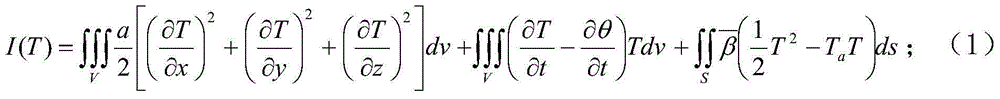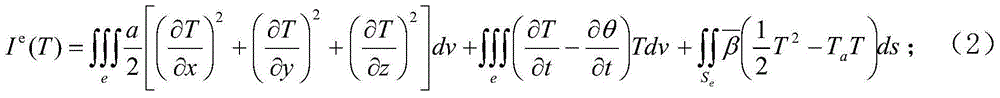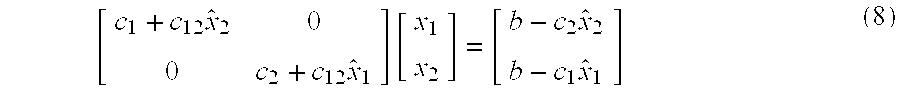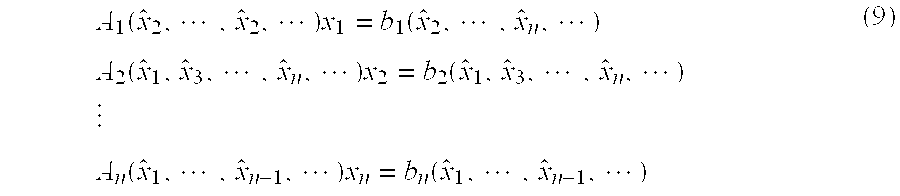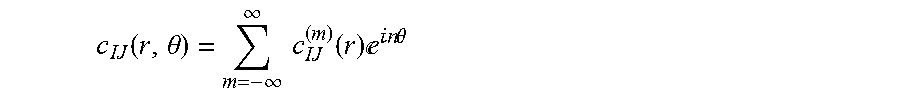Patents
Literature
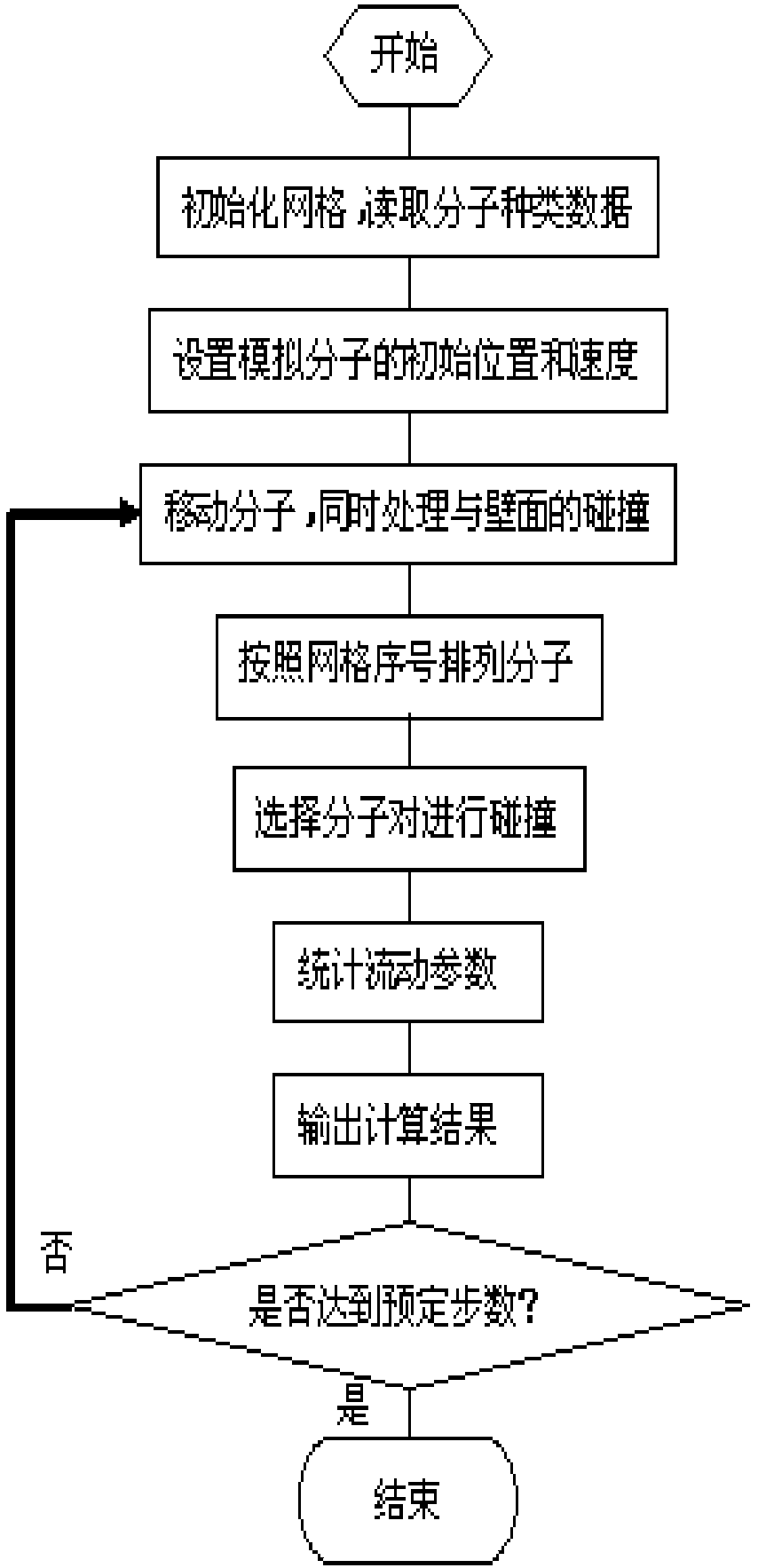
126 results about "Governing equation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
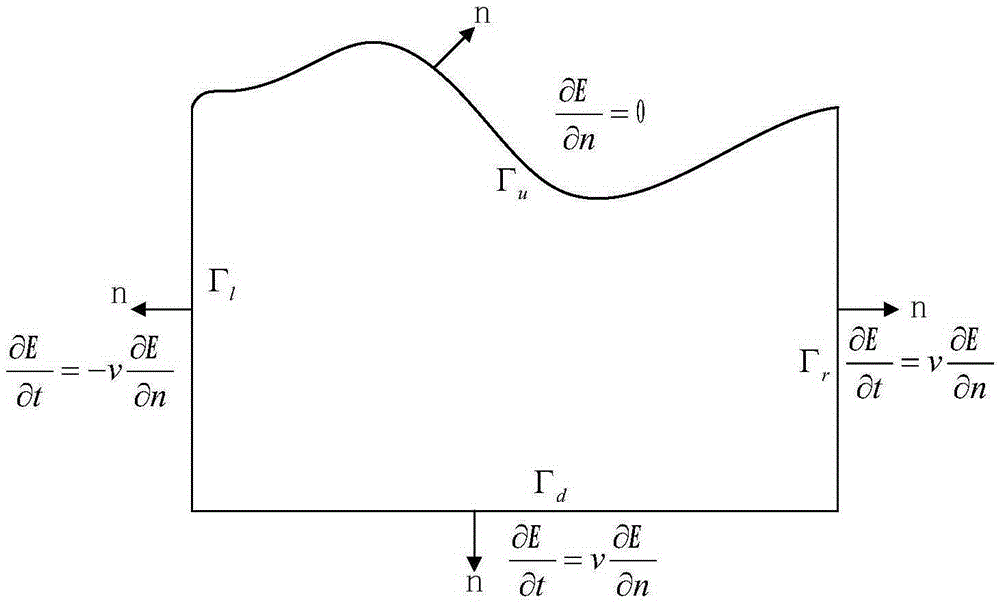
The governing equations of a mathematical model describe how the values of the unknown variables (i.e. the dependent variables) change when one or more of the known (i.e. independent) variables change.
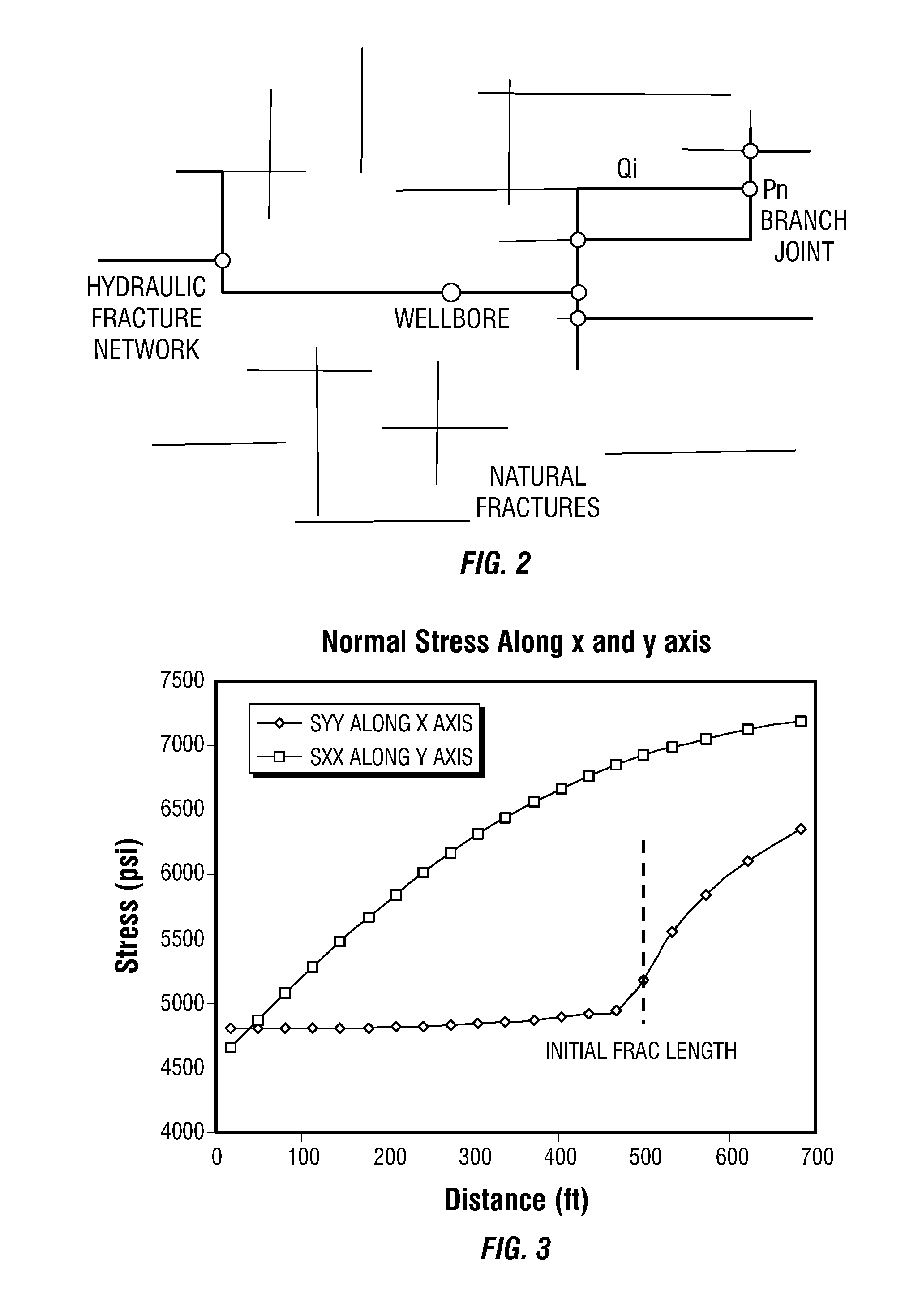
Simulations for Hydraulic Fracturing Treatments and Methods of Fracturing Naturally Fractured Formation
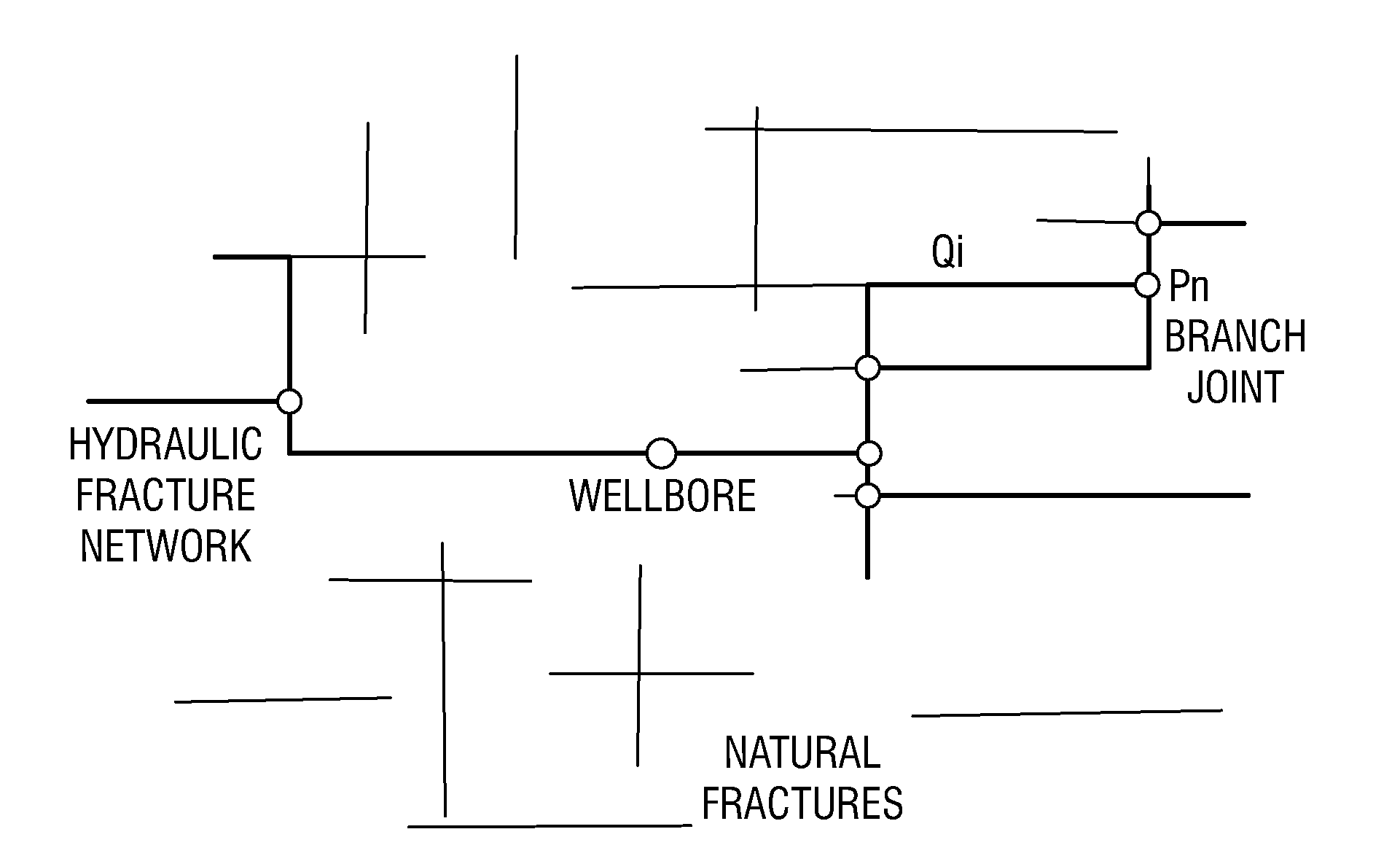
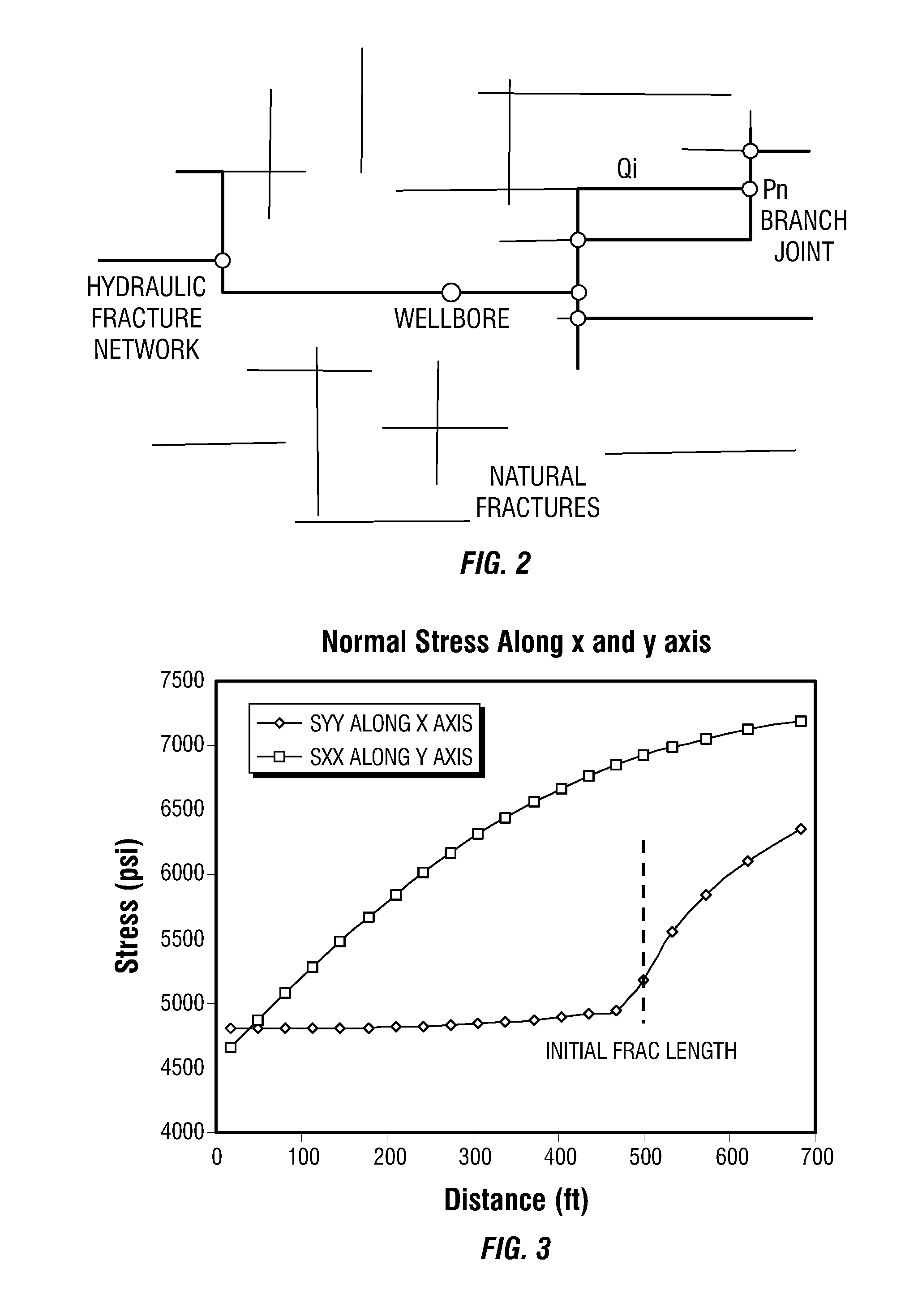
A hydraulic fracture design model that simulates the complex physical process of fracture propagation in the earth driven by the injected fluid through a wellbore. An objective in the model is to adhere with the laws of physics governing the surface deformation of the created fracture subjected to the fluid pressure, the fluid flow in the gap formed by the opposing fracture surfaces, the propagation of the fracture front, the transport of the proppant in the fracture carried by the fluid, and the leakoff of the fracturing fluid into the permeable rock. The models used in accordance with methods of the invention are typically based on the assumptions and the mathematical equations for the conventional 2D or P3D models, and further take into account the network of jointed fracture segments. For each fracture segment, the mathematical equations governing the fracture deformation and fluid flow apply. For each time step, the model predicts the incremental growth of the branch tips and the pressure and flow rate distribution in the system by solving the governing equations and satisfying the boundary conditions at the fracture tips, wellbore and connected branch joints. An iterative technique is used to obtain the solution of this highly nonlinear and complex problem.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
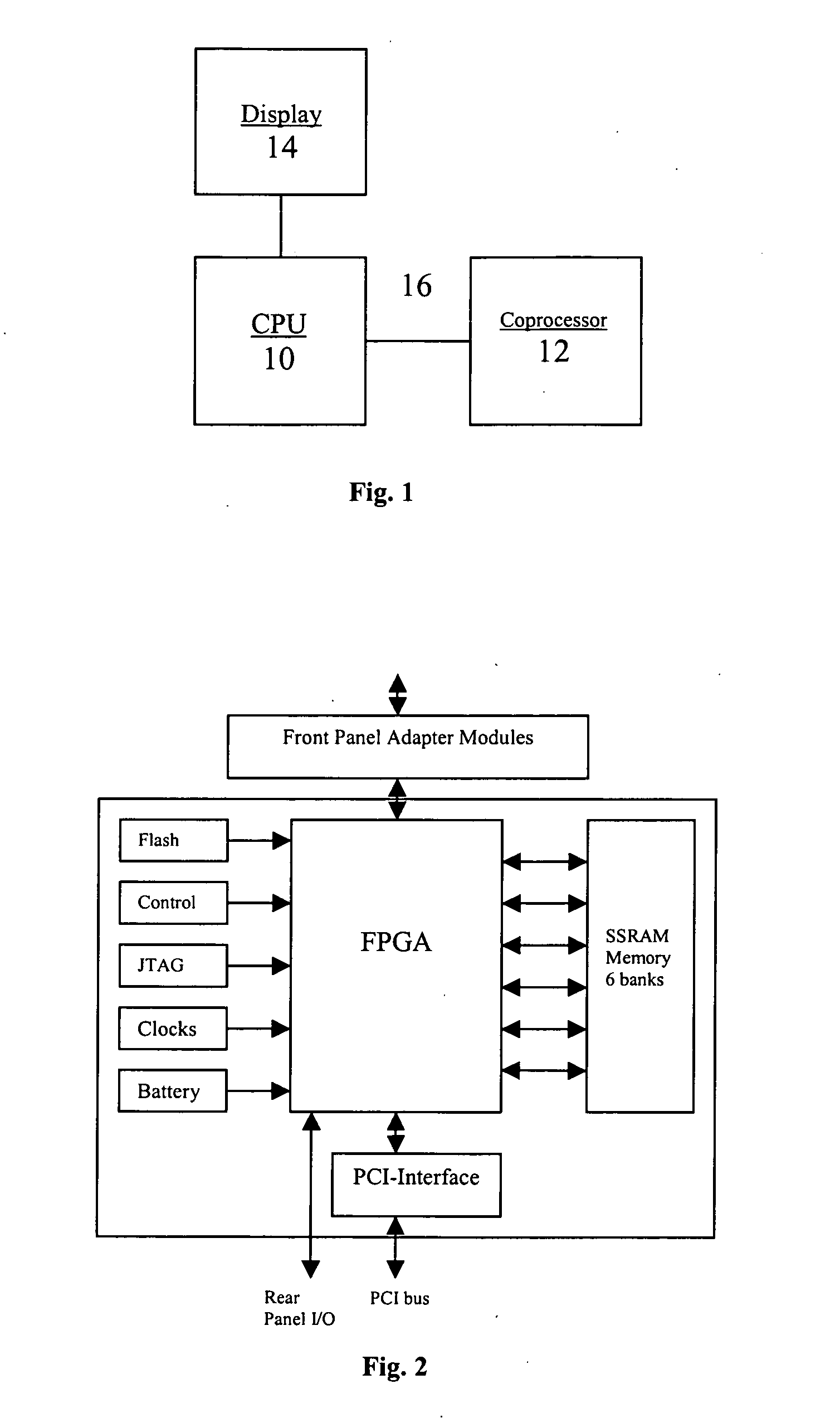
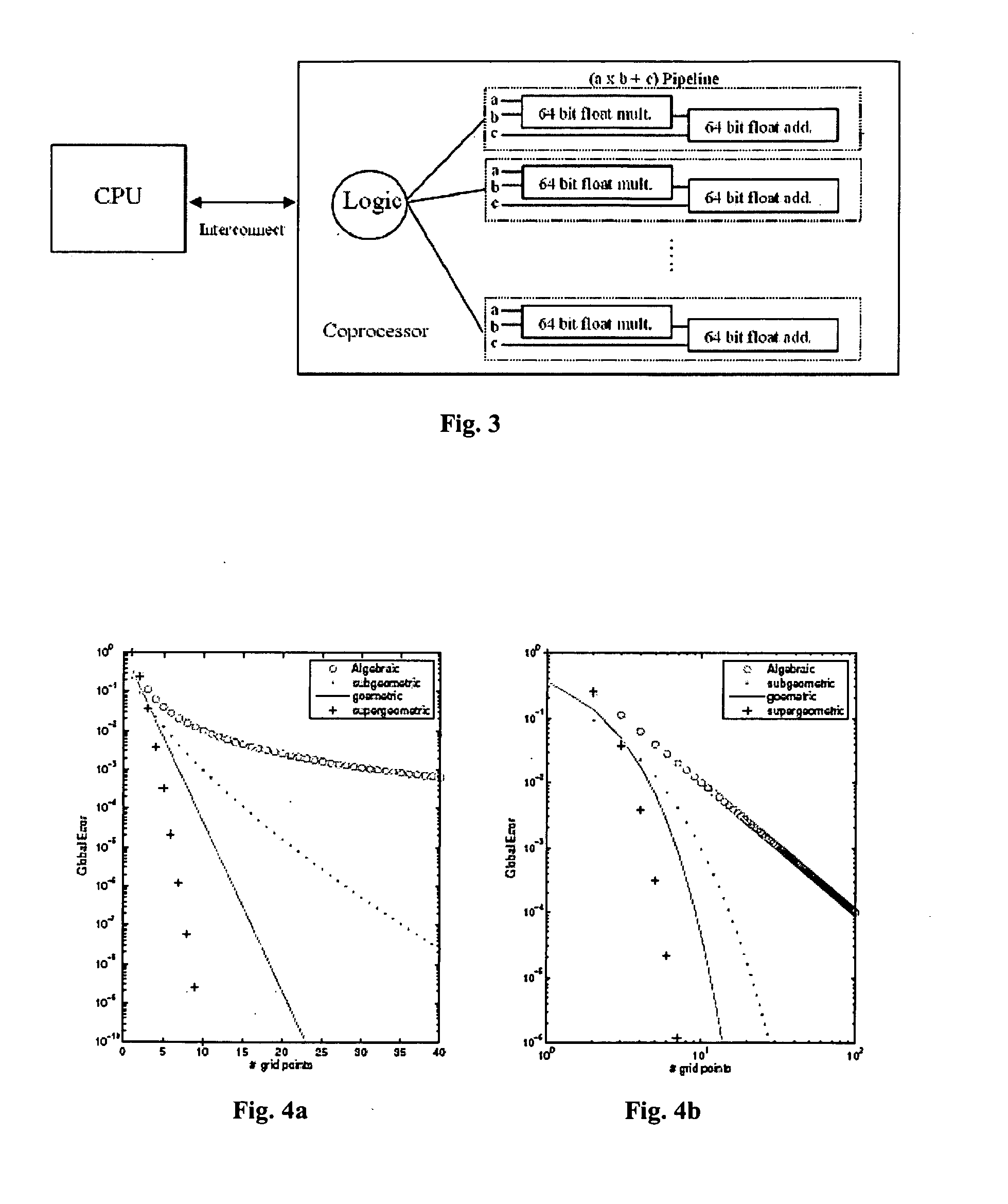
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) coprocessor-enhanced system and method
InactiveUS20070219766A1Cost-effectiveWide variety of usDesign optimisation/simulationProgram controlCoprocessorDisplay device
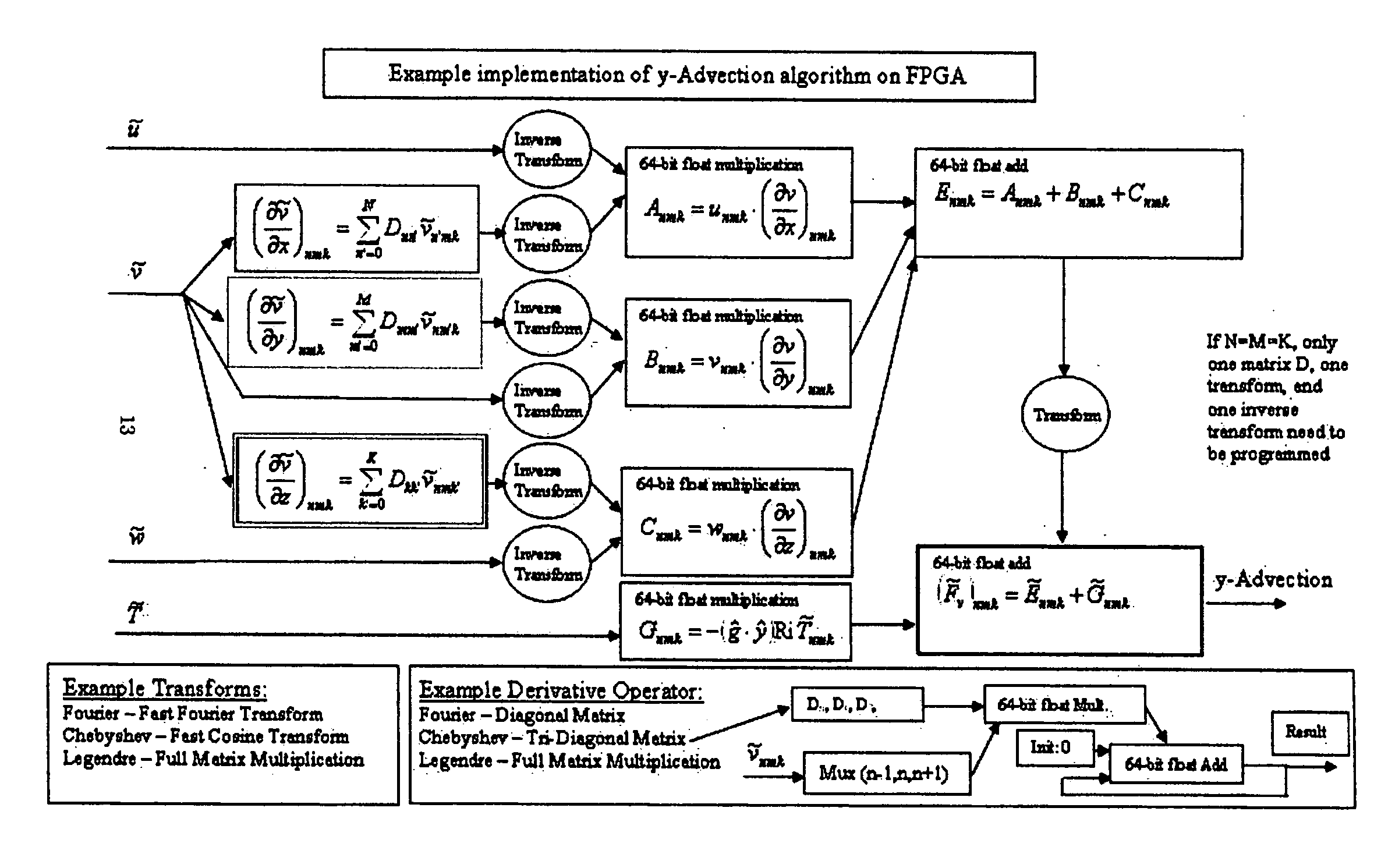
The present invention provides a system, method and product for porting computationally complex CFD calculations to a coprocessor in order to decrease overall processing time. The system comprises a CPU in communication with a coprocessor over a high speed interconnect. In addition, an optional display may be provided for displaying the calculated flow field. The system and method include porting variables of governing equations from a CPU to a coprocessor; receiving calculated source terms from the coprocessor; and solving the governing equations at the CPU using the calculated source terms. In a further aspect, the CPU compresses the governing equations into combination of higher and / or lower order equations with fewer variables for porting to the coprocessor. The coprocessor receives the variables, iteratively solves for source terms of the equations using a plurality of parallel pipelines, and transfers the results to the CPU. In a further aspect, the coprocessor decompresses the received variables, solves for the source terms, and then compresses the results for transfer to the CPU. The CPU solves the governing equations using the calculated source terms. In a further aspect, the governing equations are compressed and solved using spectral methods. In another aspect, the coprocessor includes a reconfigurable computing device such as a Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA). In yet another aspect, the coprocessor may be used for specific applications such as Navier-Stokes equations or Euler equations and may be configured to more quickly solve non-linear advection terms with efficient pipeline utilization.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Simulations for hydraulic fracturing treatments and methods of fracturing naturally fractured formation
A hydraulic fracture design model that simulates the complex physical process of fracture propagation in the earth driven by the injected fluid through a wellbore. An objective in the model is to adhere with the laws of physics governing the surface deformation of the created fracture subjected to the fluid pressure, the fluid flow in the gap formed by the opposing fracture surfaces, the propagation of the fracture front, the transport of the proppant in the fracture carried by the fluid, and the leakoff of the fracturing fluid into the permeable rock. The models used in accordance with methods of the invention are typically based on the assumptions and the mathematical equations for the conventional 2D or P3D models, and further take into account the network of jointed fracture segments. For each fracture segment, the mathematical equations governing the fracture deformation and fluid flow apply. For each time step, the model predicts the incremental growth of the branch tips and the pressure and flow rate distribution in the system by solving the governing equations and satisfying the boundary conditions at the fracture tips, wellbore and connected branch joints. An iterative technique is used to obtain the solution of this highly nonlinear and complex problem.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
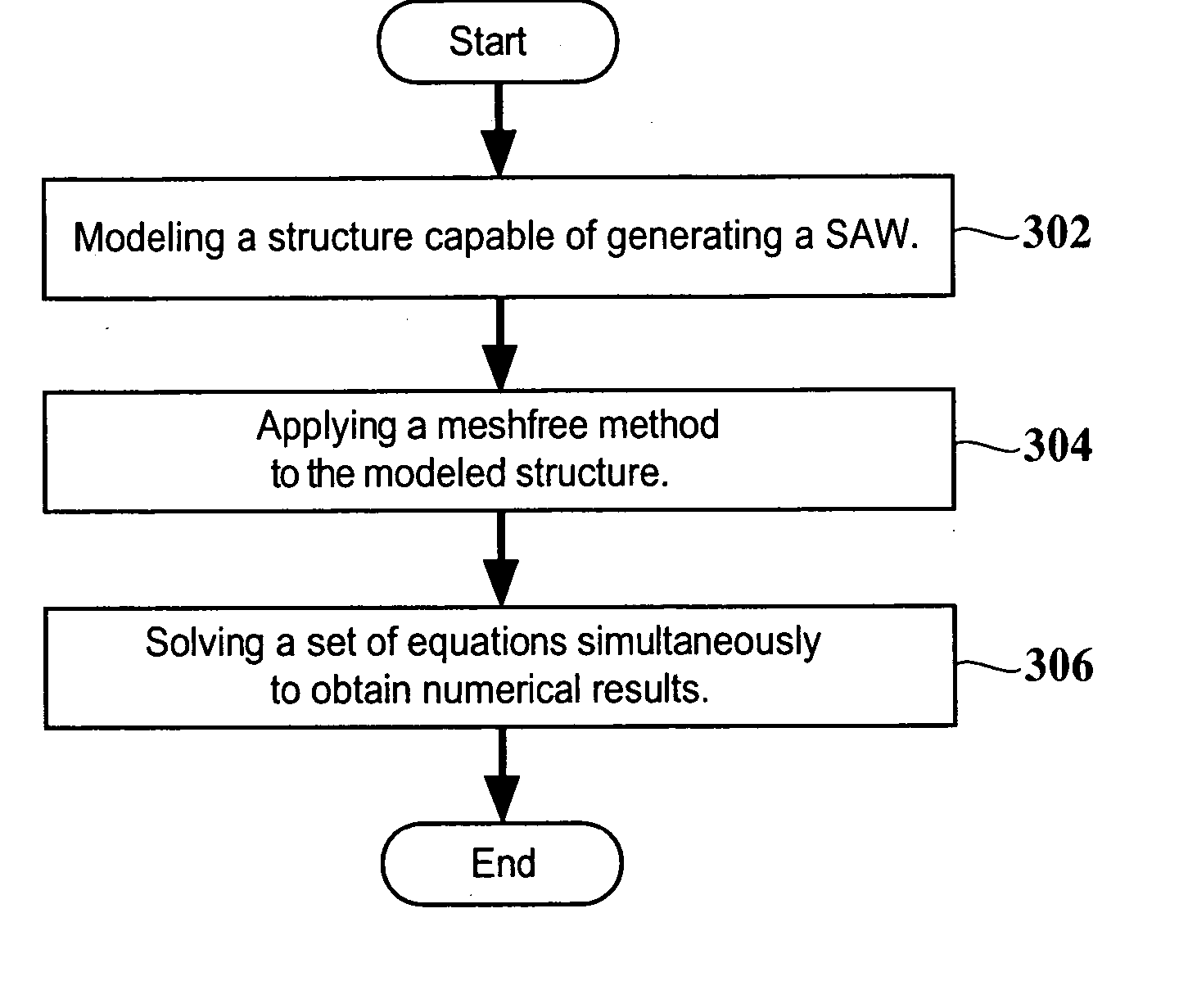
Method and system for simulating a surface acoustic wave on a modeled structure
InactiveUS20060149513A1Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationElectricityGoverning equation
A method of simulating a surface acoustic wave (SAW) on a structure that is modeled on a computer or other processor-based device enables the testing of actual SAW devices or to develop improved SAW devices. In this method, the modeled structure is preferably that of a corrugated structure that includes an electrode disposed on top of a piezoelectric substrate. A meshfree method then is applied to the modeled structure using Newton's equation of motion and Gauss's equation of charge conservation as governing equations. Subsequently, a set of equations is solved simultaneously to obtain numerical results.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Heat front capture in thermal recovery simulations of hydrocarbon reservoirs
ActiveUS20130041633A1Improve stabilityHigh temperature accuracyFluid removalComputation using non-denominational number representationEnergy balancingMathematical model
A numerical procedure is disclosed to improve the prediction of heat fronts when simulating hot fluid injection in viscous hydrocarbon reservoirs. The mathematical model is composed of the conventional governing equations that describe multiphase fluid flow and energy balance. The reservoir geometry can be partitioned into a regular Cartesian grid or an irregular corner-point geometry grid. The numerical procedure uses the finite different (FD) method to solve the flow equations and the discontinuous Galerkin (DG) method to solve the energy balance equation. The proposed FD-DG method is an alternative to the traditional solution procedure that uses the FD method to solve both the flow and the energy equations. The traditional method has the deficiency that it may require excessive number of grid cells to achieve acceptable resolution of the heat fronts. The proposed FD-DG method significantly reduces numerical dispersion near discontinuities in the solution of the energy equation and therefore provides a better capture of the heat fronts. To obtain a desired accuracy in the energy equation solution, the FD-DG method can be orders of magnitude faster than the traditional method. The superiority of the FD-DG method is that it converges on coarser grids while the traditional method requires much finer grids.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Building method for laser welding heat source model
ActiveCN103049623AEfficiency is obviousImprove efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsCouplingOpen source
The invention relates to a building method for a welding heat source model, in particular to a building method for a laser welding heat source model. The method solves the problem in laser welding simulation of large-scale complex construction members that laser heat source achieving difficulty is large, and calculating efficiency is low. The method includes: step 1, building a three-dimensional finite element grid model; step 2, building a Gaussian heat source mode of a heat source surface; step 3, expanding welding energy along the laser welding pool depth direction; and step 4, solving a governing equation based on finite element software and conducting heat-machine coupling calculation, namely building of the laser welding heat source model is finished. The building method is applied to the field of welding.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Simulation analysis method for pressure separation of spacecraft
ActiveCN108388742ASustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationBoltzmann equationContinuous flow
The invention relates to a simulation analysis method for pressure separation of a spacecraft, and belongs to the technical field of spacecraft simulation. The simulation analysis method comprises thefollowing steps: decomposing a pressure compartment into an internal continuous flow field and an external rarefied flow field for computation respectively; building a theoretical model to give the boundary condition of the entrance / exit of a computation domain; computing an internal region flow field by a CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) method, and solving an external region flow field by a DSMC (Direct simulation of Monte Carlo) method; finally determining the disturbing force of the pressure separation on two spacecrafts according to a flow field analysis result. The computed flow fieldcan be divided into two parts: a flow field inside the pressure compartment (continuous flow) and a flow field outside the spacecraft (rarefied flow). The basic governing equation of the continuous flow field in the pressure compartment is a Navier-Stokes equation, which is computed by the CFD method; the basic governing equation of the rarefied flow field outside the spacecraft is a Boltzmann equation, which is simulated by the DSMC method.
Owner:BEIJING SPACE TECH RES & TEST CENT
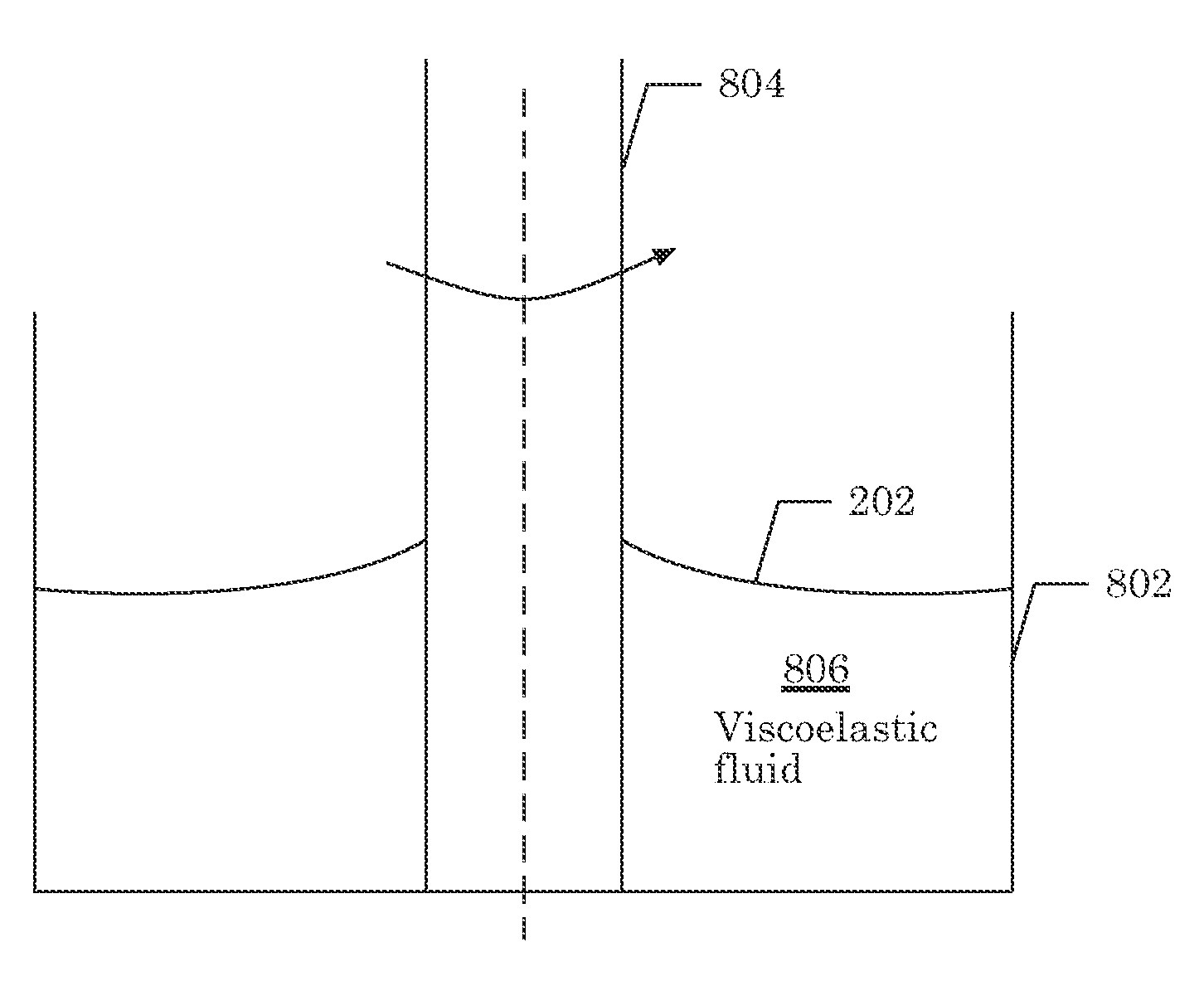
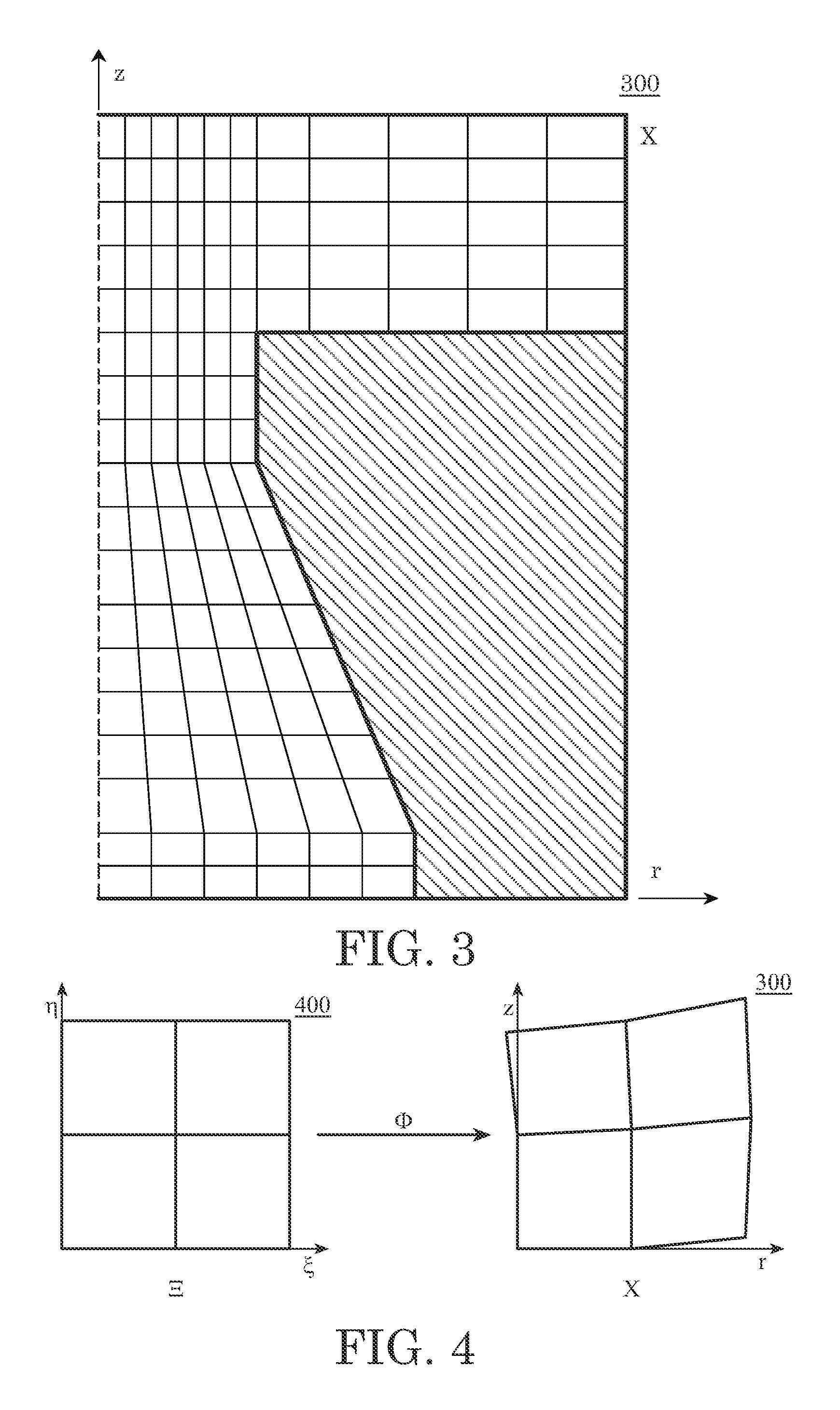
Coupled Algorithms on Quadrilateral Grids for Generalized Axi-Symmetric Viscoelastic Fluid Flows
InactiveUS20080103742A1Pipeline systemsDesign optimisation/simulationGoverning equationQuadrilateral grid
The present invention is directed towards systems and methods for simulating and analyzing viscoelastic fluid flow. The fluid flows through a channel and is ejected from a channel. The fluid has an interface between a first fluid and a second fluid. The method includes performing finite difference analysis and using a level set projection method to solve equations governing the viscoelastic flow of the fluids through the channel. The equations governing the viscoelastic flow include an azimuthal velocity term that is an approximate description of the azimuthal flow of the fluid. The equations governing the viscoelastic flow also include an approximation of the stress experienced by the fluids being simulated. The equations governing the viscoelastic flow include an advection term that includes an azimuthal velocity term. The finite difference analysis used to solve the governing equations includes a second-order Godunov type upwind scheme to update the advection terms over time. The level set for the first and second fluids is updated periodically during the simulation.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Calculating method of large-volume concrete cooling temperature field
InactiveCN104809334AReduce difficultyFast Calculation AnalysisSpecial data processing applicationsCooling effectDegrees of freedom
The invention discloses a calculating method of a large-volume concrete cooling temperature field. The method comprises the following steps: superposing the energy of concrete dissipated by the wall surface of a cooling water pipe onto a conventional fonctionelle; establishing a finite element governing equation of the concrete containing the cooling water pipe through a variational principle based on the composite fonctionelle; and then estimating an equivalent heat emission coefficient of a concrete contact surface based on the thickness and the heat conductivity coefficient of the cooling water pipe. The existence of the cooling water pipe is not considered during the mesh generation; sections intersected with concrete units are found out based on the positions of the cooling water pipe after the mesh is formed, thereby a cooling water pipe mesh is automatically formed. The method does not increase the difficulty in the mesh generation, and precisely considers the temperature change around the cooling water pipe. Therefore, the method is an efficient method for analyzing the cooling effect of the cooling water pipe; and the problems that the conventional methods are too big in the degree of freedom and are unable to be calculated by computers are solved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
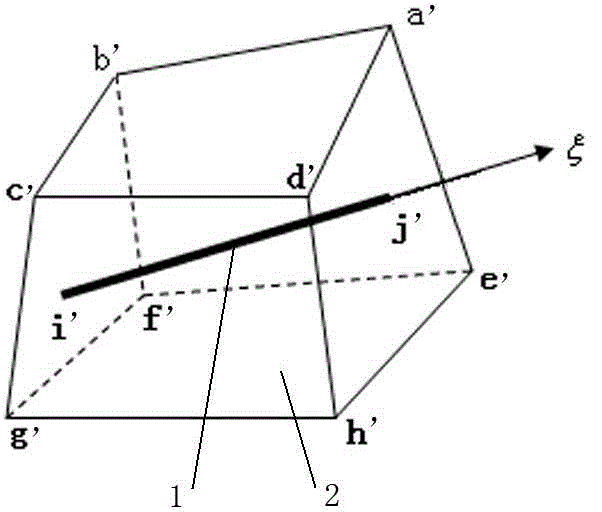
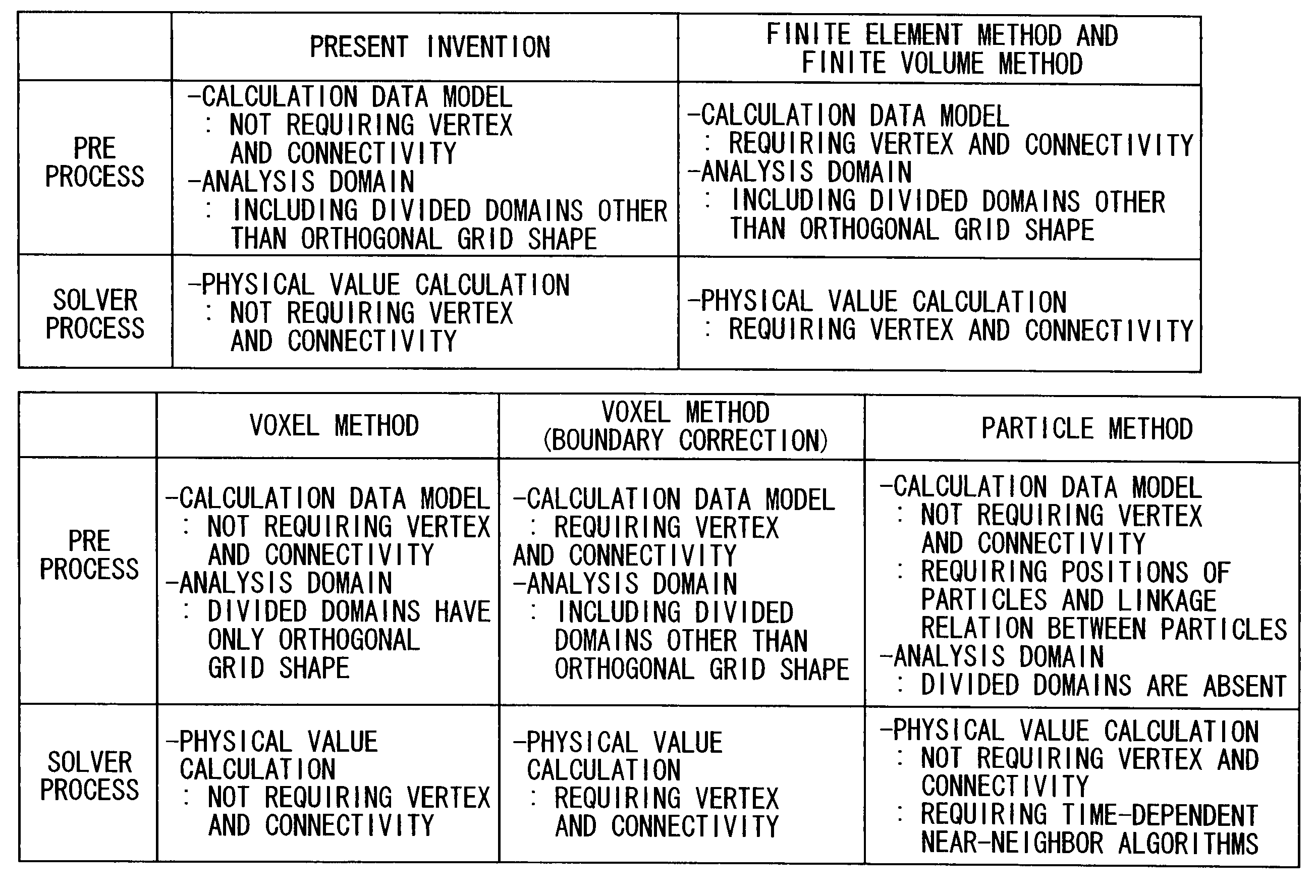
Calculation method for physical value, numerical analysis method, calculation program for physical value, numerical analysis program, calculation device for physical value, and numerical analysis device
ActiveUS20120095738A1Increase flexibilityTimely controlChemical property predictionDesign optimisation/simulationGoverning equationResidual method
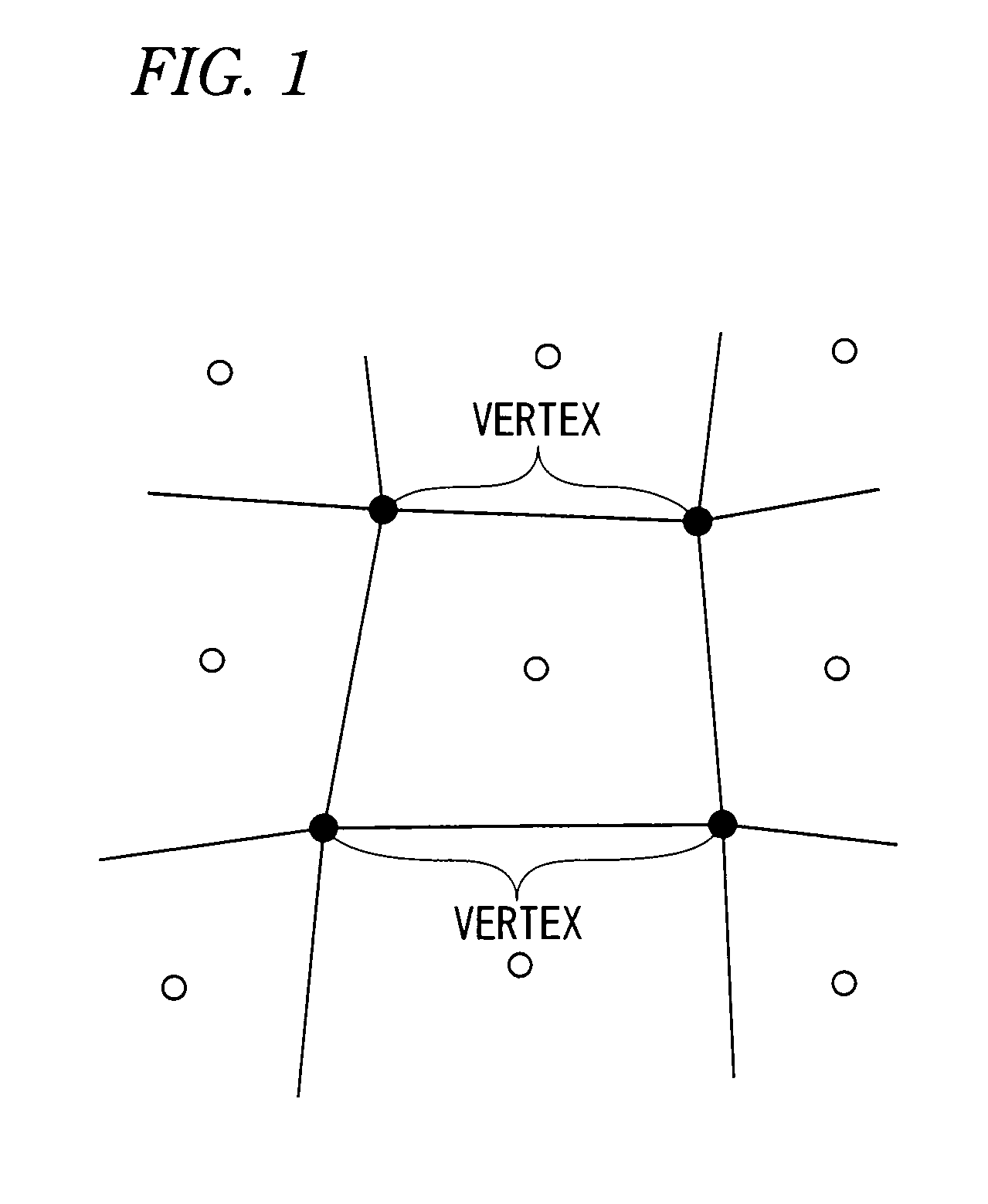
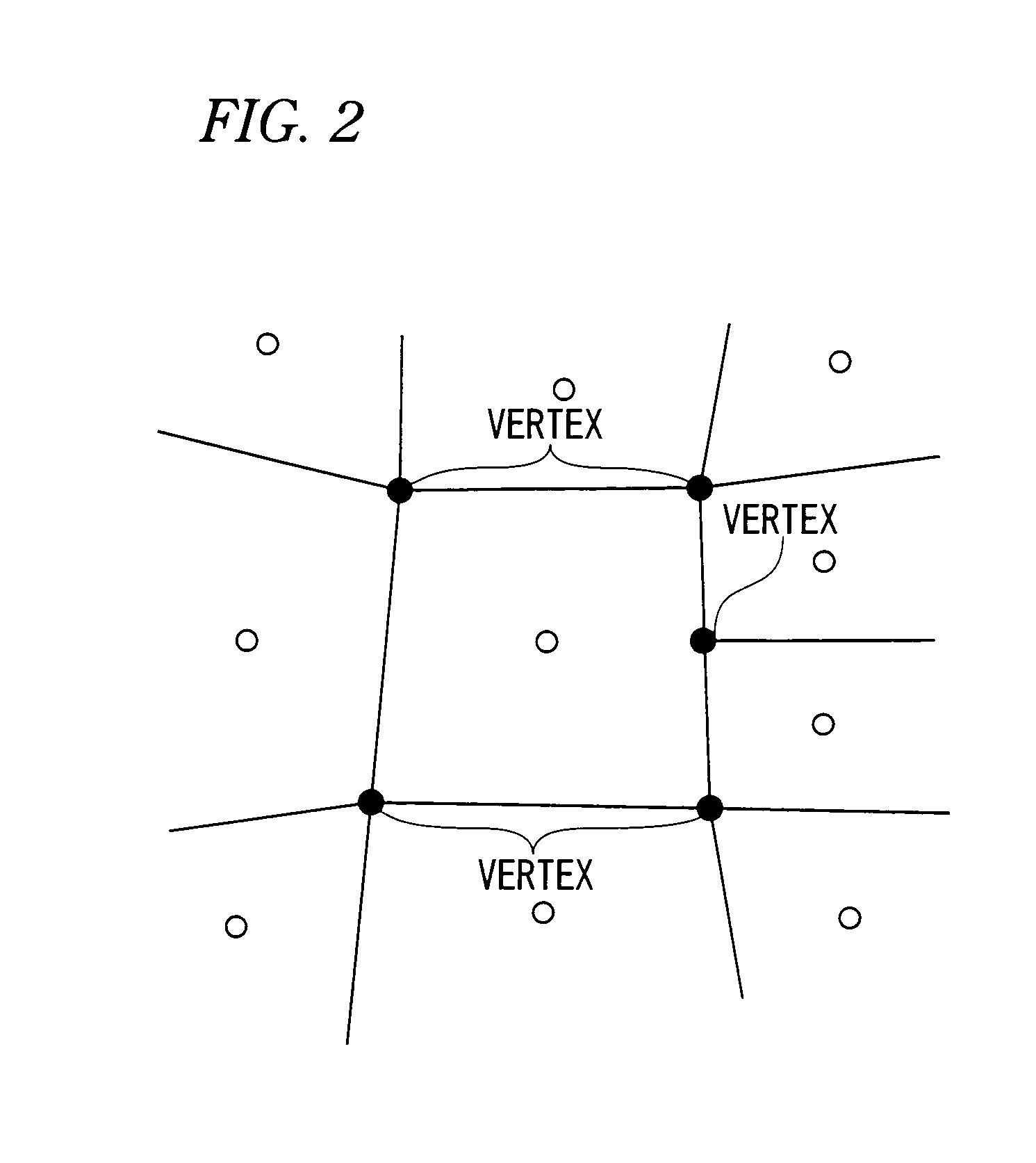
A calculation method for physical value for calculating physical values in a numerical analysis method for numerically analyzing a physical phenomenon, comprises a physical value calculation step of calculating physical values in an analysis domain divided into a plurality of divided domains, wherein in the physical value calculation step, the physical values are calculated by using: a discretized governing equation that uses values not requiring coordinates (Vertex) of vertices of the divided domains and connectivity information (Connectivity) of the vertices and that is derived on the basis of a weighted residual method; and a calculation data model in which volumes of the divided domains and characteristic values of boundary surface indicating characteristics of boundary surfaces of adjacent ones of the divided domains are provided as the values not requiring coordinates (Vertex) of vertices of the divided domains and connectivity information (Connectivity) of the vertices.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Line source time domain electromagnetic response numerical calculation method based on meshless method
ActiveCN105426339AGet rid of dependenceImprove smoothnessComplex mathematical operationsTerrainElectromagnetic response
The invention relates to a line source time domain electromagnetic response numerical calculation method based on meshless method, particularly a numerical simulation which can overcome dependence on mesh in the conventional numerical calculation method and is suitable for time domain electromagnetic surveying under complex terrain. In the line source time domain electromagnetic response numerical calculation method based on meshless method, based on a governing equation and a definite condition which the transient electromagnetic method satisfies, a generic function of a two-dimensional line source boundary value problem is established, essential boundary conditions are loaded through a penalty method, a paraxial approximate equation is provided to eliminate reflected waves at truncated boundaries, time discretization is carried out through a Crack-Nicolson format, and a recurrence equation is obtained. Based on an isoparametric element thought, units with regular shape in local coordinates are discretized to be irregular solving objects of which nodes are distributed at random. The recurrence equation is solved through a LU decomposition method, and finally, a field value of each node in a solving region is obtained. Calculation result shows that, with the method provided by the invention, a shape function has good smoothness, simulation precision is high, maximum error is not more than 1*10<-3>, and electromagnetic method high-accuracy numerical calculation is realized.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
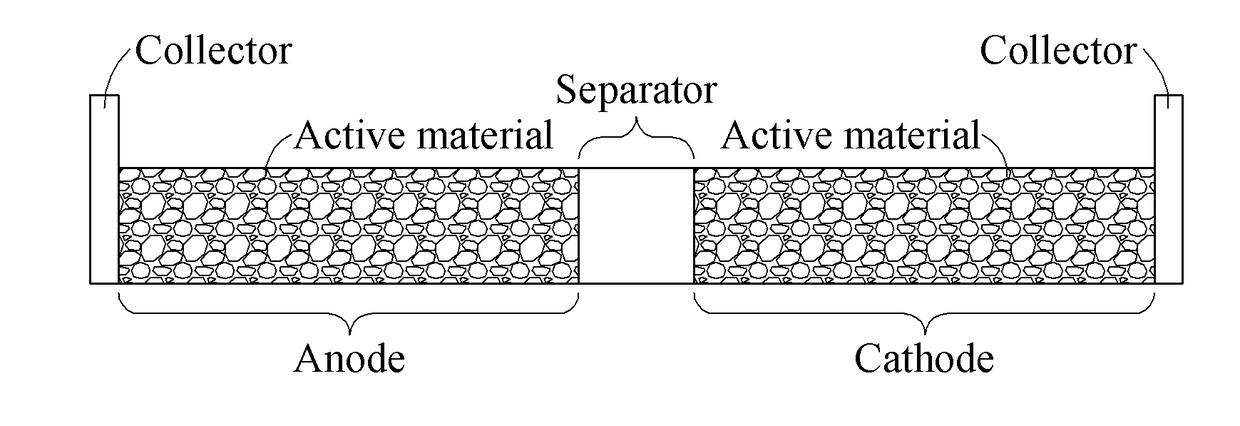
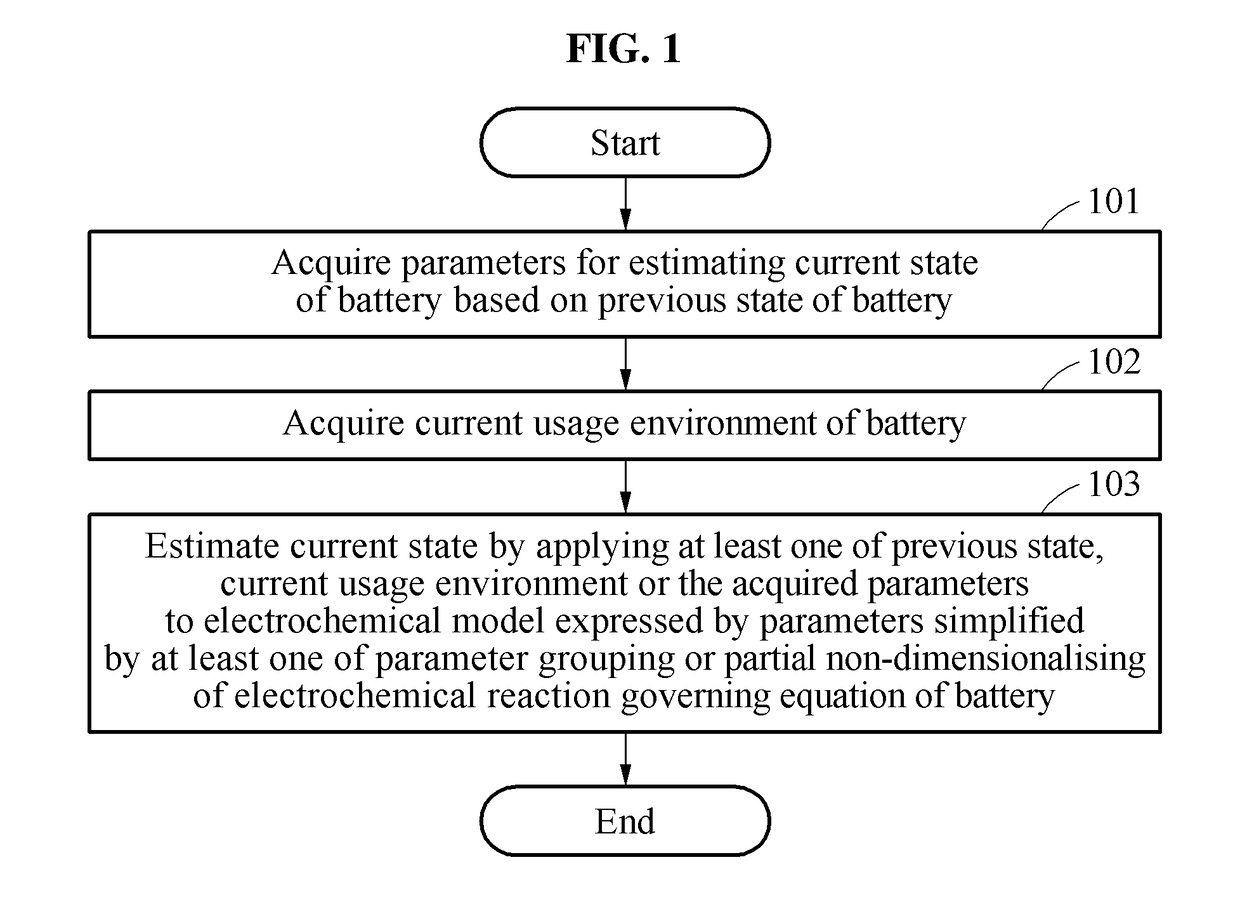
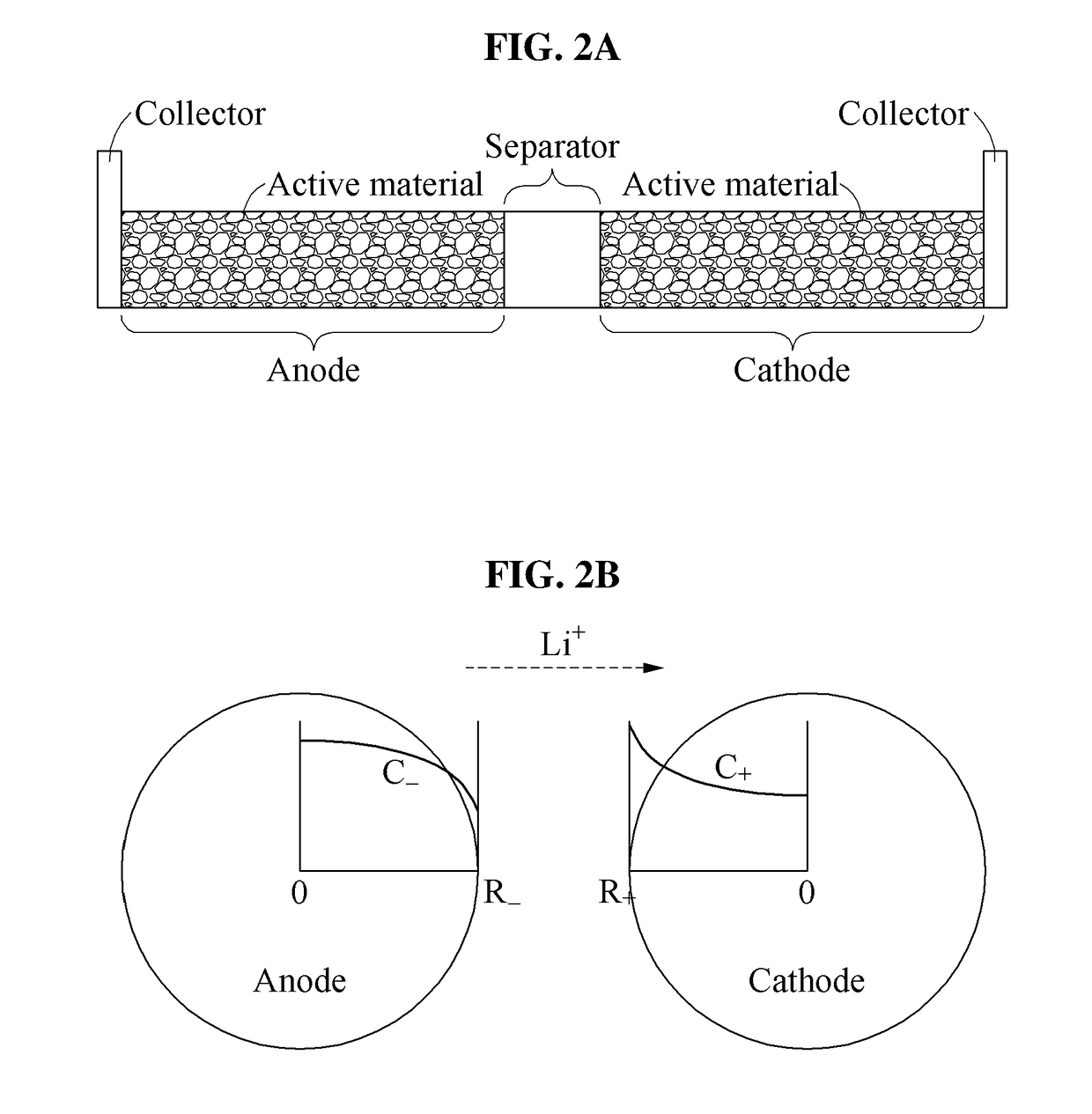
Method and apparatus estimating and controlling battery state
ActiveUS20180198300A1Well formedCircuit monitoring/indicationDifferent batteries chargingElectrochemical responseEngineering
A method of estimating a battery state includes acquiring one or more parameters for estimating a present state of the battery based on a previous state of the battery; acquiring a present usage environment of the battery; and estimating the present state by applying any one or any combination of any two or more of the previous state, the present usage environment, and the acquired one or more parameters to an electrochemical model that is expressed by simplified parameters simplified by either one or both of parameter grouping and partial non-dimensionalising of an electrochemical reaction governing equation of the battery.
Owner:OXFORD UNIV INNOVATION LTD +1
Method for predicting shape and size of CMT welding seam based on ANSYS
InactiveCN103366044AThe result is objectivePowerfulSpecial data processing applicationsElement analysisEvaporation
The invention discloses a method for predicting a shape and a size of a CMT (Cold Metal Transfer) welding seam based on ANSYS. The method comprises the steps that S1, data during a CMT welding course is acquired; S2, a finite element analysis model is established, and reinforcement of the welding seam is processed; S3, mesh dividing is performed; S4, heat source treatment is performed; S5, a governing equation is established; and S6, an transient temperature field is obtained, temperature field distribution is calculated, a time step is calculated, a self-adaption step is adopted, and the shape and the size of the cross section of the welding seam are obtained according to a calculation result of a welding temperature field, and compared with a full size of the welding seam. The prediction is performed based on the following assumptions that a boundary heat transfer condition and a geometrical shape in a width direction are symmetrical, the heat physical property of a material changes with the temperature, and evaporation of metal in a molten pool is not considered. The method is simple, convenient and quick; influences of various force on the molten pool are considered; a result is objective; very high prediction precision of the shape and the size of the CMT welding seam and detailed information of the temperature distribution of the whole CMT welding course can be obtained; set and optimized parameters can be provided for the welding course; and the applicability is high.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID +1
Urgent frequency modulation (FM) control method of energy storage system in micro-grid
InactiveCN102709928ASolving Coordinated Control ProblemsAvoid pulsed active power outputAc network load balancingMicro gas turbineElectric network
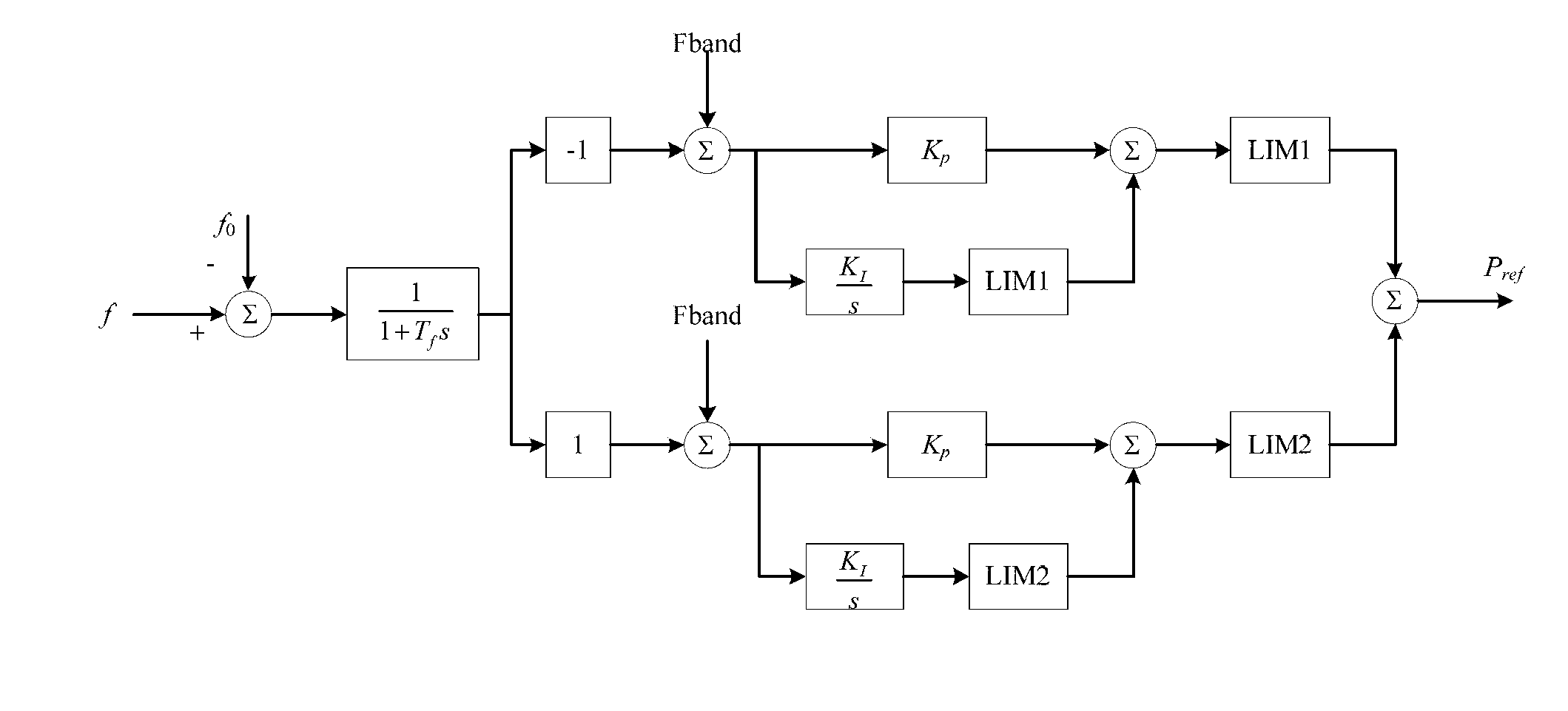
Disclosed is an urgent FM control method of an energy storage system in a micro-grid. The technical scheme includes that distributed power supplies and the energy storage system in the micro-grid are in a communication connection; a diesel-driven generator, a microturbine or other synchronous generators serves as a main power supply, the energy storage system serves as a micro-grid auxiliary adjusting unit, a PQ control method is adopted for the merging into the micro-grid through a monopolar type DC / AC or a bipolar type DC-DC / AC, and one of the functions is configured to be urgent FM. The control method includes providing an active power output reference value of the energy storage system according to the governing equation P<ref> =P0+PI*delta f; controlling the energy storage system output P to follow the active power reference value Pref by adoption of the PQ control method; and enabling the system frequency to be within an allowed range under the joint adjustment of the main power source and the energy storage system of the micro-grid. The governing equation P<ref> =P0+PI*delta f is adopted for the urgent FM function of the energy storage system in the micro-grid, wherein PI is a PI controller capable of setting a dead band, therefore urgent FM can be performed well, the problem of pulse power output or poor coordinating control of two main power sources of the energy storage system is avoided, and the system stability and service life are effectively improved.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE, CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID CO LTD
Laser powder bed melting additive manufacturing molten bath monitoring and pore controlling method
ActiveCN111283192ADescribe wellReduce dependenceAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencySolidusPowder bed
The invention discloses a laser powder bed melting additive manufacturing molten bath monitoring and pore controlling method. The method includes the steps that (1) a space powder bed three-dimensional geometrical model is established; the powder model is guided into a thermal fluid model, a thermal fluid model of the powder dimension is established, the initial and boundary conditions of computational domains are set, and meshing is performed; a powder bed melting process three-dimensional model governing equation is established, and a molten bath is simulated according to the governing equation and input parameters; (2) three-dimensional profile data, including the molten bath depth, width and length, of the molten bath are extracted according to the solidus temperature and the mesh temperature of powder and a base material at each time step; and (3) a final scanning interval is obtained according to the three-dimensional profile data of the molten bath, and an ultimate molten bath is simulated according to the governing equation, the input parameters of the step (1) and the final scanning interval. In view of the difficulties of long time and high cost of the powder bed meltingexperimental research, the reliability of a solution can be evaluated, the research and development cost can be reduced, and the forming parameters are optimized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
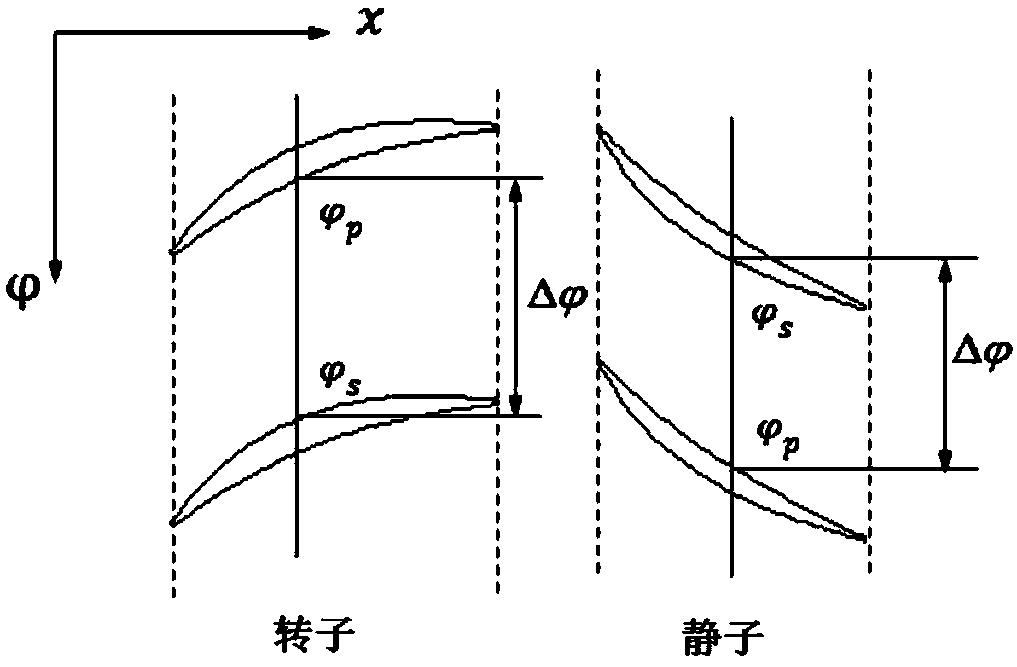
Algebraic modeling method of circumferential-direction fluctuation stress terms in turbomachine throughflow model
ActiveCN107679319AHigh precisionWell formedGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationGoverning equationComputer science
The invention relates to an algebraic modeling method of circumferential-direction fluctuation stress terms in a turbomachine throughflow model. The method includes: step 1, defining definition of governing equations and the circumferential-direction fluctuation stress terms of the throughflow model, and establishing circumferential-direction average Euler equations of considering the circumferential-direction fluctuation stress terms; step 2, adopting potential flow analysis assumption according to blade channel inlet flow characteristics; step 3, directly assuming a distribution form of flowparameters along a circumferential direction, and establishing the algebraic modeling method of the circumferential-direction fluctuation stress terms in the turbomachine throughflow model; step 4, carrying out mesh generation and flow field solving, and obtaining a three-dimensional numerical-value simulation result and a throughflow calculation result; and step 5, carrying out analysis of influences of circumferential-direction unevenness on blade channel inlet flow. The method can obtain the circumferential-direction pulsation stress terms which are in the throughflow model and induced mainly due to circulation changing, and has certain guiding significance and engineering practical-value for improving prediction precision of the throughflow model for a flow field.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Analysis of boundary and/or initial value problems in thin objects and spaces
InactiveUS20060277008A1Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationGeometric modelingGoverning equation
A method for simplifying engineering analysis of CAD geometric models, one which retains much of the accuracy of detailed finite element (FE) analysis while avoiding its computational burdens, is described. A skeleton, such as an exact or approximate medial mesh, is defined within the model, and the skeleton is then meshed. Known field values (physical values of interest, and / or their derivatives) are then “projected” onto the skeleton, as by interpolation or coordinate transformation, and these field values and the governing equations for the model and its engineering problem are then used to solve for unknown field values across all or desired portions of the skeletal mesh. The newly-determined field values may then be projected outwardly from the skeletal mesh to the remainder of the geometric model, again via interpolation or other methods. The method is found to be particularly efficient and accurate (again in comparison to standard FE methods) when applied to thin geometric objects, e.g., metal or plastic sheet, ribbed plates, thin cavities in plastics-forming molds, etc.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Multiple concurrent recursive least squares identification with application to on-line spacecraft mass-property identification
ActiveUS20050049829A1Negligible lossCosmonautic vehiclesSimulator controlGoverning equationLinear representation
The present invention is a method for identifying unknown parameters in a system having a set of governing equations describing its behavior that cannot be put into regression form with the unknown parameters linearly represented. In this method, the vector of unknown parameters is segmented into a plurality of groups where each individual group of unknown parameters may be isolated linearly by manipulation of said equations. Multiple concurrent and independent recursive least squares identification of each said group run, treating other unknown parameters appearing in their regression equation as if they were known perfectly, with said values provided by recursive least squares estimation from the other groups, thereby enabling the use of fast, compact, efficient linear algorithms to solve problems that would otherwise require nonlinear solution approaches. This invention is presented with application to identification of mass and thruster properties for a thruster-controlled spacecraft.
Owner:WILSON EDWARD
Optimal control theory based optimal design method of polymer flooding scheme
InactiveCN102352743AImprove optimization resultsFast optimizationFluid removalOptimal controlEngineering
The polymer is an expensive chemical product, and the injection of the polymer is a long and complex process. In order to scientifically decide a developing scheme for obtaining better economic benefit, the invention provides an optimal design method of a polymer flooding scheme which is based on an optimal control theory. The performance index of the optimal control problem can be the maximum net present value, the governing equation is the transfusion fluid mechanics equation of the polymer flooding process, the inequality constraints of the polymer amount and the injection density are considered, and an optimal control model of a polymer flooding distributed parameter system with the inequality constraints is built. By utilizing the Pontrjagin maximal principle, the necessary conditions of the polymer flooding optimal control problem are deduced, an improved subspace cutting off Newton method is provided and is used for solving the segment optimization problem with a decision variable boundary constraint during an SUMT (sequential unconstrained minimization technique) iterative process. The optimal design method provided by the invention is put into use in the second Gudong area of Shengli oil field, and the economic benefit of the polymer flooding is obviously improved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
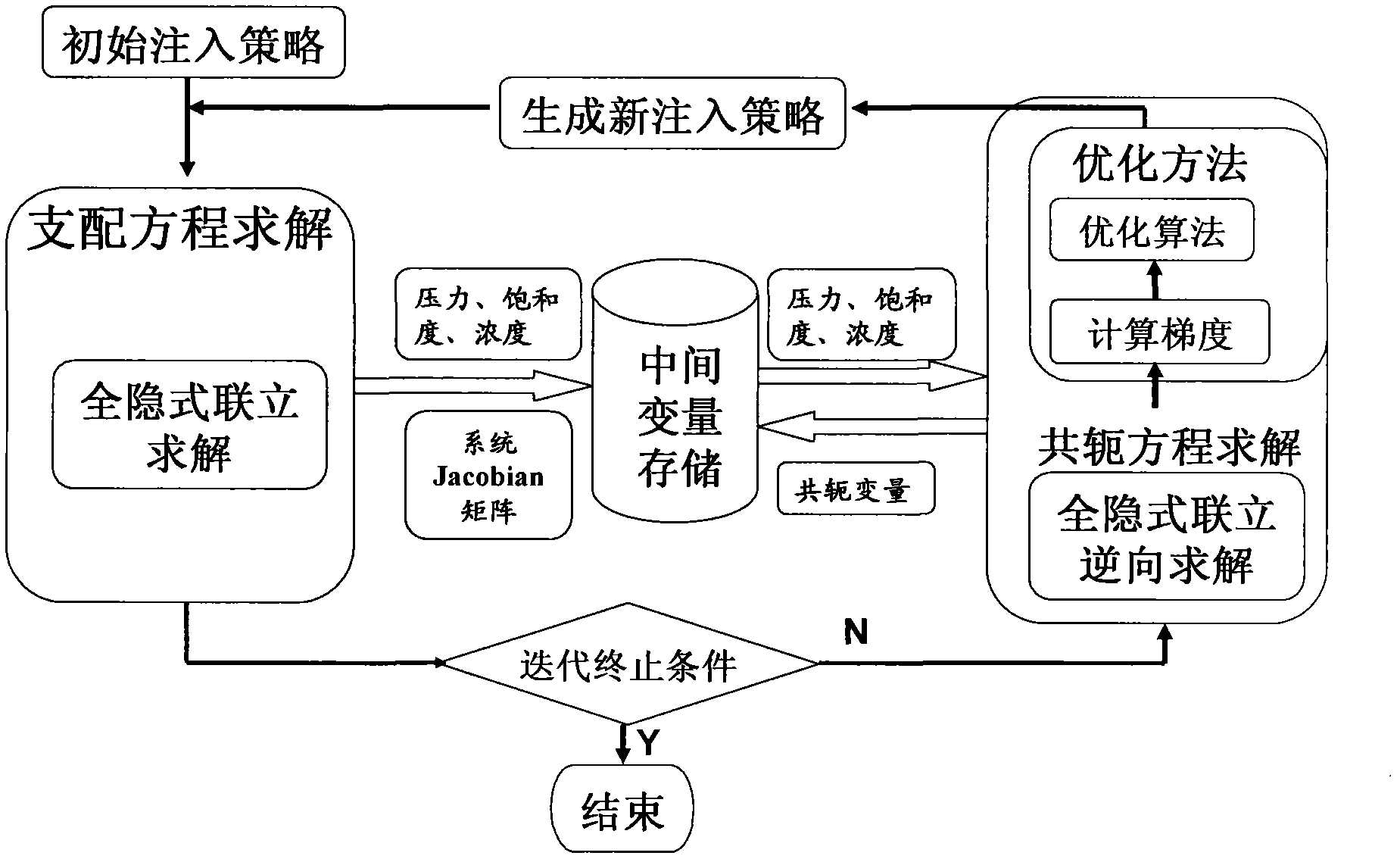
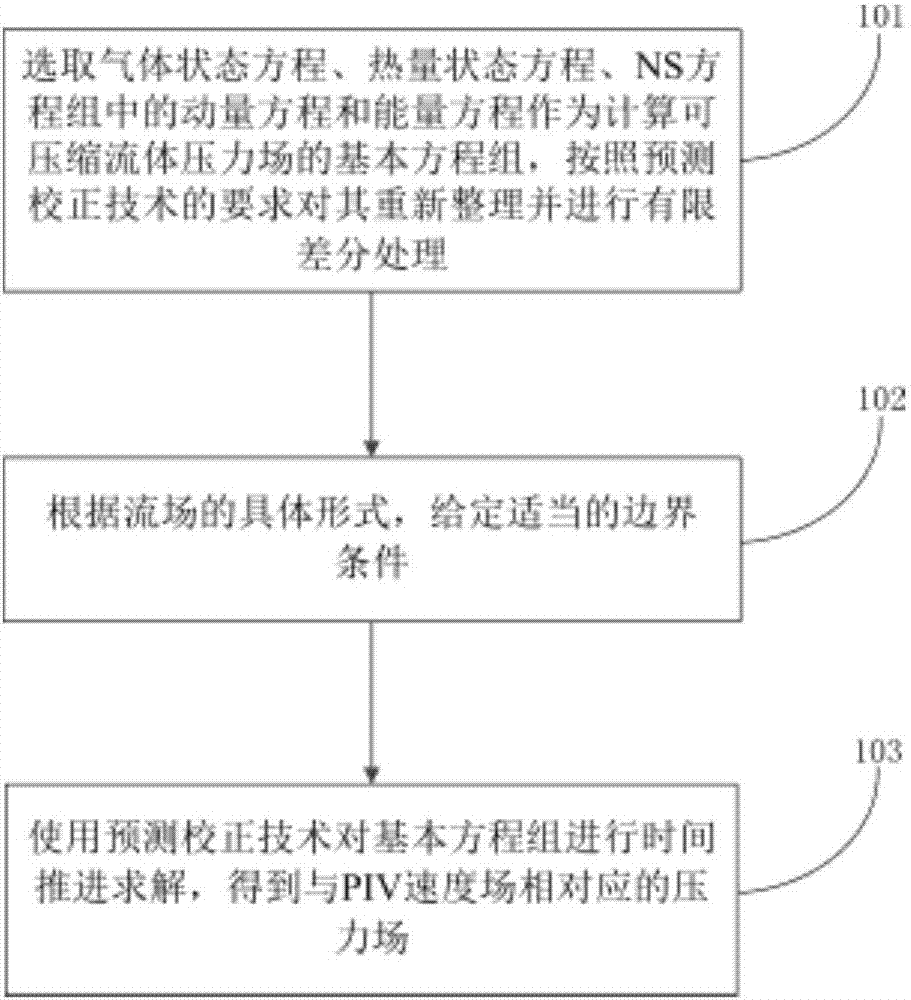
Calculation method and device of compressible fluid pressure field based on PIV (Particle Image Velocimetry) technique
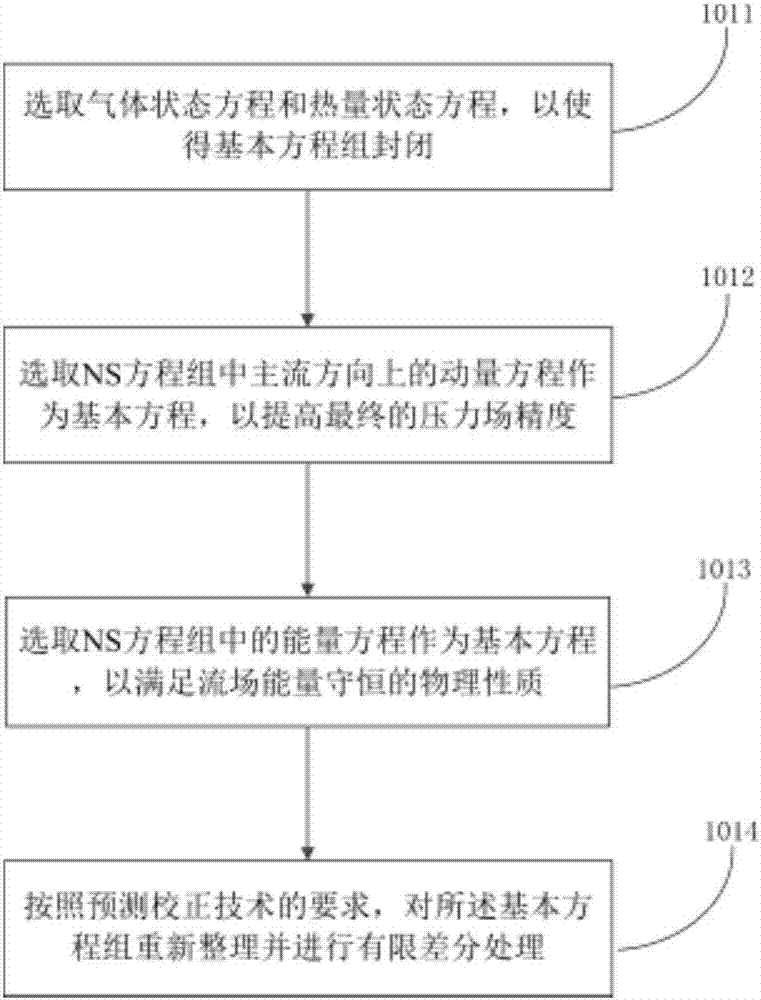
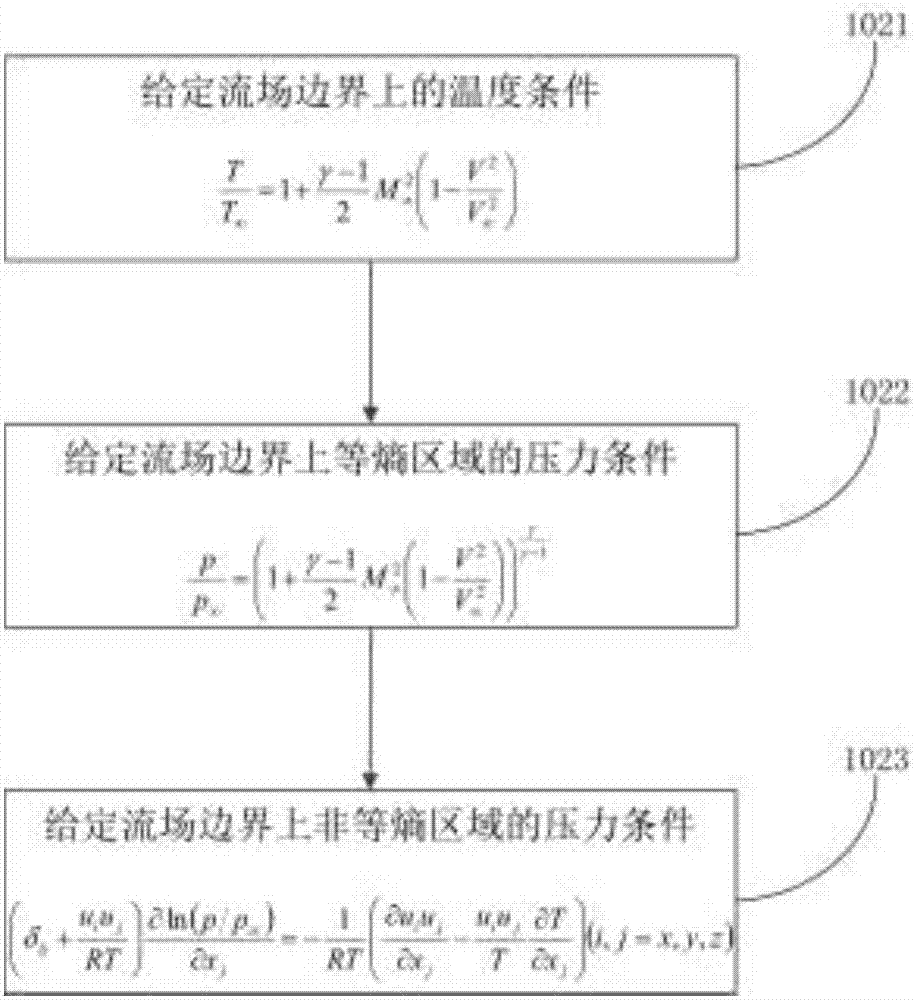
ActiveCN107066720AOvercome limitationsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsGoverning equationCorrection technique
The invention discloses a calculation method of a compressible fluid pressure field based on a PIV (Particle Image Velocimetry) technique. The method comprises the steps of selecting a gas state equation, a heat state equation, and a momentum equation and an energy equation in a hydromechanical governing equation set, namely an N-S equation set as a fundamental equation set for calculating the compressible fluid pressure field, performing rearrangement and finite difference processing on the fundamental equation set according to a requirement of a prediction-correction technique, setting an appropriate boundary condition according to a concrete form of a fluid field, and performing time stepping solution on the fundamental equation set by the prediction-correction technique to obtain the pressure field corresponding to a PIV velocity field. The invention further discloses a device for realizing the method. Therefore, a pressure field measurement scheme based on the PIV technique is provided for a compressible fluid; calculation limitation of the existing incompressible fluid pressure field is overcome; and an application scope of a fluid field pressure measurement scheme based on the PIV technique is greatly extended.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Punching method for runner cone based on three-dimensional simulation method for whole flow field of water turbine
ActiveCN106870247ASolving Unsteady Flow ProblemsGeometric CADHydro energy generationThree dimensional simulationPunching
The invention provides a punching method for a runner cone based on a three-dimensional simulation method for a whole flow field of a water turbine. The punching method comprises the steps of establishing a model test experiment system; selecting a turbulence model and performing three-dimensional unsteady simulation for the whole flow field of the water turbine by using a RANS simulation method, wherein the calculation of the three-dimensional simulation method for the whole flow field of the water turbine comprises geometric modeling, grid setting , a numerical value method, a governing equation and a boundary condition setting; and synthesizing model experiment and numerical simulation data and testing different runner cone punching models under different flow deviation working conditions. The punching method solves the problem of unsteady flow in a water turbine set in the prior art, and especially the problems of a vortex strip in a draft tube and corresponding pressure pulsation.
Owner:虚拟现实数字技术研究院(哈尔滨)有限公司
A method for processing acoustic waveforms
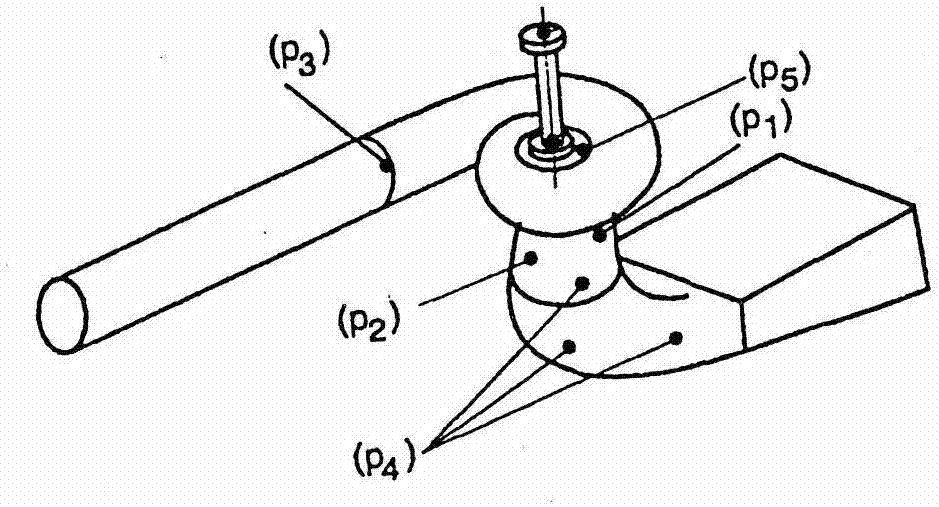
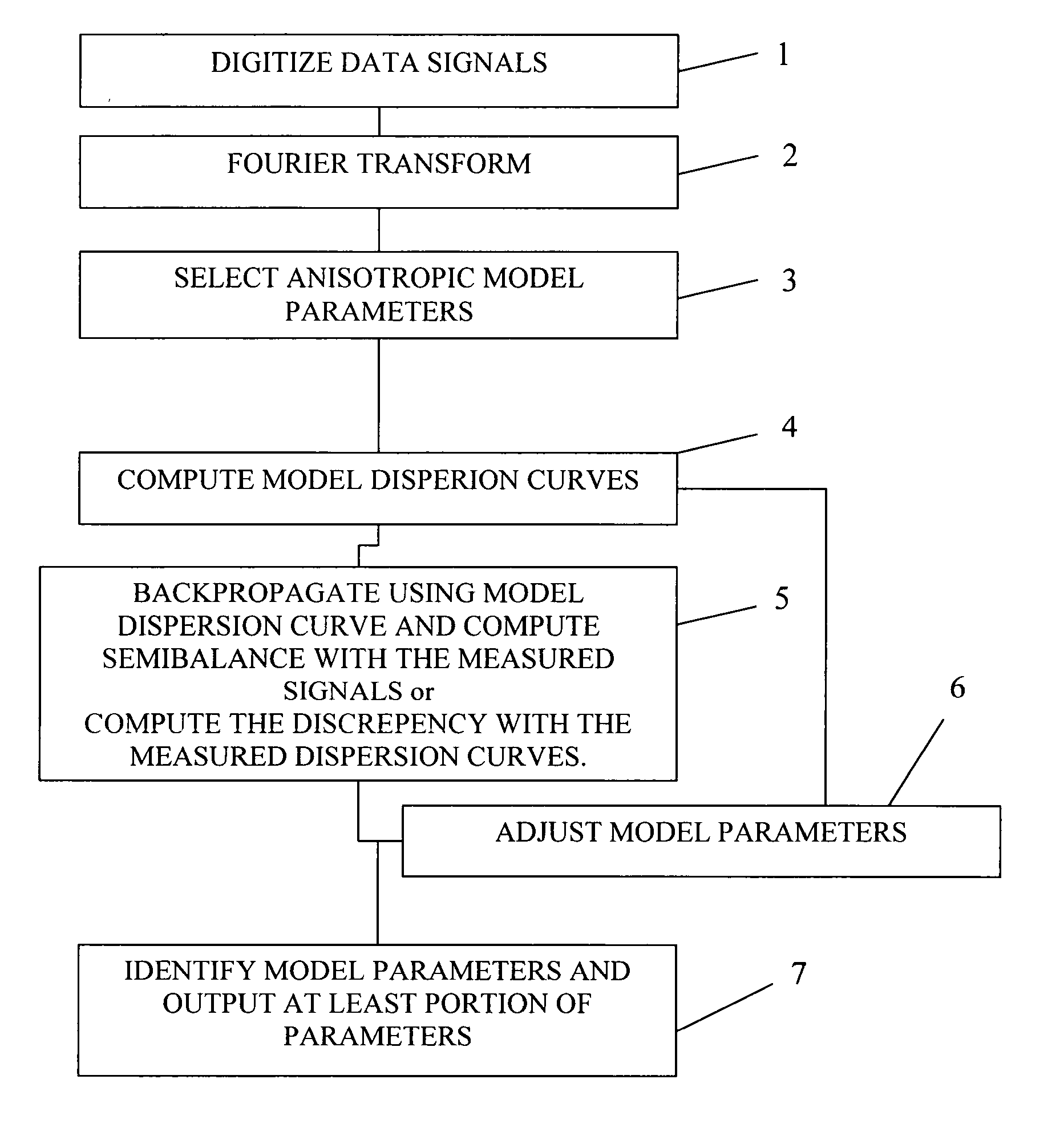
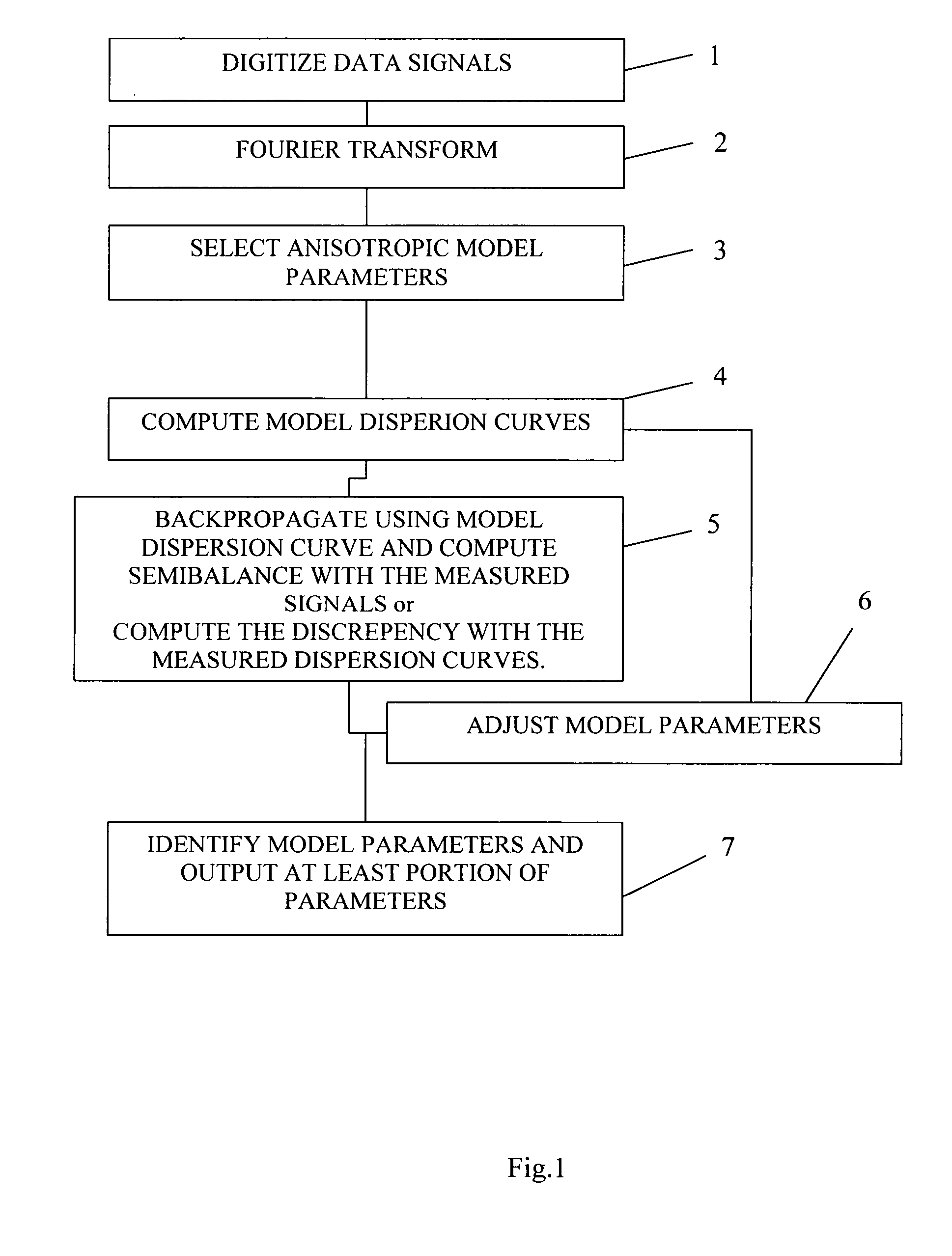
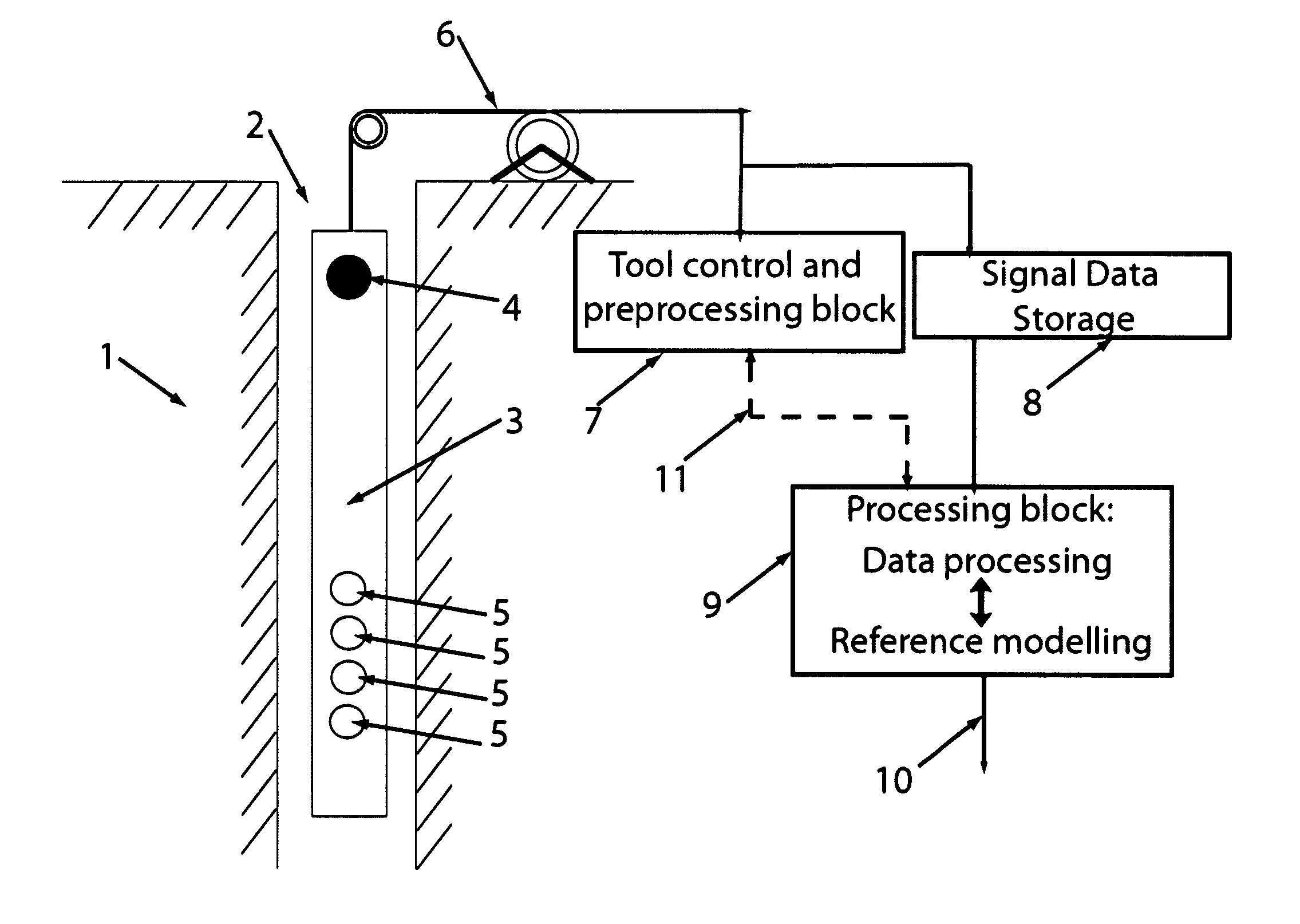
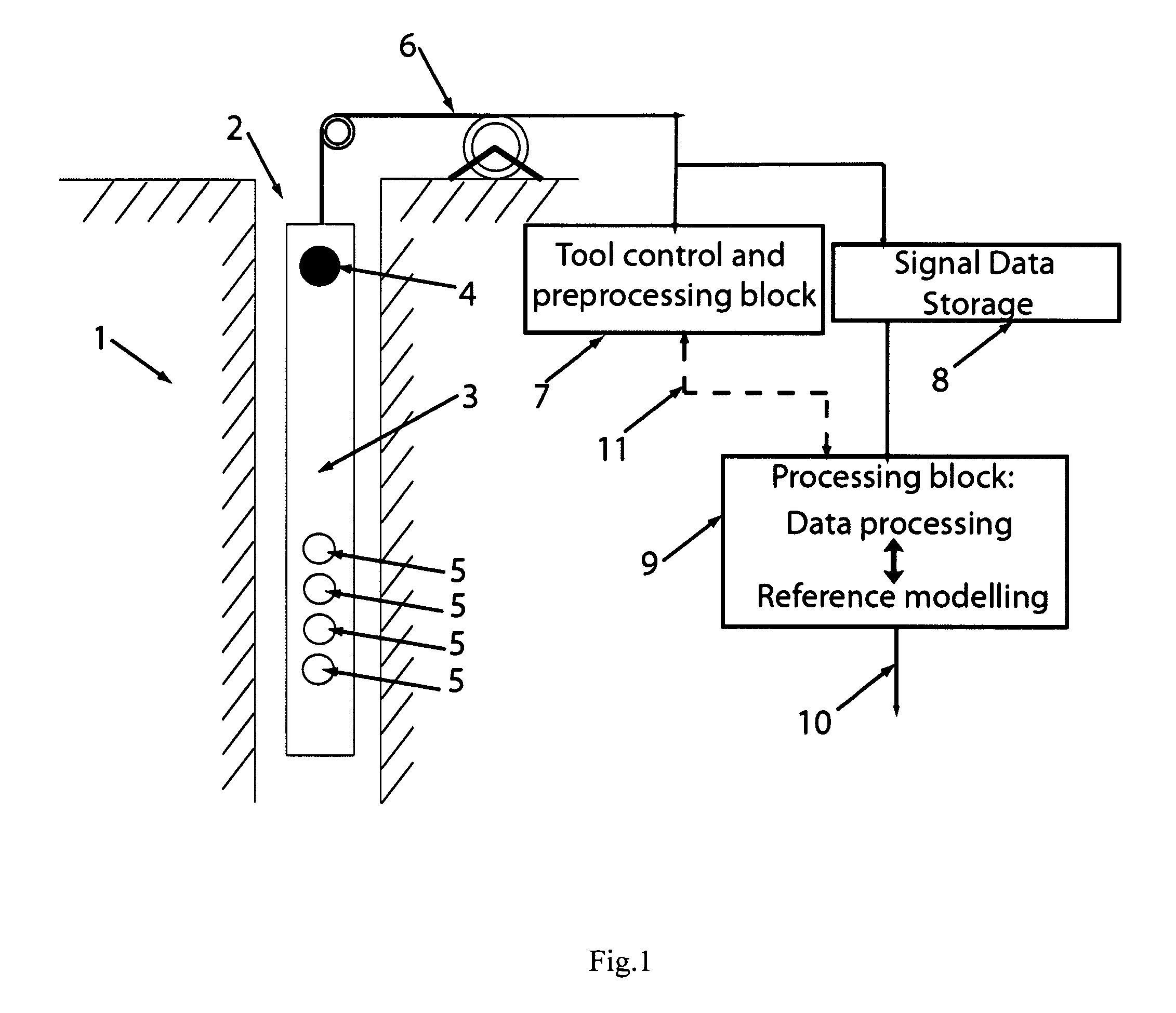
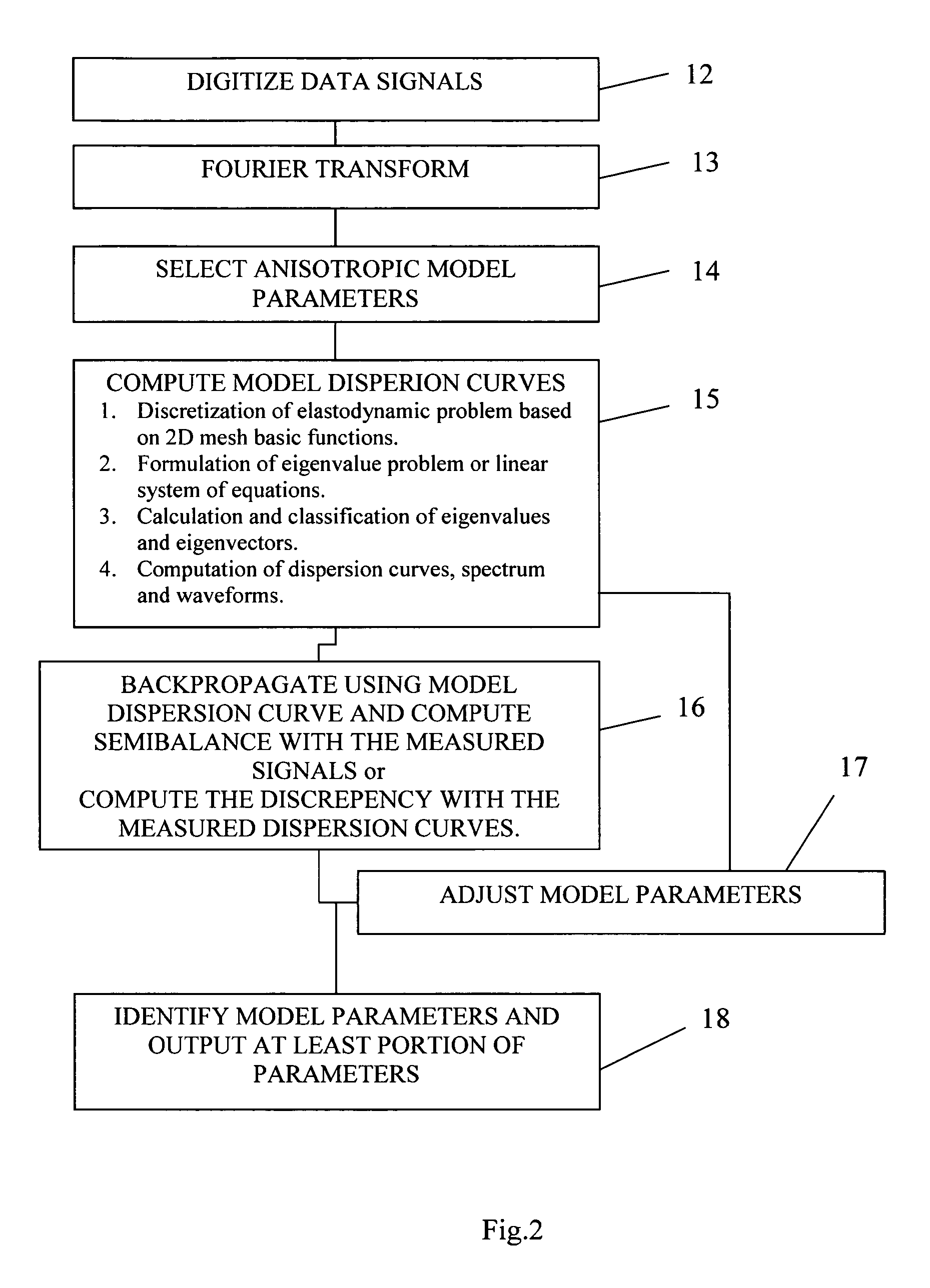
InactiveUS20150309200A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal processingRiccati equationDispersion curve
A method for processing acoustic waveforms comprises acquiring acoustic waveforms in a borehole traversing a subterranean formation and transforming at least a portion of the acoustic waveforms to produce frequency domain signals. Then model dispersion curves are generated based on an anisotropic borehole-formation model having a set of anisotropic borehole-formation parameters and by specifying governing equations and using a matrix Riccati equation approach. The frequency-domain signals are back-propagating using the model dispersion curves to correct dispersiveness of the signals and coherence of the back-propagated signals is calculated. Alternatively the difference between the measured and the model dispersion curves is determined. Model parameters are iteratively adjusted until the coherence reaches a maximum or exceeds a selected value, or alternatively until the difference between the measured and the model dispersion curves becomes minimal or is reduced to below a selected value. Then at least a portion of the set of anisotropic borehole-formation parameters is obtained.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method for simulating aircraft rock movement with RANS/LES (Reynolds average numerical simulation)/LES (large eddy simulation) mixing technique
ActiveCN104699947ASimulation is accurateAccurate predictionSpecial data processing applicationsCorrection algorithmMotion parameter
The invention discloses a method for simulating aircraft rock movement with an RANS / LES (Reynolds average numerical simulation) / LES (large eddy simulation) mixing technique, and aims to solve the problem about self-excitation rock movement under the condition that wide-range separated flow of an aircraft cannot be accurately simulated in the prior art. The method mainly comprises steps as follows: a length scale of a turbulence model is appropriately corrected on the basis of a conventional unsteady RANS method, and DES (detached eddy simulation) methods are constructed; tightly coupled solution of a flow field governing equation and a rigid body motion equation is realized in the dual-time-step pseudo time iteration process with adoption of a prediction-correction algorithm, and the changing course of aerodynamic parameters and motion parameters of the aircraft with time is obtained. On the premise that certain computational efficiency is guaranteed, self-excitation rock motion of the aircraft under the complicated flowing condition is more accurately simulated, and an effective means is provided for nonlinear coupling property evaluation of aerodynamic motion / movement of the aircraft.
Owner:INST OF HIGH SPEED AERODYNAMICS OF CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
Method for numerical simulation of steam condensation containing incoagulable gas in pipe
InactiveCN101201873AAccelerated settlementEfficient solutionSpecial data processing applicationsSteam condensationProduct gas
The invention relates to a simulation method of steam condensation number of non-condensable gas in a pipe and pertains to the mechanics field of computational fluid. The invention makes use of the CFX platform and sets source term of quality continuous equation of steam components to simulate the steam condensation process of non-condensable gas. The steps are: (1) the fluid in the flow field is set as gas mixture with changeable component mass percentage and all components respectively show steam and non-condensable gas and are in ideal state; (2) boundary conditions such as flow field area, inlet, outlet and wall are set; (3) the continuous governing equation of steam components is added with Uchida empirical correlation in the source phase of wall boundary conditions. The method of the invention makes a slight alteration on the basis of the existing calculation program of the finite volume method and accurately simulates the complex process of the change between the two phases of the steam condensation of the non-condensable gas. The treatment process is simple and efficient.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
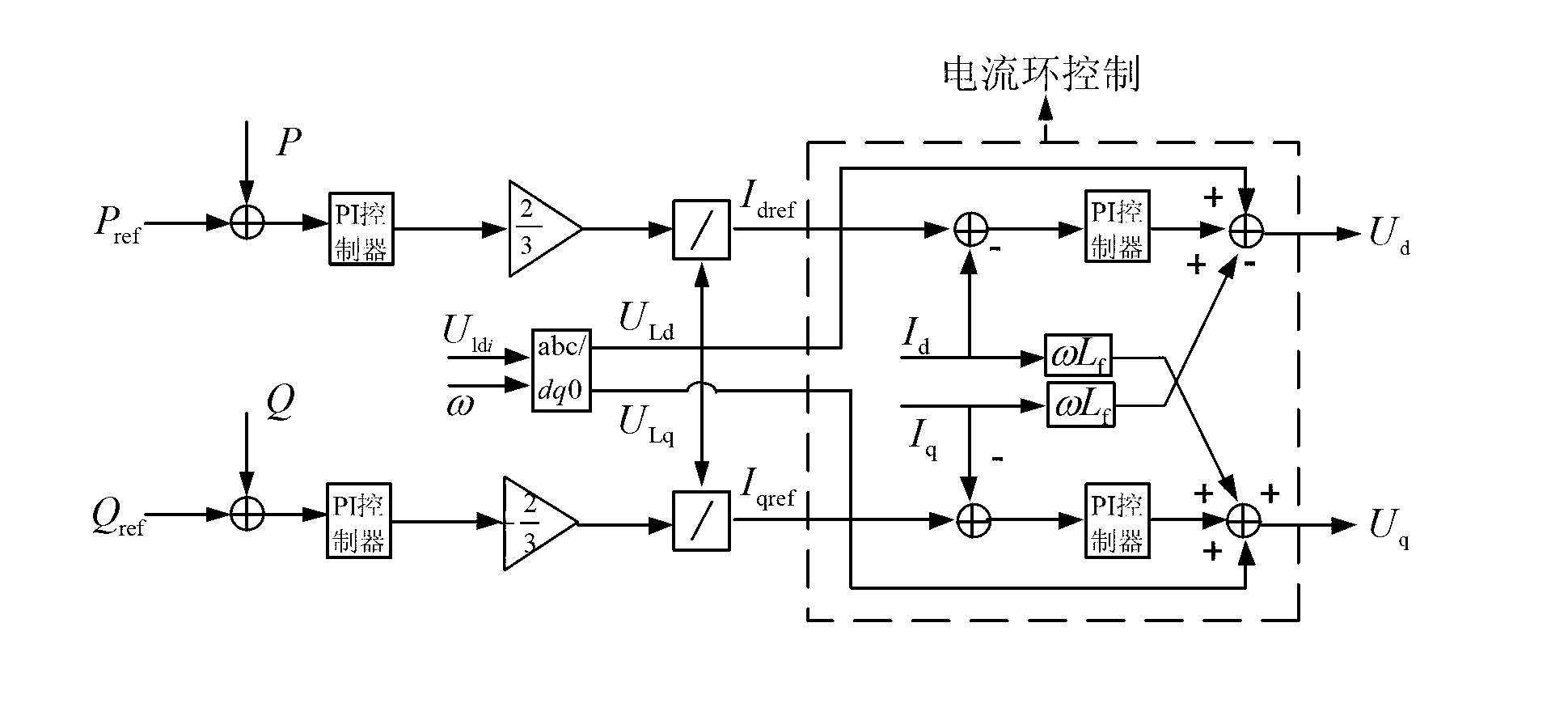
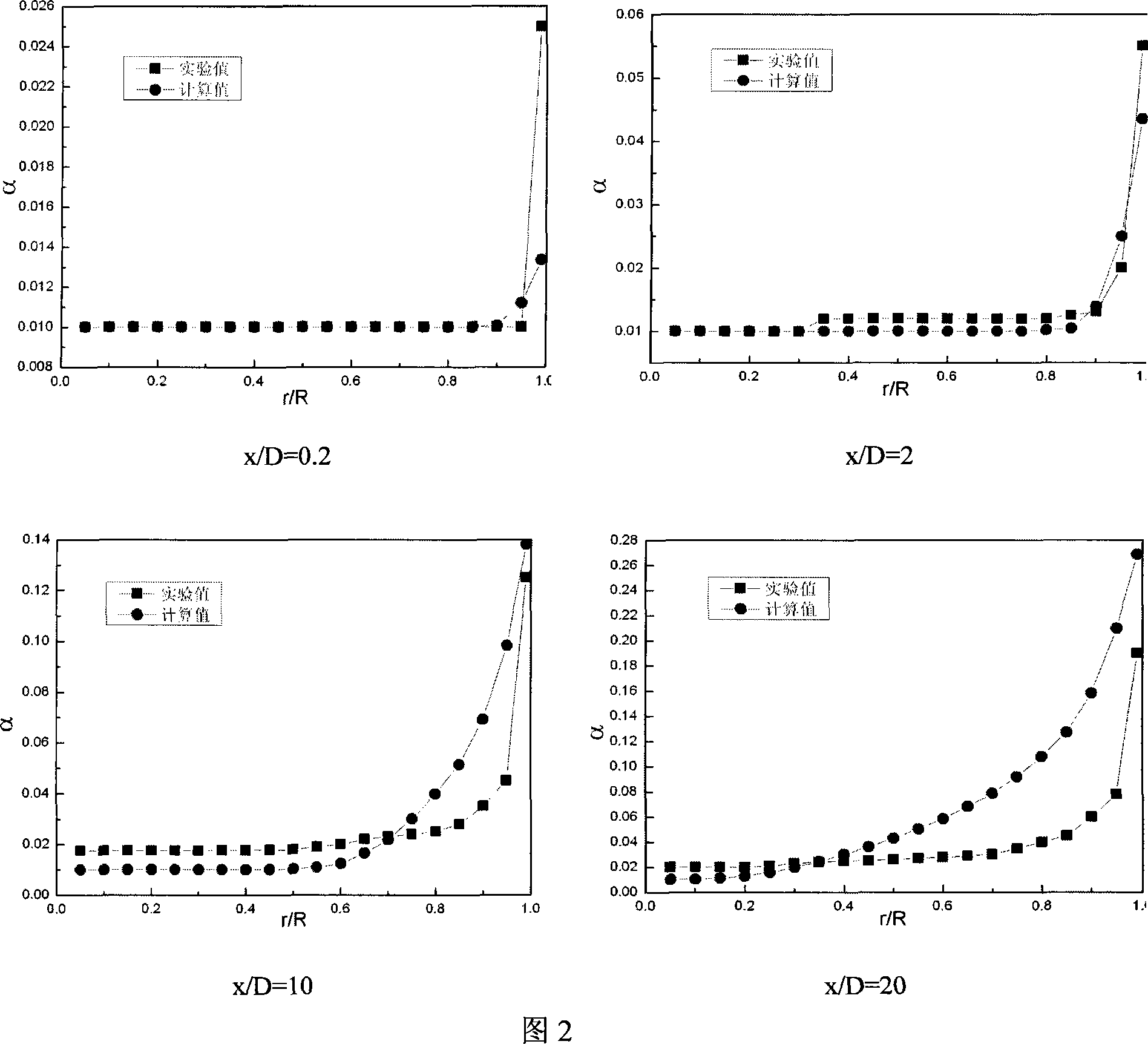
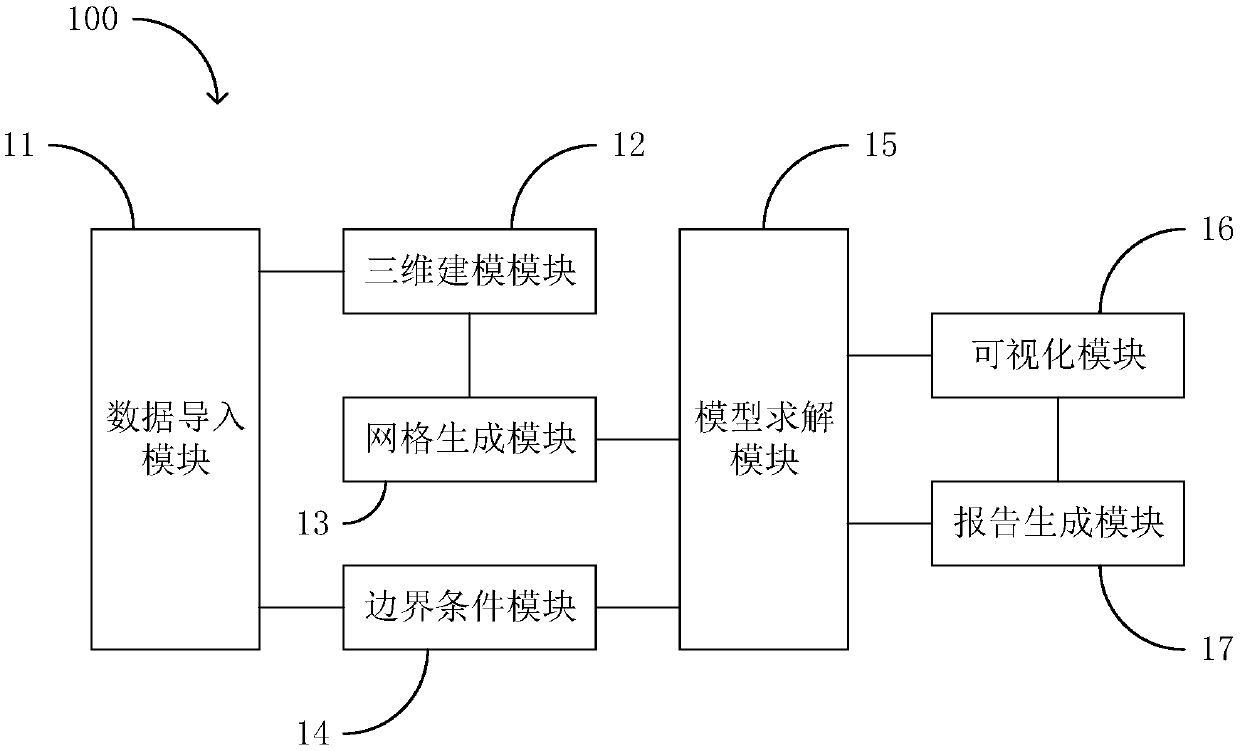
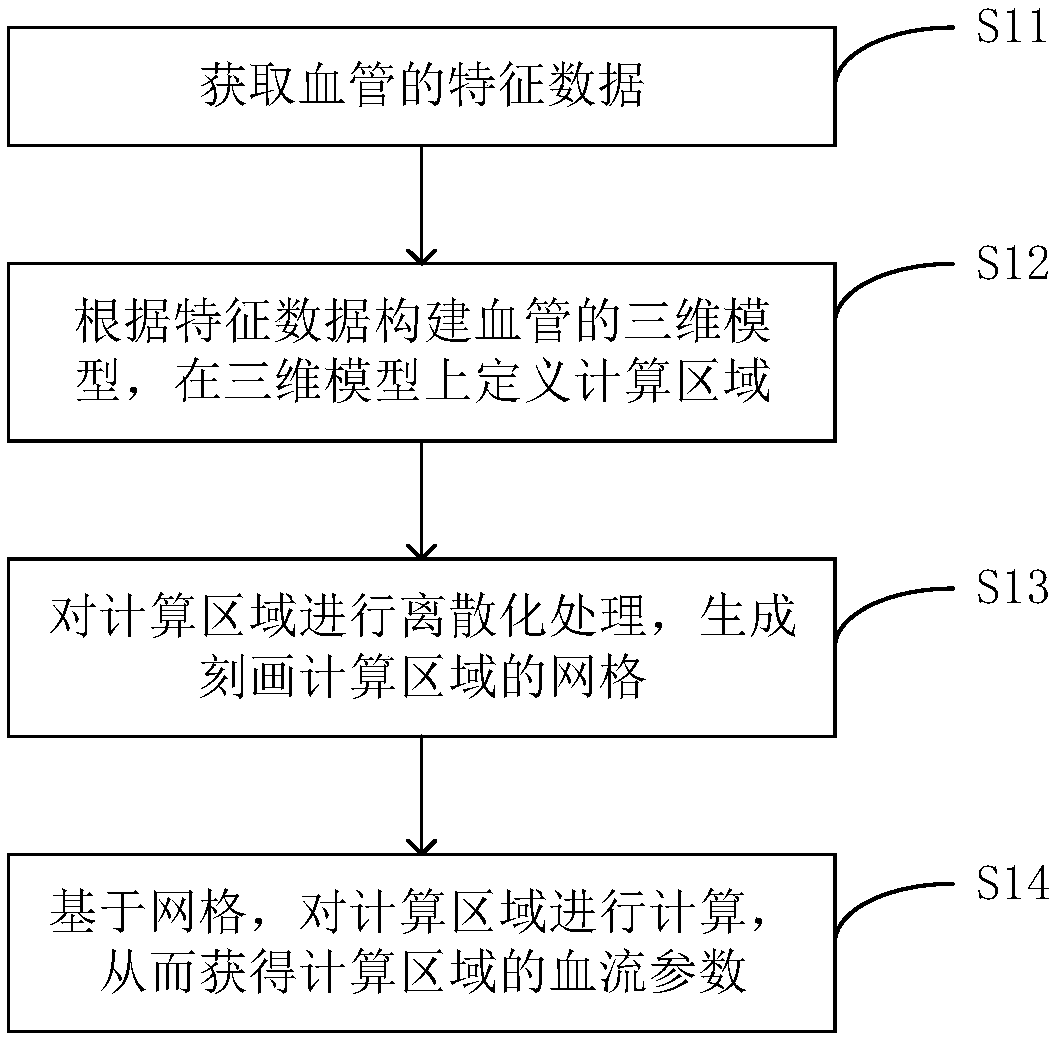
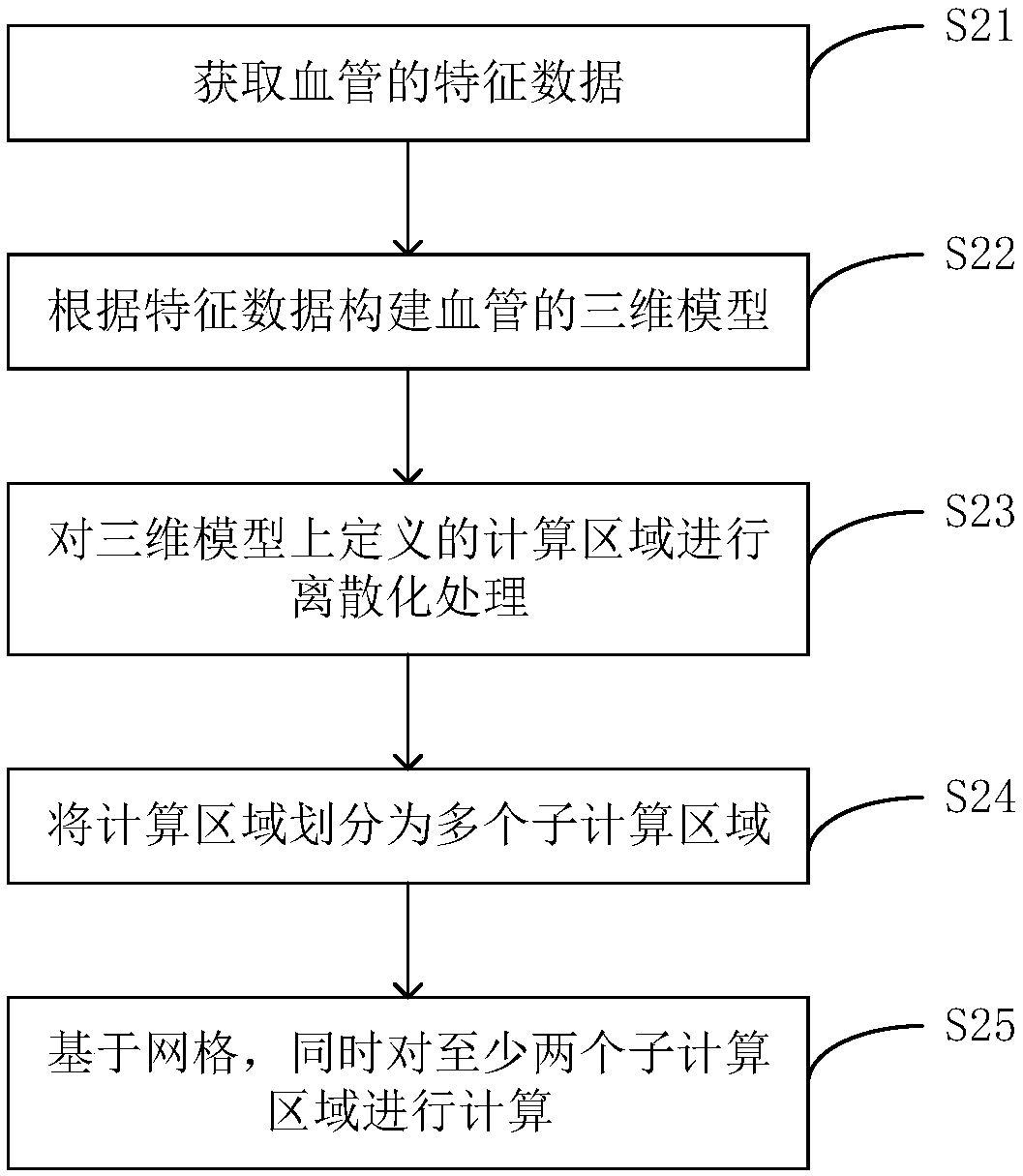
Blood vessel blood flow simulation method based on mechanics equation and related devices
PendingCN109064559AImprove simulation calculation accuracyImage generation3D modellingFully coupledMathematical model
The application discloses a blood vessel blood flow simulation method based on a mechanics equation, a blood flow simulation device, and a computer readable storage medium. The method comprises: acquiring feature data of a blood vessel; constructing a three-dimensional model of the blood vessel according to the feature data and carrying out three-dimensional model definition of a calculation area;carrying out discretization processing on the calculation area to generate a grid depicting the calculation area; constructing a physical mathematical model including a fully coupled fluid mechanicsgoverning equation and a solid mechanics governing equation, of the calculation area; on the basis of the grid, calculating the physical mathematical model and acquiring blood flow parameters and blood vessel parameters of the calculation area; and calculating change parameters of the grid based on the blood vessel parameters and thus updating the calculation area. Therefore, accurate and efficient simulation of the blood flow in a blood vessel is realized.
Owner:杭州阿特瑞科技有限公司
SH guided wave detection method for interfacial state of bonded structure
ActiveCN105486747AEasy to calculateQuick calculationAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesEpoxyWave detection
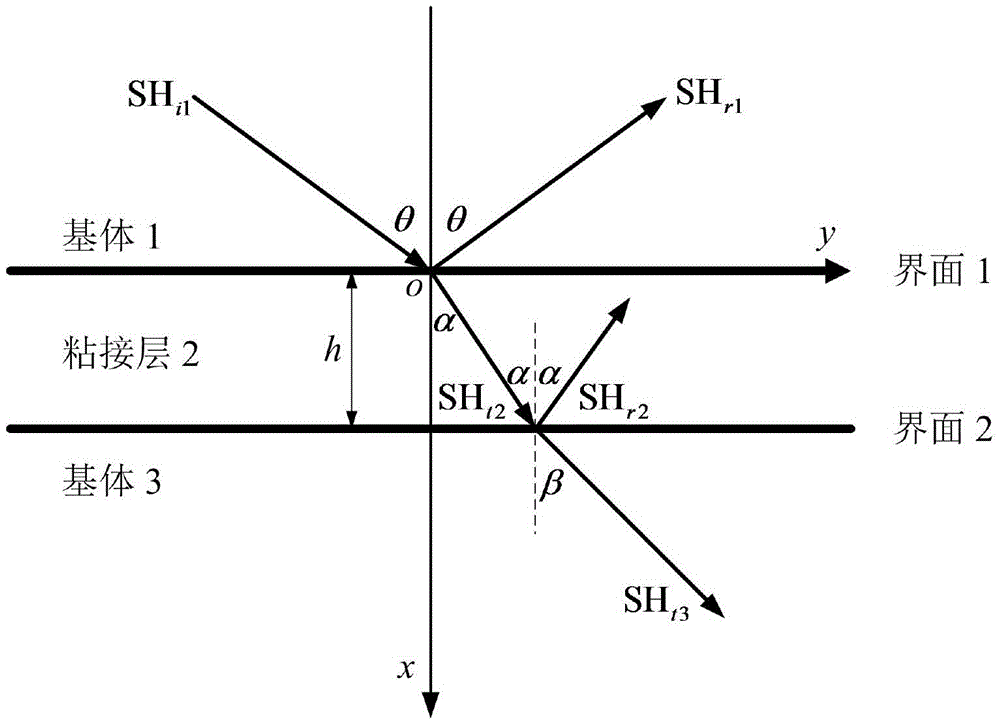
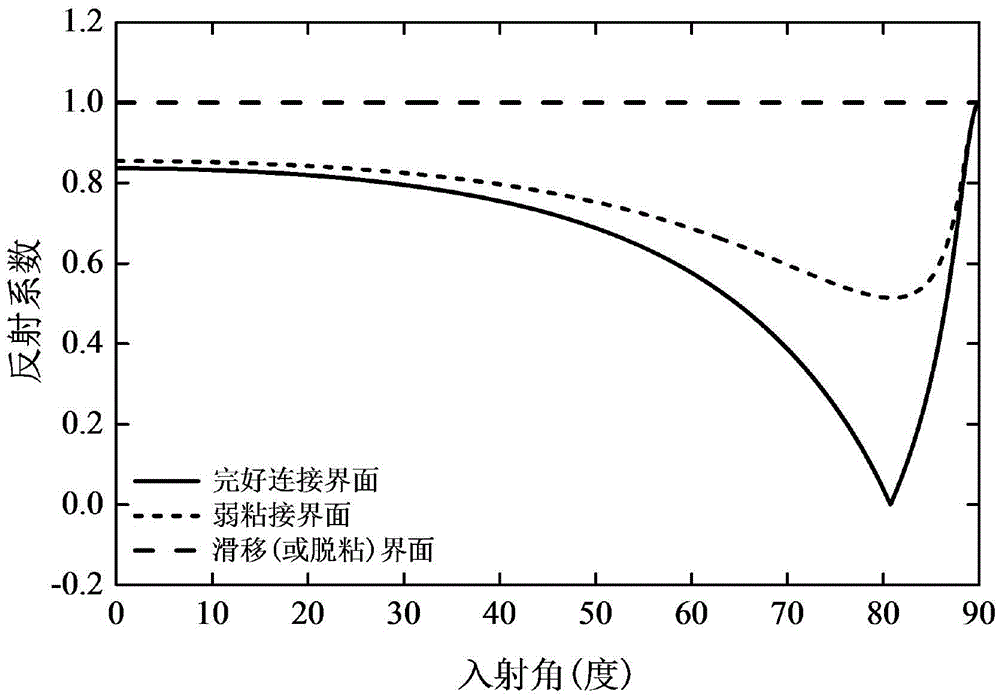
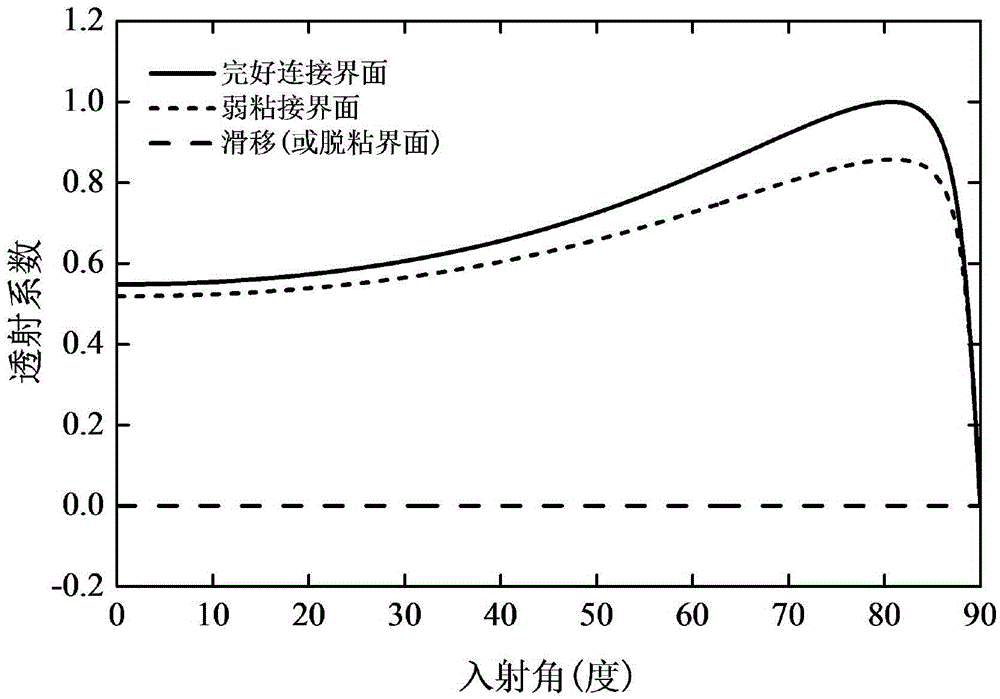
The invention provides an SH guided wave detection method for the interfacial state of a bonded structure. An expression containing a tangential rigidity coefficient K<T> for the reflection and transmission coefficients of a minimum-grade SH guided wave mode (SH<0>) in a plate-shaped bonded structure is deduced based on the governing equation of wave propagation. Taken an aluminum / epoxy resin / aluminum bonded structure as an example, the relation between incident angles and reflection or transmission characteristics of SH guided waves in different interfacial states is analyzed when the incident frequency f of the SH guided waves and the thickness h of a bonding layer are respectively set at specific values. Meanwhile, the influence of the product of frequency and thickness on reflection or transmission characteristics of the SH guided waves is discussed when the incident angles of the SH guided waves are set to be 0 DEG and 50 DEG C. How to discriminate interfacial states is also elaborated. Compared with other detection methods, the SH guided wave detection method for the interfacial state of the bonded structure has the advantages of easiness, effectiveness and practicability.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Tape muscle
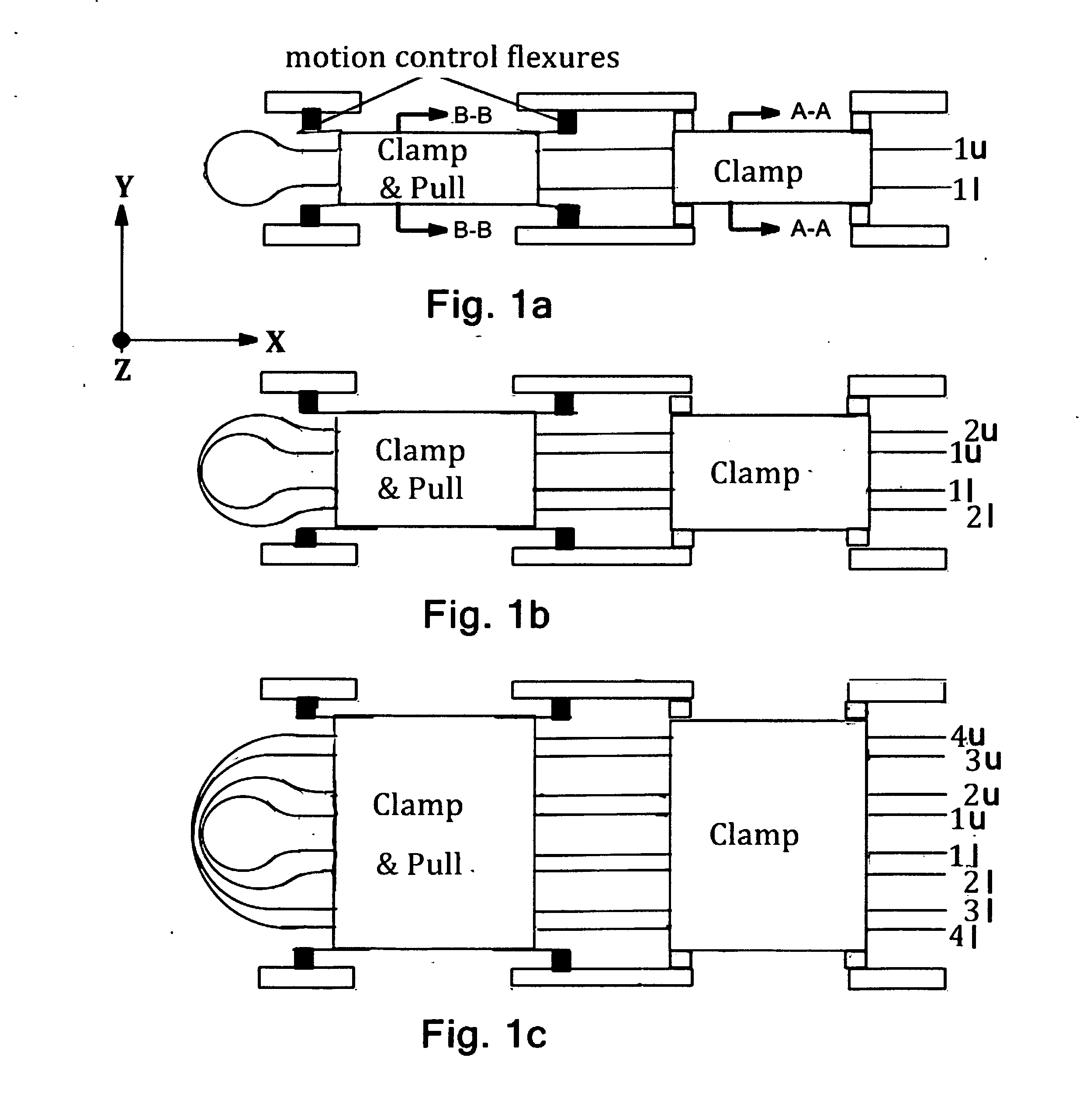
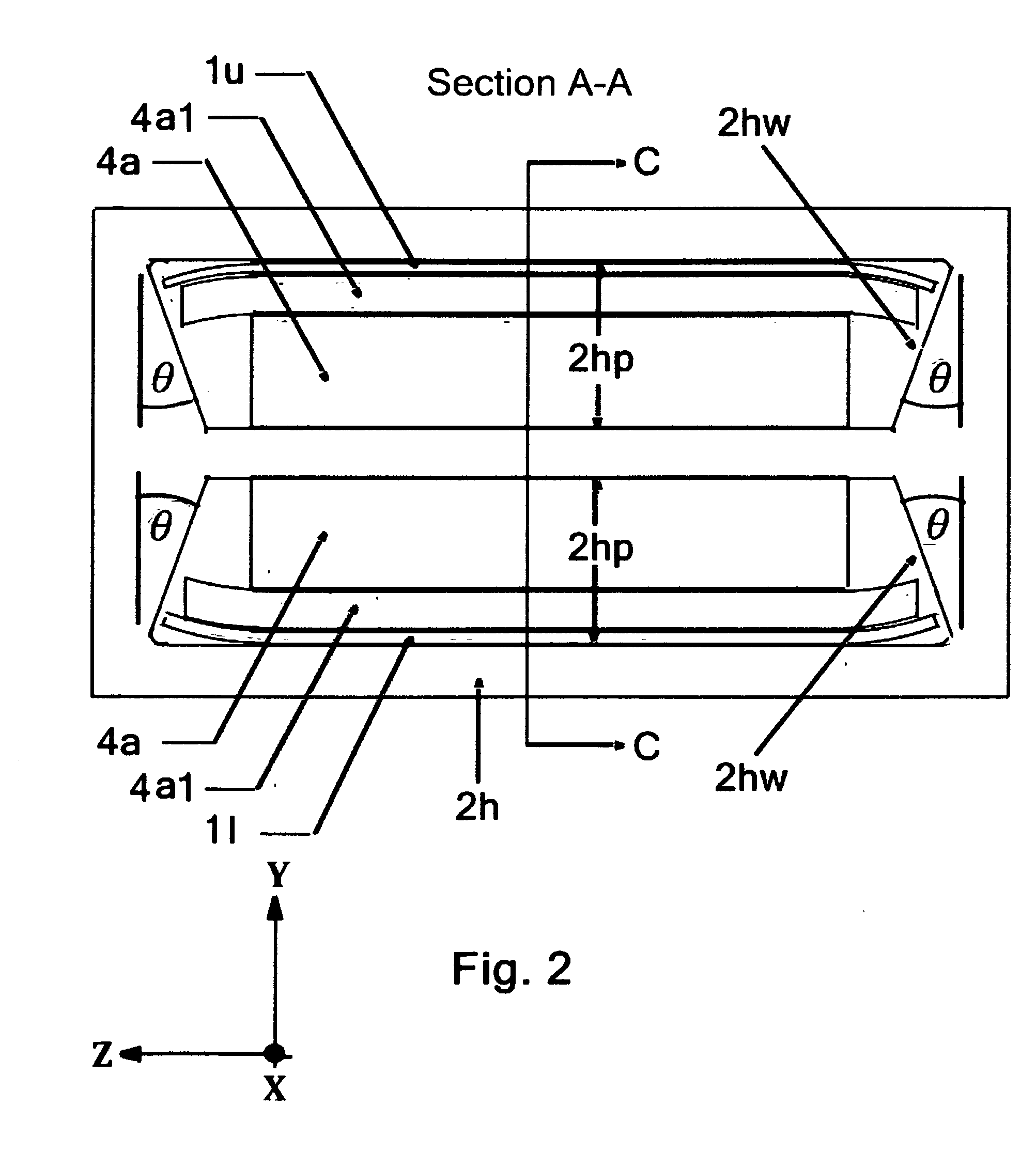
InactiveUS20120228991A1Increase clamping forceLow costProgramme-controlled manipulatorElectrostatic generators/motorsTape speedComputer module
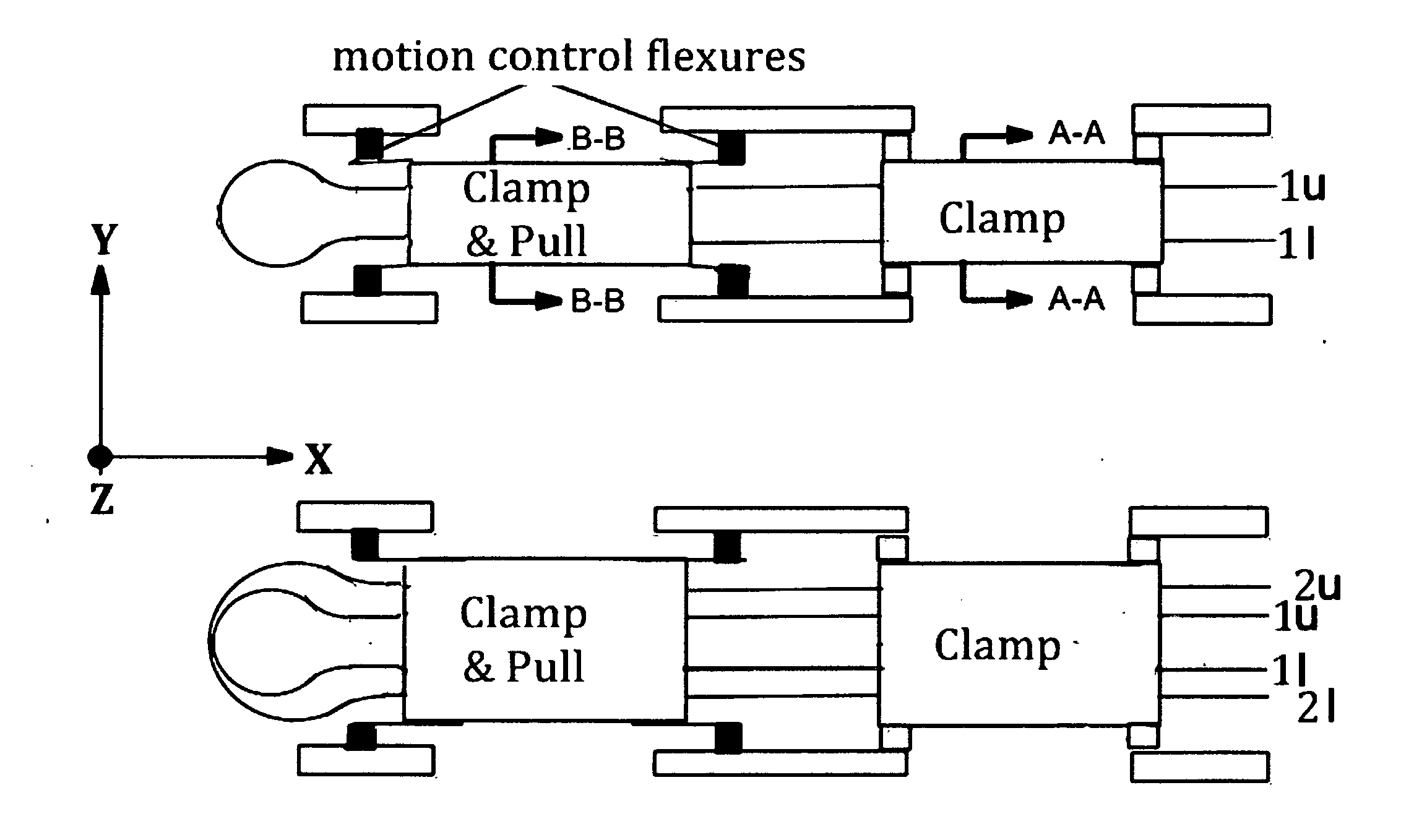
A Tape Muscle is described where multiple tape loops are independently driven by synchronized grasp and pull actions from a tandem of Clamp, Clamp & Drive modules. Each tape loop is elastically bent, with its open ends threaded through individual passageways in both modules. Tape loops are nested inside each other with all tape open ends on the same side. Each loop moves its open ends in equal, opposite directions, while the loop position remains fixed. Tape movements do not interfere with each other. The open ends of each loop attach to a shared appendage, which is pulled back and forth using tensile forces. Drive and hold forces use small angle flexure bending mechanical advantage and high force density electrostatic induction methods. Tape speed results from high frequency clock speed and novel hand-off methods. Governing equations, design details and performance estimates are provided.
Owner:VRANISH JOHN M
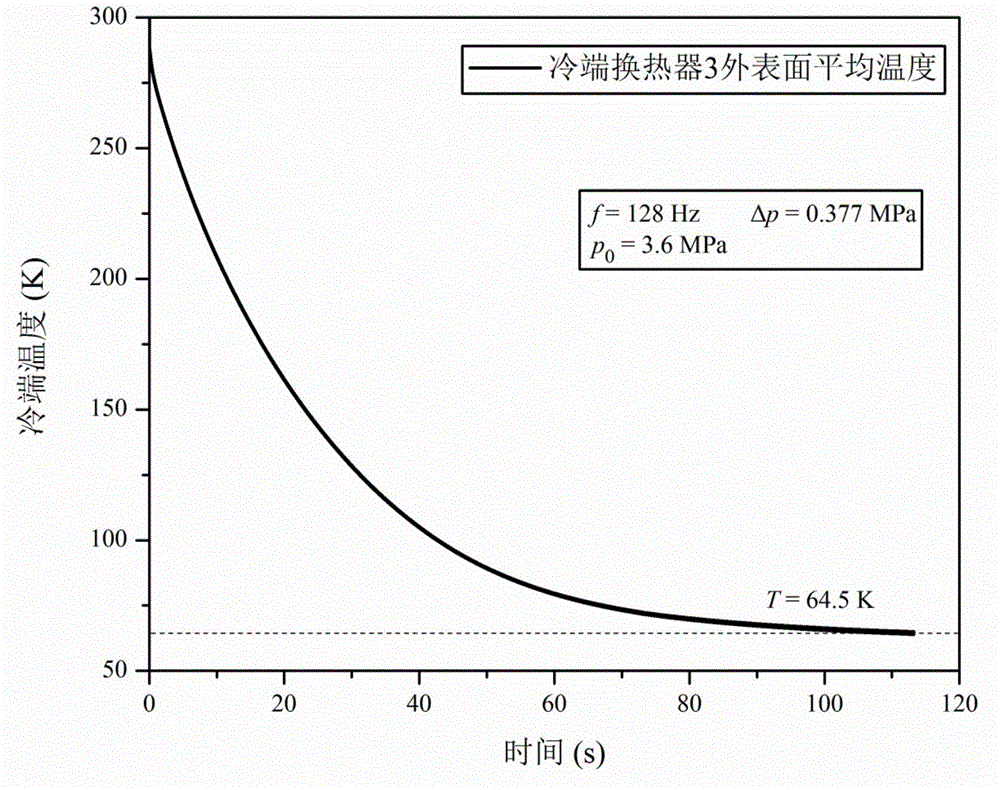
Simulation analysis method of light-weight miniature coaxial pulse tube refrigerator based on CFD technology
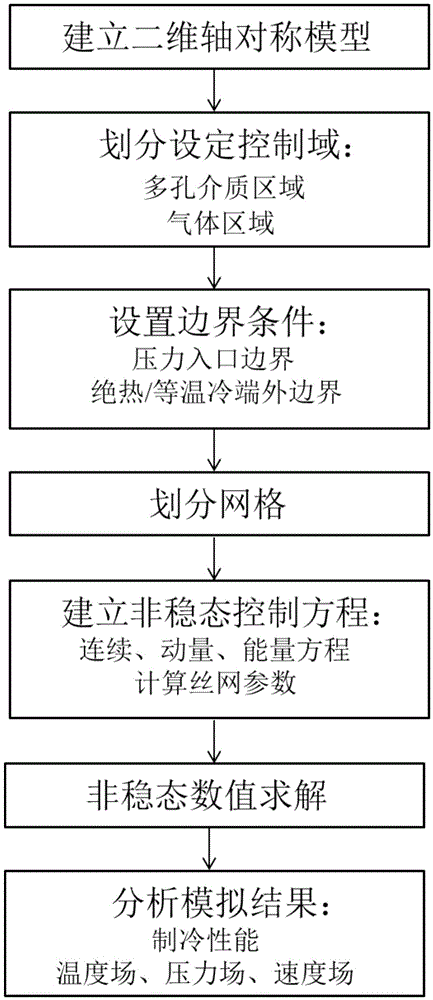
InactiveCN105526729APredicting Cooling PerformanceReduce R&D costsCompression machinesRefrigeration safety arrangementPulse tube refrigeratorEngineering
The invention discloses a simulation analysis method of a light-weight miniature coaxial pulse tube refrigerator based on a CFD technology. The simulation analysis method comprises the following steps: (1) establishing the geometric model of the light-weight miniature coaxial pulse tube refrigerator; (2) dividing and setting control areas; (3) setting boundary conditions; (4) dividing grids; (5) establishing unsteady governing equations; (6) conducting the unsteady numerical solution; and (7) analyzing the simulation result, and predicting the refrigeration performance of the light-weight miniature coaxial pulse tube refrigerator. The two-dimensional computer simulation of the light-weight miniature coaxial pulse tube refrigerator is realized through commercial computational fluid software Fluent, the refrigeration performance of the light-weight miniature coaxial pulse tube refrigerator is predicted within a shorter time, and the development cost is reduced greatly; and the operating mechanism and the fluid characteristic in a pulse tube are known deeply by analyzing the distribution of the temperature field, the pressure field and the speed filed in the light-weight miniature coaxial pulse tube refrigerator, and the simulation analysis method has important significance in the design optimization of the light-weight miniature coaxial pulse tube refrigerator.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Modeling method of using membrane humidifier to realize fuel-cell intake-air humidification
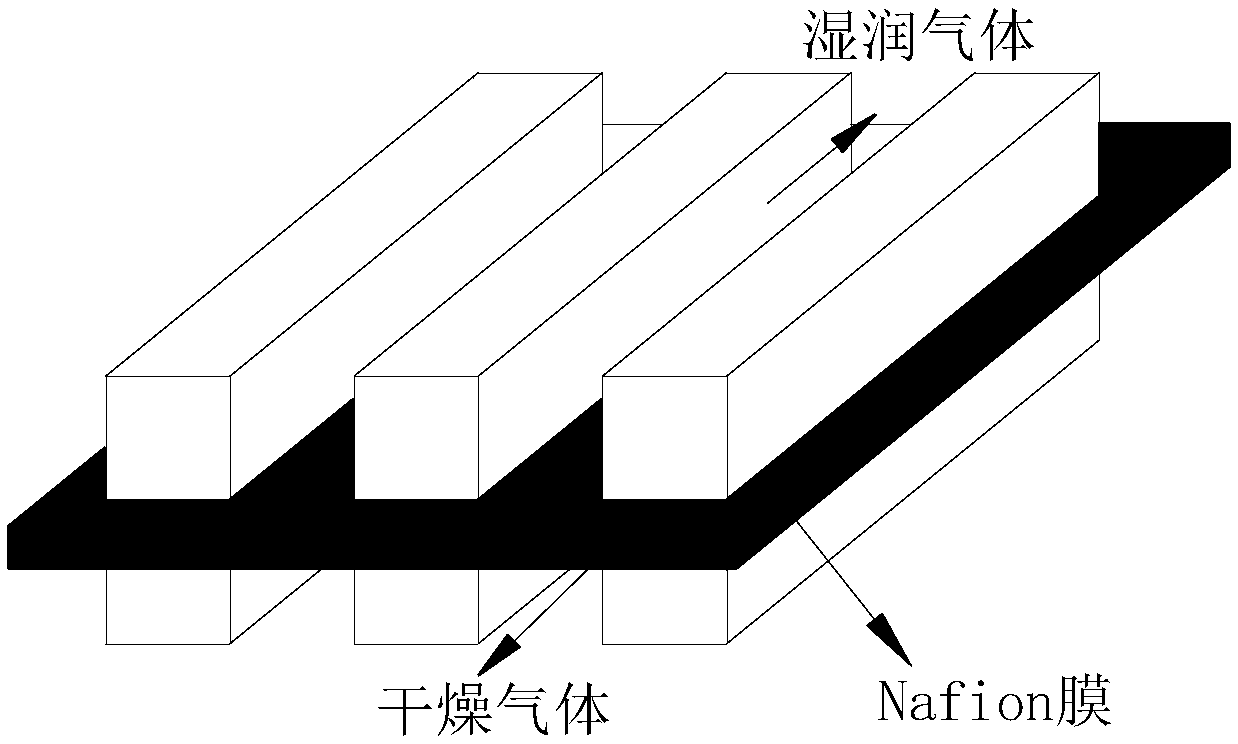
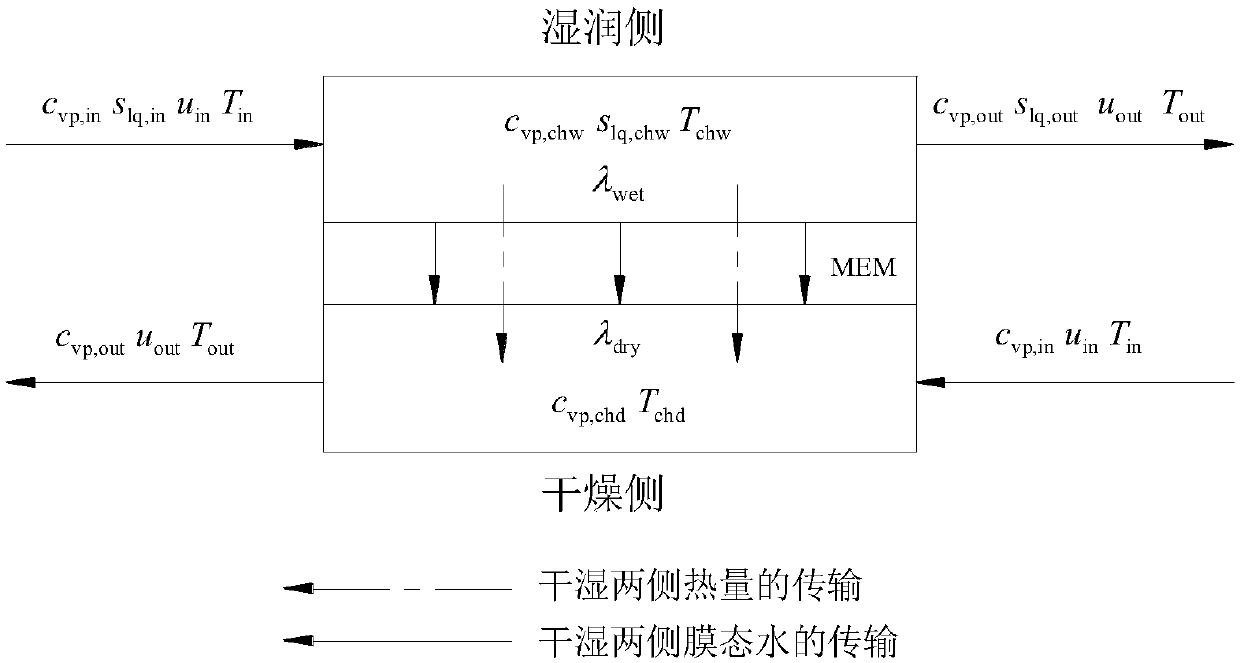
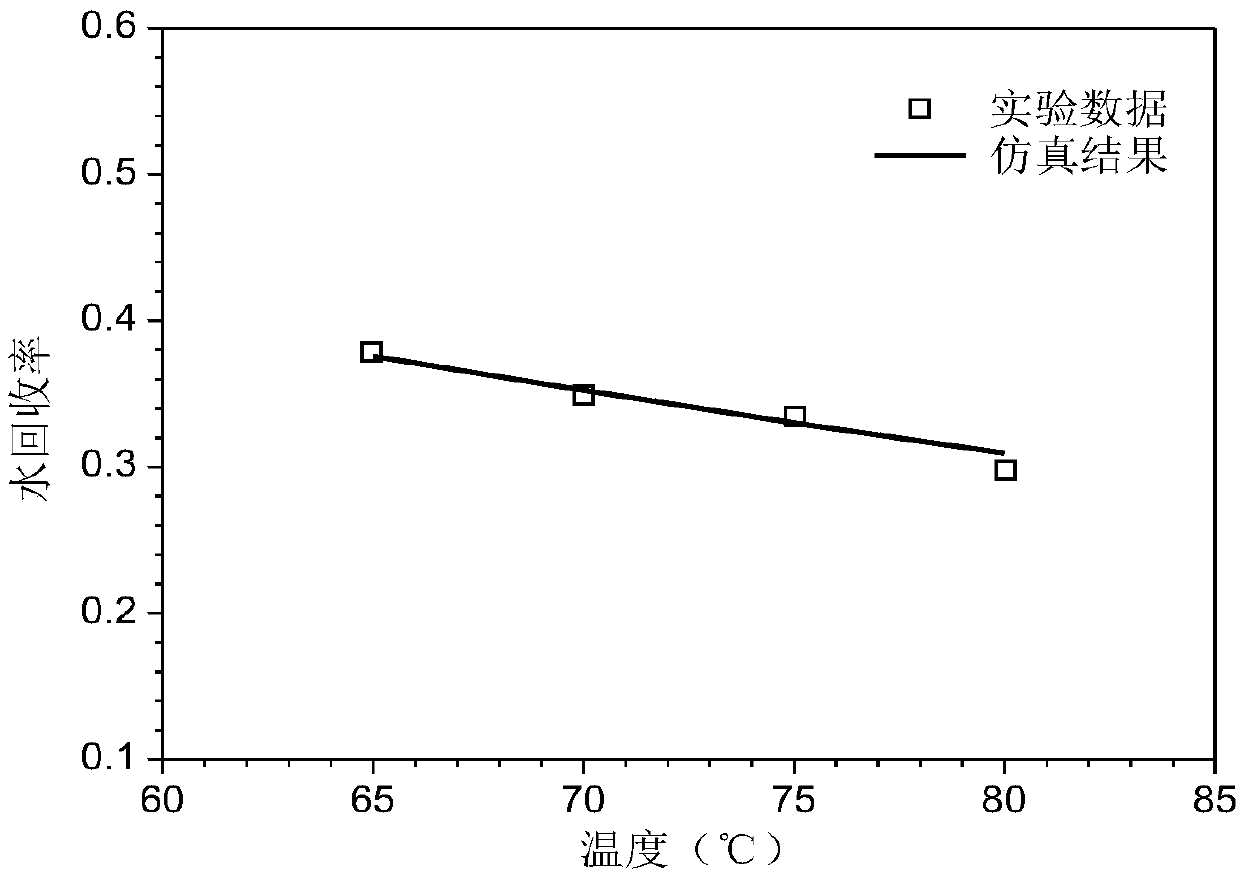
ActiveCN108875183APerformance real-time monitoringImprove computing efficiencyFuel cellsSpecial data processing applicationsLiquid waterWater vapor
The invention provides a modeling method of using a membrane humidifier to realize fuel-cell intake-air humidification. A transient simulation model of the one-dimensional flat membrane humidifier isestablished. Governing equations of the model include four conservation equations of a water content in membrane, water vapor in a flow channel, liquid water in a wet side flow channel and energy. High-heat high-humidity exhaust gas of a fuel cell stack is used to humidify desiccated low-temperature reaction gas at a humidification inlet, and a water-heat coupling transfer process inside the humidifier, phase change processes among the water vapor, the liquid water and membrane water and a combined humidification function of water and gas are fully considered. The model is based on a display format updating algorithm, the governing equations are solved at a center of each layer, calculation efficiency is high, and sufficient model accuracy can be guaranteed. The membrane humidifier model can realize coupling with the electricity stack, and a perfect humidification system is constructed through setting of boundary conditions to be used as a numerical simulation tool of heat and mass transfer analysis, structure optimization and type selection of a system, and has very high guiding significance for actual product development.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method and system for processing acoustic waveforms
InactiveUS20160334530A1Quality improvementSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingDispersion curveGoverning equation
Method for processing acoustic waveforms comprises acquiring acoustic waveforms in a borehole traversing a subterranean formation and transforming at least a portion of the acoustic waveforms to produce frequency domain signals. Then model dispersion curves, modes spectrum or waveforms are generated based on an anisotropic borehole-formation model having a set of anisotropic and geometrical borehole-formation parameters and by specifying governing equations and computational mesh based functional basis. The frequency-domain signals are back-propagating using the model dispersion curves to correct dispersiveness of the signals and coherence of the back-propagated signals is calculated. Alternatively the difference between the measured and the model dispersion curves is determined. Model parameters are iteratively adjusted until the coherence reaches a maximum or exceeds a selected value, or alternatively until the difference between the measured and the model dispersion curves becomes minimal or is reduced to below a selected value. Then at least a portion of the set of anisotropic and geometrical borehole-formation parameters is obtained.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com