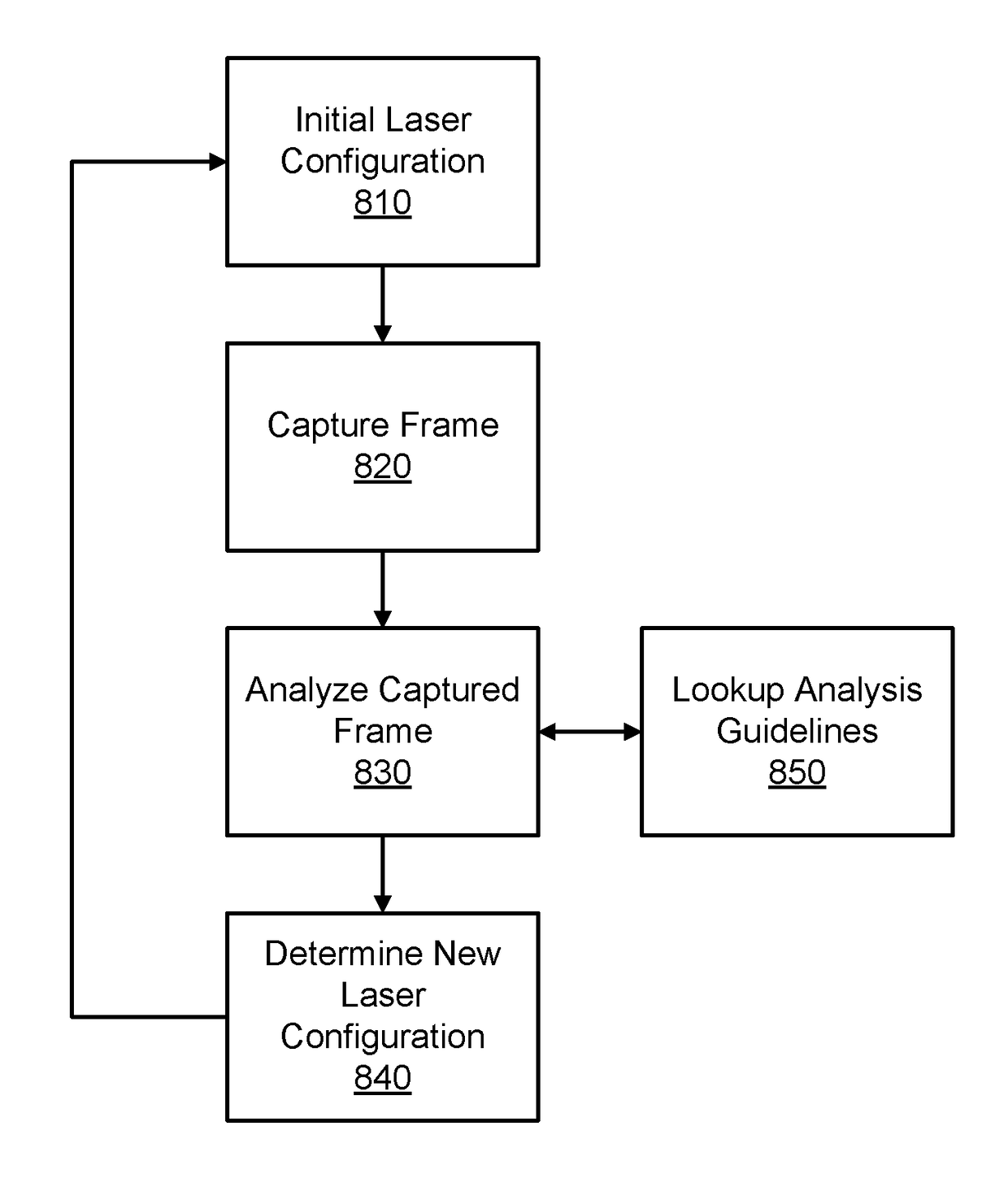
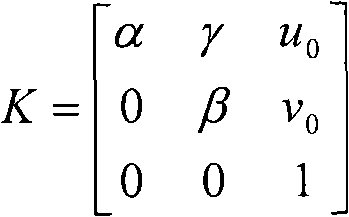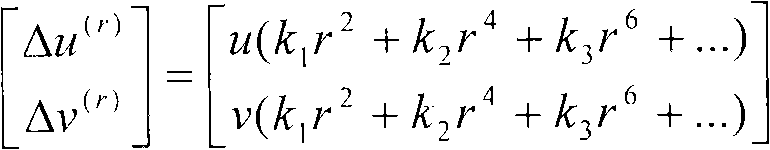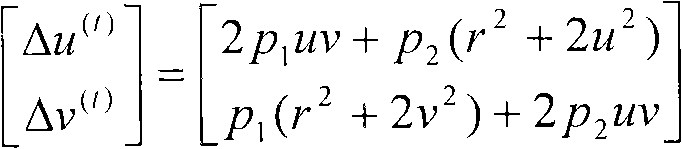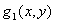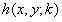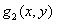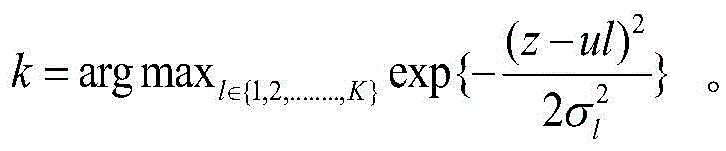Patents
Literature
106 results about "Depth mapping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method of generating surface defined by boundary of three-dimensional point cloud
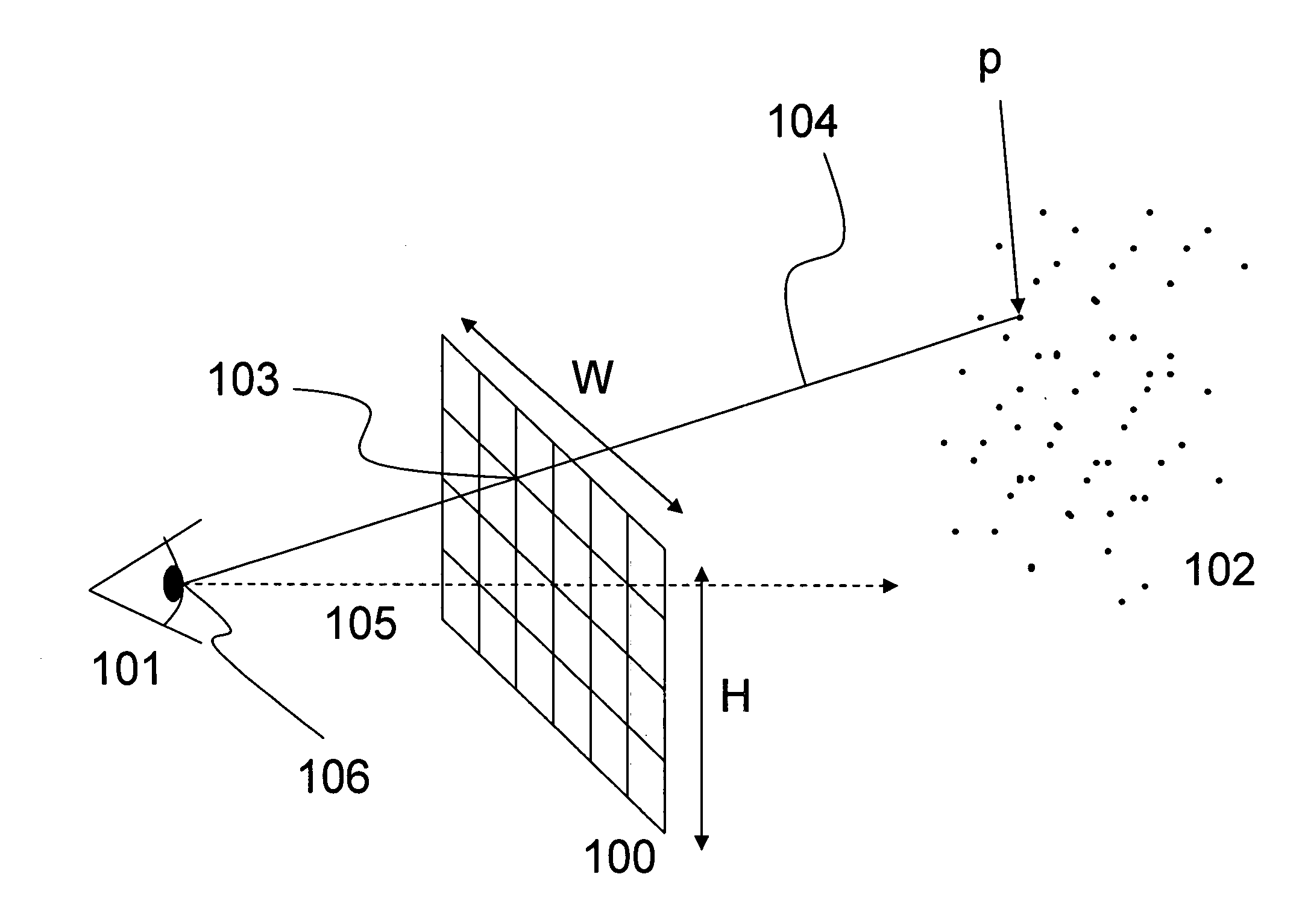
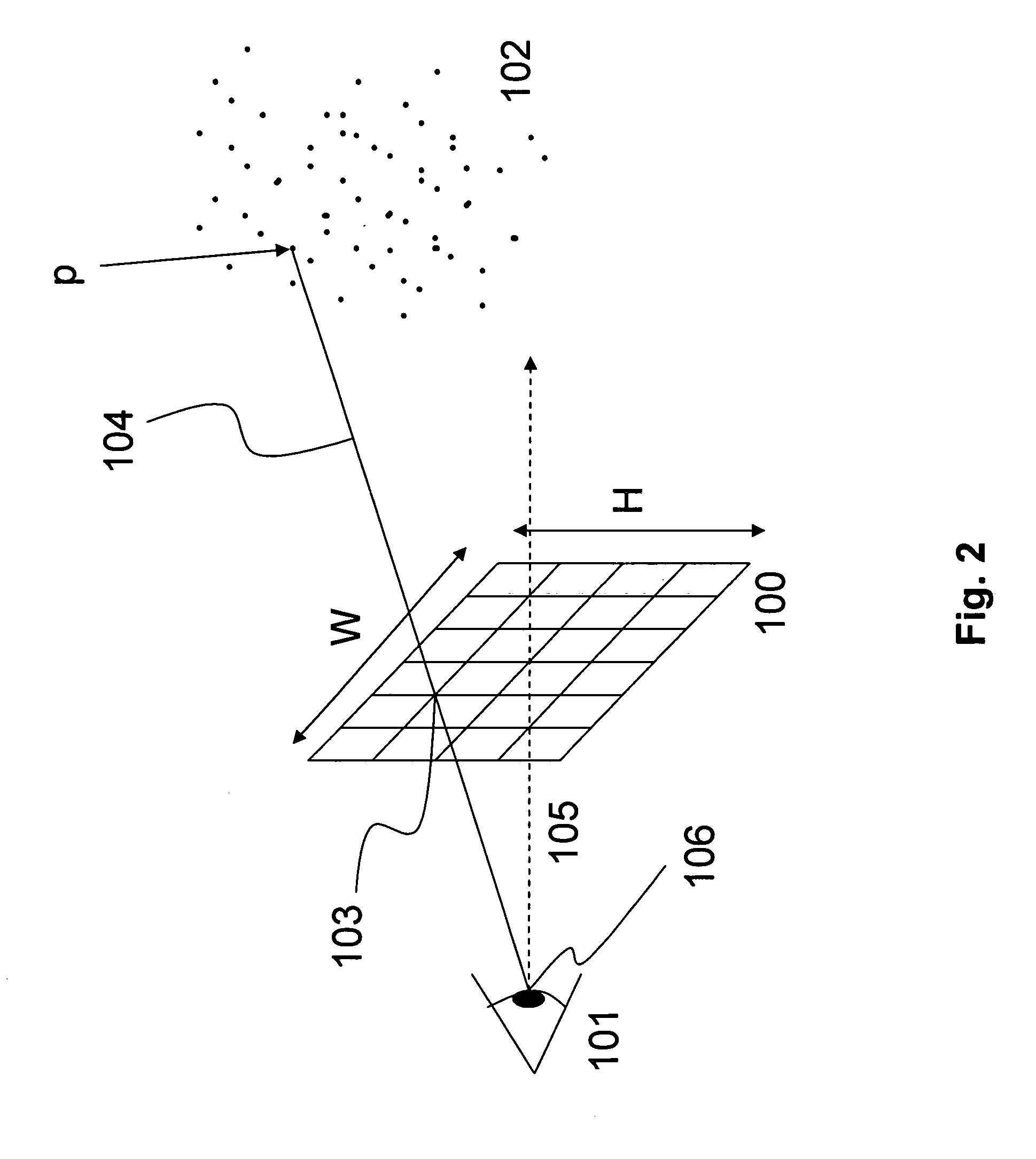
Disclosed is a method of generating a three-dimensional (3D) surface defined by a boundary of a 3D point cloud. The method comprises generating density and depth maps from the 3D point cloud, constructing a 2D mesh from the depth and density maps, transforming the 2D mesh into a 3D mesh, and rendering 3D polygons defined by the 3D mesh.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Non-Uniform Spatial Resource Allocation for Depth Mapping
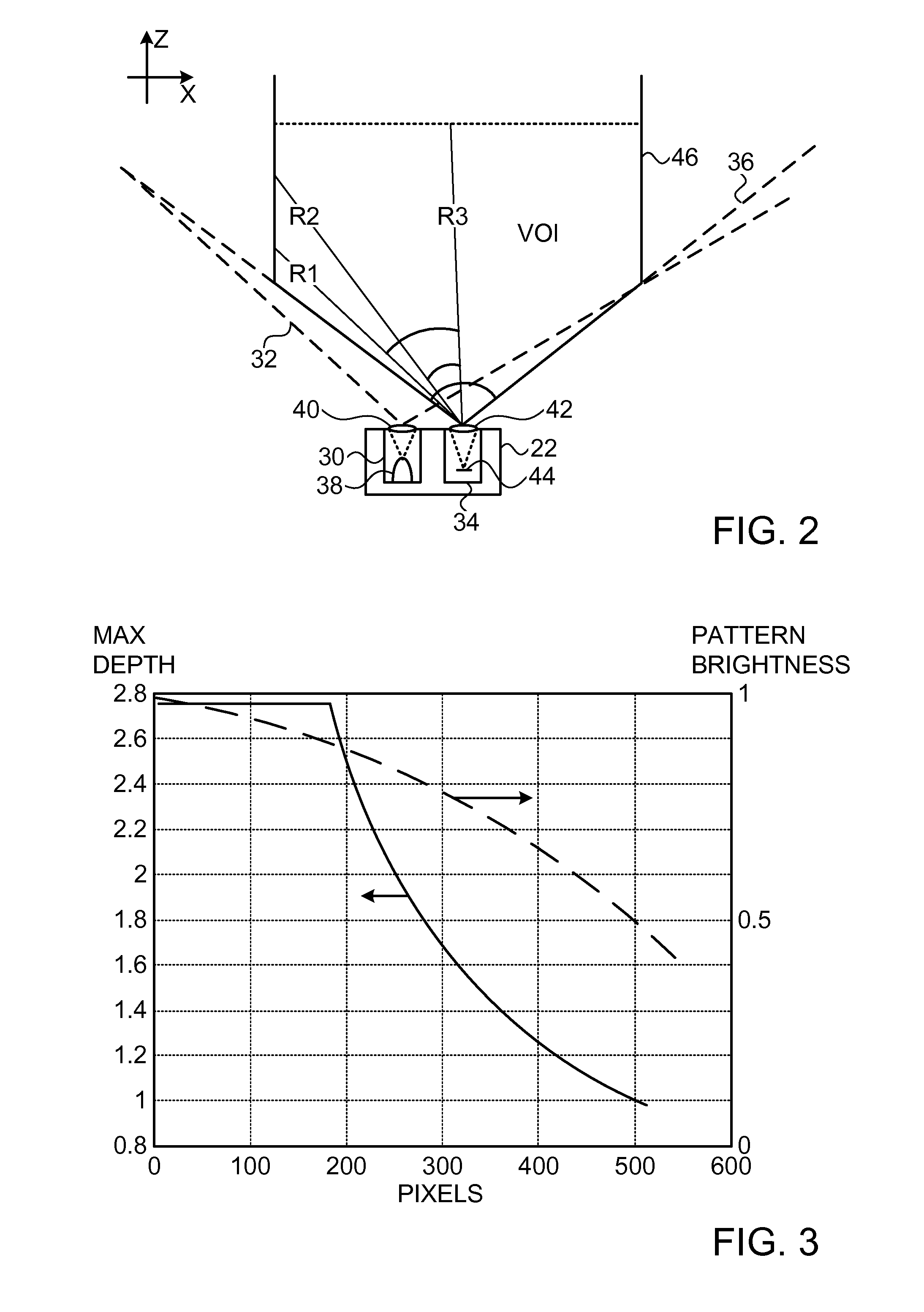
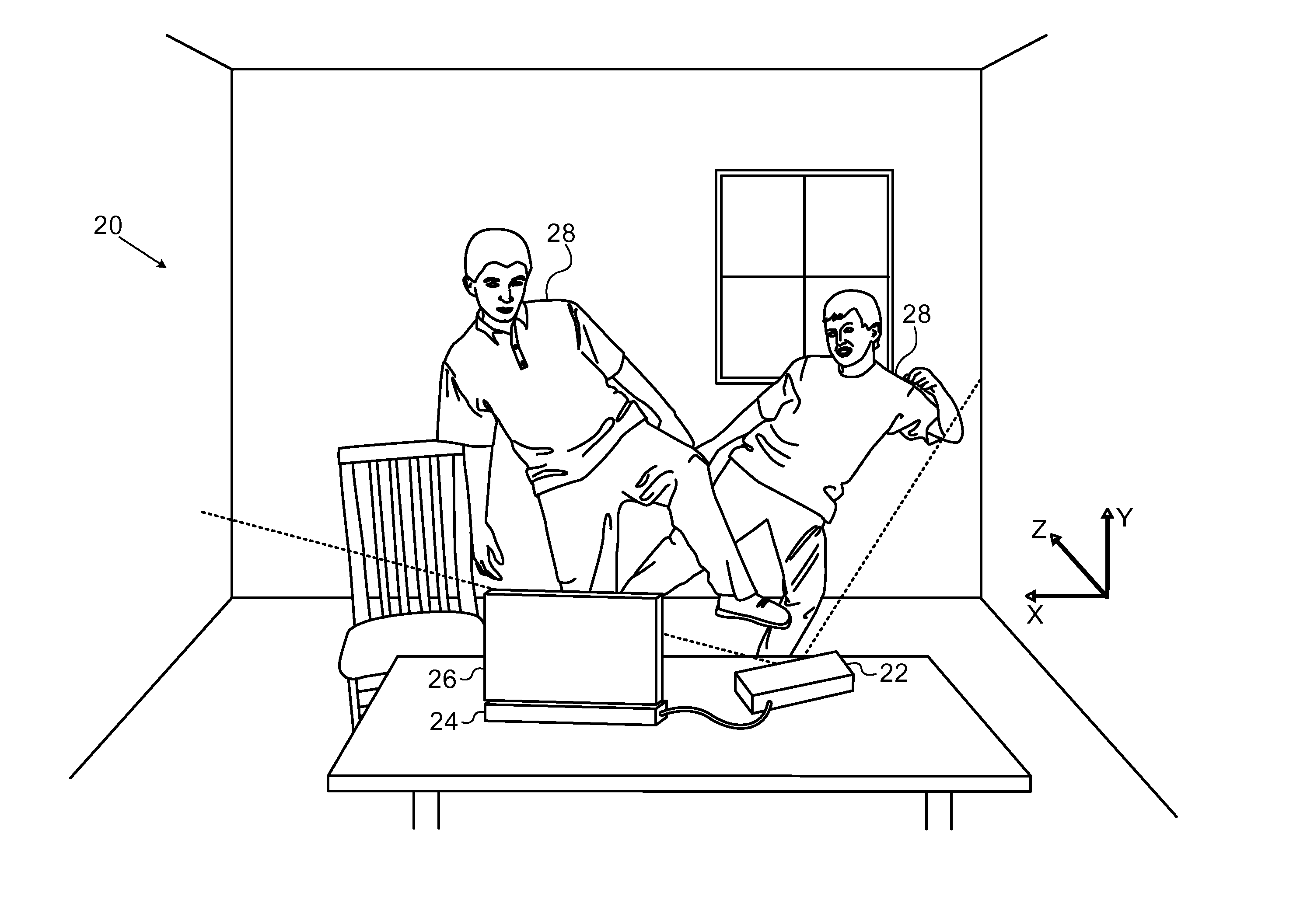
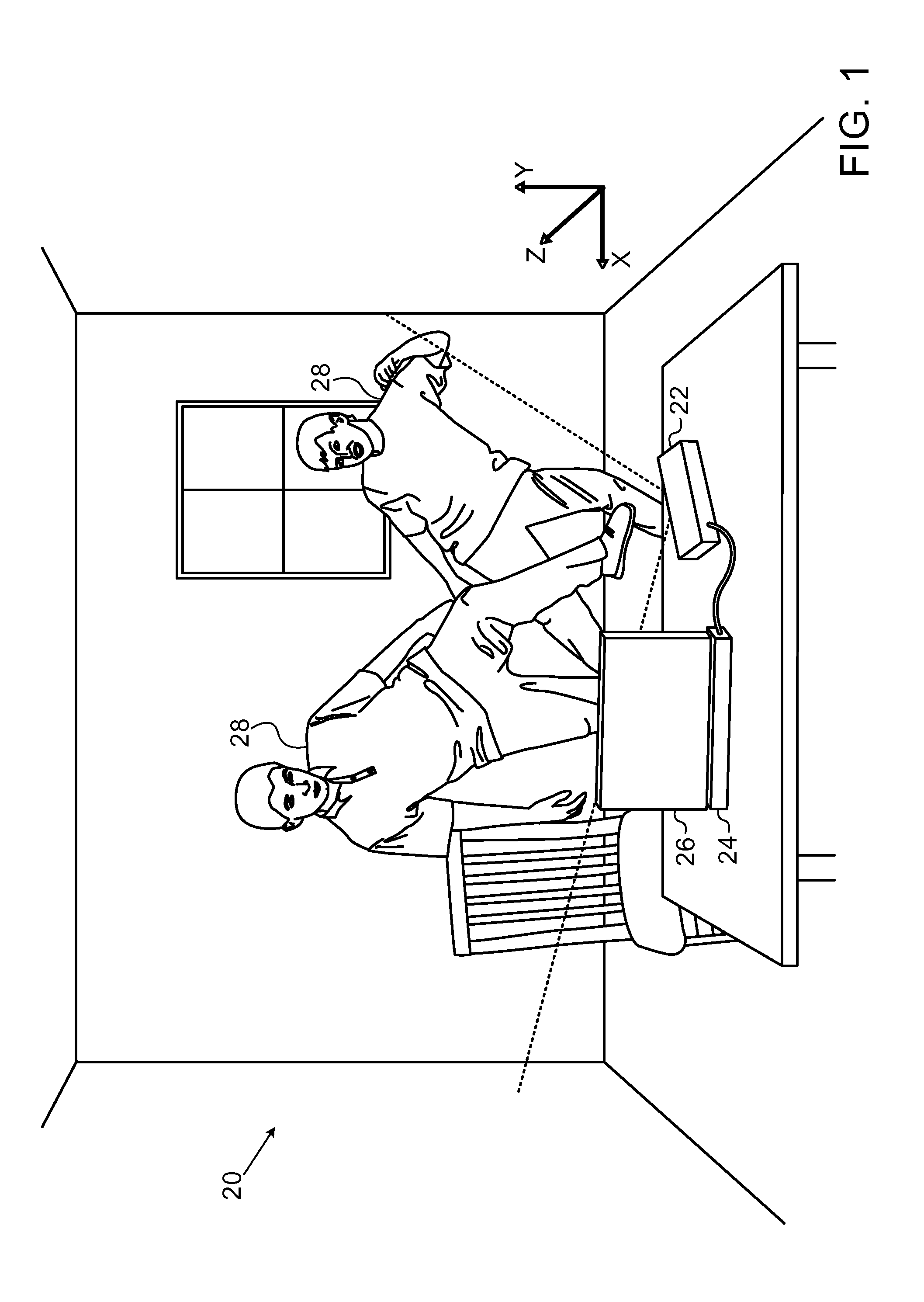
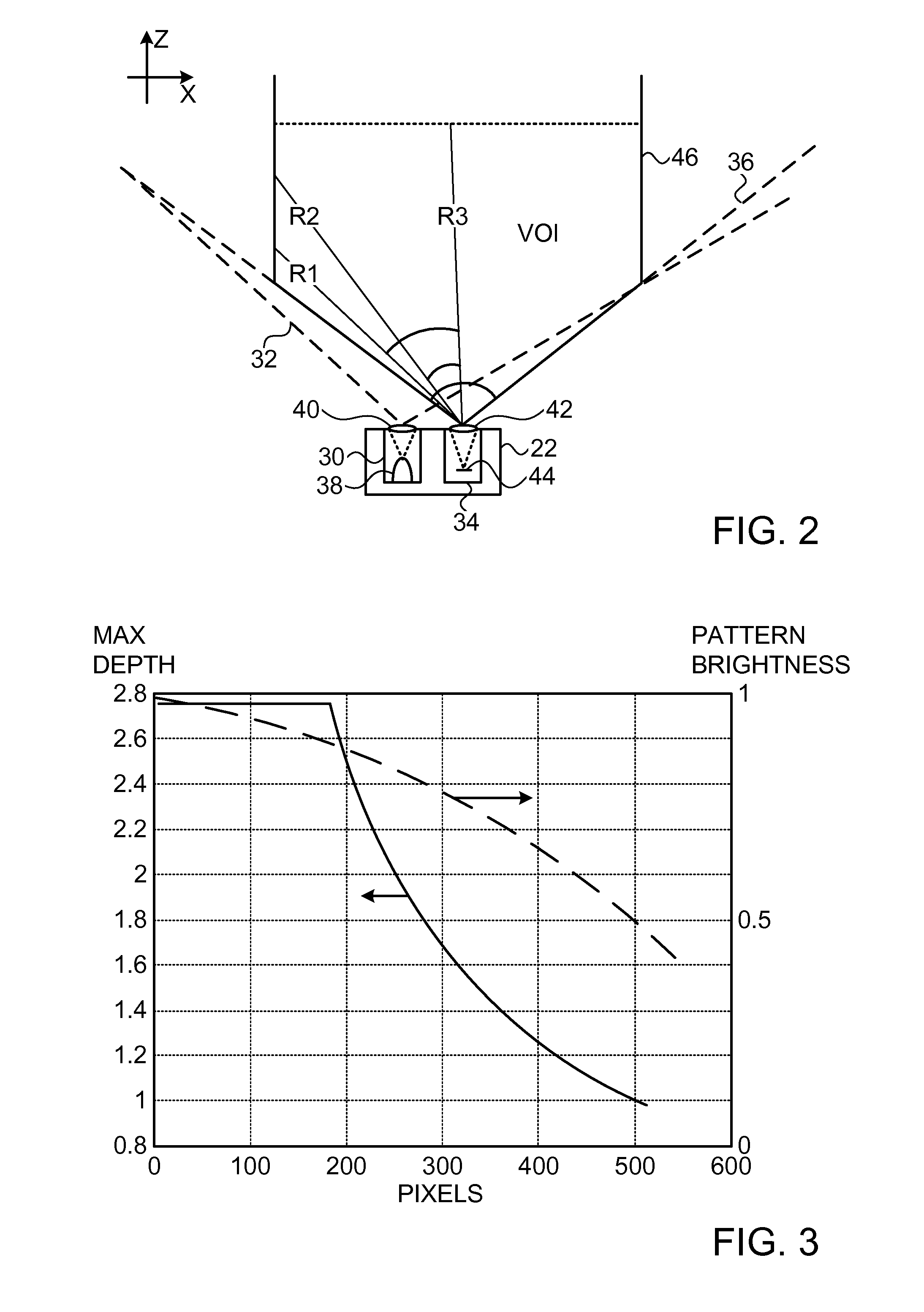
ActiveUS20110211044A1Limited resourceImprove system performanceImage enhancementImage analysisOptical radiationDepth mapping
A method for depth mapping includes providing depth mapping resources including an illumination module, which is configured to project patterned optical radiation into a volume of interest containing the object, and an image capture module, which is configured to capture an image of the pattern reflected from the object. A depth map of the object is generated using the resources while applying at least one of the resources non-uniformly over the volume of interest.
Owner:APPLE INC
Modular high-precision navigation system
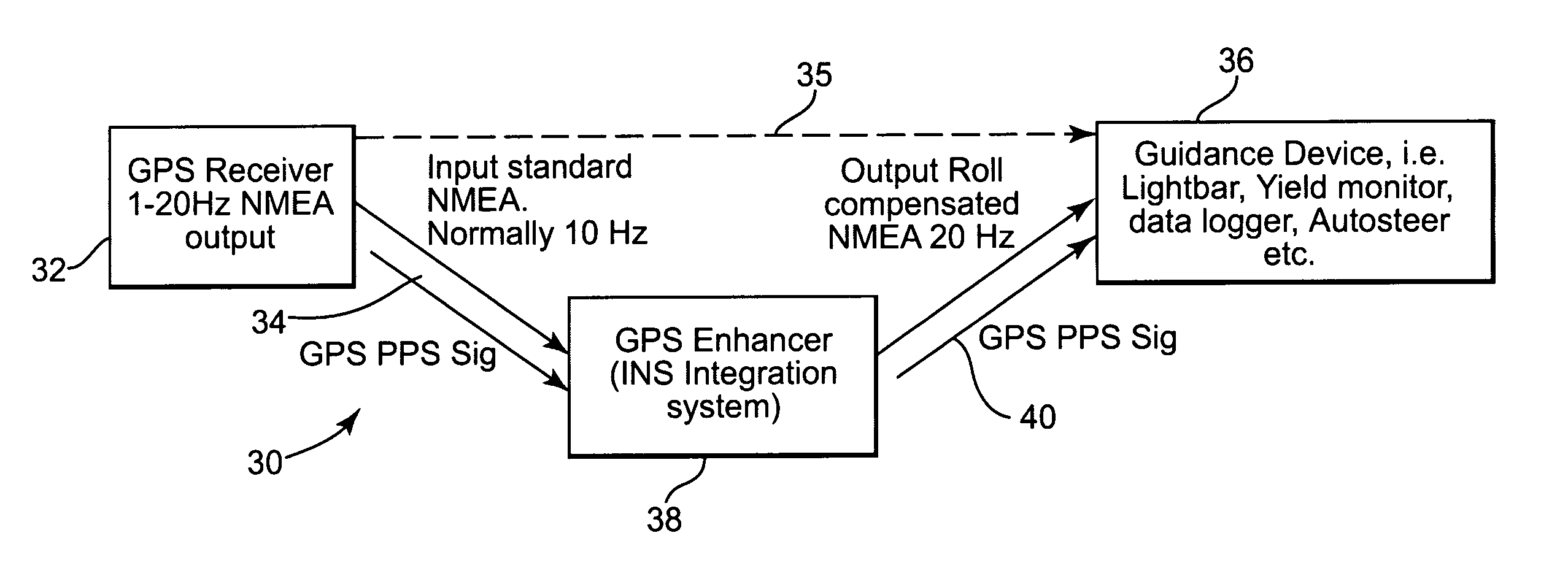
InactiveUS20070032950A1High frequencyQuality improvementPosition fixationNavigation instrumentsAviationData stream
A modular device, system and associated method, used to enhance the quality and output speed of any generic GPS engine is provided. The modular device comprises an inertial subsystem based on a solid state gyroscope having a plurality of accelerometers and a plurality of angular rate sensors designed to measure linear acceleration and rotation rates around a plurality of axes. The modular inertial device may be placed in the data stream between a standard GPS receiver and a guidance device to enhance the accuracy and increase the frequency of positional solutions. Thus, the modular inertial device accepts standard GPS NMEA input messages from the source GPS receiver, corrects and enhances the GPS data using computed internal roll and pitch information, and produces an improved, more accurate, NMEA format GPS output at preferably 2 times the positional solution rate using GPS alone. The positional solution frequency using the present invention may increase to as much as 5 times that obtained using GPS alone. Moreover, the modular inertial device may assist when the GPS signal is lost for various reasons. If used without GPS, the modular inertial device may be used to define, and adjust, a vehicle's orientation on a relative basis. The modular inertial device and architecturally partitioned system incorporated into an existing GPS system may be applied to navigation generally, including high-precision land-based vehicle positioning, aerial photography, crop dusting, and sonar depth mapping to name a few applications.
Owner:RAVEN INDUSTRIES INC
Optimal depth mapping
A method and apparatus for providing optimal correction to depth mapping between captured and displayed stereoscopic content. The solution is derived in a continuous form that can be implemented through CGI scaling techniques compatible with image rendering techniques. Similar correction can be implemented with variable depth-dependent camera separation and disparity re-mapping. The latter is applicable to correcting existing stereoscopic content.
Owner:REAID INC
Three-dimensional detection system for surface of large thin-shell object and detection method thereof
ActiveCN101995231ASimple structureFlexible structureUsing optical meansThin shellsComputer Aided Design
The invention is applied to the technical field of three-dimensional sensing, and provides a three-dimensional detection system for the surface of a large thin-shell object and a detection method thereof. The detection method comprises that: three groups of sensors project fringes to the surface of an object to be detected in the upper, middle and lower directions of the object to be detected, acquire a deformation fringe graph, acquires phase distribution information, and acquires three-dimensional depth data of each viewing field by combining phase and depth mapping principle; multi-sensor calibration information is matched with the depth data acquired by the three sensors, and multi-angle data is matched to the same coordinate system; and dimensions are acquired and models are compared, namely the measured three-dimensional data is matched with a computer-aided design (CAD) model, distances from all measuring point to the CAD model are calculated, error distribution pseudo-color pictures of the inner side face, outer side face, inner bottom surface and outer bottom surface of the object, and the related dimension of the object, such as the length, width, height, wall thickness and the like are calculated by methods such as ray tracing and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN ESUN DISPLAY
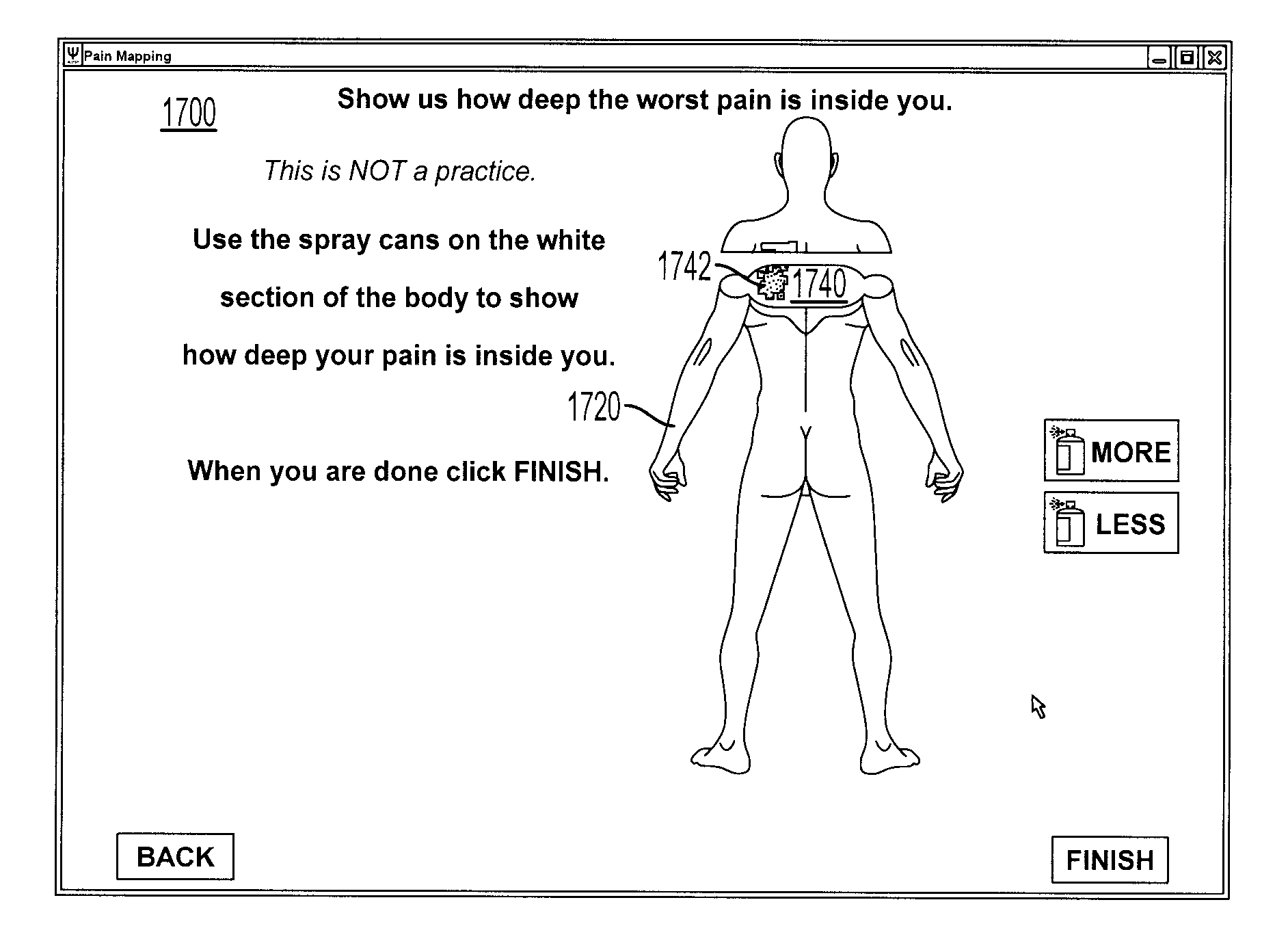
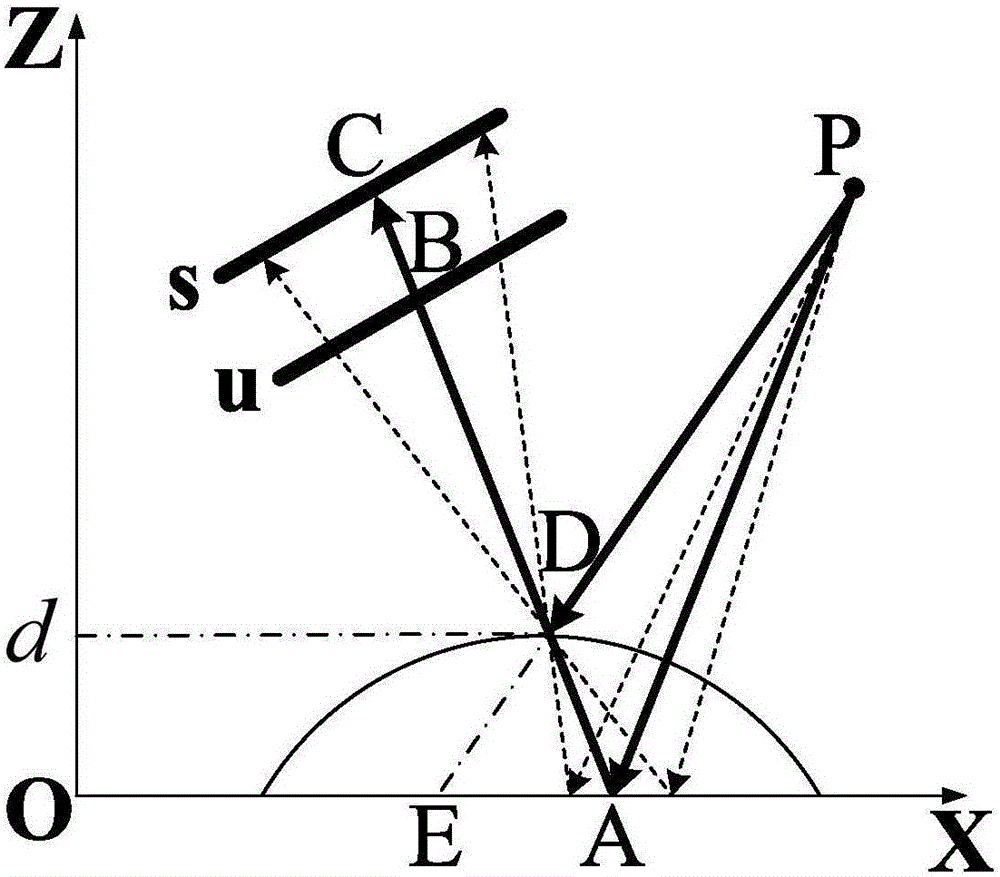
System and method for mapping pain depth
Owner:PSYCHOLOGICAL APPL
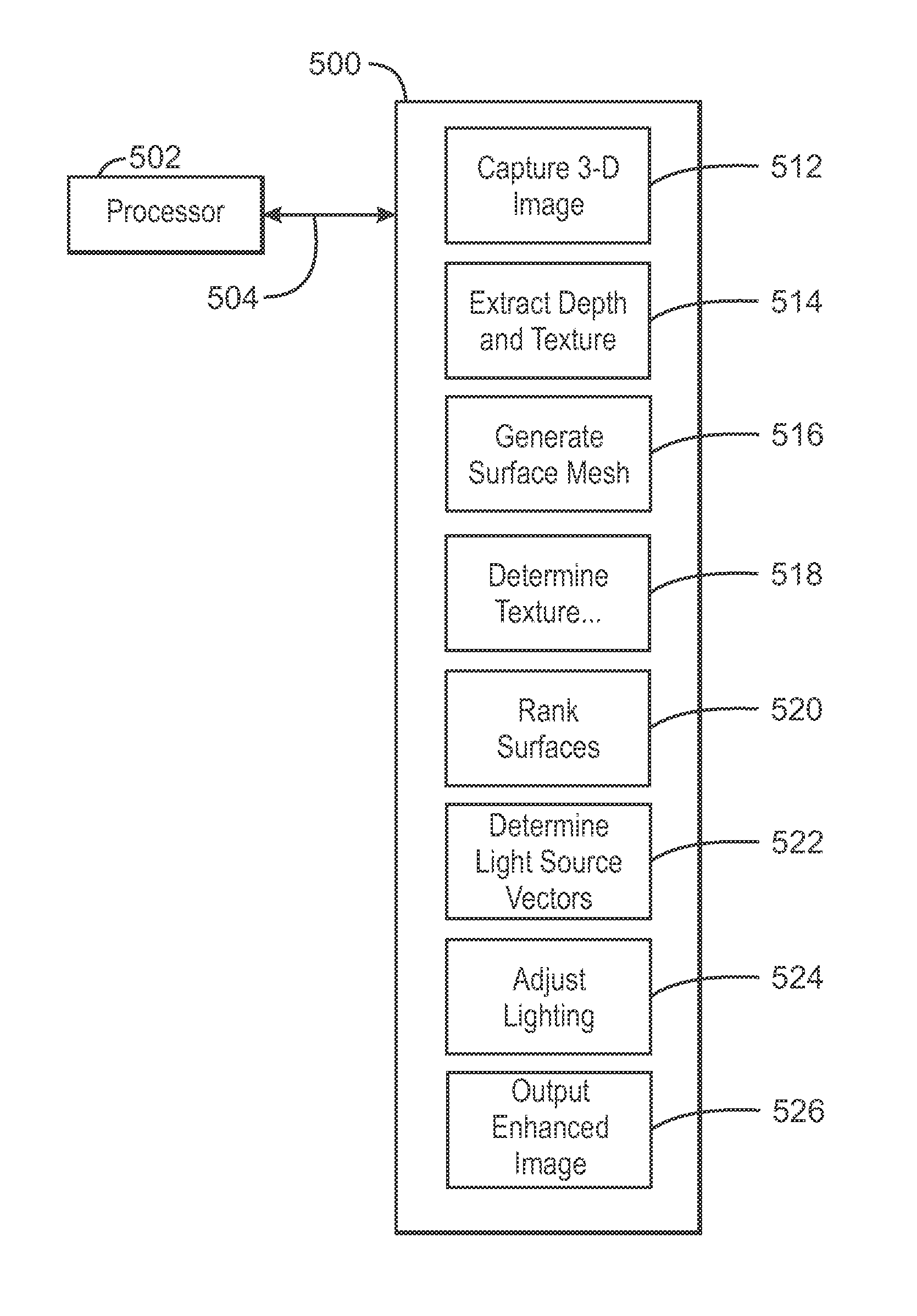
Apparatus for enhancement of 3-d images using depth mapping and light source synthesis
An apparatus for enhancing a 3-D image illuminated by a light source and having associated depth and texture information includes generating from the depth information a surface mesh having surface mesh sections. Texture sections corresponding to the surface mesh sections are determined from the texture information. The texture sections are ranked based upon their color intensity, and the characteristics of one or more light sources are adjusted to alter the color intensity of the ranked texture sections to thereby produce an enhanced image.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Stereoscopic depth mapping
Provided is a method and apparatus for linear depth mapping. Linear depth mapping includes using algorithms to correct the distorted depth mapping of stereoscopic capture and display systems.
Owner:REAID INC
Point reposition depth mapping
A method and apparatus for providing optimal correction to depth mapping between captured and displayed stereoscopic content. The solution is derived in a continuous form that can be implemented through CGI scaling techniques compatible with image rendering techniques. Similar correction can be implemented with variable depth-dependent camera separation and disparity re-mapping. The latter is applicable to correcting existing stereoscopic content.
Owner:REAID INC
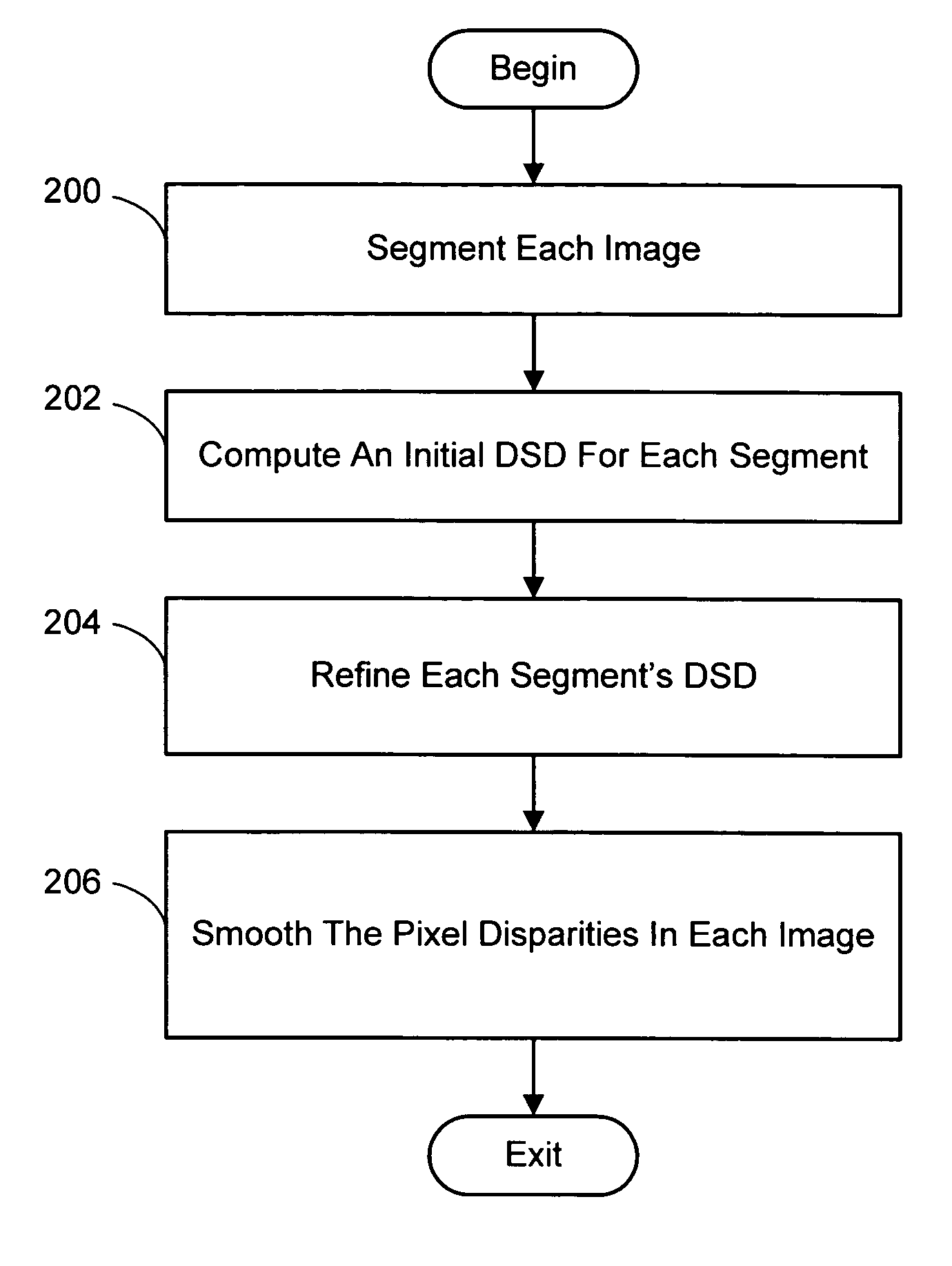
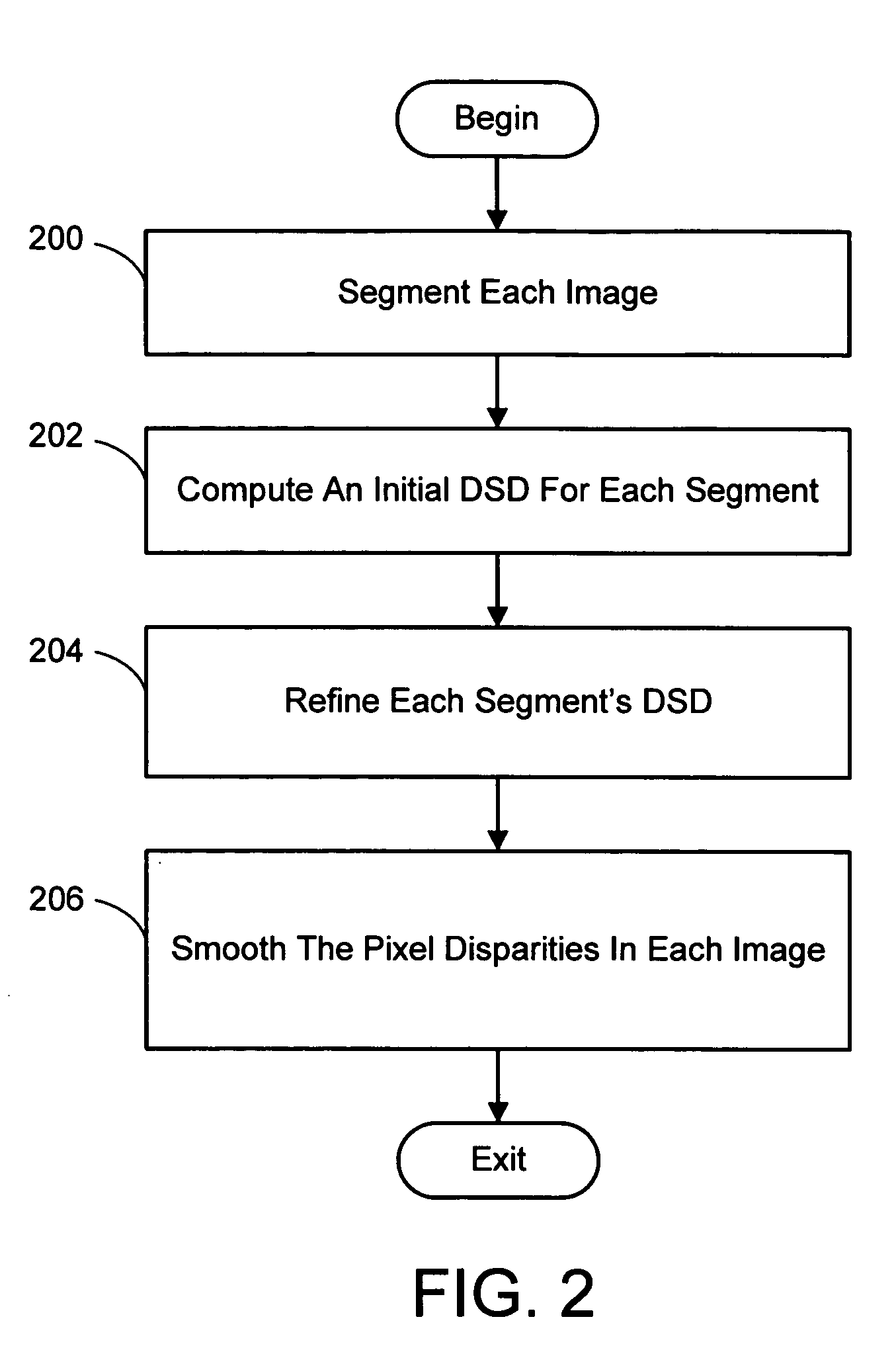
Color segmentation-based stereo 3D reconstruction system and process
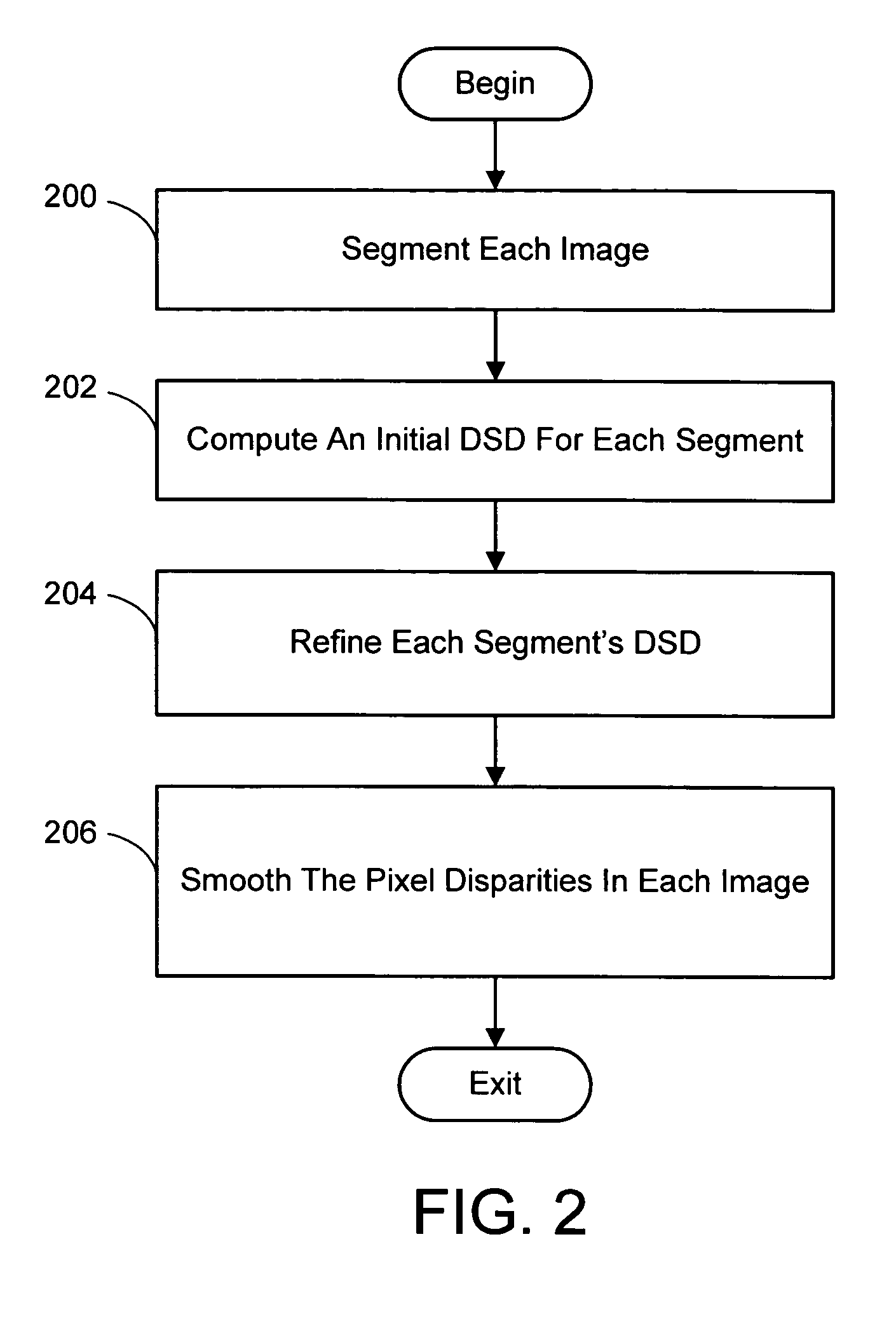
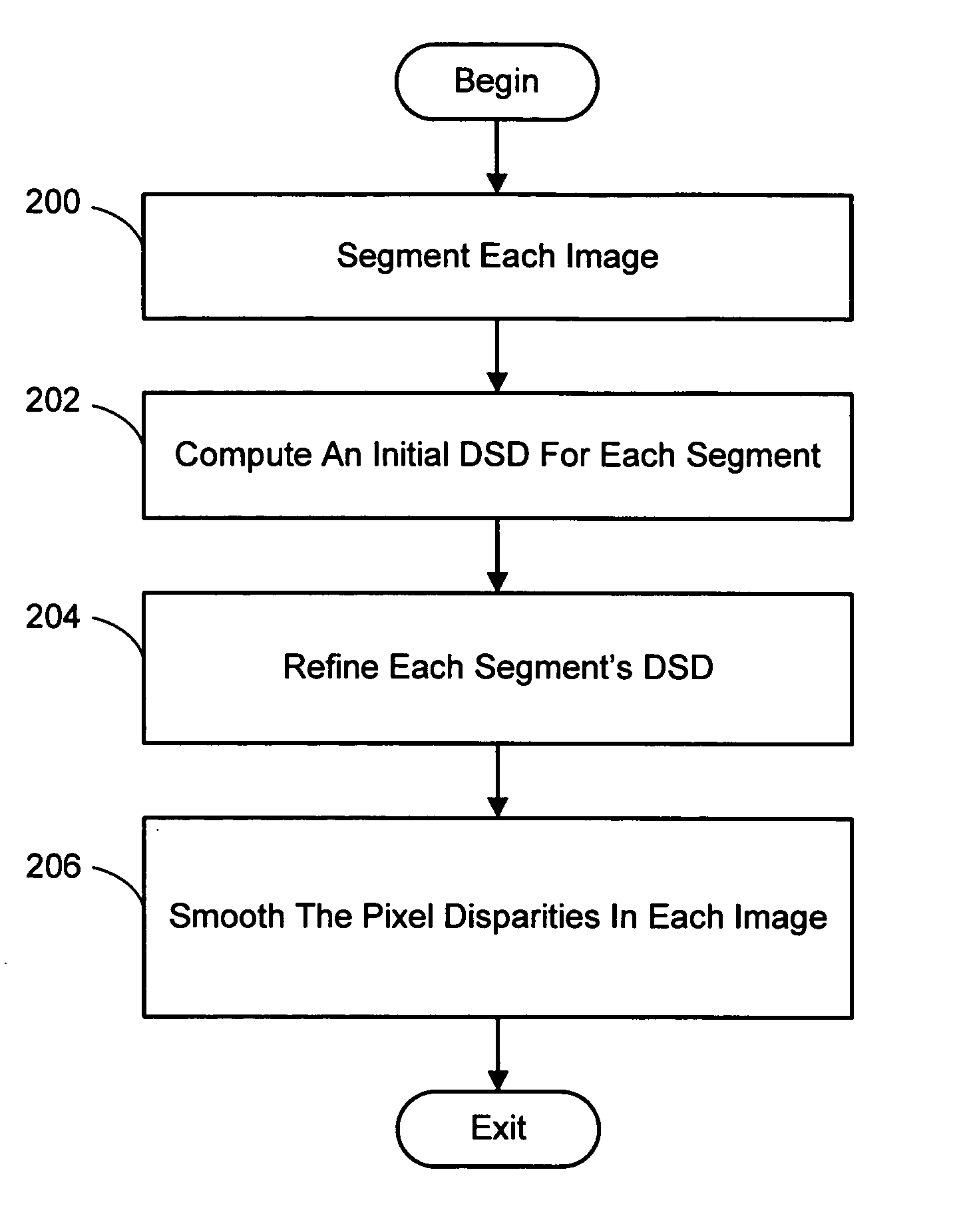
InactiveUS20050286757A1Promote resultsGood segmentation resultImage analysisAquisition of 3D object measurementsParallaxDepth mapping
A system and process for computing a 3D reconstruction of a scene from multiple images thereof, which is based on a color segmentation-based approach, is presented. First, each image is independently segmented. Second, an initial disparity space distribution (DSD) is computed for each segment, using the assumption that all pixels within a segment have the same disparity. Next, each segment's DSD is refined using neighboring segments and its projection into other images. The assumption that each segment has a single disparity is then relaxed during a disparity smoothing stage. The result is a disparity map for each image, which in turn can be used to compute a per pixel depth map if the reconstruction application calls for it.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Color segmentation-based stereo 3D reconstruction system and process employing overlapping images of a scene captured from viewpoints forming either a line or a grid
InactiveUS20050286758A1Good segmentation resultPromote resultsImage analysisAquisition of 3D object measurementsParallaxViewpoints
A system and process for computing a 3D reconstruction of a scene from multiple images thereof, which is based on a color segmentation-based approach, is presented. First, each image is independently segmented. Second, an initial disparity space distribution (DSD) is computed for each segment, using the assumption that all pixels within a segment have the same disparity. Next, each segment's DSD is refined using neighboring segments and its projection into other images. The assumption that each segment has a single disparity is then relaxed during a disparity smoothing stage. The result is a disparity map for each image, which in turn can be used to compute a per pixel depth map if the reconstruction application calls for it.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
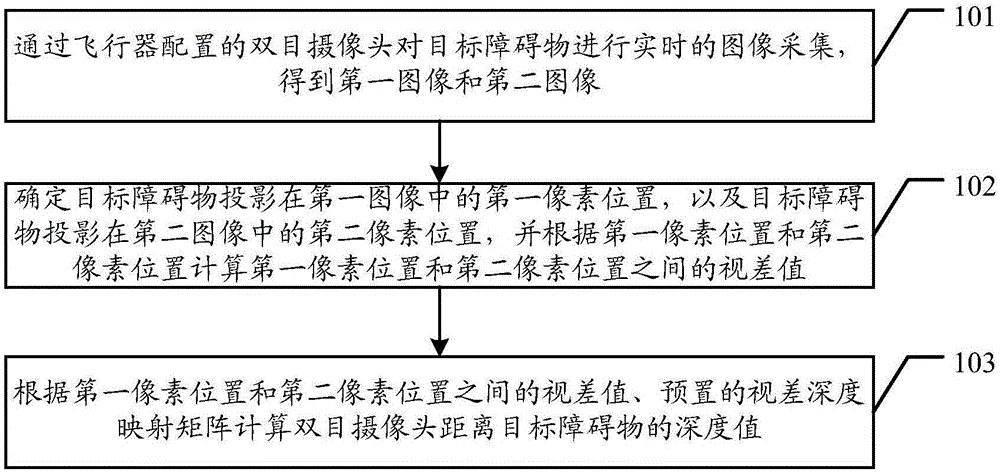
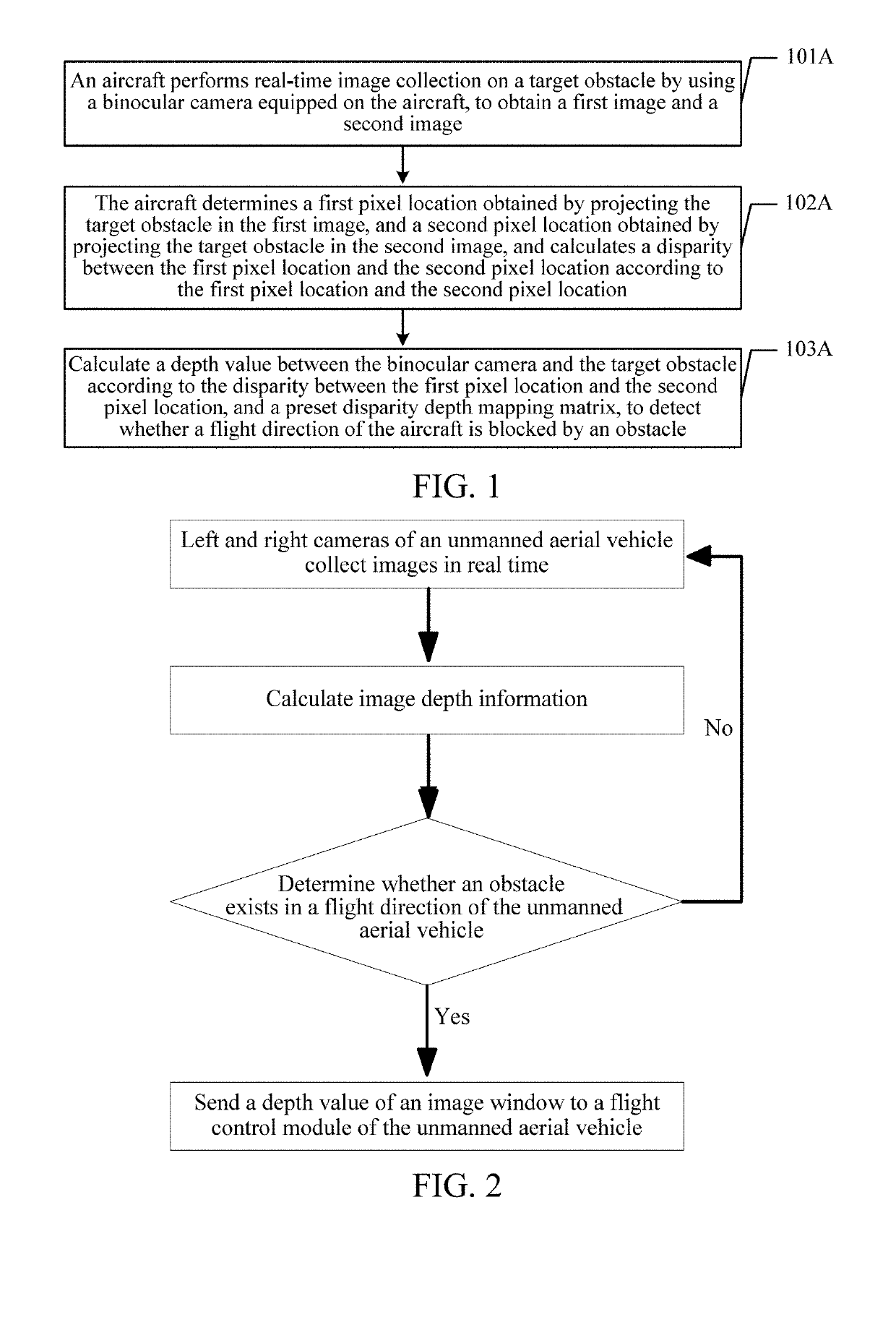
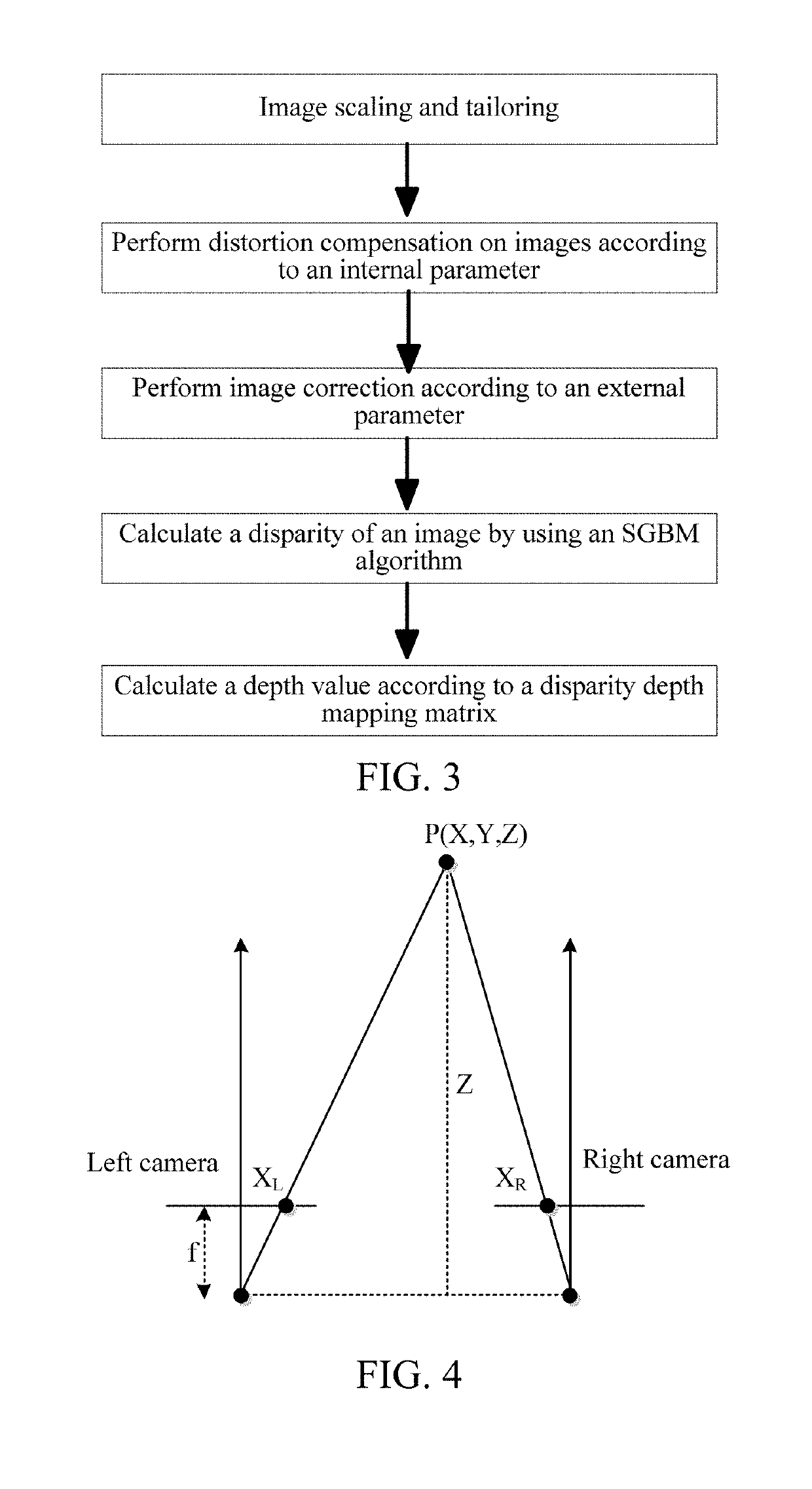
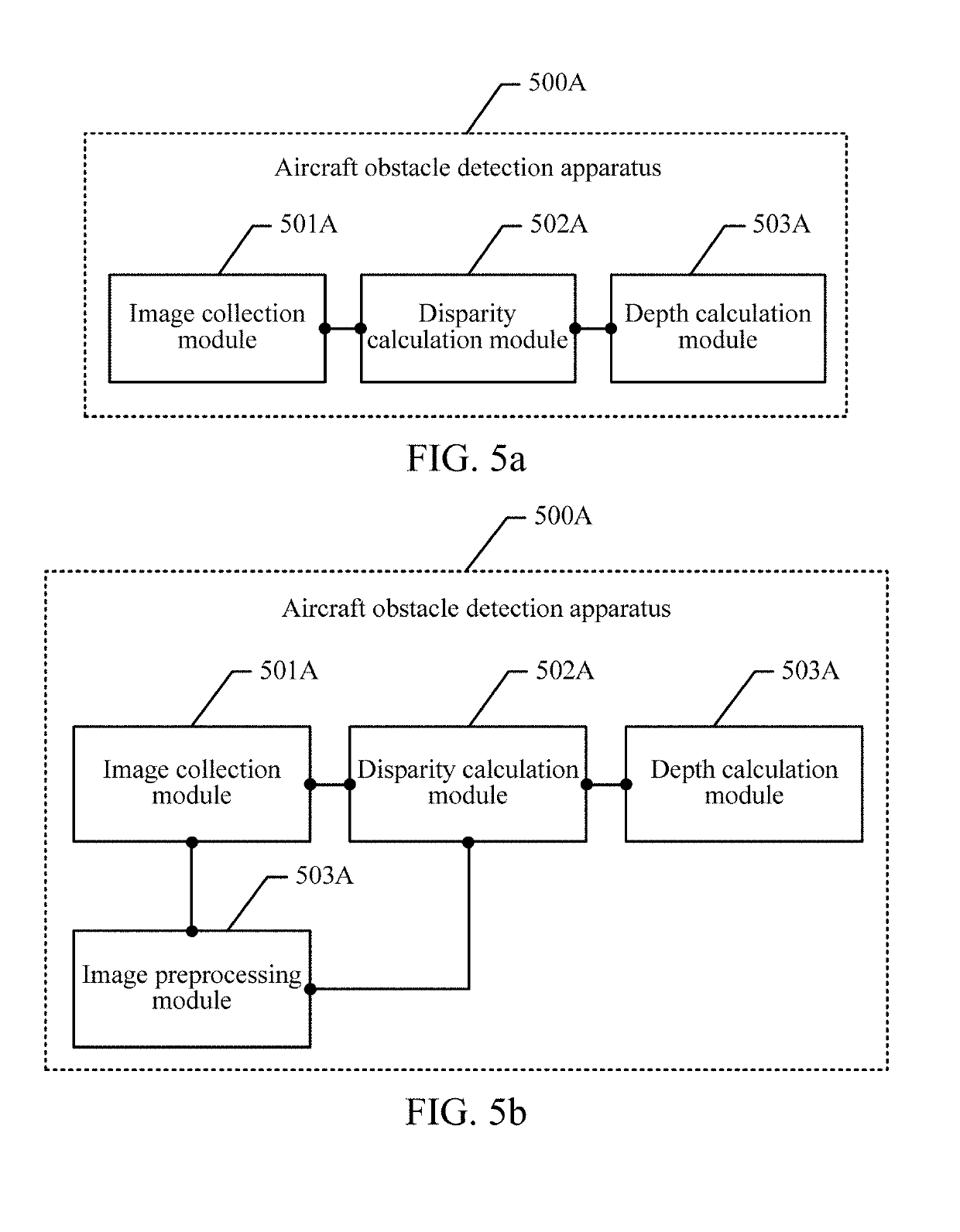
Obstacle detection method of aircraft and device
ActiveCN106529495AReduce Obstacle Detection ErrorsImprove detection accuracyScene recognitionBinocularsDepth mapping
The invention discloses an obstacle detection method of an aircraft and a device. The method and the device are used for reducing obstacle detection errors of the aircraft and improving obstacle detection precision of the aircraft. The embodiment of the invention provides an obstacle detection method of an aircraft. The detection method comprises steps of carrying out real-time image acquisition on a target obstacle through a binocular camera configured to the aircraft so as to obtain a first image and a second image, wherein the first image is obtained through shooting of a left eye in the binocular camera and the second image is obtained through shooting of a right eye in the binocular camera; determining a first pixel position, in the first image, of the projection of the target obstacle, and a second pixel position, in the second image, of the projection of the target obstacle, and calculating a parallax error value between the first pixel position and the second pixel position according to the first pixel position and the second pixel position; and according to the parallax error value between the first pixel position and the second pixel position, and a preset parallax error depth mapping matrix, calculating a depth value between the binocular camera and the target obstacle.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
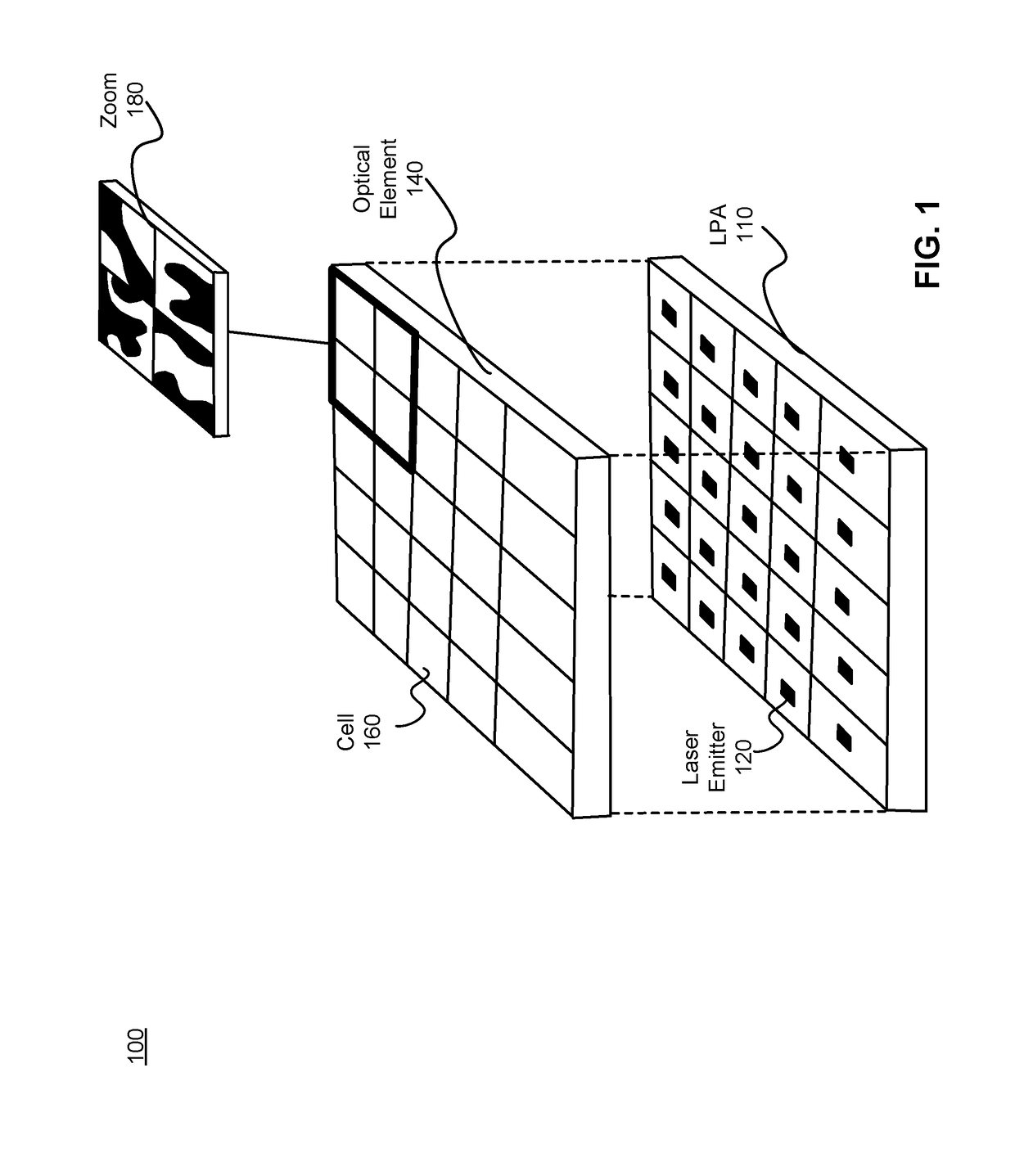
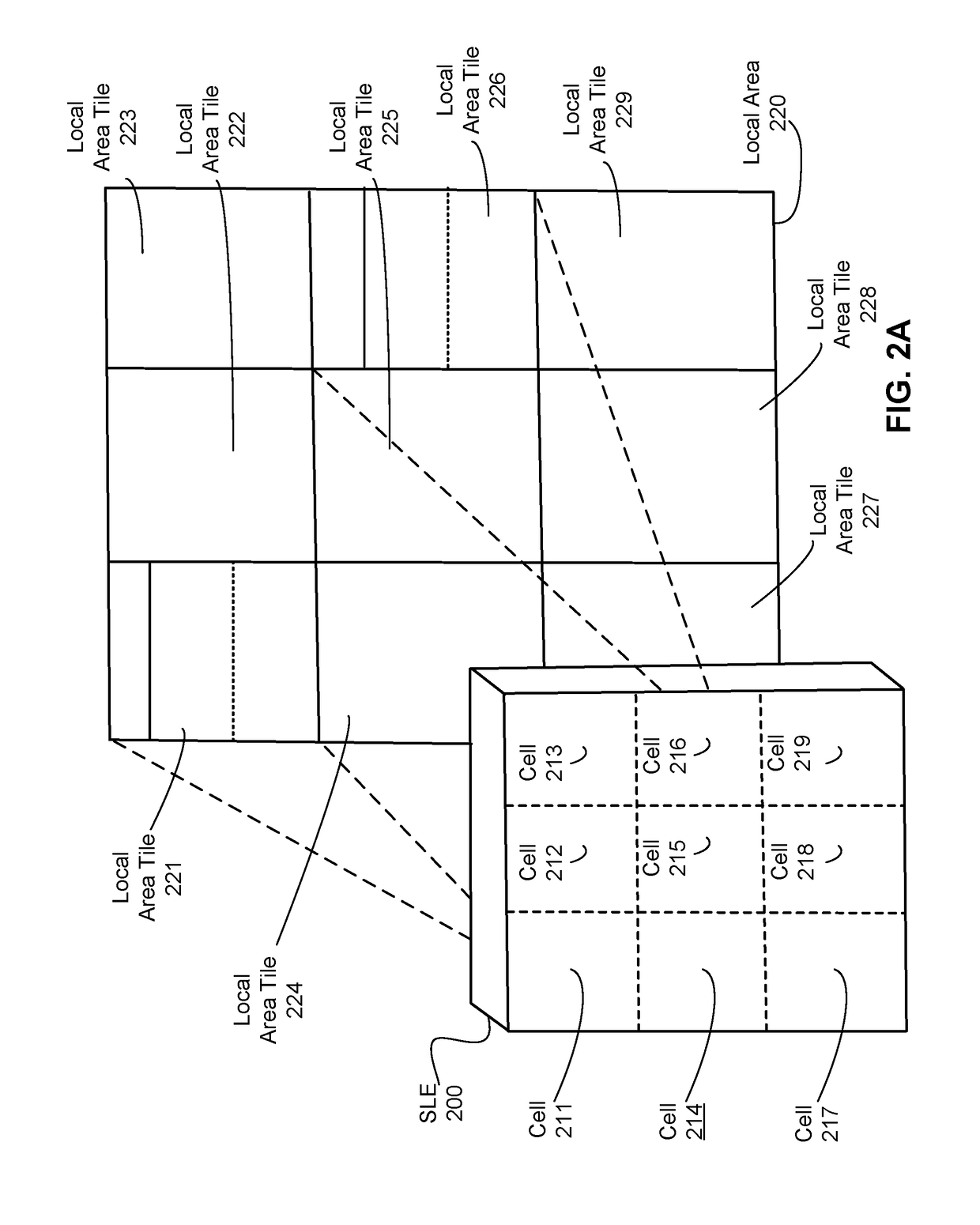
Three Dimensional Depth Mapping Using Dynamic Structured Light
ActiveUS20160286202A1High resolutionReduce resolutionInput/output for user-computer interactionSemiconductor lasersLaser arrayThree-dimensional space
Apparatus for generating a dynamic structured light pattern for optical tracking in three-dimensional space, comprises an array of lasers, such as a VCSEL laser array, to project light in a pattern into a three-dimensional space; and an optical element or elements arranged in cells. The cells are aligned with subsets of the laser array, and each cell individually applies a modulation, in particular an intensity modulation, to light from the laser or lasers of the subset, to provide a distinguishable and separately controllable part of the dynamic structured light pattern. A method of generating a structured light pattern is disclosed, in which light is provided from an array of lasers, and light is individually projected from subsets of the array of lasers to provide differentiated parts of the structured light pattern.
Owner:META PLATFORMS TECH LLC
Video game play using panoramically-composited depth-mapped cube mapping
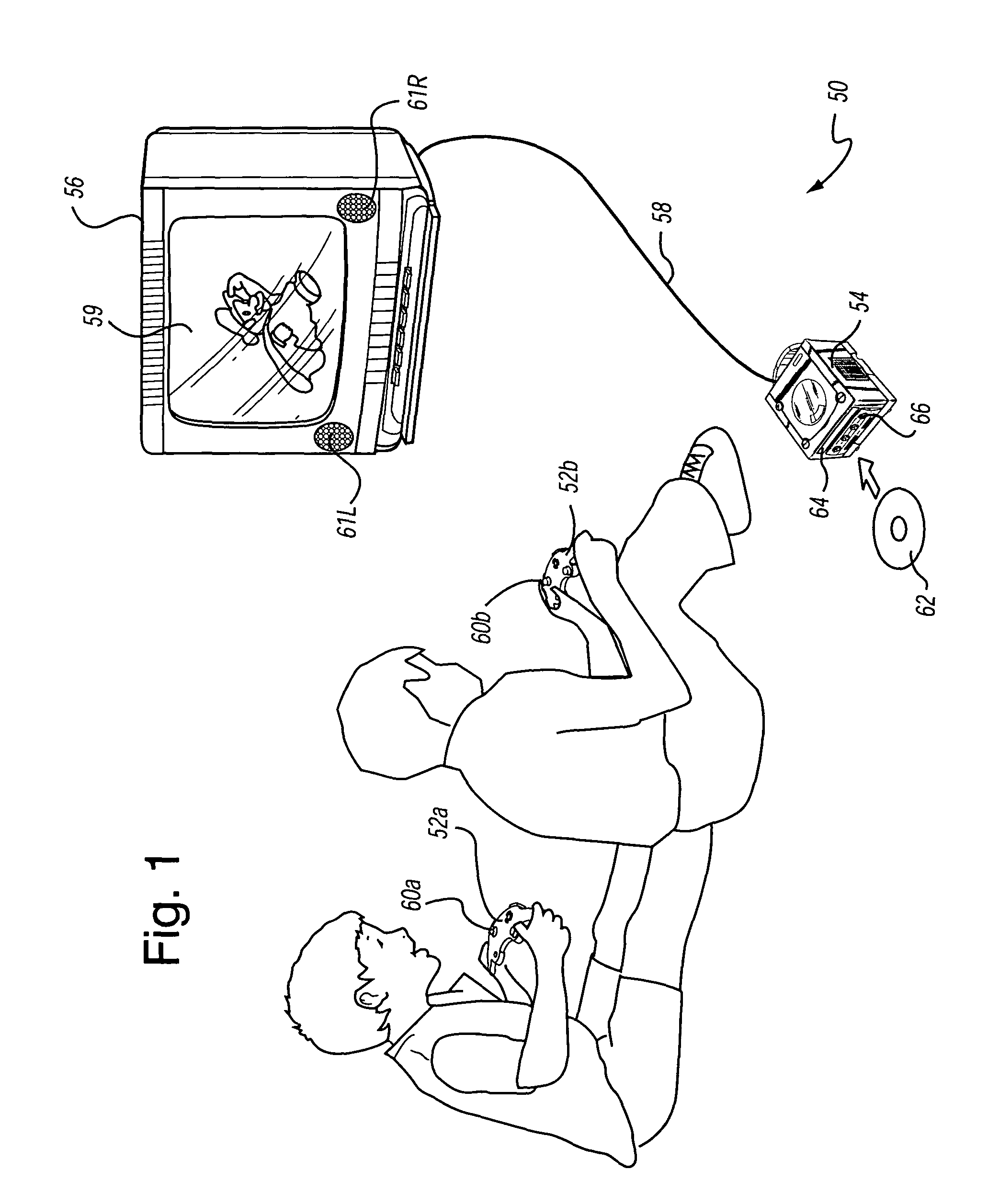
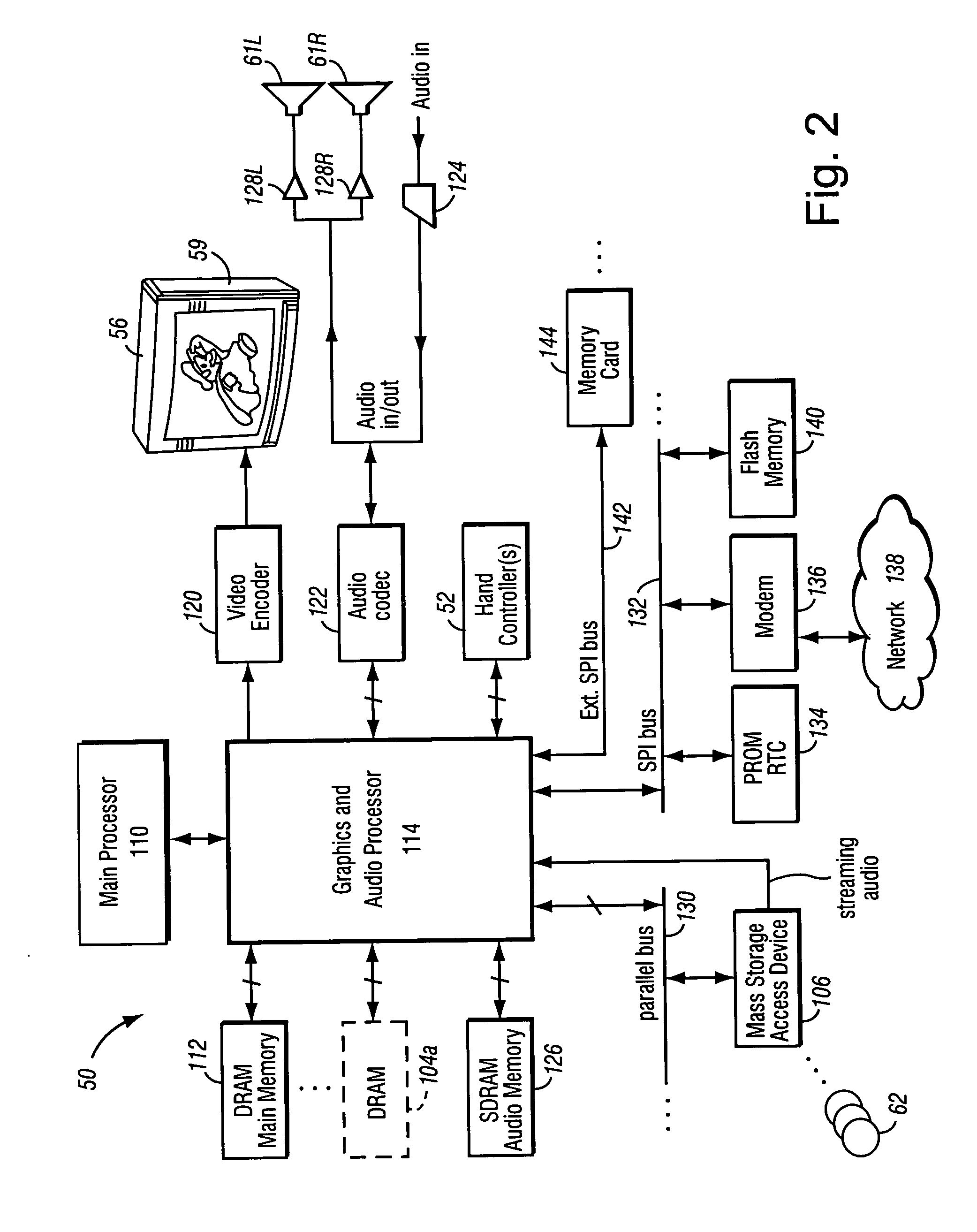
ActiveUS7256779B2More powerHighly excitingVideo games3D-image renderingThree dimensionalityDepth mapping
Video game play rendered using a panoramic view of a cube map style rendering uses an associated depth map to supply three-dimensionality to the pre-rendered scene. The resulting panoramic rendering may be indistinguishable from rendering the original scene in real-time except that the background is of pre-rendered quality.
Owner:NINTENDO CO LTD
System and methods for evaluating and monitoring wounds
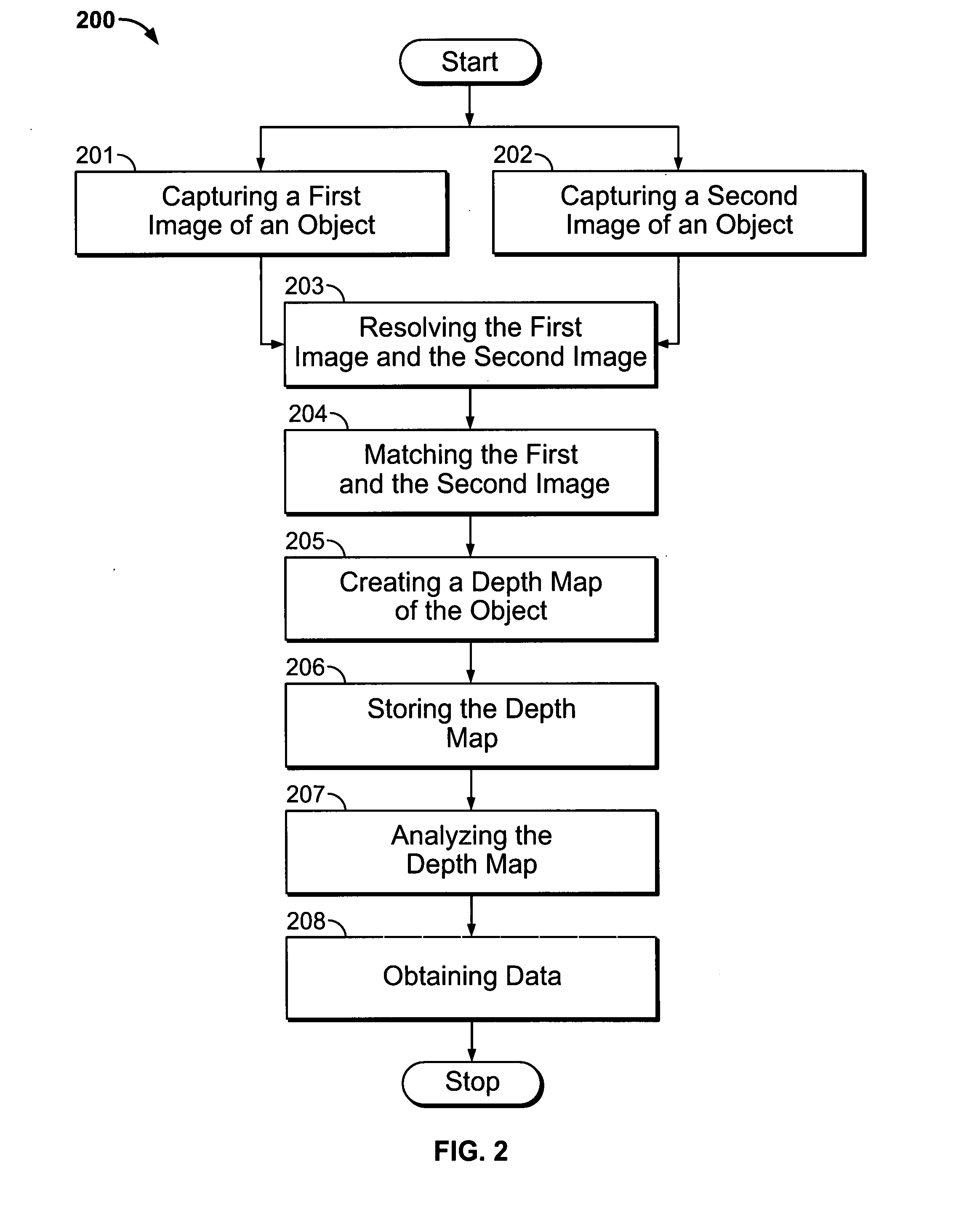
A system and methods to evaluate and monitor the healing progress of a wound. At least two optical imaging devices are mounted on a support device in order to capture images. The images are resolved in order to be matched to create a depth map of the object. The depth map can be analyzed to obtain data, such as the length, width, and depth of the wound and the area and volume of the wound.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
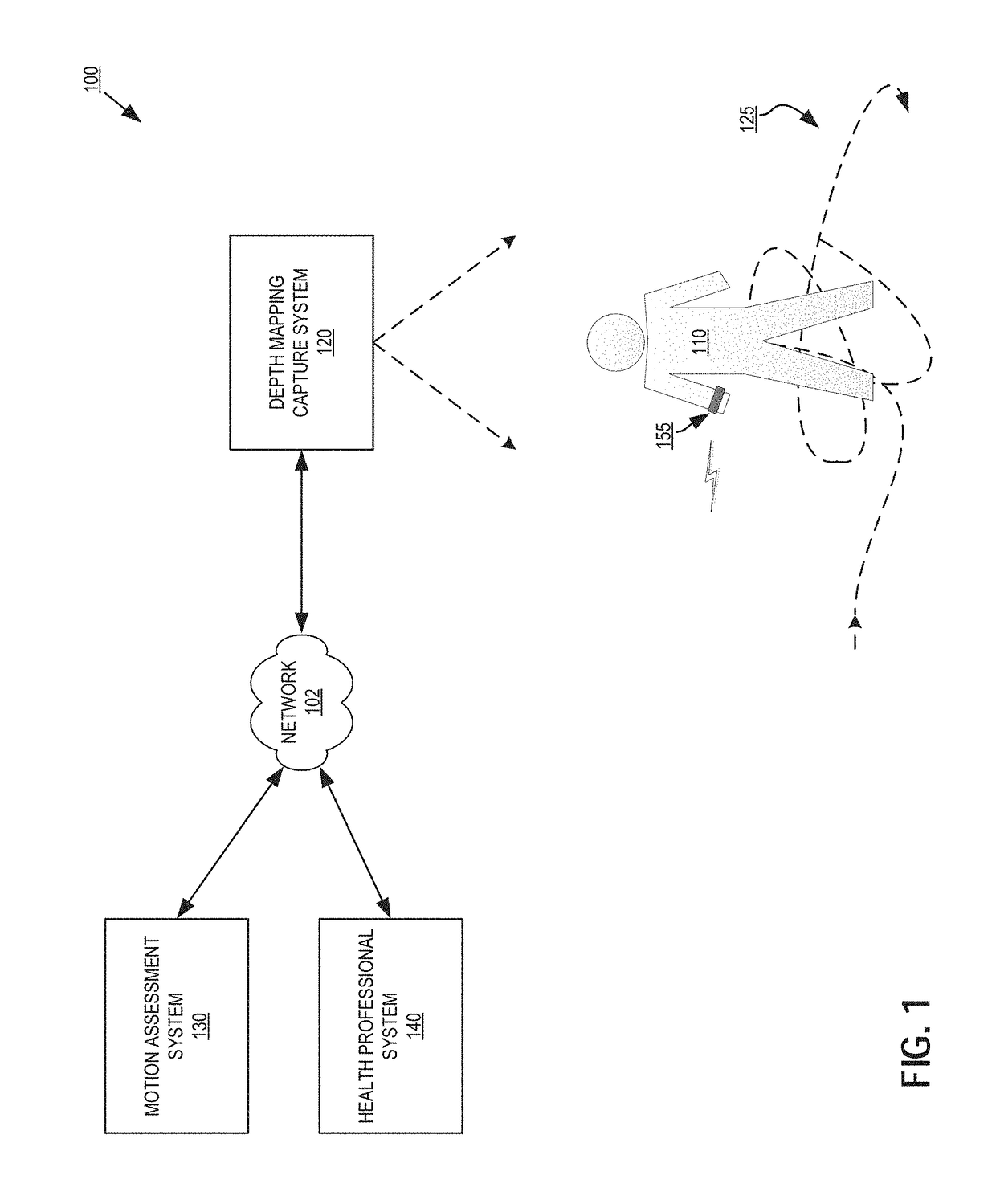
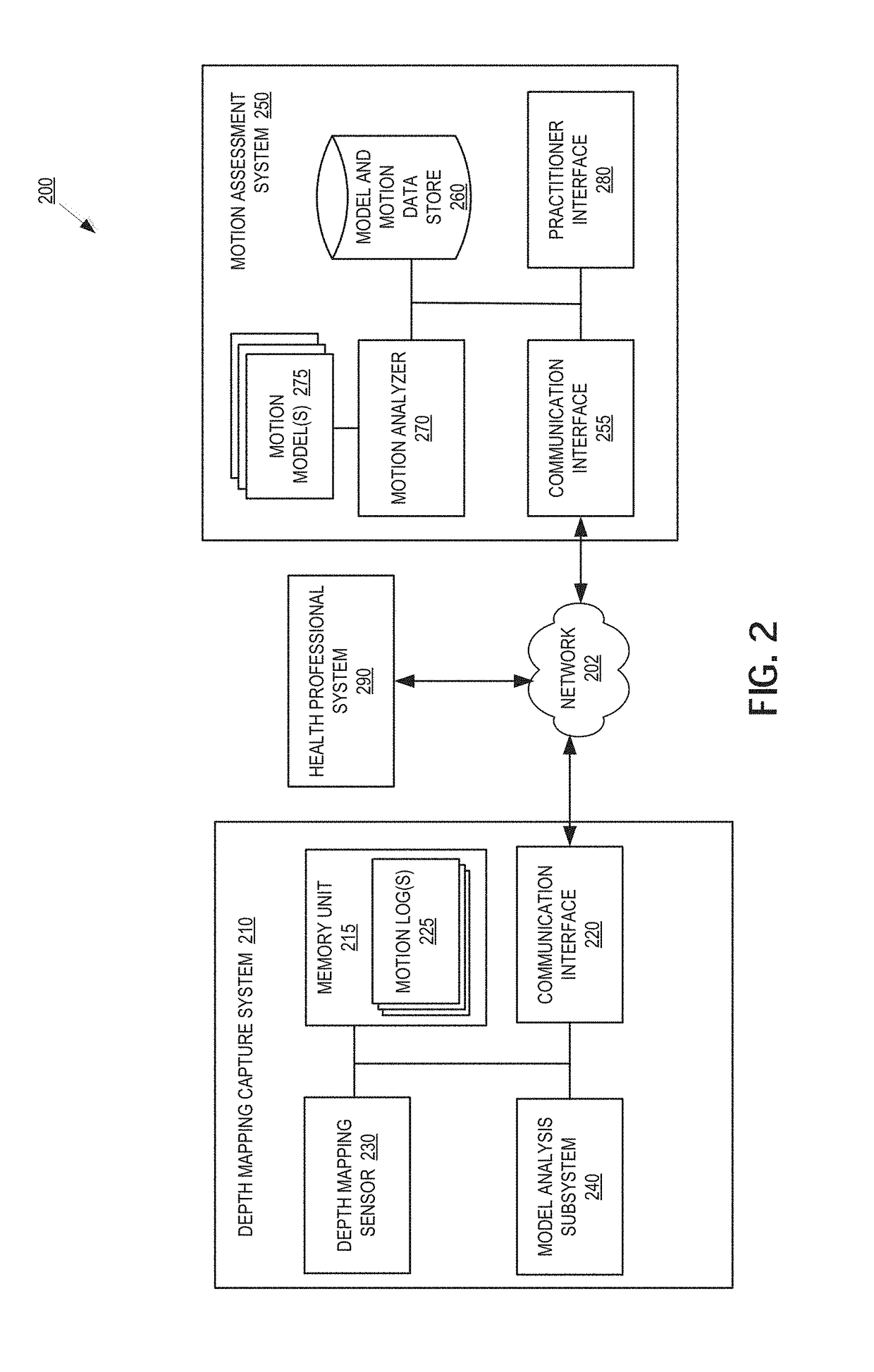
Disease and fall risk assessment using depth mapping systems
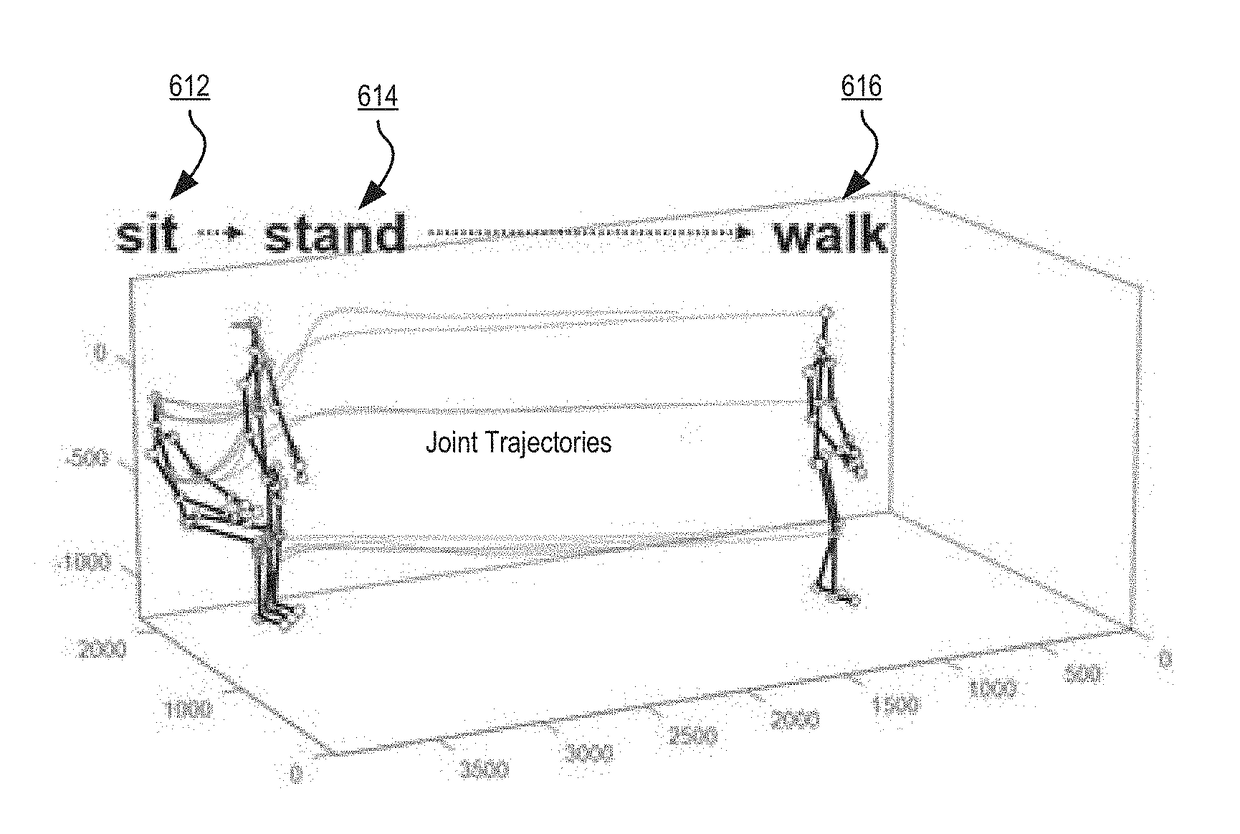
An apparatus, system and process for tracking and analyzing target person movements, captured while the target person is performing ordinary tasks outside of a medical context, for medical diagnosis and treatment review are described. The method may include constructing a model of a target person from three-dimensional (3D) image data of the target person performing an activity over a period of time. The method may also include tracking movement of the model of the target person in the 3D image data over the period of time, and detecting one or more motion features in the movement of the model of the target person that are relevant to diagnosis, treatment, care, or a combination thereof, of a potential chronic neurodegenerative or musculoskeletal medical condition. The method may also include computing a risk score associated with likelihood of the target person having the medical condition based on the detected motion features.
Owner:VERILY LIFE SCI LLC
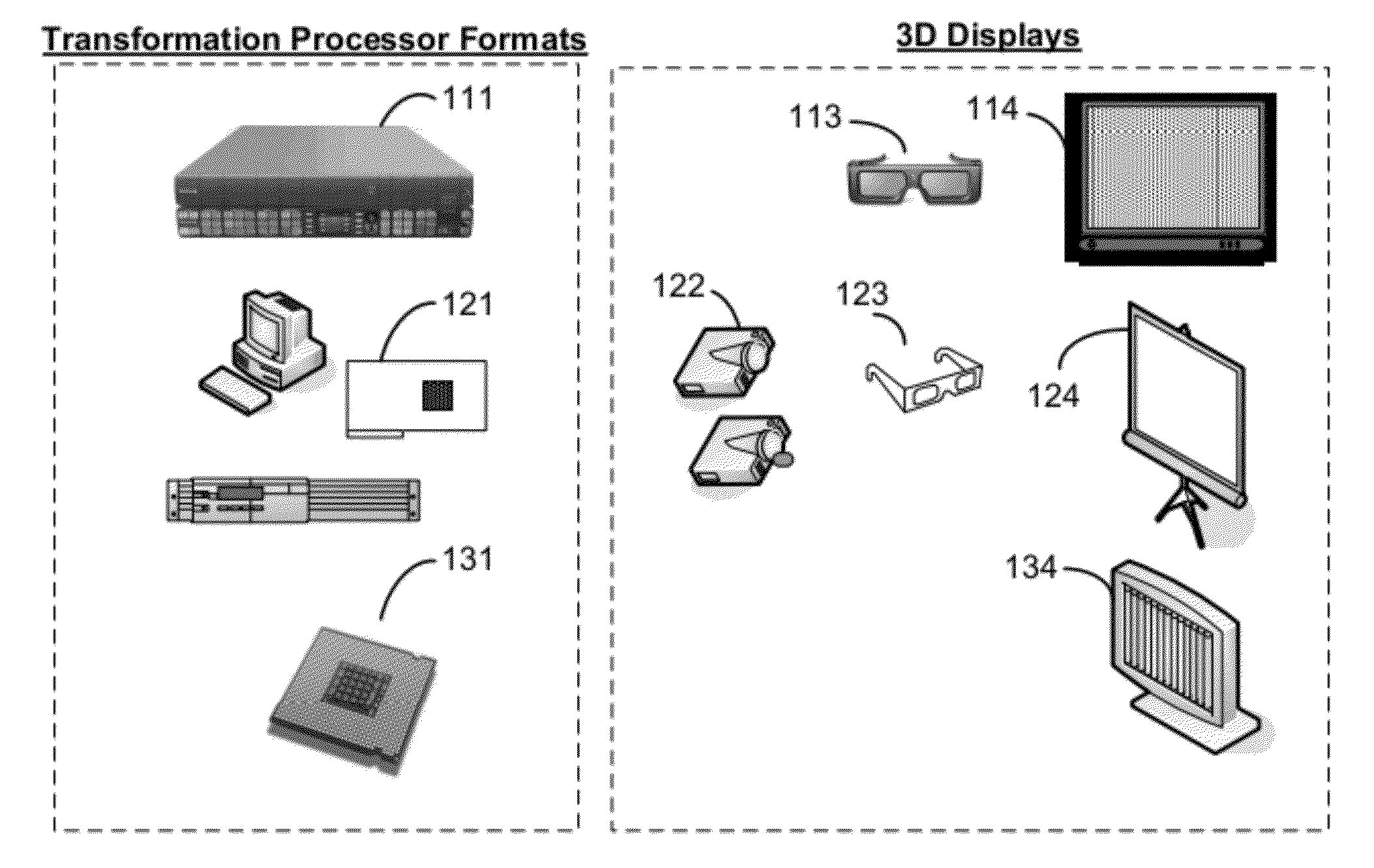
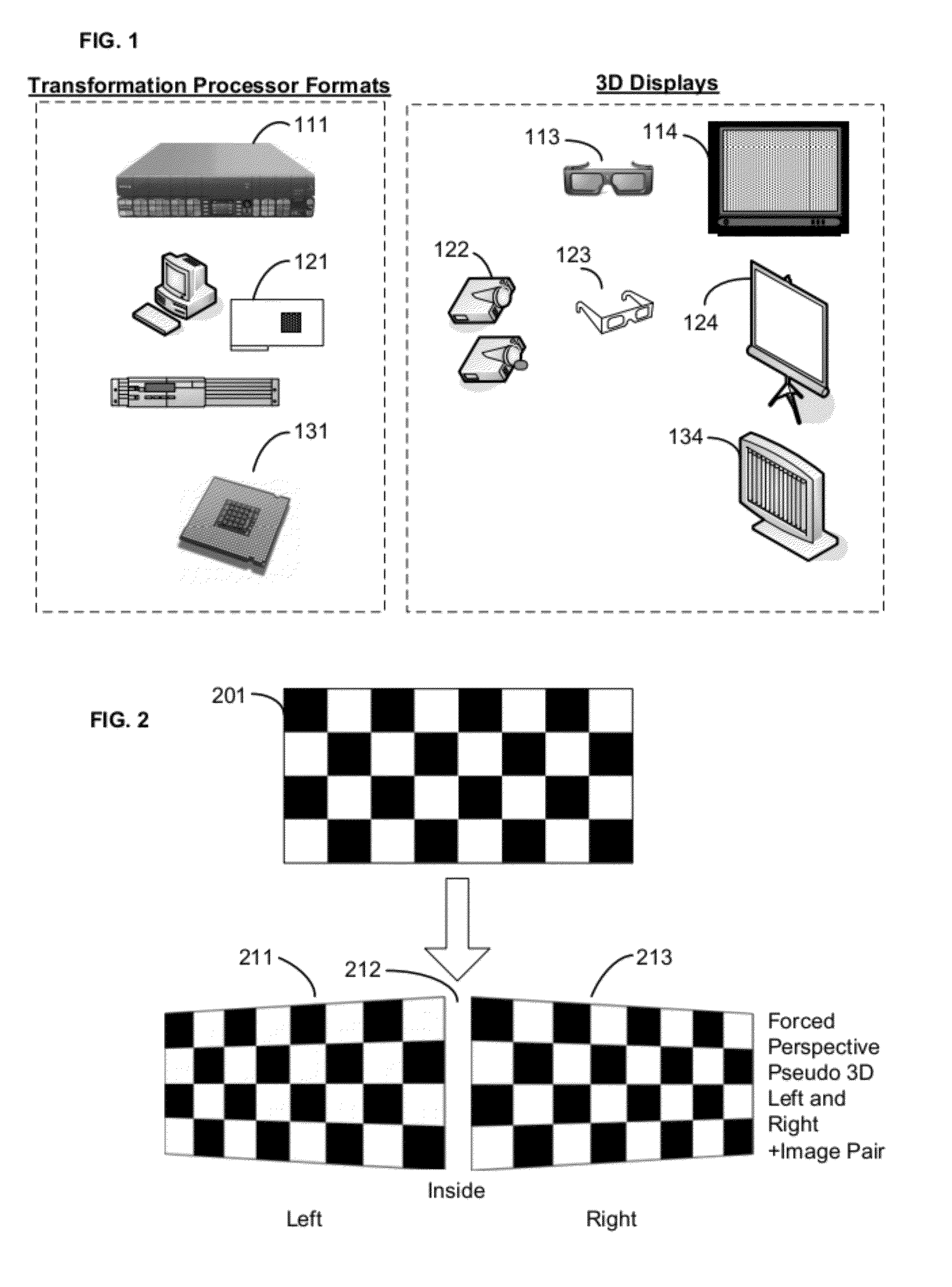
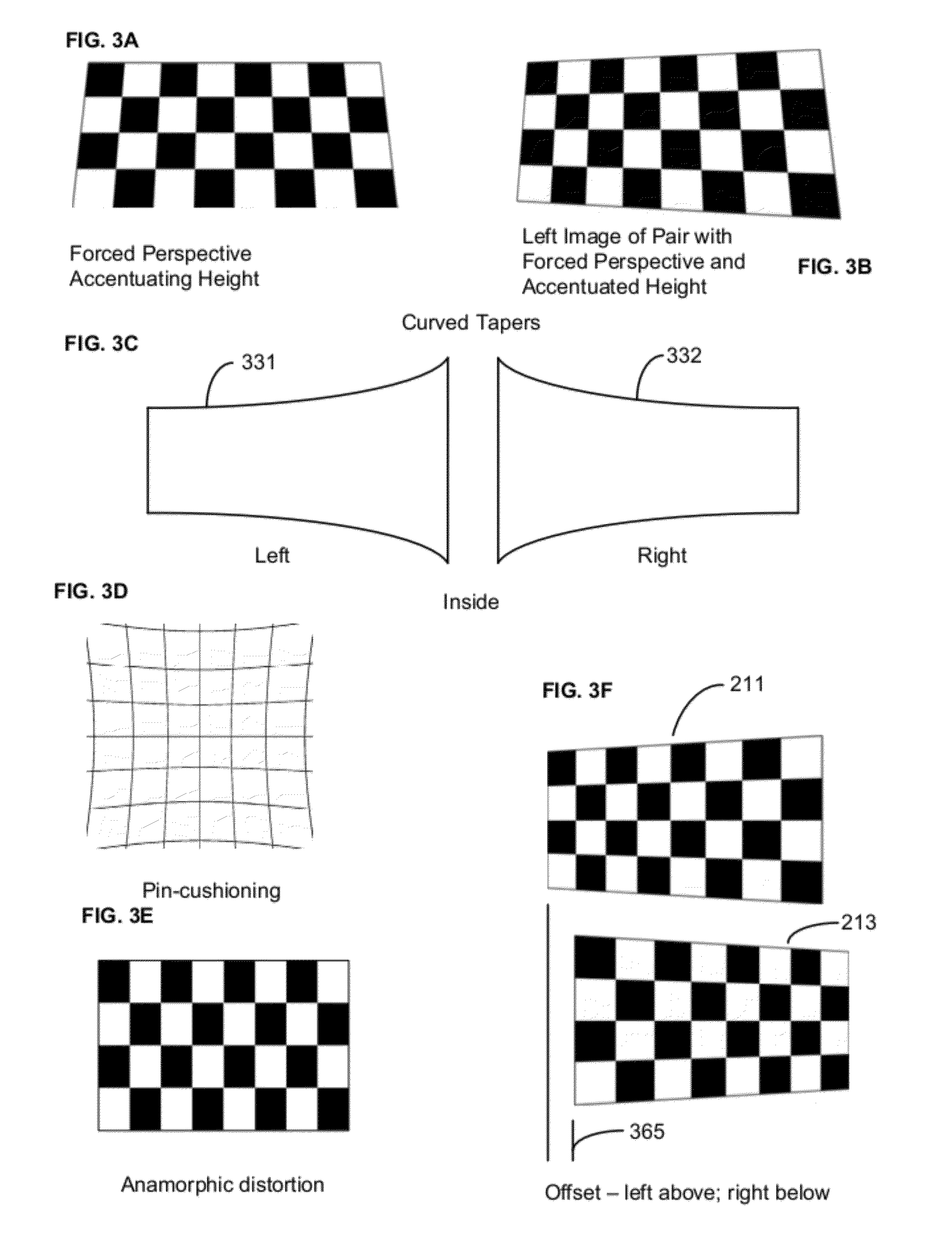
Pseudo-3d Forced Perspective Methods And Devices
The present invention relates to conversion of 2D media to pseudo-3D left and right image pairs. In particular, it relates to imposing forced perspective on left and right versions of a 2D image. The distorted pair of images, when displayed, will be interpreted by a viewer as a 3D image. The pseudo-3D forced perspective image pairs can be produced without depth mapping of objects in scenes and without comparing the position of objects in successive image frames.
Owner:TERANEX SYST
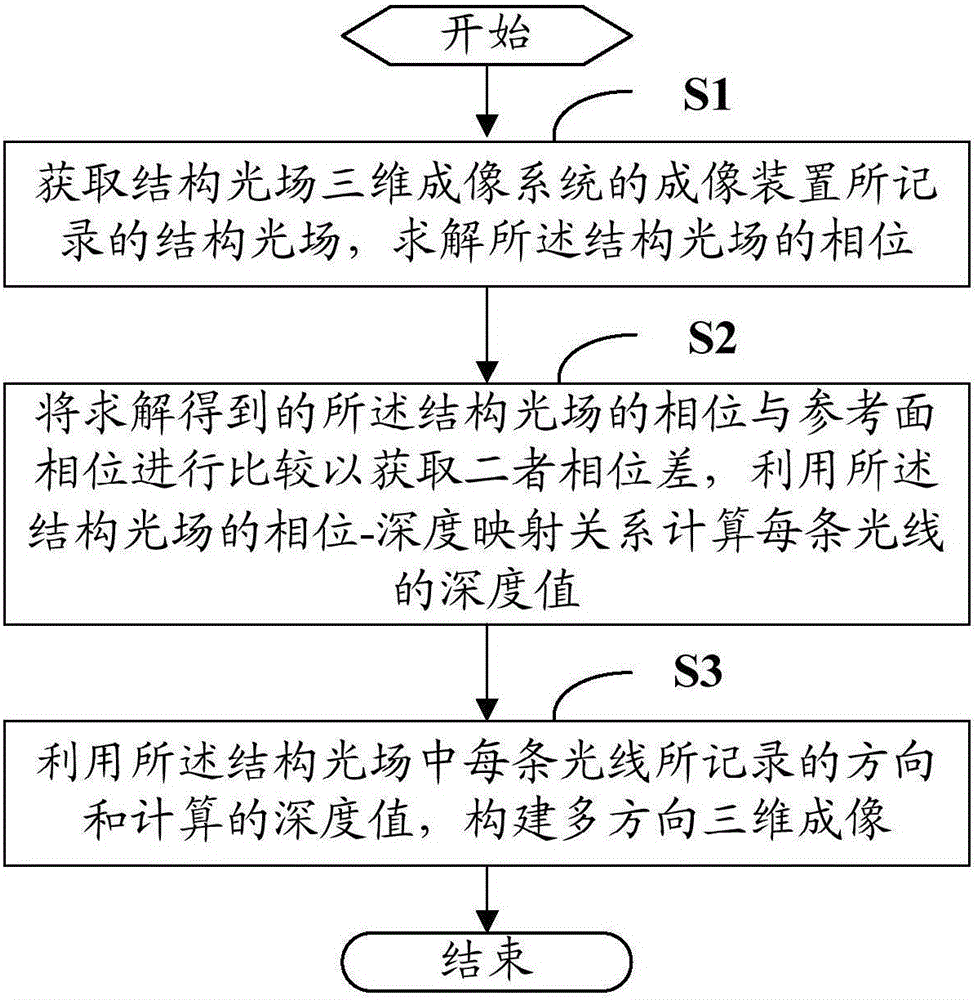
A structured light field three-dimensional imaging method and a system thereof
ActiveCN106257995AMeet imaging requirementsMeet the measurement requirementsUsing optical meansDigital imagingPhase difference
A structured light field three-dimensional imaging method is provided. The method includes acquiring a structure light field recorded by an imaging device of a structured light field three-dimensional imaging system, solving the phase of the structured light field, comparing the solved phase of the structured light field with a reference plane phase to acquire a phase difference, calculating a depth value of each light line by utilizing a phase-depth mapping relation of the structured light field, and constructing multi-direction three-dimensional imaging by utilizing a direction and the calculated depth value of each light line in the structured light field. The structured light field three-dimensional imaging system is also provided. The structured light field is acquired by combining light field imaging and structured lighting in the technical scheme. The mapping relation between the phase and a scene depth of the structured light field is deduced. One time of collection and multi-direction three-dimensional imaging can be achieved. The method and the system facilitate further research of structured light field three-dimensional imaging theories and applications and meet requirements on multi-view three-dimensional digital imaging and measurement.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
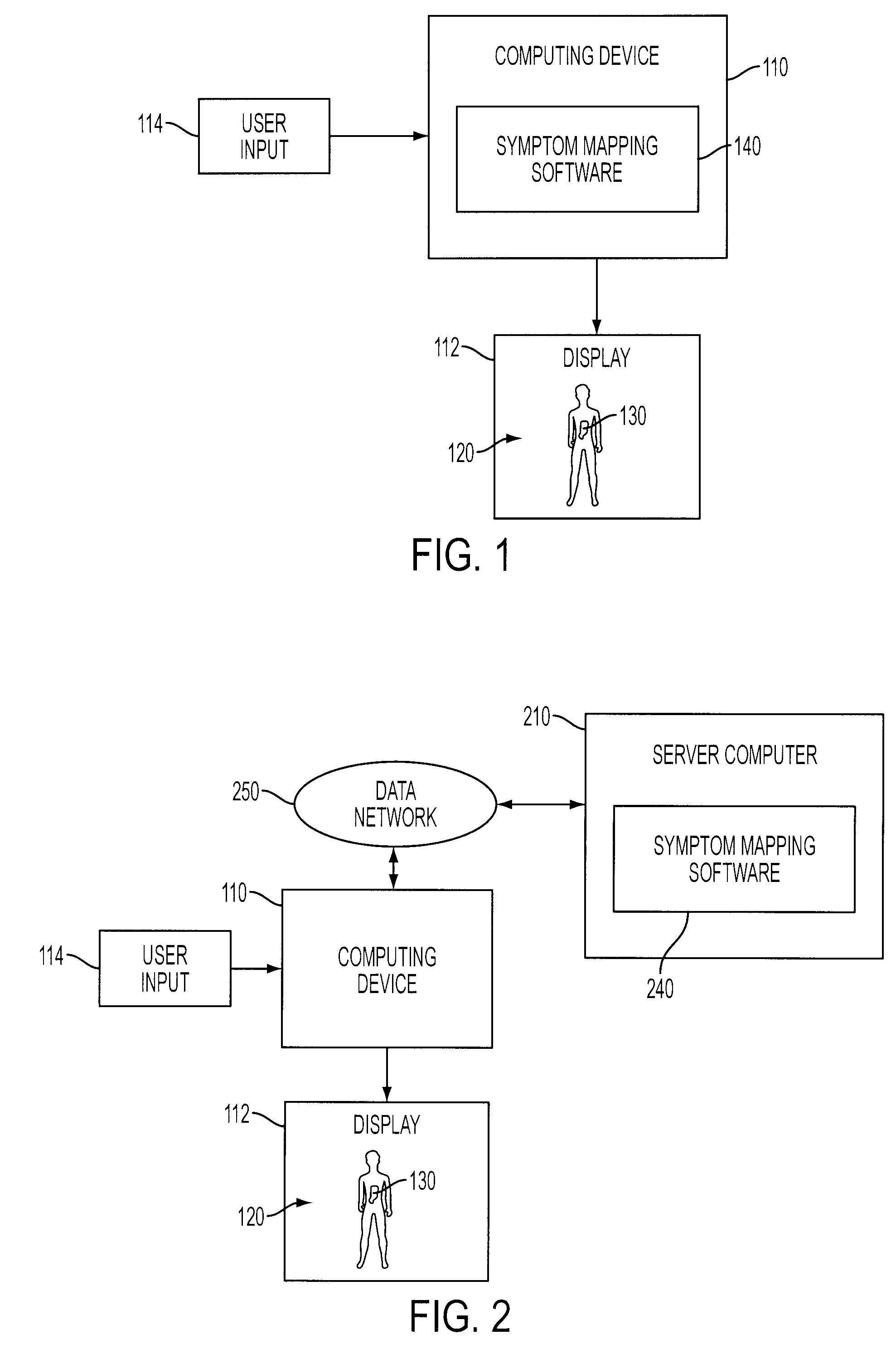
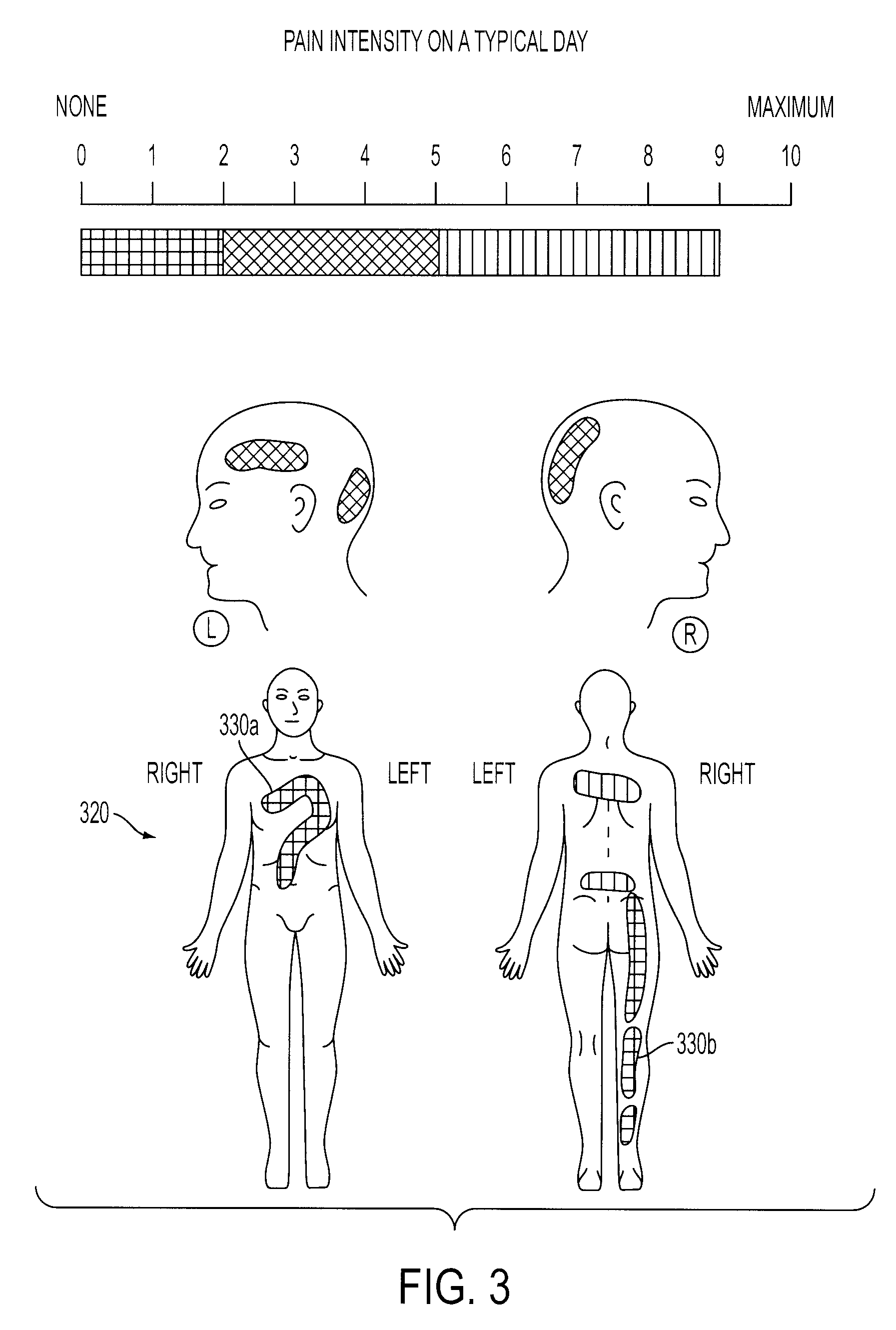
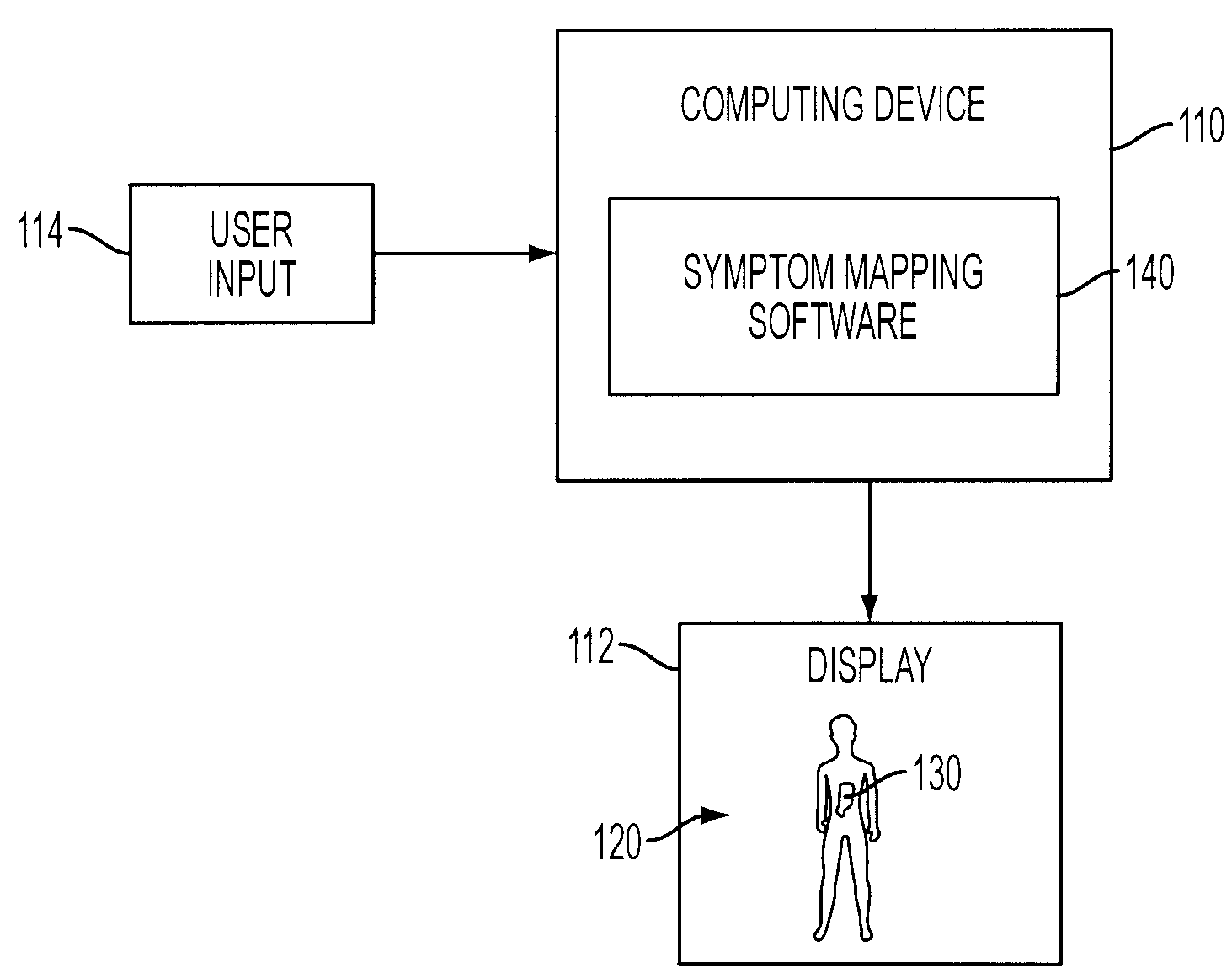
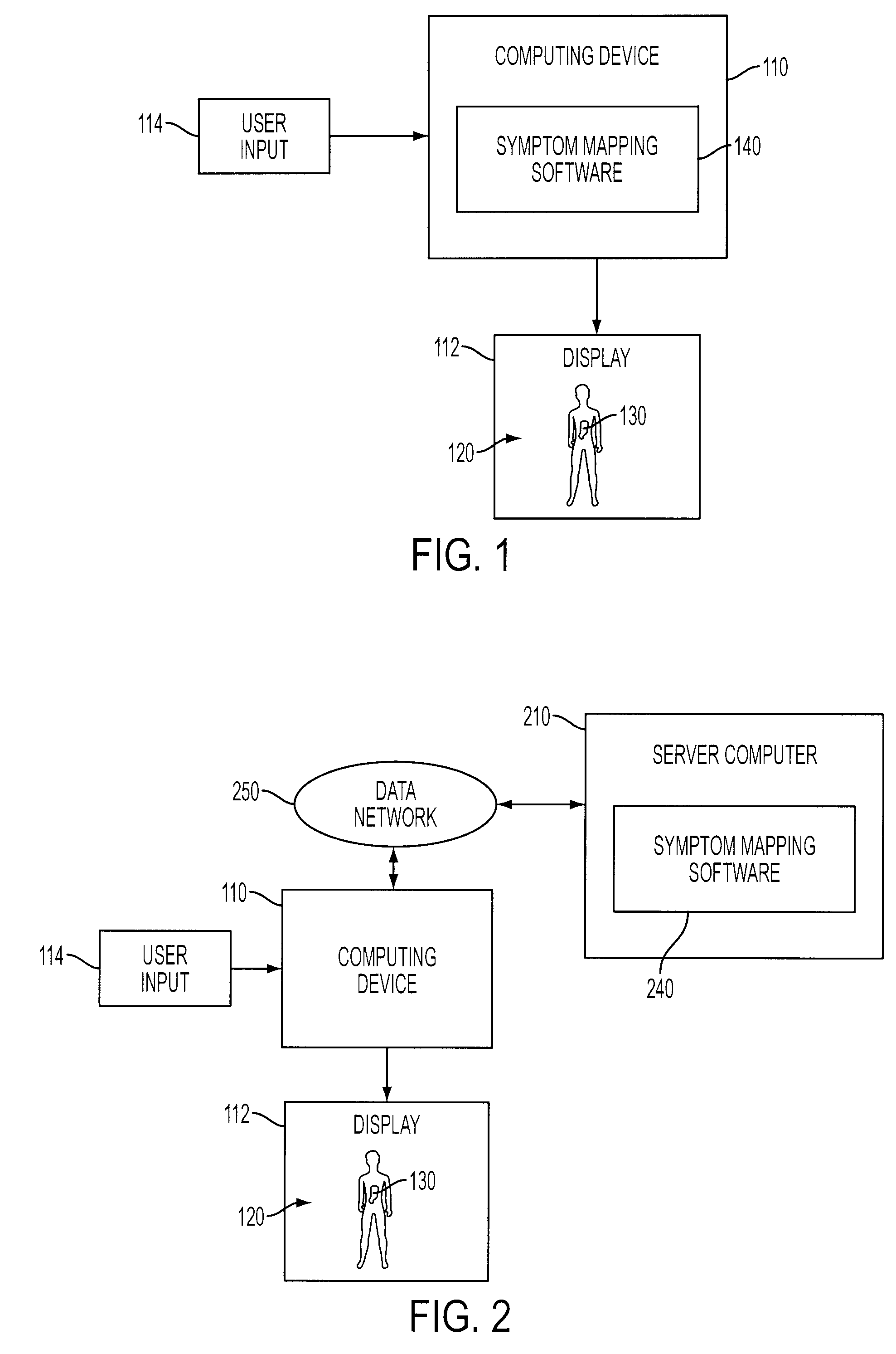
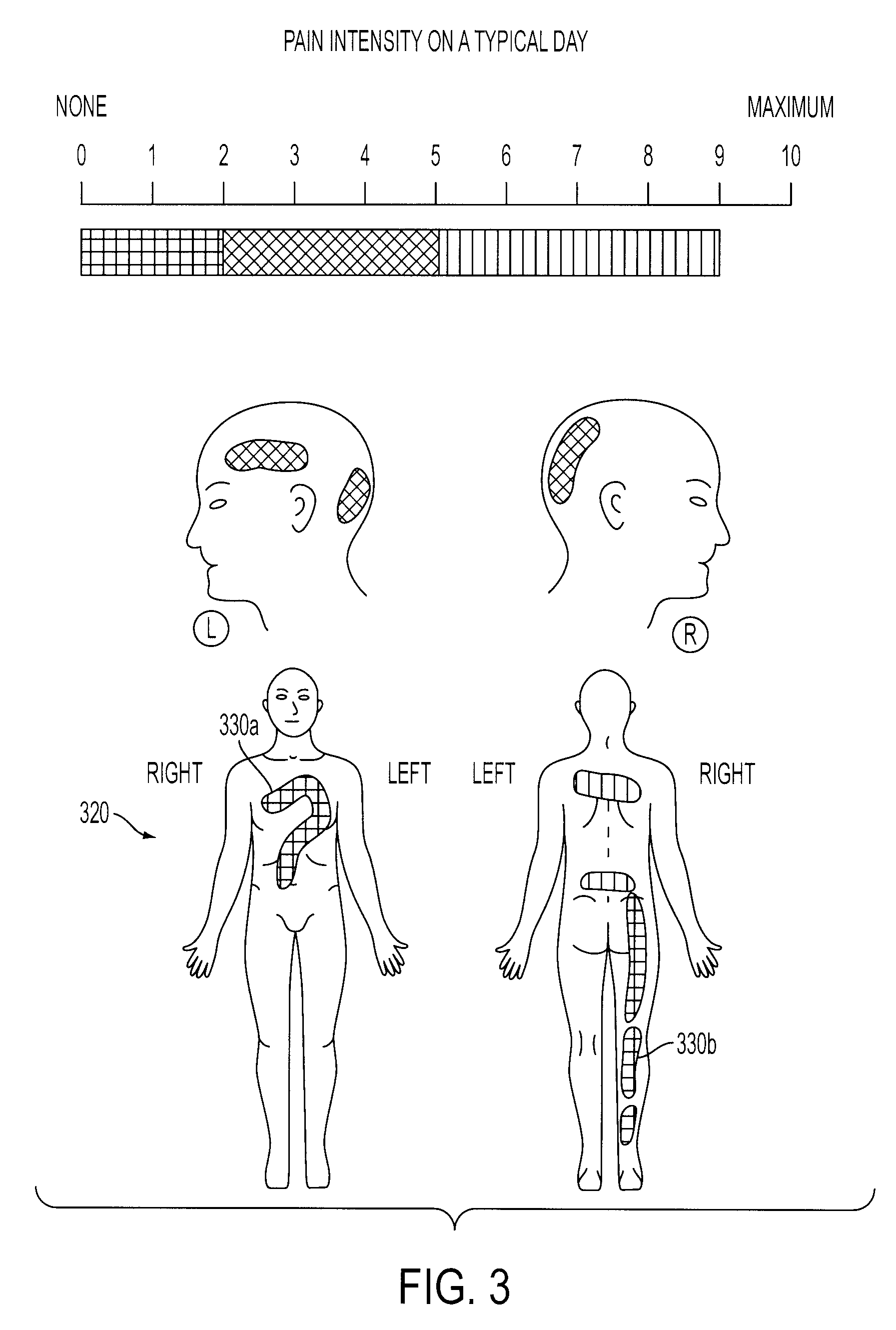
System And Method For Mapping Pain Depth
A pain depth mapping system and method may be used to map the location and depth of pain experienced by a user (e.g., a patient). The pain depth mapping system and method is capable of displaying one or more body representations with symptom representations representing the location of the pain. The pain depth mapping system and method allows the user to delineate one or more user-defined pain depth regions on a cross-section of the body representation with the symptom representations to form a pain map. The symptom mapping system and method may also allow the user to vary the pain intensity represented by the symptom representations as the user delineates the user-defined pain depth region(s).
Owner:PSYCHOLOGICAL APPL
Non-uniform spatial resource allocation for depth mapping
ActiveUS8982182B2Improve system performanceLimited resourceInput/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementOptical radiationComputer module
Owner:APPLE INC
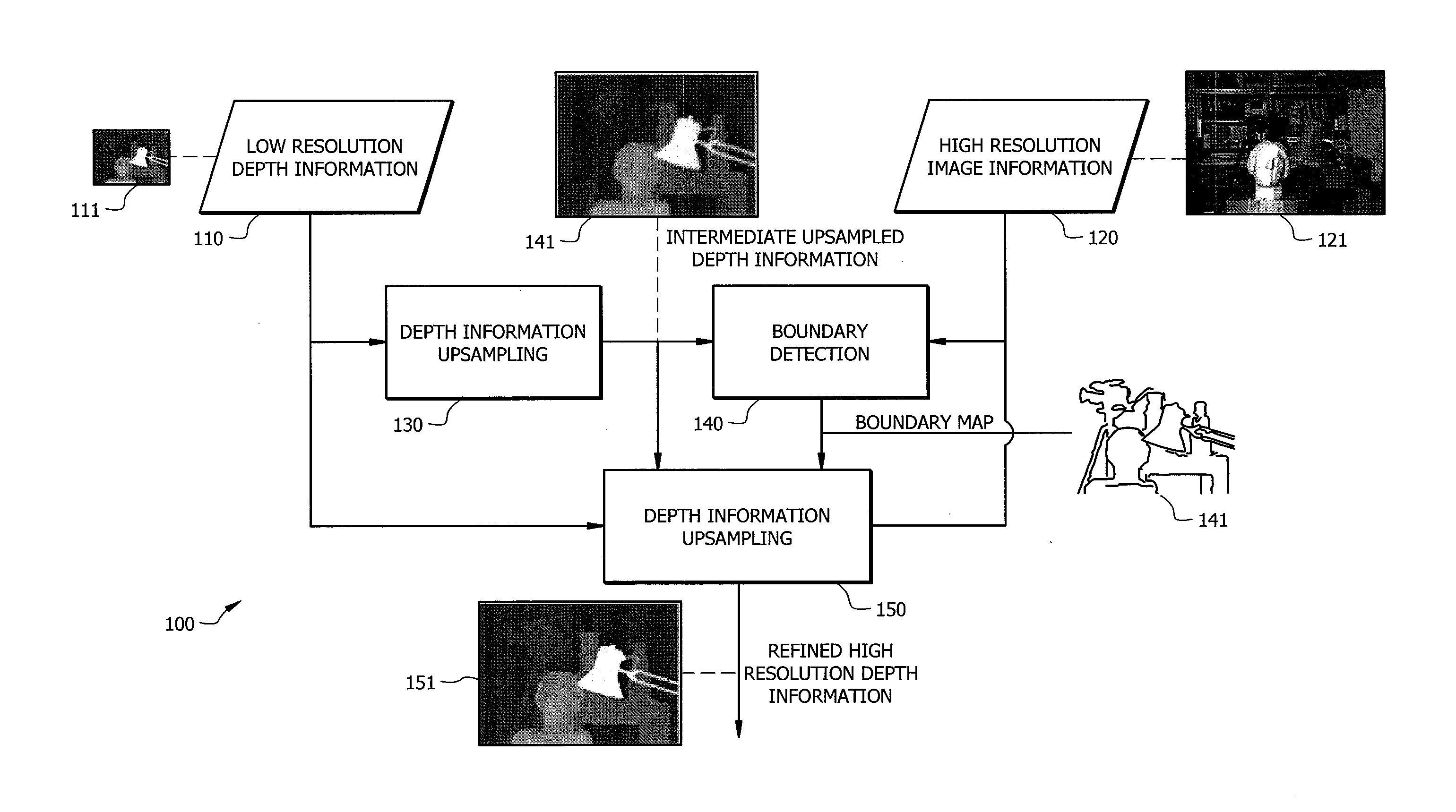
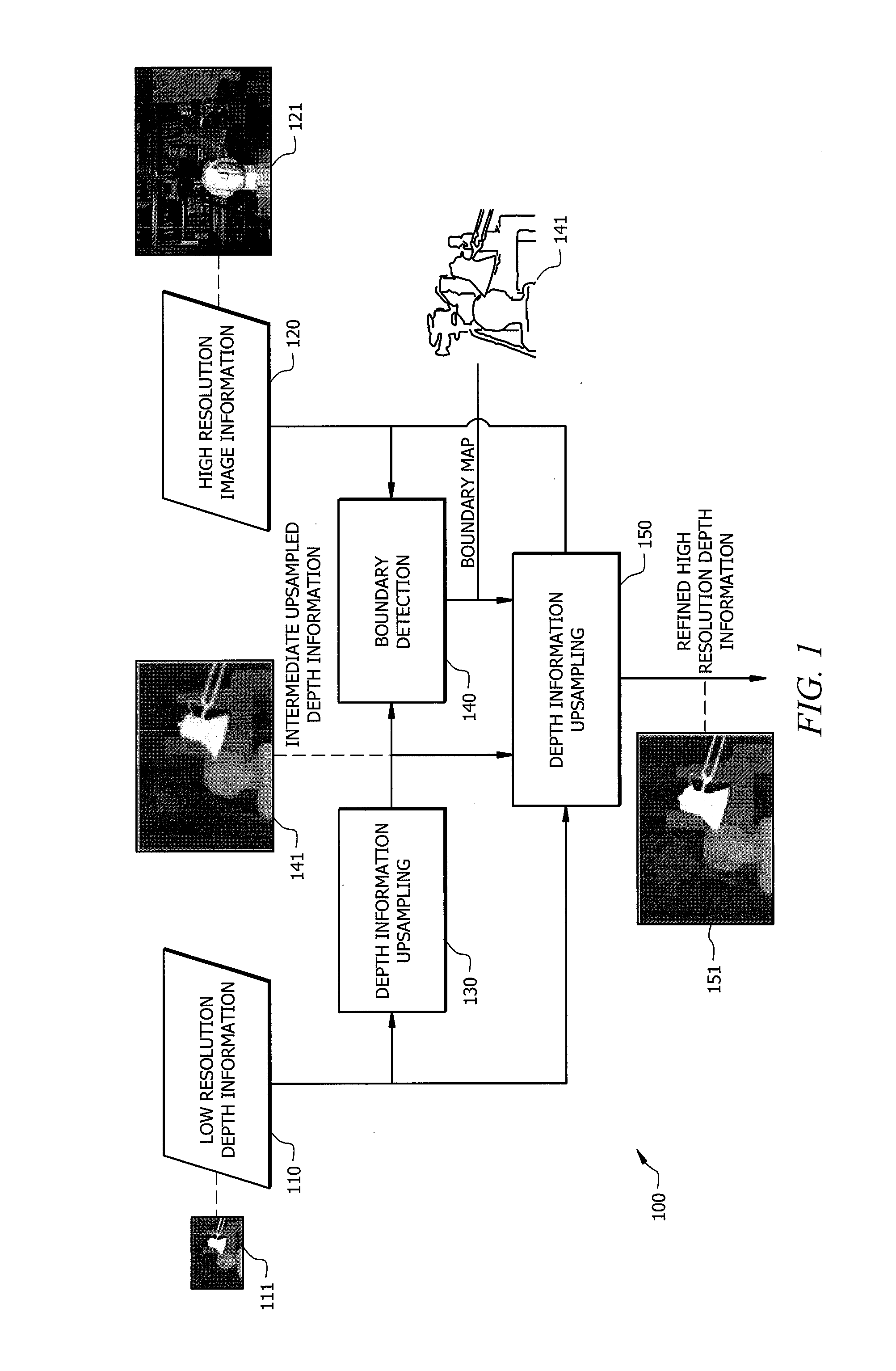
Boundary-based high resolution depth mapping
ActiveUS20140169701A1High resolutionMore accurate and reliable high resolution depth informationGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionImage resolutionHigh resolution image
Systems and methods which provide generation of high resolution depth maps from low resolution depth information using boundary-based processing techniques are disclosed. Boundary-based depth processing provided by embodiments implements boundary detection and boundary-based interpolation algorithms for providing high resolution depth information from low resolution depth information and high resolution image information. Boundary detection algorithms are implemented according to embodiments to detect object boundaries (e.g., depth discontinuities), where the low resolution depth samples are typically inaccurate and generally in need of refining. Boundary-based interpolation algorithms are implemented according to embodiments of the invention to refine intermediate upsampled depth information (e.g., spatially interpolated low resolution depth information), using the boundary information provided by a boundary detection algorithm, and provide high resolution depth information.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
Device and method for measuring scene depth
ActiveCN102997891AAccurate estimateRealize measurementOptical rangefindersPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
The invention provides a device and a method for measuring scene depth. The device comprises a camera shooting part, a data processing part and an interface control part. The method comprises the steps of firstly utilizing a calibrated camera to acquire a first defocusing image at the uncertain depth, and then adopting a camera which is parallel to the calibrated camera and has the same parameters to acquire a second defocusing image at a different depth position, wherein the change of the depth causes the change of the defocusing degree of the image; establishing the corresponding relation of a point spread function according to different scattering degrees in the two images, and establishing a depth mapping relation according to the corresponding pixel coordinate; and finally estimating the actual scene depth and estimating the two-dimension sizes such as the height and the width of an object. According to the invention, measurement on the distance and size of the object in the scene in a complex environment can be realized without using a mechanical motion part or measuring information of parameters of the camera, thereby bringing convenience for implementers, and being applicable to the field of security protection of squares, bulk warehouses, markets, airports and traffic management.
Owner:南京光蓝物联网科技有限公司
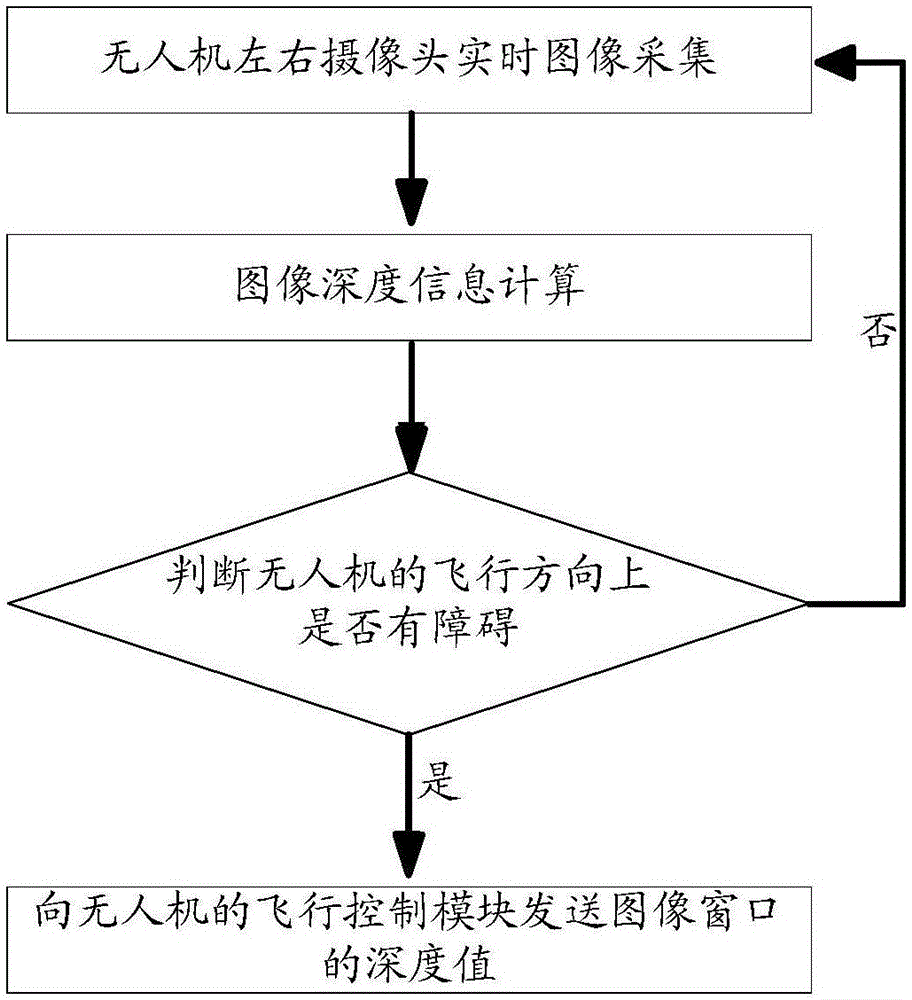
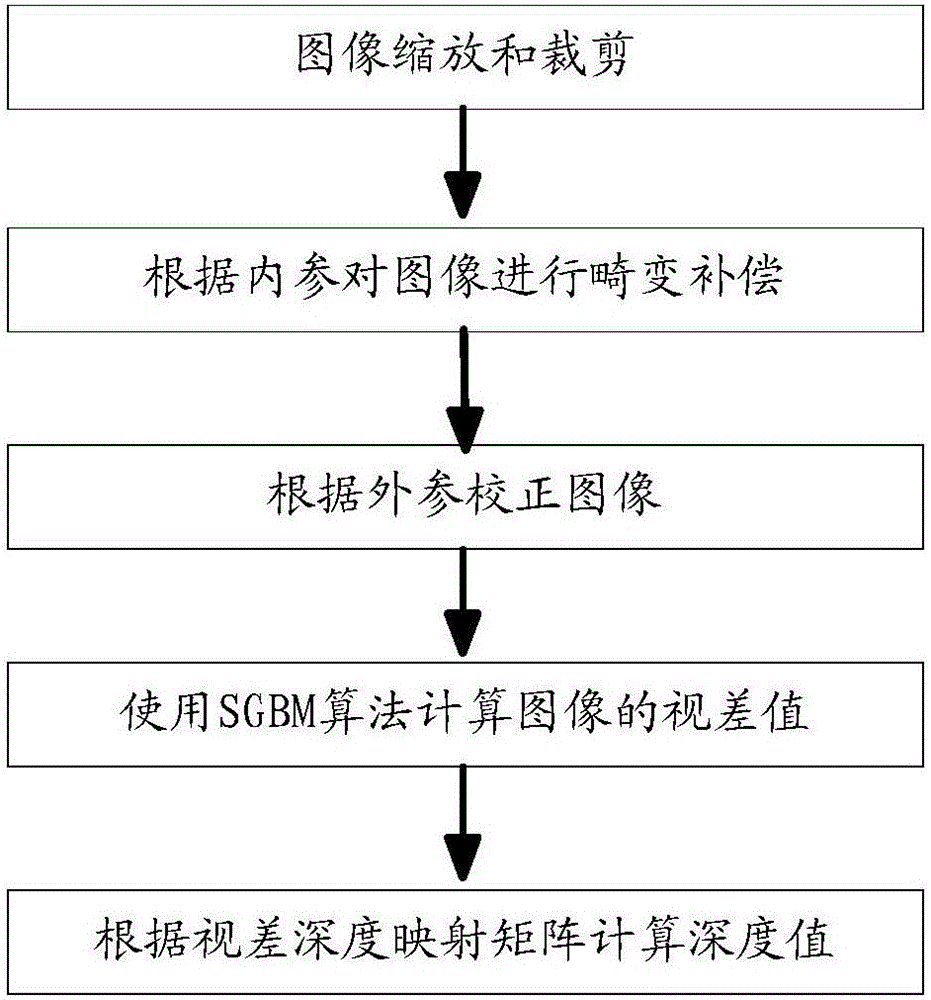
Aircraft information acquisition method, apparatus and device
ActiveUS20190206073A1Reduce aircraft obstacle detection errorImprove aircraft obstacle detection precisionImage enhancementImage analysisParallaxFlight direction
The present disclosure discloses an aircraft (e.g., unmanned aerial obstacle detection method and apparatus, to reduce aircraft obstacle detection errors, and improve aircraft obstacle detection precision. The apparatus performs image collection on a target obstacle by using a binocular camera, to obtain a first image and a second image. After determining a first pixel location obtained by projecting the target obstacle in the first image, and a second pixel location obtained by projecting the target obstacle in the second image, the apparatus calculates a disparity between the first pixel location and the second pixel location and a depth value between the binocular camera and the target obstacle according to the disparity and a preset disparity-to-depth mapping matrix, to detect whether a flight direction of the aircraft is blocked by an obstacle.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
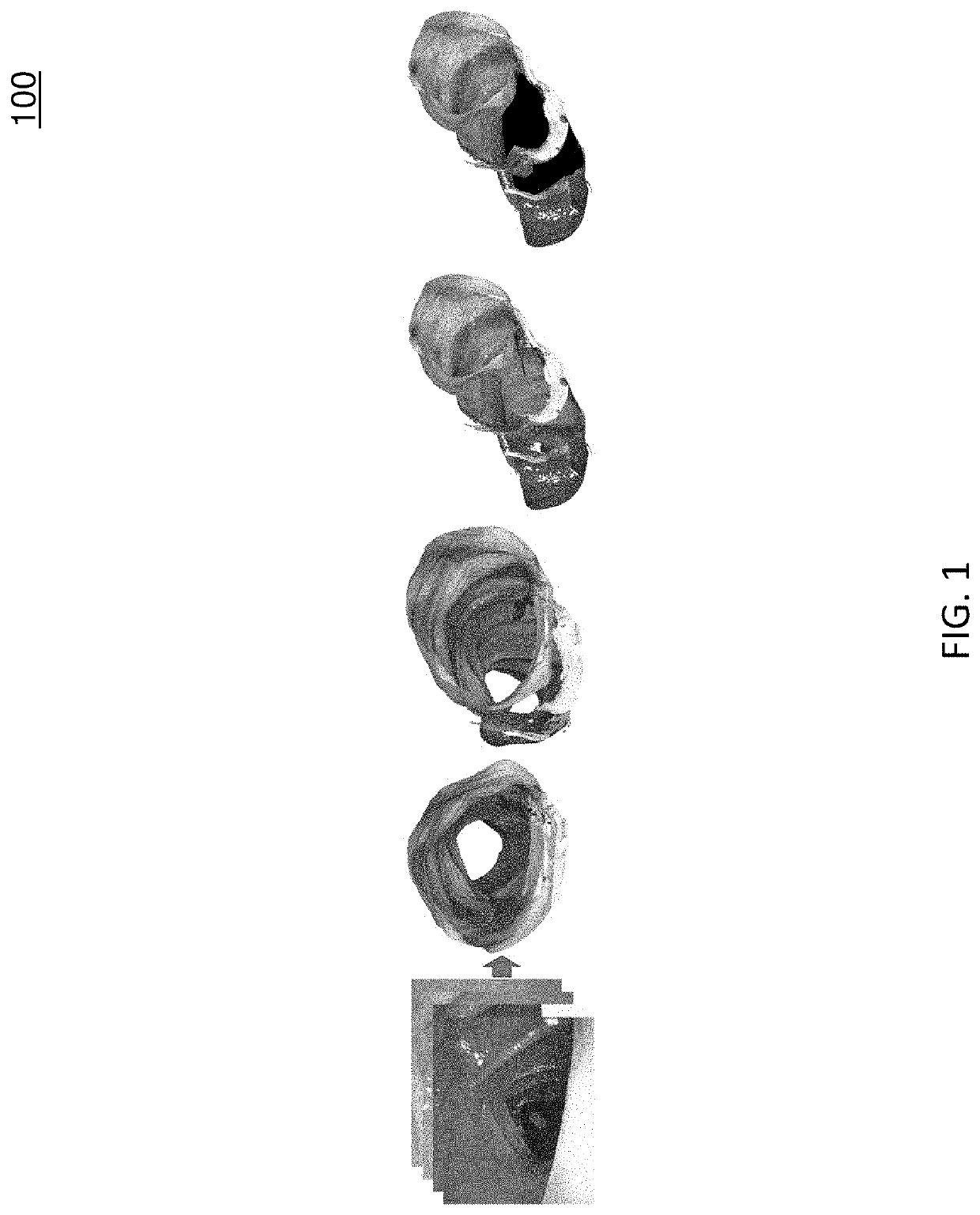
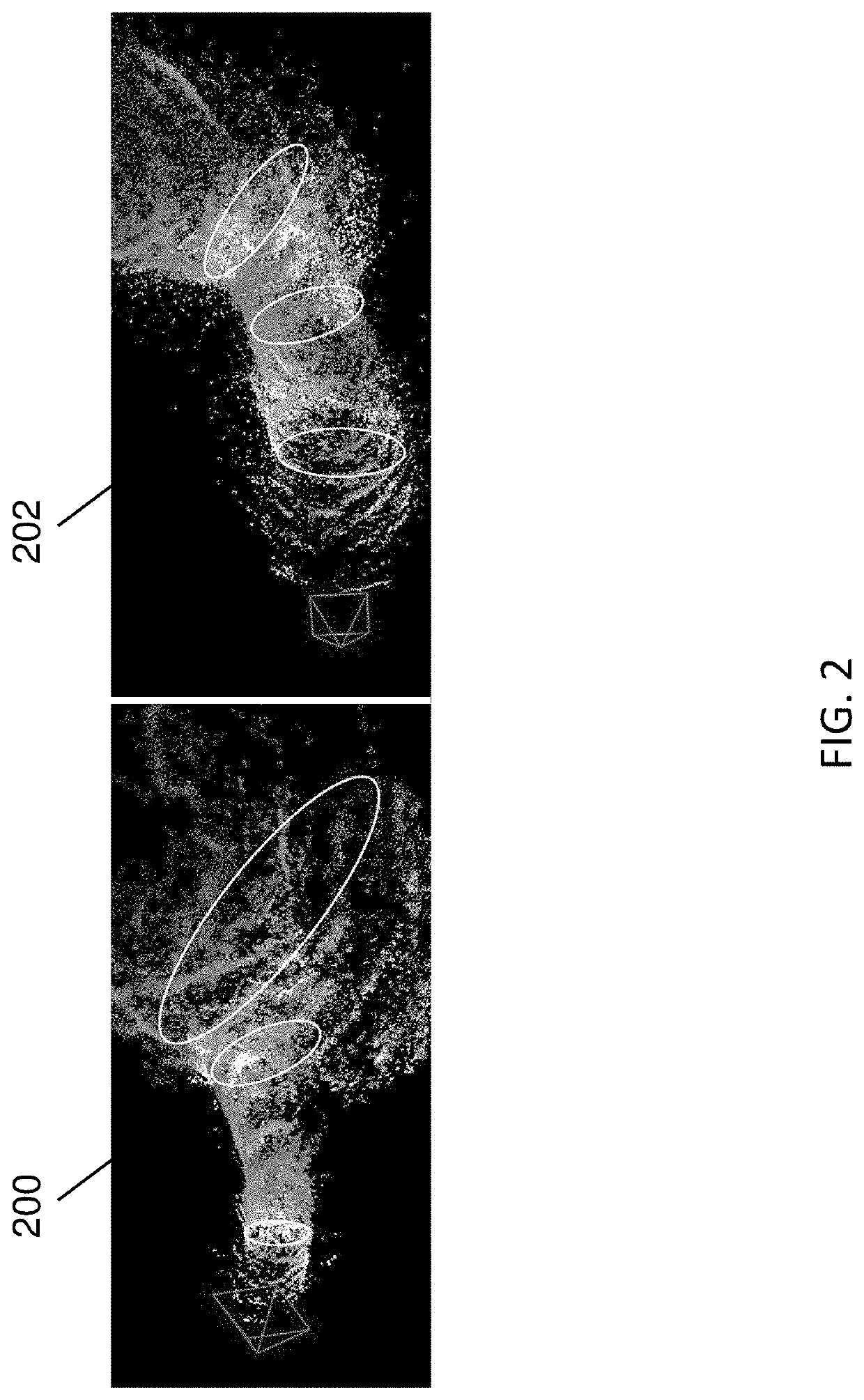
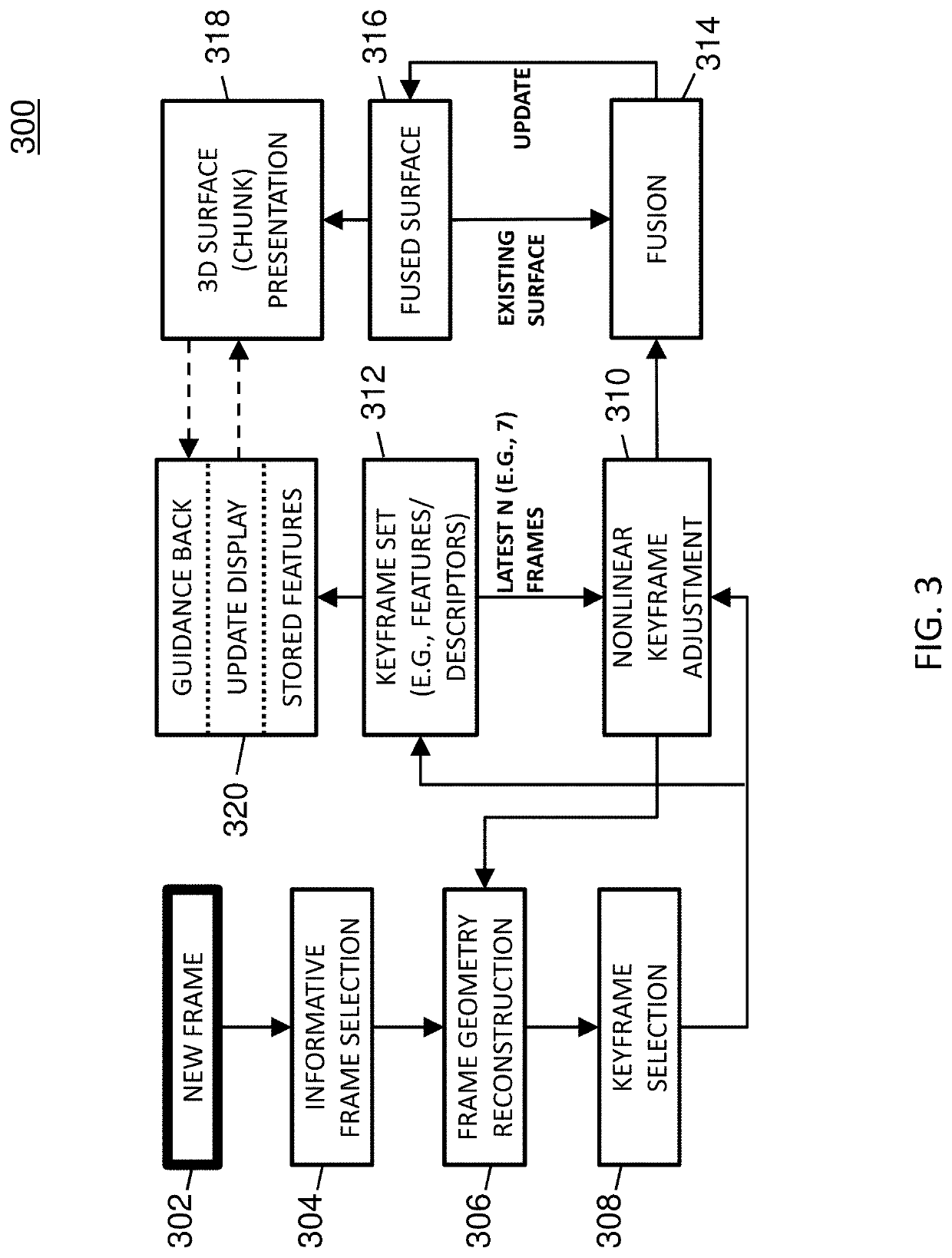
Methods, systems, and computer readable media for three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction of colonoscopic surfaces for determining missing regions
Methods, systems, and computer readable media for deriving a three-dimensional (3D) surface from colonoscopic video are disclosed. According to one method for deriving a 3D surface from colonoscopic video, the method comprises: performing video frame preprocessing to identify a plurality of keyframes of a colonoscopic video, wherein the video frame preprocessing includes informative frame selection and keyframe selection; generating, using a recurrent neural network and direct sparse odometry, camera poses and depth maps for the keyframes; and fusing, using SurfelMeshing and the camera poses, the depth maps into a three-dimensional (3D) surface of a colon portion, wherein the 3D surface indicates at least one region of the colon portion that was not visualized.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
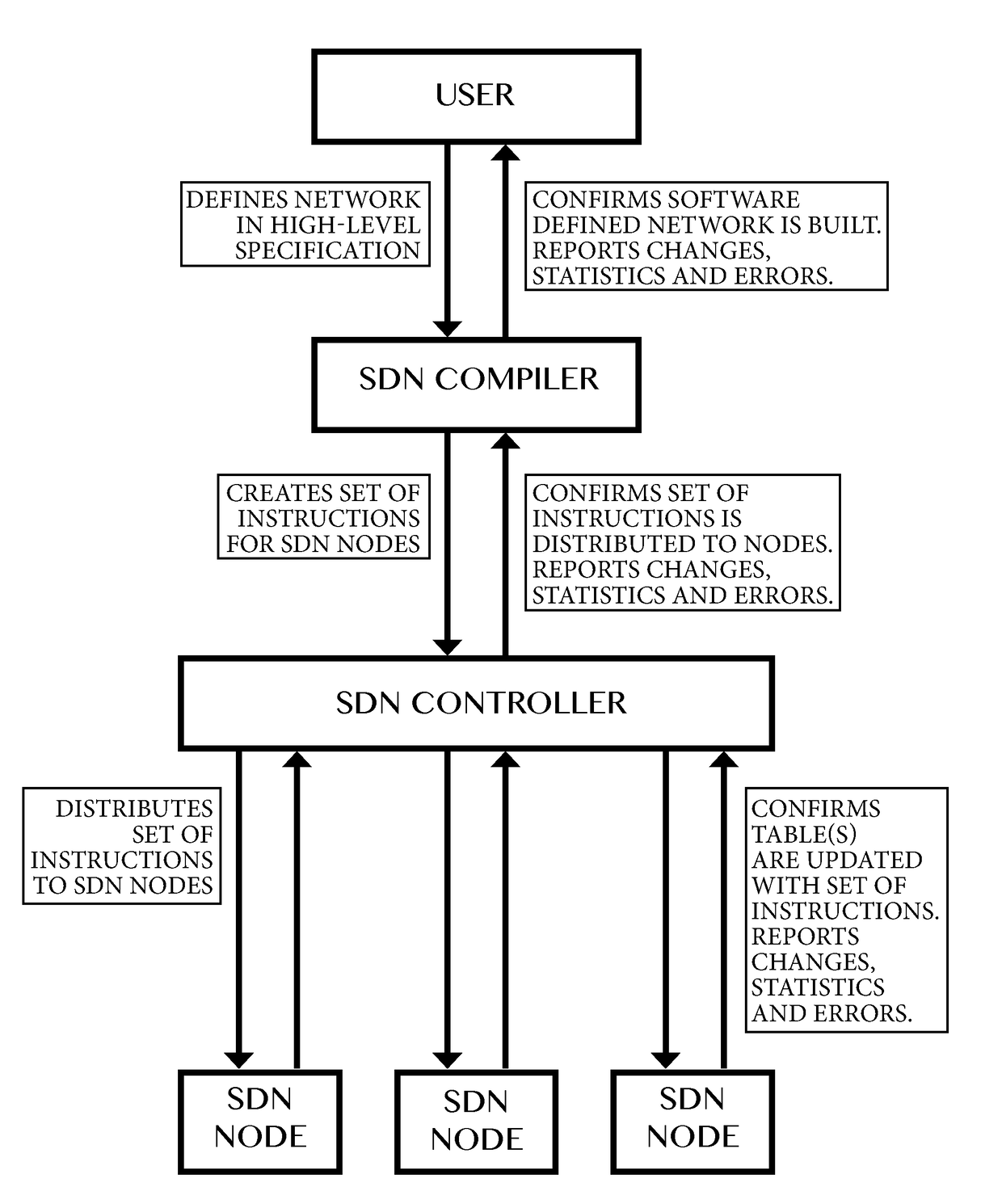
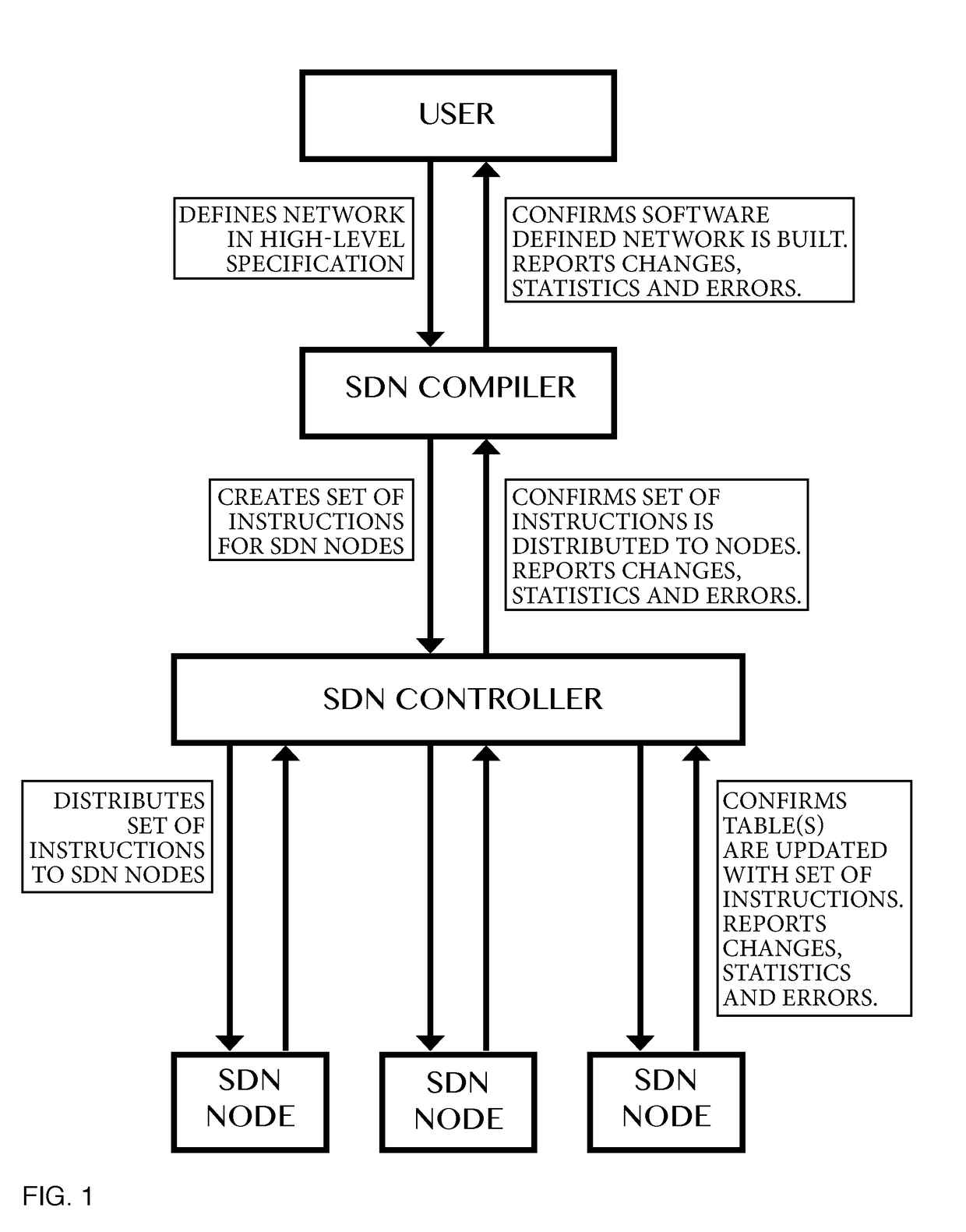
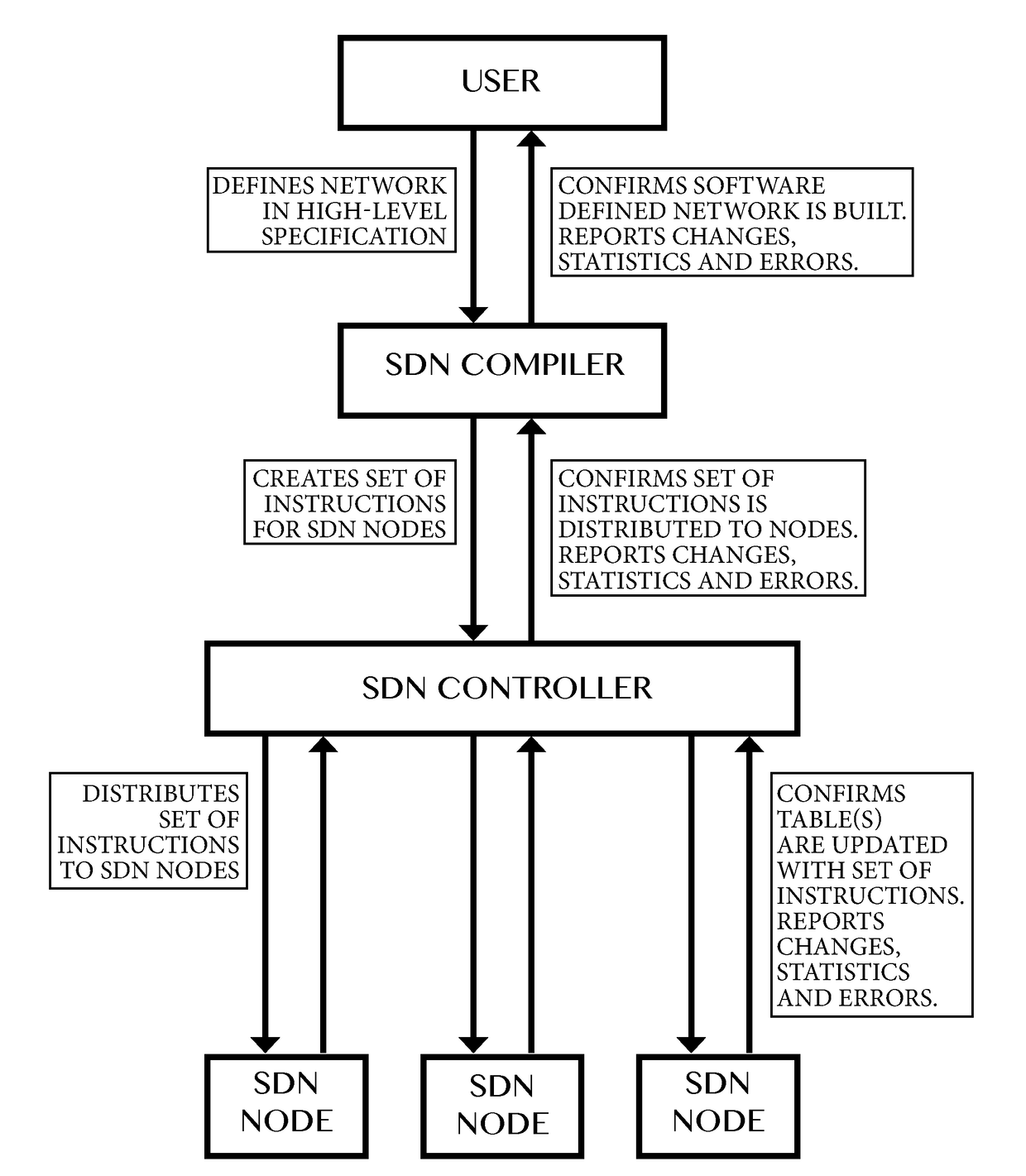
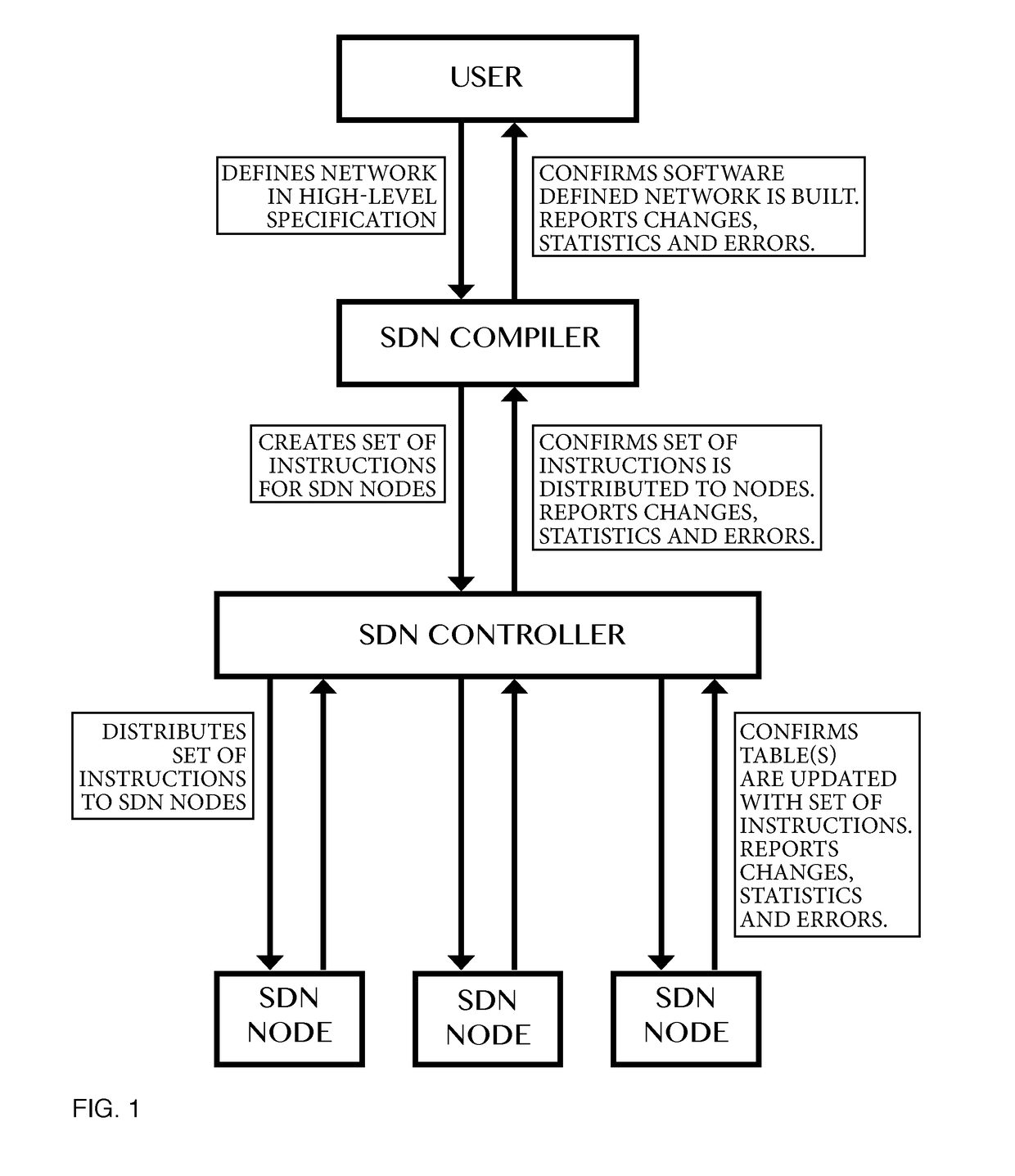
Compiler for and method of software defined networking, storage and compute performing operations
ActiveUS20170302530A1Increasing network programmabilityTightly coupledData switching networksMultiplexingDepth mapping
Method of and a compiler for controlling a network based on a logical network model. The network has physical nodes and logical nodes. The physical nodes are interconnected by physical links in accordance with a physical network layout. The logical network model has logical nodes indicated with a logical node name which refers to at least one physical node in the network. The method uses a depth-mapping relation defining how the logical nodes are mapped to the physical nodes. The method includes creating logical links between the logical nodes in dependence on the physical paths between the physical nodes and on the depth-mapping relation. The method uses edge-relationships between logical link, logical path, physical link, physical path and depth-mapping relations. Logical paths in the logical network are transformed into a physical path comprising of physical links between the physical nodes through recursive calculation and forwarding instructions are created for the physical nodes, in dependence on the edge-relationships and point-of-attachment names between physical links and physical nodes. A user of a compiler may specify additional operations other than switching, multiplexing or de-multiplexing to be performed at a logical node on packet or signal. Said packet or signal may be identified with a logical identifier identifying at least one logical link or logical path, and said additional operation may be specified at a logical node, providing programmability of additional operations in said logical network model. Said additional operations will, if possible, be performed by physical or virtual resources represented by physical nodes.
Owner:WOLTING HLDG
Saliency based disparity mapping
ActiveUS20140313191A1High disparityLarge shiftSteroscopic systems3D-image renderingParallaxDisplay device
A three dimensional [3D] image signal is processed for rendering 3D image data (33) on a specific 3D display, e.g. an auto-stereoscopic display. A first depth map (34) and saliency of the 3D image data are determined. A display depth sub-range (35) of a usable depth range (36) of the 3D display is determined and provides a higher 3D image quality for a viewer than the 3D image quality across the usable depth range. A depth mapping function is determined in dependence of the saliency data. The depth mapping function maps the first depth map to a second depth map for generating views for the 3D display. Advantageously the salient range of depth values is mapped towards the display depth sub-range.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Stereoscopic depth mapping
Provided is a method and apparatus for linear depth mapping. Linear depth mapping includes using algorithms to correct the distorted depth mapping of stereoscopic capture and display systems.
Owner:REAID INC
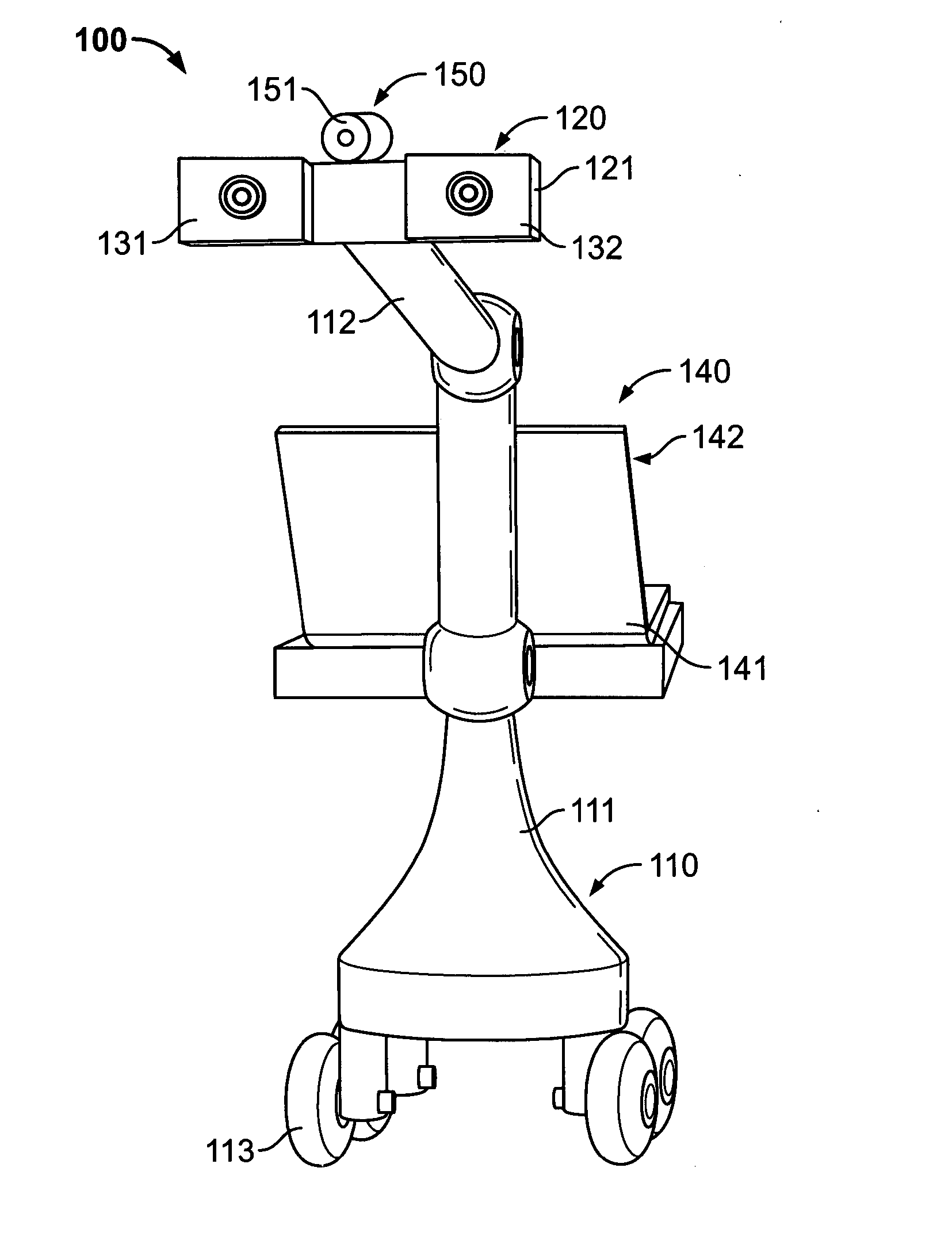
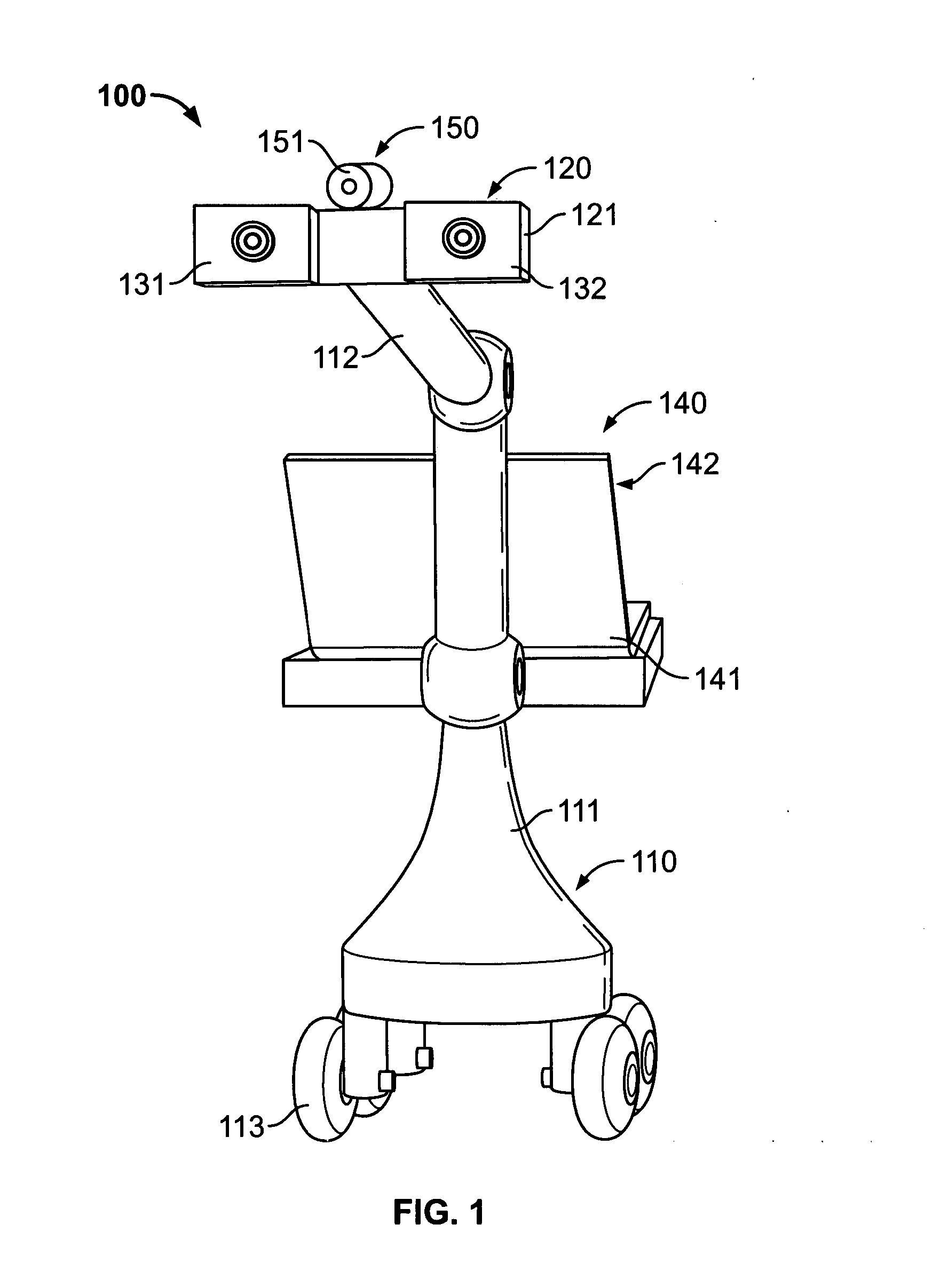
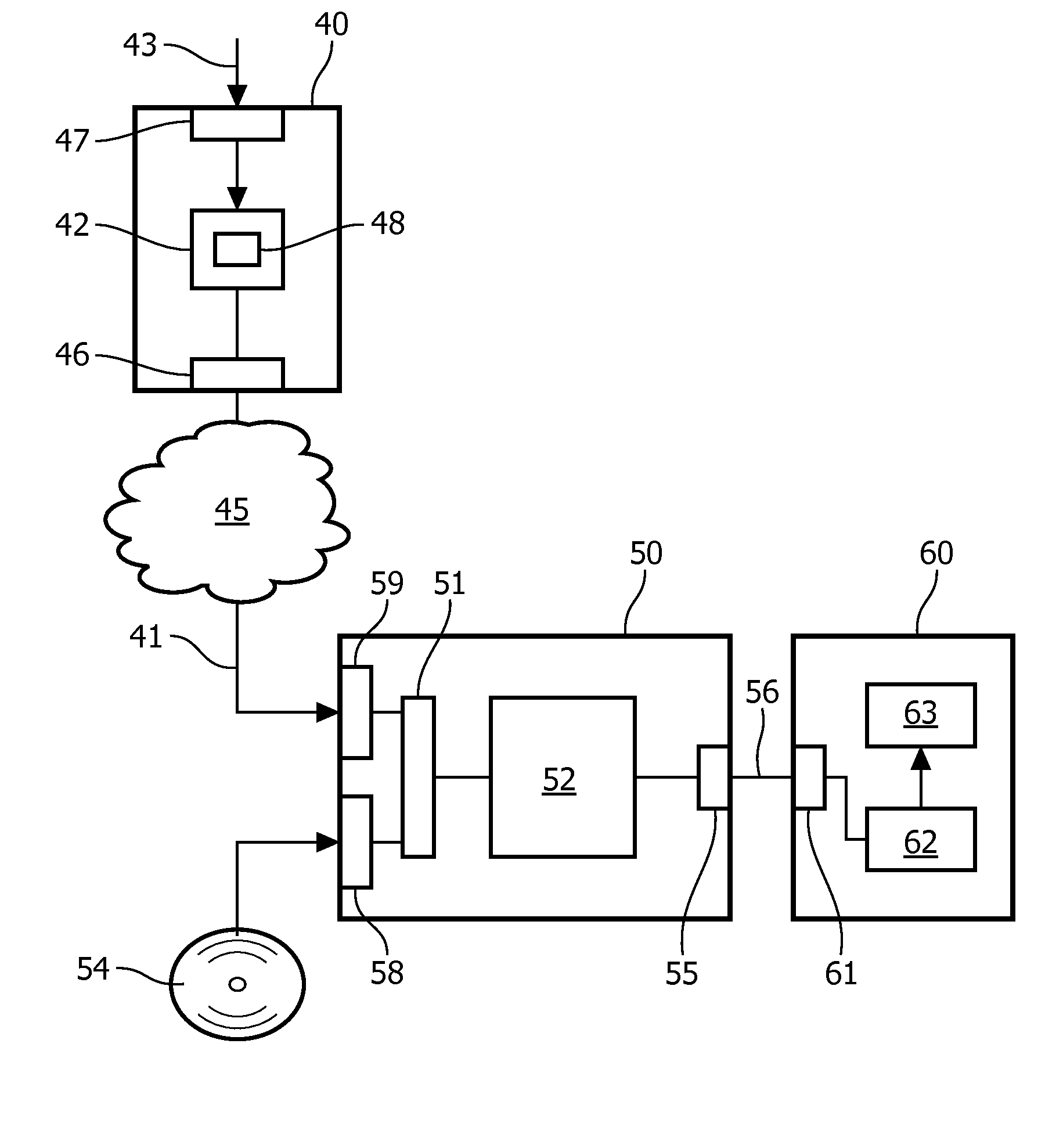
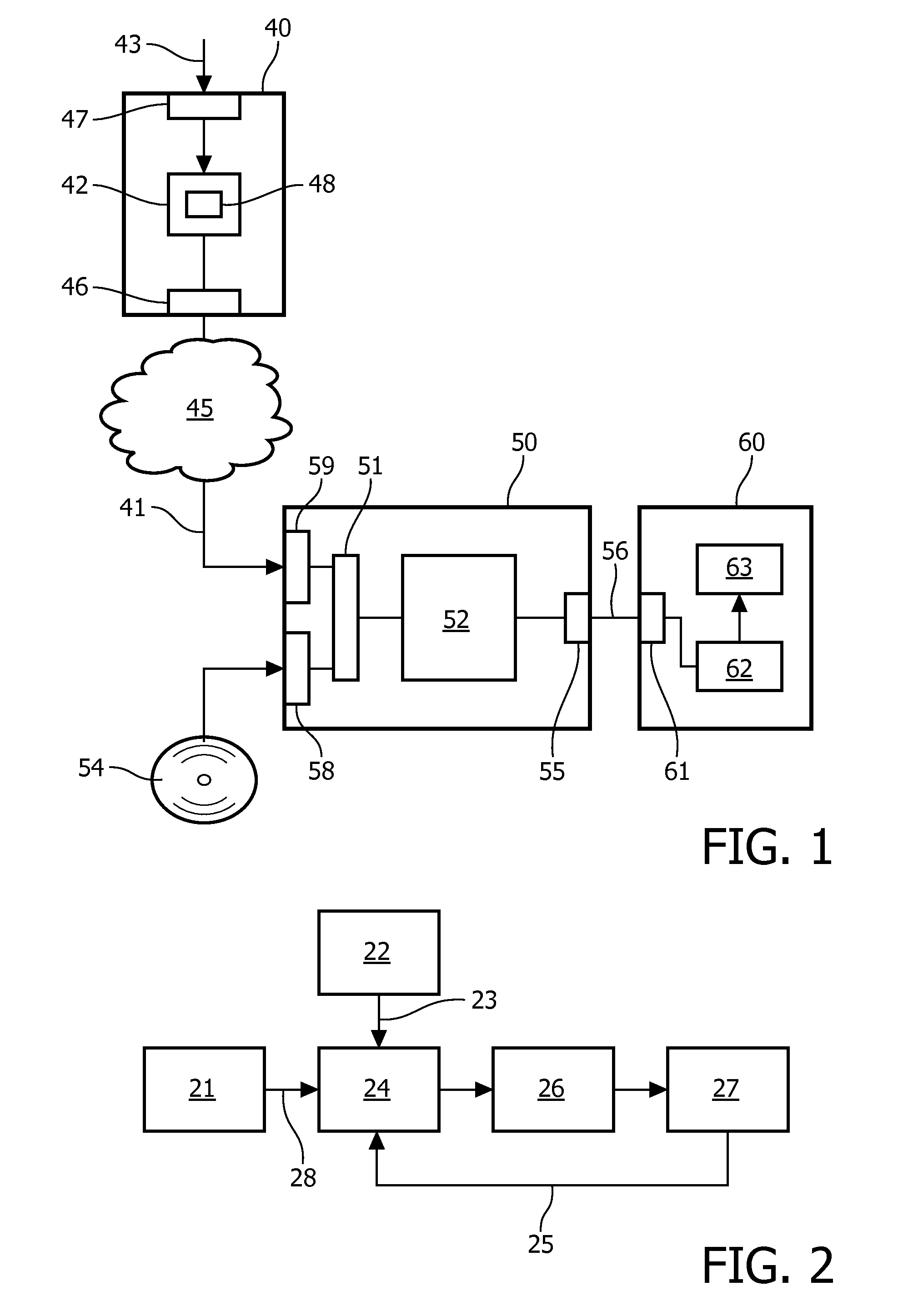
Depth mapping with a head mounted display using stereo cameras and structured light
ActiveUS20180157342A1Input/output for user-computer interactionLaser detailsDisplay deviceStereo cameras
A tracking system generates a structured light pattern in a local area. The system includes an array of lasers that generate light. The array of lasers includes a plurality of lasers and an optical element. The plurality of lasers are grouped into at least two subsets of lasers, and each of the at least two subsets of lasers is independently switchable. The optical element includes a plurality of cells that are each aligned with a respective subset of the array of lasers. Each cell receives light from a corresponding laser of the array of lasers, and each cell individually applies a modulation to the received light passing through the cell to form a corresponding portion of the structured light pattern that is projected onto a local area.
Owner:META PLATFORMS TECH LLC
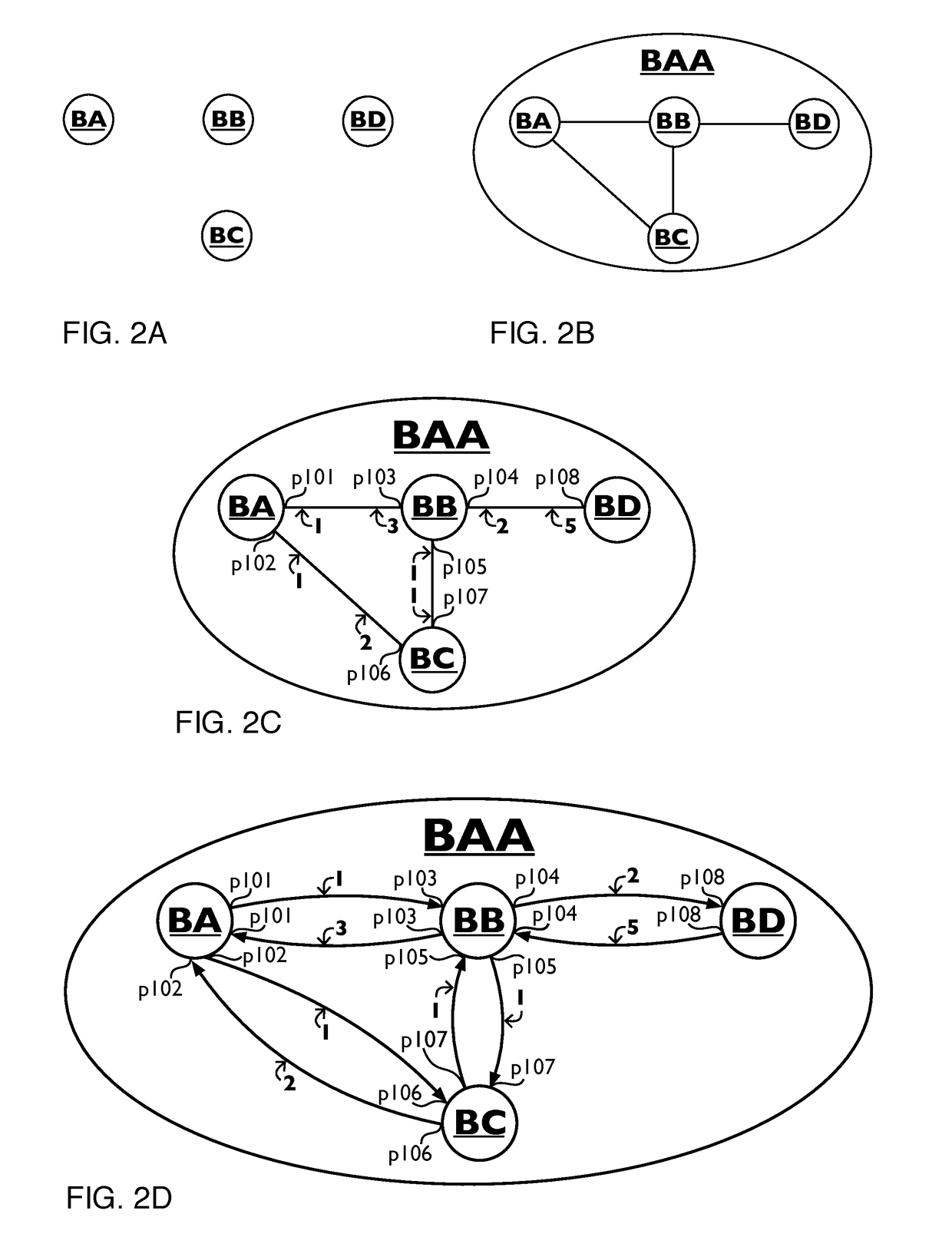
Compiler for and method of software defined networking, storage and compute determining physical and virtual resources
ActiveUS20170310574A1Less complex forwarding hardwareEasy to operateData switching networksDepth mappingLogical network
Method of and a compiler for controlling a network based on a logical network model. The compiler determines physical and / or virtual resources, comprising of physical nodes and physical links, against which the logical model can be compiled. The network has known physical nodes, unknown physical nodes and logical nodes. The known physical nodes are “physical nodes” which are existing or still to be setup (virtual) nodes in the network. The known physical nodes are interconnected by physical links in accordance with a physical network layout. The logical network model has logical nodes indicated with a logical node name which refers to at least one known physical node or one unknown physical node in the network. The method uses a depth-mapping relation defining how the logical nodes are mapped to the known physical nodes and the unknown physical nodes. The term “unknown physical node” is used to define an imaginary physical node to which logical nodes can be mapped through depth-mappings and which are to be substituted by a physical node of the network of which the physical node name is stored. The method includes creating logical links between the logical nodes in dependence on the paths between the known physical nodes and / or the unknown physical nodes and on the depth-mapping relation. Known physical nodes are determined for unknown physical nodes and known physical paths are determined for unknown physical paths between unknown physical nodes by performing a search. The method uses edge-relationships between logical link, logical path, physical link, physical path and depth-mapping relations. Logical paths in the logical network are transformed into a physical path comprising of physical links between the physical nodes through recursive calculation and forwarding instructions are created for the physical nodes, in dependence on the edge-relationships and point-of-attachment names between physical links and physical nodes.
Owner:WOLTING HLDG
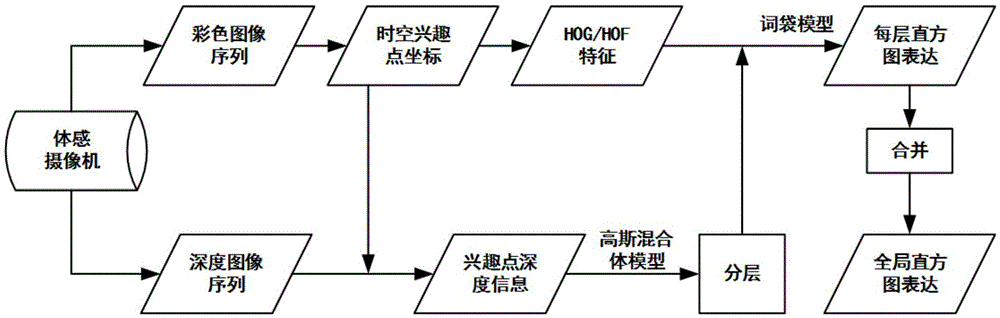
Human motion recognition feature expression method based on depth mapping
InactiveCN105590096AImprove accuracyEasy to operateCharacter and pattern recognitionColor imageCluster algorithm
The invention relates to the technical field of pattern recognition and specifically to a human motion recognition feature expression method based on depth mapping. The human motion recognition feature expression method based on depth mapping is easy to implement, increases the accuracy of motion recognition, and comprises steps of: extracting, from a color image sequence of a motion-sensing video camera, a human motion space-time interest point p; computing a light stream feature and a gradient feature in the color image sequence by revolving around the human motion space-time interest point p; finding out, from a depth image sequence of the motion-sensing video camera, a corresponding human motion space-time interest point p' and acquiring the depth value of the p'; dividing the p into N layers according to the depth value of the p' and on the basis of a Gaussian mixture model, constructing multichannel expression based on depth mapping, clustering the space-time interest point of each layer by using a clustering algorithm and expressing the space-time interest point of each layer by using a bag-of-word model to obtain a histogram vector; and connecting the feature expression of each layer to form a feature S=(H1,..,Hi,..,Hn). The method is mainly used in the aspect of human motion recognition.
Owner:YUNCHENG UNIVERISTY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com