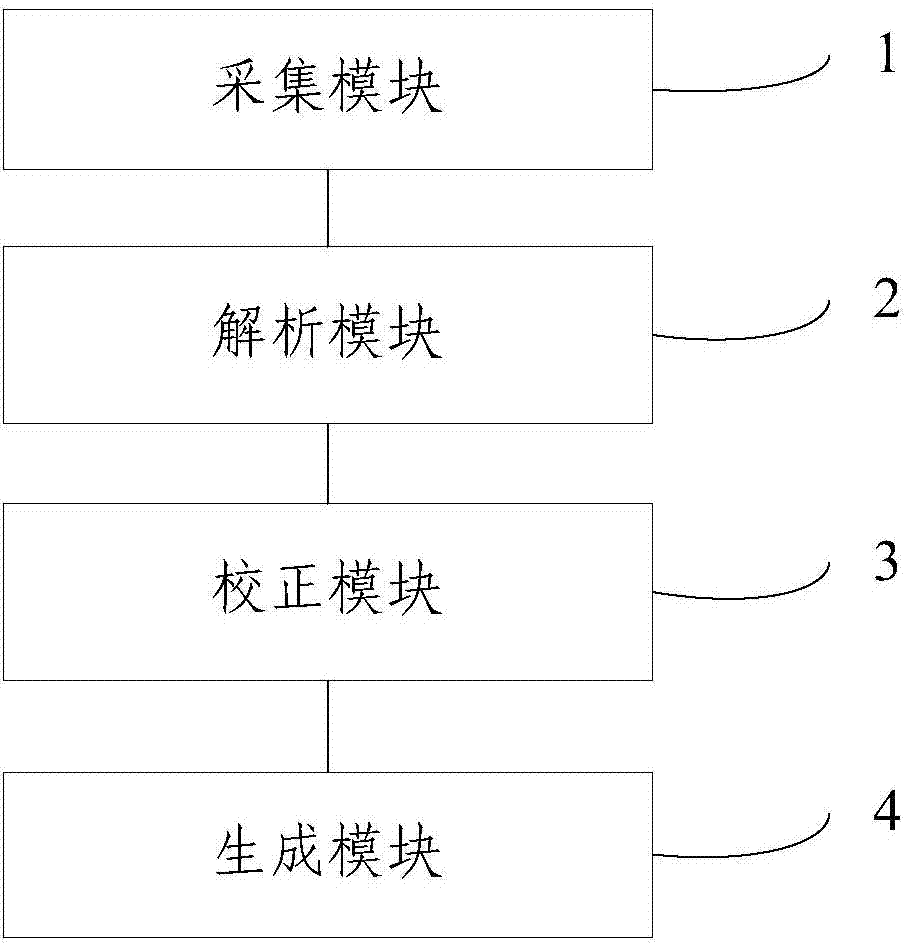
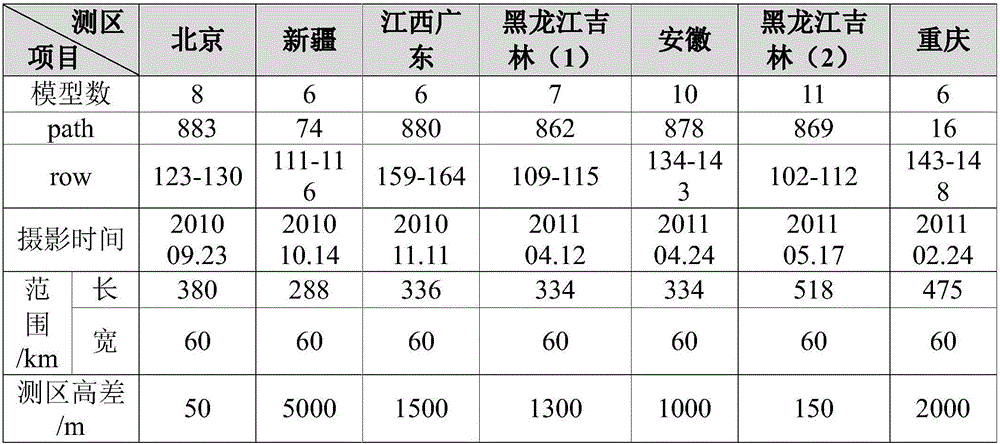
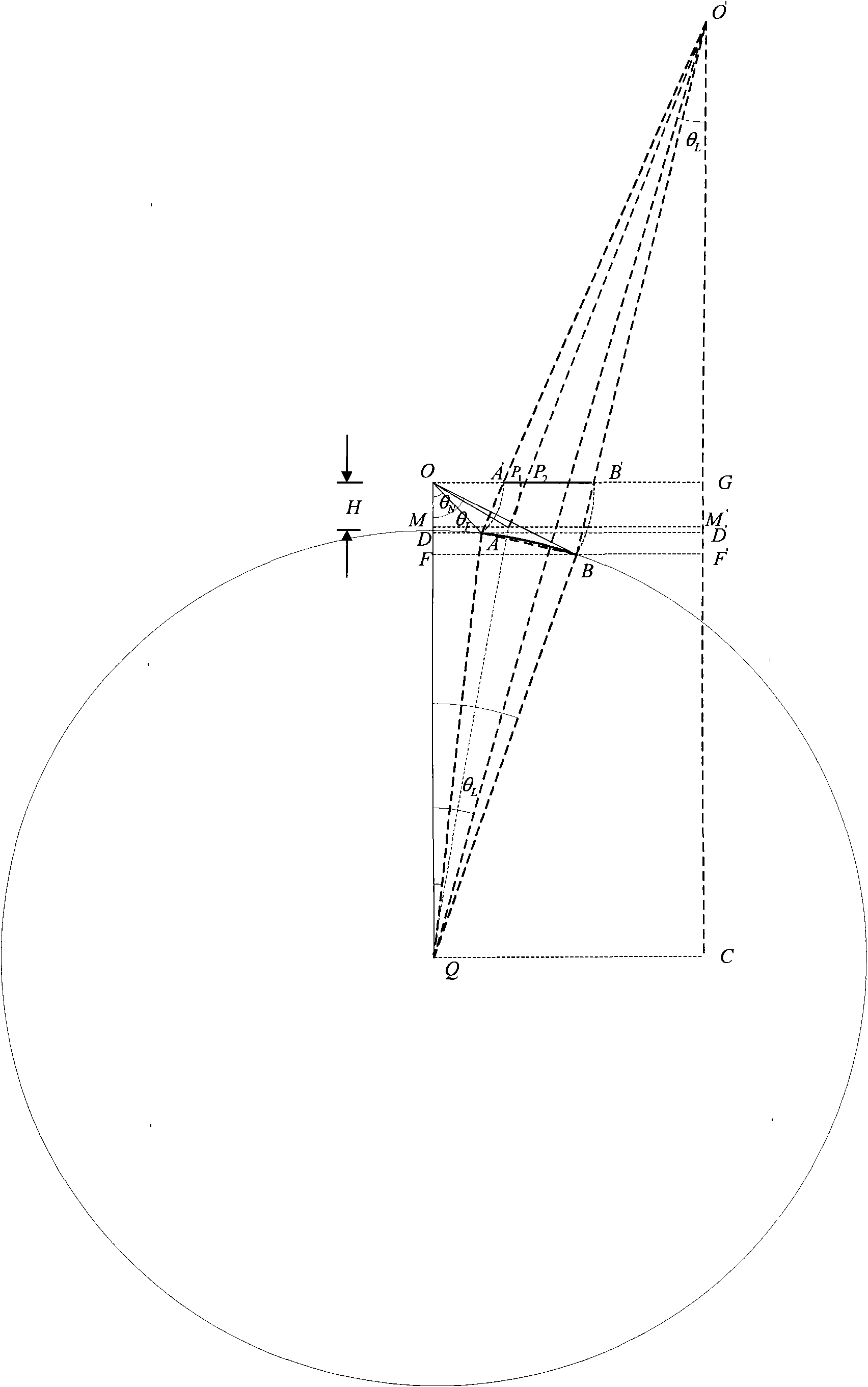
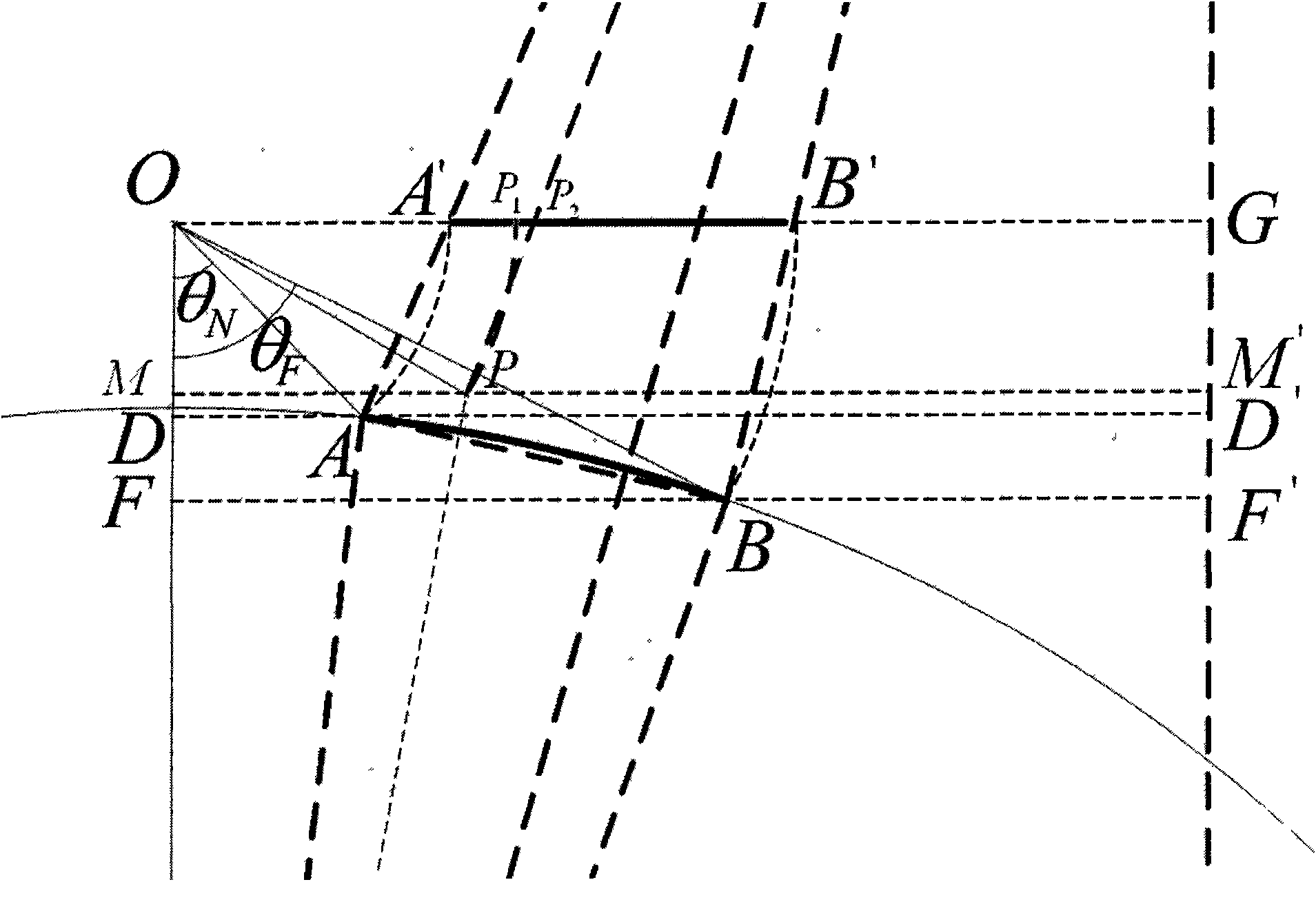
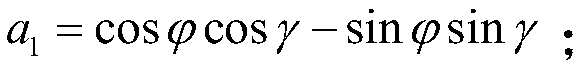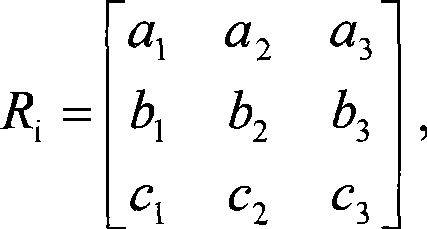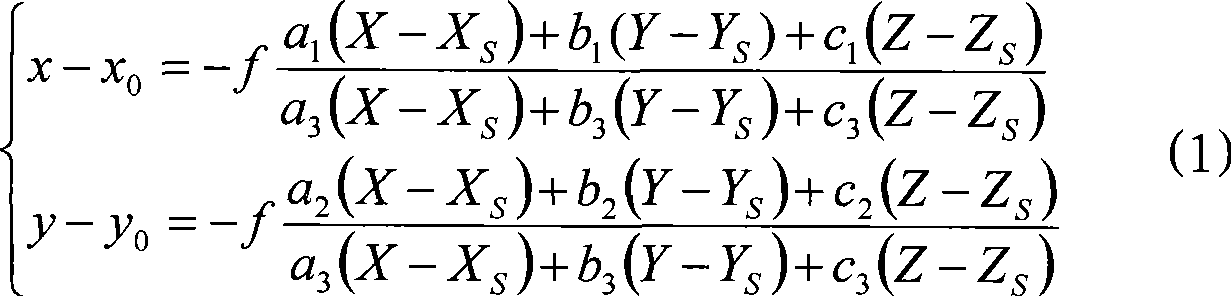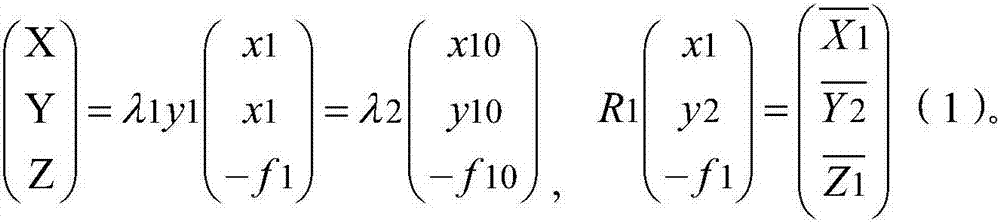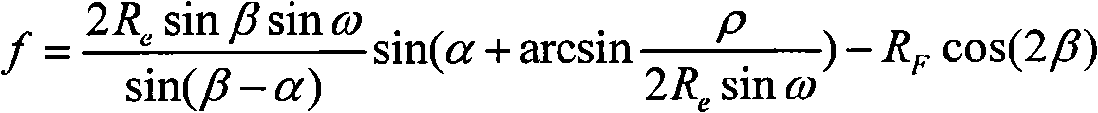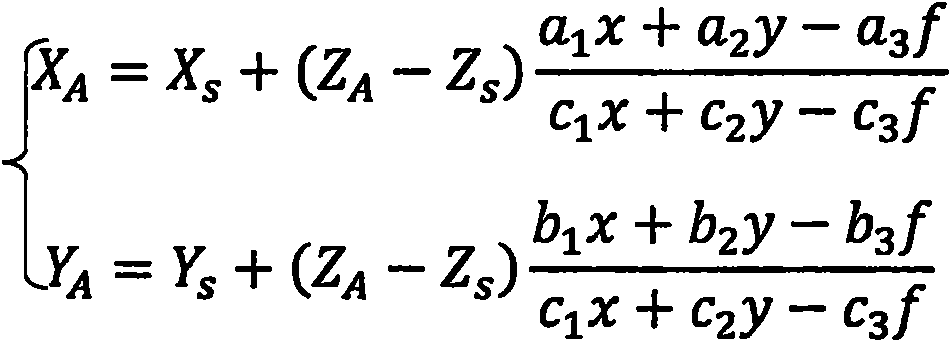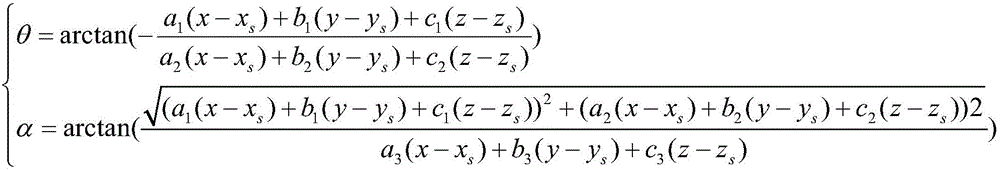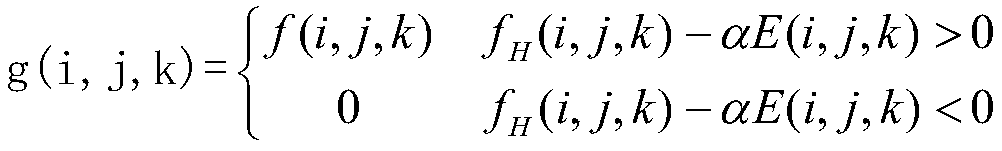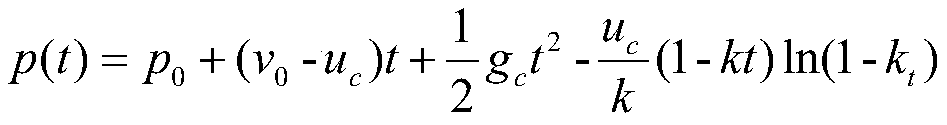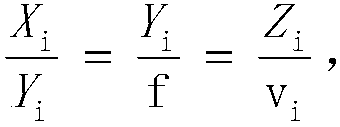Patents
Literature
100 results about "Collinearity equation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
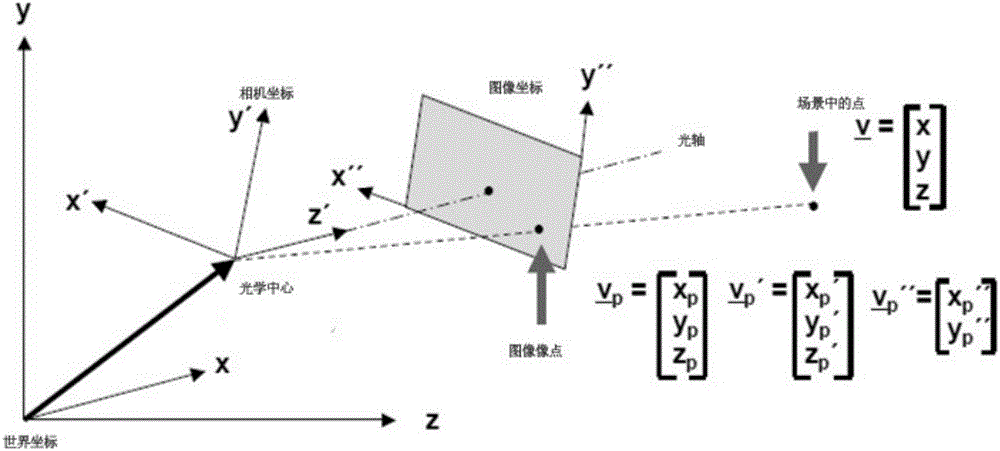
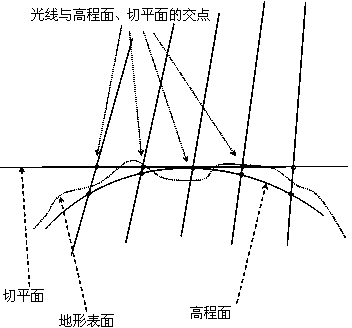
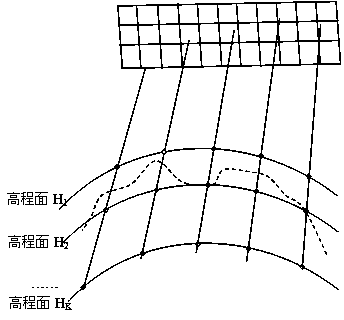
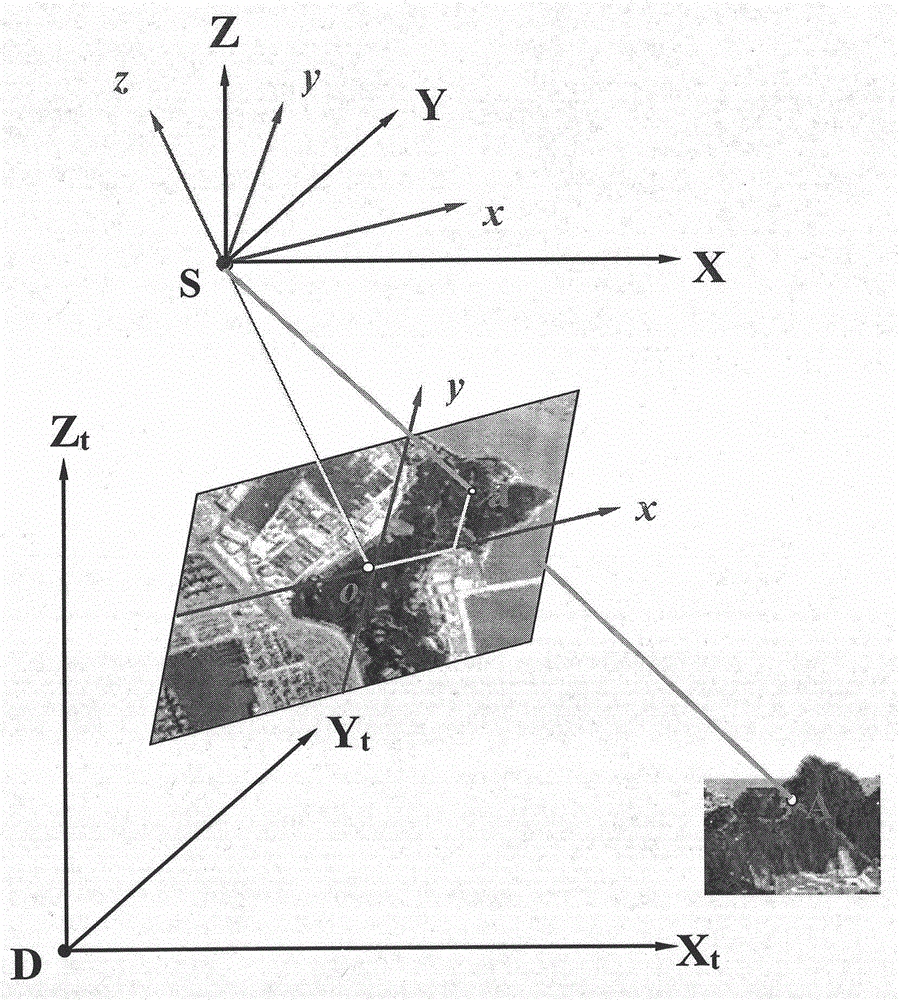
The collinearity equations are a set of two equations, used in photogrammetry and remote sensing to relate coordinates in a sensor plane (in two dimensions) to object coordinates (in three dimensions). The equations originate from the central projection of a point of the object through the optical centre of the camera to the image on the sensor plane.
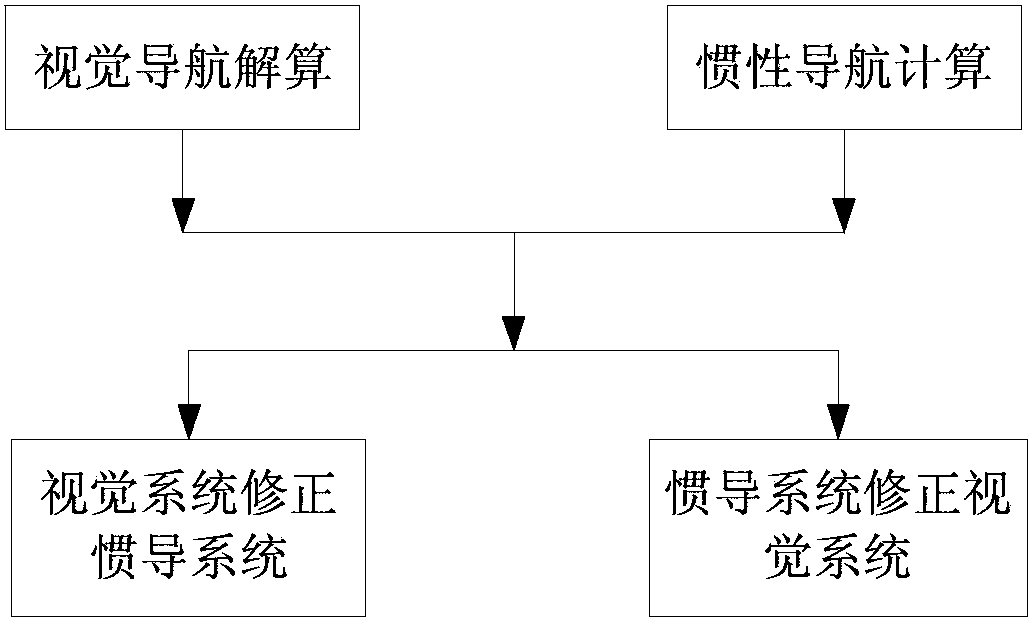
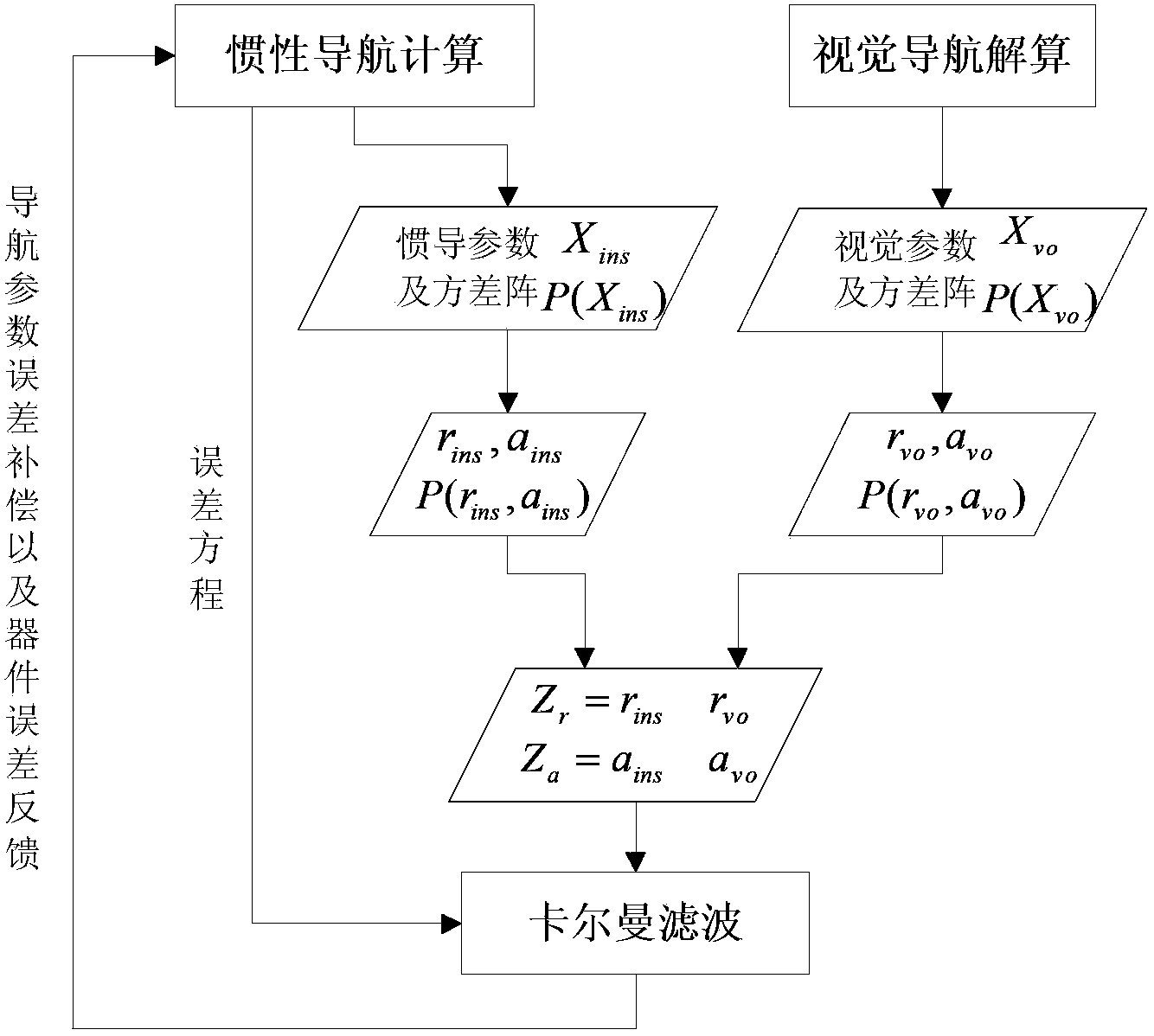
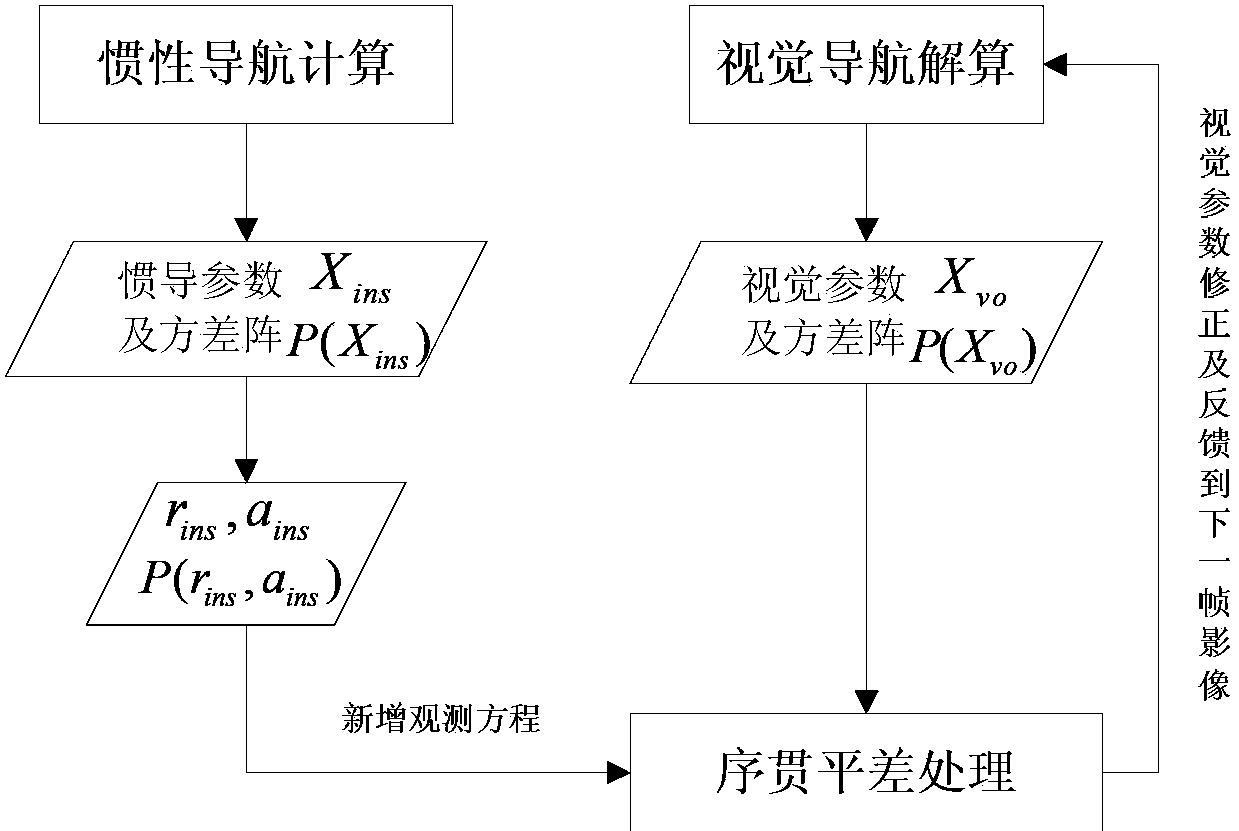
Visual navigation/inertial navigation full combination method
InactiveCN103424114AHigh precisionReduce precisionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsComputer visionLeast squares
The invention relates to a visual navigation / inertial navigation full combination method. The method comprises the following steps: first, calculation of visual navigation: observation equations are listed based on collinearity equations, carrier positions and attitude parameters are obtained through the least square principle and adjustment,, and variance-covariance arrays among the parameters are calculated; second, calculation of inertial navigation: navigation calculation is carried out in the local horizontal coordinates, carrier positions, speeds and attitude parameters of each moment are obtained, variance-covariance arrays among the parameters are calculated; third, correction of the inertial navigation system through the visual system: by means of the Kalman filtering, navigation parameter errors and device errors of the inertial navigation system are estimated, and subjected to compensation and feedback correction, and therefore the optimal estimated values of all the parameters of the inertial navigation system are obtained; fourth, correction of the visual system through the inertial navigation system: all the parameters of the visual system are corrected through the sequential adjustment treatment. Compared to the prior art, the method has advantages of rigorous theories, stable performances, high efficiency and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
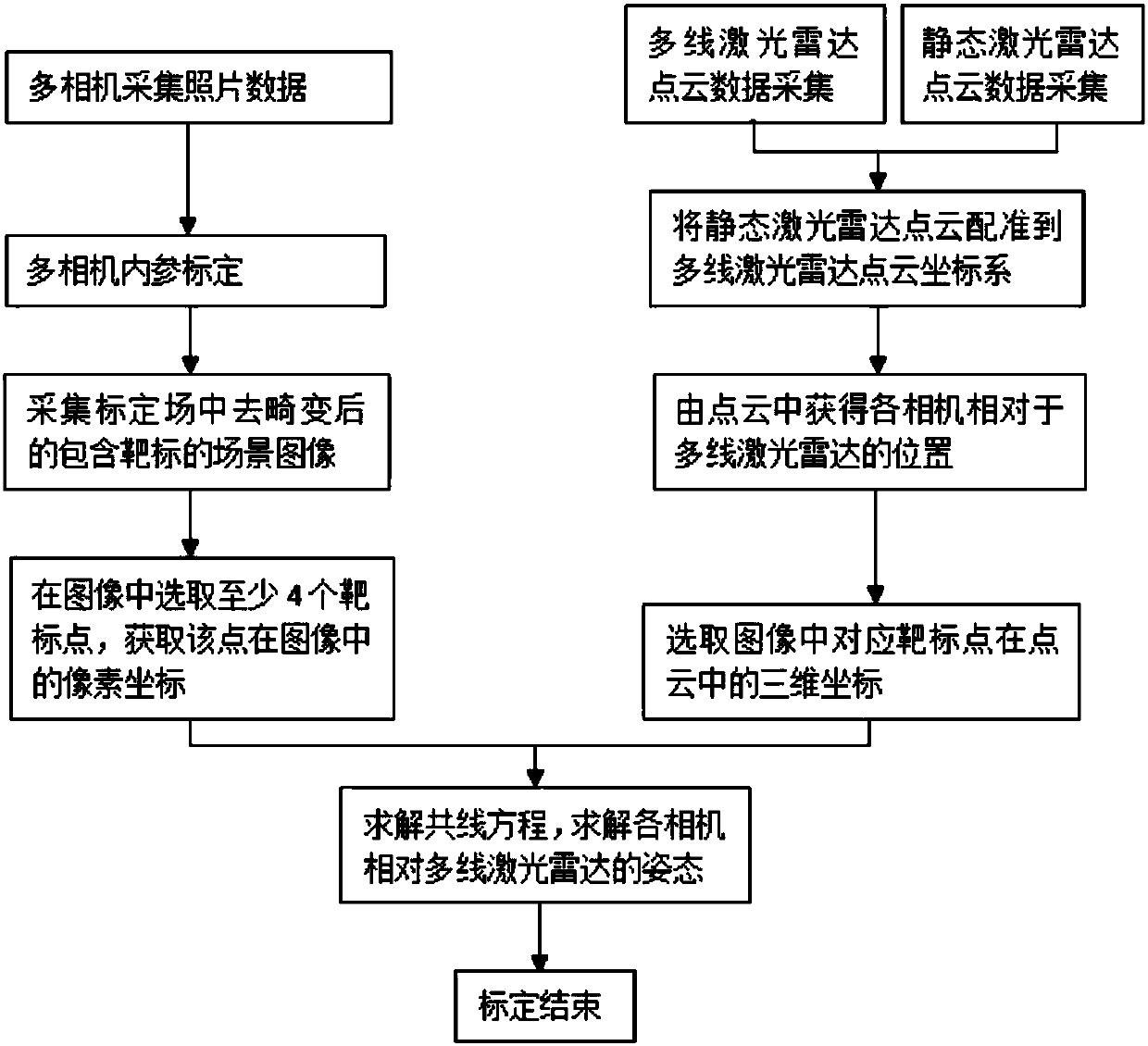
Multi-line laser radar and multi-path camera mixed calibration method
ActiveCN108020826AEasy to implementLow costTelevision system detailsImage enhancementReference modelPoint cloud
The invention discloses a multi-line laser radar and multi-path camera mixed calibration method. The method comprises the following steps of S1, collecting the original image data of a multi-path camera, the point cloud data of a multi-line laser radar and the point cloud data of a static laser radar; S2, solving an internal reference model of each camera; S3, subjecting images acquired by each camera to de-distortion treatment and obtaining corrected images; S4, registering the point cloud data of the static laser radar into the point cloud coordinate system of the multi-line laser radar; S5, acquiring the position (Xs,Ys,Zs) of each camera in the point cloud coordinate system of the multi-line laser radar in the point cloud data which are well registered in the step S4; S6, selecting the pixel coordinates (u,v) of at least four target objects in the corrected images of each camera and the corresponding three-dimensional coordinates (Xp,Yp,Zp) of the target objects in the point cloud with the multi-line laser radar as an coordinate origin; S7, according to the internal reference model of each camera, the position (Xs,Ys,Zs) of each camera, the pixel coordinates (u,v) of target objects corresponding to the camera, and the corresponding three-dimensional coordinates (Xp,Yp,Zp), establishing a collinear equation. In this way, the attitude angle elements of each camera and the cosines of the camera in nine directions can be figured out. Therefore, the calibration is completed.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
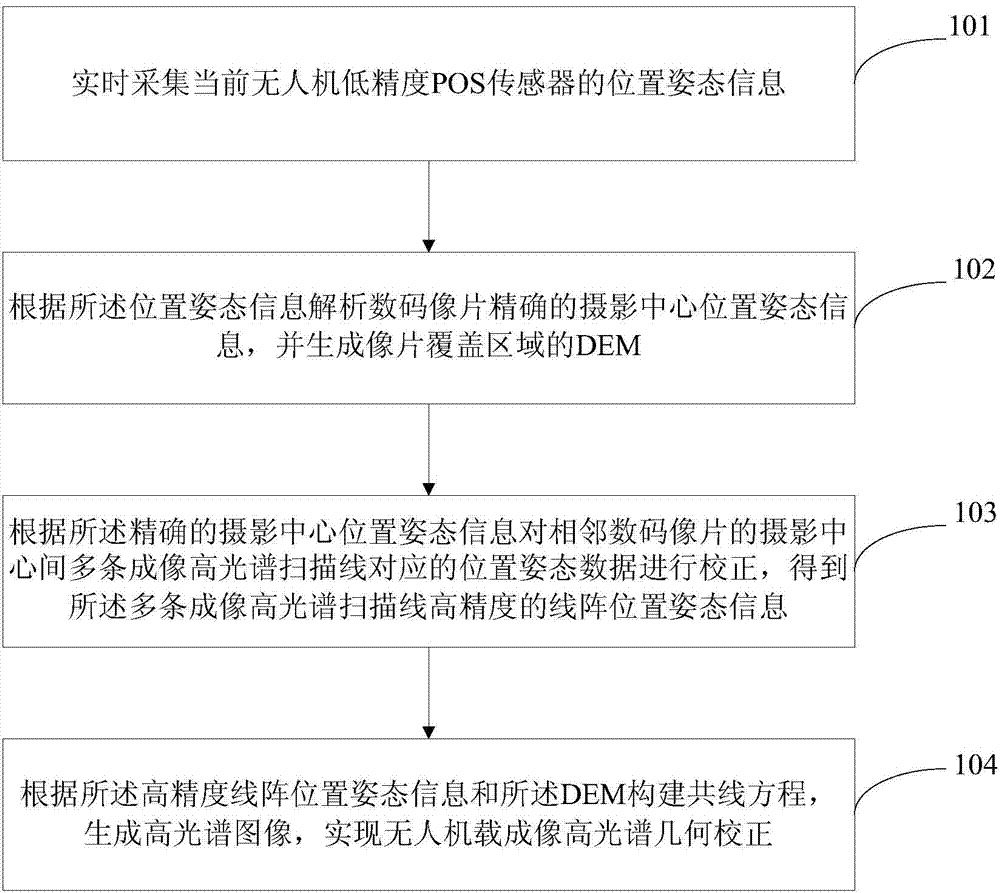
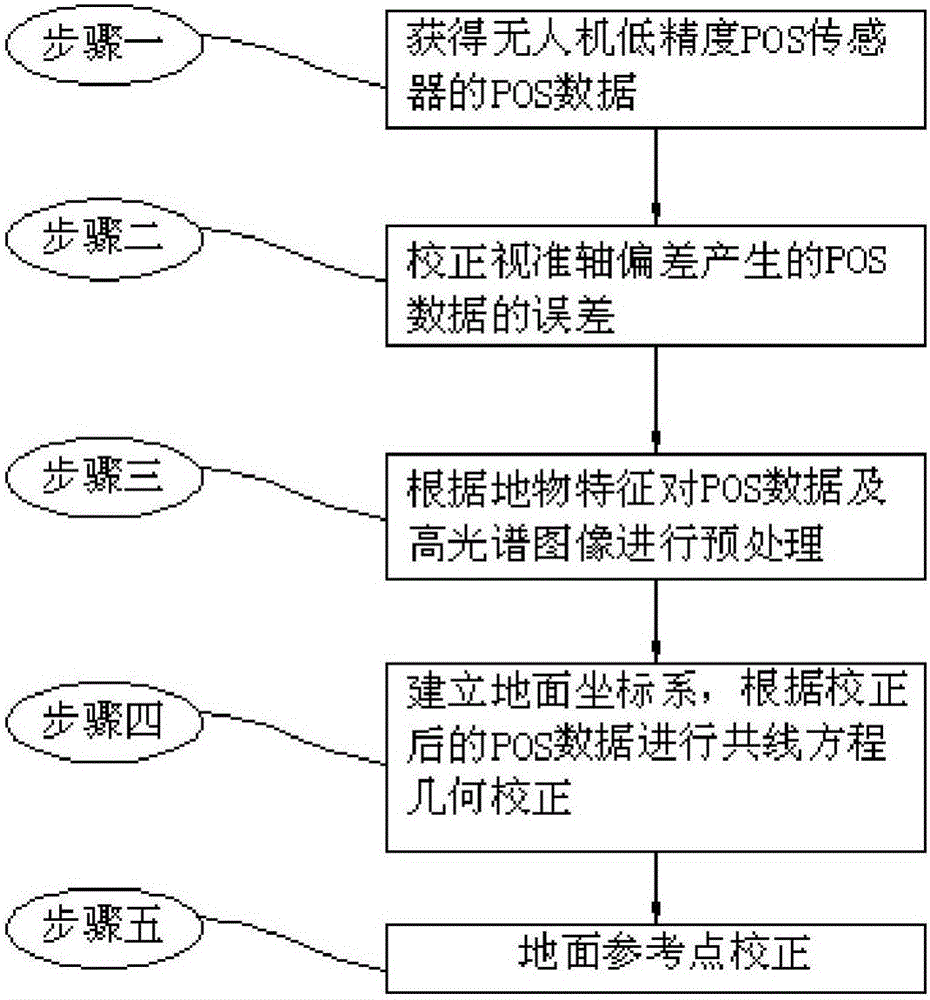
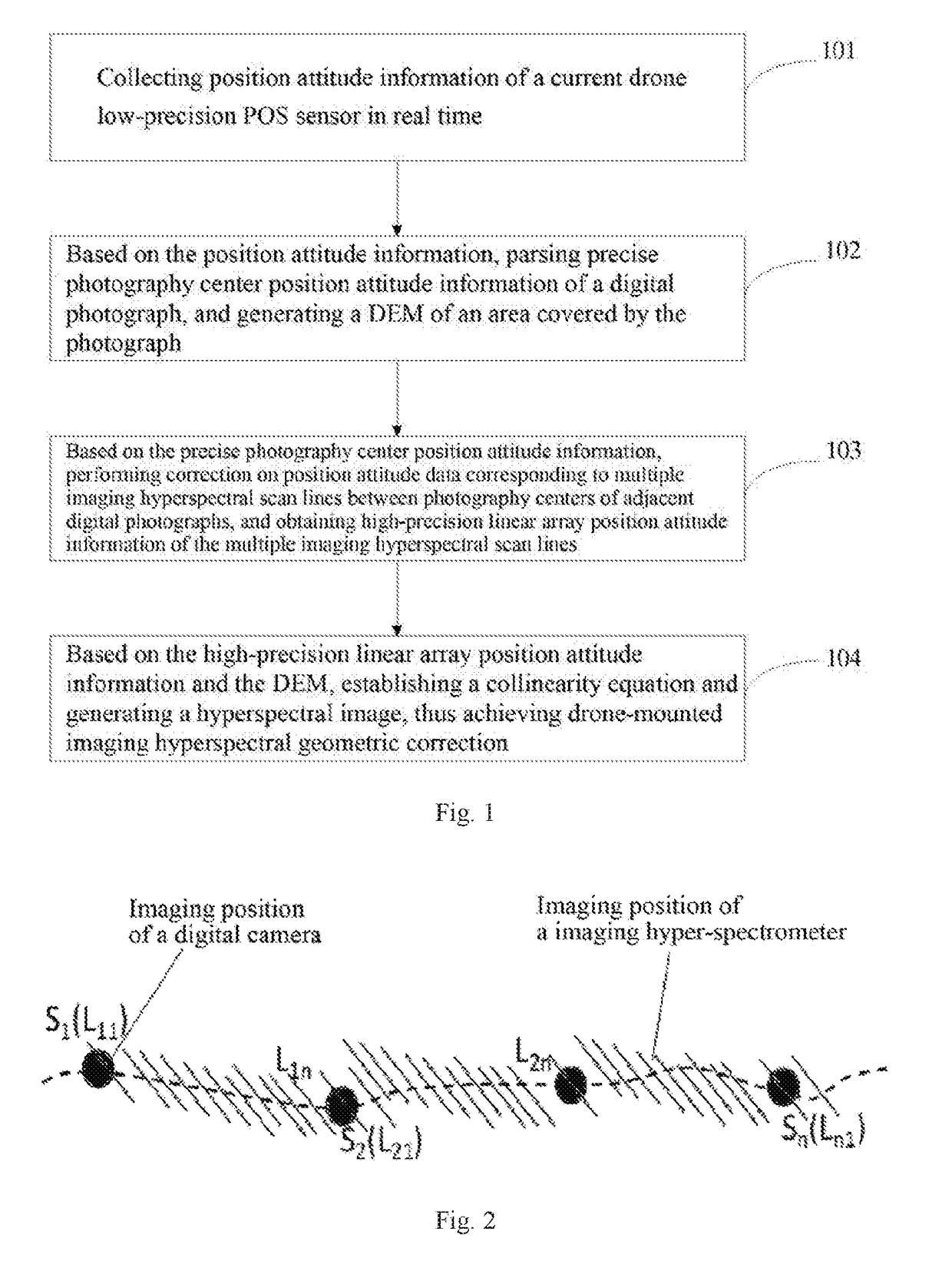
Method and system for geometric correction of UAV (unmanned aerial vehicle) loaded imaging hyperspectrum
The invention relates to a method and a system for the geometric correction of UAV (unmanned aerial vehicle) loaded imaging hyperspectrum. The method comprises the steps of collecting the position and attitude information of the POS sensor with low precision of an existing UAV; analyzing the precise position and attitude information in the photographing centre of a numerical code photograph according to the position and attitude information, so as to generate a DEM (Dynamic Effect Model) of a photograph covering area; correcting position and attitude data corresponding to a plurality of imaging hyperspectral scanning lines in the photographing centre of an adjacent numerical code photograph according to the precise position and attitude information of the photographing centre, so as to obtain the linear array position and attitude information with high precision of the plurality of imaging hyperspectral scanning lines; building a collinearity equation according to the linear array position and attitude information with high precision and the DEM, so as to generate a hyperspectral image. The POS information with high precision is calculated by calculating the area array imaging data of the UAV, the POS data with low precision of the UAV can be optimized, the precise geometric correction of the scanning lines of an imaging hyperspectral imager can be realized, and the technical support is provided for the extensive application of UAV loaded imaging hyperspectrum.
Owner:NONGXIN TECH BEIJING CO LTD
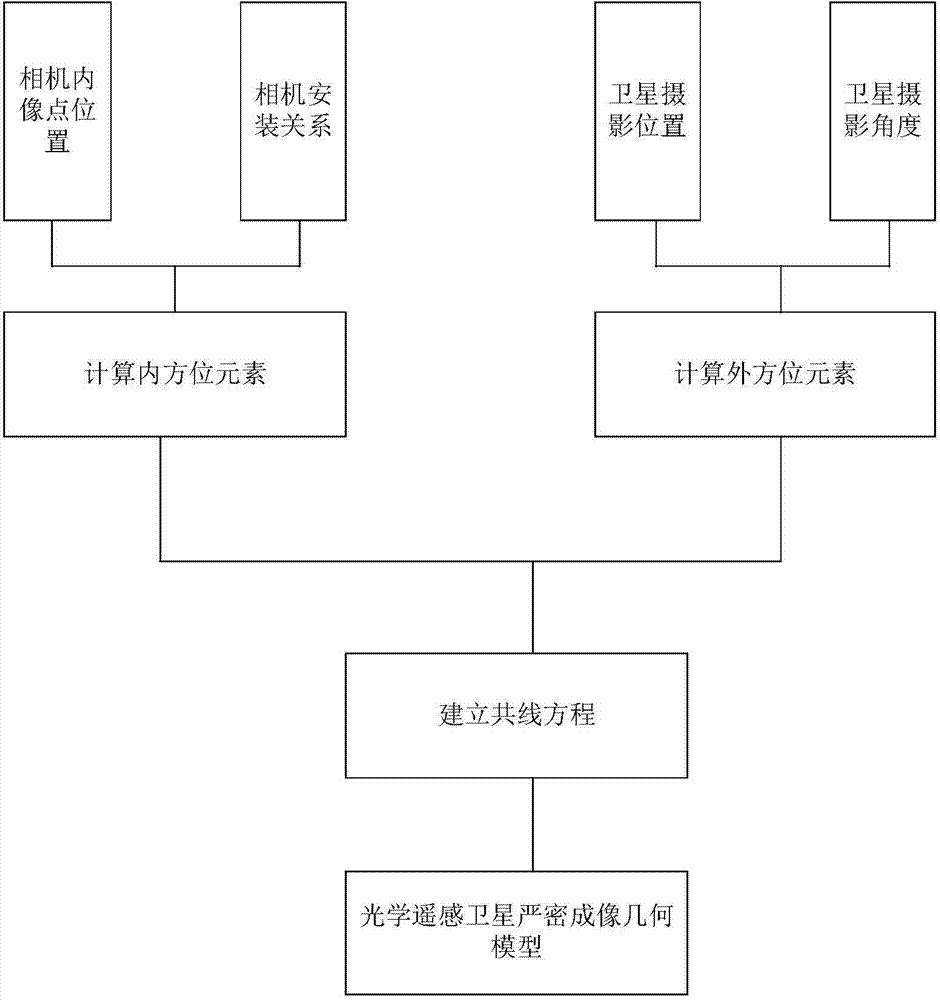
Optical remote sensing satellite rigorous imaging geometrical model building method
ActiveCN104764443AAccurate descriptionPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryGyroscopeRemote sensing satellite
The invention provides an optical remote sensing satellite rigorous imaging geometrical model building method. The optical remote sensing satellite rigorous imaging geometrical model building method comprises the following steps that the geometrical relationship between the image point coordinates of an optical remote sensing satellite and the satellite is determined according to design parameters and on-orbit calibration parameters of an optical remote sensing satellite camera and the installation relation of the camera and the satellite; the shooting position of a satellite image is determined according to the GPS carried by the optical remote sensing satellite, the observation data of a laser corner reflector and the installation relation of the laser corner reflector and the satellite; the shooting angle of the satellite image is determined according to a star sensor carried by the optical remote sensing satellite and the observation data of a gyroscope and the installation relation of the gyroscope and the optical remote sensing satellite, a collinearity equation of all image points of the optical remote sensing satellite is built, and a rigorous imaging geometrical model of optical remote sensing satellite images is formed. The optical remote sensing satellite rigorous imaging geometrical model building method is the basis of optical remote sensing satellite follow-up geometrical imaging processing and application.
Owner:SATELLITE SURVEYING & MAPPING APPL CENTSASMAC NAT ADMINISTATION OF SURVEYING MAPPING & GEOINFORMATION OF CHINANASG
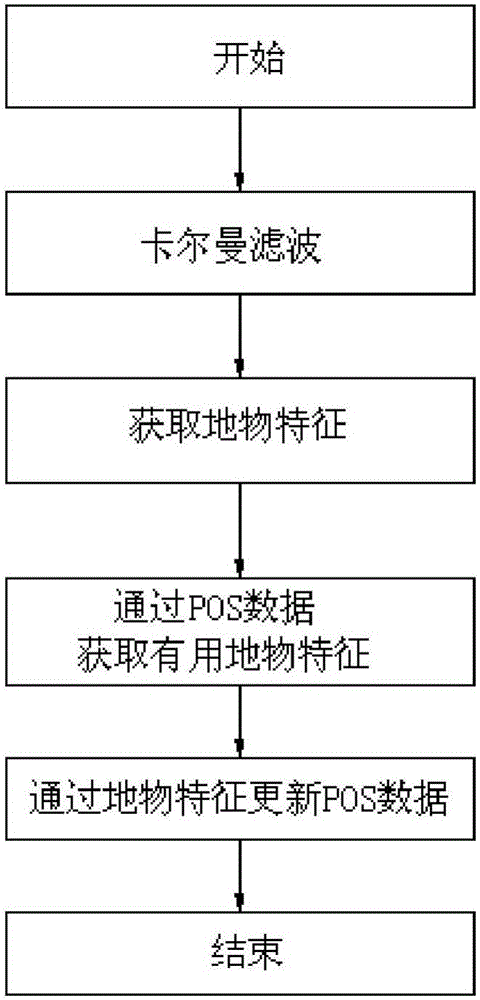
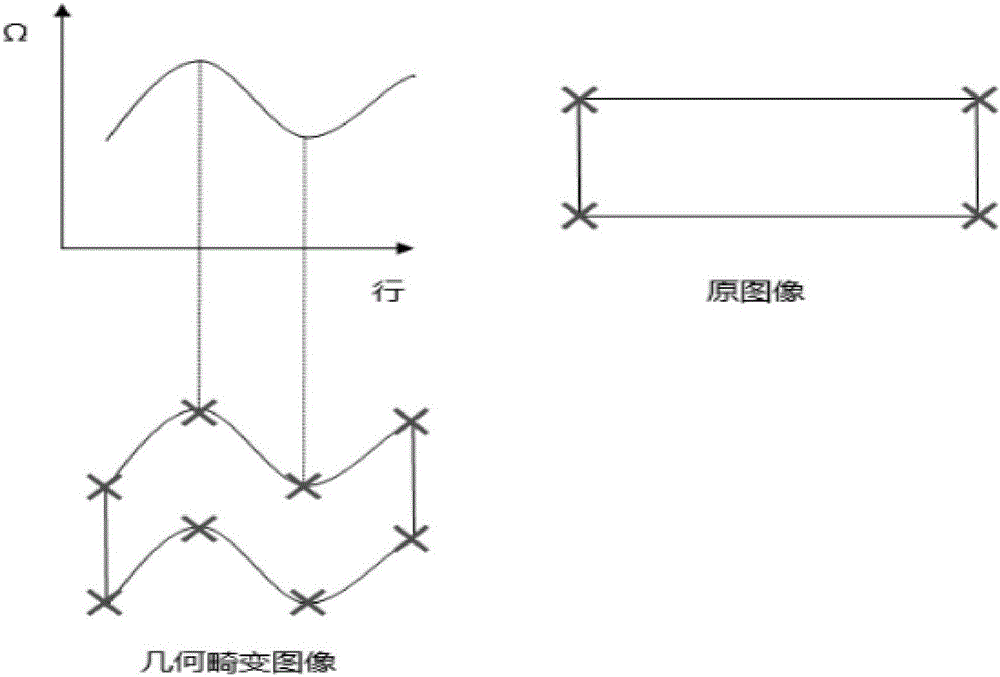
Geometric correction method of airborne imaging hyperspectrum of unmanned aerial vehicle
ActiveCN106127697ALow-precision POS data optimizationHigh precisionImage enhancementImage analysisAngular pointUncrewed vehicle
The invention discloses a geometric correction method of an airborne imaging hyperspectrum of an unmanned aerial vehicle. At present, an image obtained according to POS (Positioning and Orientation System) data exhibits an overlarge deviation with practicality, and the point, line and surface distortion of scenery is large and is difficult in geometric fine correction through polynomial correction. The method comprises the following steps: collecting the position gesture information of a low-precision POS sensor of a current unmanned aerial vehicle to correct a collimation axis error; according to the angular point and outline information of ground object characteristics, preprocessing the POS data to obtain corresponding elements of exterior orientation; carrying out collinearity equation correction; and through a ground correction point, carrying out polynomial correction. By use of the geometric correction method, a relationship between natural ground object characteristics and the own error of the sensor is considered, correction accuracy is improved, the aerial photography low-precision POS data of the unmanned aerial vehicle is optimized, the aerial photography image of the unmanned aerial vehicle can be accurately corrected only by carrying the low-precision POS sensor and a hyperspectral imager, and technical support is provided for the wide application of the current low-cost imaging hyperspectrum of an unmanned aerial vehicle.
Owner:天岸马科技(黑龙江)有限公司
Lunar rover binocular vision navigation system calibration method
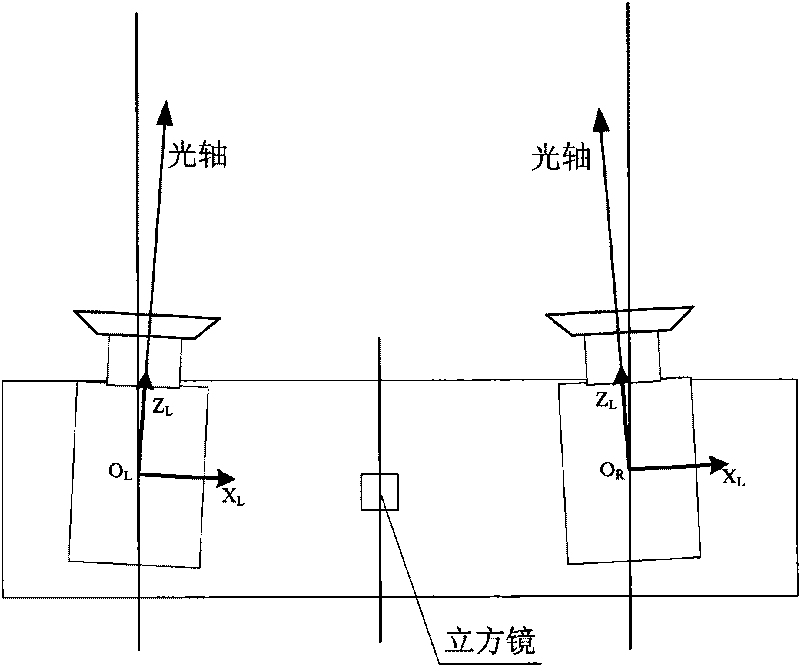
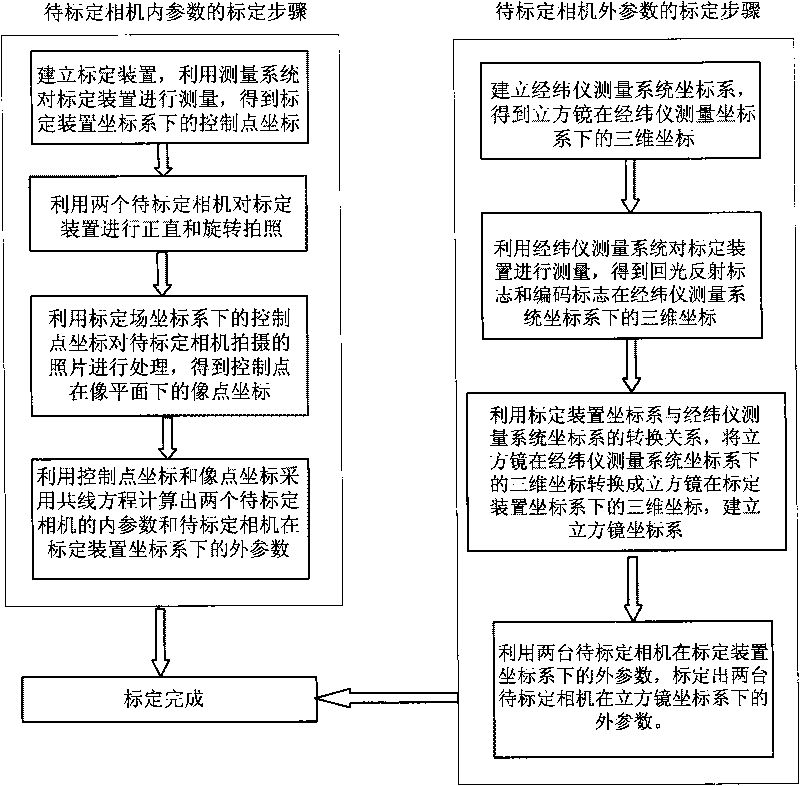
ActiveCN101876555AHave visibilitySolve problems that cannot be obtained by direct measurement methodsMeasurement devicesTheodolitePrism
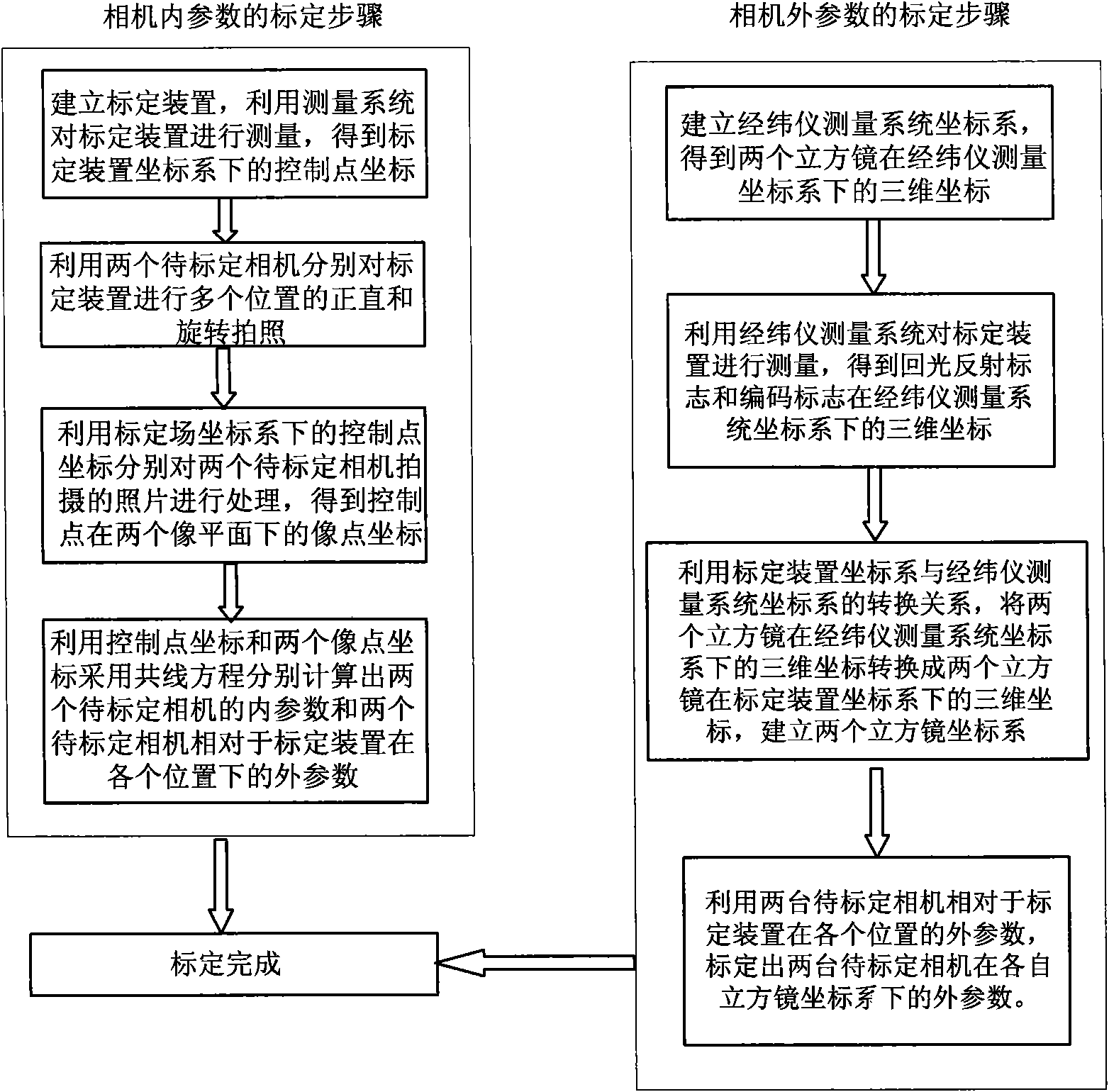
The invention discloses a lunar rover binocular vision navigation system calibration method. A measurement system measures a calibration device comprising a light-reflecting measurement mark and a coded mark to obtain a control point coordinate, two cameras to be calibrated respectively shoot the calibration device, and internal parameters of the two cameras to be calibrated and external parameters of the two cameras to be calibrated at different positions relative to the calibration device can be calibrated by adopting a collinearity equation; and a theodolite measurement system is matched with the calibration device to calibrate respective prism square coordinate system of the two cameras to be calibrated, and respective external parameters of the two cameras to be calibrated are calibrated by utilizing the respective prism square coordinate system and the external parameters of the two cameras to be calibrated at different positions relative to the calibration device respectively. The lunar rover binocular vision navigation system calibration method radically solves the problem that a coordinate system of a camera cannot be obtained by a direct measurement method, and makes the coordinate system of the camera visible; meanwhile, the lunar rover binocular vision navigation system calibration method has the advantages of simple operation, high calibration precision and high work efficiency.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
GPS//INS data direct directing precision assessment method
InactiveCN101509784AInnovative designHigh degree of automationInstruments for road network navigationPicture interpretationBundle methodBundle methods
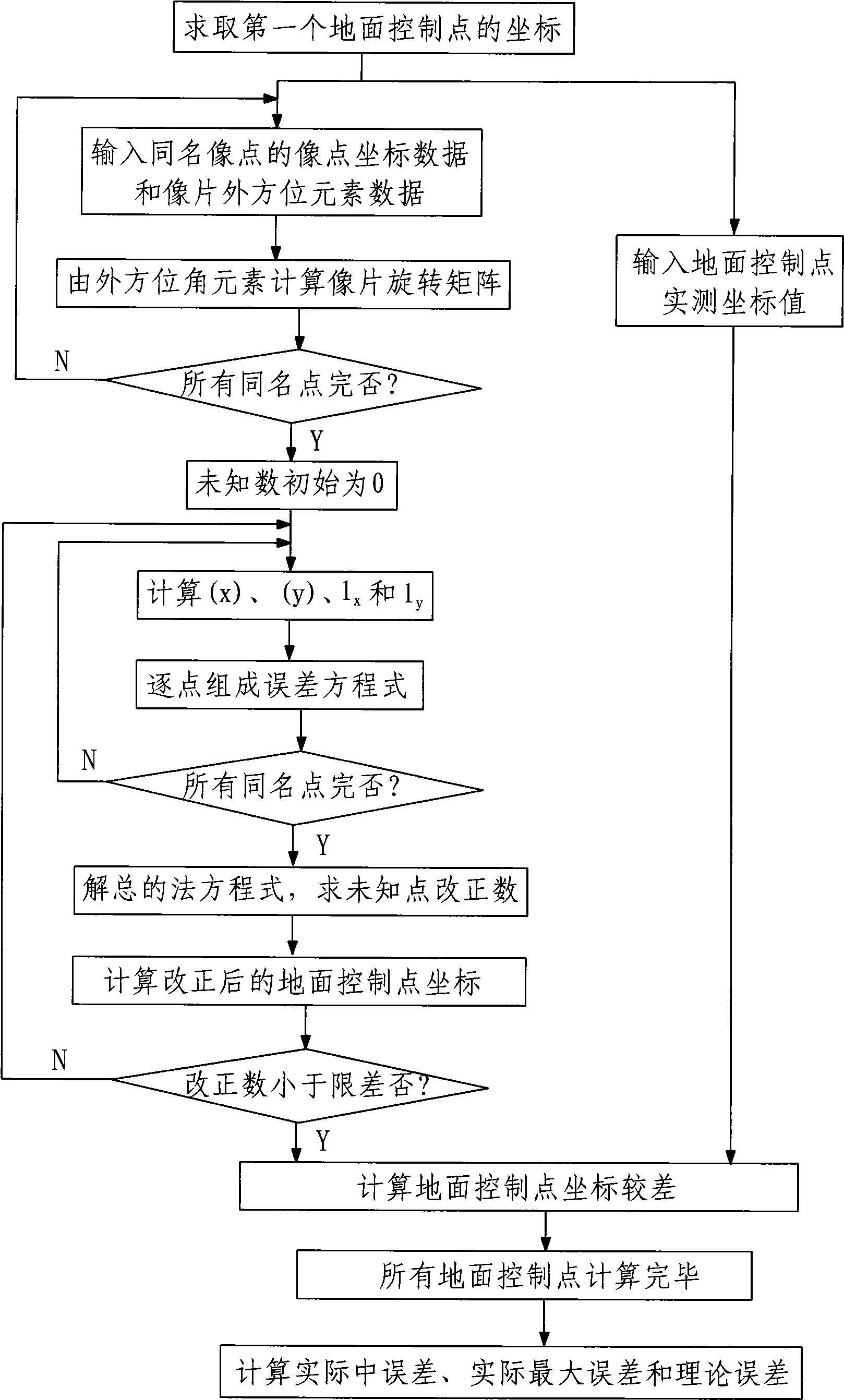
The invention discloses a GPS / INS data direct orientation precision evaluation method, which takes photogrammetric emphasis equation collinearity equation as base and a multi-piece forward intersection of a bundle method as theory basis; the evaluation method is combined with the least square principle for obtaning the coordinate of a ground control point object by compensating calculation; and then a comparison with the actually measured coordinate of the ground control point is carried out for obtaining the error value of the coordinate by the statistics so as to evaluate the direct orientation precision of the outer orientation elements obtained by the GPS / INS system. The method has high evaluation precision and small measurement error, and the evaluation result can be used for manufacture practice directly, thus being capable of effectively avoiding the measurement error of the picpointed coordinate added in manual stereomeasurement; and the algorithm is not limited by image number.
Owner:XIAN MEIHANG INFORMATION IND
Calibration method for lunar rover binocular vision navigation system
ActiveCN101726318AHave visibilityImprove the problem of low calibration accuracyMeasurement devicesTheodoliteLight reflection
The invention relates to a calibration method for a lunar rover binocular vision navigation system, which is designed against the characteristics of the binocular vision navigation system and comprises the steps of utilizing a measurement system for measuring a calibration device containing a back light reflection measurement mark and an encoding mark, obtaining a control point coordinate, utilizing a camera to be calibrated to carry out photographing on the calibration device, and then adopting a collinearity equation for calibrating internal parameters of the camera to be calibrated and external parameters of the camera to be calibrated under a coordinate system of the calibration device; and utilizing a theodolite measurement system to be matched with the calibration device for calibrating the coordinate system of a prism square, and utilizing the relationship between the coordinate system of the prism square and the external parameters of the camera for calibrating the external parameters of the camera to be calibrated under the coordinate system of the prism square. The calibration method makes full use of known information of a large number of control points of the calibration device, and an industrial measurement system is matched, thereby improving the problem of low calibration precision of the external parameters of the traditional camera, realizing simple operation and high calibration precision, completing the calibration of the internal parameters of the camera to be calibrated and the relative external parameters, completing the calibration within a hour and greatly improving the working efficiency.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
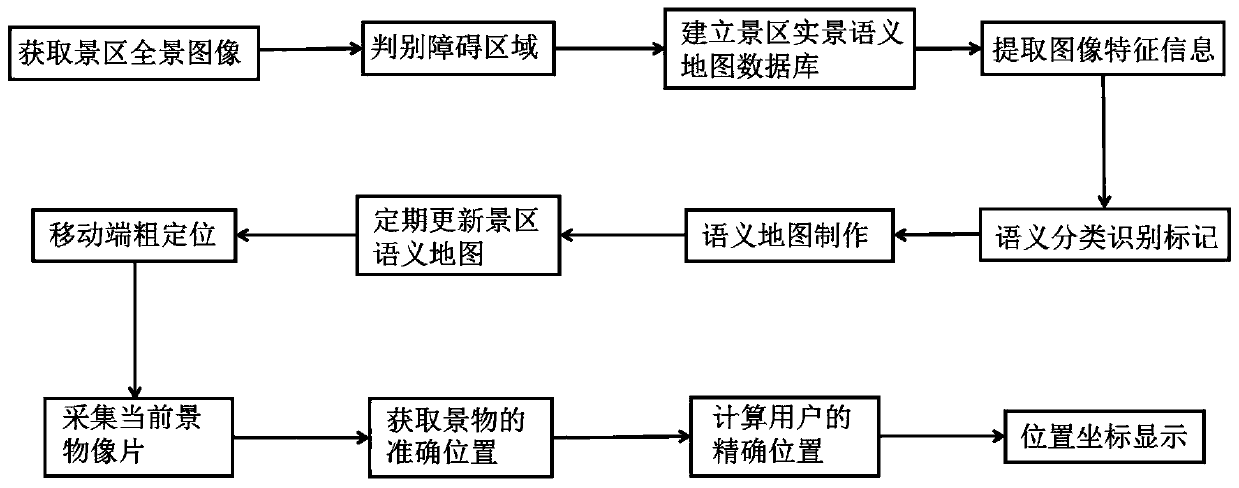
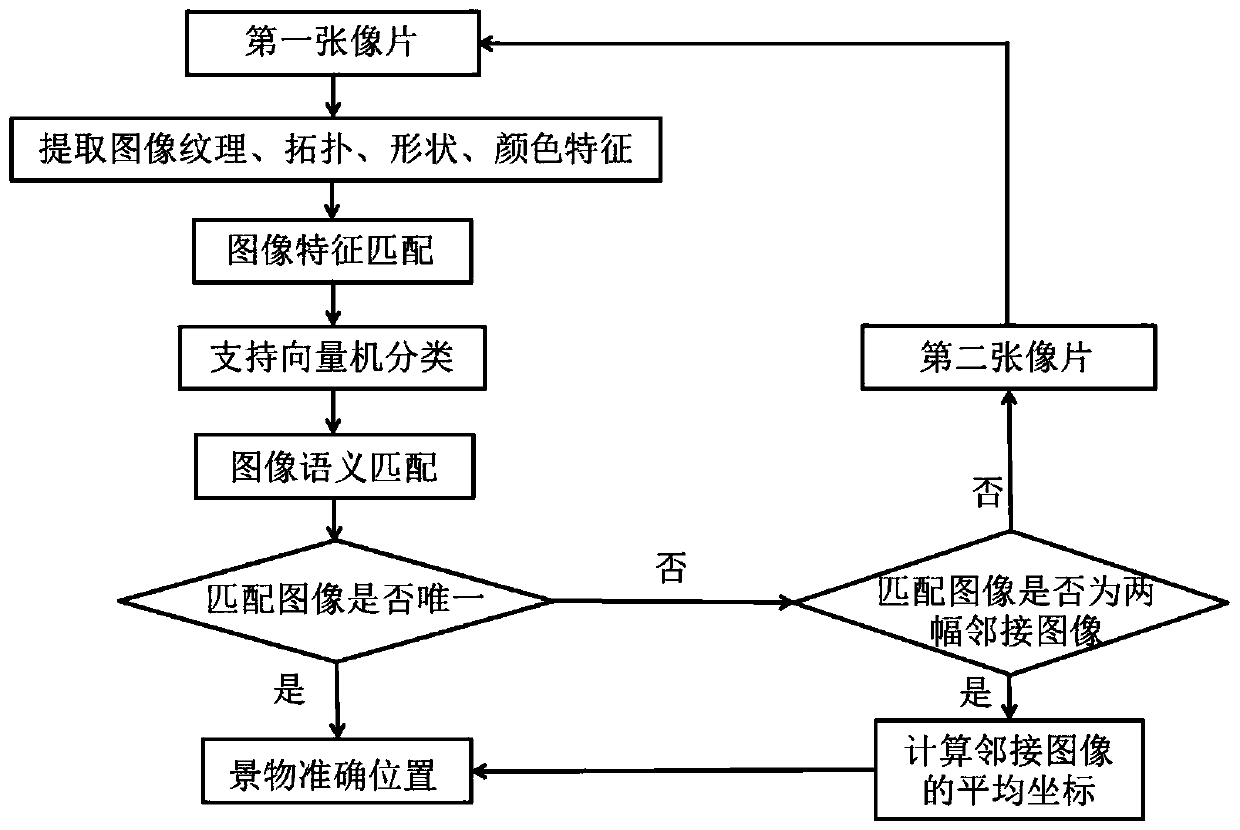
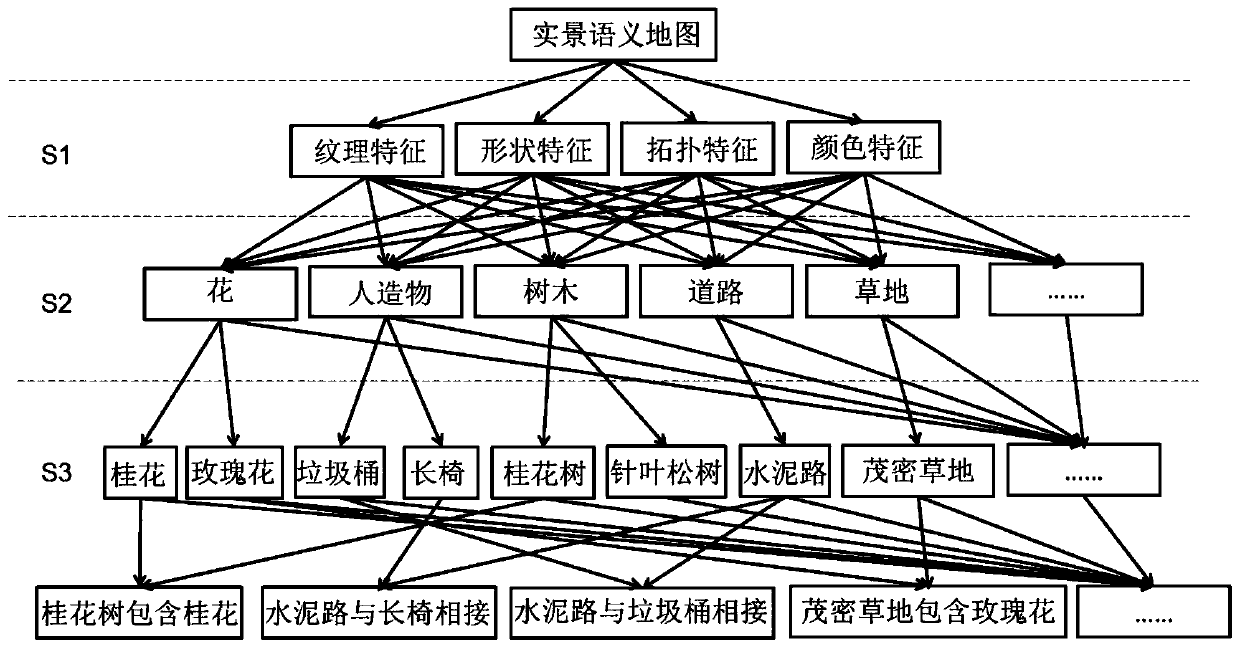
Generation and auxiliary positioning method for live-action semantic map of smart scenic spot
ActiveCN110866079APrecise positioningResolve locationGeographical information databasesSpecial data processing applicationsElectronic mapPhysics
The invention discloses a generation and auxiliary positioning method of a live-action semantic map of a smart scenic spot. The generation and auxiliary positioning method comprises the following steps: acquiring a scenic spot panoramic image and positioning information, extracting scenic spot image features to perform semantic description and scene classification identification marking, and establishing a scenic spot live-action semantic map database; collecting a scene stereo image pair at the current position by a user; matching the photo image features and the semantic information with theimage features and the semantics of the local semantic map of the scenic spot respectively; and acquiring a scenery image closest to the photographic film, extracting the spatial position informationof the scenery image marked in the semantic map, resolving the accurate position of the user photography through a spatial forward intersection collinear equation, and displaying the position coordinates of the user on the scenic spot electronic map in real time. According to the generation and auxiliary positioning method, the fine position of the user is calculated through the main steps, and the defects of insufficient live-action semantic information and inaccurate positioning in an electronic map are overcome.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
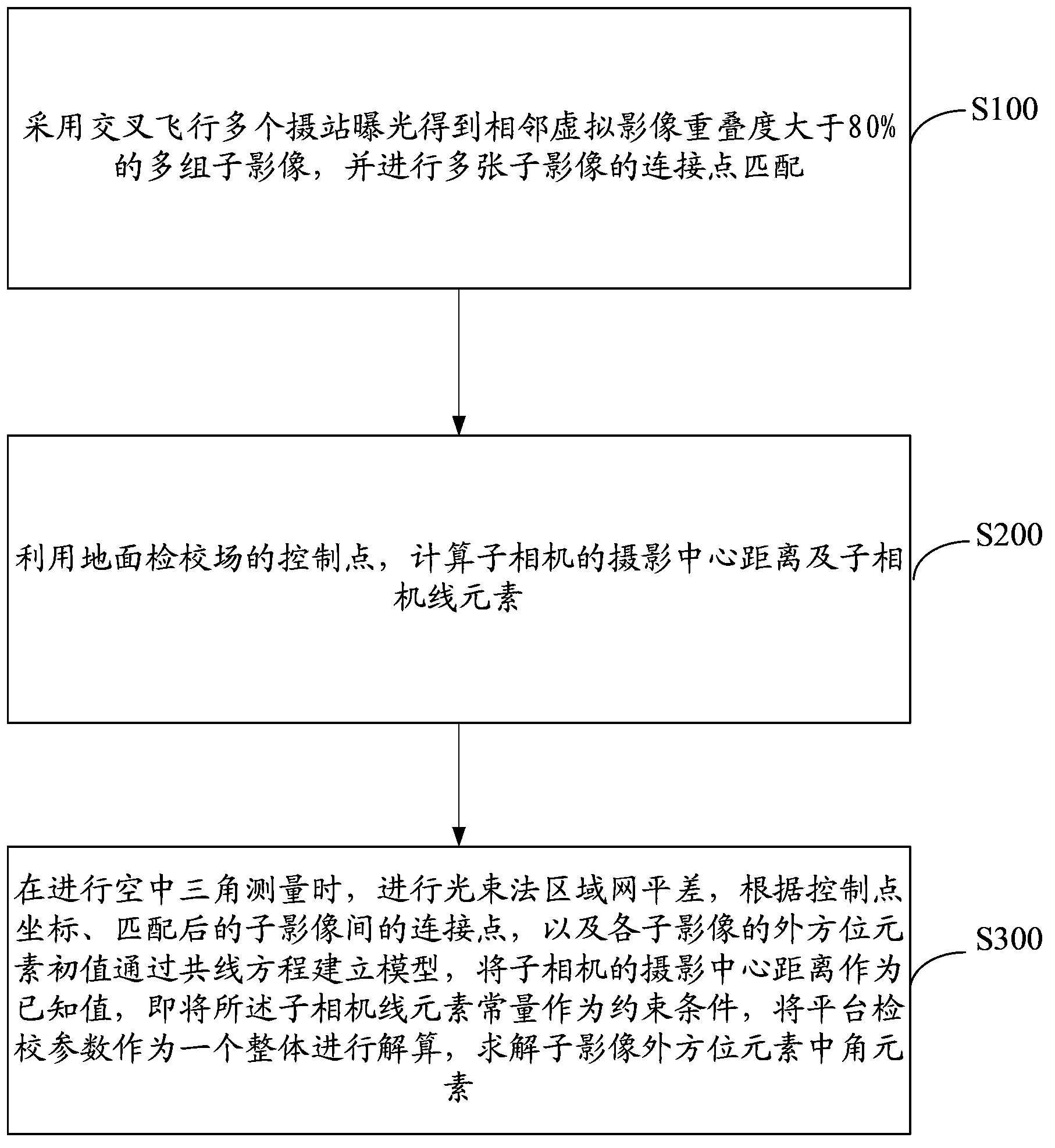
Multi-area array aerial camera platform calibration method with constraint condition
The invention discloses a multi-area array aerial camera platform calibration method with a constraint condition. The method includes: employing a data acquisition strategy of multiple cross flying camera station exposure to acquire multiple groups of sub-images with an adjacent virtual image overlap degree of more than 80%; making use of the control point of a ground calibration field to calculate a photographing centre distance of sub-cameras and a sub-camera line element; during aerotriangulation, conducting bundle block adjustment, according to the control point coordinate, the connection points among matched sub-images, and the external orientation element initial value, establishing a model through a collinearity equation, adopting the photographing centre distance of the sub-cameras as a given value, i.e. taking the sub-camera line element constant as the constraint condition, and taking platform calibration parameters as a whole to perform calculation to solve the angle elements in the external orientation elements of the sub-images. According to the calibration method, a lot of uniformly distributed connection points are matched, precision of the platform calibration parameters is improved through the constraint condition, higher stitching precision of the generated virtual images can be guaranteed, and the mapping precision can be higher.
Owner:CHINA TOPRS TECH
Method and device for acquiring coordinates of point cloud by oblique photography
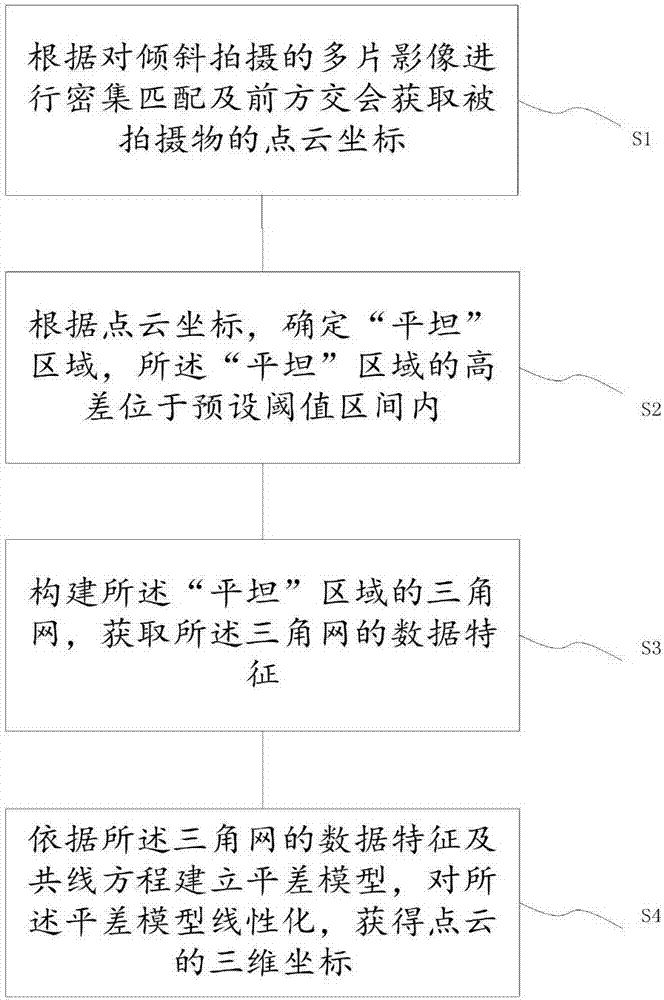
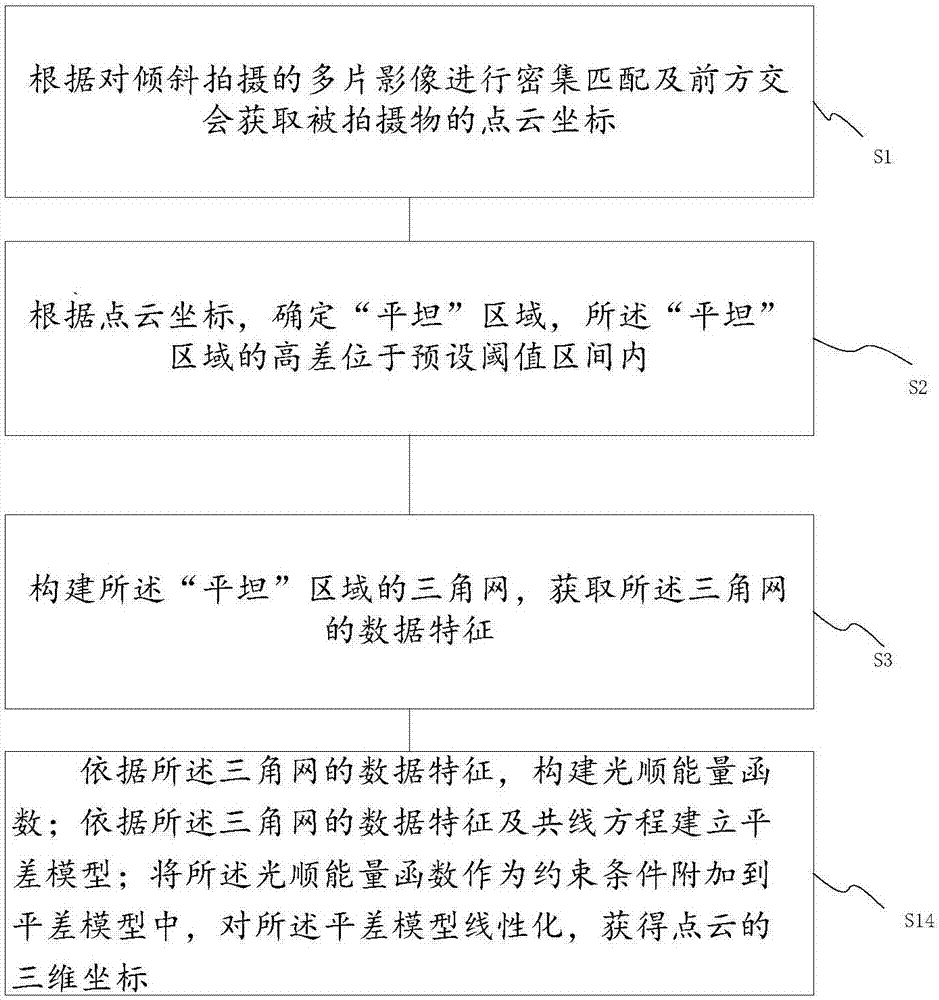
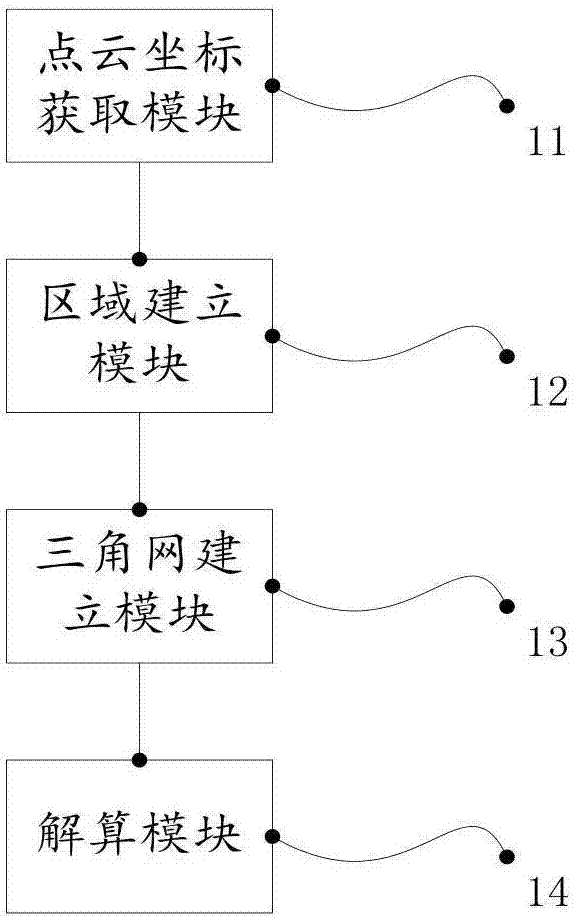
InactiveCN107067394AImprove accuracyReduce point cloud elevation non-uniform variationImage enhancementImage analysisPoint cloudTriangulation
The invention provides a method and a device for acquiring coordinates of a point cloud by oblique photography, so as to solve the problem of inconsistency existing between the point cloud position and the actual position in oblique photography measurement. The method comprises steps: through carrying out dense matching and forward intersection on multiple images obtained through oblique photography, point cloud coordinates of a photographed object are acquired; according to the point cloud coordinates, flat areas are determined, wherein the altitude difference among the flat areas is located in a preset threshold interval; a triangulation network for the flat areas is built, and data features of the triangulation network are acquired; and according to a collinearity equation and a smoothing energy function, an adjustment model is built, the adjustment model is linearized, and three-dimensional coordinates of the point cloud are acquired. The method uses the flat areas as constraint conditions for point cloud calculation, error match phenomena of the point cloud caused by altitude difference changes can be reduced, and the point cloud position and the actual position are thus consistent.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF ELECTRONICS & INFORMATION TECH OF CETC
Video measurement based quantitative background schlieren method
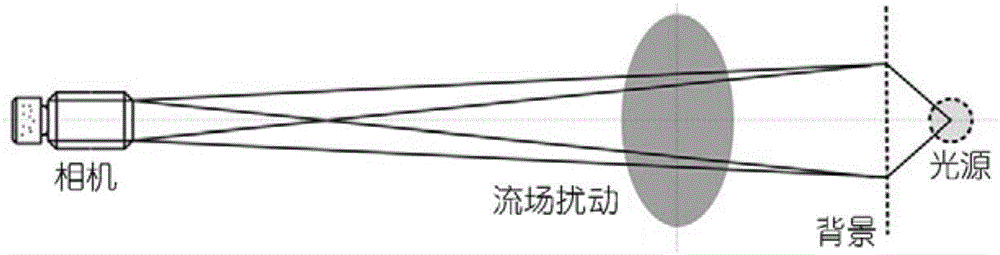
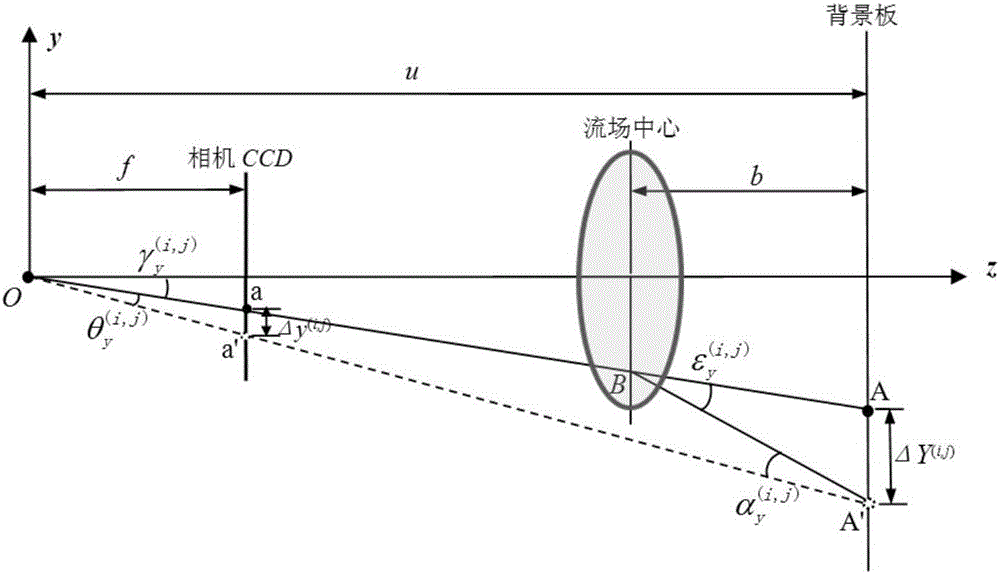
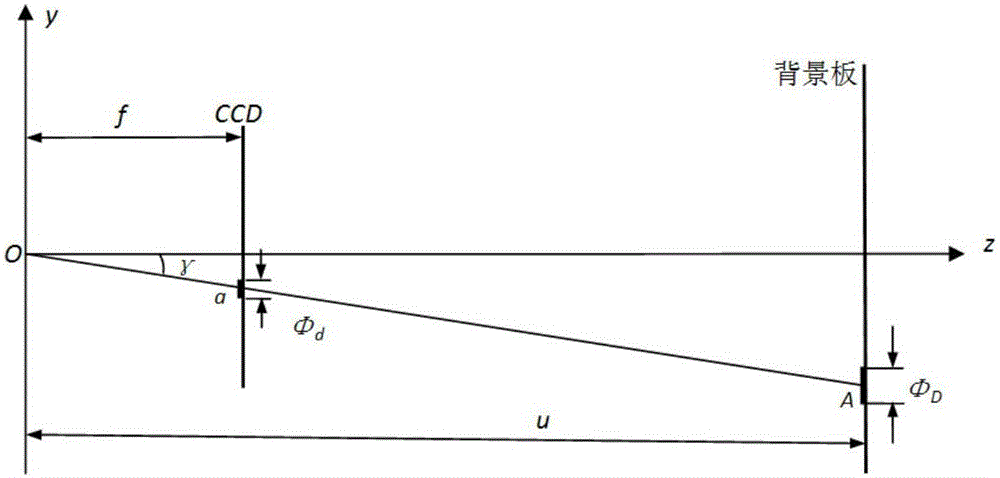
ActiveCN106290256AEliminate errorsAccurate measurementPhase-affecting property measurementsPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryImaging processingMutual correlation
The invention discloses a video measurement (VM) based quantitative background schlieren (BOS) method. A VM technology and a BOS light path are combined, and small evenly distributed round points are adopted as BOS background points, so that on one hand, a VM mature round marking point image processing technology is utilized to ensure the point positioning accuracy of small round point imaging is up to 0.02 pixels; on the other hand, the defection displacements produced by light beams starting from the small background round points to the photographing center of a camera and penetrating through a flow field on a background board are accurately calculated through a collinearity equation, an exact defection angle calculation formula is given to accurately obtain the defection angles and light path differences of all the background point positions, accordingly the errors produced by an existing BOS adopting a parallel light deflection angle calculation formula are eliminated, and the adverse effect on the limit of existing BOS measurement and BOS measurement accuracy of an image mutual-correlation technology is overcome.
Owner:INST OF HIGH SPEED AERODYNAMICS OF CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
Method for measuring three-dimensional information of person or object through monitoring video or vehicle-mounted camera
InactiveCN106323241APhotogrammetry/videogrammetryClosed circuit television systemsVideo monitoringStereo matching
The invention discloses a method for measuring three-dimensional information of a person or an object through a monitoring video or a vehicle-mounted camera, and relates to the technical field of video monitoring. The method comprises the following steps: 1, acquiring two or more images in different visual angles according to a video monitoring picture; 2, calibrating the camera, and establishing a mapping relation between 3D to 2D (three-dimensional to two-dimensional); 3, extracting a feature point, performing stereo matching, and calculating the three-dimensional information of the feature point of the object to be measured in the video picture according to the perspective transformation principle and a collinearity equation; and 4, establishing a perspective transformation relation between coordinates of a space object point of the feature point and coordinates of a picture image point through close shot photographic measurement. The method can be used for measuring the three-dimensional information of the person or the object through the monitoring video or the vehicle-mounted camera.
Owner:广东警官学院
EEG electrode space positioning method based on up shot measure
InactiveCN1405736AAchieve the expected purpose2D-image generationCamerasComputer graphics (images)Three-dimensional space
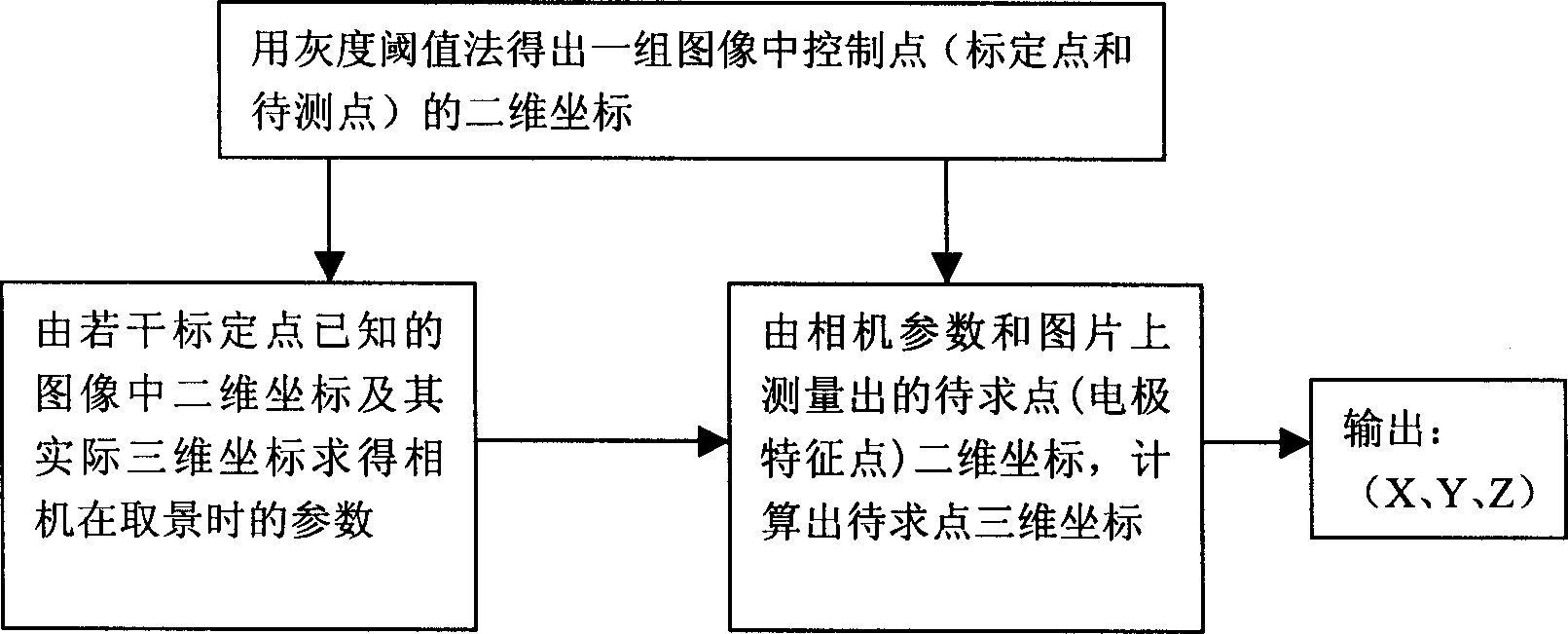
The invention belongs to the technique area of the 3D space orientation, including following steps. The system is composed of the some calibrated objects with the aiming points, the electrode cap having the fixed space positions with calibrated objects, the non-measuring camera, the image processor and the computer. The space coordinate measure of the electrode is completed through the following three steps. The 2D coordinates of the control points (the aiming points and the points to be measured) in the group of image are obtained by using the image recognition method (such as gray scale threshold method). The parameter of the camera at the shooting time can be solved inversely by the collinearity equation in the close-range photogrammetry from the 2D coordinates of the aiming points in the image and its actual 3D coordinates.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Multi-lens sensor-based image fusion method
ActiveCN107492069AReal geographical environment sceneImage enhancementImage analysisThree-dimensional spaceMathematical model
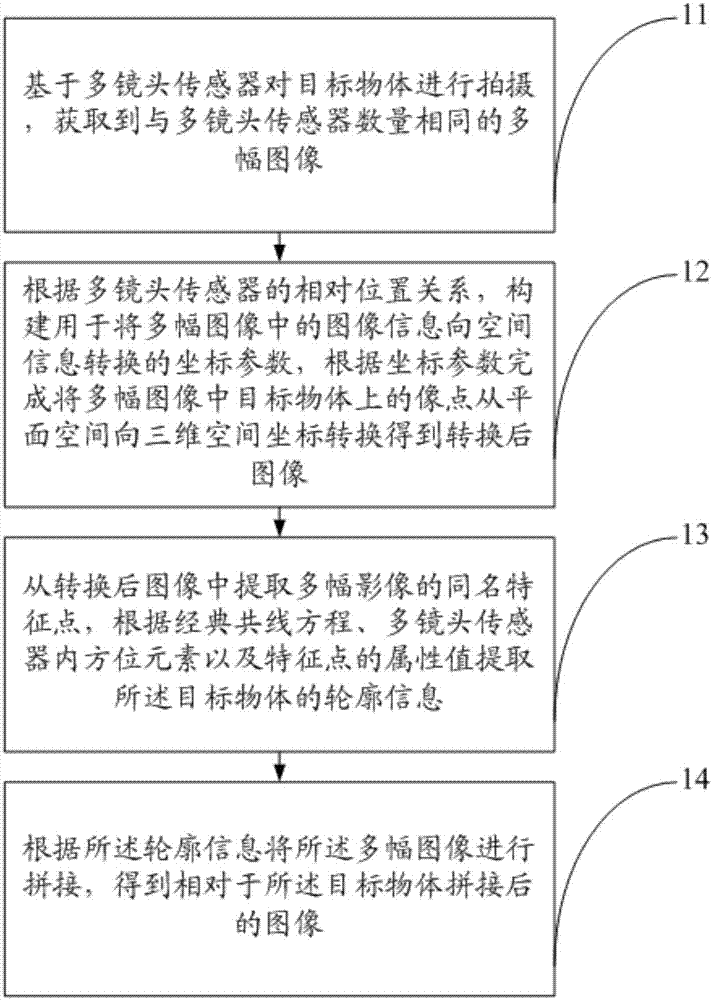
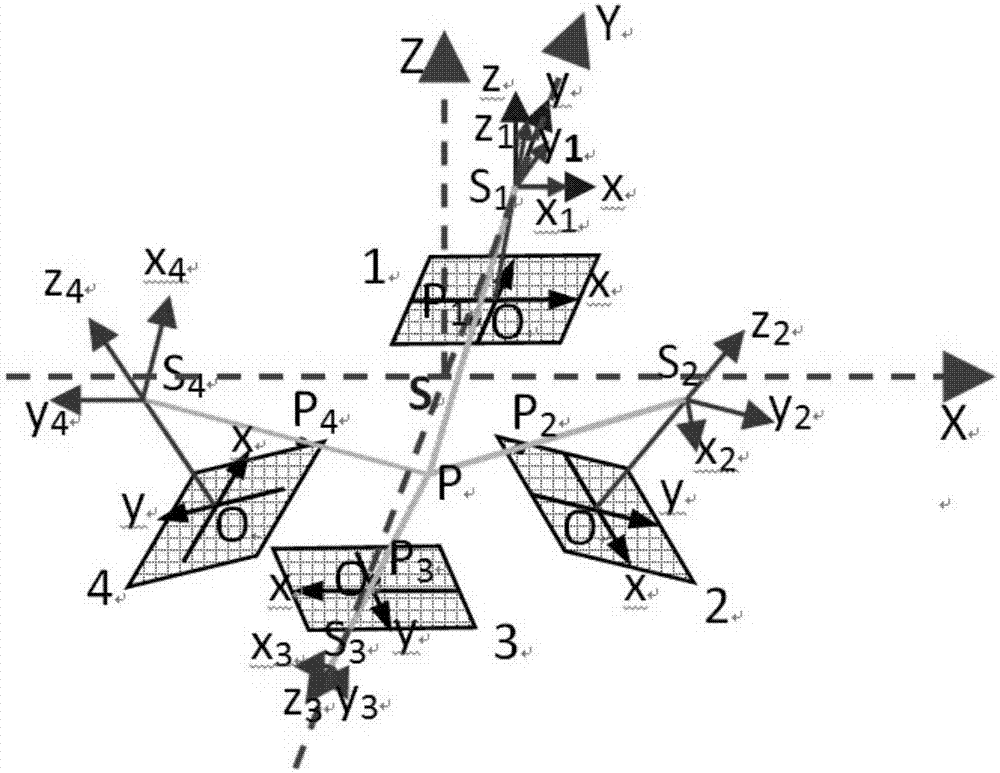
The invention provides a multi-lens sensor-based image fusion method, and belongs to the field of image synthesis. The method includes: acquiring multiple images on the basis of a multi-lens sensor; constructing coordinate parameters according to a relative position relationship of the multi-lens sensor, and completing coordinate transformation, which is of image points on a target object in the multiple images, from plane space and to three-dimensional space, according to the coordinate parameters to obtain transformed images; extracting contour information of the target object according to classical collinearity equations, orientation elements in the multi-lens sensor and attribute values of feature points; and splicing the multiple images according to the contour information to obtain a spliced image. Through above processing, the five images can be spliced into the one image, and relative space relationships between different regions in the target object can be obtained on the basis of the obtained image to establish a strict spatial mathematical model of a multi-lens camera. On the basis of the technology, a user can carry out fast unmanned-aerial-vehicle line inspection of transmission lines, fuse the images collected by multiple lenses, and establish a real geographical environment scene.
Owner:NINGBO POWER SUPPLY COMPANY STATE GRID ZHEJIANG ELECTRIC POWER +1
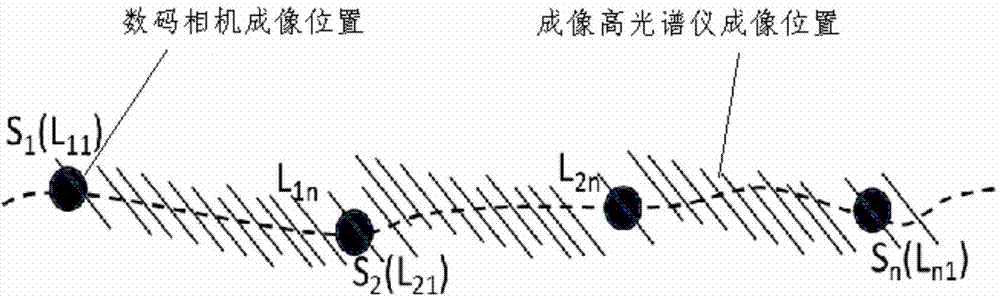
Drone-mounted imaging hyperspectral geometric correction method and system
ActiveUS20170200259A1Provide supportImage enhancementTelevision system detailsScan lineDigital pictures
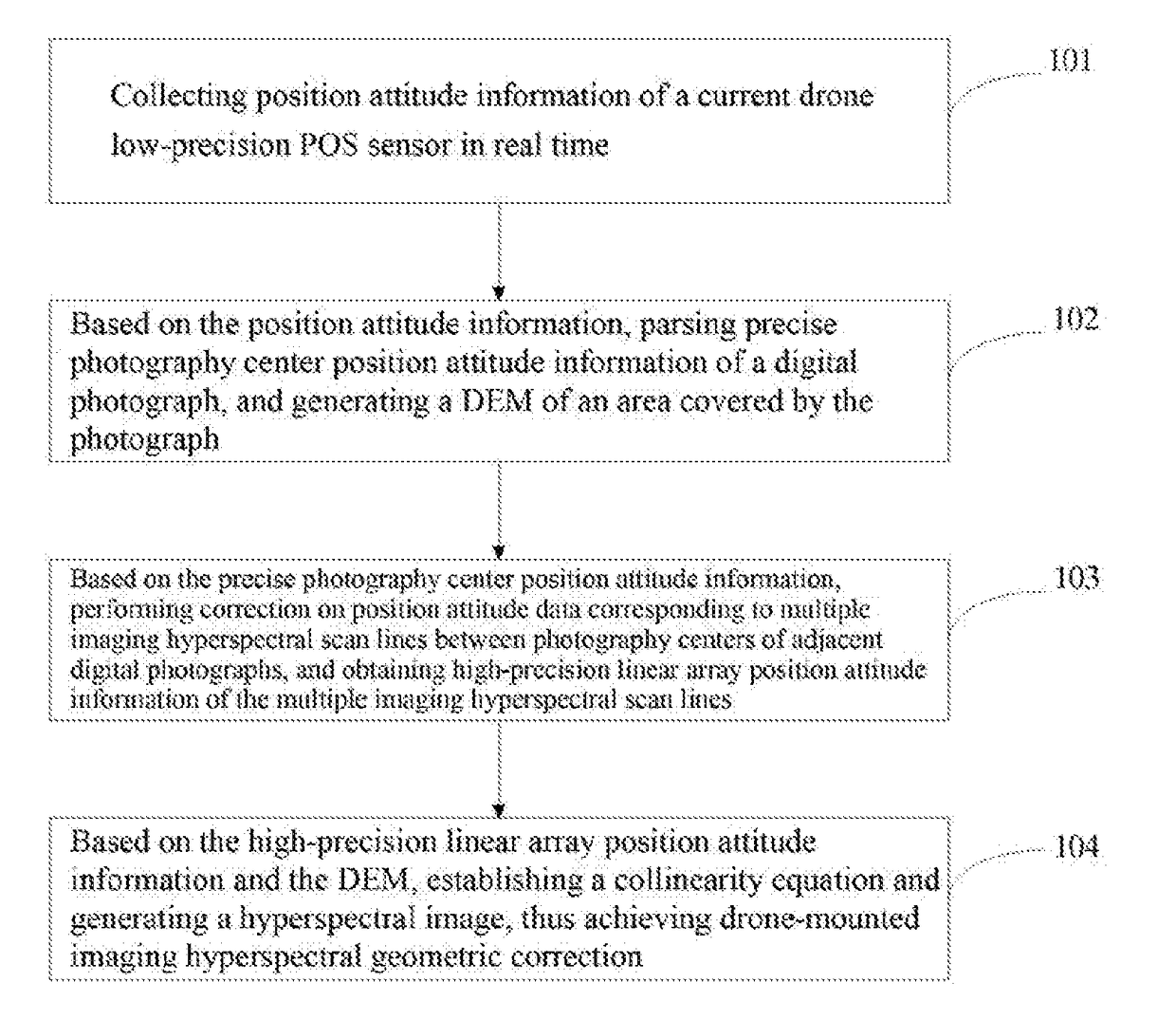
Related are a drone-mounted imaging hyperspectral geometric correction method and a system, comprising: collecting position attitude information of a current drone low-precision POS sensor in real time; based on the position attitude information, parsing precise photography center position attitude information of a digital photograph, and generating a DEM of an area covered by the photograph; based on the precise photography center position attitude information, performing correction on position attitude data corresponding to multiple imaging hyperspectral scan lines between photography centers of adjacent digital photographs, and obtaining high-precision linear array position attitude information of the multiple imaging hyperspectral scan lines; based on the high-precision linear array position attitude information and the DEM, establishing a collinearity equation and generating a hyperspectral image.
Owner:BEIJING RES CENT FOR INFORMATION TECH & AGRI
Calibration method for image measuring system
ActiveCN101482410ASmall footprintEasy to keepPicture taking arrangementsVisual field lossSmall footprint
The invention relates to a scaling method in image measuring system, which comprises: placing simple scaling targets on the scaled plane in order, superposing and imaging; calculating out the coordinate of every point on the image plane; calculating out the coordinate of every scaled point on the scaled plane by using the geometric constant principle between the scaled plane and the image plane; and inputting the coordinates into the conllinear equation of the scaled plane and the image plane to obtain the relation between the scaled plane and the image plane. The invention is especially suitable for industrialized large visual field image measuring system, can meet the real-time requirement of production site, can increase the scaling target placing time according to the scaling precision requirement to realize high precision scaling, avoids the constraint scaling by plane fixing mechanical devices in the existing technologies, and achieves the advantages of fast, simple, efficient, reliable, small scaling target occupation area, easy keeping and high precision.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Thermal infrared image stitching method
ActiveCN107403410AHigh feasibilityImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisThermal infraredPositioning system
The invention relates to a thermal infrared image stitching method, which comprises the following steps that: calibrating an infrared thermal imager to obtain an inner orientation element, and carrying out aerial survey on ground through the aircraft carried infrared thermal imager and a positioning and orientation system to obtain an infrared image sequence and position gesture data; according to the inner orientation element, the infrared image sequence and the position gesture data at a corresponding photographing moment, adopting a collinearity equation method to carry out geometric coarse correction on each image in the infrared image sequence to obtain a value file and an absolute coordinate file; carrying out image preprocessing on the value file to carry out image stretching to obtain an area of which the gray level distribution is relatively centralized and continuous; adopting an SIFT (Scale-Invariant Feature Transform) feature point matching method and a gray level distribution method to carry out image matching on two images before and after stretching is carried out; utilizing an absolute coordinate difference value between correct matching points in the two images to carry out integral error correction on the absolute coordinate file of the rear image; and on GIS (Geographic Information System) software, on the basis of the absolute coordinate file, carrying out the embedding of mass images.
Owner:INST OF DEFENSE ENG ACADEMY OF MILITARY SCI PLA CHINA
Geometric pretreatment method for vertical rail swing images of satellite-borne linear array sensor
InactiveCN103778610ARealize splicingEliminate internal geometric distortionImage enhancementPretreatment methodRectangular coordinates
The invention discloses a geometric pretreatment method for vertical rail swing images of a satellite-borne linear array sensor. The geometric pretreatment method comprises steps of establishing a collinearity equation model of original single-frame images according to the imaging geometry of the original single-frame images; performing geometric correction treatment on all the original single-frame images, dividing all the original single-frame images into virtual three-dimensional grids, resolving rational polynomial model coefficients corresponding to the original single-frame images, establishing a positive and negative calculation relation of each original single-frame image coordinate and a tangent plane image coordinate, and performing geometric correction on all the original single-frame images on the basis of a rational polynomial model to obtain frame images under an object space tangent plane coordinate, wherein the geometric correction treatment comprises constructing a mutual conversion relation of an object space local coordinate and a geocentric rectangular coordinate and constructing a mutual conversion relation of the tangent plane image coordinate and the object space local coordinate; splicing all the frame images under the object space tangent plane coordinate on the basis of the coordinate to obtain the spliced images; resolving the rational polynomial model coefficients corresponding to the spliced images.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Satellite image positioning method and device
The embodiment of the invention provides a satellite image positioning method and device applied to a charge-coupled device image sensor. By adoption of the method and device provided by the embodiment of the invention, under the condition of no ground control point, orbit determination and attitude determination data and coordinate value data of connection points of satellite images shot by a camera of a satellite under the orbit determination and attitude determination data can be obtained only according to external calibration, and spatial attitude data in the orbit determination and attitude determination data of the satellite are corrected. Specifically, the orbit determination and attitude determination data and a corresponding relation between the connection point coordinates and ground coordinate values corresponding to the connection points are utilized, an exterior orientation element equation of the spatial attitude data changing with time is built through a quadratic polynomial, and based on a collinearity equation, the ground coordinate values of the connection points are obtained and the least square method is utilized to perform iteration to solve the spatial attitude data.
Owner:SPACE STAR TECH CO LTD
Strict collinearity equation model of satellite-borne SAR image
InactiveCN101571593ASatisfy the ground positioningRadio wave reradiation/reflectionCentral projectionComputer vision
The invention discloses a strict collinearity equation model of a satellite-borne SAR image. In the model, the derivation is carried out aiming at an earth ellipsoid model, a virtual projection center is built at each orientation of the SAR image, and a computing method of external parameter and equivalent focal length of a virtual projection center sensor and a revision method from a slant-distance image to a central projection image are derived. The method solves the following problems: (1), an approximate collinearity equation model is not strict; and (2), a ground control point is required to carry out image geocoding when the external parameter of the sensor is unknown.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Measurement method for relative exterior orientation elements by using arbitrary photographic image pair of ground without any known photogrammetric control point
ActiveCN105241422ADetermine Relative Outer Orientation ElementsSimple and fast operationPicture interpretationObservation pointNormal case
The invention discloses a measurement method for relative exterior orientation elements by using an arbitrary photographic image pair of ground without any known photogrammetric control point. The measurement method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: directed at a mark-free condition, selecting two observation points near a to-be-measured area by utilizing arbitrary photogrammetric measurement technology, subjecting a to-be-measured object to nearly horizontal normal case photographing with a fixed-focus camera so as to obtain stereoscopic image pairs, and calculating the relative exterior orientation elements of the camera by utilizing a collinearity equation mathematic model and more than 6 corresponding image points; vertically placing two fixed-length sighting rods near the to-be-measured object, respectively photographing the two observation points, then calculating coordinates of object space of a rod endpoint through the lengths of the fixed-length sighting rods, and calculating the relative exterior orientation elements of the camera by utilizing a mathematic model and point coordinates; and vertically placing a fixed-length sighting rod near the to-be-measure object, then selecting more than 3 known points in a photographed image and calculating the relative exterior orientation elements of the camera during photographing by utilizing the length of the fixed-length sighting rod and the three known points.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Incident-angle-based laser point cloud reflection intensity correction method
InactiveCN108830921AAchieve seamless texture mappingHigh precisionImage enhancementImage analysisAngle of incidencePoint cloud
The invention discloses an incident-angle-based laser point cloud reflection intensity correction method. The method comprises: step one, generating a depth image by interpolation of a certain grid according to a fitting plane reference plane; step two, with a digital differential correction technique, generating a reference plane image by using registration parameters, depth image models and thecollinear equations of the image and the point cloud; step three, carrying out rough matching by using SIFT matching, and carrying out dense matching on dense feature points extracted by a uniform grid by using a rough matching result as a constraint condition and other constraint conditions; step four, establishing a triangulation network by using a dense matching result, correcting an overlappedreference image based on radiation transformation parameters, and generating a corrected image by using an interpolating RGB method; and step five, according to a relationship between a depth image model and the reference image, generating a seamless color model for the corrected reference image by using a texture mapping technique.
Owner:陈年康
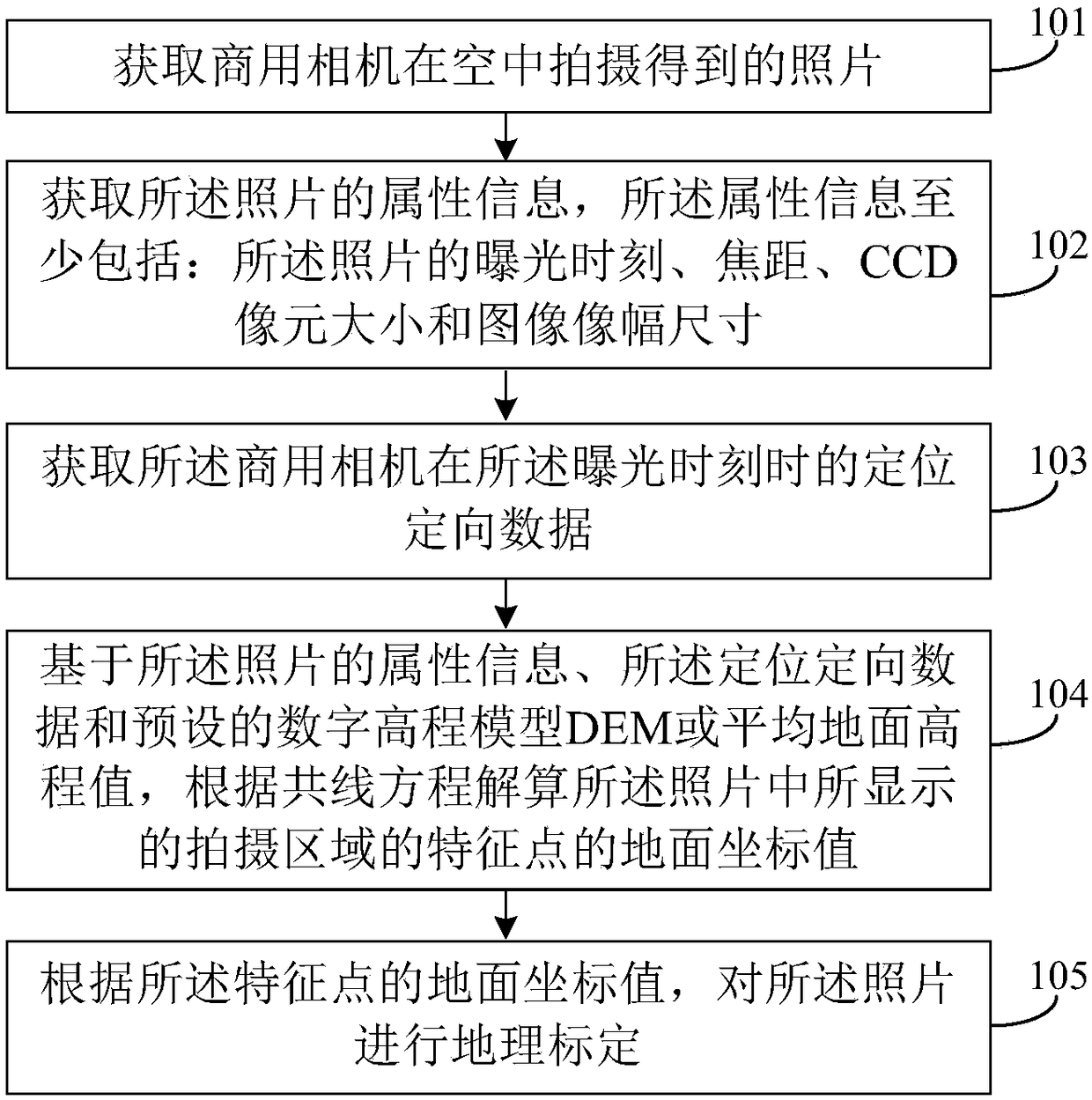
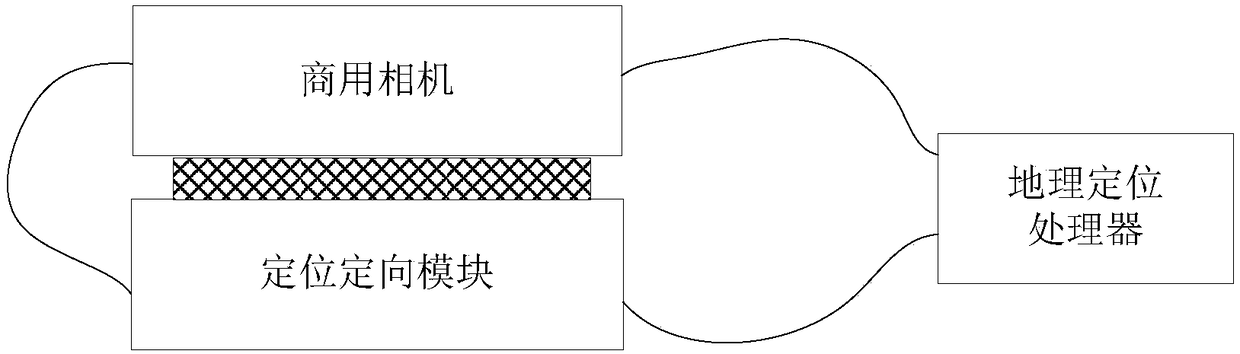
Method for realizing geographic calibration of commercial camera photo based on positioning and orientation data
InactiveCN108492334AMeet needsImage enhancementImage analysisCollinearity equationDigital elevation model
The invention relates to a method for realizing the geographic calibration of a commercial camera photo based on positioning and orientation data. The method comprises a step of acquiring a photo taken by a commercial camera in the air, a step of acquiring attribute information of the photo, wherein the attribute information includes an exposure time, a focal length, a CCD pixel size and an imageframe size, a step of obtaining the positioning and orientation data of the commercial camera at the exposure time, a step of solving a ground coordinate value of a characteristic point of a shootingarea displayed in the photo according to a collinearity equation based on the attribute information, the positioning and orientation data and a digital elevation model (DEM) or average ground elevation value, and a step of carrying out geographic calibration on the photo according to the ground coordinate value of the characteristic point. It can be seen that the geographic calibration of the photo is carried out through obtaining the positioning and orientation data of the commercial camera in taking the photo based on the photo attribute information, the positioning and orientation data, andthe DEM or average ground elevation value, and the position information of photo center point and corner point of the photo taken by the commercial camera, photo covering ground range information andactual location information of any target in the photo can be determined.
Owner:中国海监南海航空支队
Monocular camera-based planar moving target visual navigation method and system
ActiveCN112179357AHigh precisionImprove robustnessInstruments for road network navigationImage analysisPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
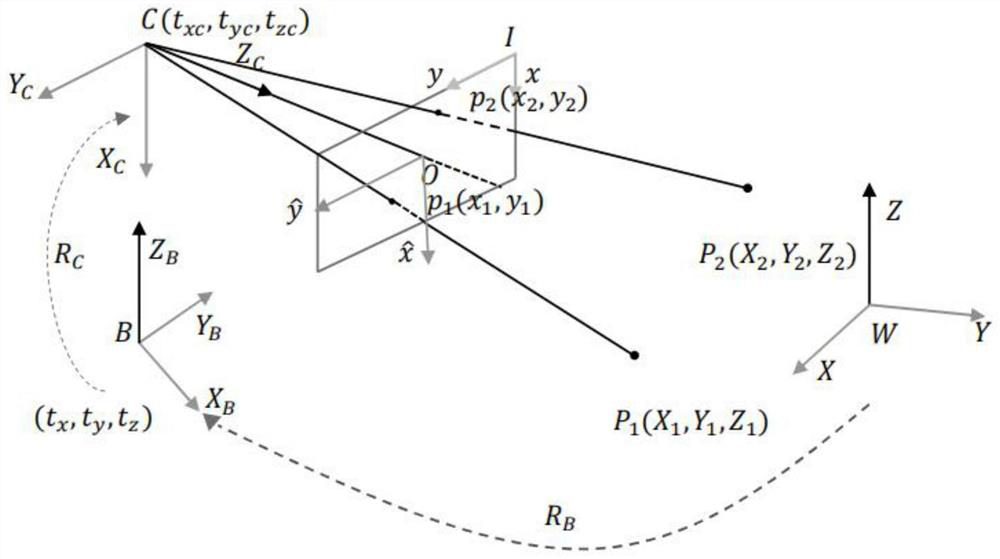
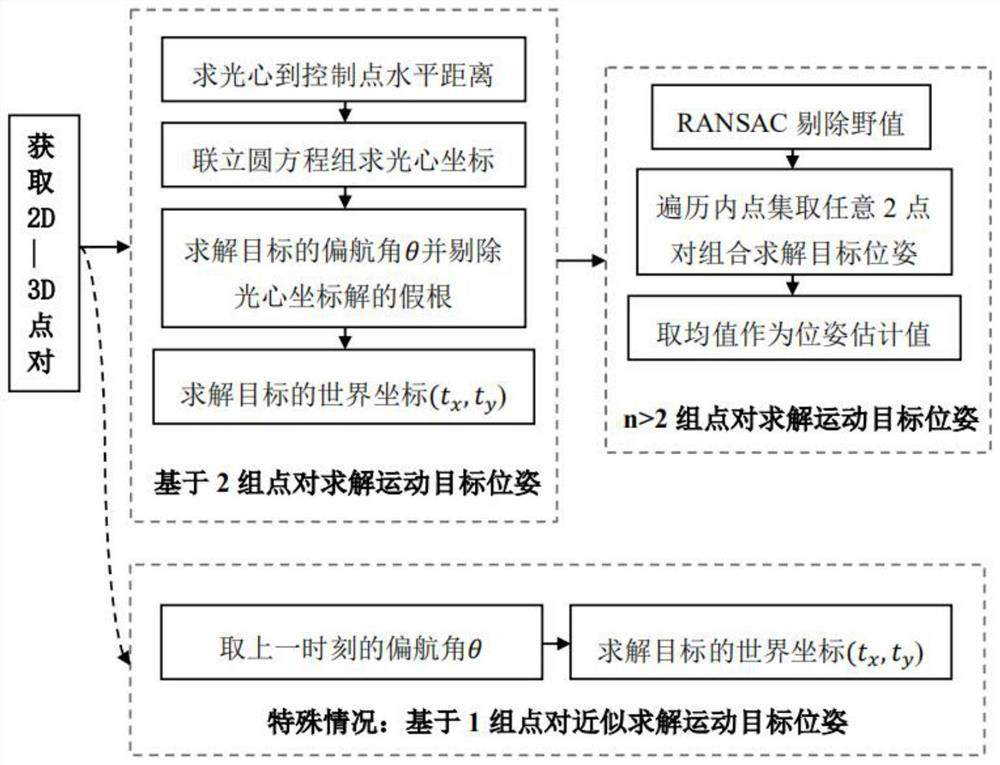
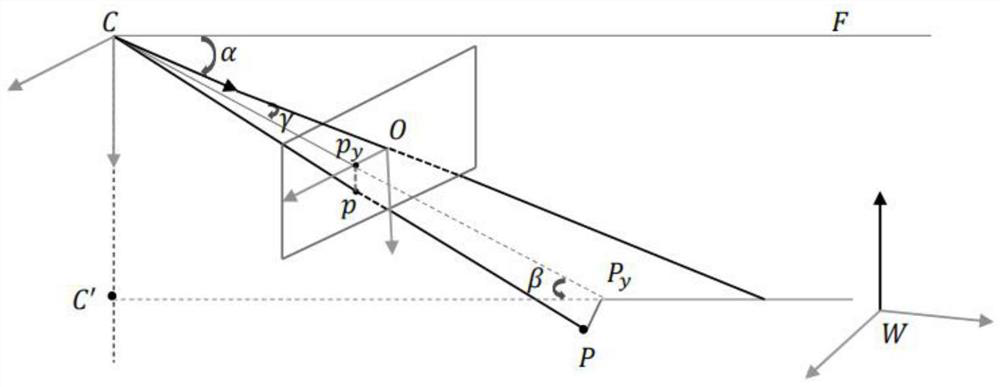
The invention relates to a monocular camera-based planar moving target visual navigation method and system. The method comprises the following steps of establishing a world coordinate system, a cameracoordinate system, a moving target coordinate system and a picture plane coordinate system, enabling the monocular camera to form a 2D-3D point pair by acquiring a control point and an image point pair of the control point falling on an image plane physical coordinate system in real time in the advancing process of the moving target, conducting coordinate transformation on the 2D-3D point pairs according to a coordinate system, and solving the pose of a moving target, and assisting the moving target to move forward according to the moving target pose. According to the method, an idea method of space geometry modeling and an RANSAC algorithm are adopted, a set of all possible positions of a camera optical center is modeled into a space circle with a control point as the circle center and the distance from the control point to the optical center as the radius, unknown position parameters and attitude parameters in a collinear equation are decoupled and then solved respectively, and meanwhile, the RANSAC algorithm is used for eliminating outliers; and the method is a high-speed, high-robustness and high-precision real-time visual navigation method.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
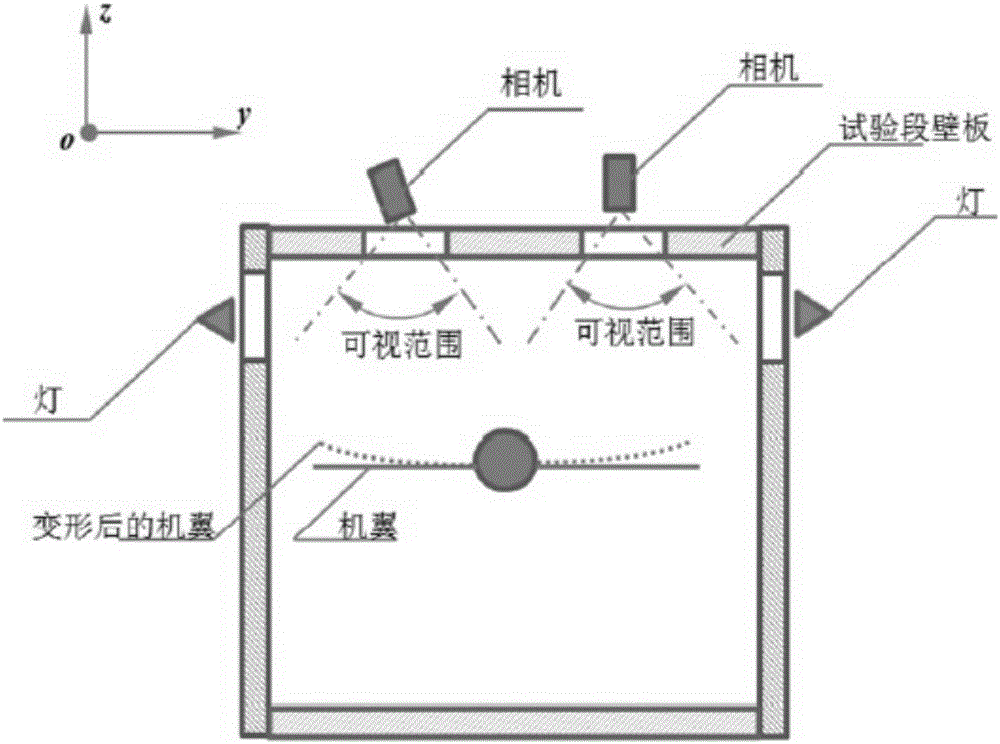
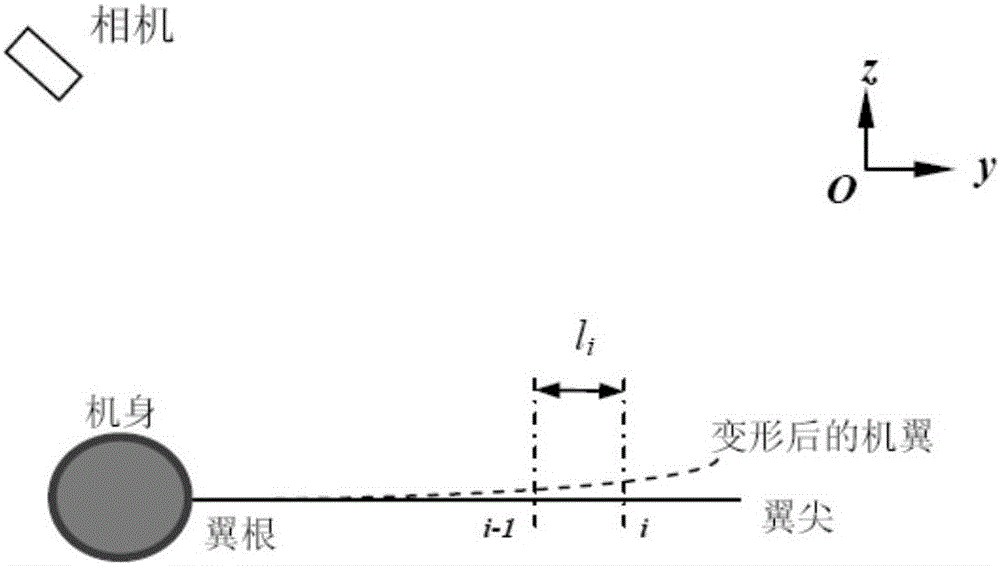
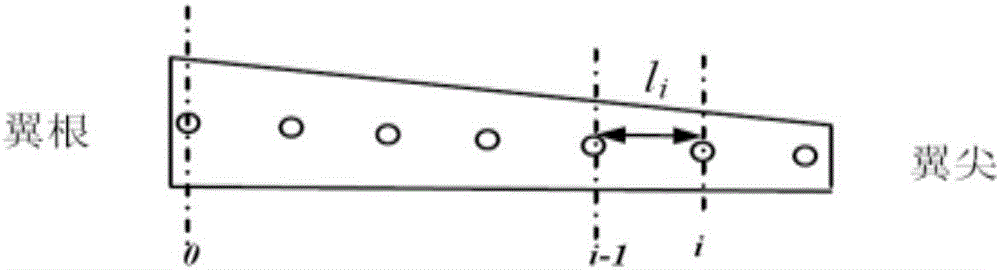
Monocular video high precision measuring method for wing wind tunnel test model elastic deformation
ActiveCN106323587AGuaranteed accuracyReduce hardware costsAerodynamic testingObservational errorMeasurement device
The invention discloses a monocular video high precision measuring method for wing wind tunnel test model elastic deformation. Based on a fact that relative deformation of two adjacent cross sections of a wing wind tunnel test model is small linear elasticity deformation, coordinate figures of corners and deformation mark points Y of all cross sections are orderly calculated from a wing root according to a superposition principle; a conventional monocular video measuring method is adopted, the coordinate figures of the deformation mark points Y are brought in a collinearity equation, and deformation data of the mark points on all the cross sections can be orderly obtained. Via the monocular video high precision measuring method, monocular video measurement errors of wing wind tunnel test model elastic deformation can be greatly reduced, only one camera needs to be used, multi-view video measurement precision can be obtained, hardware cost of a measurement device can be lowered, tedious homonymous point matching work of multi-view video measurement can be prevented, the monocular video high precision measuring method is particularly suitable for an environment where camera installation positions are limited, and the monocular video high precision measuring method has great engineering application prospects.
Owner:INST OF HIGH SPEED AERODYNAMICS OF CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
Method for positioning forest fire at night via unmanned aerial vehicle
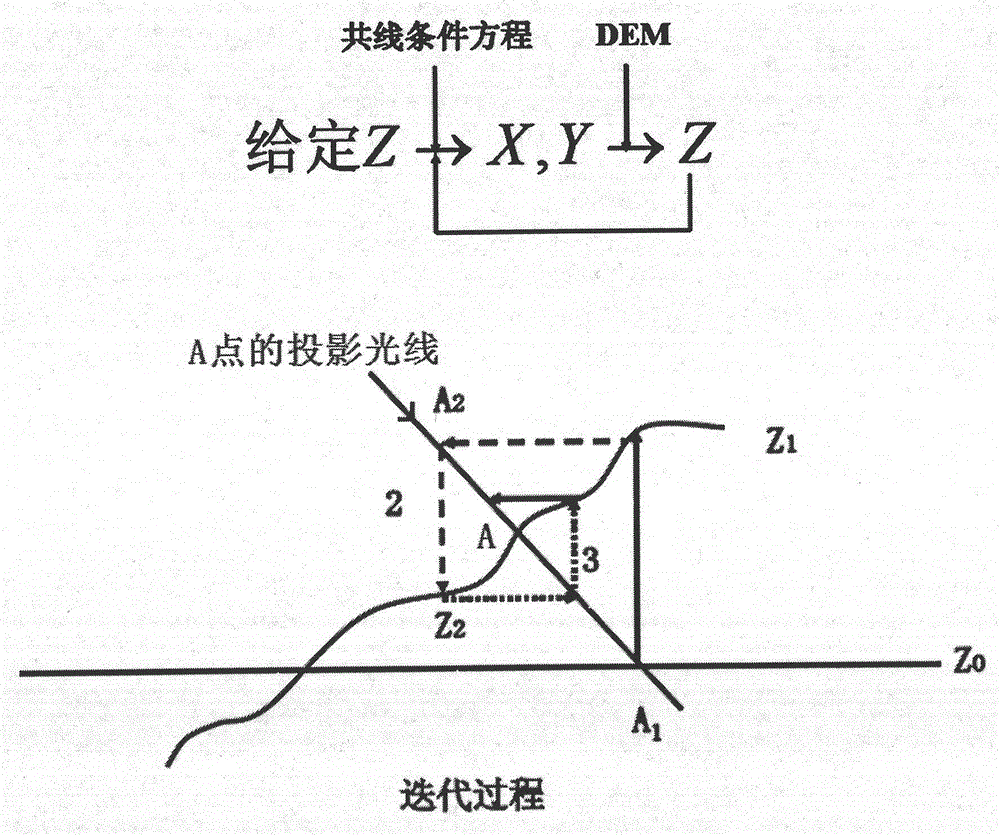
The invention provides a method for positioning a forest fire at night via an unmanned aerial vehicle. An unmanned aerial vehicle with a POS system and a digital camera is used for positioning a forest fire at night. The onboard POS system can directly record six exterior orientation elements of an image shot by the camera at a certain moment; the interior orientation elements of the image shot by the camera are x0, y0 and f; it is supposed that any object space point A is a fire point, the object space coordinates of A is XA, YA and ZA, the image plane coordinates of a corresponding image point a of A is x and y, and an equation set for resolving the space coordinates of A is obtained through the collinearity equations; since only the direction of the fire point A can be obtained according to the position of a when the orientation of the aviation image in space is determined, the spatial position of the fire point A can be determined as long as the elevation of the point is obtained; and the projection light (XA and YA) of the fire point A can be determined in virtue of the equation set, and the spatial position of the fire point A can be obtained as the elevation information (ZA) of DEM data is used and an iterative solving method is employed.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Photogrametry method based on double panorama
ActiveCN106123863AEasy to operateImprove accuracyPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryObject pointStereo image
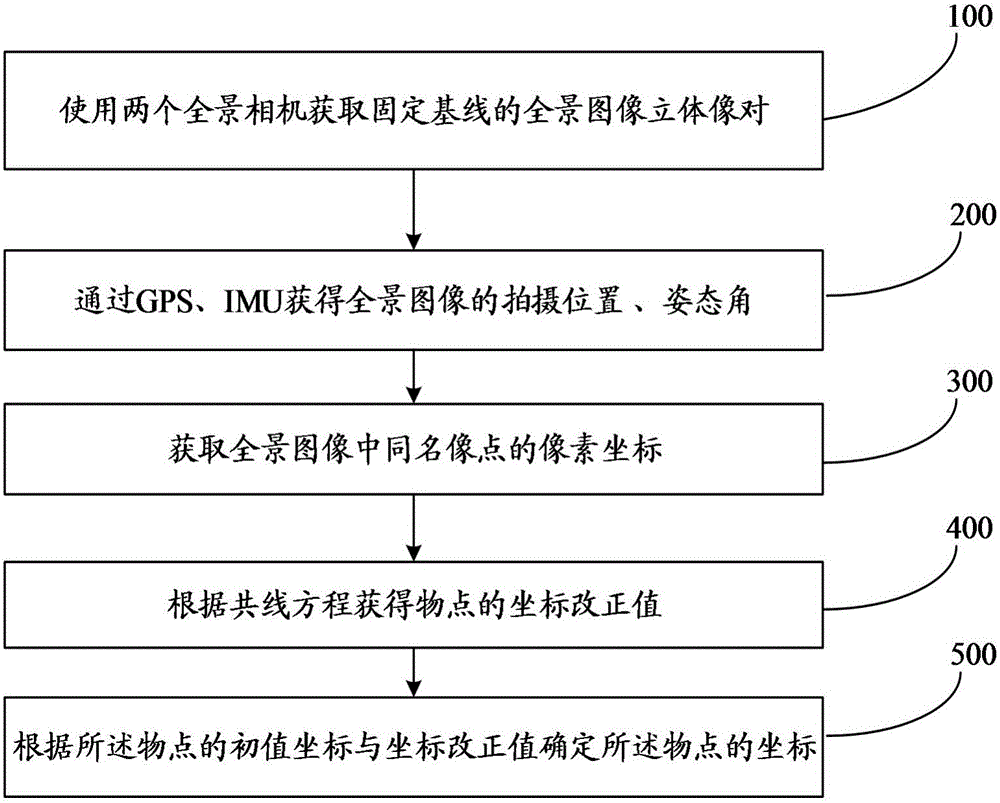
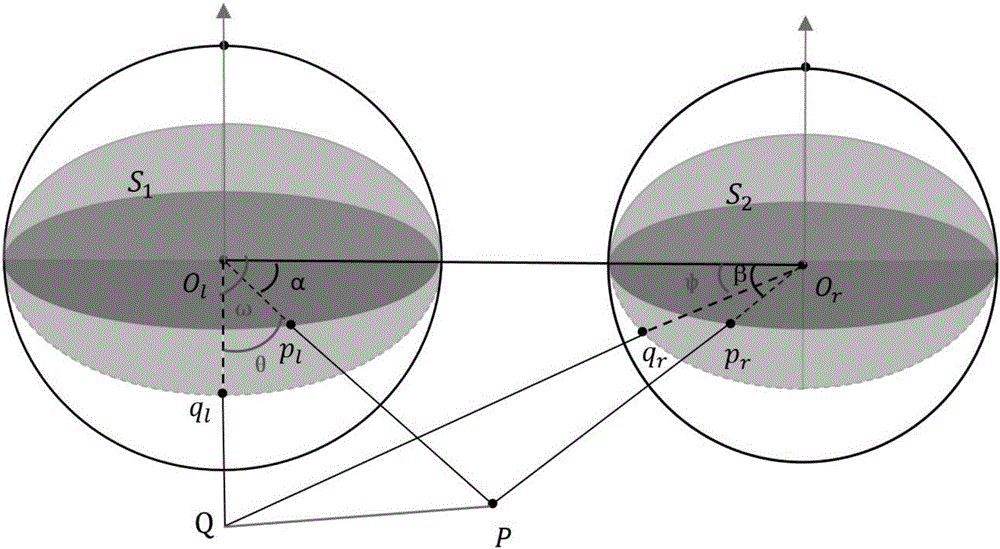
The present invention discloses a photogrametry method based on double panorama. The photogrametry method comprises: 1, acquiring the panorama image stereo image pair of a fixed baseline by using two panorama cameras; 2, acquiring the shooting position and the attitude angle of the panorama image through GPS and IMU; 3, acquiring the coordinates of image points having the same name in the panorama image; 4, acquiring the coordinate correction value of an object point according to a collinearity equation; and 5, determining the coordinate of the object point according to the original value coordinate and the coordinate correction value of the object point. According to the present invention, the pixel coordinate of the object point in the panorama image can be accurately determined by acquiring the panorama image through the two panorama image cameras and by acquiring the coordinates of the pair of the image points having the same name, and the advantages of convenient operation, convenient operation, high accuracy, effective measurement efficient improving and cost reducing are provided.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
Ballistic missile three-dimensional trajectory estimation method based on infrared early warning image
ActiveCN111462182AReduce mistakesImprove trajectory accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisTrajectory of a projectileInfrared remote sensing
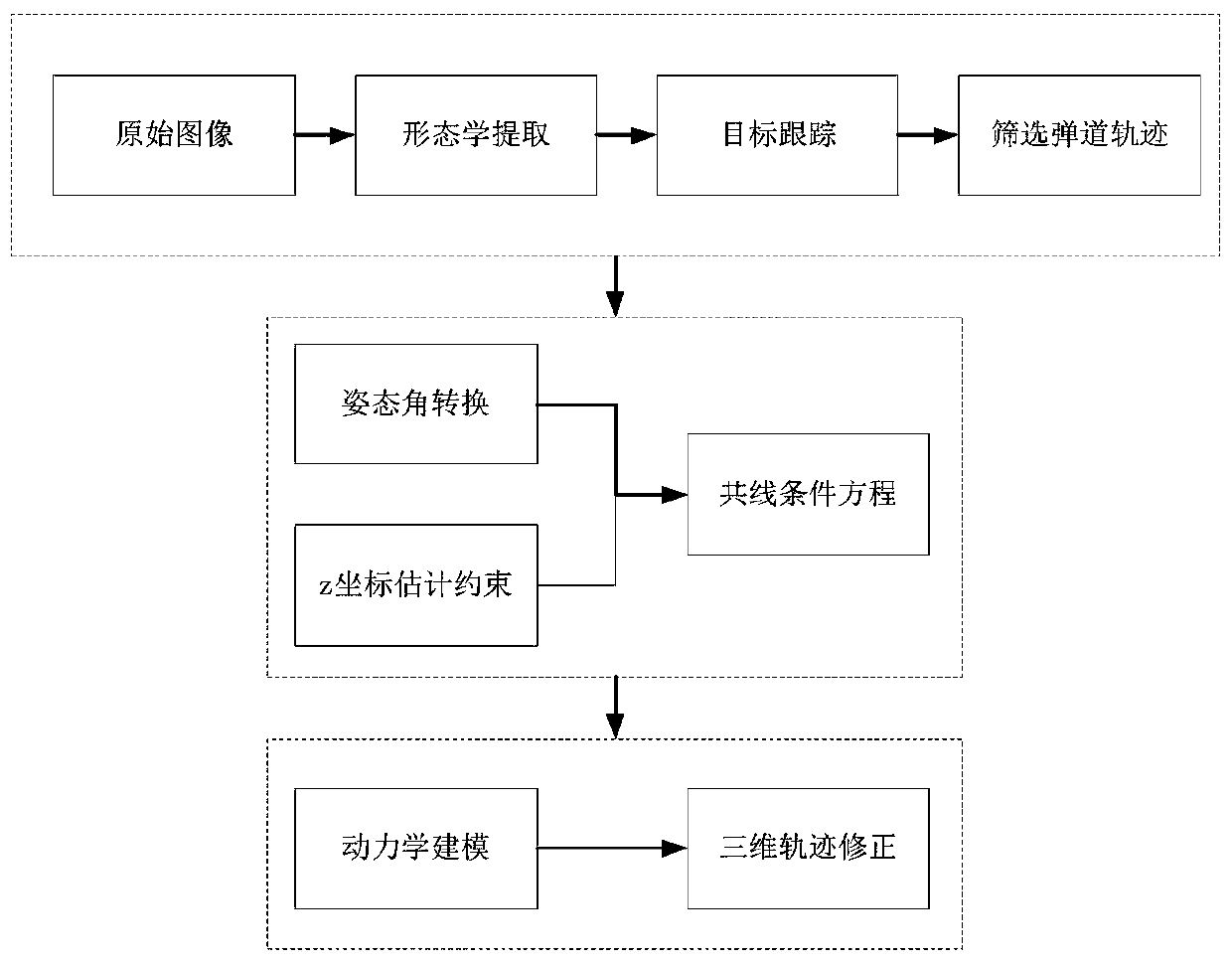
The invention discloses a ballistic missile three-dimensional trajectory estimation method based on an infrared early warning image, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the point target detection of a pre-obtained missile infrared remote sensing image in a continuous time sequence, and extracting the pixel coordinates of the mass center of a target of each image point; according to the extracted time and space information of the target point, tracking the target and obtaining a motion trail; conducting ballistic missile trajectory screening on ballistic missile motion characteristic analysis; unifying the attitude data and the orbit data of the missile target in a coordinate system; predicting a target three-dimensional trajectory through a collinear equation and a constraintcondition in a z direction according to the image plane two-dimensional trajectory; and correcting the error track according to the kinematic model of the missile and the constraint condition of the active section of the missile. According to the method, three dimensions are estimated from two dimensions, and a new scheme is provided for tracking and early warning of missiles.
Owner:SUZHOU ZHONGKE IMAGE SKY REMOTE SENSING TECH CO LTD
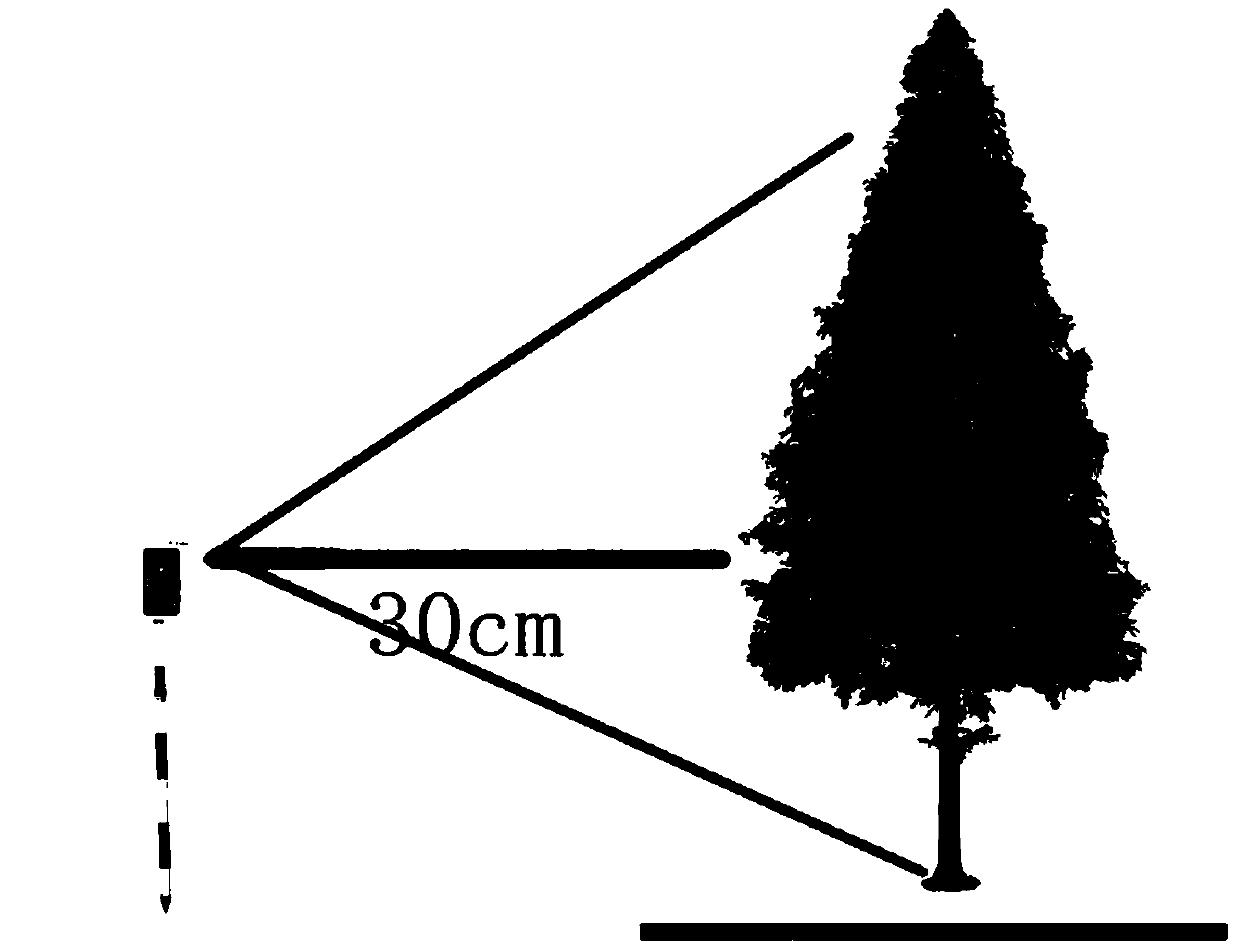
Intelligent mobile phone tree measuring device and tree measuring method thereof
InactiveCN110411360AReduce the intensity of measurement workRealize measurementUsing optical meansAlgorithmDiameter at breast height
The invention discloses an intelligent mobile phone tree measuring device and a tree measuring method thereof. An intelligent mobile phone is erected by utilizing a flower rod, a standing tree in a to-be-measured area is measured by normal case photography, and coordinates B, L and H and rotation angles phi, omega and kappa can be determined according to a mobile phone positioning function and anelectronic compass; and by utilizing a collinearity equation principle, according to the distance between the flower rod and the to-be-measured tree, the focal length f and image point image space coordinates (ui, vi) of corresponding feature points, object space coordinates (Xi, Yi, Zi) of corresponding points are calculated out, and then the diameter-at-breast-height value of the standing tree is calculated.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com