Patents
Literature
398results about "Aquisition of 3D object measurements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
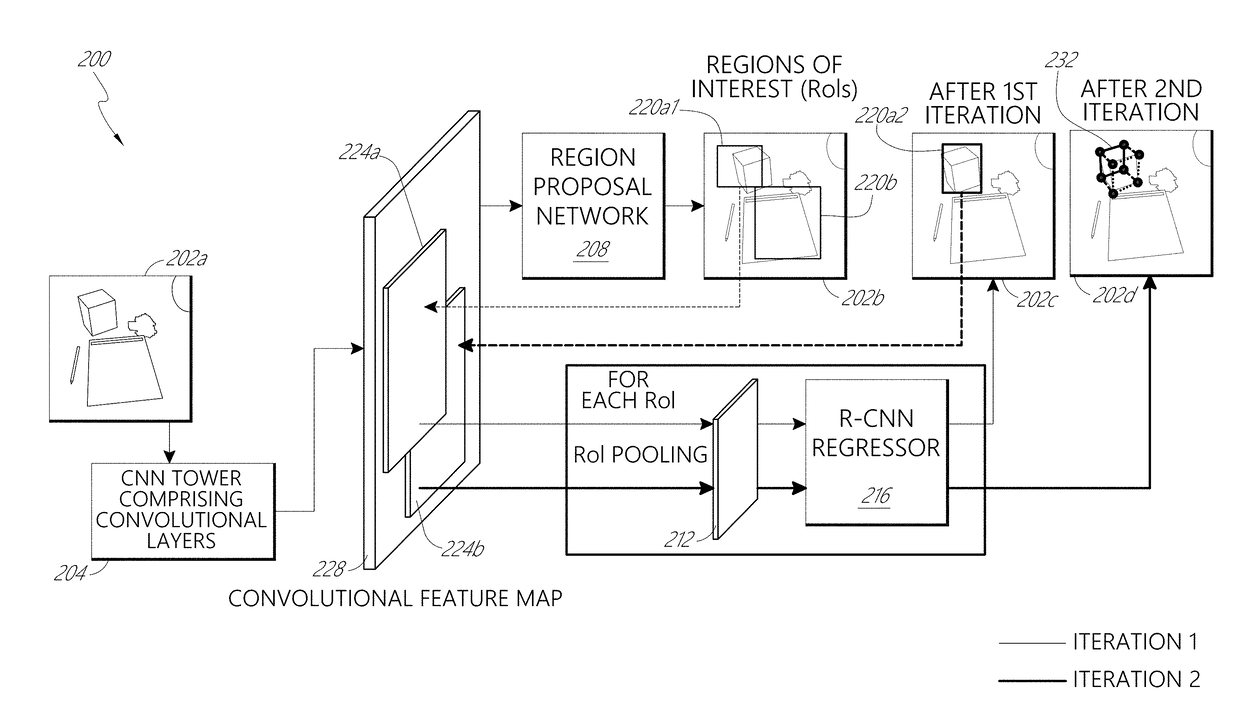
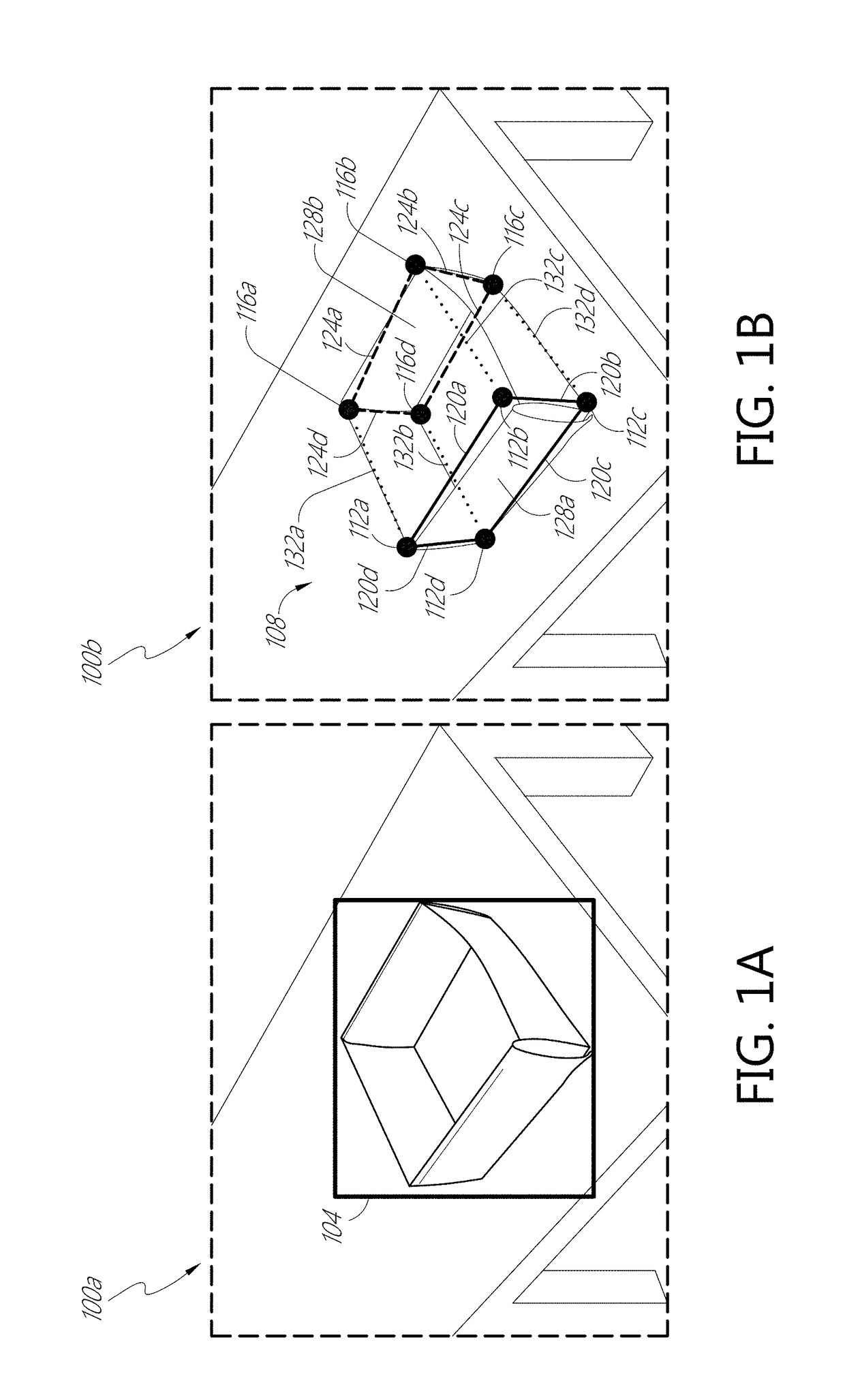
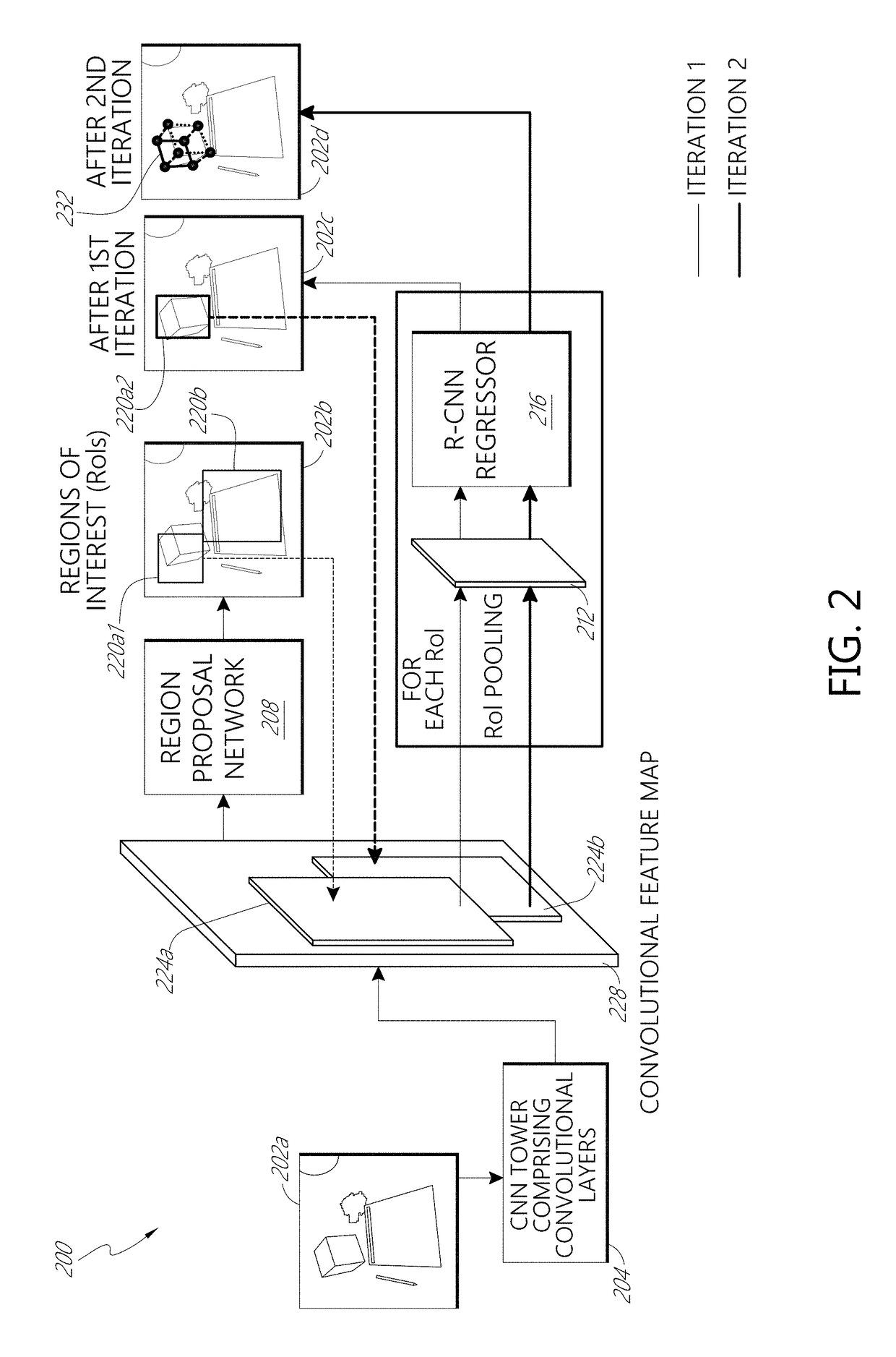
Deep learning system for cuboid detection
Systems and methods for cuboid detection and keypoint localization in images are disclosed. In one aspect, a deep cuboid detector can be used for simultaneous cuboid detection and keypoint localization in monocular images. The deep cuboid detector can include a plurality of convolutional layers and non-convolutional layers of a trained convolution neural network for determining a convolutional feature map from an input image. A region proposal network of the deep cuboid detector can determine a bounding box surrounding a cuboid in the image using the convolutional feature map. The pooling layer and regressor layers of the deep cuboid detector can implement iterative feature pooling for determining a refined bounding box and a parameterized representation of the cuboid.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
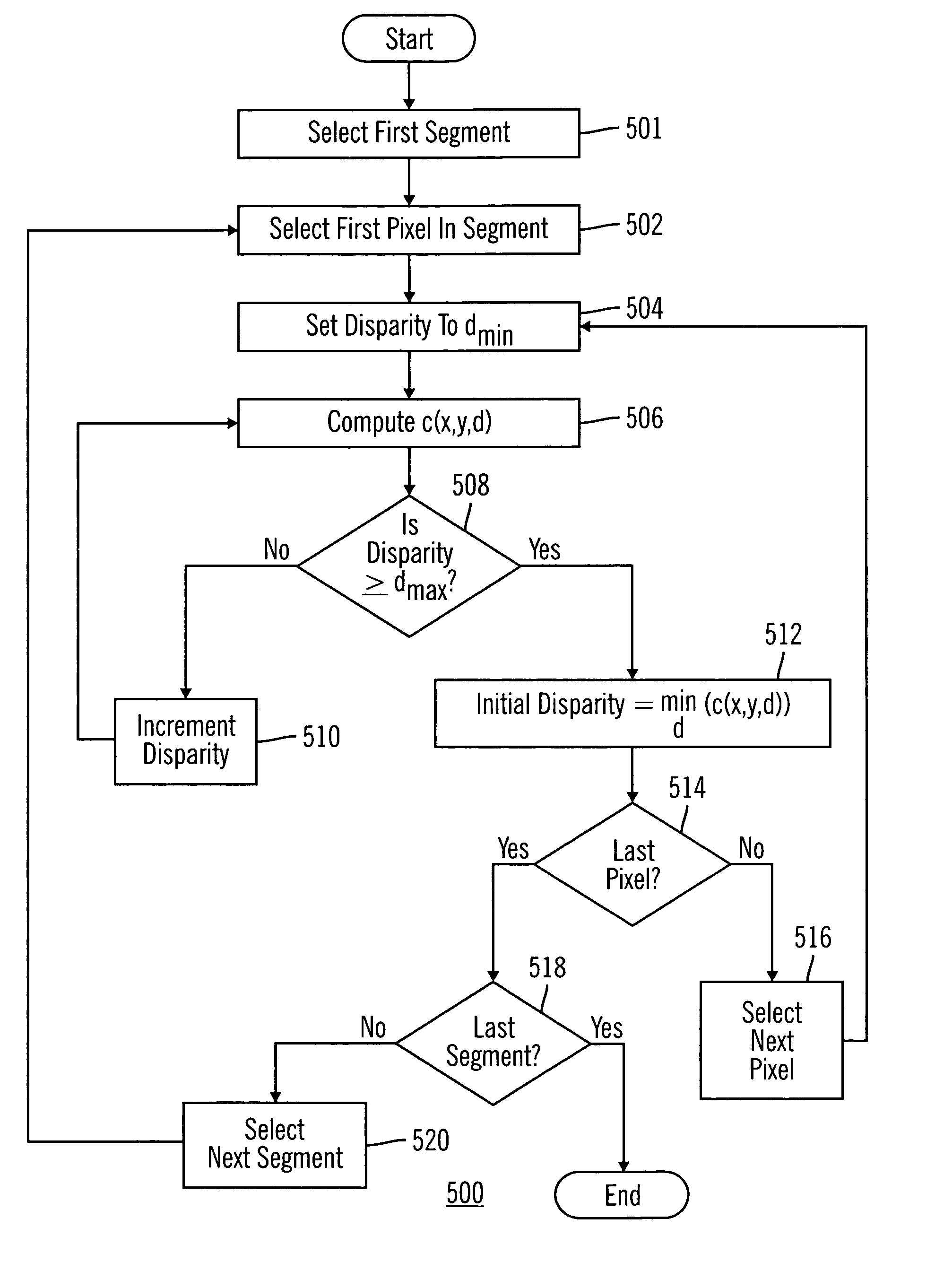
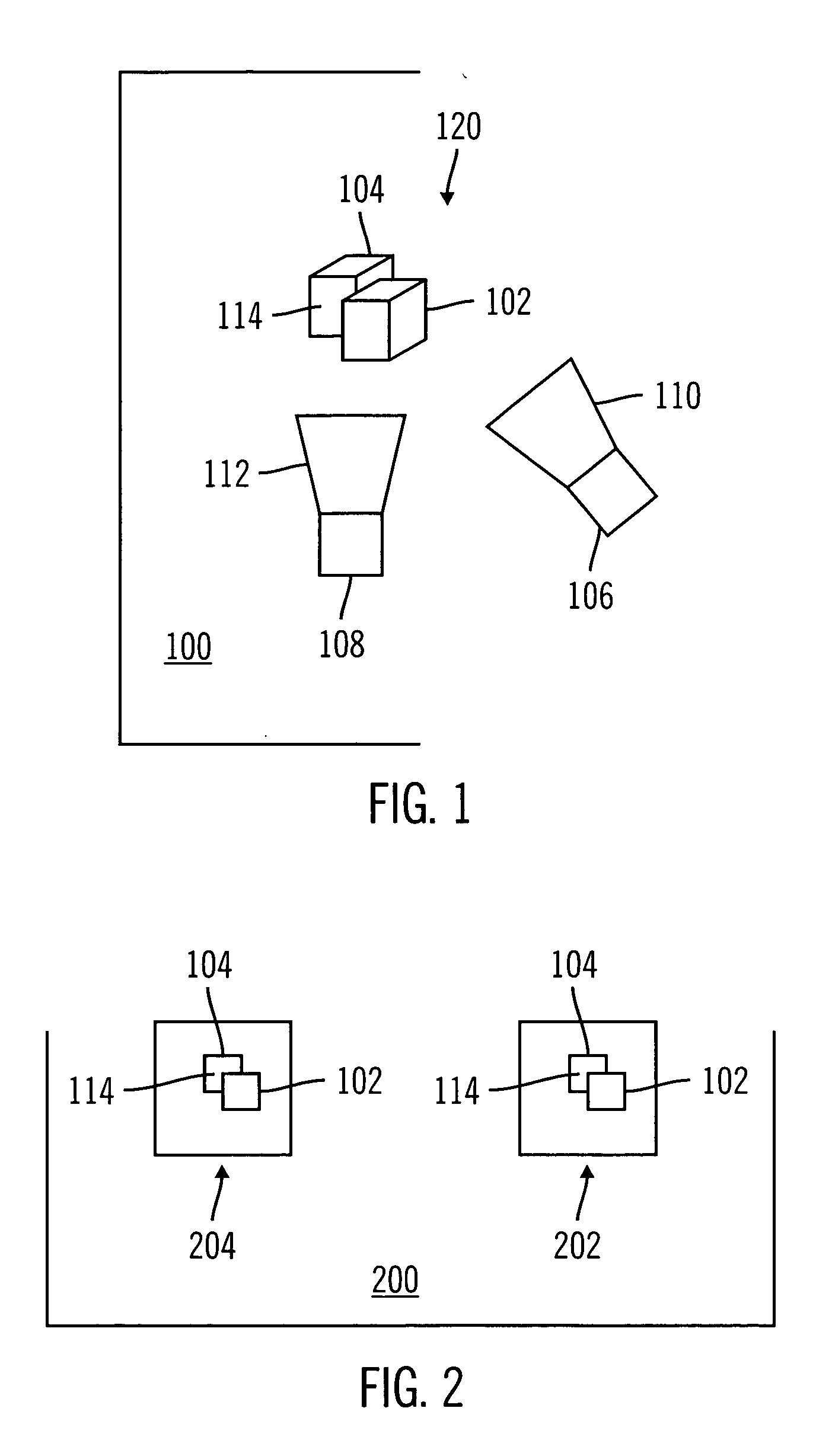
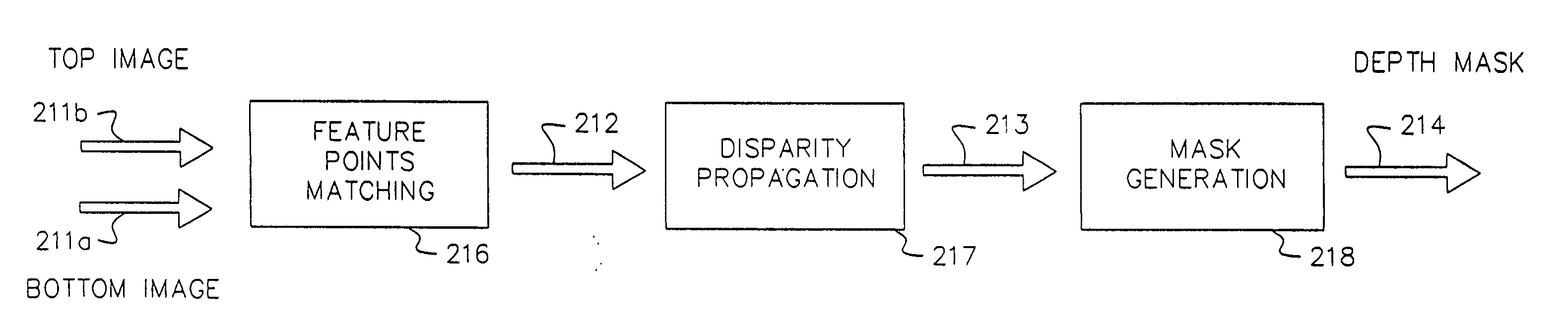
Segment based image matching method and system
An image matching method and system for use with multiple images of a scene captured from different angles. Image matching is performed by identifying a plurality of segments within at least two images, determining an initial disparity values for pixels in the images and then determining initial disparity planes for the segments by fitting a plane to initial disparity values for the segments. A refined disparity plane set is created by iteratively refitting the disparity planes by using various fitting cost functions and weighted linear systems. A labeling of each segment to a disparity plane is made by minimizing a global energy function that includes energy terms for segment to disparity plane matching as well as penalizing disparity plane discontinuities between adjacent image segments.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
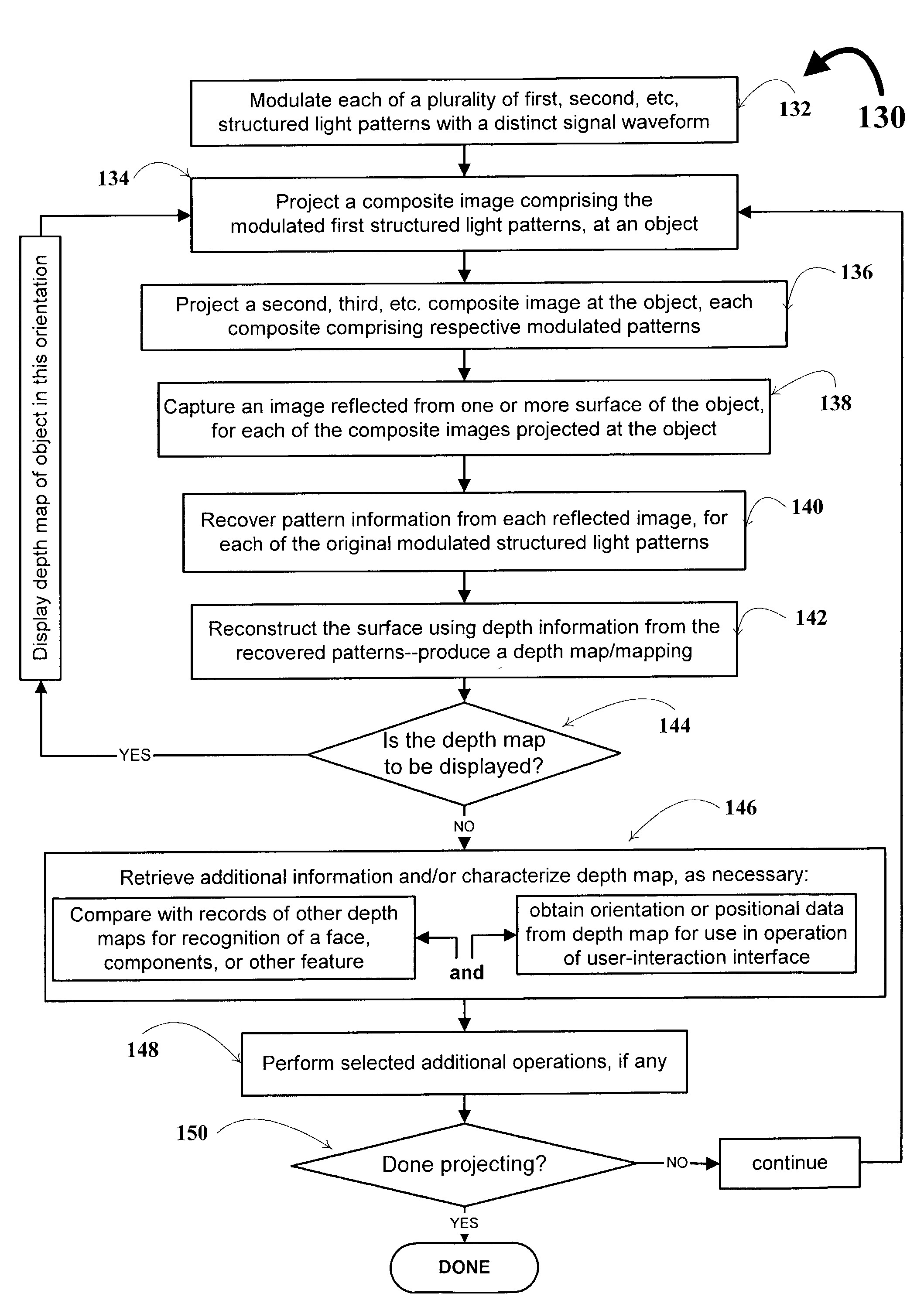
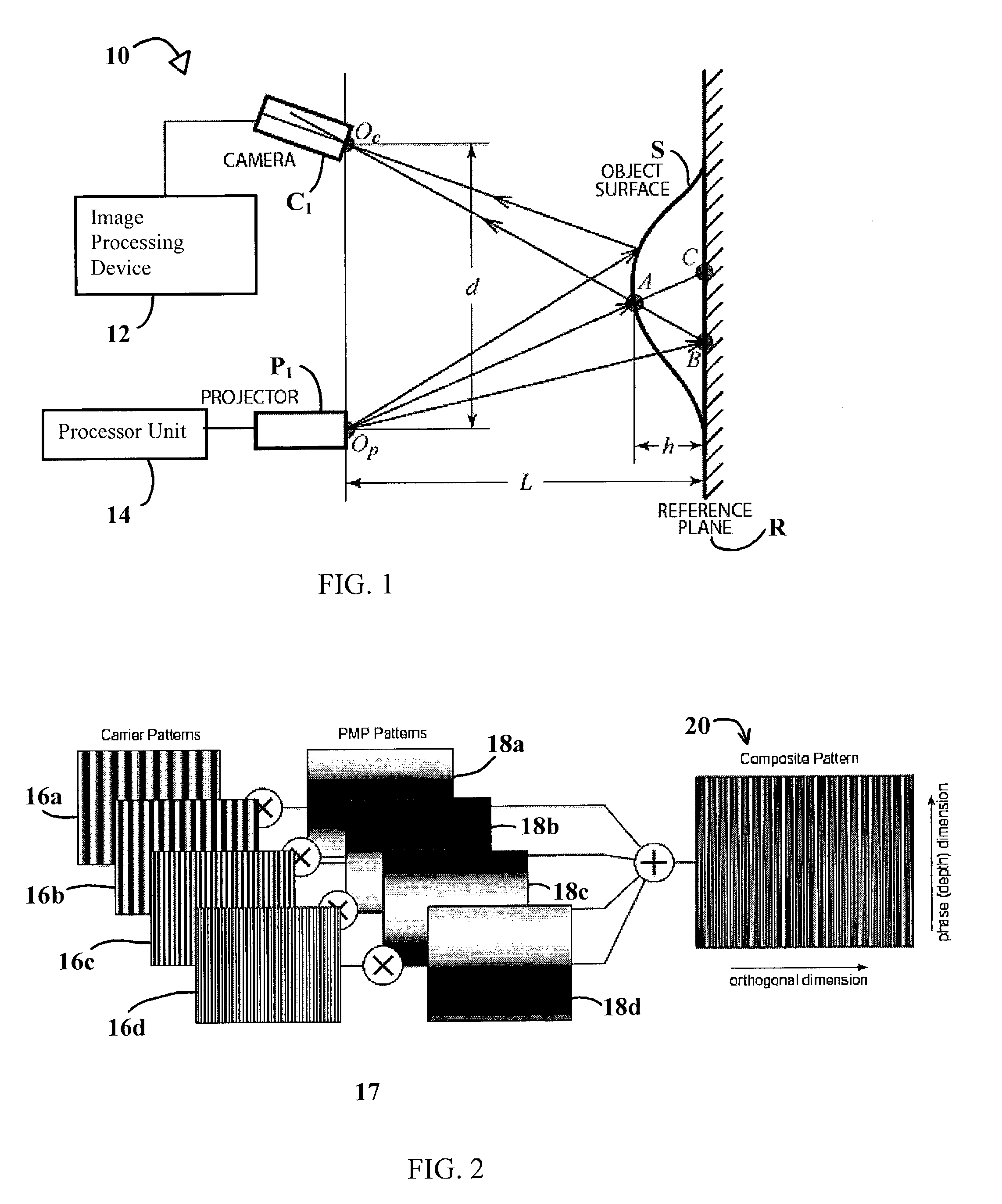
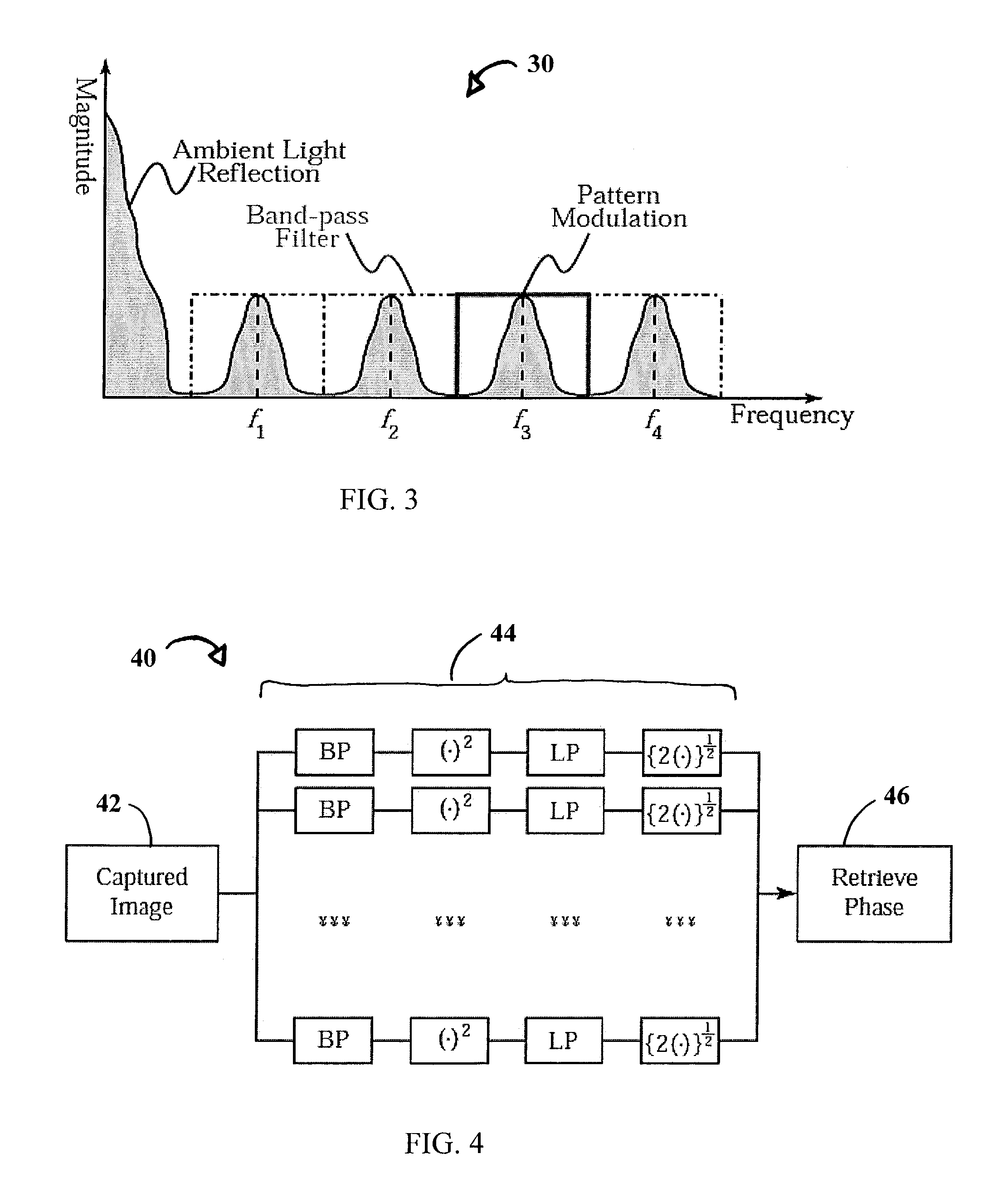
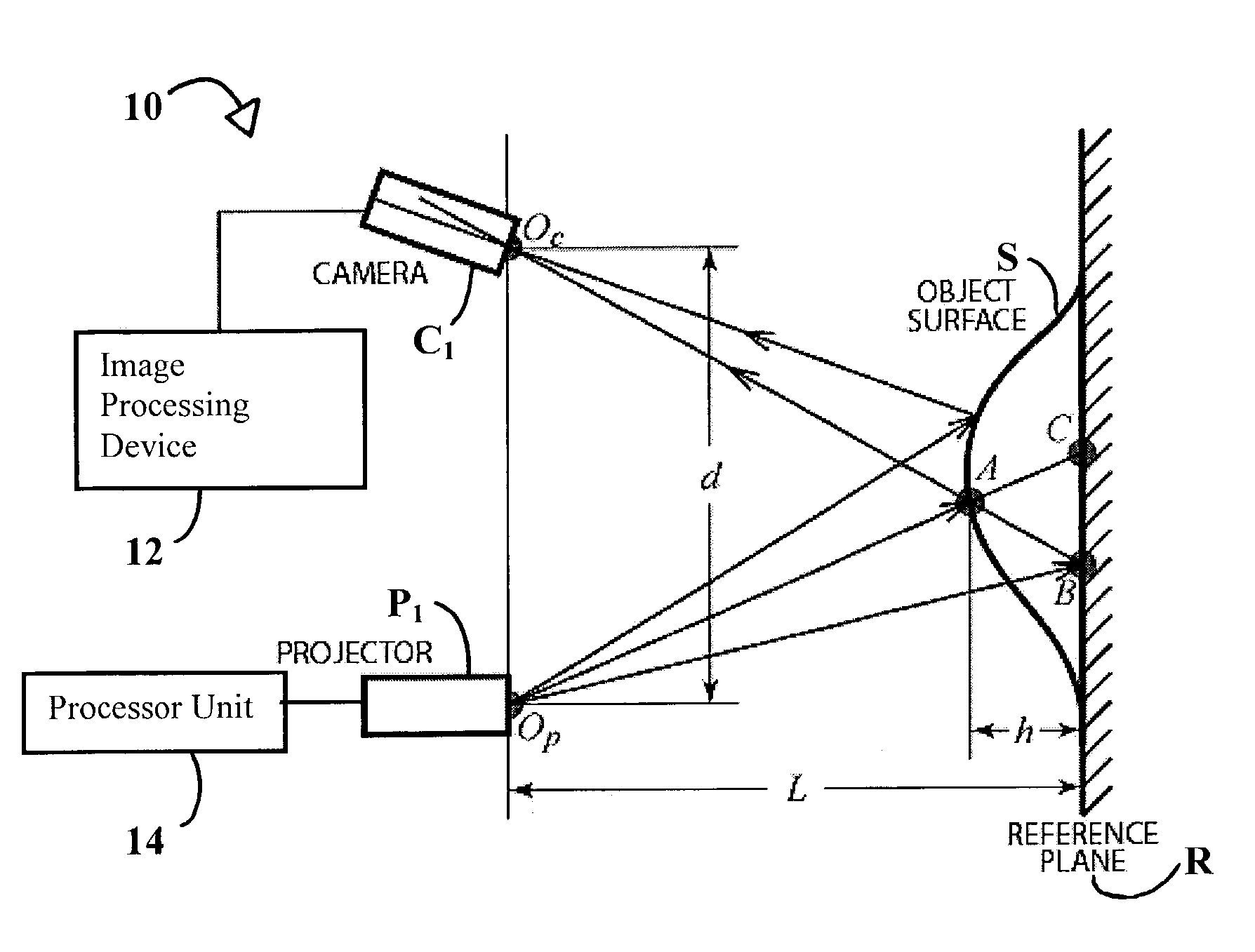
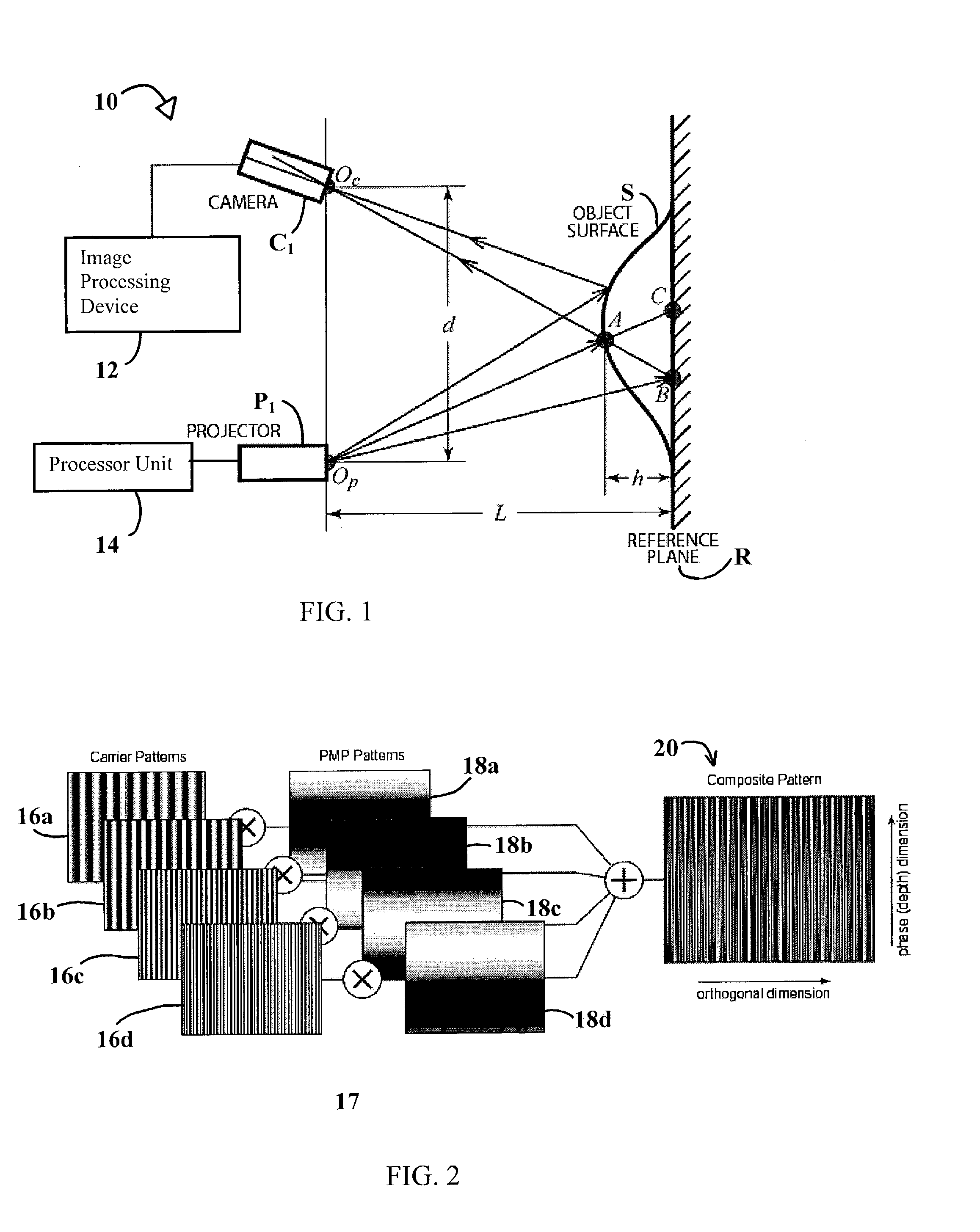
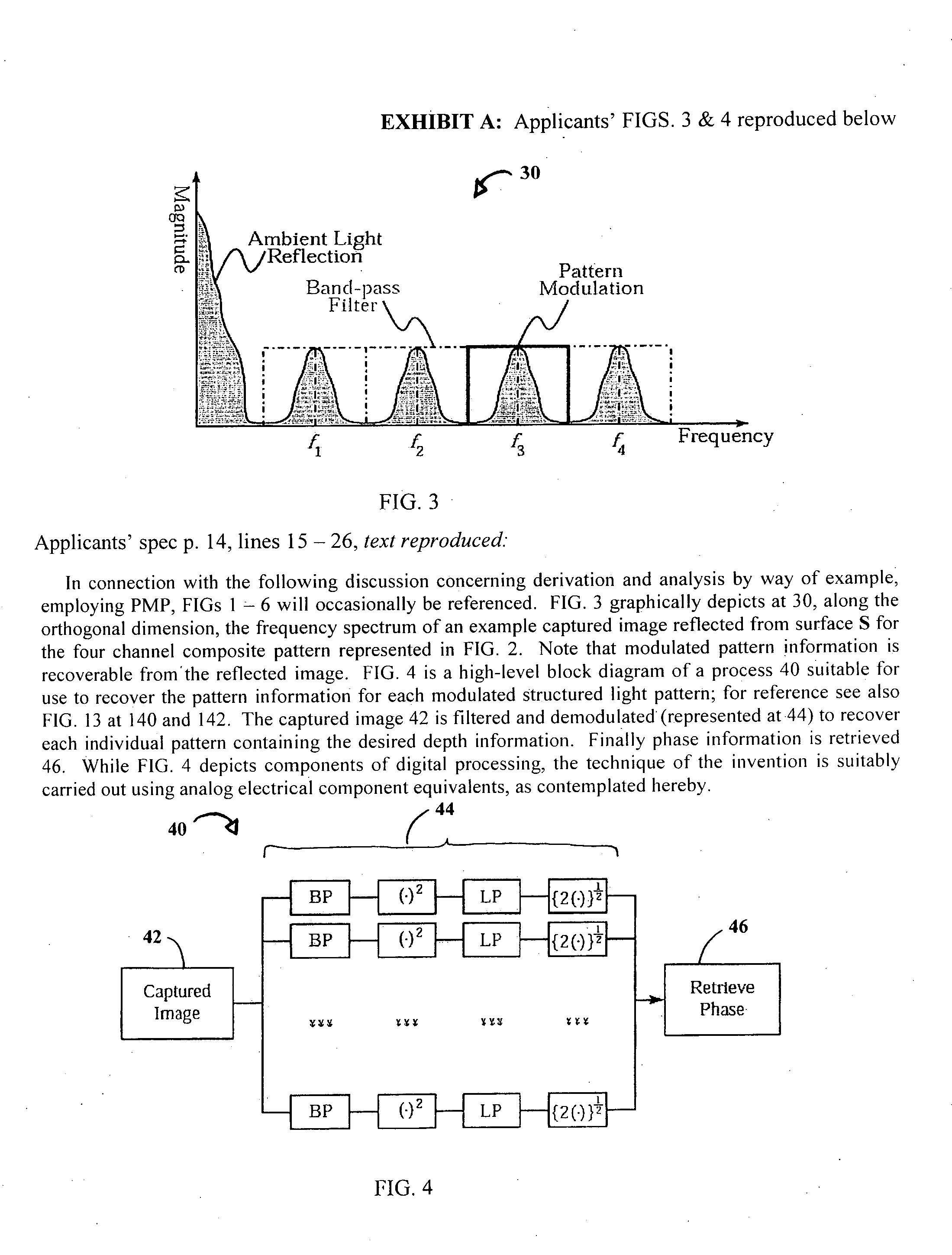
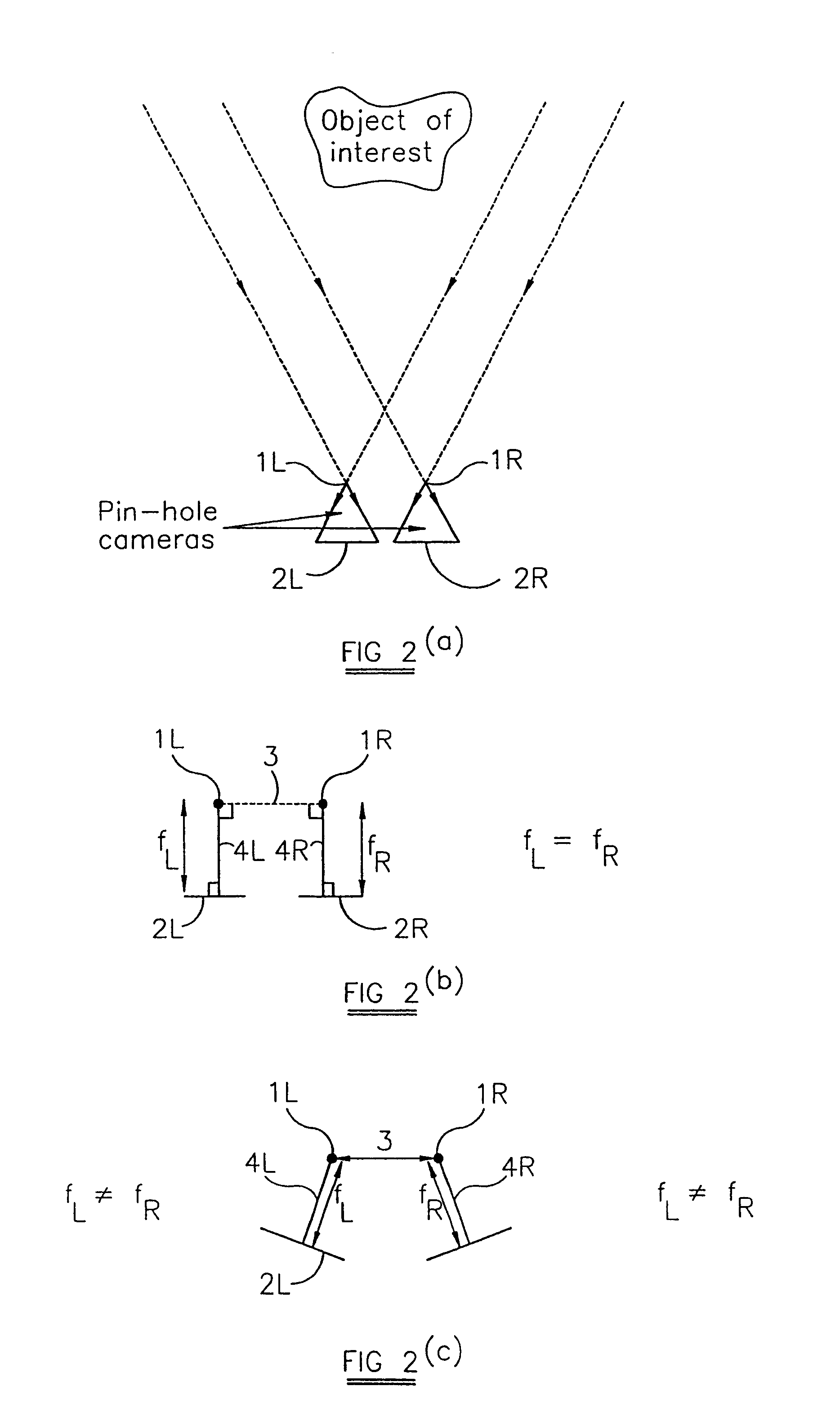
System and technique for retrieving depth information about a surface by projecting a composite image of modulated light patterns
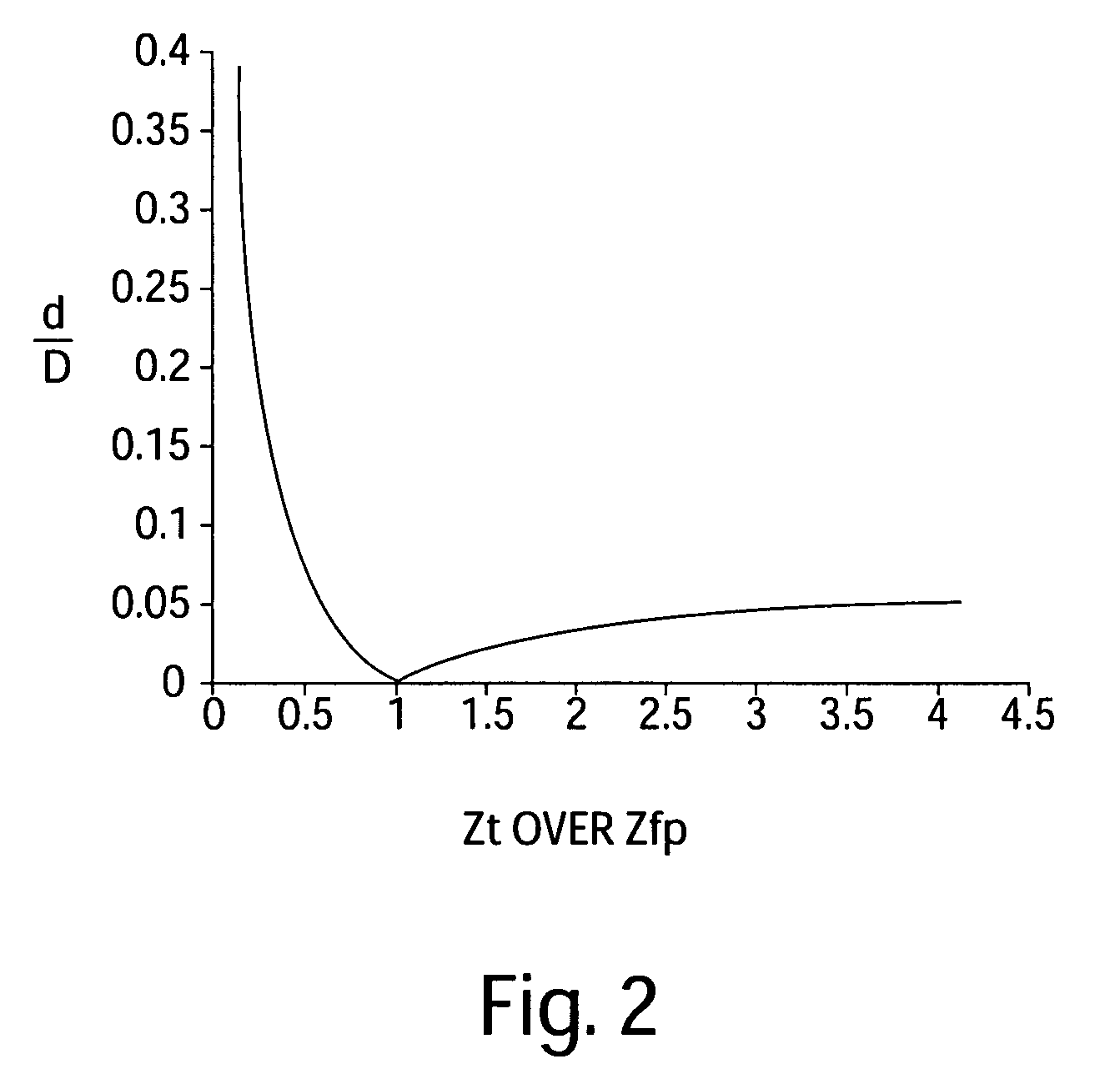
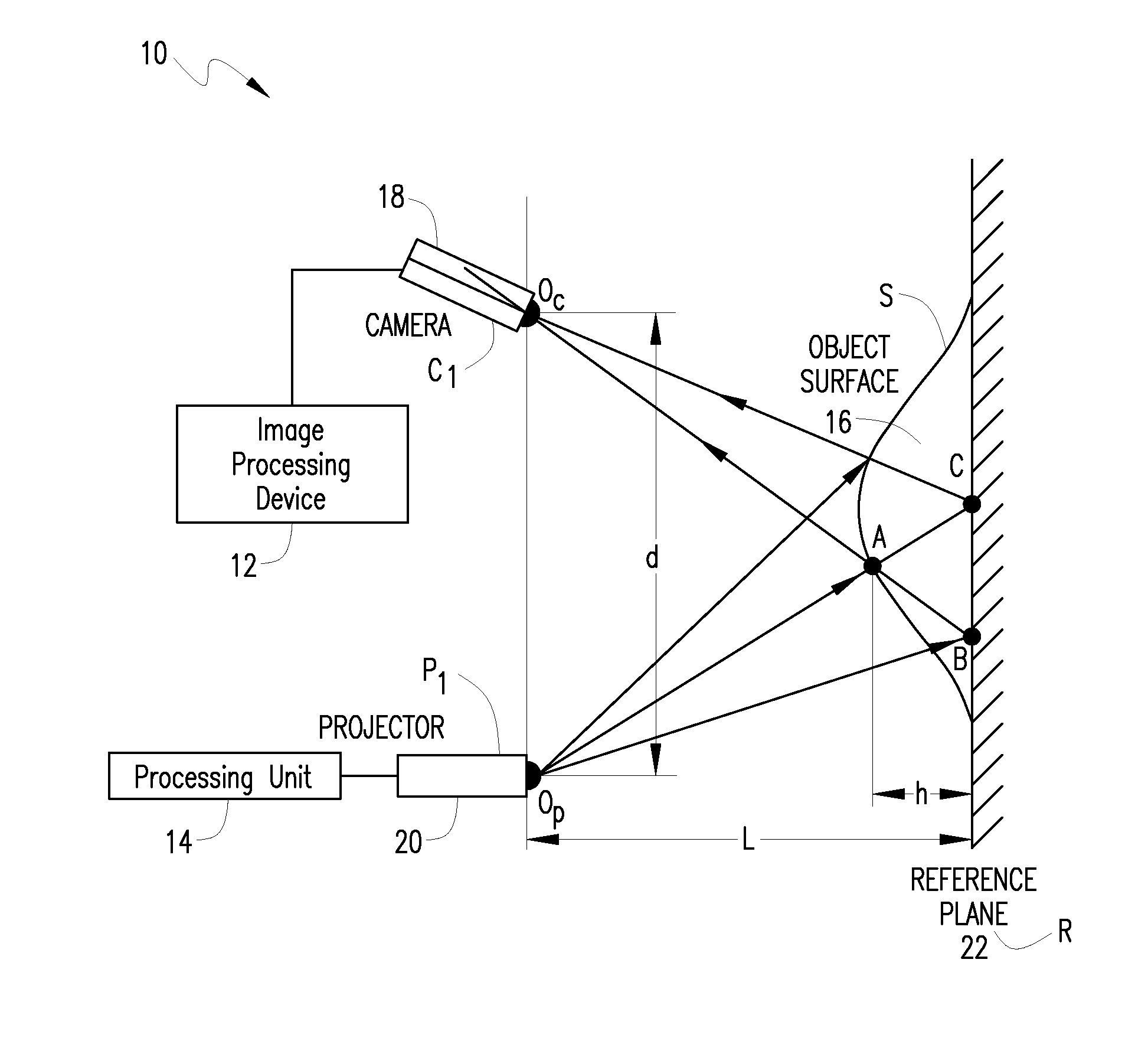
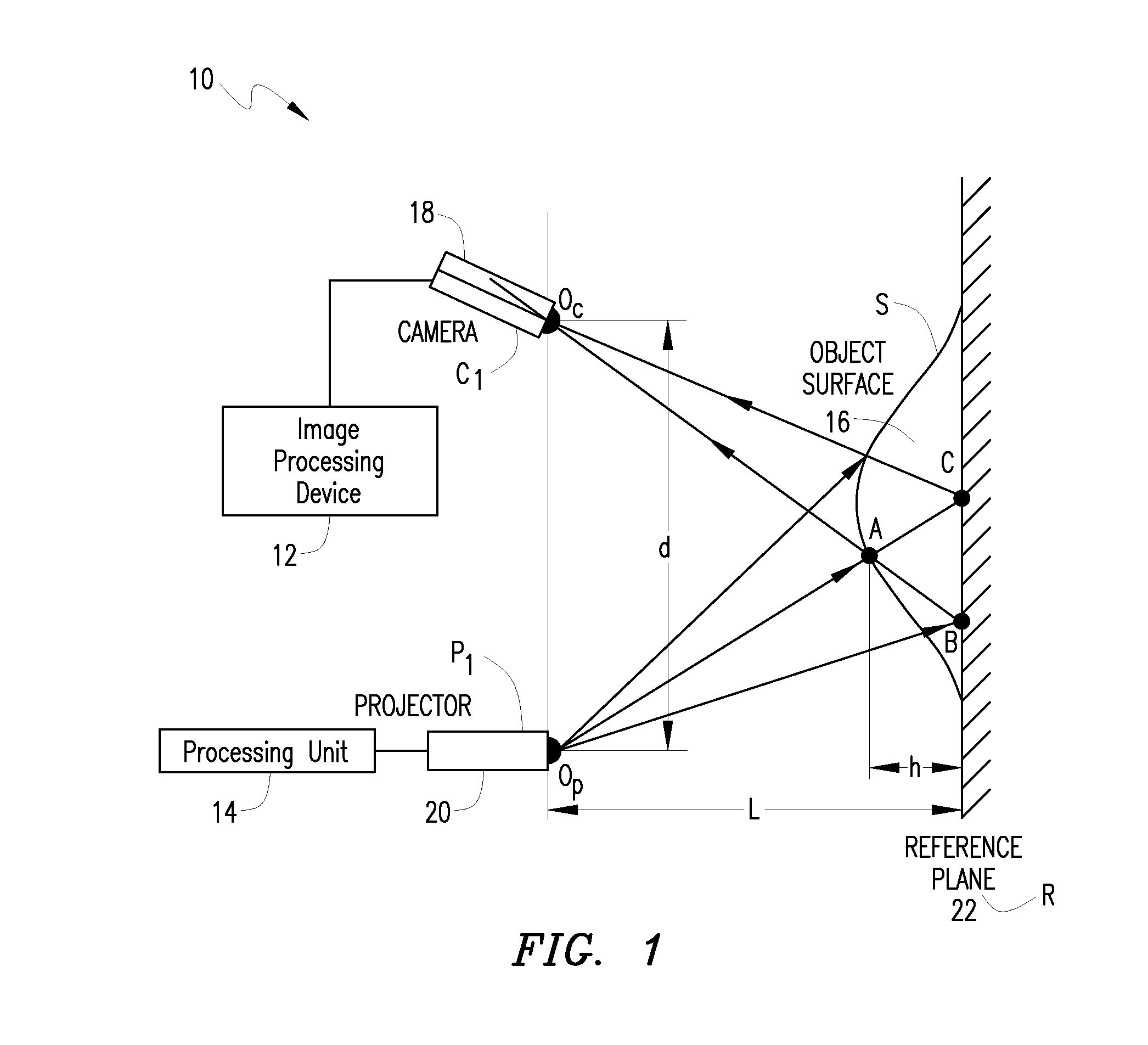
InactiveUS7440590B1More detailed and large depth mappingLimited bandwidthProjectorsCathode-ray tube indicatorsInteraction interfaceTelecollaboration
A technique, associated system and program code, for retrieving depth information about at least one surface of an object. Core features include: projecting a composite image comprising a plurality of modulated structured light patterns, at the object; capturing an image reflected from the surface; and recovering pattern information from the reflected image, for each of the modulated structured light patterns. Pattern information is preferably recovered for each modulated structured light pattern used to create the composite, by performing a demodulation of the reflected image. Reconstruction of the surface can be accomplished by using depth information from the recovered patterns to produce a depth map / mapping thereof. Each signal waveform used for the modulation of a respective structured light pattern, is distinct from each of the other signal waveforms used for the modulation of other structured light patterns of a composite image; these signal waveforms may be selected from suitable types in any combination of distinct signal waveforms, provided the waveforms used are uncorrelated with respect to each other. The depth map / mapping to be utilized in a host of applications, for example: displaying a 3-D view of the object; virtual reality user-interaction interface with a computerized device; face—or other animal feature or inanimate object—recognition and comparison techniques for security or identification purposes; and 3-D video teleconferencing / telecollaboration.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
System and technique for retrieving depth information about a surface by projecting a composite image of modulated light patterns
InactiveUS20080279446A1Reduce system costInformation can be reducedUsing optical meansAquisition of 3D object measurementsInteraction interfaceTelecollaboration
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
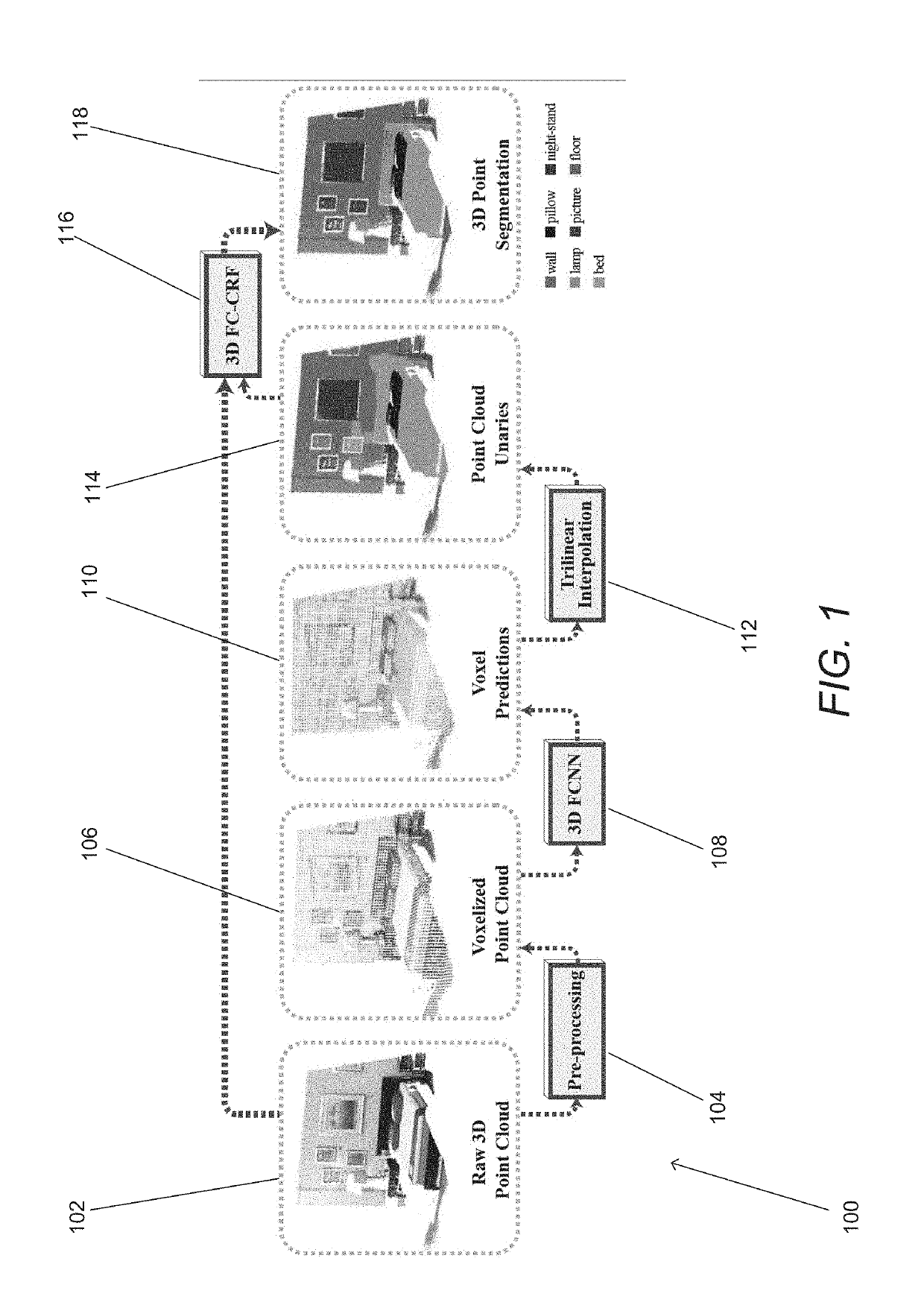
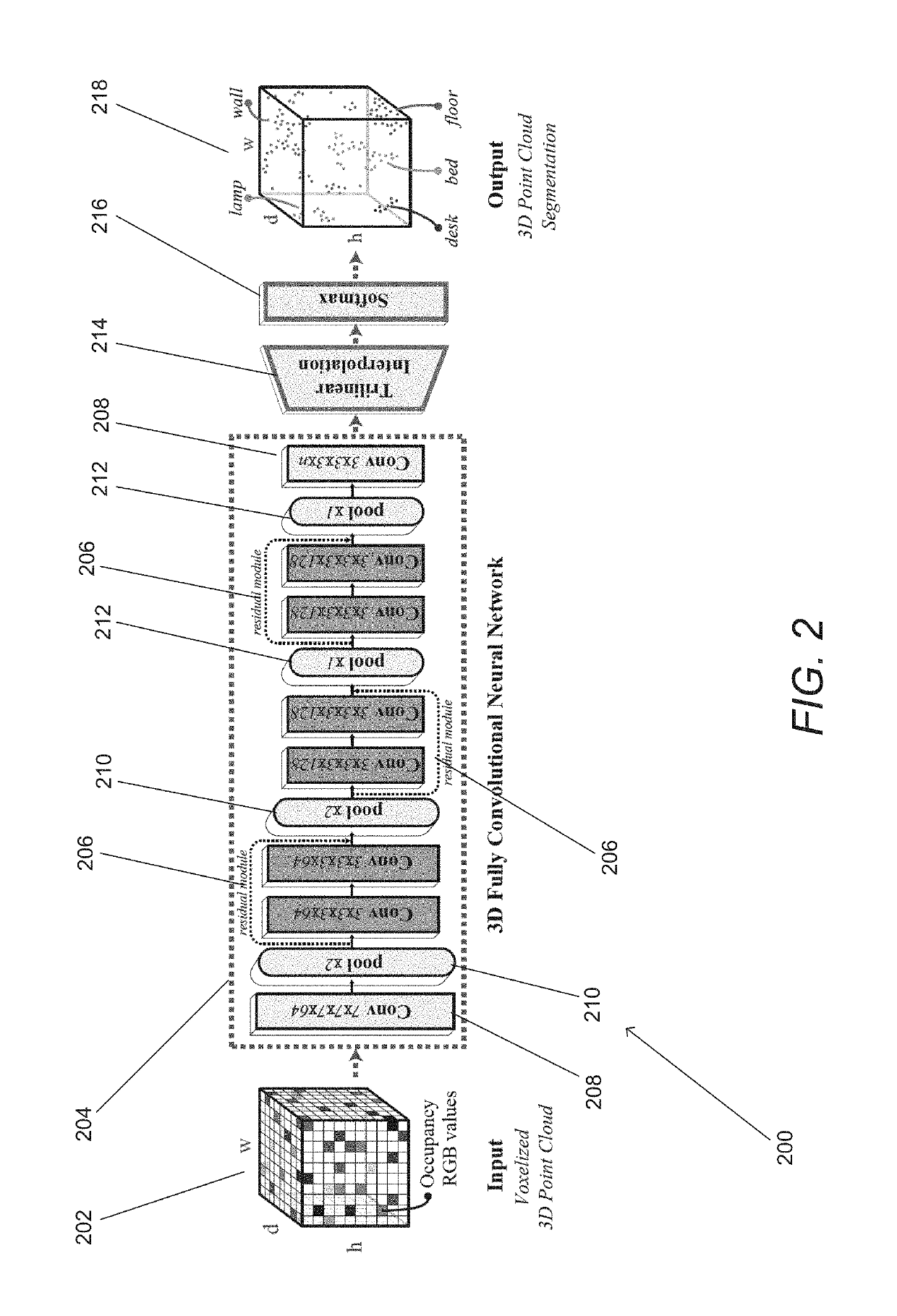
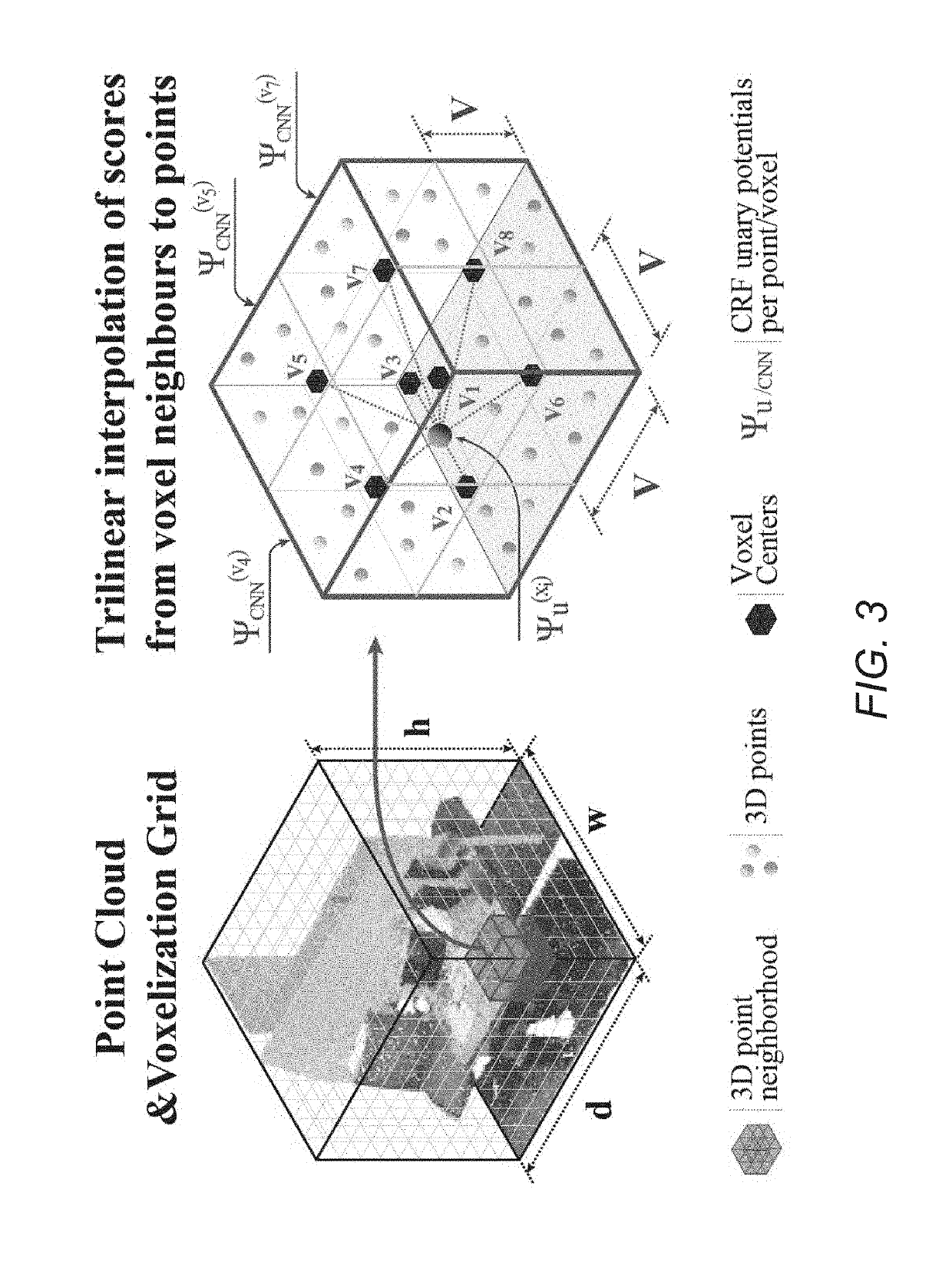
Systems and Methods for Semantic Segmentation of 3D Point Clouds
Systems and methods for obtaining 3D point-level segmentation of 3D point clouds in accordance with various embodiments of the invention are disclosed. One embodiment includes: at least one processor, and a memory containing a segmentation pipeline application. In addition, the segmentation pipeline application configures the at least one processor to: pre-process a 3D point cloud to group 3D points; provide the groups of 3D points to a 3D neural network to generate initial label predictions for the groups of 3D points; interpolate label predictions for individual 3D points based upon initial label predictions for at least two neighboring groups of 3D points including the group of 3D points to which a given individual 3D point belongs; refine the label predictions using a graph neural network; and output a segmented 3D point cloud.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
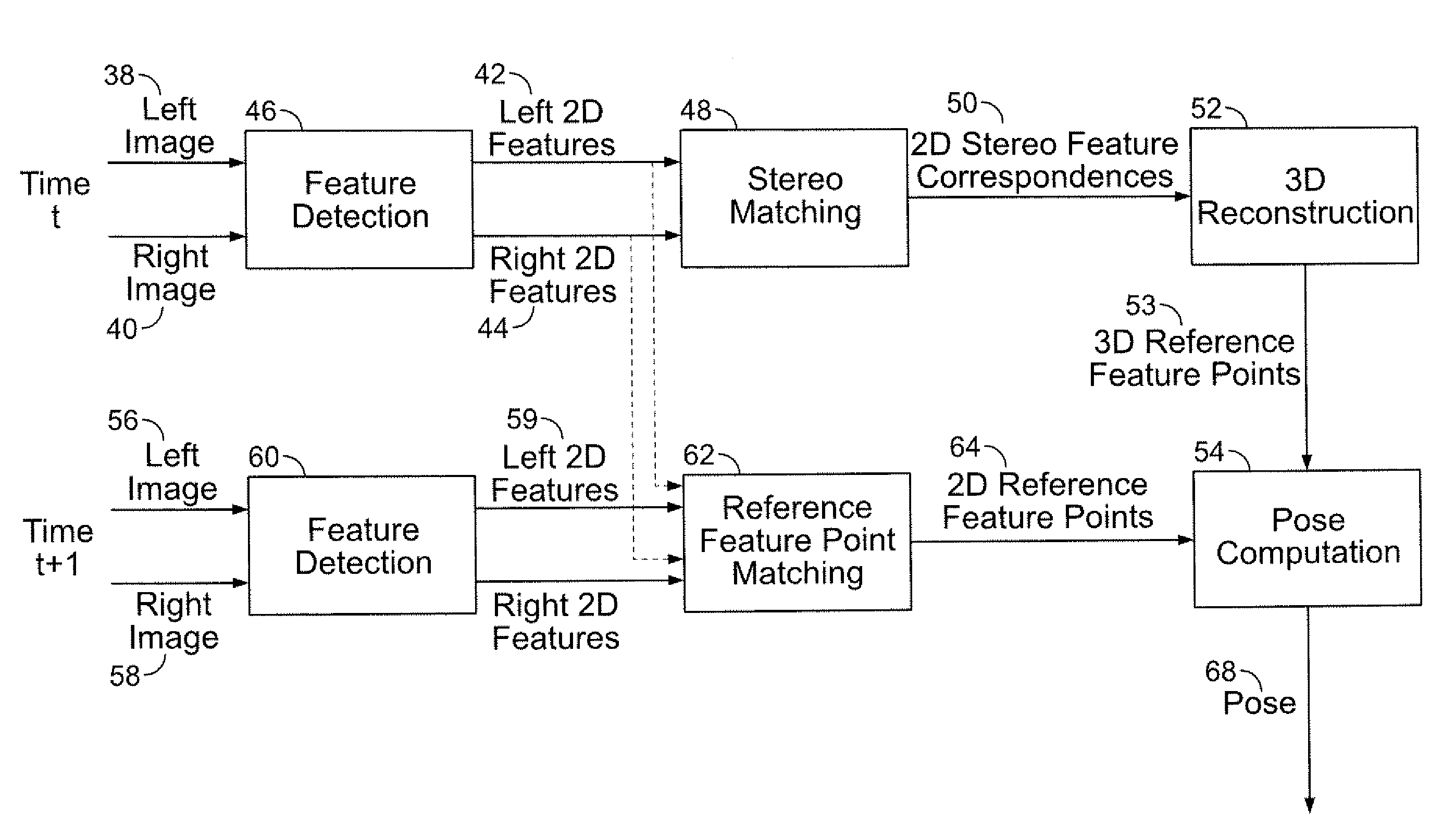
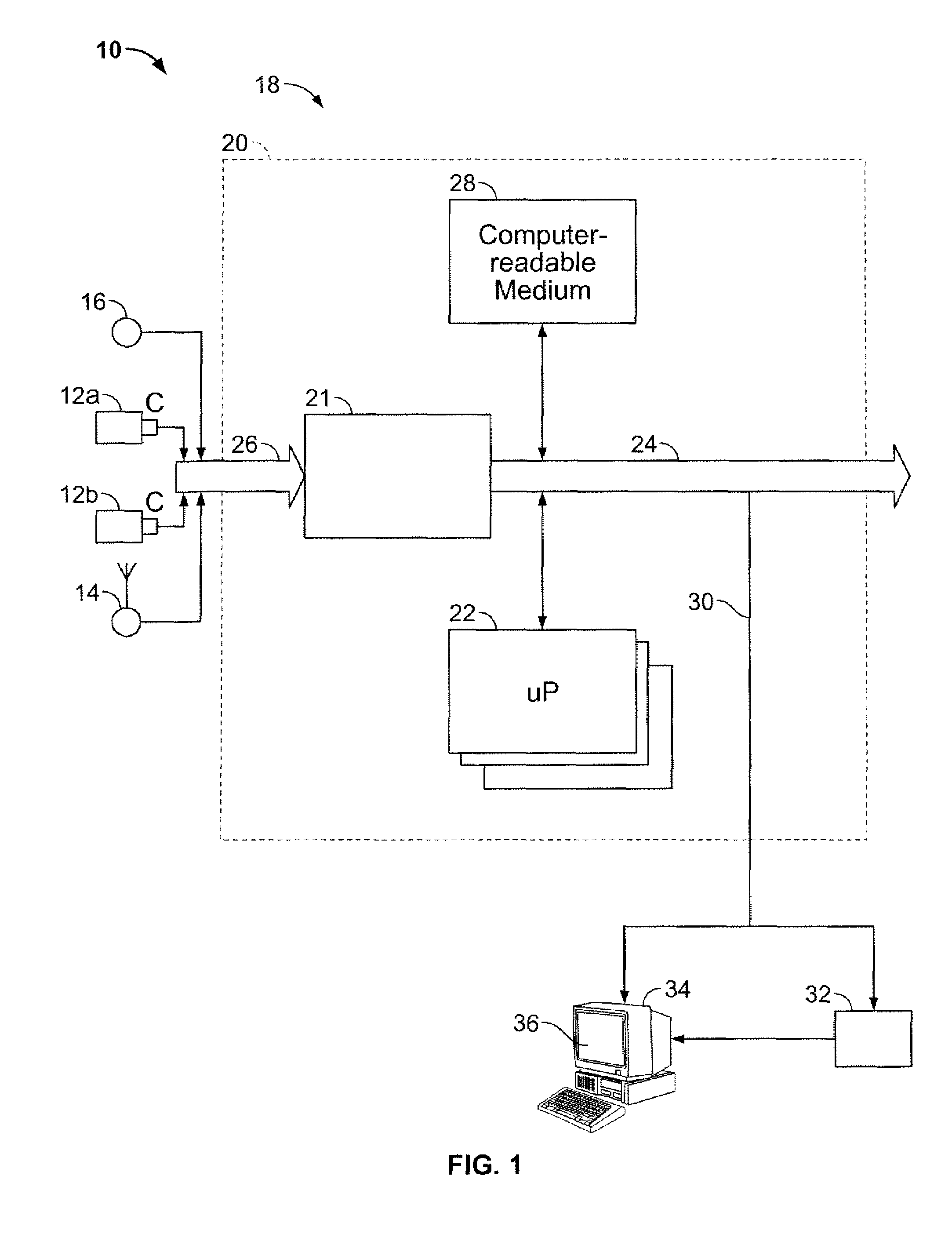
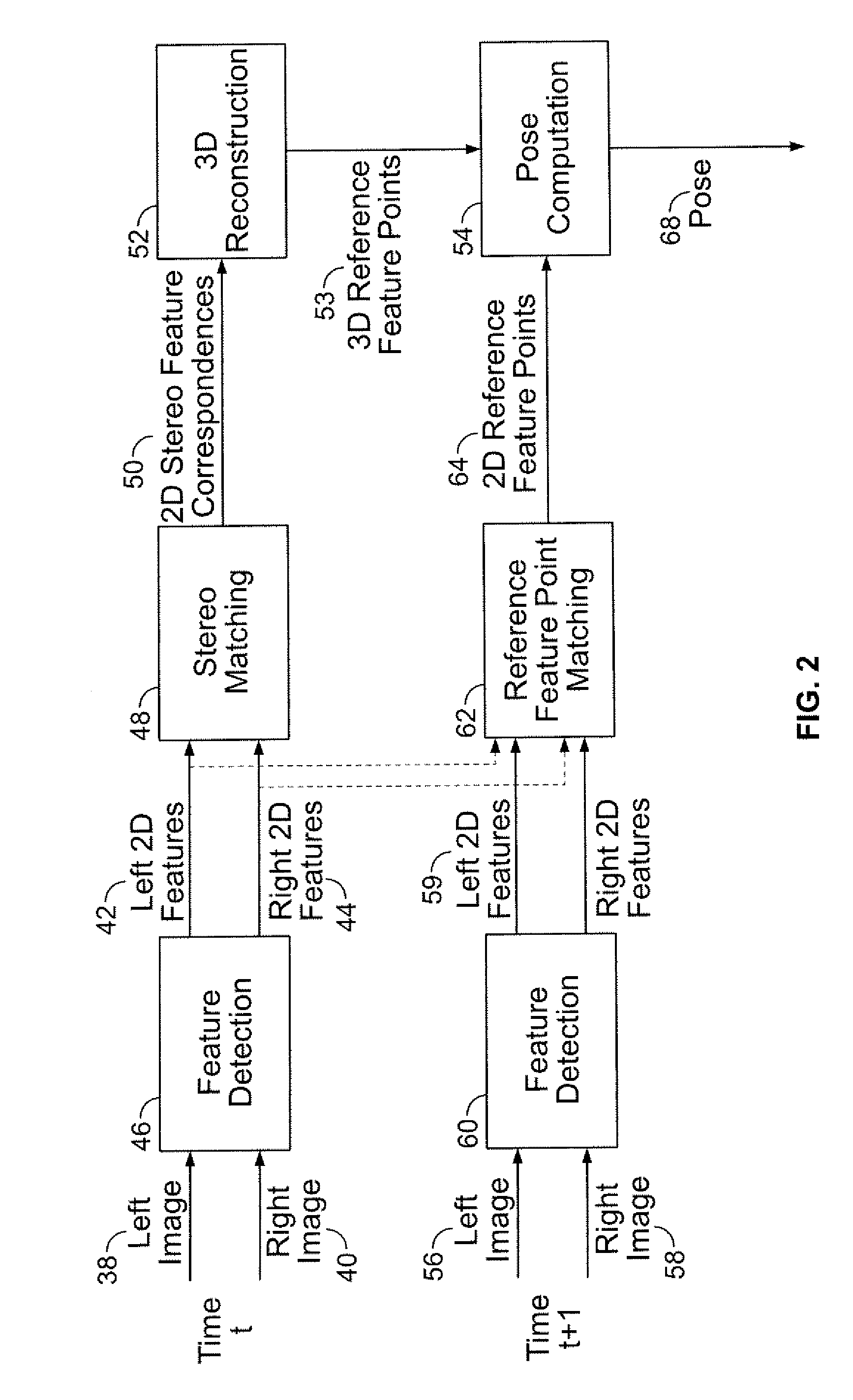
Stereo-Based Visual Odometry Method and System
ActiveUS20080144925A1Minimizes projectionImage enhancementImage analysisStereo imageVisual perception
A method for estimating pose from a sequence of images, which includes the steps of detecting at least three feature points in both the left image and right image of a first pair of stereo images at a first point in time; matching the at least three feature points in the left image to the at least three feature points in the right image to obtain at least three two-dimensional feature correspondences; calculating the three-dimensional coordinates of the at least three two-dimensional feature correspondences to obtain at least three three-dimensional reference feature points; tracking the at least three feature points in one of the left image and right image of a second pair of stereo images at a second point in time different from the first point in time to obtain at least three two-dimensional reference feature points; and calculating a pose based on the at least three three-dimensional reference feature points and its corresponding two-dimensional reference feature points in the stereo images. The pose is found by minimizing projection residuals of a set of three-dimensional reference feature points in an image plane.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
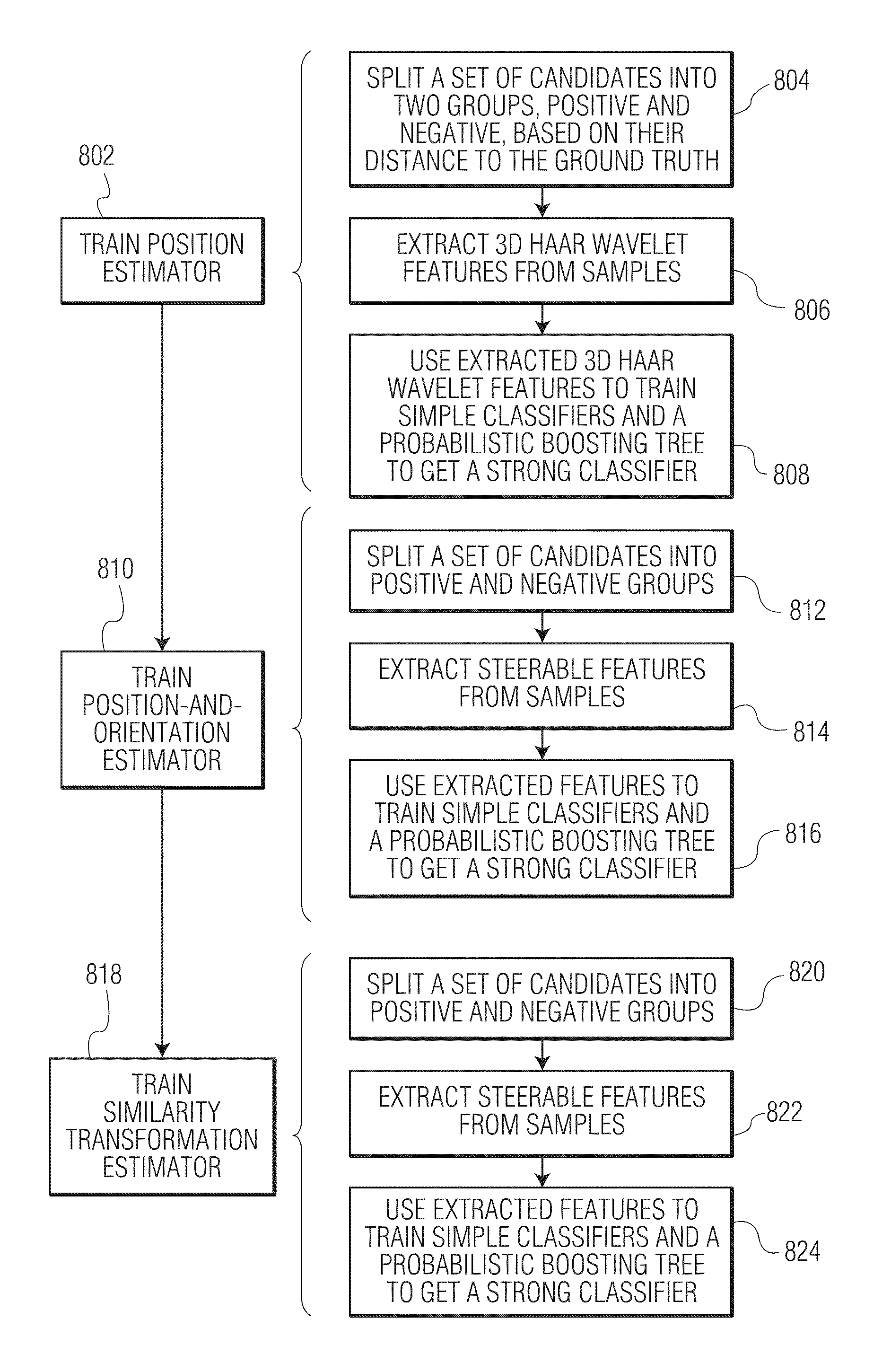
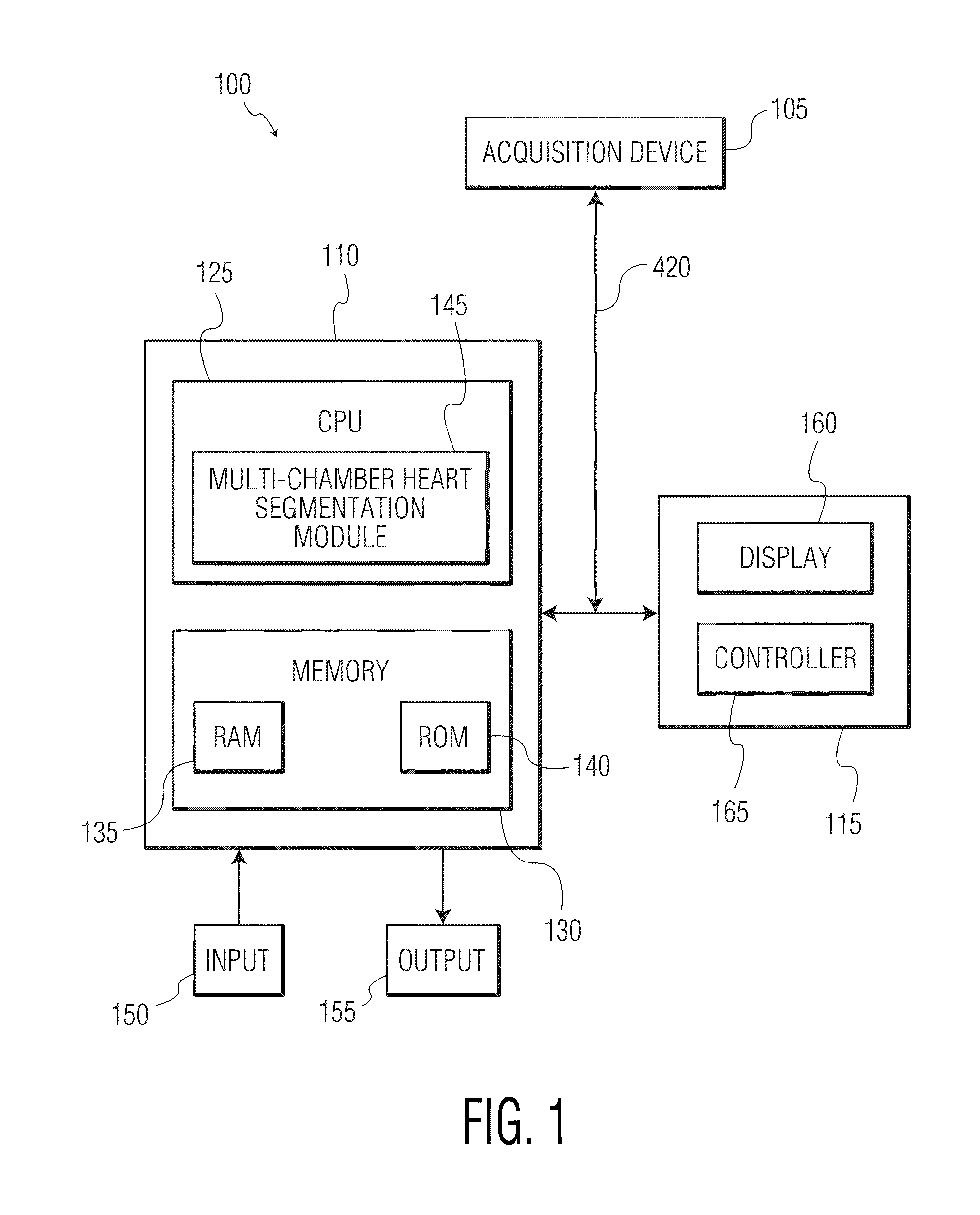
System and method for segmenting chambers of a heart in a three dimensional image
InactiveUS7916919B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementFeature recognitionCardiology
A system and method for segmenting chambers of a heart in three dimensional images is disclosed. A set of three dimensional images of a heart is received. The shape of the heart in the three dimensional images is localized. Boundaries of the chambers of the heart in the localized shape are identified using steerable features.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
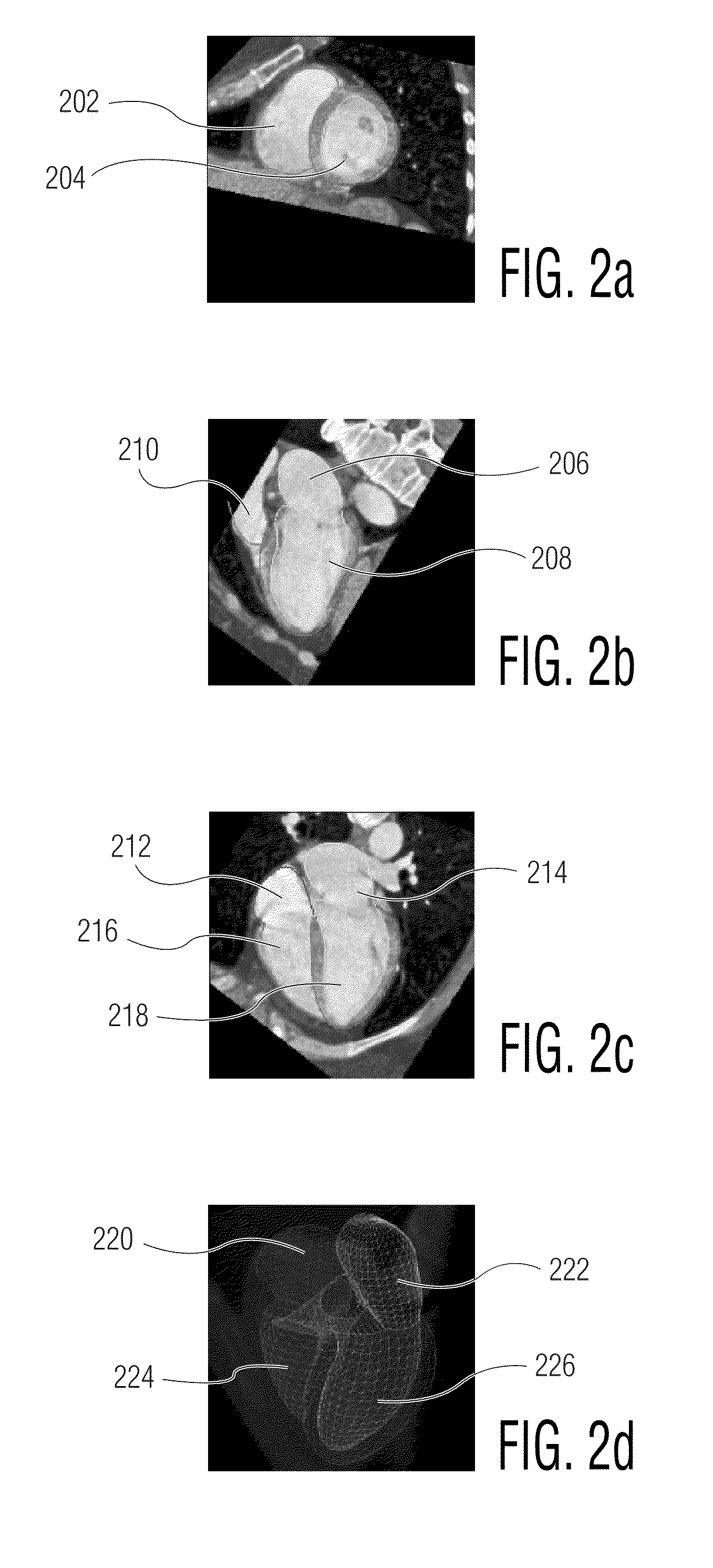
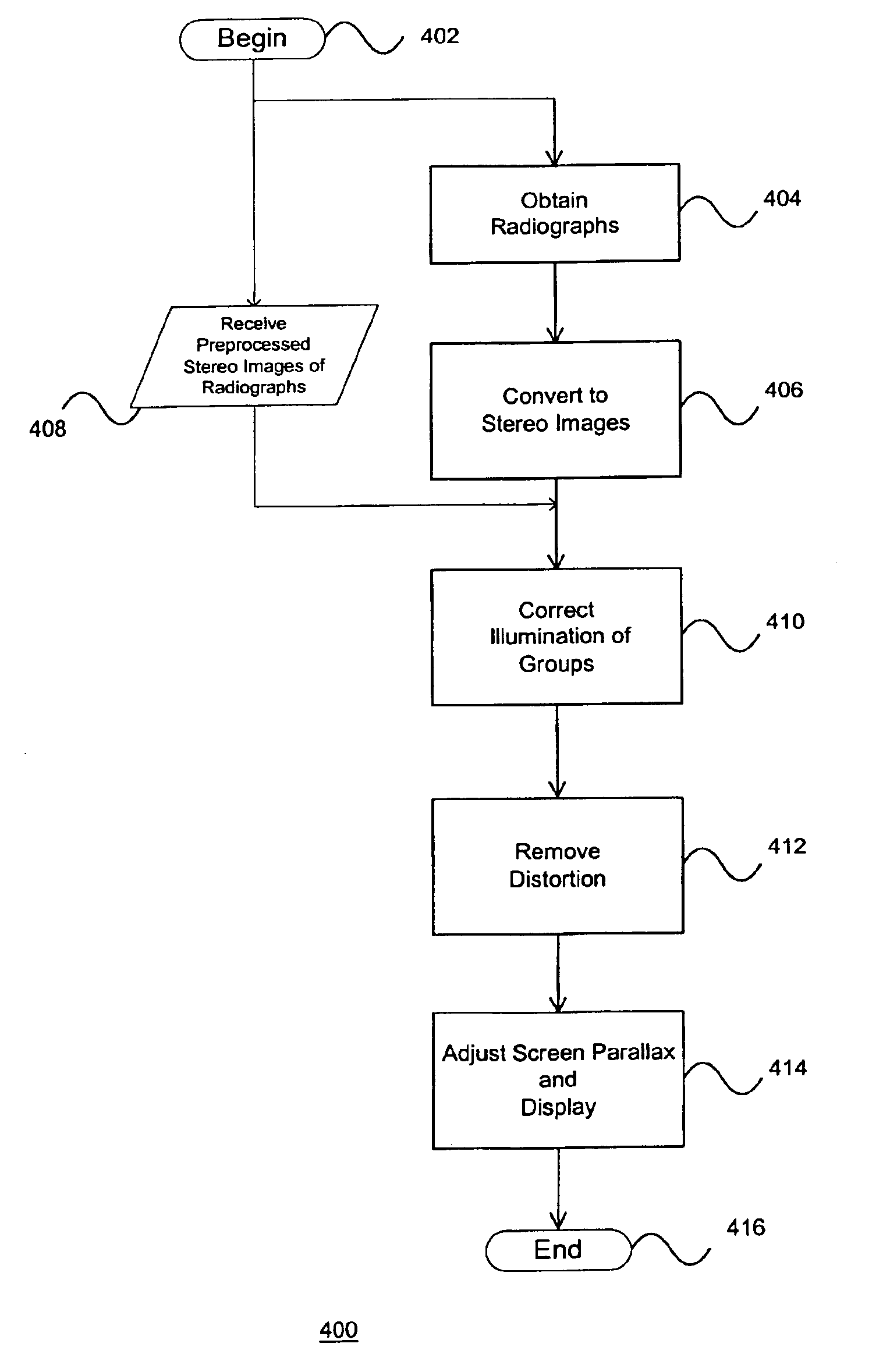
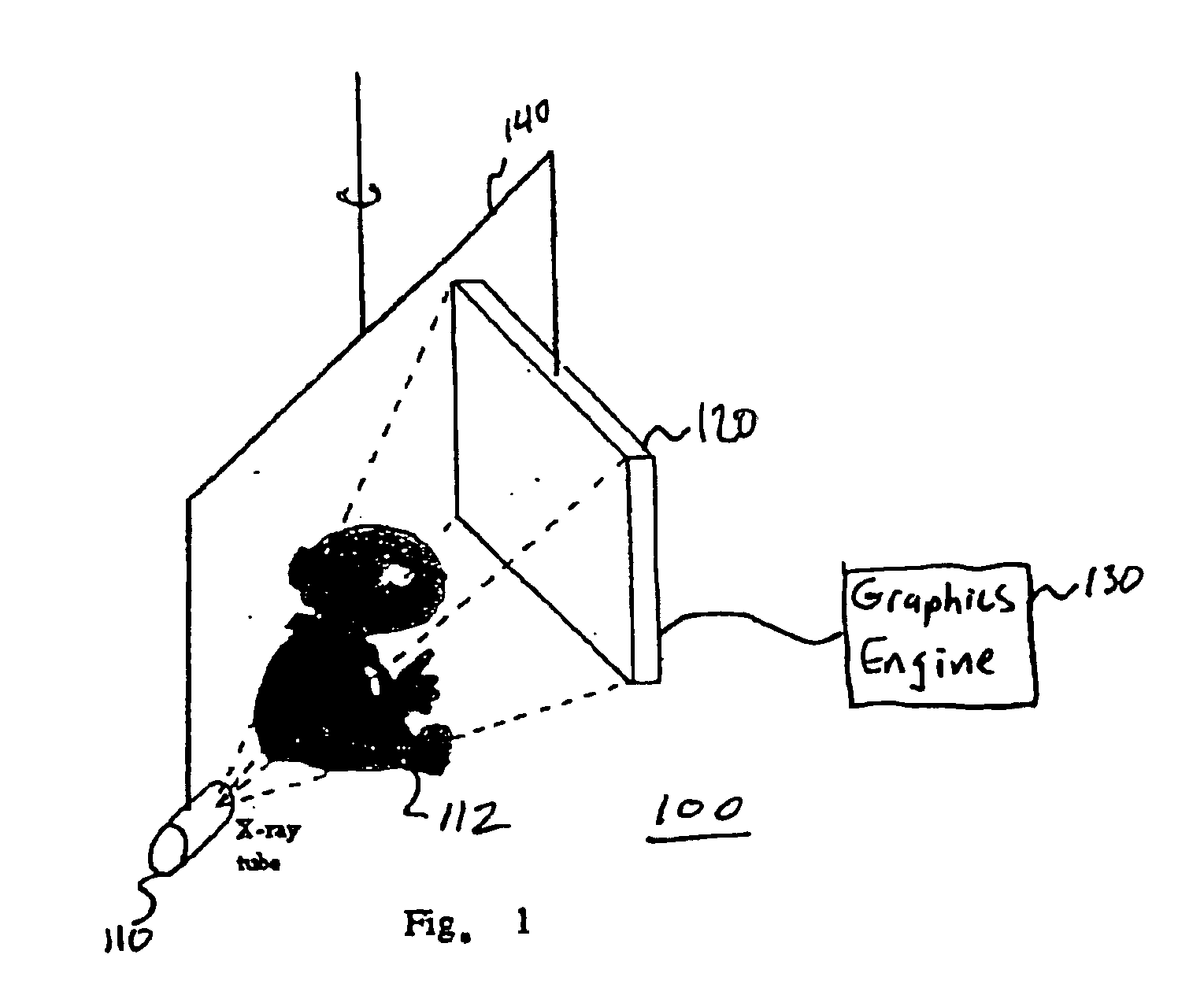
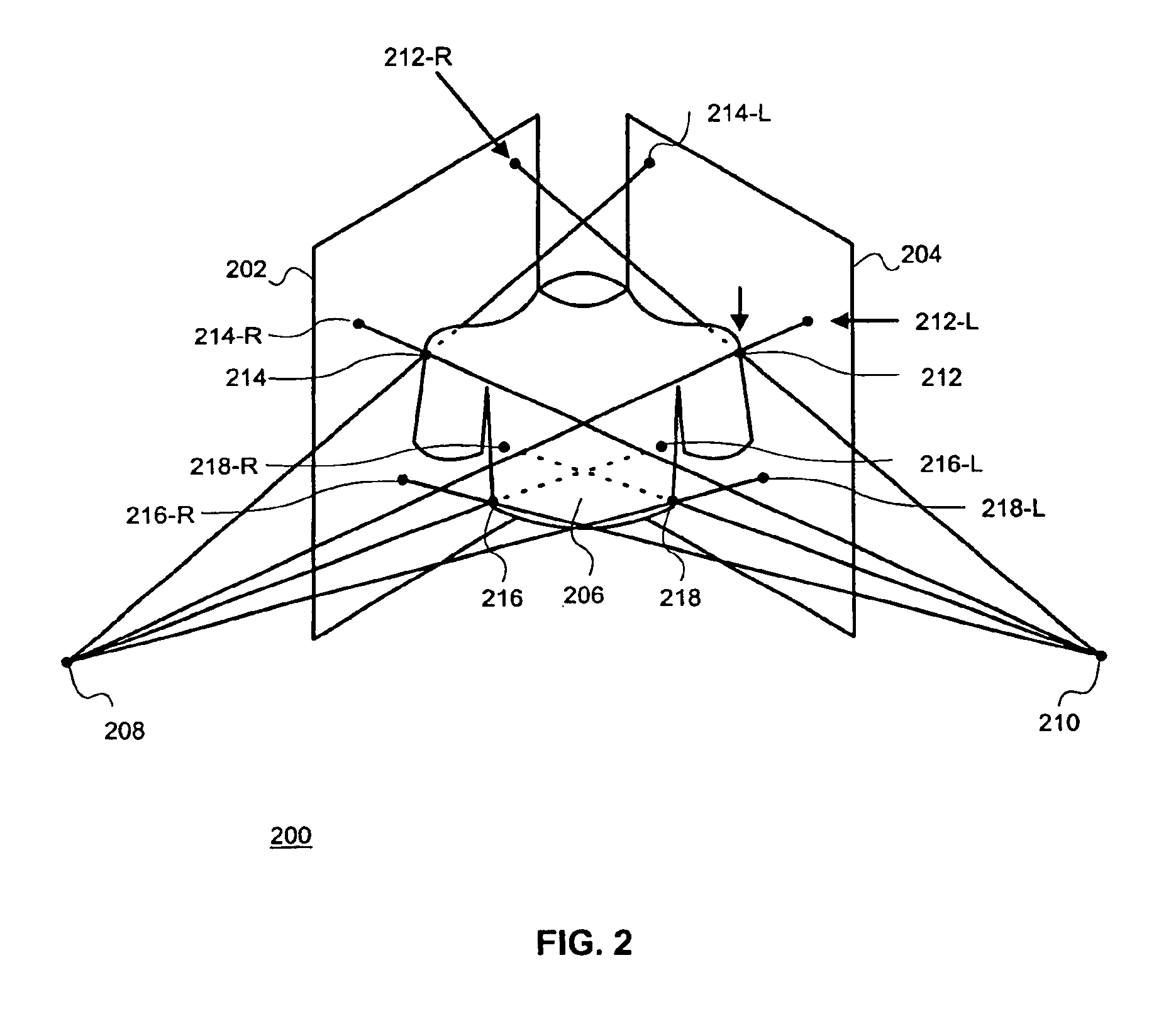
Stereo image processing for radiography
InactiveUS6862364B1Reduce and eliminate illumination errorConvenient lightingImage enhancementImage analysisParallaxX-ray
Pairs of stereo Xray radiographs are obtained from an X-ray imaging system and are digitized to form corresponding pairs of stereo images (602, 604). The pairs of stereo images (602, 604) are adjusted (410) to compensate for gray-scale illumination differences by grouping and processing pixel groups in each pair of images. Distortion in the nature of depth plane curvature and Keystone distortion due to the toed-in configuration of the X-ray imaging system are eliminated (412). A screen parallax for the pair of stereo images is adjusted (414) to minimize depth range so as to enable a maximum number of users to view the stereoscopic image, and particular features of interest.
Owner:CANON KK
Systems and methods for visual classification with region proposals
Systems and method are provided for controlling an autonomous vehicle. A camera configured to capture an image, and a controller can execute an autonomous driving system (ADS) that classify that image. The ADS comprises a classification system for classifying objects in an environment within a driveable area of the autonomous vehicle. The classification system comprises a processor configured to execute a region proposal generator module and an image classification module. The region proposal generator module generates a set of bounding box region proposals for the image. The bounding box region proposals are selected areas of the image that include objects to be classified. The image classification module classifies, via a neural network executed by the processor, the objects from the image that are within one of the bounding box region proposals
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
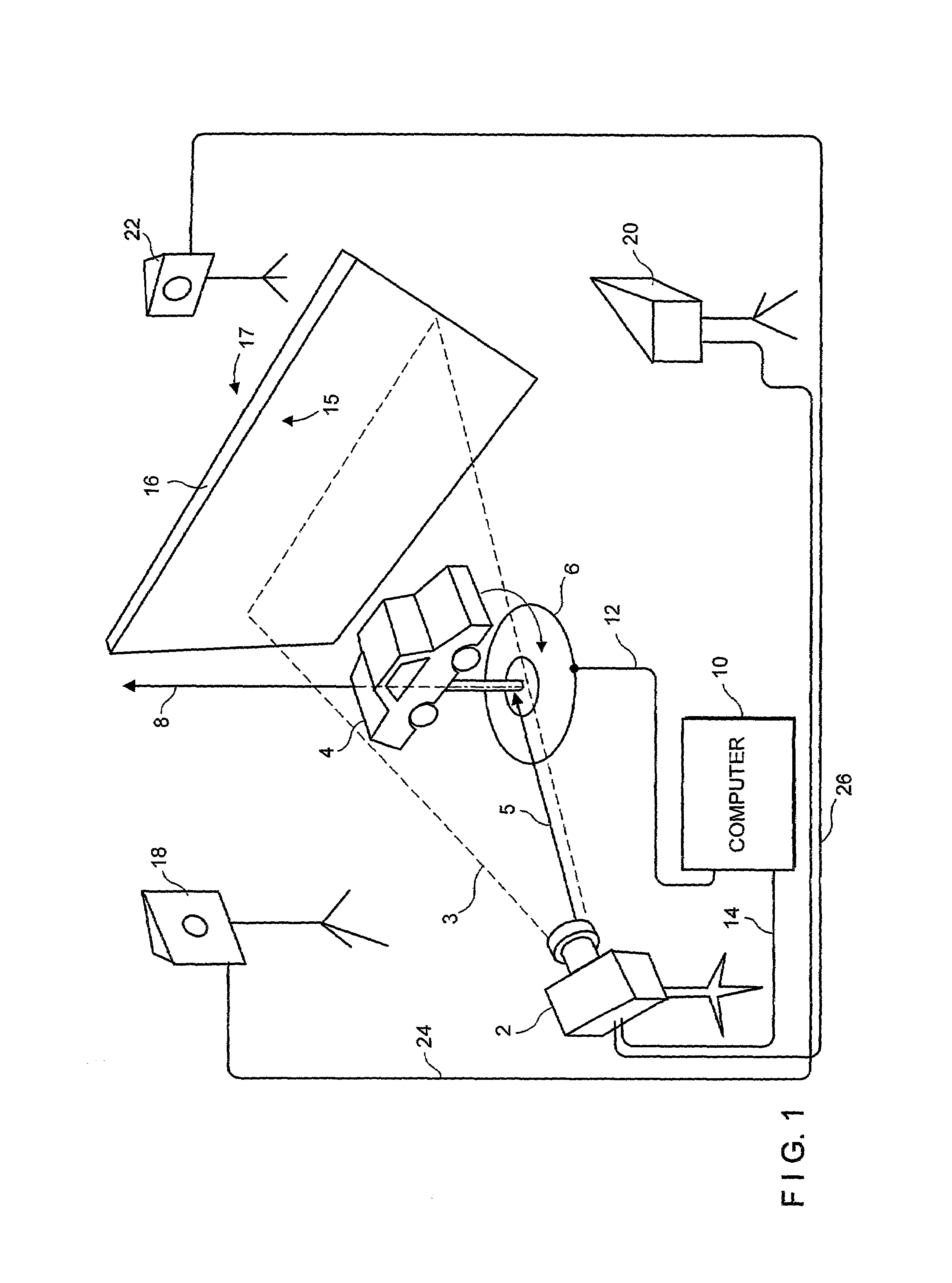
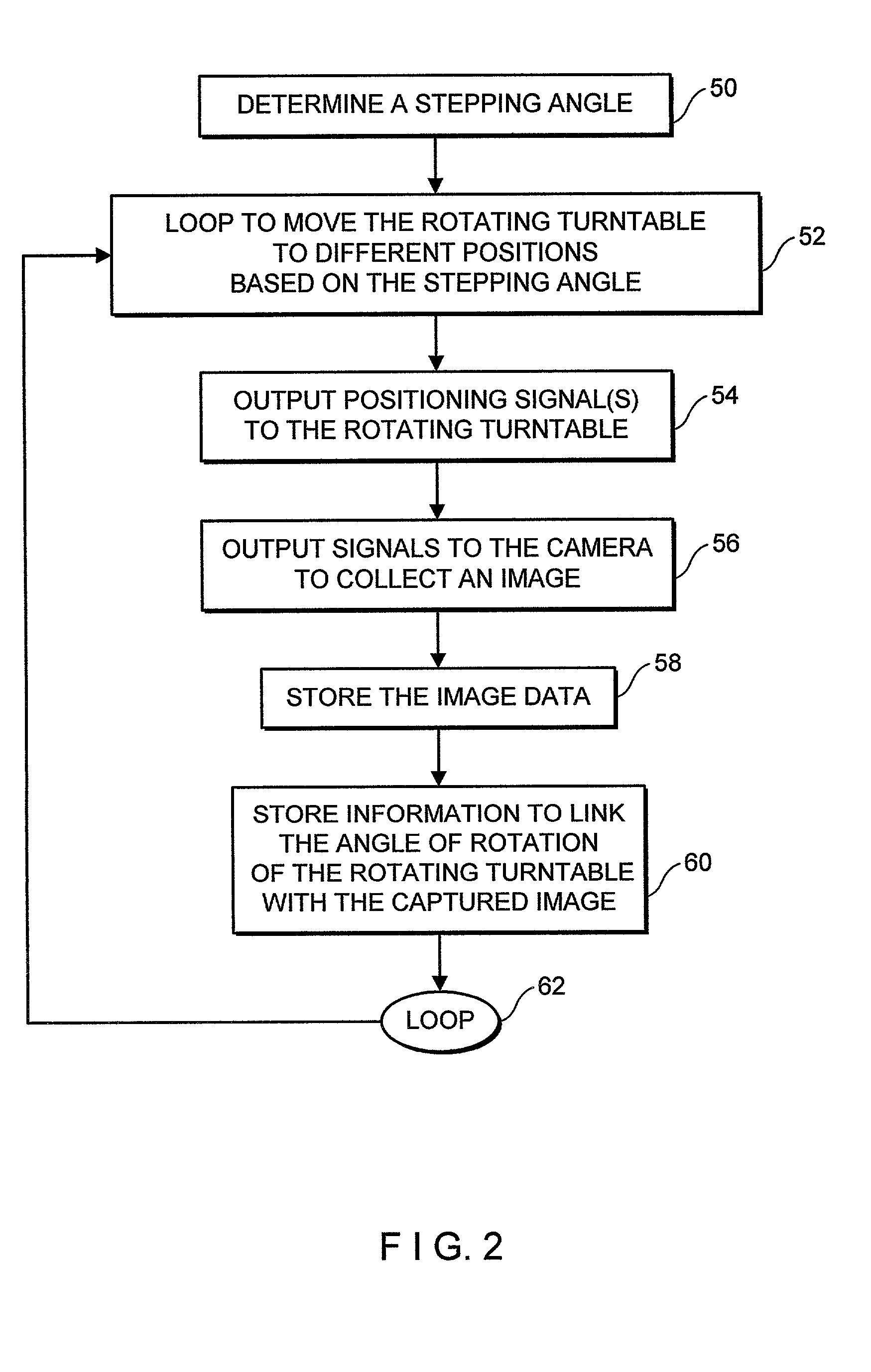
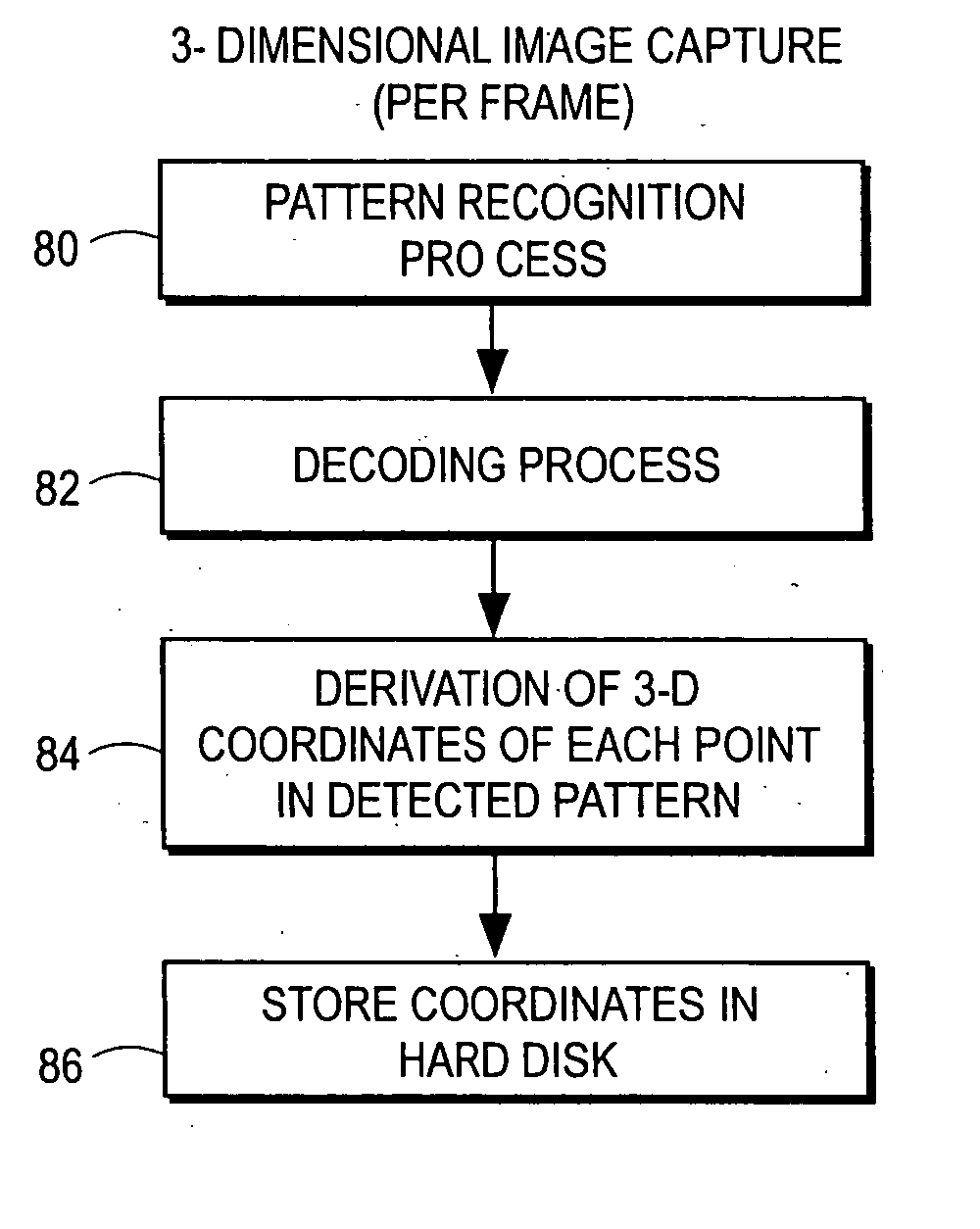
System and method of three-dimensional image capture and modeling
InactiveUS7065242B2Eliminate needImprove accuracyImage data processing detailsAquisition of 3D object measurementsOne passObject based
System and method for constructing a 3D model of an object based on a series of silhouette and texture map images. In the exemplary embodiment an object is placed on a rotating turntable and a camera, which is stationary, captures images of the object as it rotates on the turntable. In one pass, the system captures a number of photographic images that will be processed into image silhouettes. In a second pass, the system gathers texture data. After a calibration procedure (used to determine the camera's focal length and the turntable's axis of rotation), a silhouette processing module determines a set of two-dimensional polygon shapes (silhouette contour polygons) that describe the contours of the object. The system uses the silhouette contour polygons to create a 3D polygonal mesh model of the object. The system determines the shape of the 3D model analytically-by finding the areas of intersection between the edges of the model faces and the edges of the silhouette contour polygons. The system creates an initial, (rough) model of the 3D object from one of the silhouette contour polygons, then executes an overlaying procedure to process each of the remaining silhouette contour polygons. In the overlaying process, the system processes the silhouette contour polygons collected from each silhouette image, projecting each face of the (rough) 3D model onto the image plane of the silhouette contour polygons. The overlaying of each face of the (rough) 3D model onto the 2D plane of the silhouette contour polygons enables the present invention to determine those areas that are extraneous and should be removed from the (rough) 3D model. As the system processes the silhouette contour polygons in each image it removes the extraneous spaces from the initial object model and creates new faces to patch “holes.” The polygonal mesh model, once completed, can be transformed into a triangulated mesh model. In a subsequent step, the system uses a deterministic procedure to map texture from the texture images onto the triangles of the 3D mesh model, locating that area in the various texture map images that is “best” for each mesh triangle.
Owner:SIZMEK TECH
Methods and apparatus for 3D surface imaging using active wave-front sampling
InactiveUS20080212838A1Compensating for such errorImage enhancementImage analysis3d surfacesImage capture
According to one aspect, a method of determining motion of at least one feature present in a plurality of images, the plurality of images captured by a single camera of a scene, each of the plurality of images resulting from light passing through an aperture positioned at a different location for each of the plurality of images is provided. The method comprises determining the motion, in integer pixel units using a first tracking algorithm, of the at least one feature between a first image of the plurality of images and a second image of the plurality of images to obtain an integer pixel measurement of the motion, offsetting the first image and the second image according to the integer pixel measurement, determining the motion, in sub-pixel units using a second tracking algorithm, between the at least one feature in the offset first image and the second image to obtain a sub-pixel measurement, and combining the integer pixel measurement and the sub-pixel measurement to form an estimate of the motion of the at least one feature.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
System and method for 3D imaging using structured light illumination
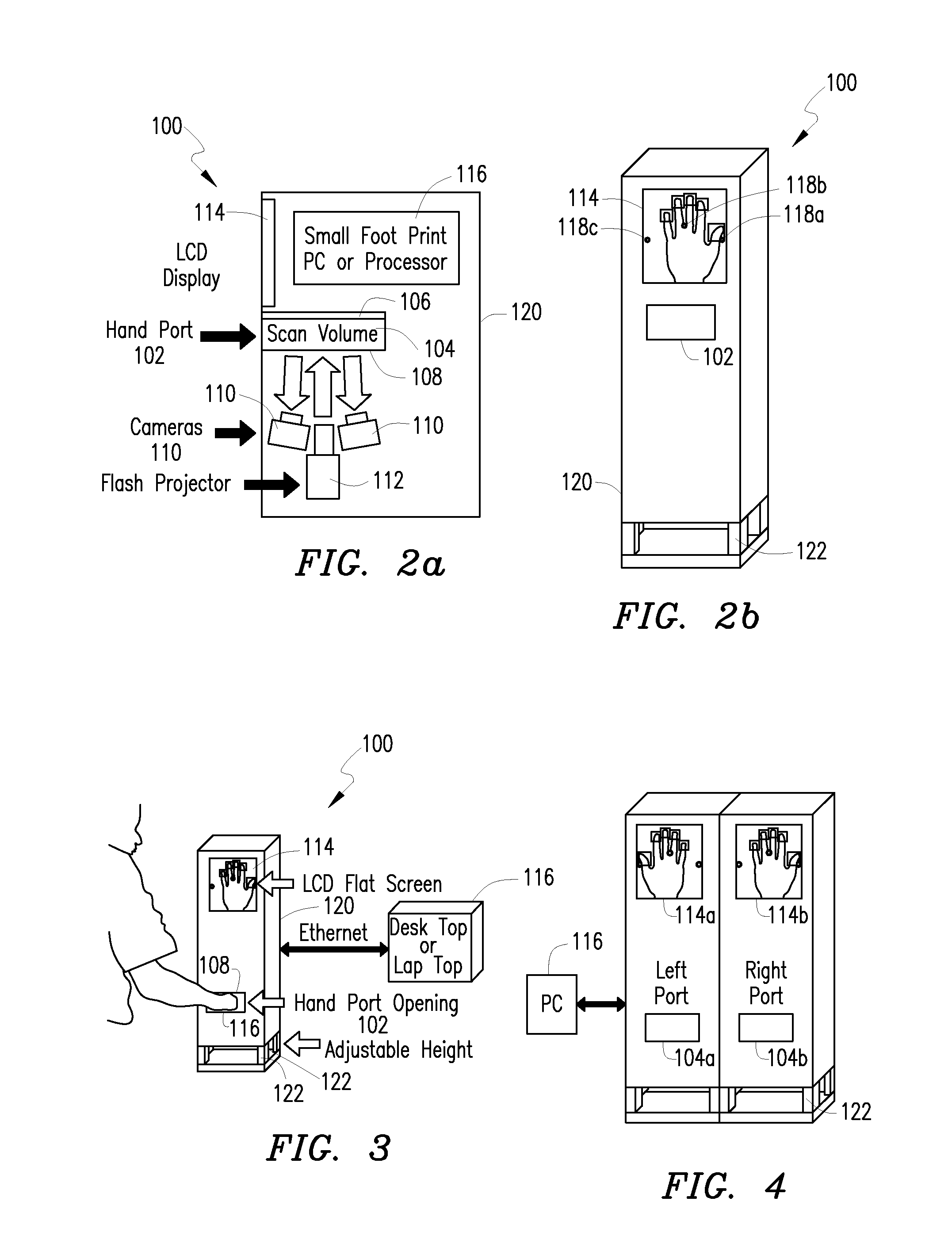
InactiveUS8224064B1Acquisition speed is fastMore robust to extremely worn ridges of the fingersImage enhancementImage analysisRandom noiseComputer science
A biometrics system captures and processes a handprint image using a structured light illumination to create a 2D representation equivalent of a rolled inked handprint. The biometrics system includes an enclosure with a scan volume for placement of the hand. A reference plane with a backdrop pattern forms one side of the scan volume. The backdrop pattern is preferably a random noise pattern and the coordinates of the backdrop pattern are predetermined at system provisioning. The biometrics system further includes at least one projection unit for projecting a structured light pattern onto a hand positioned in the scan volume on or in front of the backdrop pattern and at least two cameras for capturing a plurality of images of the hand, wherein each of the plurality of images includes at least a portion of the hand and the backdrop pattern. A processing unit calculates 3D coordinates of the hand from the plurality of images using the predetermined coordinates of the backdrop pattern to align the plurality of images and mapping the 3D coordinates to a 2D flat surface to create a 2D representation equivalent of a rolled inked handprint. The processing unit can also adjust calibration parameters for each hand scan from calculating coordinates of the portion of backdrop pattern in the at least one image and comparing with the predetermined coordinates of the backdrop pattern.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
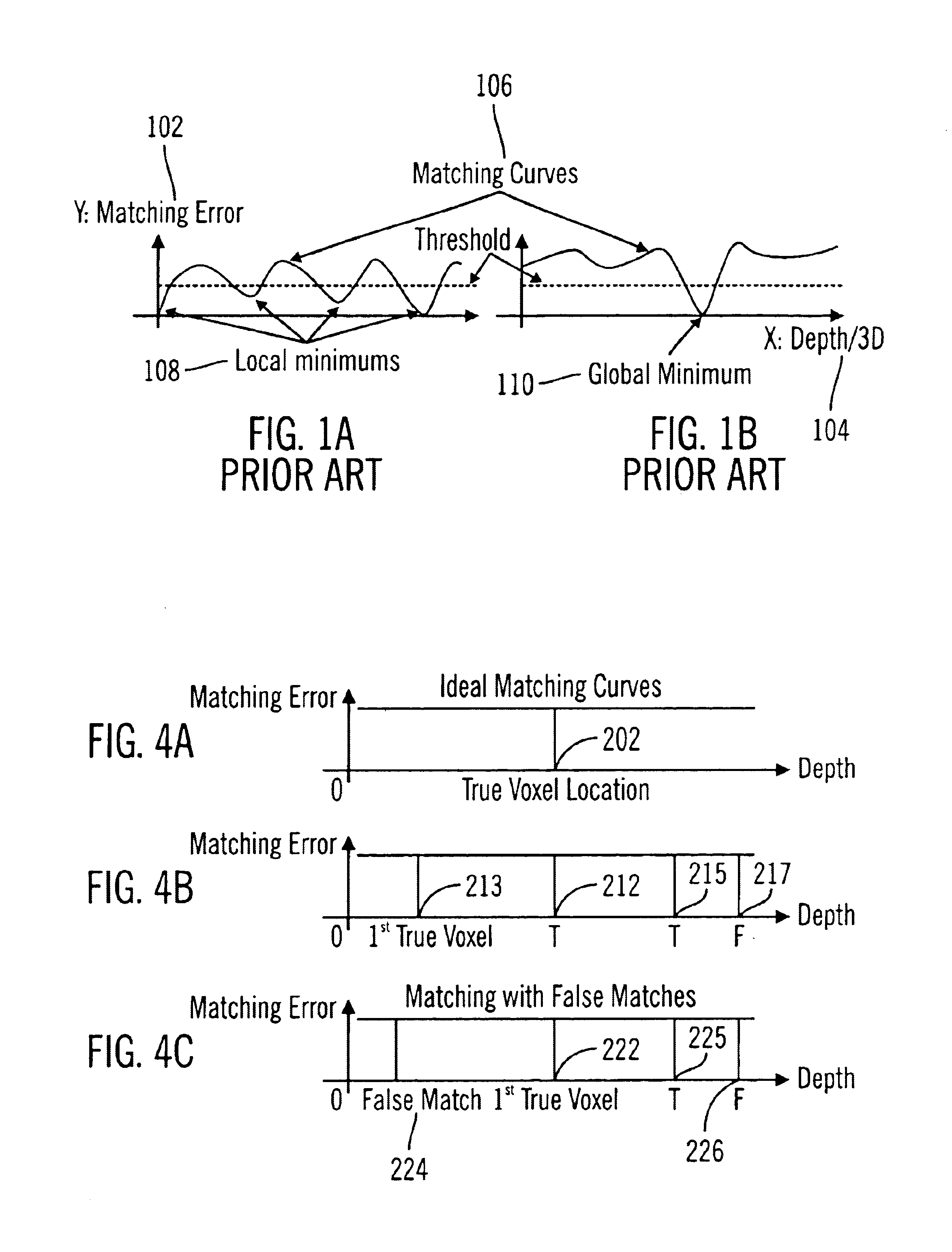
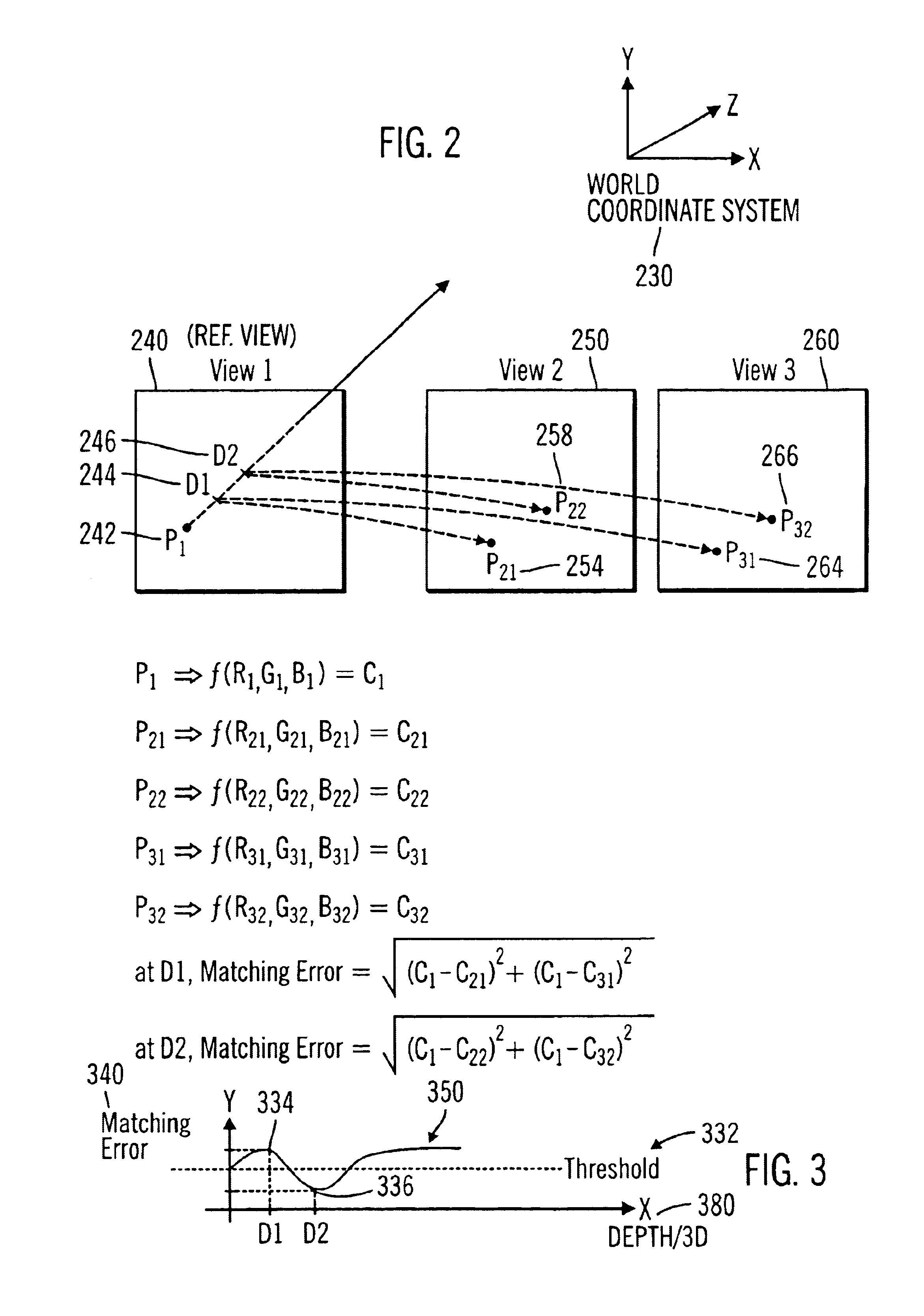
Method and system for 3D reconstruction of multiple views with altering search path and occlusion modeling
An image processing system and method reconstructs 3D image information corresponding to a scene from a plurality of 2D images of the scene. The method receives a plurality of image features corresponded between different 2D views of the scene, the corresponded image features deviating between different views as a result of camera relative motion. The method determines image features of the received plurality of image features that are occluded views, determines image features of the received plurality of image features that are confident seeds associated with 3D depth information, and propagates 3D depth information from the confident seeds to neighboring image features, while avoiding image features that have been determined to be occluded views. The 3D image information can be rendered and displayed such as for a virtual walkthrough of the scene.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
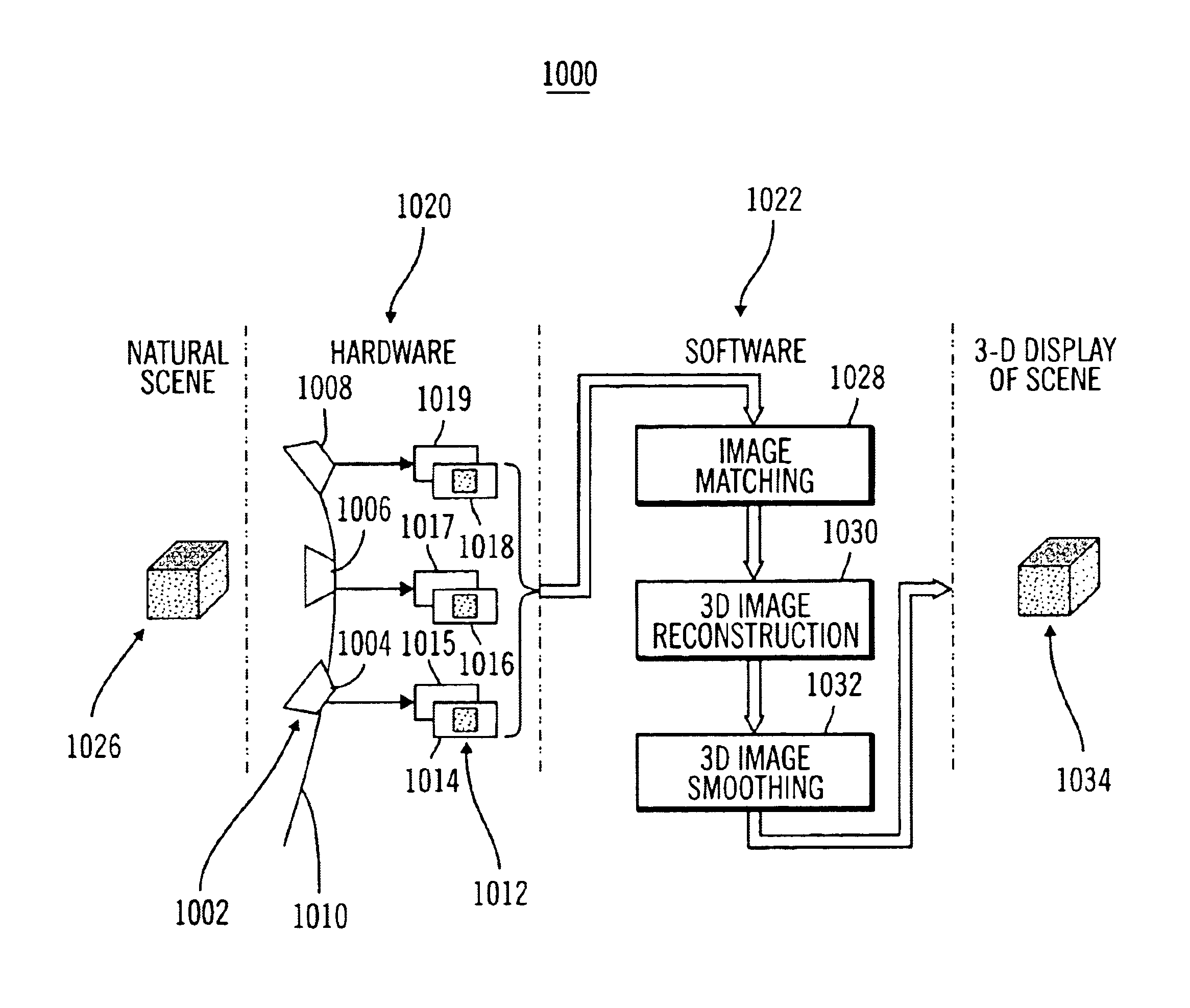
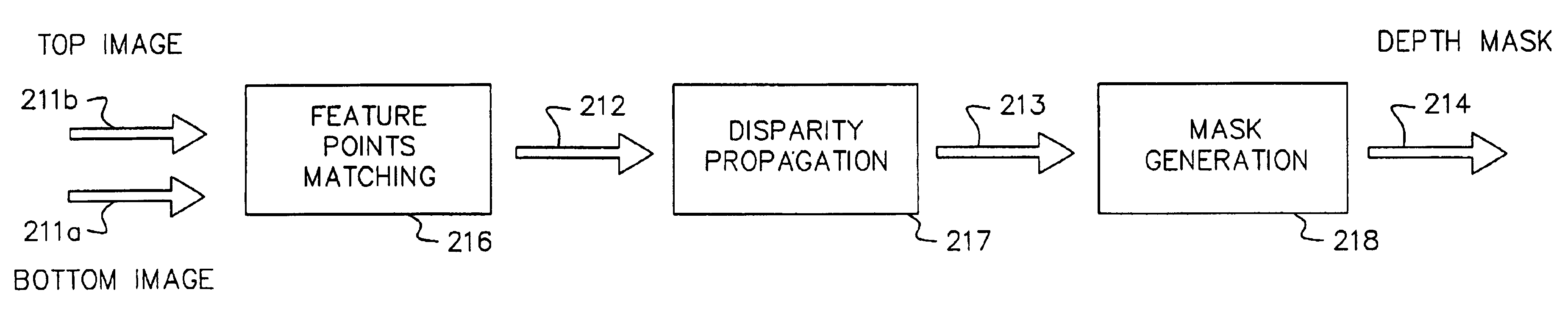
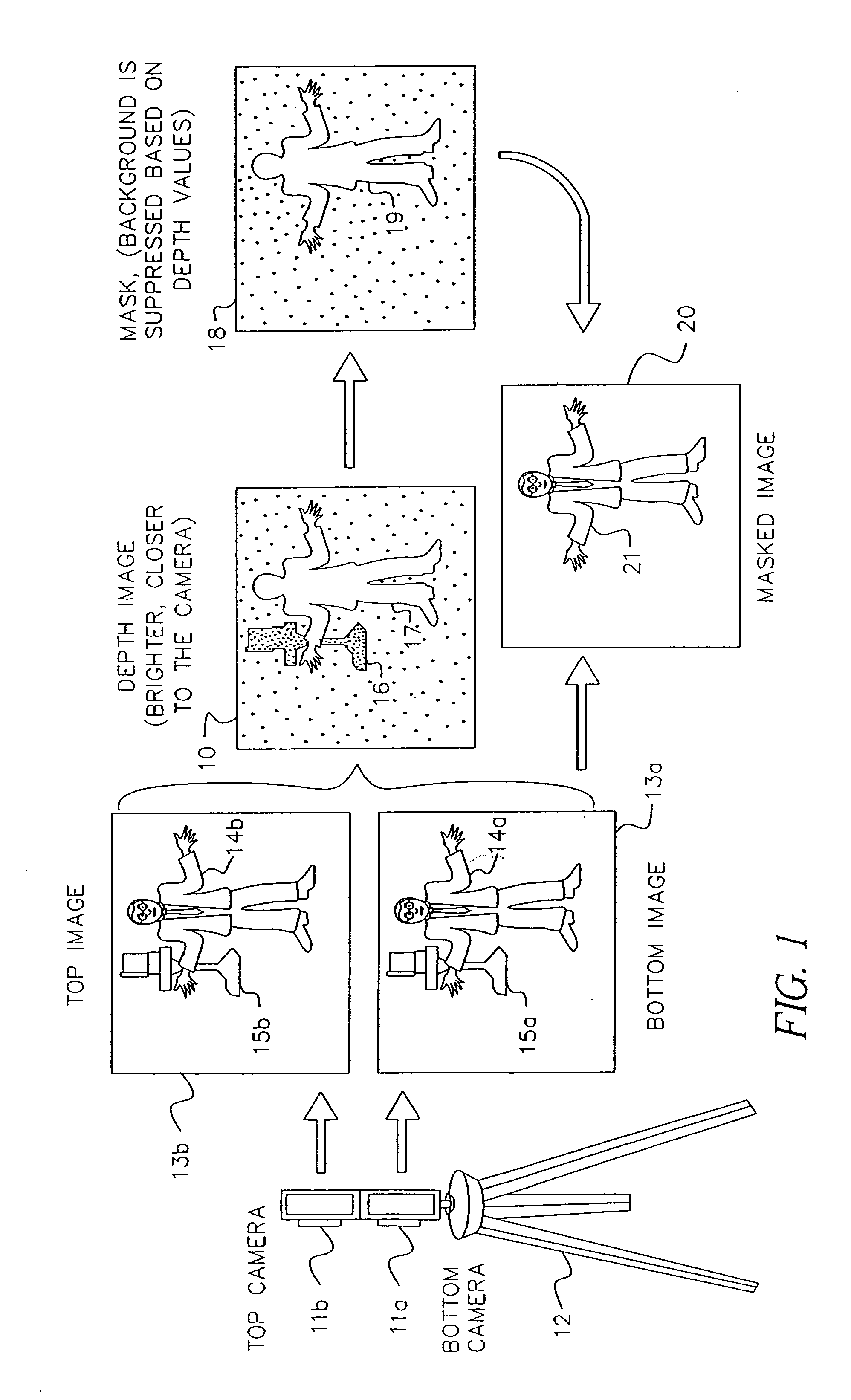
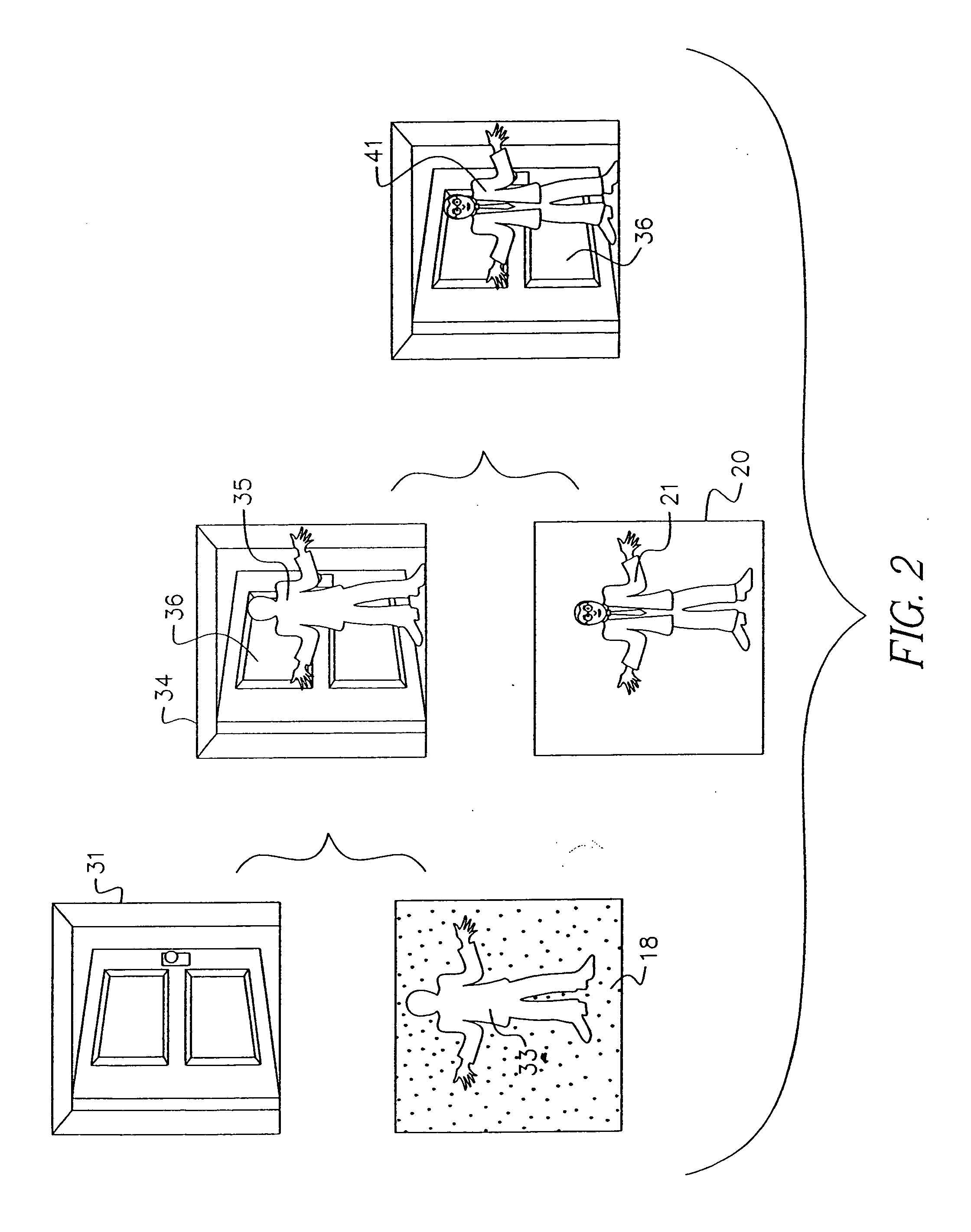
Method for forming a depth image from digital image data
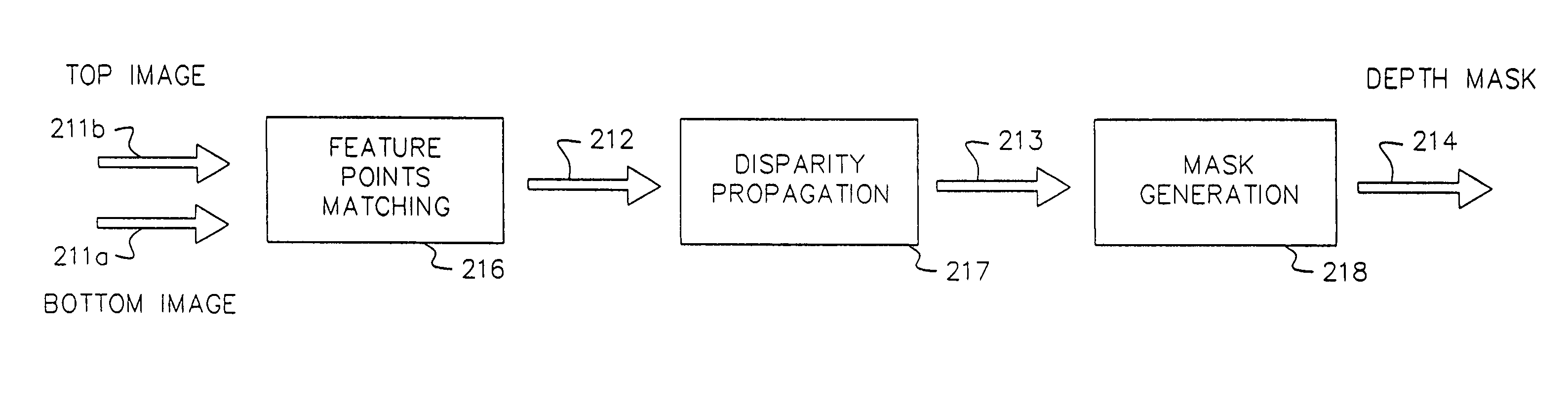
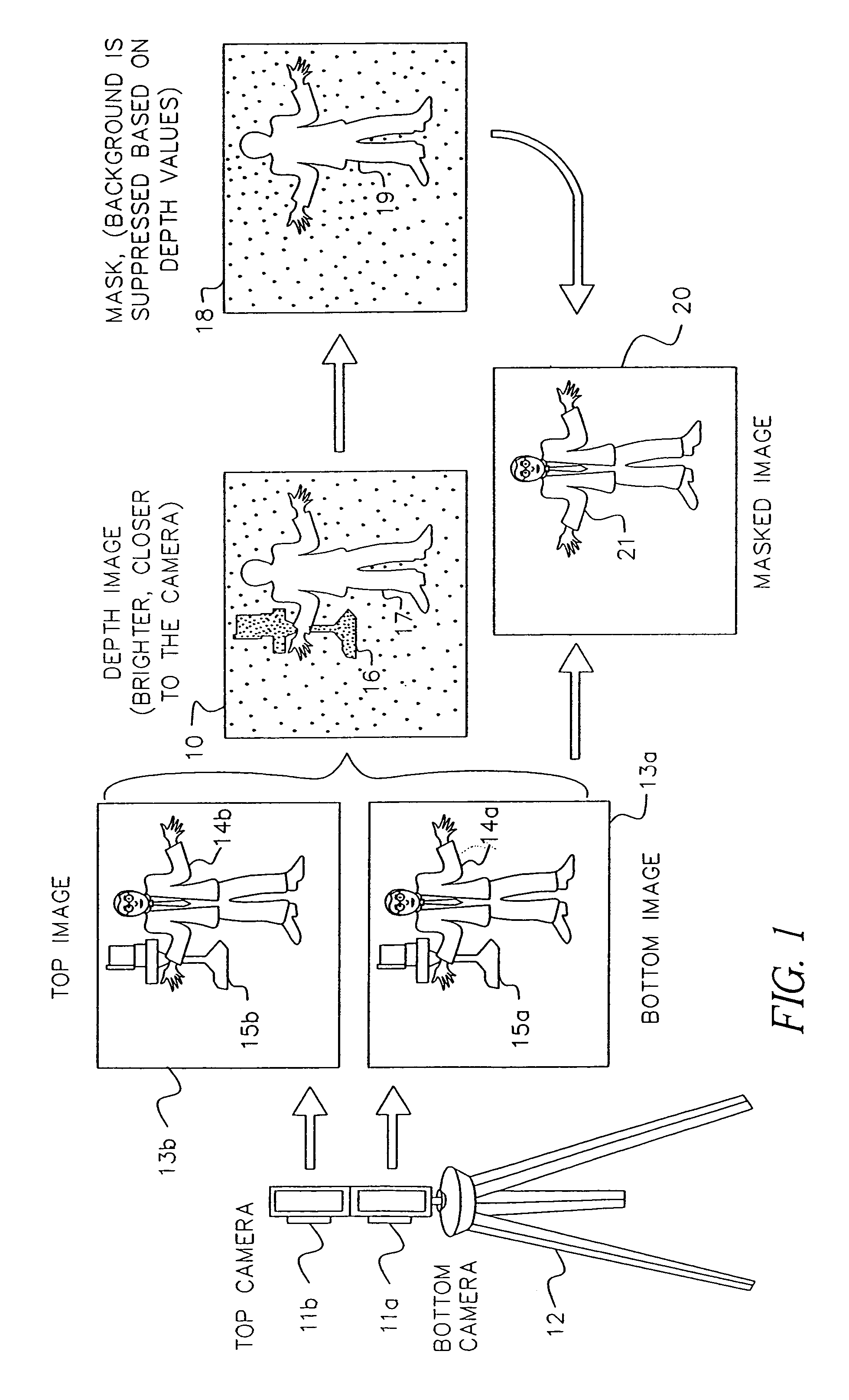
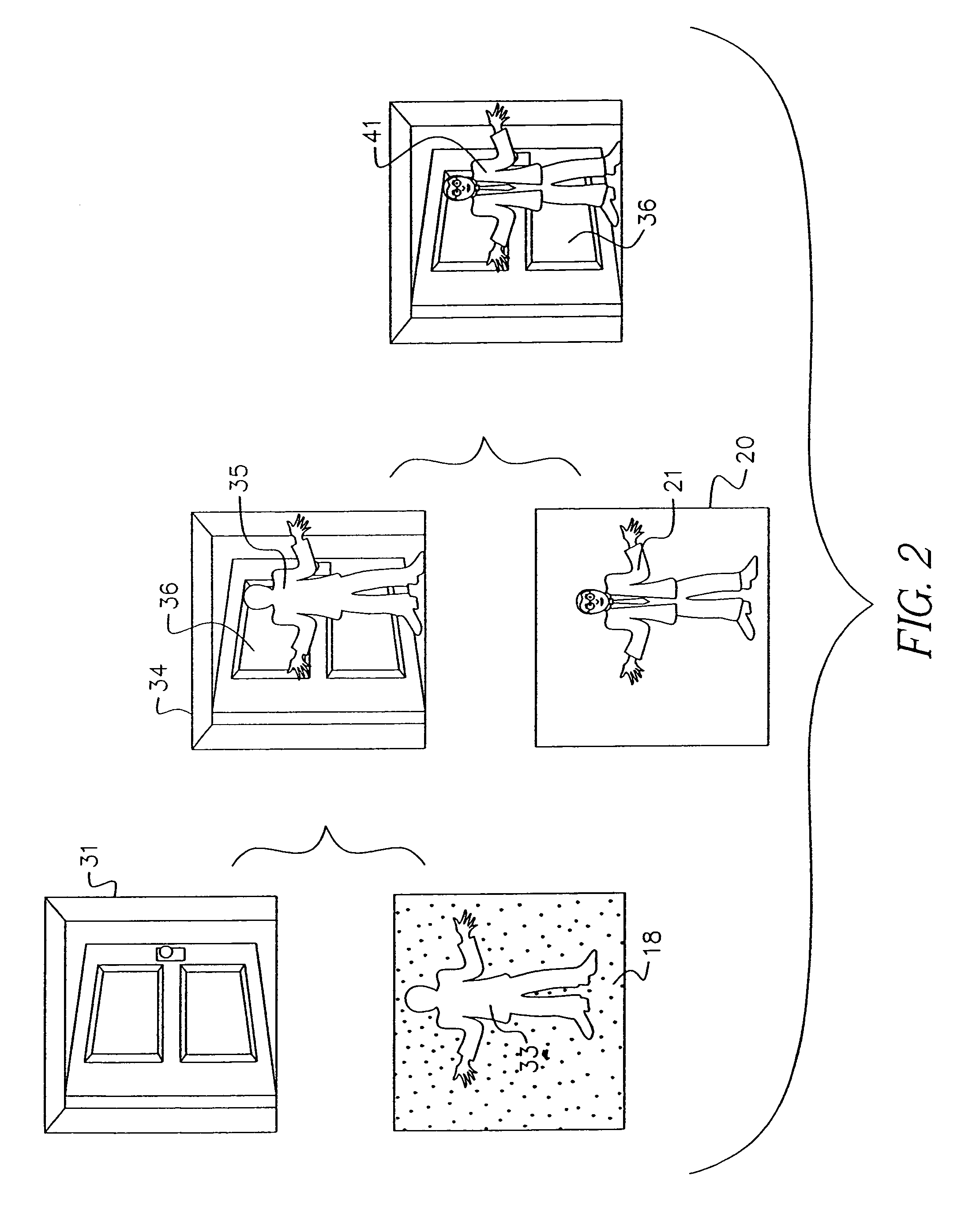
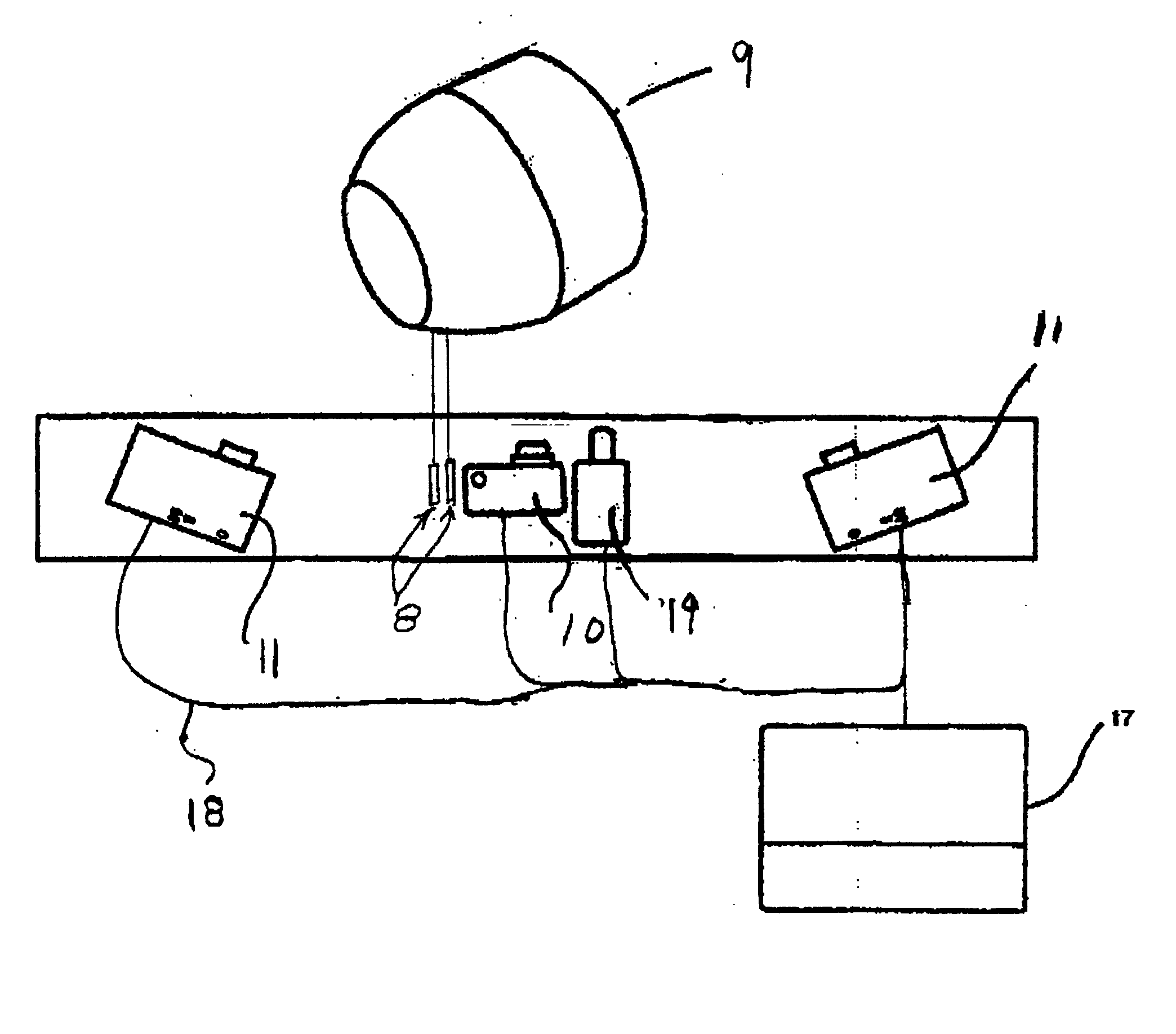
A computer vision / image processing method generates a depth map useful in producing a foreground depth mask for 2D / 3D image editing. The method uses image data from a plurality of scenes. Feature points on each of the vertical scan lines in each of the scene images are used to search for corresponding feature points on the corresponding vertical lines in other images. The corresponding feature-point search is performed by using a bipartite match network with a feature-point-ordering constraint and a disparity-limit constraint, and produces an individual feature-point depth map for each input image. A sparse feature-point depth map of the scene is obtained after applying a consistency test to all the individual depth maps. A complete feature-point depth map is produced by applying a color property assisted depth propagation process to the sparse feature-point depth map. Foreground and background separation is then conducted in the depth domain by using the order statistics of the depth data extracted the feature-point depth map. A foreground feature-point depth map is obtained from the separation operation. The final foreground depth mask is generated by applying a color aided eight-nearest-neighbor LMS interpolation process to the foreground feature-point depth map.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
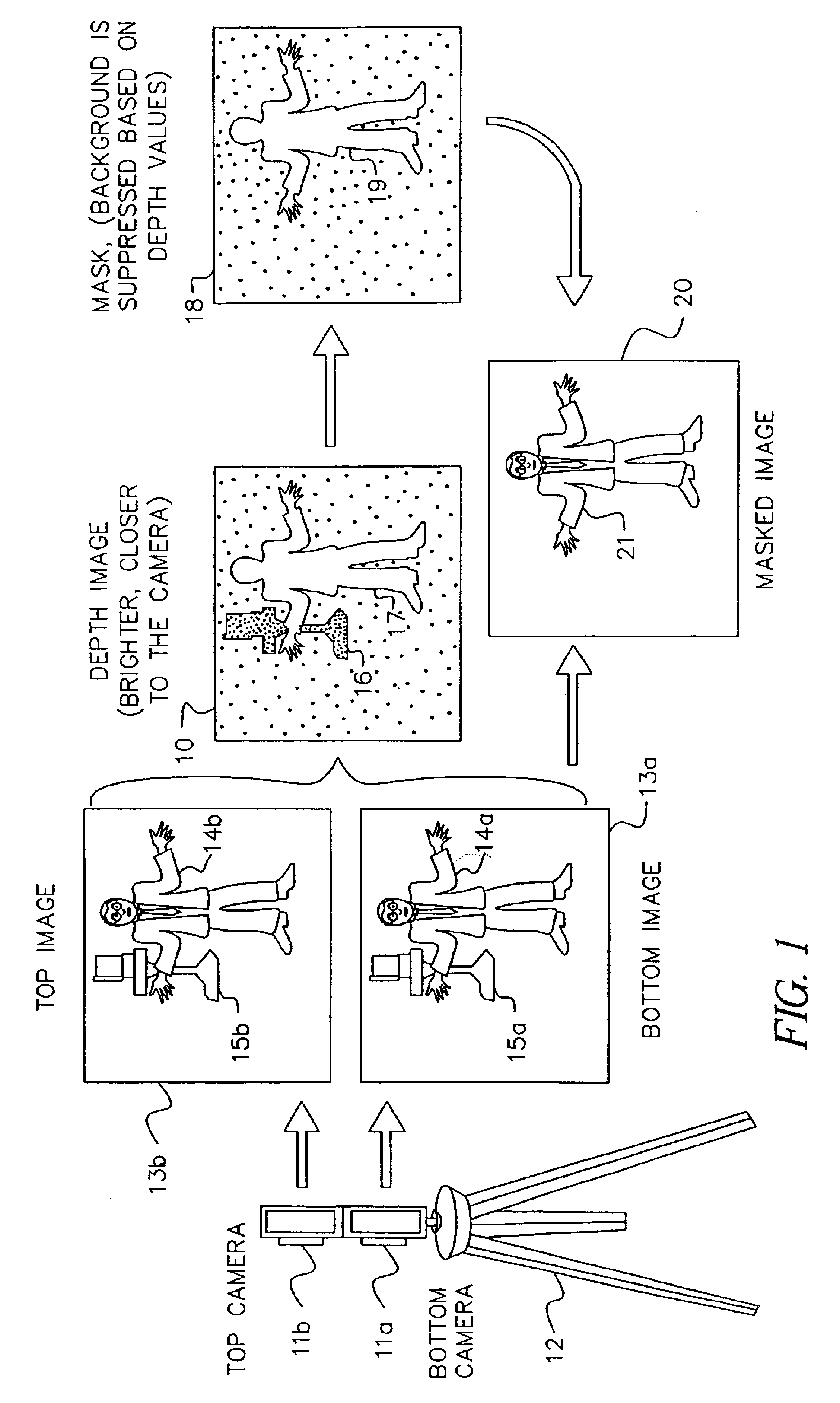
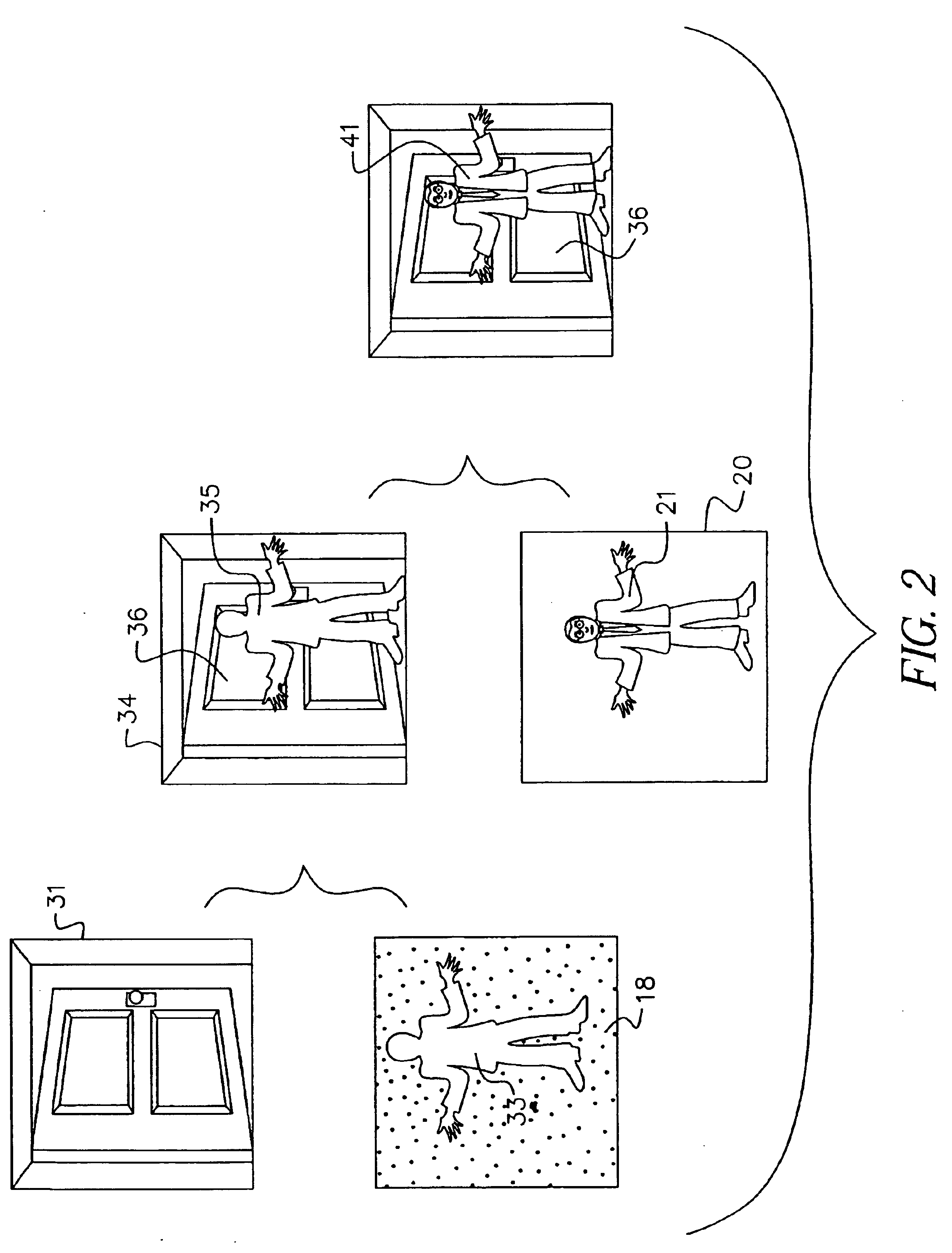
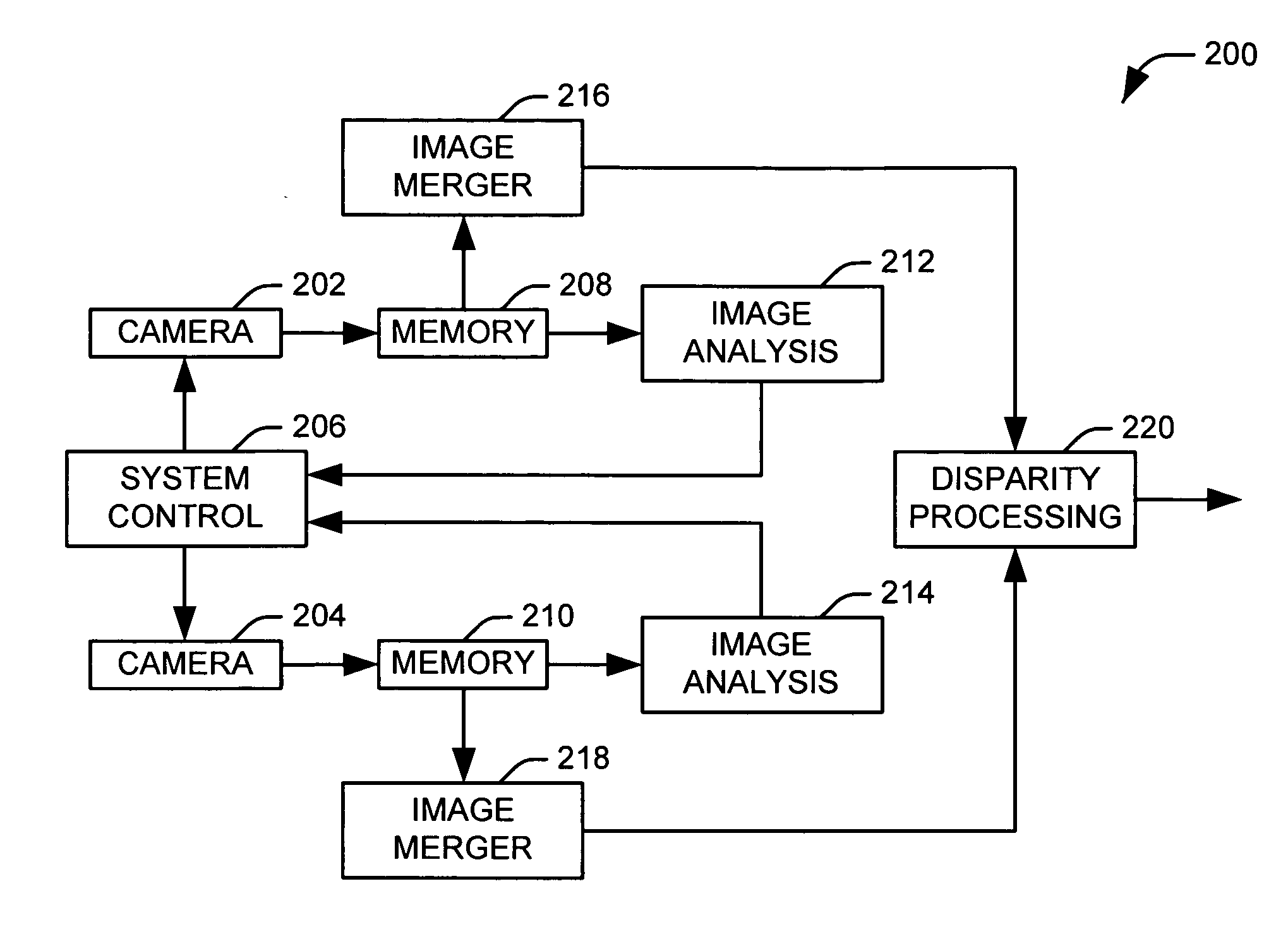
Method and apparatus for enhancing the dynamic range of stereo vision system
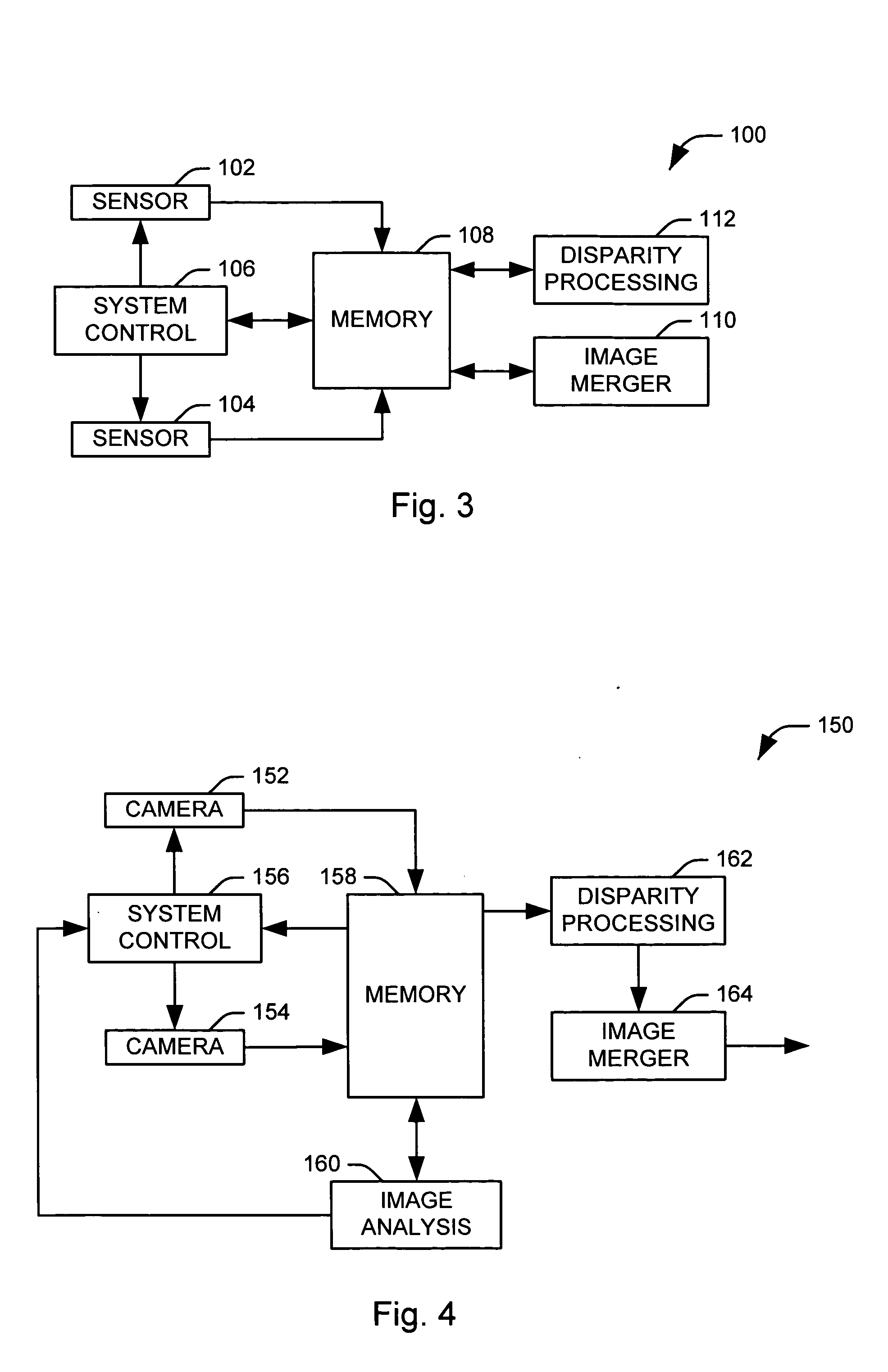
Systems and methods are provided for producing a stereo disparity map representing an imaged subject. A plurality of sensors (102 and 104) are operative to produce a plurality of images. Each image has an associated exposure according to an exposure level of an associated sensor. A system control (106) determines exposure levels for the plurality of sensors according to an exposure selection algorithm. A disparity processing component (112) is operative to generate a stereo disparity map from a plurality of images. An image merger (110) is operative to merge a plurality of images to produce a composite image having an increased dynamic range.
Owner:TRW AUTOMOTIVE US LLC
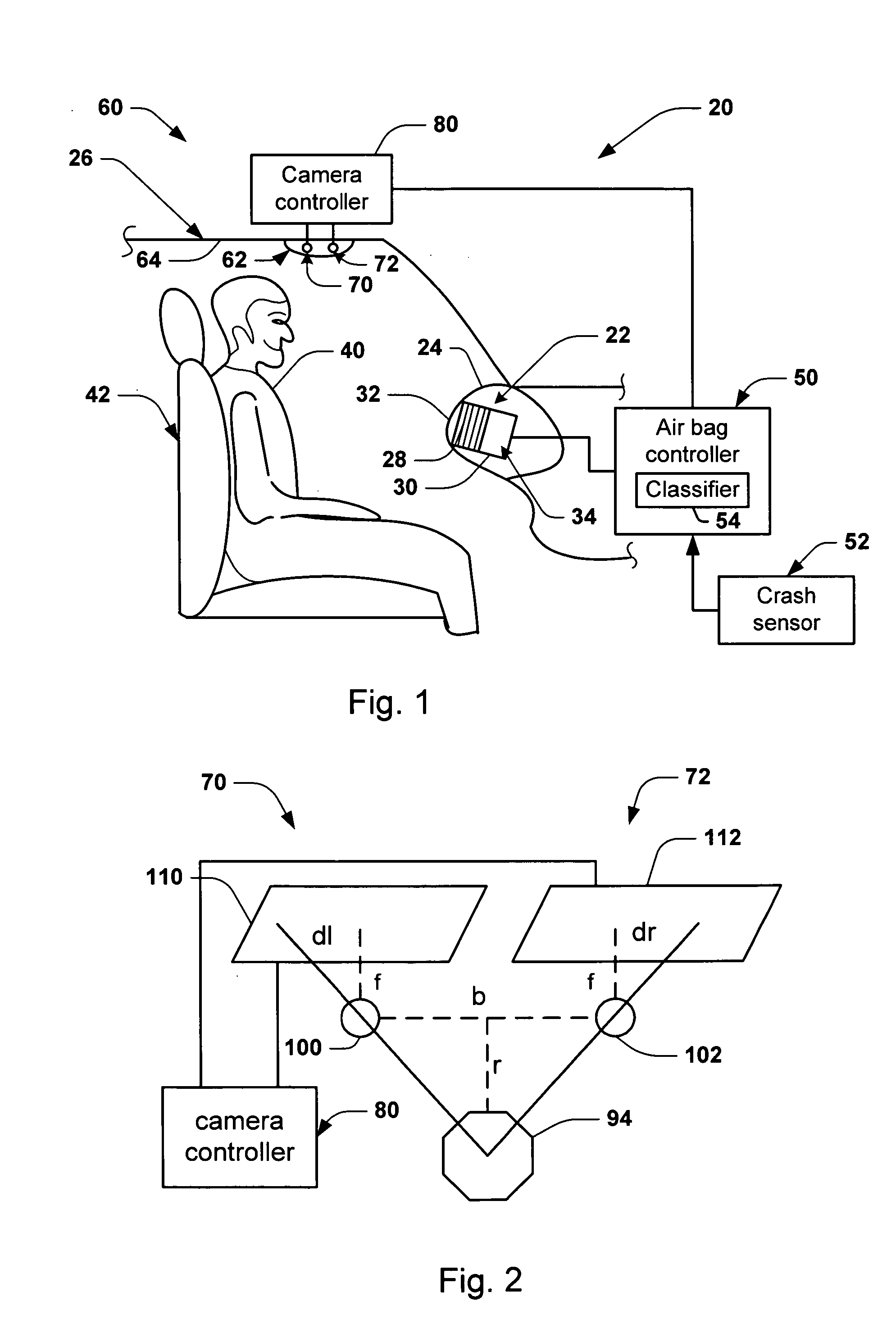
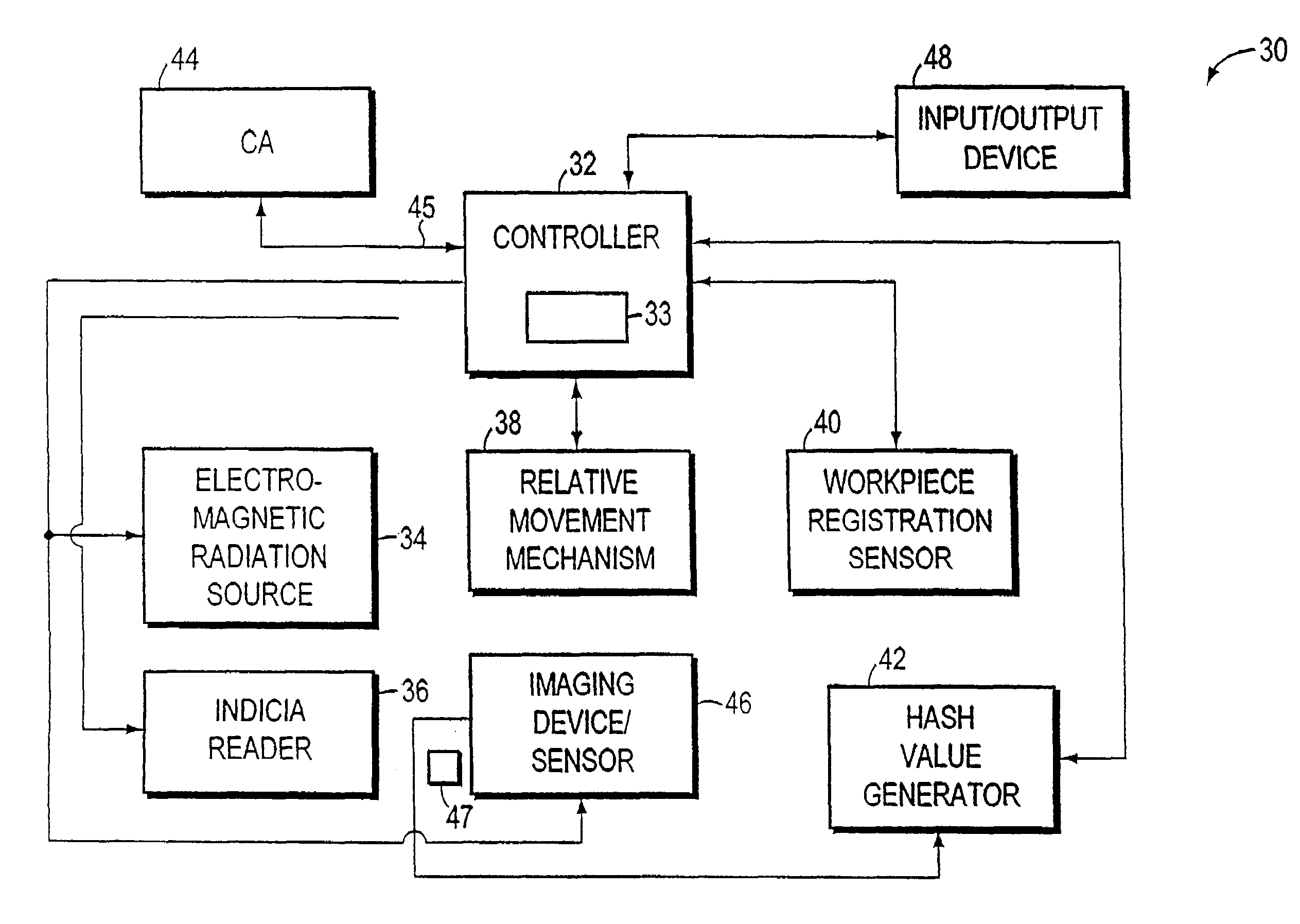
System and method for authentication of a workpiece using three dimensional shape recovery
ActiveUS7251347B2Programme controlElectric signal transmission systemsRelevant informationComputer graphics (images)
A workpiece authentication system uses shape recovery techniques to extract explicit three dimensional (“3-D”) features of the surface geometry of the designated portion of a workpiece from images produced using different lighting conditions. The system then bases authentication on the 3-D surface features. The system recovers surface normals, or equivalently gradients, for selected locations within a designated portion of the workpiece from multiple enrollment images produced under different illumination conditions. The system then encodes the surface normal information into authentication indicia that is placed on the workpiece and / or stores the surface normals or related information. Thereafter, the system determines that a given workpiece is authentic if the surface normals recovered from various verification images correspond to the stored surface normal information or the surface normal information encoded into the indicia. Alternatively, the system may use the surface normals to predict what an image should contain when the workpiece is subjected to a particular lighting condition. The system then determines that the workpiece is authentic if the predicted image and the image produced using the workpiece correspond. The system may instead encode brightness patterns associated with one or more enrollment images into the indicia. The system then recovers surface normals from images produced during verification operations, predicts what the brightness image should contain and compares the enrollment image to the prediction.
Owner:ESCHER GROUP
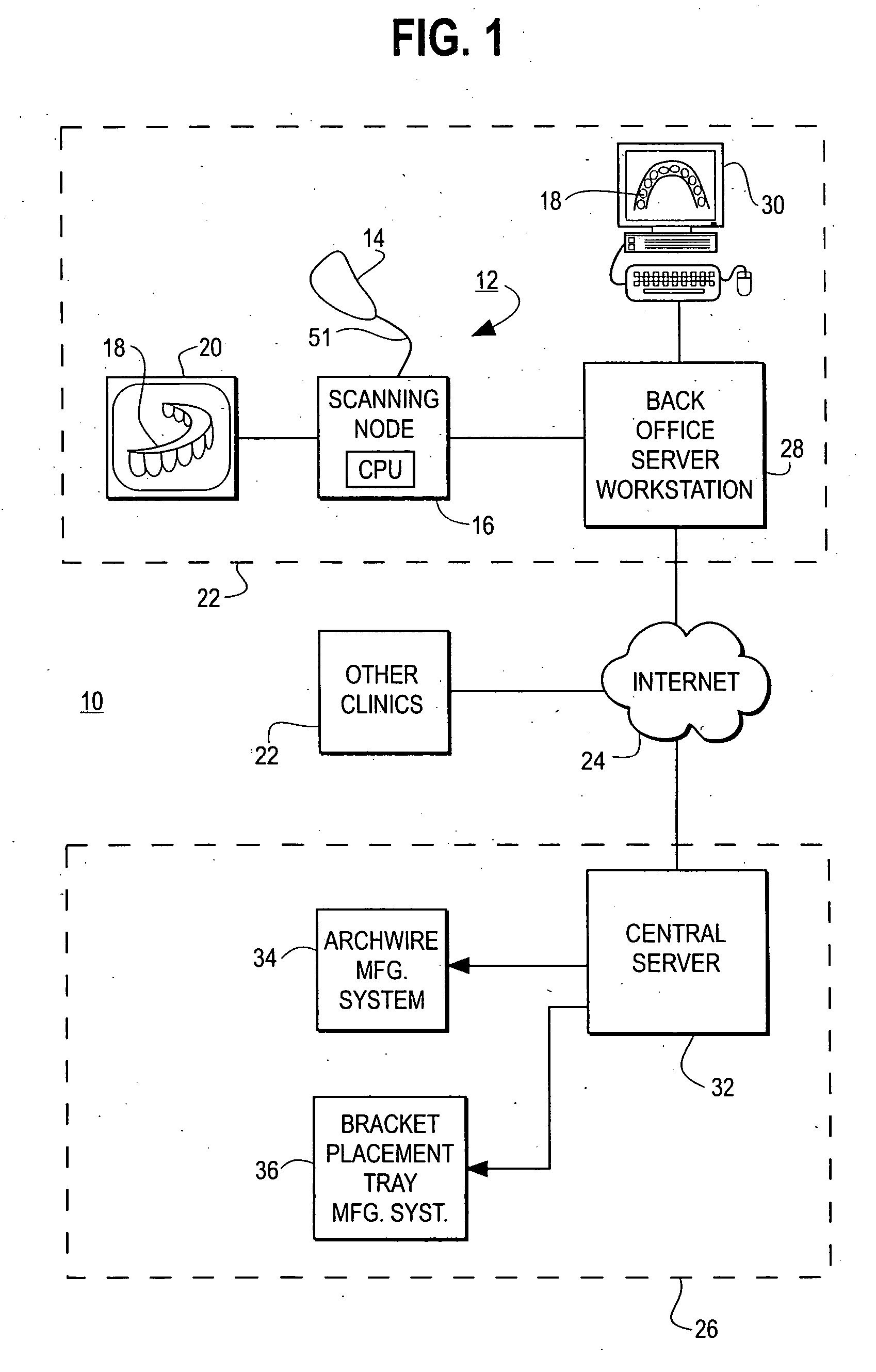
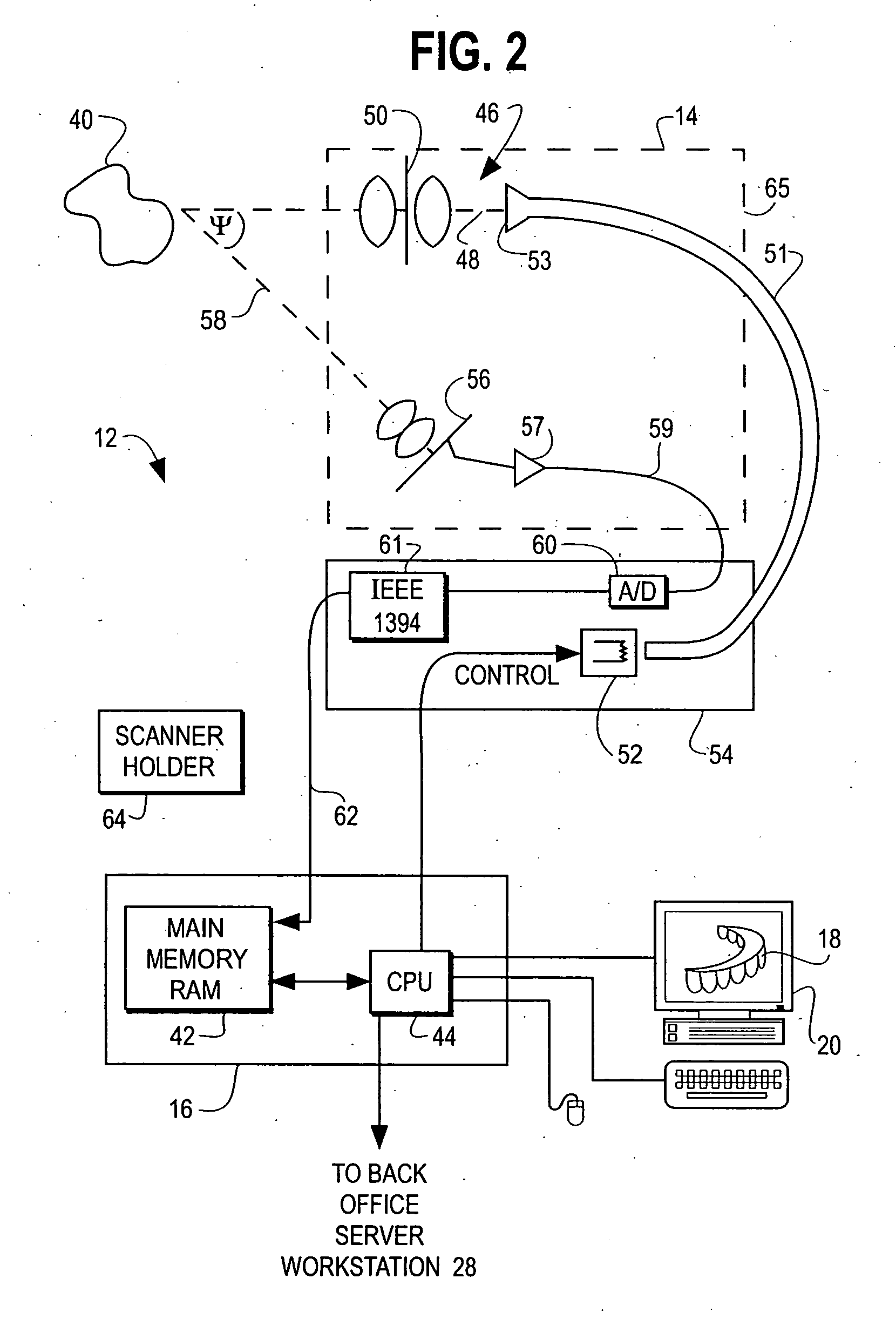
Methods for registration of three-dimensional frames to create three-dimensional virtual models of objects
A method and system are provided for constructing a virtual three-dimensional model of an object using a data processing system, and at least one machine-readable memory accessible to said data processing system. A set of at least two digital three-dimensional frames of portions of the object are obtained from a source, such as a computing system coupled to an optical or laser scanner, CT scanner, Magnetic Resonance Tomography scanner or other source. The at least two frames comprise a set of point coordinates in a three dimensional coordinate system providing differing information of the surface of the object. The frames provide a substantial overlap of the represented portions of the surface of the object, but do not coincide exactly for example due to movement of the scanning device relative to the object between the generation of the frame. Data representing the set of frames are stored in the memory. The data processing system processes the data representing the set of frames with said data processing system so as to register the frames relative to each other to thereby produce a three-dimensional virtual representation of the portion of the surface of the object covered by said set of frames. The registration is performed without using pre-knowledge about the spatial relationship between the frames. The three-dimensional virtual model or representation is substantially consistent with all of the frames.
Owner:ORAMETRIX
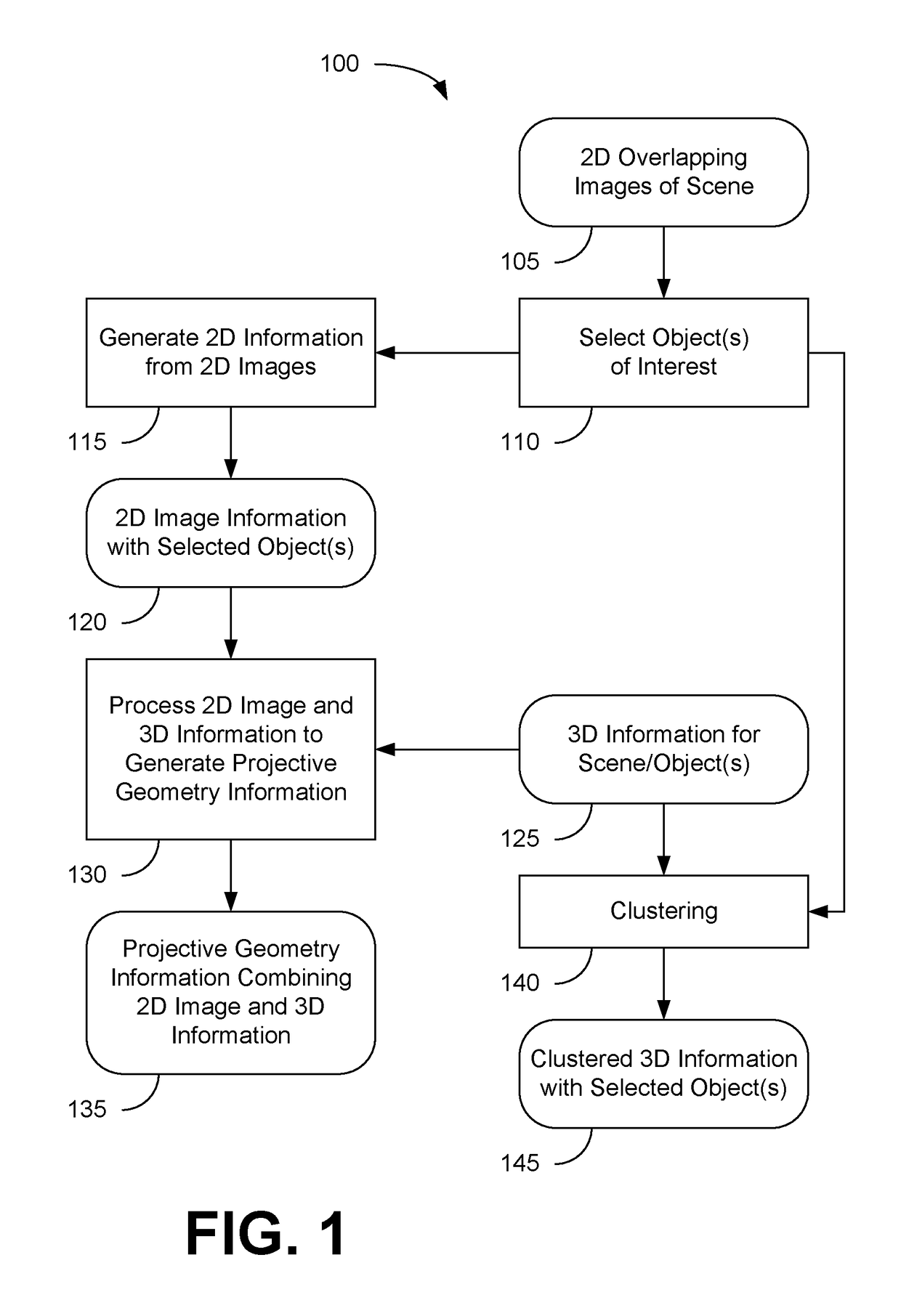
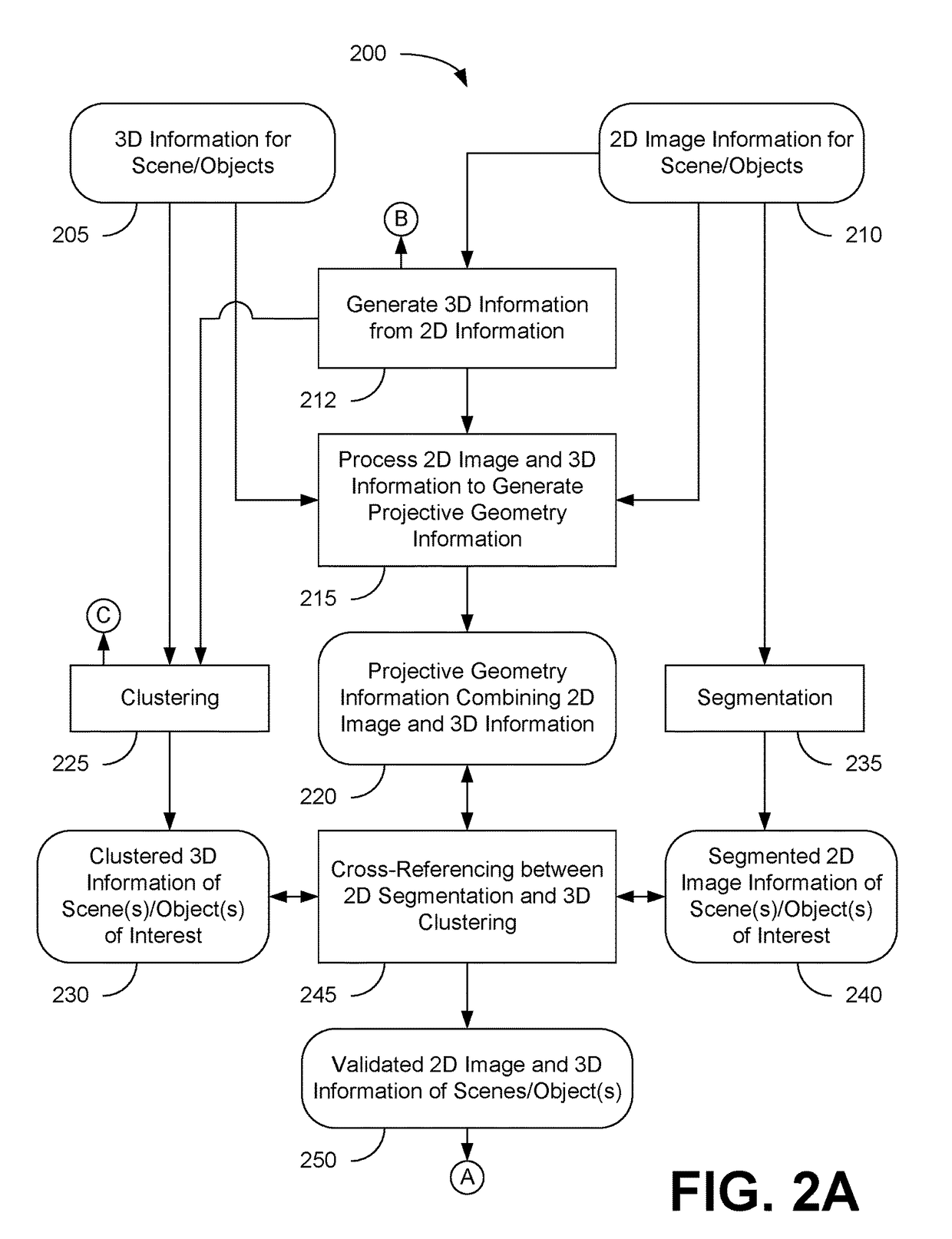
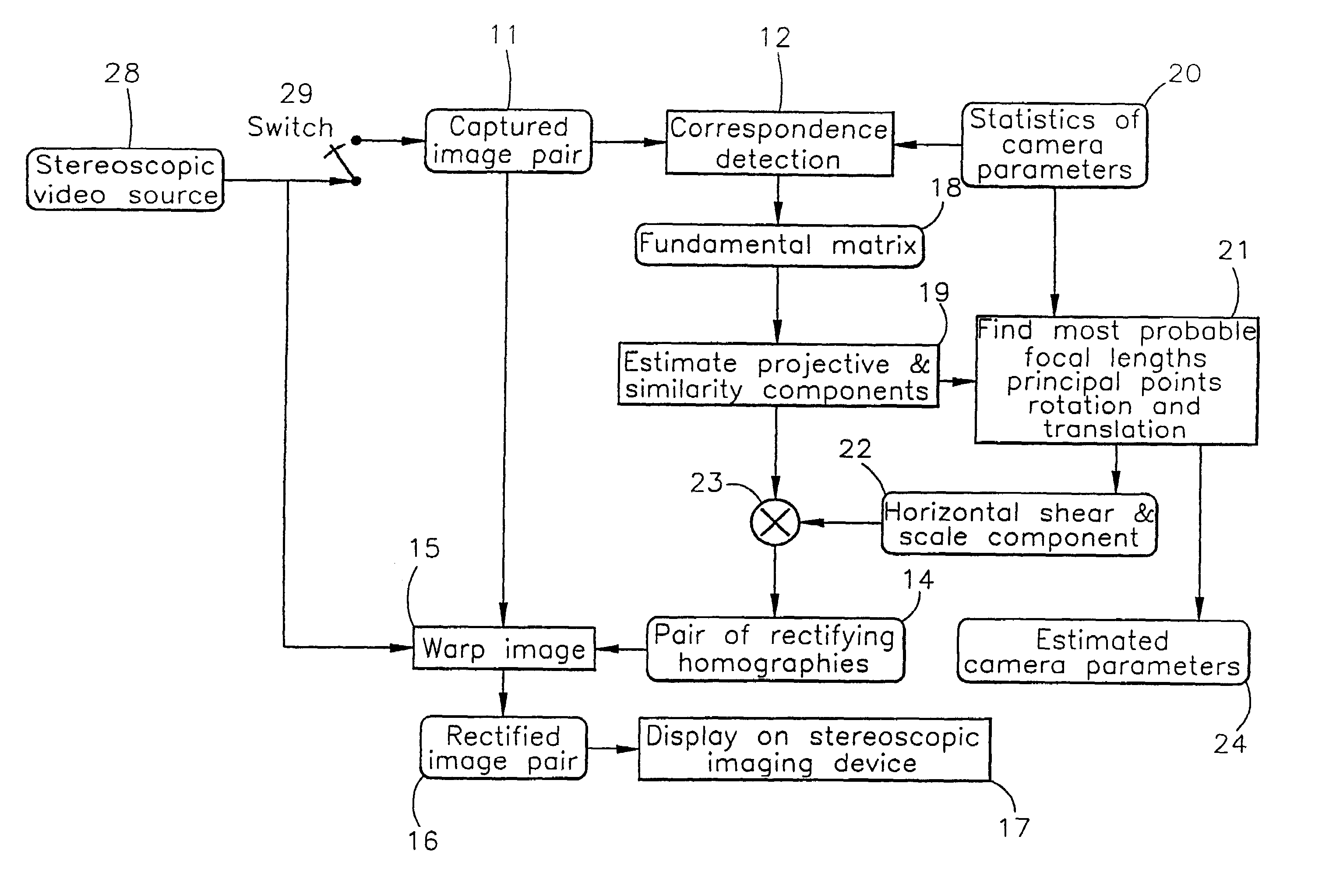
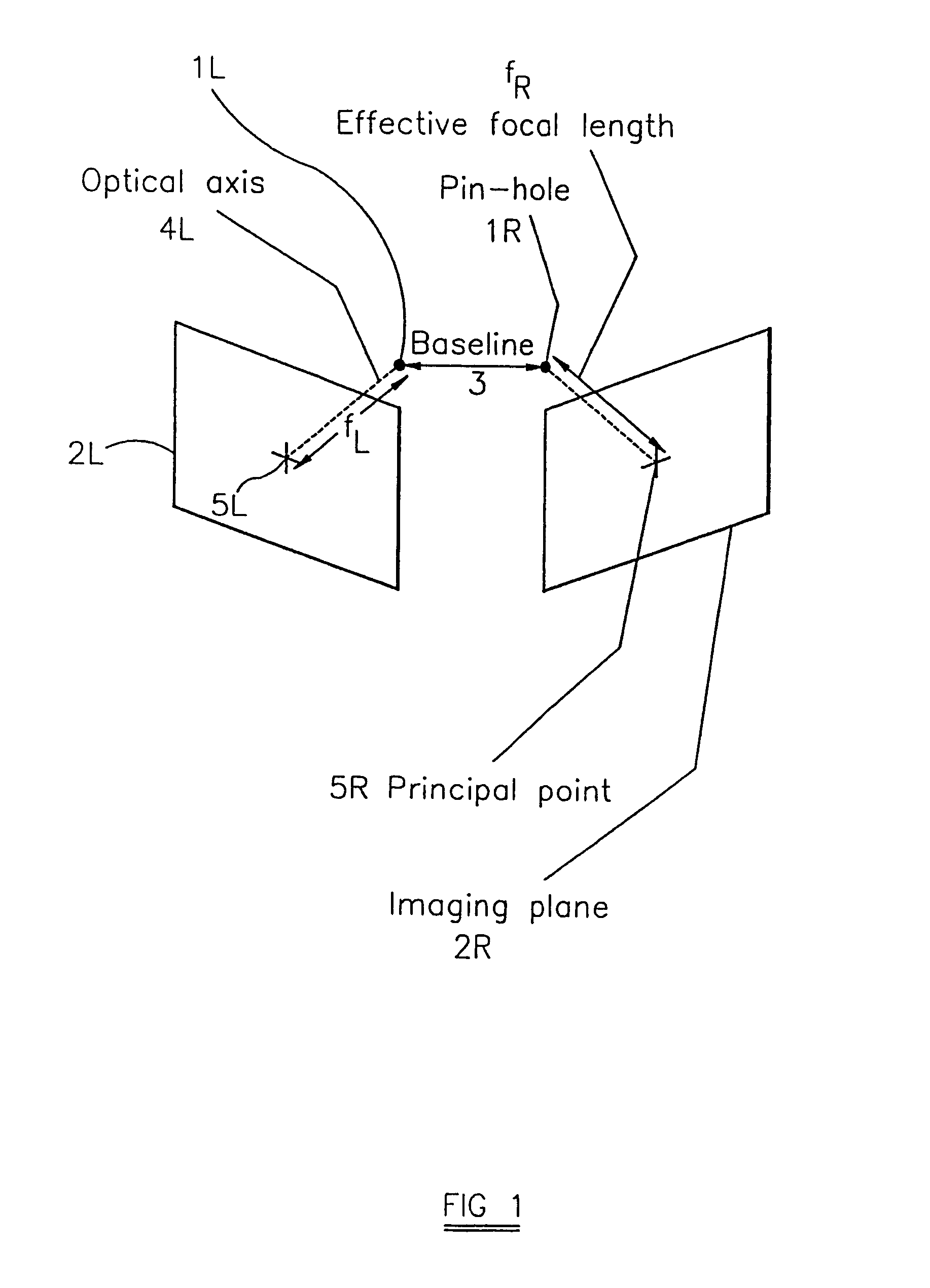
Method of and apparatus for rectifying a stereoscopic image
ActiveUS7113632B2Processing power requiredEasy to handleImage data processing detailsAquisition of 3D object measurementsComputer graphics (images)Display device
A method of rectifying a stereoscopic image consisting of left and right captured images comprises determining left and right rectification transformations. According to one aspect of the invention, statistics of the parameters of the stereoscopic image capture device used to capture the left and right images are used in the determination of the left and / or right rectification transformation.According to another aspect of the invention, the left and right rectification transformations are constrained to correspond to a transformation to a virtual alignment to a parallel camera set-up.Once the left and right rectification transformations have been determined they are preferably used to rectify the left and right images to eliminate, or substantially eliminate, vertical disparity from the rectified image pair. The left and right rectified images may then be displayed on a stereoscopic display device for viewing by an observer, or they may alternatively be stored for later use.
Owner:SHARP KK
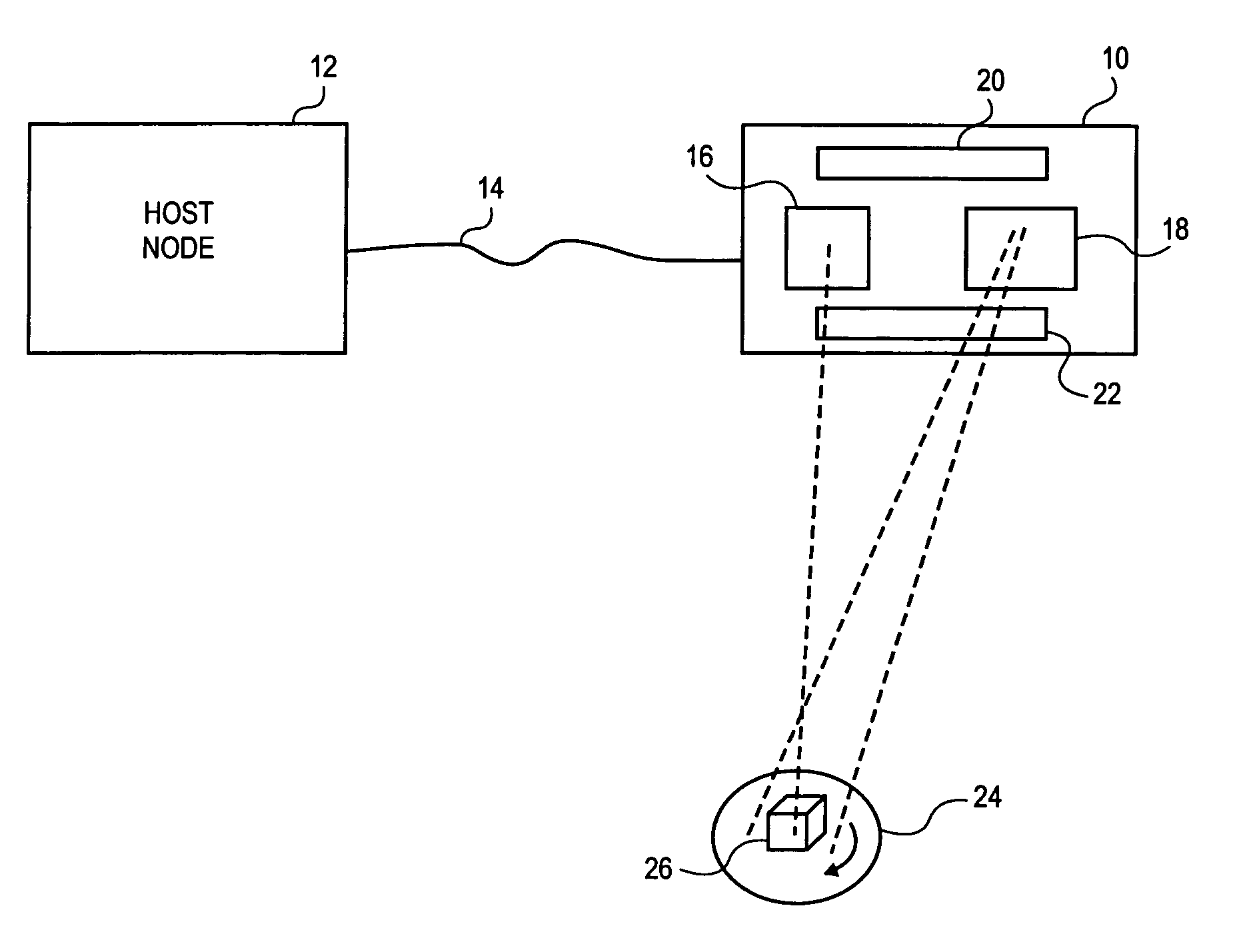
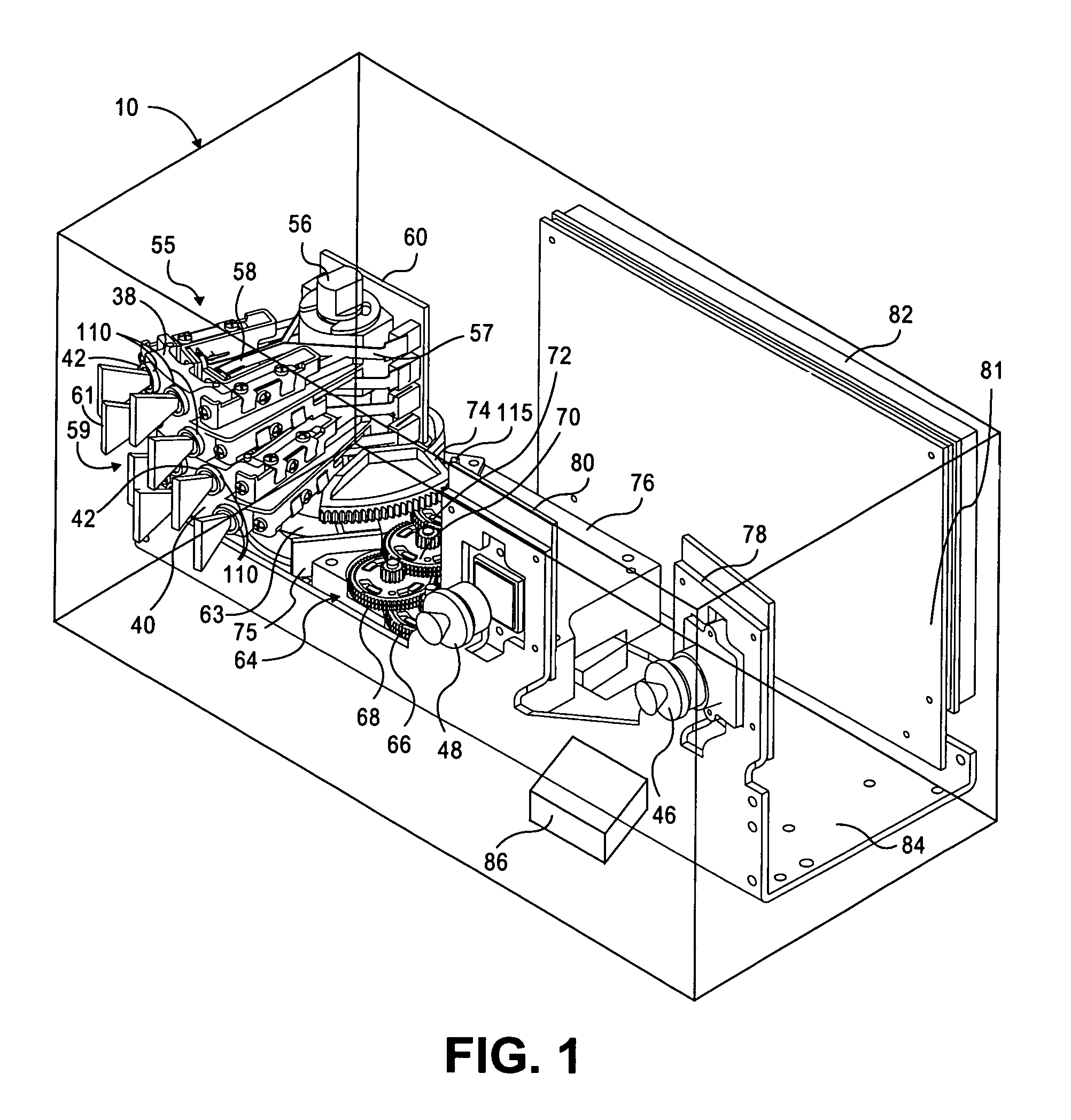
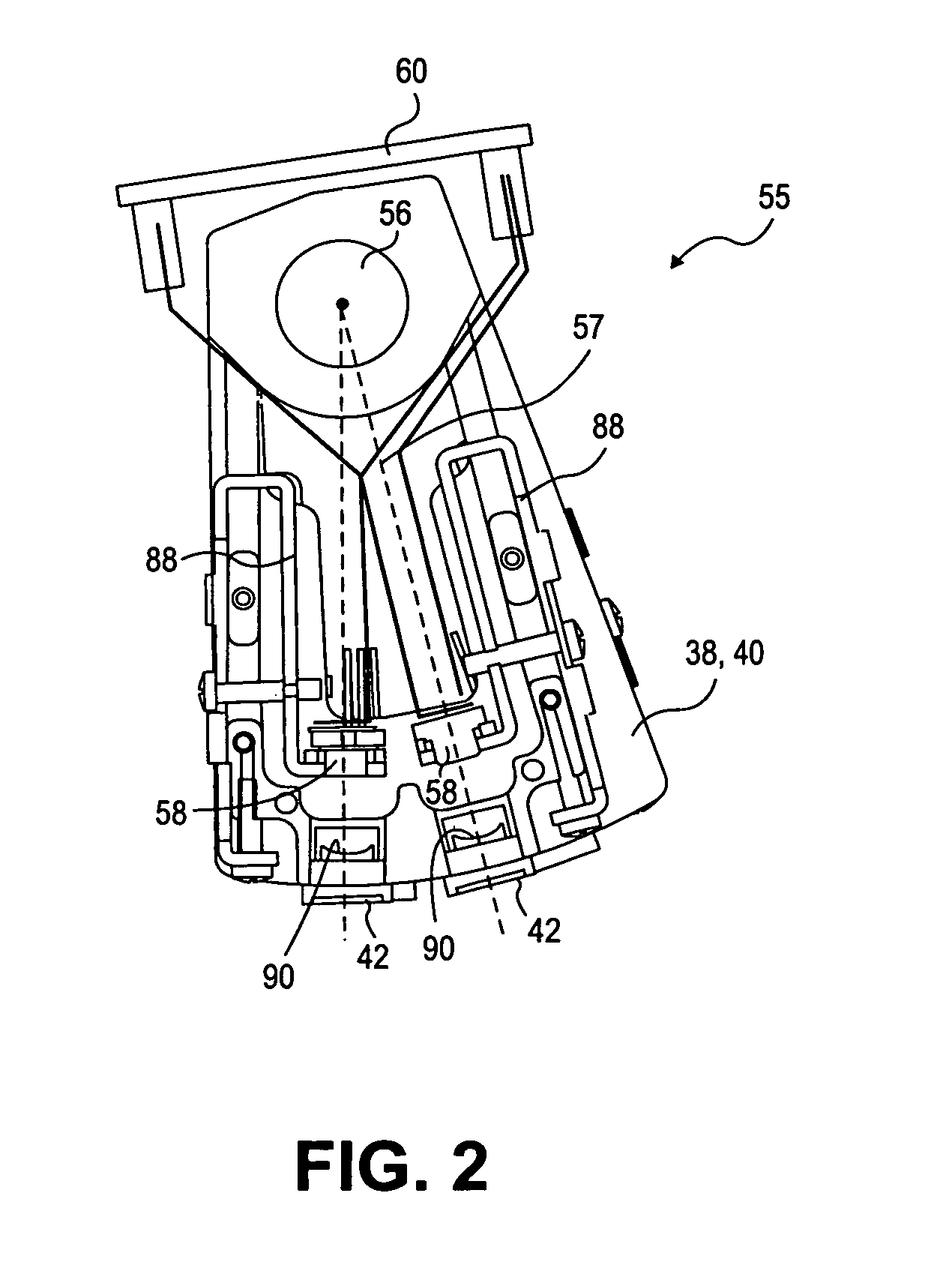
Multiple laser scanner
ActiveUS7995834B1Beam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansTriangulationLaser scanning
A method and system to capture geometry of a three dimensional target while disambiguating multiple projected target elements. The system projects at least three light pattern elements toward a target at a diverse spacing relative to each other. The system captures at least one image of the target while illuminated by at least one of the pattern elements. The pattern elements are moved relative to the target. The system disambiguates one pattern element from any other contained within an image of the target, at least in part based on the diverse spacing. The system measures triangulation locations of points on a three-dimensional surface of the target.
Owner:NEXTPAT
Method for forming a depth image
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Method and apparatus for dynamic space-time imaging system
A method for creating a 3D map of the surface contours of an object includes projecting a variety of patterns onto the object, and imaging the patterns as they fall on the object to encode the topographic features of the object. The images are processed in a computer program in a manner such that a complete 3D map of the surface of the object is obtained in digital form. Reiteration of the method can detect motional variation such as a breathing human, flexure of a complex mechanical structure, or a stress-strain testing of an airplane, vehicle, beam, bridge, or other structure.
Owner:4D IMAGING +1
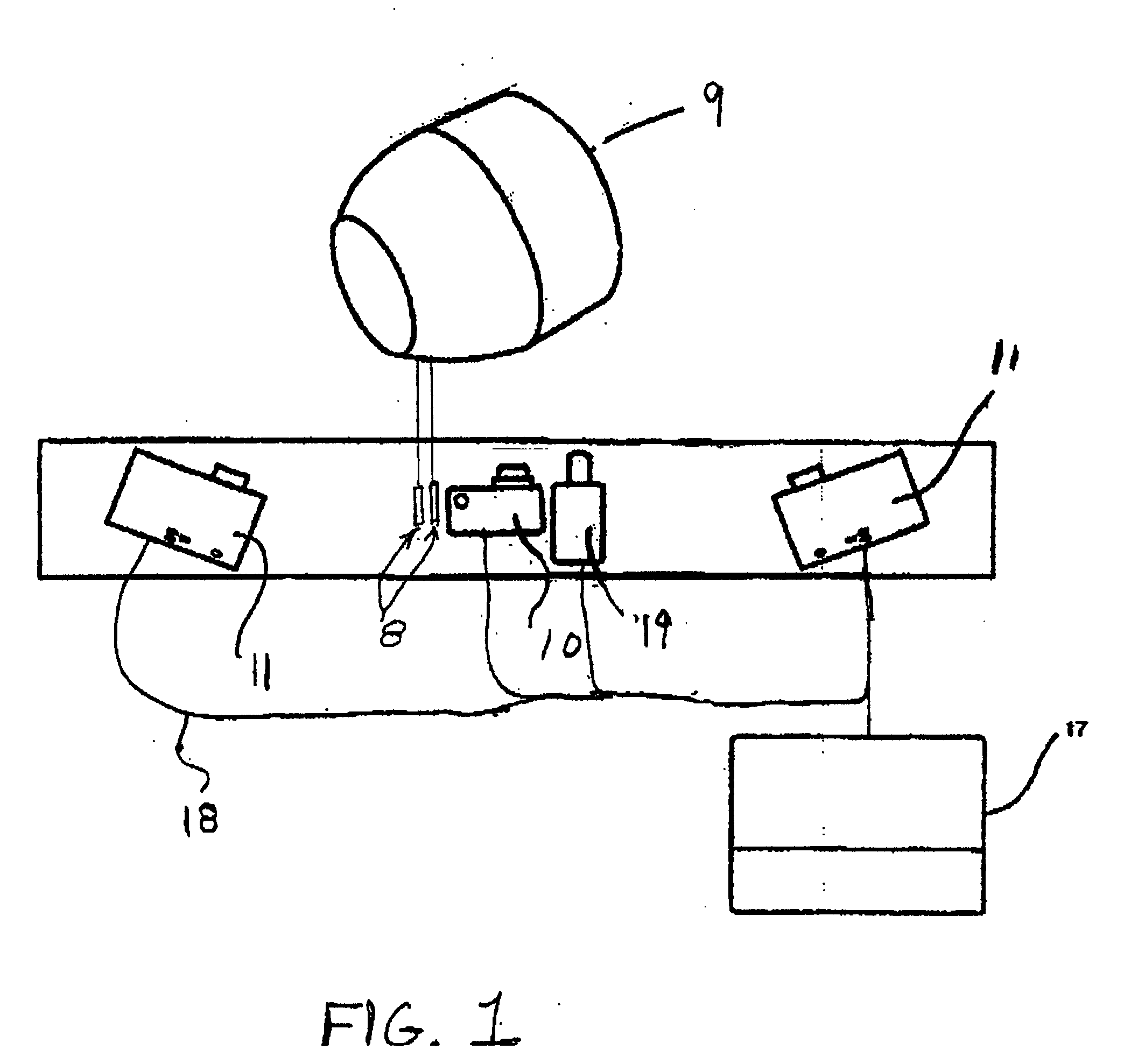
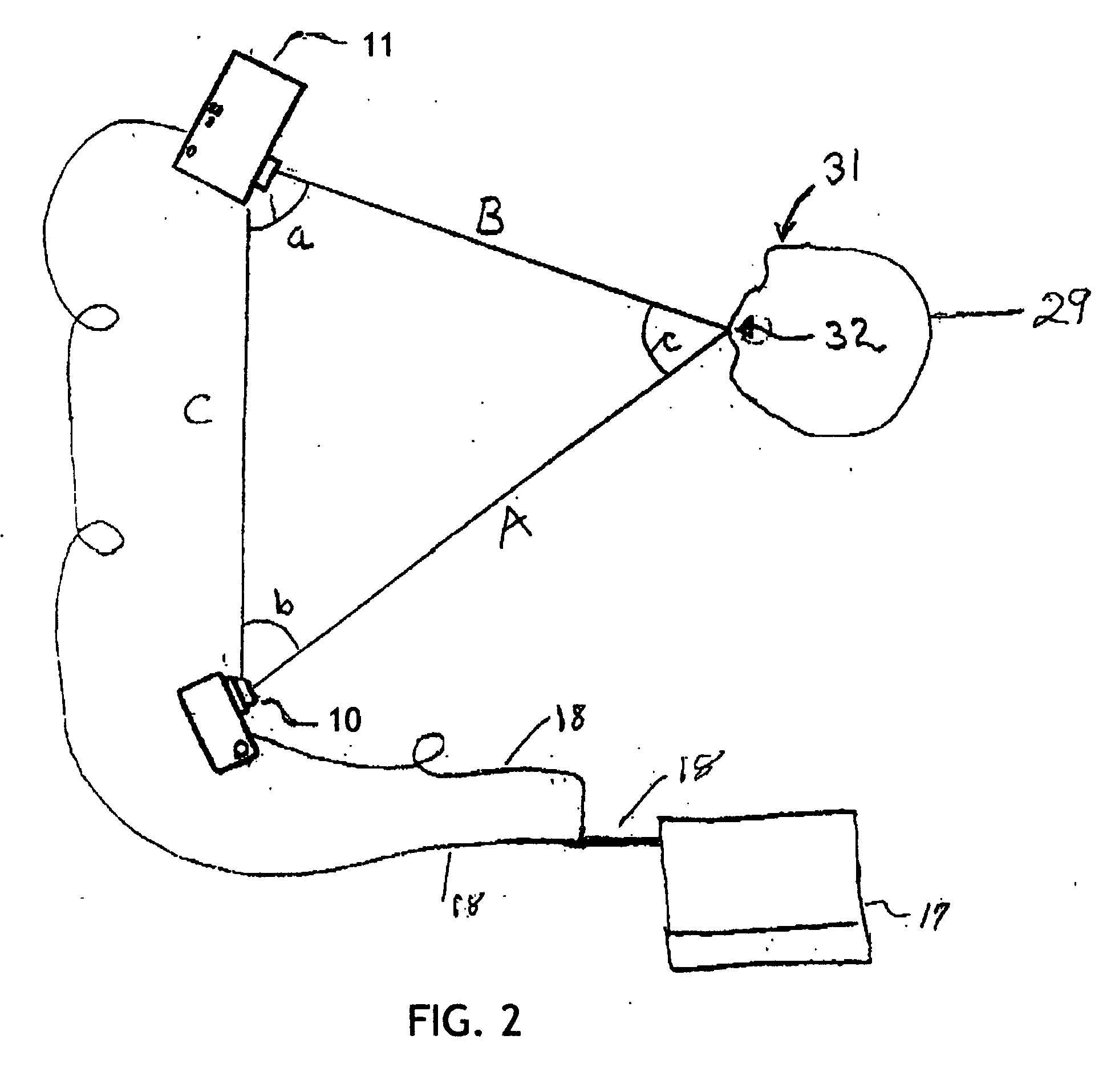
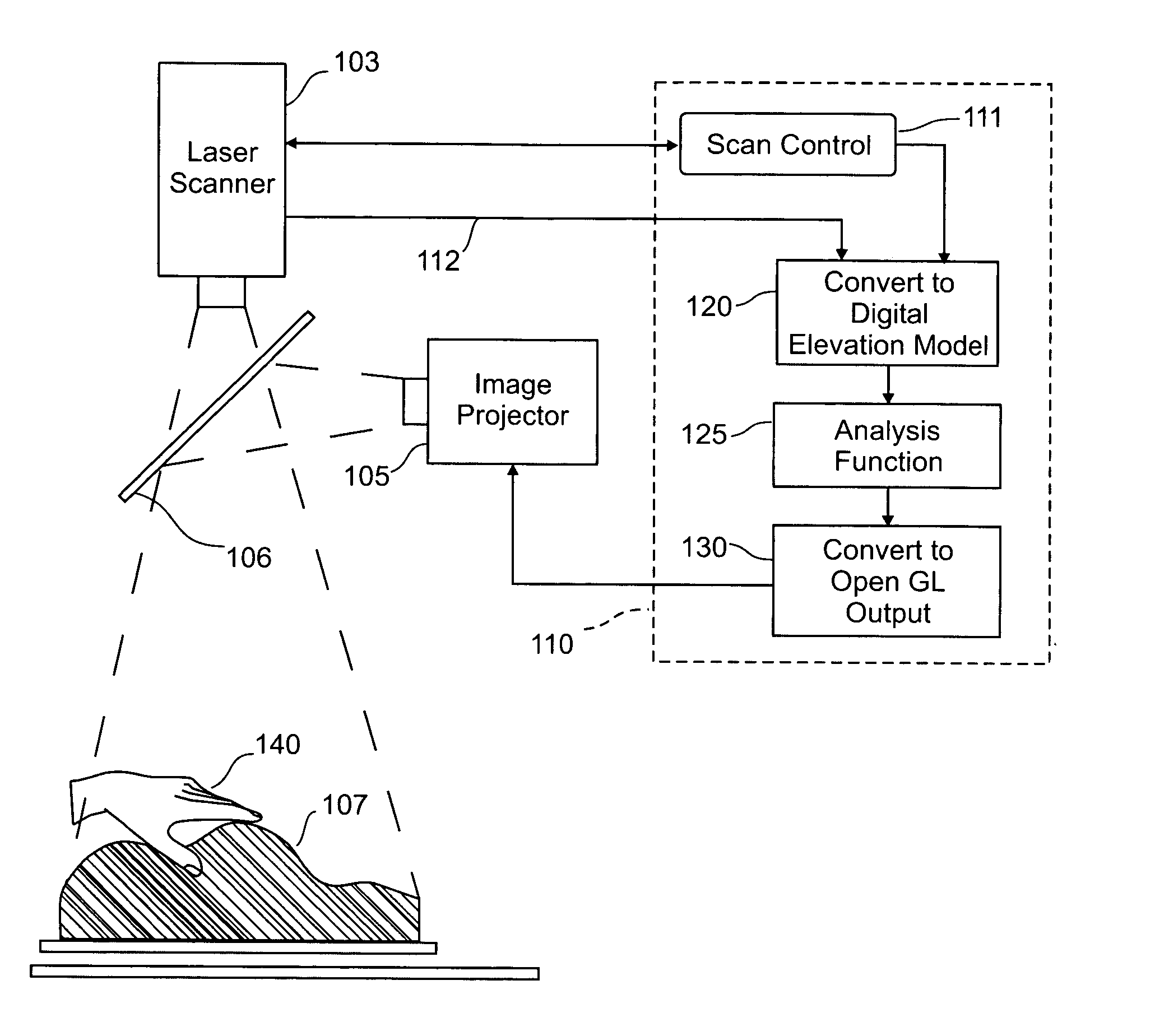
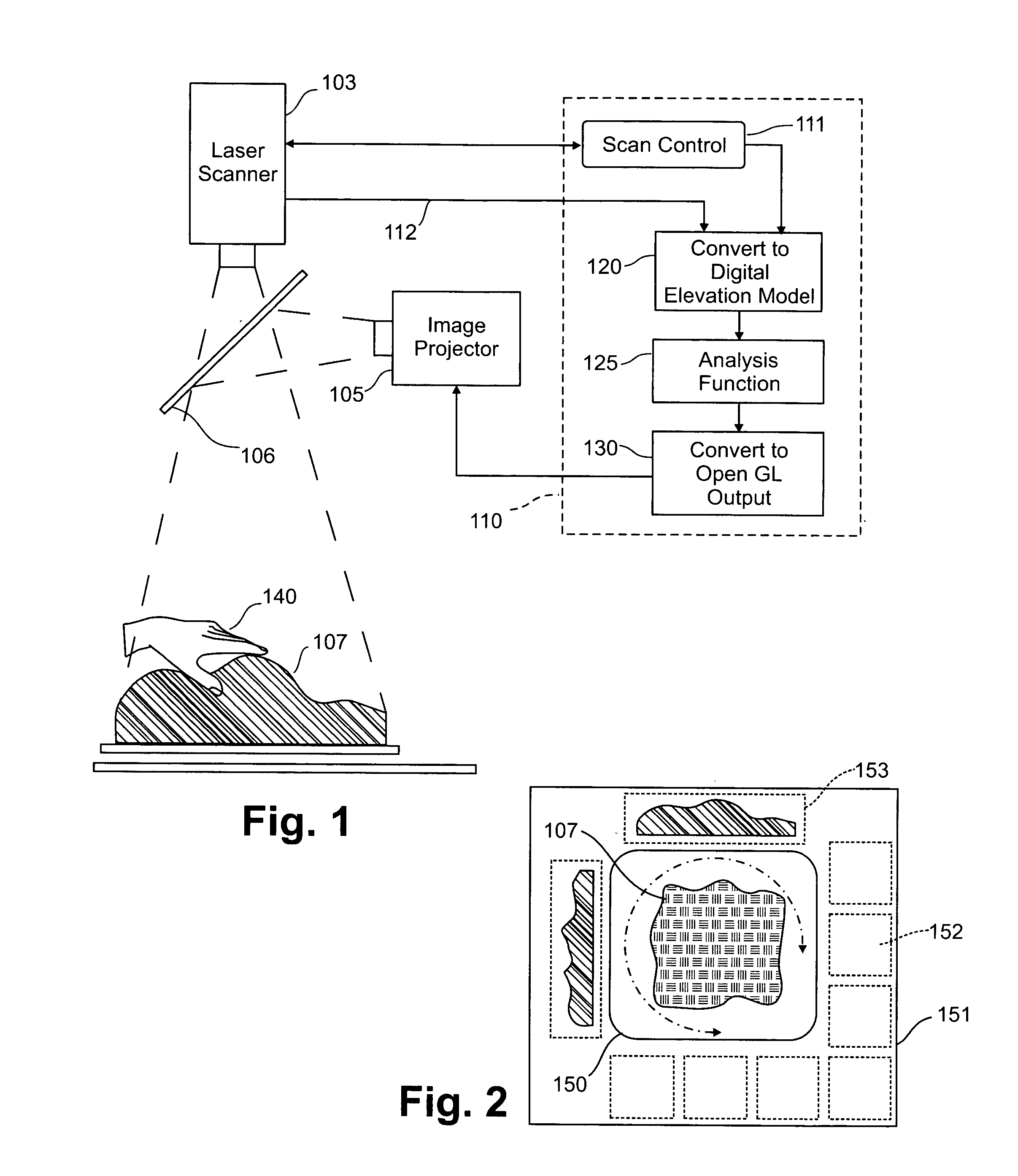
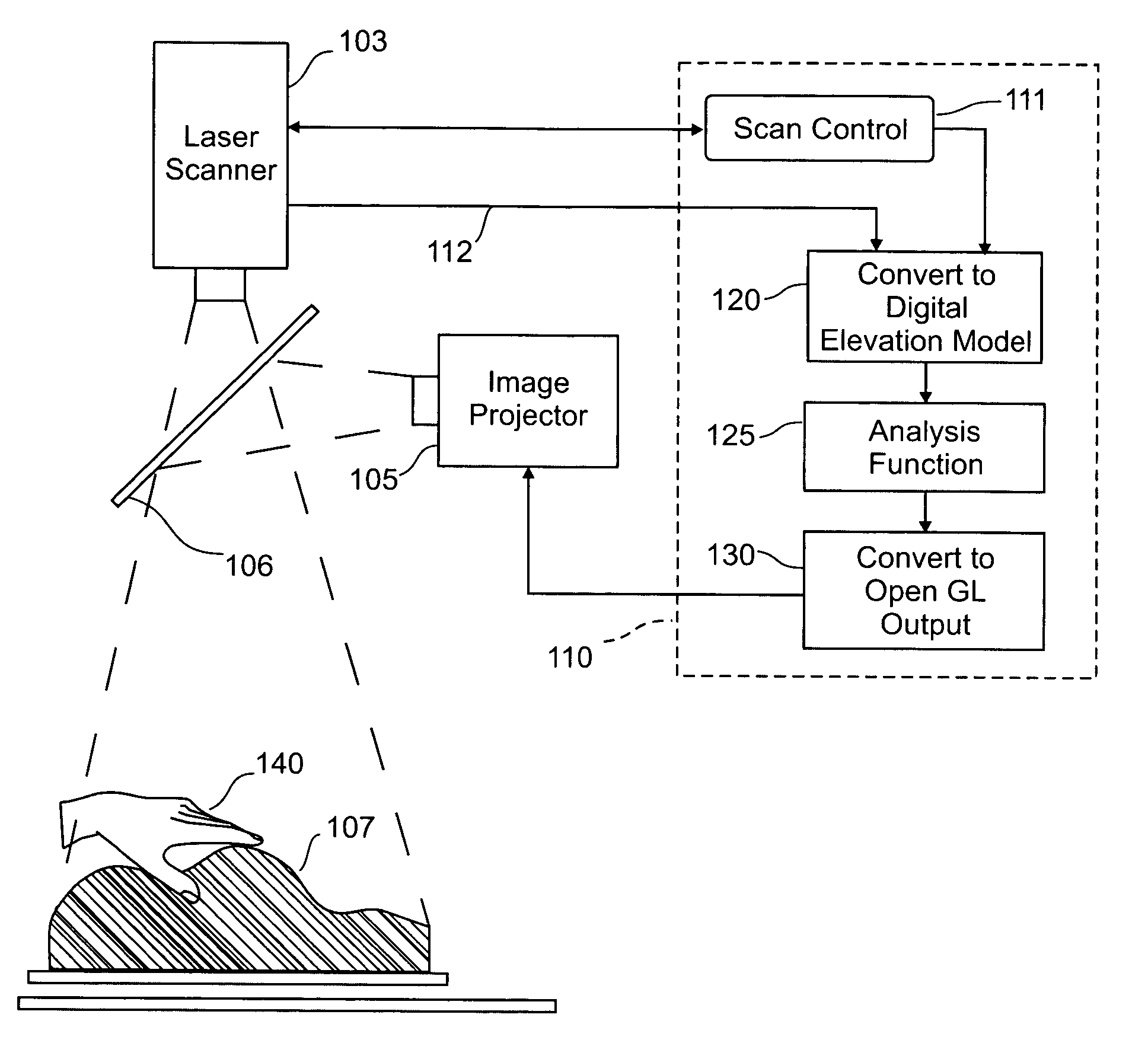
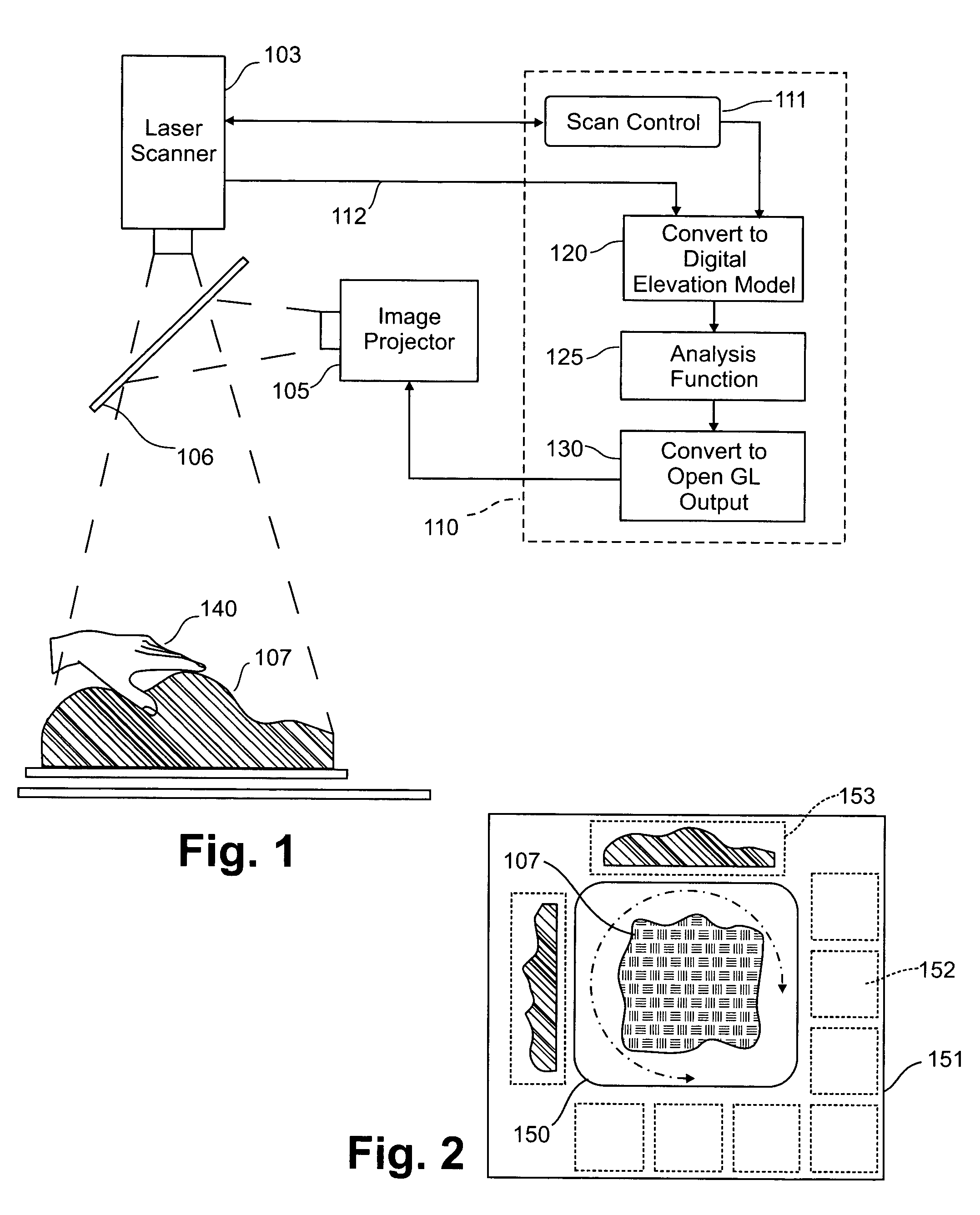
Three dimensional tangible interface for interacting with spatial-temporal data using a laser scanner
InactiveUS20050017967A1Efficient representationQuickly define and understandImage analysisCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)Laser scanning
An interface that allows a user to model and analyze the properties of three dimensional surface and the regions surrounding such surfaces. The user manipulates a deformable physical modeling material that defines the geometry of a surface. A position sensor such as a laser scanner captures position data specifying the geometry of the surface. A processor processes the geometry data using a selected analysis function to produce result data representing computed characteristics of the surface or its surrounding region. The result data projected as an image onto the deformable surface. The interface permits the user to modify a surface geometry and directly visualize the characteristics of the modified geometry in real time.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method for forming a depth image
InactiveUS20050129305A1Easy to shapeImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingReference image
A computer vision / image processing method generates a depth map. In one embodiment, the present invention provides a method of forming a relative depth map from at least three x-ray images of a patient taken from different perspectives. The method includes the steps of: (a) selecting one of the x-ray images as a reference image; (b) identifying corresponding objects within the reference image and the other images; (c) computing a disparity between the identified corresponding objects; and (d) generating the relative depth map from the disparities.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
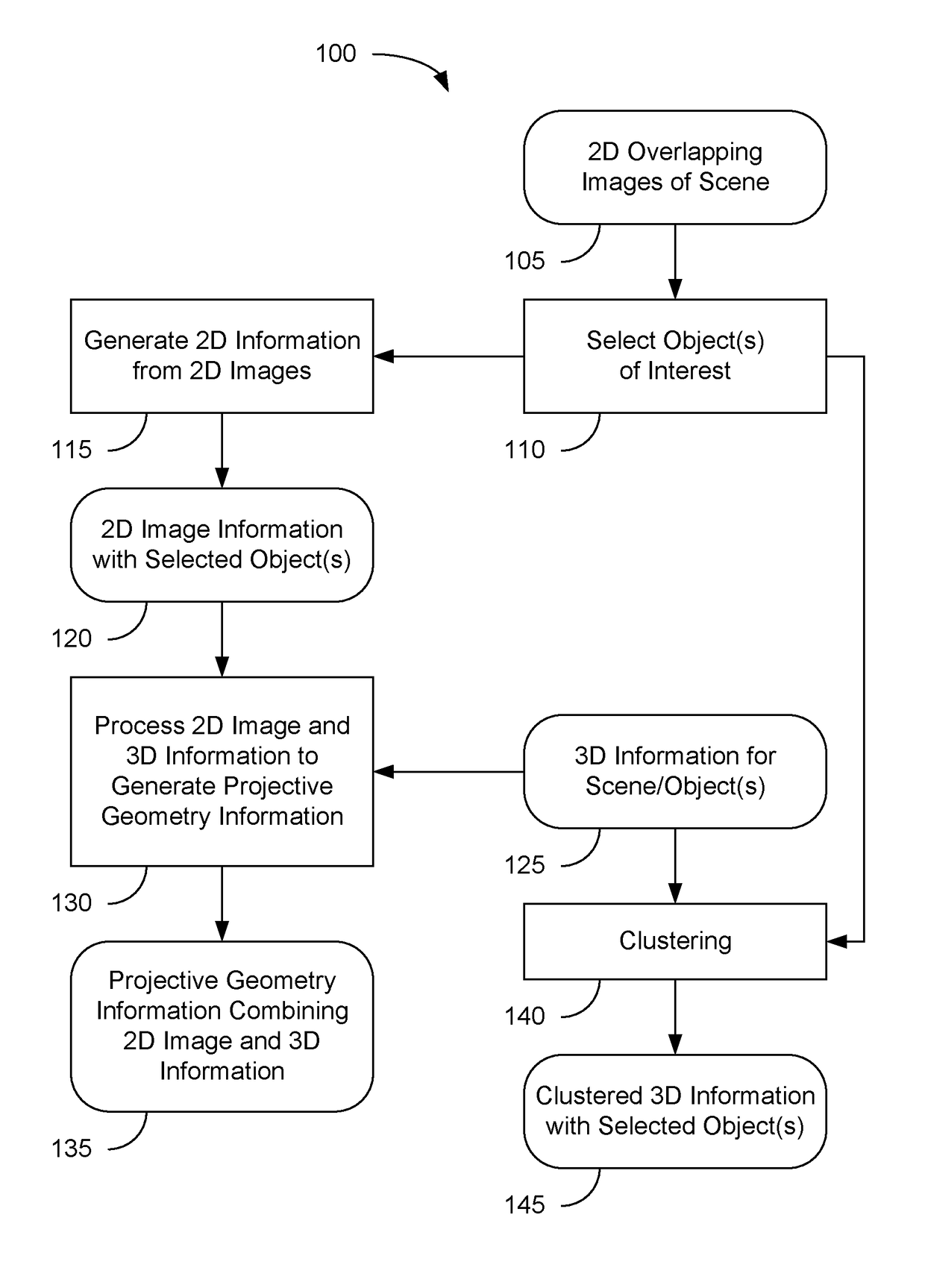
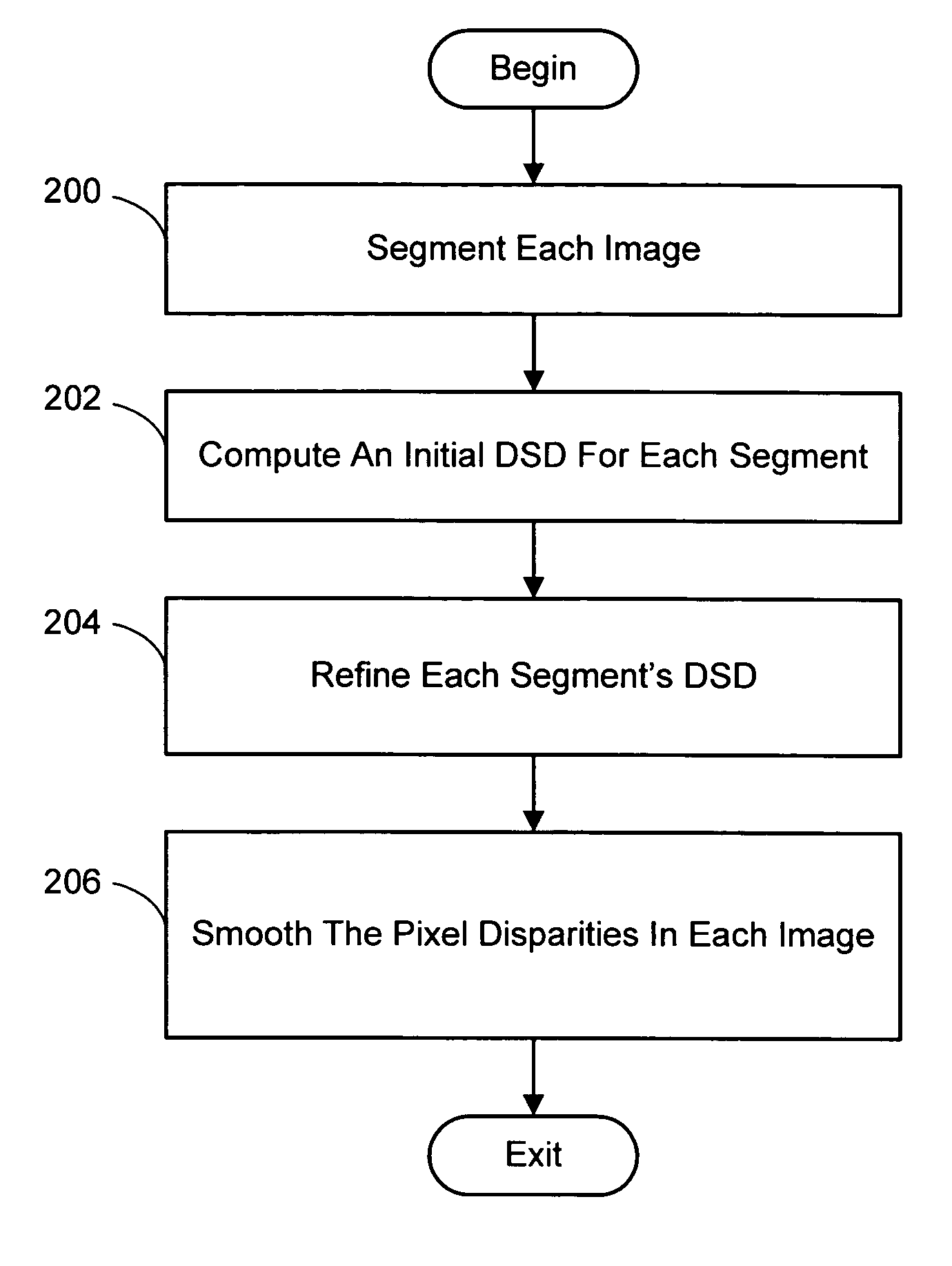
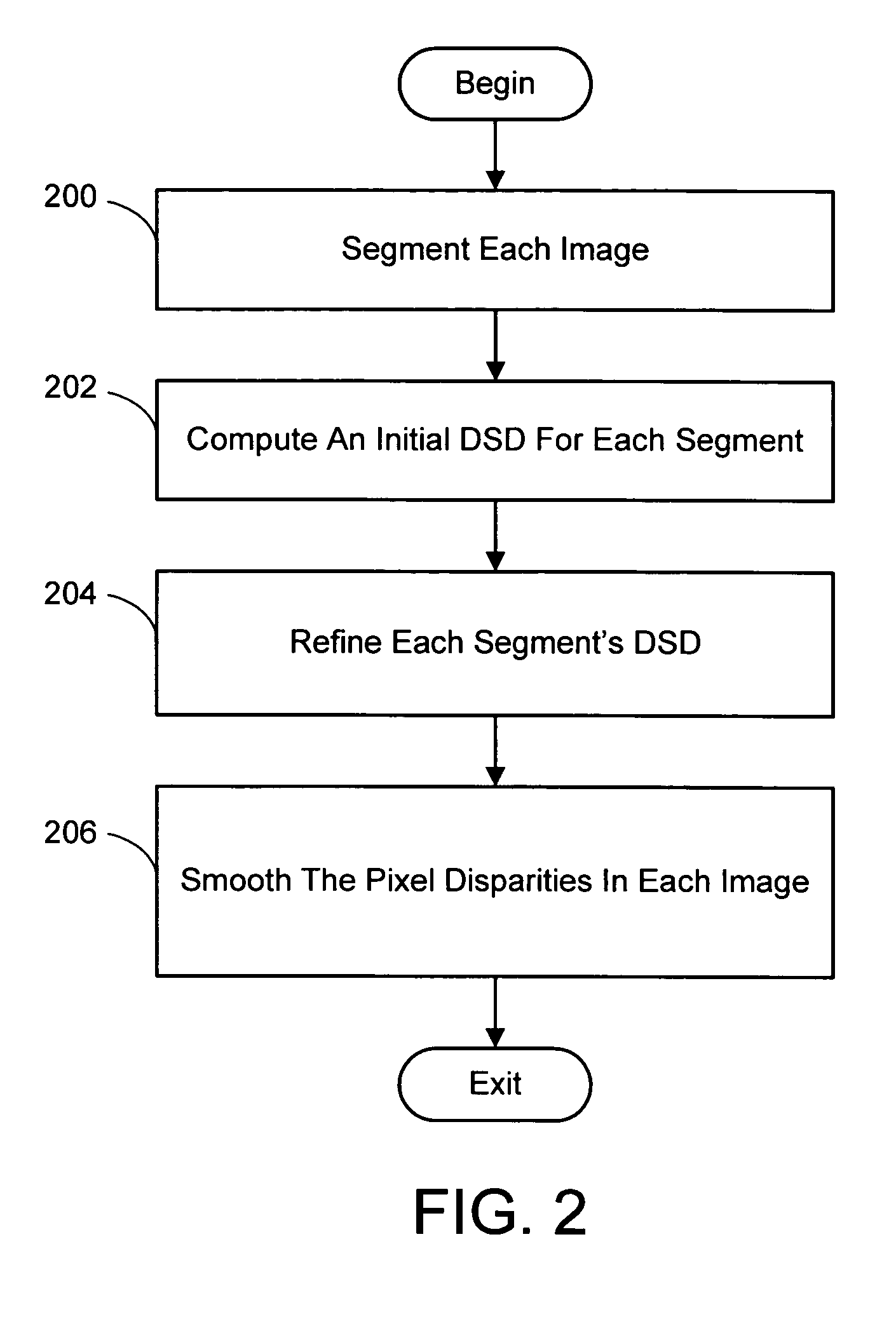
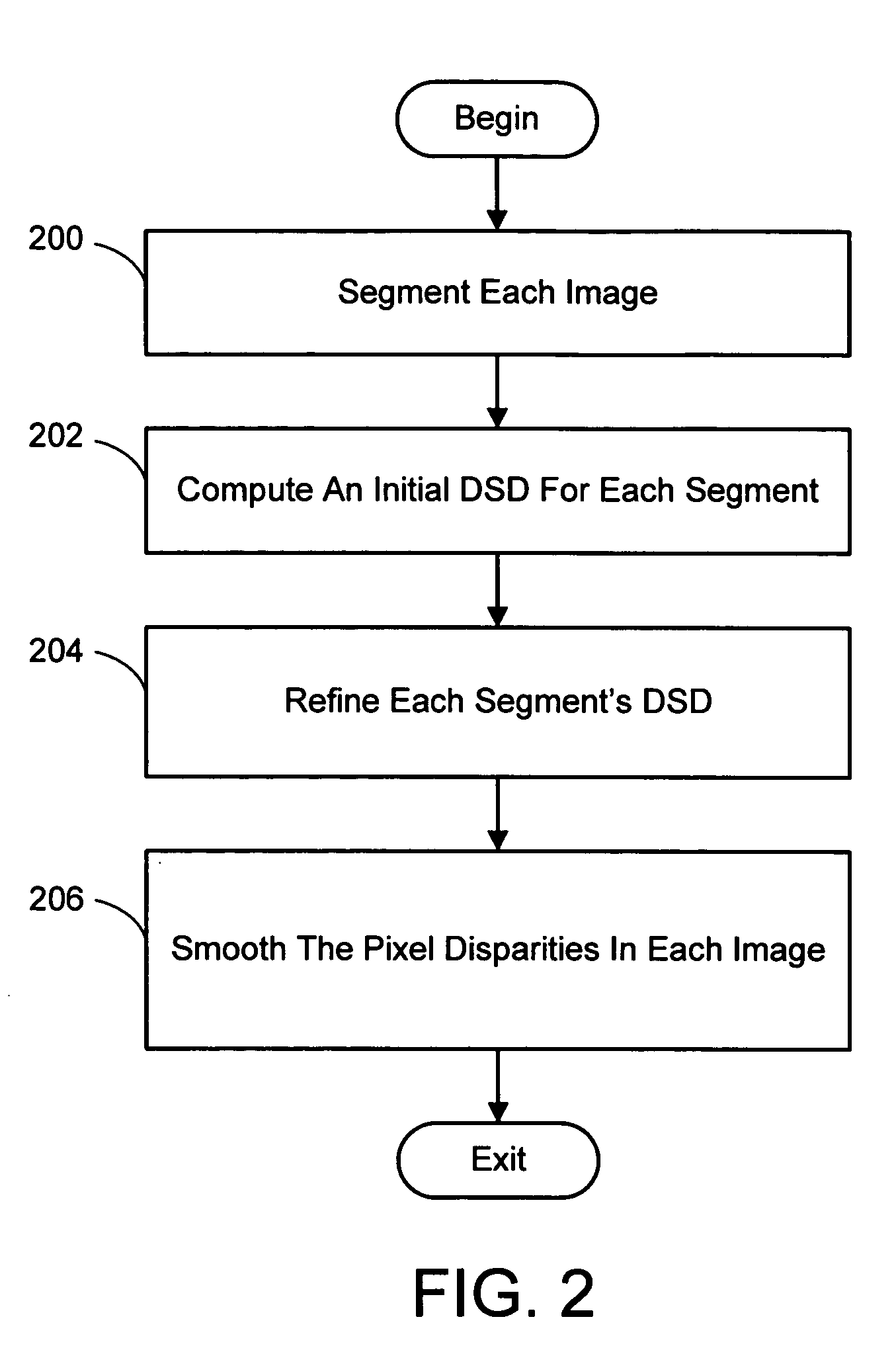
Color segmentation-based stereo 3D reconstruction system and process
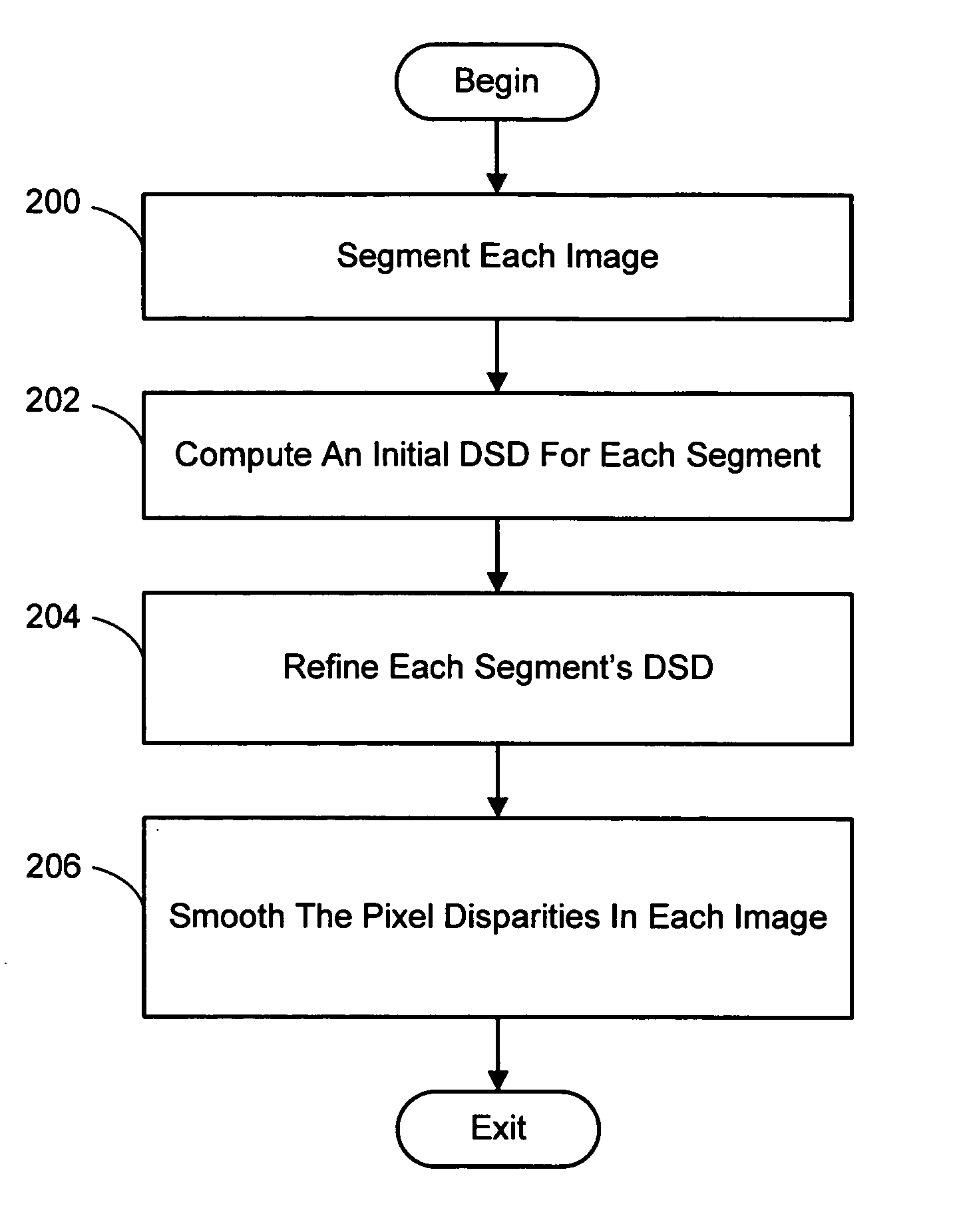
InactiveUS20050286757A1Promote resultsGood segmentation resultImage analysisAquisition of 3D object measurementsParallaxDepth mapping
A system and process for computing a 3D reconstruction of a scene from multiple images thereof, which is based on a color segmentation-based approach, is presented. First, each image is independently segmented. Second, an initial disparity space distribution (DSD) is computed for each segment, using the assumption that all pixels within a segment have the same disparity. Next, each segment's DSD is refined using neighboring segments and its projection into other images. The assumption that each segment has a single disparity is then relaxed during a disparity smoothing stage. The result is a disparity map for each image, which in turn can be used to compute a per pixel depth map if the reconstruction application calls for it.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Three dimensional tangible interface for interacting with spatial-temporal data using a laser scanner
InactiveUS7181363B2Efficient representationQuickly define and understandImage analysisIncline measurementComputer graphics (images)Laser scanning
An interface that allows a user to model and analyze the properties of three dimensional surface and the regions surrounding such surfaces. The user manipulates a deformable physical modeling material that defines the geometry of a surface. A position sensor such as a laser scanner captures position data specifying the geometry of the surface. A processor processes the geometry data using a selected analysis function to produce result data representing computed characteristics of the surface or its surrounding region. The result data projected as an image onto the deformable surface. The interface permits the user to modify a surface geometry and directly visualize the characteristics of the modified geometry in real time.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
3D (three-dimensional) sight direction estimation method for robot interaction object detection
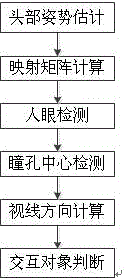
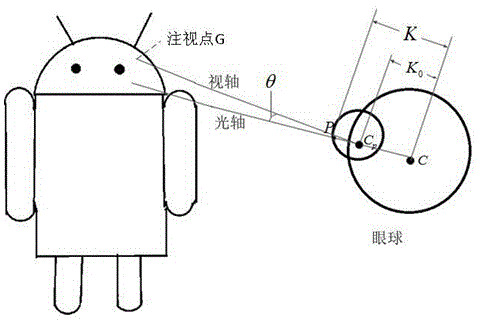
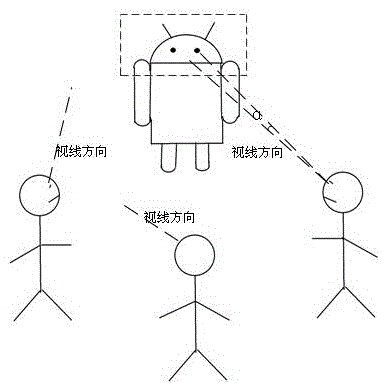
ActiveCN104951808ASimple hardwareEasy to implementAquisition of 3D object measurementsHough transformEstimation methods
The invention discloses a 3D (three-dimensional) sight direction estimation method for robot interaction object detection. The method comprises steps as follows: S1, head posture estimation; S2, mapping matrix calculation; S3, human eye detection; S4, pupil center detection; S5, sight direction calculation; S6, interaction object judgment. According to the 3D (three-dimensional) sight direction estimation method for robot interaction objection detection, an RGBD (red, green, blue and depth) sensor is used for head posture estimation and applied to a robot, and a system only adopts the RGBD sensor, does not require other sensors and has the characteristics of simple hardware and easiness in use. A training strong classifier is used for human eye detection and is simple to use and good in detection and tracking effect; a projecting integral method, a Hough transformation method and perspective correction are adopted when the pupil center is detected, and the obtained pupil center can be more accurate.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Color segmentation-based stereo 3D reconstruction system and process employing overlapping images of a scene captured from viewpoints forming either a line or a grid
InactiveUS20050286758A1Good segmentation resultPromote resultsImage analysisAquisition of 3D object measurementsParallaxViewpoints
A system and process for computing a 3D reconstruction of a scene from multiple images thereof, which is based on a color segmentation-based approach, is presented. First, each image is independently segmented. Second, an initial disparity space distribution (DSD) is computed for each segment, using the assumption that all pixels within a segment have the same disparity. Next, each segment's DSD is refined using neighboring segments and its projection into other images. The assumption that each segment has a single disparity is then relaxed during a disparity smoothing stage. The result is a disparity map for each image, which in turn can be used to compute a per pixel depth map if the reconstruction application calls for it.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
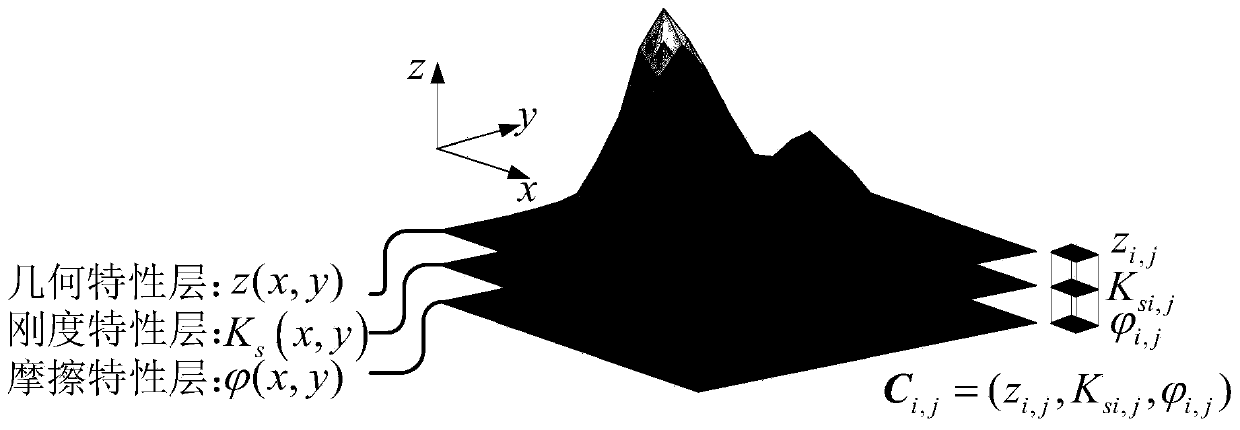
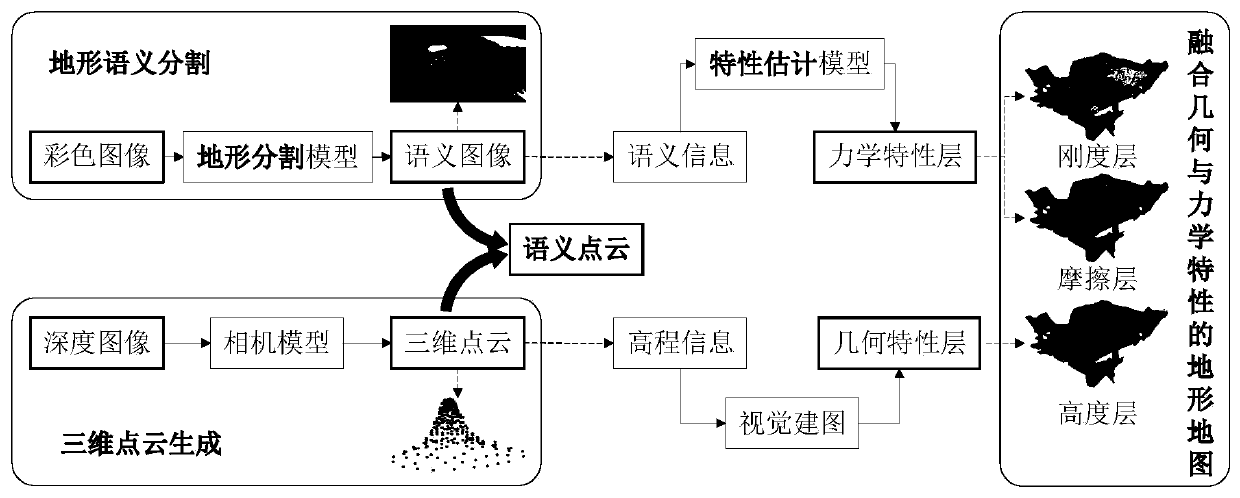
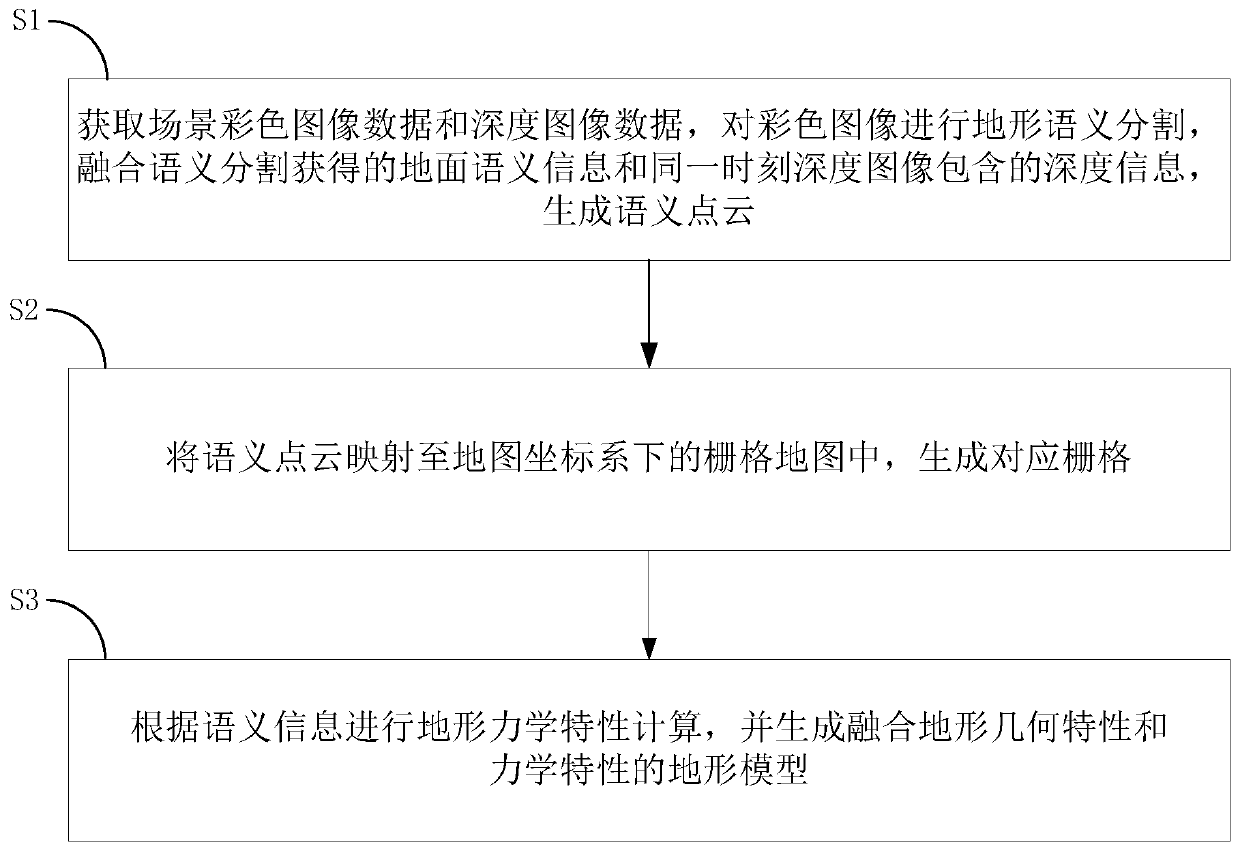
Terrain modeling method and system fusing geometric characteristics and mechanical characteristics
The invention provides a terrain modeling method and system integrating the geometric characteristics and the mechanical characteristics, and relates to the technical field of environment modeling. The method comprises the following steps of obtaining a color image and a depth image of a detection area, carrying out terrain semantic segmentation on the color image, and fusing a semantic segmentation result and the depth information contained in the depth image at the same moment to generate a semantic point cloud; mapping the semantic point cloud into a grid map under a map coordinate system to generate the corresponding grids, and updating the elevation values and the semantic information in the semantic point cloud to the corresponding grids; and performing ground mechanical property calculation according to the semantic information, updating a calculation result to the corresponding grid, and generating a terrain model. According to the method, the mechanical property parameters are added into topographic factors, and the topographic characterization is innovatively carried out from two dimensions of geometric properties and mechanical properties. The ground pressure-bearing characteristic and the shear characteristic of a non-contact area are deduced in advance in a visual perception mode, and the perception range is expanded.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
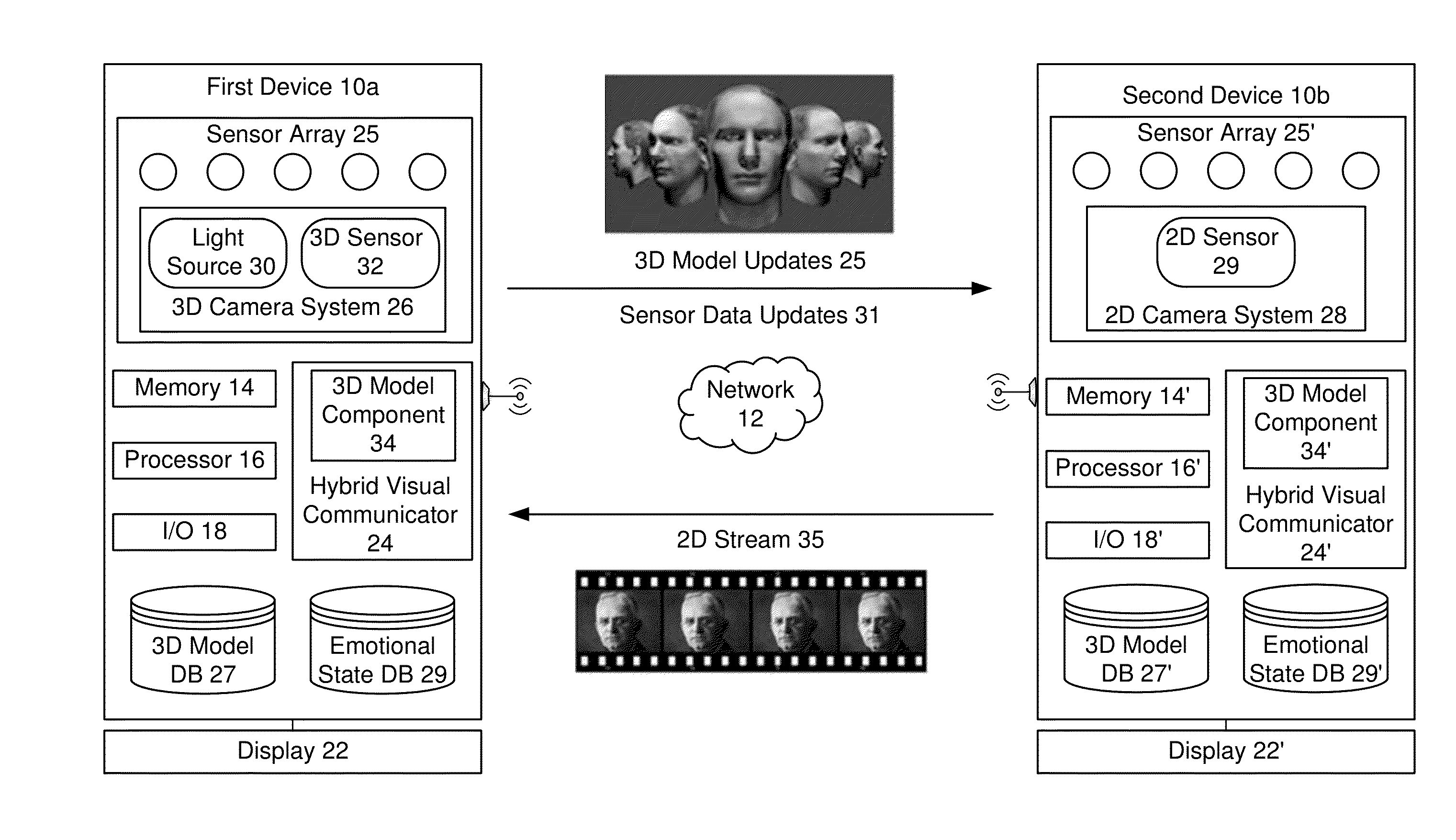
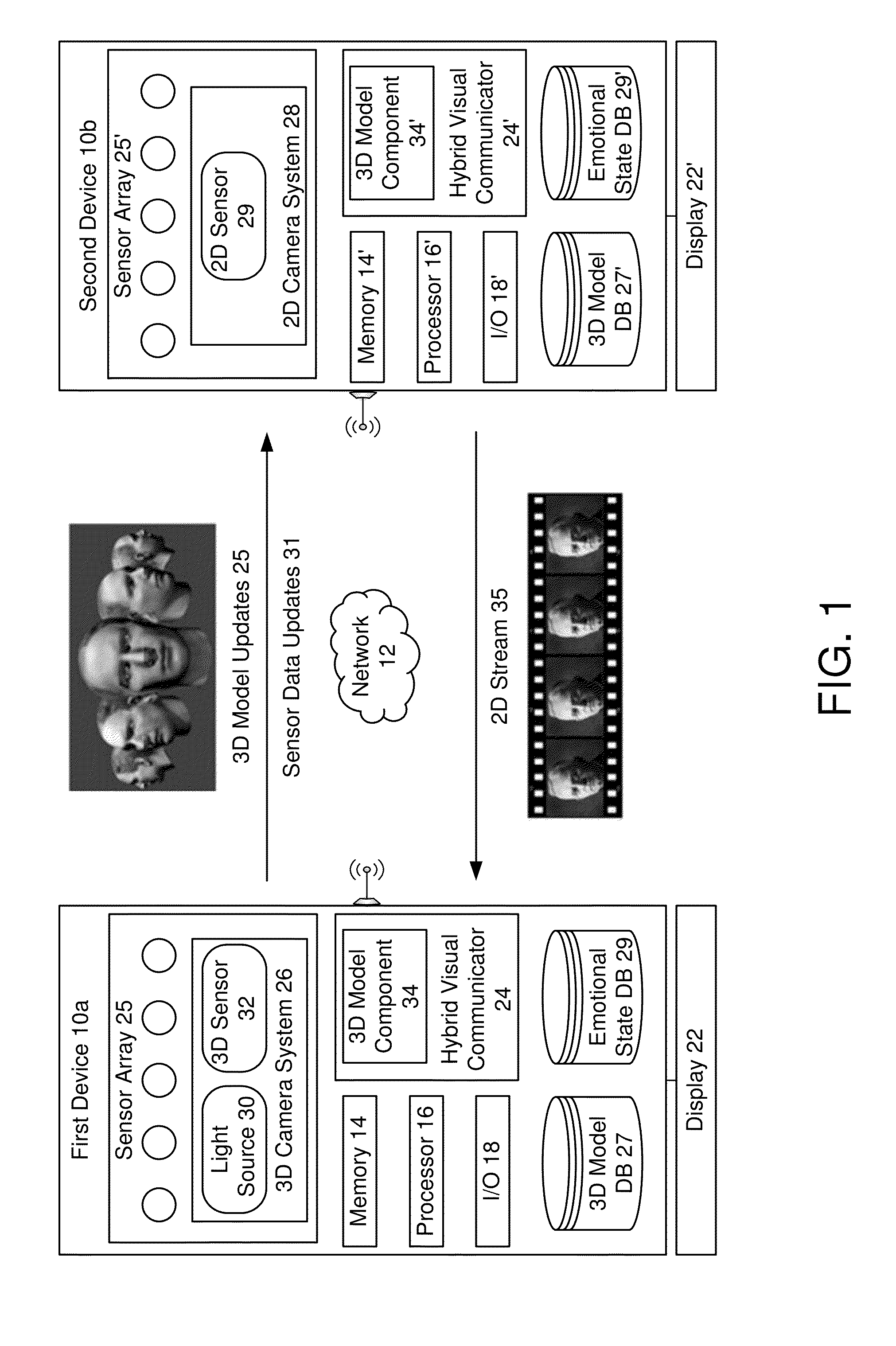
Hybrid visual communication
ActiveUS20150042743A1Lower latencyLess bandwidthDetails involving processing stepsDetails involving 3D image dataSensor arrayComputer graphics (images)
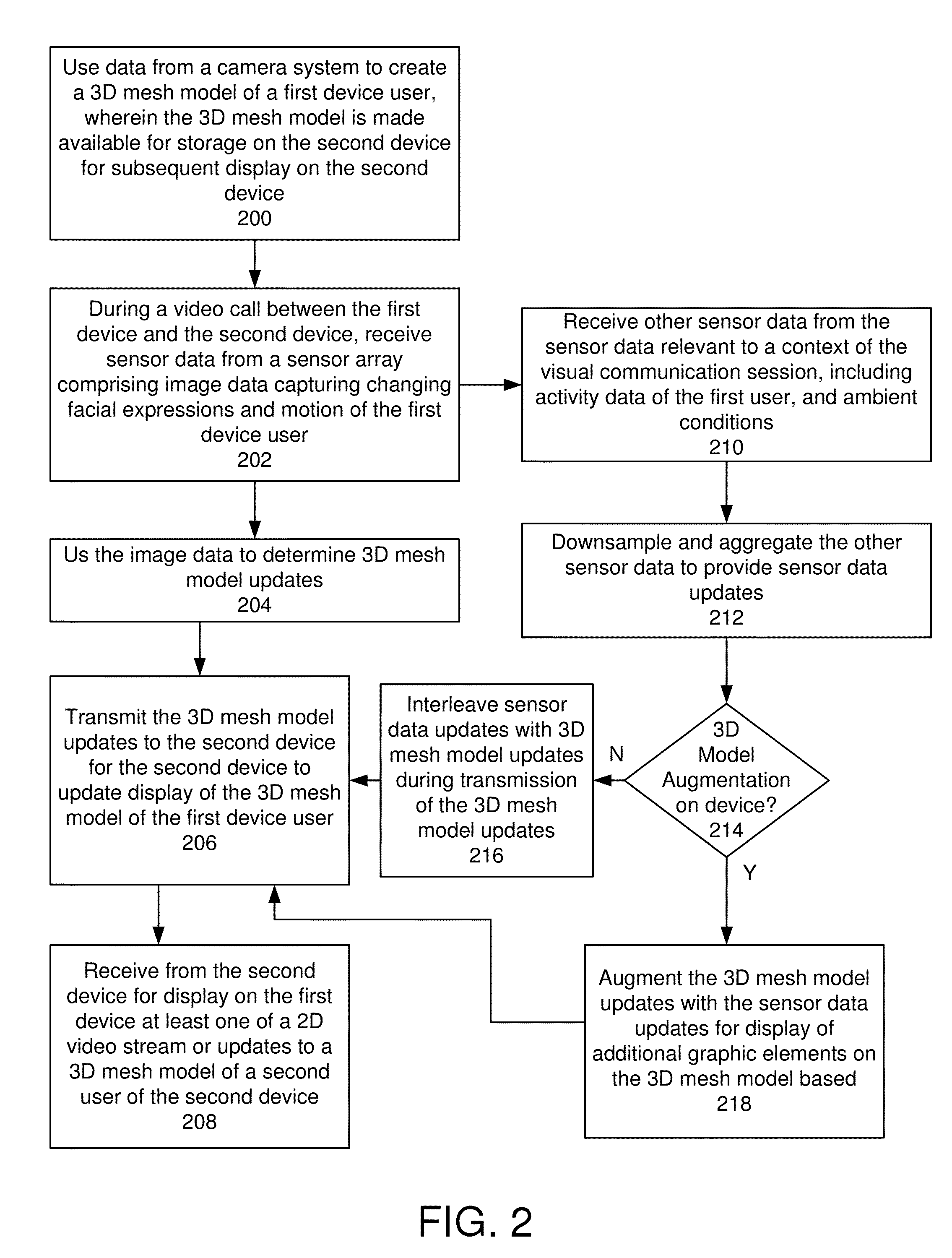
Exemplary embodiments for visual communication between a first device and a second device, comprising: using data from a camera system to create a 3D mesh model of a first device user, wherein the 3D mesh model is made available for storage on the second device for subsequent display on the second device; during the visual communication session between the first device and the second device, receiving sensor data from a sensor array, including image data capturing changing facial expressions and motion of the first device user; using the image data to determine 3D mesh model updates; transmitting the 3D mesh model updates to the second device for the second device to update display of the 3D mesh model of the first device user; and receiving from the second device for display on the first device at least one of a 2D video stream or updates to a 3D mesh model of a second device user.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com