Method for accurately reconstructing dissimilar material microcosmic finite element grid model on basis of CT (computed tomography) images
A technology of heterogeneous materials and CT images, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problems of limited grid quality, easy loss of small information, low precision of finite element analysis, etc., to improve The effect of precision
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
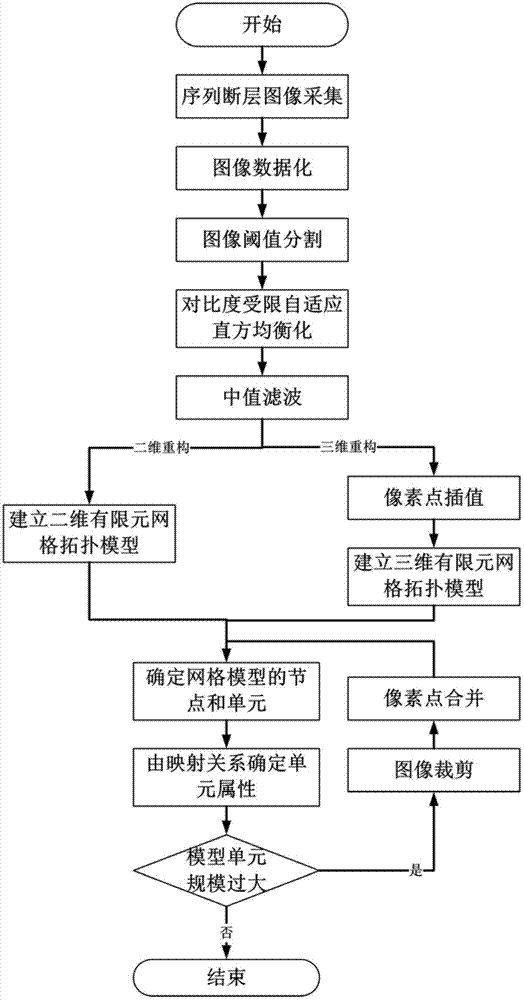
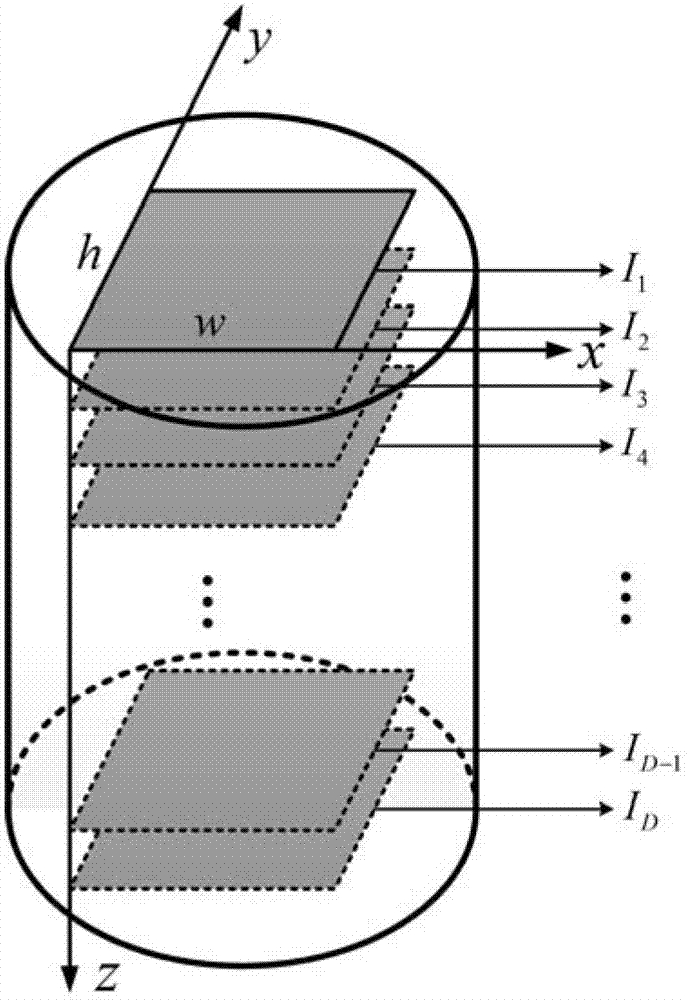
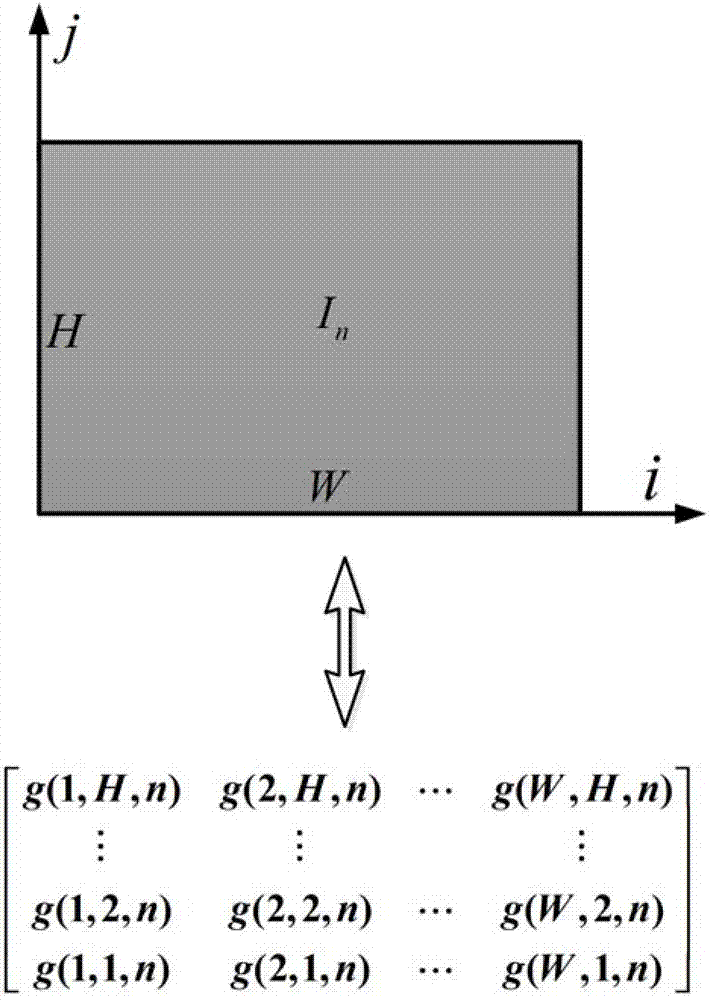
[0070] The present invention first collects sequential tomographic images of heterogeneous materials through industrial CT, and digitizes the collected images; then thresholds the images through gray histograms and cumulative distribution functions, and uses contrast-limited adaptive histogram Value filtering and pixel point interpolation improve the accuracy of the image reflecting the real microstructure of the material; then, on the basis of establishing the finite element grid topology model, the unit material properties of the model are determined through the mapping relationship between the topology model and the tomographic image, and the image Clipping and pixel binning reduce the size of the elements in the finite element mesh model. The specific implementation process of the whole finite element mesh model reconstruction is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the specific technical problems are described in detail below according to the process.
[0071] 1. Sequence imag...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com