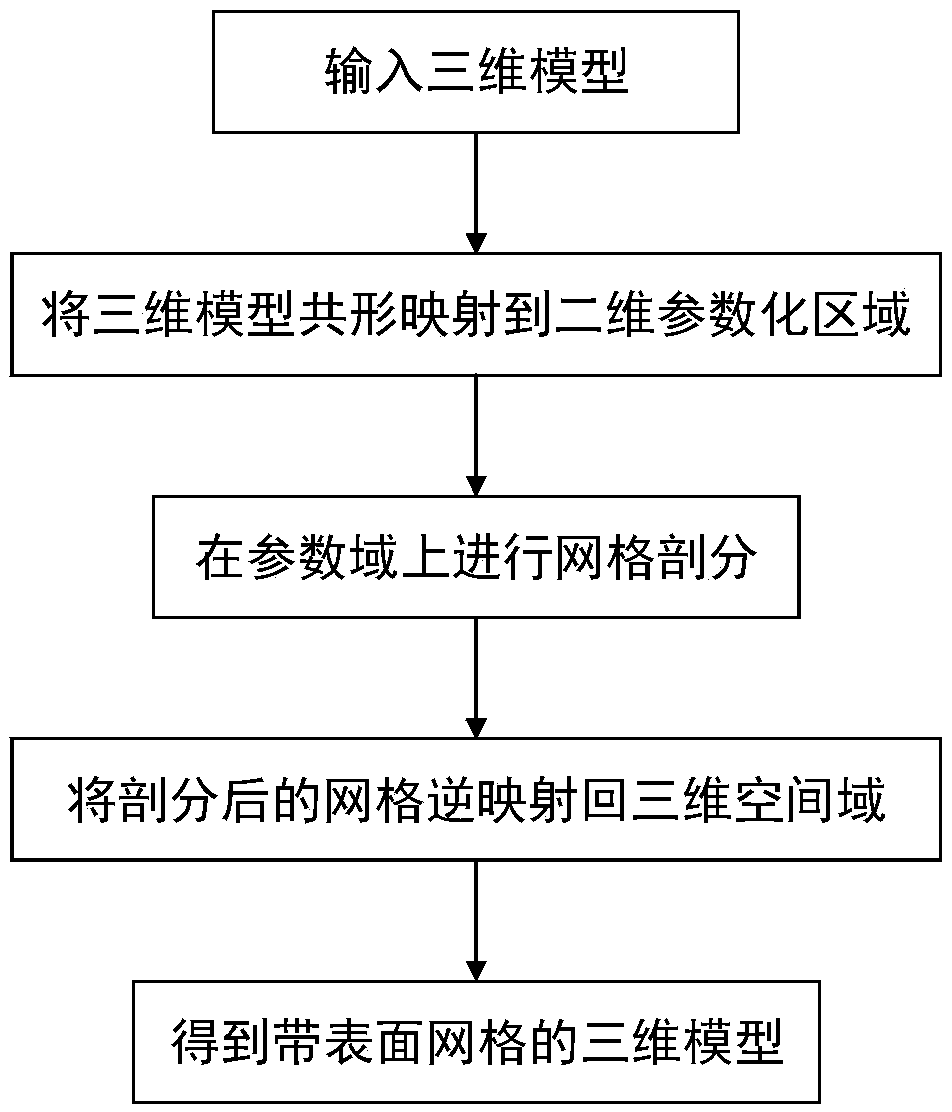
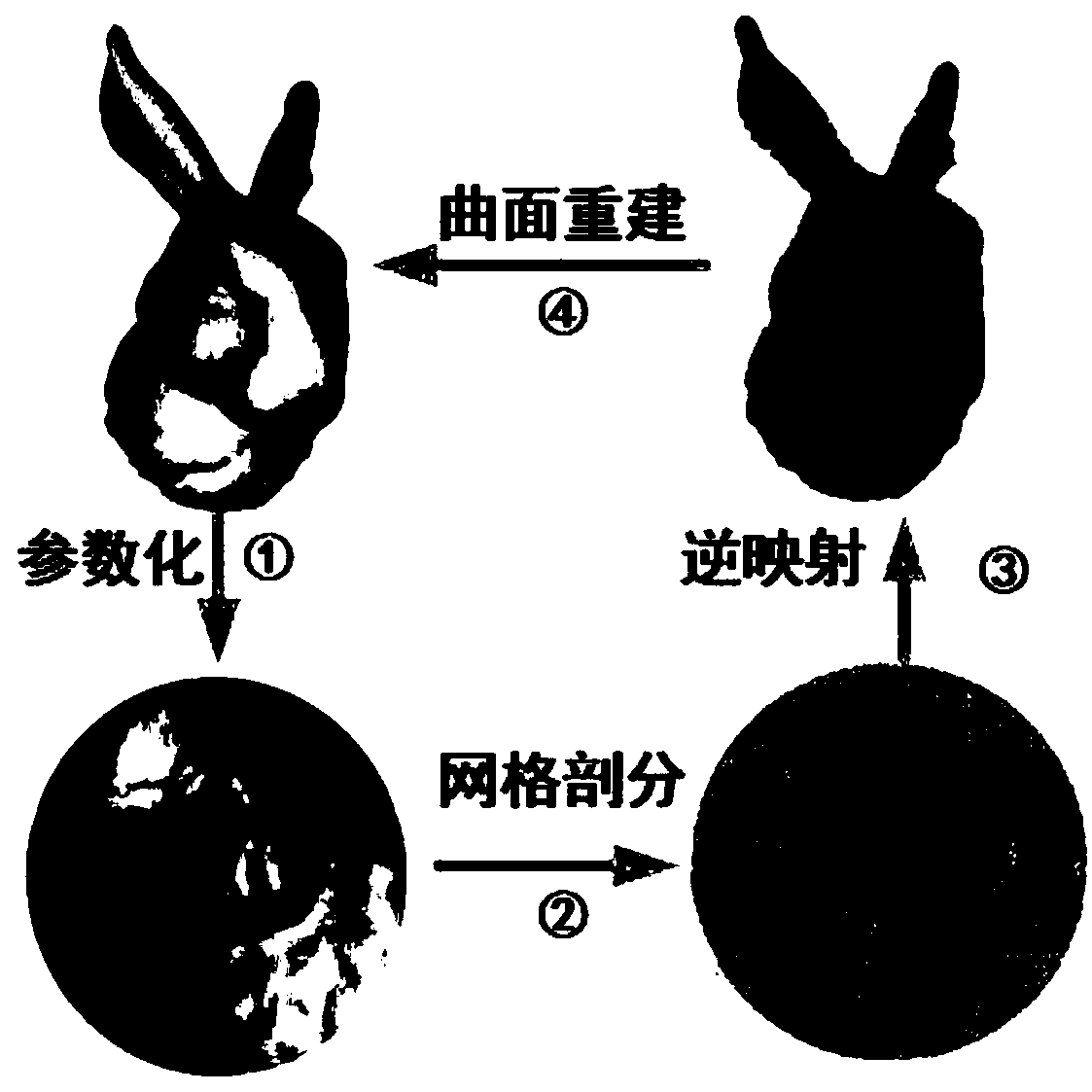
A surface mesh generation method of a digital model based on conformal geometry
PendingCN109377561AEasy split operationQuality improvement3D modellingNODALComputer graphics (images)
The invention provides a surface mesh generation method of a digital model based on conformal geometry, which aims at simplifying the surface mesh generation problem of a three-dimensional model to atwo-dimensional plane for processing, wherein the method comprises according to the topological information of the three-dimensional model, selecting the conformal mapping function from the three-dimensional model to the two-dimensional parameter region, and then generating the finite element mesh on the parameter region, in the mesh generation of parametric domain, generating the triangular element or quadrilateral element, and then mapping the mesh of parametric domain into the mesh of spatial domain by conformal inversion according to the mapping function from parametric domain to spatial domain, and keeping the topological relationship between nodes unchanged, so that the mesh of spatial domain is the surface mesh of the 3D model. Compared with the mesh generation on the surface of 3Dmathematical model directly, the mesh generation on parameterized area is simpler and has less computational complexity. The surface mesh generated by this method is of high quality and high precision.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
Unconstrained paving and plastering method for generating finite element meshes
ActiveUS7671858B1Computation using non-denominational number representationComplex mathematical operationsComputer softwareComputer science
Computer software for and a method of generating a conformal all quadrilateral or hexahedral mesh comprising selecting an object with unmeshed boundaries and performing the following while unmeshed voids are larger than twice a desired element size and unrecognizable as either a midpoint subdividable or pave-and-sweepable polyhedra: selecting a front to advance; based on sizes of fronts and angles with adjacent fronts, determining which adjacent fronts should be advanced with the selected front; advancing the fronts; detecting proximities with other nearby fronts; resolving any found proximities; forming quadrilaterals or unconstrained columns of hexahedra where two layers cross; and establishing hexahedral elements where three layers cross.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com