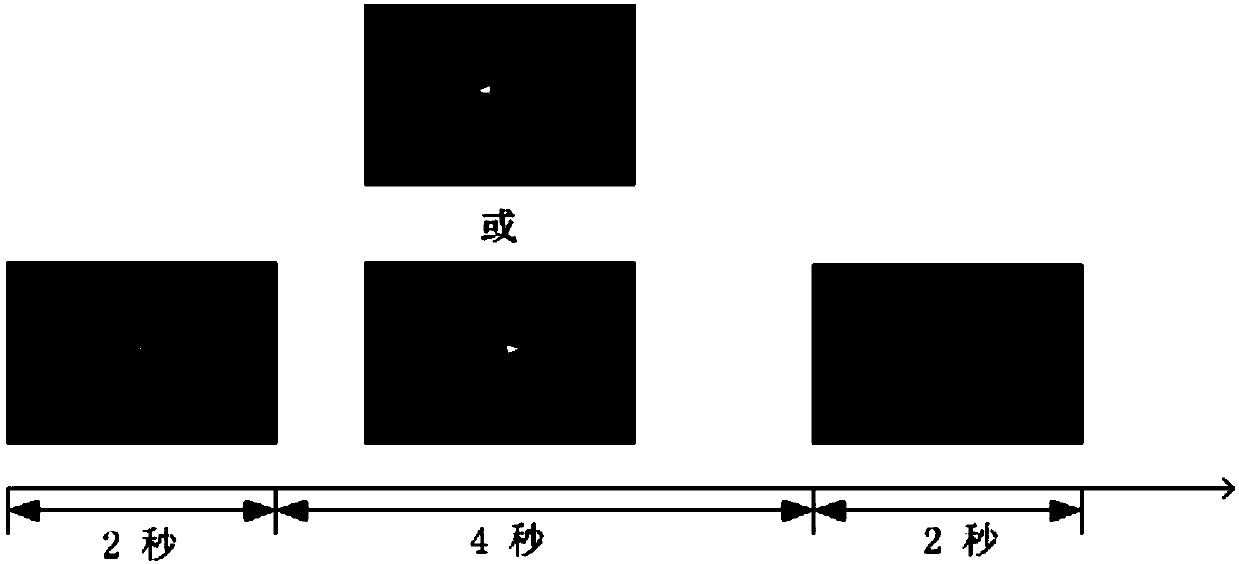
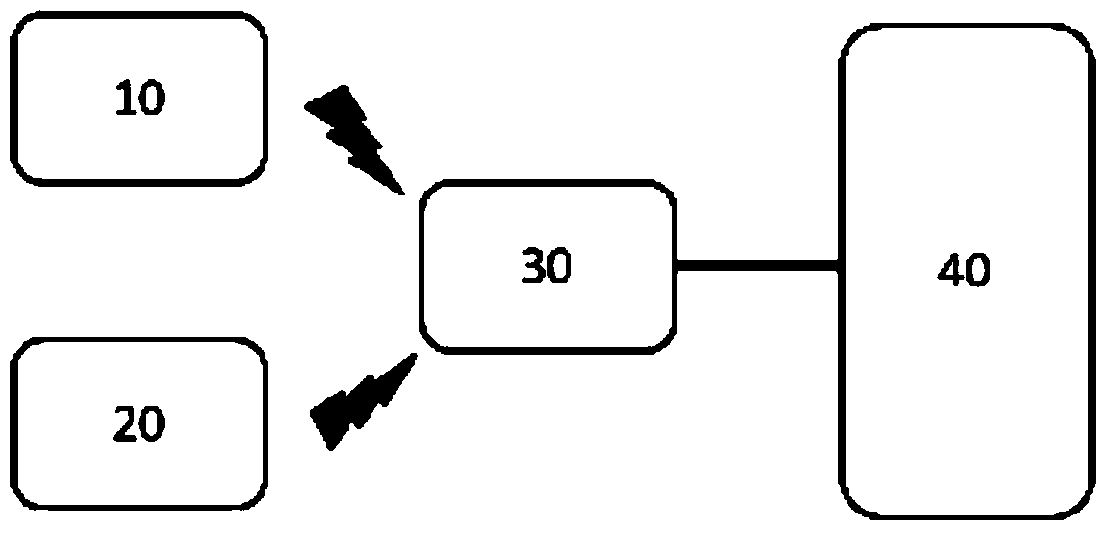
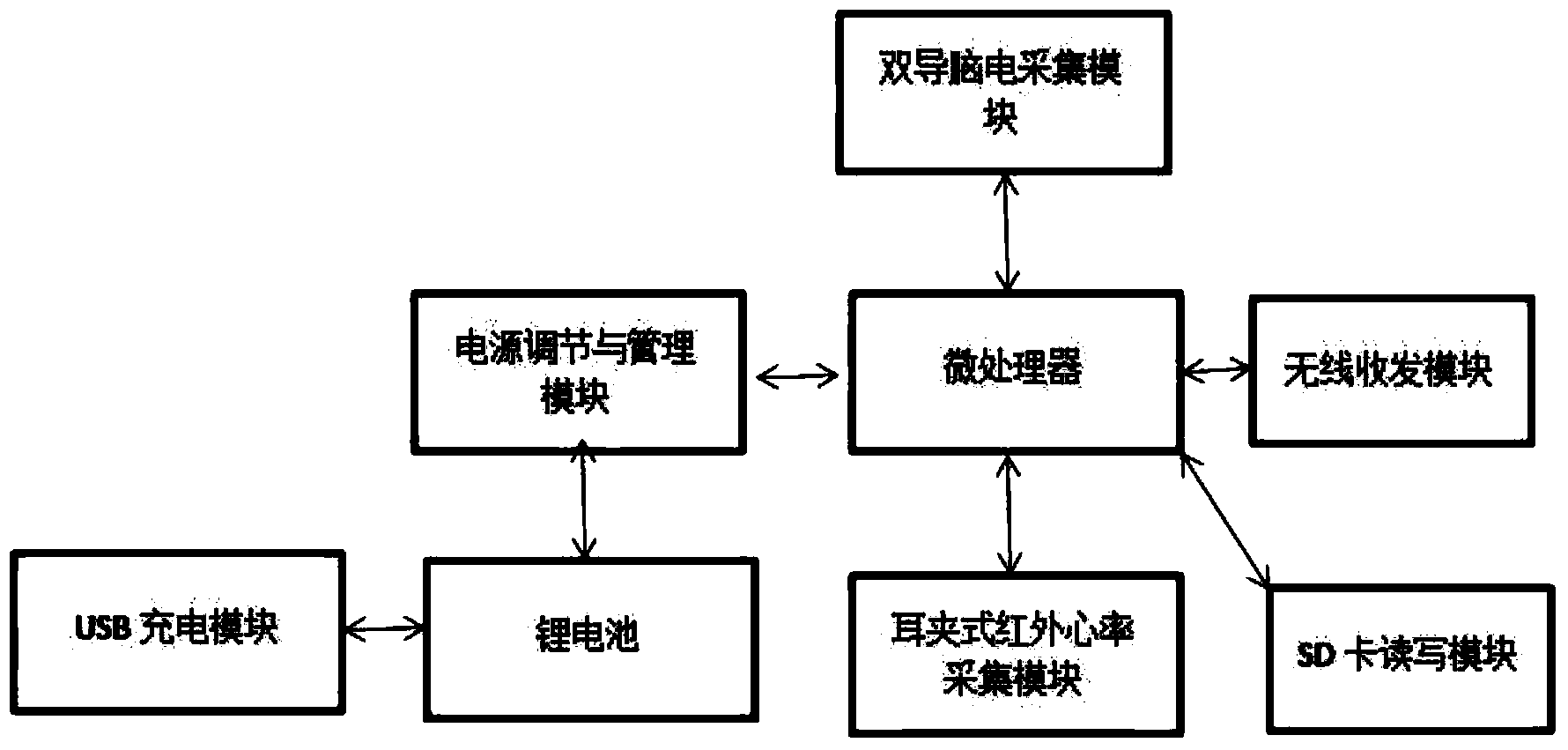
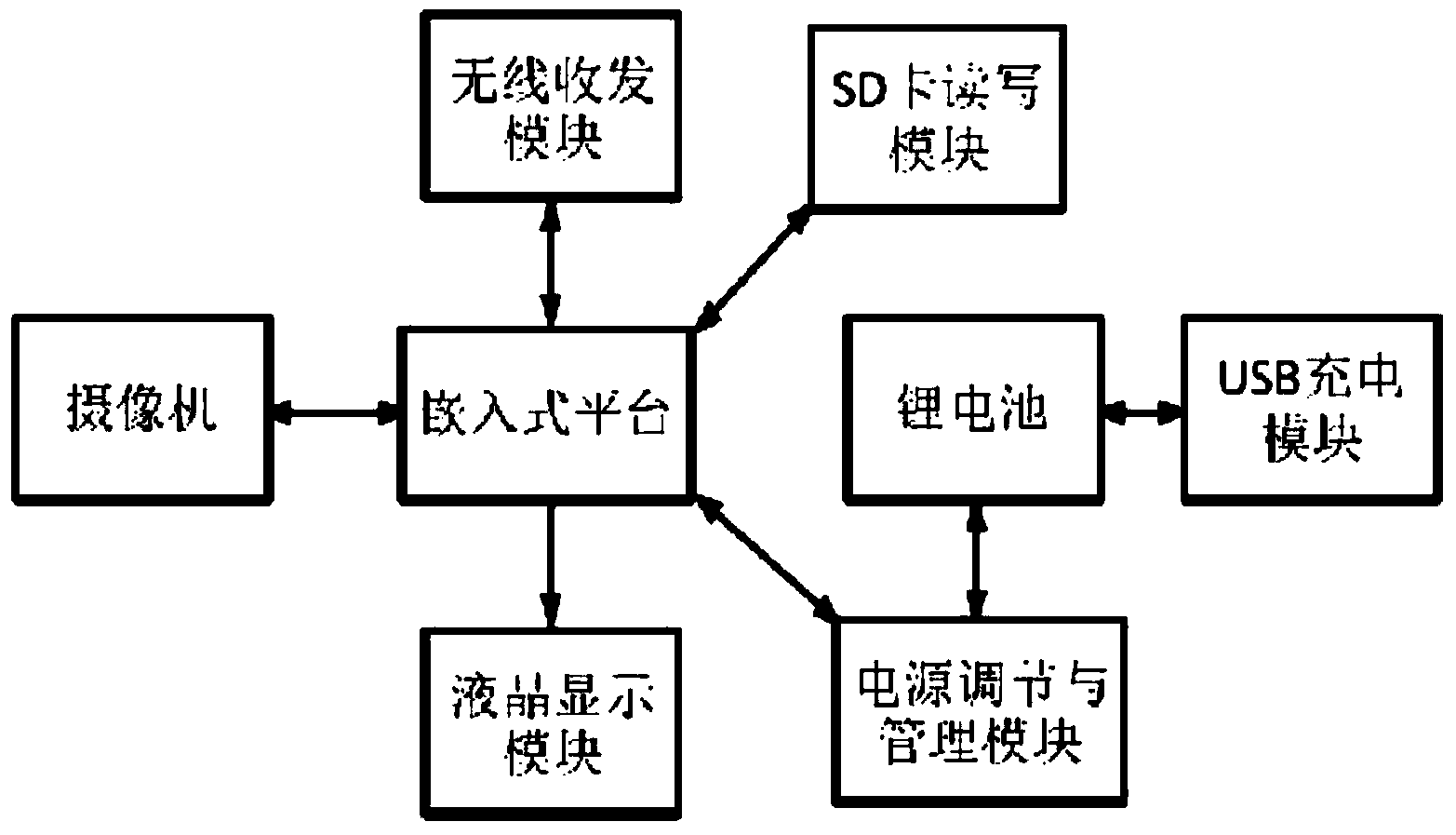
Patents
Literature
508 results about "Brain–computer interface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A brain–computer interface (BCI), sometimes called a neural-control interface (NCI), mind-machine interface (MMI), direct neural interface (DNI), or brain–machine interface (BMI), is a direct communication pathway between an enhanced or wired brain and an external device. BCI differs from neuromodulation in that it allows for bidirectional information flow. BCIs are often directed at researching, mapping, assisting, augmenting, or repairing human cognitive or sensory-motor functions.
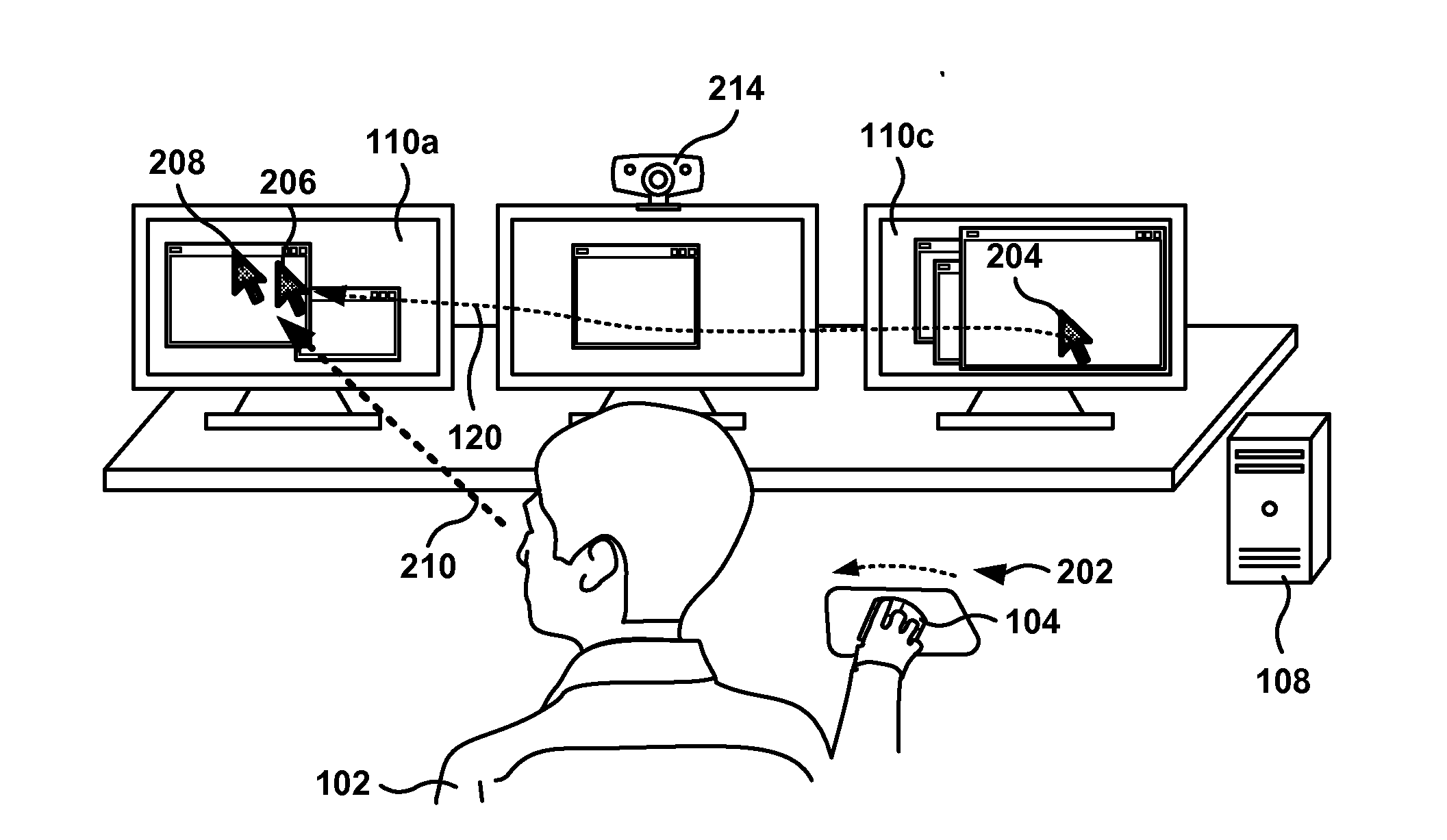
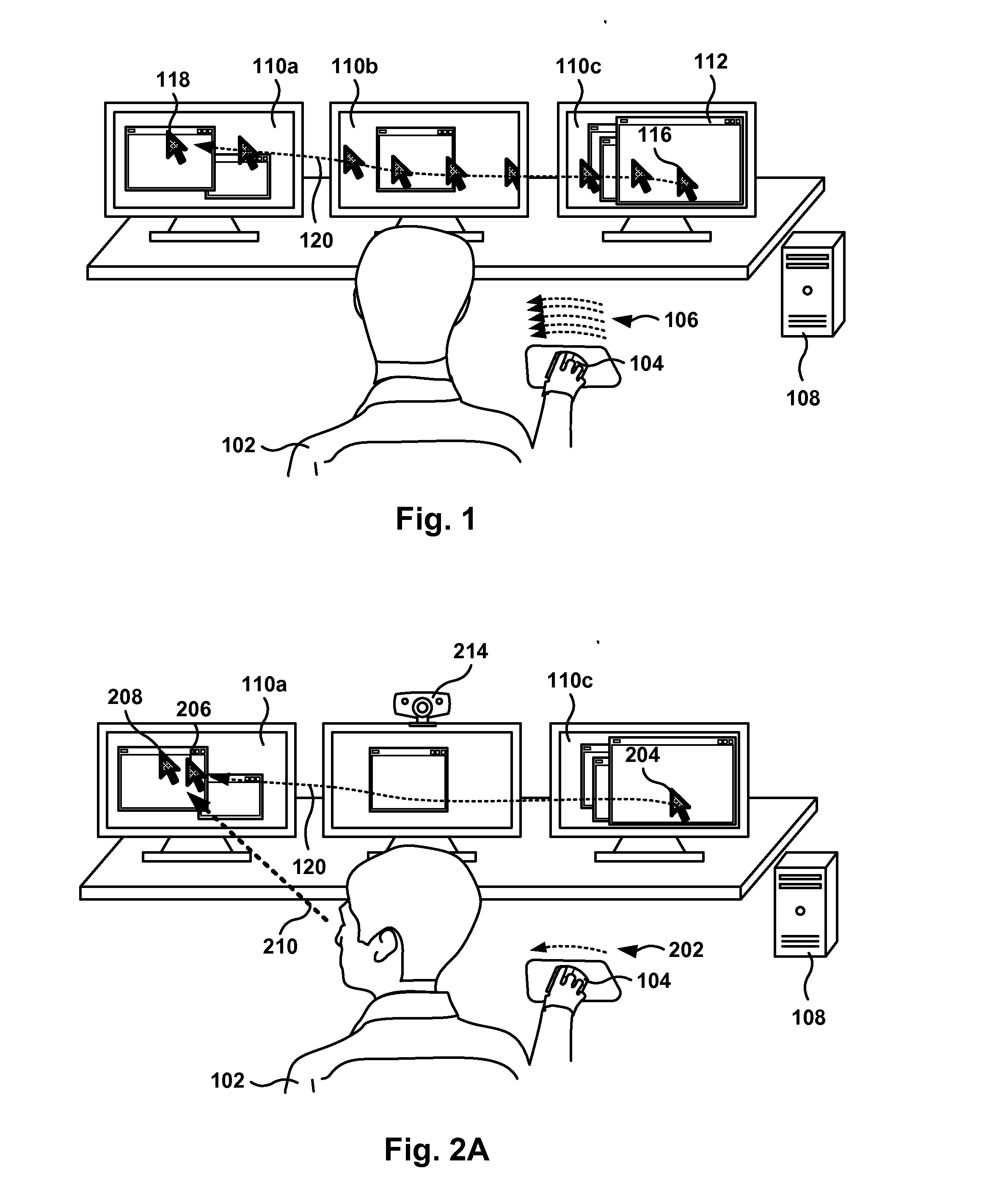
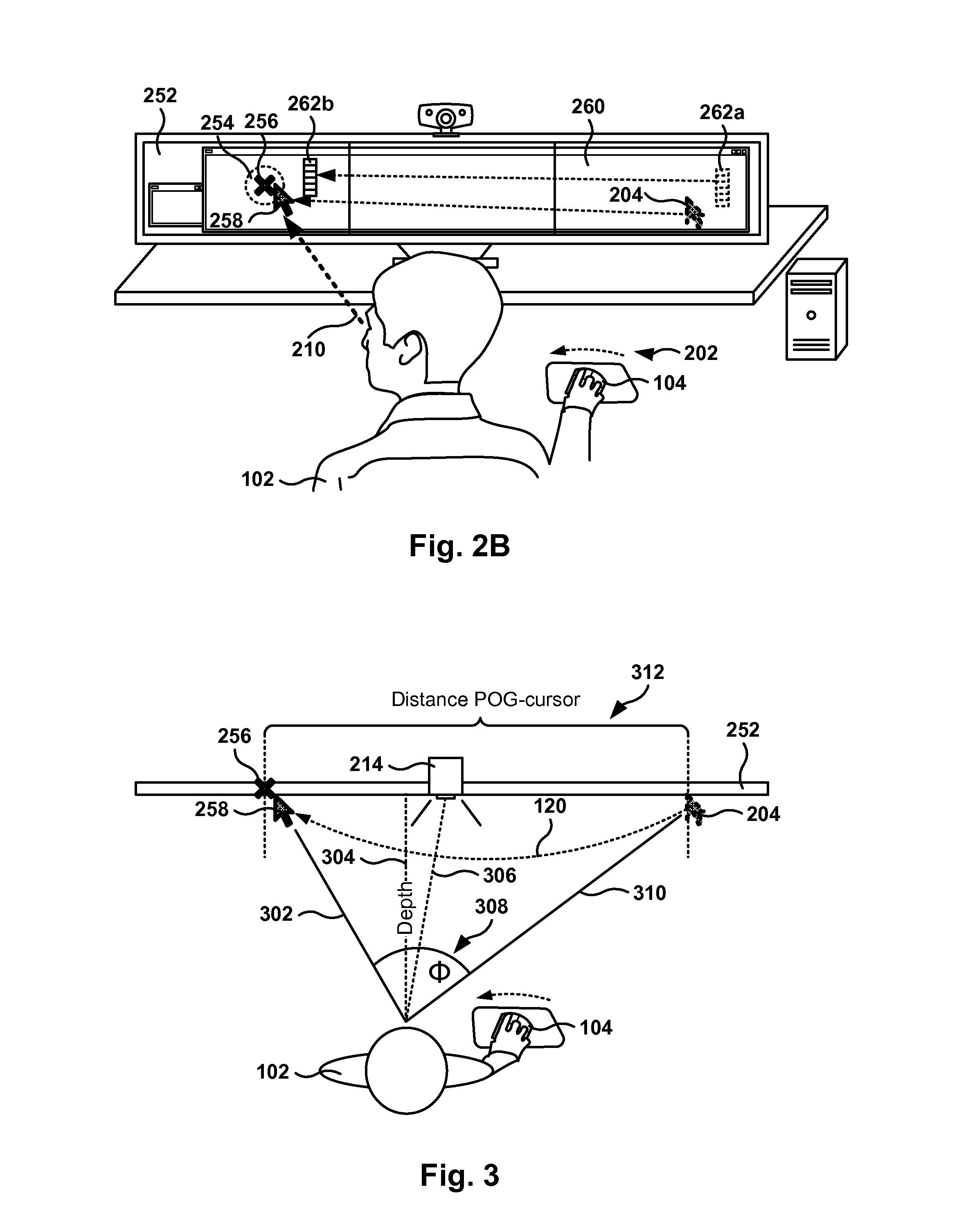
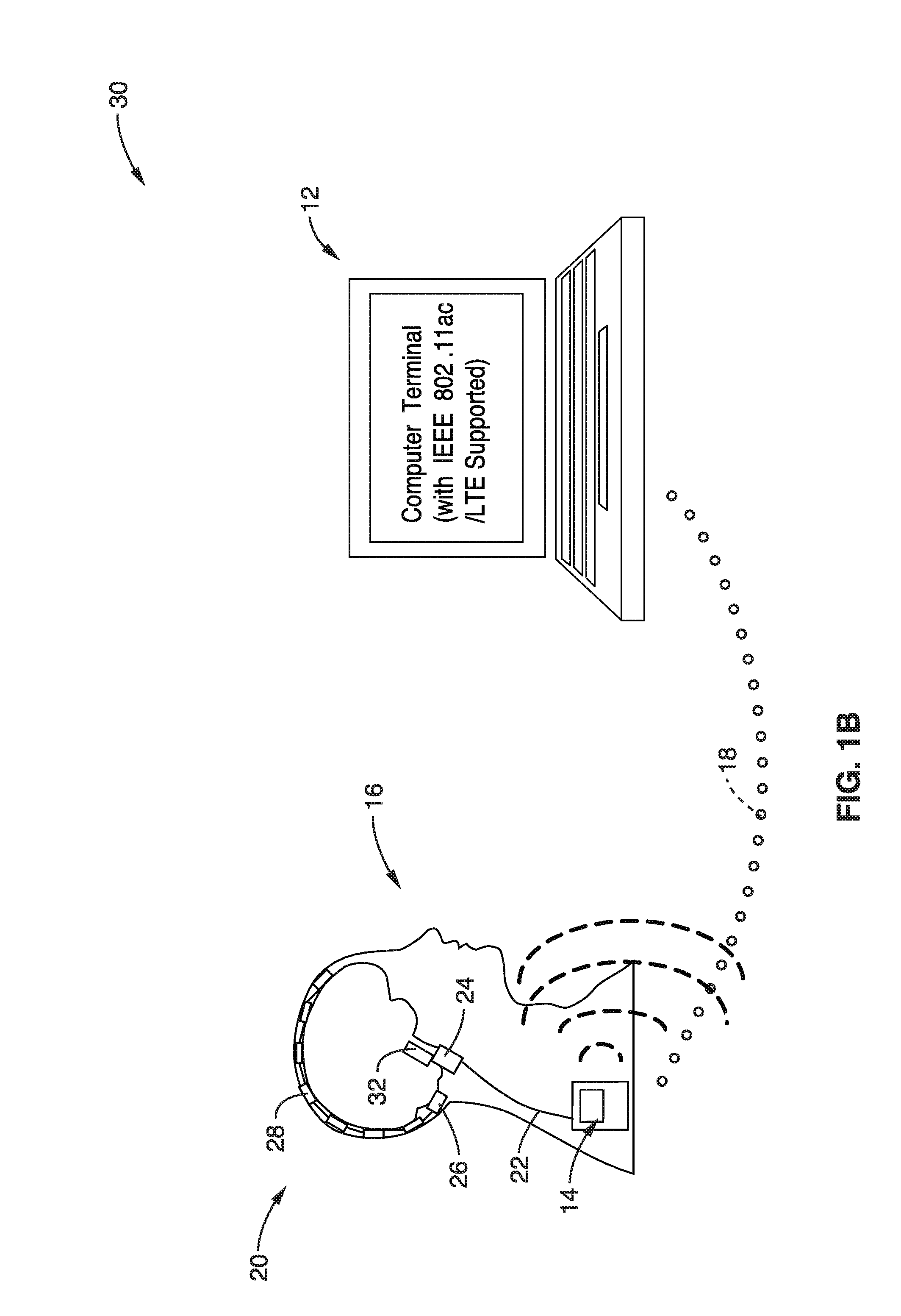
Gaze-Assisted Computer Interface
ActiveUS20120272179A1Input/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsGraphical user interface
Methods, systems, and computer programs for interfacing a user with a Graphical User Interface (GUI) are provided. One method includes an operation for identifying the point of gaze (POG) of the user. The initiation of a physical action by the user, to move a position of a cursor on a display, is detected, where the cursor defines a focus area associated with a computer program executing the GUI. Further, the method includes an operation for determining if the distance between the current position of the cursor and the POG is greater than a threshold distance. The cursor is moved from the current position to a region proximate to the POG in response to the determination of the POG and to the detection of the initiation of the physical action.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
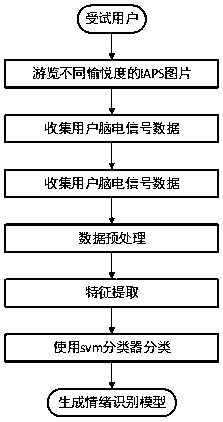
Method and apparatus for quantitatively evaluating mental states based on brain wave signal processing system
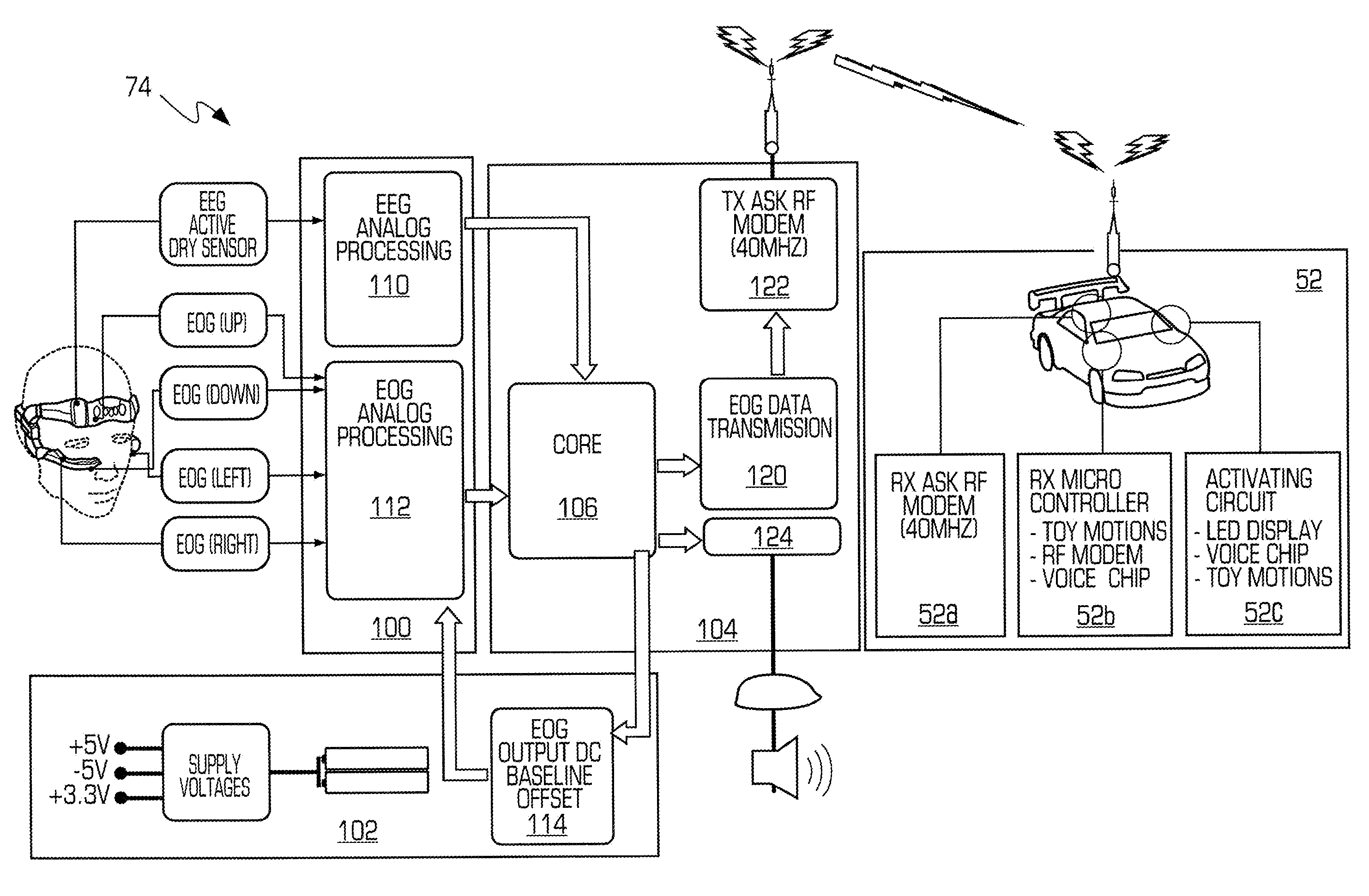
A noise-free portable EEG system is provided. The system has hardware and software and can evaluate mental state quantitatively. The quantitative data of mental states and their levels can be applied to various areas of brain-machine interface including consumer products, video game, toys, military and aerospace as well as biofeedback or neurofeedback.
Owner:NEUROSKY
Wireless wearable big data brain machine interface
ActiveUS20160323000A1Circuit arrangementsDiagnostic recording/measuringComputer hardwareShortest distance
A wireless wearable high data throughput (big data) brain machine interface apparatus is presented. An implanted recording and transmitting module collects neural data from a plurality of implanted electrodes and wirelessly transmits this over a short distance to a wearable (not implanted) receiving and forwarding module, which communicates the data over a wired communication to a mobile post processing device. The post processing device can send this neural data to an external display or computer enabled device for viewing and / or manipulation. High data throughput is supported by aggregating multiple groups of electrodes by multiple n-channel recording elements, which are multiplexed and then modulated into high frequency wireless communications to the wearable module. Embodiments include use of multiple radiators (multiple polarizations and / or spatially distributed), with beam alignment adjustment.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Computer interface having a single window mode of operation
InactiveUS6957395B1Reduce confusionMinimal amountProgram controlMemory systemsHuman–machine interfaceComputer monitor
A computer-human interface manages the available space of a computer display in a manner which reduces clutter and confusion caused by multiple open windows. The interface includes a user-selectable mode of operation in which only those windows associated with the currently active task are displayed on the computer monitor. All other windows relating to non-active tasks are minimized by reducing them in size or replacing them with a representative symbol, such as an icon, so that they occupy a minimal amount of space on the monitor's screen. When a user switches from the current task to a new task, by selecting a minimized window, the windows associated with the current task are automatically minimized as the window pertaining to the new task is displayed at its normal size. As a result, the user is only presented with the window that relates to the current task of interest, and clutter provided by non-active tasks is removed.
Owner:APPLE INC
Computer interface system for tracking of radio frequency identification tags
ActiveUS7102509B1Electric signal transmission systemsMultiple keys/algorithms usageTransceiverDiagnostic information
A method for operating with multiple protocols for handling communications comprising the steps of obtaining information from sensors and related input devices utilizing specialized tamper resistant passive transceivers working with active pulse type transceivers to create historical maps of information on people or objects. This includes steps of: a) identifying recording information, b) sending and receiving prompts, c) associating the call with timers, d) monitoring passive transceivers with low level diagnostic information, e) monitoring the transceivers with voice recognition software, f) recording associated data, g) identifying the users, the key words or phrases within the recorded data, h) naming the recording and i) saving the data in a protected format.
Owner:GLOBAL TELLINK
Computer interfaces including physiologically guided avatars
This invention provides user interfaces that more intuitively display physiological data obtained from physiological monitoring of one or more subjects. Specifically, the user interfaces of this invention create and display one or more avatars having behaviors guided by physiological monitoring data. The monitoring data is preferably obtained when the subject is performing normal tasks without substantial restraint. This invention provides a range of implementations that accommodate user having varying processing and graphics capabilities, e.g., from handheld electronic devices to ordinary PC-type computers and to systems with enhanced graphics capabilities.
Owner:ADIDAS
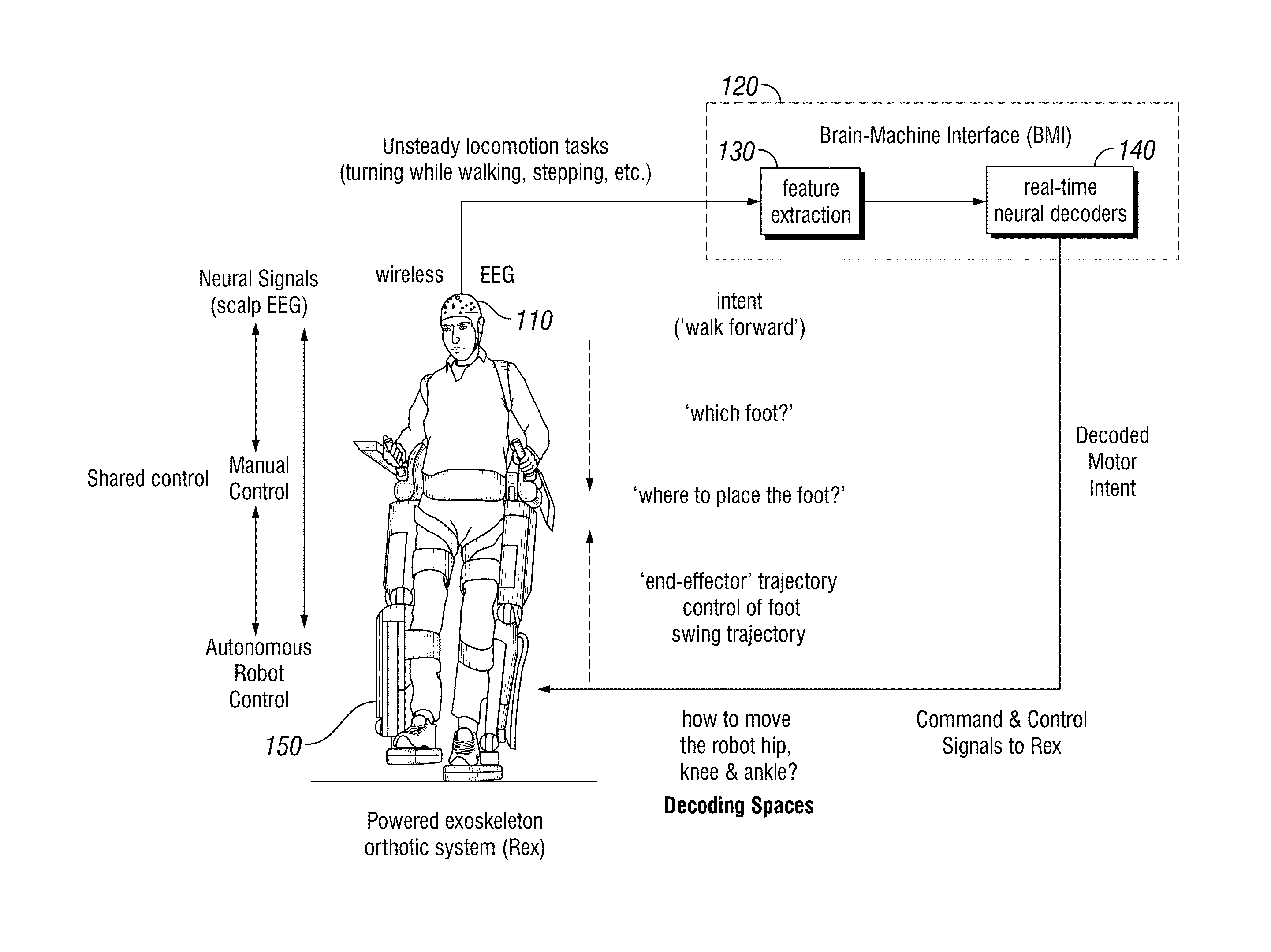
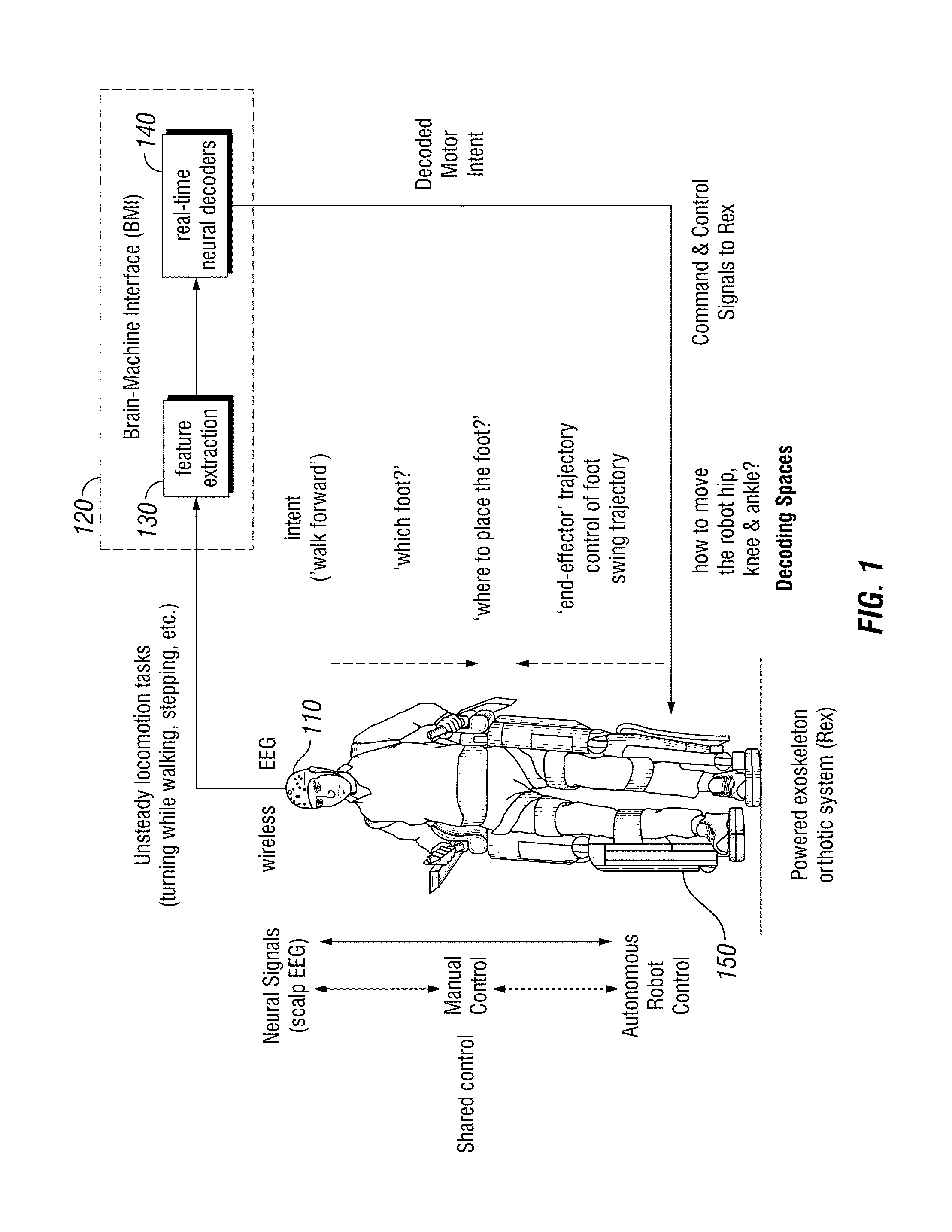
Methods for closed-loop neural-machine interface systems for the control of wearable exoskeletons and prosthetic devices
Brain-Machine Interface (BMI) systems or movement-assist systems may be utilized to aid users with paraplegia or tetraplegia in ambulation or other movement or in rehabilitation of motor function after brain injury or neurological disease, such as stroke, Parkinson's disease or cerebral palsy. The BMI may translate one or more neural signals into a movement type, a discrete movement or gesture or a series of movements, performed by an actuator. System and methods of decoding a locomotion-impaired and / or an upper-arm impaired subject's intent with the BMI may utilize non-invasive methods to provide the subject the ability to make the desired motion using an actuator or command a virtual avatar.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
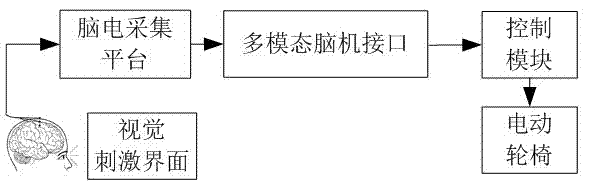
Intelligent wheelchair based on multimode brain-machine interface
InactiveCN102309380AImprove practicalityImprove transfer rateInput/output for user-computer interactionWheelchairs/patient conveyanceHuman–machine interfaceHuman–computer interaction
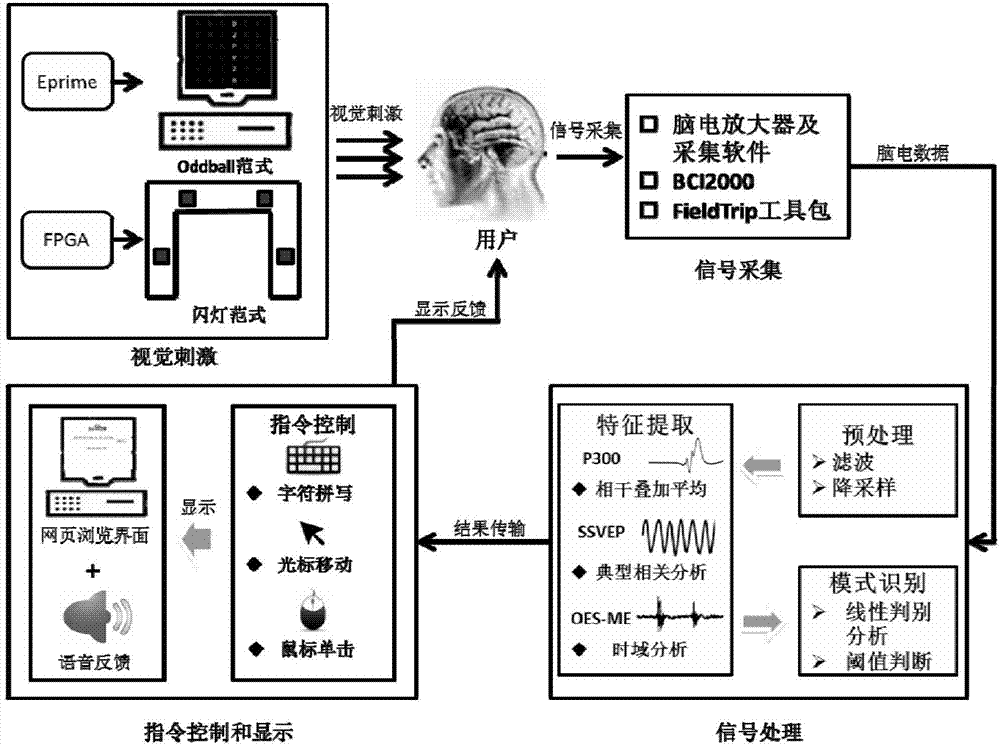
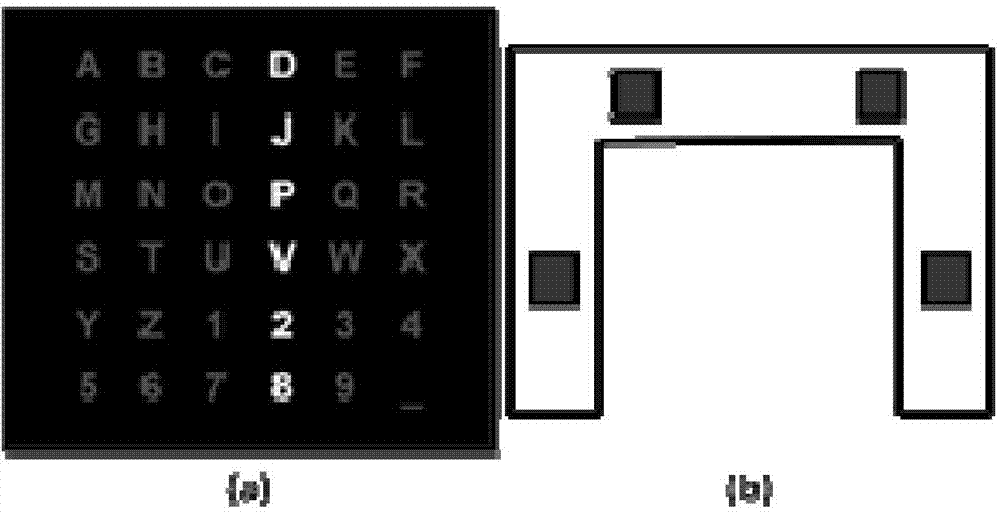
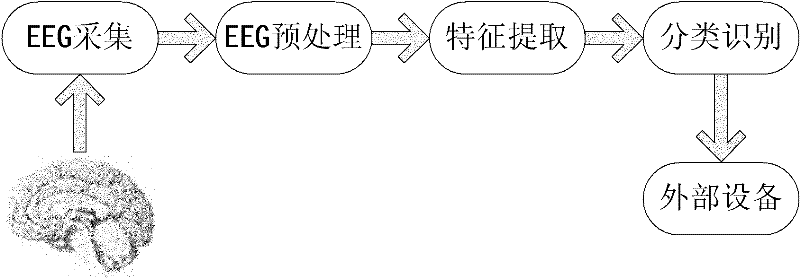
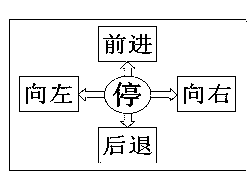
The invention discloses an intelligent wheelchair based on a multimode brain-machine interface, comprising a visual stimulus interface, a brain-electrical acquisition platform, the multimode brain-machine interface, a control module and an electric wheelchair which are connected in sequence, wherein a subject expresses control intention by watching the visual stimulus interface and active movement imagery; after finishing acquisition, amplification, filtering and digitalization of brain-electrical signals, the brain-electrical acquisition platform transmits the brain-electrical signals to the multimode brain-machine interface, then preprocessing, characteristic extraction and classification are carried out on real-time brain-electrical signals, the control intention of the subject is converted into an instruction which is sent to a communication unit of the control module, and the wheelchair is controlled by a controller, so that the seven types of movement such as starting, stopping, backward movement, leftward rotation, rightward rotation, acceleration and speed reduction of the wheelchair are realized. The intelligent wheelchair can help the patients with severe paralysis to expand new information output channels for the brain, provides a new idea for the study and the practice on multiple degree of freedom of the brain-machine interface, and has various values in the aspects such as medical rehabilitation, experiment on medical physiology and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
A method and apparatus for quantitatively evaluating mental states based on brain wave signal processing system
Owner:NEUROSKY
Detection circuit for high-performance brain electrical signal of brain-machine interface
InactiveCN101433461AMeet the testing requirementsSimple structureInput/output for user-computer interactionDiagnostic recording/measuringLow noiseHuman–machine interface
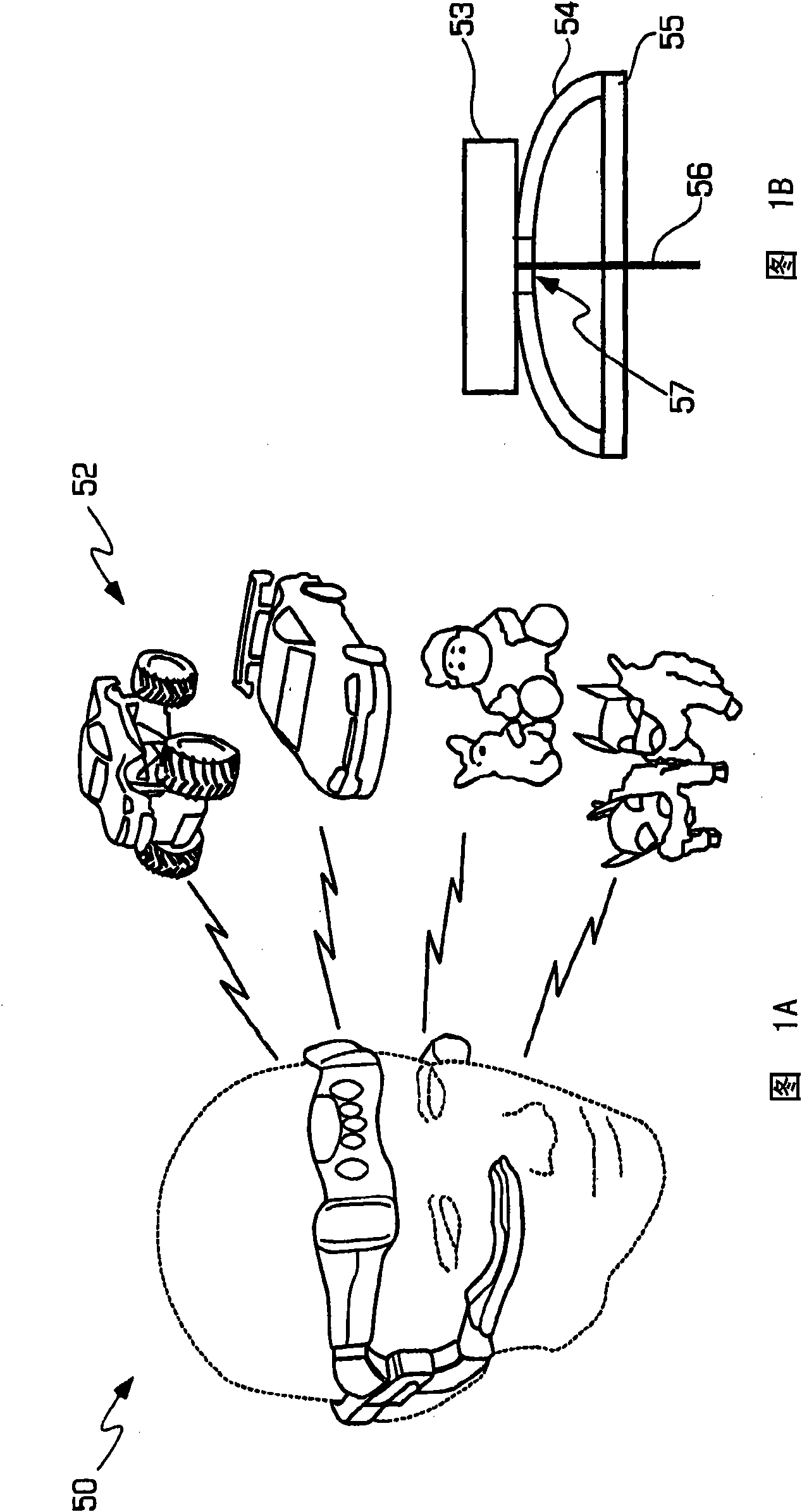
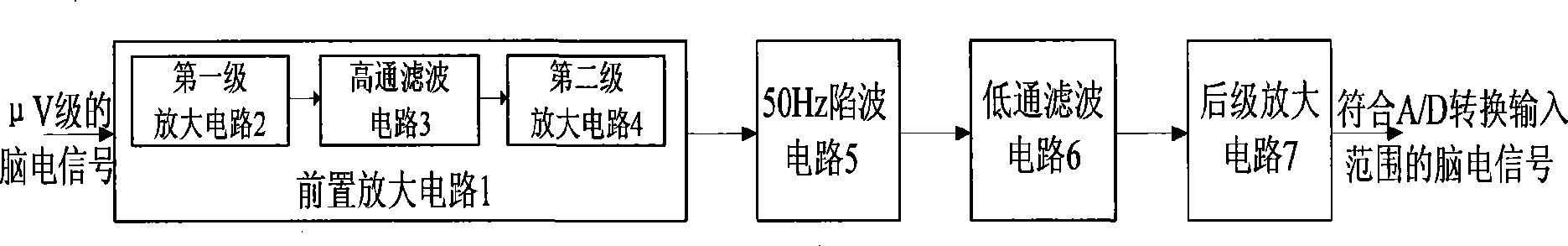
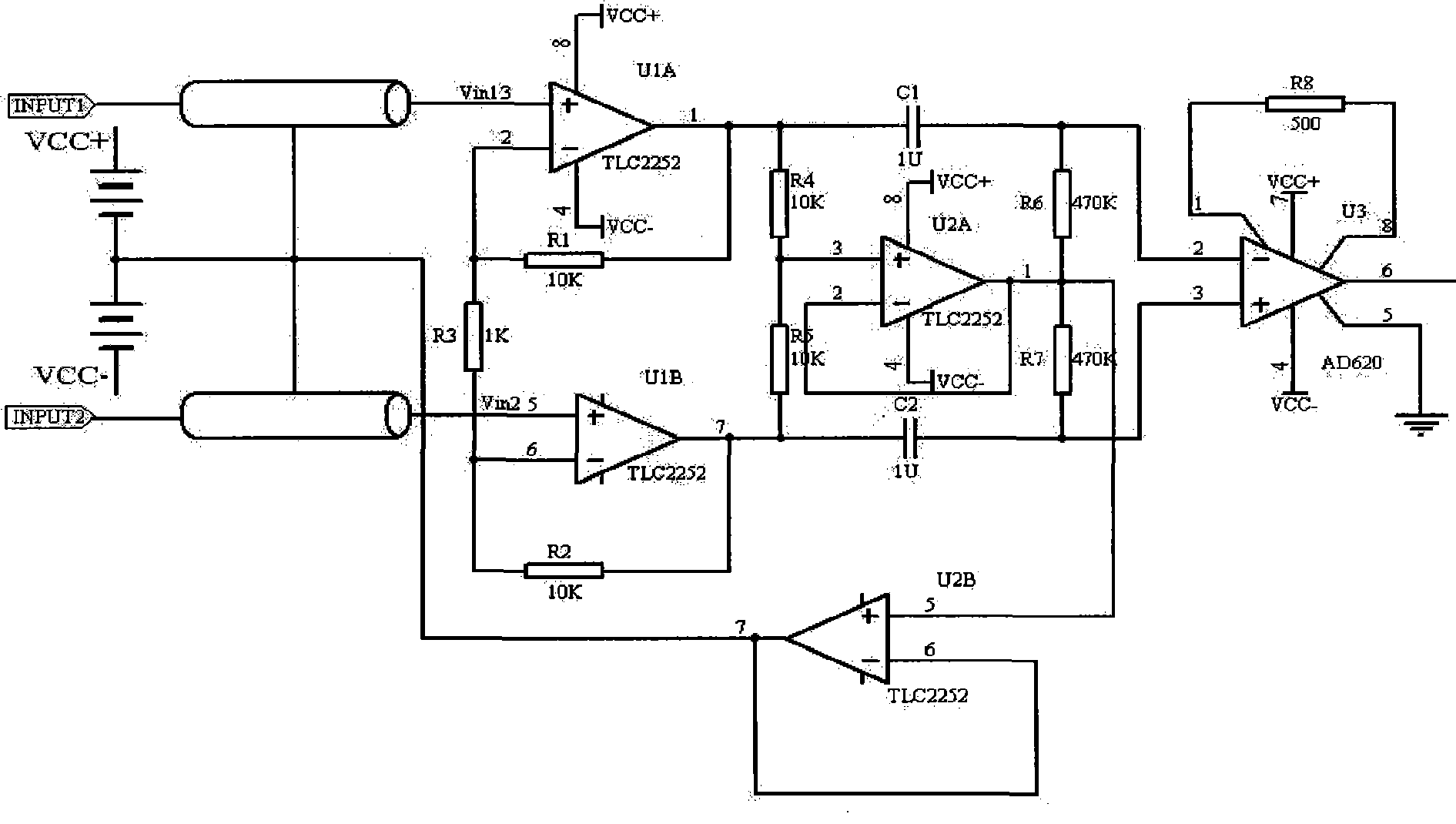
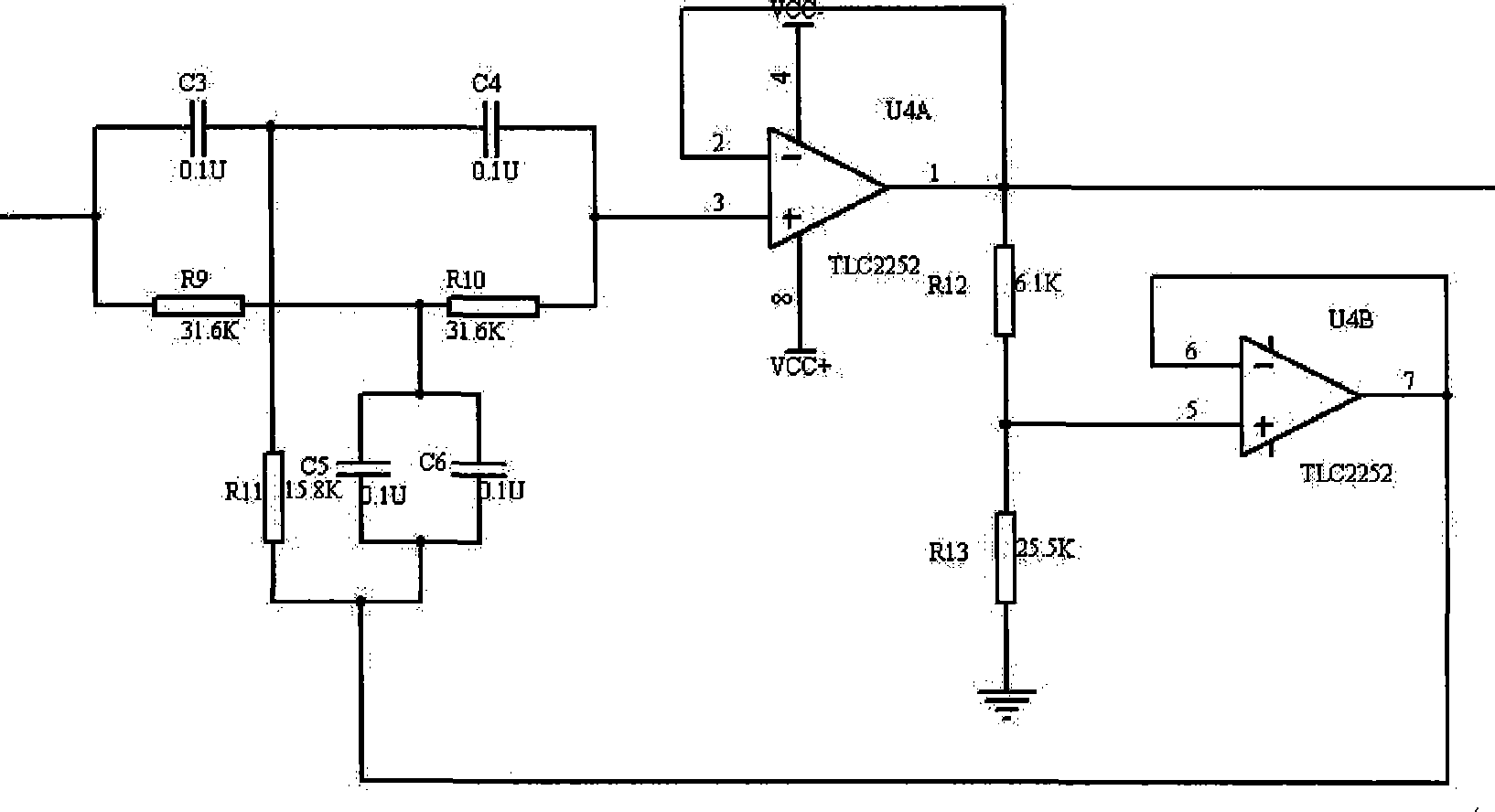
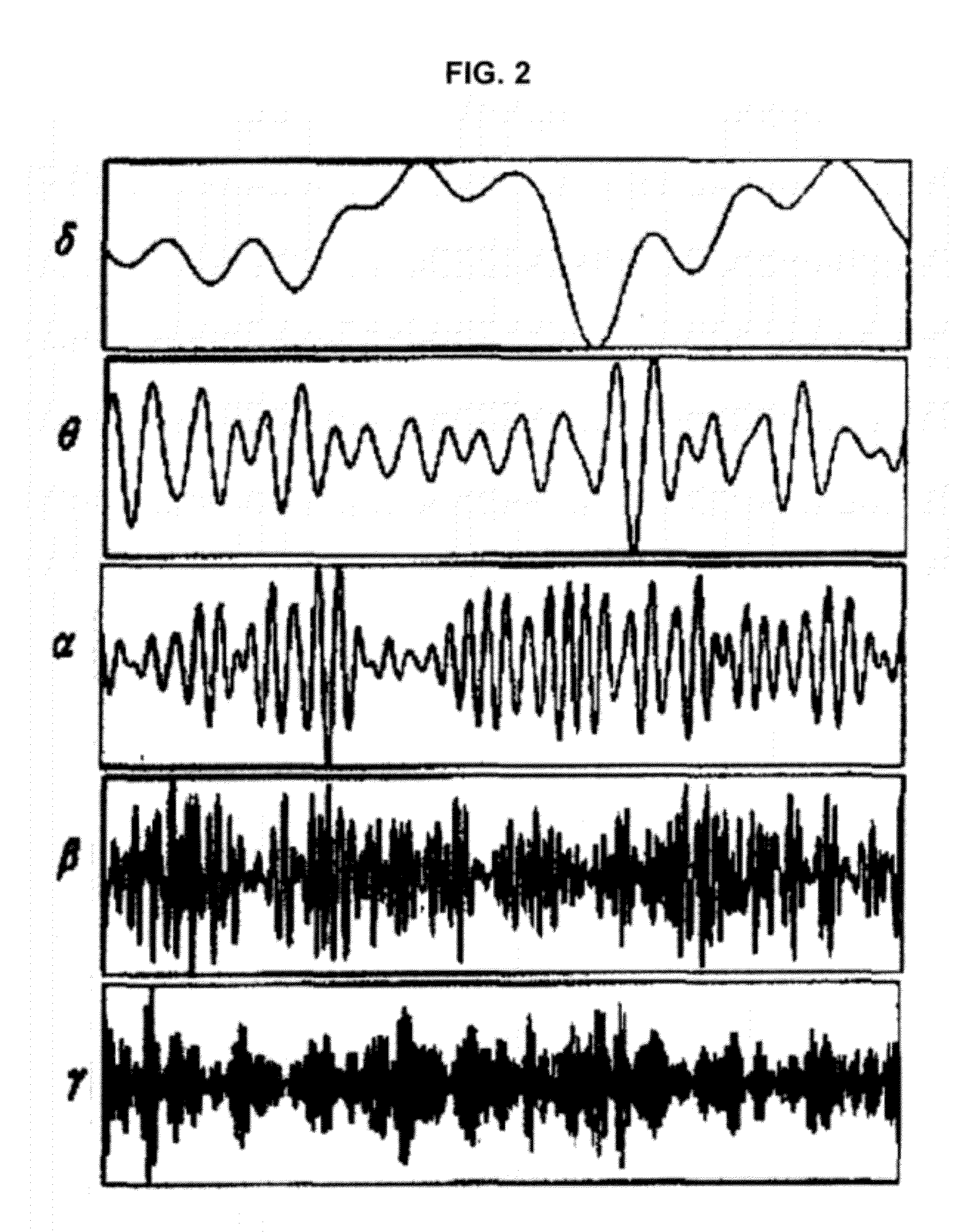
The invention relates to a high-performance EEG signal detection circuit provided with a brain-machine interface. The detection circuit comprises a pre-amplifier circuit and a post-amplifier circuit, wherein the pre-amplifier circuit consists of a first-level amplifier circuit and a second-level amplifier circuit which are connected by a high-pass filter circuit; and the pre-amplifier circuit is connected with the post-amplifier circuit by a 50Hz trap circuit and a low-pass filter circuit. The detection circuit has the characteristics of high input impedance, high common mode rejection ratio, high gain, low noise and low drift, and has the advantages of simple structure, strong capacity of resisting disturbance and good reliability. The invention can be used as a high-performance EEG signal detection circuit, and lay a foundation for realizing the brain-machine interface.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
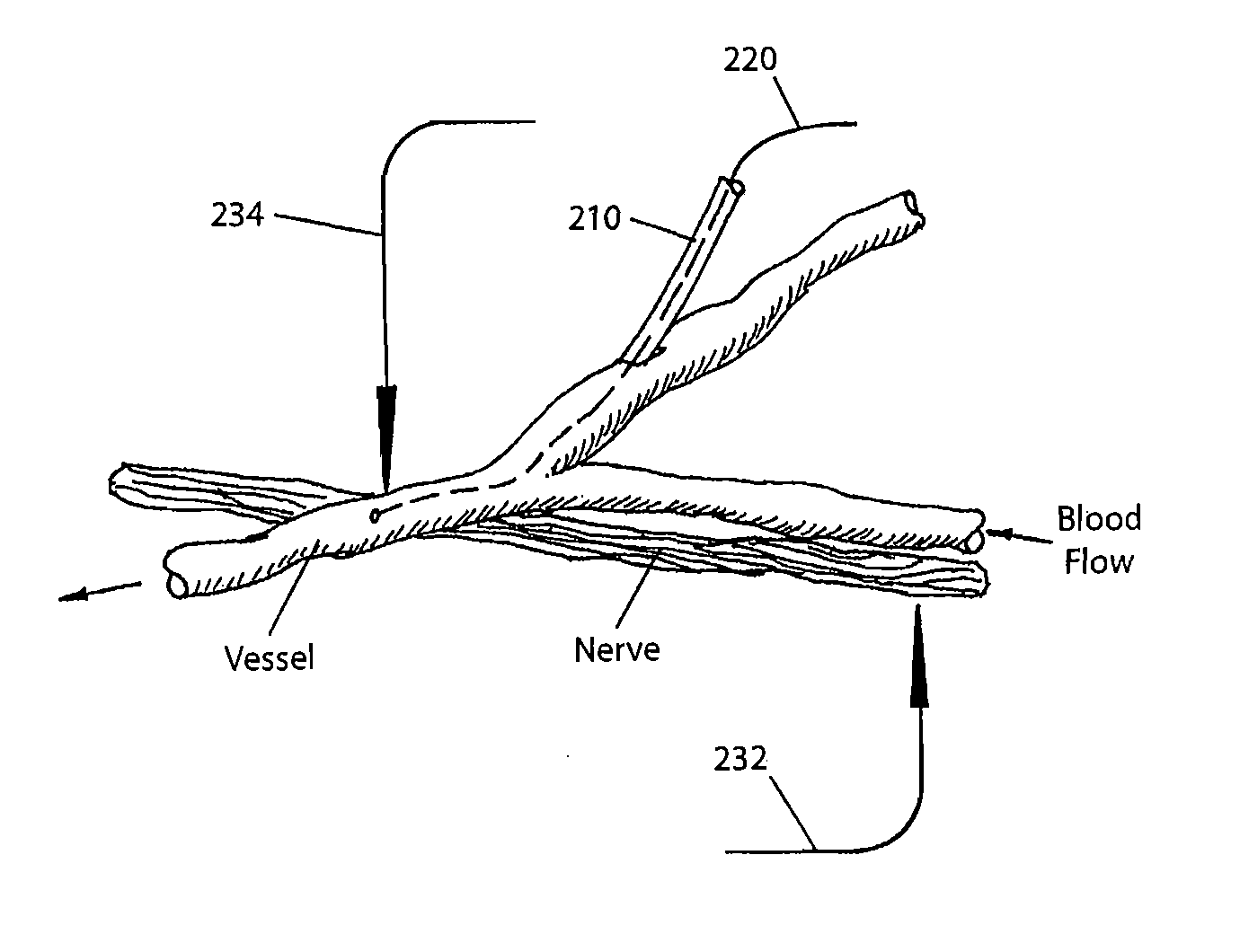
Brain-machine interface systems and methods
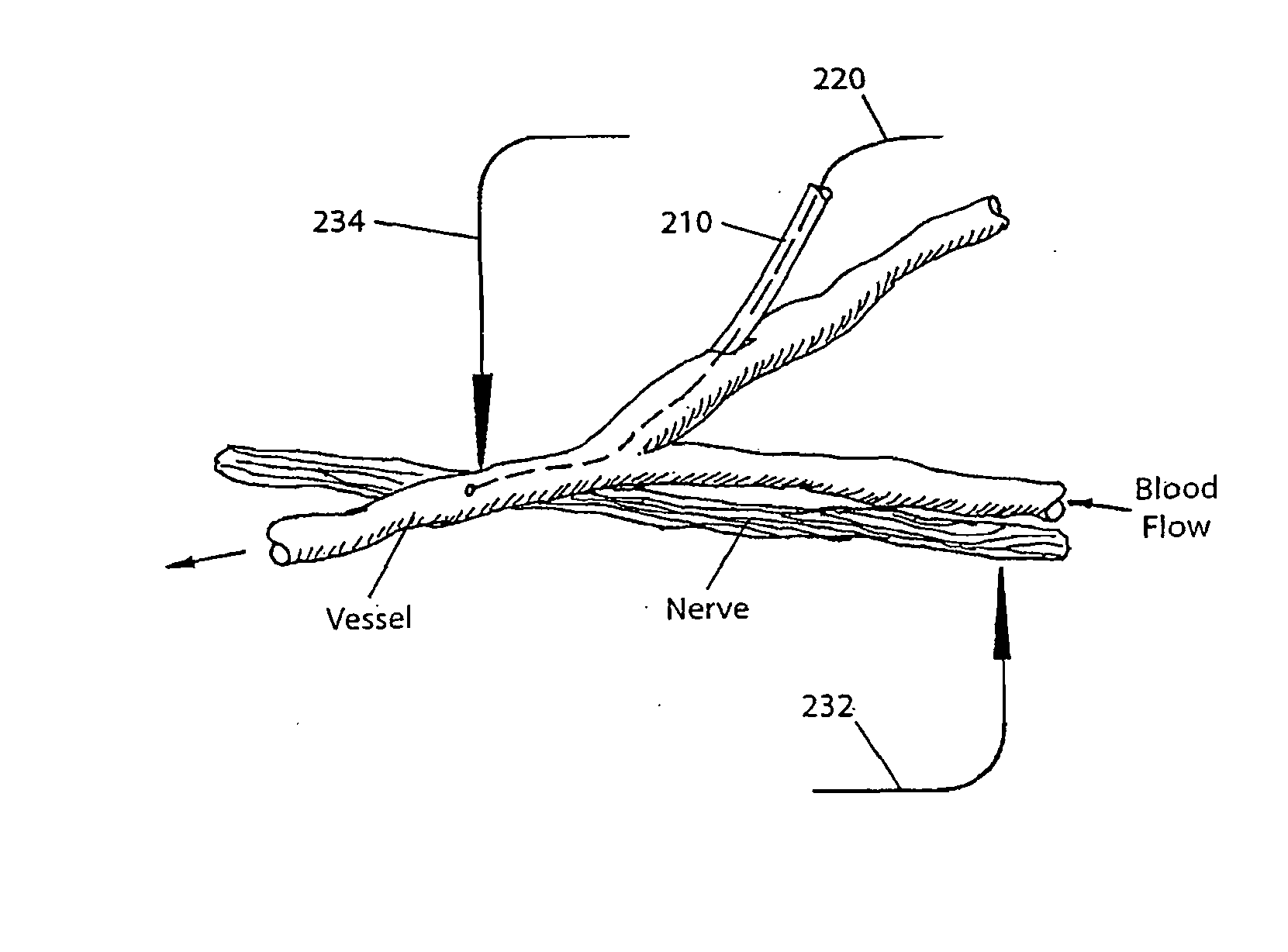
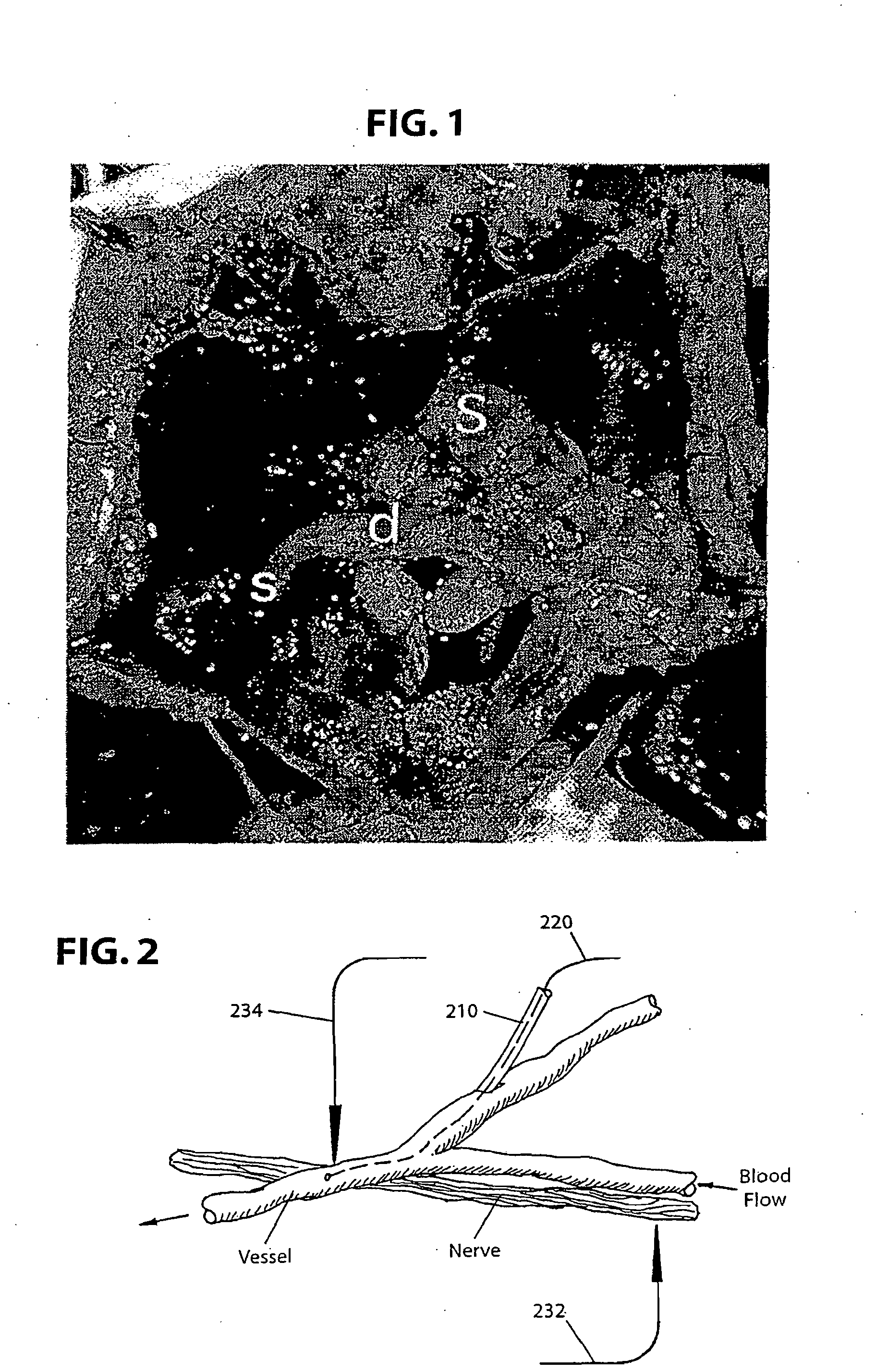
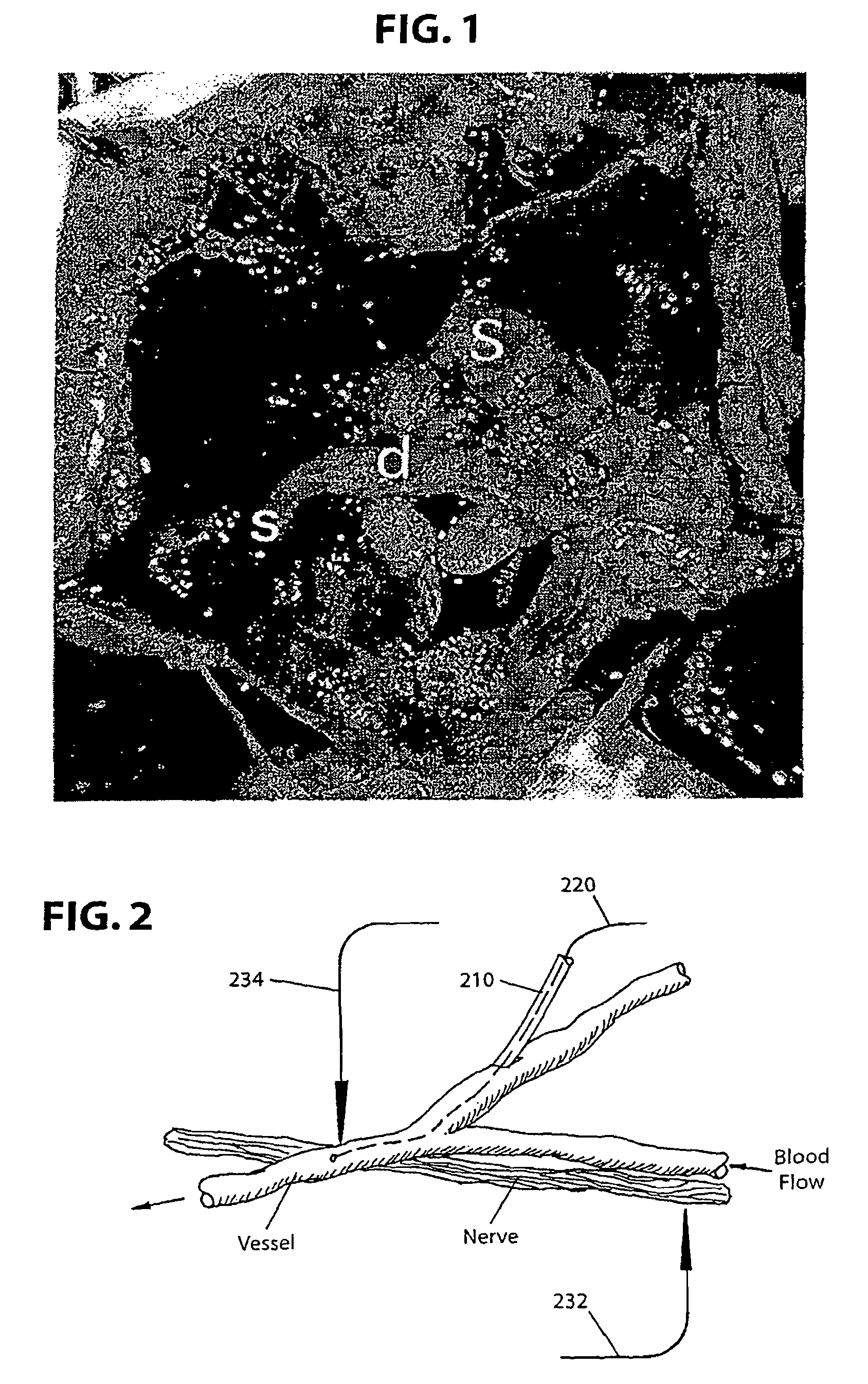
InactiveUS7257439B2Not disruptSmall sizeElectroencephalographyTransvascular endocardial electrodesRadiologyBrain–computer interface
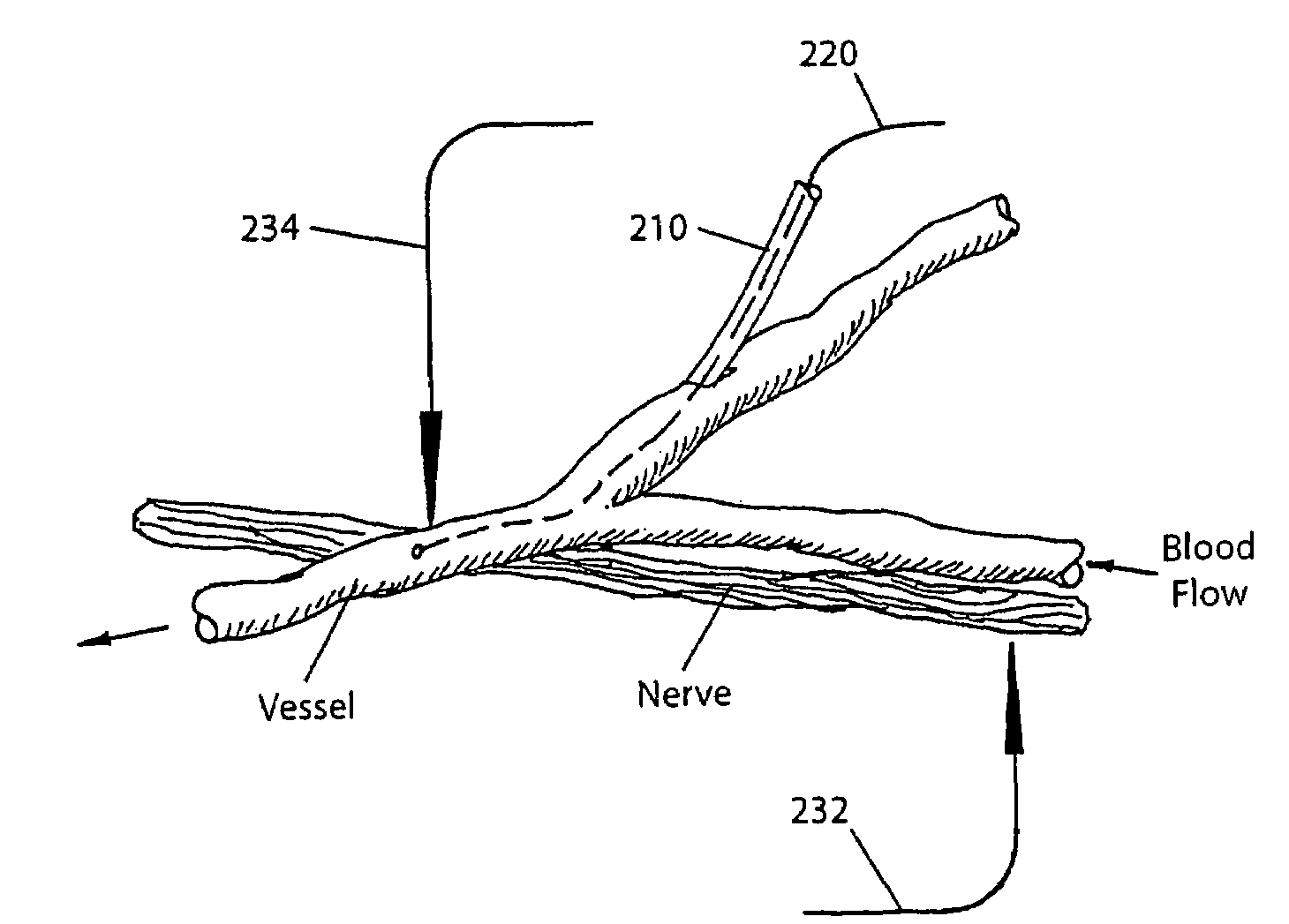
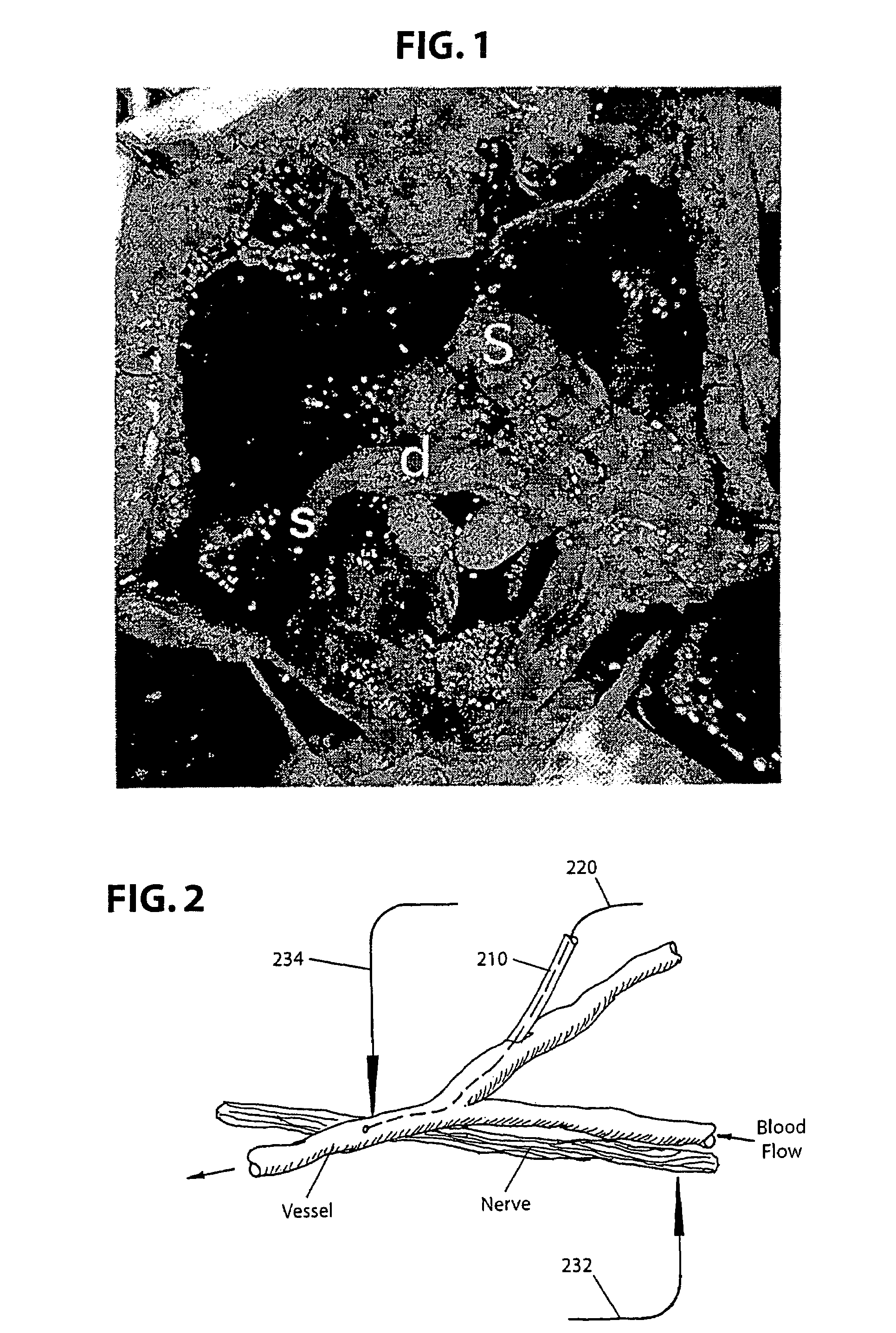
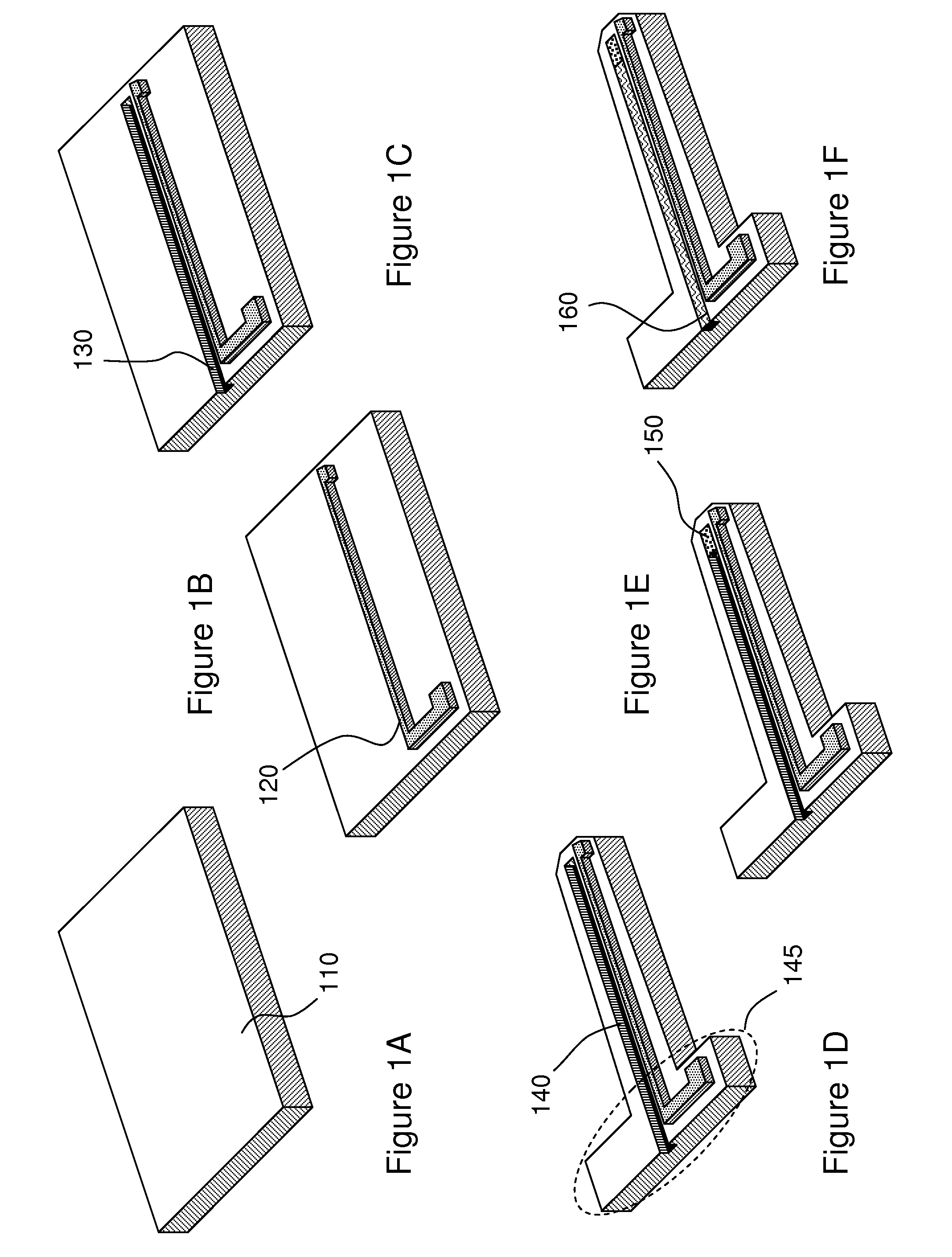
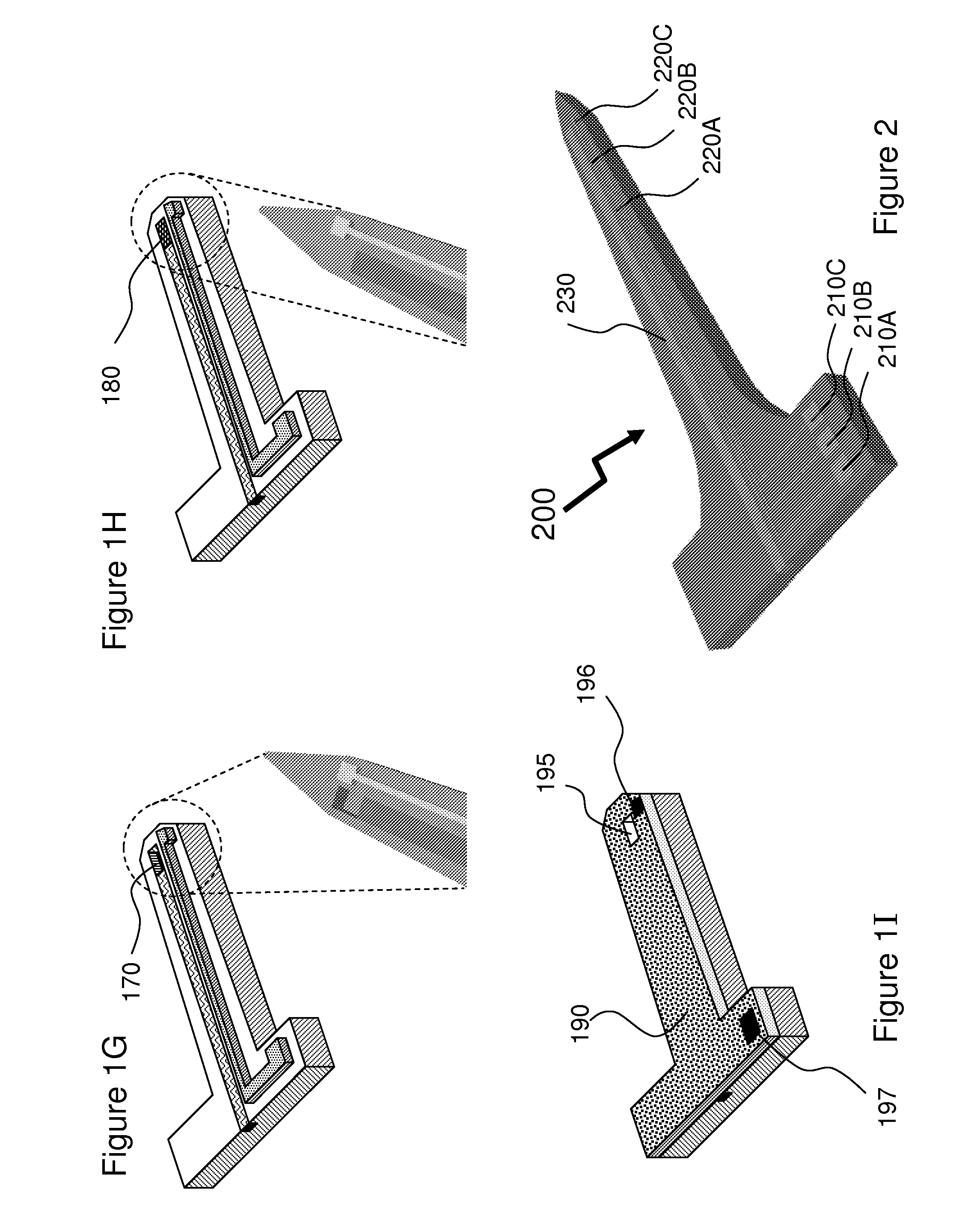
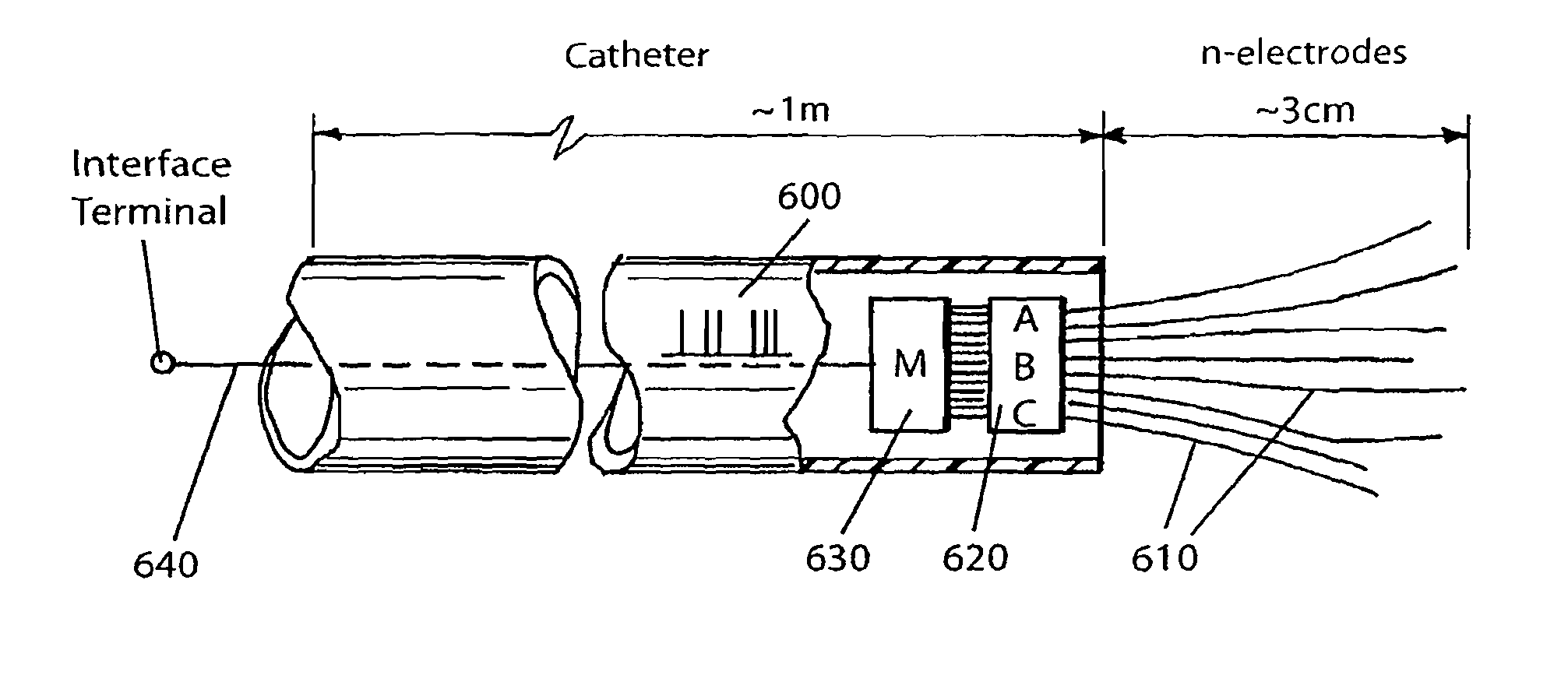
A system and method for interfacing a brain with a machine. An exemplary embodiment of the present invention employs a vascular approach in which one or more nano-electrodes are deployed in vasculature having a close geometric relationship with proximal innervation. Each nano-electrode is preferably deployed in a blood vessel so that its sensing end is at or near a nerve passing close to or intersecting the blood vessel. The sensing end of each nano-electrode is adapted so as to be carried along in the blood stream so as to position the sensing end at a desired point within the blood vessel. An array of nano-electrodes of varying lengths can be used to monitor multiple nerves or neurons along a blood vessel.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
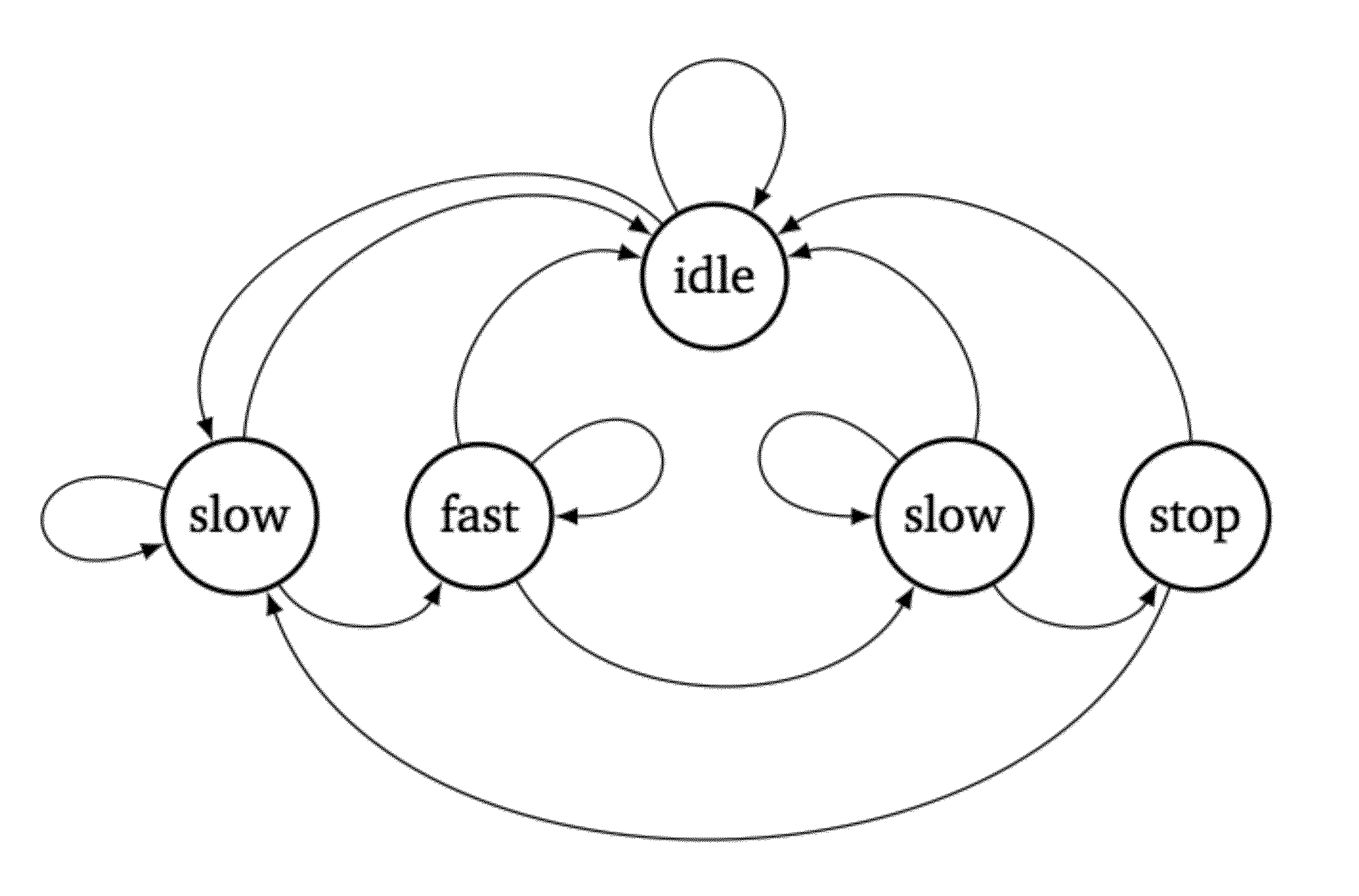
Brain Machine Interface utilizing a Discrete Action State Decoder in Parallel with a Continuous Decoder for a Neural Prosthetic Device
ActiveUS20140081454A1Improve performanceReliable decodingMathematical modelsComputer controlControl systemEngineering
A brain machine interface for control of prosthetic devices is provided. In its control, the interface utilizes parallel control of a continuous decoder and a discrete action state decoder. In the discrete decoding, we not only learn states affiliated with the task, but also states related to the velocity of the prosthetic device and the engagement of the user. Moreover, we not only learn the distributions of the neural signals in these states, but we also learn the interactions / transitions between the states, which is crucial to enabling a relatively higher level of performance of the prosthetic device. Embodiments according to this parallel control system enable us to reliably decode not just task-related states, but any “discrete action state,” in parallel with a neural prosthetic “continuous decoder,” to achieve new state-of-the-art levels of performance in brain-machine interfaces.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
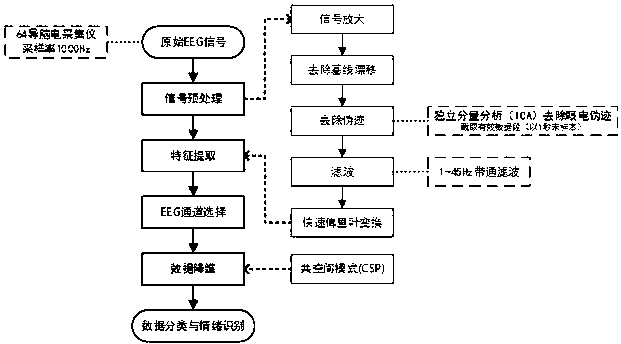
Electroencephalogram signal characteristic extracting method
InactiveCN103110418ARevealing fractal propertiesDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsComplex network analysisAlgorithm
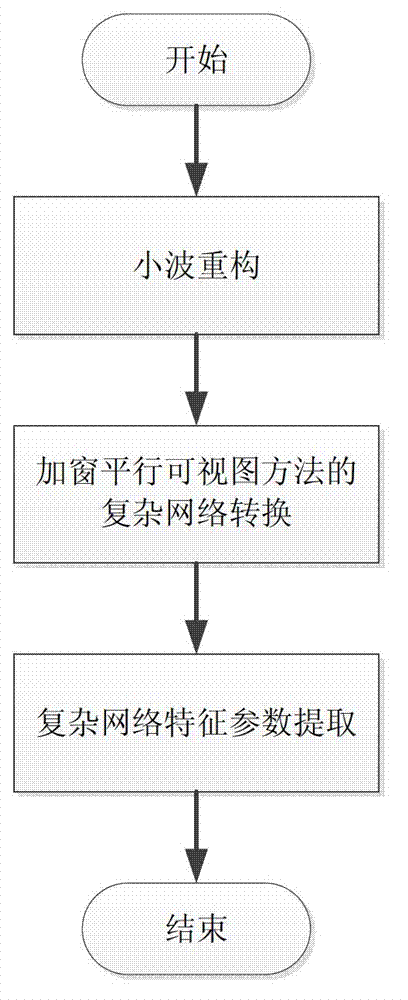
The invention provides an electroencephalogram signal characteristic extracting method. Network average route lengths and clustering coefficients are calculated through wavelet reconstruction, windowing horizontal visibility map complex network conversion and complex network analysis. The average route lengths and clustering coefficients composed of electroencephalogram signals are calculated to achieve characteristic analysis of electroencephalogram signals and chaotic time sequence signals of the electroencephalogram signals of different rhythms. The electroencephalogram signal characteristic extracting method has the advantages that one-dimensional chaotic time sequences are converted into complex networks, according to analysis of network characteristic parameters, fractal characters of the electroencephalogram signals are revealed, the complex non-linearity signals of the electroencephalogram signals are depicted from a brand new angle. The electroencephalogram signal characteristics can be applied to automatic diagnosis of mental disease and a characteristic identifying module of a brain-machine port system. The electroencephalogram signal characteristic extracting method can effectively distinguish the electroencephalogram signals of an epilepsia attach stage and an epilepsia non-attach stage, the equation p<0.1 is met after Mann-Whitney detection, and the electroencephalogram signal characteristic extracting method can be applied to epilepsia electroencephalogram automatic identification.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
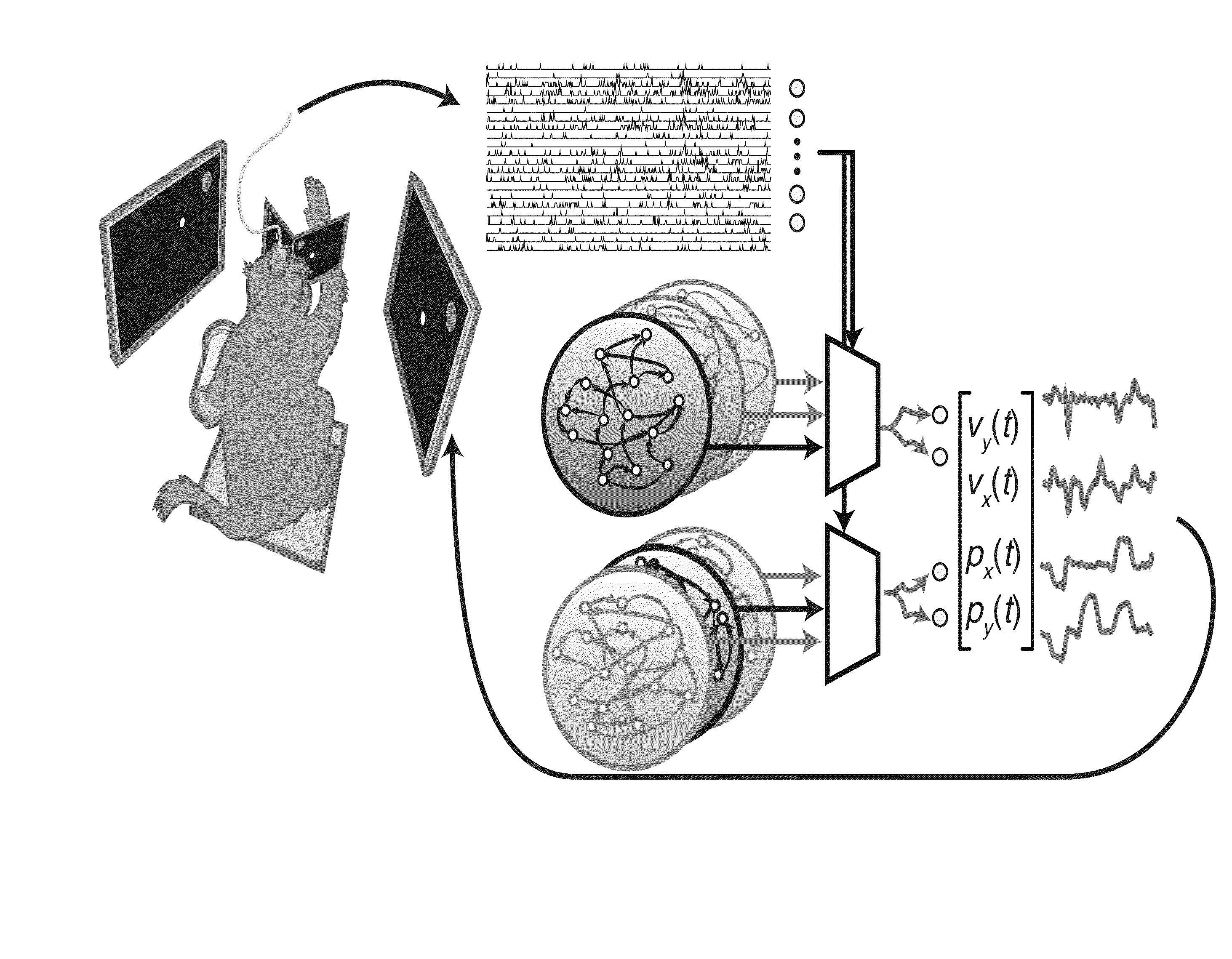
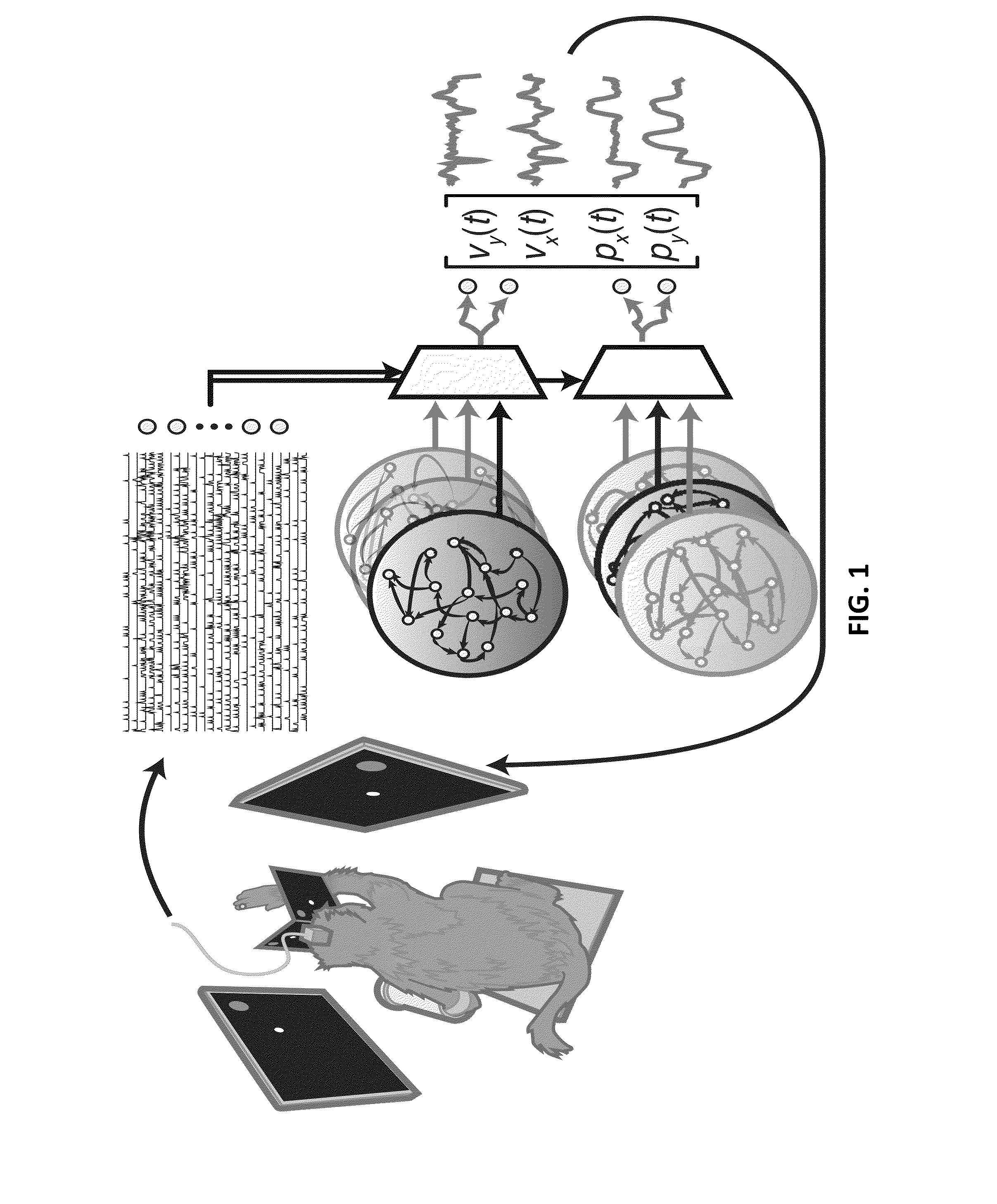
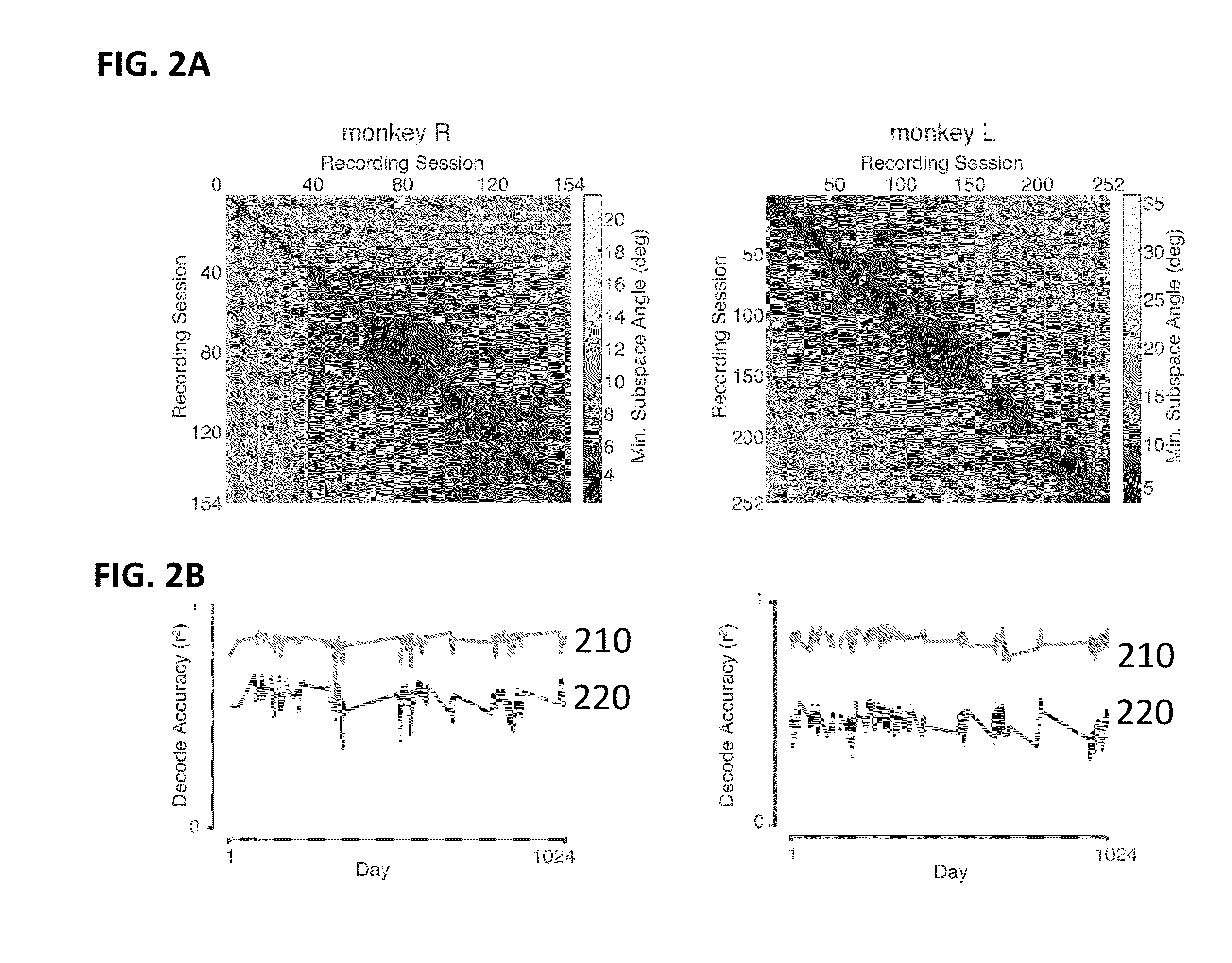
Multiplicative recurrent neural network for fast and robust intracortical brain machine interface decoders
ActiveUS20160048753A1Digital computer detailsDiagnostic recording/measuringNerve networkClinical settings
A brain machine interface (BMI) to control a device is provided. The BMI has a neural decoder, which is a neural to kinematic mapping function with neural signals as input to the neural decoder and kinematics to control the device as output of the neural decoder. The neural decoder is based on a continuous-time multiplicative recurrent neural network, which has been trained as a neural to kinematic mapping function. An advantage of the invention is the robustness of the decoder to perturbations in the neural data; its performance degrades less—or not at all in some circumstances—in comparison to the current state decoders. These perturbations make the current use of BMI in a clinical setting extremely challenging. This invention helps to ameliorate this problem. The robustness of the neural decoder does not come at the cost of some performance, in fact an improvement in performance is observed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
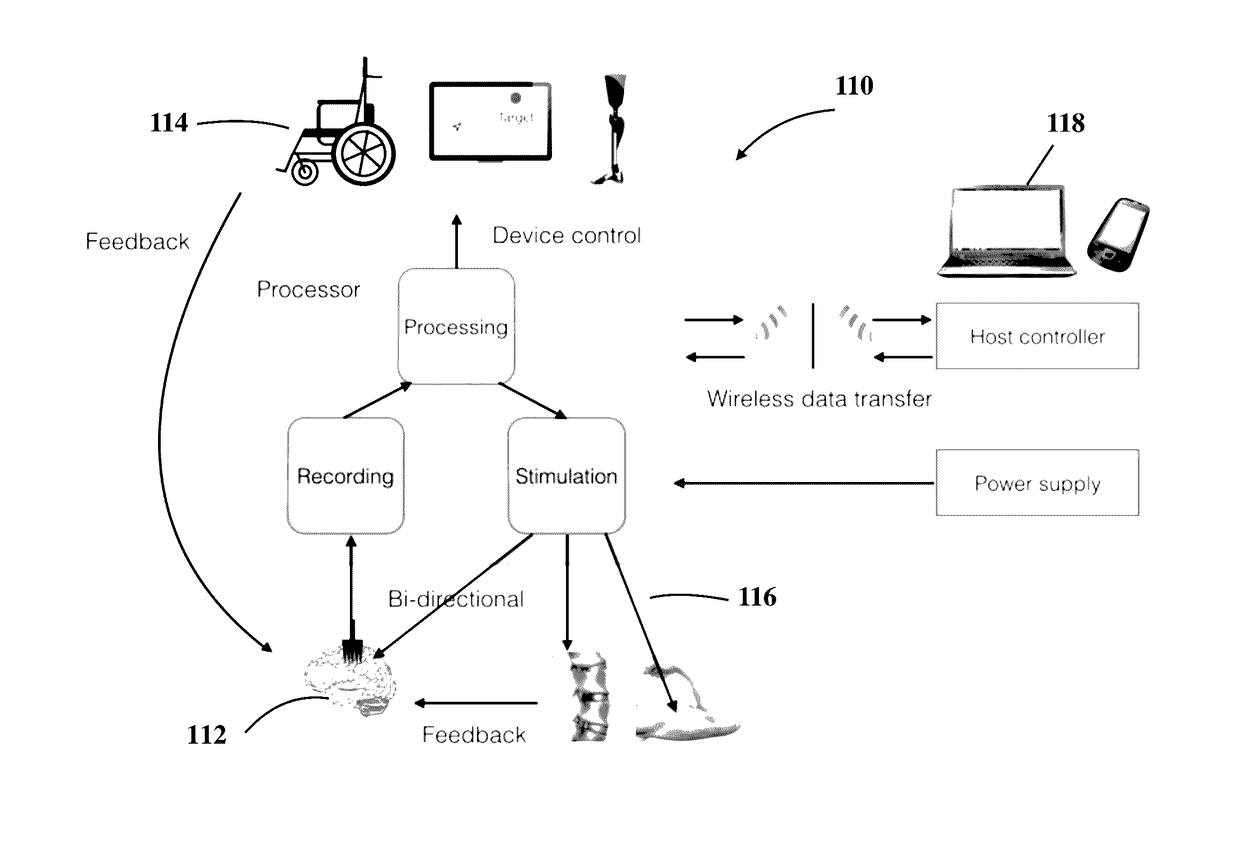
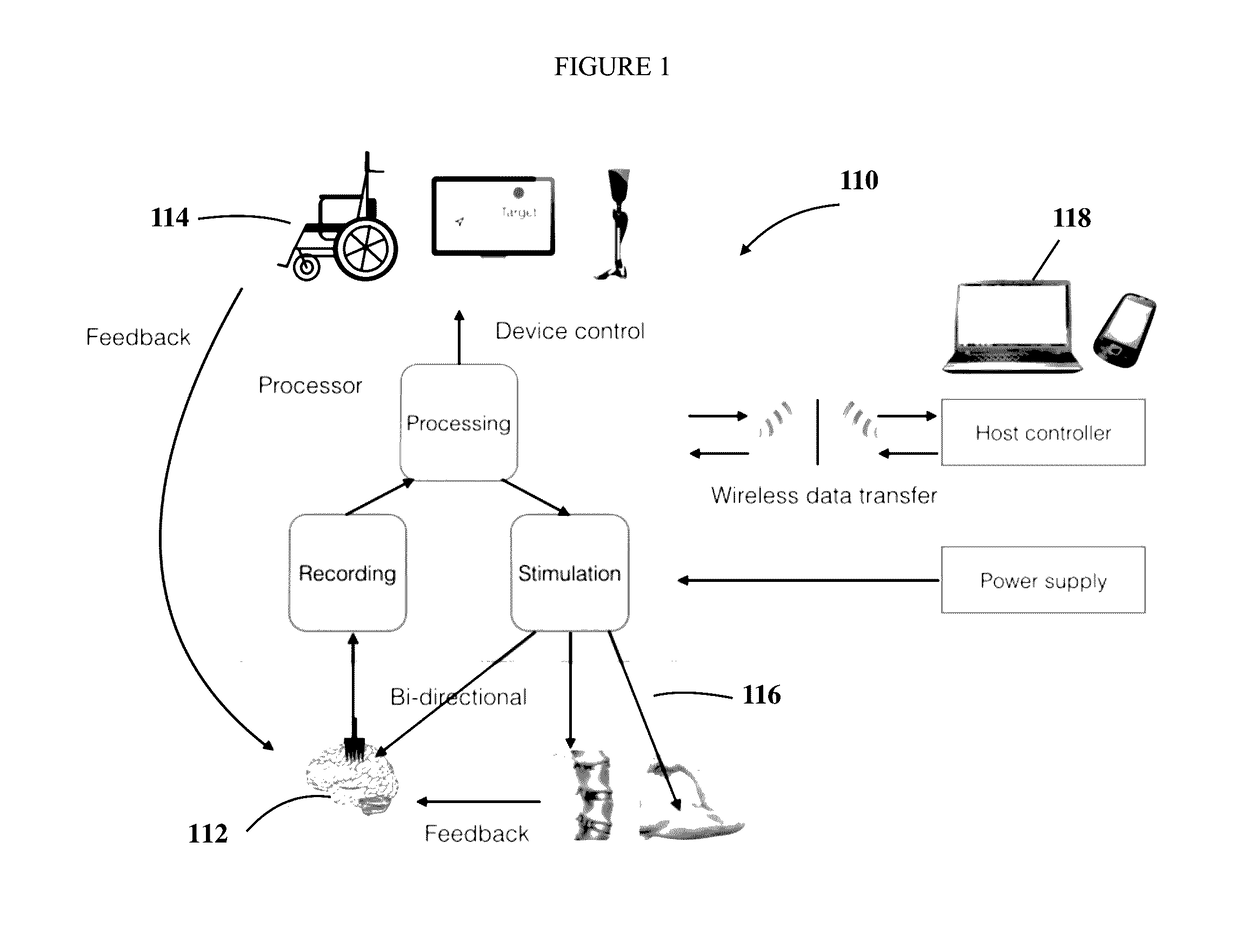
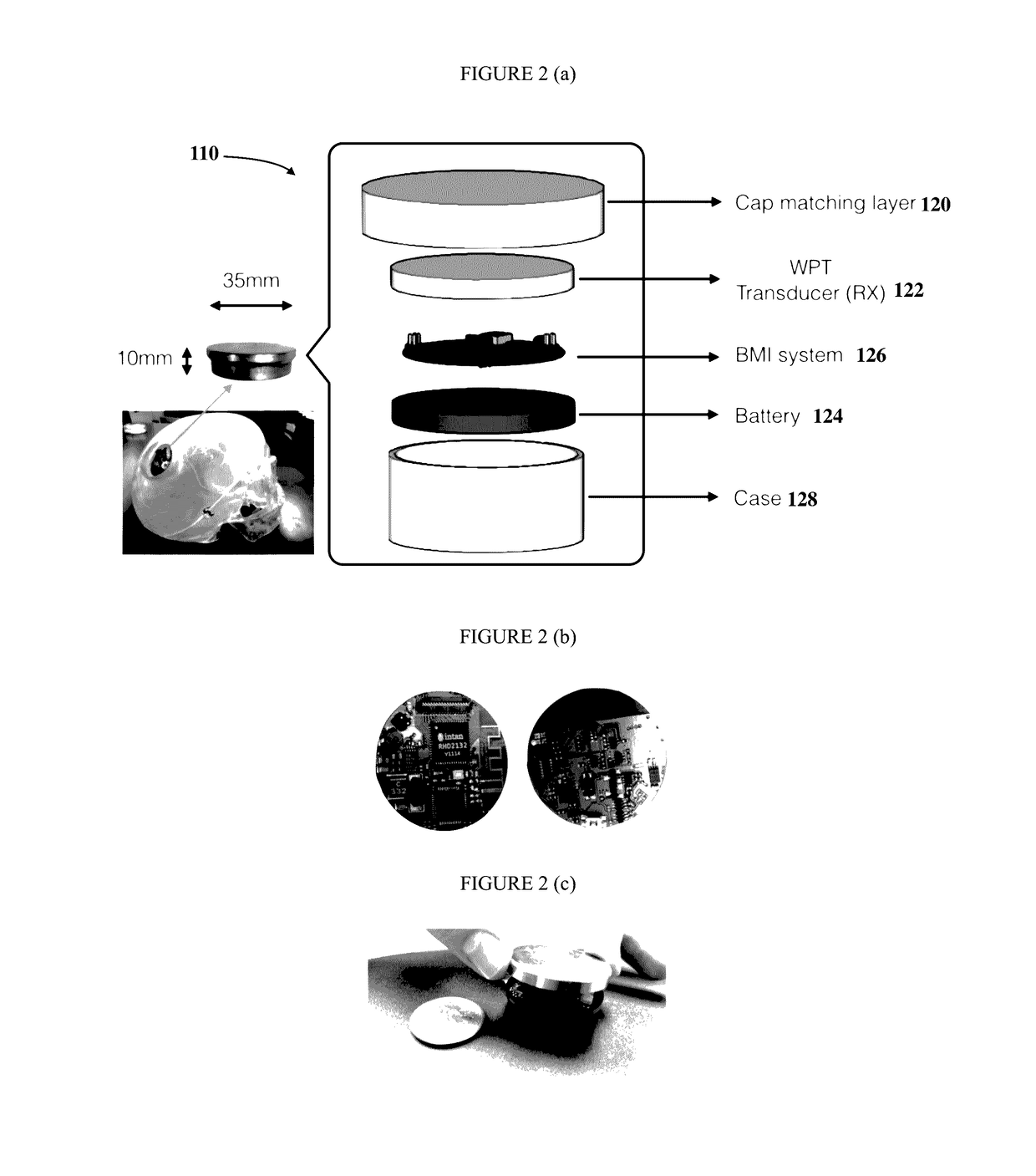
Apparatus and method of implantable bidirectional wireless neural recording and stimulation
ActiveUS20170108926A1Avoid tissue damageSpeed up the processInput/output for user-computer interactionSpinal electrodesBattery chargeElectrical battery
A device and method is described for electronic human prosthetics, and specifically a skull- and / or spine implantable bi-directional neural-communication / brain-machine interface (BBMI) device where the input, output and on-board computing are combined into a single unit to form a compact neuro-prosthetics device. This invention is also directed to a fully implantable wireless spinal electronic recording and stimulation system using the BBMI in a human. The bi-directional devices (BBMIs) communicate with other bi-directional brain-machine interface devices (BBMI) and / or with external controllers wirelessly. The compact implantable stimulator has ultrasonic secondary battery charging system. One or more BBMI can be wirelessly connected so that a closed loop of BBMIs, or a BBMI and an external controller, can wirelessly send trigger pulses to this fully implanted stimulator over the spinal cord.
Owner:SAN DIEGO STATE UNIV RES FOUND +1
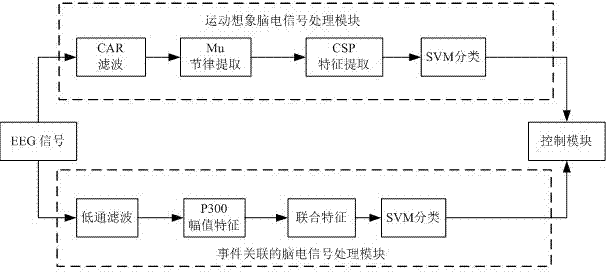
Tri-modal serial brain-computer interface method based on multi-information fusion
ActiveCN103699226AExpand applicable environmentExpand objectInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingSocial benefitsBrain computer interfacing
The invention discloses a tri-modal serial brain-computer interface method based on multi-information fusion. The method includes the steps: stimulating a testee by the aid of two visual stimulus paradigms; extracting electroencephalogram data of the testee; setting relevant parameters, reading the electroencephalogram data, preprocessing the electroencephalogram data, extracting characteristics, recognizing modes and acquiring final mode recognition results; converting the final mode recognition results into control instructions, and fulfilling specific tasks by executing the control instructions. A mixed-paradigm brain-computer interface introduces electrophysiology control signals except for electroencephalogram signals, and application environments and objects of the brain-computer interface are expanded to some extent. The tri-modal serial brain-computer interface method has the advantages of high stability, more options, wide application range and the like, and a foundation is laid for the brain-computer interface to step into a wide-range time application stage as soon as possible. The method can be used for fields such as electronic entertainment and industrial control, a perfect brain-computer interface system can be obtained, and the method is expected to obtain considerable social benefits and economic benefits.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
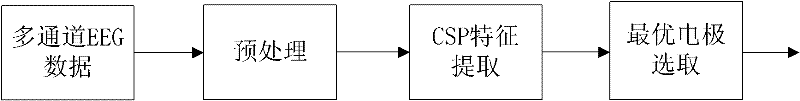
Optimal electrode assembly automatic selecting method of brain-machine interface
InactiveCN102542283AClassification accuracy dropsIncrease processing rateInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionSupport vector machineHuman–machine interface
The invention provides an optimal electrode assembly automatic selecting method of a brain-machine interface, which relates to the field of brain-machine interfaces. According to the invention, the automatic selection of the optimal electrode is realized; and the optimal electrode assembly automatic selection of an imagery motion brain-machine interface is realized by using a combined method of a common special pattern (CSP) and a support vector machine (SVM). The automatic selection of the optimal electrode assembly in the brain-machine interface has important effects on simplifying a brain-machine interface system and increasing system classification recognition rate and data transmission efficiency; and by using relevant property of an optimal support vector machine SVM linear kernel function as the optimal electrode screening index, redundant electrodes can be effectively deleted, the number of the electrodes can be obviously reduced, the useful electrodes can be kept, the system performance can be improved, and the precondition can be created to improve the popularization of a brain-machine interface technology.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Conducting polymer nanowire brain-machine interface systems and methods
InactiveUS20100106259A1Not disrupt brain activitySmall sizeNanoinformaticsInternal electrodesNanowireConductive polymer
The present invention relates to conducting polymer nanowires and their use in a brain-machine interface which is secure, robust and minimally invasive. In accordance with a first aspect of the present invention, a vascular-based brain-machine interface comprising conducting polymer nanowires is disclosed.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV +1
BCI (brain-computer interface) method for multi-modal signals
ActiveCN104182042AHigh precisionOvercoming illiteracyInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingFeature vectorBrain computer interfacing
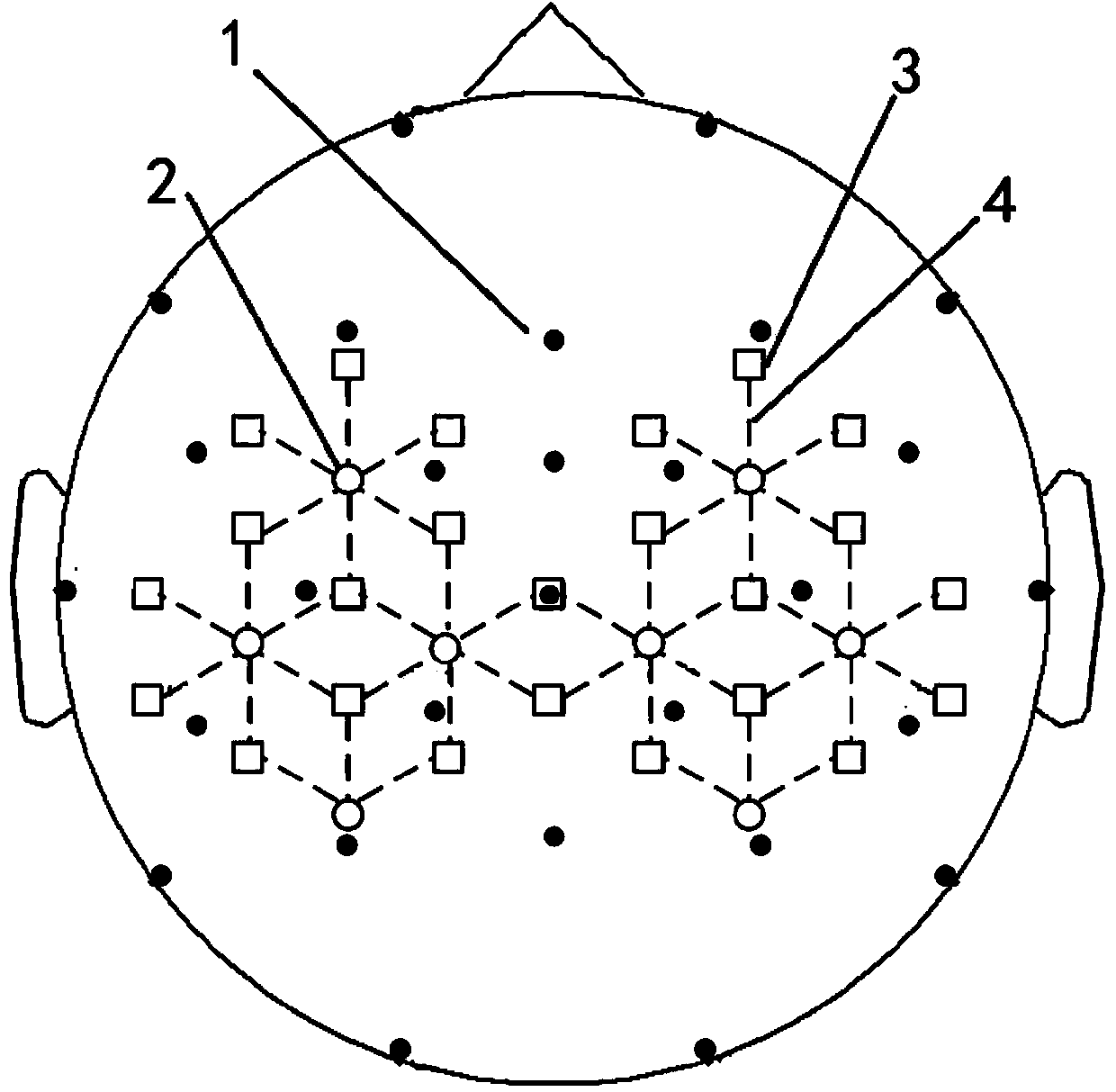
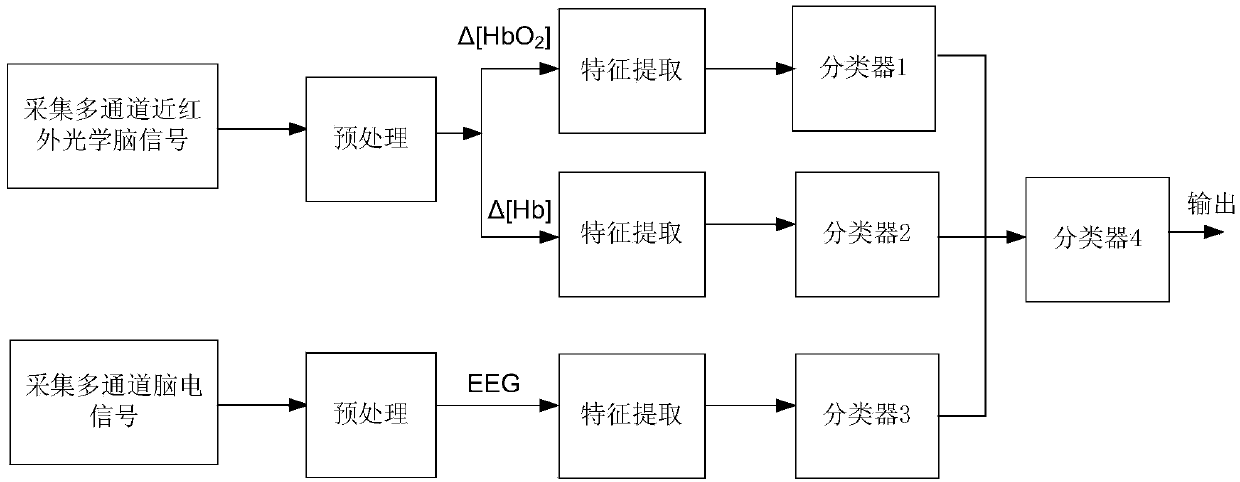
The invention discloses a BCI (brain-computer interface) method for multi-modal signals. The BCI method for multi-modal signals comprises a calibration stage and an identification stage. At the calibration stage, synchronously collected EEG and near infrared optical brain signals are pretreated respectively, so as to obtain signals in three modes; characteristics of the signals in the three modes are extracted respectively; the characteristic vector is adopted to train a classifier 1, a classifier 2 and a classifier 3; then, output signals of the three trained classifiers are adopted to train a classifier 4; at the identification stage, synchronously collected EEG and near infrared optical brain signals are pretreated; characteristics of the synchronously collected EEG and near infrared optical brain signals are extracted; the characteristic vectors of the signals in the three modes are input to the classifier 1, the classifier 2 and the classifier 3 respectively; then, the classification results of the three classifiers are input to the classifier 4; lastly, the brain-computer interface for the multi-modal signals outputs results. The BCI method for the multi-modal signals has the advantages of improving the precision of the BCI for single-modal signals and effectively overcoming the illiteracy phenomenon of the BCI for single-modal signals.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Brain-machine interface system based on cognition and emotional state multi-mode perception
InactiveCN104391569AEfficient matchingAchieve perceptionInput/output for user-computer interactionSensorsEmotional perceptionCognition
The invention discloses a brain-machine interface system based on cognition and emotional state multi-mode perception. The brain-machine interface system comprises a portable type physiological signal collection and analysis system, a behavior recognition system based on video analysis, a wireless gateway and data fusion and feedback computer system. According to the brain-machine interface system, an analysis and feedback problem of brain high-grade functions including cognition / emotion and the like can be solved and the limitation of brain specificity theories of traditional cognition and emotional separation is broken through, and the multi-mode brain-machine interface system based on cognition and emotional perception and calculation under an emotional- cognition integrated framework is constructed; a calculation principle of a cognition / emotion grade brain-machine fusion is disclosed, and efficient match between brains and machines is realized.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
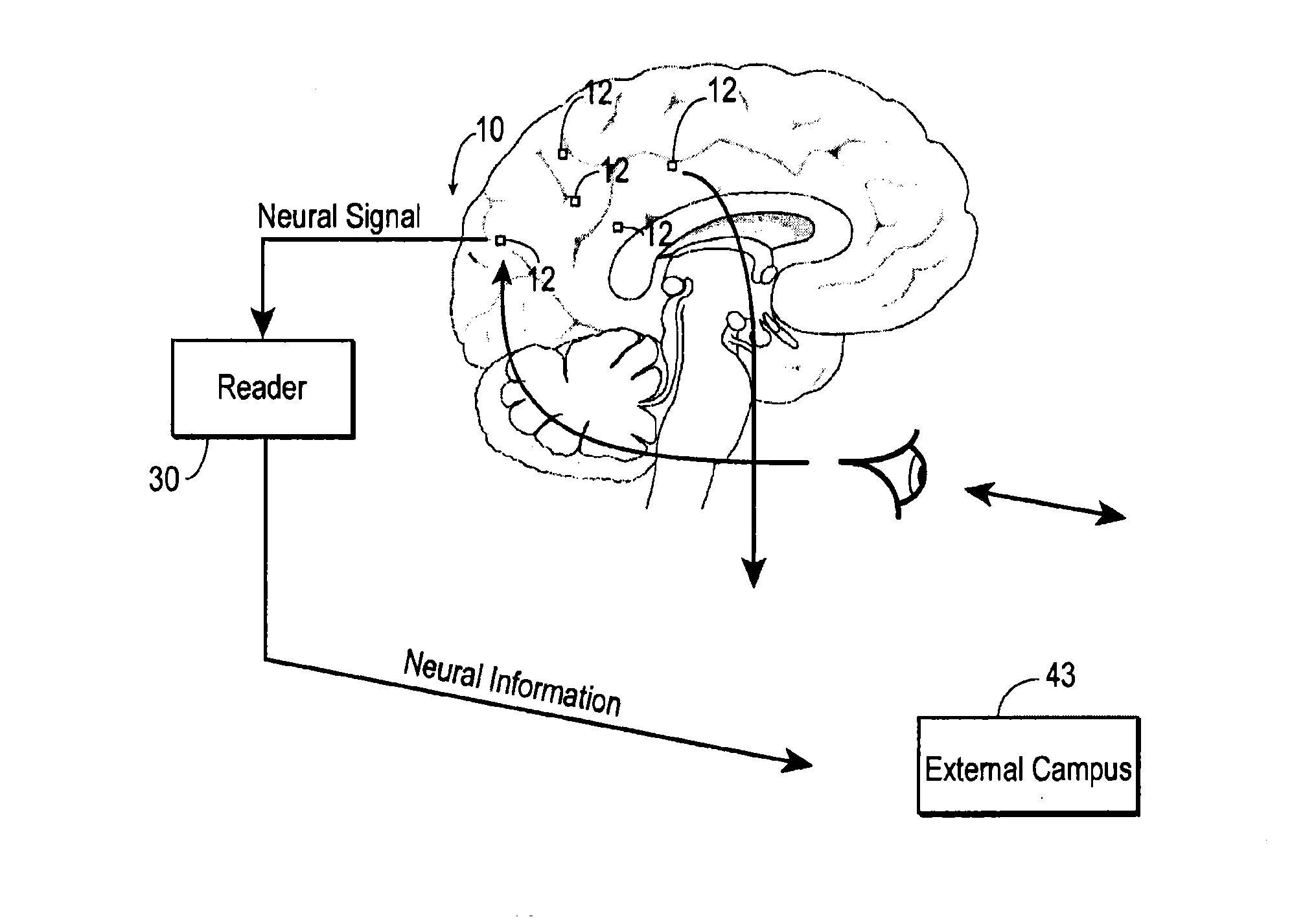
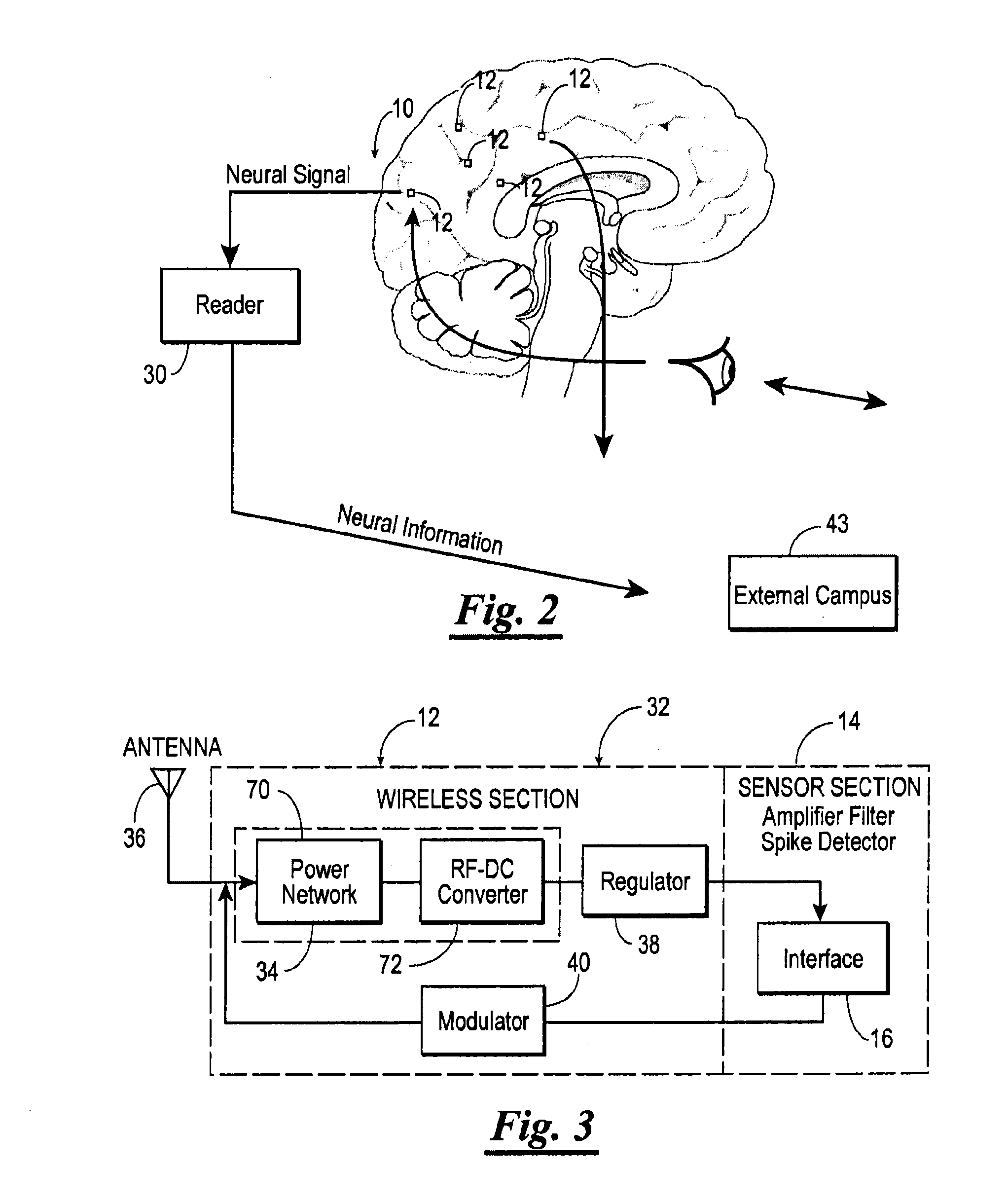
Brain Machine Interface Device
A distributed real-time wireless neural interface including a reader and an array of distinct recording devices having a wireless section and a sensor section. The reader outputs and receives radio-frequency signals. The wireless section of the array includes an rf power converter, an antenna, a regulator, and a modulator. The antenna receives the radio-frequency signals output by the reader and provides the radio-frequency signals to the rf power converter which converts such radio-frequency signals to power signals. The regulator receives the power signals and regulates such power signals to provide stable power signals. The sensor section receives the stable power signals and is adapted to detect neural activity and provide output signals containing information indicative of such neural activity to the modulator. The modulator receives the power signals and the output signals from the sensor section communicates the information in the output signals to the reader via the antenna.
Owner:RENNAKER II ROBERT L
Optically interrogated solid state biosensors incorporating porous materials—devices
ActiveUS8263986B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringWaveguide
Quantitative understanding of neural and biological activity at a sub-millimeter scale requires an integrated probe platform that combines biomarker sensors together with electrical stimulus / recording sites. Optically addressed biomarker sensors within such an integrated probe platform allows remote interrogation from the activity being measured. Monolithic or hybrid integrated silicon probe platforms would beneficially allow for accurate control of neural prosthetics, brain machine interfaces, etc as well as helping with complex brain diseases and disorders. According to the invention a silicon probe platform is provided employing ultra-thin silicon in conjunction with optical waveguides, optoelectronic interfaces, porous filter elements, and integrated CMOS circuitry. Such probes allowing simultaneously analysis of both neural electrical activities along with chemical activity derived from multiple biomolecular sensors with porous membrane filters. Such porous silicon and polymer filters providing biomolecular filtering and optical filtering being compatible with post-processing wafers with integrated CMOS electronics.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Readiness potential-based brain-computer interface device and method
InactiveUS20120226185A1Cancel noiseElectroencephalographyMedical automated diagnosisReadiness PotentialsBrain–computer interface
The present invention provides a brain-computer interface device. The brain-computer interface device may include: a preprocessor for preprocessing a readiness potential signal measured by a brain wave detection device; a noise eliminator for eliminating noise from the preprocessed readiness potential signal; a signal processor for extracting features related to a user's intention by calculating at least one of the intensity of the readiness potential signal from which noise is eliminated, the phase of the readiness potential signal, the place where the readiness potential signal is generated, and the time when the readiness potential signal is generated; and a data classifier for classifying the extracted features to determine the user's intention.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Bioelectric electrode
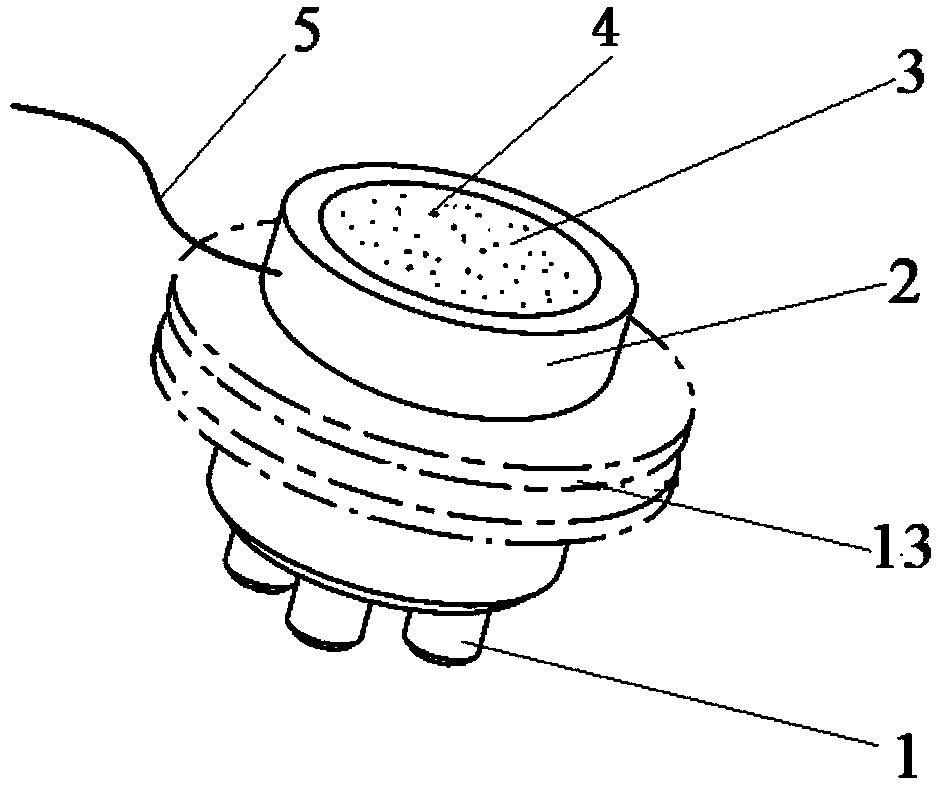
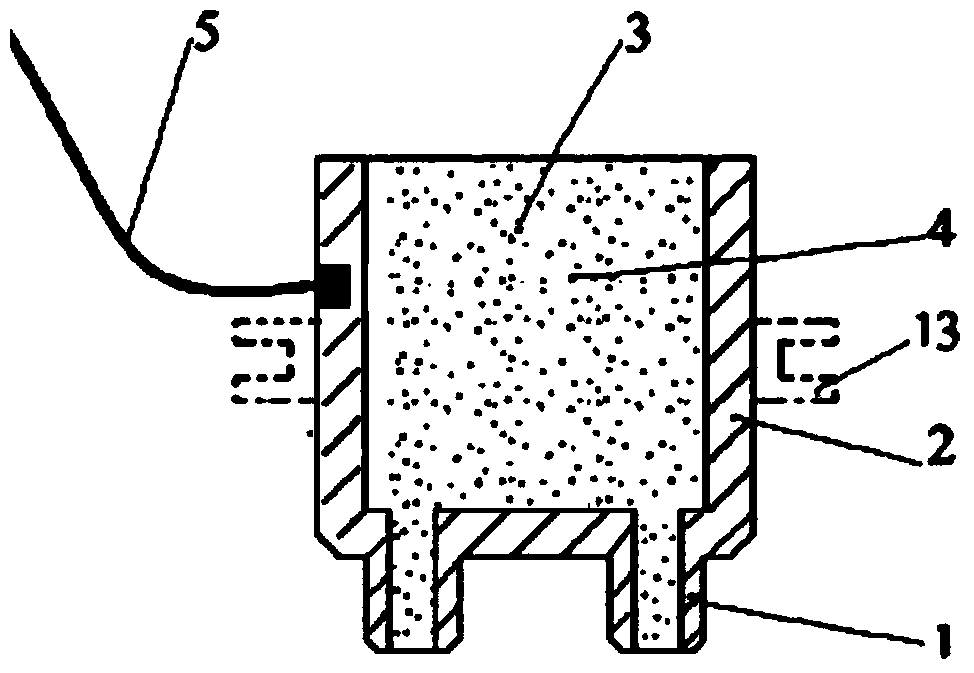
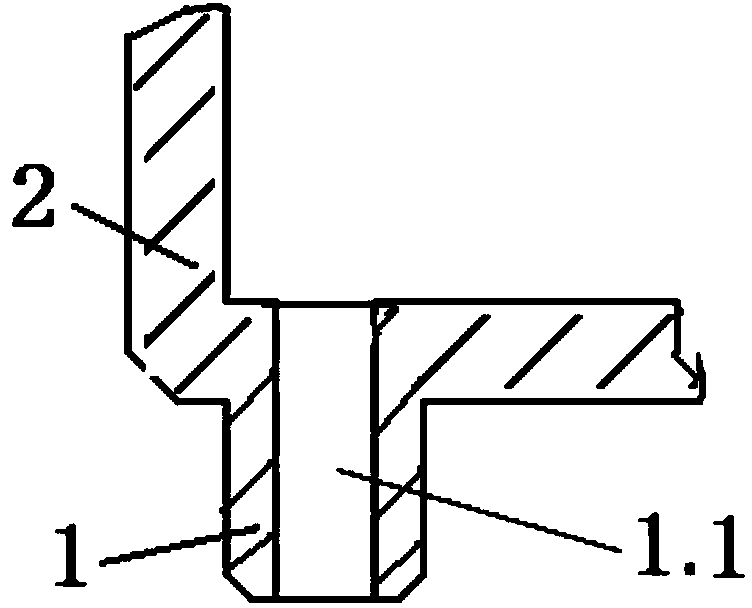
ActiveCN104068853AImpedance stabilityIncrease contactDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFamily healthInsulator (electricity)
The invention relates to a bioelectric electrode which is extensively applied to bioelectric recording, measurement and stimulation, including high-density electrode measurement, medical facilities, mobile equipments, family health care, psychological cognition, games, a brain-computer interface, rehabilitation training and the like, and is particularly applicable to electroencephalogram measurement. An electrode tip is a columnar pipe, and the middle part of the electrode tip is provided with an electrolyte circulating hole; one end of the electrode tip is a working end in contact with a living body, and the other end of the electrode tip is an electrolyte entering end; the electrode tip is located on one end plane of an electrode body; the middle part of the electrode body is provided with a cavity used for accommodating an electrolyte and communicating with a middle through hole; the electrode tip is a conductor, and the electrode body is either a conductor or an insulator; the electrode tip is communicated with an external circuit directly through the electrode body. The bioelectric electrode provided by the invention has the main advantages of being simple in structure, low and stable in electrode impedance, low in measurement noise, small in artifact, convenient and comfortable to use, and an electrolyte ion conductor and an electrode tip electronic conductor are simultaneously in contact with the skin, thereby being applicable to the relevant applications of bioelectricity recording, measuring and stimulation.
Owner:SUZHOU GREENTEK
Collaborative filtering recommendation system and method for assisting in preference acquisition by utilizing electroencephalogram signal
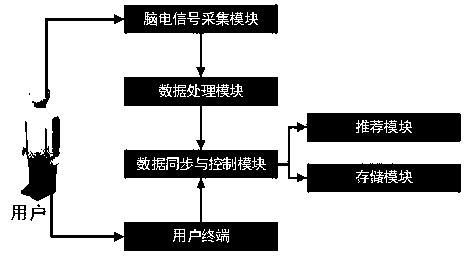
ActiveCN108446635ARecommendation results are objectiveRecommended results are accurateBuying/selling/leasing transactionsPhysiological signal biometric patternsBrain computer interfacingMiniaturization
The invention discloses a collaborative filtering recommendation system and method for assisting in preference acquisition by utilizing an electroencephalogram signal. Through electroencephalogram signal data, a user emotion tendency is calculated and an implicit feedback acts on preference scoring of commodities browsed by a user; and in a recommendation process, a classification result of the electroencephalogram signal data is brought into a calculation category, so that the recommendation accuracy of the recommendation system is improved. By adopting the recommendation method for deeply mining user preferences, the user can quickly find required data from overloaded information data. On the other hand, along with miniaturization and productization of electroencephalogram equipment, therecommendation method provided by the invention provides a new direction for next development of the recommendation system in combination with professional knowledge of the field of brain-computer interfaces.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Brain- machine interface systems and methods
InactiveUS20080015459A1Not disruptSmall sizeElectroencephalographyTransvascular endocardial electrodesRadiologyBrain–computer interface
A system and method for interfacing a brain with a machine. An exemplary embodiment of the present invention employs a vascular approach in which one or more nano-electrodes are deployed in vasculature having a close geometric relationship with proximal innervation. Each nano-electrode is preferably deployed in a blood vessel so that its sensing end is at or near a nerve passing close to or intersecting the blood vessel. The sensing end of each nano-electrode is adapted so as to be carried along in the blood stream so as to position the sensing end at a desired point within the blood vessel. An array of nano-electrodes of varying lengths can be used to monitor multiple nerves or neurons along a blood vessel.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Multimodal closed-loop brain-computer interface and peripheral stimulation for neuro-rehabilitation
InactiveUS20200038653A1Input/output for user-computer interactionElectrotherapyStatistical analysisCerebral damage
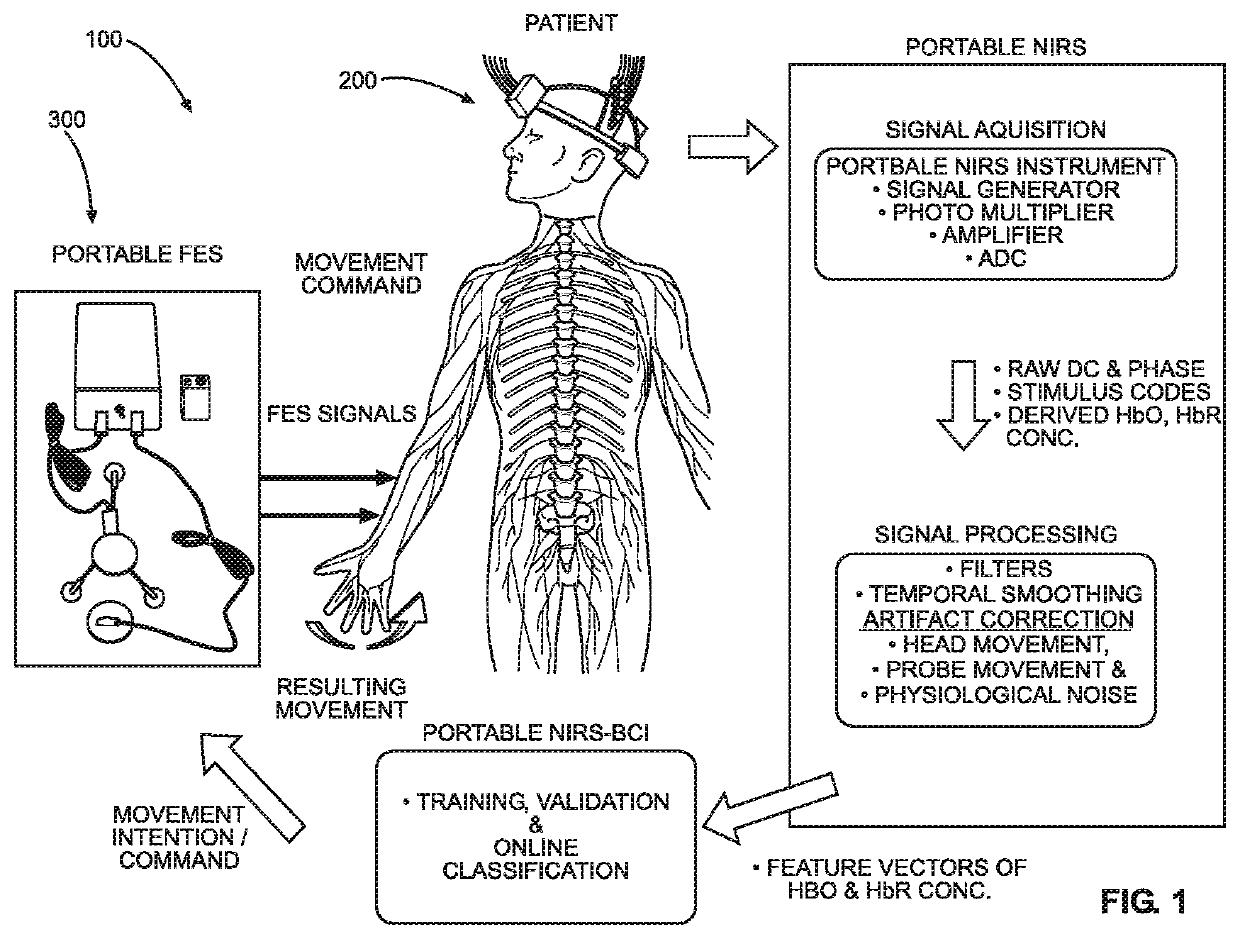
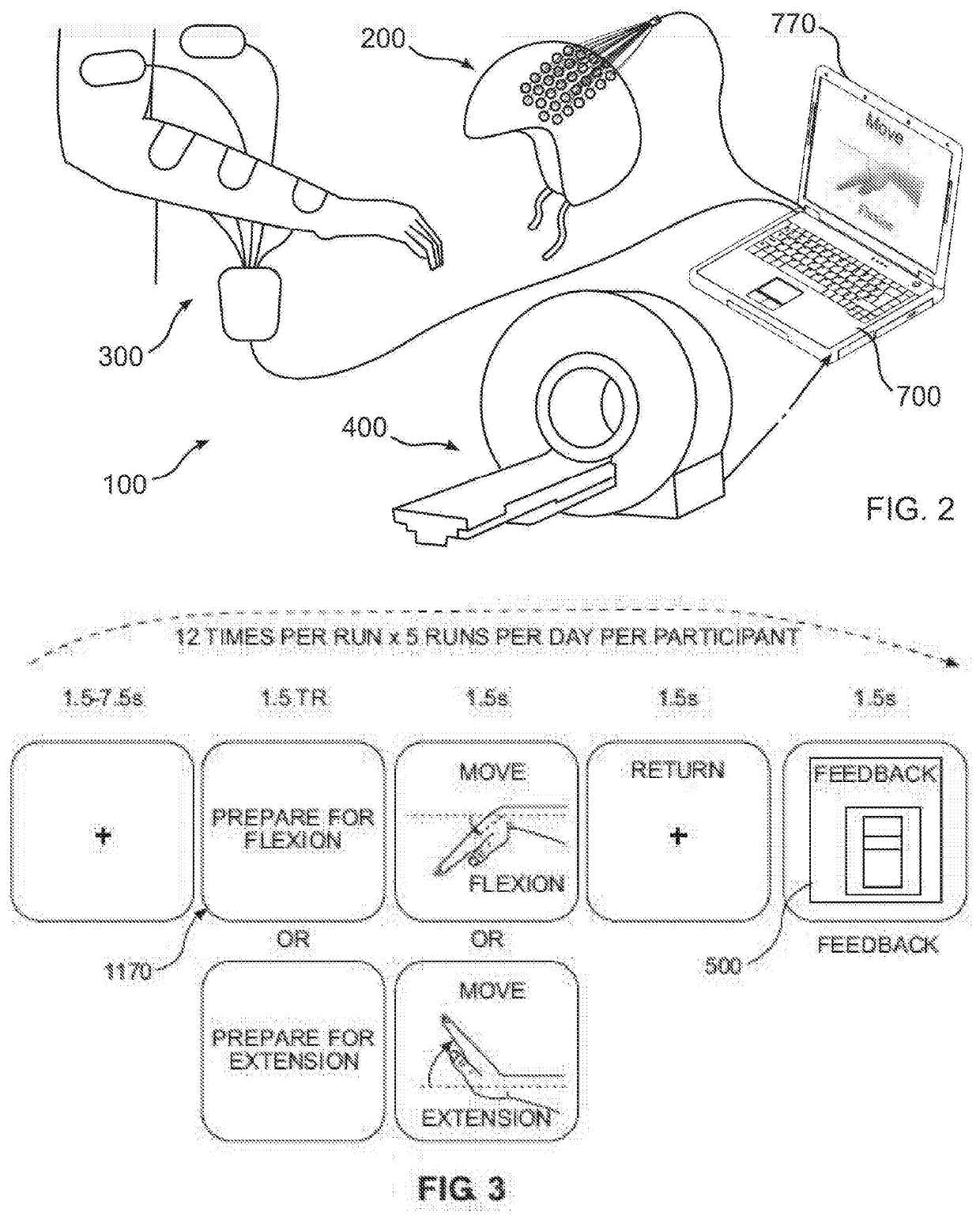
Brain impairment, for example due to stroke, is corrected in order to improve body movement. An fNIRS device is positioned over the motor cortex of non-impaired individuals, and blood oxygen in locations of the brain is analyzed to determine brain activity corresponding to a particular body movement. The movements are statistically analyzed, and are compared with fNIRS data gathered from a movement impaired individual attempting the same movement. A weighted value corresponding to the desired brain activity is generated using the statistical analysis, and is graphically displayed to the movement impaired individual during the attempts. This produces a feedback loop relating to the movement which can be repeated to produce brain plasticity in the impaired individual to facilitate the movement. Additionally, correct brain activity can be used to cause the application of an electrical signal to muscles of the body to produce the desired movement.
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS +1
Optical neuron stimulation prosthetic using silicon carbide
InactiveUS20140067023A1Eliminate needLittle immune responseSurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismNeuronal stimulationNervous system
The microfabricated prosthetic device uses local, direct, and wavelength-specific optical stimulation to achieve an action potential from a single or small group of neurons within the central nervous system (CNS). The device is biocompatible, mechanically flexible, and optically transparent. The device can also use integrated electrodes for additional input / output (IO) locations, signal verification, feedback, wireless communication, and characterization of the electrochemically-evoked potential received from the activated neuron. The purpose of the device is to act as a neural interface prosthetic. The prosthetic is designed as the central component of a brain machine interface (BMI).
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Handicapped-helping control system based on electroencephalogram/voice instructions
InactiveCN103099693AIncrease diversityImprove accuracyInput/output for user-computer interactionWheelchairs/patient conveyanceBluetoothDigital signal
The invention discloses a handicapped-helping control system based on electroencephalogram / voice instructions. The handicapped-helping control system is composed of a computer, a brain wave collection device, a brain-and-computer port device, a Bluetooth headset, a home furnishing control device, a wheel chair control device and an electric wheel chair, wherein the brain wave collection device collects electroencephalogram signals of a user through the brain-and-computer port device, and the computer receives the electroencephalogram signals and enables the electroencephalogram signals to be converted into computer keyboard events. The Bluetooth headset enables the voice instructions sent by the user to be transmitted to the computer in a wireless mode, a voice recognition procedure conducts recognition process for the voice instructions, and the voice instructions are converted into the computer keyboard events. The computer keyboard events are then converted into digital events, control for common household appliances is achieved through the home furnishing control device, control electric potentials of the electric wheel chair is changed through the wheel chair control device, and functions of advancing, retreating, going left, going right and stopping of the wheel chair are achieved. The handicapped-helping control system achieves the purposes that the handicapped and the like having limb inconvenience or language inconvenience achieve independent living and independent tripping, has great contribution to relieving of psychological stress of the handicapped, and is simple in structure, low in cost and easy to operate.
Owner:王禹
Brain-machine interface systems and methods
InactiveUS8447392B2Not disruptSmall sizeElectroencephalographyTransvascular endocardial electrodesProximal pointRadiology
A system and method for interfacing a brain with a machine. An exemplary embodiment of the present invention employs a vascular approach in which one or more nano-electrodes are deployed in vasculature having a close geometric relationship with proximal innervation. Each nano-electrode is preferably deployed in a blood vessel so that its sensing end is at or near a nerve passing close to or intersecting the blood vessel. The sensing end of each nano-electrode is adapted so as to be carried along in the blood stream so as to position the sensing end at a desired point within the blood vessel. An array of nano-electrodes of varying lengths can be used to monitor multiple nerves or neurons along a blood vessel.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com