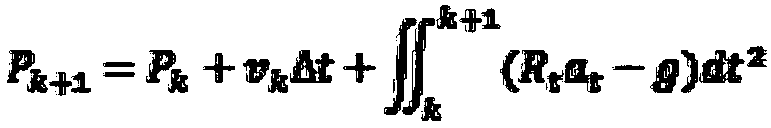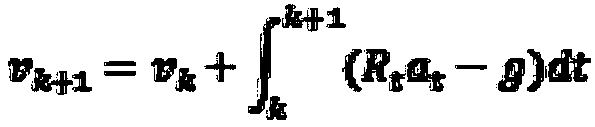Patents
Literature
135 results about "Odometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Odometry is the use of data from motion sensors to estimate change in position over time. It is used in robotics by some legged or wheeled robots to estimate their position relative to a starting location. This method is sensitive to errors due to the integration of velocity measurements over time to give position estimates. Rapid and accurate data collection, instrument calibration, and processing are required in most cases for odometry to be used effectively.
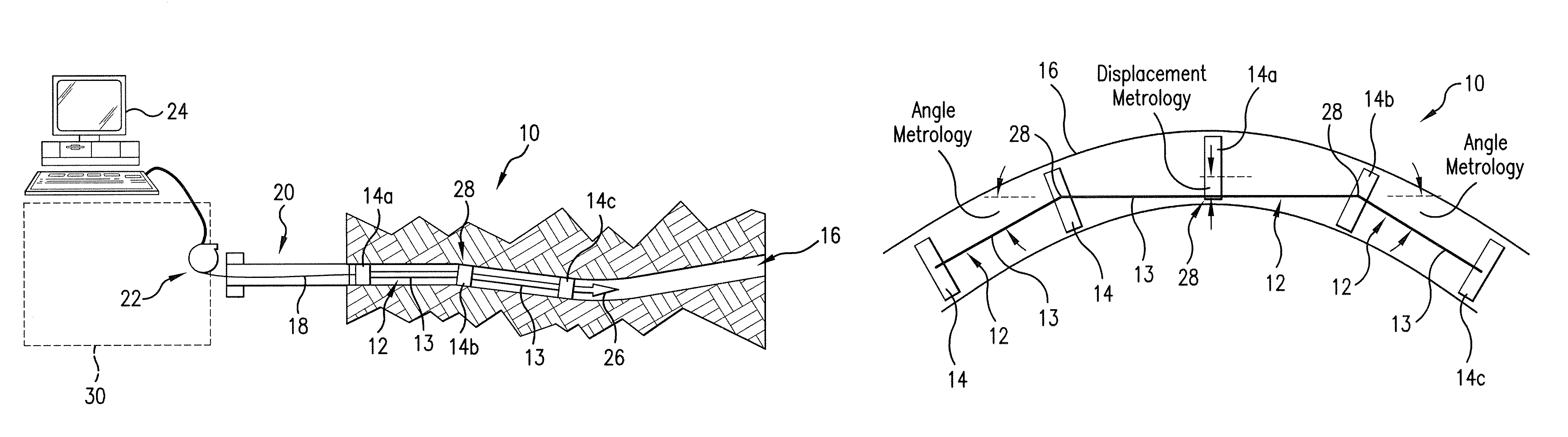
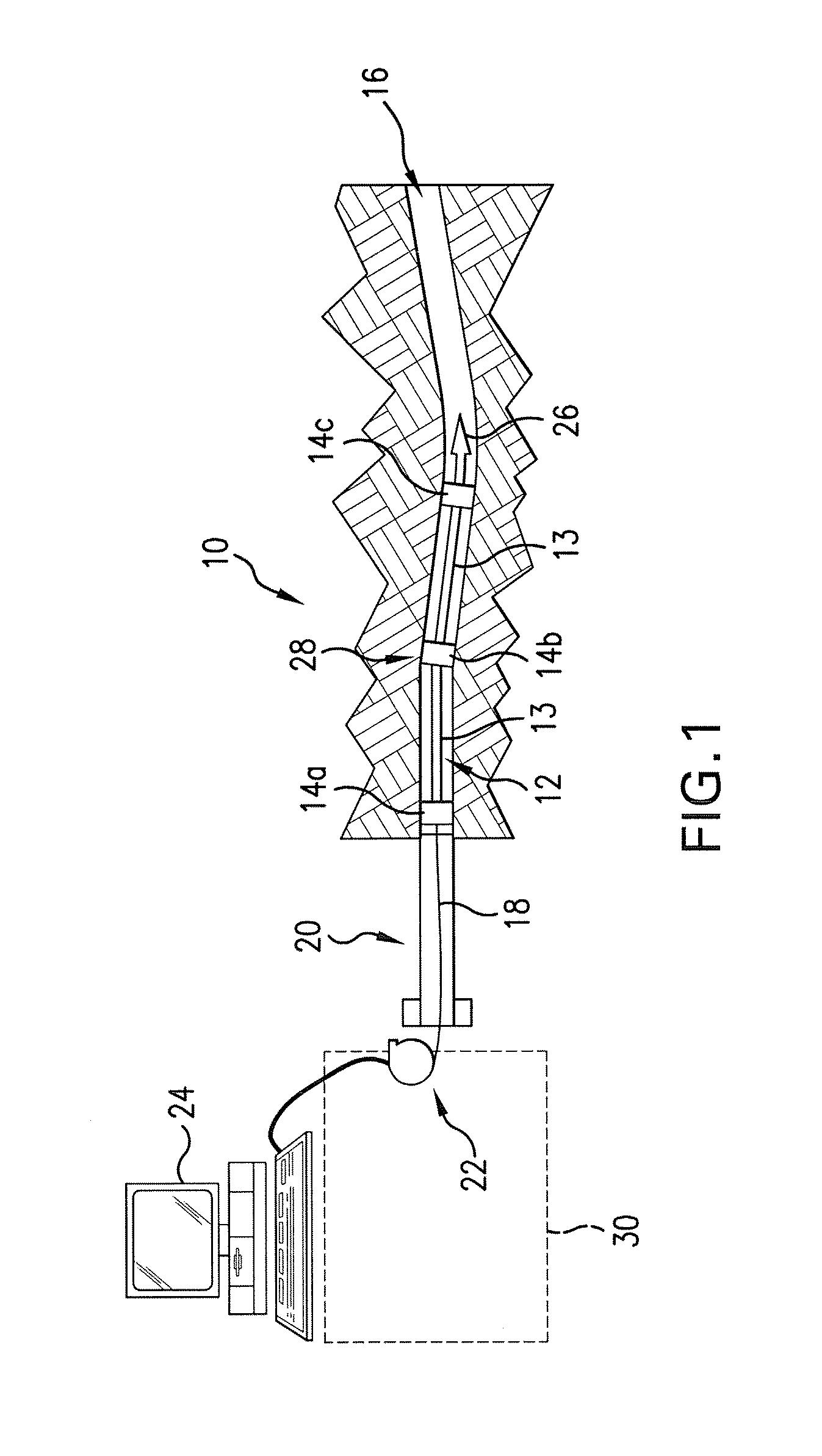
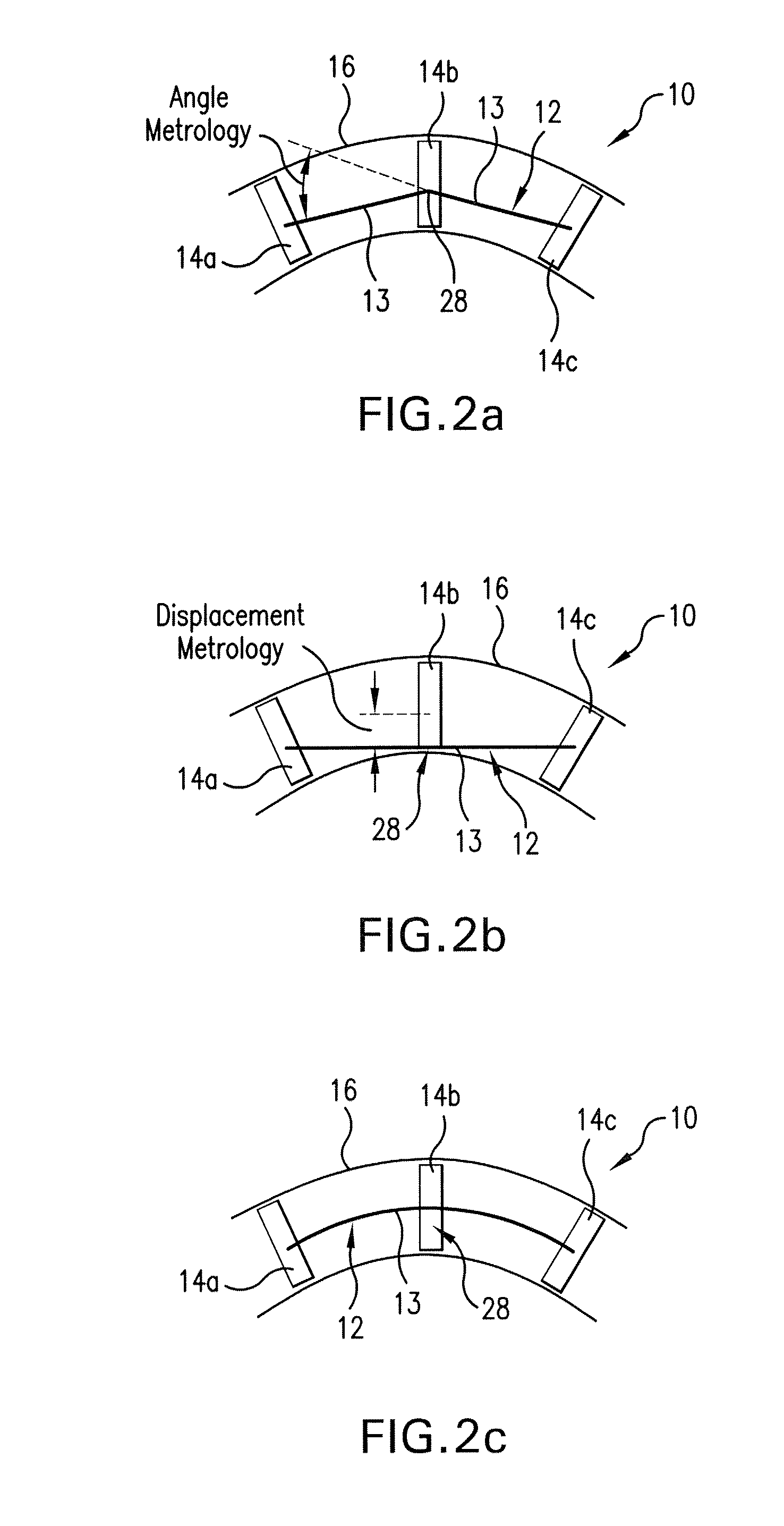
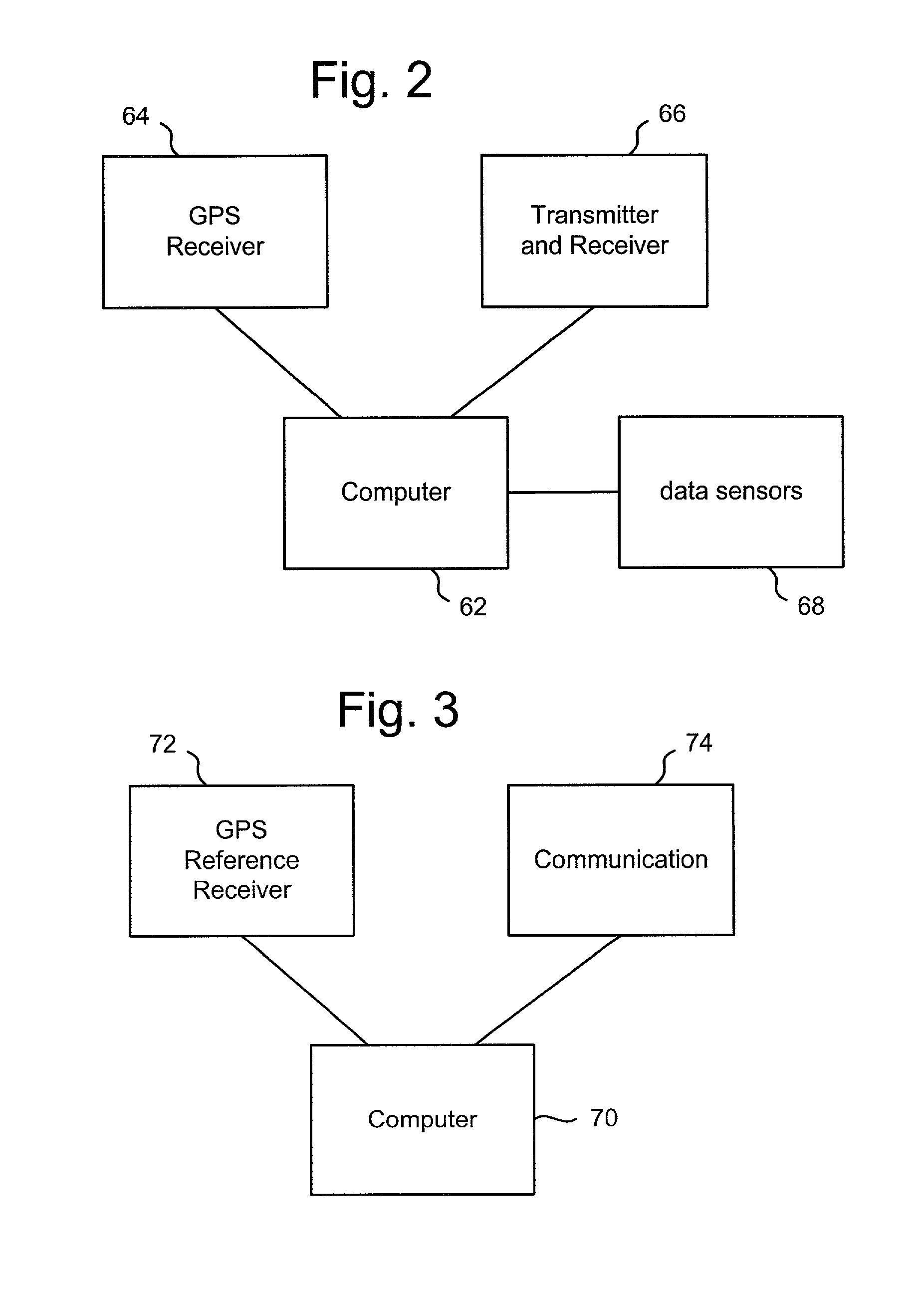
Self-contained positioning method and system thereof for water and land vehicles
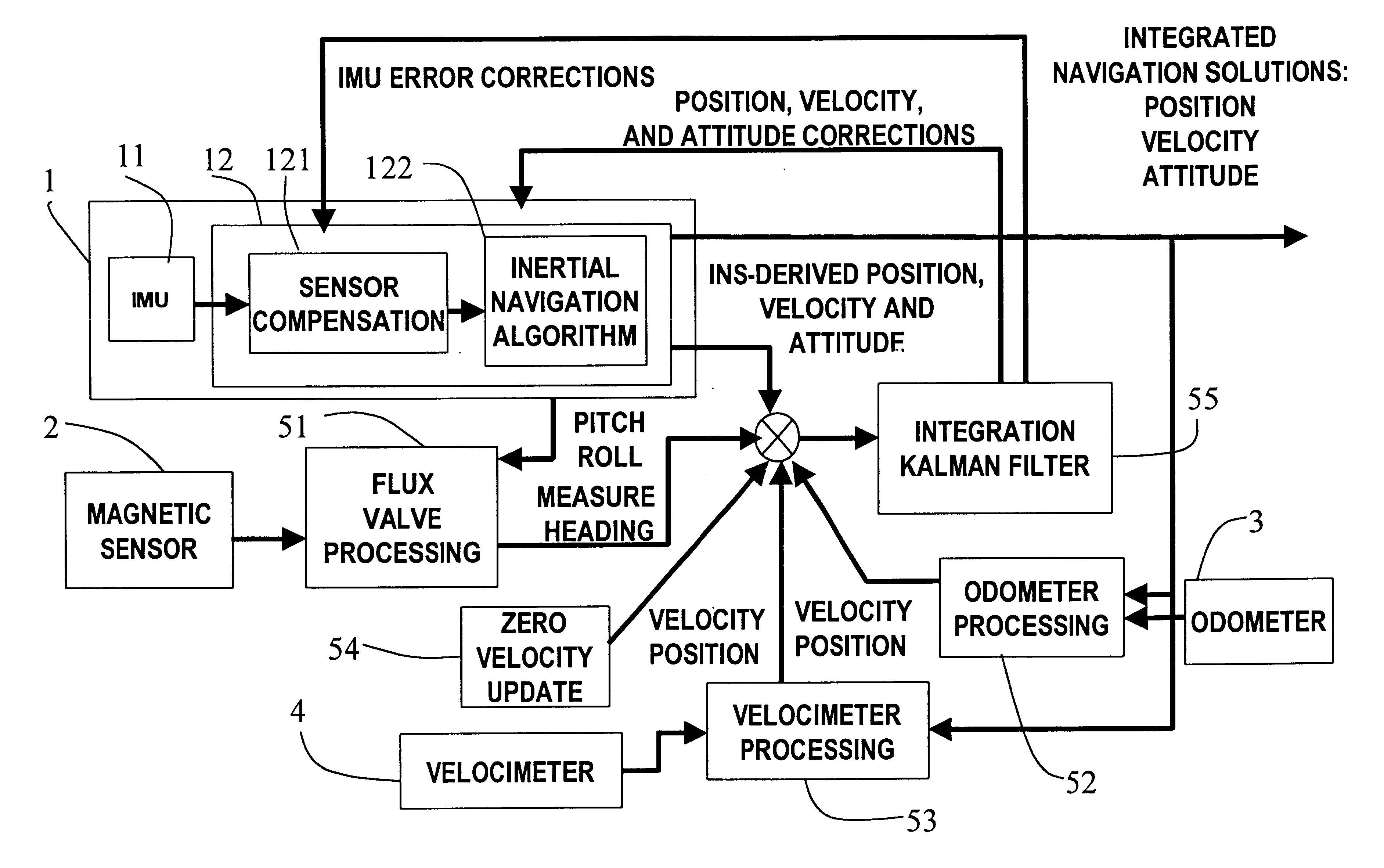
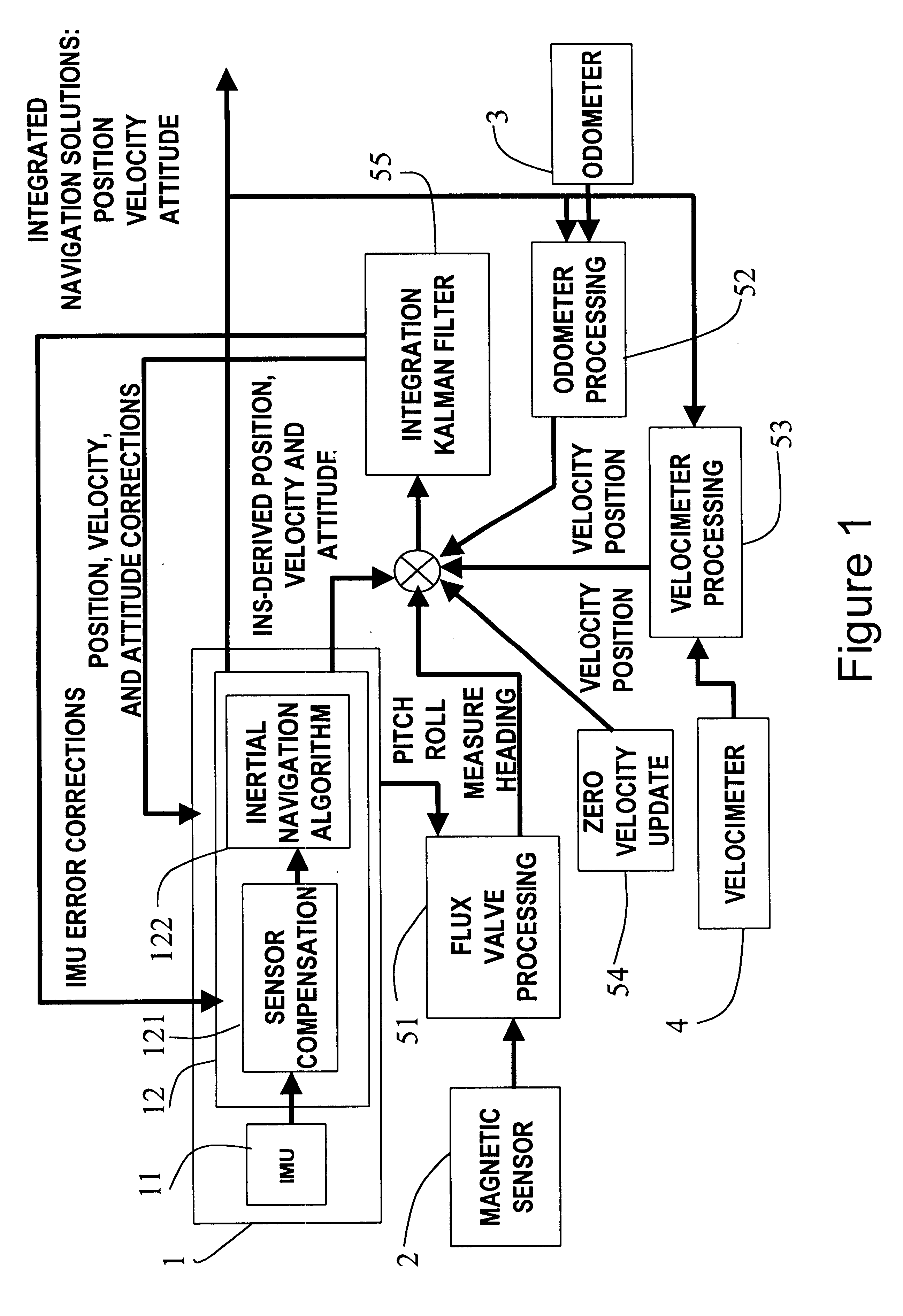
A positioning method and system for water and land vehicles is disclosed for highly accurate and self-contained operation. In which, an inertial navigation system (INS) is built on the micro MEMS (MicroElectroMechanicalSystem) IMU that is the core of the position determination system. To compensate the error of the INS, multiple navigation sensors are integrated into the system. The magnetic sensor is used as a magnetic field sensor to measure the heading of the vehicle. The odometer is used to measure the distance when the vehicle is on land. An automated Zero velocity updating method is used to calibrate the ever increasing INS errors. When the vehicle is in the water, a velocimeter is used to measure water speed for the INS aiding.
Owner:AMERICAN GNC
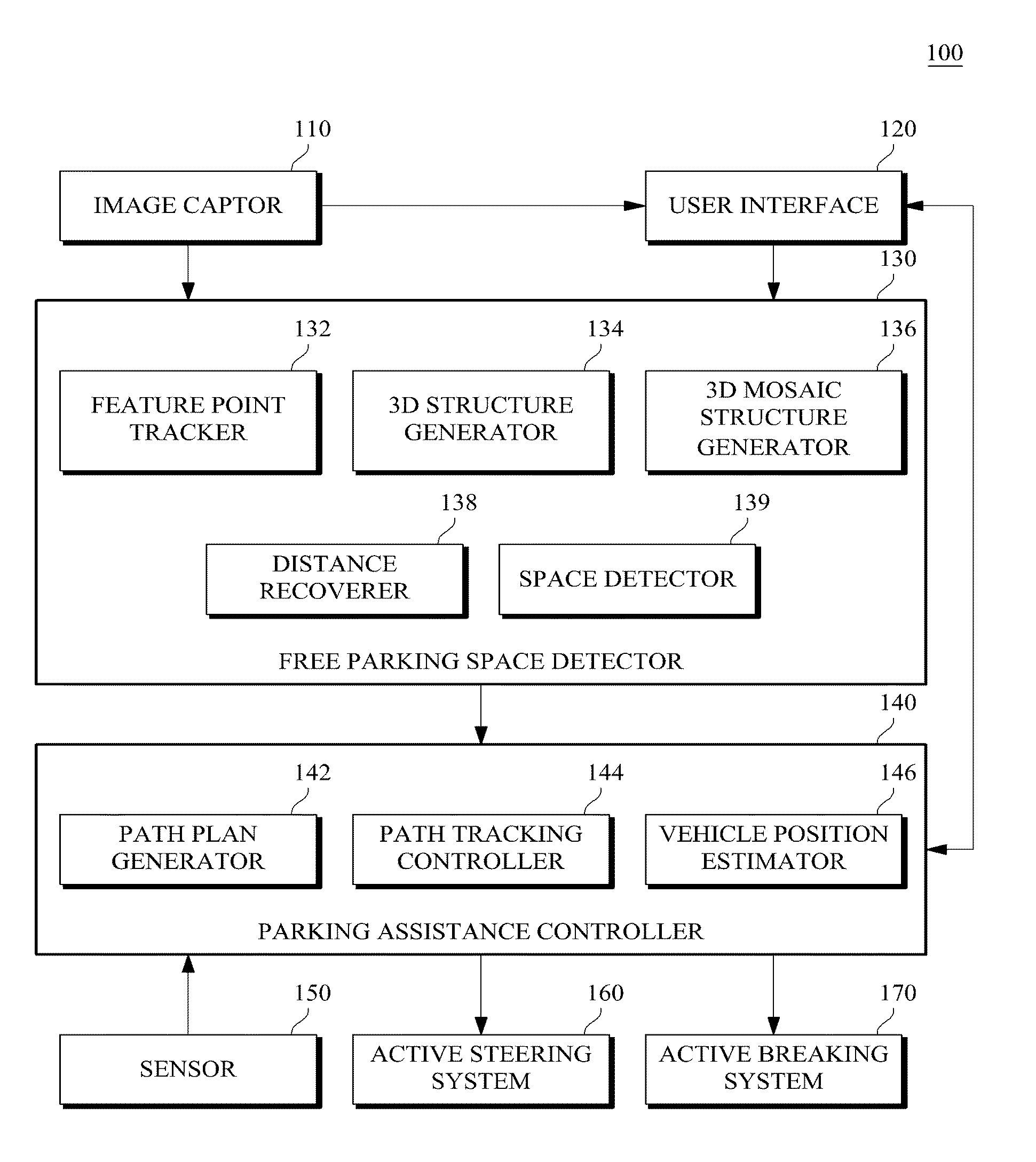
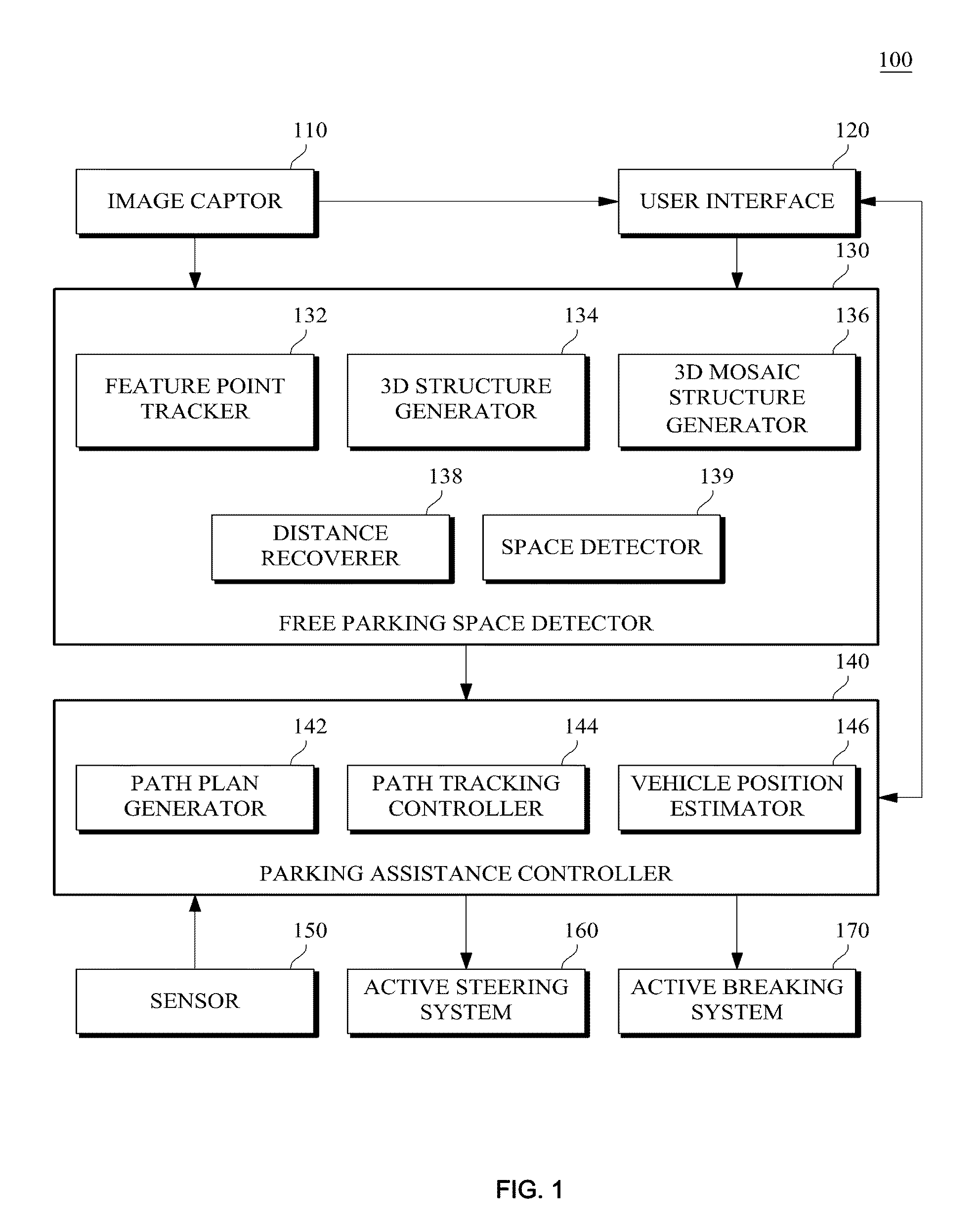
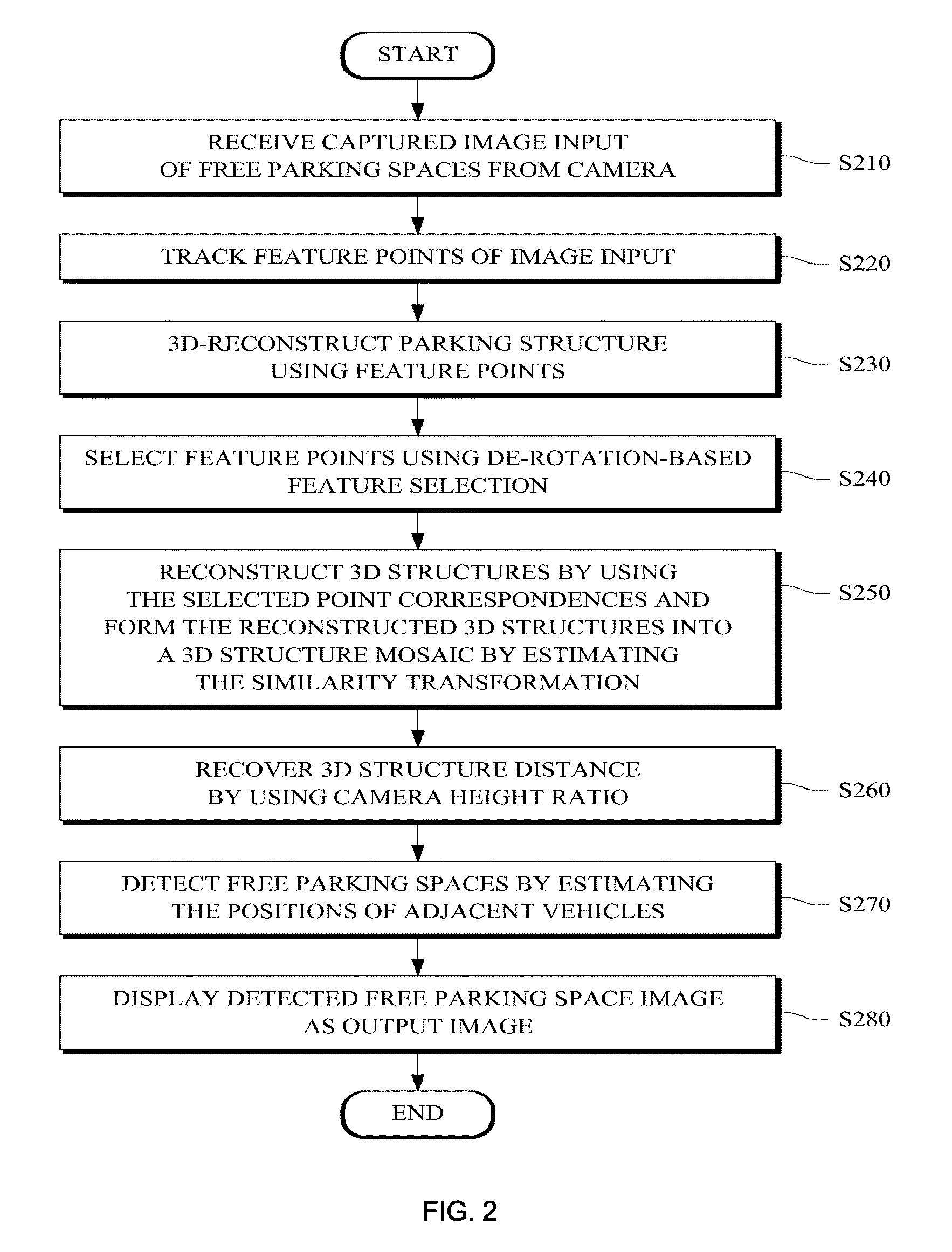
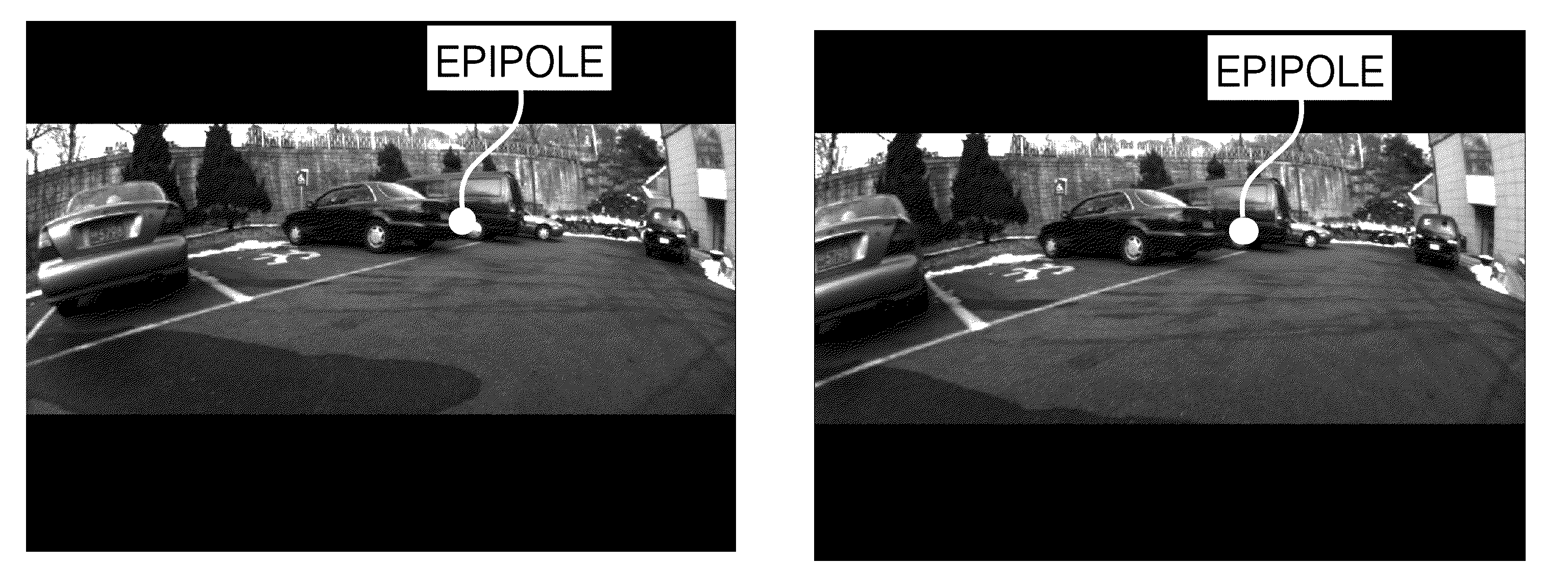
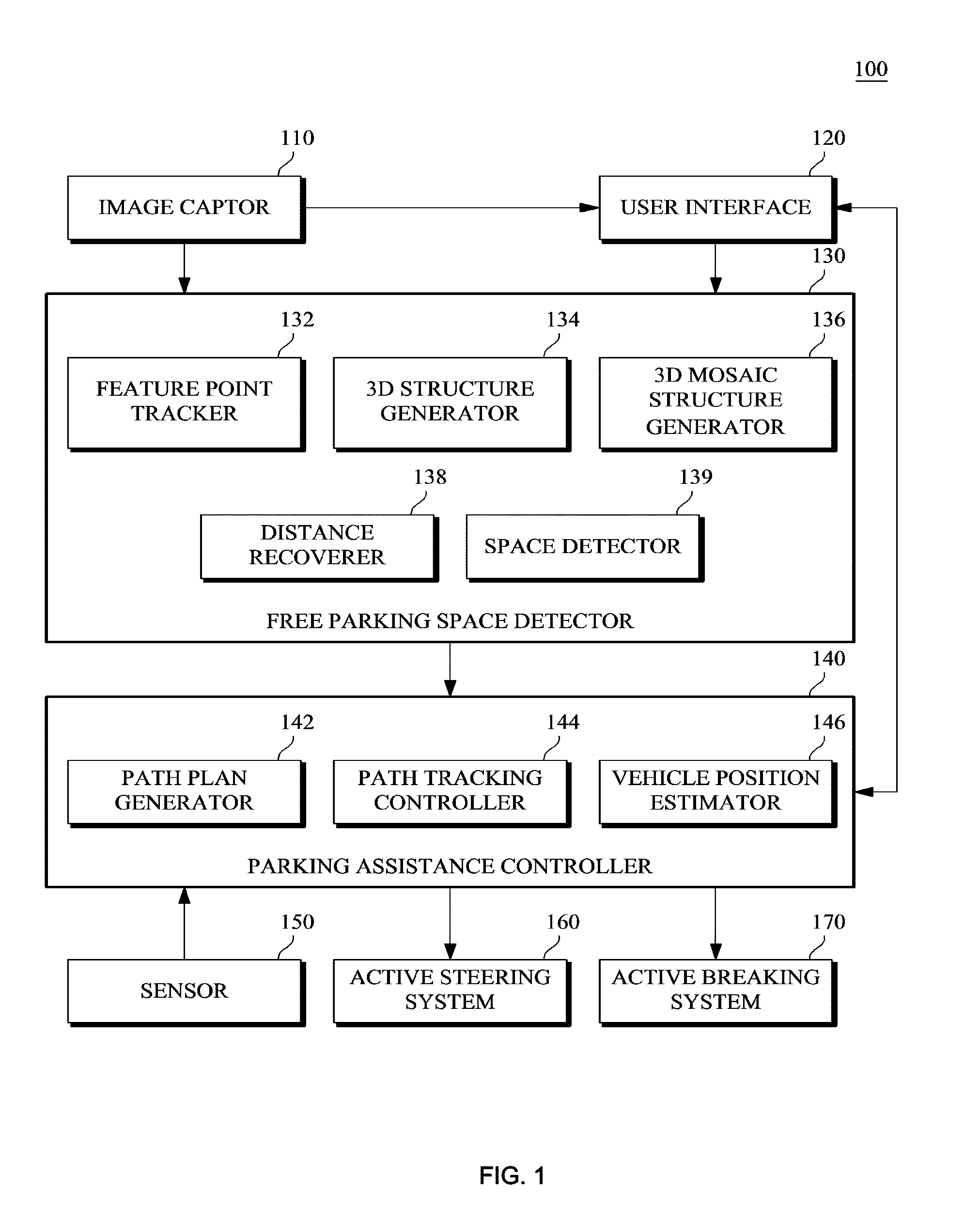
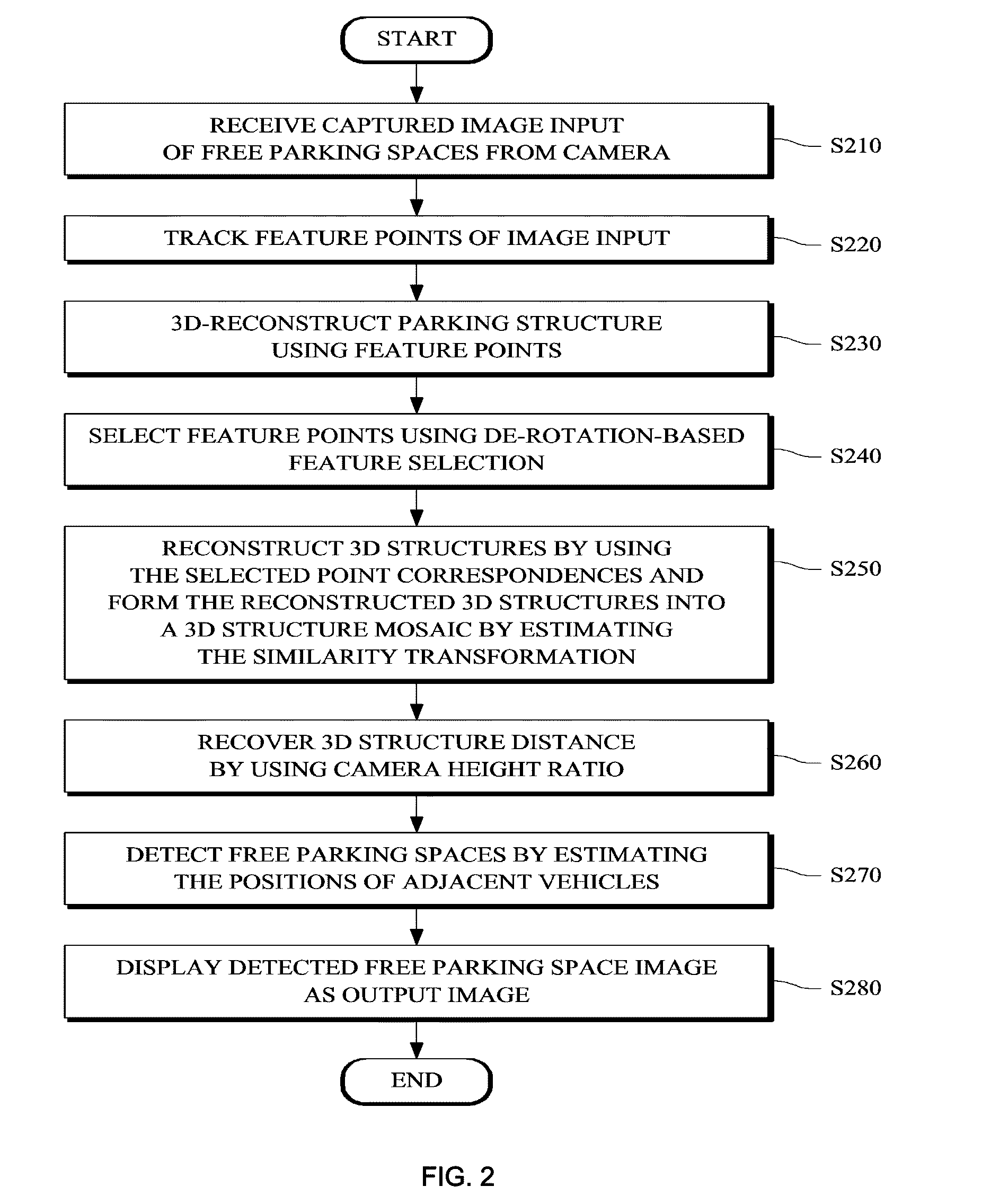
Monocular motion stereo-based free parking space detection apparatus and method
ActiveUS20090243889A1Solve the degradation problemEffective positioningImage enhancementImage analysisOdometryBase free
A monocular motion stereo-based automatic free parking space detection system is disclosed. The system acquires image sequences with a single rearview fisheye camera, three-dimensionally reconstructs the vehicle rearview by using point correspondences, and recovers metric information from a known camera height to estimate the positions of adjacent vehicles thereby detecting the free parking spaces. By using de-rotation-based feature selection and 3D structure mosaicking the degradation of the 3D structure near the epipole is solved and it is not necessary to use the unreliable odometry due to its accuracy depending on road conditions.
Owner:HL KLEMOVE CORP
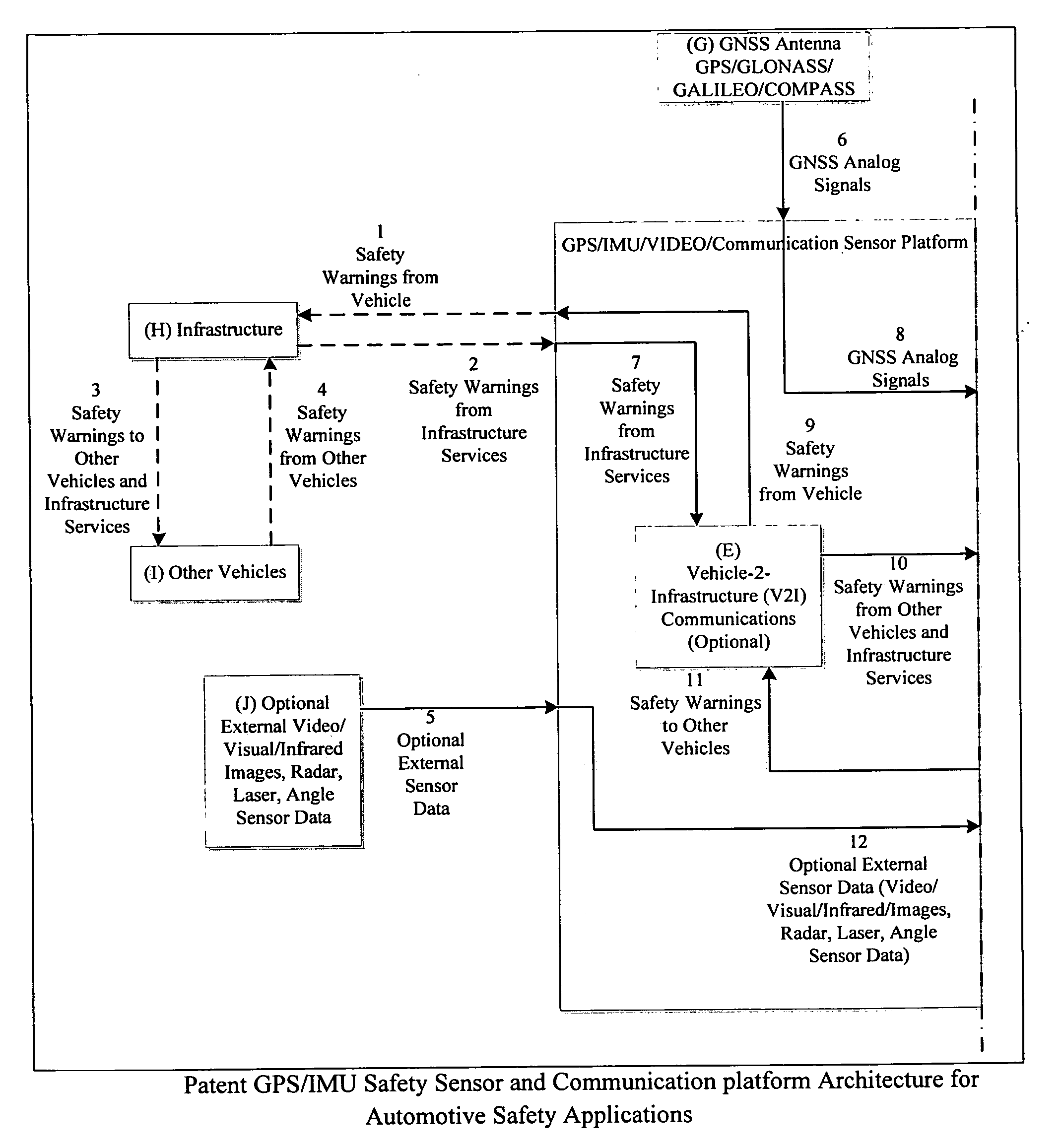
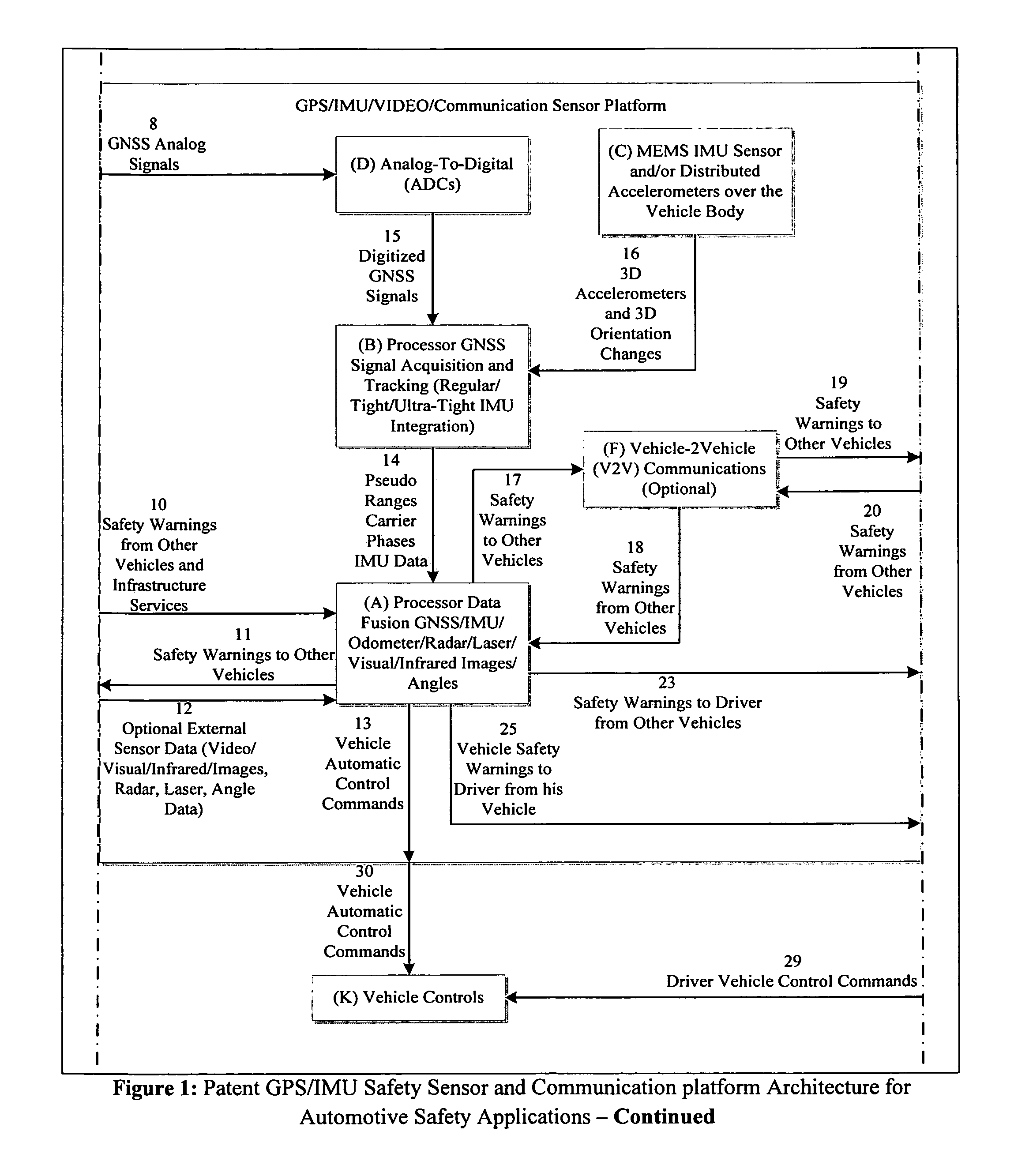
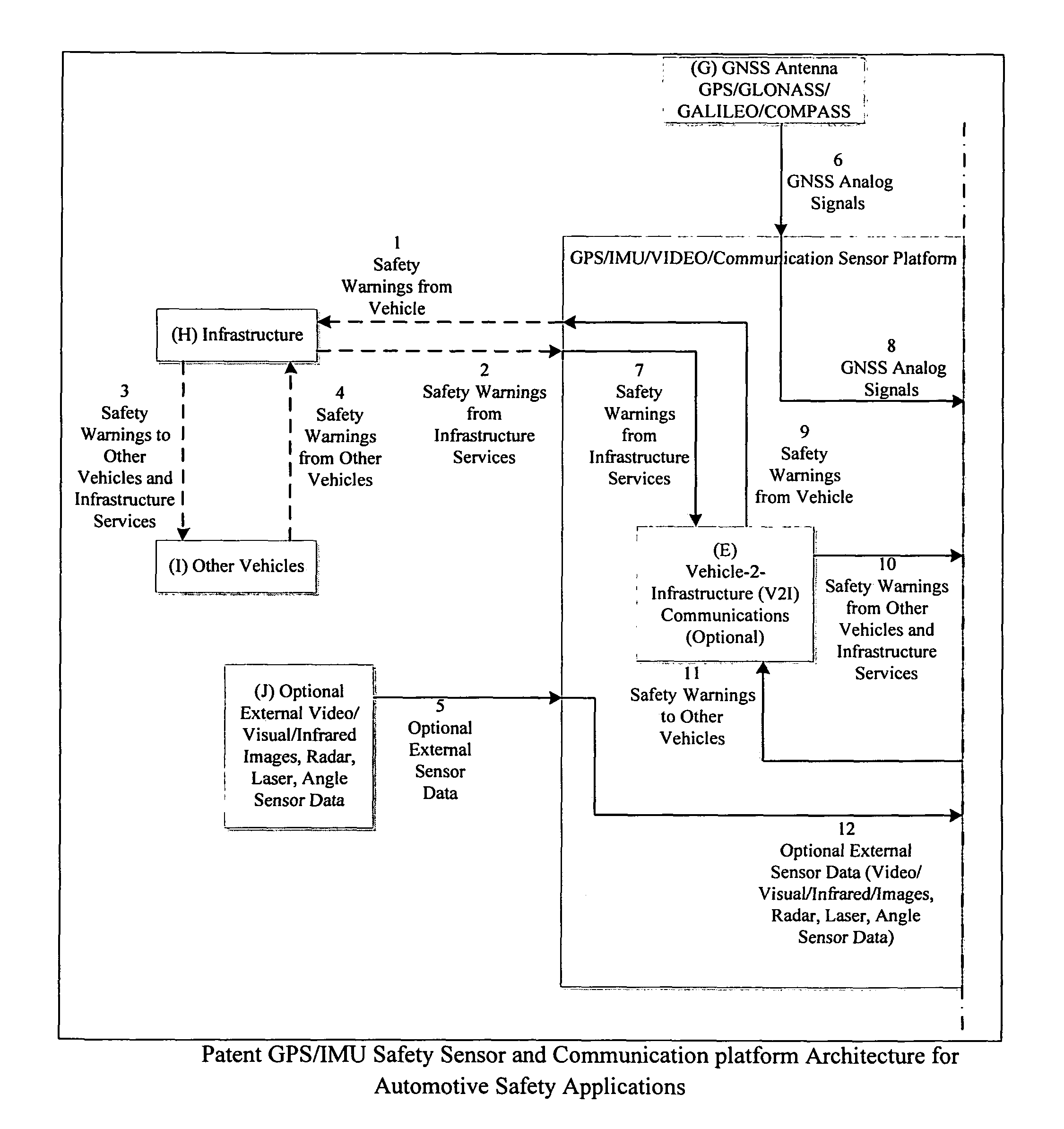
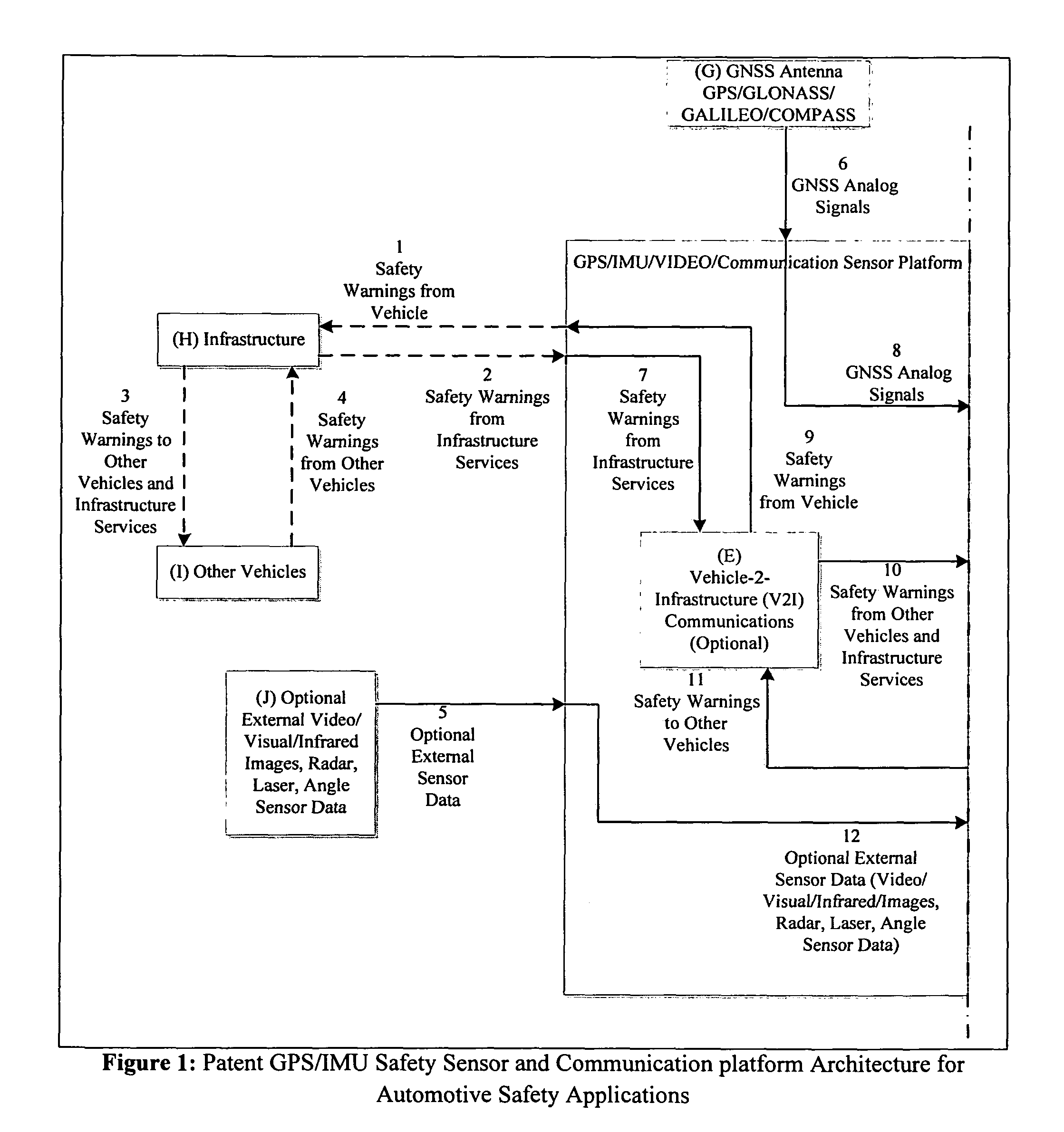
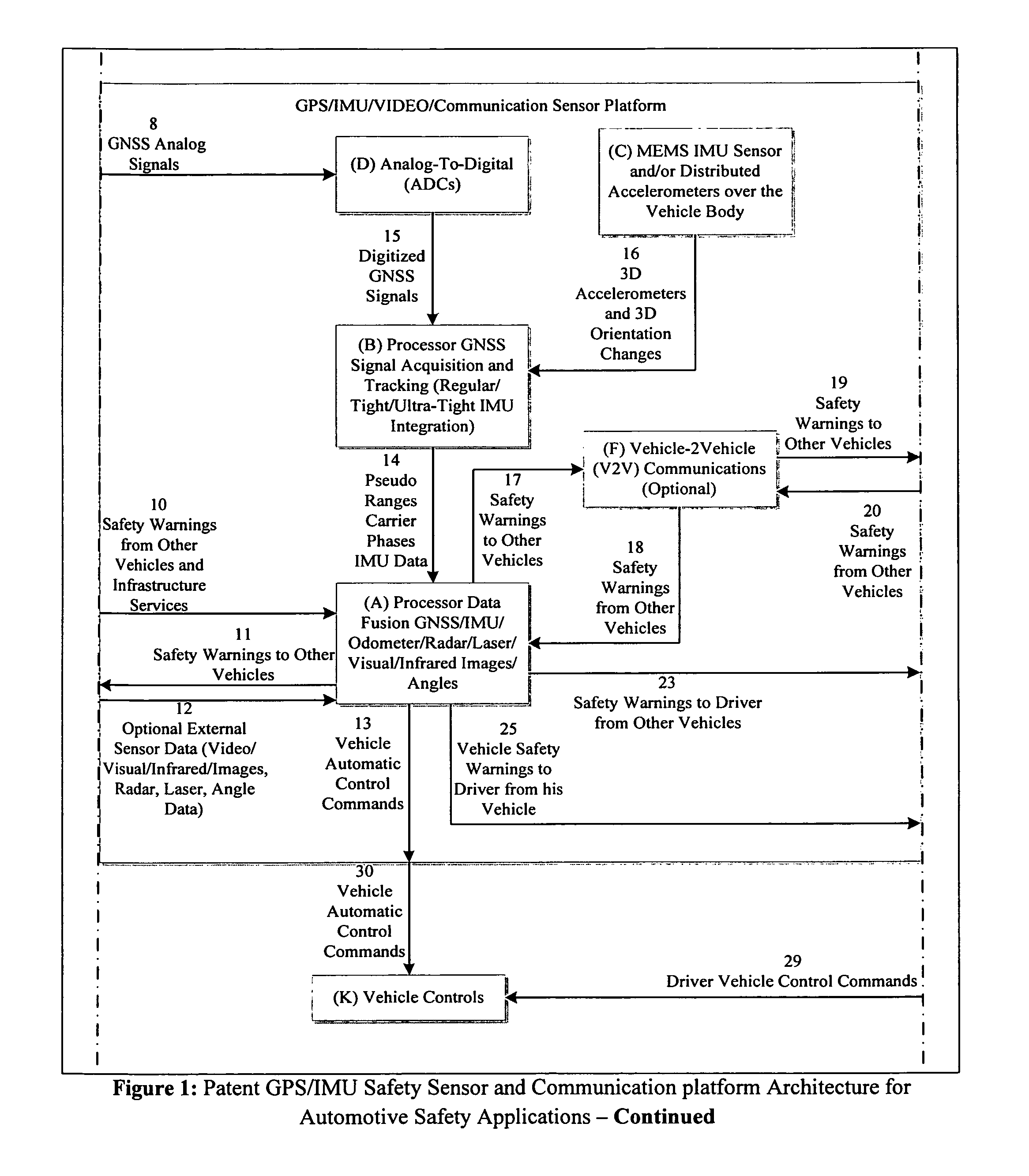
GPS/IMU/Video/Radar absolute/relative positioning communication/computation sensor platform for automotive safety applications
ActiveUS20120290146A1Establish situational awarenessPrevent unavoidable accidentsDigital data processing detailsAnti-collision systemsDriver/operatorAccelerometer
A GPS / IMU safety sensor platform is proposed, consisting of data fusion Processors, GNSS Signal Acquisition and Tracking Processors, MEMS IMU sensors, one or multiple accelerometers able to provide orientation information, optional V2V communication modules, and optional V2I communication modules. The data fusion processors provide interface ports to GNSS / IMU processors, odometers, video (Visual / Infrared) cameras installed in the vehicle, V2V relative positioning sensors (laser, radar or any other distance measuring), and V2V and V2I communication modules. The data fusion processors are interfaced to a driver warning system and optionally to the vehicle controls for providing safety warning messages to drivers, or for automatic control the vehicle for preventing and reducing accidents.
Owner:UATC LLC
Spatial data collection apparatus and method
A spatial data collection apparatus collects and correlates spatial data for use in creating floor plans, maps and models of existing spaces. The apparatus includes a mobile platform with wheels to allow movement around a space. One or more positional sensors on the platform generate positional data related to a position of the platform. The positional data can include odometry data and optionally gyroscopic data for correcting the odometry data. One or more range-finding devices on the platform measure and calculate range data (e.g., 2-D or 3-D) relating to distances and angles between the platform and objects in the space. The apparatus collects, fuses and correlates the positional data and range data to produce spatial data and stores the spatial data for transfer to a PC for use in creating, viewing and / or editing a map of the space. The apparatus can also record media files (e.g., audio, video, or images) to be associated with locations within the map.
Owner:ORMON CORP
Centralizer-based survey and navigation device and method
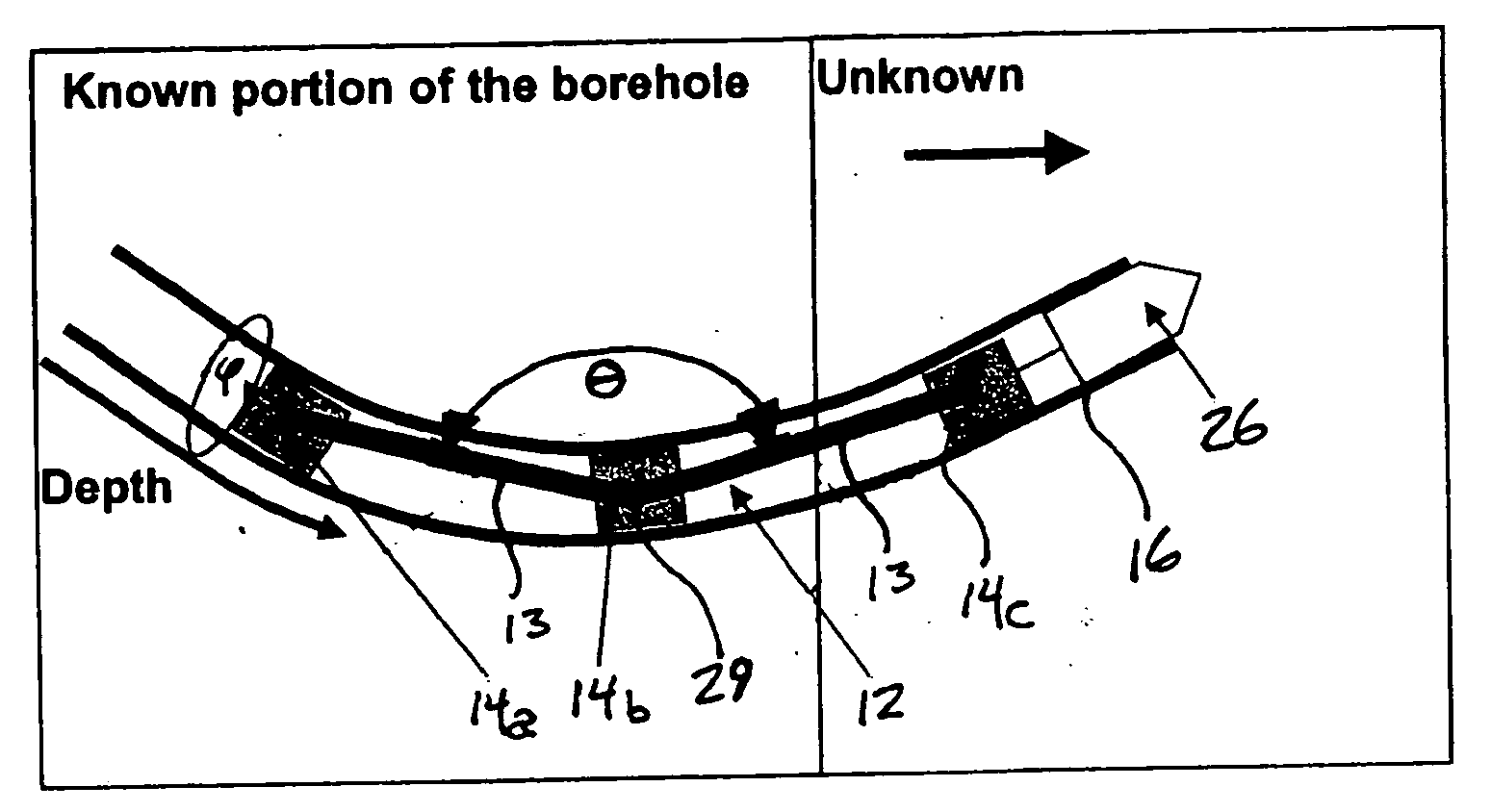
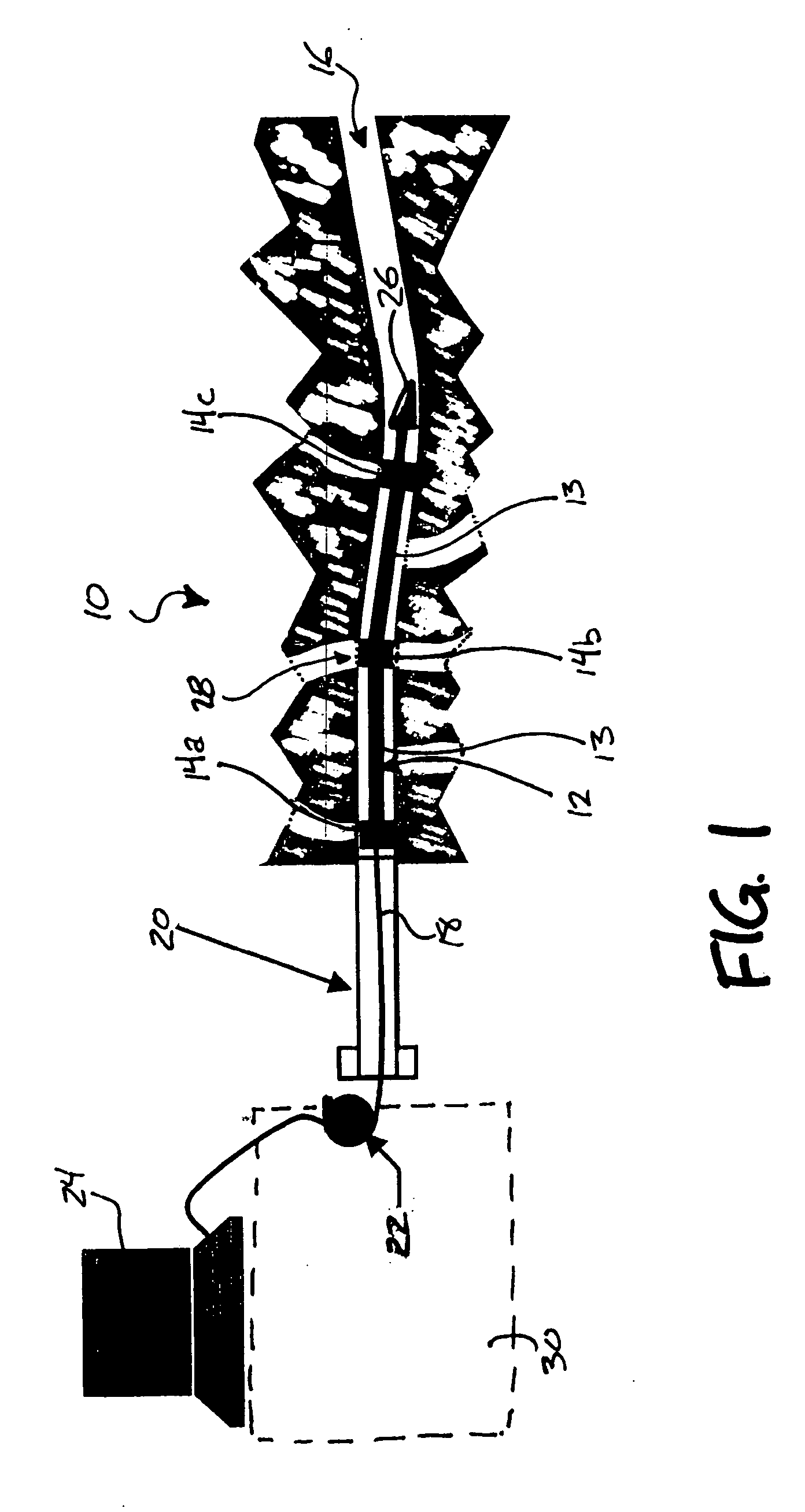
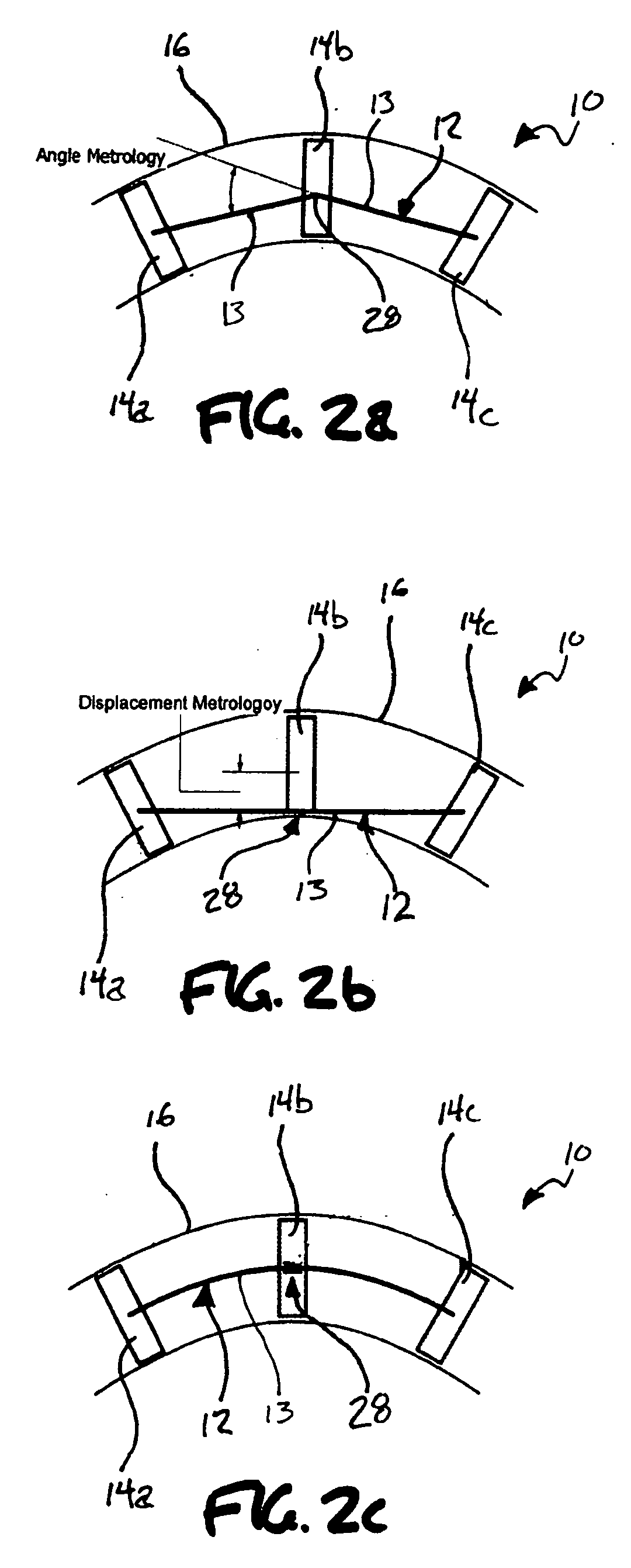
A Centralizer based Survey and Navigation (CSN) device designed to provide borehole or passageway position information. The CSN device can include one or more displacement sensors, centralizers, an odometry sensor, a borehole initialization system, and navigation algorithm implementing processor(s). Also, methods of using the CSN device for in-hole survey and navigation.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
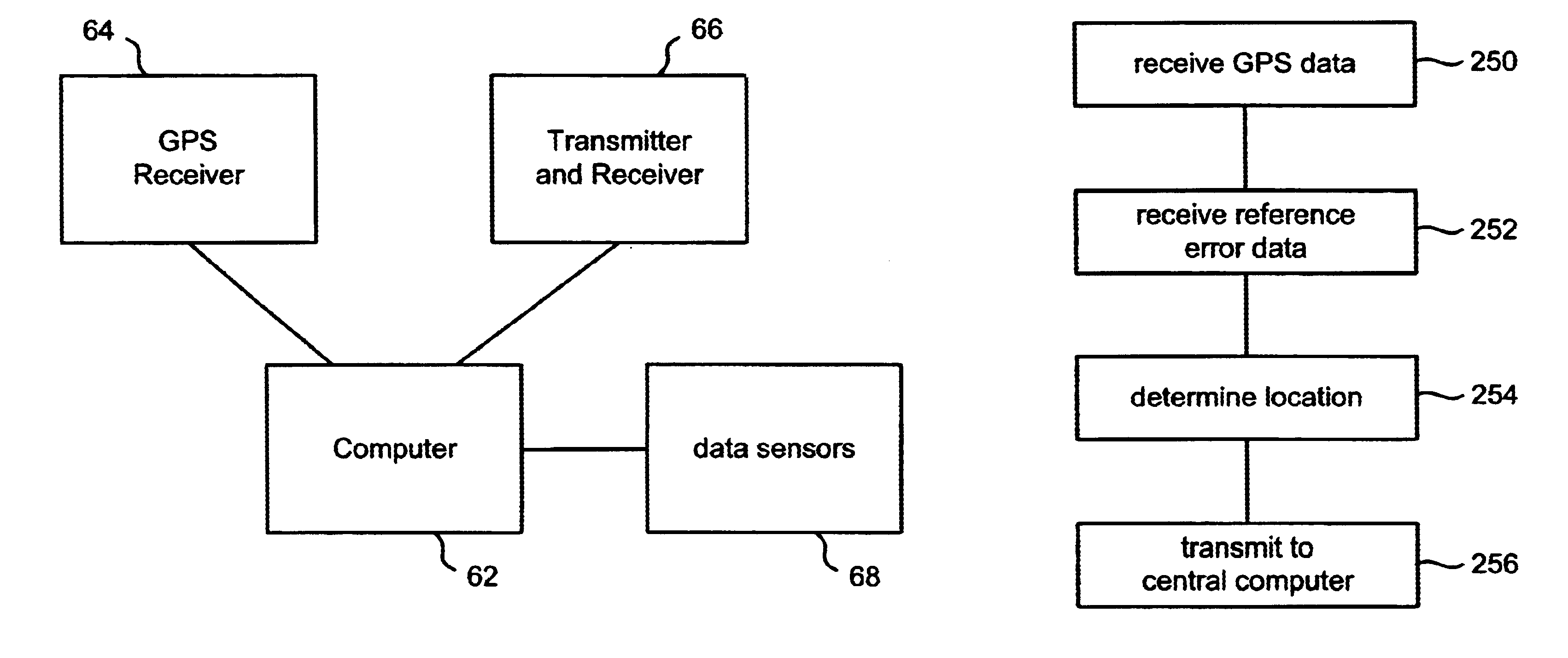
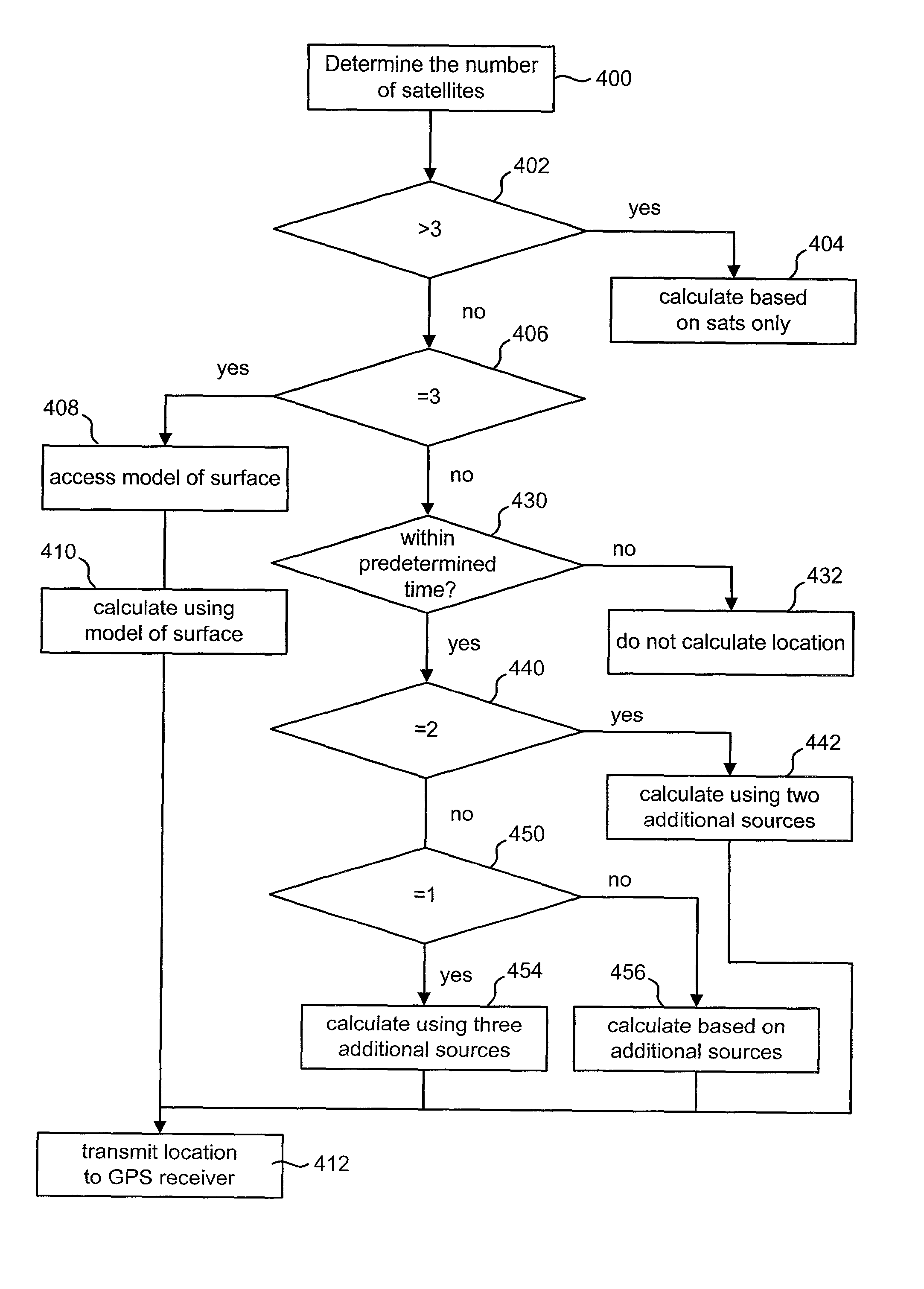
Locating an object using GPS with additional data
A system is disclosed that uses GPS and additional data to determine the location of an object. Typically, GPS receivers need valid data from four satellites to accurately determine a three dimensional location. If a GPS receiver is receiving valid data from fewer than four satellites, then additional data is used to compensate for the shortage of satellites in view of the GPS receiver. Examples of additional data includes a representation of the surface that the object is traveling on, an accurate clock, an odometer, dead reckoning information, pseudolite information, and error correction information from a differential reference receiver. An exemplar use of the disclosed system is to concurrently track a set of one or more automobiles during a race. The determined locations of the automobile can be used to provide route information, to generate statistics and / or to edit video of one or more of the automobiles.
Owner:SPORTSMEDIA TECH CORP
Autonomous inspector mobile platform
ActiveUS8024066B2Streamlined and low cost inspectionInexpensive and easily deployed/operatedPipe elementsColor television detailsOdometryMeasurement device
An autonomous inspector mobile platform robot that is used to inspect a pipe or network of pipes. The robot includes a locomotion device that enables the device to autonomously progress through the pipe and accurately track its pose and odometry during movement. At the same time, image data is autonomously captured to detail the interior portions of the pipe. Images are taken at periodic intervals using a wide angle lens, and additional video images may be captured at locations of interest. Either onboard or offboard the device, each captured image is unwarped (if necessary) and combined with images of adjacent pipe sections to create a complete image of the interior features of the inspected pipe. Optional features include additional sensors and measurement devices, various communications systems to communicate with an end node or the surface, and / or image compression software.
Owner:REDZONE ROBOTICS
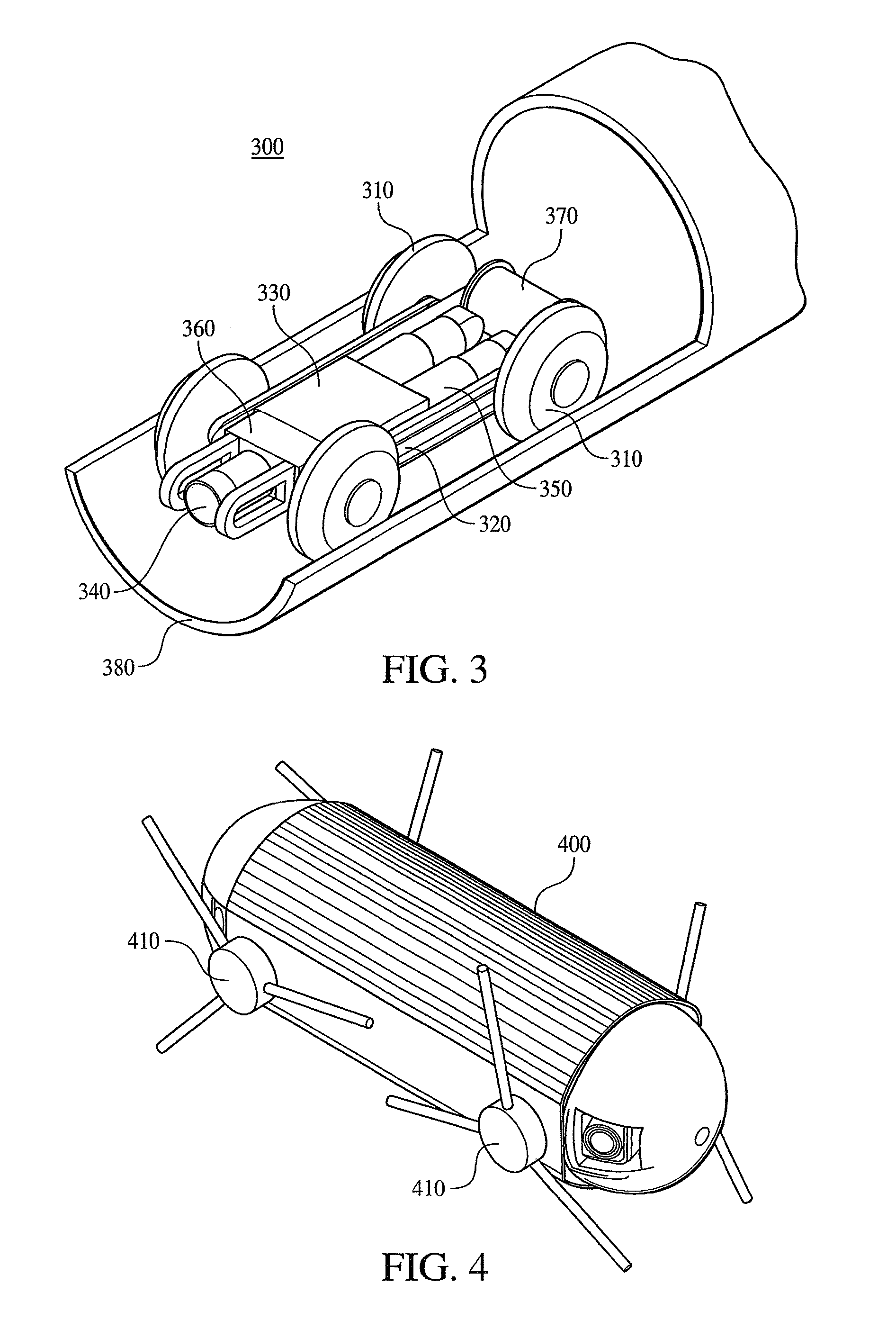
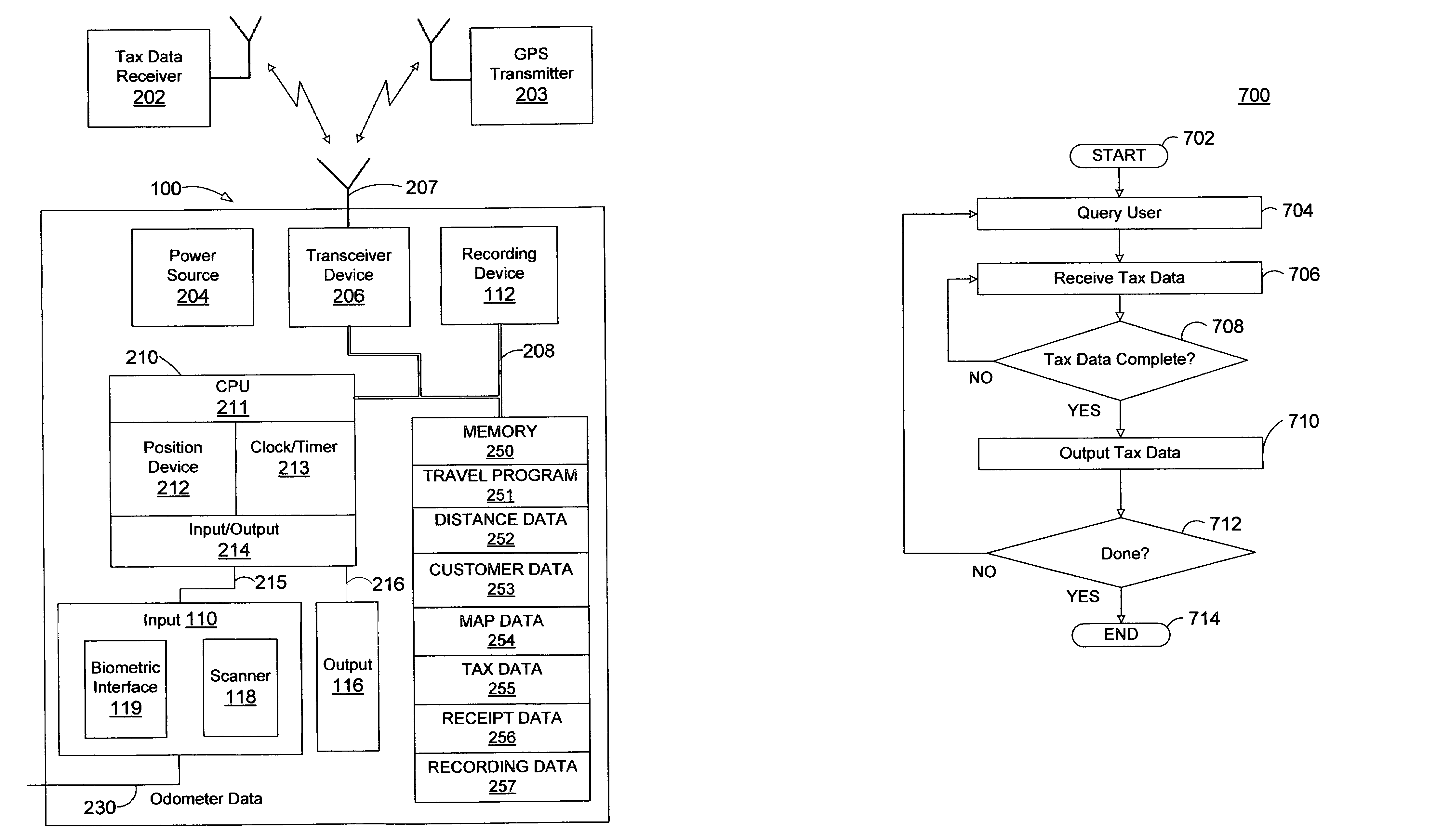
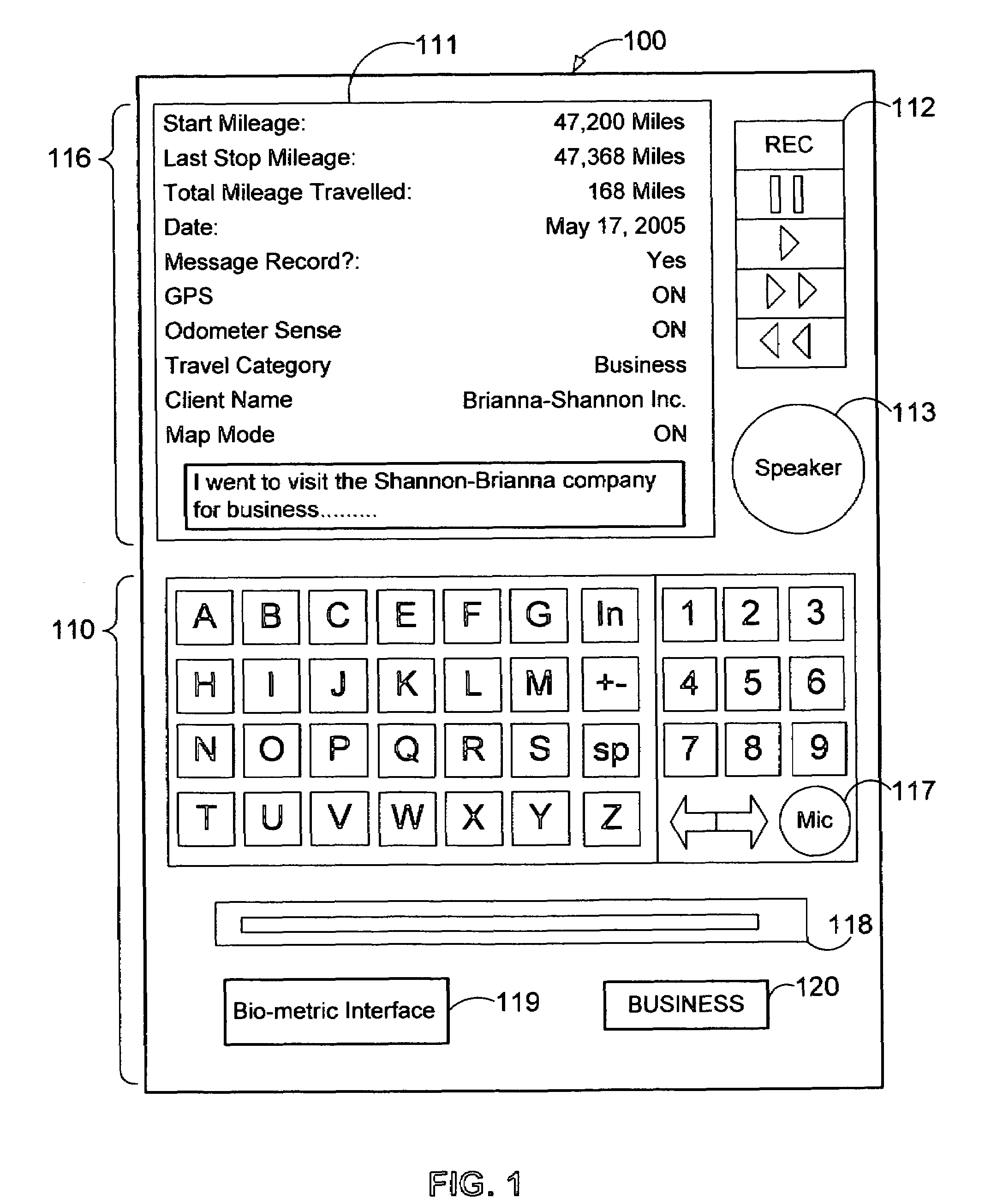
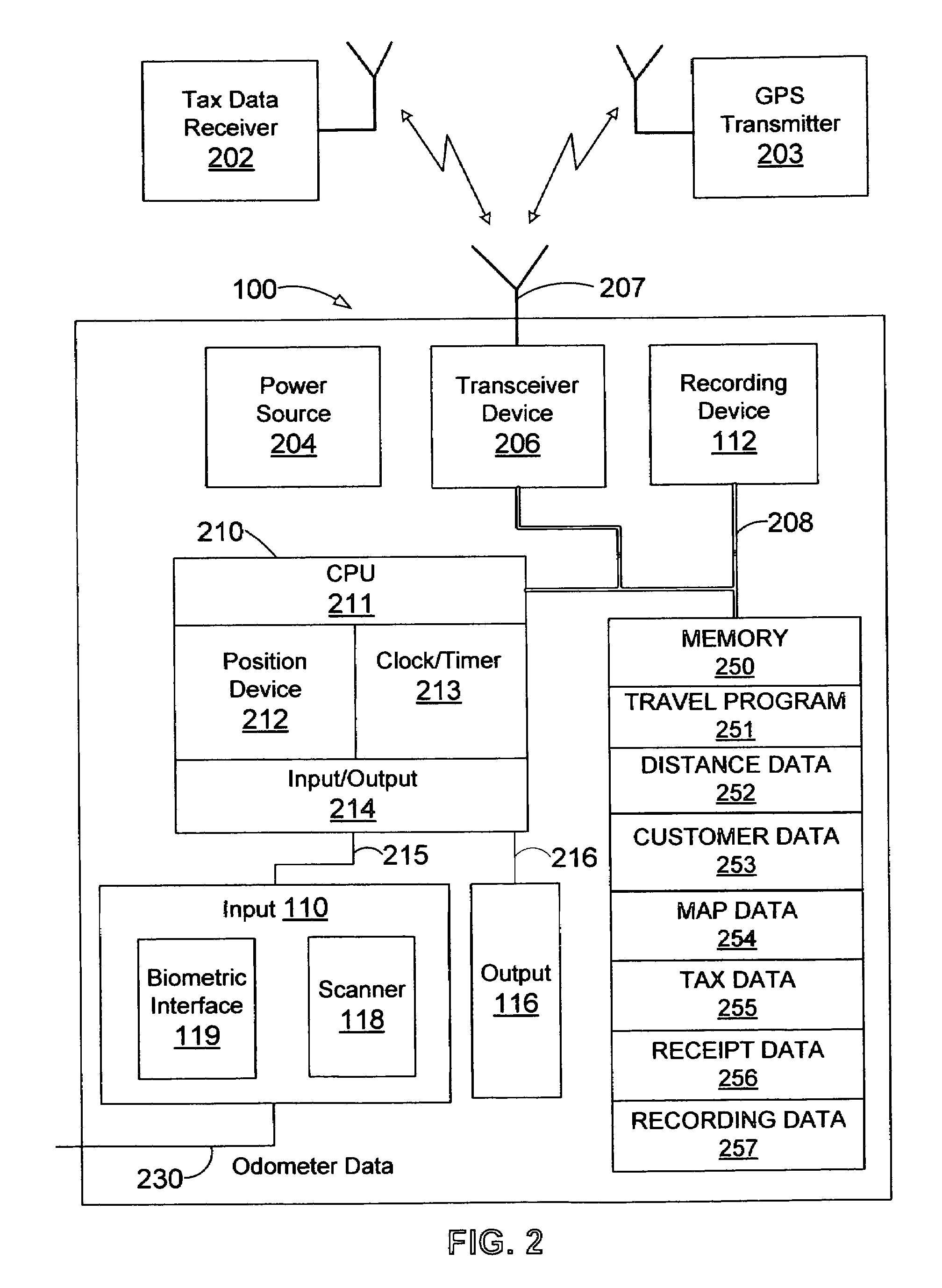
Apparatus and method for tracking vehicle travel and expenditures
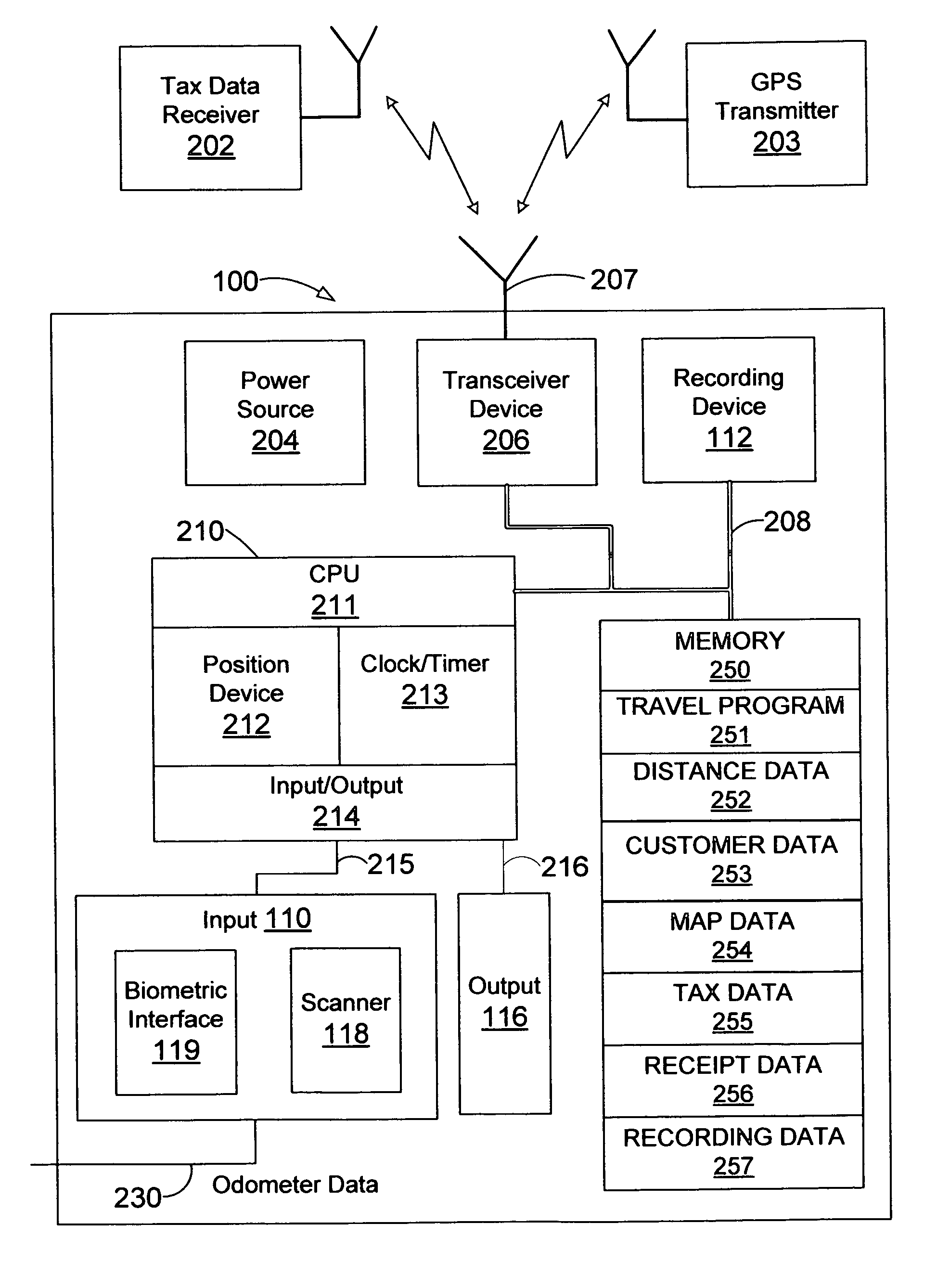
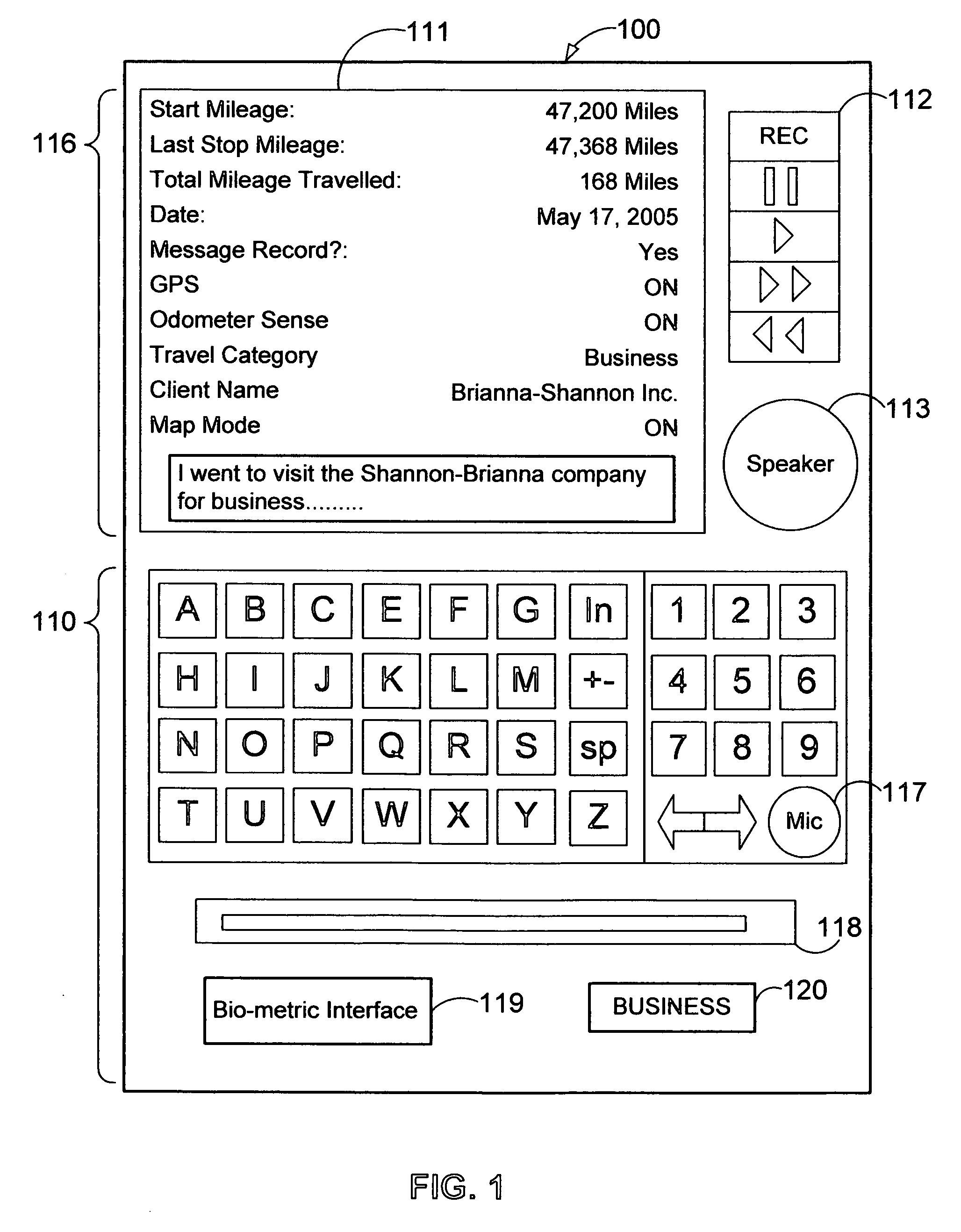
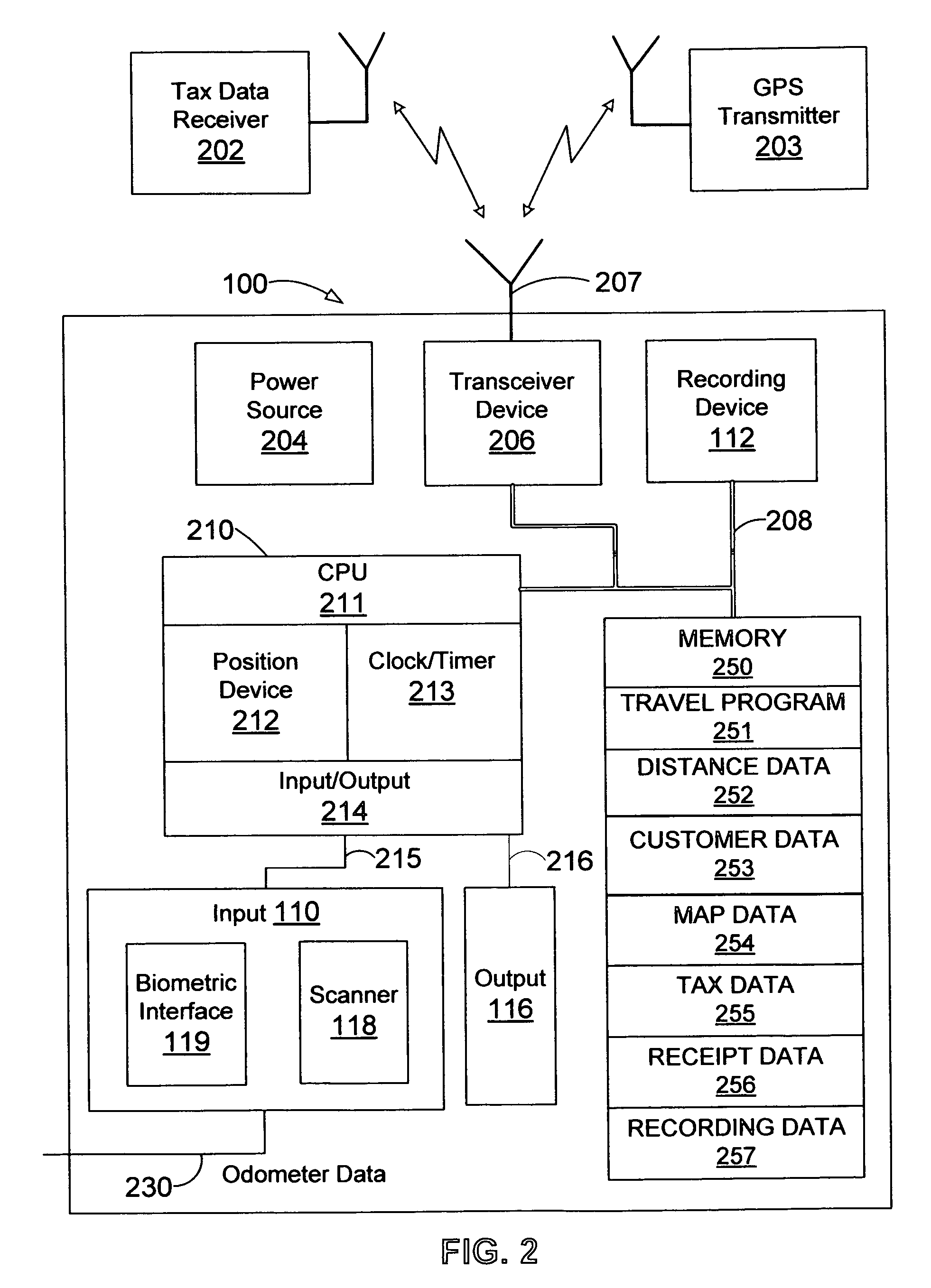
A system and method is provided to track and log the distance traveled by a vehicle during a trip and other expenditures related to the trip. The system is capable of categorizing the trip as business or pleasure. In one embodiment, a tracking device receives global positioning data and / or distance data from the vehicle's odometer. The system receives and stores travel data such as voice, geographic location, receipts, time, date, notes, pictures, etc. to provide verification for the purpose of the trip. In one configuration, the system queries the user for verification data at various intervals such as when the user starts the trip or when the motion of the vehicle has stopped for a predetermined length of time. The system can display the trip information to the user and allow the user to output the travel data to another device such as a printer and / or a third party, etc.
Owner:HARDY CYNTHIA
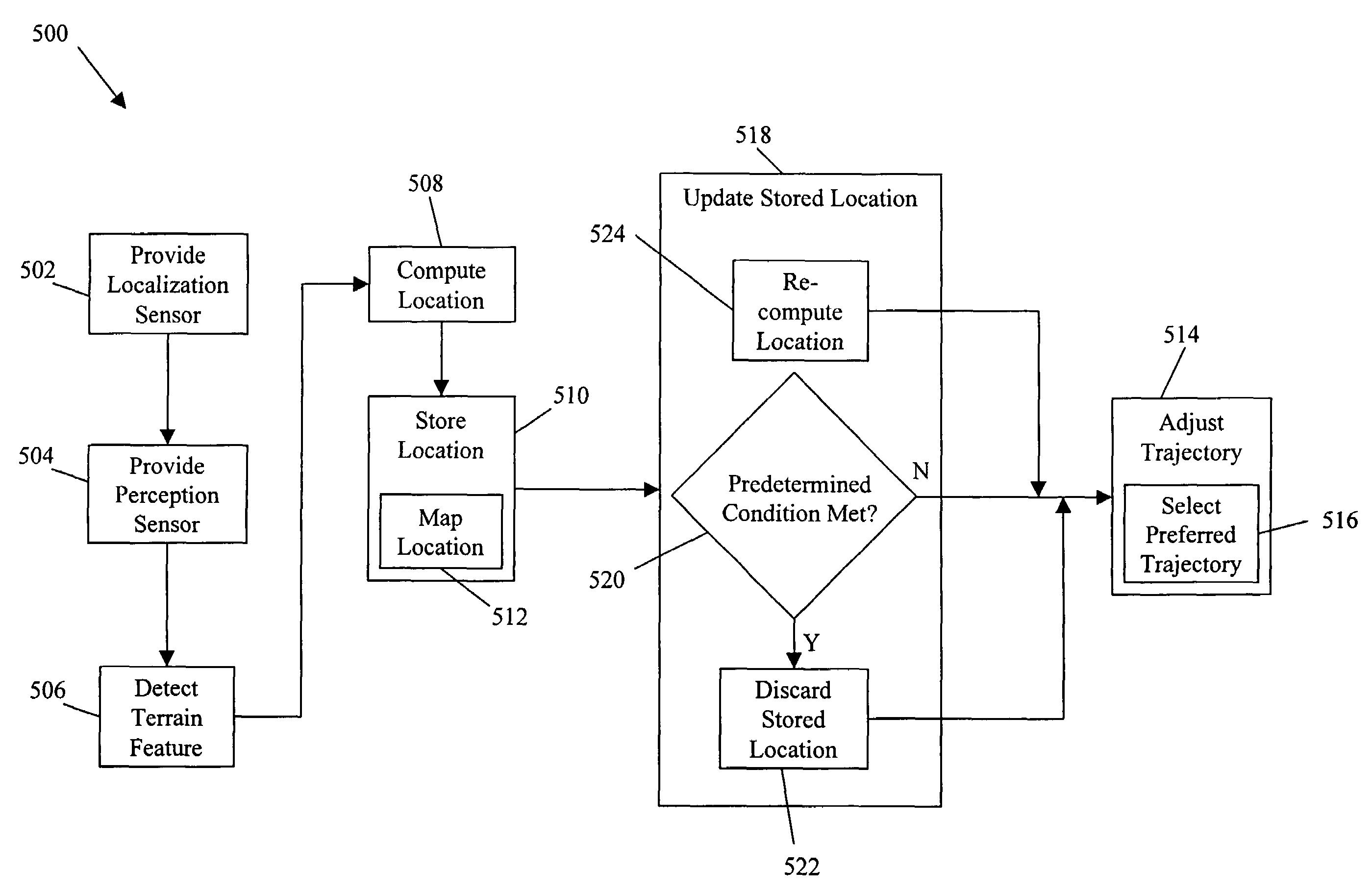
System and method for terrain feature tracking
System and method for tracking obstacles by an autonomous vehicle. Localization sensors (i.e., sensors to measure pitch, roll, and yaw, and systems including an inertial navigation system, a compass, a global positioning system, or an odometer) detect the position of the vehicle. Perception sensors (e.g., LIDAR, stereo vision, infrared vision, radar, or sonar) assess the environment about the vehicle. Using these sensors, locations of terrain features relative to the vehicle are computed and kept up-to-date. The vehicle trajectory is adjusted to avoid terrain features that are obstacles in the path of the vehicle.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
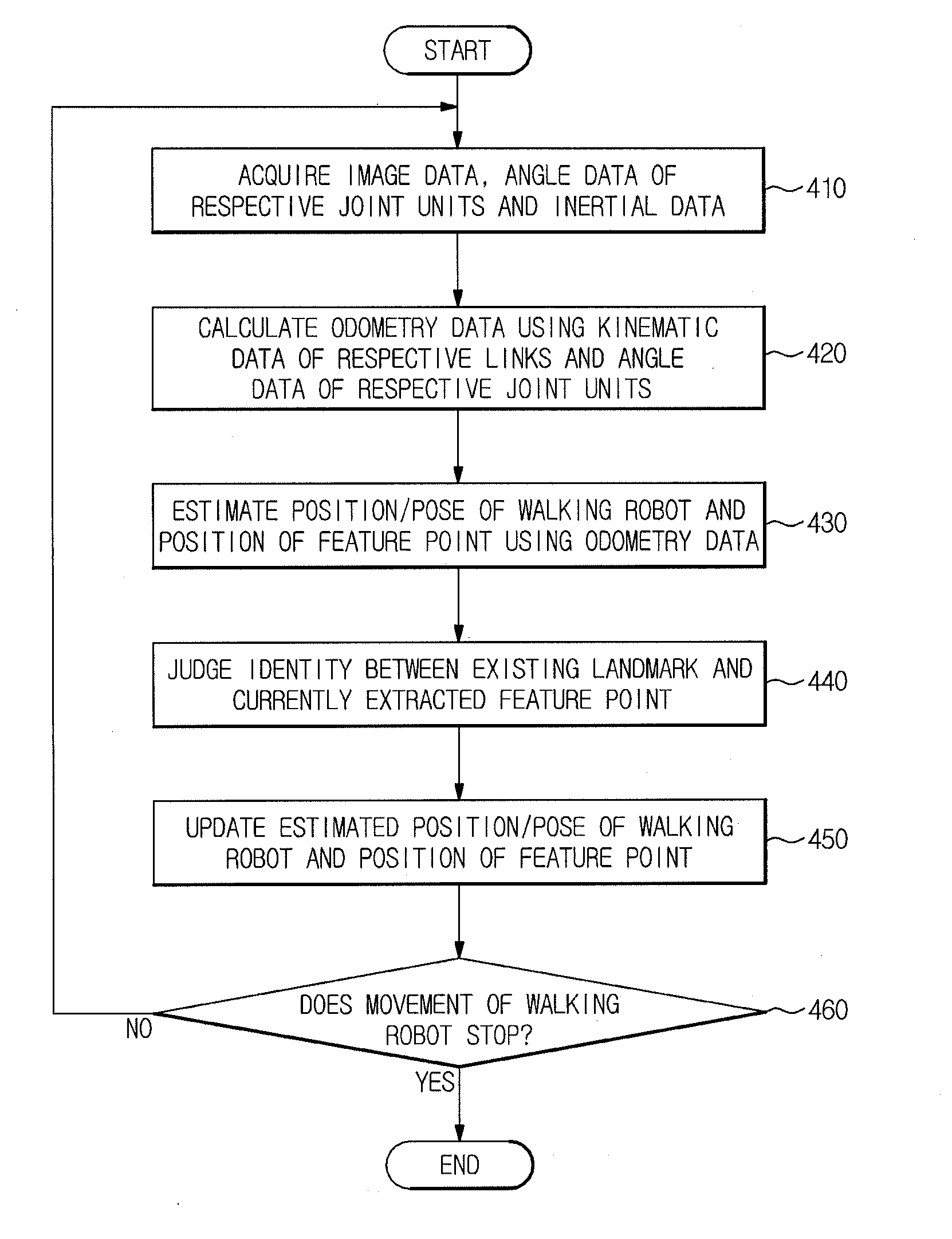
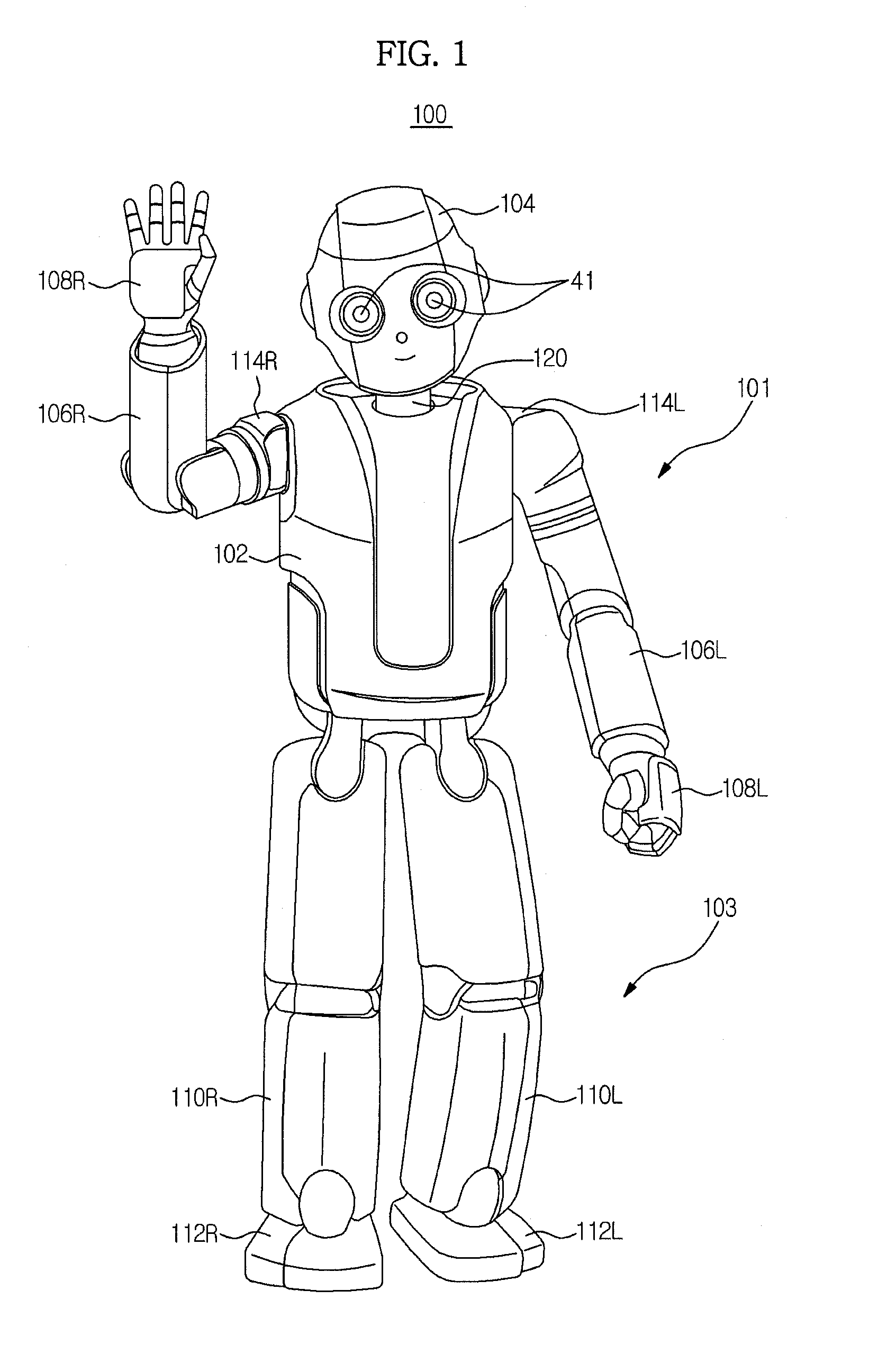
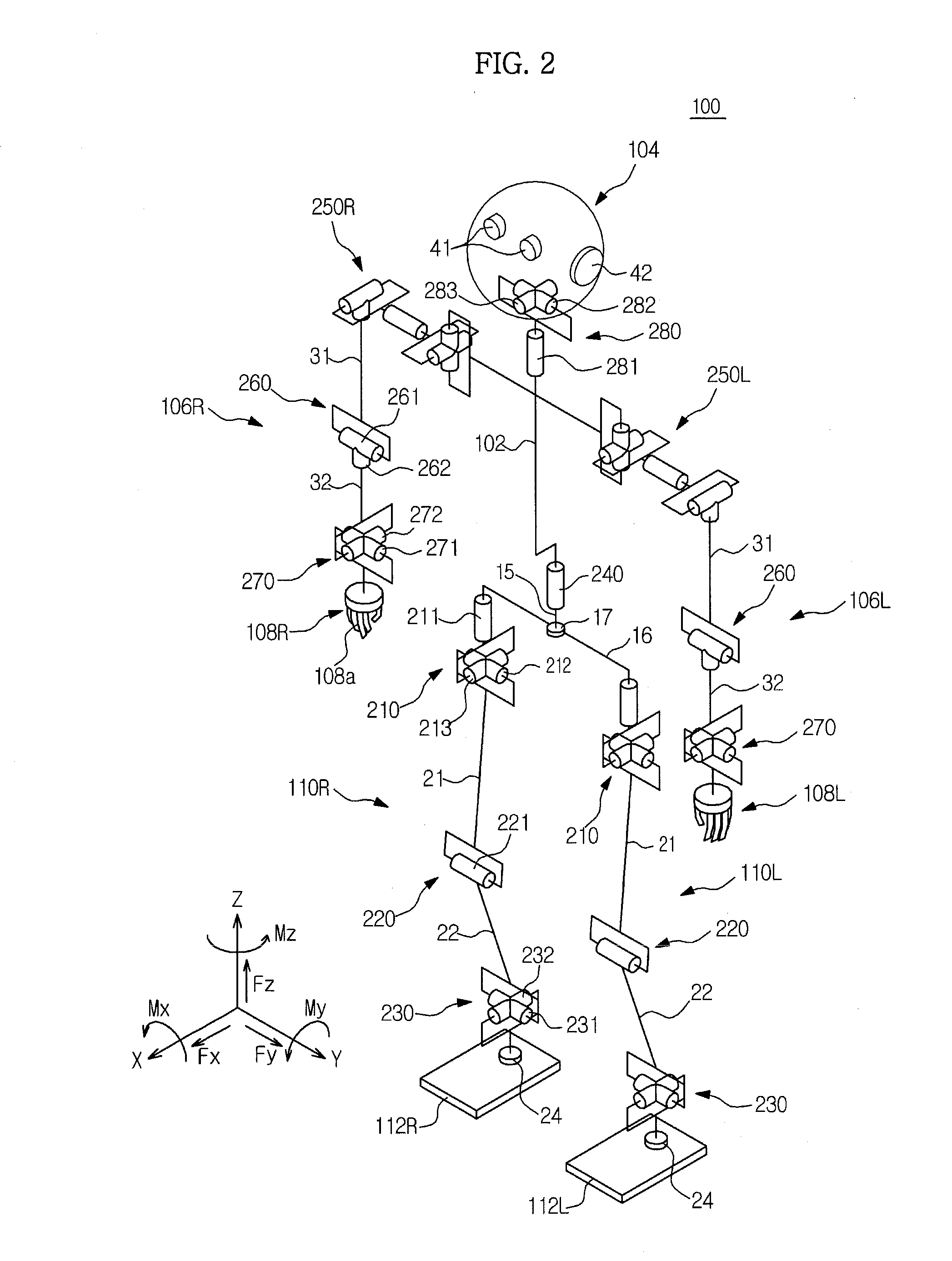
Walking robot and simultaneous localization and mapping method thereof
ActiveUS20120155775A1Improve accuracyFast convergenceProgramme-controlled manipulatorImage analysisOdometryComputer science
A walking robot and a simultaneous localization and mapping method thereof in which odometry data acquired during movement of the walking robot are applied to image-based SLAM technology so as to improve accuracy and convergence of localization of the walking robot. The simultaneous localization and mapping method includes acquiring image data of a space about which the walking robot walks and rotational angle data of rotary joints relating to walking of the walking robot, calculating odometry data using kinematic data of respective links constituting the walking robot and the rotational angle data, and localizing the walking robot and mapping the space about which the walking robot walks using the image data and the odometry data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Locating an object using GPS with additional data
A system is disclosed that uses GPS and additional data to determine the location of an object. Typically, GPS receivers need valid data from four satellites to accurately determine a three dimensional location. If a GPS receiver is receiving valid data from fewer than four satellites, then additional data is used to compensate for the shortage of satellites in view of the GPS receiver. Examples of additional data includes a representation of the surface that the object is traveling on, an accurate clock, an odometer, dead reckoning information, pseudolite information, and error correction information from a differential reference receiver. An exemplar use of the disclosed system is to concurrently track a set of one or more automobiles during a race. The determined locations of the automobile can be used to provide route information, to generate statistics and / or to edit video of one or more of the automobiles.
Owner:SPORTSMEDIA TECH CORP
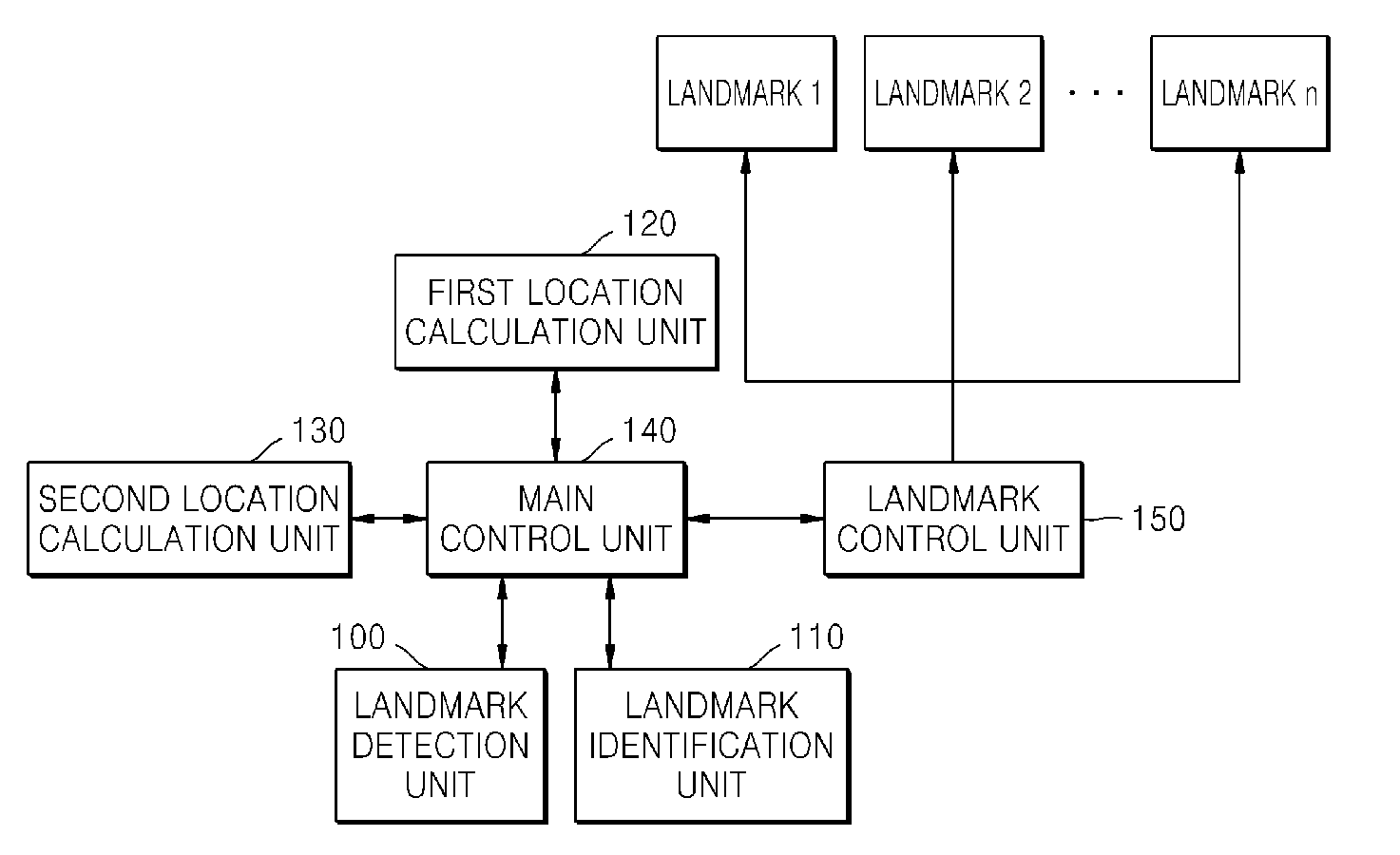
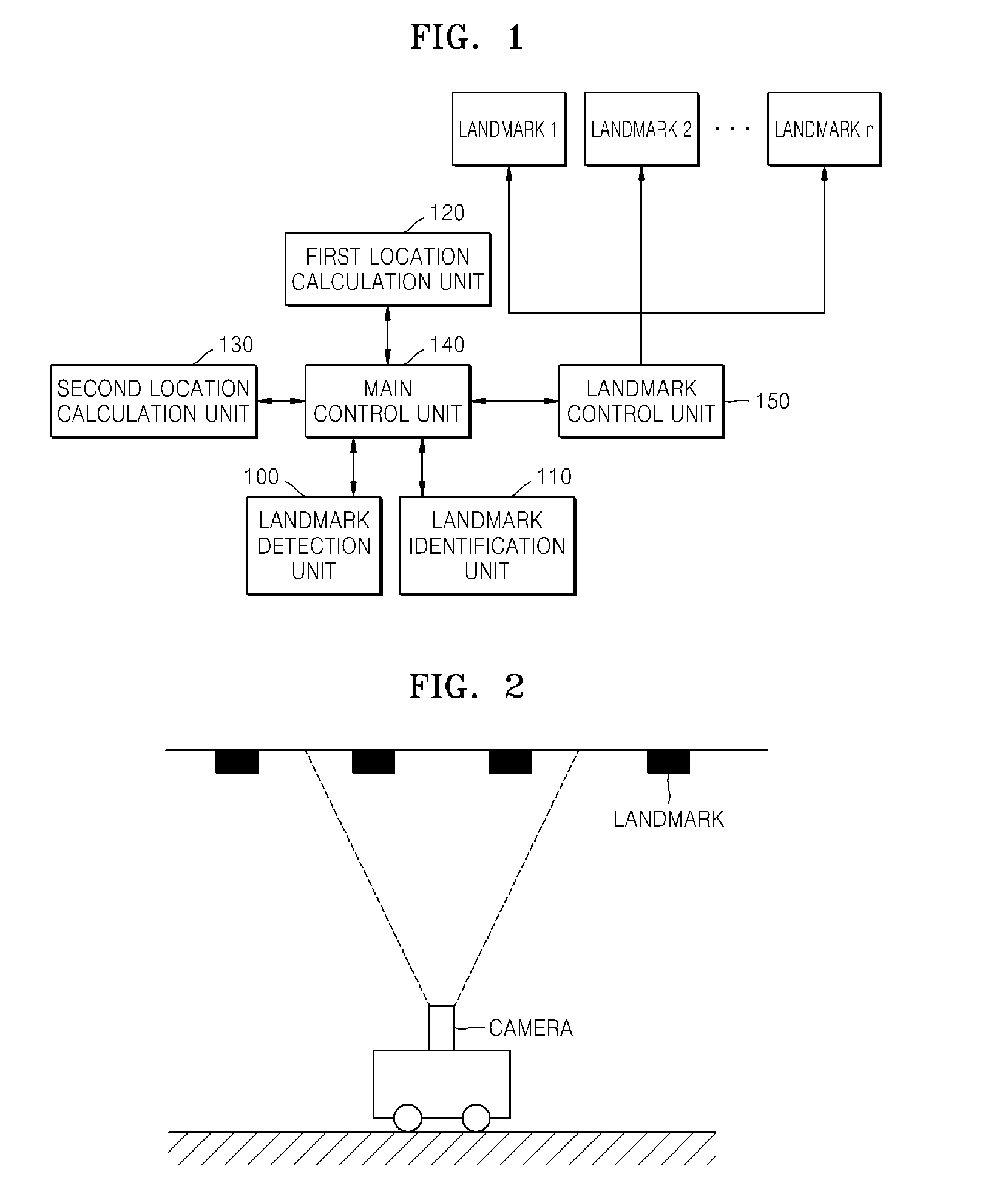
System and method for calculating location using a combination of odometry and landmarks
Disclosed is a system and method for calculation a location in a real-time manner using a combination of odometry and artificial landmarks. The system for calculating a location comprising a landmark detection unit detecting an image coordinates value of the artificial landmark corresponding to a location in a two-dimensional image coordinate system with respect to a mobile robot from an image obtained by photographing a specific space where the artificial landmarks are provided; a landmark identification unit comparing a predicted image value of the artificial landmark, obtained by converting a location coordinates value of the artificial landmark into an image coordinates value corresponding to the location in the two-dimensional image coordinate system with respect to a location coordinates value corresponding to a location in an actual three-dimensional spatial coordinate system of the mobile robot, with an image coordinates value detected by the landmark detection unit to detect the location coordinates value of the artificial landmark; a first location calculation unit calculating a current location coordinates value of the mobile robot using a predetermined location calculation algorithm based on the image coordinates value detected by the landmark detection unit and the location coordinates value detected by the landmark identification unit; a second location calculation unit calculating a current location coordinates value of the mobile robot using a predetermined location calculation algorithm based on odometry information of the mobile robot; and a main control unit updating the current location coordinates value of the mobile robot, using the location coordinates value calculated by the first location calculation unit when the location coordinates value calculated by the first location calculation unit exists, or using the location coordinate value obtained from the second location calculation unit when the location coordinates value calculated by the first location calculation unit does not exist.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Apparatus and method for tracking vehicle travel and expenditures
InactiveUS7599770B2Registering/indicating working of vehiclesRoad vehicles traffic controlThird partyOdometry
A system and method is provided to track and log the distance traveled by a vehicle during a trip and other expenditures related to the trip. The system is capable of categorizing the trip as business or pleasure. In one embodiment, a tracking device receives global positioning data and / or distance data from the vehicle's odometer. The system receives and stores travel data such as voice, geographic location, receipts, time, date, notes, pictures, etc. to provide verification for the purpose of the trip. In one configuration, the system queries the user for verification data at various intervals such as when the user starts the trip or when the motion of the vehicle has stopped for a predetermined length of time. The system can display the trip information to the user and allow the user to output the travel data to another device such as a printer and / or a third party, etc.
Owner:HARDY CYNTHIA
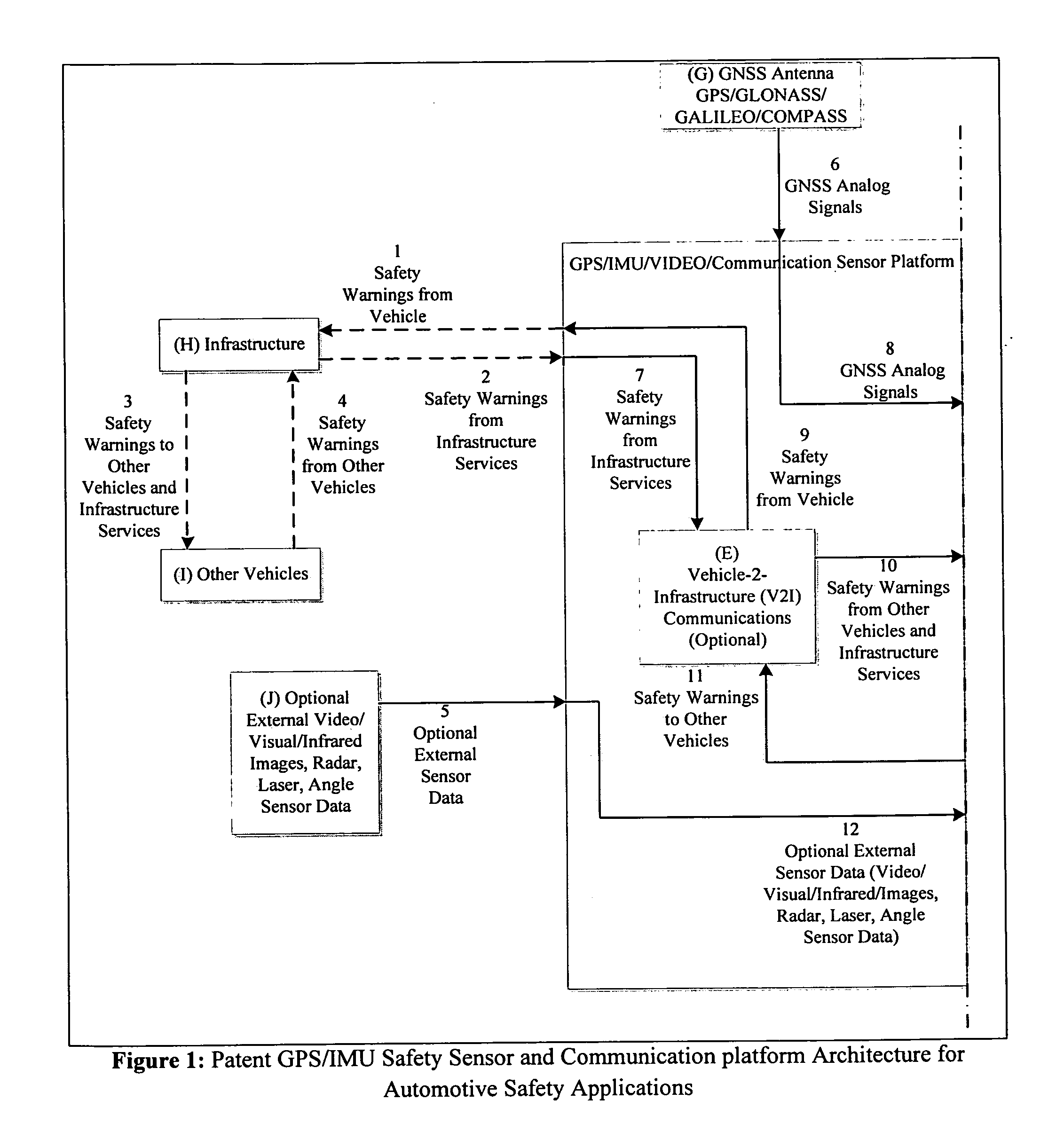
GPS/IMU/video/radar absolute/relative positioning communication/computation sensor platform for automotive safety applications
ActiveUS8639426B2Prevent unavoidable accidentsAnalogue computers for vehiclesInstruments for road network navigationAccelerometerAutomatic control
A GPS / IMU safety sensor platform is proposed, consisting of data fusion Processors, GNSS Signal Acquisition and Tracking Processors, MEMS IMU sensors, one or multiple accelerometers able to provide orientation information, optional V2V communication modules, and optional V2I communication modules. The data fusion processors provide interface ports to GNSS / IMU processors, odometers, video (Visual / Infrared) cameras installed in the vehicle, V2V relative positioning sensors (laser, radar or any other distance measuring), and V2V and V2I communication modules. The data fusion processors are interfaced to a driver warning system and optionally to the vehicle controls for providing safety warning messages to drivers, or for automatic control the vehicle for preventing and reducing accidents.
Owner:UATC LLC
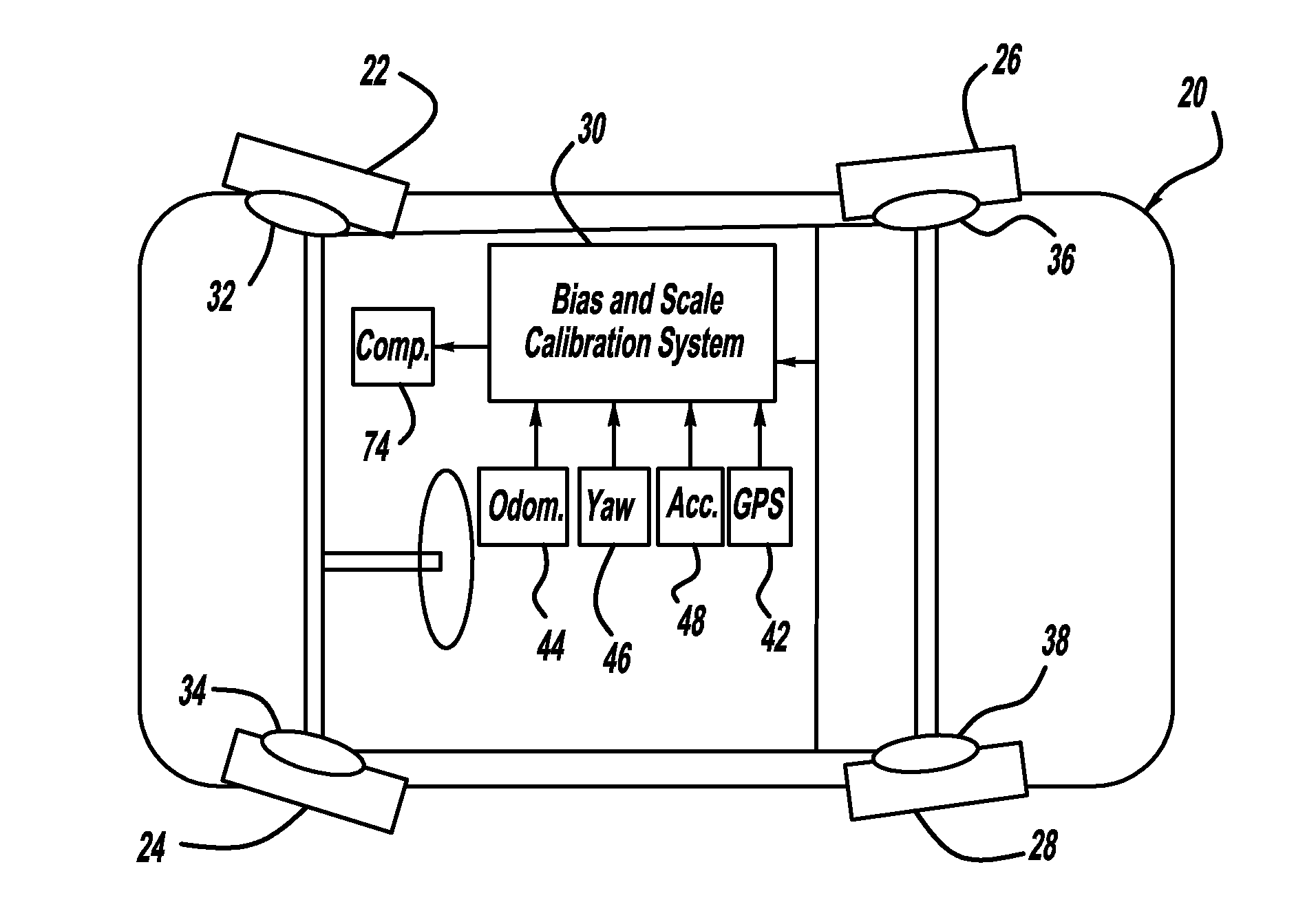
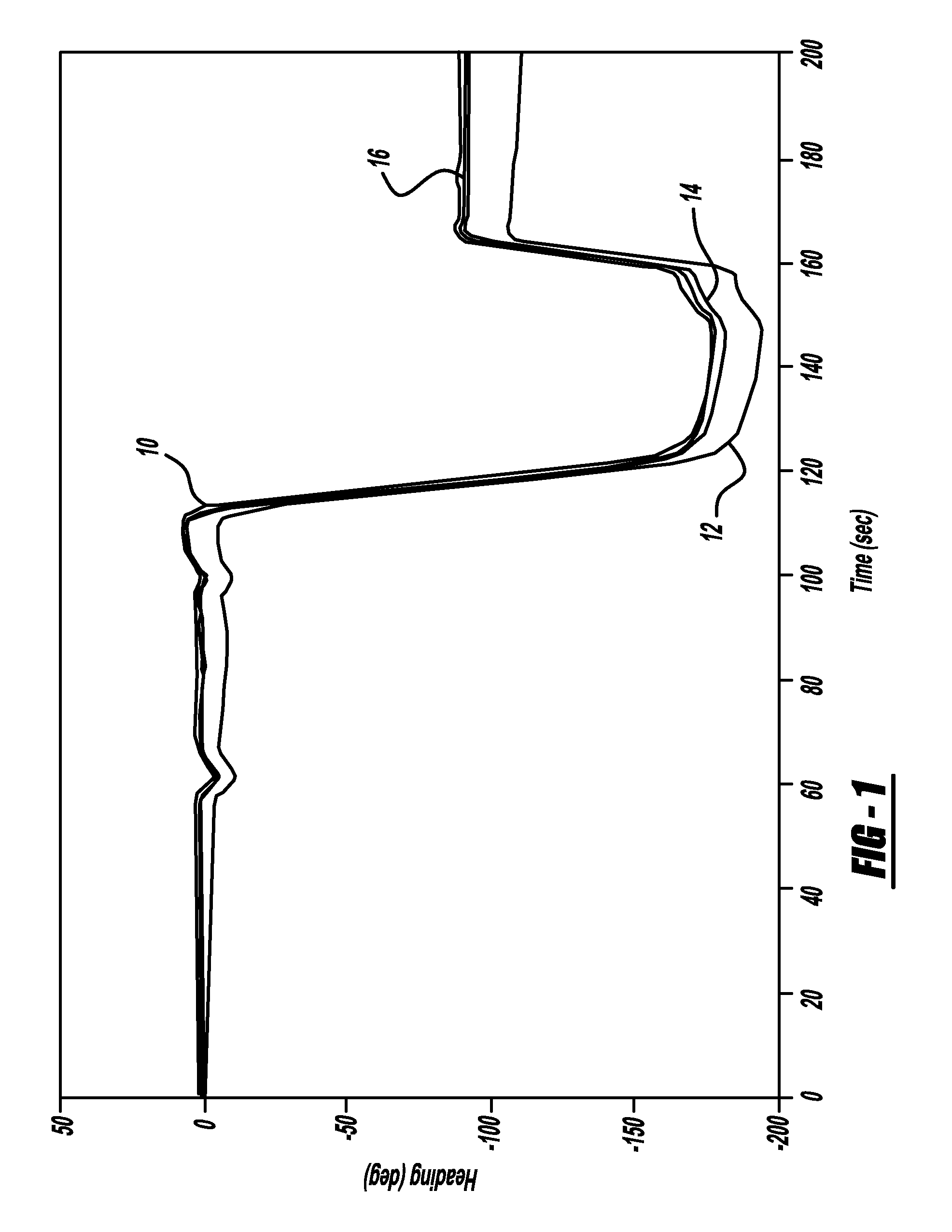
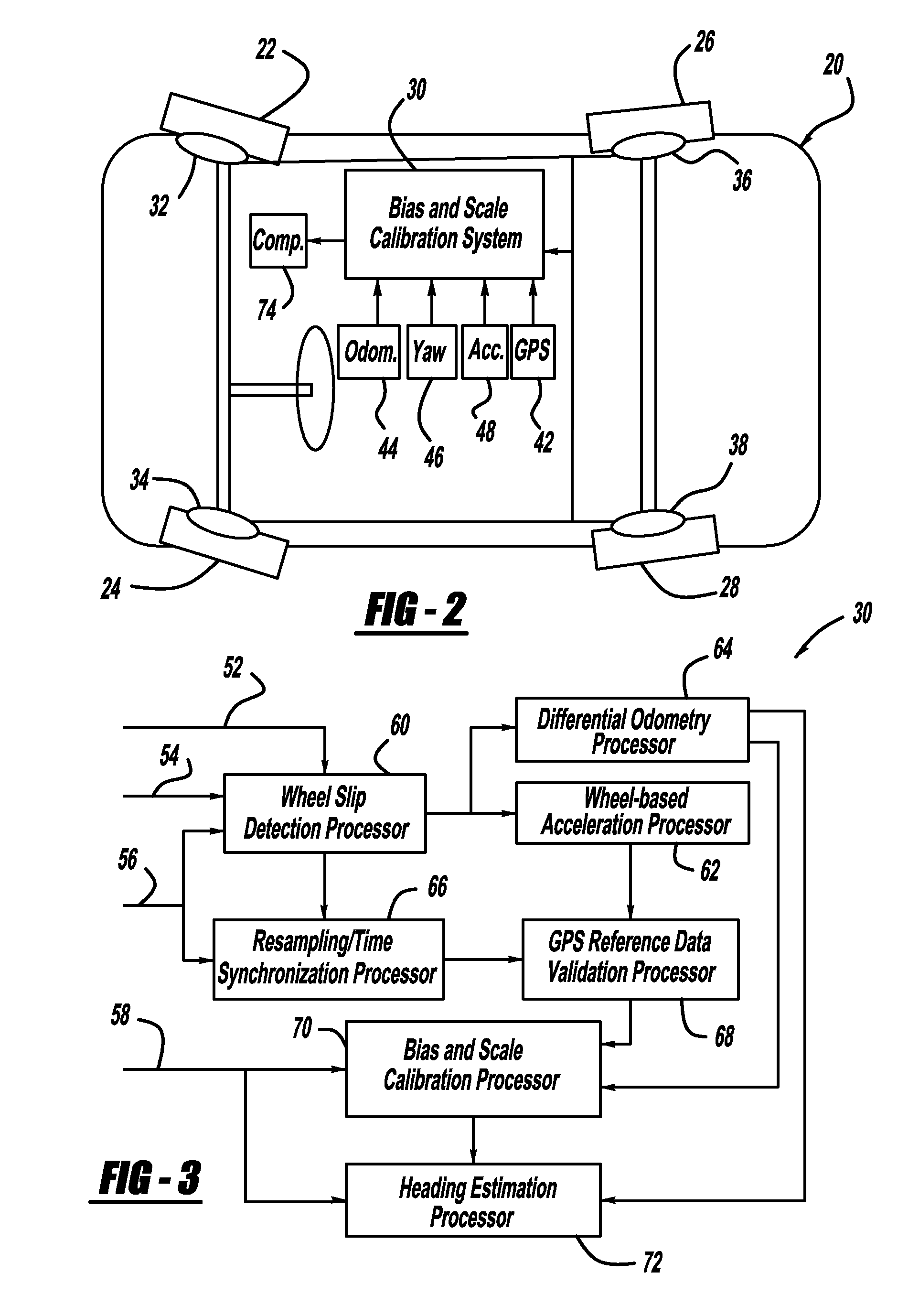
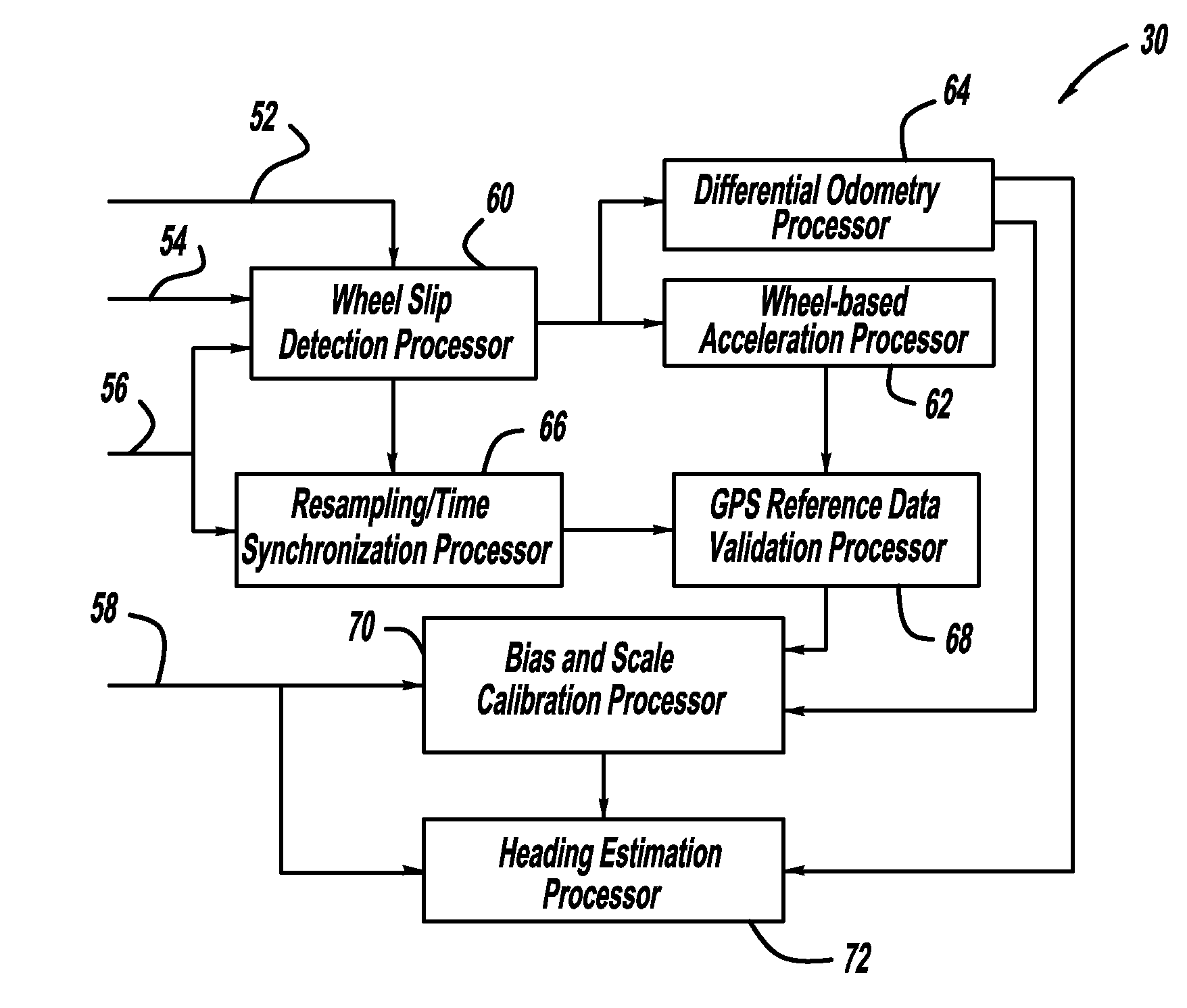
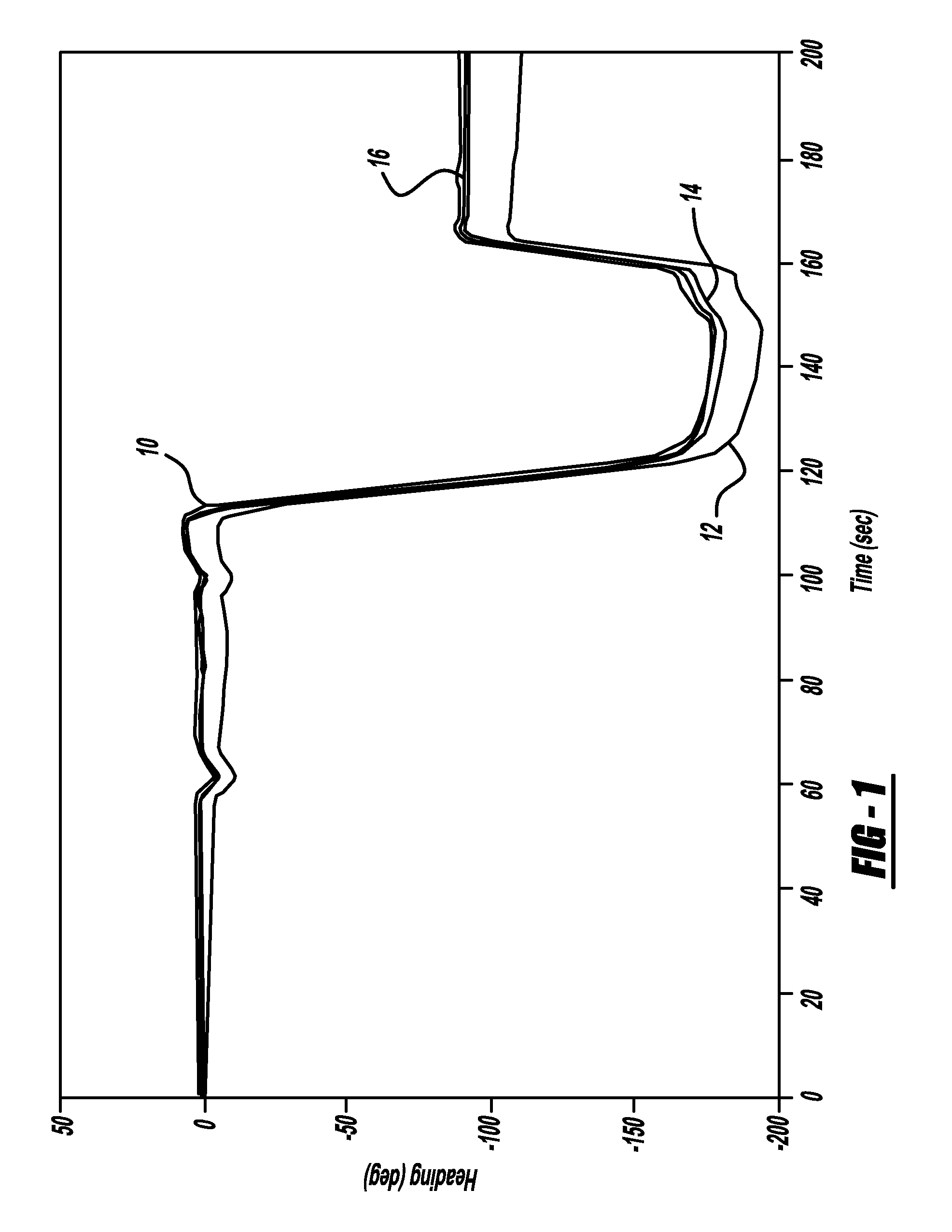
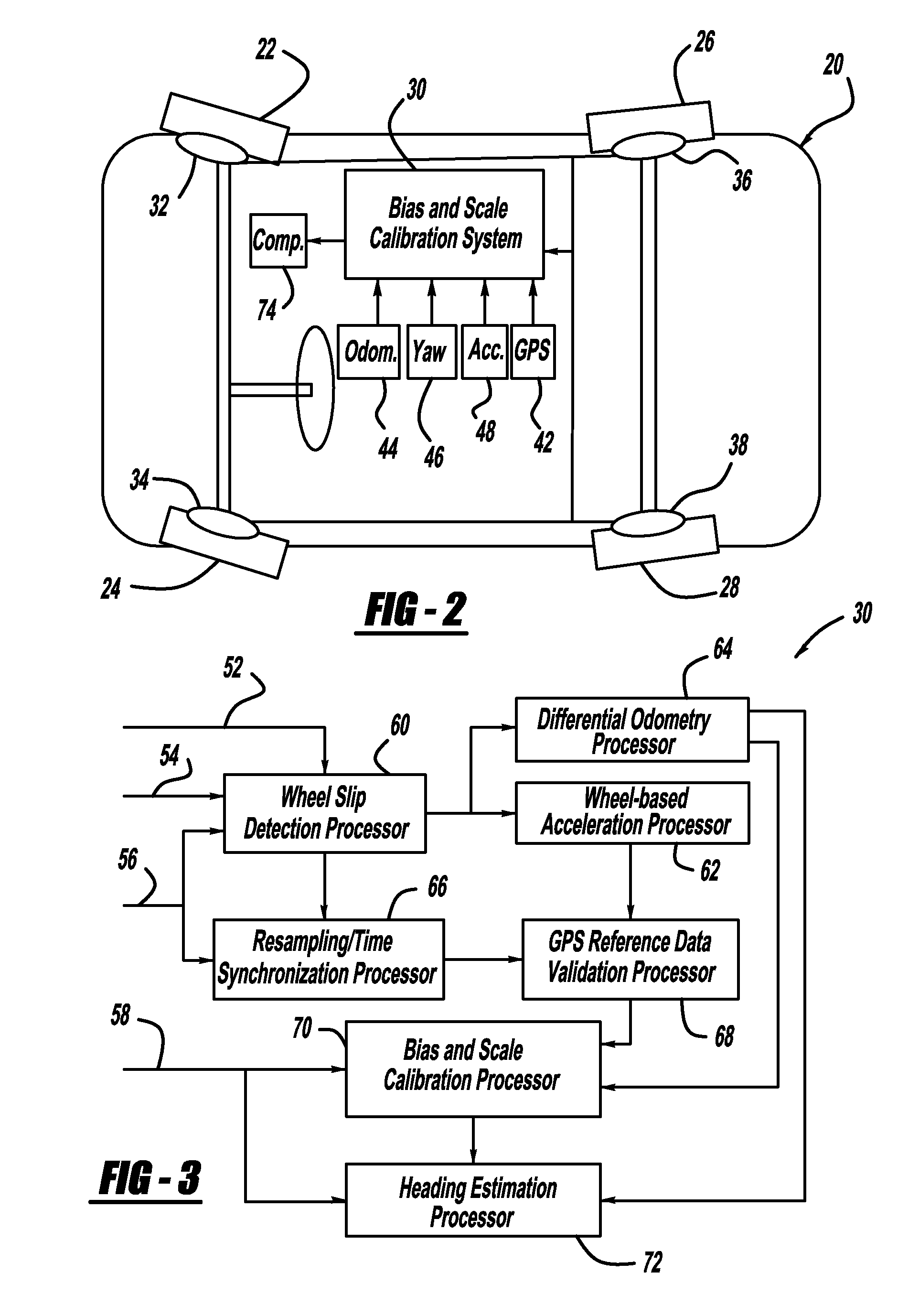
GPS-based in-vehicle sensor calibration algorithm
ActiveUS20090005985A1Digital data processing detailsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsOdometryData validation
A system and method for calibrating the bias and scale factors of a heading rate sensor, such as a yaw-rate sensor, using GPS signals. The system receives wheel speed or rotation signals, a vehicle odometer reading, GPS signals and yaw-rate signals. The system includes a wheel-slip detection processor that determines whether there is wheel-slip based on the wheel speed signals and the GPS signals. The system also includes a wheel-based acceleration processor that estimates vehicle acceleration. The system also includes a differential odometry processor that determines vehicle heading based on wheel speed. The system also includes a GPS reference data validation processor that determines whether the GPS signals are valid using the estimated vehicle acceleration and wheel speeds. The valid GPS signals are then used to calibrate the yaw-rate sensor signals, which can be used for vehicle heading purposes.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
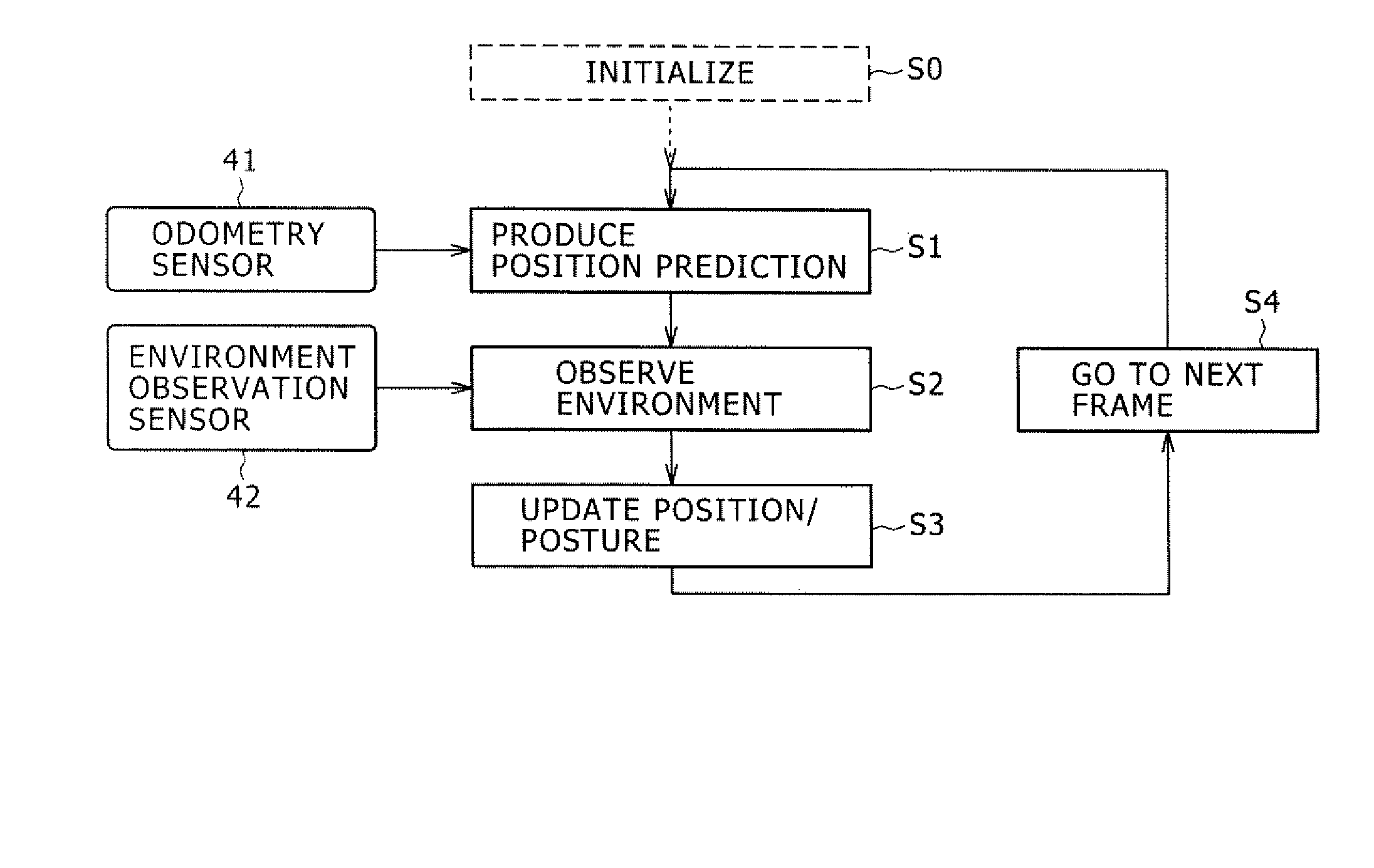
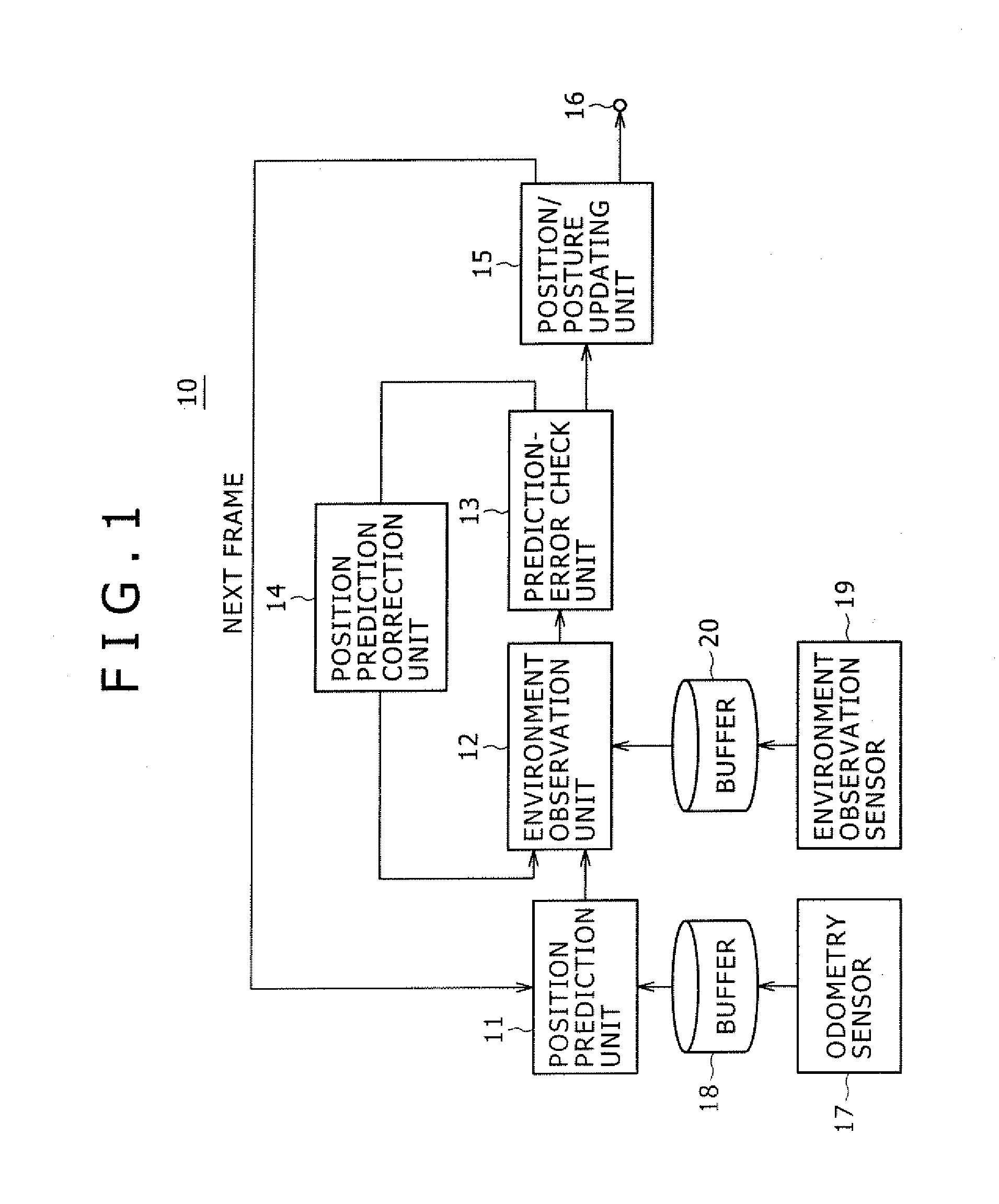
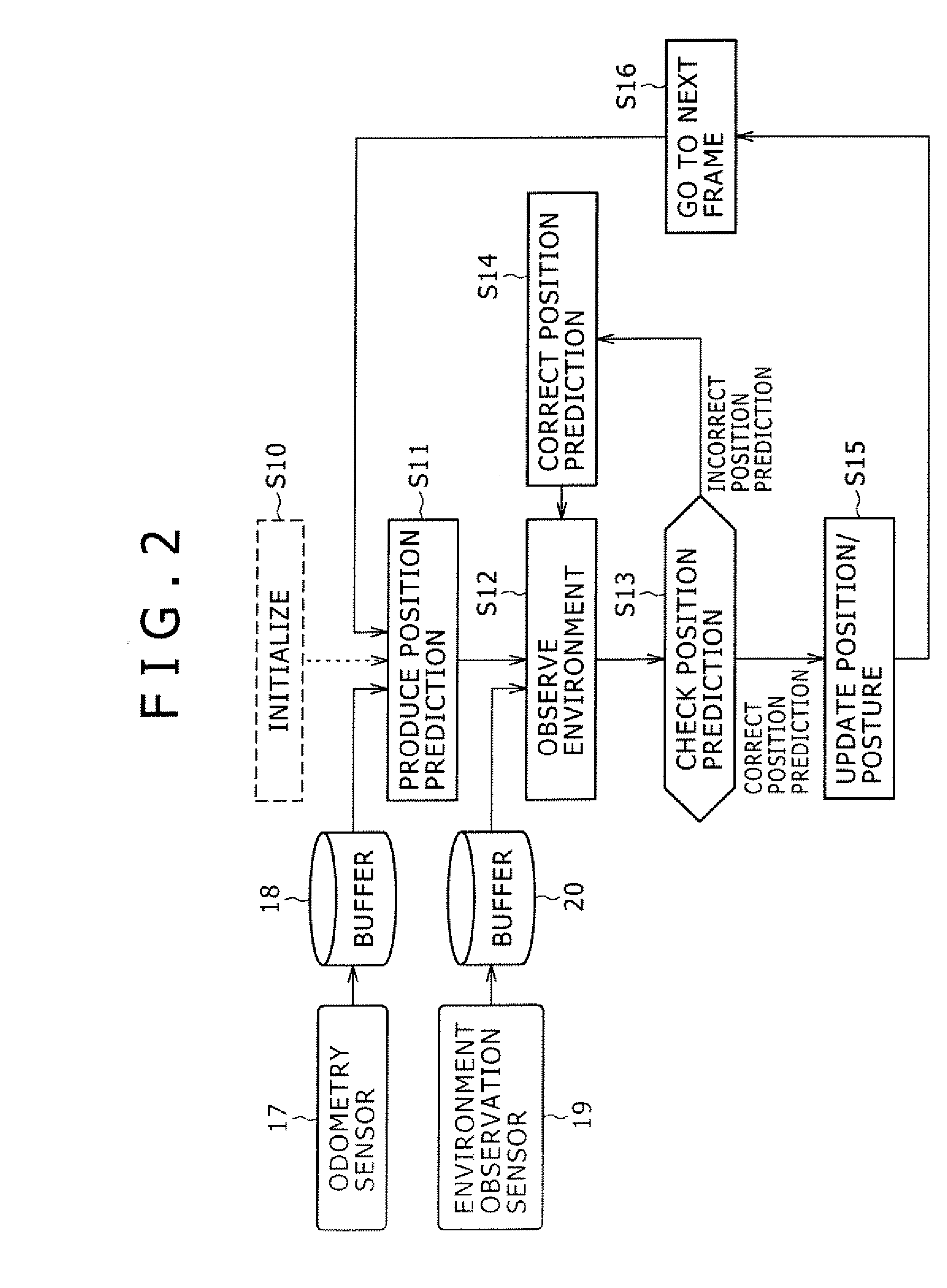
Position Estimation Apparatus, Position Estimation Method and Program Recording Medium
InactiveUS20070265741A1Navigation by speed/acceleration measurementsComplex mathematical operationsOdometryError check
The present invention provides a position estimation apparatus capable of determining whether an estimated value deviates from an actual value and trying a process to correct the estimated value if the estimated value is determined to be incorrect. The position estimation apparatus employs a position prediction unit configured to produce a prediction of the position of a mobile object having an odometry sensor mounted thereon, an environment observation unit configured to keep track of each feature point in the environment of the mobile object, a prediction-error check unit configured to determine whether the position prediction produced by the position prediction unit is correct or incorrect, a position-prediction correction unit configured to correct a wrong position prediction and a position / posture updating unit configured to update the position and / or posture of the mobile object on the basis of a correct position prediction.
Owner:SONY CORP
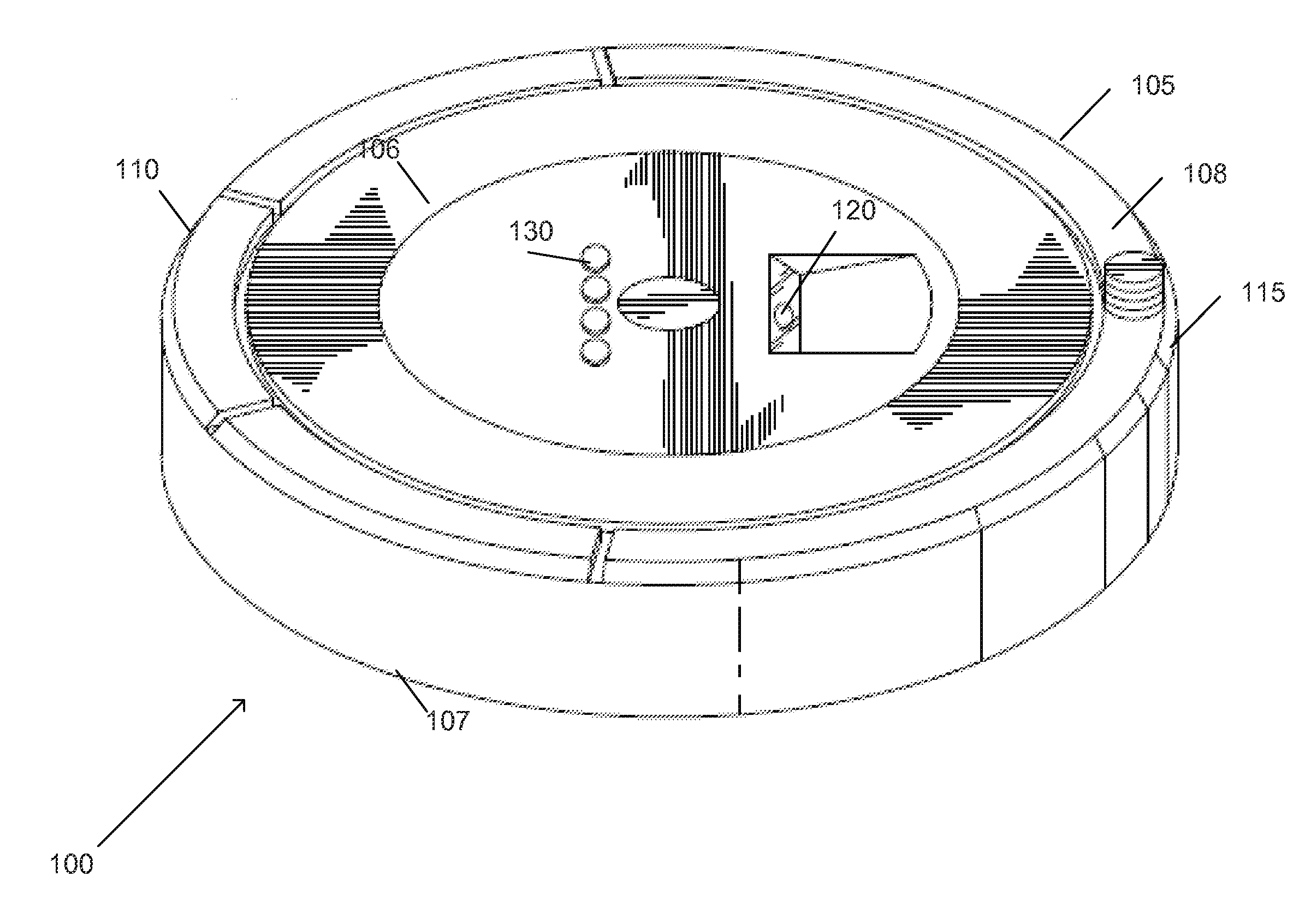
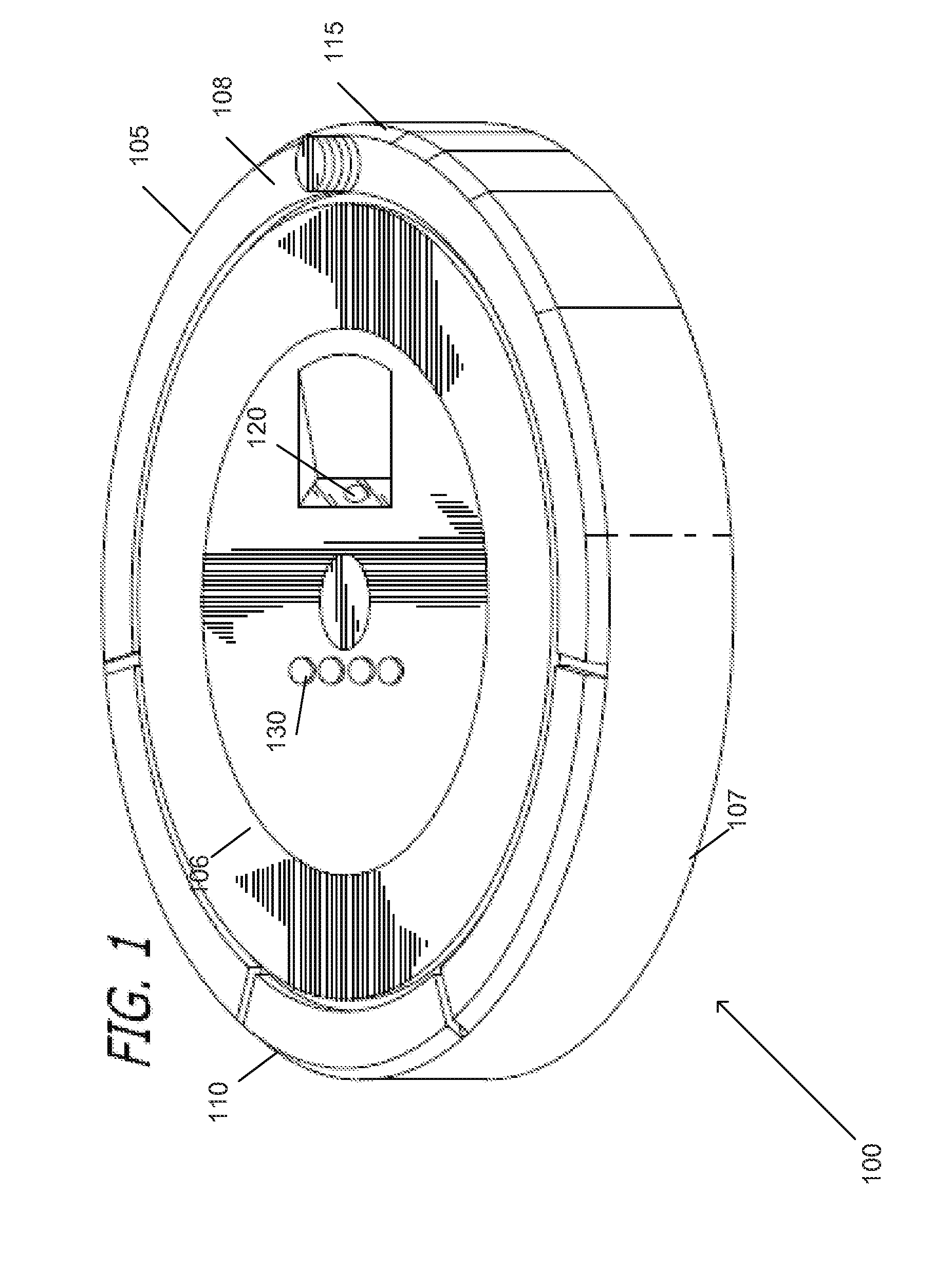
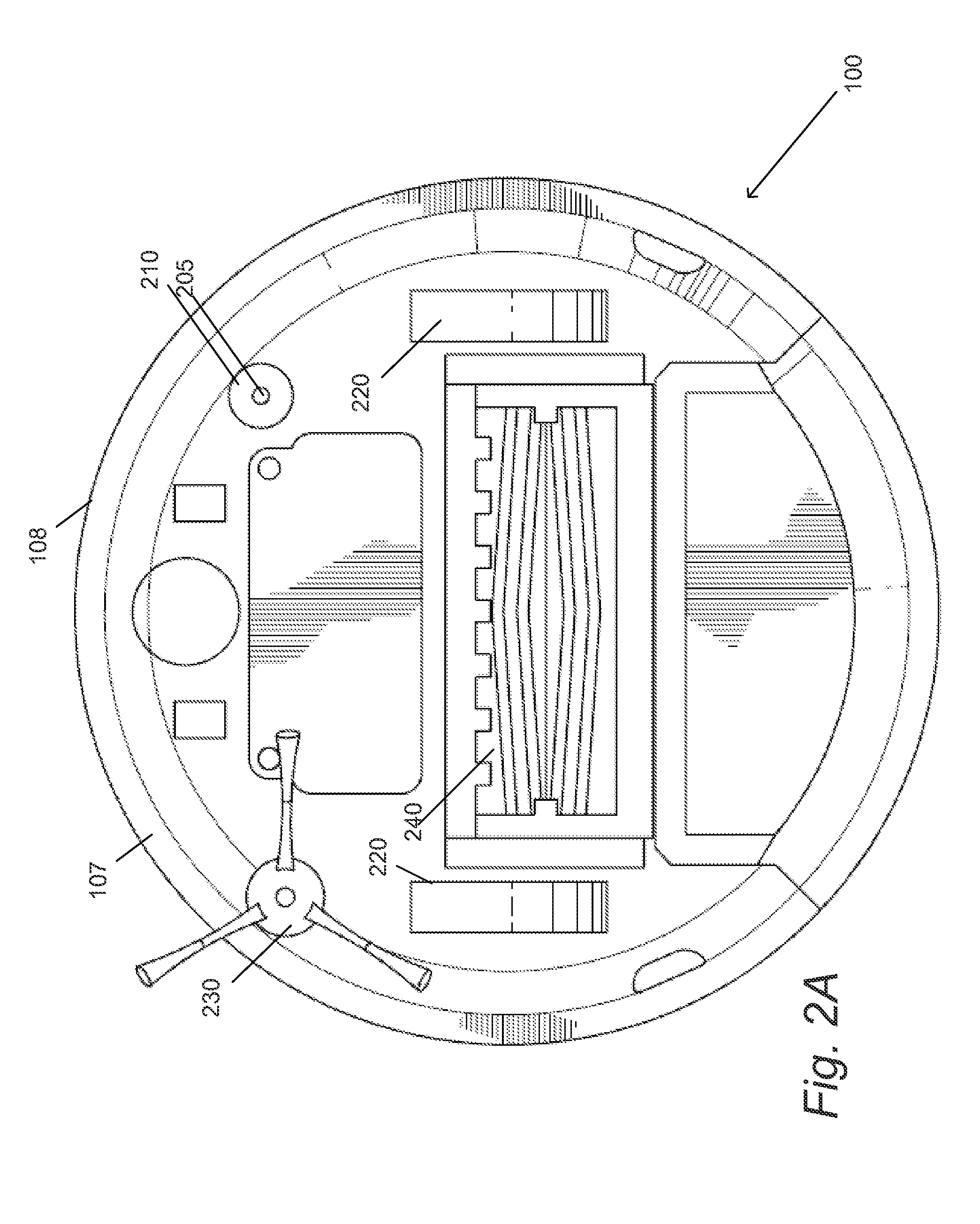
Systems and Methods for Use of Optical Odometry Sensors In a Mobile Robot
Systems and methods for use of optical odometry sensor systems in a mobile robot. The optical odometry sensor system is positioned within a recessed structure on an underside of the mobile robot body and configured to output optical odometry data. The optical odometry sensor system includes an optical odometry camera that includes a telecentric lens configured to capture images of a tracking surface beneath the body and having a depth of field that provides a range of viewing distances at which a tracking surface is captured in focus from a first distance within the recessed structure to a second distance below the underside of the mobile robot body.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
Monocular motion stereo-based free parking space detection apparatus and method
ActiveUS8134479B2Solve the degradation problemEffective positioningImage enhancementImage analysisOdometryBase free
A monocular motion stereo-based automatic free parking space detection system is disclosed. The system acquires image sequences with a single rearview fisheye camera, three-dimensionally reconstructs the vehicle rearview by using point correspondences, and recovers metric information from a known camera height to estimate the positions of adjacent vehicles thereby detecting the free parking spaces. By using de-rotation-based feature selection and 3D structure mosaicking the degradation of the 3D structure near the epipole is solved and it is not necessary to use the unreliable odometry due to its accuracy depending on road conditions.
Owner:HL KLEMOVE CORP
Sensor odometry and application in crash avoidance vehicle
A method for determining an actual trajectory of a vehicle using object detection data and vehicle dynamics data. An object detection system identifies point objects and extended objects in proximity to the vehicle, where the point objects are less than a meter in length and width. An updated vehicle pose is calculated which optimally transposes the point objects in the scan data to a target list of previously-identified point objects. The updated vehicle pose is further refined by iteratively calculating a pose which optimally transposes the extended objects in the scan data to a target model of previously-identified extended objects, where the iteration is used to simultaneously determine a probability coefficient relating the scan data to the target model. The updated vehicle pose is used to identify the actual trajectory of the vehicle, which is compared to a planned path in a collision avoidance system.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
SLAM (simultaneous localization and mapping) method combining GPS (global positioning system) and radar odometer
ActiveCN109507677AEfficient integrationImplement the buildMaps/plans/chartsSatellite radio beaconingSimultaneous localization and mappingTimestamp
An SLAM (simultaneous localization and mapping) method combining GPS (global positioning system) and radar odometer comprises the steps of 1) acquiring differential GPS data and point cloud data fromlaser radar; 2) processing the GPS data to obtain displacement (X, Y, Z) and attitude RPY (rolling, pitching and yawing) angles; 3) matching the GPS data and point cloud data of LiDAR by means of timestamp aligning; 4) checking reliability of the GPS data according to the attitude data from GPS processing of step 2) and the point cloud data of LiDAR; 5) using a LOAM (Lidar odometry and mapping) method to acquire (X, Y, Z) and RPY angles; 6) in a place with reliable GPS data, using the GPS-acquired attitude as a final attitude; in a section with unreliable GPS data, using GPS attitudes of startpoint and endpoint of the section to optimize the attitude of the LOAM method to acquire a final attitude; 7) using the attitude output in step 6) to transform point cloud data of laser radar to a world coordinate system to obtain a final global map. The method herein is suitable for construction of large-range city three-dimensional maps.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Centralizer-based survey and navigation device and method
A Centralizer based Survey and Navigation (CSN) device designed to provide borehole or passageway position information. The CSN device can include one or more displacement sensors, centralizers, an odometry sensor, a borehole initialization system, and navigation algorithm implementing processor(s). Also, methods of using the CSN device for in-hole survey and navigation.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
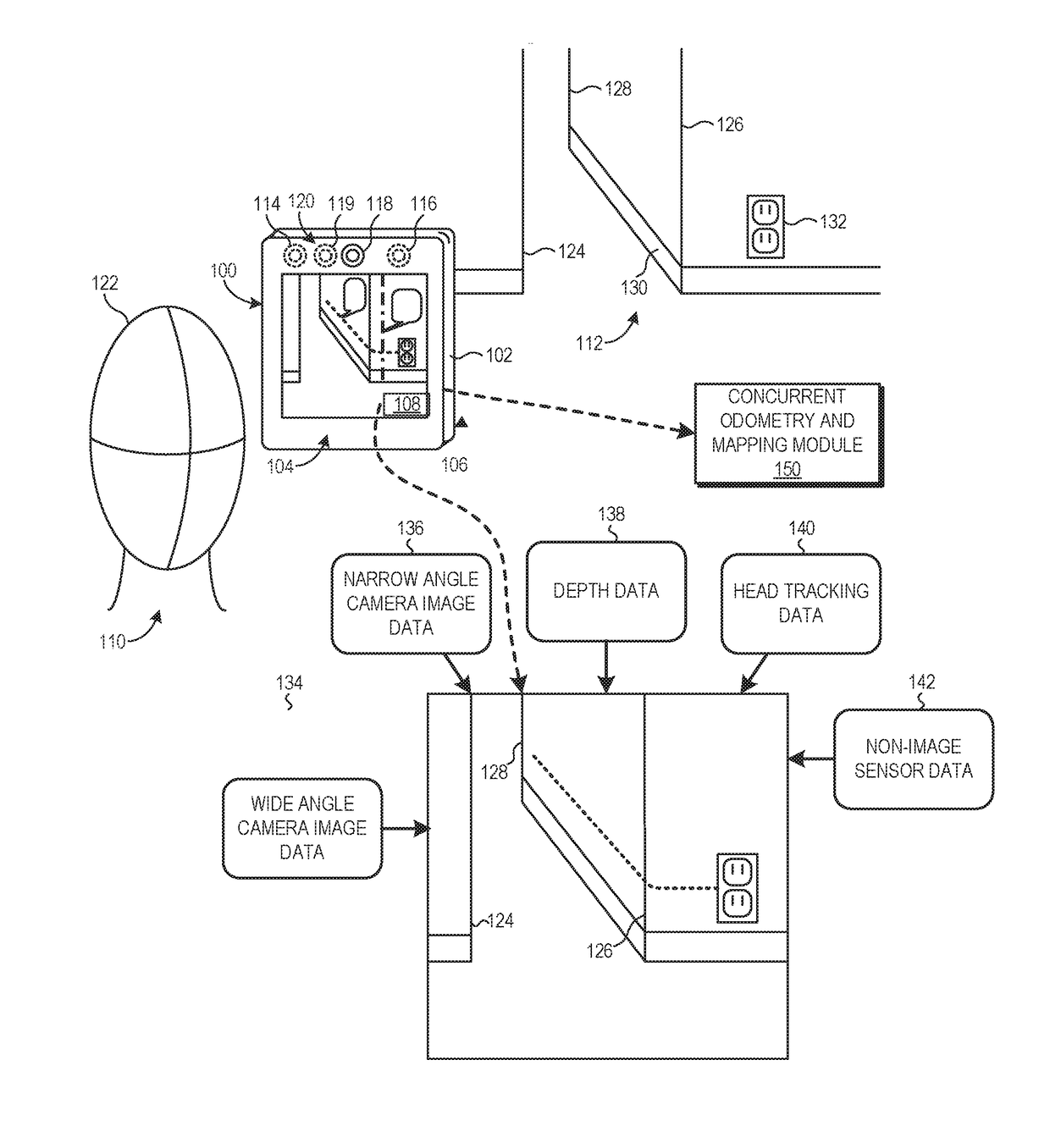
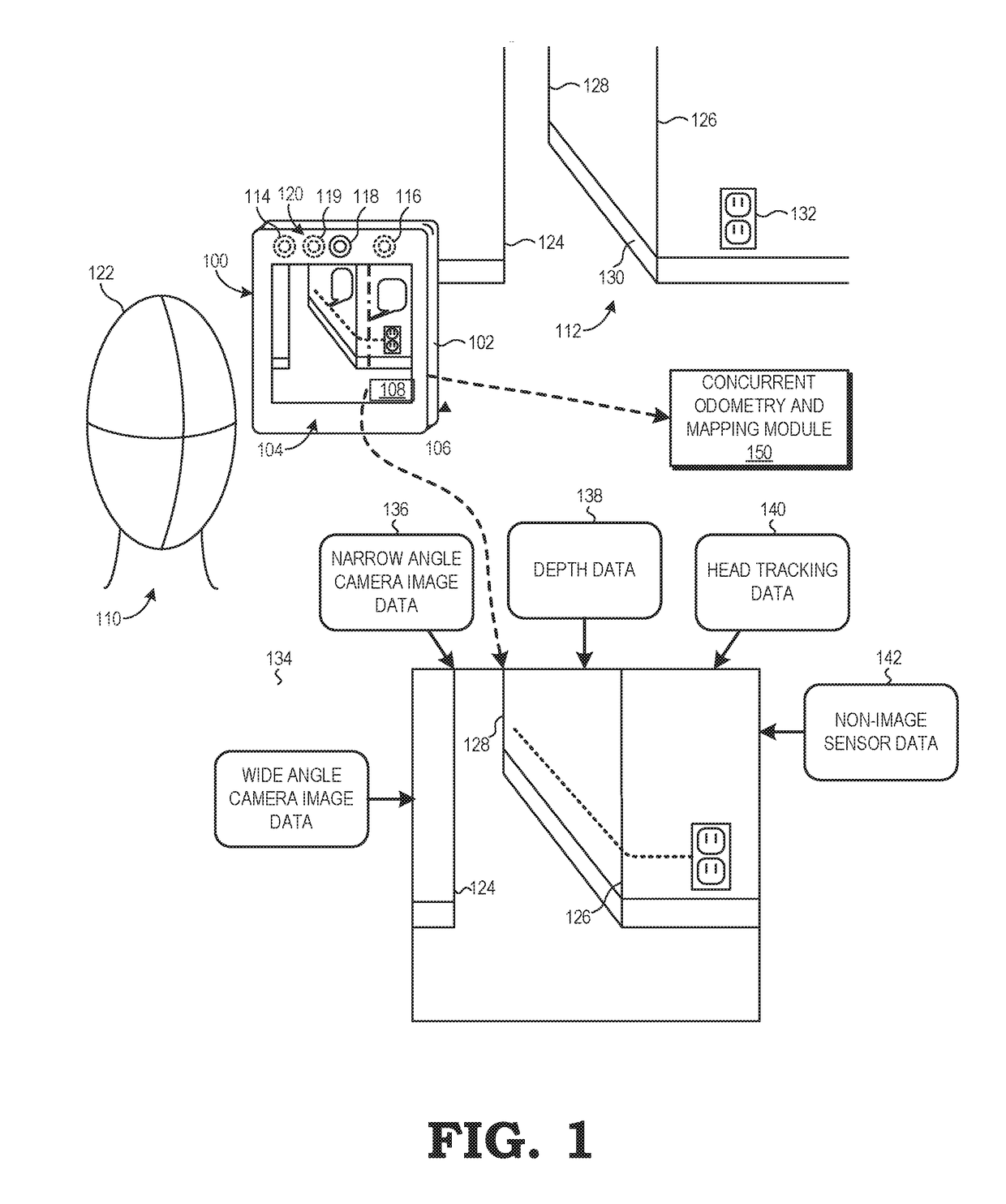
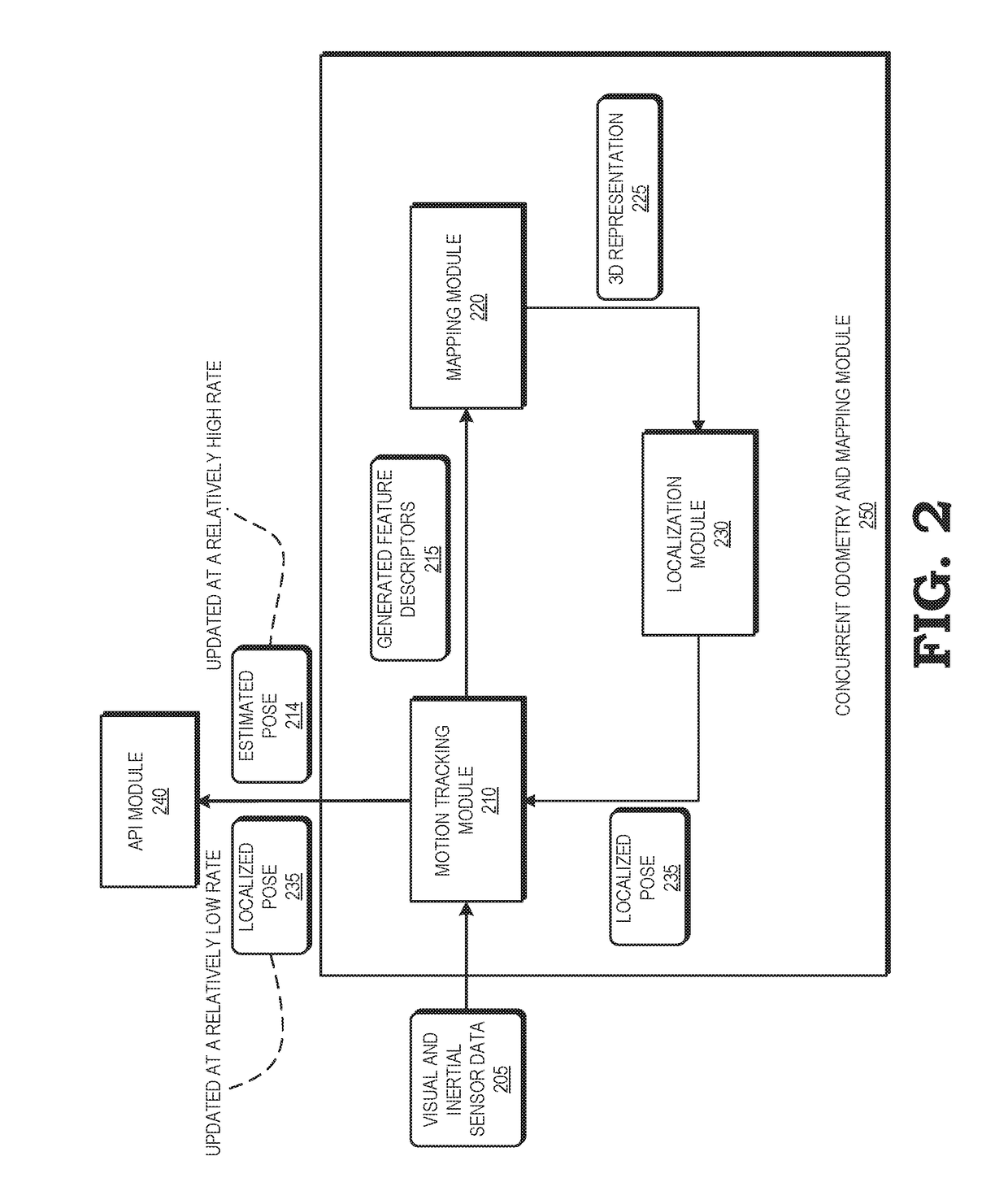
System and method for concurrent odometry and mapping
ActiveUS20170336511A1Limiting utility and effectivenessImage enhancementImage analysisOdometryVisual appearance
An electronic device tracks its motion in an environment while building a three-dimensional visual representation of the environment that is used to correct drift in the tracked motion. A motion tracking module estimates poses of the electronic device based on feature descriptors corresponding to the visual appearance of spatial features of objects in the environment. A mapping module builds a three-dimensional visual representation of the environment based on a stored plurality of maps, and feature descriptors and estimated device poses received from the motion tracking module. The mapping module provides the three-dimensional visual representation of the environment to a localization module, which identifies correspondences between stored and observed feature descriptors. The localization module performs a loop closure by minimizing the discrepancies between matching feature descriptors to compute a localized pose. The localized pose corrects drift in the estimated pose generated by the motion tracking module.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
GPS-based in-vehicle sensor calibration algorithm
ActiveUS7957897B2Digital data processing detailsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsOdometryData validation
A system and method for calibrating the bias and scale factors of a heading rate sensor, such as a yaw-rate sensor, using GPS signals. The system receives wheel speed or rotation signals, a vehicle odometer reading, GPS signals and yaw-rate signals. The system includes a wheel-slip detection processor that determines whether there is wheel-slip based on the wheel speed signals and the GPS signals. The system also includes a wheel-based acceleration processor that estimates vehicle acceleration. The system also includes a differential odometry processor that determines vehicle heading based on wheel speed. The system also includes a GPS reference data validation processor that determines whether the GPS signals are valid using the estimated vehicle acceleration and wheel speeds. The valid GPS signals are then used to calibrate the yaw-rate sensor signals, which can be used for vehicle heading purposes.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Inertial navigation unit enhaced with atomic clock
InactiveUS20160349379A1Low drift rateCapablePosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingRelative motionVisual perception
An atomic clock is used in conjunction with the GNSS receiver and the inertial sensors, creating a more capable inertial navigation system (INS). The system is composed of a GNSS receiver, an accurate clock, and a mechanism for measuring relative pose changes. The system being presented utilizes an inertial measurement unit (IMU) to provide the relative pose changes, but other mechanisms can be used—like visual and ladar odometry. The GNSS receiver measures the pseudo-ranges to the GNSS satellites in the field of view. These measurements are “time tagged” with the accuracy of the atomic clock. The relative motion between the pseudo-ranges is measured using the IMU. Finally, the lock is achieved by filtering these measurements. The filtering mechanism can vary, from the traditional Kalman Filters to other mechanisms that attempt to minimize the mean square error.
Owner:ROBOTIC RES OPCO LLC
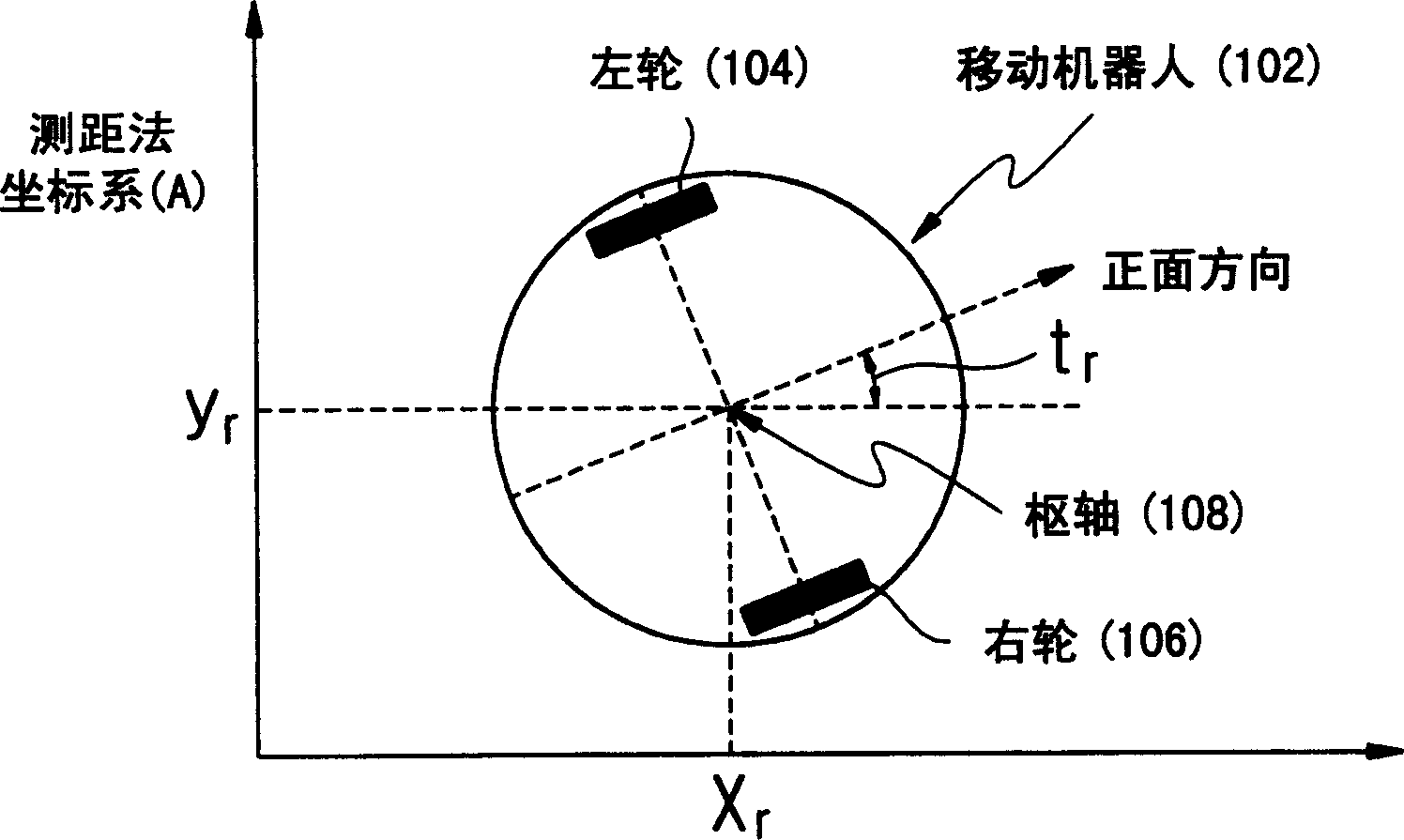
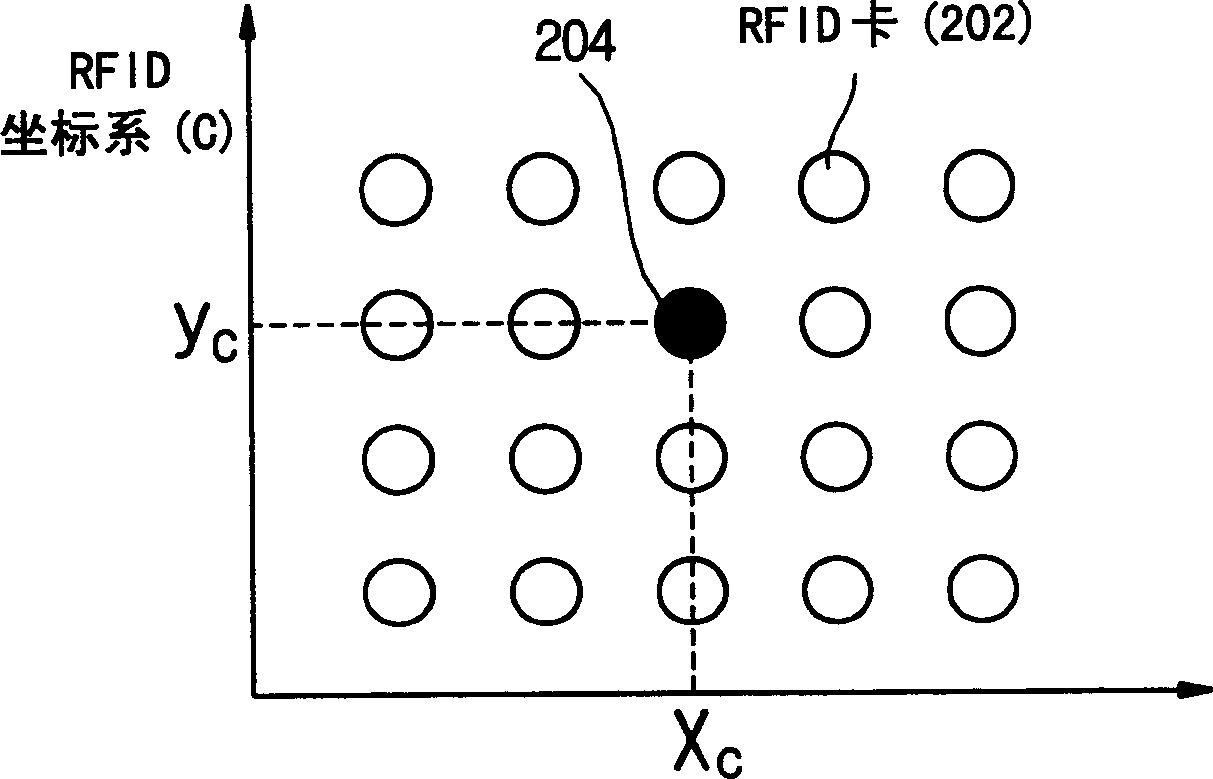
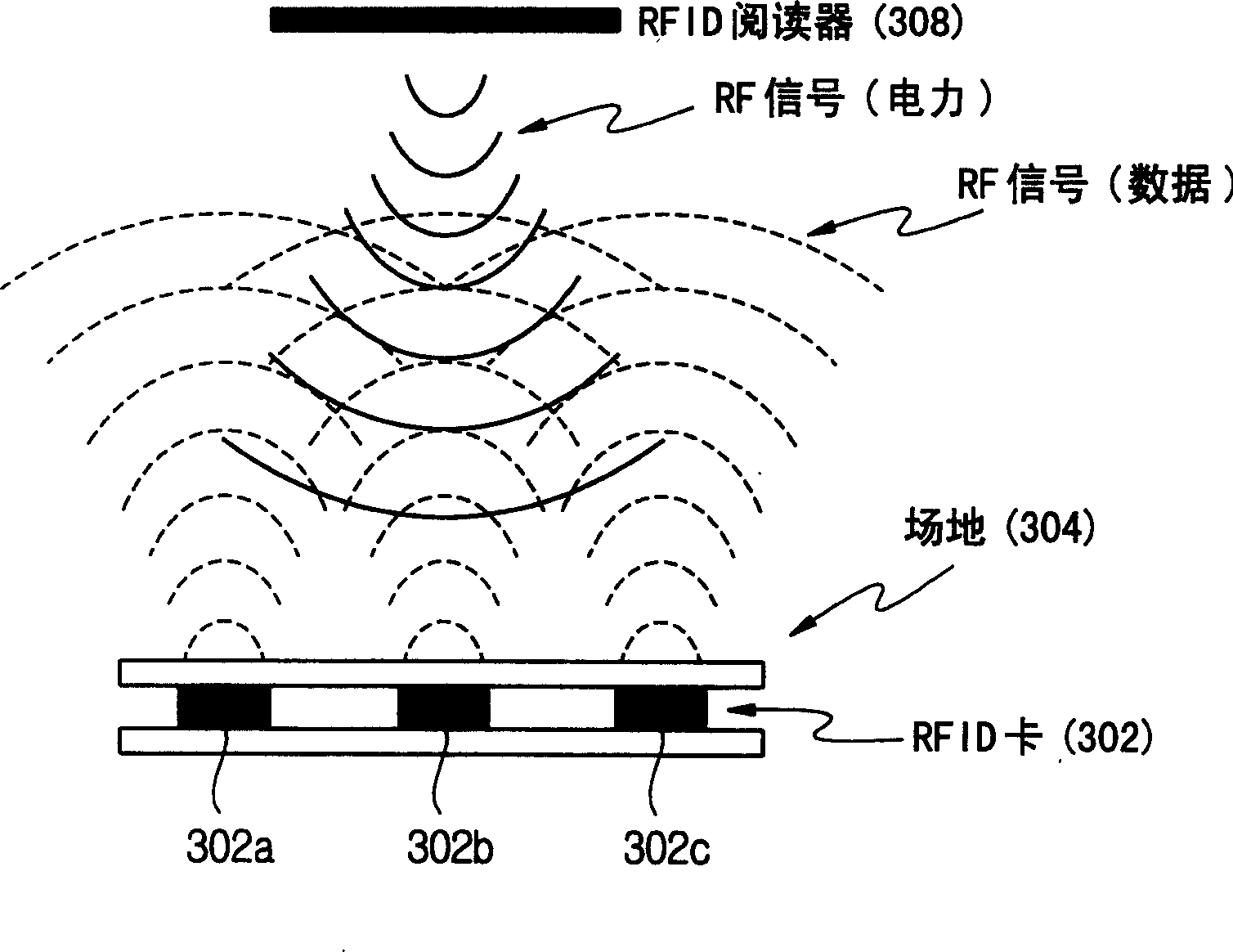
Apparatus and method of recognizing position and direction of mobile robot
InactiveCN1467480ARecognition stabilityHigh sampling rateProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorOdometryComputer vision
An apparatus and method of recognizing a position and direction of a mobile robot includes obtaining absolute coordinates at a current position of the mobile robot and relative coordinates for a moving displacement of the mobile robot. Therefore, the position and direction of the mobile robot are recognized by reflecting the relative coordinates on the absolute coordinates. Accordingly, the present invention operates odometry and RFID coordinate systems in combination with each other, thus obtaining a high sampling rate by the odometry coordinate system while restricting an error range within a predetermined level by the RFID coordinate system.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
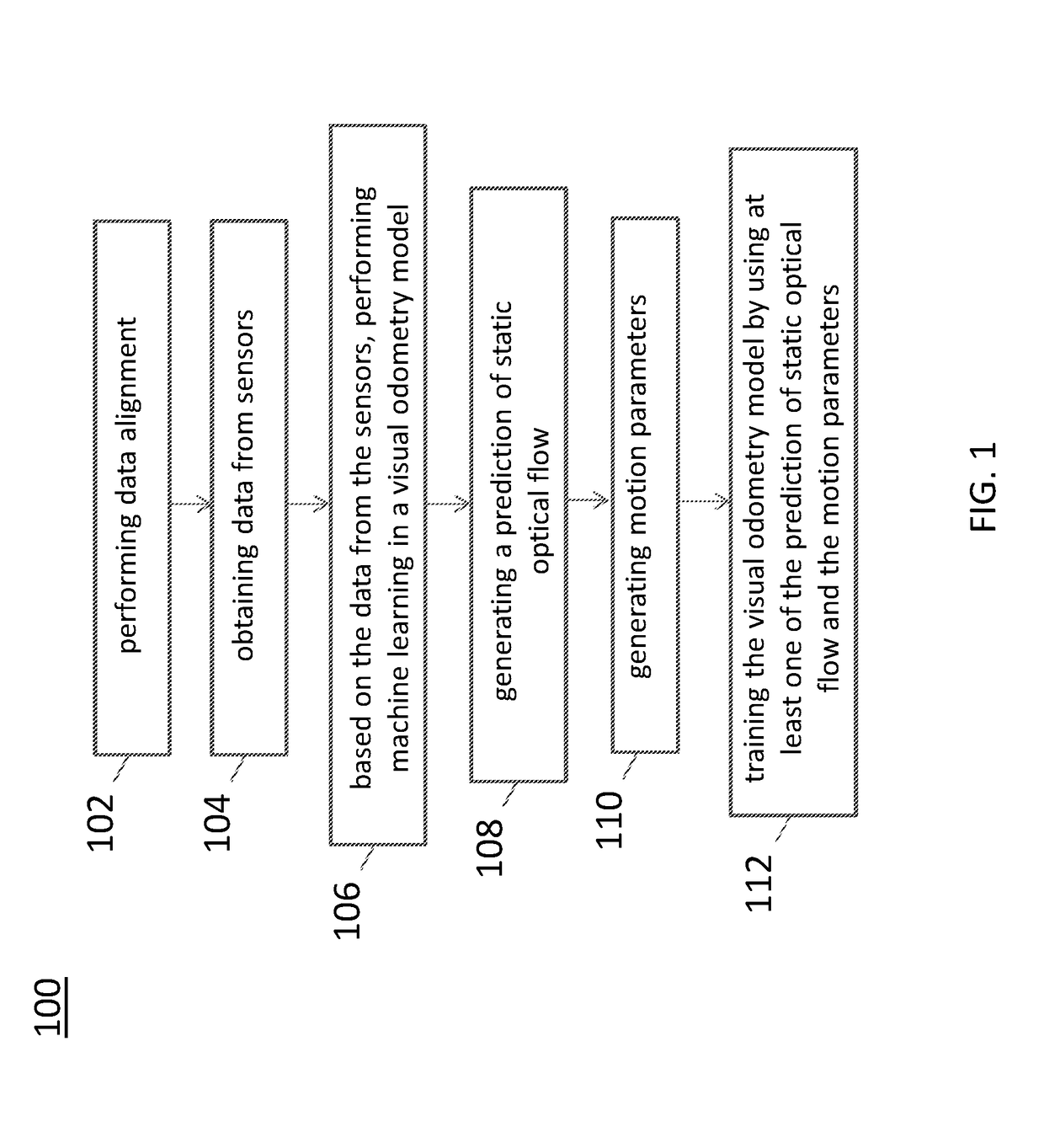
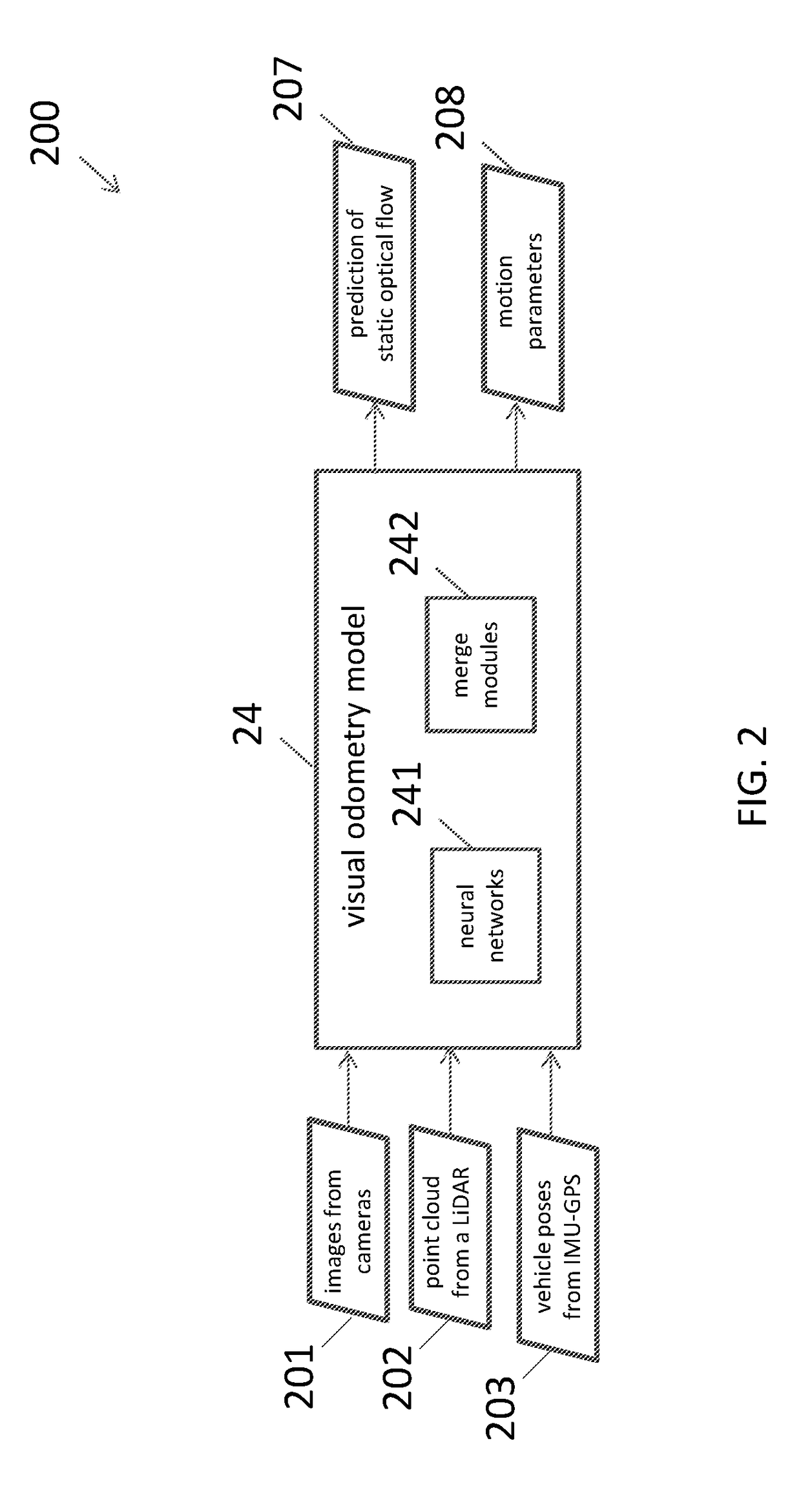
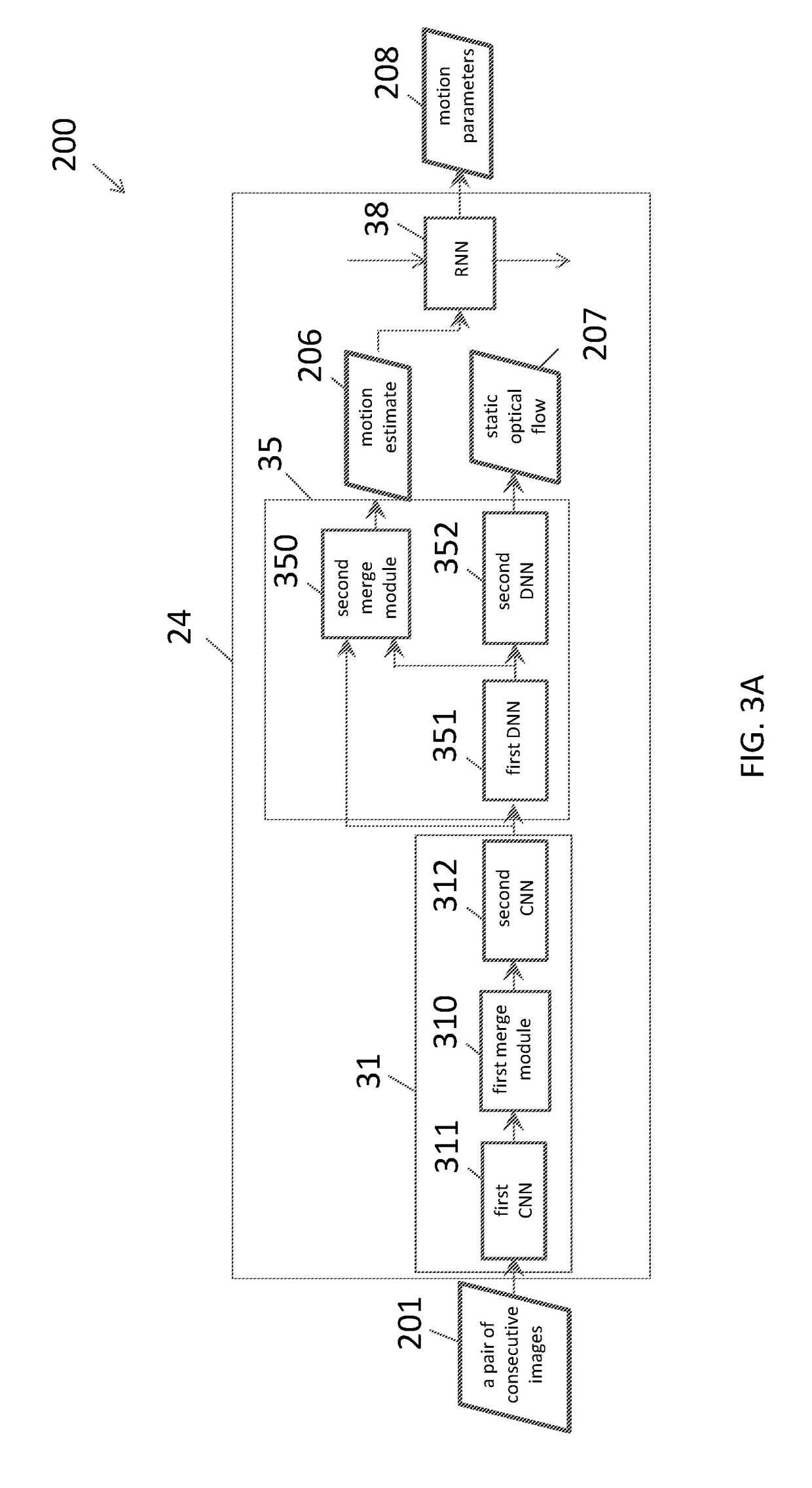
Neural network architecture system for deep odometry assisted by static scene optical flow
ActiveUS20190079534A1Reduce accumulated errorsImage enhancementInstruments for road network navigationStructure of Management InformationNetwork architecture
A system for visual odometry is disclosed. The system includes: an internet server, comprising: an I / O port, configured to transmit and receive electrical signals to and from a client device; a memory; one or more processing units; and one or more programs stored in the memory and configured for execution by the one or more processing units, the one or more programs including instructions for: extracting representative features from a pair input images in a first convolution neural network (CNN) in a visual odometry model; merging, in a first merge module, outputs from the first CNN; decreasing feature map size in a second CNN; generating a first flow output for each layer in a first deconvolution neural network (DNN); merging, in a second merge module, outputs from the second CNN and the first DNN; generating a second flow output for each layer in a second DNN; and reducing accumulated errors in a recurrent neural network (RNN).
Owner:TUSIMPLE INC
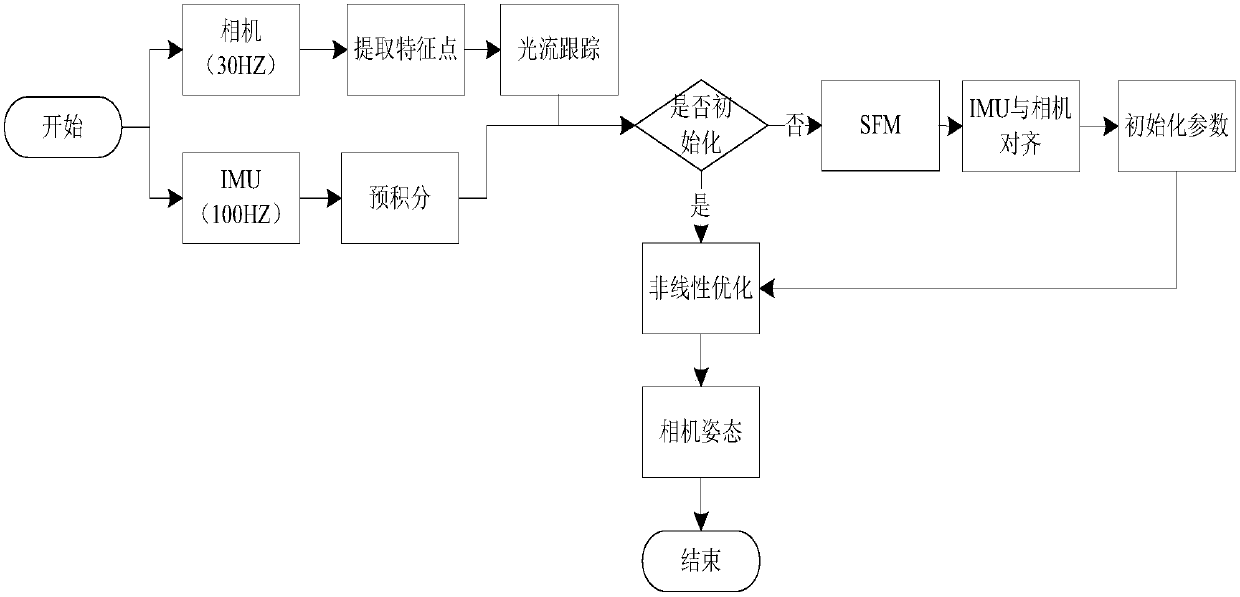
Monocular vio (Visual-Inertial Odometry) based mobile terminal AR method
InactiveCN107767425ARun in real timeAvoid offsetImage enhancementImage analysisSimultaneous localization and mappingOdometry
The invention provides a monocular vio (Visual-Inertial Odometry) based mobile terminal AR method, which comprises the steps of performing image acquisition and inertial data acquisition respectivelyby using a camera and an IMU; extracting feature points of each image acquired by the camera, and setting the extracted feature points to be key frames; calculating corresponding IMU position and rotation information of two images in a pre-integration manner; acquiring a tracked feature point in the key frames, and calculating the pose of each key frame according to the feature point; calculatingan external parameter between the camera and the IMU according to a condition that displacement and rotation information acquired by the IMU is equal to displacement and rotation information measuredby the camera between the two frame; initializing the speed, the acceleration and a scale factor of the IMU; acquiring the pose of the camera by using tight coupling nonlinear optimization, and then superimposing a virtual object to achieve an AR effect. The mobile terminal AR method adopts the IMU to make up defects of VSLAM (Virtual Simultaneous Localization and Mapping), and is not affected byenvironmental feature points within a short time; and deviation is prevented by using alignment of the VSLAM and the IMU when the time is long.
Owner:NANJING WEIJING SHIKONG INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Apparatus of controlling movement of mobile robot mounted with wide angle camera and method thereof
ActiveUS20170153646A1Reduce positioningAccurate estimateProgramme-controlled manipulatorImage enhancementOdometryMedicine
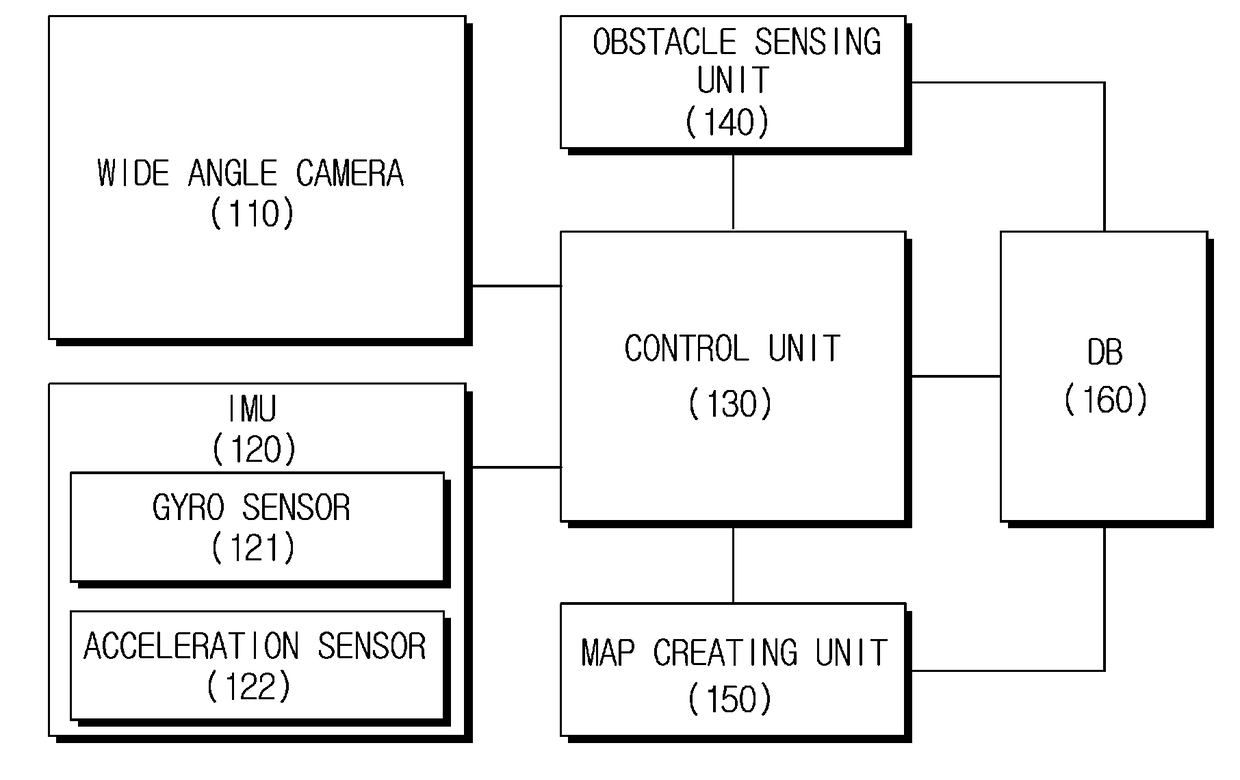
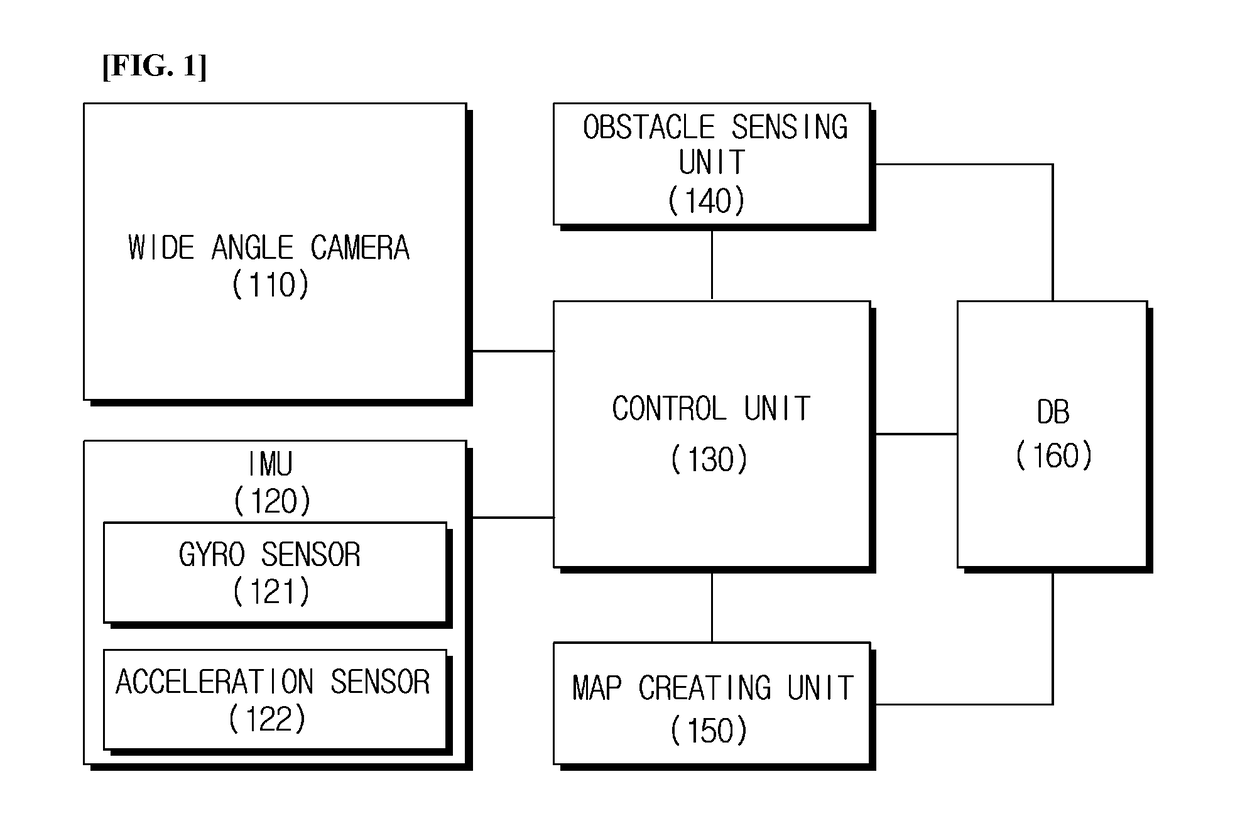
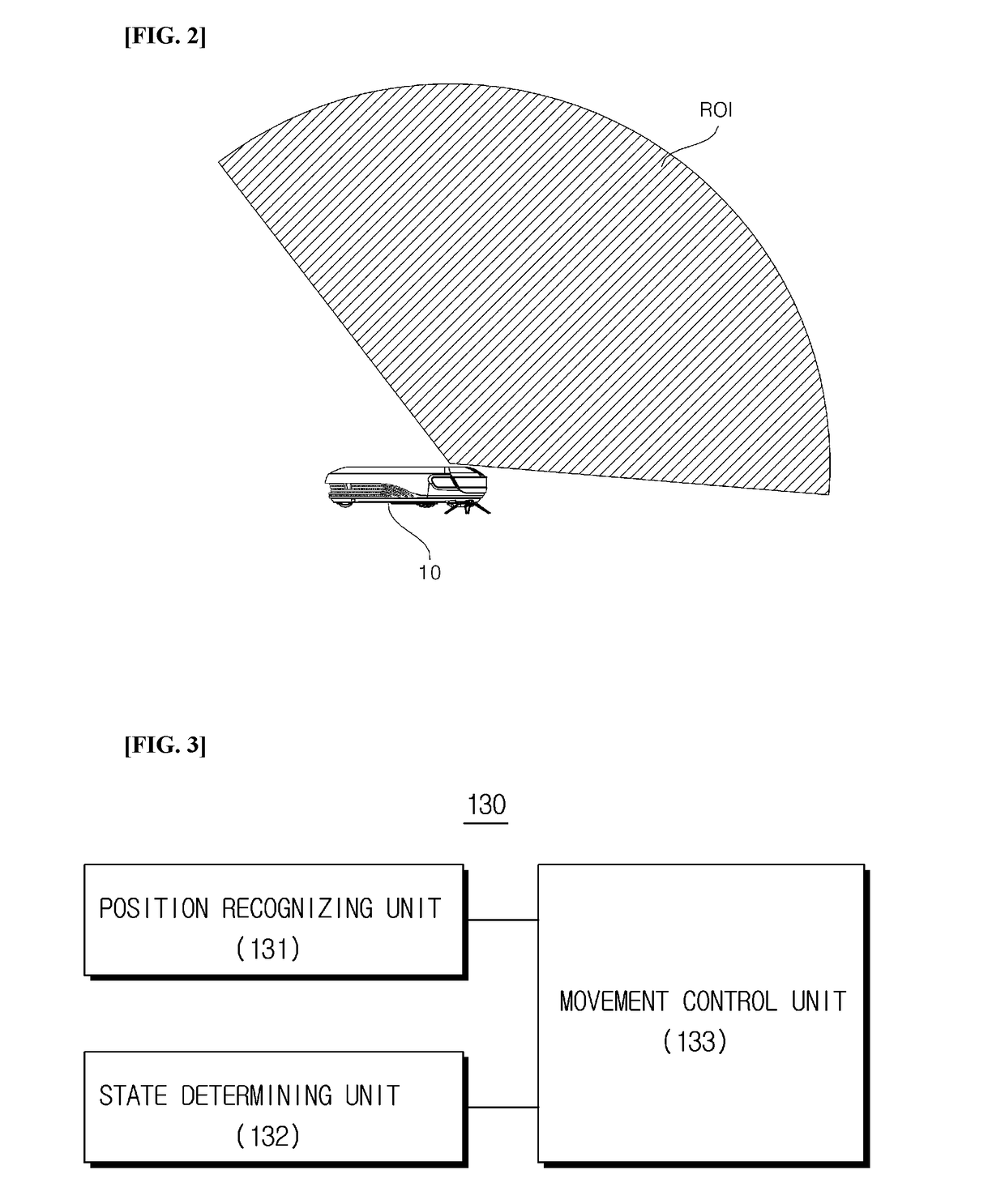
Disclosed are an apparatus of controlling movement of a mobile robot mounted with a wide angle camera and a method thereof. An apparatus of recognizing a position of a mobile robot includes two wide angle cameras which obtain one pair of stereo images on a region of interest including a vertical direction and a horizontal direction in accordance with movement of a mobile robot; an inertial measurement unit (IMU) which obtains inertial information of a mobile robot; a position recognizing unit which predicts a movement point using one between first odometry information calculated based on at least one pair of stereo images and second odometry information calculated based on the inertial information and estimates a current position using the predicted movement point and a previously stored key frame, by a position recognizing unit; and a movement control unit which controls movement of the mobile robot based on the estimated position.
Owner:YUJIN ROBOT
System and method for calibrating vehicle dynamics expectations for autonomous vehicle navigation and localization
InactiveUS20180188031A1Precise NavigationAccurately determine its locationInstruments for road network navigationAutonomous decision making processVehicle dynamicsOdometry
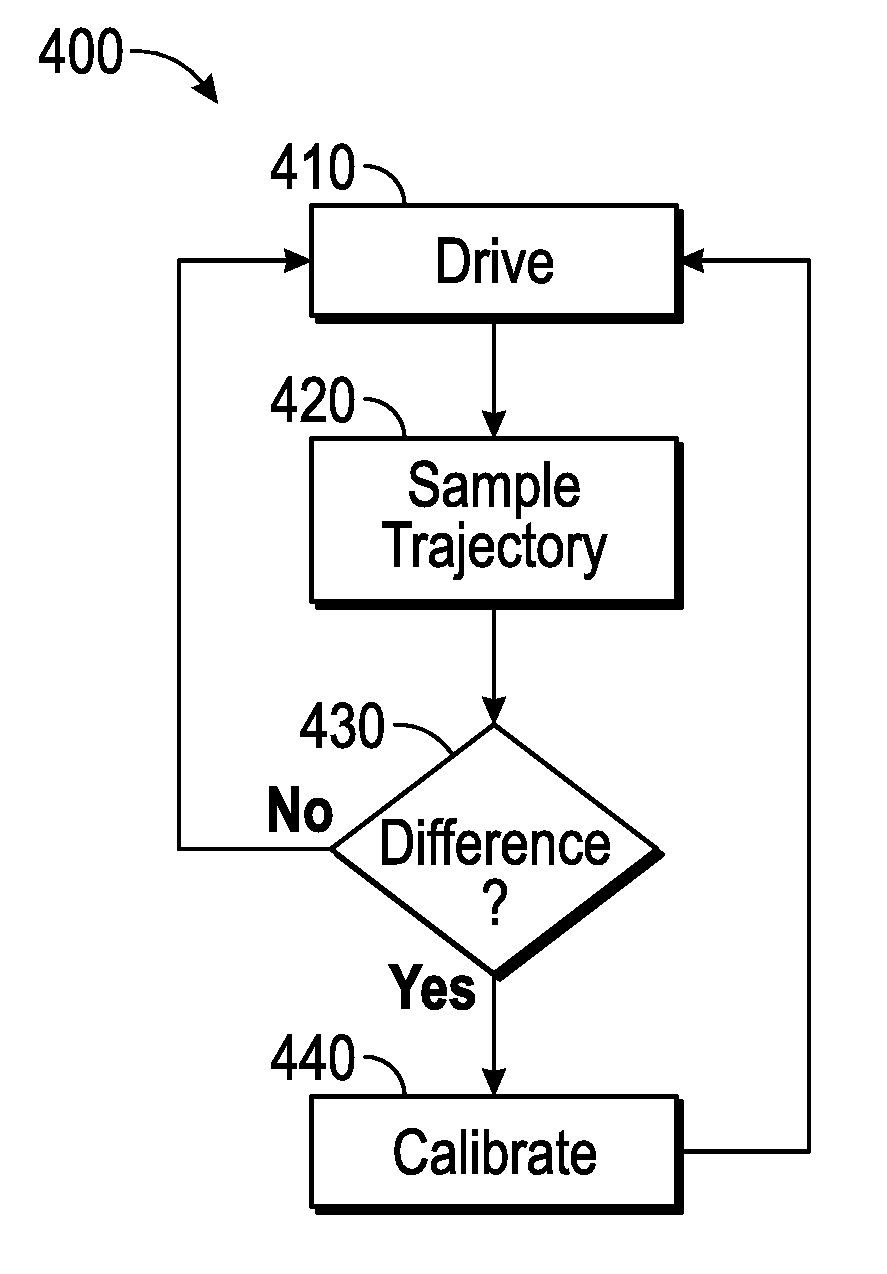
A system that performs a method is disclosed. While navigating a vehicle along a path, the system determines a starting point along the driving path, and monitors a vehicle trajectory, wherein the vehicle trajectory comprises odometry information. The system calculates an expected ending point of the vehicle trajectory using the starting point, the odometry information, and vehicle dynamics expectations, and determines whether there is a difference between the ending point and the expected ending point that is greater than a threshold distance. In response to the determination: in accordance with a determination that the difference between the ending point and the expected ending point is greater than the threshold distance, the system calibrates the vehicle dynamics expectations. In accordance with a determination that the difference between the ending point and the expected ending point is not greater than the threshold distance, the system foregoes calibrating the vehicle dynamics expectations.
Owner:FARADAY&FUTURE INC
Intelligent wheel chair control method based on brain computer interface and automatic driving technology
InactiveUS20170095383A1Reduce mental burdenInput/output for user-computer interactionEnsemble learningBrain computer interfacingAngular velocity
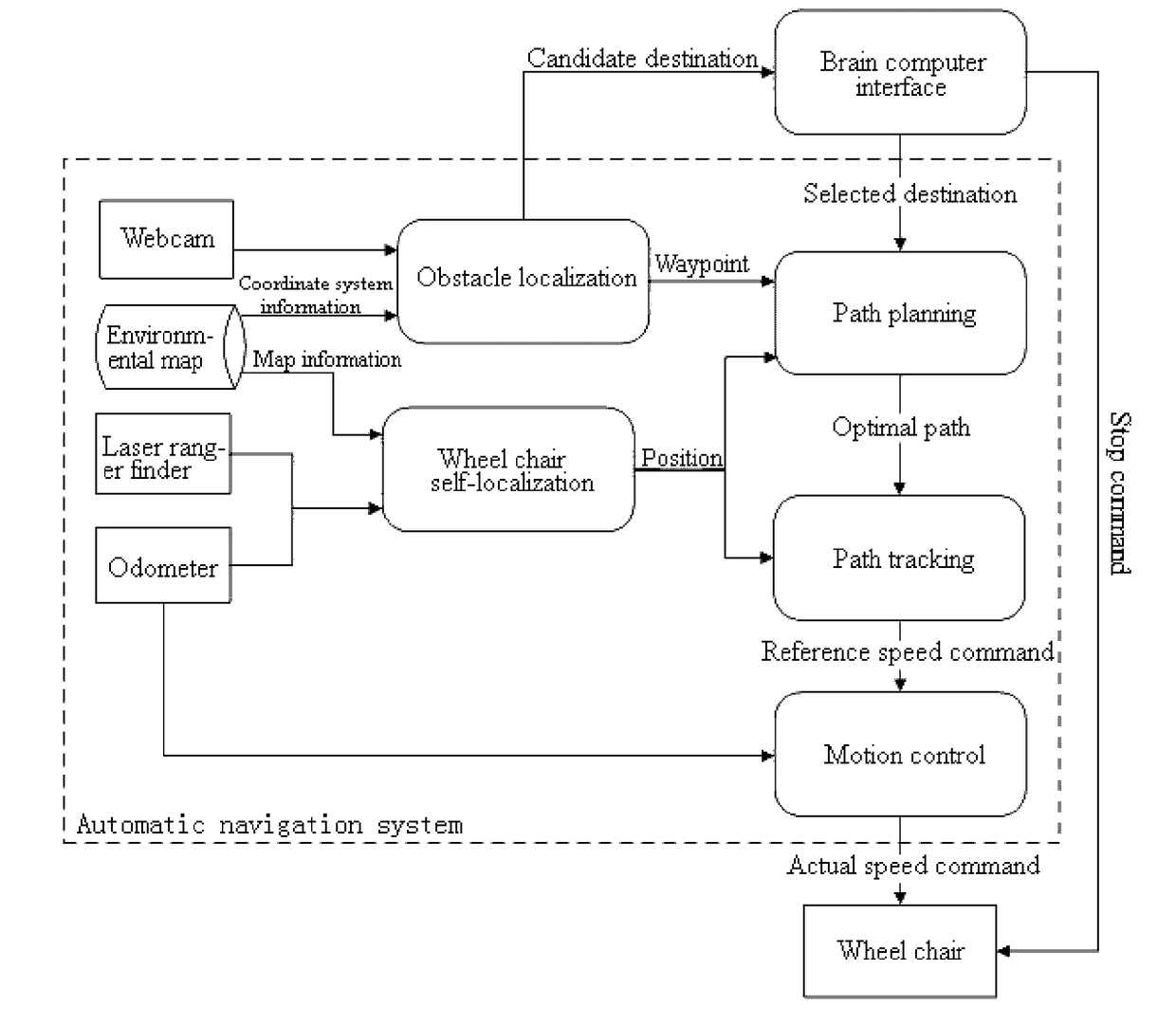
Disclosed is an intelligent wheel chair control method based on a brain computer interface and an automatic driving technology. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring current pictures by webcams to perform obstacle localization; generating candidate destinations and waypoints for path planning according to the current obstacle information; performing self-localization of the wheel chair; selecting a destination by a user through the brain computer interface (BCI); planning an optimal path according to the current position of the wheel chair as a starting point and the destination selected by the user as an end point in combination with the waypoints; calculating a position error between the current position of the wheel chair and the optimal path as the feedback of aPID path tracking algorithm; and calculating a reference angular velocity and linear velocity by means of the PID path tracking algorithm and transmitting them to a PID motion controller, converting odometry data from encoders into current angular and linear velocities as a feedback of the PID motion controller, and controlling the driving of the wheel chair in real time to the destination. The intelligent wheel chair control method greatly relieves the mental burden of a user, can adapt to changes in the environment, and improves the self-care ability of patients with severe paralysis.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com