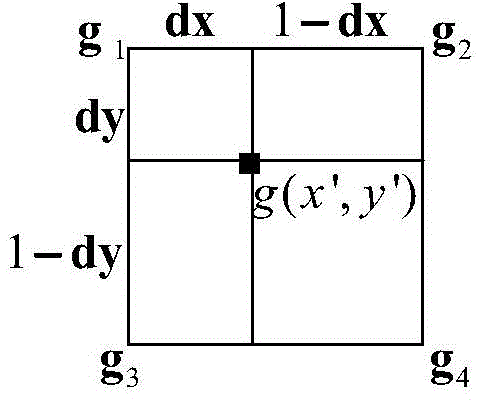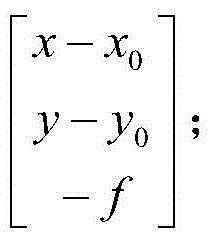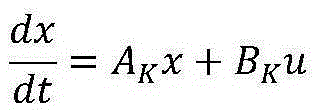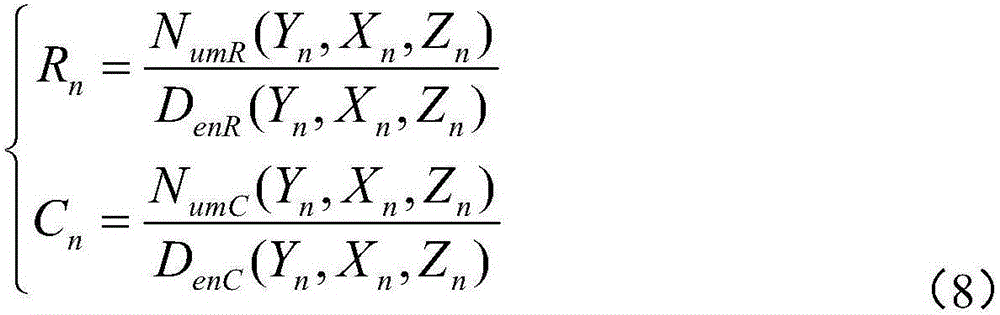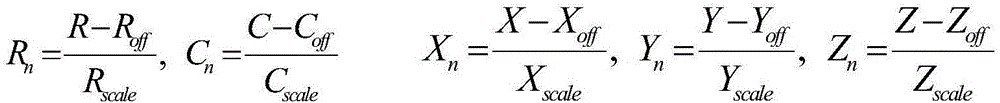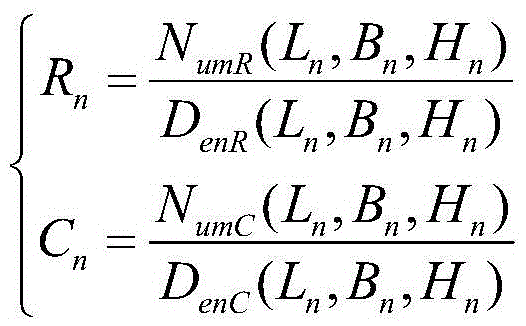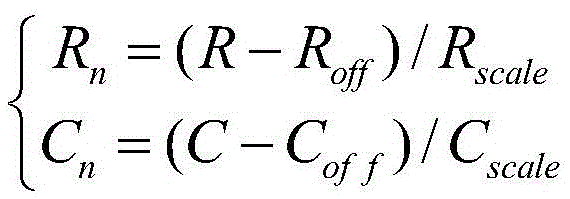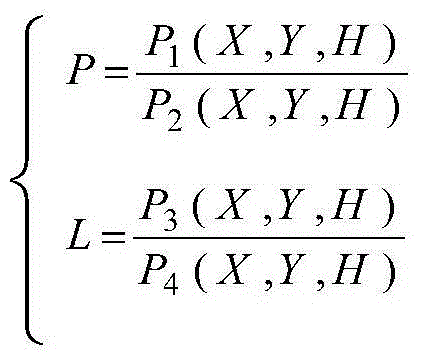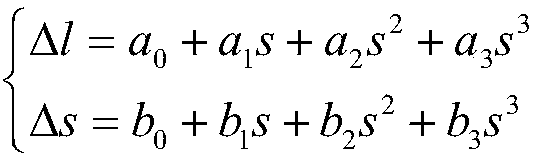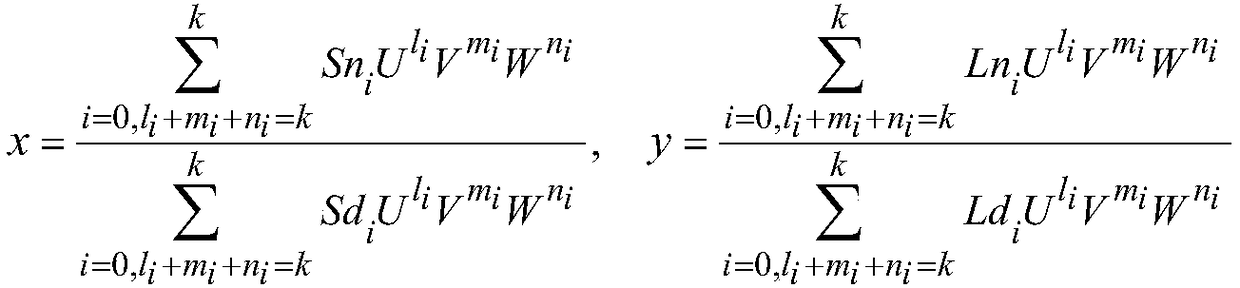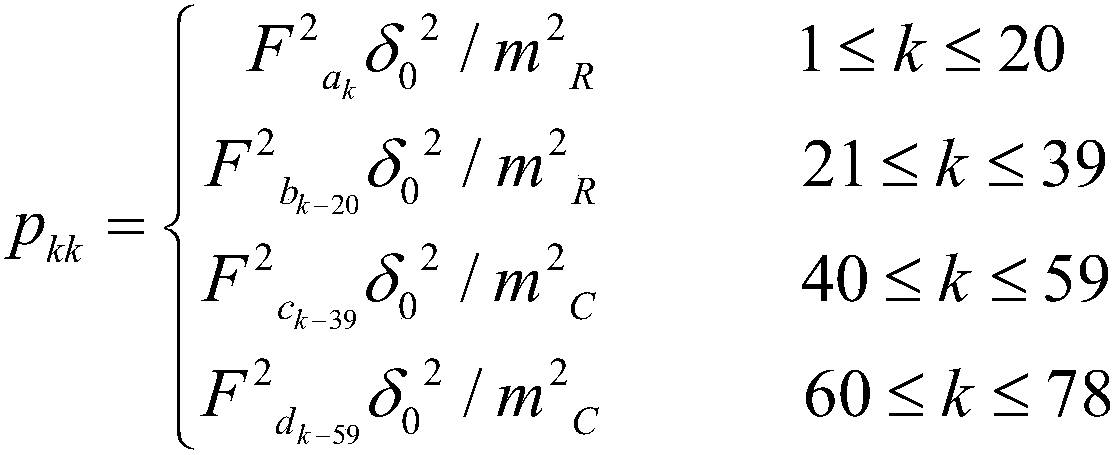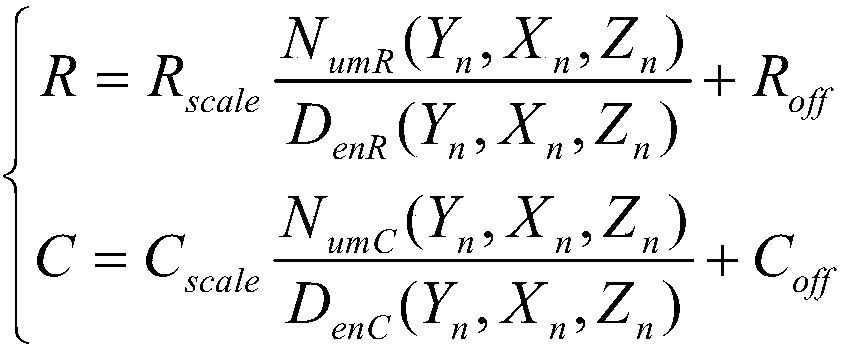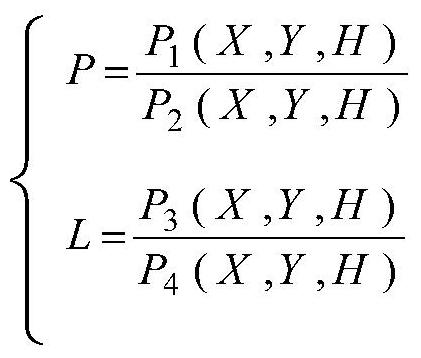Patents
Literature
48 results about "Rational polynomial" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A rational polynomial is a polynomial having rational coefficients. While the term "rational polynomial" is sometimes used as a synonym for rational function, this usage is strongly discouraged since by analogy with complex polynomial and integer polynomial, "rational polynomial" should properly refer to a polynomial with rational coefficients.
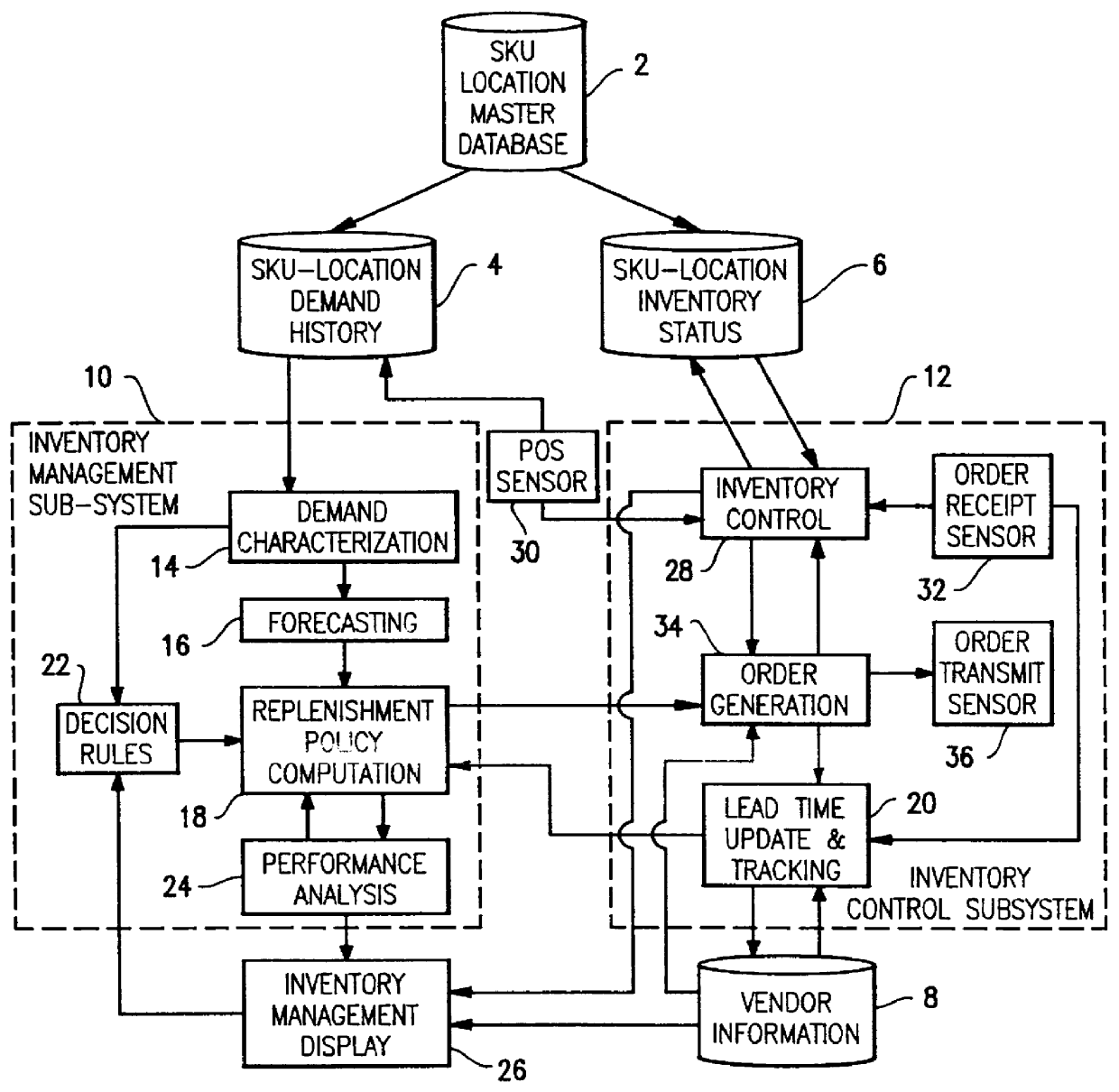
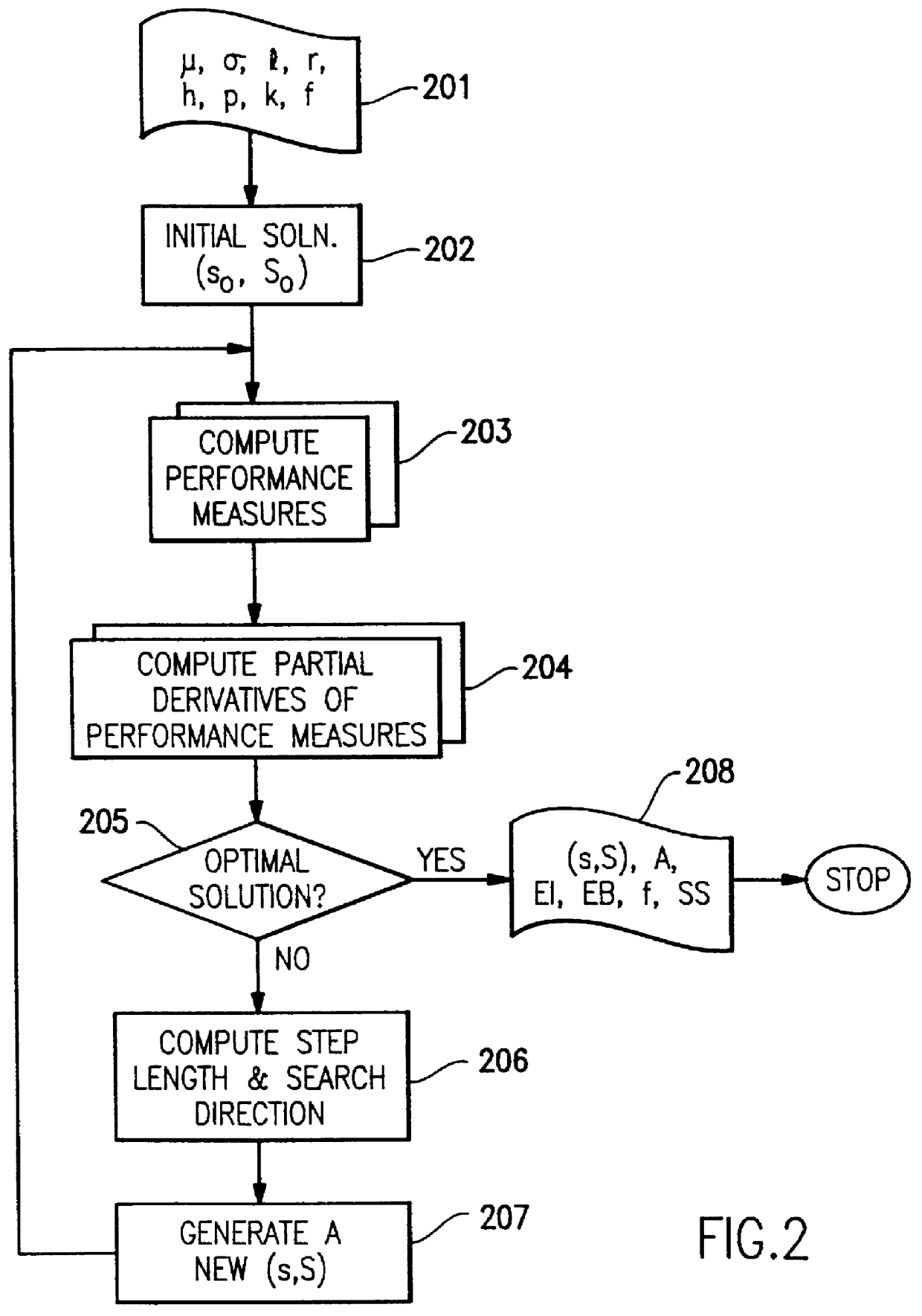
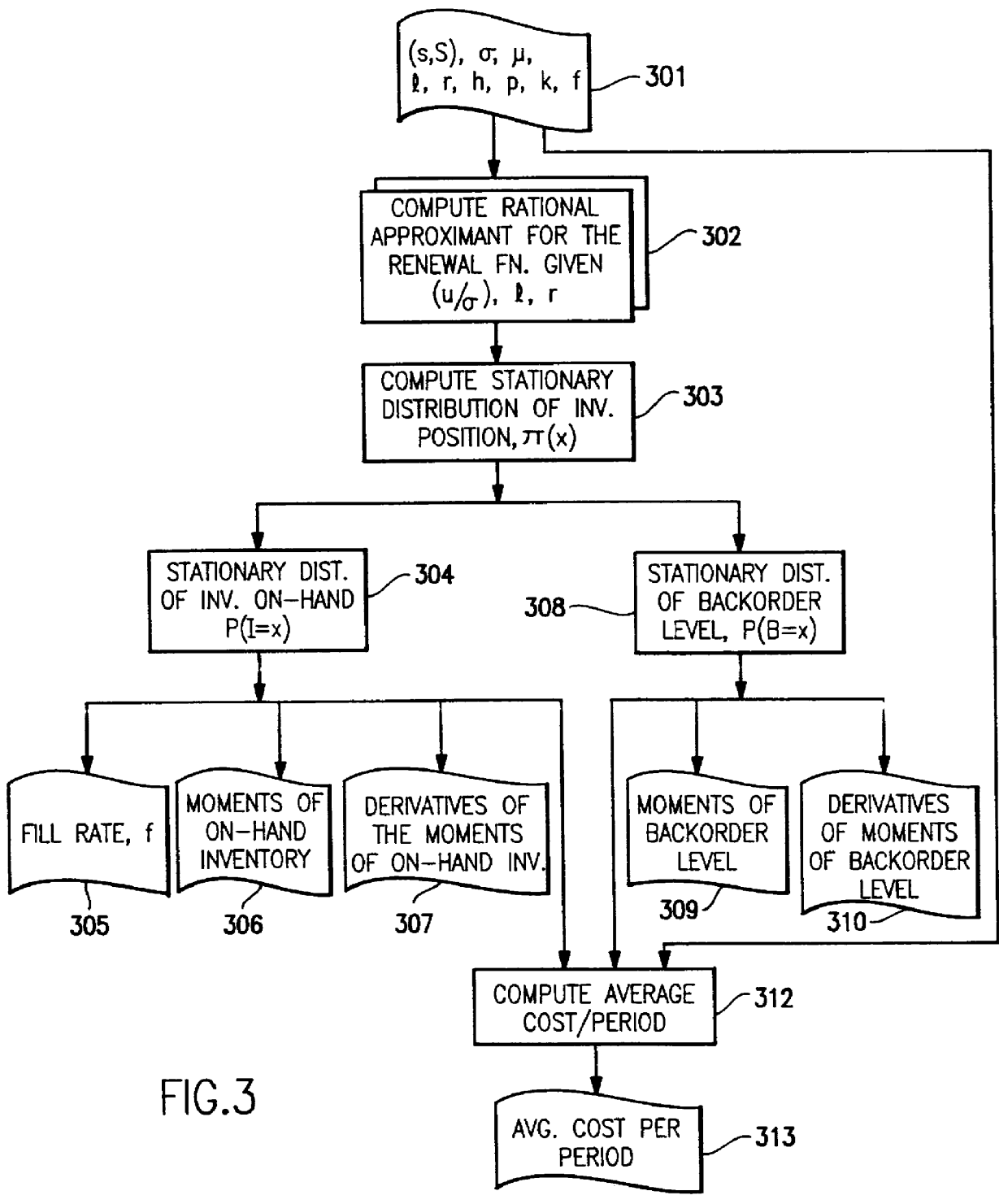
Method for fast and accurate evaluation of periodic review inventory policy
InactiveUS6144945AThe process is fast and accurateLogisticsSpecial data processing applicationsRegular distributionComputational problem
A computer implemented process is provided for fast and accurate evaluation of the performance characteristics of the periodic-review (s,S) inventory policy with complete back ordering. This policy has an underlying stochastic process that is a renewal process. The method provides a novel computer implementation of a fast and accurate way to compute approximations of the renewal function. In order to overcome the computational problems in evaluating renewal functions numerically, an approximation scheme has been devised whereby the renewal function of the truncated normal distribution can be characterized by two parameters: (1) its coefficient of variation, and (2) the point at which the function needs to be evaluated. This approximation is derived in two stages. In the first stage, a class of rational polynomial approximations are developed to the renewal function, called Pad+E,acu e+EE approximants. In the second stage, polynomial expressions are derived for each coefficient of the Pad+E,acu e+EE approximants in terms of the coefficient of variation of the distribution.
Owner:IBM CORP
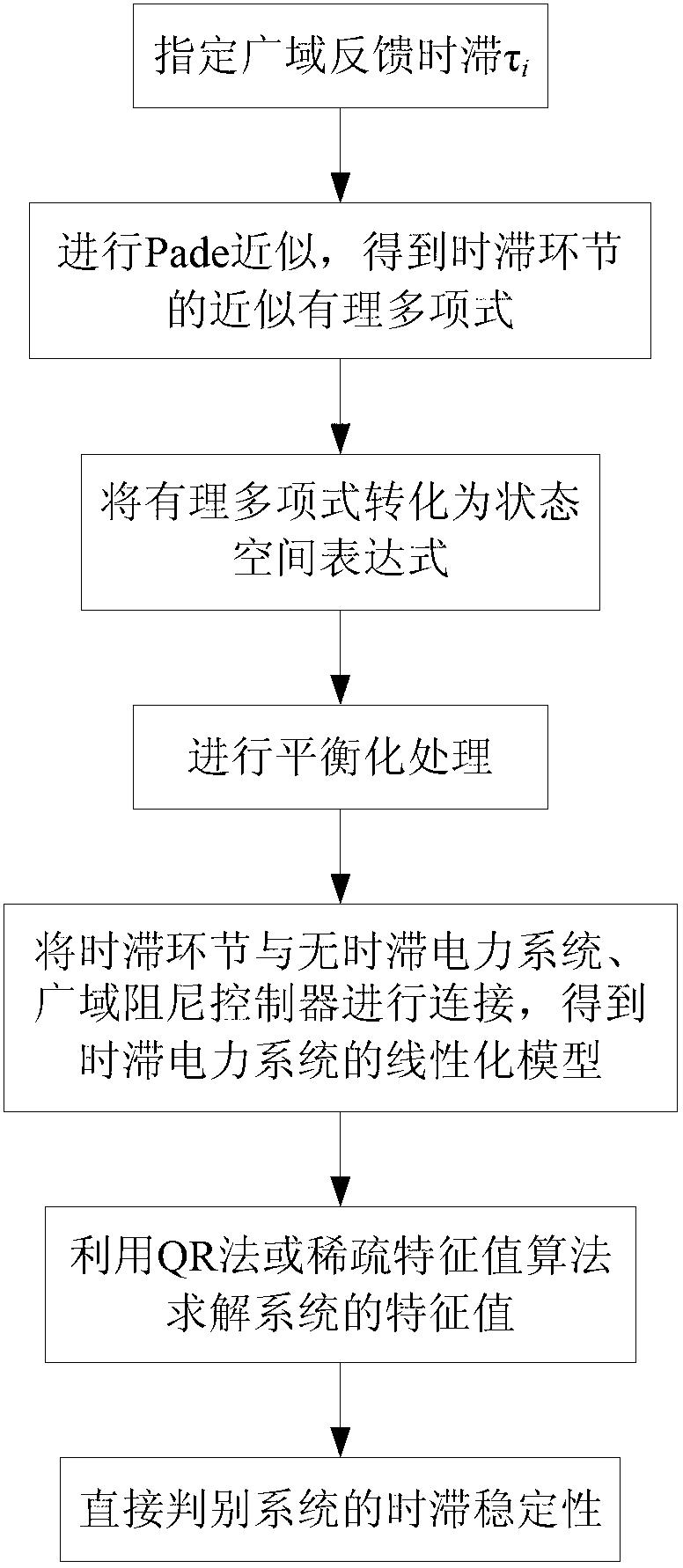
Method for calculating time-lag electric power system eigenvalue and discriminating stability based on Pade approximation
The invention discloses a method for calculating time-lag electric power system eigenvalues and discriminating stability based on Pade approximation. The method uses Pade approximation to make wide area feedback time-lag approximate to a rational polynomial. Though connecting with an electric power system without time-lag and a wide area damping controller, a linearized model of the time-lag electric power system is established. Finally, part of characteristic roots of the time-lag system is directly obtained according to a system state matrix, and then time-lag stability of the system is determined. According to an eigenvalue calculating result of a four-machine two-region example system, the method can relatively accurately solve part of the eigenvalues and eigenvectors which are corresponding to dynamic elements in the time-lag system. The method can conveniently and accurately determine time-lag stability of the system, correctly solve the number of the eigenvalues which are corresponding to a time-lag link and calculate precision which is related to order of the rational polynomial. In addition, the method is advantaged by small calculated amount, and short calculating time.
Owner:RES INST OF ECONOMICS & TECH STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER
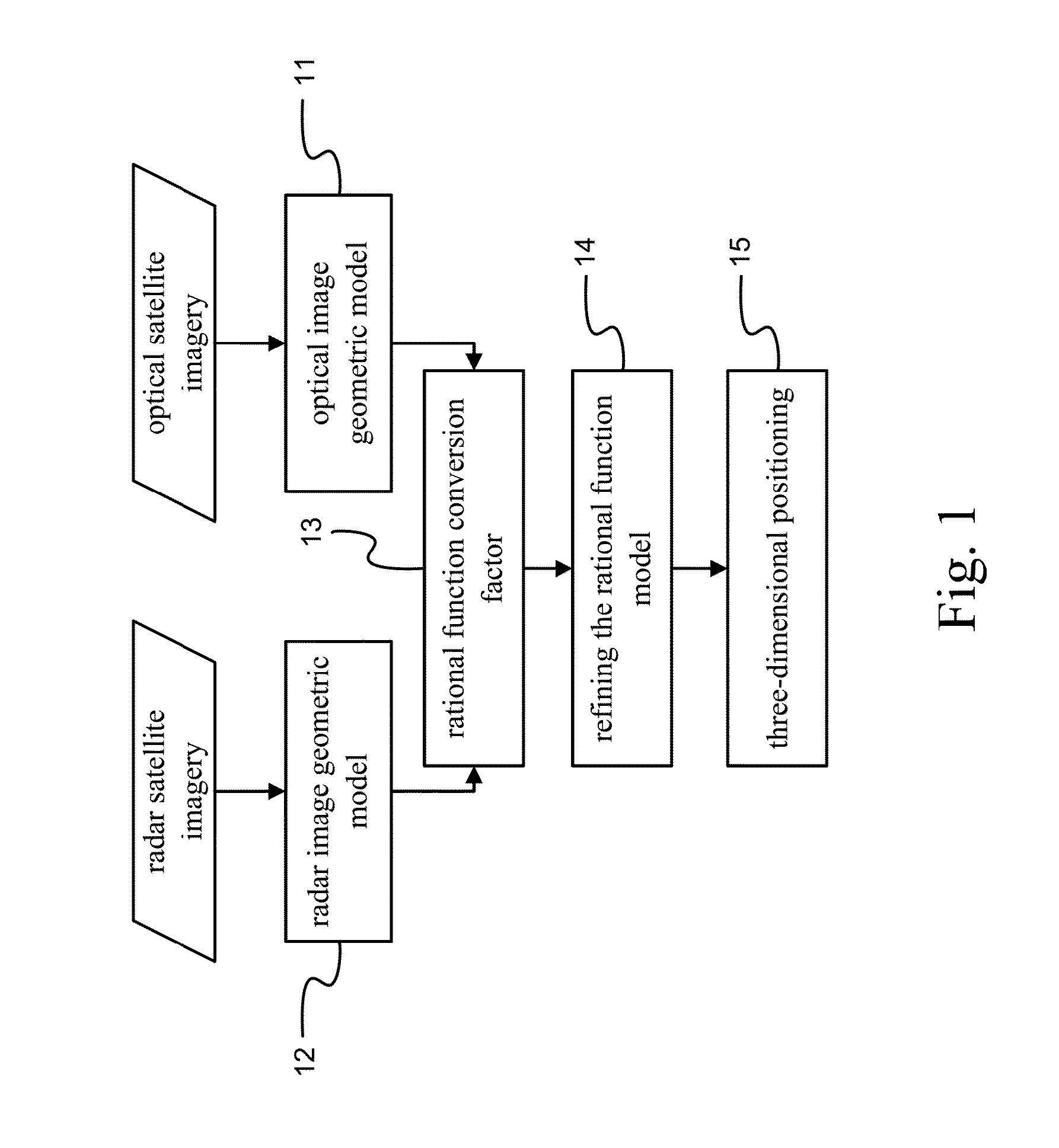
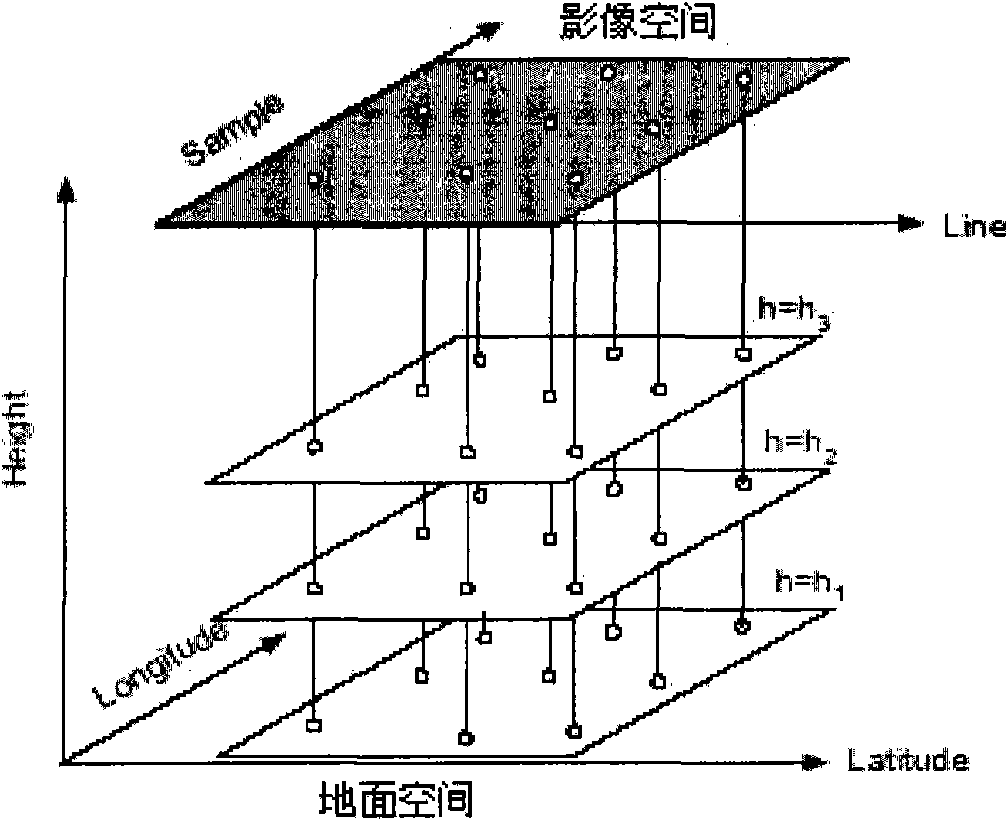
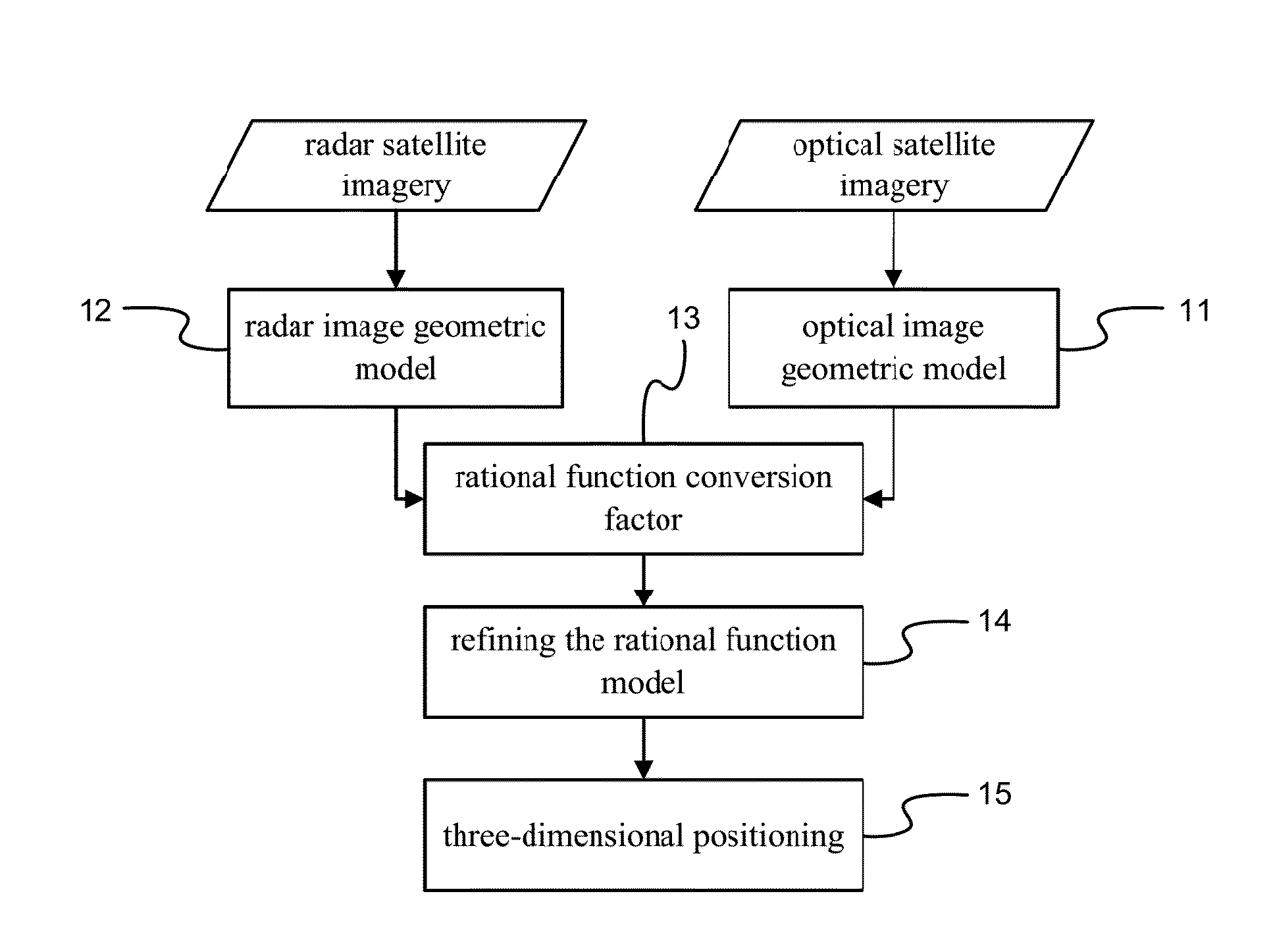
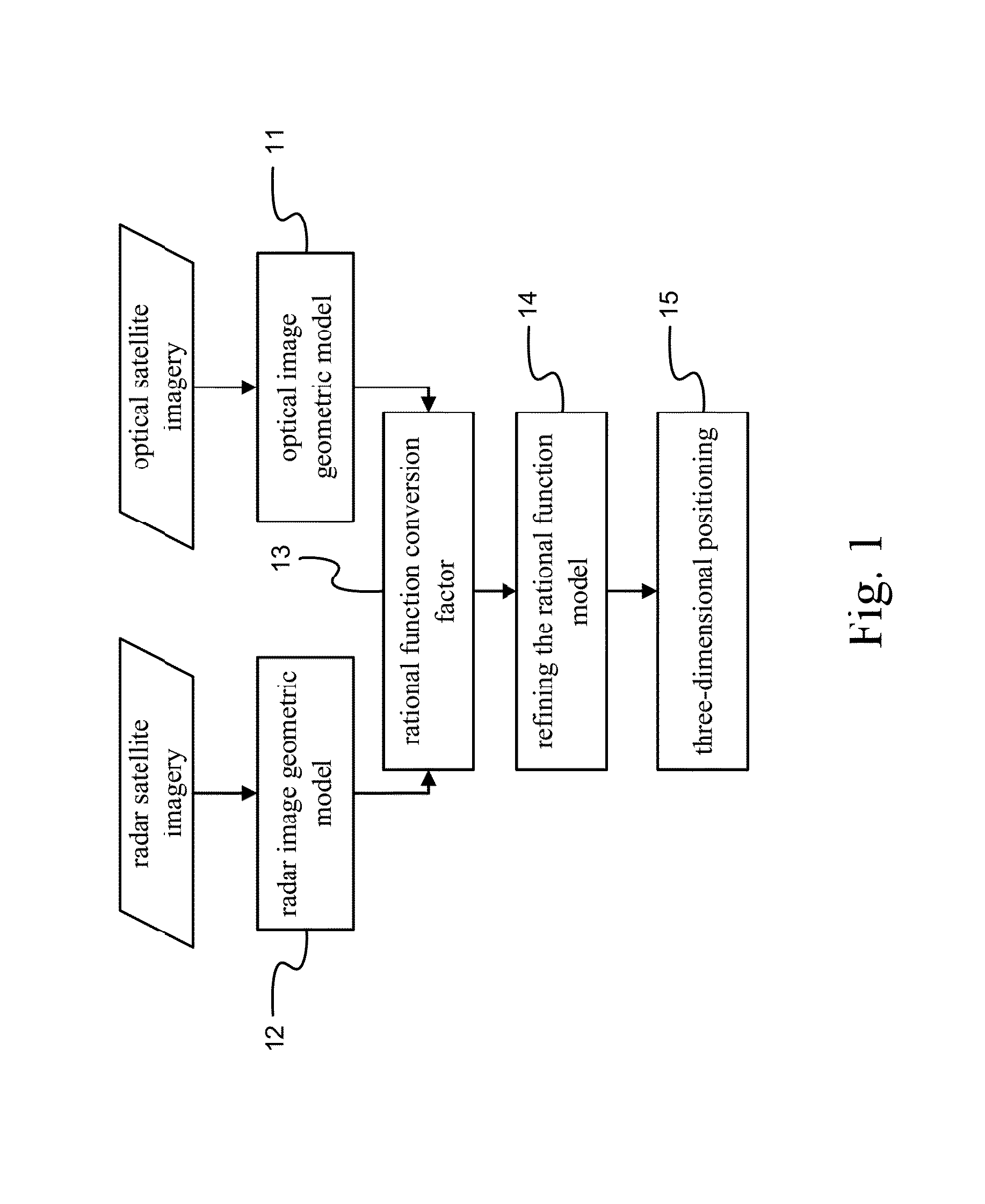
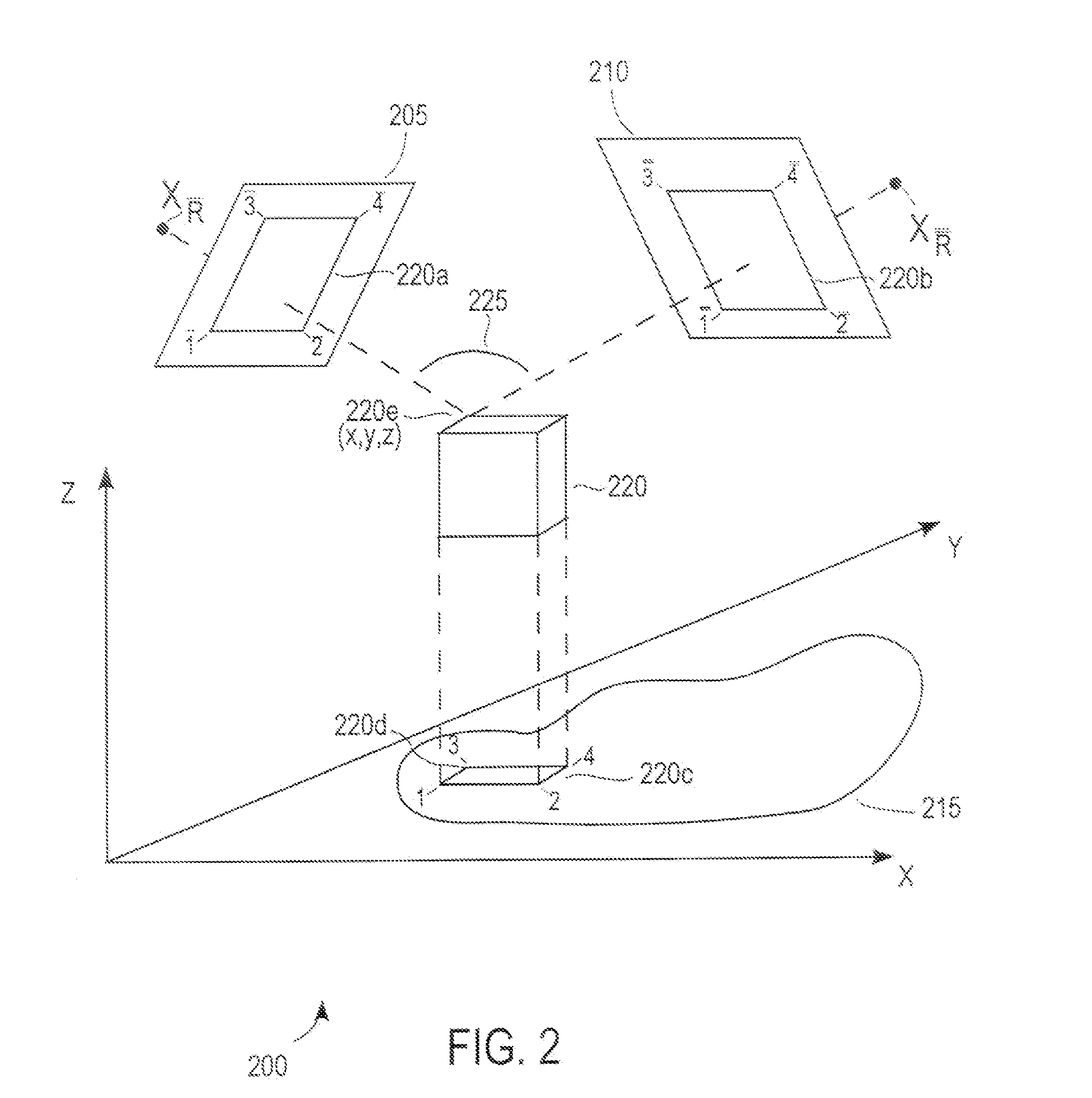
Three-dimensional positioning method
InactiveUS20140191894A1Improve shortcomingsImage enhancementImage analysisRadarConversion coefficients
A three-dimensional positioning method includes establishing the geometric model of optical and radar sensors, obtaining rational function conversion coefficient, refining the rational function model and positioning the three-dimensional coordinates. Most of the radar satellite companies and part of the optical satellite only provide satellite ephemeris data, rather than the rational function model. Therefore, it is necessary to obtain the rational polynomial coefficients from the geometric model of optical and radar sensors; followed by refining the rational function model by the ground control points, so that object image space intersection is more serious; and then followed by measuring the conjugate point on the optical and radar images. Finally, the observation equation is established by the rational function model to solve the three-dimensional coordinates. It is obvious from the above results that the integration of optical and radar images does achieve the three-dimensional positioning.
Owner:NAT CENT UNIV
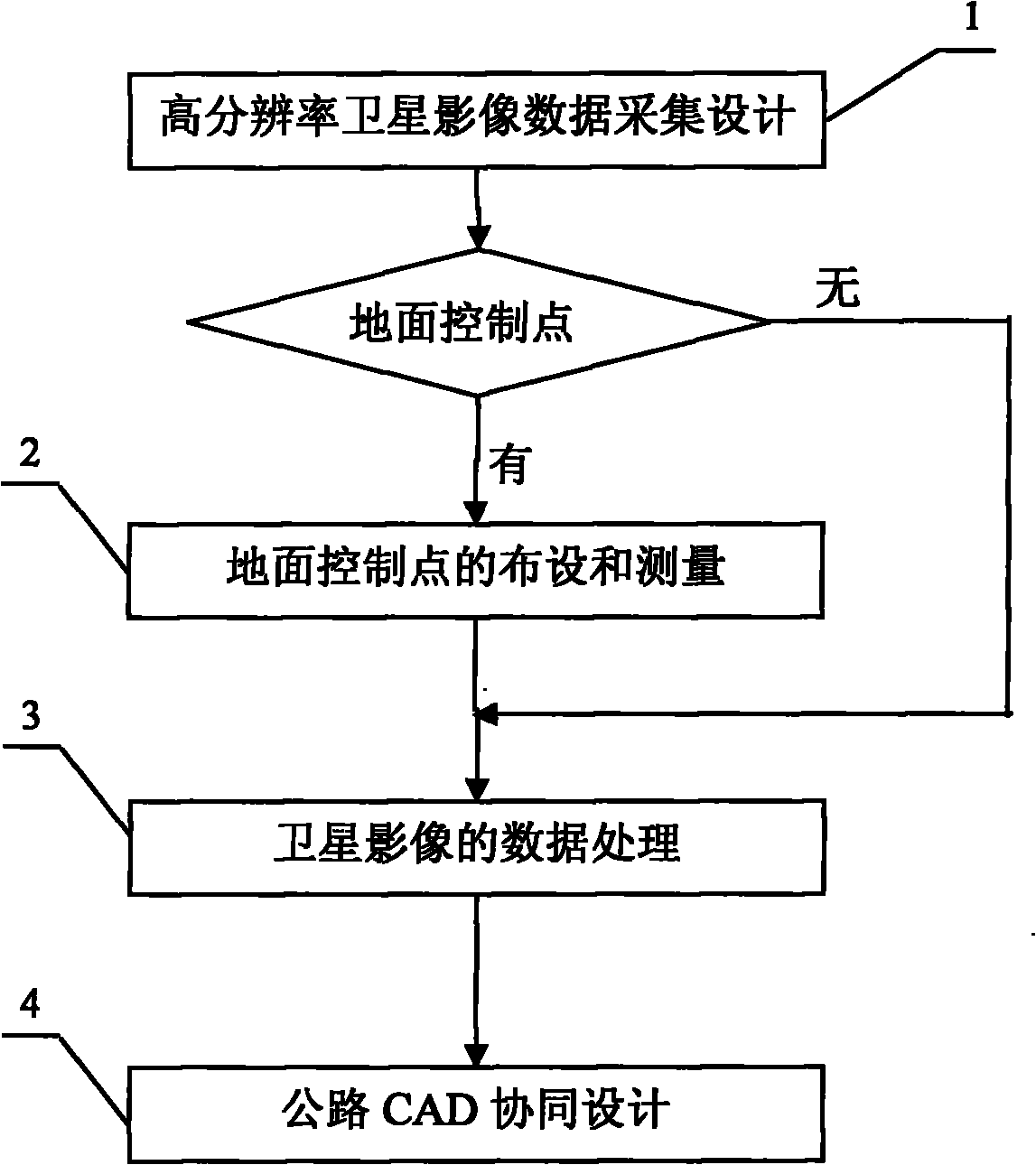
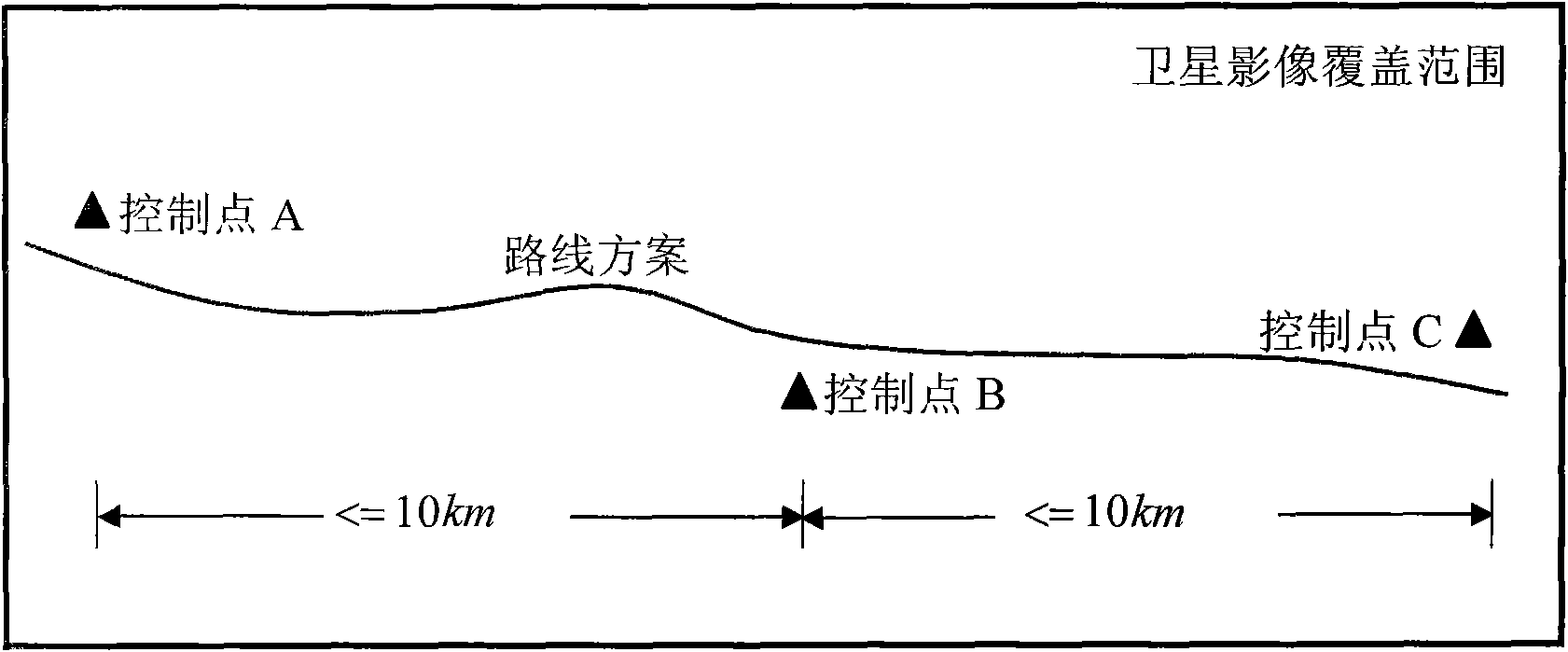
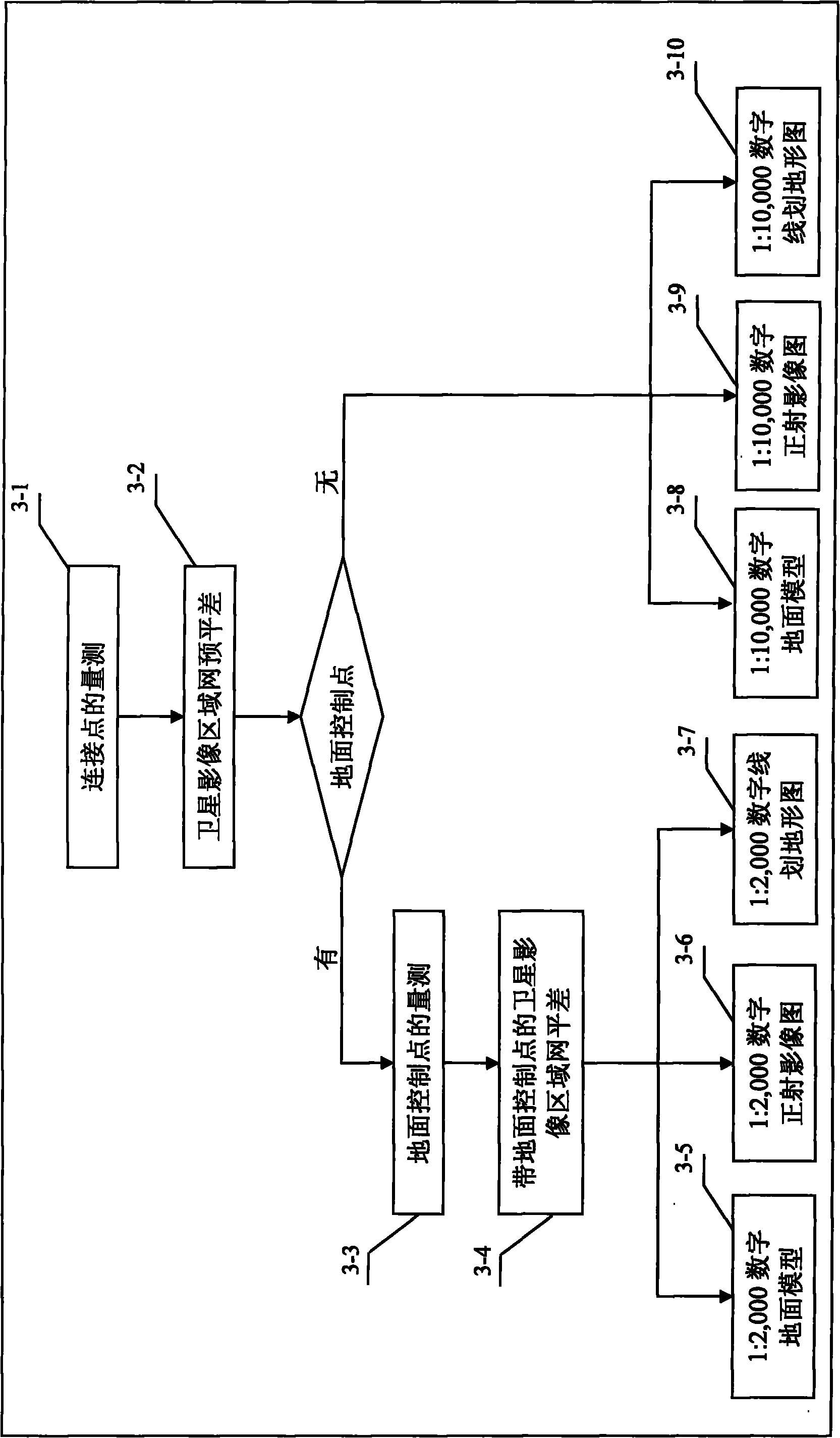
Road survey and design method based on high-resolution satellite image
ActiveCN101814102AReduce field workShorten the test and design cycleElectromagnetic wave reradiationSpecial data processing applicationsTopographic mapOrthophotomap
The invention discloses a road survey and design method based on a high-resolution satellite image, which comprises the following steps: A, determining a scope to be covered by a satellite image according to a route scheme, selecting a high-resolution satellite and a sensor for collection, and designing and collecting three-dimensional images of the high-resolution satellite; B, when a scale of 1 to 2,000 is formed, laying and measuring field ground control points and laying control points along the route; C, generating a digital ground model, a digital orthophotomap and a digital line topographic map for the road route area through area adjustment of the three-dimensional images of the high-resolution satellite based on rational polynomial parameters of the images of the high-resolution satellite; and D, calculating engineering quantities and generating route design drawings and tables through measurement of the high-resolution satellite and collaborative design of the road CAD. The invention realizes the measurement of the high-resolution satellite and the collaborative design of the road CAD, thereby greatly reducing the field workload, shortening the survey and design period, and producing significant economic and social benefits.
Owner:CCCC SECOND HIGHWAY CONSULTANTS CO LTD
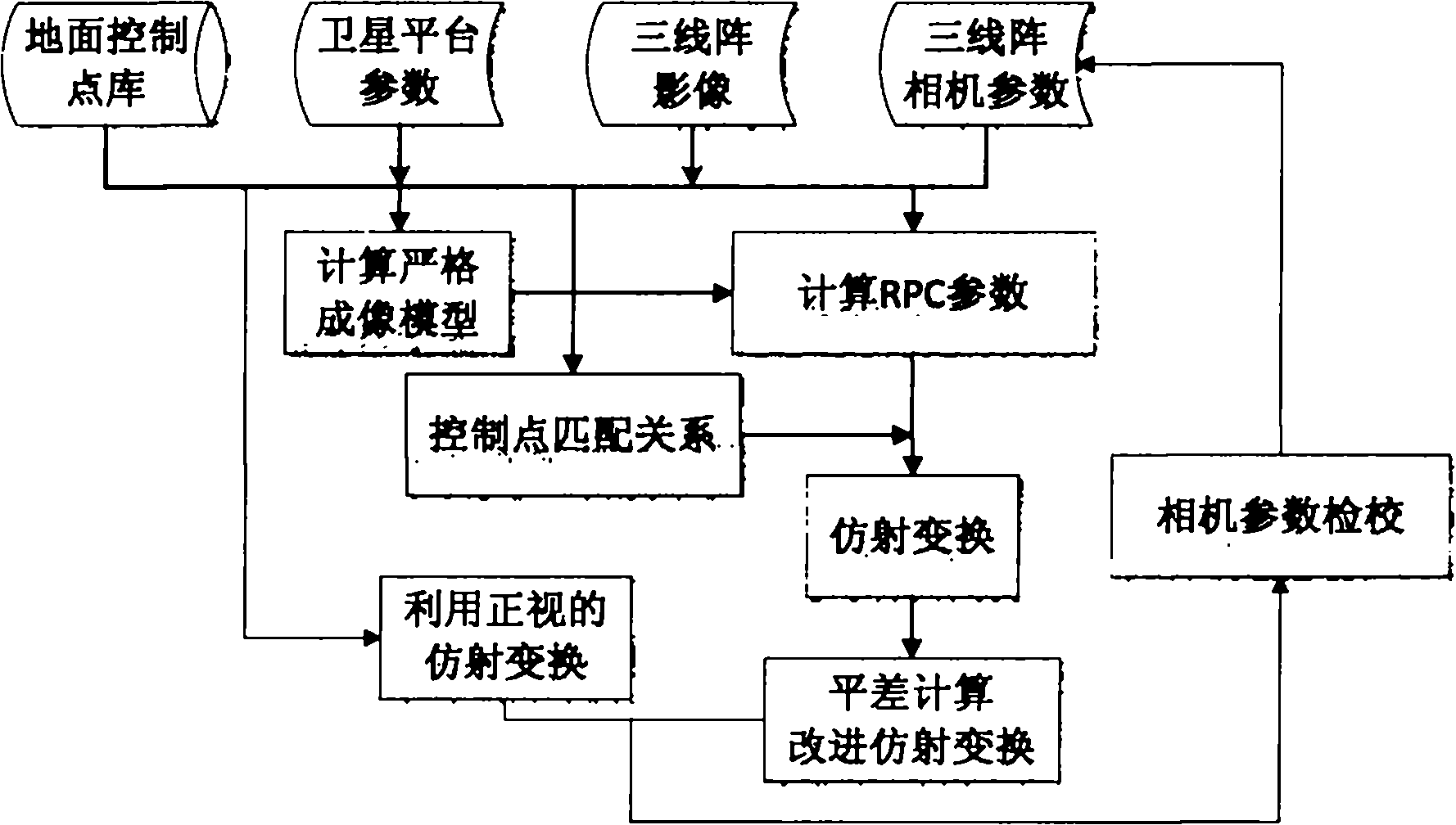
RPC-based method for improving and calibrating block adjustment of three-linear array three-dimensional satellite
ActiveCN102168972ASolve computational difficultiesImprove compatibilityPicture interpretationArea networkImage matching
The invention relates to a rational-polynomial-coefficients (RPC)-based method for improving and calibrating the block adjustment of a three-linear array three-dimensional satellite, which comprises the following steps of: (1) determining the mapping relationship between ground points and image points, namely a strict imaging model; (2) solving RPC parameters of each image in three linear arrays according to the strict imaging model, and searching for connection points among the three linear arrays by image matching; (3) listing three affine transformation formulas of fore sight, front sight and back sight of the three-linear array images; (4) establishing an error equation and solving to acquire corrections of affine transformation parameters, and revising the affine transformation formulas by utilizing the corrections; (5) listing the affine transformation formulas of the fore sight and the back sight again by utilizing camera parameters and the revised affine transformation formula of the front sight; and (6) solving the revised affine transformation formulas of the fore sight and the back sight in the step (4) and the listed affine transformation formulas of the fore sight and the back sight in the step (5) simultaneously to acquire the corrections of the camera parameters, and revising the camera parameters to improve and calibrate the block adjustment of the three-linear array three-dimensional satellite.
Owner:CHINA CENT FOR RESOURCES SATELLITE DATA & APPL
Method for splicing ZY3 satellite three-line-scanner image and multispectral image
ActiveCN103914808AFacilitate subsequent geometry processingEasy to handle geometryGeometric image transformationImaging processingImaging modalities
The invention relates to a method for splicing a ZY3 satellite three-line-scanner image and a multispectral image. The method includes the following steps of building a precise imaging geometrical model of a real CCD linear array, building a precise imaging geometrical model of a virtual CCD linear array according to the precise imaging geometrical model of the real CCD linear array, building a rational polynomial model of the spliced images, and finishing splicing of the ZY3 satellite three-line-scanner image and the multispectral image. By the inner view field splicing scheme based on the virtual CCD linear array, a distortionless CCD array is built on a focal plane, and reimaging is carried out on a plurality of original CCD imaging images according to a line central projection imaging method, so that line central projection seamless splicing of the CCD imaging images is achieved. The method can be widely applied to image processing of the ZY3 satellite.
Owner:SATELLITE SURVEYING & MAPPING APPL CENTSASMAC NAT ADMINISTATION OF SURVEYING MAPPING & GEOINFORMATION OF CHINANASG
Three-dimensional positioning method
InactiveUS20160259044A1Improve shortcomingsEffectively improves the shortcomingsImage enhancementImage analysisRadarGeometric modeling
A three-dimensional positioning system includes establishing a geometric model for optical AND radar sensors, obtaining rational function conversion coefficients, refining the rational function model and positioning three-dimensional coordinates. The system calculates rational polynomial coefficients from a geometric model of optical AND radar sensors, followed by refining a rational function model by determined ground control points and object image space intersection. The system then measures one or more conjugate points on the optical and radar images. Finally, an observation equation is established by the rational function model to solve and display three-dimensional coordinates.
Owner:NAT CENT UNIV
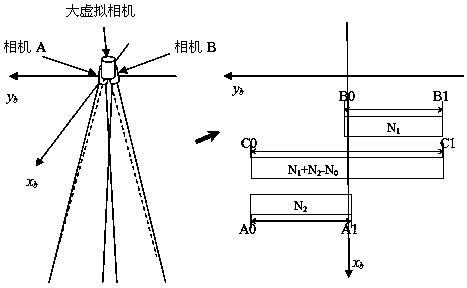
Narrow-view-field double-camera image fusion method based on large virtual camera
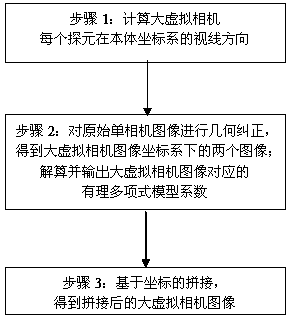
InactiveCN103697864ARealize splicingNo human intervention requiredGeometric image transformationPicture interpretationCamera imageBack calculation
The invention discloses a narrow-view-field double-camera image fusion method based on a large virtual camera. The narrow-view-field double-camera image fusion method comprises the steps of constructing the large virtual camera according to two single cameras, and constructing geometric imaging parameters of the large virtual camera according to geometric imaging parameters of the two single cameras; constructing corresponding geometric imaging models according to the geometric imaging parameters of the two cameras and the large virtual cameras; calculating and outputting a rational polynomial model coefficient corresponding to the large virtual camera; respectively performing indirect-method geometric correction on images of the two single cameras according to a coordinate forward calculation process and a coordinate back calculation process based on the geometric imaging models to obtain two images under an image coordinate system of the large virtual camera, and obtaining a fused image of the large virtual camera. According to the narrow-view-field double-camera image fusion method based on the large virtual camera, the concept of the large virtual camera is ingeniously used; high-precision fusion of the images of the two cameras in a narrow view field is realized, and the rational polynomial model coefficient corresponding to the large virtual camera is supplied; furthermore, the processing procedure is fully automatic, and manual intervention is not needed; the narrow-view-field double-camera image fusion method is applicable to a ground preprocessing procedure.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
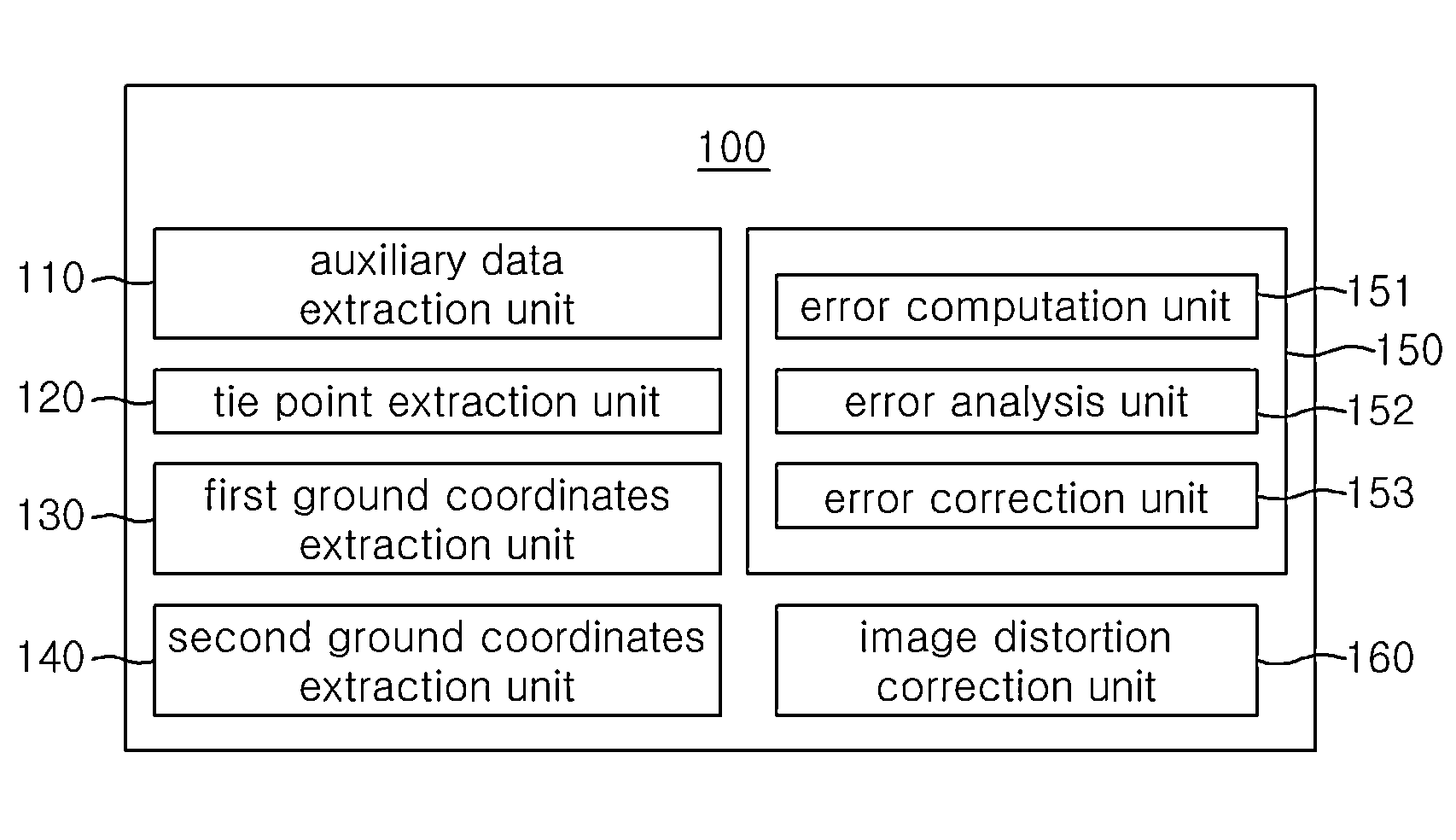
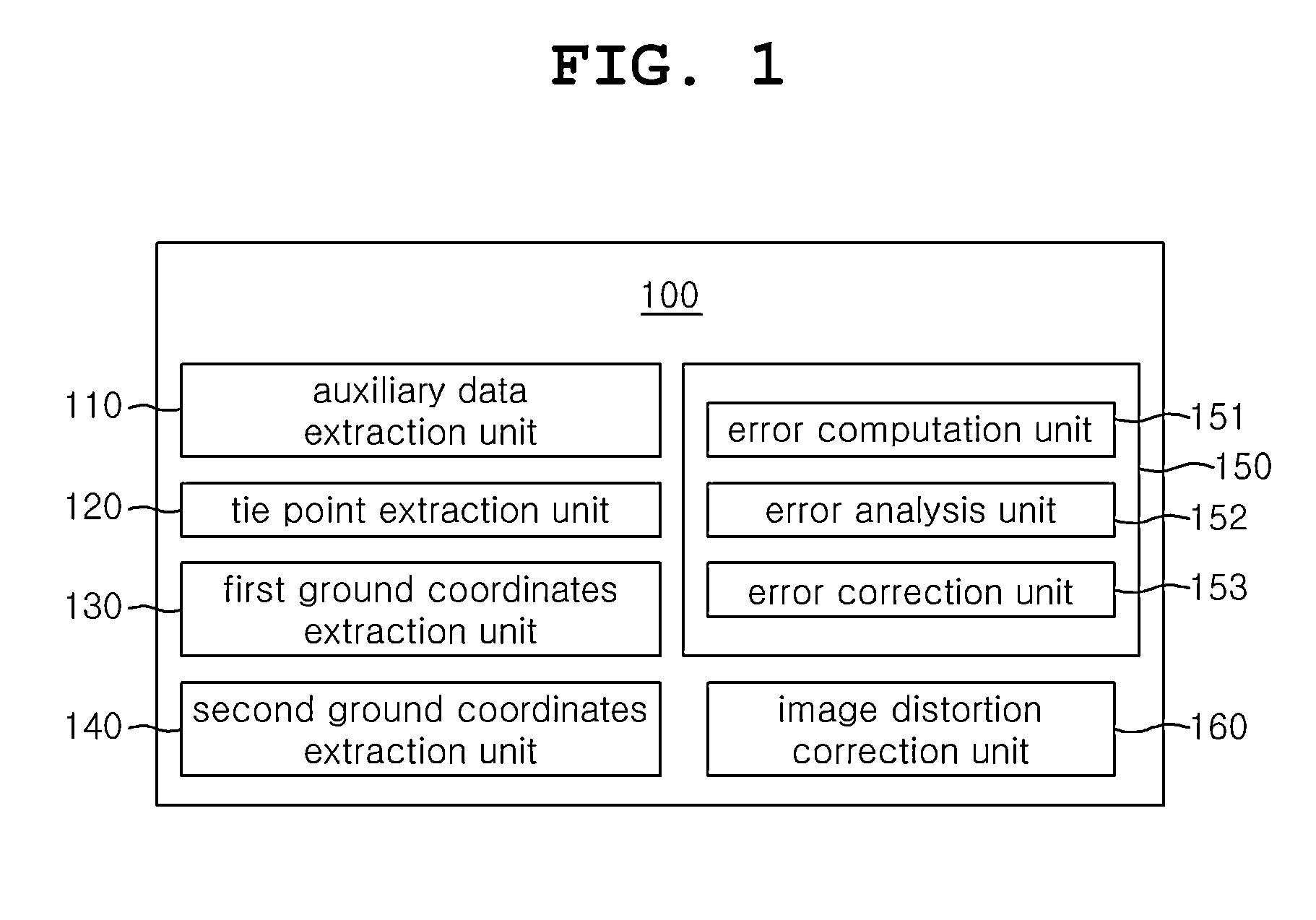
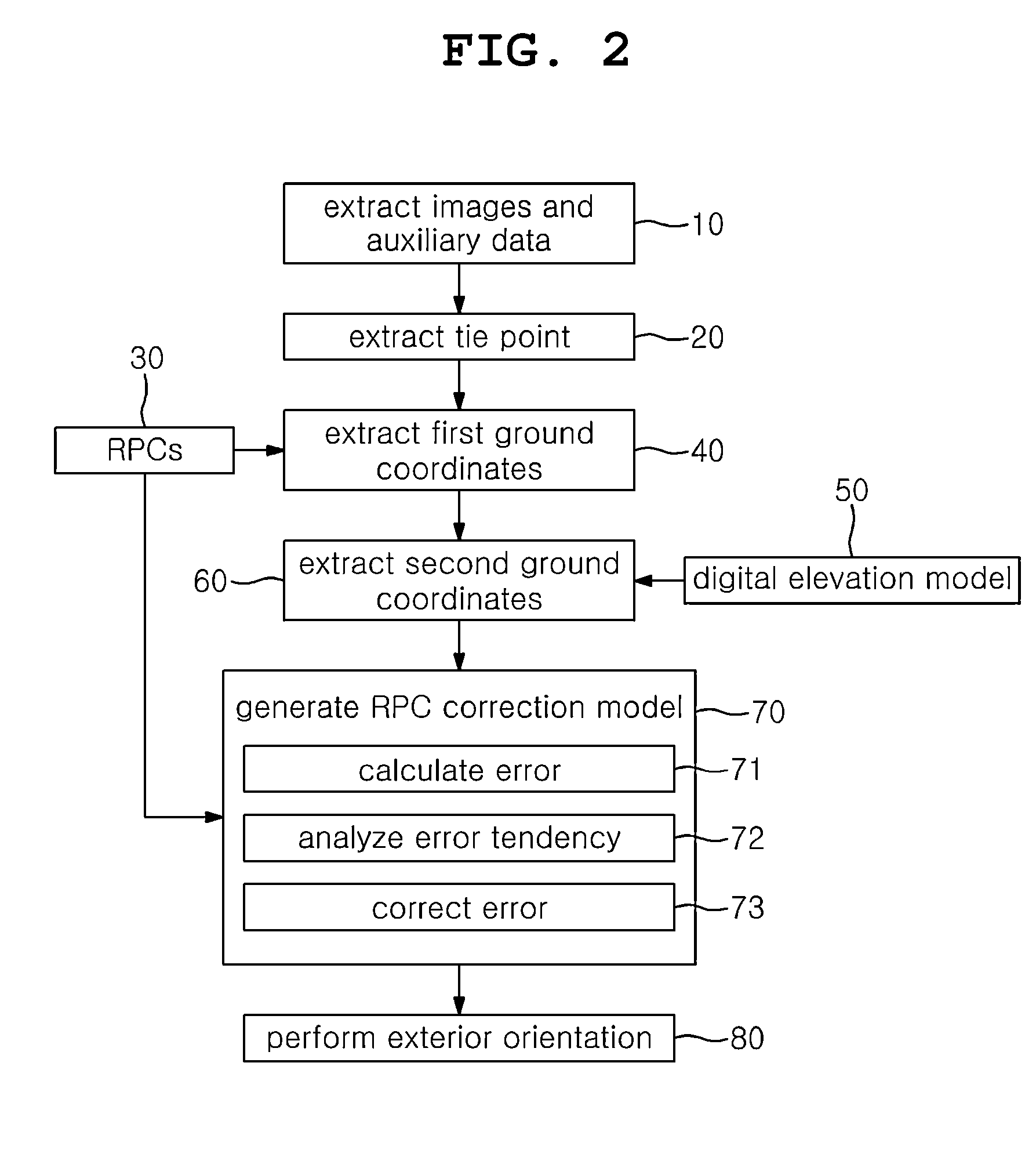
System and method for automatic geometric correction using rpc
ActiveUS20150042648A1Low costShorten the timeImage enhancementTelevision system detailsCorrelation coefficientImage matching
The present invention relates to a technique for correcting a geometric image error calculated as a rational polynomial coefficient (RPC) only through a corresponding point extracted from a digital elevation model (DEM) and a stereoscopic image without direct measurement of a ground control point (GCP). To this end, a system for automatic geometric correction using an RPC in accordance with the present invention comprises: an auxiliary data extraction unit; a corresponding point extraction unit; a first ground coordinate extraction unit; a second ground coordinate extraction unit; an RPC correction model generation unit; and an image distortion correction unit. The auxiliary data extraction unit extracts two or more different images captured from the same ground surface and auxiliary data of the two or more different images. The corresponding point extraction unit extracts a corresponding point from the two or more different images through image matching. The first ground coordinate extraction unit extracts first ground coordinates from the corresponding point and an RPC model of the auxiliary data. The second ground coordinate extraction unit extracts second ground coordinates by using the first ground coordinates and a correlation coefficient of a DEM. The RPC correction model generation unit generates an RPC correction model by correcting the RPC model on the basis of the second ground coordinates. The image distortion correction unit corrects distortion of an image by allocating ground coordinates to each image coordinates of the image by using the second ground coordinates and the RPC correction model.
Owner:UNIV OF SEOUL IND COOP FOUND
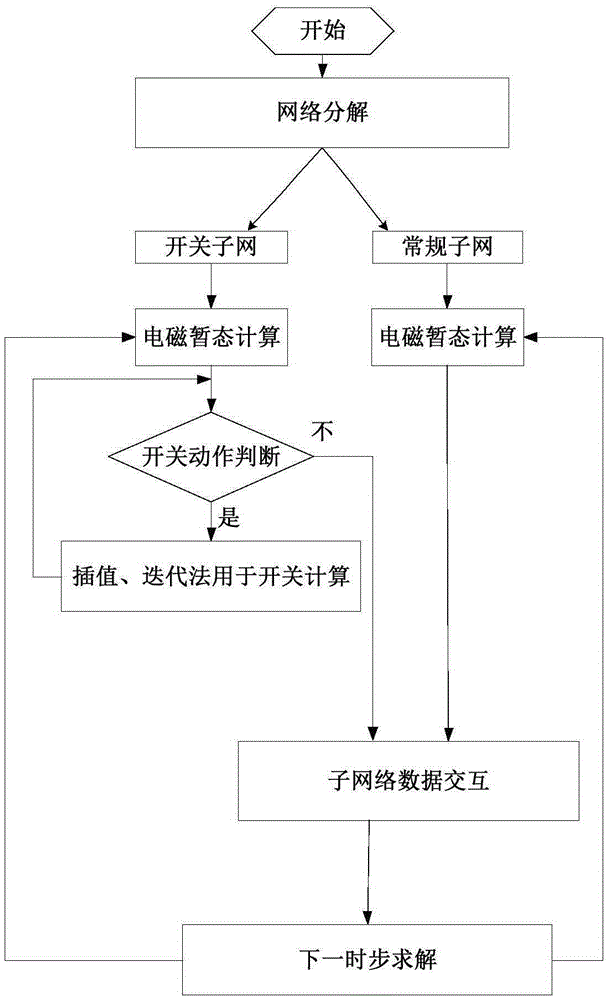
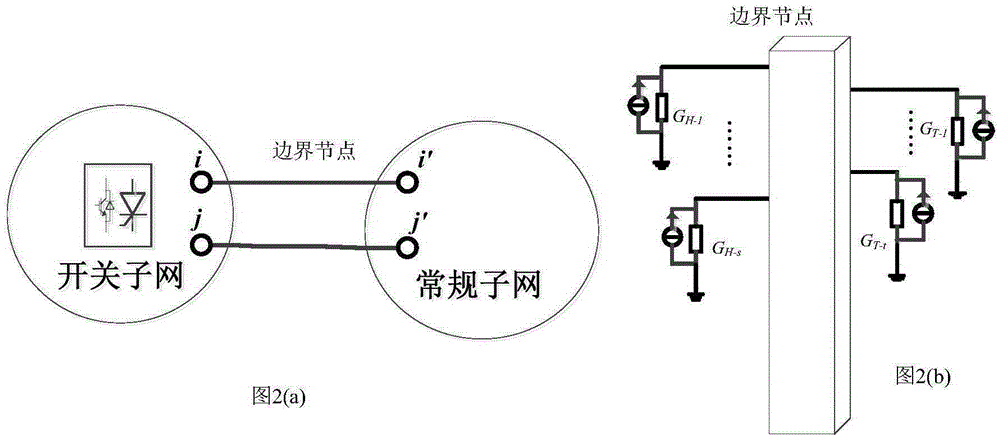
Electromagnetic transient simulation method containing switching characteristic sub-network
InactiveCN105260516AEliminate numerical oscillationsEliminate numerical oscillation problemsSpecial data processing applicationsCapacitanceTransient analysis
The invention relates to an electromagnetic transient simulation method containing a switching characteristic sub-network, and belongs to the technical field of electromagnetic transient analysis in electric power systems. According to the simulation method, a breaker and electronic power switching elements are designed into an independent switching sub-network; the network only comprises an electronic power sub-switch, the breaker and related elements (resistors, inductors, capacitors and the like); the network performs modeling through a rational polynomial approximation based exponential fitting method provided by the invention; and the rest of networks perform modeling by a conventional method (an implicit trapezoid method, a backward Euler method, a damping trapezoidal method or a modified combining form thereof). In offline / real-time calculation, only the switching sub-network performs iteration or interpolation calculation, and the rest of networks do not participate in iteration or interpolation. The switching sub-network adopts a high-order algorithm provided by the invention, so that numerical oscillation can be immunized; and meanwhile, the workload of model modification is relatively low, so that engineering promotion is facilitated.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +3
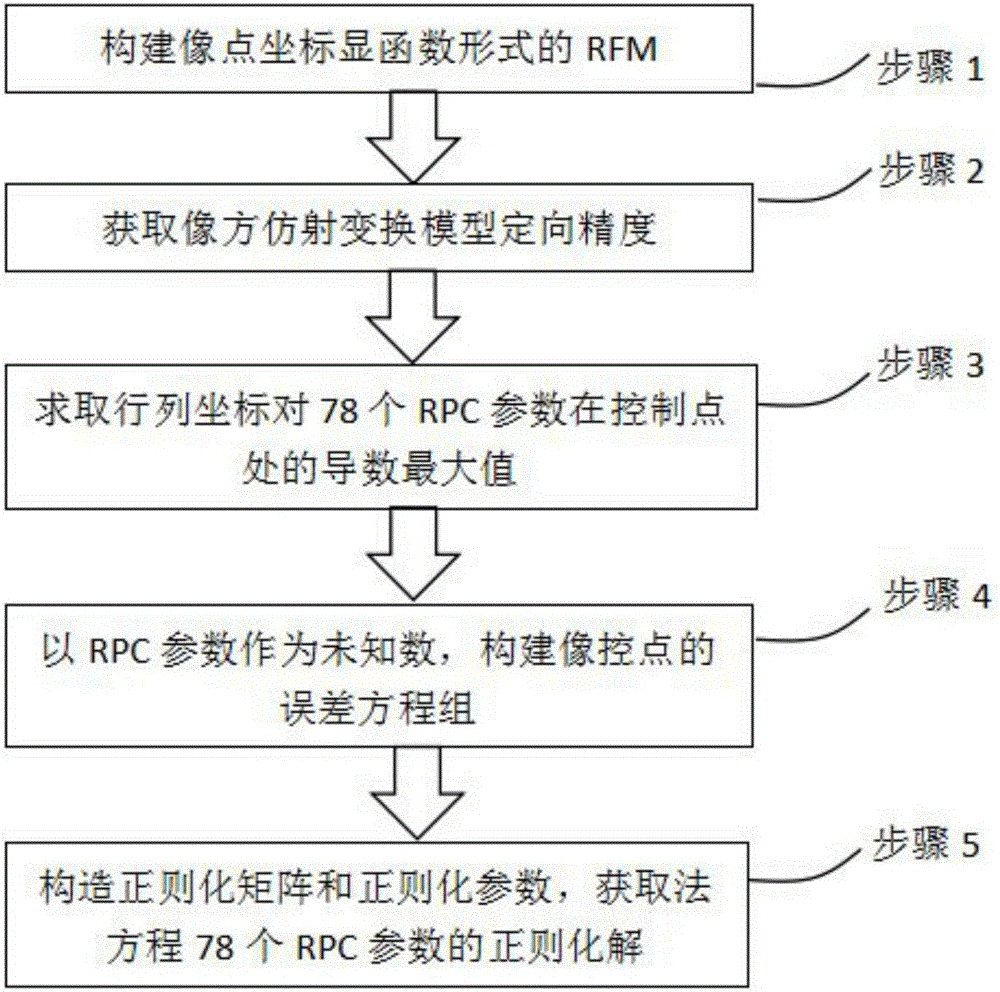
Method of realizing satellite remote sensing image high precision geometric correction through slightly modifying RPC parameters
ActiveCN105761228APrevent morbidityImproved accuracy of image correctionImage enhancementImage analysisRecursive modelSelf adaptive
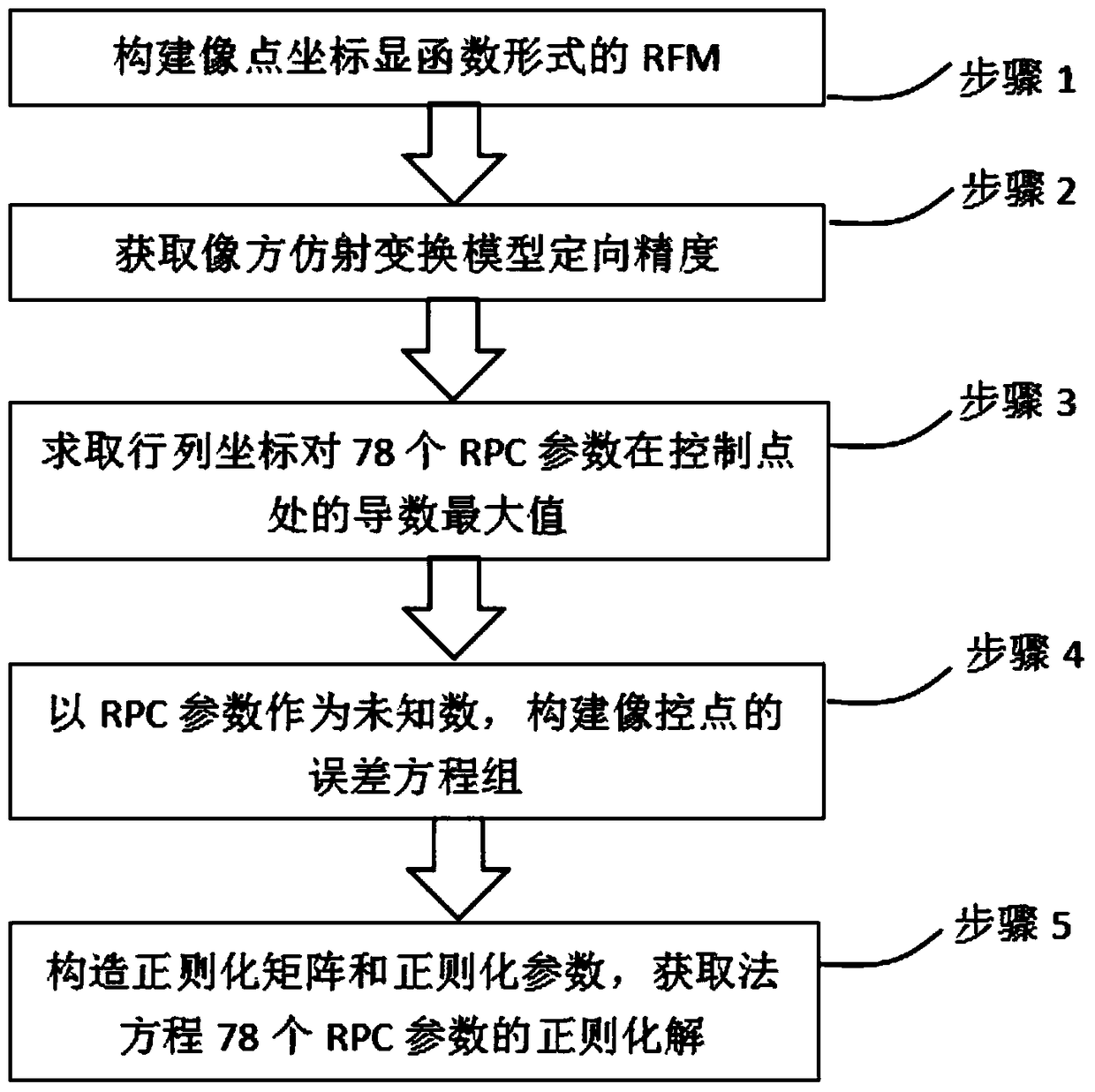
Provided is a method of realizing satellite remote sensing image high precision geometric correction through slightly modifying RPC parameters, which realizes image high precision geometric correction through adjusting 78 rational polynomial coefficients in RPC parameters of an RPC model after traditional RPC image space affine transformation parameter orientation, wherein a normal equation ill-conditioned problem utilizes precision information after image space affine transformation orientation to adaptively construct a regularizer and regularization parameters, thereby realizing robust resolution of 78 RPC parameters of satellite remote sensing images. Under the condition of sufficient ground control points, the method can obtain higher geometric correction precision than a traditional image space affine transformation RFM recursive model and a precise model, and has obvious advantages than traditional methods in the remote sensing image automatic matching and correction filed based on existing reference geographic data.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF SURVEYING & MAPPING
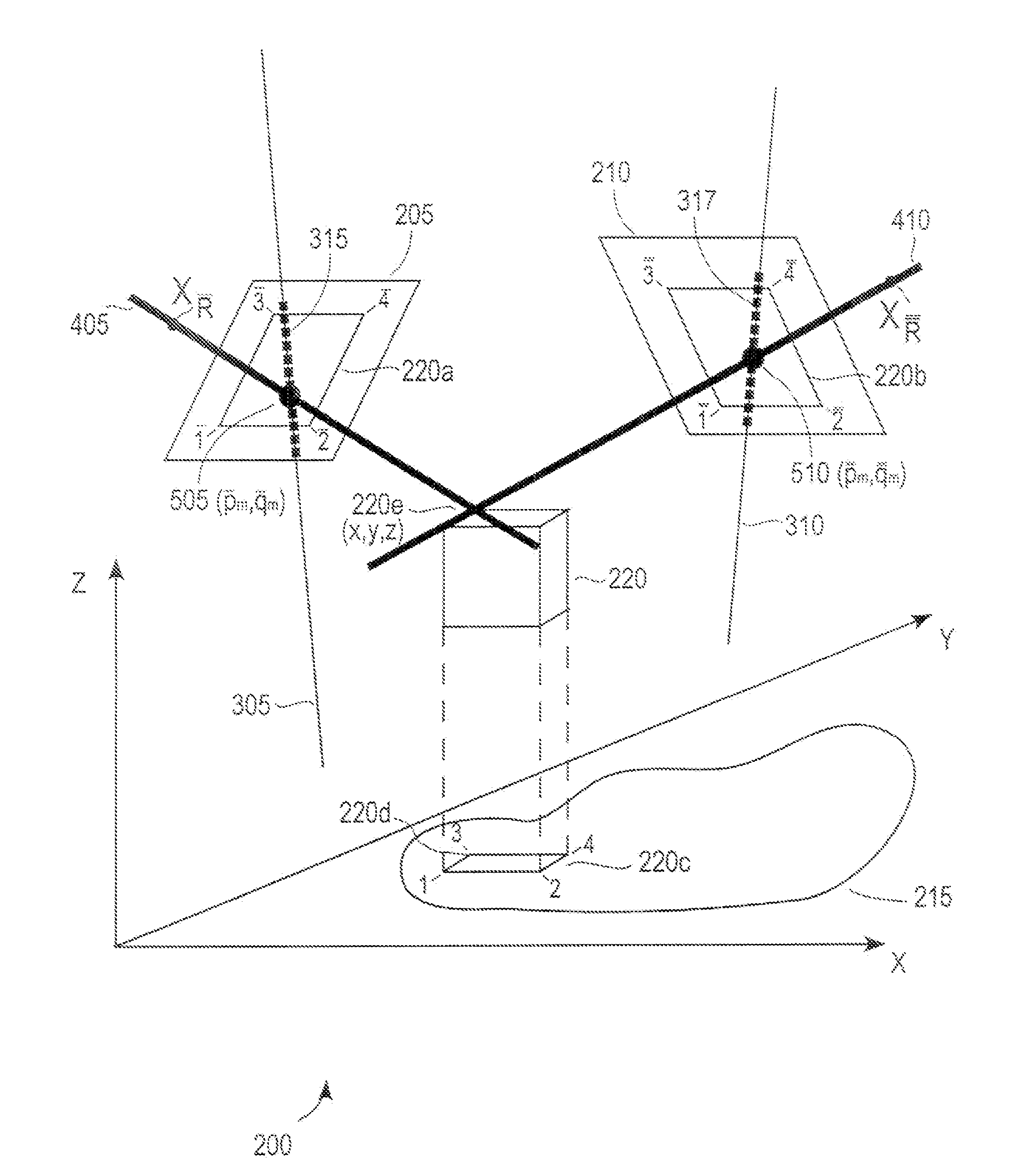
Method and system for three-dimensional feature attribution through synergy of rational polynomial coefficients and projective geometry
InactiveUS7343035B1Low costScene recognitionAquisition of 3D object measurementsSpatial imageAerial photography
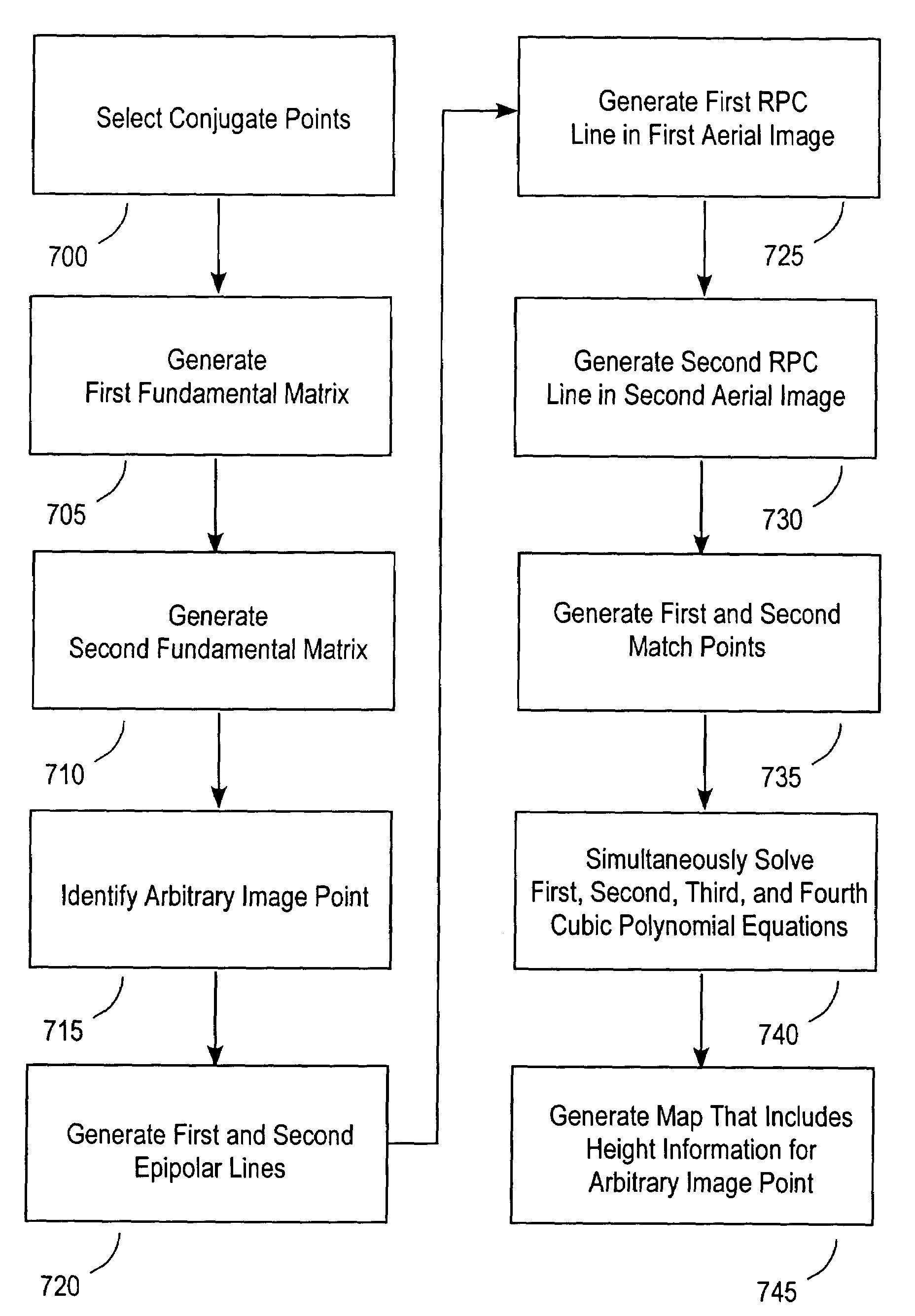
A method is provided for generating height information for an arbitrary-image point on a rectified image and for generating a representation of the rectified image that includes the height information. According to an exemplary embodiment, height information is generated for an arbitrary-image point on the rectified image from first and second aerial images having respective first and second sets of rational polynomial coefficients (RPCs) and projective geometrical relationships, such that the first and second aerial images and the rectified image include overlapping image locations.
Owner:OPEN INVENTION NEWTORK LLC
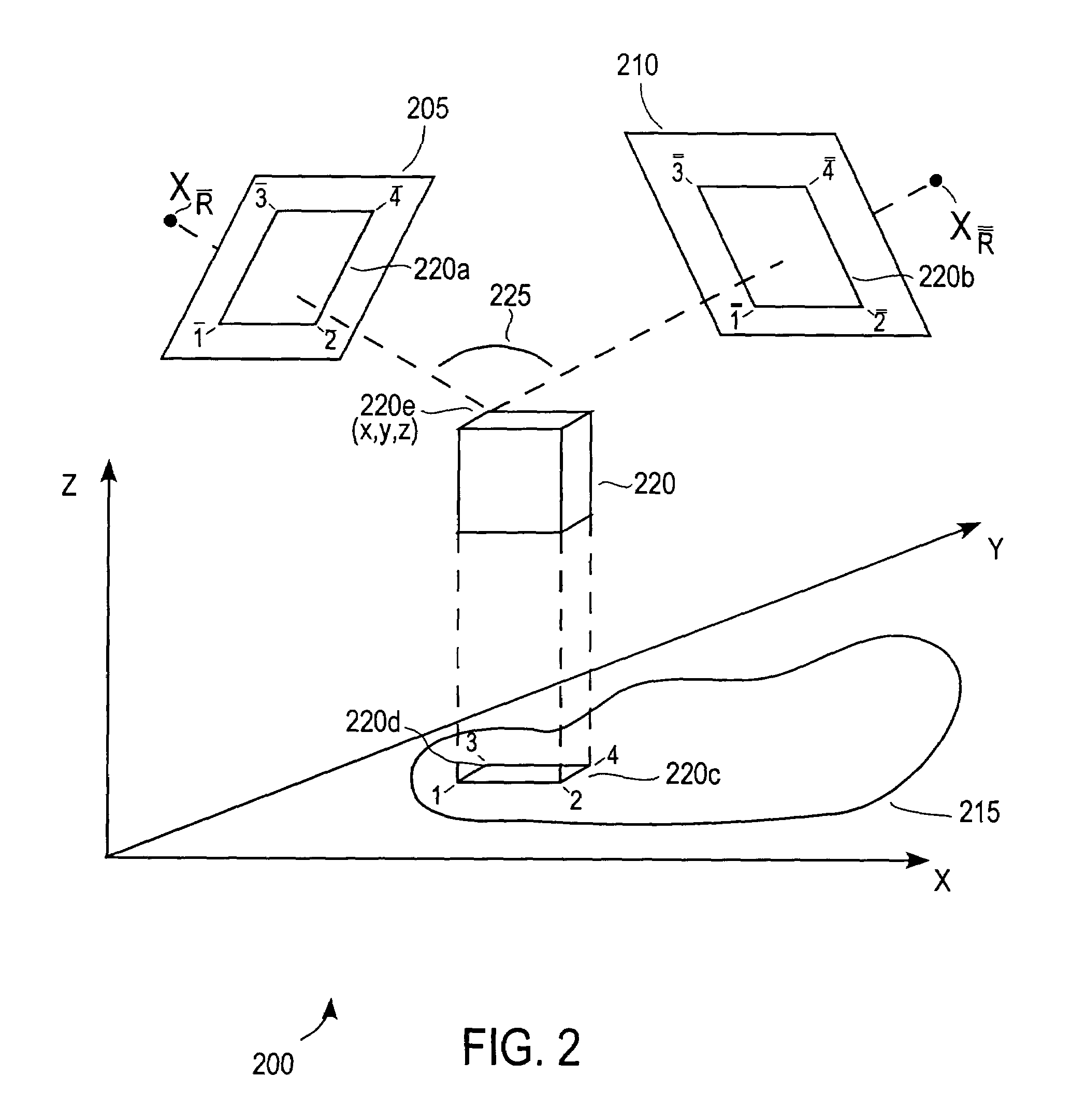
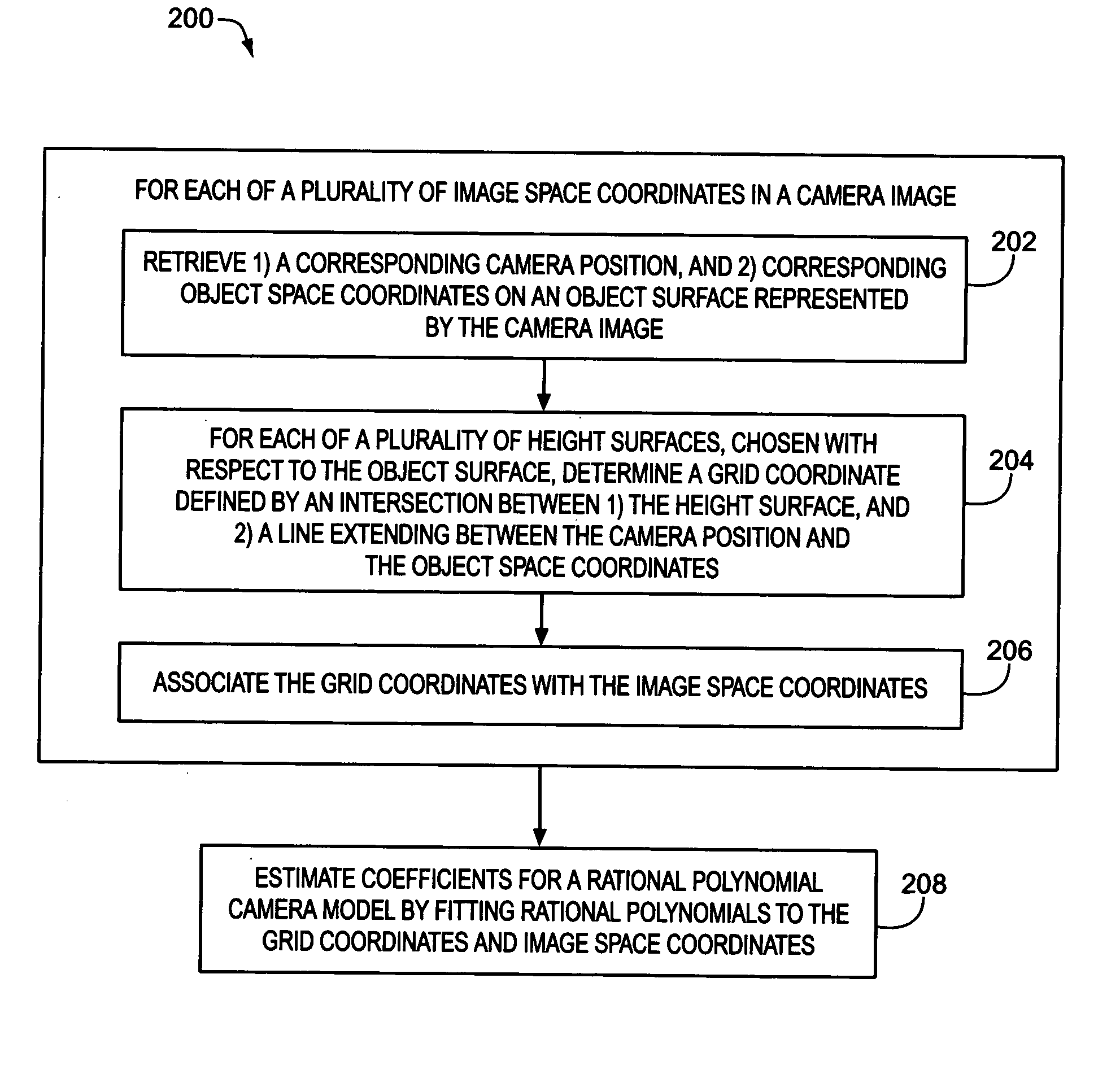
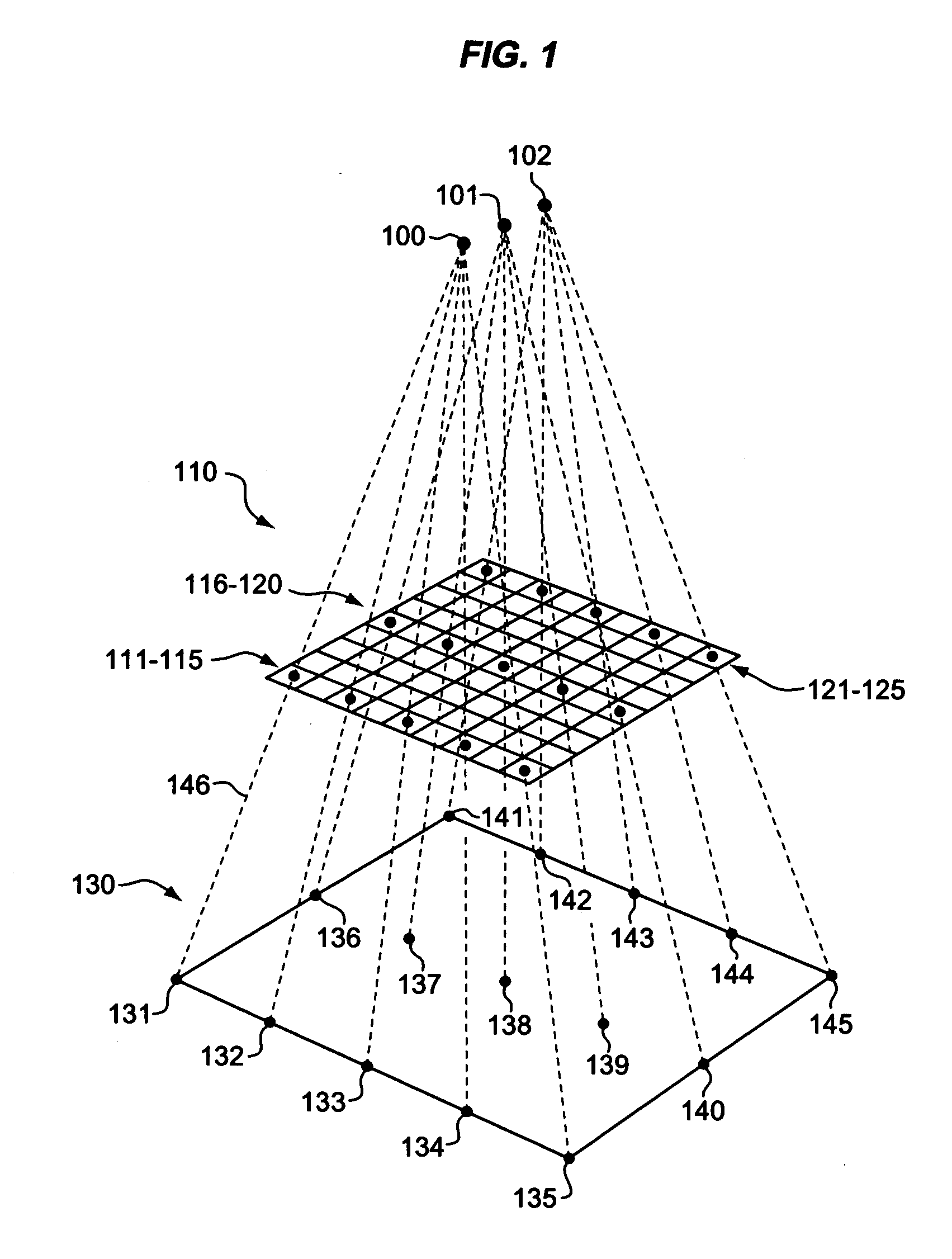
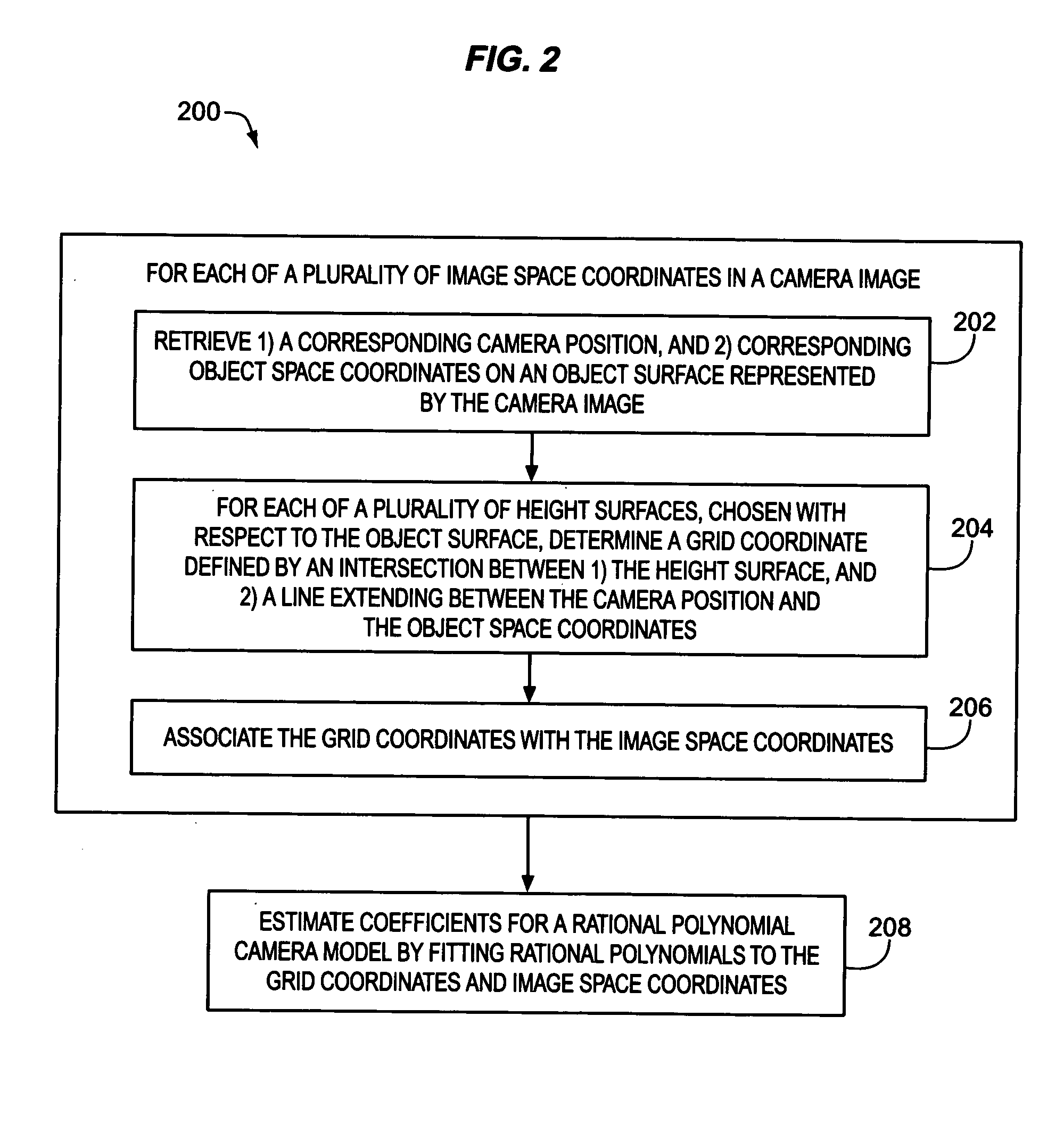
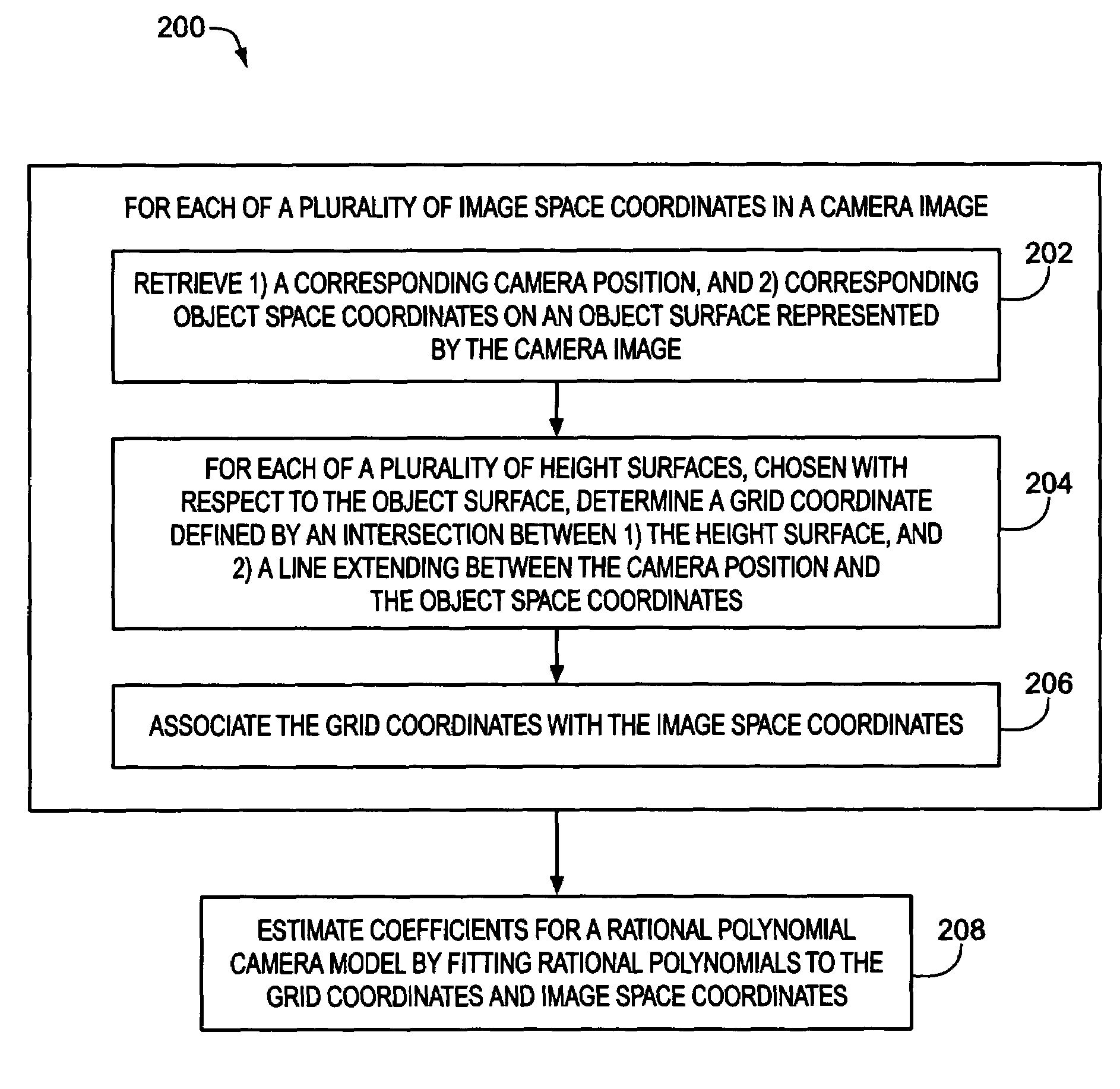
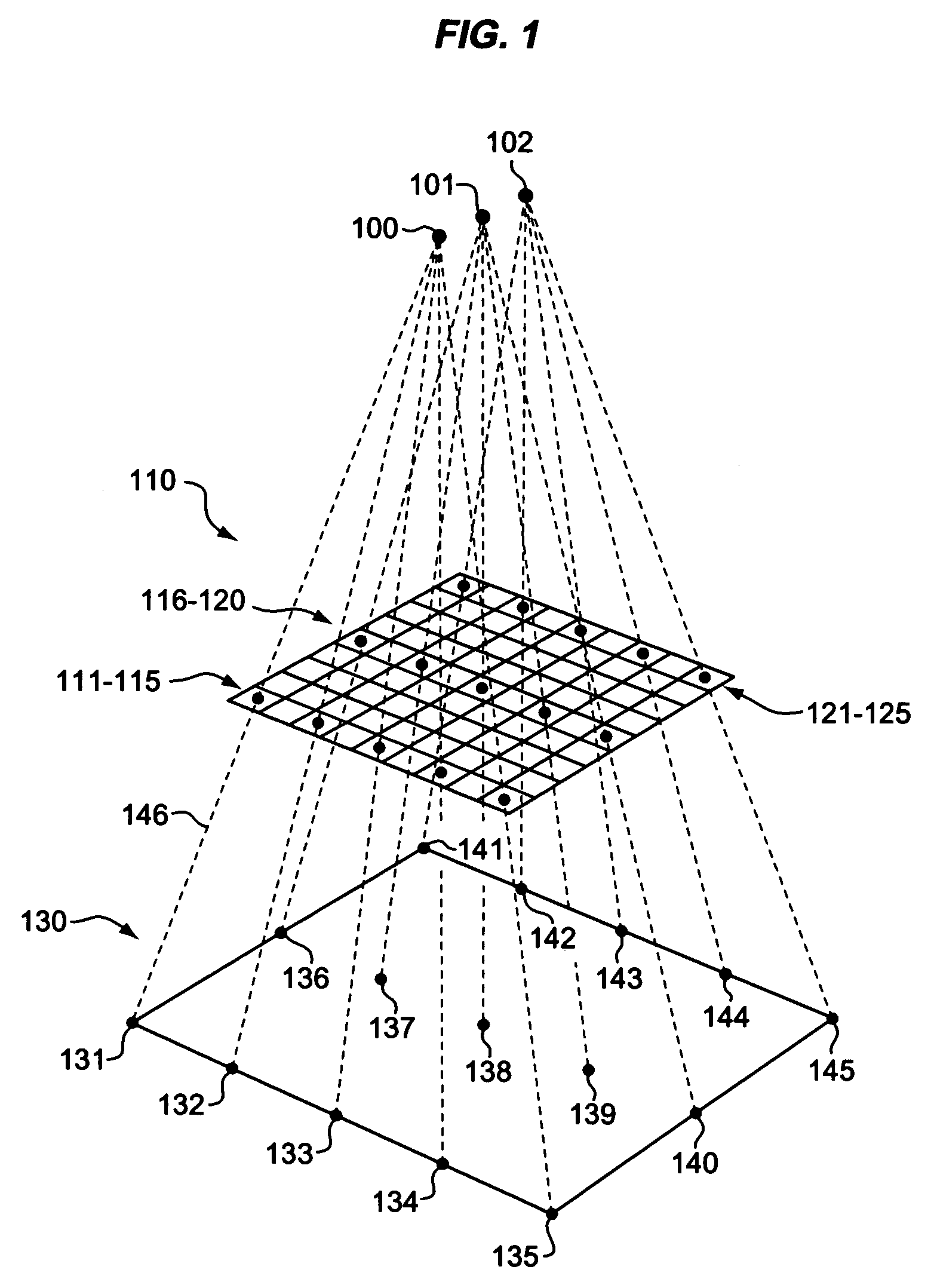
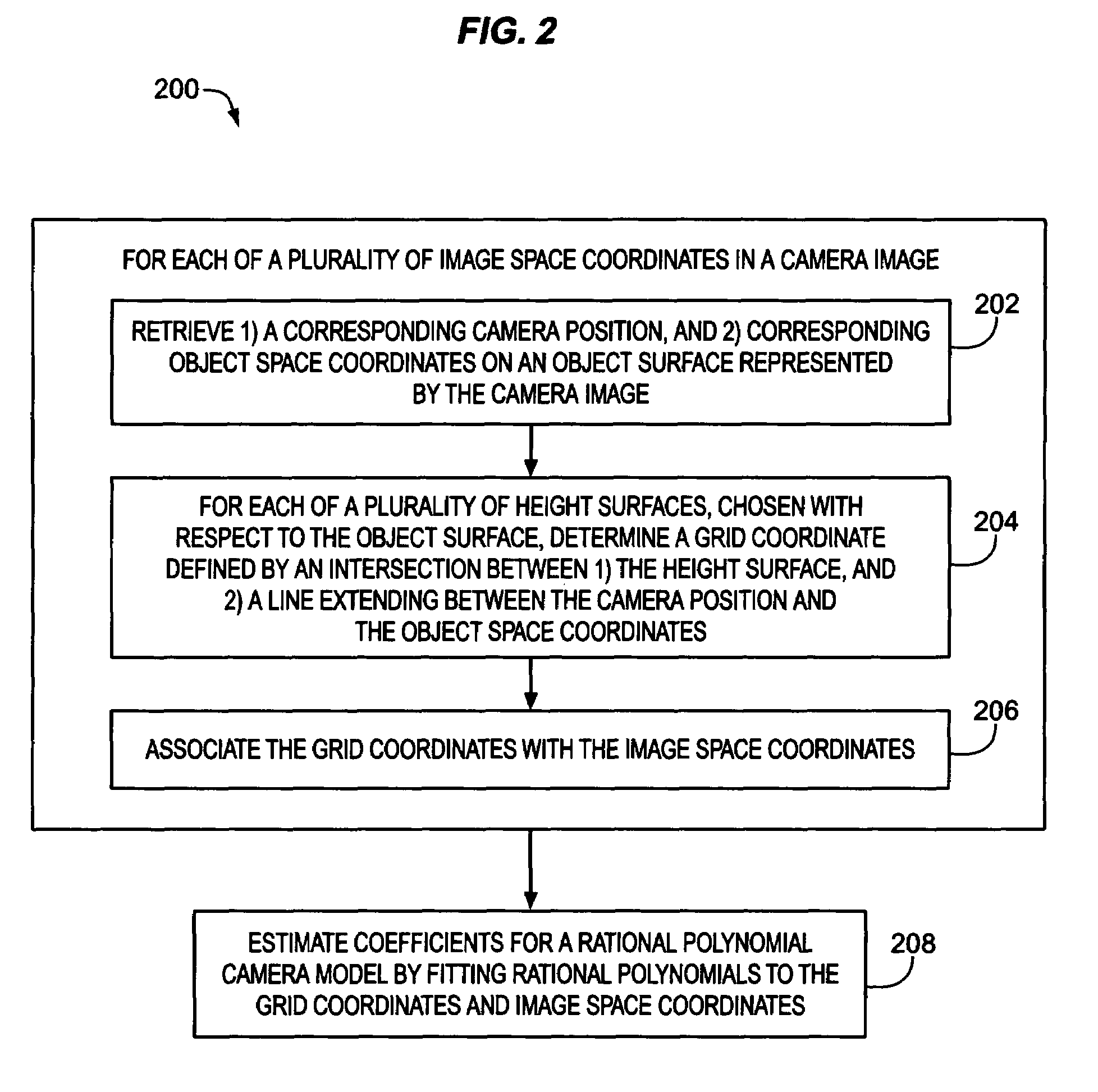
Estimation of coefficients for a rational polynomial camera model
One aspect of the invention is embodied in a number of machine-readable media having stored thereon sequences of instructions which, when executed by a machine, cause the machine to perform a number of actions. The actions include, for each of a plurality of image space coordinates of a camera image, retrieving 1) a corresponding camera position, and 2) corresponding object space coordinates on an object surface that is represented by the camera image. Then, for each of a plurality of height surfaces (chosen with respect to the object surface), a grid coordinate defined by an intersection between the height surface, and a line extending between the camera position and the object space coordinates, is determined. The determined grid coordinates are then associated with their corresponding image space coordinates. Finally, coefficients for a rational polynomial camera model are estimated by fitting rational polynomials to at least the grid coordinates and image space coordinates.
Owner:MAXAR INTELLIGENCE INC
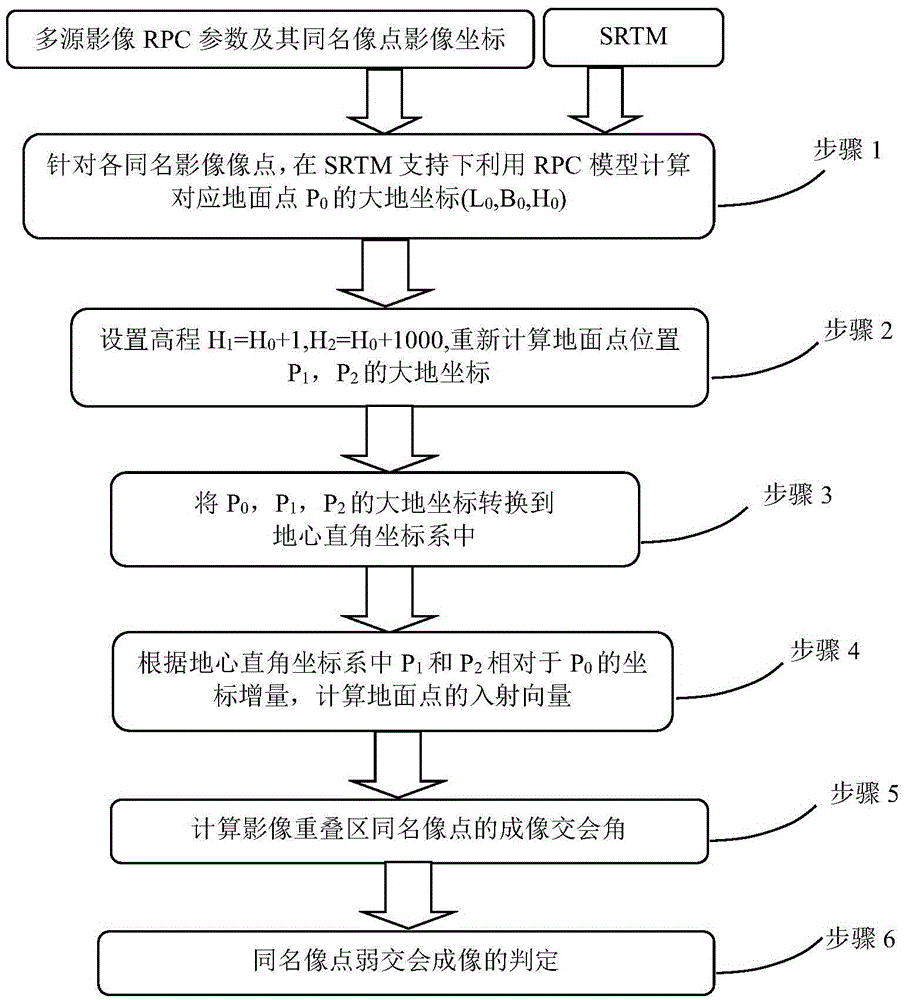
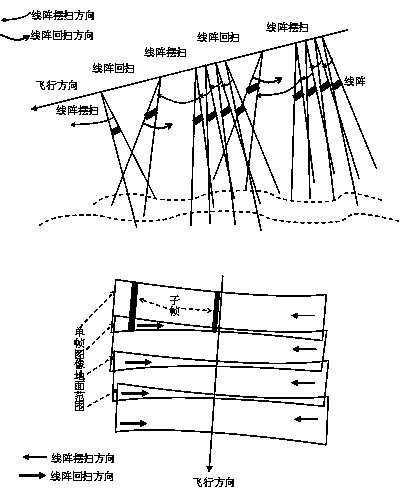
Method for probing multi-source satellite image corresponding image point imaging intersection angles
The invention discloses a method for probing multi-source satellite image corresponding image point imaging intersection angles by utilizing remote position control (RPC), which is a detection method suitable for homogenous or heterogeneous satellite remote-sensing image corresponding image point imaging intersection angles based on rational polynomial RPC parameters and global shuttle radar topography mission (SRTM) data, and further counts angles of incidence of ground targets and imaging intersection angles of any two image corresponding image point ground targets by utilizing RPC models to count changes of ground point position vectors through elevation change. The method for detecting the multi-source satellite image corresponding image point imaging intersection angles can obtain imaging intersection angles of superimposed image corresponding points by utilizing RPC parameters under the situation that the positions of sensors are not known, and provides an effective method for detecting RPC model positioning imaging intersection angles, and can supply basic information for preventing a ground point coordinate solving ill-posed problem which is caused by weak intersection imaging in image geometric processing.
Owner:GUIZHOU TDT TECH CO LTD
Geometric pretreatment method for vertical rail swing images of satellite-borne linear array sensor
InactiveCN103778610ARealize splicingEliminate internal geometric distortionImage enhancementPretreatment methodRectangular coordinates
The invention discloses a geometric pretreatment method for vertical rail swing images of a satellite-borne linear array sensor. The geometric pretreatment method comprises steps of establishing a collinearity equation model of original single-frame images according to the imaging geometry of the original single-frame images; performing geometric correction treatment on all the original single-frame images, dividing all the original single-frame images into virtual three-dimensional grids, resolving rational polynomial model coefficients corresponding to the original single-frame images, establishing a positive and negative calculation relation of each original single-frame image coordinate and a tangent plane image coordinate, and performing geometric correction on all the original single-frame images on the basis of a rational polynomial model to obtain frame images under an object space tangent plane coordinate, wherein the geometric correction treatment comprises constructing a mutual conversion relation of an object space local coordinate and a geocentric rectangular coordinate and constructing a mutual conversion relation of the tangent plane image coordinate and the object space local coordinate; splicing all the frame images under the object space tangent plane coordinate on the basis of the coordinate to obtain the spliced images; resolving the rational polynomial model coefficients corresponding to the spliced images.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
NURBS figure laser broom method
InactiveCN101920603AImplement sweeperEasy to integratePrintingSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsLaser engraving
The invention discloses a method for realizing NURBS figure laser broom processing in the technical fields of laser marking and laser engraving processing. The method comprises that: a NURBS expression in an iteration form is converted into an expression in a rational polynominal form, an intersection point of a scanning line and a closed NURBS contour is calculated, laser on / off delay compensation is carried out, a laser motion path is generated, and a multi-task-based control framework is realized. In the method, the closed contour described by the NURBS expression can be received, motion control and laser control instructions are generated, a motion mechanism is driven to move, and the laser on / off control is carried out in the motion process, so fill lines are generated in the closed NURBS contour to generate a NURBS figure.
Owner:东莞市升力智能科技有限公司
High-resolution remote sensing image ortho-rectification method based on floating control point
ActiveCN103530628ARealize Image CorrectionExact geographic coordinatesCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorSupport vector machine
Owner:SHANGHAI URBAN CONSTR DESIGN RES INST GRP CO LTD
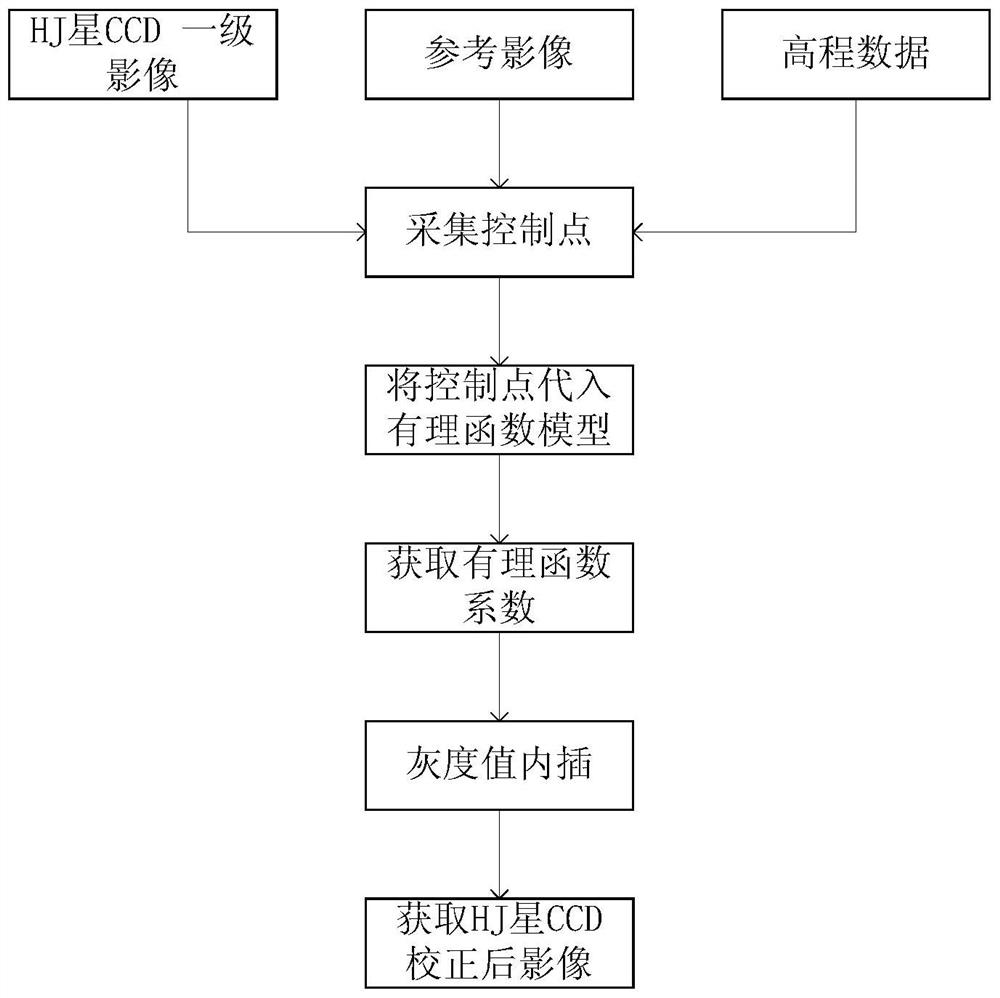
Orthographic correction method of CCD image of HJ-1 satellite
ActiveCN104537614AHigh positioning accuracyMultiple lossesImage enhancementPolynomial methodElevation data
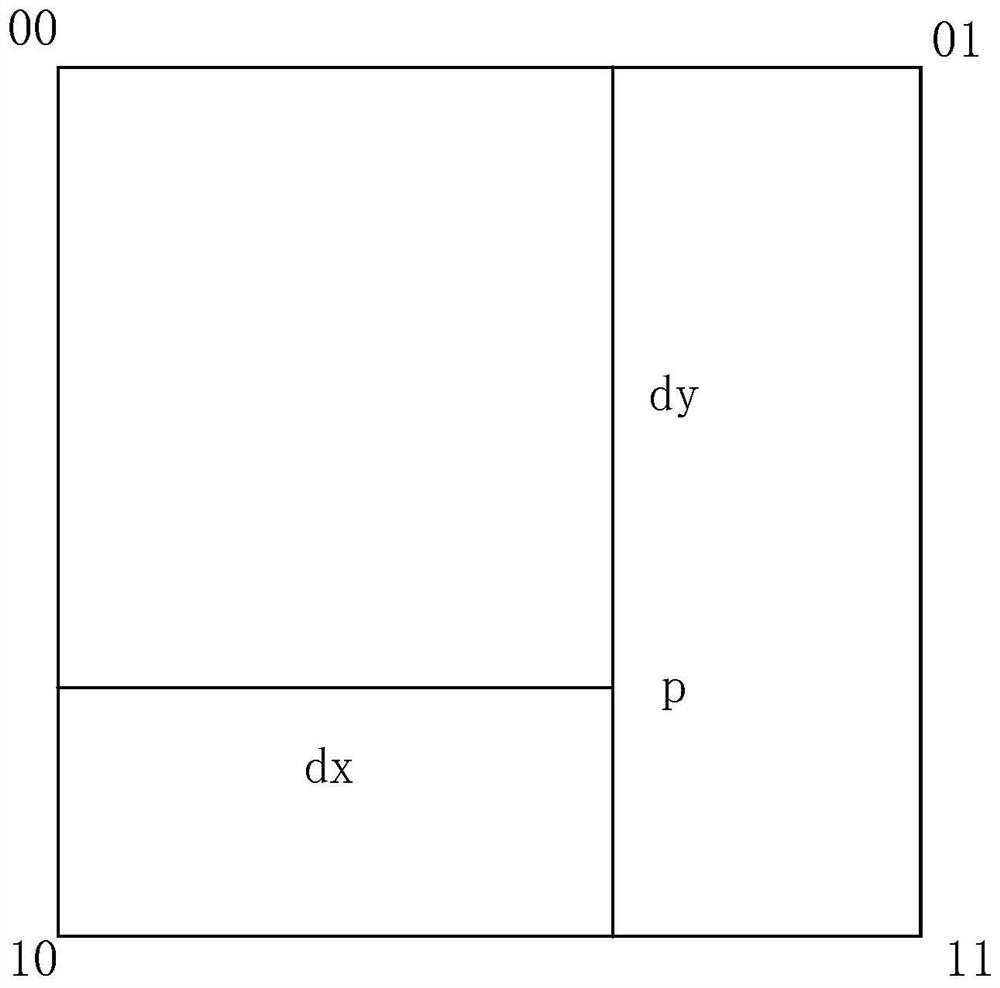
The invention relates to an orthographic correction method of a CCD image of an HJ-1 satellite. A first-stage image of a CCD of an HJ satellite as well as corresponding altitude data and reference data are introduced; ground control points are collectedly uniformly at the first-stage image of the CCD of the HJ satellite; coordinates of the collected control points are introduced into a cubic rational function model and calculation is carried out to obtain a rational polynomial coefficient (RPC), so that a corresponding rational function model is obtained; pixel coordinates of all points of the first-stage image of the CCD of the HJ-1 satellite are inputted into the rational function model to obtain coordinates corresponding to all points of an image after orthographic correction; and with a bilinear interpolation method, interpolation of gray values of all points of the image after correction is carried out on points with pixel coordinates in an entire row or column mode, thereby obtaining an orthographic correction image. According to the invention, compared with the traditional polynomial method, the provided orthographic correction method enables the precision to be improved.
Owner:CHINA CENT FOR RESOURCES SATELLITE DATA & APPL
Satellite image system error correction method based on RPC model
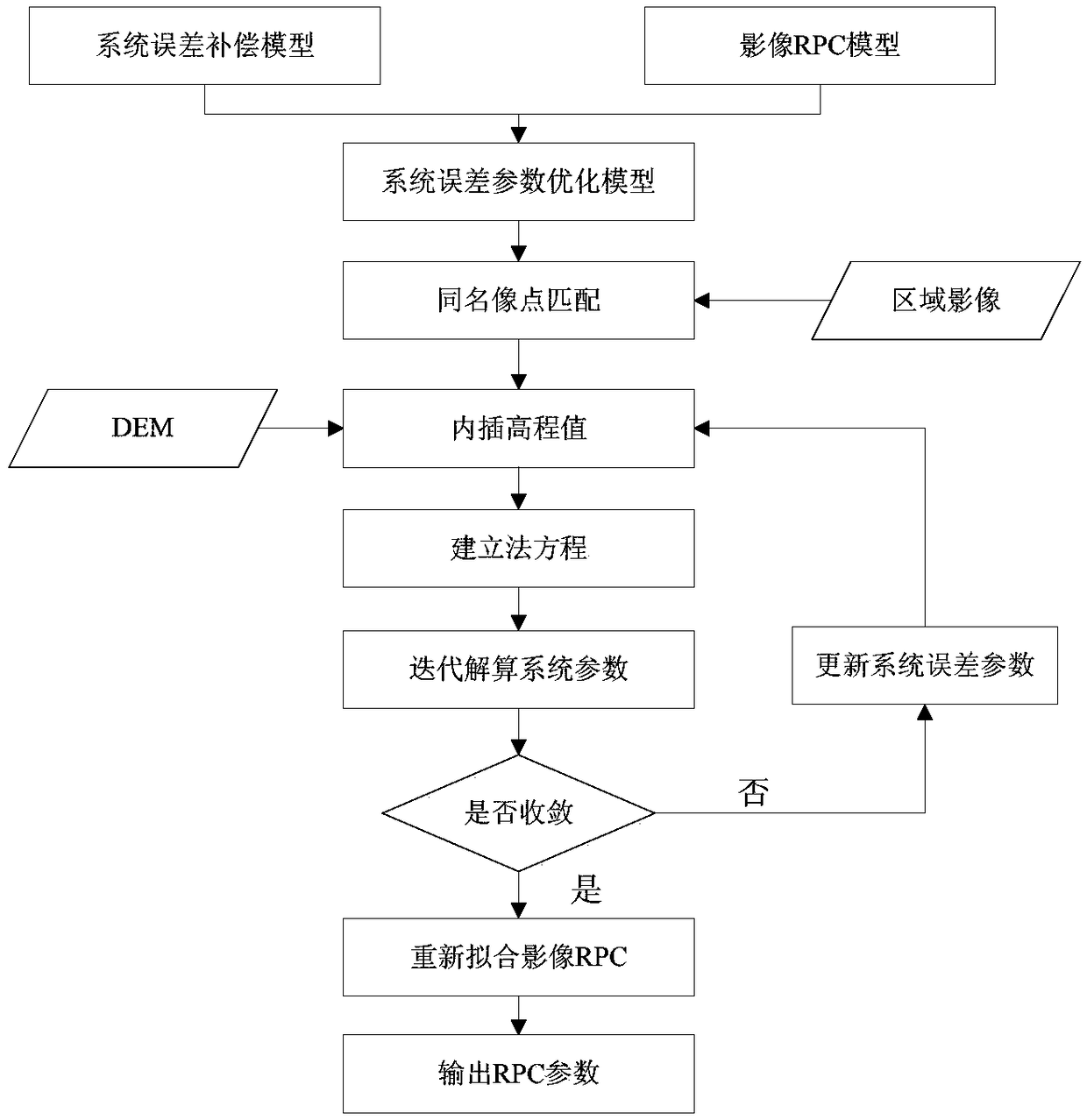
The invention discloses a satellite image system error correction method based on a RPC model. An improvement model of system errors is pushed to a generalized rational polynomial model from a rigorous geometric imaging model, and then improvement of the image system errors is pushed to a satellite image product stage from pre-processing resolving. According to the satellite image system error correction method based on the RPC model, by adding a generalized error compensation model to a RPC model image space to build an optimization model of the system errors, and then using mutual constraintconditions between overlapping region images and absolute constraint conditions of control points within a period of time, error parameters are resolved.
Owner:CHINA CENT FOR RESOURCES SATELLITE DATA & APPL
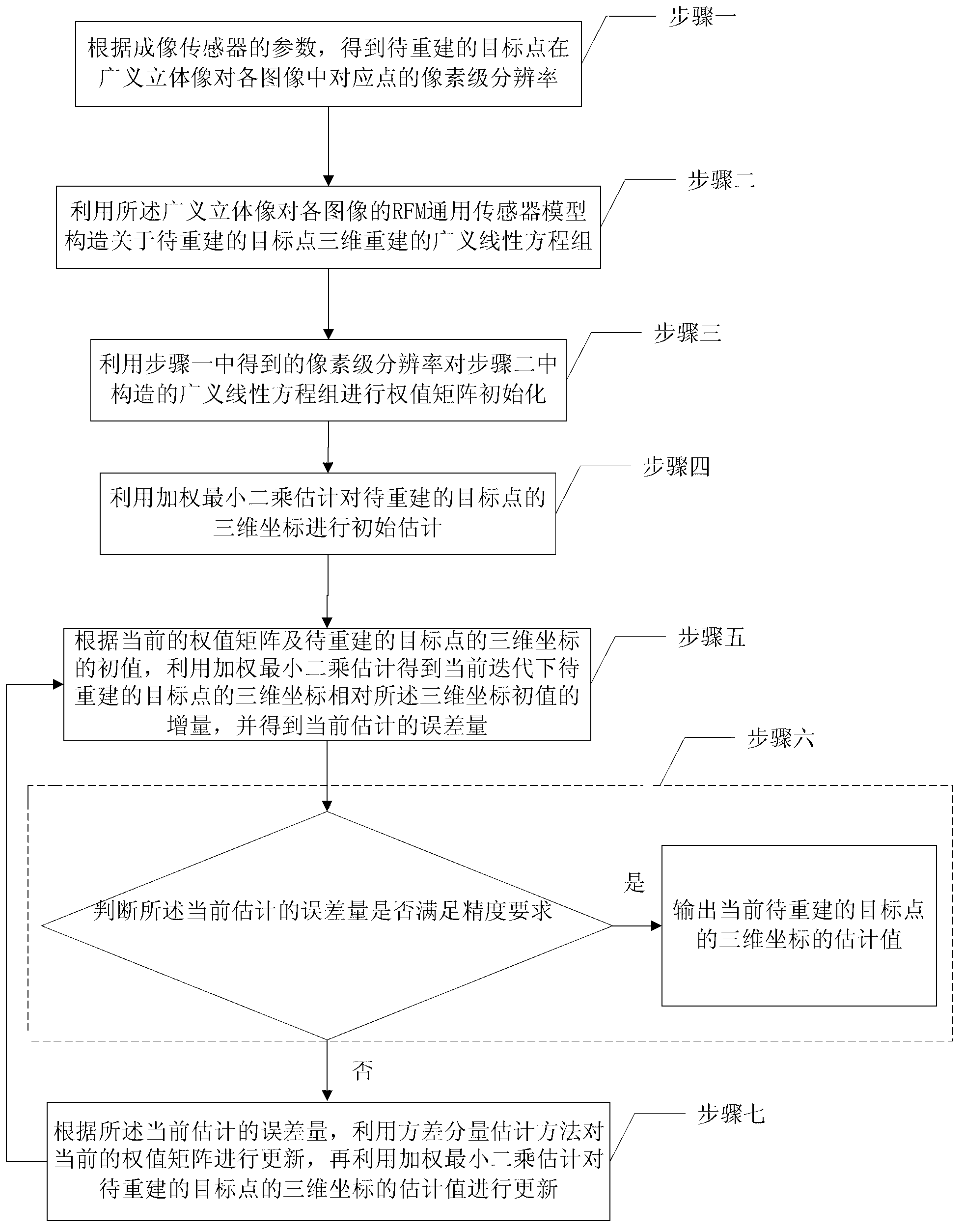
Generalized stereopair three-dimensional reconstruction method adopting variance component estimation
ActiveCN103021021AAddressing severe imbalancesHigh precision3D modellingImaging conditionEstimation methods
The invention relates to a generalized stereopair three-dimensional reconstruction method adopting variance component estimation, relates to a three-dimensional reconstruction method and aims at solving the problem that a generalized linear equation set with serious unbalancedness exists in the traditional generalized stereopair three-dimensional reconstruction method based on RFM (Rational Function Model) when the pixel resolution difference of same images and the resolution difference of images with different imaging conditions are serious because of a large angle facing to different imaging systems. The generalized stereopair three-dimensional reconstruction method disclosed by the invention realizes that a variance component estimation method is embedded into a classical three-dimensional reconstruction method based on the front convergence of a rational polynominal model RFM by utilizing the pixel-level resolution relation of corresponding target points, which are to be reconstructed, of a generalized stereopair and realizes the weight value matrix self-adaption adjustment in the process of iteratively solving an unknown three-dimensional coordinate, thereby effectively enhancing the three-dimensional reconstruction accuracy and enhancing the feasibility of the three-dimensional reconstruction of the generalized stereopair; and in addition, the generalized stereopair three-dimensional reconstruction method is used for the three-dimensional reconstruction of the generalized stereopair.
Owner:严格集团股份有限公司
Method for automatically optimizing and solving parameters of rational function model based on embedded regression
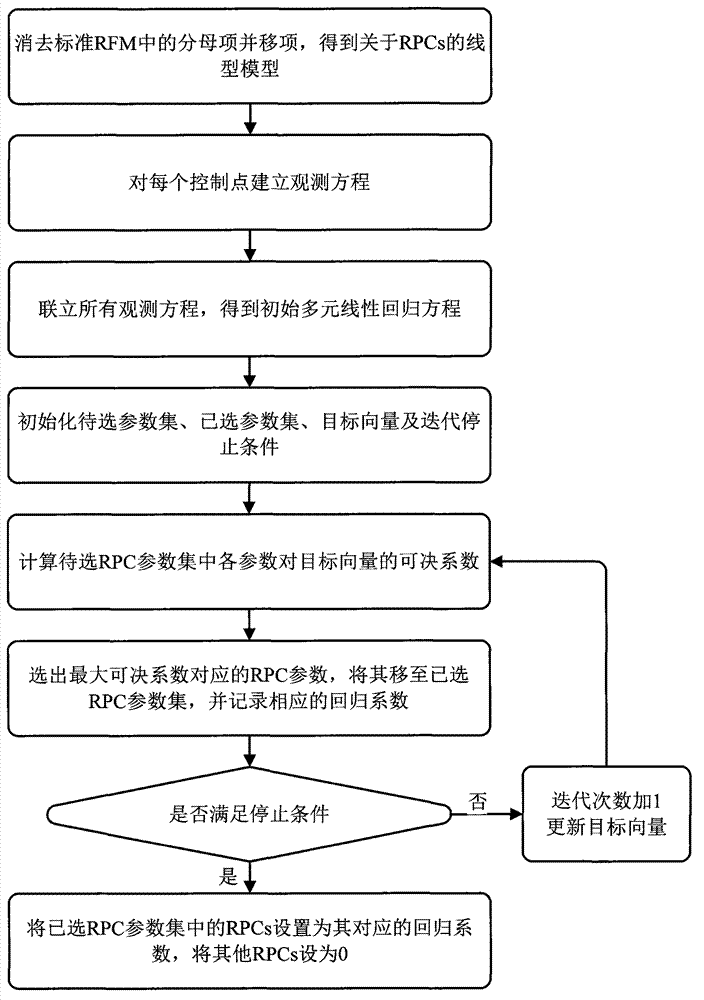
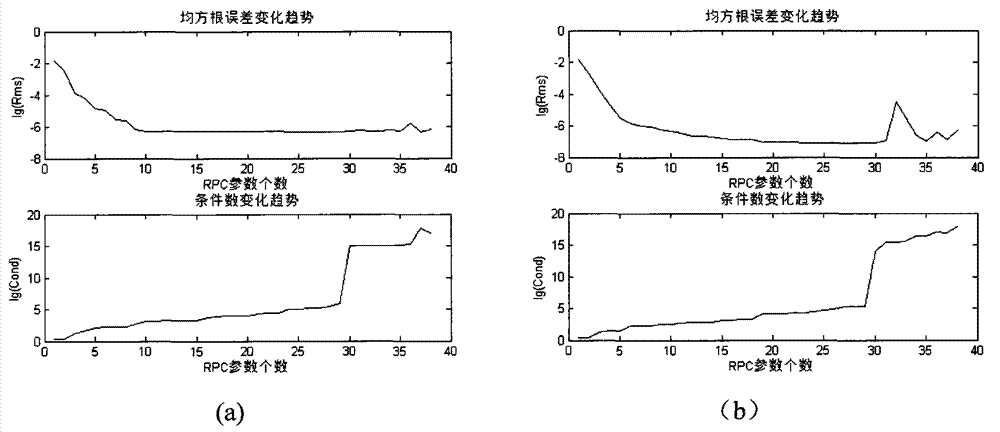
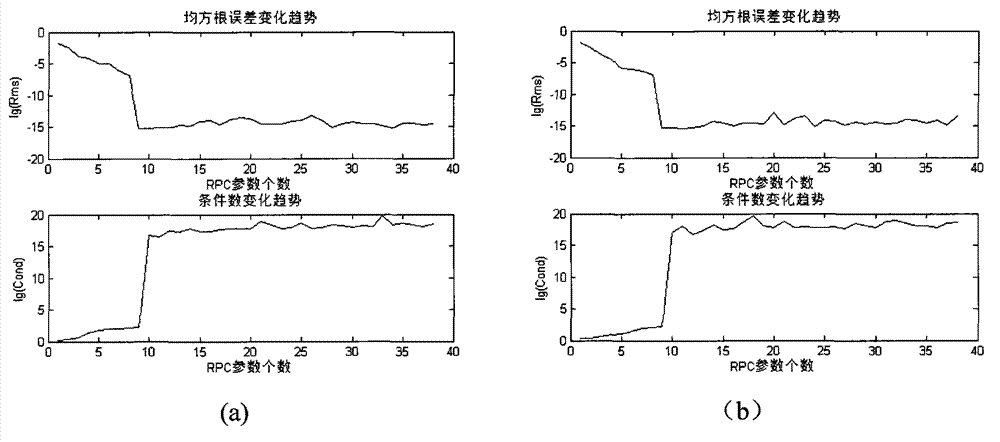
InactiveCN102855221AReduce usageImprove calibration accuracyComplex mathematical operationsAlgorithmImage correction
The invention aims to convert a problem for solving rational polynomial coefficients (RPCs) into a multi-element linear regression problem with multi-collinearity, and provides an embedded regression method for automatically optimizing parameters of a rational function model by taking a determination coefficient as an evaluation rule. Coefficients with obvious influence in the rational function model are gradually introduced, and redundant coefficients with low influence are eliminated, so that the RPCs can be automatically optimized and solved, and the brief rational function model is obtained. By the method, the rational function model can be automatically simplified, the using amount of control points is reduced, and the image correction and collimation precision is improved.
Owner:CENT FOR EARTH OBSERVATION & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method and system for three-dimensional feature attribution through synergy of rational polynomial coefficients and projective geometry
InactiveUS20080310681A1Scene recognitionAquisition of 3D object measurementsSpatial imageRational polynomial coefficient
Owner:OPEN INVENTION NEWTORK LLC
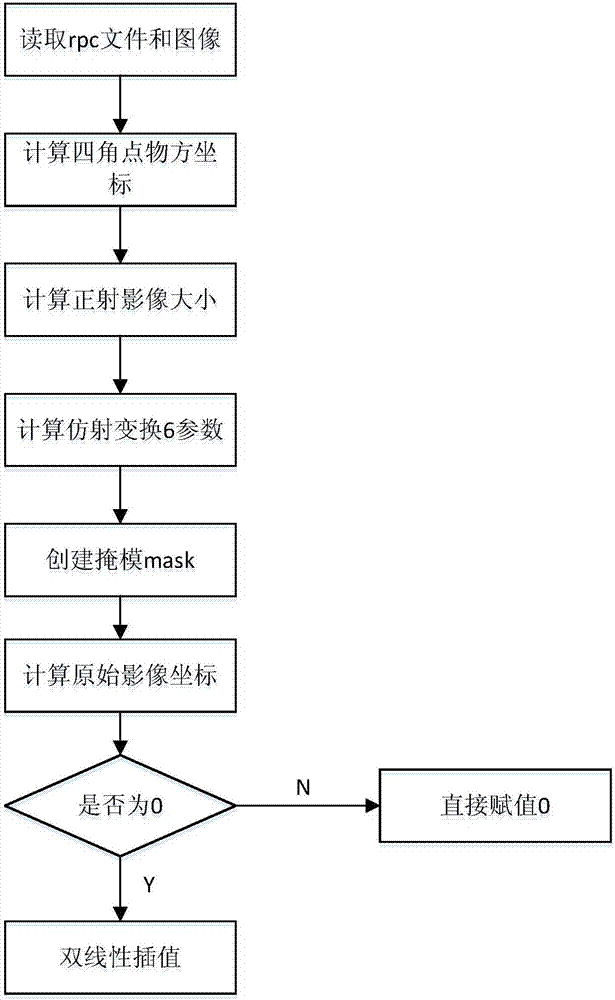
Ortho-rectification processing method for night images
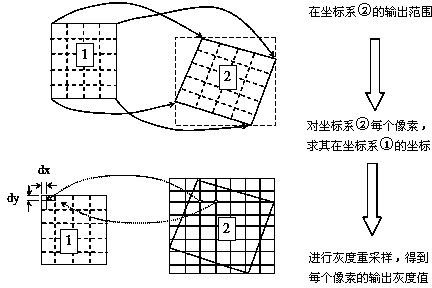
ActiveCN107516291AImprove the efficiency of orthorectificationSmall amount of calculationGeometric image transformationPixel mappingLarge size
The invention relates to an ortho-rectification processing method for night images and relates to the field of remote sensing image processing. The method includes steps of creating an orthographic output image in a manner of mapping the output image to an original image pixel by pixel, acquiring a gray value through interpolation on the original image and bestowing the gray value to a corresponding position of the output image. According to the invention, as for a night image with a large size black area, based on a prior remote sensing image ortho-rectification algorithm, a rational polynomial coefficient based ortho-rectification model is adopted for ortho-rectification. Through pixel-by-pixel mapping of the output image to the original image, only ortho-rectification calculation of the original image is required and point-by-point calculation is saved, so that a large amount of calculation is reduced and the efficiency of night image ortho-rectification is improved substantially. According to the invention, ortho-rectification can be performed on the night images effectively targeting at characteristics of the night images and flexible and quick ortho-rectification can be achieved.
Owner:CHANGGUANG SATELLITE TECH CO LTD
High-resolution satellite image and rational polynomial parameter transformation method
PendingCN109239745AExpand practical application scenariosImprove applicabilitySatellite radio beaconingSatellite imageWorkstation
The invention relates to a high-resolution satellite image and rational polynomial parameter transformation method so as to adapt to requirements of a mapping workstation in the aspects of a data volume, an image angle and the like and ensure that accuracy after transformation still meets the mapping requirement. The high-resolution satellite image and rational polynomial parameter transformationmethod comprises the steps of: compiling a grid on an original image at a certain interval; in a set elevation range, replicating such grid at different elevations, and acquiring three-dimensional coordinates of each point on all the grids; when image space coordinates and the elevations are known, determining ground coordinates of each grid point by rational polynomial forward transformation; after a coordinate system of the image is transformed, determining new coordinates of all the grid points, wherein the new coordinates of the grid points correspond to object space coordinates; accordingto the transformed image, solving a normalized parameter of a rational polynomial after transformation; and when the normalized parameter is known, carrying out iteration on a corresponding relationship between the new coordinates of the grid points and the object space coordinates E, N and H to resolve a new rational polynomial parameter.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY ERYUAN ENG GRP CO LTD
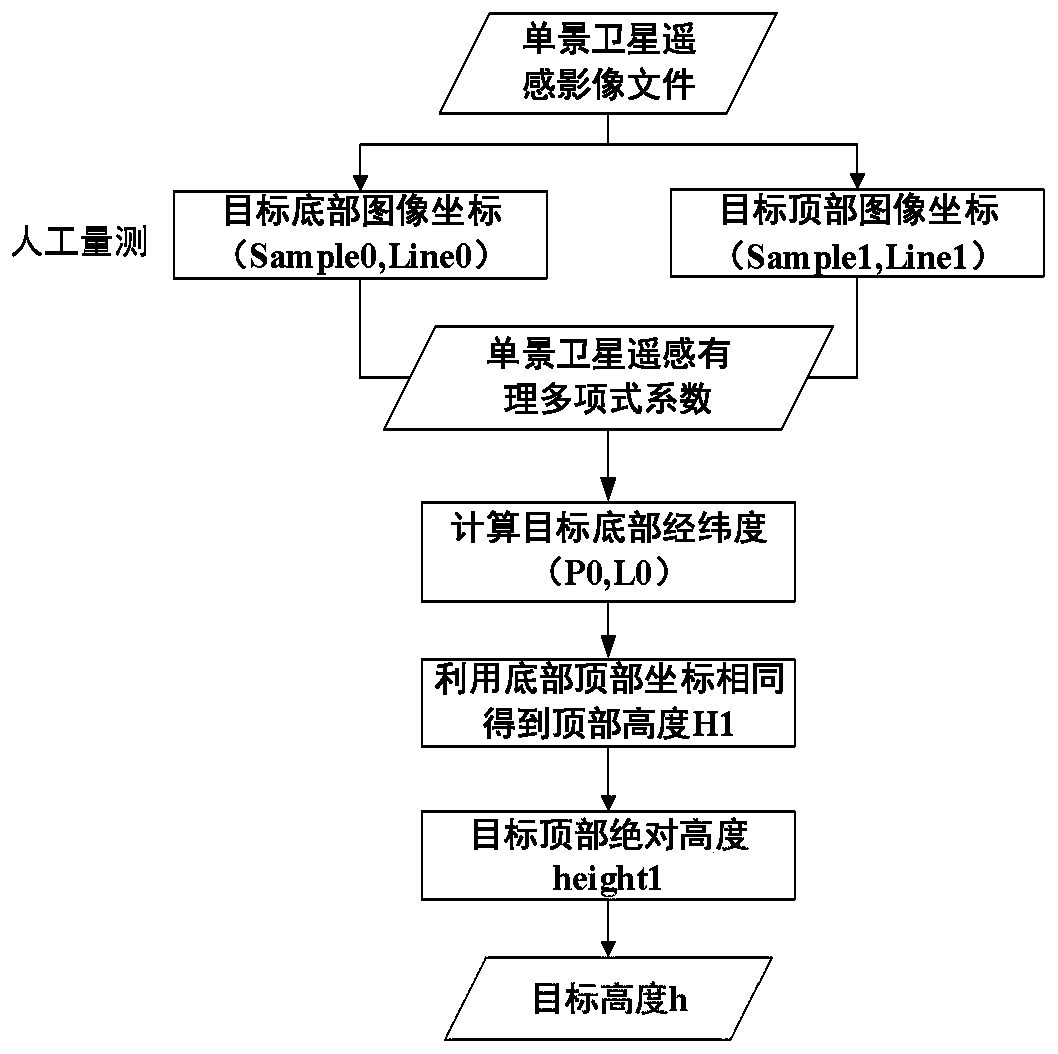
Rational polynomial coefficient-based single satellite-borne remote sensing image target height calculation method
ActiveCN111597496ARealization of direct solutionImprove calculation accuracyHeight/levelling measurementComplex mathematical operationsLongitudeRemote sensing
The invention discloses a rational polynomial coefficient-based single satellite-borne remote sensing image target height calculation method. The rational polynomial coefficient-based single satellite-borne remote sensing image target height calculation method comprises the following steps of obtaining a bottom coordinate and a top coordinate of a target on a remote sensing image; determining a relationship between original data image plane coordinates and ground three-dimensional coordinates through rational polynomial coefficients; expressing target bottom coordinates in a form of the rational polynomial coefficients; expressing the top coordinates of the target in the form of rational polynomial coefficients; directly solving the top height of the regularized target based on the featurethat the bottom longitude and latitude of the target are consistent with the top longitude and latitude; performing inverse transformation by adopting a regularization formula to obtain a target topabsolute height; and performing difference between the target top height and the bottom height to obtain a target height. The rational polynomial coefficient-based single satellite-borne remote sensing image target height calculation method does not need to use a spatial triangular relation between a satellite or the sun and a target, is higher in calculation precision, and directly observes the target body while shadow information of the target is not needed, and the calculation process is simple, convenient and efficient.
Owner:AEROSPACE INFORMATION RES INST CAS
Estimation of coefficients for a rational polynomial camera model
ActiveUS7421151B2Image enhancementImage analysisCamera imageIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
One aspect of the invention is embodied in a number of machine-readable media having stored thereon sequences of instructions which, when executed by a machine, cause the machine to perform a number of actions. The actions include, for each of a plurality of image space coordinates of a camera image, retrieving 1) a corresponding camera position, and 2) corresponding object space coordinates on an object surface that is represented by the camera image. Then, for each of a plurality of height surfaces (chosen with respect to the object surface), a grid coordinate defined by an intersection between the height surface, and a line extending between the camera position and the object space coordinates, is determined. The determined grid coordinates are then associated with their corresponding image space coordinates. Finally, coefficients for a rational polynomial camera model are estimated by fitting rational polynomials to at least the grid coordinates and image space coordinates.
Owner:MAXAR INTELLIGENCE INC
Ortho-correction method for high-resolution remote sensing images based on floating control points
ActiveCN103530628BRealize Image CorrectionExact geographic coordinatesCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorTest sample
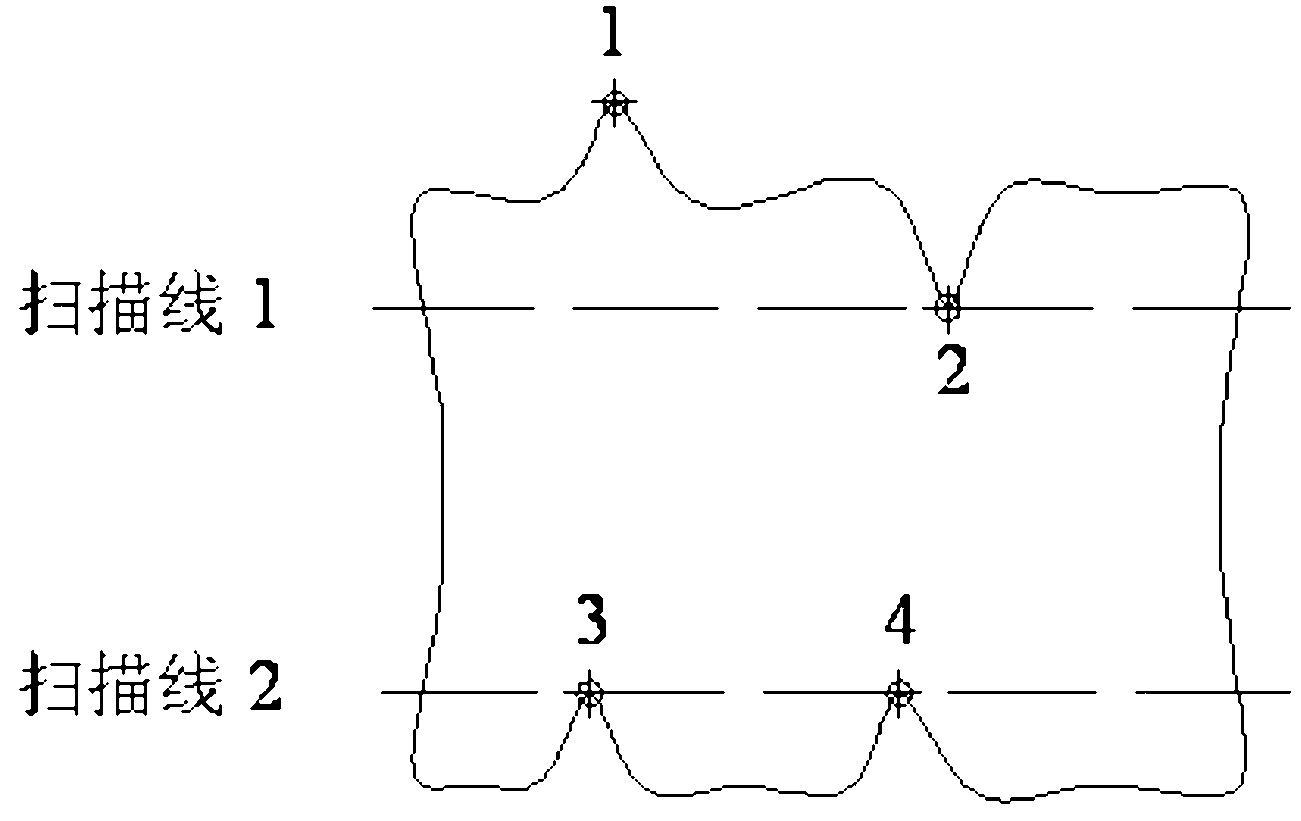
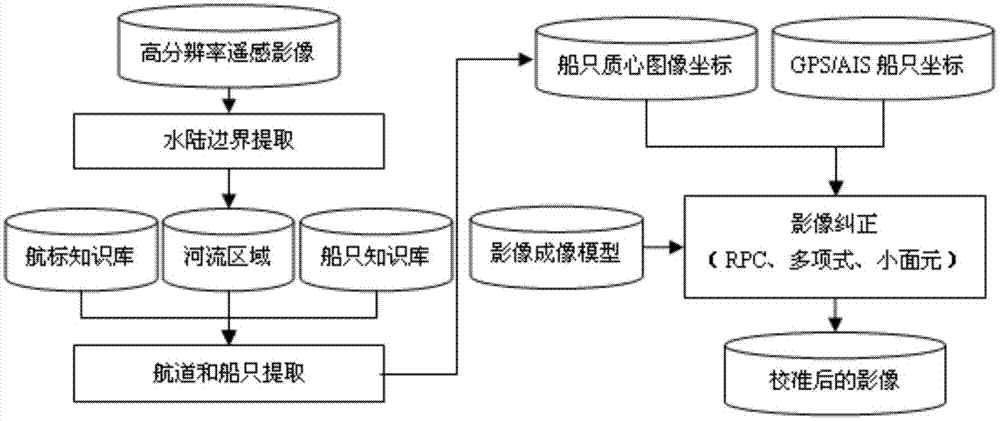
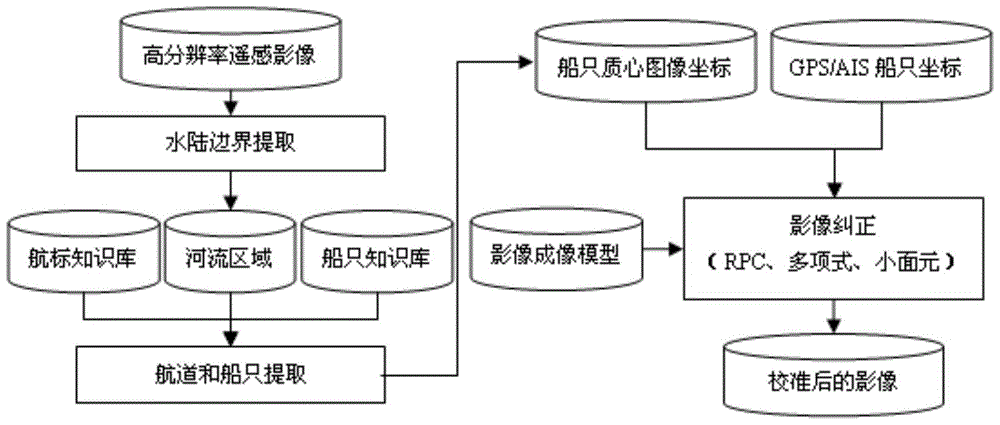
The invention discloses a high-resolution remote sensing image orthorectification method based on floating control points, comprising the steps of: step S101, extracting land and water boundaries based on the high-resolution remote sensing image, and selecting small targets in the water area as candidate targets for ship recognition ; Step S102, construct feature vector; Step S103, construct training and test sample library; Step S104, utilize SVM or ANN method, based on training and test sample library training classifier, complete ship identification, obtain the image coordinates of ship; Step S105, For the identified ship, use morphological subdivision to obtain its geometric centerline, and use the geometric centerline to complete the matching with the tangent direction of the AIS track of the ship, thereby obtaining accurate GPS positioning information of the ship; step S106, based on The ship's image coordinates and geographic coordinates constitute the control points, and the satellite rational polynomial correction model is optimized to obtain high-precision orthophotos.
Owner:SHANGHAI URBAN CONSTR DESIGN RES INST GRP CO LTD
High-precision geometric correction method of satellite remote sensing imagery by slightly correcting rpc parameters
ActiveCN105761228BPrevent morbidityImproved accuracy of image correctionImage enhancementImage analysisTransformation parameterRemote sensing
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF SURVEYING & MAPPING
A Method of Orthorectification for CCD Image of Environment-1 Satellite
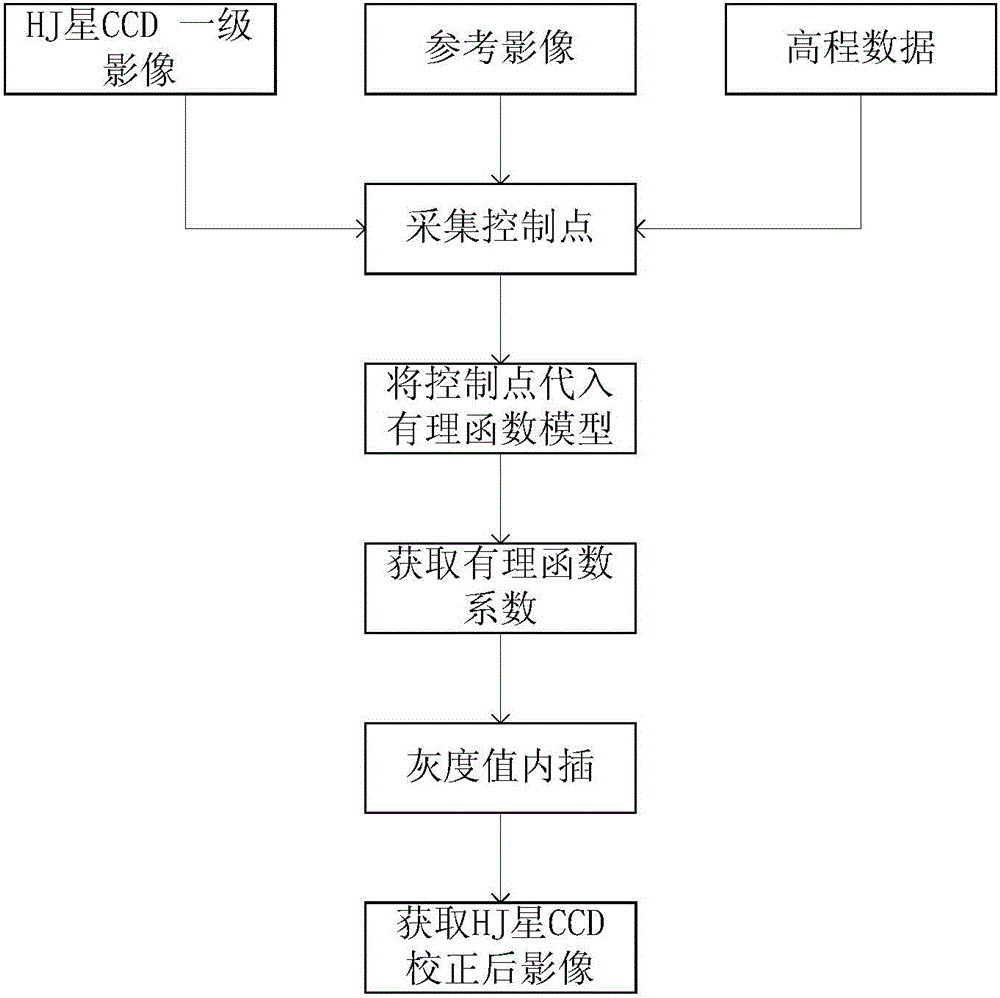
A method for orthorectification of the CCD image of the Environment-1 satellite. First, import the HJ star CCD first-level image and the corresponding elevation data and reference data, and then uniformly collect ground control points on each HJ star CCD first-level image. The coordinates of the control points are imported into the cubic rational function model, and the rational polynomial coefficient (RPC) is calculated to obtain the corresponding rational function model, and then the pixel coordinates of all points in the first-level CCD image of the Environment-1 satellite are input into the rational function model to obtain Corresponding to the coordinates of each point of the orthorectified image, and then adopting the bilinear interpolation method to interpolate the gray value of each point of the corrected image to the point whose pixel coordinates are the entire row and column, and obtain the orthorectified image. Compared with the traditional polynomial method, the method of the invention can obtain higher precision.
Owner:CHINA CENT FOR RESOURCES SATELLITE DATA & APPL
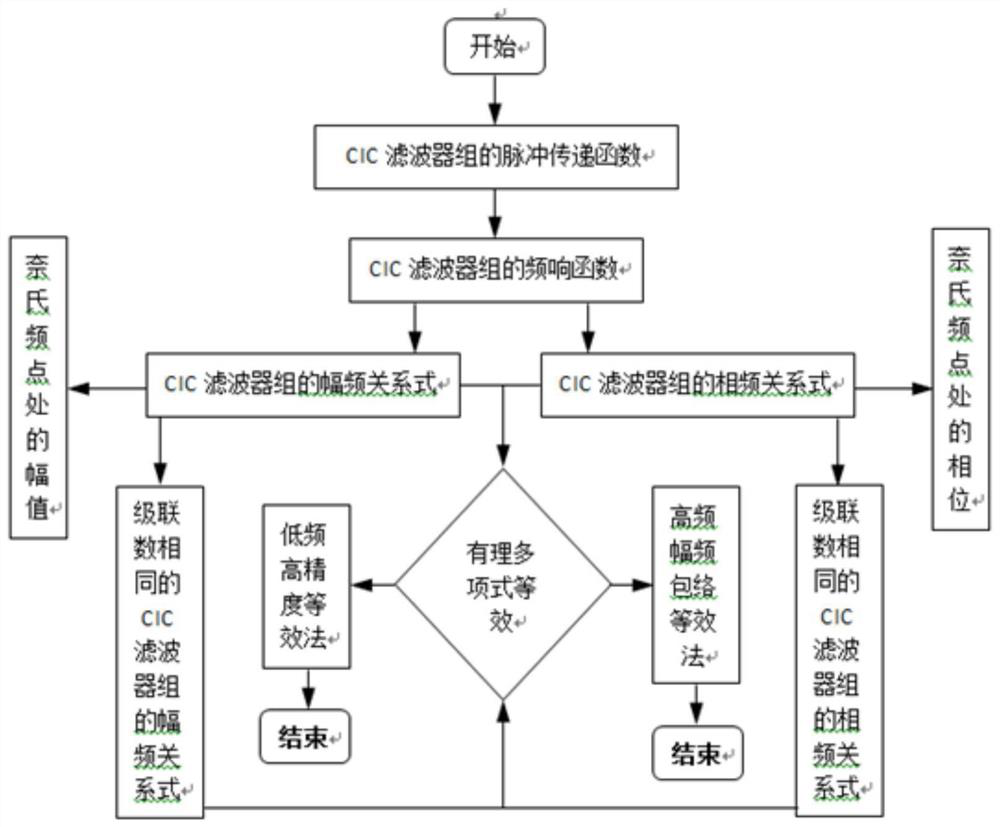
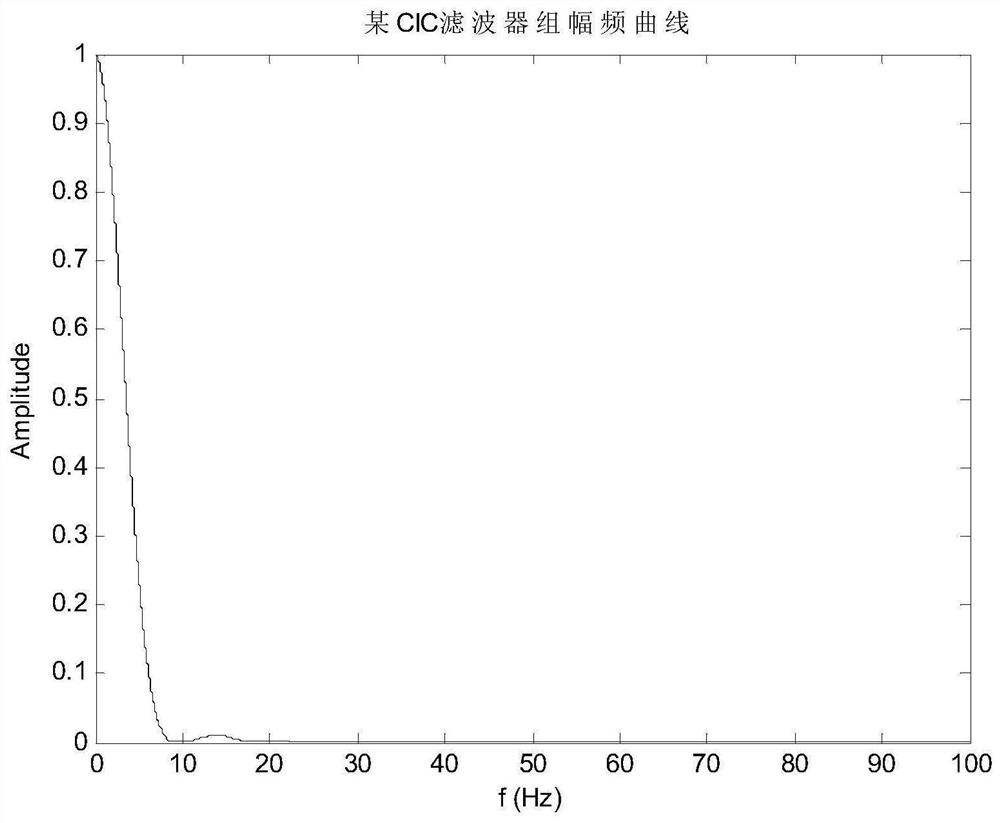
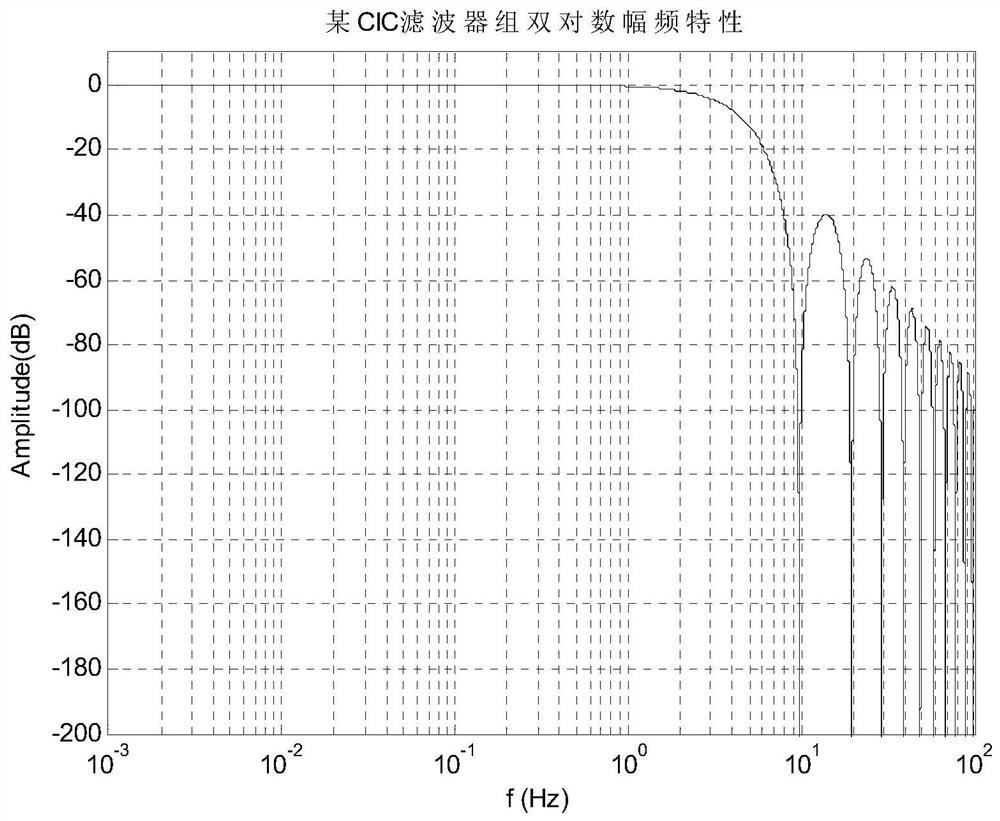
Transfer function equivalence method of CIC filter bank
ActiveCN111641400AEasy to drawIt is convenient to calculate the amplitude-frequency equivalent errorDigital technique networkHarmonic reduction arrangementLoop controlControl system
The invention discloses amplitude-frequency and phase-frequency response expressions of a common CIC filter bank, and discloses two methods for carrying out rational polynomial transfer function equivalence on the frequency response characteristics of the common CIC filter bank, so that the frequency domain design of a drag-free controller and the rapid simulation of a closed-loop control system are successfully realized. A low-frequency high-precision equivalent method can achieve very high equivalent precision in a low frequency band, but a high-frequency upwarp phenomenon exists. The upwarpcan be inhibited by introducing high-resistance filtering, so that the analysis and design of a control system can be normally carried out. An equivalent result of a high-frequency amplitude-frequency envelope equivalence method is generally simple, and great convenience is brought to analysis, design and rapid simulation of the control system; and a certain error only exists in a low-frequency-band local part. The method belongs to the technical field of control technology and signal processing based on a CIC filter bank.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com