Method for calculating time-lag electric power system eigenvalue and discriminating stability based on Pade approximation
A power system and discrimination method technology, applied in the direction of electrical components, circuit devices, AC network circuits, etc., can solve problems such as lack of measurement methods, poor control effects, and limited power grid transmission capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
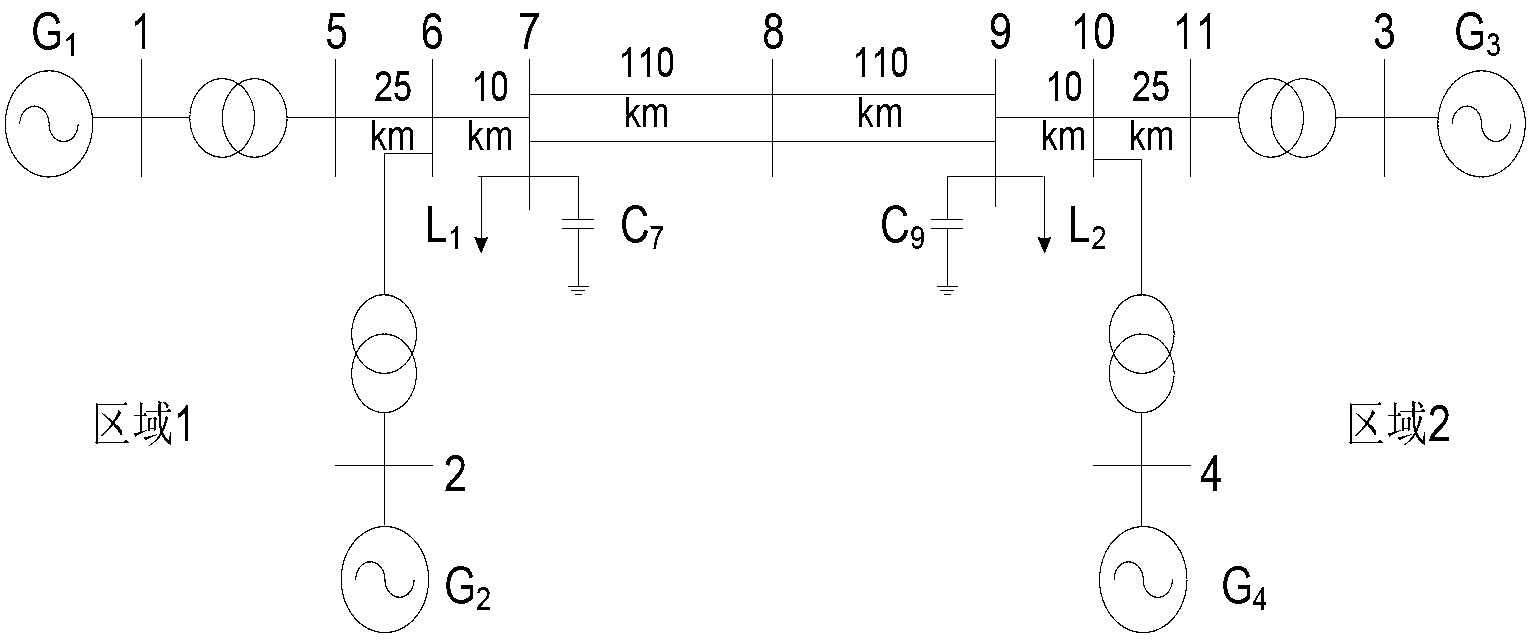
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0091] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
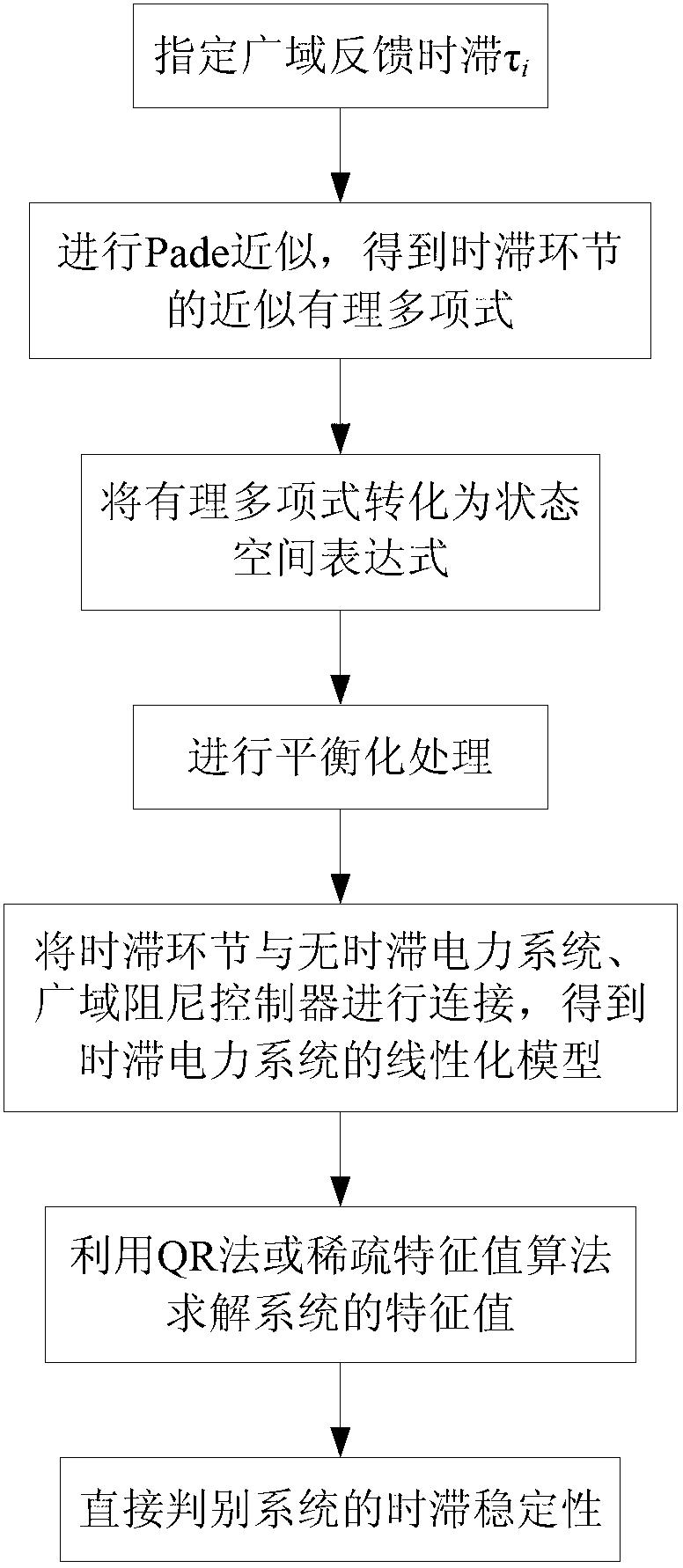
[0092] Such as figure 1 As shown, a Pade approximation-based eigenvalue calculation and stability discrimination method for time-delayed power systems, the specific steps are as follows:
[0093] Step 1: Specify the wide-area feedback delay τ i and Pade approximation order k;
[0094] Step 2: Perform Pade approximation to obtain the approximate rational polynomial of the delay link;
[0095] Step 3: Transform rational polynomials into state space expressions;
[0096] Step 4: Perform balance processing;
[0097] Step 5: Connect the time-delay link with the time-delay-free power system and the wide-area damping controller to obtain the linearized model of the time-delay power system;
[0098] Step 6: Use the QR method or the sparse eigenvalue algorithm to solve the eigenvalues of the system;
[0099] Step seven: directly judge the time-delay stabi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com