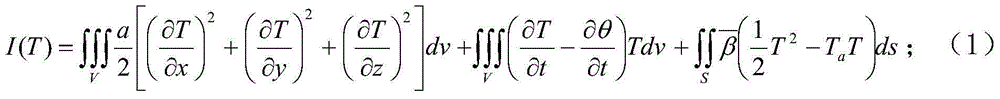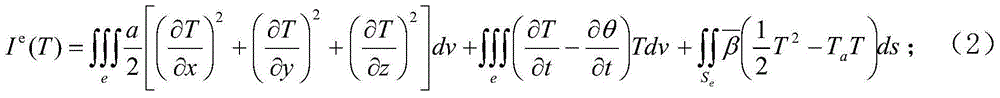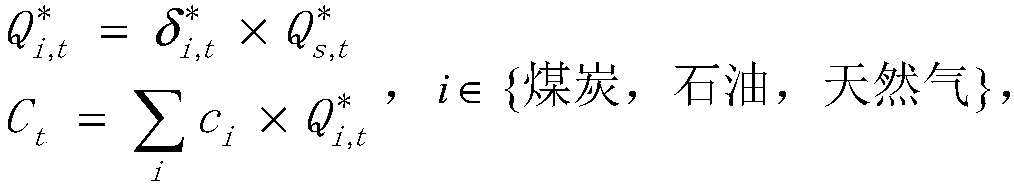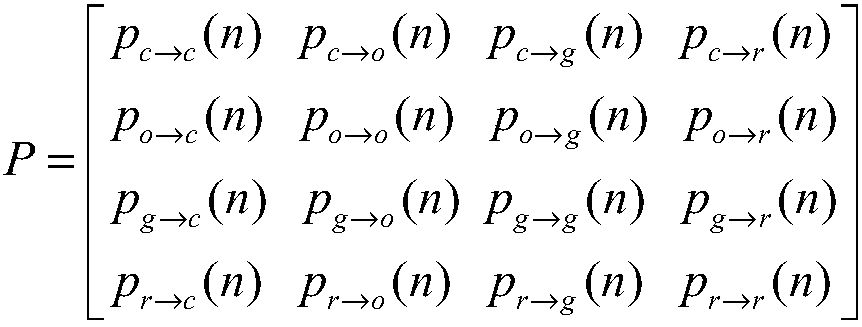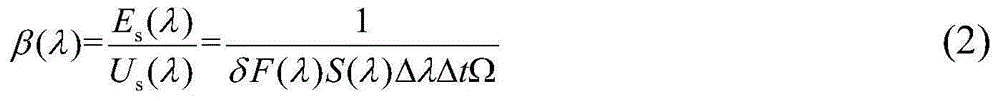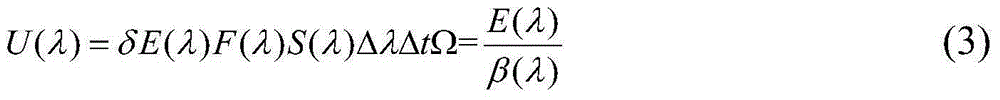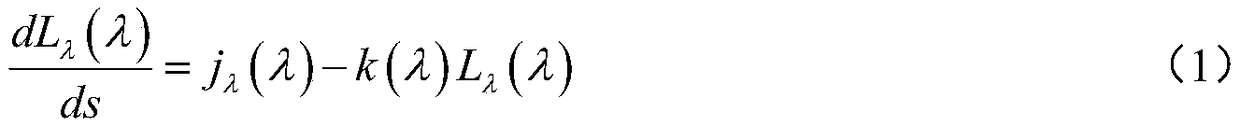Patents
Literature
74 results about "Emission coefficient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Emission coefficient is a coefficient in the power output per unit time of an electromagnetic source, a calculated value in physics. The emission coefficient of a gas varies with the wavelength of the light. It has units of ms−3sr−1.
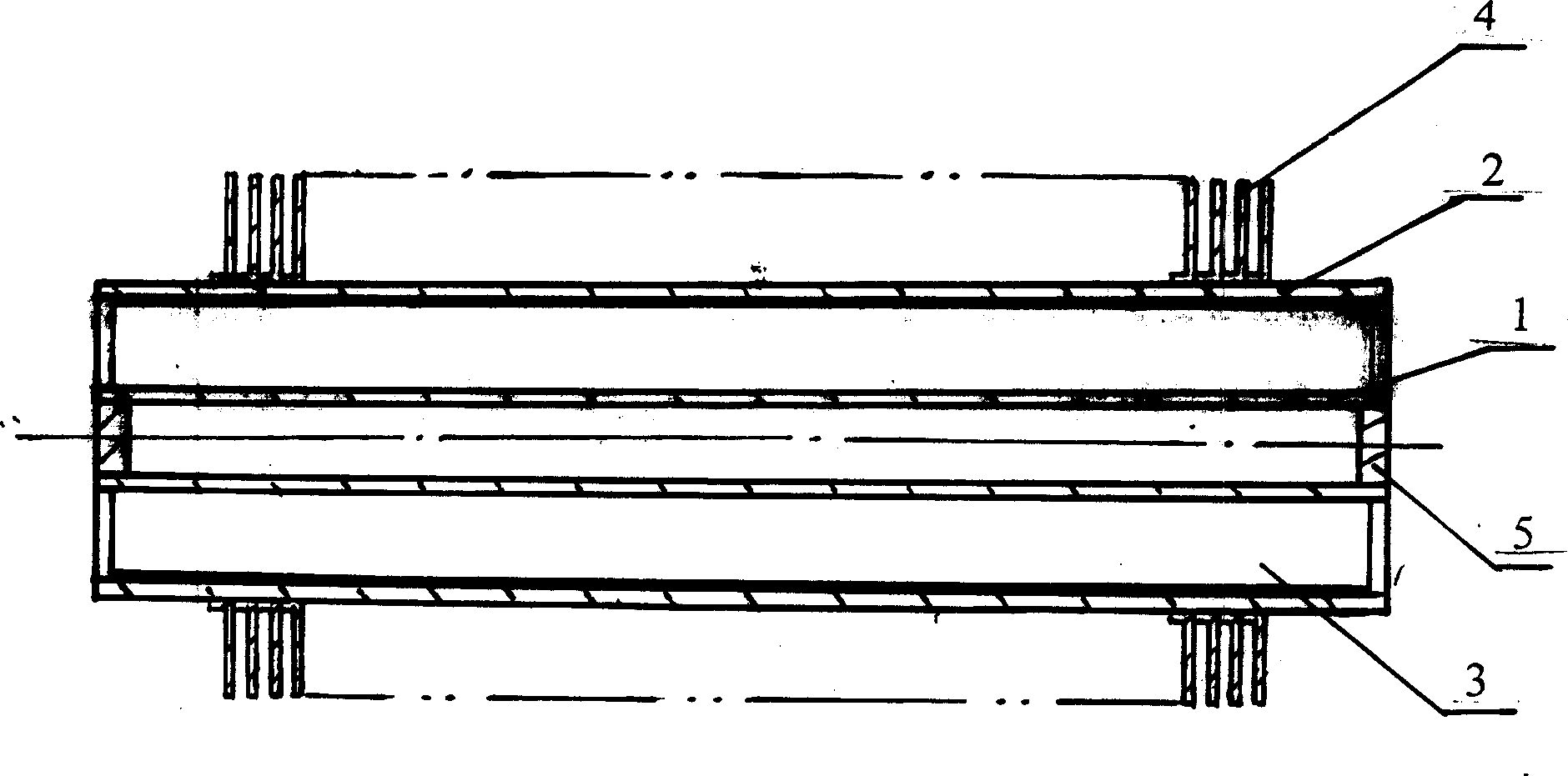
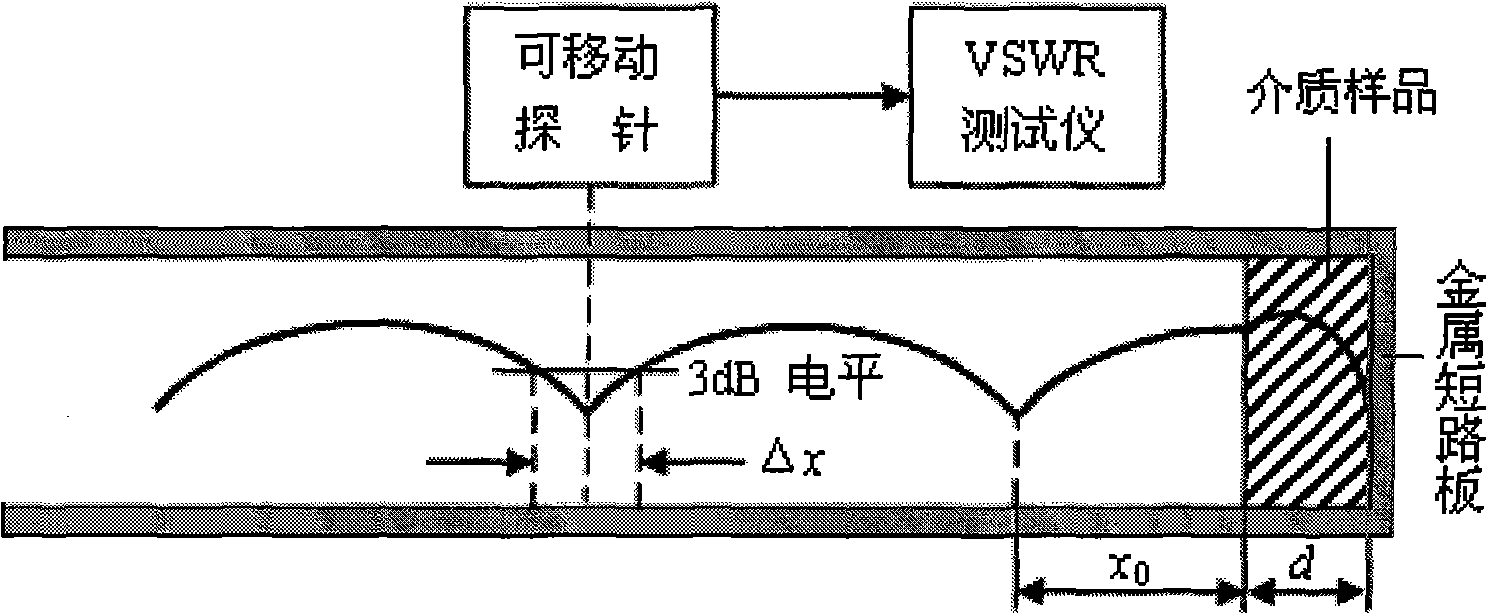
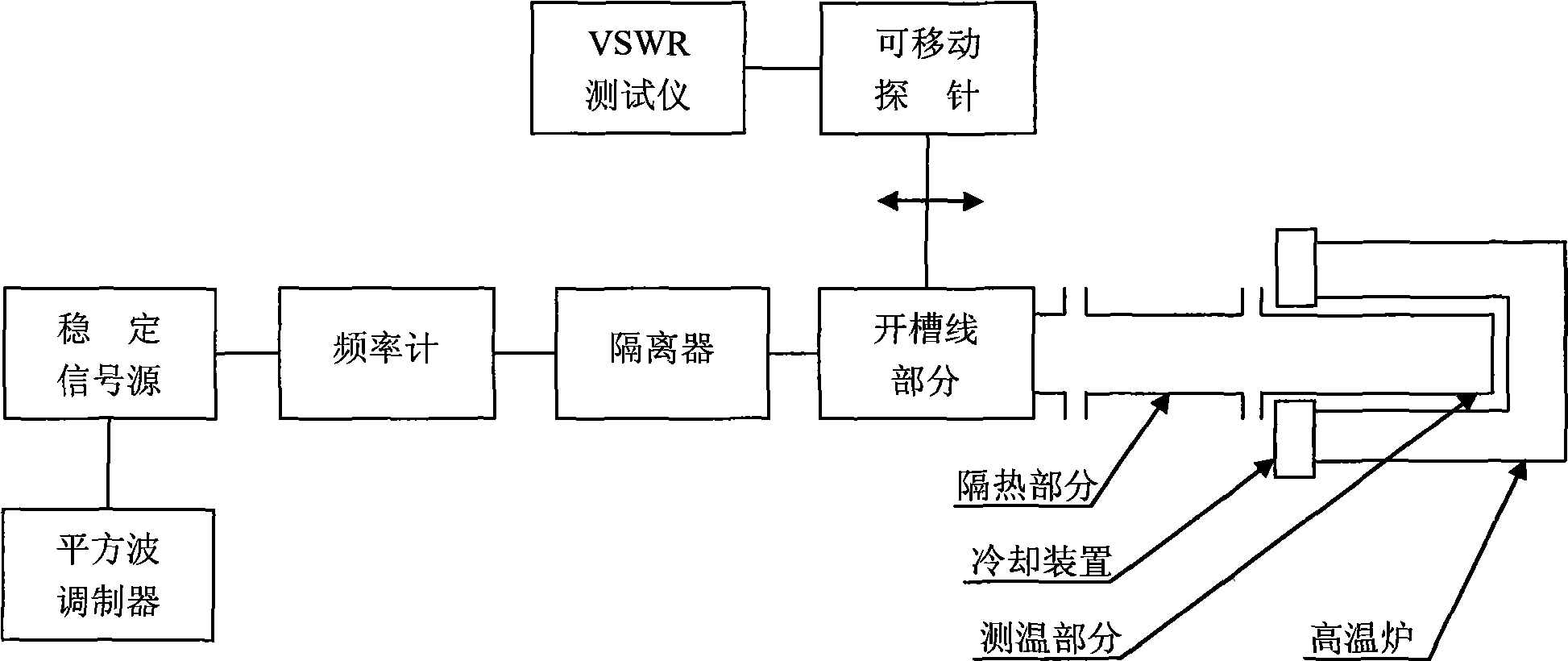
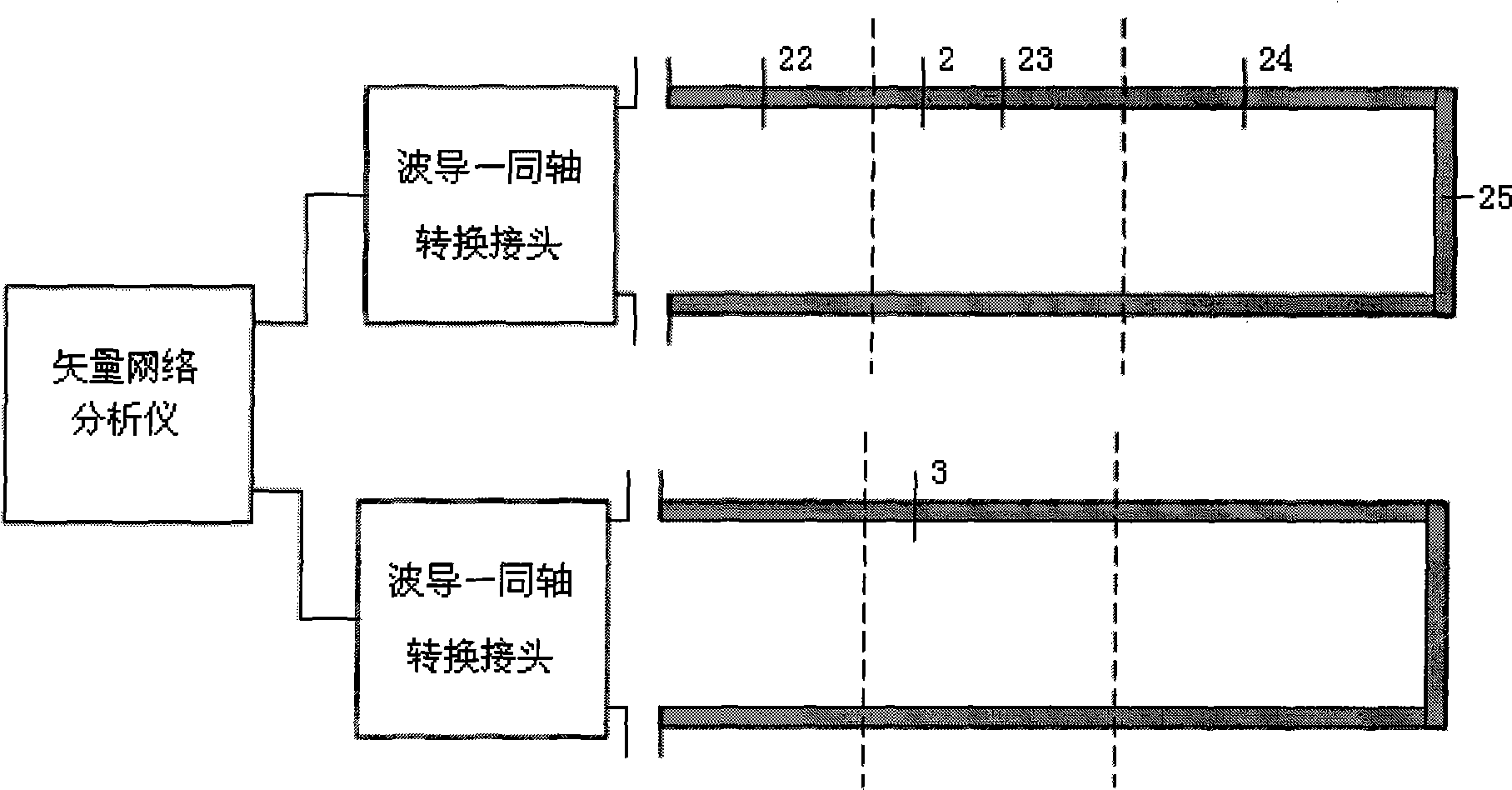
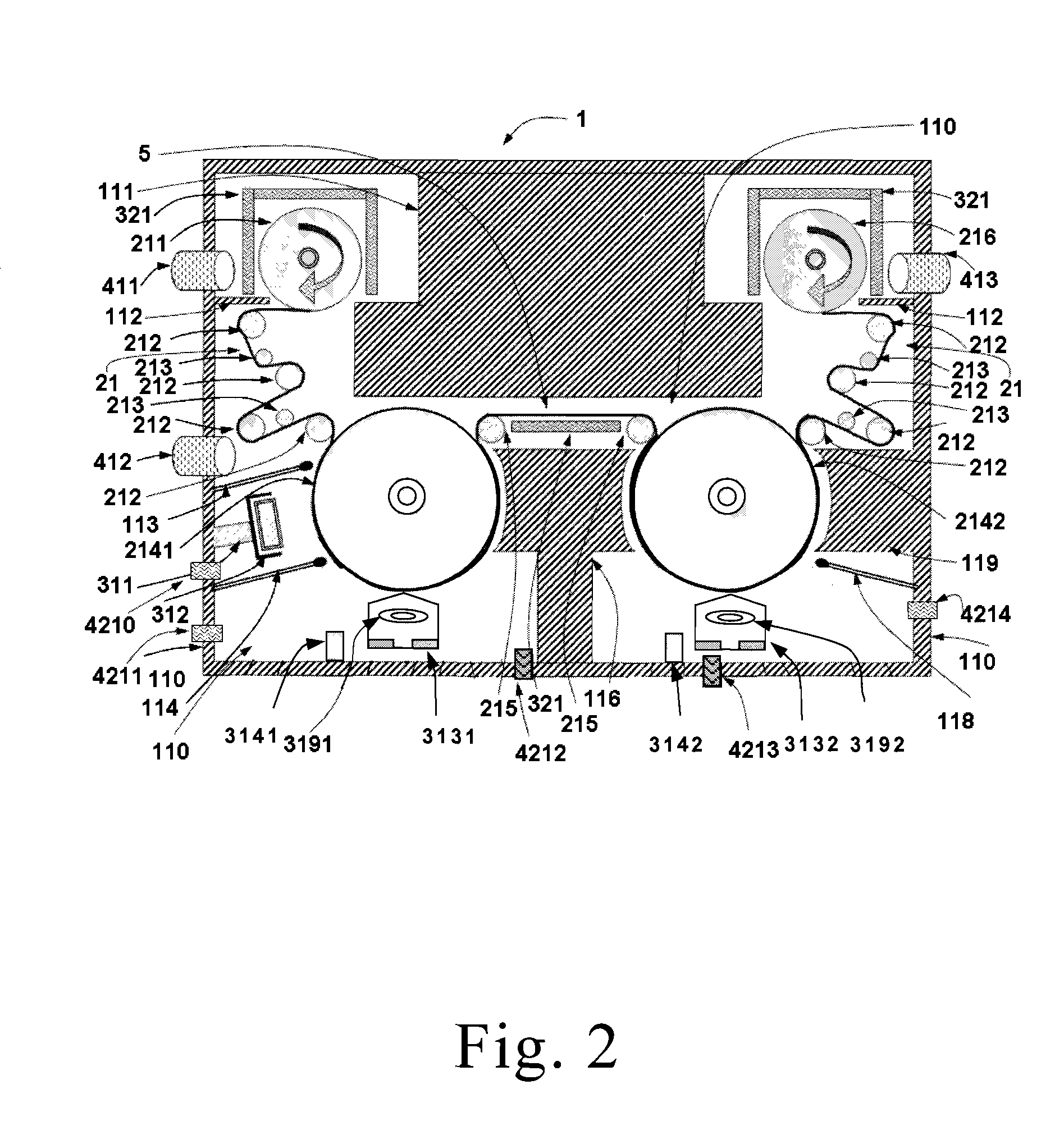
Method for measuring high-temperature complex dielectric constants based on terminal short-circuit method
InactiveCN101545931AHigh precisionReduce test errorResistance/reactance/impedenceDielectricMethod test
The invention belongs to the technical field of microwaves and millimeter waves, and in particular relates to a method for measuring complex dielectric constants of microwave and millimeter wave dielectric materials. When the method tests the complex dielectric constants of high-temperature dielectric materials by adopting a terminal short-circuit method, two same rectangular test waveguides are connected with a vector network analyzer respectively, and each rectangular test waveguide is formed by connecting a radiating waveguide, a heat insulation waveguide, a high-temperature waveguide and a short-circuit board sequentially; and the method comprises the following steps: firstly, measuring emission coefficients of two waveguides at room temperature; secondly, loading a dielectric sample to be tested in one of the test waveguides; thirdly, measuring the emission coefficients of the two waveguides at high test temperature, and correcting the emission coefficient of the waveguide loaded with the test sample by using the emission coefficient of an empty waveguide to further obtain the complex dielectric constant of the dielectric sample to be tested through calculation. By using the method for measuring the high temperature complex dielectric constants of the dielectric materials, the test error can be reduced so that the precision of the test result is higher; and simultaneously, the method only performs the high-temperature measurement once, so that the test efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Thin film deposition apparatus and method of manufacturing organic light-emitting display device by using the same
InactiveUS20110123707A1Manufactured usingMaximized ratioElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesCrucibleDisplay device
A thin film deposition apparatus including a deposition source having a crucible to contain a deposition material and a heater to heat and vaporize the deposition material; a nozzle unit disposed at a side of the deposition source along a first direction and having a plurality of nozzle slits to discharge the deposition material that was vaporized; a plurality of emission coefficient increasing units disposed toward the nozzle unit within the deposition source and increasing a quantity of motion of the deposition material that is discharged toward the nozzle unit; a patterning slit sheet disposed opposite to the nozzle unit and having a plurality of patterning slits arranged along the first direction; and a barrier plate assembly disposed between the nozzle unit and the patterning slit sheet along the first direction, and having a plurality of barrier plates that partition a space between the nozzle unit and the patterning slit sheet into a plurality of sub-deposition spaces.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Carbon emission calculation method based on entire life cycle of building
InactiveCN104268807AData processing applicationsTechnology managementEnterprise life cycleEmission standard
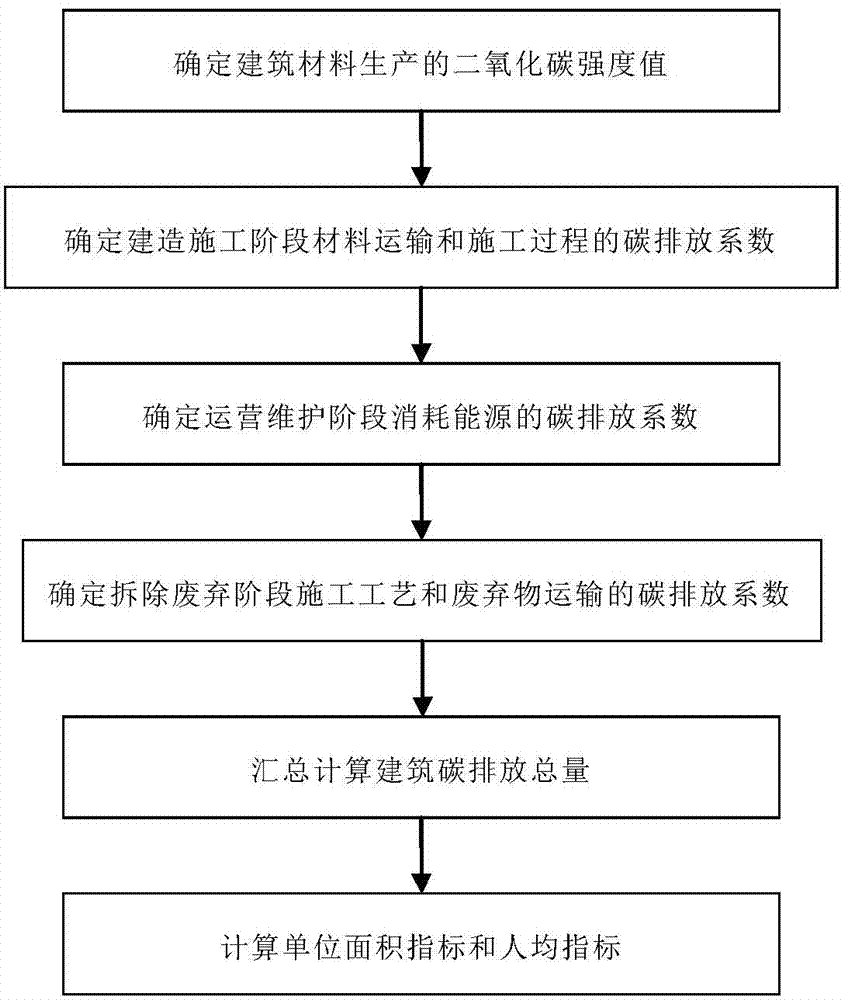
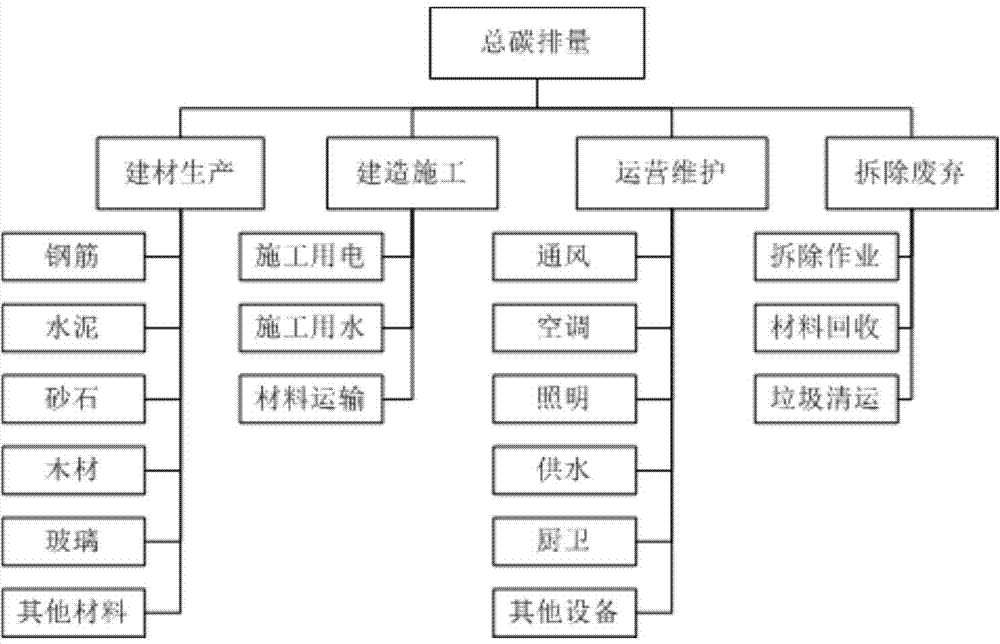
The invention provides a carbon emission calculation method based on the entire life cycle of a building and relates to the technical field of carbon emission calculation. According to the features of carbon emission, carbon emission calculation is divided into four stages of building material production, building construction, operation maintenance and waste dismantlement. The method includes the steps that a carbon dioxide intensity value of building material production is determined; carbon emission coefficients in the material transportation and construction processes in the building construction stage are determined; carbon emission coefficients of consumed energy in the operation maintenance stage are determined; carbon emission coefficients of the construction technology and waste transportation in the waste dismantlement stage are determined; the total carbon emission amount of the building is calculated through collection; the unit area index and the per capita index are calculated, the indexes of the total carbon emission amount, the unit area carbon emission amount and the per capita carbon emission amount of the building in the entire life cycle are acquired, the carbon emission standard which the low-carbon building can reach is checked, assessment and affirmation are conducted, effective measures such as design, construction and operation are taken in each stage of the building, the carbon emission of the building is reduced, and the low-carbon level of the building is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIANKE ENG CONSULTING
Intelligent prediction method and system for road traffic pollution source
ActiveCN105206056AImprove air qualityThe issue of improving total emissionsDetection of traffic movementInformation repositoryEmission standard
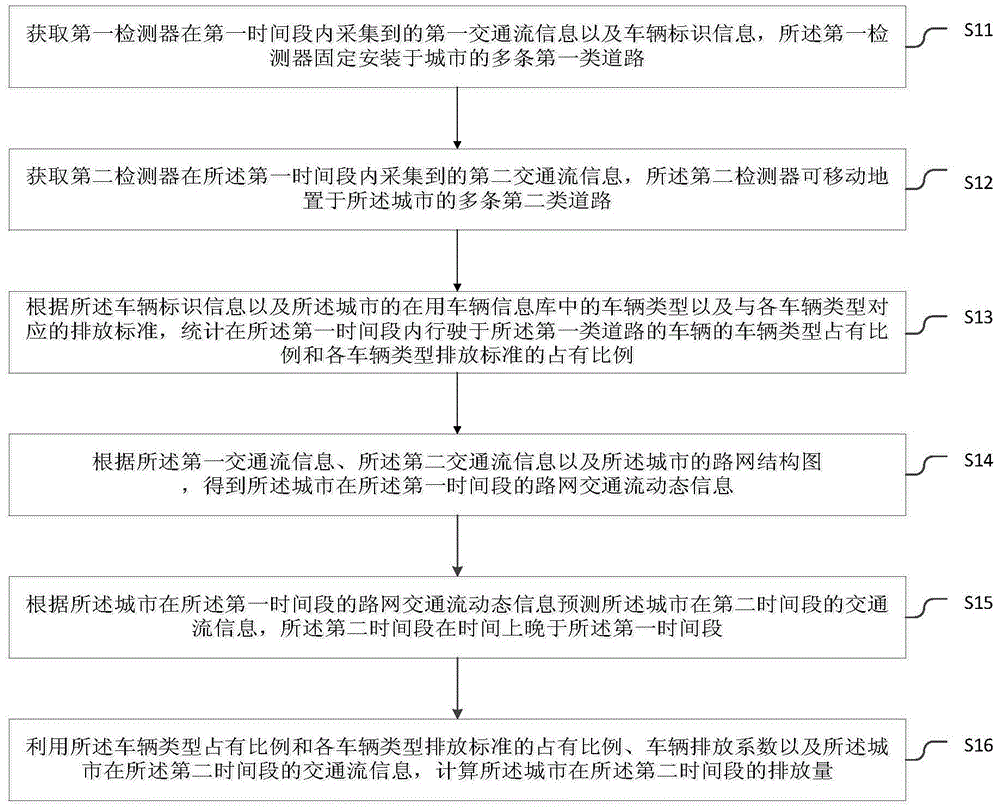
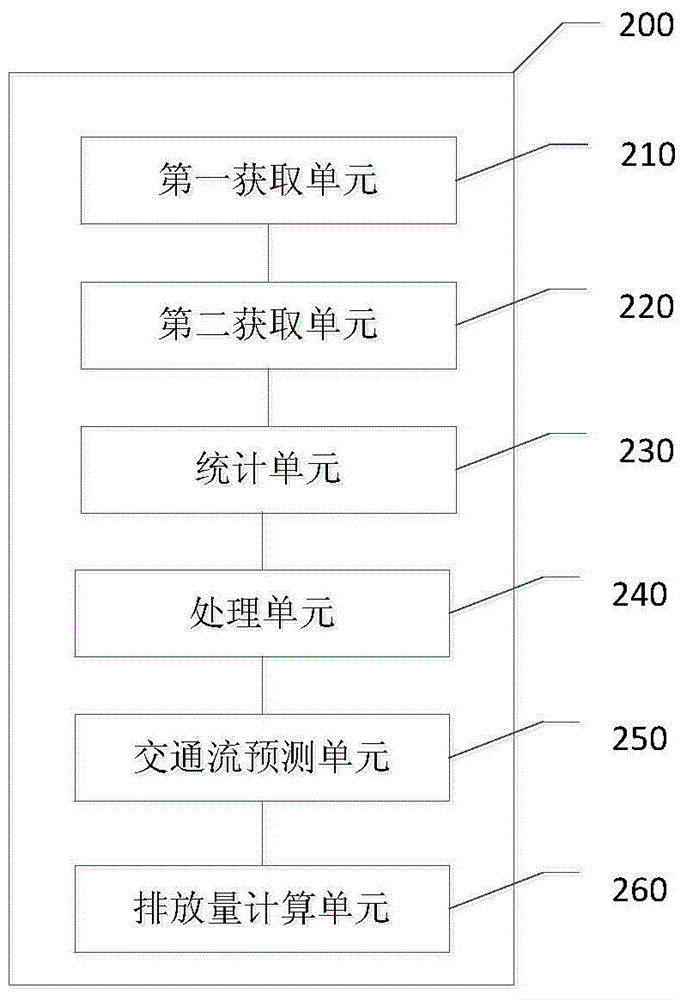
The invention discloses an intelligent prediction method and system for a road traffic pollution source, and belongs to the field of traffic pollution and environment monitoring. The method comprises the steps of obtaining first traffic flow information and vehicle identification information collected by a first detector within a first period of time; obtaining second traffic flow information collected by a second detector within a second period of time; conducting statistics on the occupation rate of vehicle types of vehicles driven in a first road within the first period of time and the occupation rate of emission standards of the vehicle types according to the vehicle identification information and urban in-use vehicle information base; obtaining urban road network traffic flow dynamic information within the first period of time according to the first and second traffic flow information and an urban road network structure chart, and predicting the urban traffic flow information within the second period of time; calculating the urban emission load within the second period of time by means of the occupation rate of the vehicle types, the occupation rate of the emission standards of the vehicle types, vehicle emission coefficients and the urban traffic flow information within the second period of time.
Owner:ZHUHAI GAOLING INFORMATION TECH COLTD
Secondary-emission rare earth-molybdenum material and its preparing process
InactiveCN1360079AImprove machinabilityThe secondary emission coefficient is constantMagnetronsGas discharge connecting/feedingHigh resistanceSecondary emission
A two-element rare-earth / molybdenum material as secondary emission material is characterized by that it contains La2O3 and Y2O3 in a weight ratio of 1:3, and is preapred through adding La2O3 and Y2O3in the form of aqueous solution of their nitrates to molybdenum oxide or Mo powder, treating in hydrogen at 500-550 deg.C for 1-5 hr, reducing at 800-1000 deg.C, and powder metallurgy to obtain said secondary emission material, which has advantages of high emission coefficient, stability and mechinability and high resistance to expose in atomosphere.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Calculating method of large-volume concrete cooling temperature field
InactiveCN104809334AReduce difficultyFast Calculation AnalysisSpecial data processing applicationsCooling effectDegrees of freedom
The invention discloses a calculating method of a large-volume concrete cooling temperature field. The method comprises the following steps: superposing the energy of concrete dissipated by the wall surface of a cooling water pipe onto a conventional fonctionelle; establishing a finite element governing equation of the concrete containing the cooling water pipe through a variational principle based on the composite fonctionelle; and then estimating an equivalent heat emission coefficient of a concrete contact surface based on the thickness and the heat conductivity coefficient of the cooling water pipe. The existence of the cooling water pipe is not considered during the mesh generation; sections intersected with concrete units are found out based on the positions of the cooling water pipe after the mesh is formed, thereby a cooling water pipe mesh is automatically formed. The method does not increase the difficulty in the mesh generation, and precisely considers the temperature change around the cooling water pipe. Therefore, the method is an efficient method for analyzing the cooling effect of the cooling water pipe; and the problems that the conventional methods are too big in the degree of freedom and are unable to be calculated by computers are solved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Method for preparing black titanium oxide coating on titanium surface
InactiveCN101775633AUniform surfaceHigh blacknessSurface reaction electrolytic coatingMicro arc oxidationPlasma electrolytic oxidation
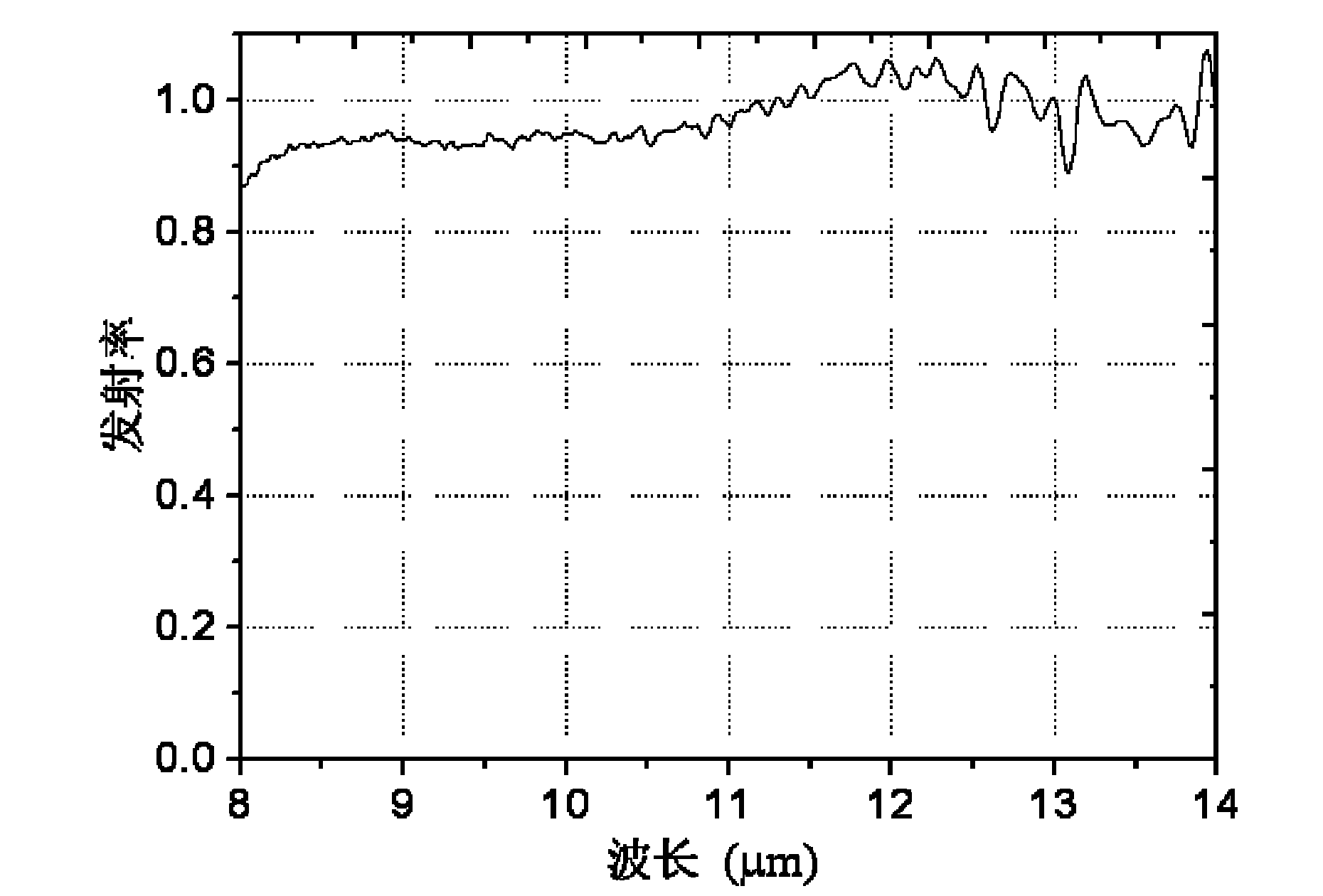
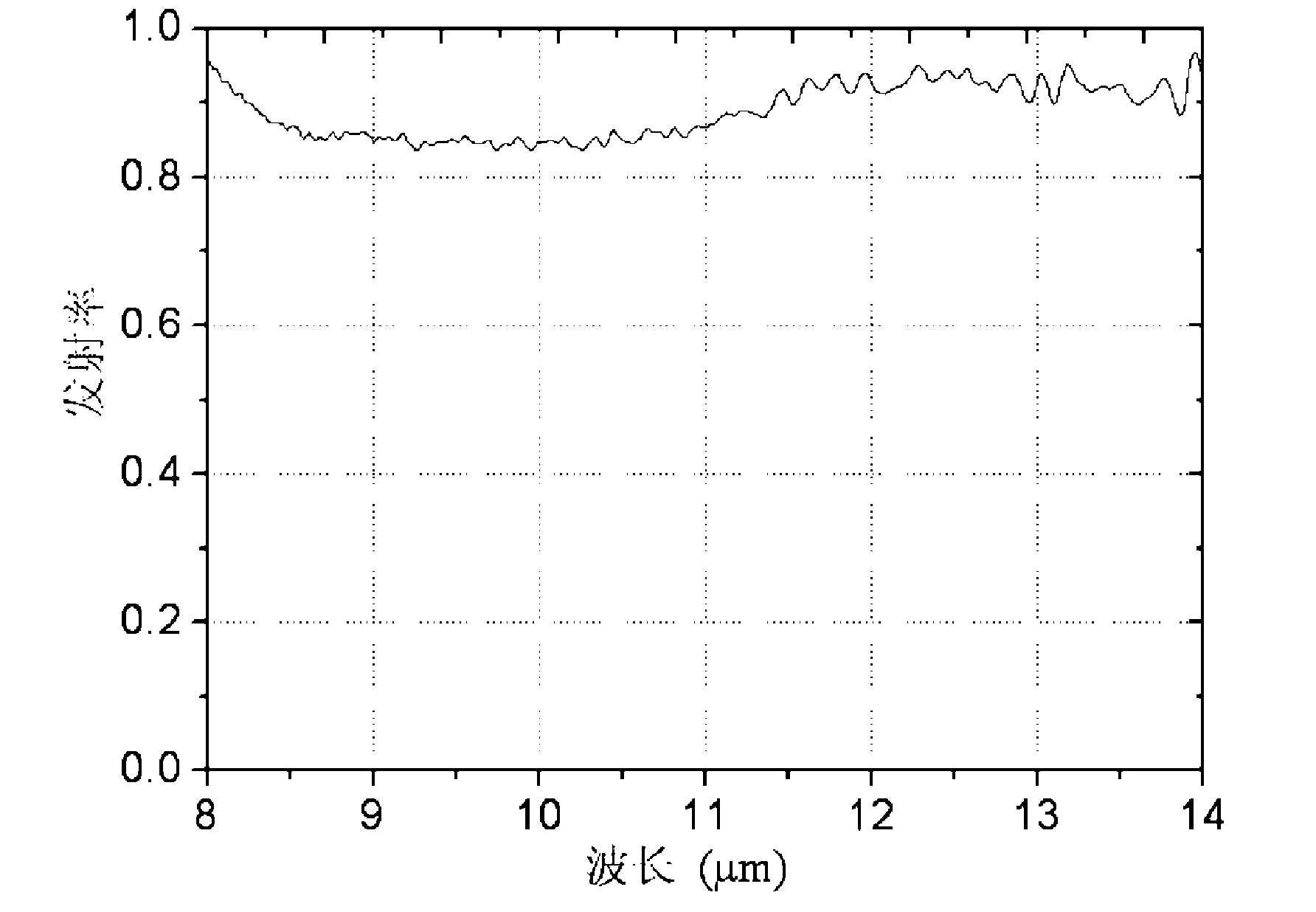
The invention discloses a method for preparing a black titanium oxide coating on a titanium surface, which relates to a method for preparing a micro-arc oxidation coating on a titanium surface. The invention solves the problems of complexity, high energy consumption and high cost of the traditional preparation process of forming a black titanium oxide film on the titanium surface. The method is characterized in that a titanium part is taken as the anode after being degreased, stainless steel is taken as the cathode, the anode and the cathode are soaked in an electrolyte, and micro-arc oxidation is carried out after electrical parameters are regulated, thereby the black titanium oxide coating on the titanium surface is obtained. The invention simplifies the process and has simple operation, energy and time saving and low cost by adopting a single-step micro-arc oxidation process; the obtained black titanium oxide coating is even and has high blackness, and the emission coefficient is 0.85 to 1.0 within the infrared wavelength range of 8 to 14mum; and the reflection coefficient of the wavelength of the black titanium oxide coating is 0.02 to 0.15, and thereby, the black titanium oxide coating is used for the field of military thermal control and civil decorative coatings. The invention is not limited by the shape and the dimension of the part, thereby being suitable for industrial mass production.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
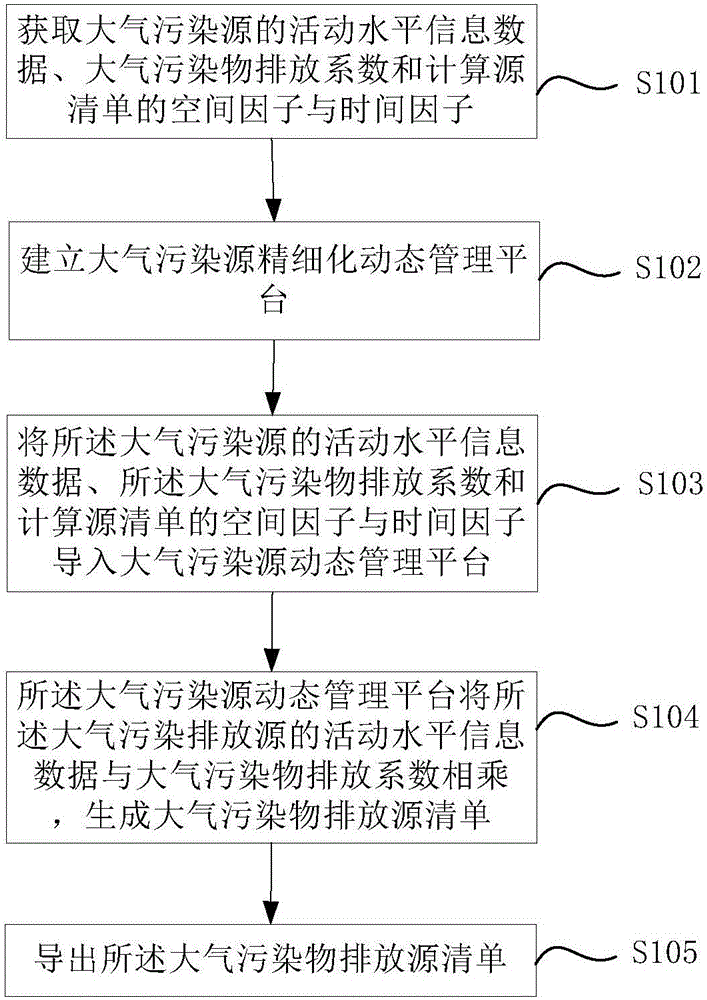
Refined dynamic air pollutant emission source list management method
The invention discloses a refined dynamic air pollutant emission source list management method. The method comprises steps that the activity level information data of an air pollution source is acquired; an air pollutant emission coefficient is acquired; a refined dynamic air pollution source management platform is established; the activity level information data of the air pollution emission source and the air pollutant emission coefficient are inputted to the dynamic air pollution source management platform; the activity level information data of the air pollution emission source and the air pollutant emission coefficient multiply in the dynamic air pollutant source management platform to generate an air pollution source list; the air pollution source list is led out. Through the method, the activity level information data of the air pollution emission source and the air pollutant emission coefficient are acquired, the refined dynamic air pollution source management platform is utilized to generate the air pollutant emission source list, knowledge of an emission condition of air pollutants is facilitated, and the method is applicable to city group air pollution control, key air pollution source control and air quality simulation.
Owner:湖南省环境保护科学研究院
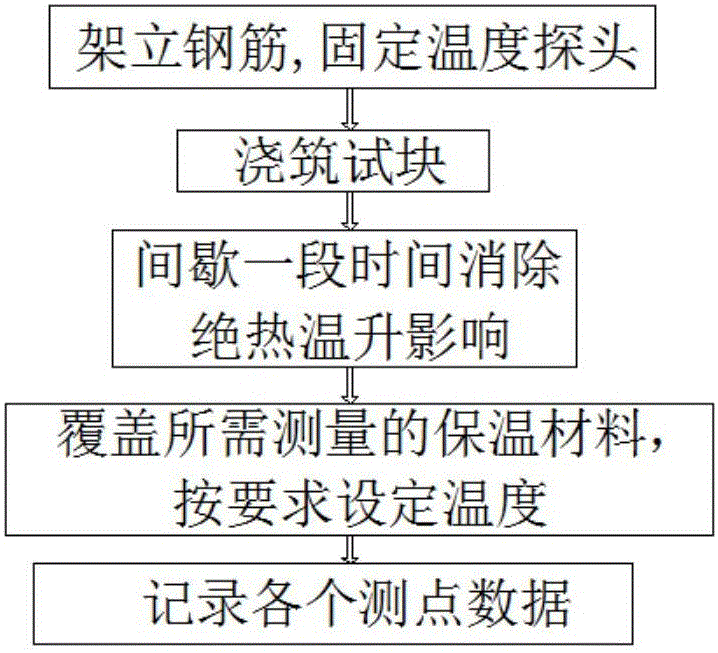
Method for indoor measurement surface heat emission coefficient of concrete
ActiveCN105842278APrecise inversionExact heat release coefficientMaterial heat developmentMaterial testing goodsAutomatic controlField conditions
The invention discloses a method for indoor measurement of the surface heat emission coefficient of concrete. According to the method, the temperature of the environment where an experiment block is located, the moisture content of a heat preservation material and other parameters can be precisely controlled, the surface heat emission coefficient of the experiment block is subjected to high-precision inverse analysis and calculation, and then the surface heat emission coefficient of the concrete covering the heat preservation material (including a water containing frozen heat preservation material) can be precisely tested. The method comprises the steps that 1, the experiment block is manufactured, and a certain number of temperature testing points are buried in the experiment block; 2, the experiment block with the heat preservation material laid is placed in a freezing and thawing test box for automatically controlling and recording the temperatures of the testing points, the temperature of an antifreezing solution and the temperature in the box, wherein the heat preservation material comprises a water containing frozen material, and reasonable temperature value is set for an experiment; 3, according to experiment data, inverse analysis is carried out to obtain the experiment block surface heat emission coefficient beta1 of the experiment block with the heat preservation material laid under the experiment condition; 4, through formula derivation and calculation, the surface heat emission coefficient betaS of the concrete under the field condition is obtained.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
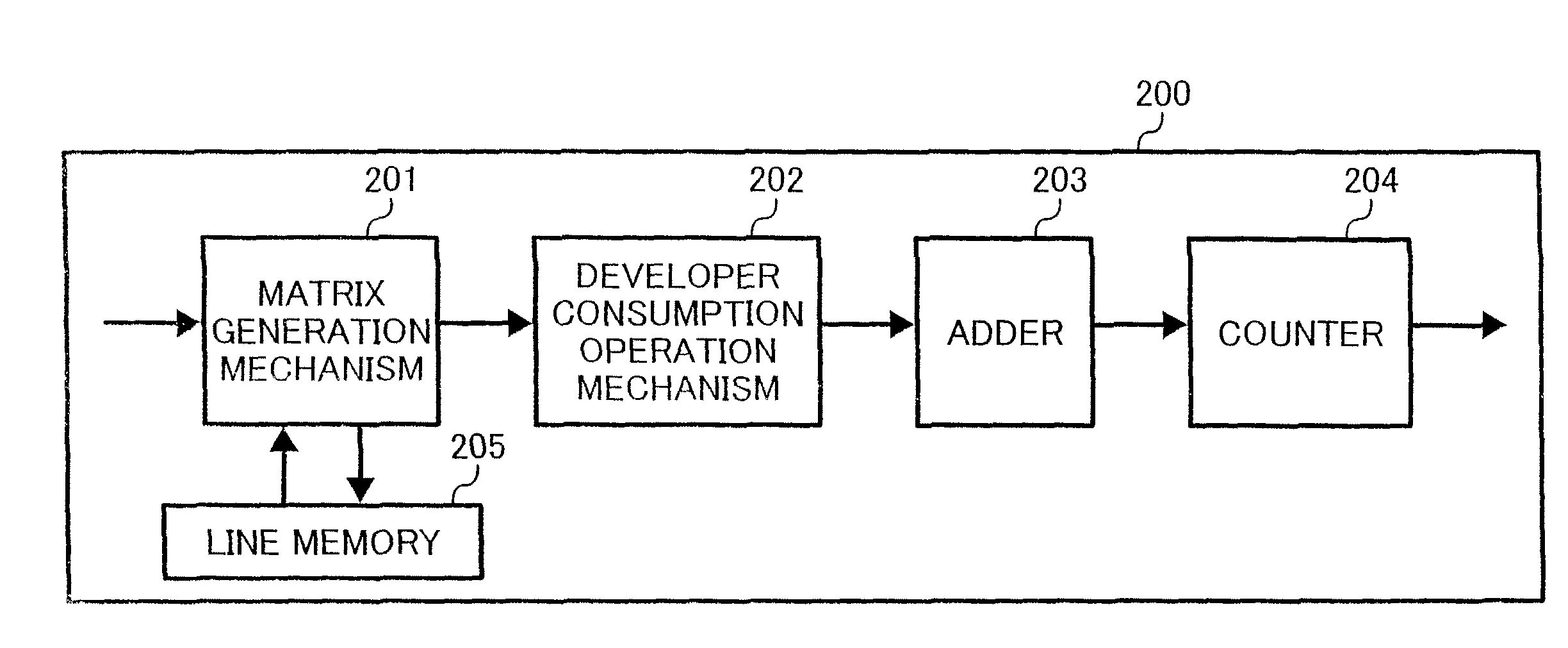
Method and apparatus for determining developer consumption, and image forming apparatus
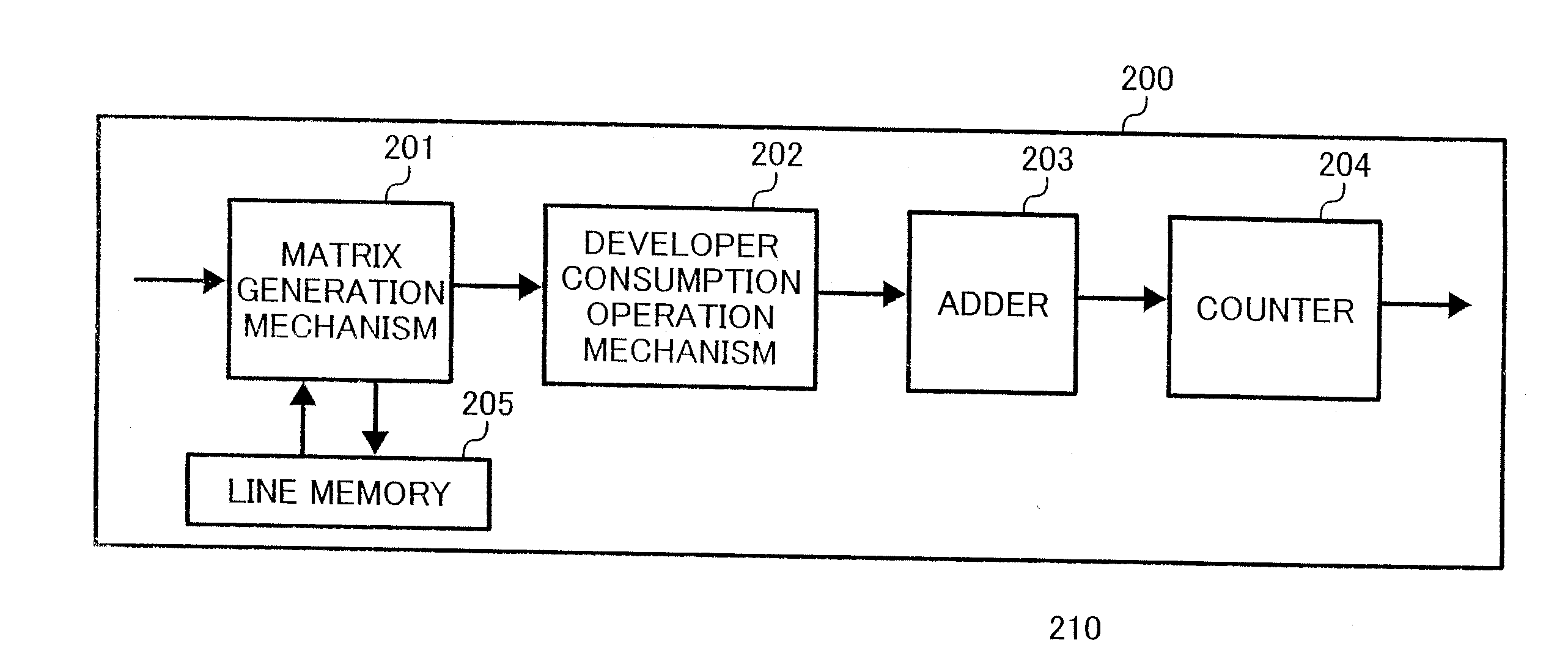
InactiveUS20070103717A1Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsWeight coefficientImage formation
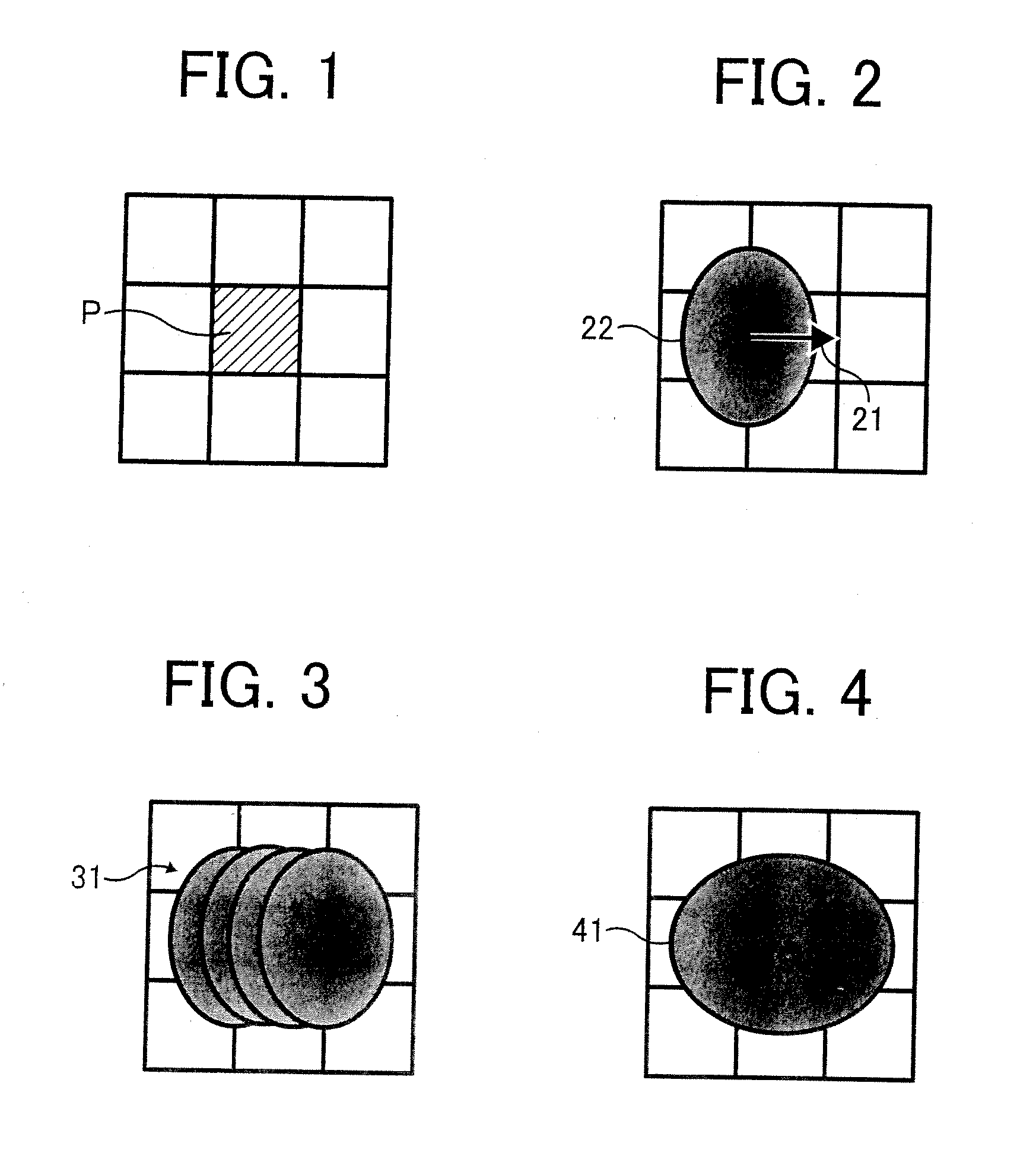
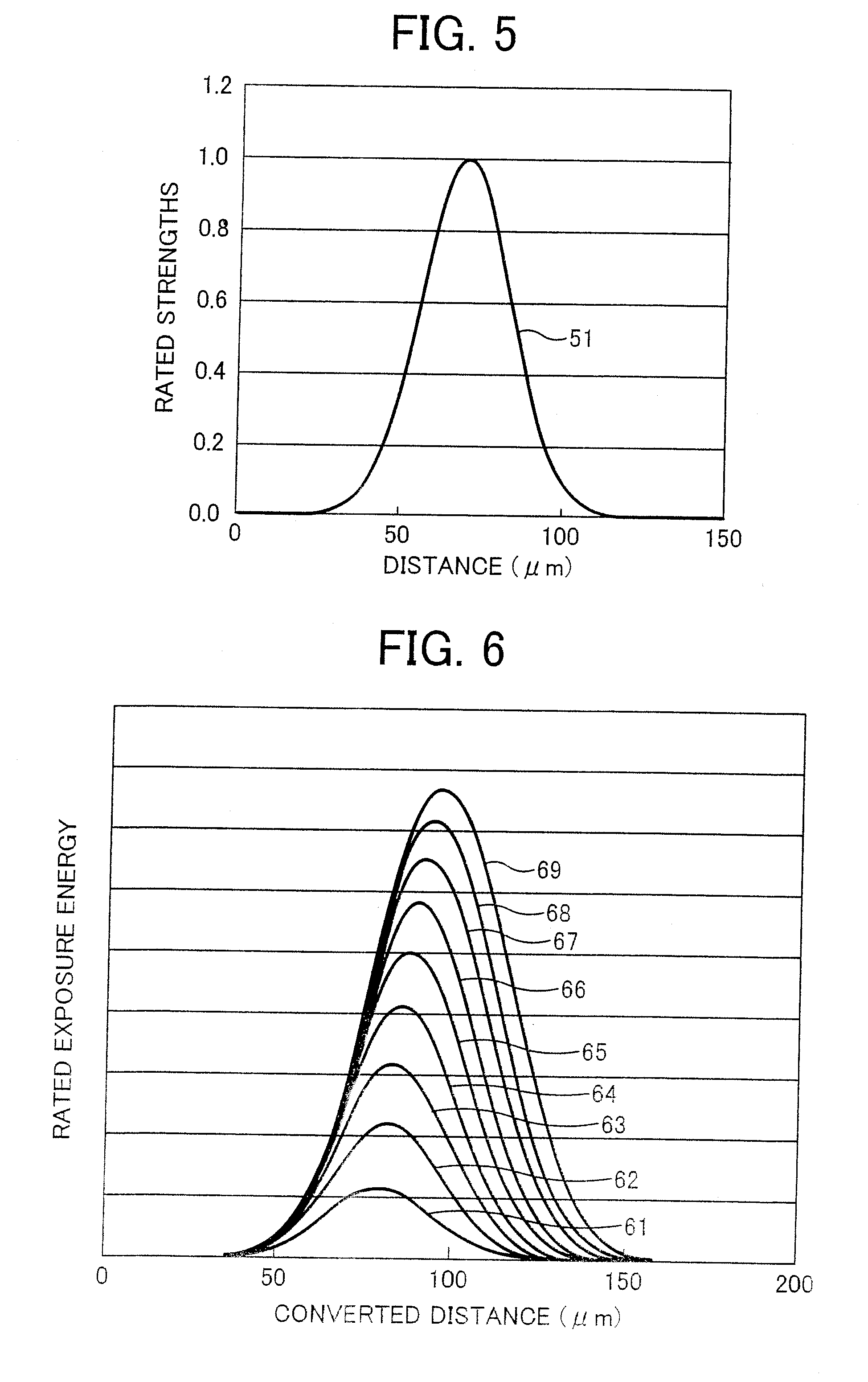
A developer consumption determining method for determining a developer consumption of an image forming apparatus includes the steps of dividing one of writing pixels into a plurality of sub-pixels in a main scanning direction, determining a weighting coefficient for each of surrounding sub-pixels of one of the sub-pixels located within a predetermined distance from the one of the sub-pixels on the basis of positional relationships, determining respective emission coefficients for the surrounding sub-pixels on the basis of one of durations and exposures of the light beams applied to the surrounding sub-pixels, summing products of the weighting coefficients of the surrounding sub-pixels and the respective emission coefficients to obtain total exposure for the one of the sub-pixels, repeating for all of the sub-pixels the steps of determining the weighting coefficient, determining respective emission coefficients, and summing products, and summing the total exposures for all the sub-pixels to determine the developer consumption.
Owner:RICOH KK
Lock head construction emulation method considering soft foundation consolidation and concrete creep
ActiveCN106202649AConsider elastoplastic consolidation behaviorComprehensive calculationGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationStress distributionEngineering
The invention discloses a lock head construction emulation method considering soft foundation consolidation and concrete creep. The lock head construction emulation method comprises the steps of: 1, determining thermal parameters of concrete and a soft foundation, a creep calculation parameter of the concrete, a consolidation parameter of the foundation and an elastoplasticity mechanical parameter of the foundation; 2, establishing a finite element network of a lock head structure; 3, determining time steps of calculation, an initial temperature of the concrete and an equivalent heat emission coefficient of a concrete heat insulating measure; 4, according to the thermal parameters, a time-history analysis step, an initial condition and an air temperature, predicting and calculating a temperature field; 5, calculating a pore pressure and ground stress distribution of the excavated soft foundation; and 6, applying a temperature load, a foundation initial pore pressure, a ground stress of the foundation and other loads which need to be considered to carry out stress calculation. The method disclosed by the invention comprehensively considers a creep feature of the concrete and an elastoplasticity consolidation feature of the soft foundation, and can relatively perfectly predict a stress of the lock head structure in the construction period.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Method and system for enhancing microscopy image
InactiveUS20110317000A1Accurate valueLess subjectColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsMicroscopic imageLight attenuation
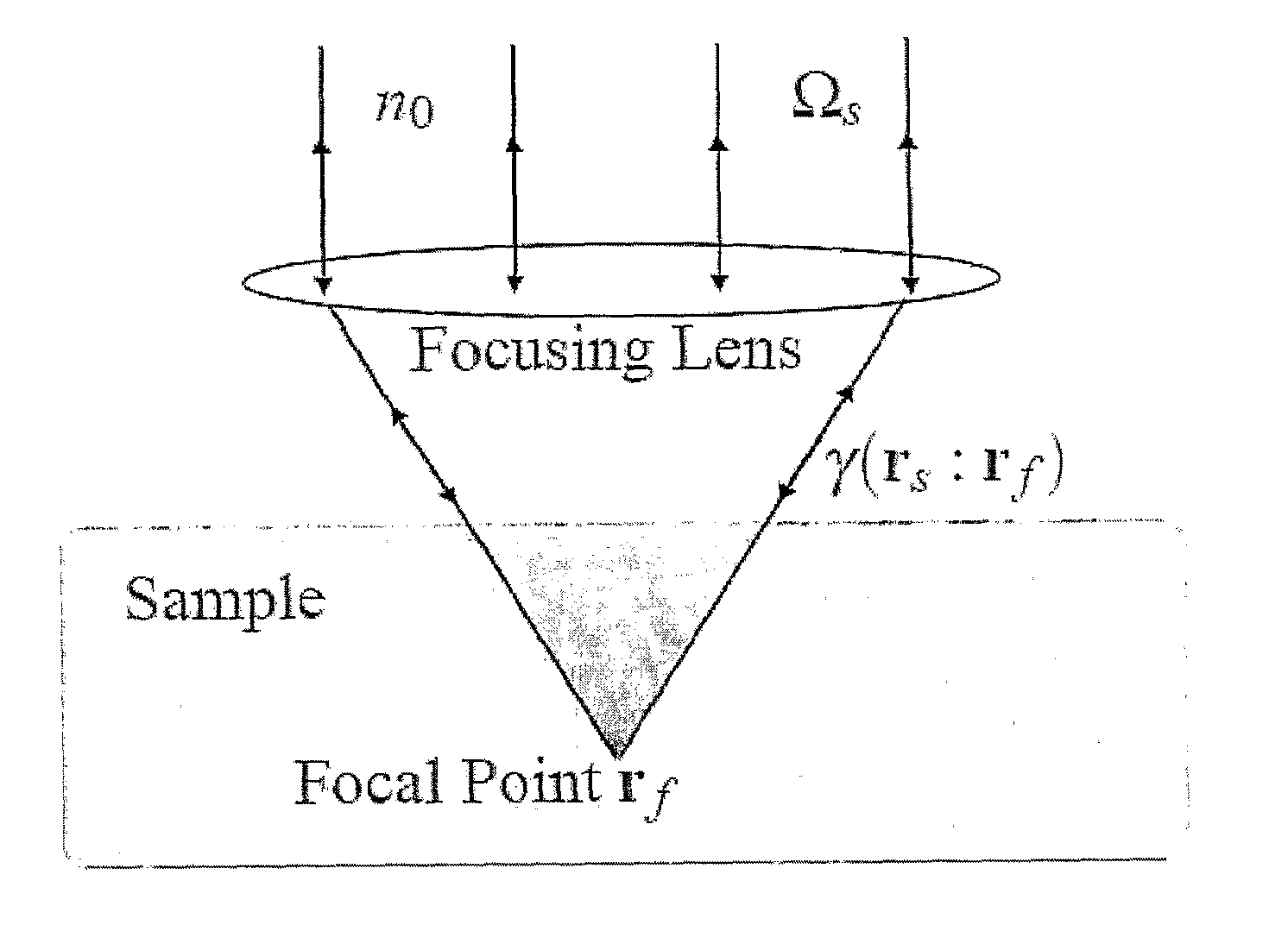
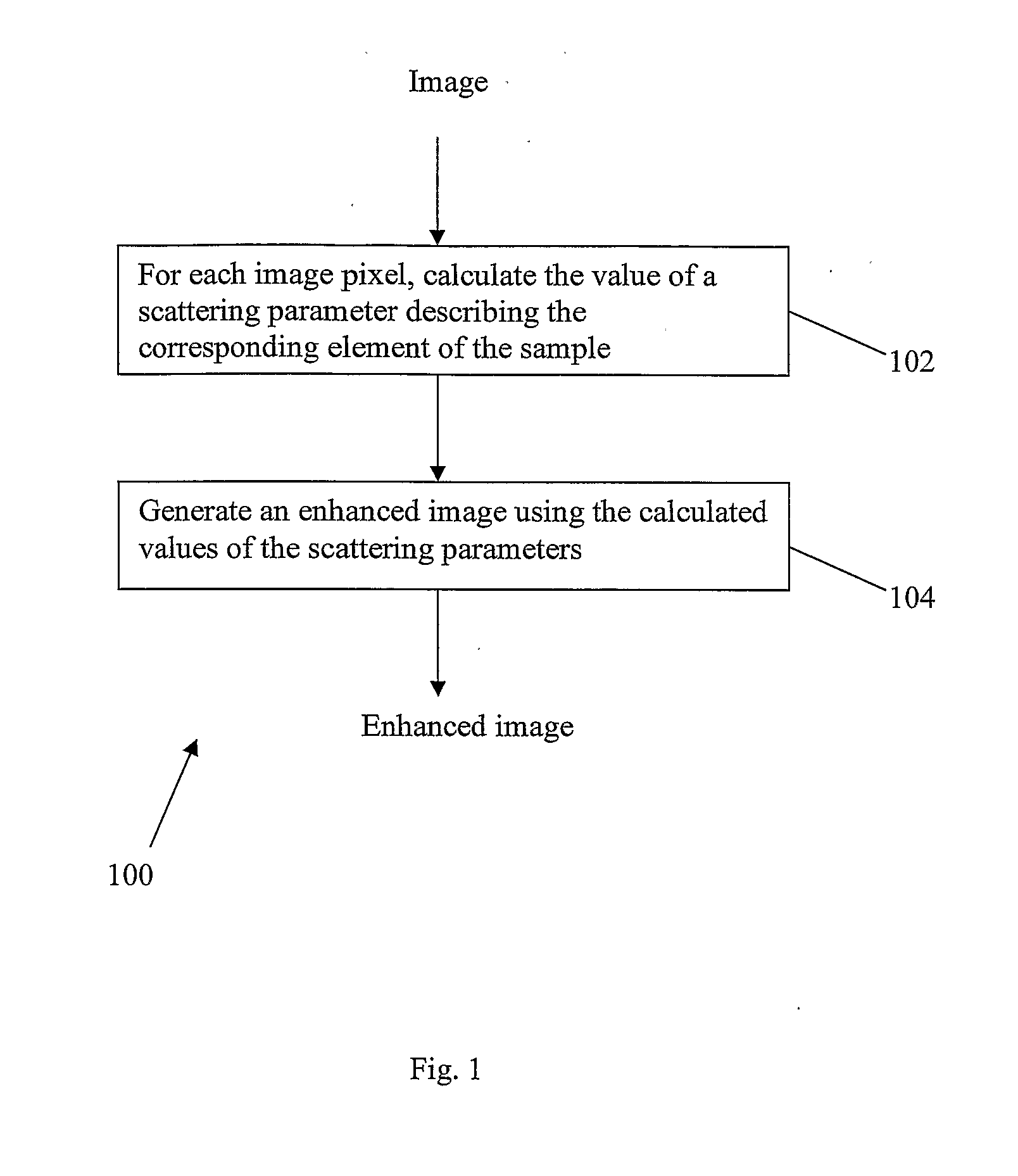
A microscopy image, formed by illuminating a sample by shining light onto it in an illumination direction and capturing scattered light, is used to produce an enhanced image. This is done using an expression which links the intensity of the portions of the image to respective values of a scattering parameter at multiple respective elements of the sample. The scattering parameter may be an emission coefficient ρem or else equal to an absorption coefficient ραb. This expression is solved to find the values of the scattering parameter. The scattering parameter is used to construct an enhanced image, for example an image which maps the variation of the scattering parameter itself. Provided the scattering parameter is found accurately, the enhanced image should be less subject than the original image to degradation due to non-uniform light attenuation and scattering.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
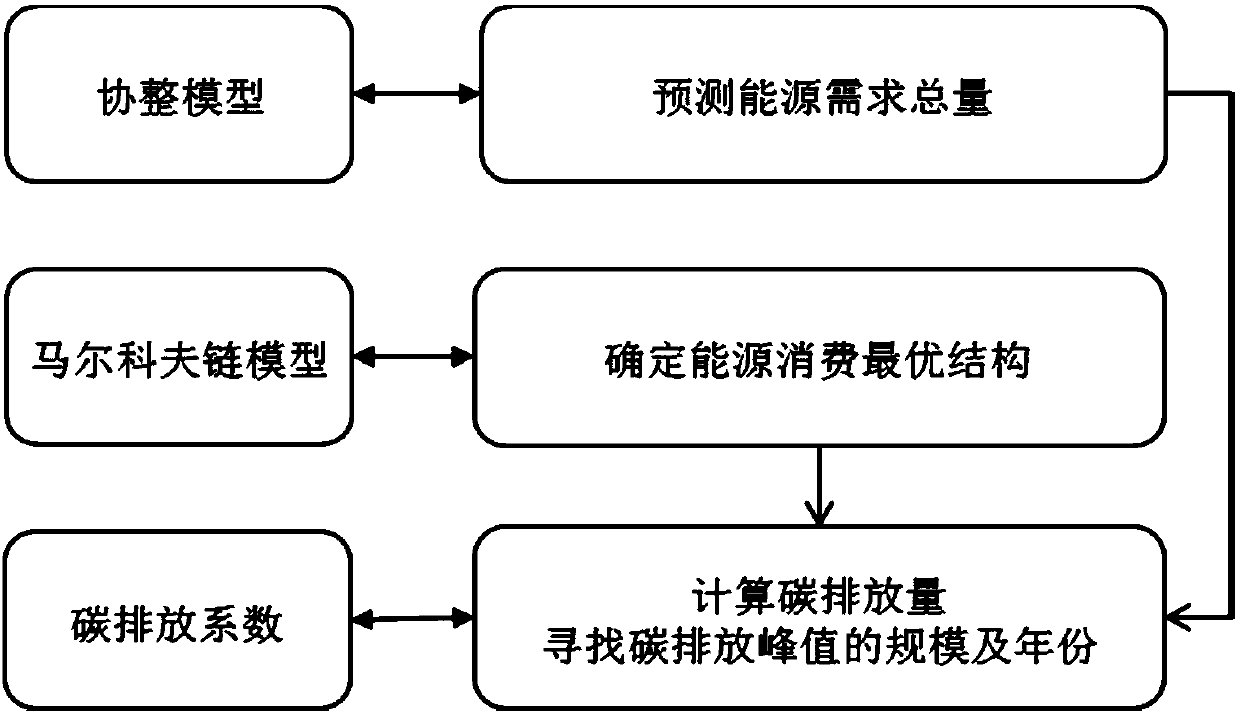
Method and system for calculating carbon emission peak value based on energy consumption structure optimization
InactiveCN107609676AIn line with the actual carbon emission curveForecastingTechnology managementMarkov chainEnvironmental resource management
The invention discloses a method and a system for calculating a carbon emission peak value based on energy consumption structure optimization. A scale interval and an occurrence time range of the carbon emission peak value can be calculated by an existing Kuznets curve. However, the movement of the carbon emission peak value cannot be accurately estimated when environmental governance is carried out and an energy policy changes. The technical scheme adopted by the method comprises the steps of (1) constructing a co-integration model and predicting total energy consumption; (2) calculating an optimal energy consumption structure by use of a Markov chain model under the situation of natural evolution and planning constraint; and (3) calculating carbon emissions under different situations according to results obtained in the previous two steps by use of an international standard carbon emission coefficient, and finding out the scale and the occurrence year of the carbon emission peak value. According to the calculation method, the carbon emission peak value is calculated based on the energy consumption structure optimization, the relation among economic development, energy consumptionand environmental constraint is comprehensively balanced, and the formulation of an energy development strategy can be supported.
Owner:STATE GRID ZHEJIANG ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY ECONOMIC TECHN INST +1
Illumination apparatus with a heat sink
InactiveUS20110170302A1Cut surfaceAvoid contactPoint-like light sourceLighting heating/cooling arrangementsEngineeringLight-emitting diode
An illumination apparatus is provided. The illumination apparatus may include at least one light-emitting diode; and at least one heat sink for cooling the light-emitting diode, wherein at least one component of the illumination apparatus provided for thermal discharge has an emission coefficient of more than 0.75.
Owner:OSRAM GMBH
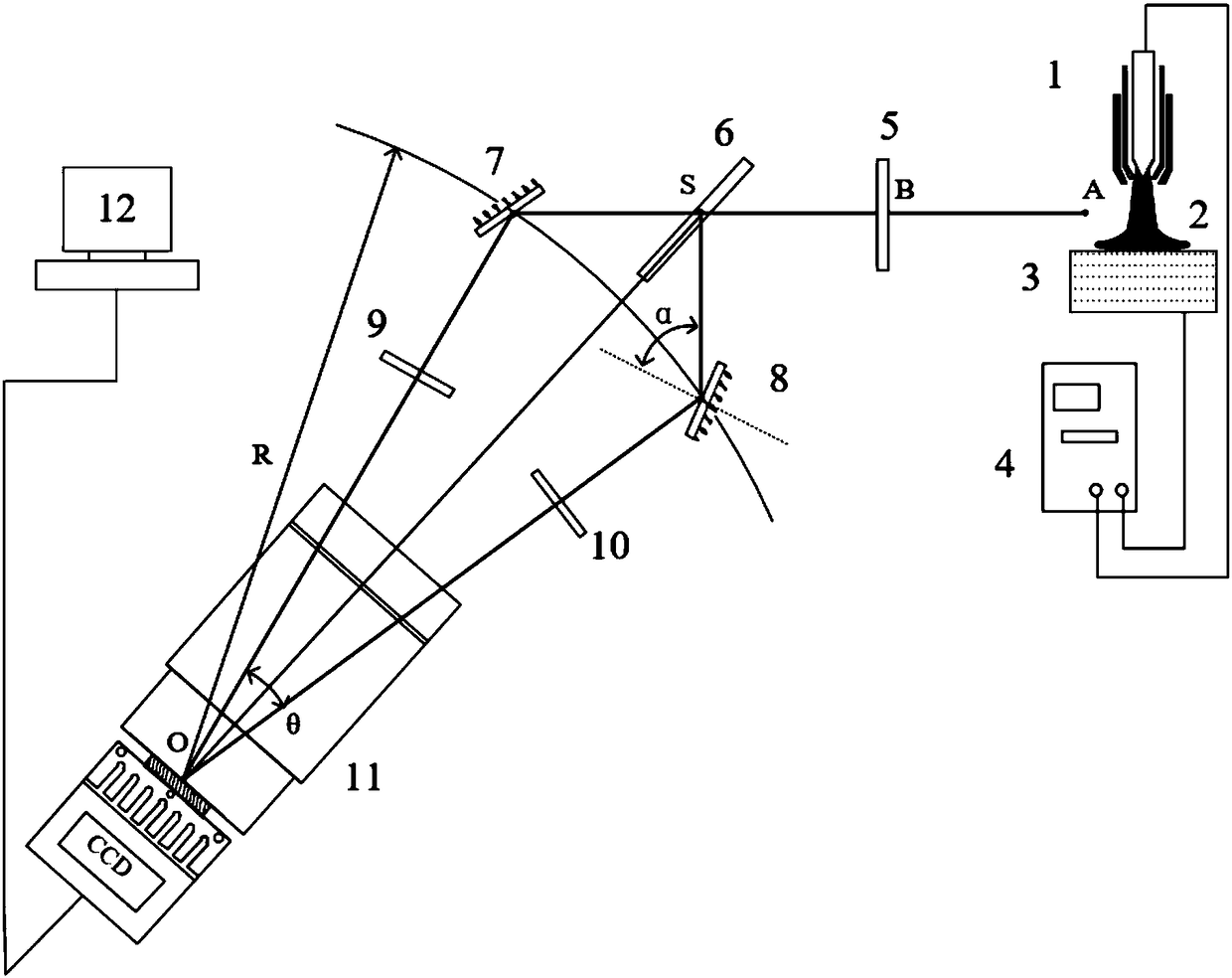
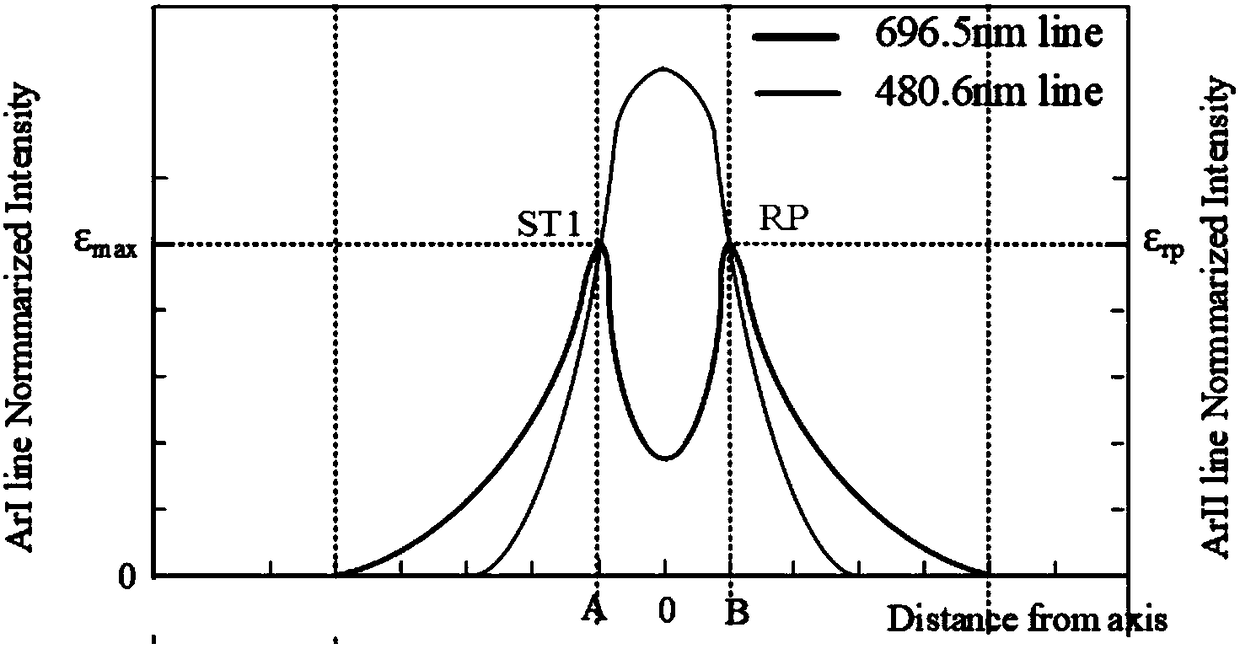
Double-spectral line feature-based standard temperature method
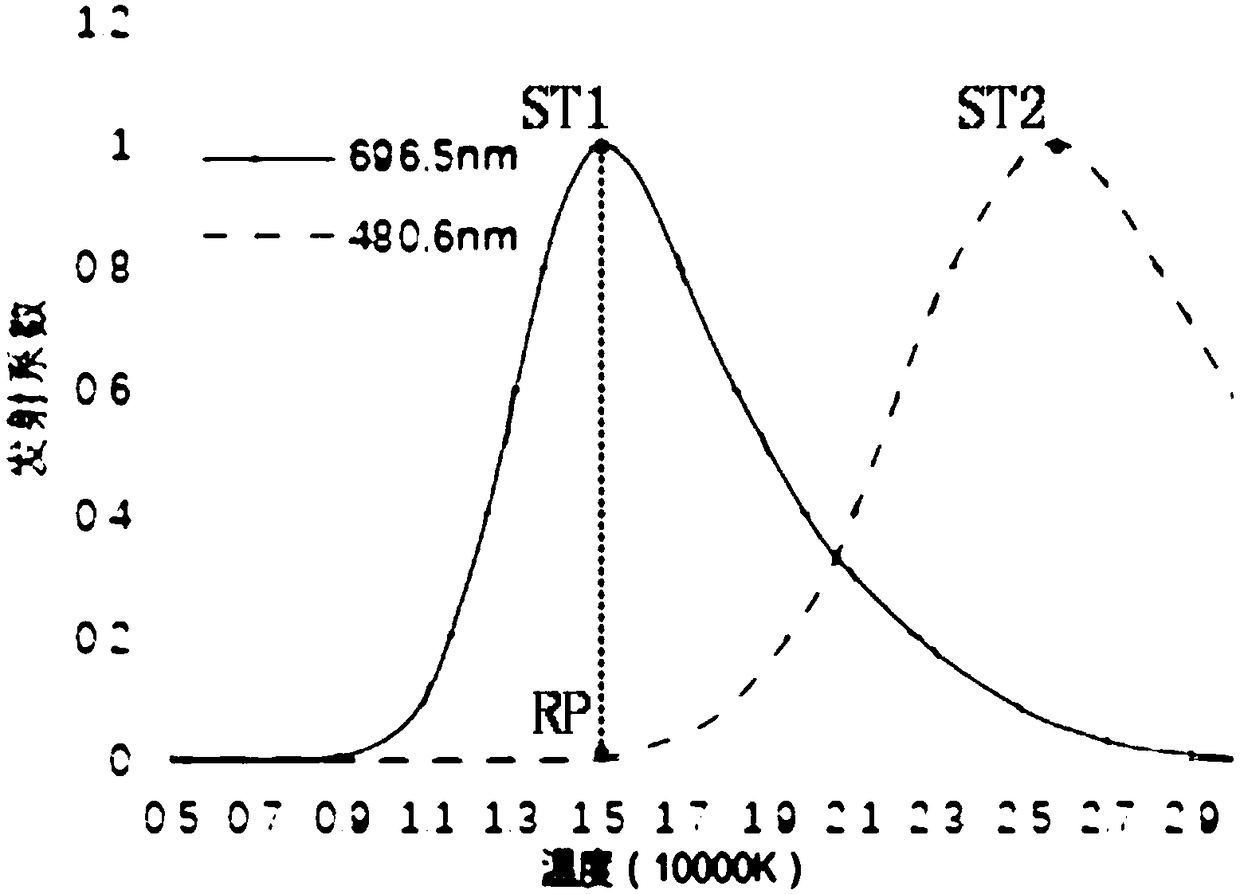
ActiveCN108225569AGood spacing consistencyHigh precisionRadiation pyrometryLuminous intensityImaging quality
The invention discloses a double-spectral line feature-based standard temperature method, relating to the field of measuring the temperature of thermal plasma. The method comprises the following steps: dividing a welding arc into two identical to-be-measured targets through a beam splitting system, respectively two arc light beams by using a high-speed camera and a narrow-band filter, to obtain anatomic spectral line and a primary ionization spectral line. In order to overcome errors brought due to factors of camera dark current, photon overflow and the like, the imaging quality of two arc narrow-band images is needed to be guaranteed in once exposure, the highest luminous intensity value in the two images should be not lower than 50% of maximum measurement range of the camera. During measurement, the highest luminance value of the two arc narrow-band images is controlled 80%-90% of the maximum light exposure. A three-dimensional arc emission coefficient field is reduced by utilizingan ML-EM iterative reconstruction algorithm. The two collected images have good time and space consistency; the automatic judgment of high-temperature and low-temperature areas of the arc can be completed, and the problem that the temperature at the central area of the arc cannot automatically judged during the measurement process of single spectral line can be solved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
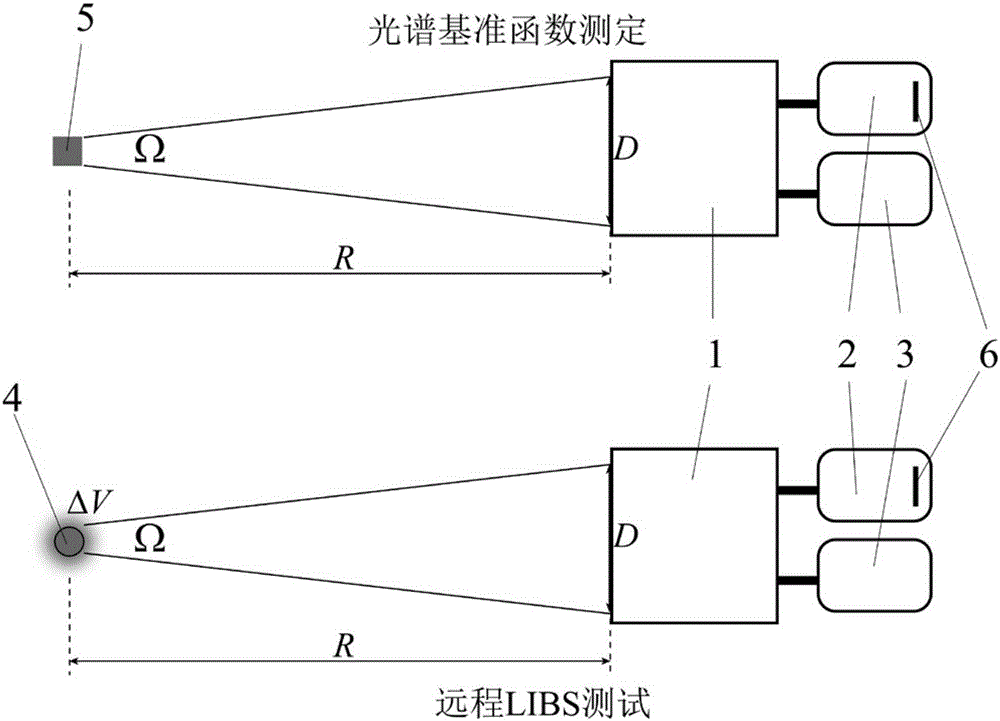
Calibration-free remote quantitative laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy analysis method
ActiveCN105203526AHigh precisionAnalysis by thermal excitationLaser-induced breakdown spectroscopyAnalysis method
The invention discloses a calibration-free remote quantitative laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) analysis method. According to the method, a spectrum reference function reflecting the relation between LIBS spectrometer detector digital voltage output and a target laser-induced plasma emission coefficient is tested firstly, then a geometrical relationship model of an LIBS emitting and receiving optical system is established, and then the spectrum reference function and the geometrical relationship model are fit in CF-LIBS quantitative calculation, so that quantitative LIBS detection is achieved. The method has the advantage that due to the fact that the spectrum reference function and the geometrical relationship model of the LIBS emitting and receiving optical system are fit in CF-LIBS quantitative calculation, precision is quite high.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
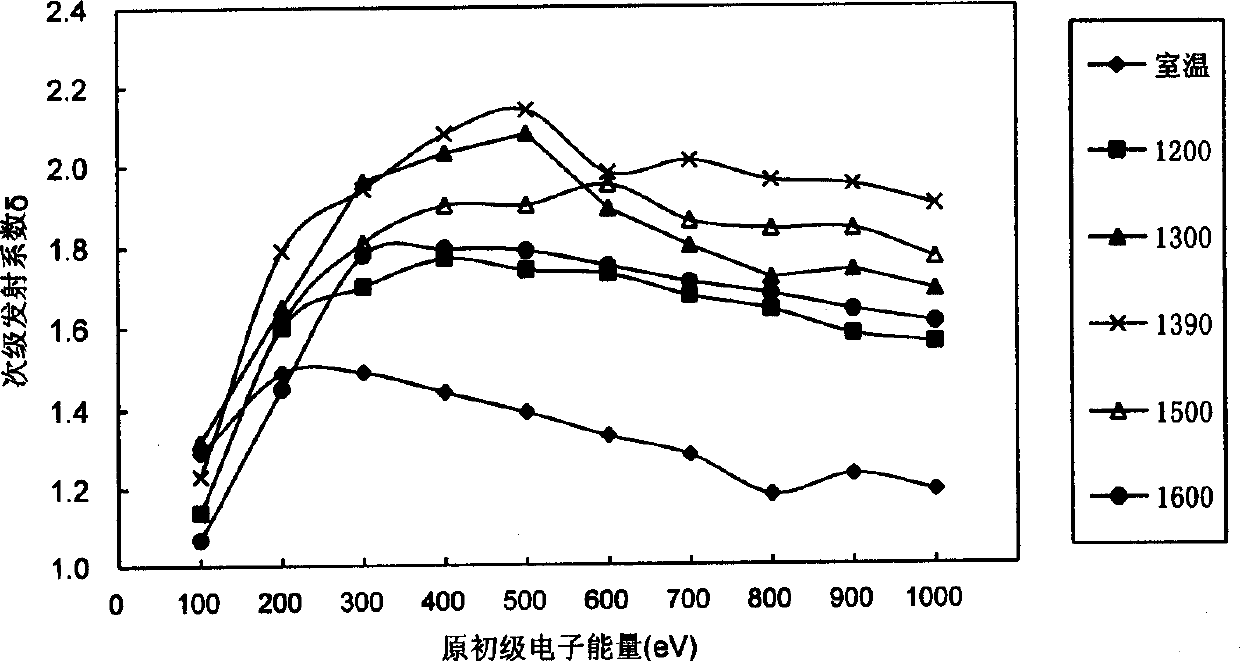
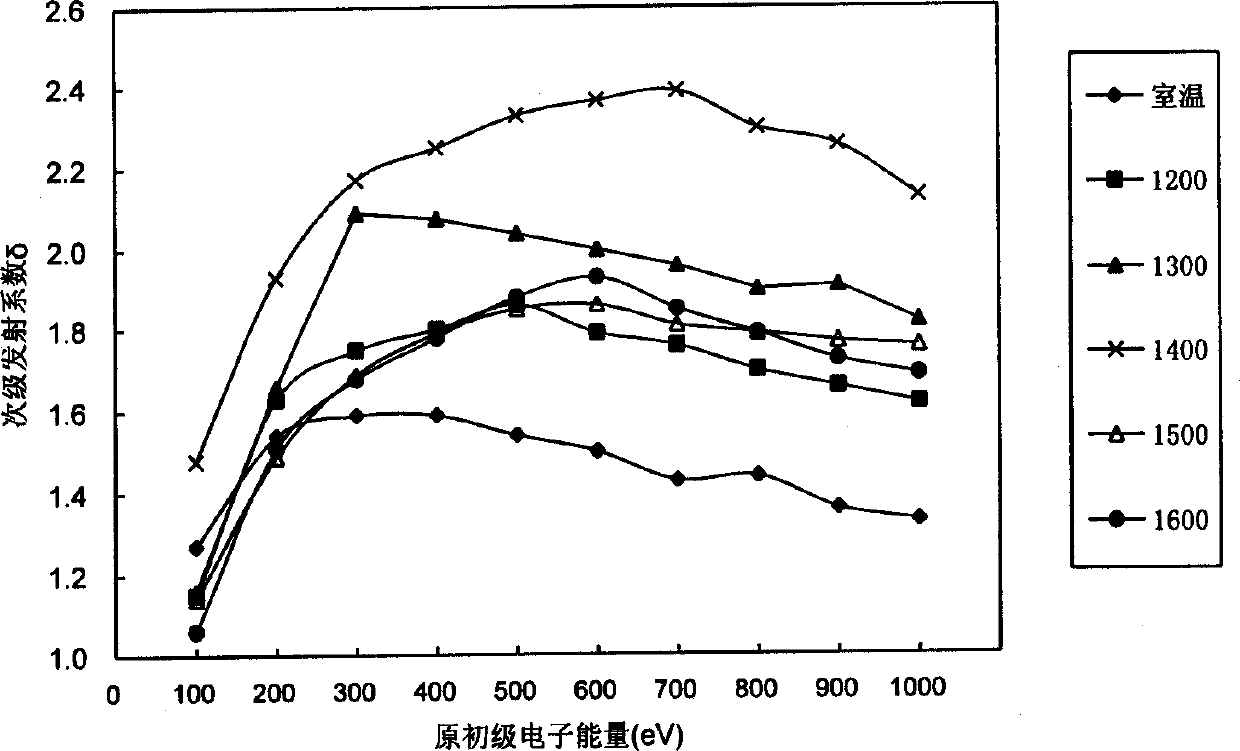
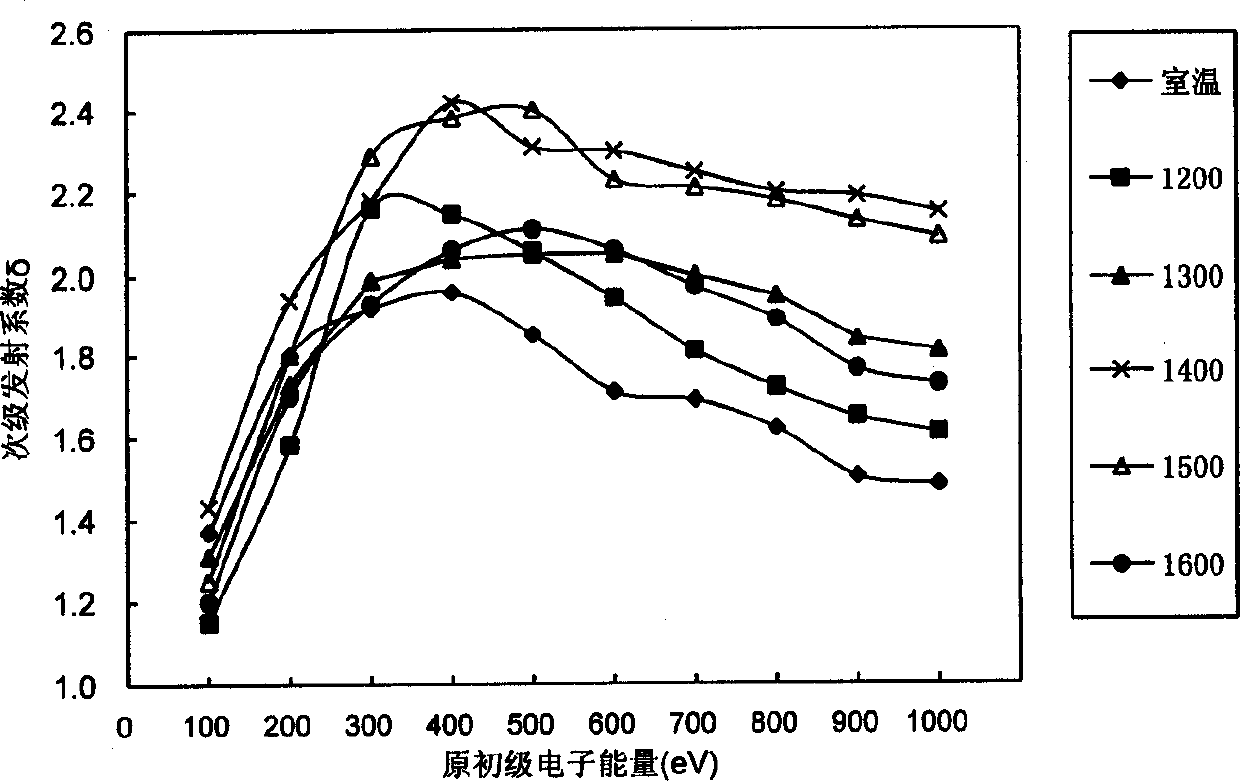
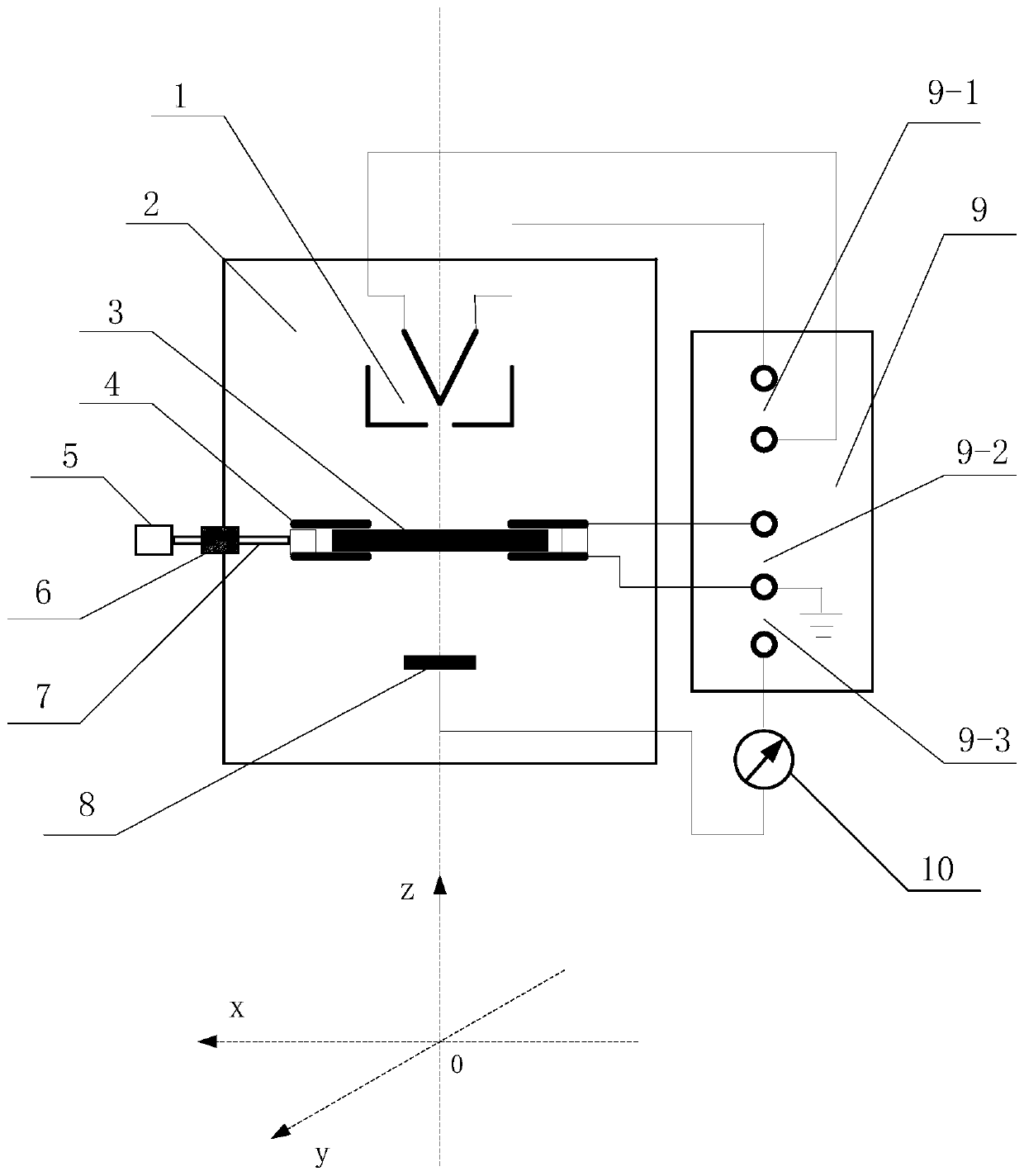
Device and method for measuring secondary electron emission coefficient of material
The invention discloses a device and method for measuring a secondary electron emission coefficient of a material. The device is characterized in that an electronic gun, a test fixture and a collection pole are sequentially and parallelly arranged from top to bottom in a vacuum chamber along the central axis z of the vacuum chamber; a micro-channel plate is mounted on the test fixture and comprises an input end and an output end, and the input end faces the electronic gun; working power supplies are located outside the vacuum chamber and comprise the electronic gun power supply, the micro-channel plate power supply and the collection pole power supply which are sequentially connected with the electronic gun, the micro-channel plate and the collection pole correspondingly; an ampere meter is located outside the vacuum chamber and located between the collection pole power supply and the collection pole; and a manipulator is connected with a moving guiding rod in the vacuum chamber through a corrugated pipe. According to the method, an output current of the micro-channel plate is proportional to the secondary electron emission coefficient of the material on the input end, and meanwhile, the secondary electron emission coefficient of the material is measured by taking the secondary electron emission coefficient of the nickel-chromium electrode material as the reference, wherein theinput end of the micro-channel plate is plated with the nickel-chromium electrode material.
Owner:NORTH NIGHT VISION TECH
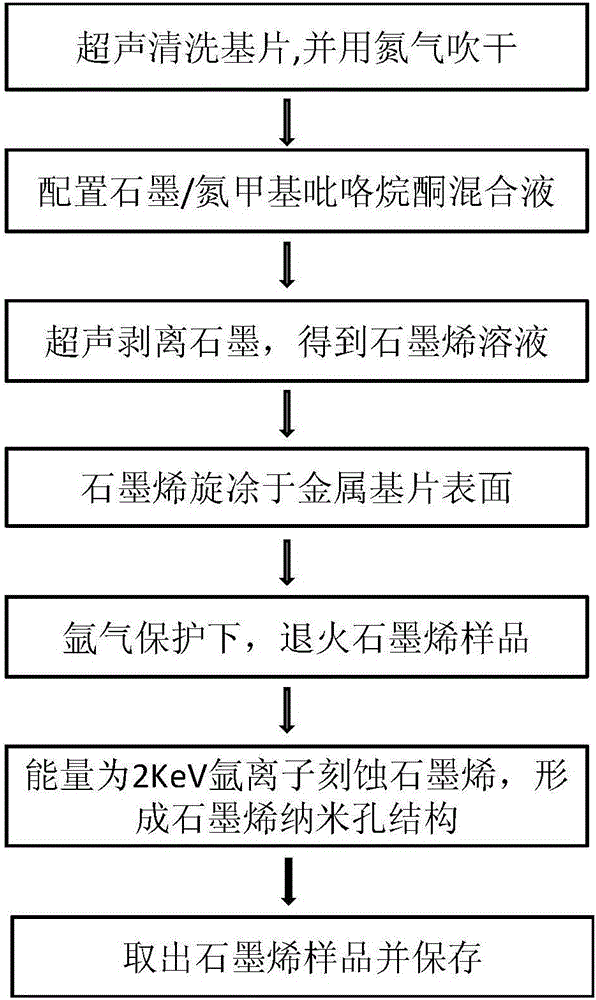
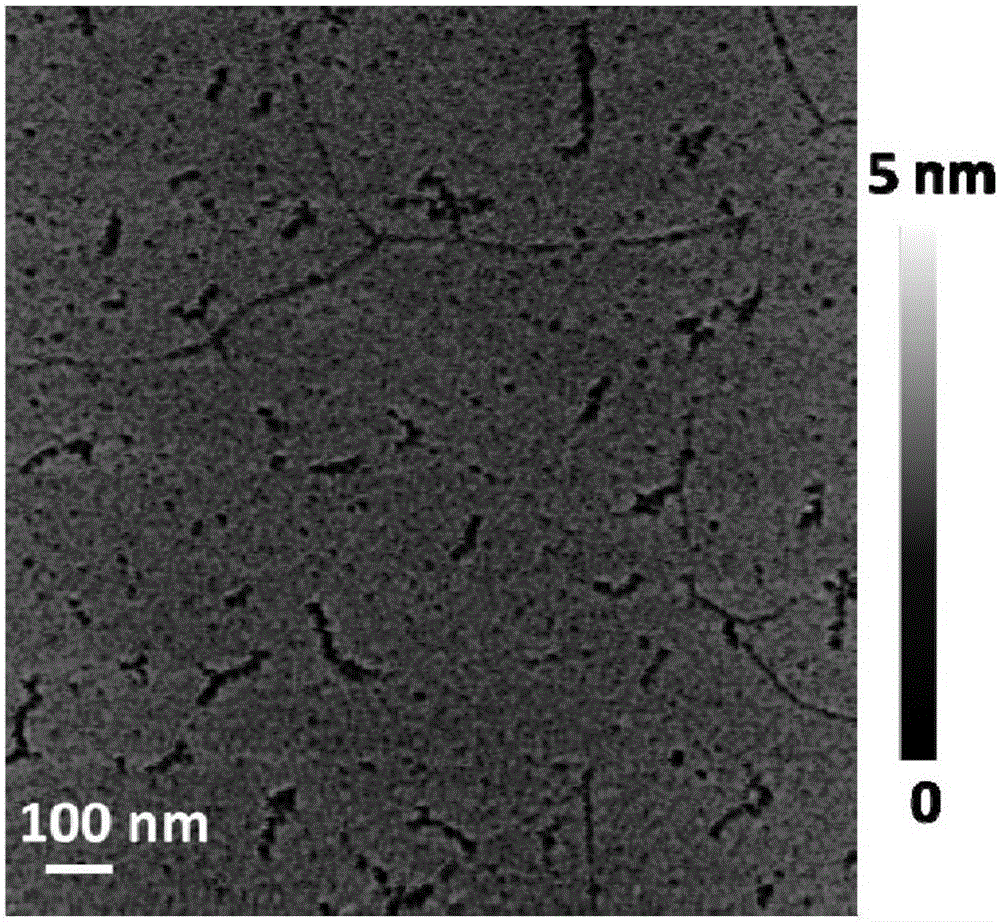
Method for etching graphene nanopores to reduce secondary electron emission coefficient
Provided is a method for etching graphene nanopores to reduce a secondary electron emission coefficient. The method combines with two different methods to coat a material having a low secondary electron emission coefficient and prepare a trap structure on the surface: the surface is coated with graphene having the low secondary electron emission coefficient, and then nanopores are prepared by adopting an argon ion etching technology. Technically, different secondary electron emission inhibiting effects are achieved by controlling the graphene coating thickness on the surface and the porosity and depth-to-width ratio of the nanopores. It is found through an experimental study that graphene with the thickness ranging from several nanometers to more than ten nanometers deposits on a metal substrate, the secondary electron emission coefficient can be reduced from about 2.0 to 1.5-1.1, and after the graphene nanopores are etched by using argon ions, the secondary electron emission coefficient of the surface is reduced to 0.9, and controllable adjustment from 1.5 to 0.9 of the electron emission coefficient is achieved. The method is simple, convenient and high in stability, and the influence on device surface insertion loss of a conducting coating with nanoscale thickness in a surface loss-less state is smaller. By the adoption of the technical scheme, the secondary electron emission coefficient can be effectively reduced, and the method has a wide application prospect in the fields of particle accelerators, vacuum transmission lines and high-power microwave components.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Real-time inversion analysis method of concrete dam block surface heat emission coefficient
ActiveCN110055927AReduce the numberRealize automatic inversionBarrages/weirsHydraulic engineering apparatusTemperature controlFinite element method
The invention provides a real-time inversion analysis method of concrete dam block surface heat emission coefficient. The real-time inversion analysis method monitors climatic conditions around a damblock, dam block surface temperature and a temperature inside the dam block in real time; temperature variation parameters inside the dam body are calculated by a direct solution method, by combiningwith shape parameters and material thermodynamic and mechanical parameters of the dam body, an interpolation and iteration method is used for inversely analyzing and determining the dam block surfaceheat emission coefficient based on a finite element method, temperature control and cracking prevention can be carried out better, and the accuracy and calculation efficiency are higher.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES +1
Internal and external fin tube and fin tube group
InactiveCN1400447ACompact designReasonable structural designStationary tubular conduit assembliesHeat conductingHeat transfer efficiency
The present invention discloses a kind of inner-outer fin tube and fin tube group, and it is formed from inner core, outer tube, fin A and fin B. It is characterized by that it in the interior of outer tube the inner core is set, between inner core and outer tube the fin A is mounted and between outer tube and outer wall the fin B is mounted. Said invented fin tube and fin tube group are equiopedwith high-efficiency compact secondary heat-conducting surface respectively on inner wall and outer wall of heat-exchange tube, and can be used in the heat exchanger in which the heat emission coefficients of its two side heat exchange fluids are smaller and / or approximate. The structure of said heat exchange is more reasonable, compact and high in heat-conductive efficiency, specially it is applicable to gas-gas medium heat exchange.
Owner:吕钢岭
High-tenacity high-strength far infrared ceramic and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103664218AHigh far infrared radiation emissivityHigh hardnessTemperature resistanceFar infrared
The invention relates to a far infrared ceramic material, in particular to a high-tenacity high-strength far infrared ceramic and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises steps as follows: (1), alpha-Al2O3 and nano ZrO2 (2Y) precursors are weighed proportionally, put into an aqueous alkaline solution, stirred and mixed, and a high-dispersion and uniformly mixed two-phase aqueous suspension of alpha-Al2O3 and nano ZrO2 (2Y) is prepared; (2) the two-phase aqueous suspension prepared in the step (1) is calcinated into powder; and (3) toughened SiC crystal whisker, the powder prepared in the step (2) and MgO powder are uniformly and proportionally mixed and subjected to compression molding, high-temperature vacuum sintering and furnace cooling, and a ceramic material is prepared. The high-tenacity high-strength far infrared ceramic material has higher far infrared radiation emissivity, and a test shows that the far infrared emission coefficient of the far infrared ceramic material is larger than 0.8; and the ceramic material has high hardness, high temperature resistance, chemical corrosion resistance and abrasion resistance, the service life of the far infrared ceramic is prolonged, and the far infrared ceramic can be applied in more application fields.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
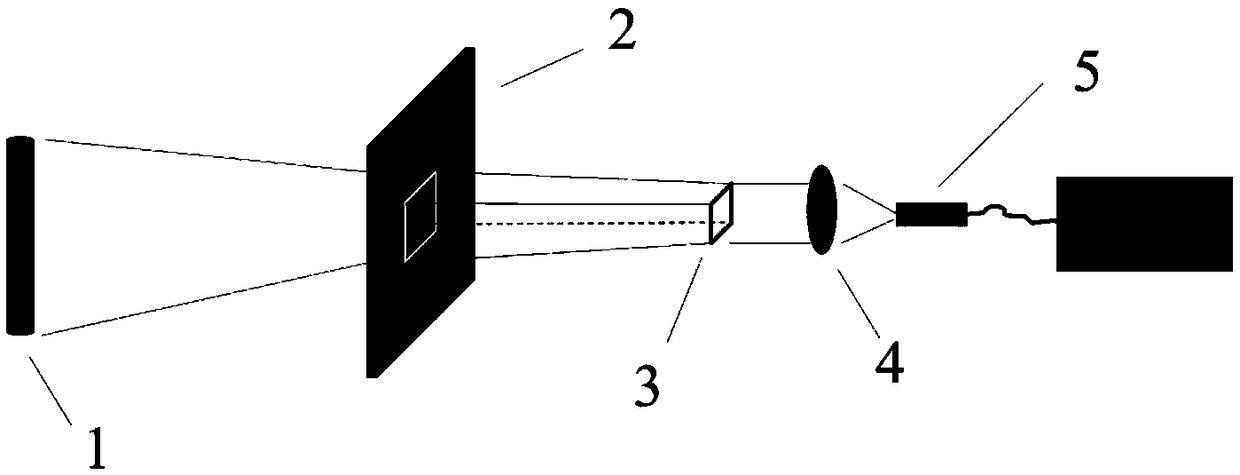
Continuous spectrum absolute intensity diagnosis method for electron density of Ar jet plasmas under different pressures
InactiveCN109302789AReduce light intensity requirementsLow costPlasma techniqueRadianceDiagnosis methods
The invention provides a continuous spectrum absolute intensity diagnosis method for the electron density of Ar jet plasmas under different pressures. The method includes the following steps that: step 1, the intensity change process of a light beam in jet plasmas is described; step 2, absolute radiance is determined; step 3, the expression of the emission coefficient of a continuous spectrum in the plasmas is determined; step 4, the emission coefficient expressions of the recombination process of electrons and ions, the collision effect of the electrons and ions, and the collision effect of the electrons and neutral atoms are defined, wherein the recombination process of the electrons and the ions, the collision effect of the electrons and ions, and the collision effect of the electrons and neutral atoms are respectively represented by three symbols descried in the descriptions of the invention; step 5, an average collision cross section QAr(Te) is fitted; step 6, a total emission coefficient is obtained; step 7, the expression of the total emission coefficient of which the form has been adjusted is obtained; step 8, the equation for the total emission coefficient is solved; and step 9, Taylor expansion is performed on the sign of evolution of a solution, so that the electron density is obtained. The diagnosis method of the invention has the advantages of wide application range and low cost.
Owner:INST OF DEFENSE ENG ACADEMY OF MILITARY SCI PLA CHINA +1
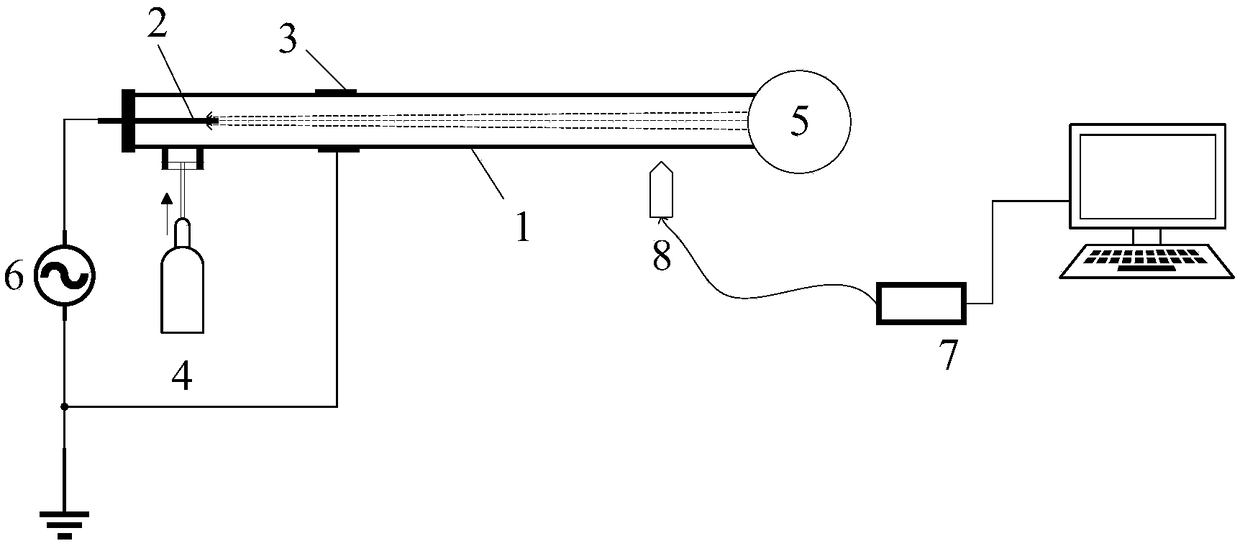
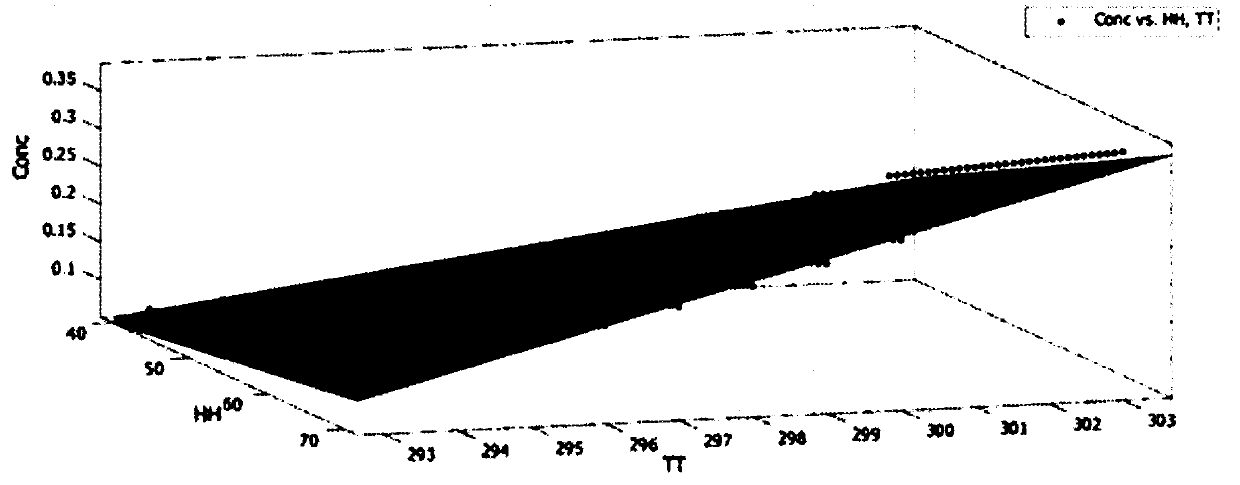
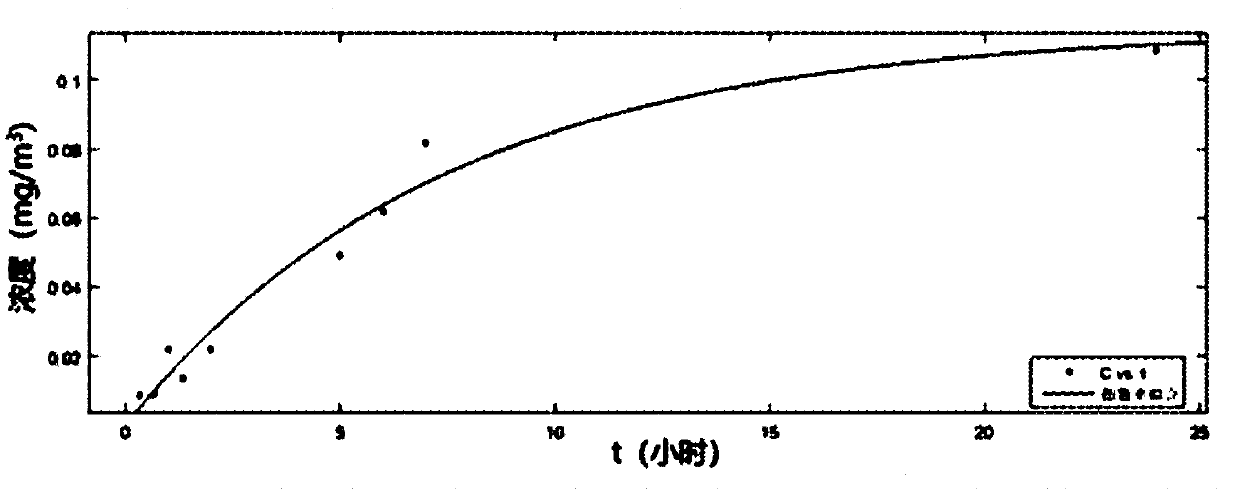
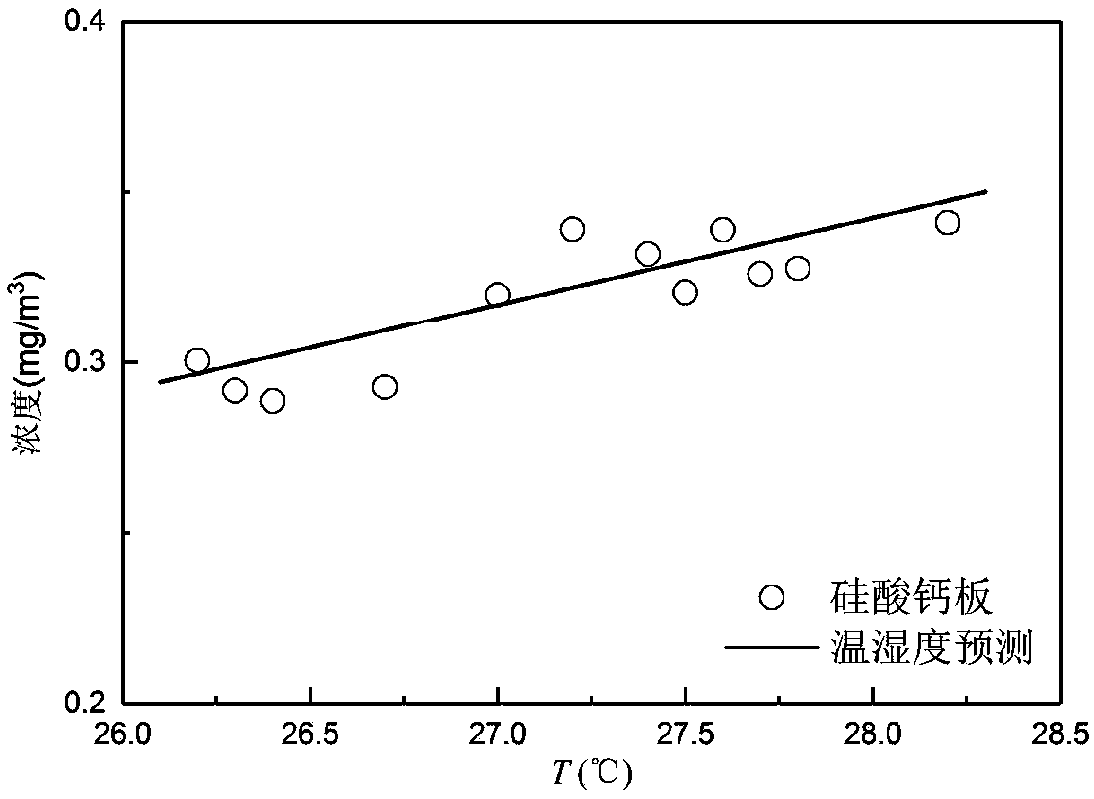
Method for predicting release concentration of formaldehyde in decorative materials under conditions of different temperature and humidity
InactiveCN109540819ARelease concentration changeImprove reliabilityColor/spectral properties measurementsComplex mathematical operationsTemporal changeConcentration curve
The invention relates to the technical field of decorative materials detection, and discloses a method for predicting the release concentration of the formaldehyde in decorative materials under conditions of the different temperature and humidity. The method comprises steps of: performing fitting on the temperature and humidity coefficients, according to the existing formaldehyde concentration data and an equation (7); measuring the formaldehyde release concentration by the spectrophotometry or the like for the materials placed in an environmental chamber, recording data for 24 hours, and recording the temperature and humidity data of the environment chamber in the measurement process at the same time; drawing a measured concentration curve over time, and obtaining an emission coefficientk and a limiting concentration C0 by data fitting, according to the exponential law of the formula (5); and substituting the bearing rate L, the prediction time t, the limiting concentration C0, the emission coefficient k, the predicted temperature T, and the predicted humidity RH into the prediction equation (7), so that the formaldehyde release concentration of the material under the condition of predicting indoor temperature and humidity is calculated, and the prediction is finished. According to the method for predicting the release concentration of the formaldehyde in decorative materialsunder conditions of different temperature and humidity, the method has the advantage of predicting the release concentration of the formaldehyde in the building decorative materials under conditionsof different temperature and humidity.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRANDLAND DECORATION GROUP
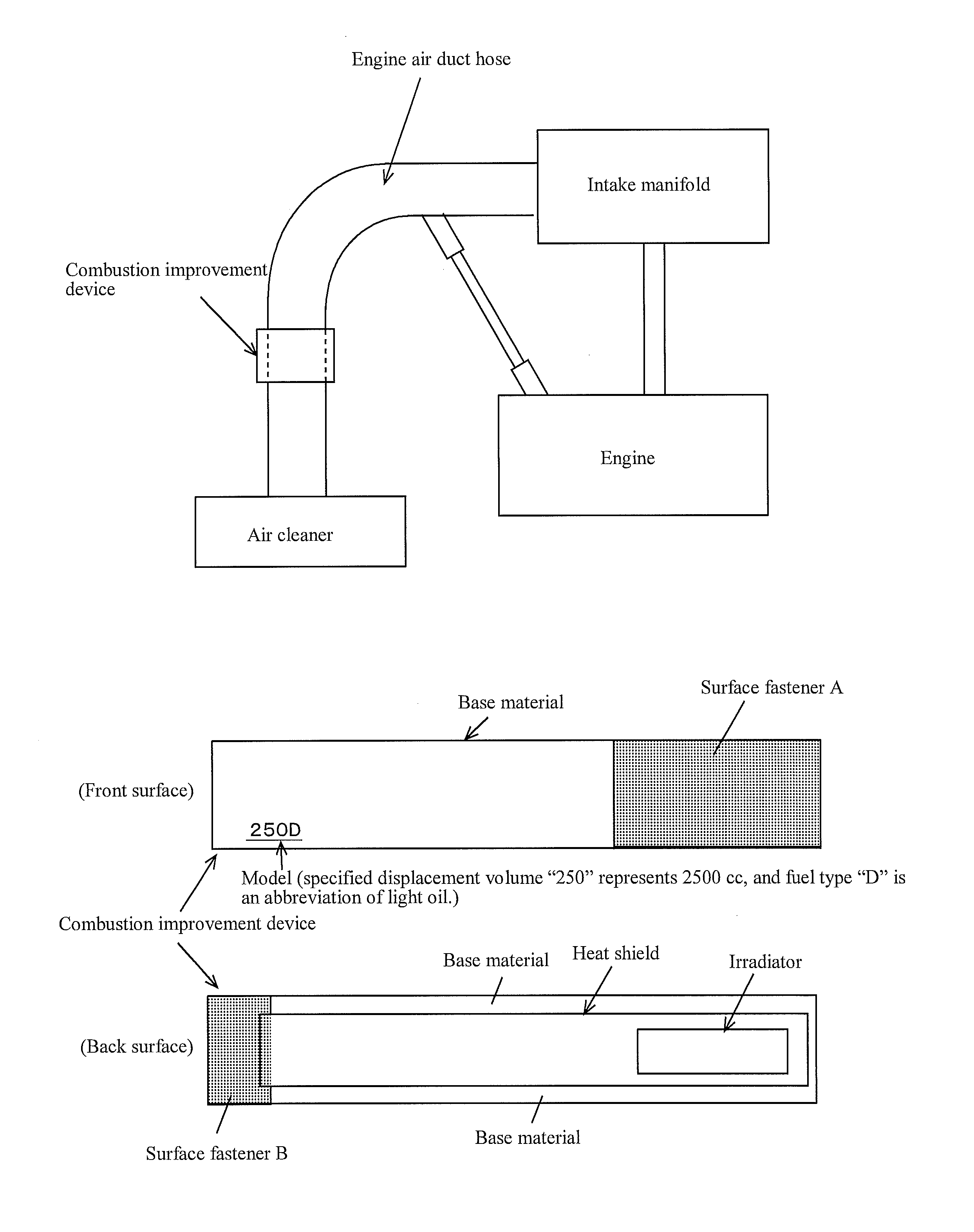
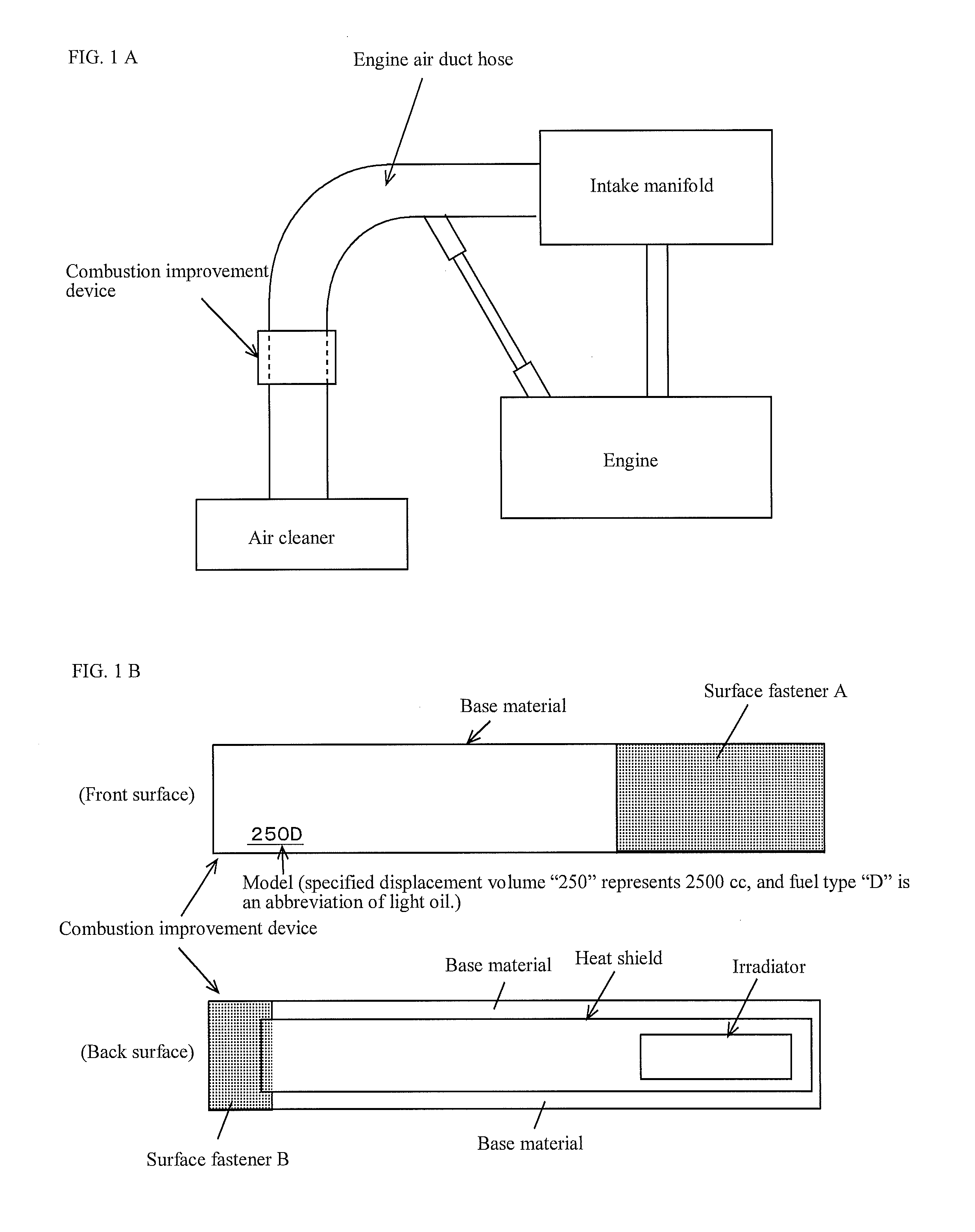
Device for calculating amount of reduced fuel consumption, and program for displaying calculation, as well as device for calculating amount of reduced co2 exhaust, and program for displaying calculation
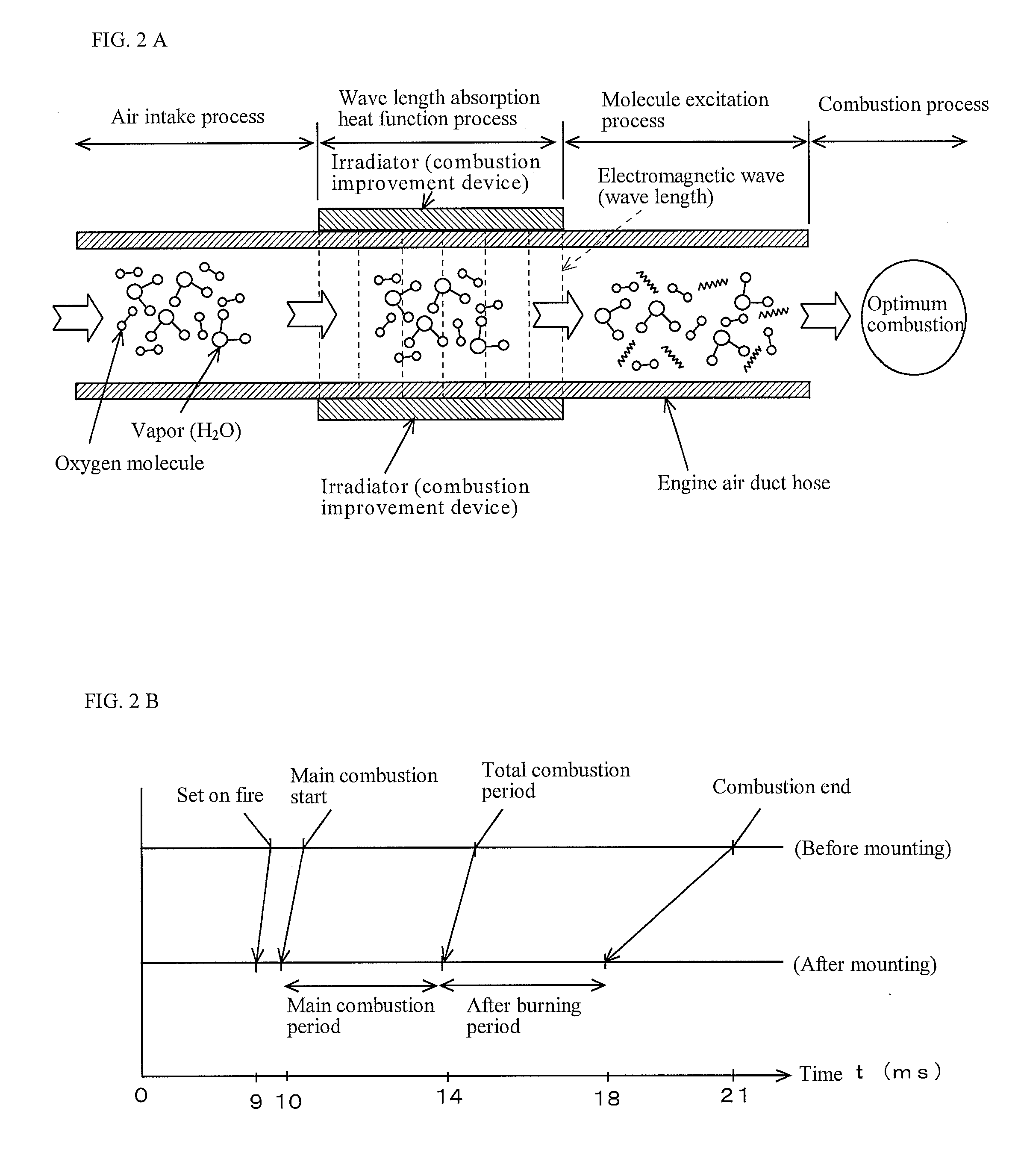
InactiveUS20150122001A1Facilitate fuel combustionEfficient fuel consumptionEngine testingWork measurementCombustionEngineering
PROBLEM TO BE SOLVED: To provide a fuel consumption reduction amount calculation device, a fuel consumption reduction amount calculation and display program, a carbon dioxide emission reduction amount calculation device, and a carbon dioxide emission reduction amount calculation and display program, that digitize the fuel consumption reduction amounts or CO2 emission reduction amounts of a vehicle or a drier or the other heating appliances.SOLUTION: A fuel consumption reduction amount calculation device 10 inputs base line data 14 and 16 of a vehicle before mounting a combustion improvement device and project data 18 and 20 of the vehicle after mounting the combustion improvement device, and displays a value calculated by subtracting annual fuel consumption amount taken from project data from a value calculated by dividing annual travel distance taken from the project data by the fuel consumption rate taken from the base line data. Also, a carbon dioxide emission reduction amount calculation device 34 displays a value calculated by subtracting an emission amount that is calculated by multiplying an emission coefficient by the annual fuel consumption amount taken from project data from the emission amount calculated by multiplying the annual fuel consumption amount taken from the project data by the annual travel distance taken from the project data divided by the fuel consumption rate taken from the base line data.
Owner:JAPAN ECO SUPPORTER +1
Portable reflectometer and method for characterising the mirrors of solar thermal power plants
ActiveCN103097877ARealize measurementWith high toleranceScattering properties measurementsReflective surface testingData acquisitionDiffuse reflection
The invention relates to a portable reflectometer and to a method for characterising the collector mirrors used in solar power plants for the in-field characterisation of reflection coefficients. The equipment includes all of the components required for this measurement, such as a module to measure the reflection coefficient of the mirror, an electronic data acquisition and processing system, a system for processing data and controlling the equipment, a system for storing the data of interest, a user interface system, and a system allowing communication between the aforementioned systems and an outer casing. The equipment can be used to characterise the specular reflection coefficient of flat or curved mirrors of different thicknesses, without requiring adjustments to be made to the equipment, minimising the influence of diffuse reflection on the measurement.
Owner:ABENGOA SOLAR NEW TECH SA
Method and apparatus for determining developer consumption, and image forming apparatus
InactiveUS7973952B2Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsWeight coefficientImage formation
A developer consumption determining method for determining a developer consumption of an image forming apparatus includes the steps of dividing one of writing pixels into a plurality of sub-pixels in a main scanning direction, determining a weighting coefficient for each of surrounding sub-pixels of one of the sub-pixels located within a predetermined distance from the one of the sub-pixels on the basis of positional relationships, determining respective emission coefficients for the surrounding sub-pixels on the basis of one of durations and exposures of the light beams applied to the surrounding sub-pixels, summing products of the weighting coefficients of the surrounding sub-pixels and the respective emission coefficients to obtain total exposure for the one of the sub-pixels, repeating for all of the sub-pixels the steps of determining the weighting coefficient, determining respective emission coefficients, and summing products, and summing the total exposures for all the sub-pixels to determine the developer consumption.
Owner:RICOH KK
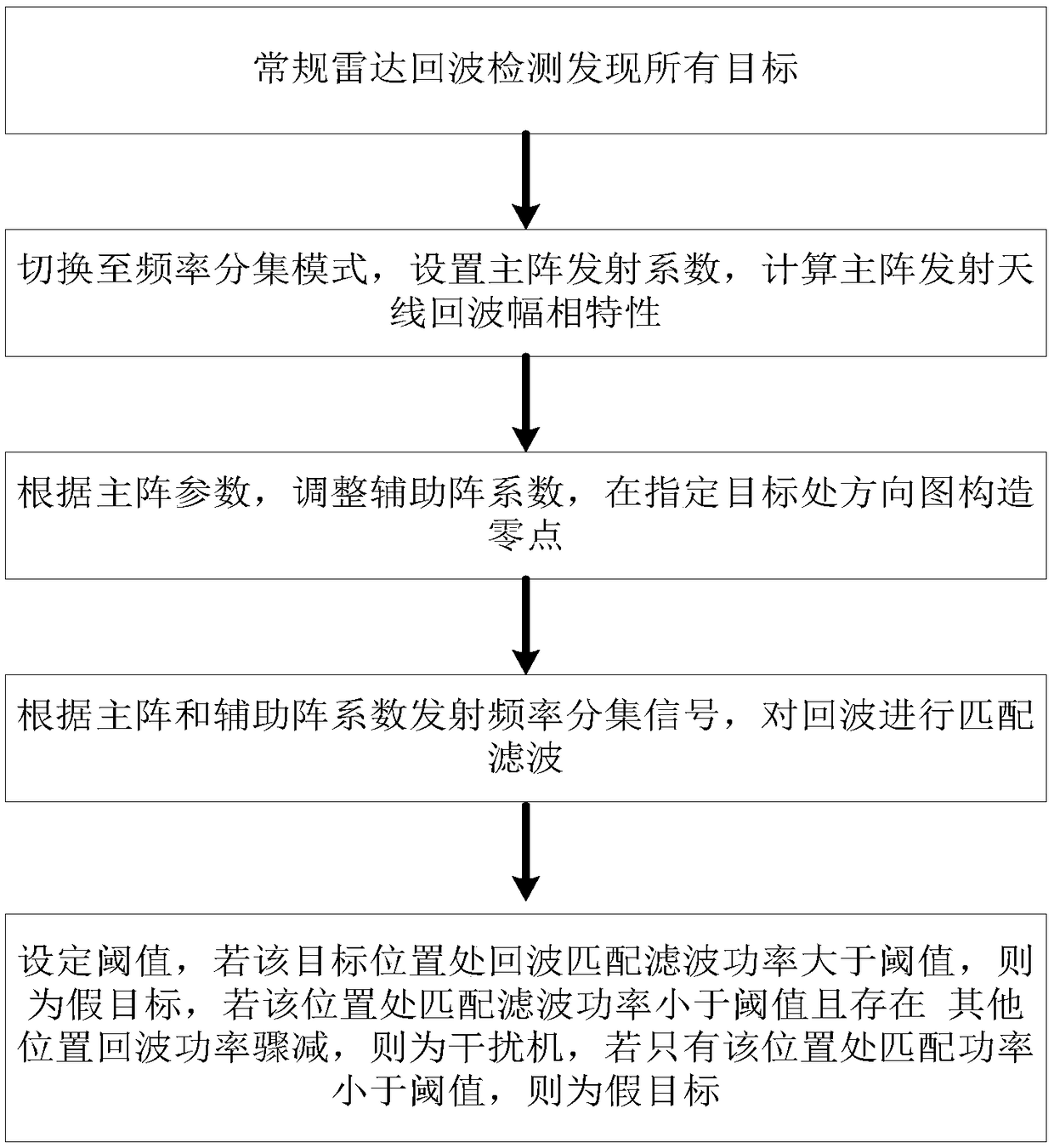
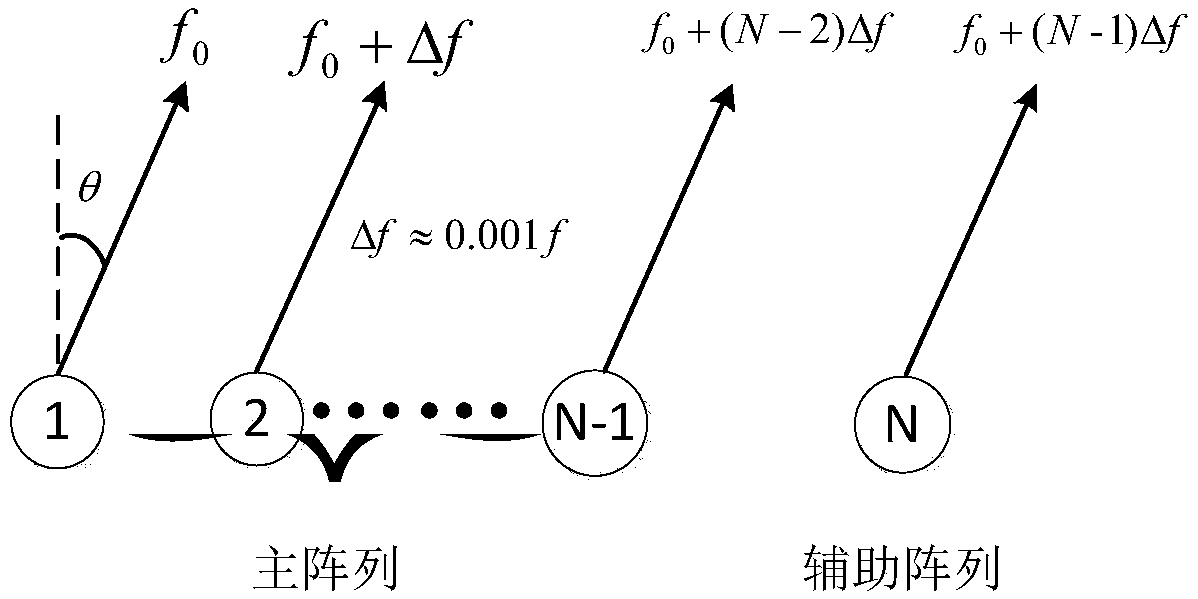
Frequency diversity array deception jamming suppression method based on auxiliary array element
ActiveCN108919205ASuppress interferenceImprove anti-false target abilityWave based measurement systemsICT adaptationRadarEngineering
The invention discloses a frequency diversity array deception jamming suppression method based on an auxiliary array element. Main lobe deception jamming is mainly suppressed. The frequency diversityarray deception jamming suppression method comprises the specific steps that conventional radar emission and receiving systems are adopted, all targets of the airspace at the moment are obtained; switching is conducted into a frequency diversity mode, main array emission coefficients are set, and the echo amplitude phase characteristics of a main array emitting antenna are calculated; according tothe main array emission coefficients, auxiliary array element coefficients are adjusted, and a zero point is constructed in a directional diagram at the specified target; echoes of emission frequencydiversity signals of the main array coefficients and the auxiliary array coefficients are subjected to matching filtering; and a threshold value is set, if the echo matching filter power at the specified target position is larger than the threshold value, it is judged to be a false target, if the echo power at the specified target position is smaller than the threshold value and the echo power atother positions is suddenly decreased, it is judged to be a jammer, and if only the echo matching filter power at the position is smaller than the threshold value, it is judged to be the false target.
Owner:THE 724TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND
Manufacturing method for far-infrared irradiating substrate
InactiveUS20090098307A1Contributes to evaporating efficiencyContributes to the evaporating efficiencyVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingFar infraredMaterials science
A manufacturing method for a far-infrared irradiating substrate is provided. The manufacturing method comprises steps of providing a substrate, providing a far-infrared irradiating material and evaporating the far-infrared irradiating material to form a thin film onto the substrate. The far-infrared irradiating substrate provided by the present invention not only has a high emission coefficient of far-infrared ray, but also do not cause a potential exposure of an ionizing radiation.
Owner:NAT APPLIED RES LAB +1
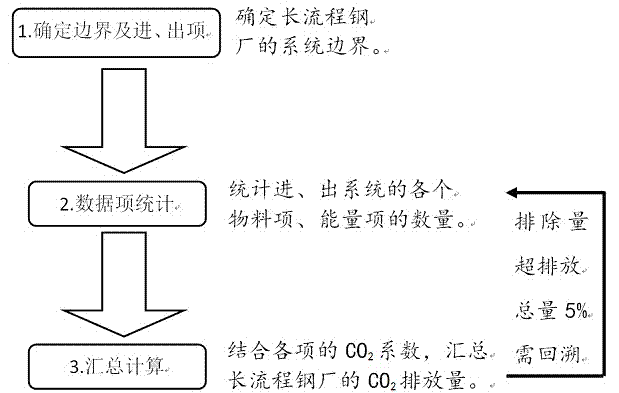
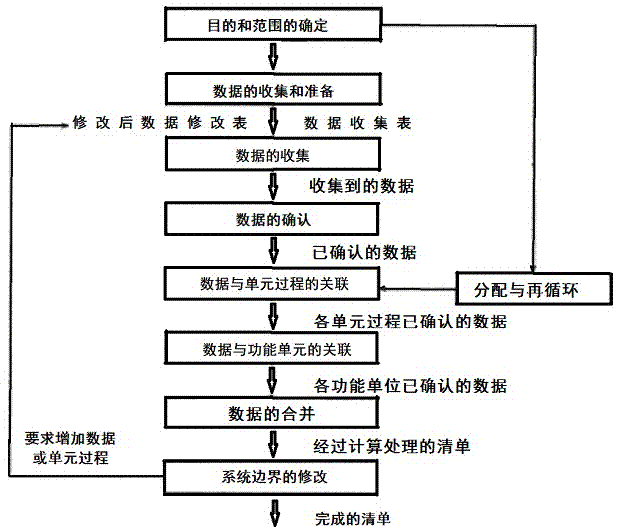
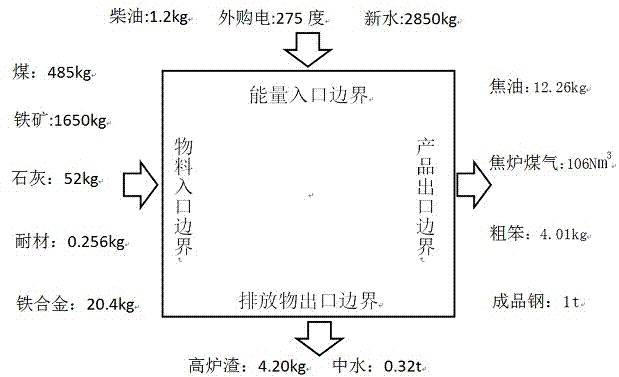
Input-output method-based blast furnace-converter long-process steel production process CO2 emission examining method
InactiveCN103870881ACope wellConducive to coping with the carbon tax system that may be implemented in the futureData processing applicationsTechnology managementEnergy depletionMaterials science
An input-output method-based blast furnace-converter long-process steel production process CO2 emission examining method is used for examining the emission load of CO2 per ton of steel of a long-process steel plant on the basis of consumption data of raw materials going in and out of the steel plant and energy. The examining method comprises the steps that firstly a material inlet, an energy source inlet, a product outlet and an emission outlet of a production system of the steel plant are determined and form the system boundary of the steel plant; the consumption of the raw materials going in and out of the system boundary and that of energy items are counted, and the CO2 emission of each raw material or that of each energy item is obtained by multiplying the consumption of the raw material or that of the energy item by a CO2 emission coefficient; the CO2 emission of all material items entering the system and that of the energy items are summed, and the summed result is subtracted by deduction carbon equivalent values of byproducts and emissions to obtain the total CO2 emission of the plant; the total CO2 emission is divided by total steel output to obtain the CO2 emission value per ton of steel of the steel plant. Although the precision is not high, the examining time and manpower demands can be remarkably reduced by using secondary data of the steel plant.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Charging-free electron beam cure of dielectric material
InactiveUS20090181534A1Alleviates undesirable charging effectHigh hardnessLiquid surface applicatorsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectricitySemiconductor
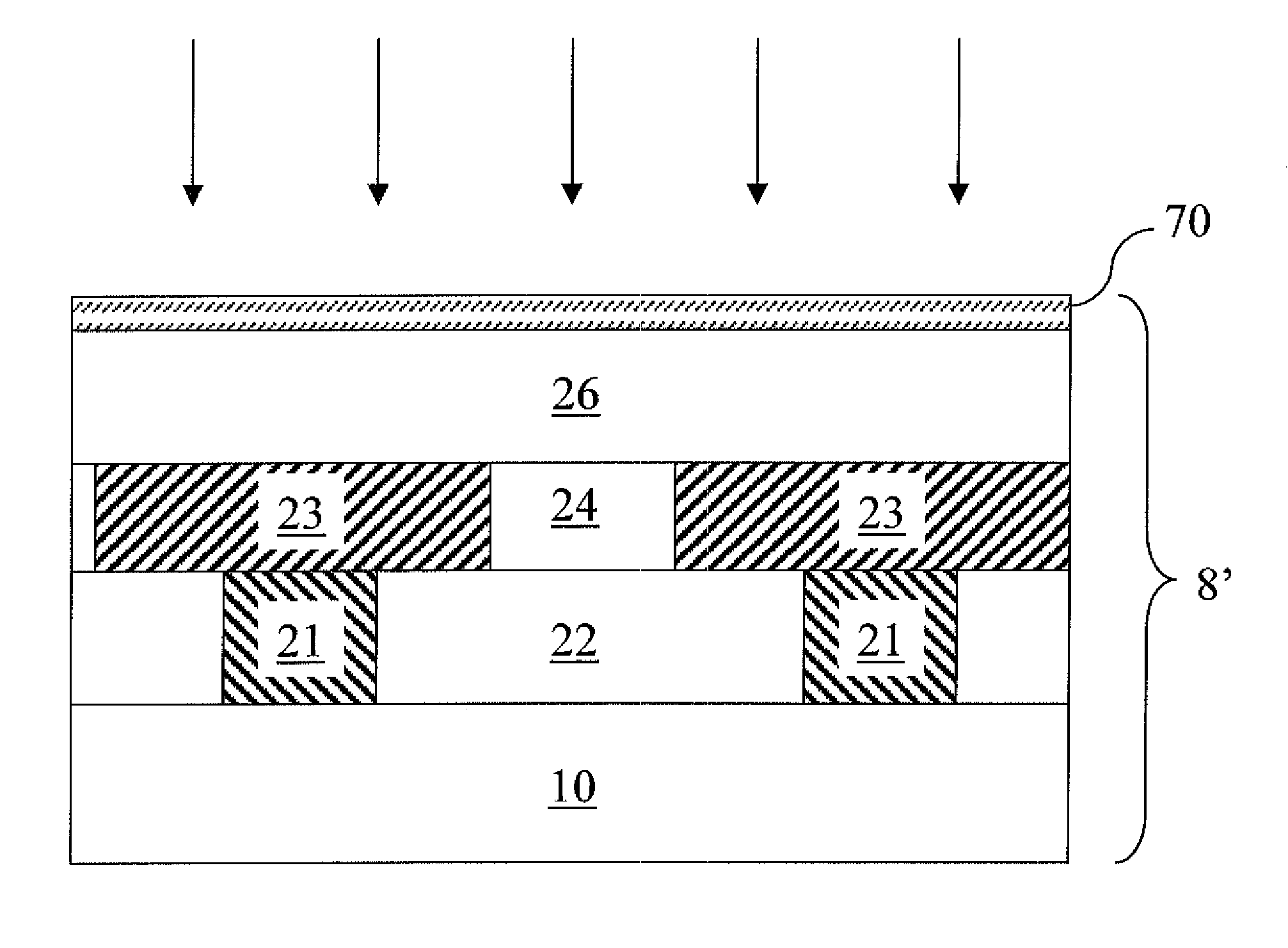
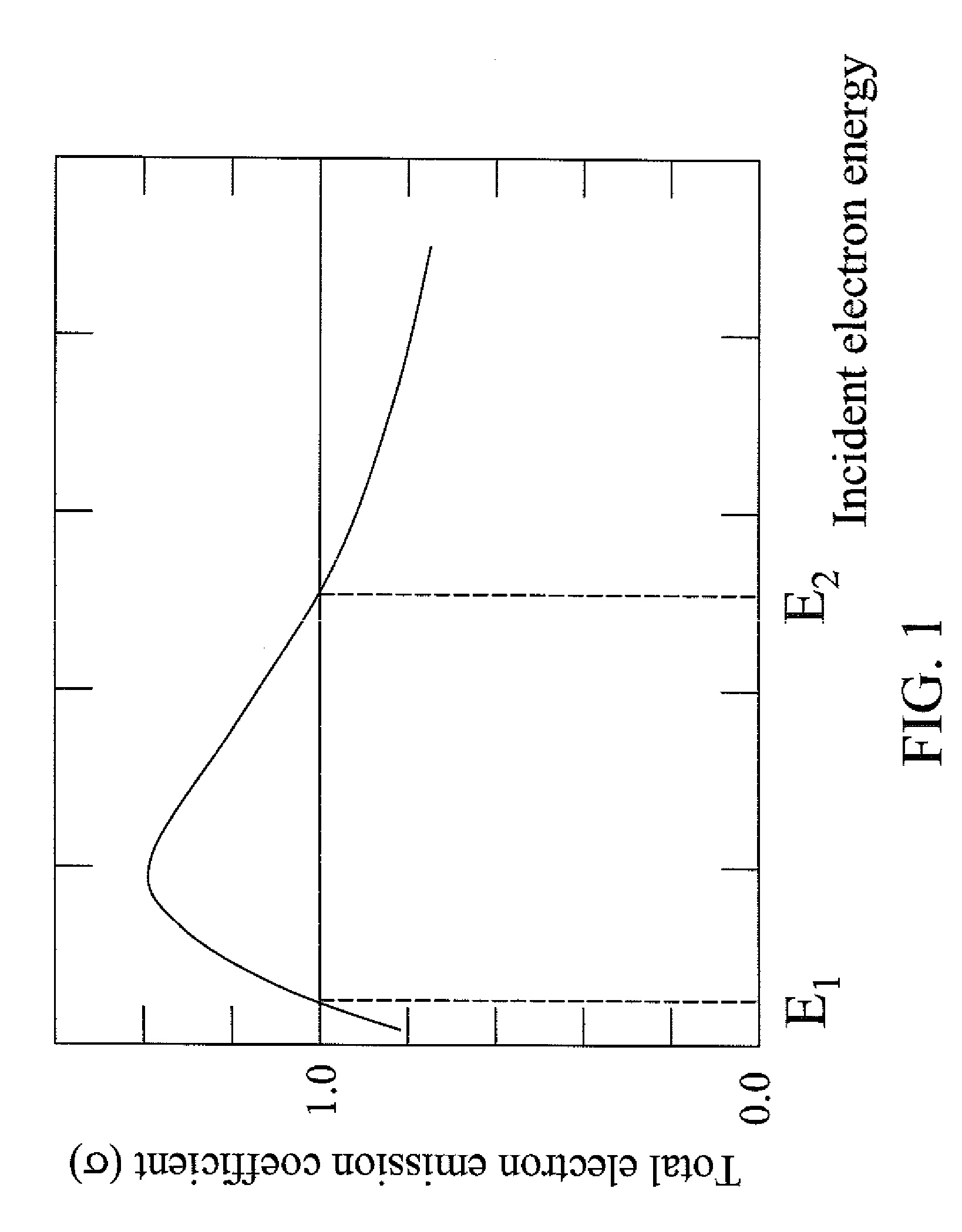
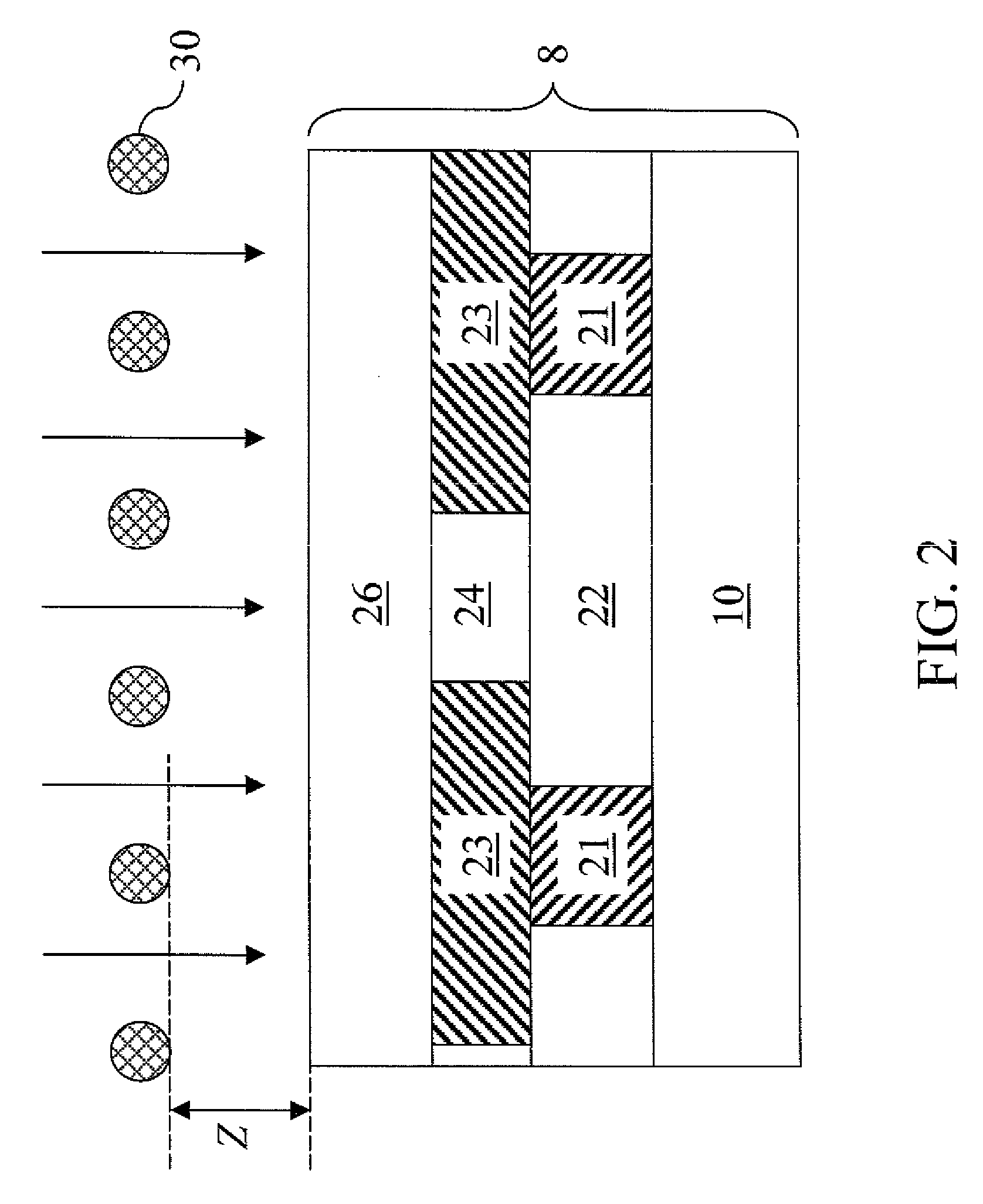
An ultra low-k dielectric material layer is formed on a semiconductor substrate. In one embodiment, a grid of wires is placed at a distance above a top surface of the ultra low-k dielectric material layer and is electrically biased such that the total electron emission coefficient becomes 1.0 at the energy of electrons employed in electron beam curing of the ultra low-k dielectric material layer. In another embodiment, a polymeric conductive layer is formed directly on the ultra low-k dielectric material layer and is electrically biased so that the total electron emission coefficient becomes 1.0 at the energy of electrons employed in electron beam curing of the ultra low-k dielectric material layer. By maintaining the total electron emission coefficient at 1.0, charging of the substrate is avoided, thus protecting any device on the substrate from any adverse changes in electrical characteristics.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com