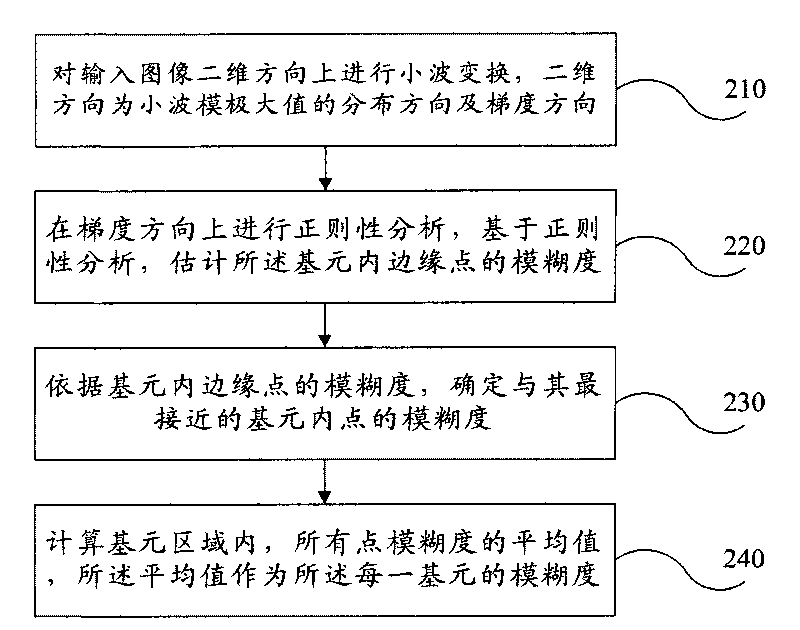
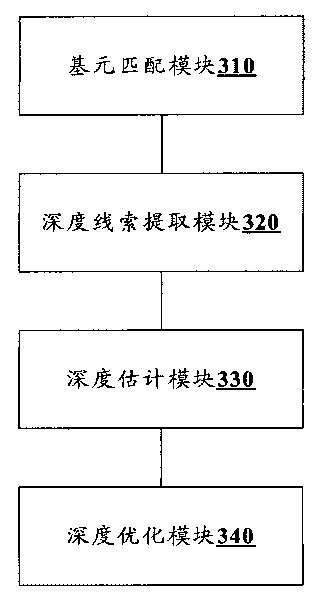
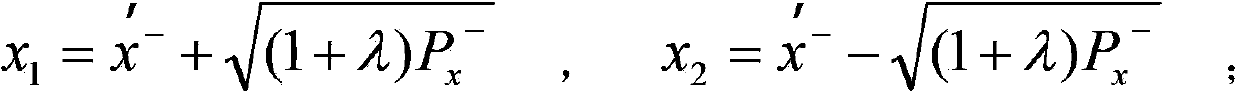Patents
Literature
104 results about "Relative depth" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
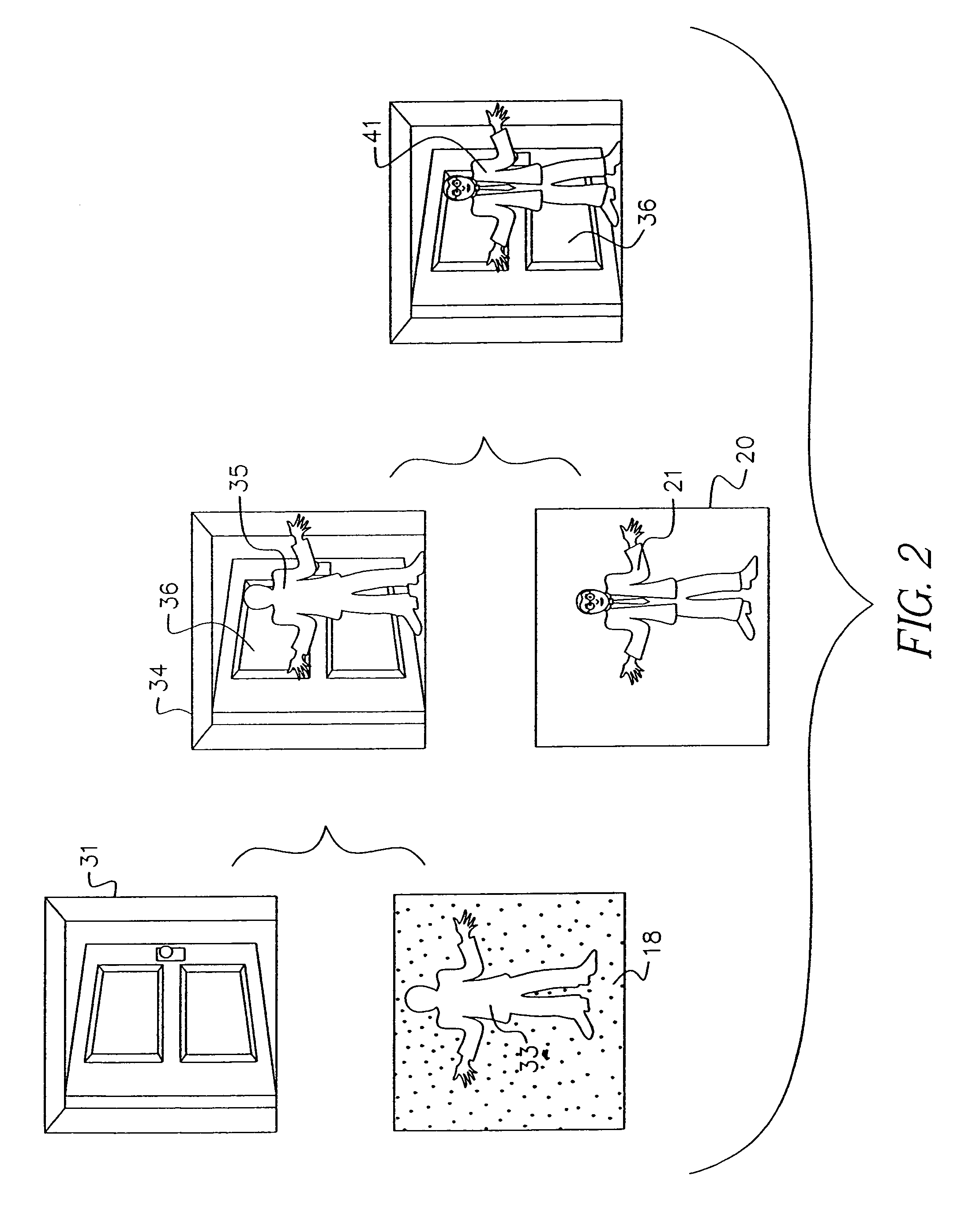
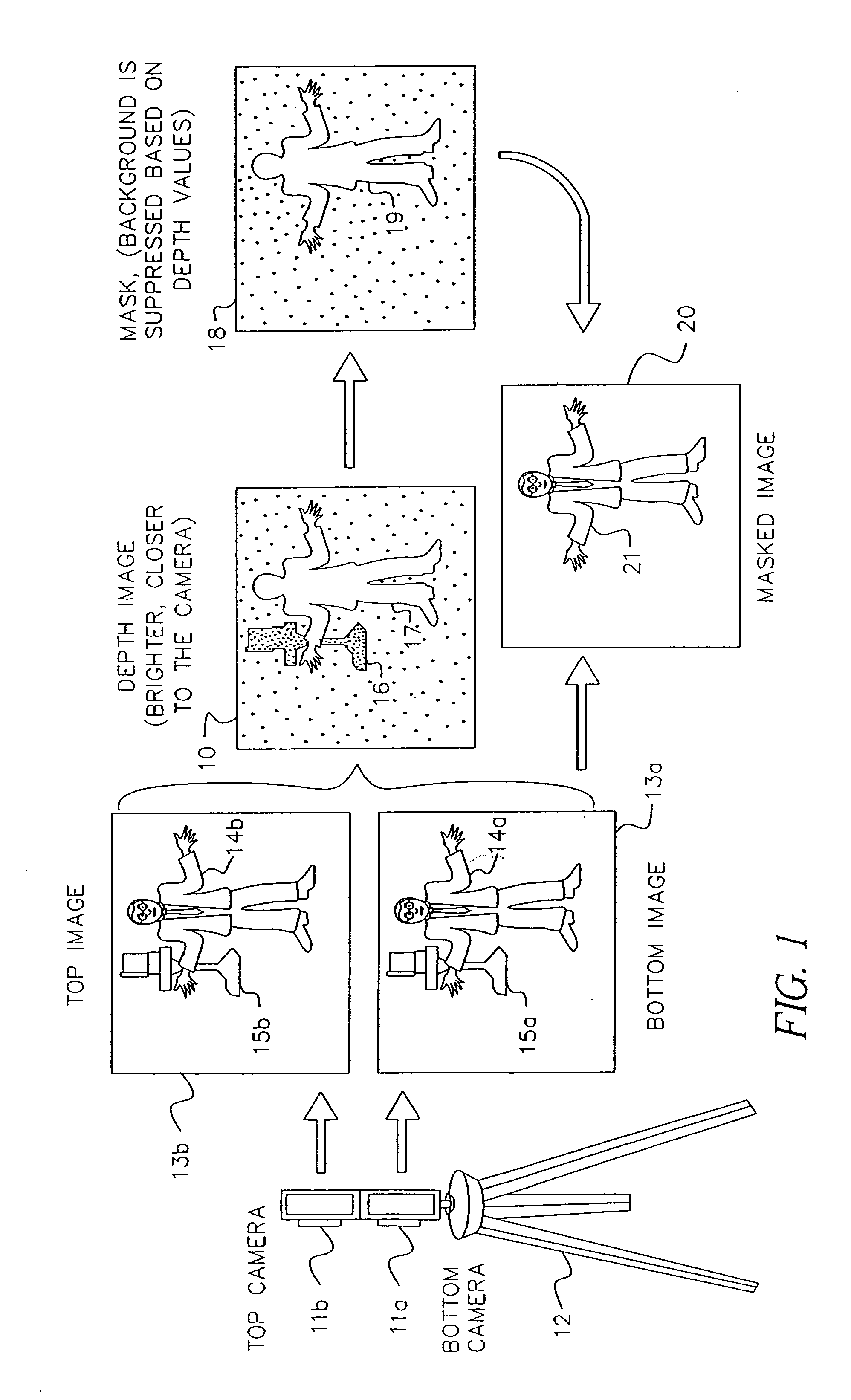
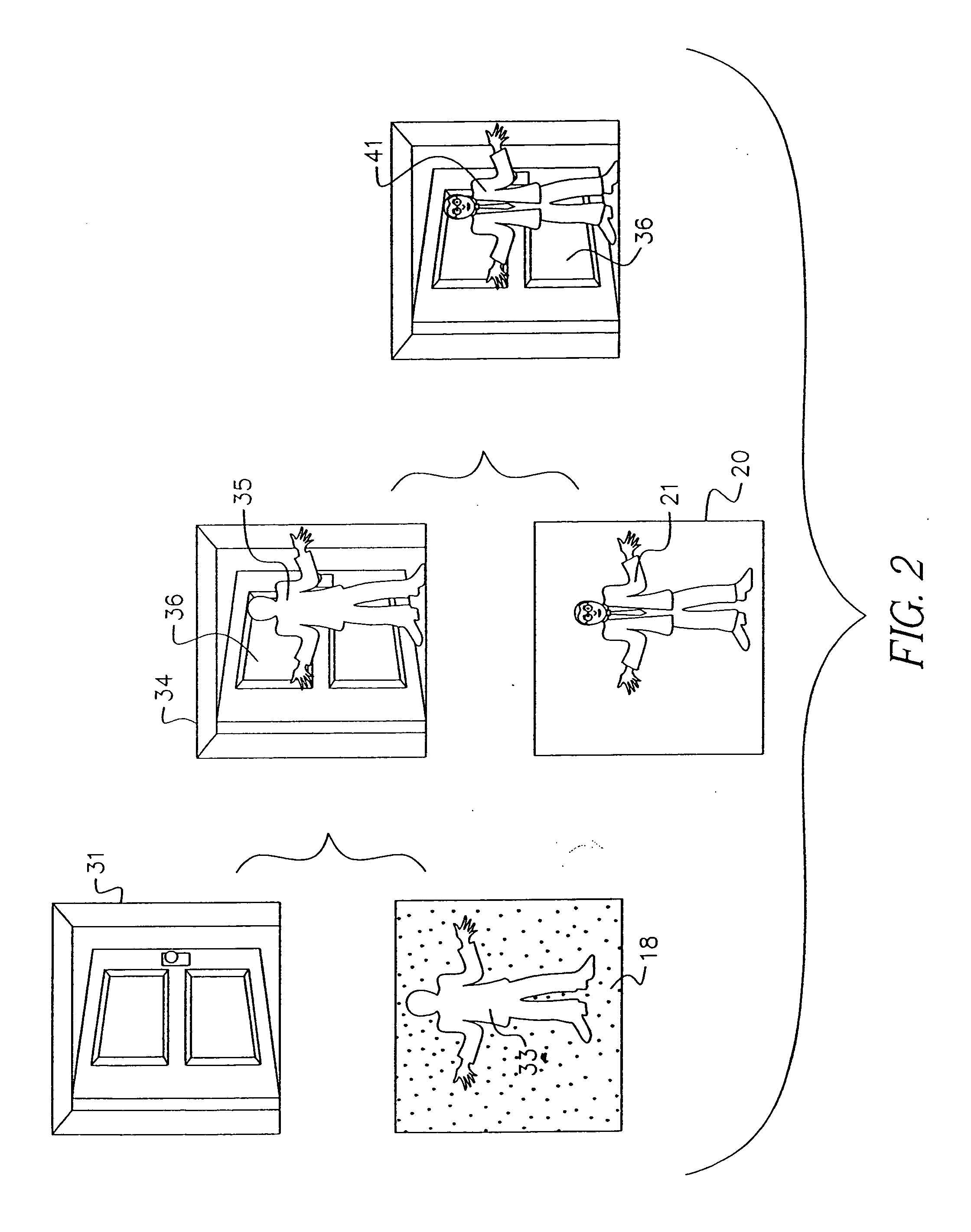
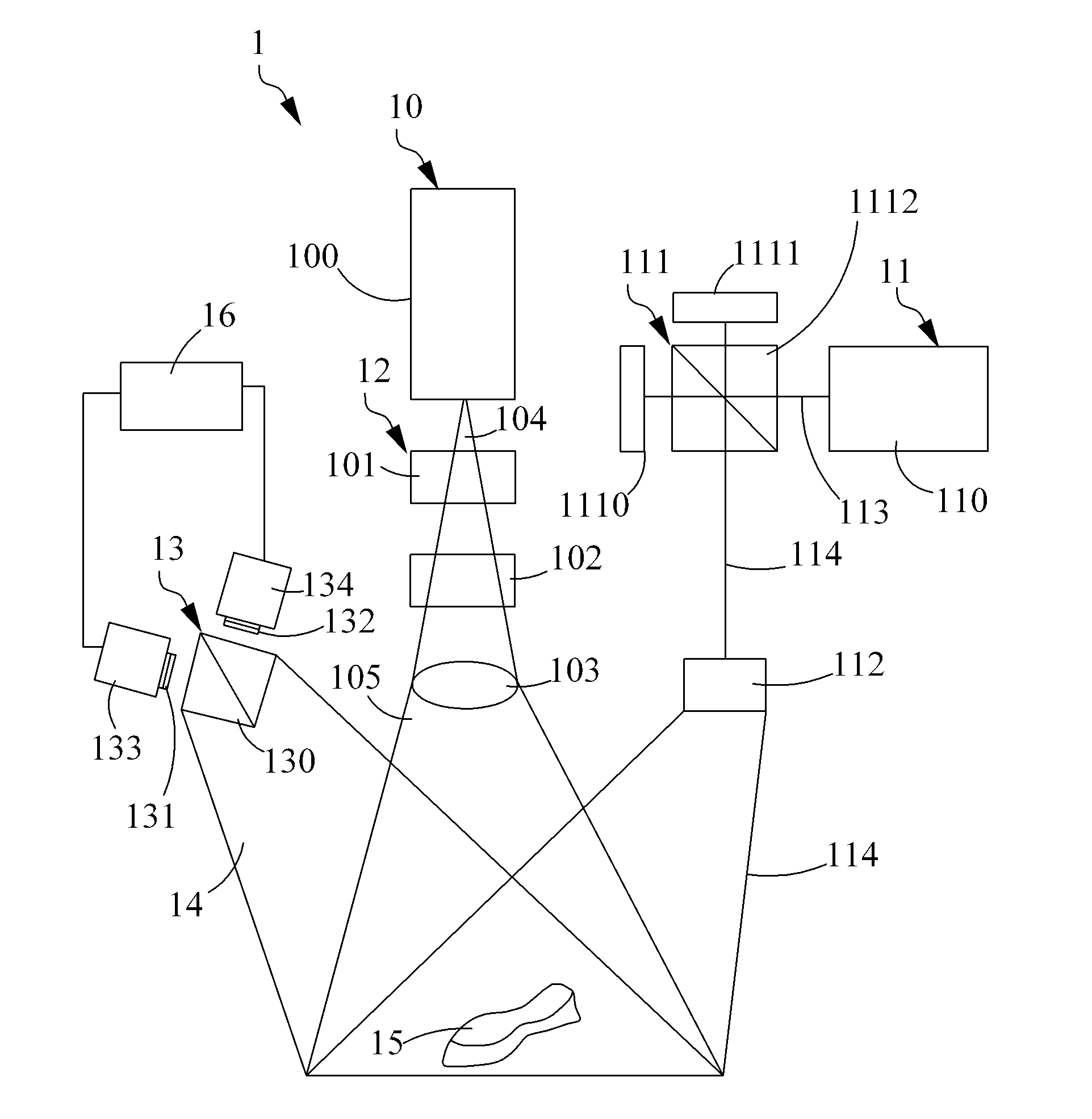
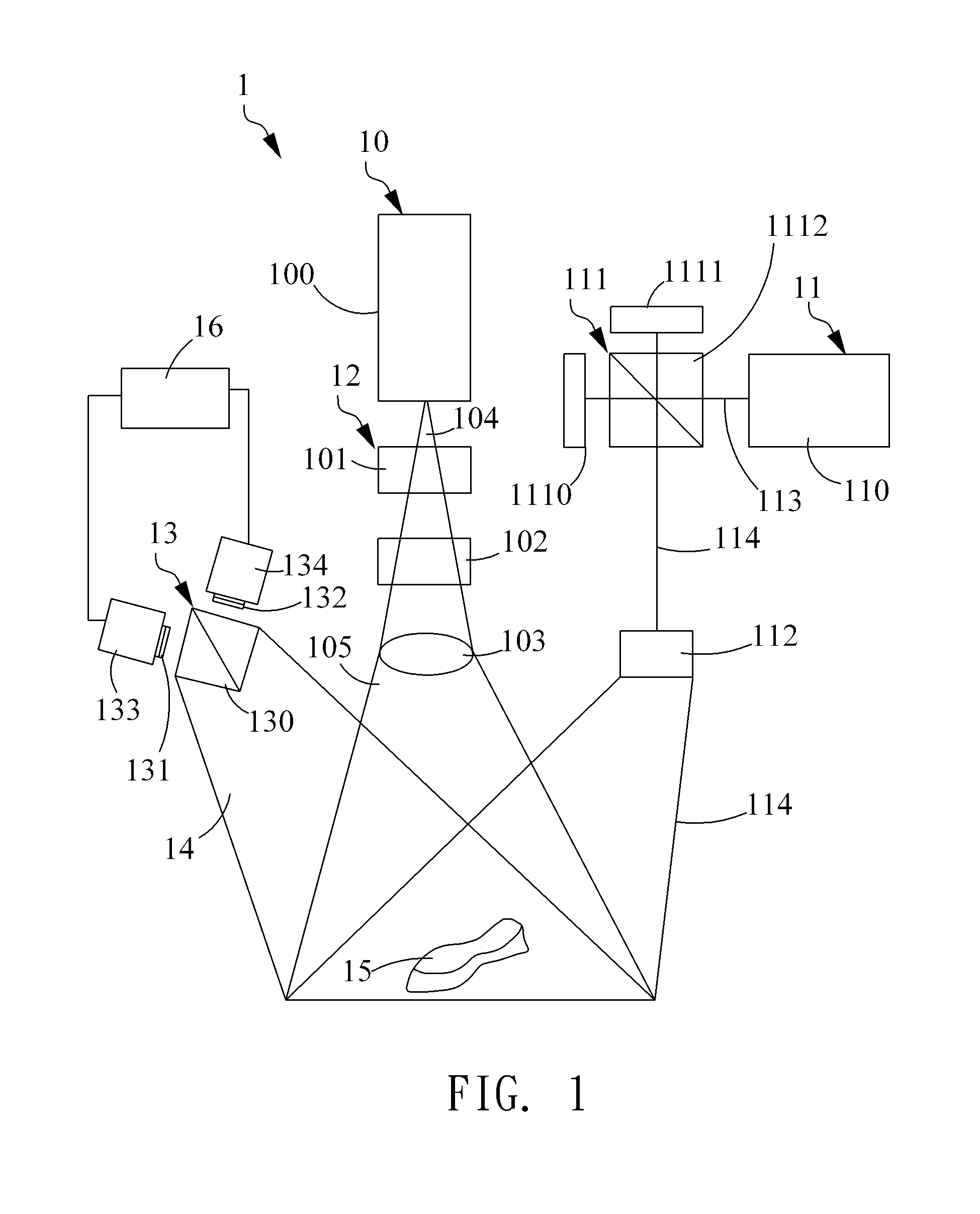
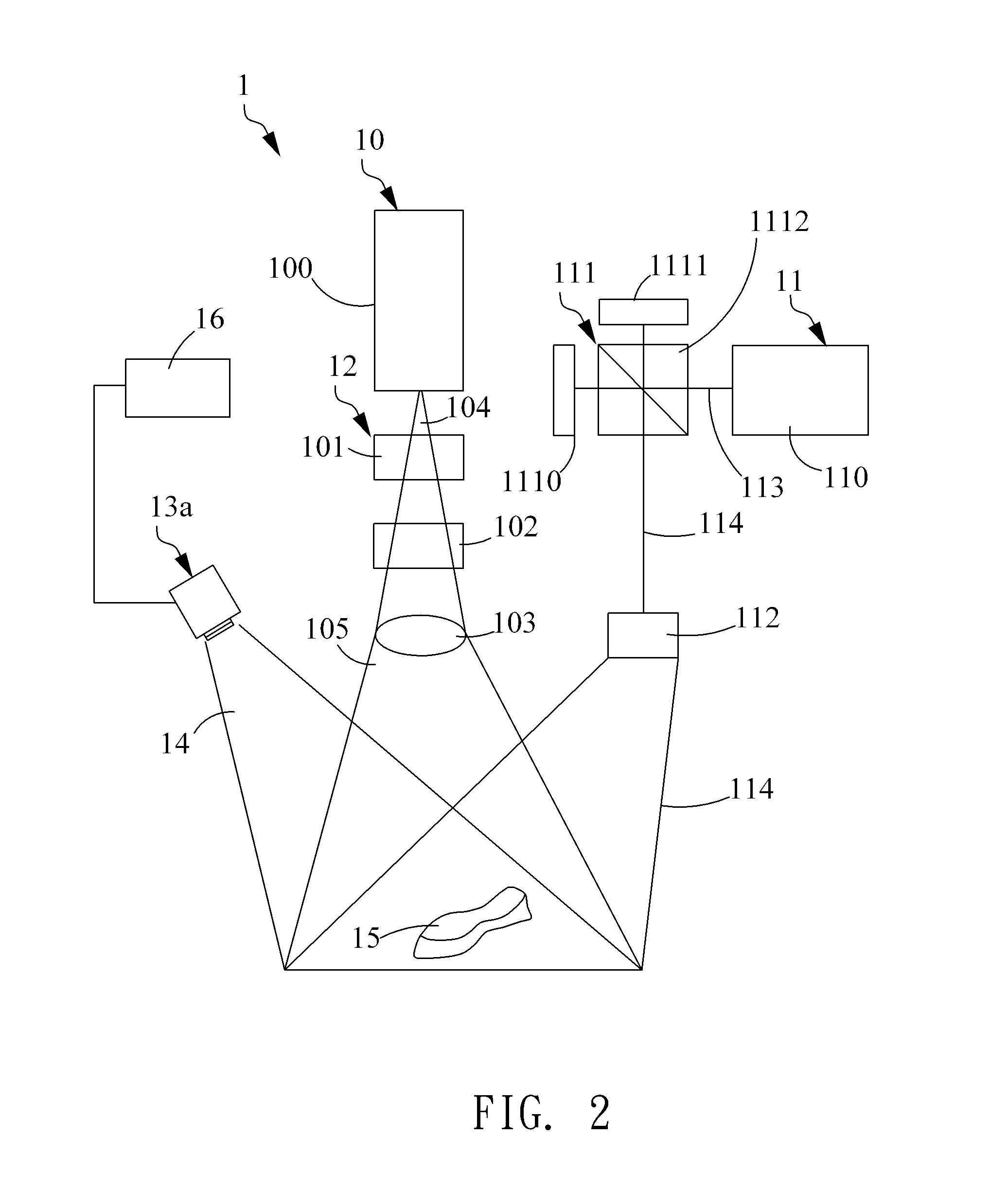
Apparatus and methods for determining the three-dimensional shape of an object using active illumination and relative blurring in two images due to defocus
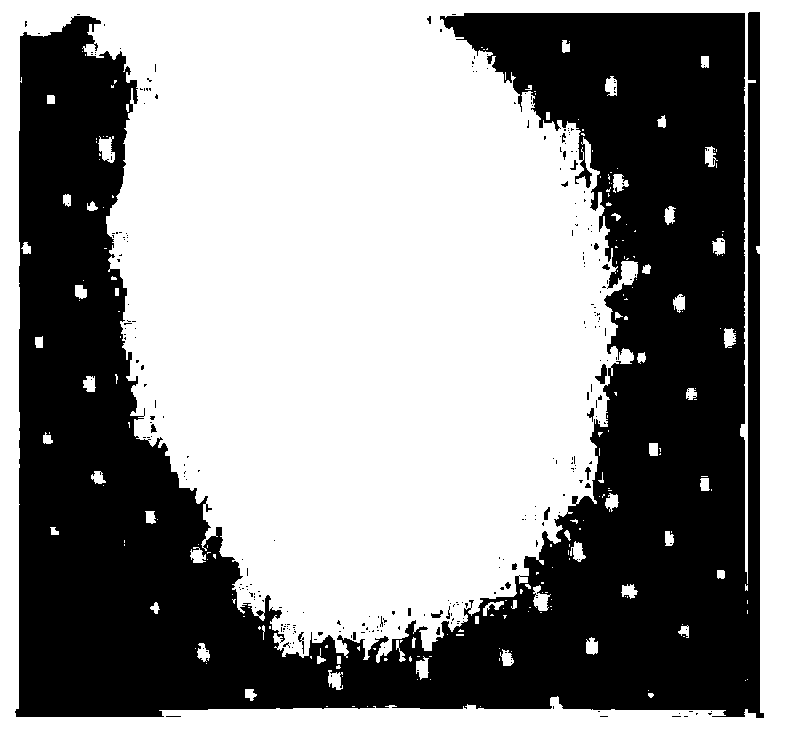
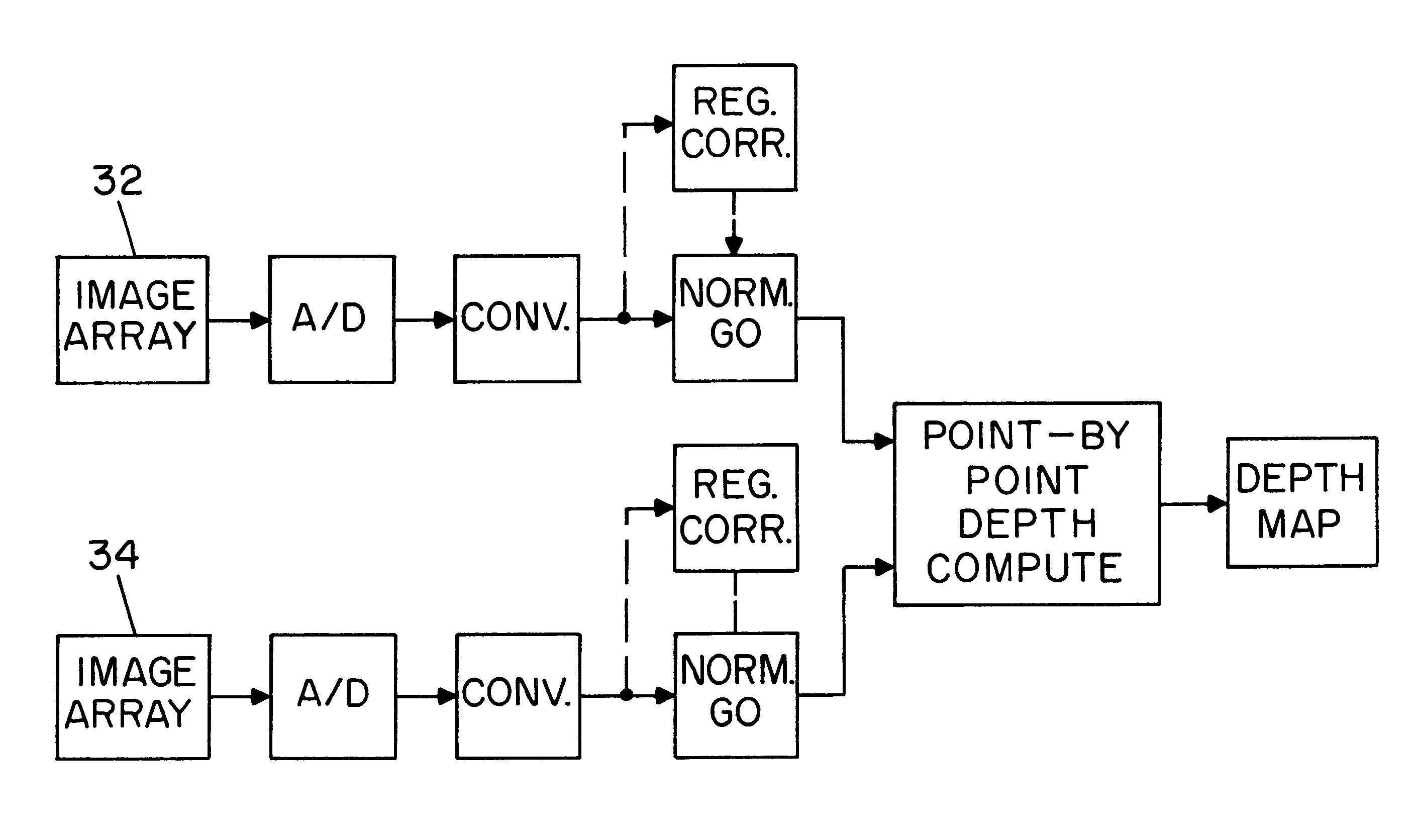
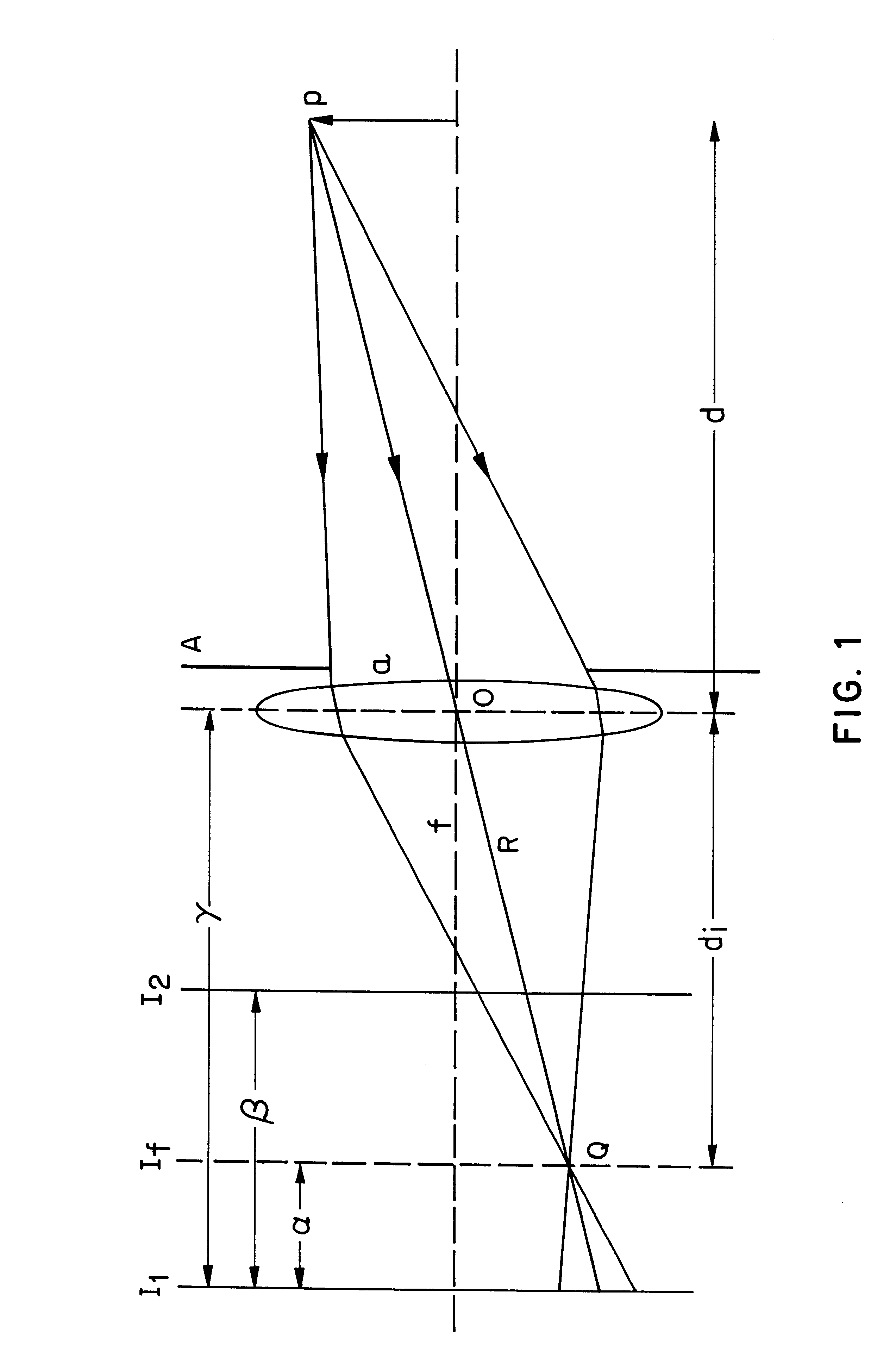
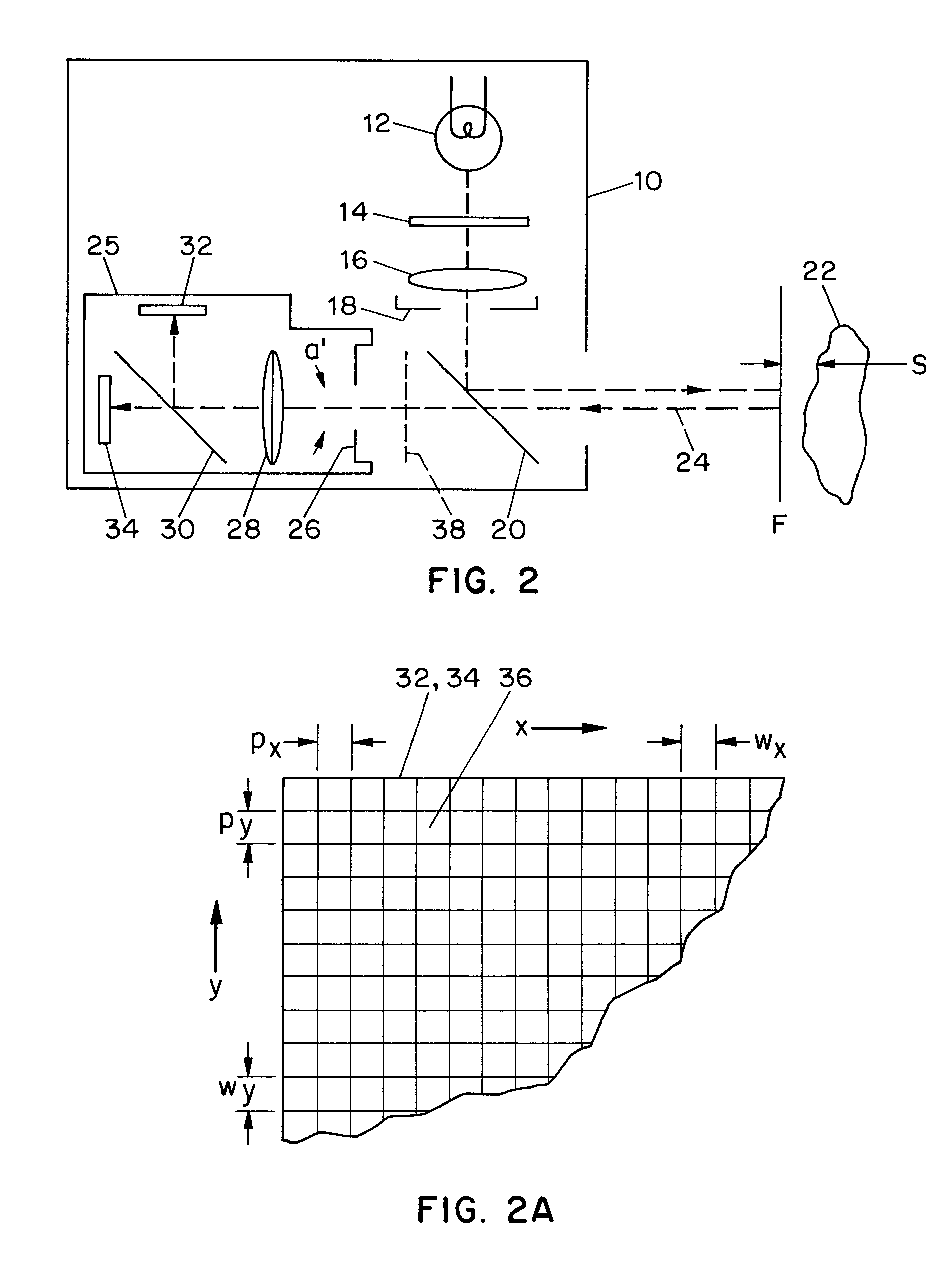
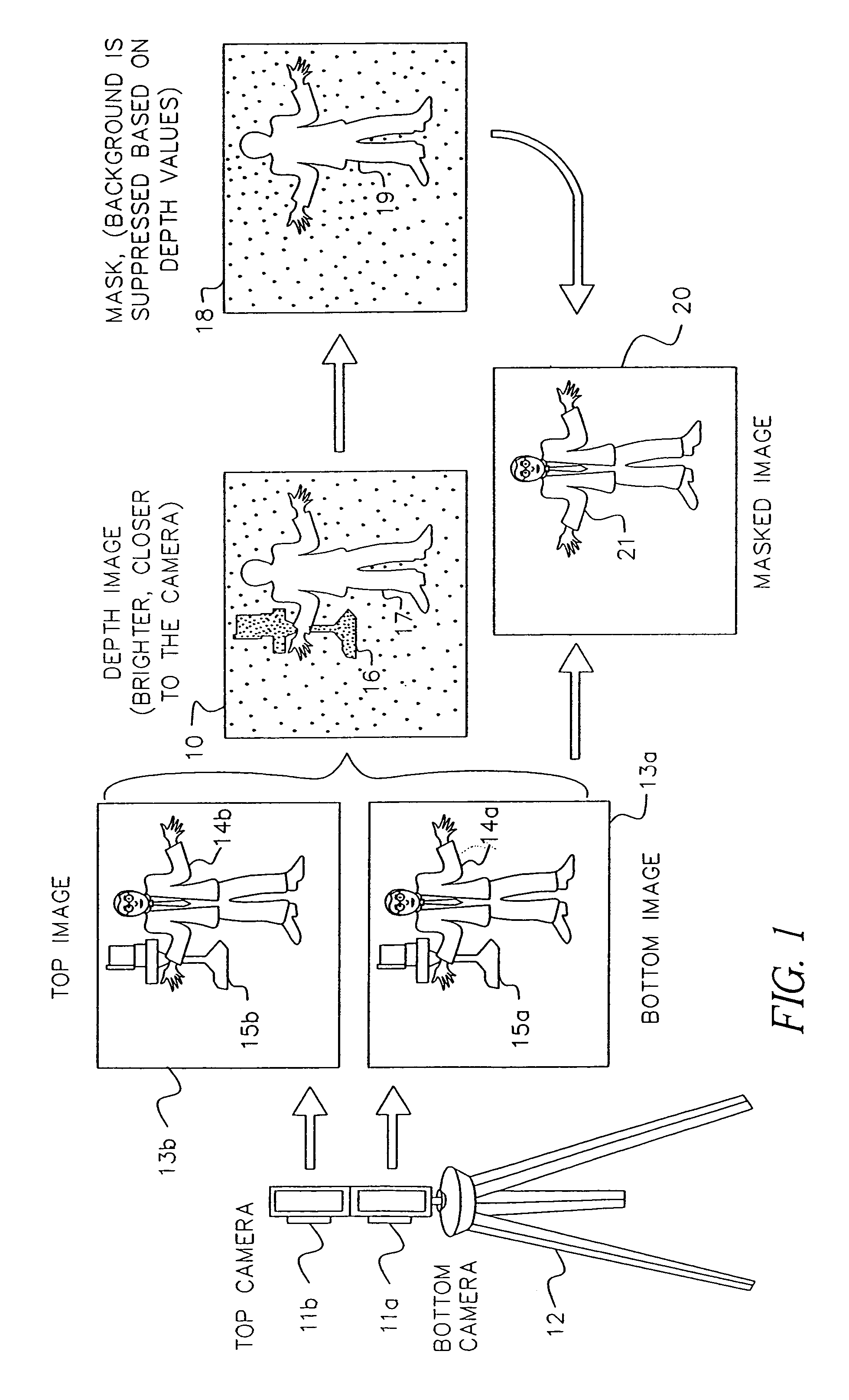
A method and apparatus for mapping depth of an object (22) in a preferred arrangement uses a projected light pattern to provide a selected texture to the object (22) along the optical axis (24) of observation. An imaging system senses (32, 34) first and second images of the object (22) with the projected light pattern and compares the defocused of the projected pattern in the images to determine relative depth of elemental portions of the object (22).
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
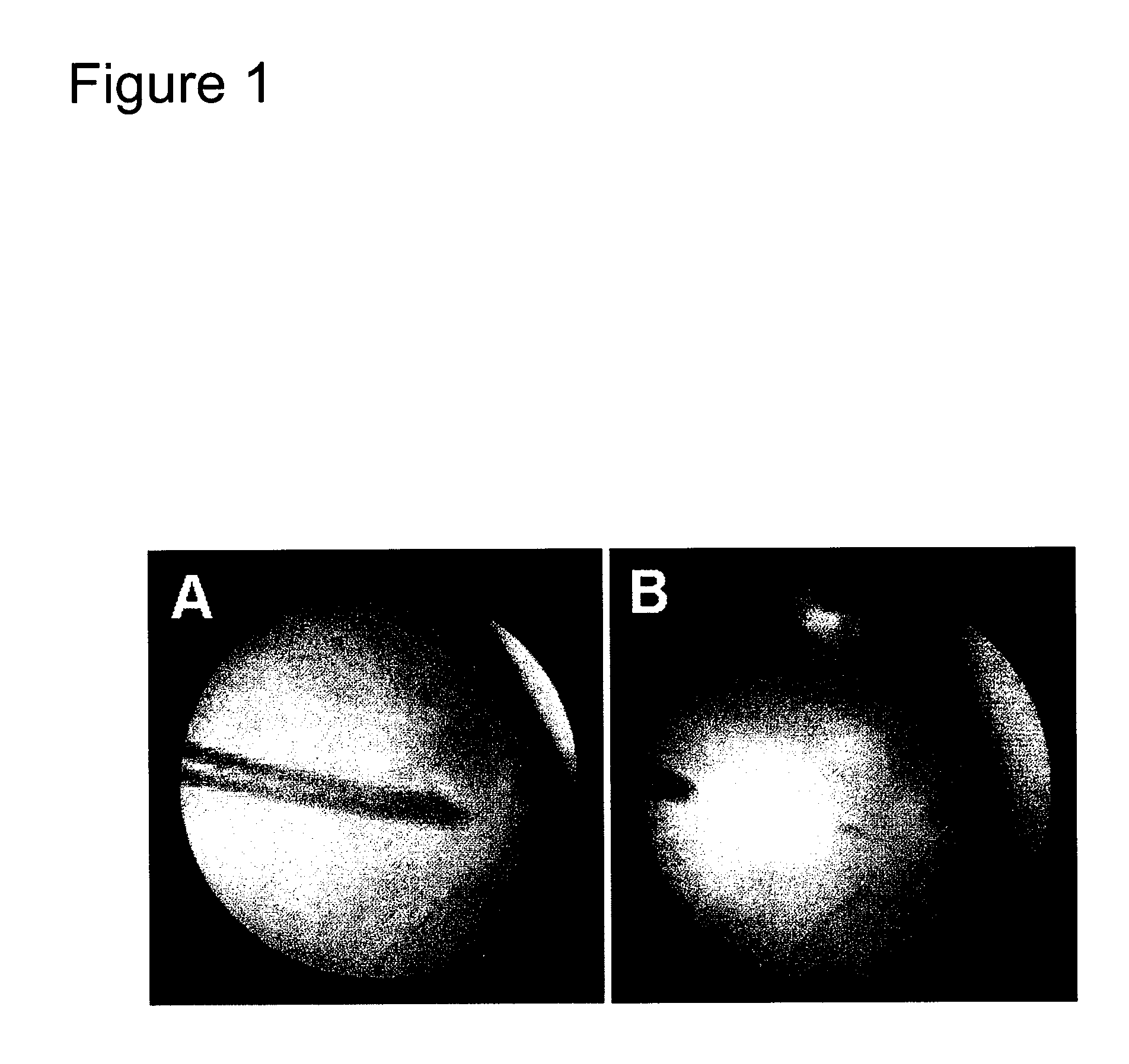
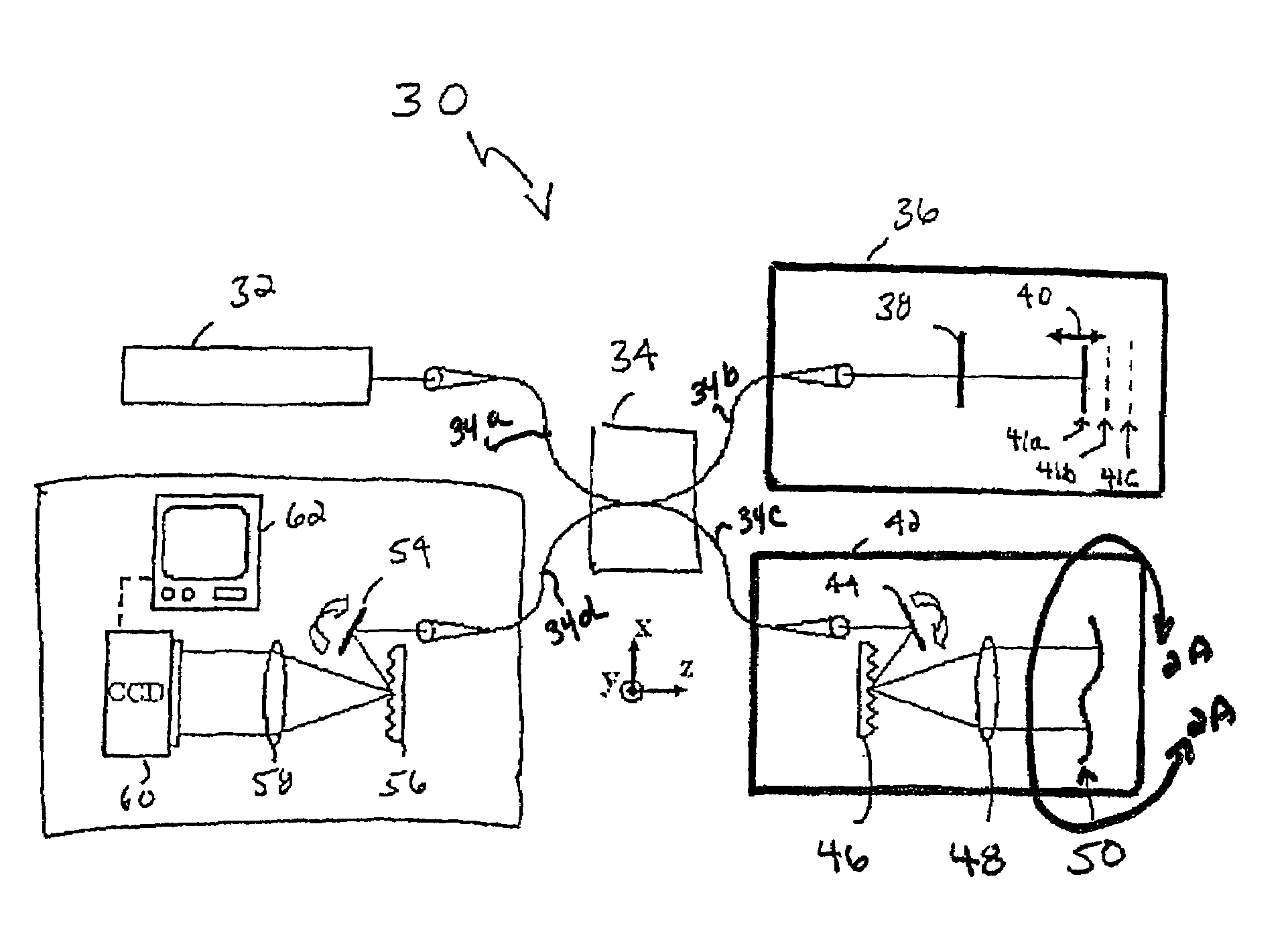
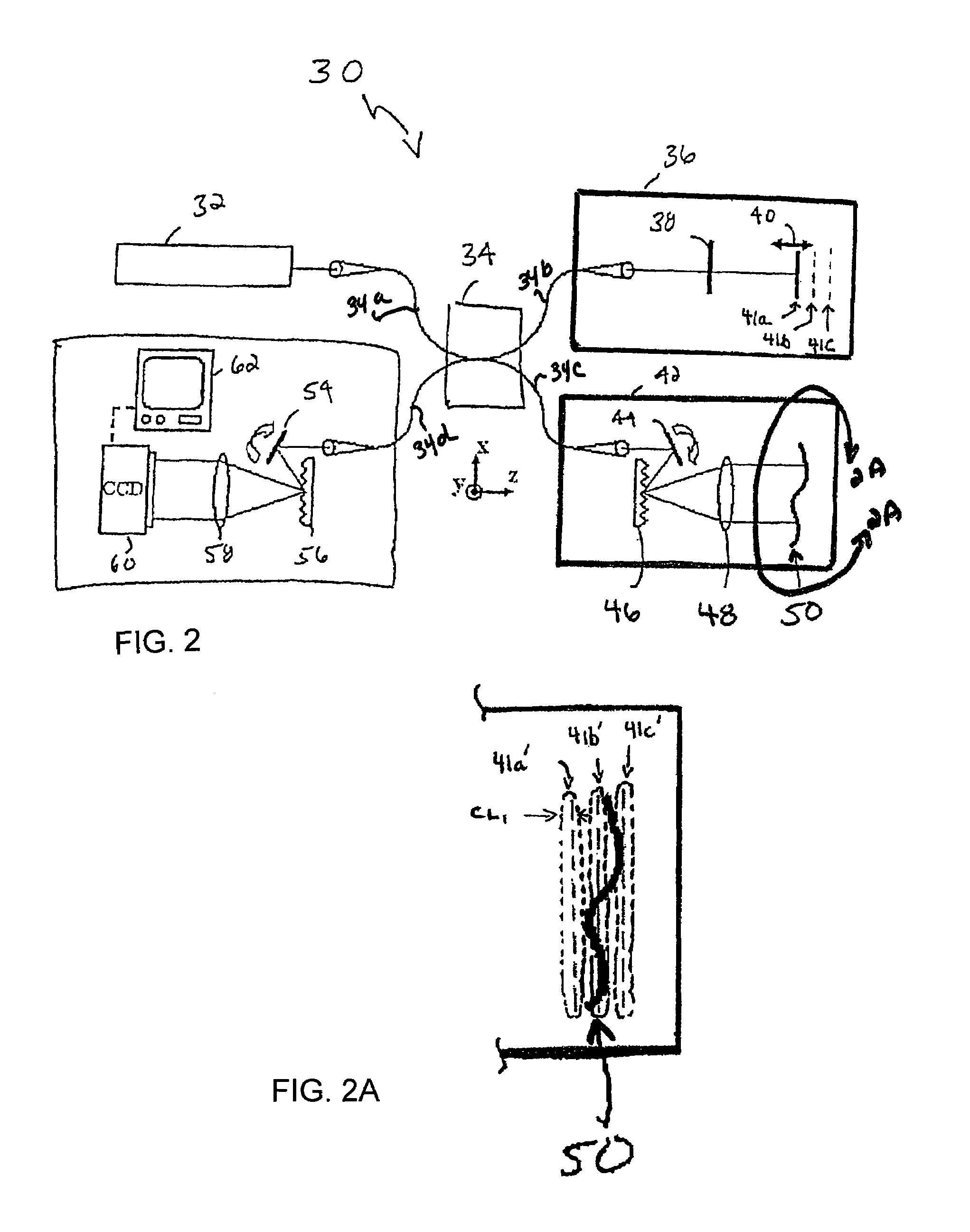
Apparatus and method for obtaining and providing imaging information associated with at least one portion of a sample, and effecting such portion(s)
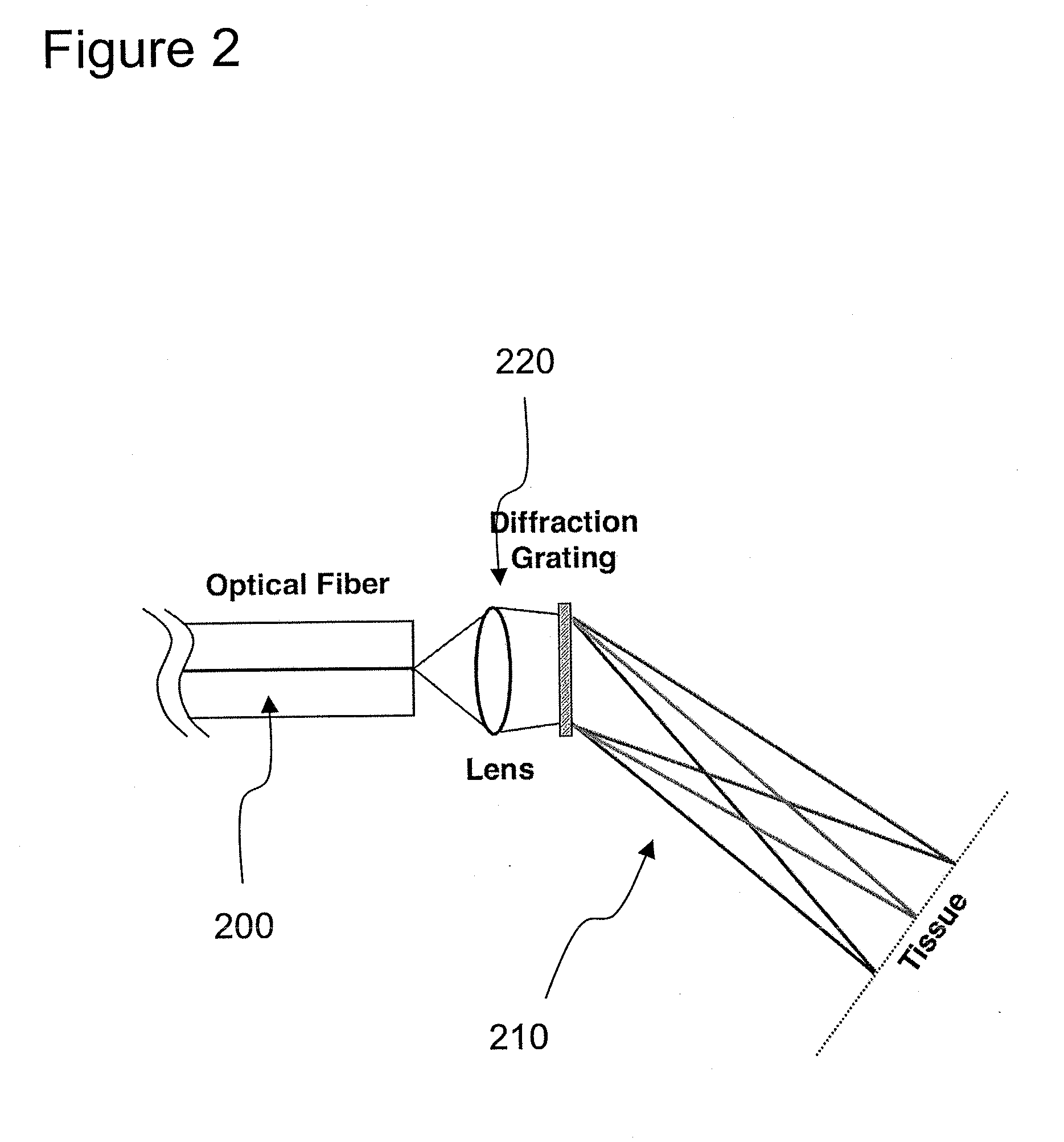
ActiveUS20080097225A1Treatment safetyImprove image qualityRadiation pyrometryDiagnostics using lightRelative phaseElectromagnetic radiation
Exemplary apparatus and process can be provided for imaging information associated with at least one portion of a sample. For example, (i) at least two first different wavelengths of at least one first electro-magnetic radiation can be provided within a first wavelength range provided on the portion of the sample so as to determine at least one first transverse location of the portion, and (ii) at least two second different wavelengths of at least one second electro-magnetic radiation are provided within a second wavelength range provided on the portion so as to determine at least one second transverse location of the portion. The first and second ranges can east partially overlap on the portion. Further, a relative phase between at least one third electro-magnetic radiation electro-magnetic radiation being returned from the sample and at least one fourth electro-magnetic radiation returned from a reference can be obtained to determine a relative depth location of the portion. First information of the portion based on the first transverse location and the relative depth location, and second information of the portion based on the second transverse location and the relative depth location can be obtained. The imaging information may include the first and second information.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
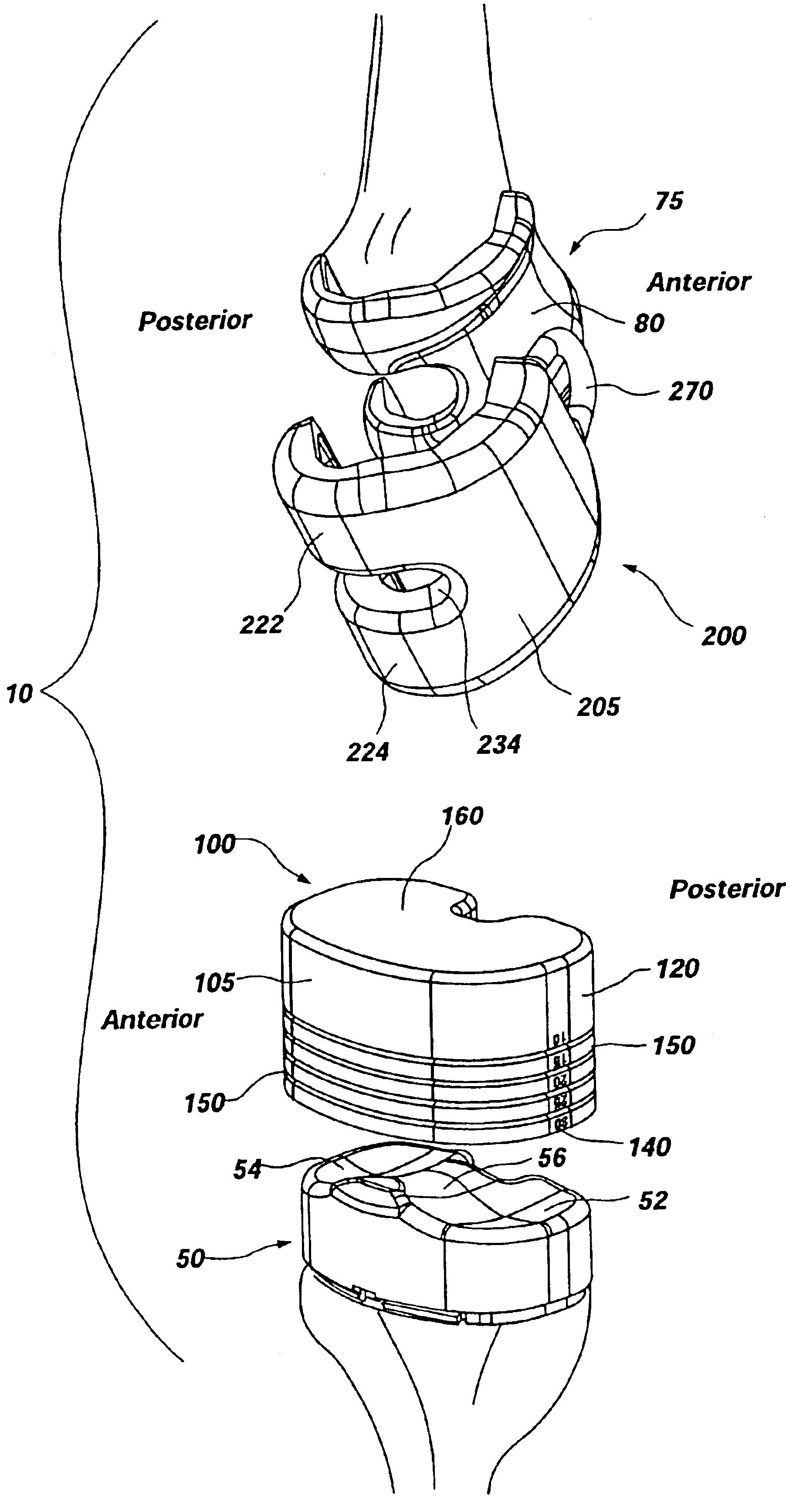
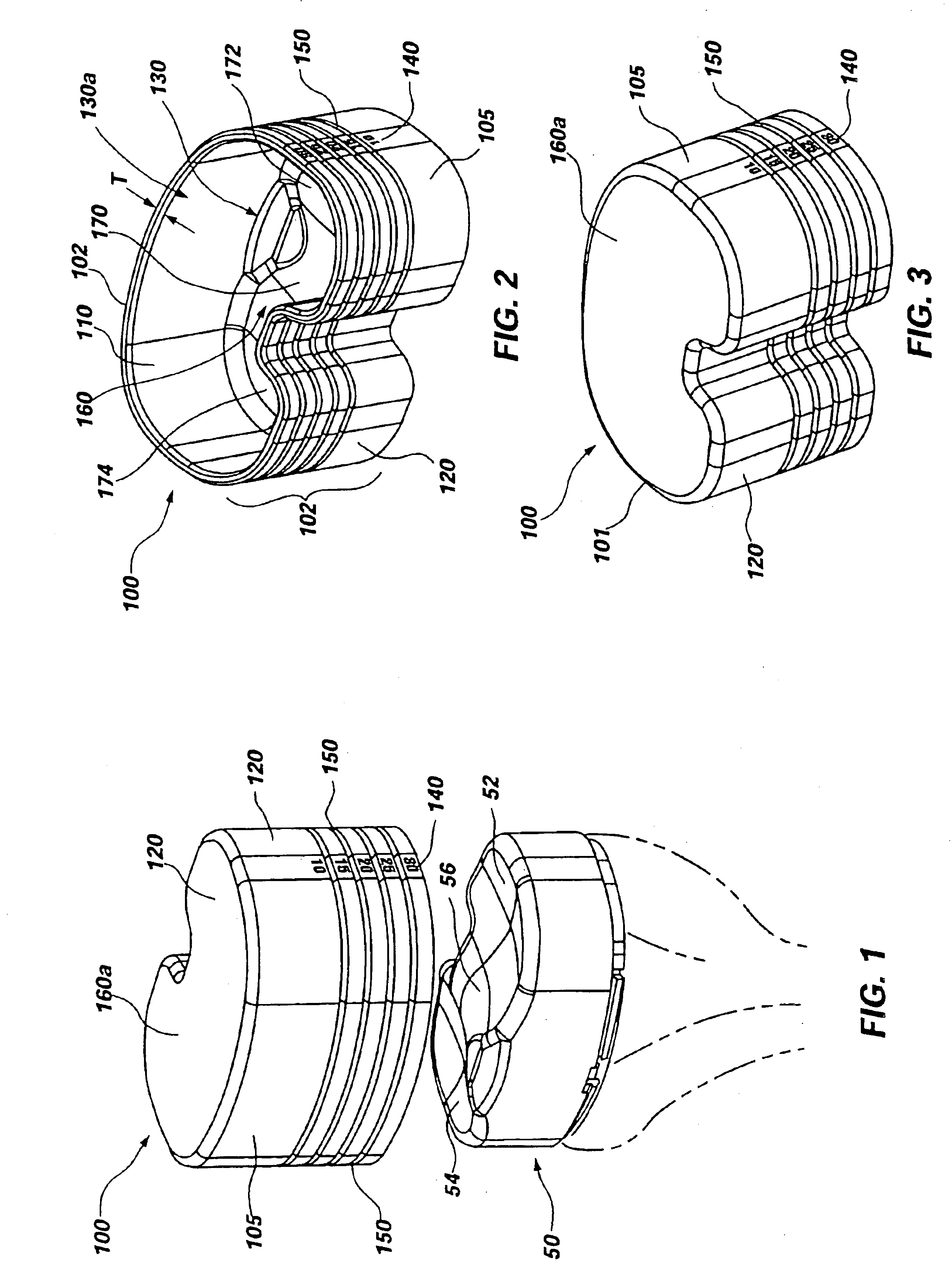
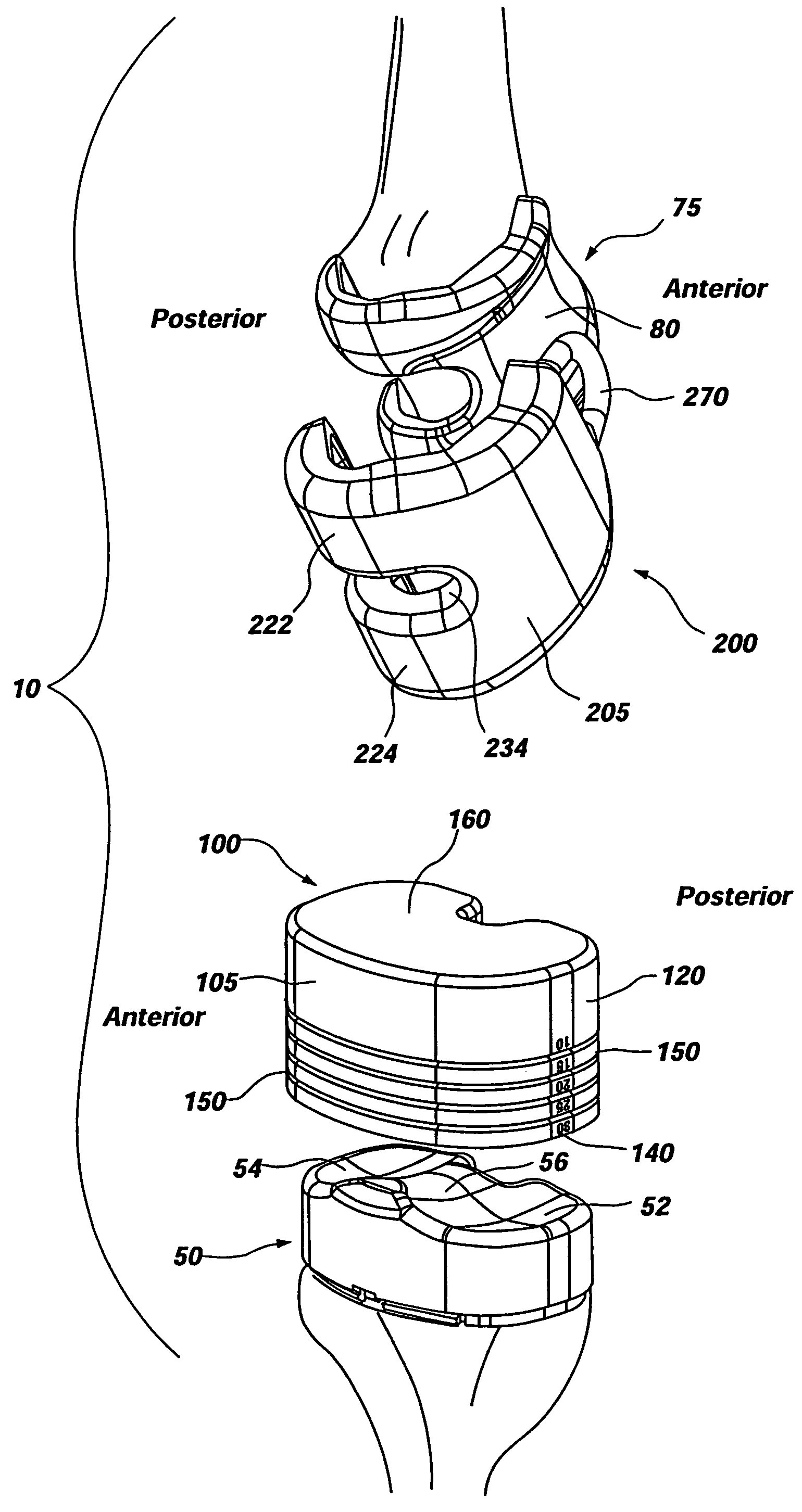
Disposable knee mold
An orthopedic implant device and method is disclosed. Specifically, a knee mold system is disclosed, including elastic tibial and femoral molds, each of which may be configured and dimensioned as a unitary mold for in situ placement during a surgical procedure. Each mold may be manufactured from an elastic material that may be disposable. The tibial mold may further comprise a sidewall forming a cavity, markings for relative depth measurement, and depth rings for use as a guide for scoring, cutting, and / or trimming and tearing away an excess portion of the tibial mold. The femoral mold may further comprise a sidewall defining a cavity, two legs extending from a body of the femoral mold for forming the artificial condyles, and an eyelet for aiding in placement and removal of the femoral mold. The resulting prosthetic tibial and femoral components may form an articulation surface that mimics, at least in part, the natural articulation surface of the knee.
Owner:ORTHO DEV CORP
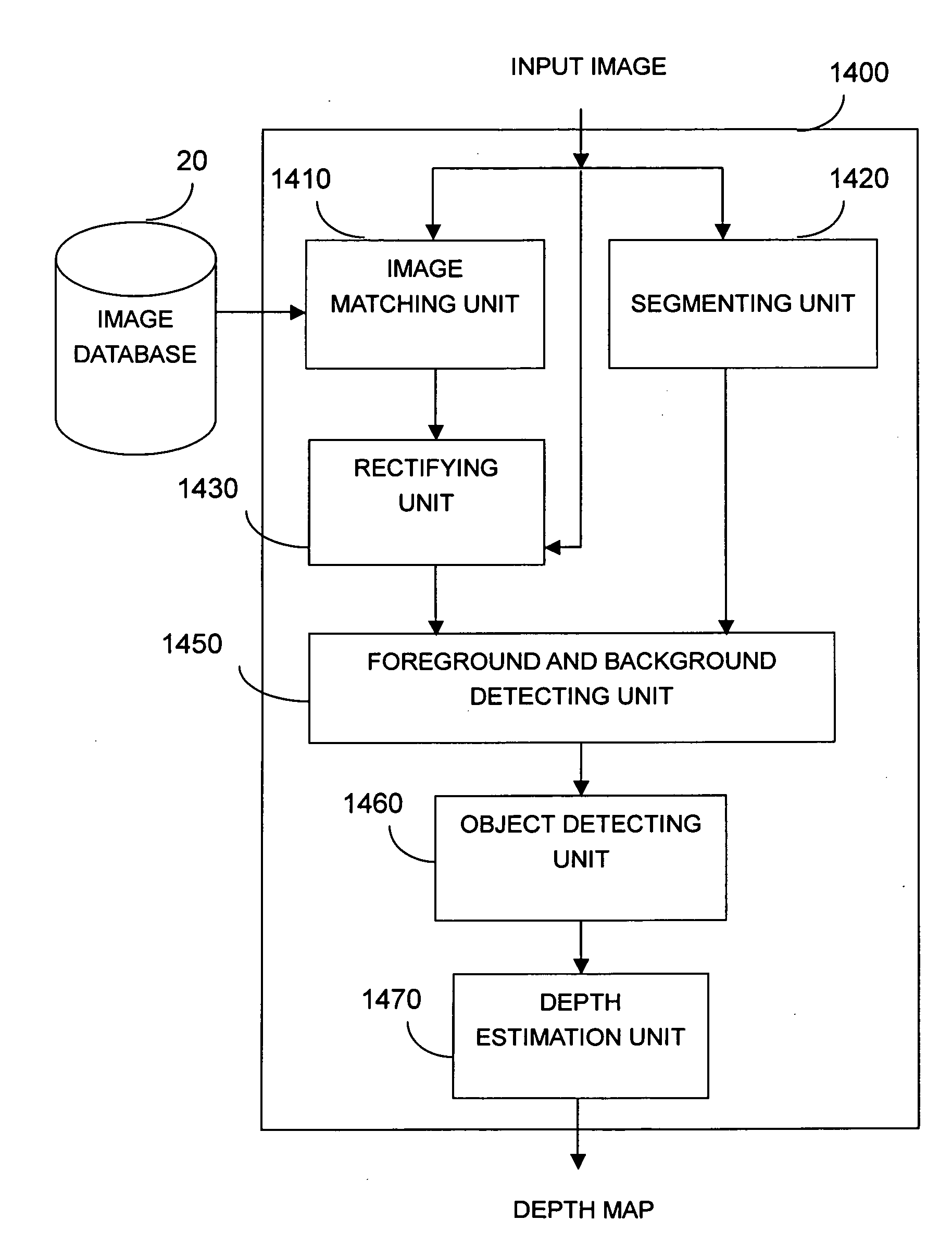
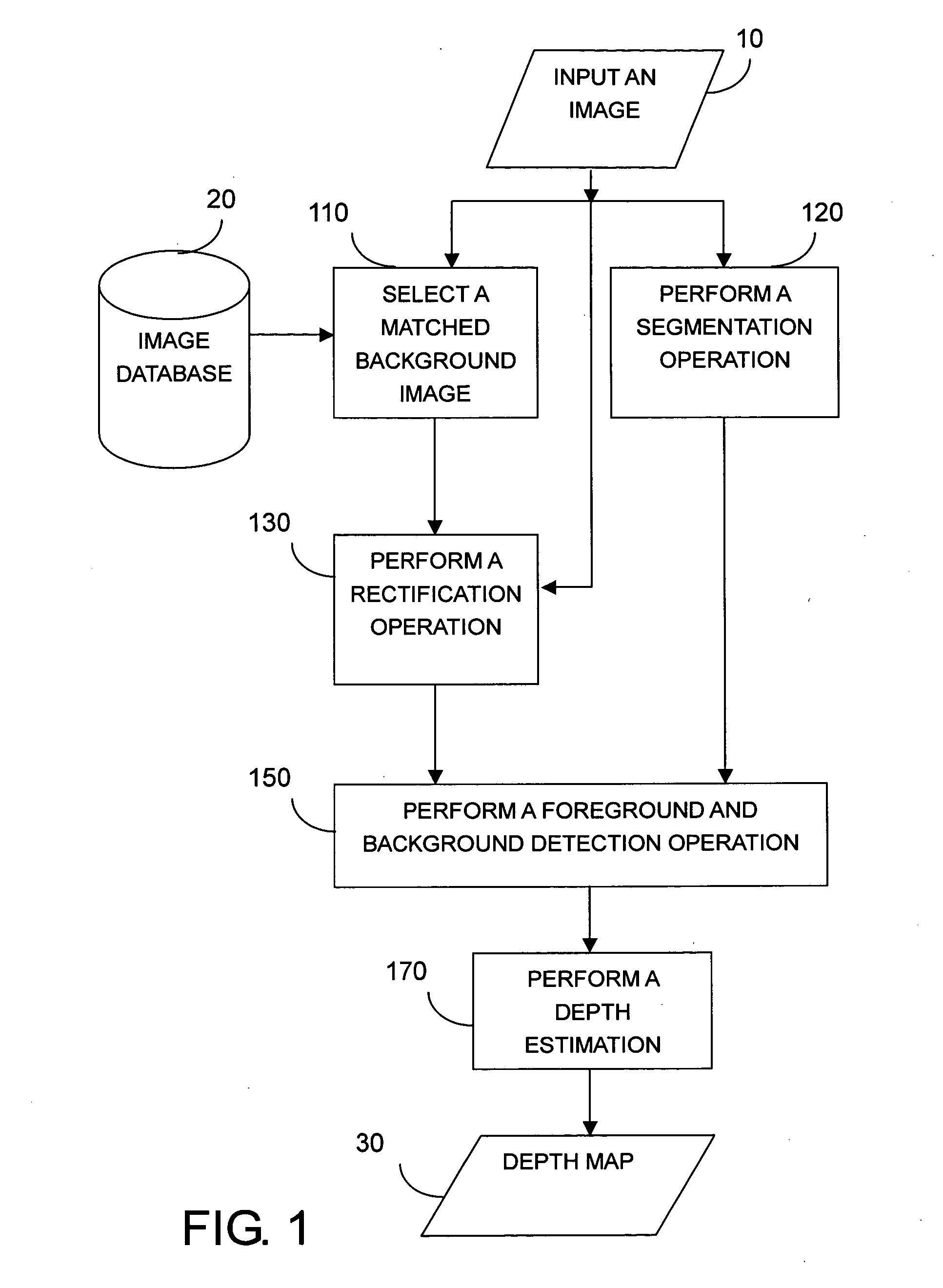
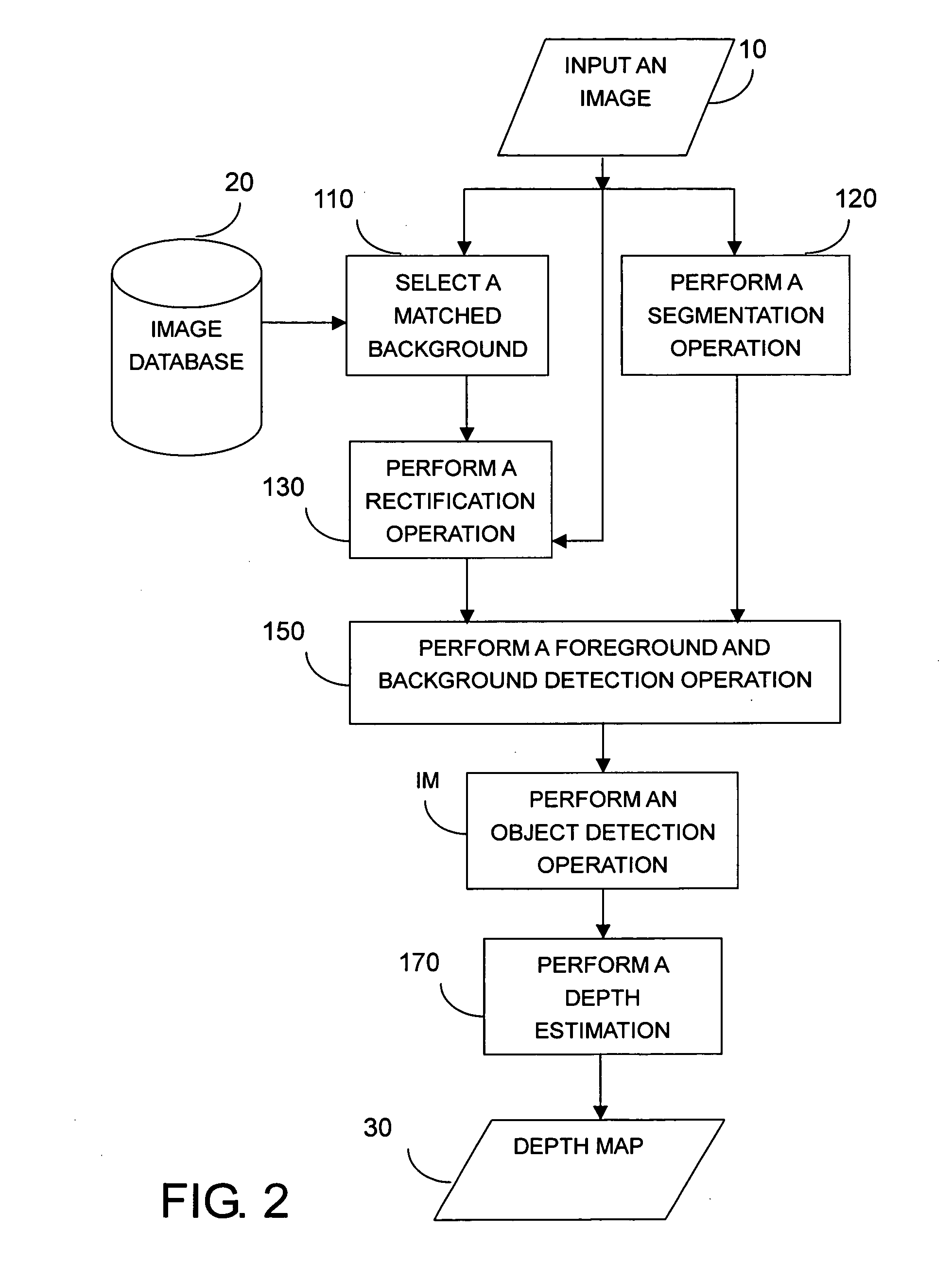
Example-Based Two-Dimensional to Three-Dimensional Image Conversion Method, Computer Readable Medium Therefor, and System
ActiveUS20100014781A1Character and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsGraphics3d image
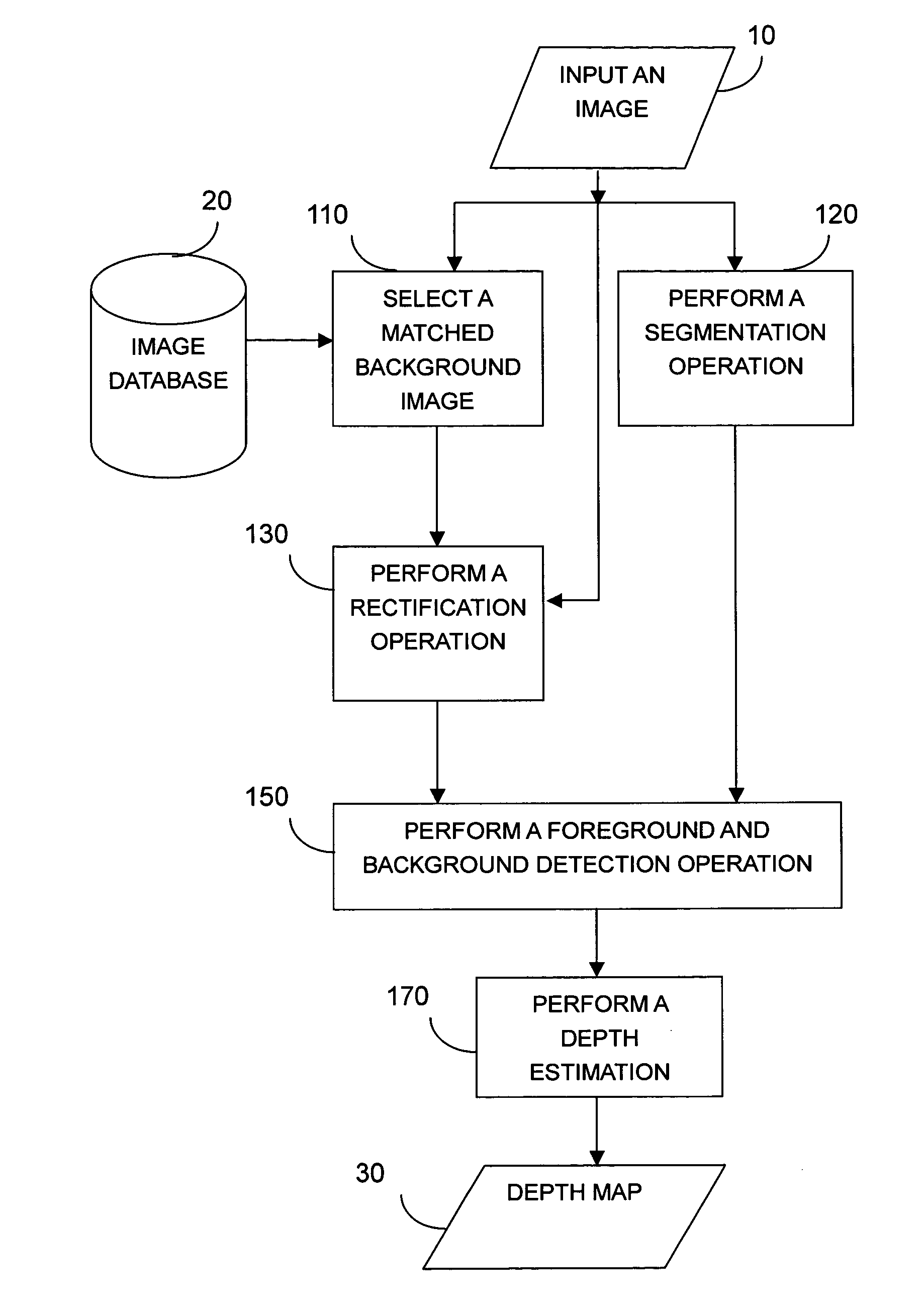
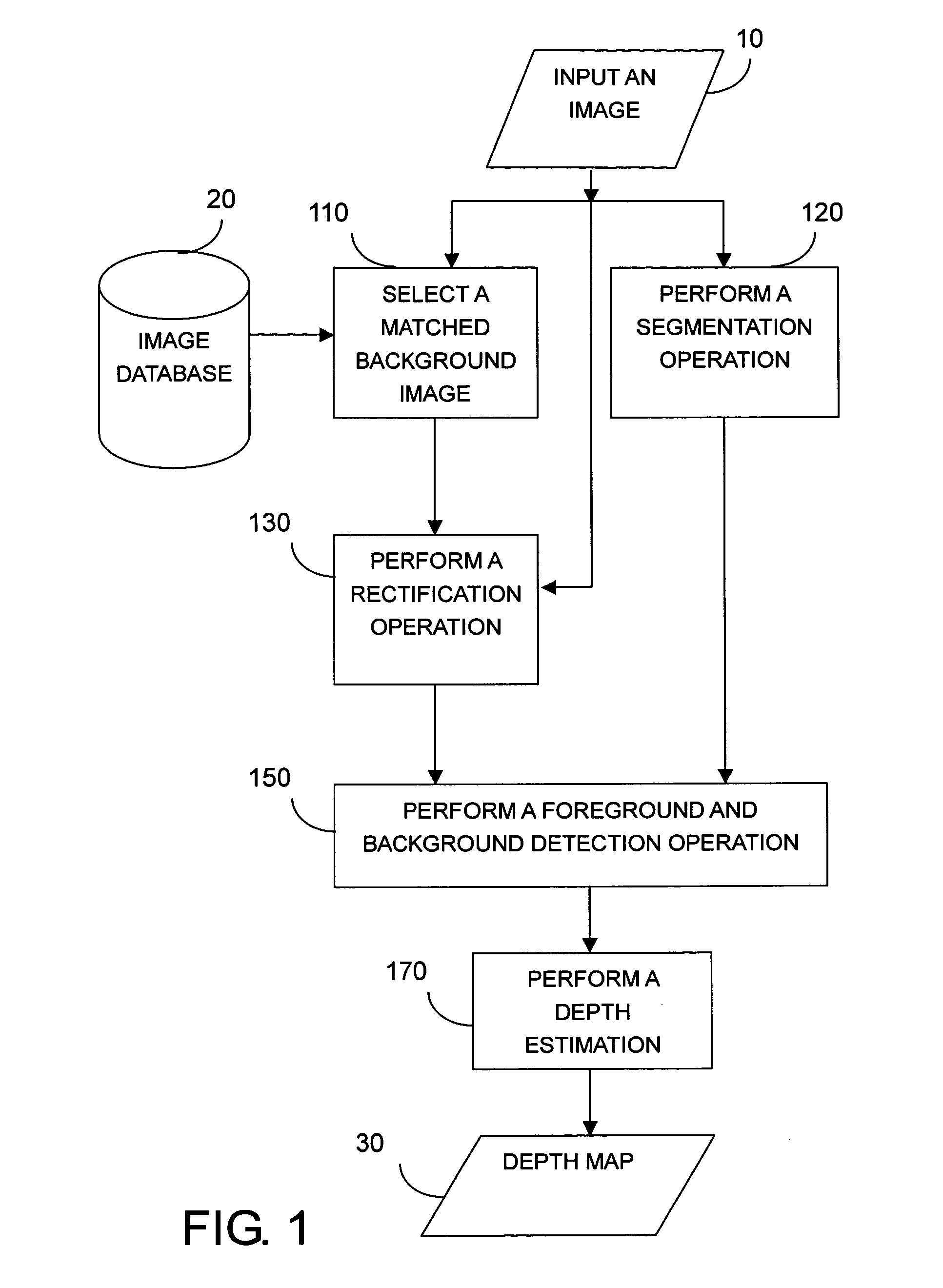
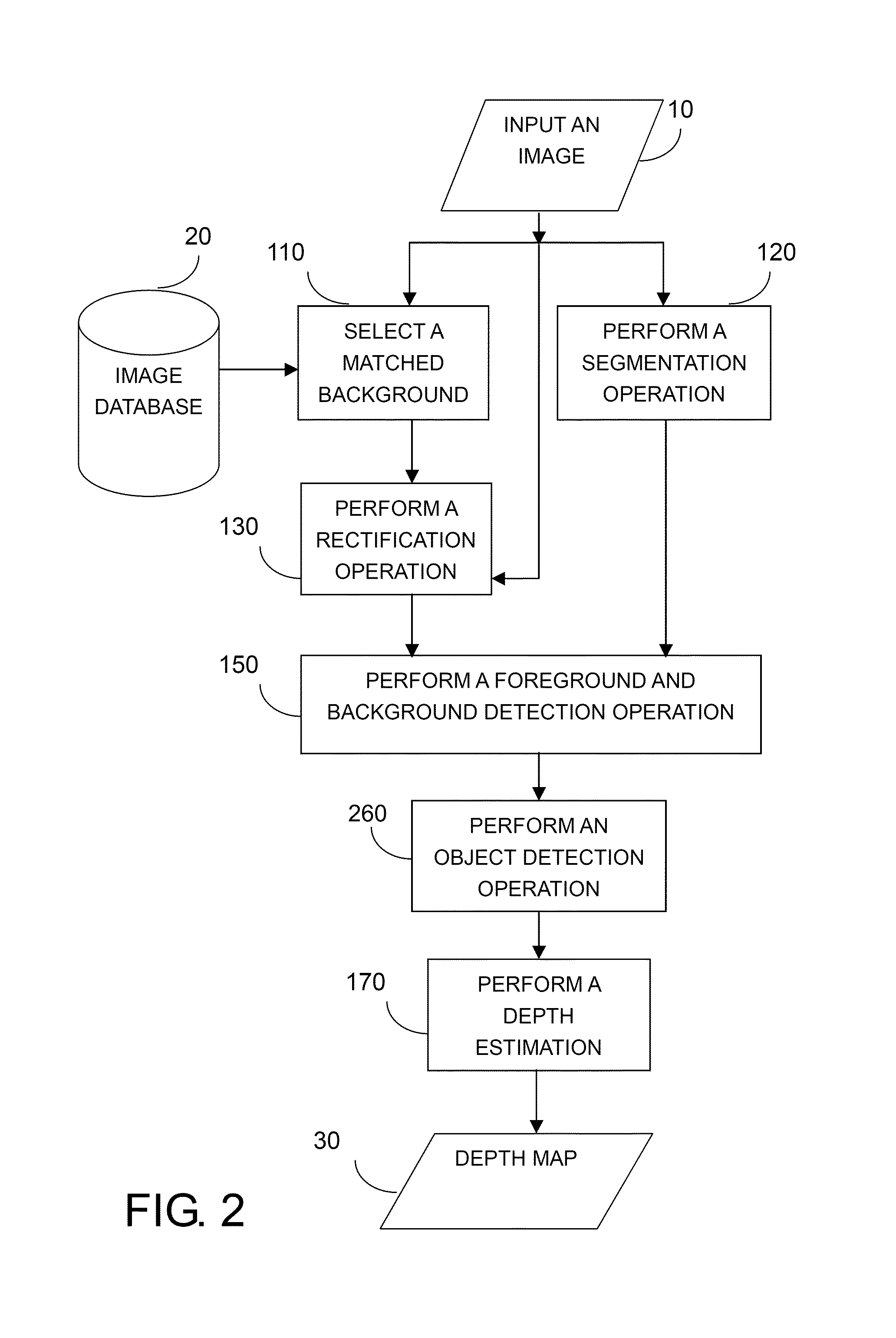
An example-based 2D to 3D image conversion method, a computer readable medium therefor, and a system are provided. The embodiments are based on an image database with depth information or with which depth information can be generated. With respect to a 2D image to be converted into 3D content, a matched background image is found from the database. In addition, graph-based segmentation and comparison techniques are employed to detect the foreground of the 2D image so that the relative depth map can be generated from the foreground and background information. Therefore, the 3D content can be provided with the 2D image plus the depth information. Thus, users can rapidly obtain the 3D content from the 2D image automatically and the rendering of the 3D content can be achieved.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
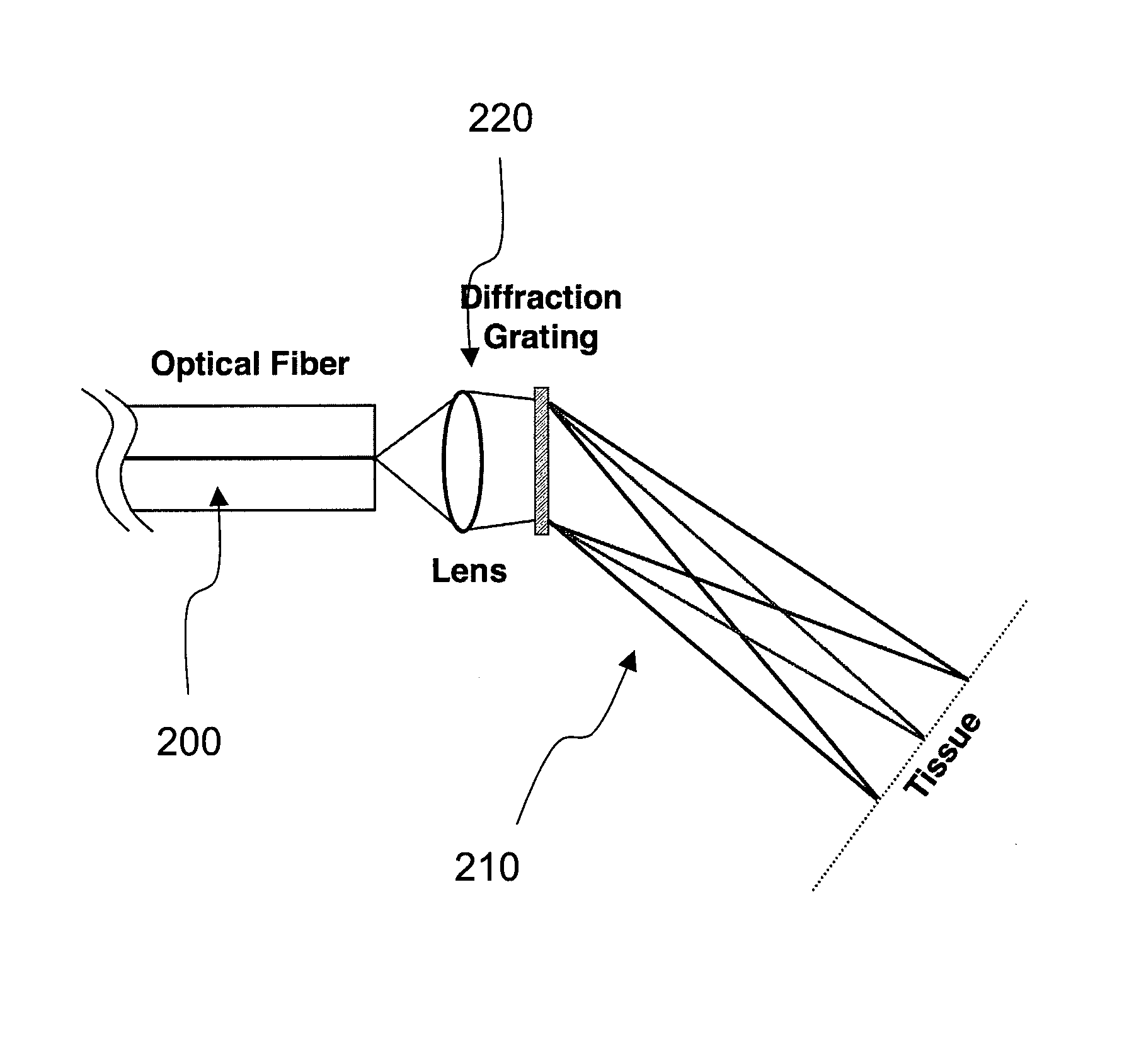
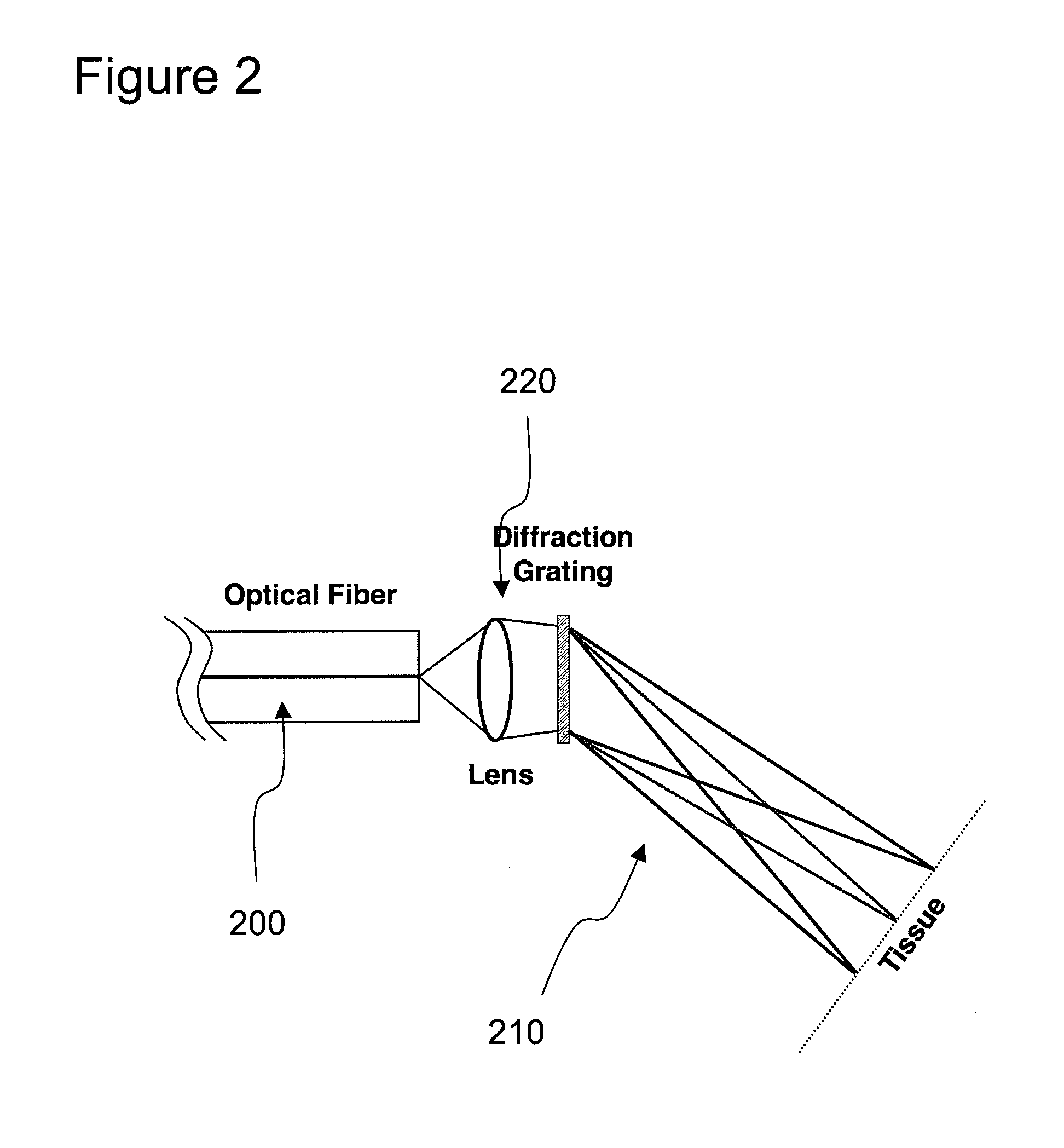
Method and apparatus for three-dimensional spectrally encoded imaging
A method and apparatus for providing information associated with at least one portion of a sample can be provided. For example, at least one wavelength of electro-magnetic radiation provided on a sample can be encoded to determine at least one transverse location of the portion. A relative phase between at least one first electro-magnetic radiation electro-magnetic radiation being returned from a sample and at least one second electro-magnetic radiation returned from a reference can be obtained to determine at least one relative depth location of the portion. Further, the information of the portion can be provided based on the transverse location and the relative depth location. For example, the information can be depth information and / or three-dimensional information associated with the portion of the sample.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
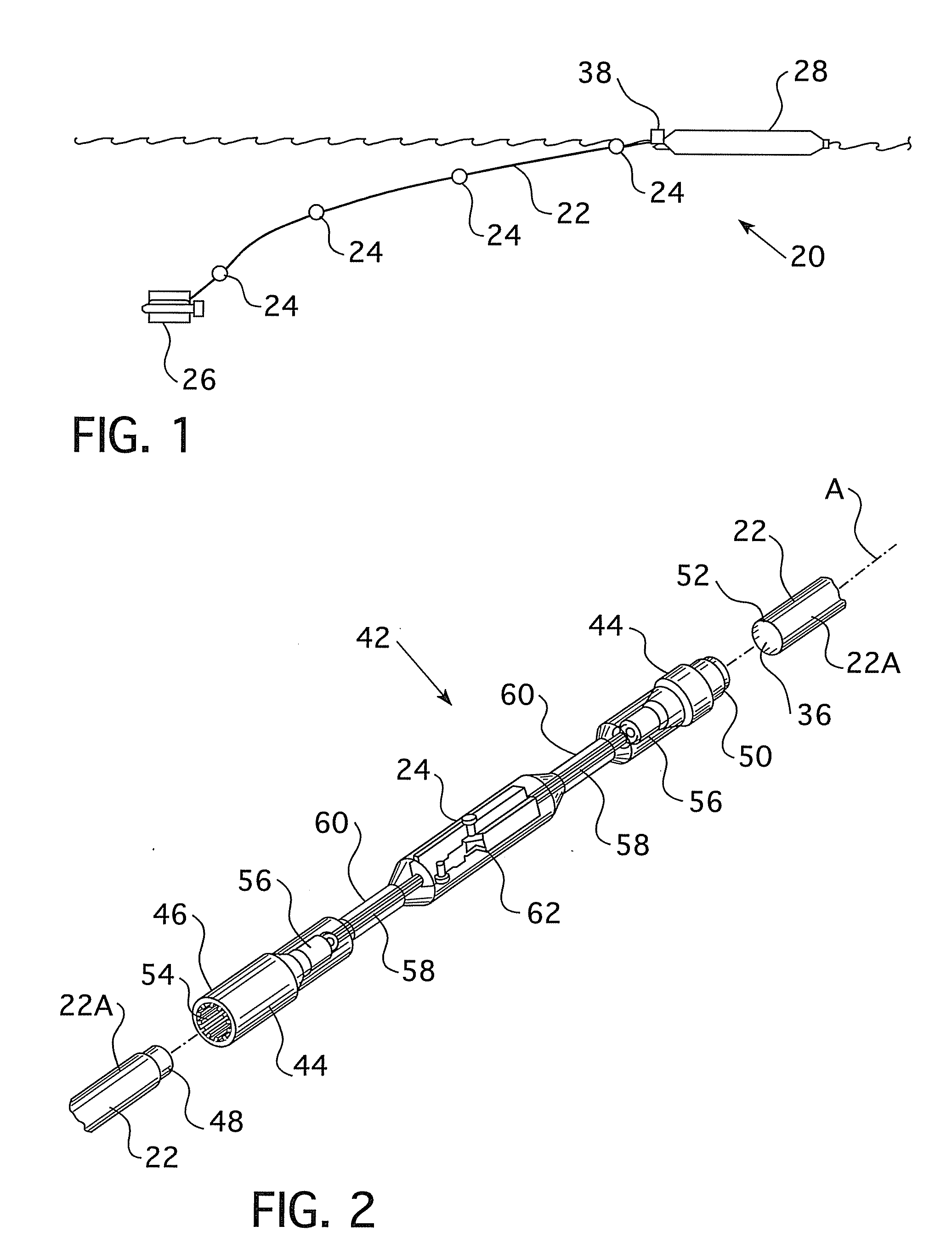
Smart tether system for underwater navigation and cable shape measurement
ActiveUS20080300821A1Digital computer detailsMechanical clearance measurementsRelative pressureUnderwater navigation
A position sensing system including a flexible tether and at least one sensor at least partially embedded within a portion of the flexible tether is disclosed. The sensor may be adapted to detect a sensor position factor. The system also includes a communication device adapted to transmit the sensor position factor from the sensor, and a signal processor adapted to receive the sensor position factor. The signal processor is also adapted to calculate at least one of the shape or orientation of the flexible tether from the sensor position factor. The sensor position factor may be relative orientation, relative depth, relative pressure, presence of a magnetic field, presence of an electric field, acceleration, or relative rate of rotation. The system may also include a probe connected to the flexible tether, and the signal processor may calculate the orientation of the probe from the sensor position factor.
Owner:KCF TECHNOLOGIES
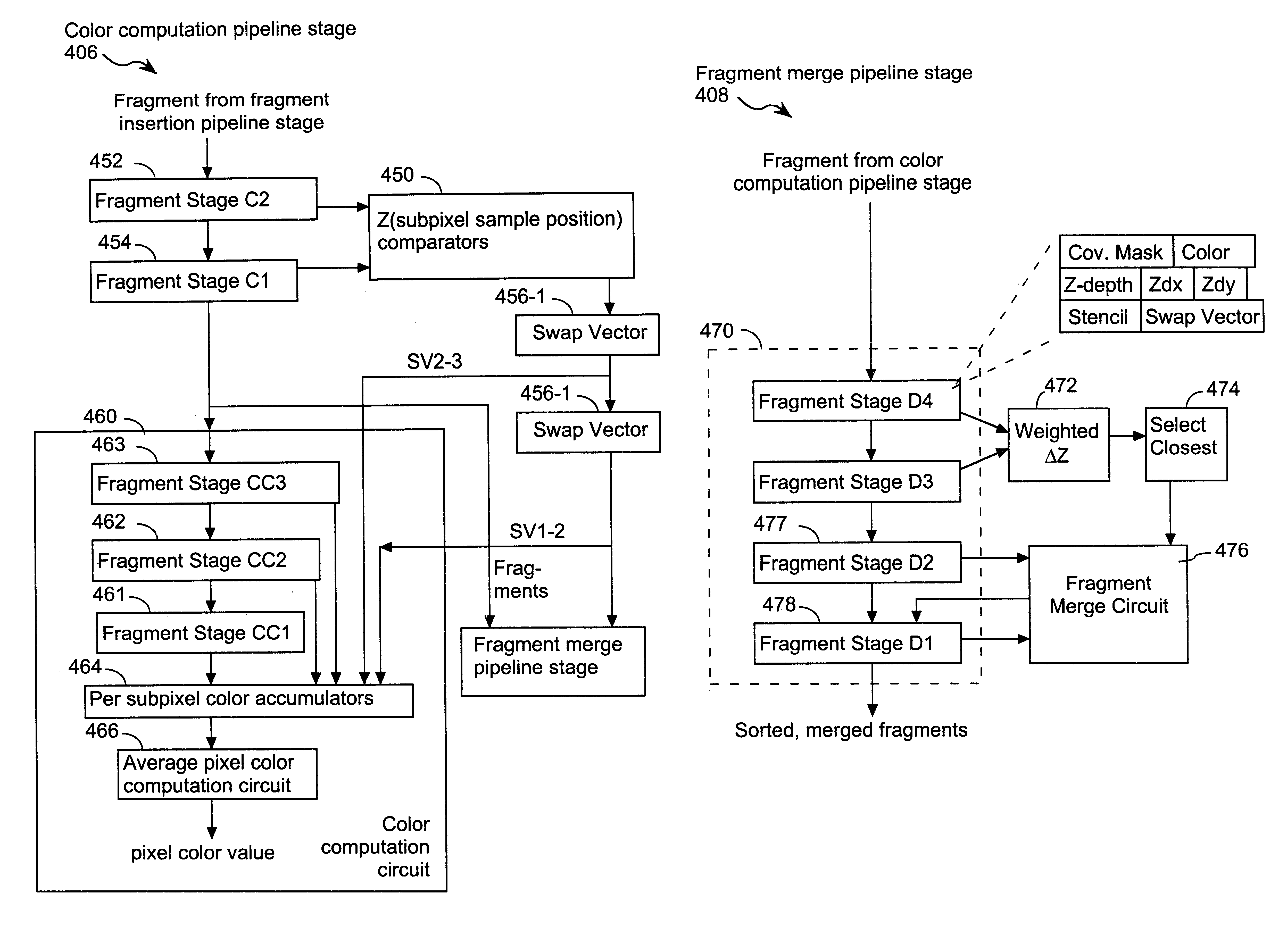
Method and apparatus for compositing colors of images using pixel fragments with Z and Z gradient parameters
InactiveUS7064771B1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsProcessor architectures/configurationGraphicsRelative depth
A graphics data processing apparatus includes a graphics memory having pixel storage for storing up to a predetermined number of fragment values for the pixel. Each stored fragment value is associated with a fragment of an image that is visible in that pixel. When a new fragment is determined to be visible in the pixel, but all the available fragment values for the pixel are already in use, one of the previously stored fragment values is either replaced by, or combined with the fragment value for the new fragment. The resulting new fragment value is used to determine the color of the pixel. Alternately, if the new fragment is determined to be totally occluded by one or more of the other fragments, the new fragment may be discarded. Z-depth and Z gradient information is stored each fragment. This Z information is used to determine the relative depth values of the fragments, which in turn is used to determine which fragment to discard or to combine with another fragment when all the available fragment values for a pixel are already in use.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Stereo reconstruction employing a layered approach
InactiveUS6348918B1Improve performanceDepth accurateImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
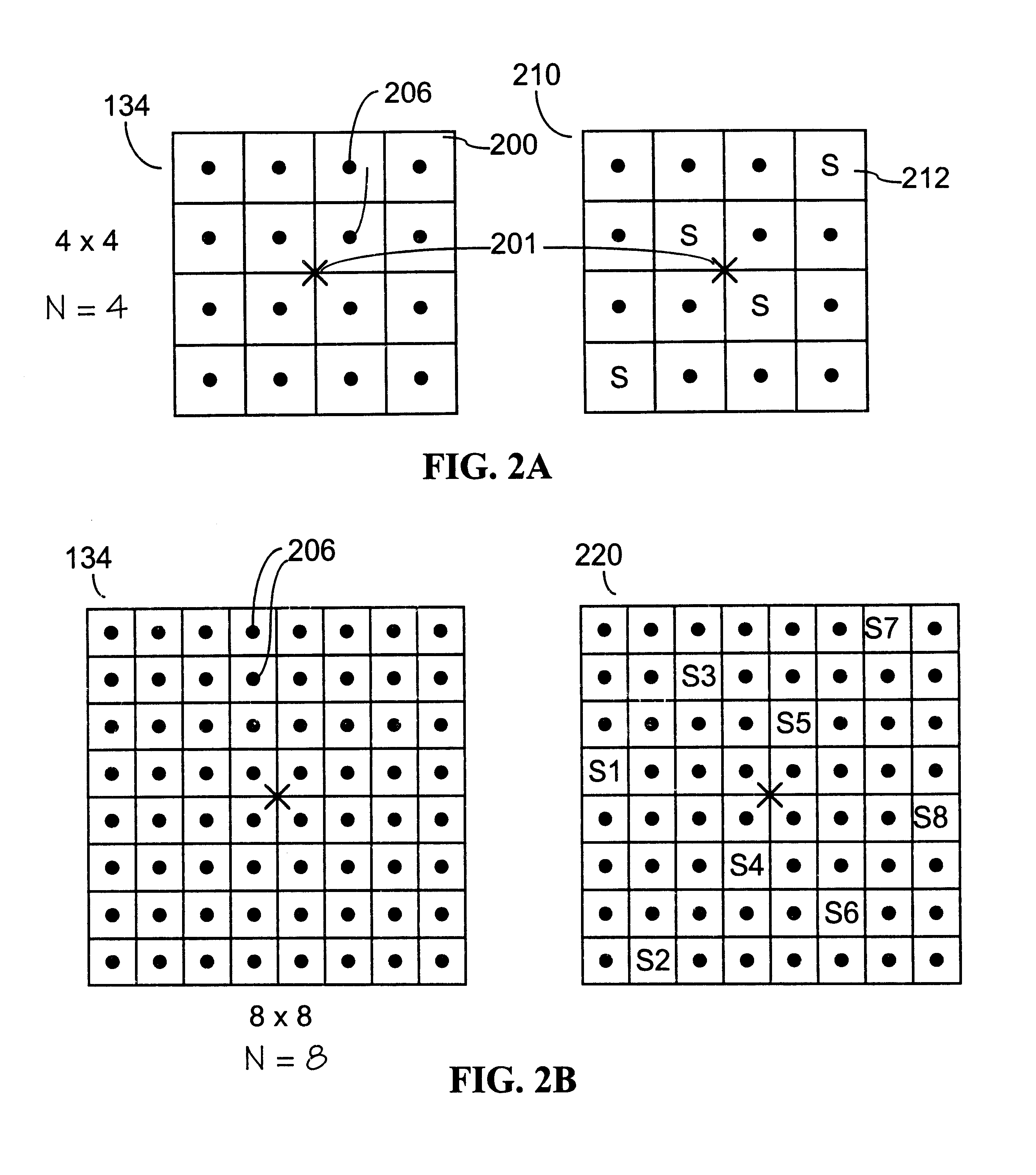
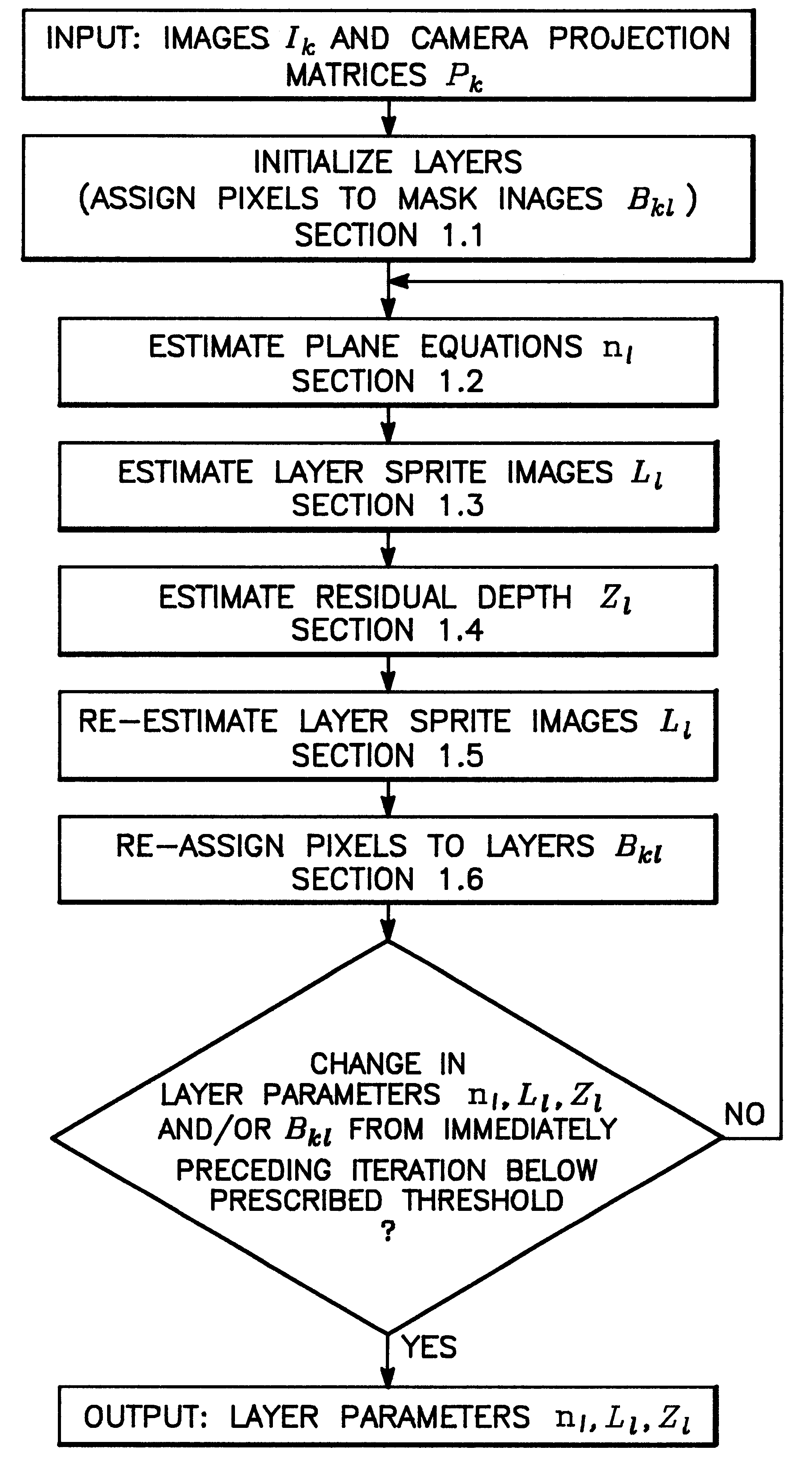
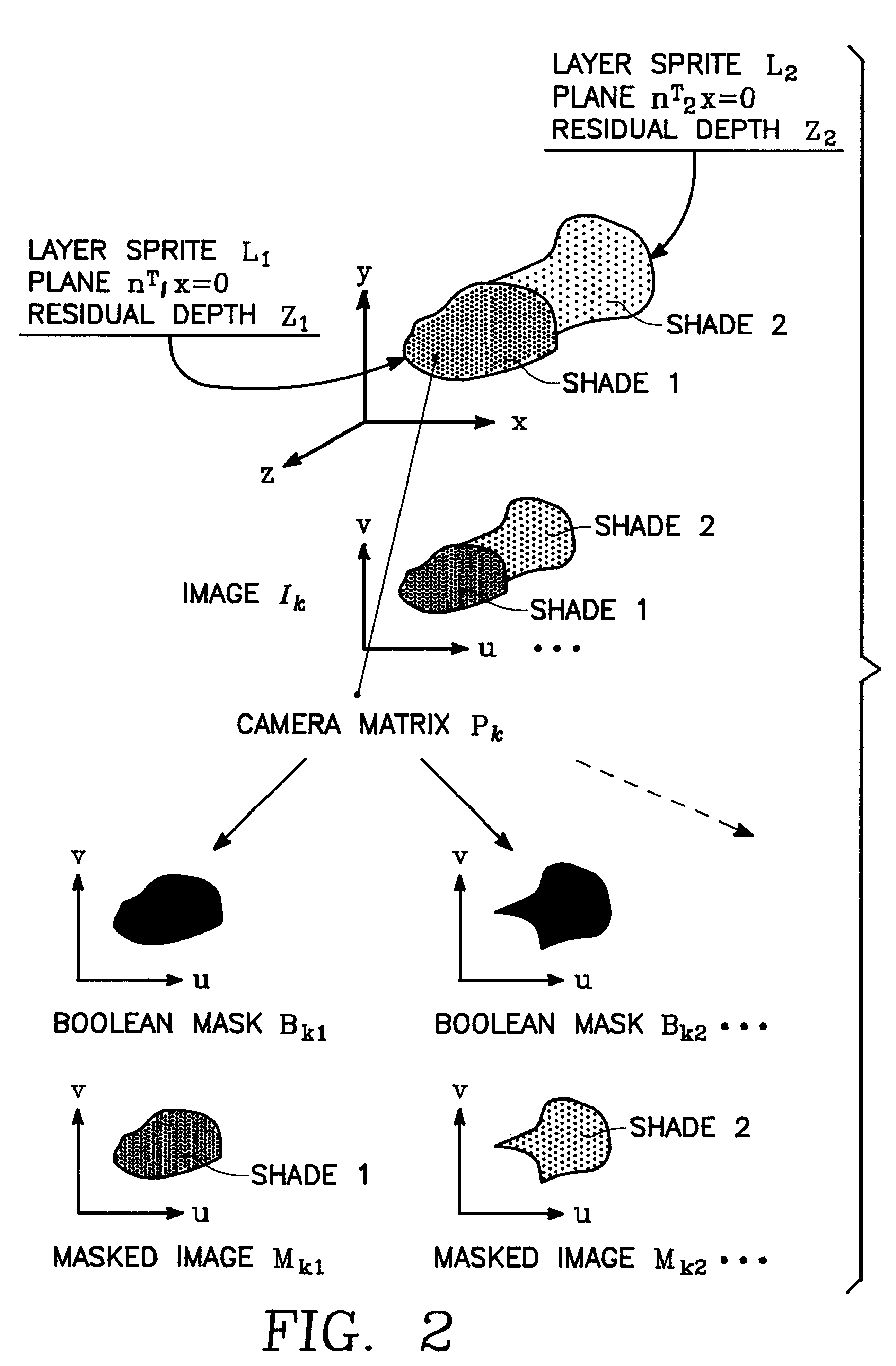
A system and method for extracting structure from stereo that represents the scene as a collection of planar layers. Each layer optimally has an explicit 3D plane equation, a colored image with per-pixel opacity, and a per-pixel depth value relative to the plane. Initial estimates of the layers are recovered using techniques from parametric motion estimation. The combination of a global model (the plane) with a local correction to it (the per-pixel relative depth value) imposes enough local consistency to allow the recovery of shape in both textured and untextured regions.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Example-based two-dimensional to three-dimensional image conversion method, computer readable medium therefor, and system
An example-based 2D to 3D image conversion method, a computer readable medium therefore, and a system are provided. The embodiments are based on an image database with depth information or with which depth information can be generated. With respect to a 2D image to be converted into 3D content, a matched background image is found from the database. In addition, graph-based segmentation and comparison techniques are employed to detect the foreground of the 2D image so that the relative depth map can be generated from the foreground and background information. Therefore, the 3D content can be provided with the 2D image plus the depth information. Thus, users can rapidly obtain the 3D content from the 2D image automatically and the rendering of the 3D content can be achieved.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Method of forming a temporary prosthetic joint using a disposable mold
An orthopedic implant device and method is disclosed. Specifically, a knee mold system is disclosed, including elastic tibial and femoral molds, each of which may be configured and dimensioned as a unitary mold for in situ placement during a surgical procedure. Each mold may be manufactured from an elastic material that may be disposable. The tibial mold may further comprise a sidewall forming a cavity, markings for relative depth measurement, and depth rings for use as a guide for scoring, cutting, and / or trimming and tearing away an excess portion of the tibial mold. The femoral mold may further comprise a sidewall defining a cavity, two legs extending from a body of the femoral mold for forming the artificial condyles, and an eyelet for aiding in placement and removal of the femoral mold. The resulting prosthetic tibial and femoral components may form an articulation surface that mimics, at least in part, the natural articulation surface of the knee.
Owner:ORTHO DEV CORP
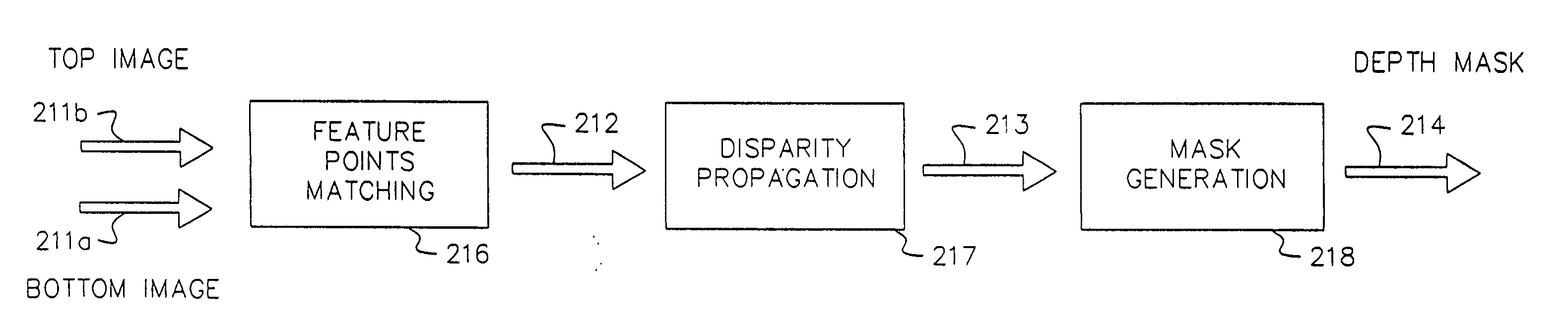
Method for forming a depth image
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Method for forming a depth image
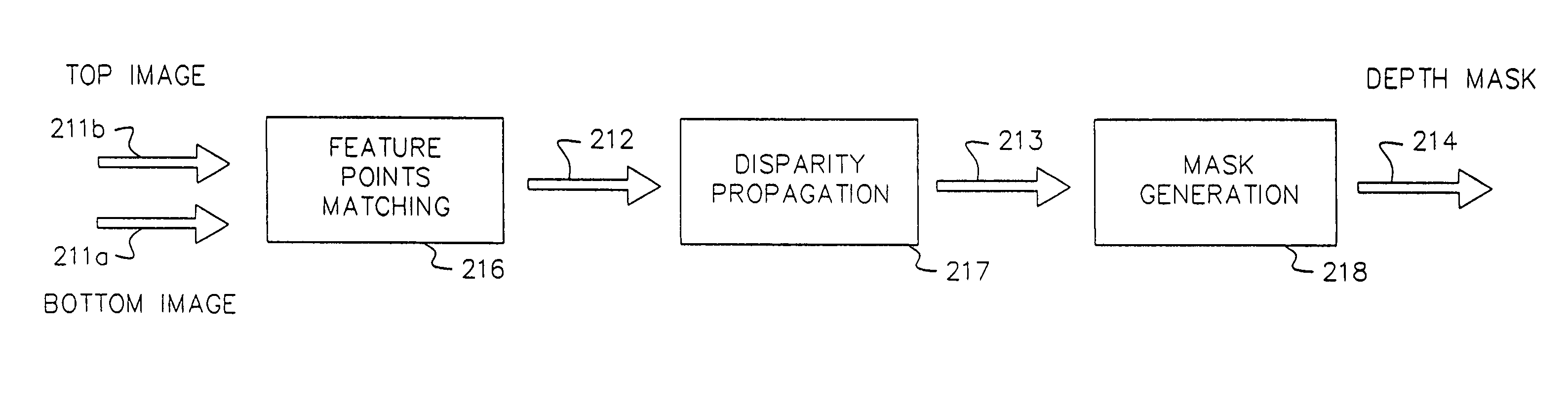
InactiveUS20050129305A1Easy to shapeImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingReference image
A computer vision / image processing method generates a depth map. In one embodiment, the present invention provides a method of forming a relative depth map from at least three x-ray images of a patient taken from different perspectives. The method includes the steps of: (a) selecting one of the x-ray images as a reference image; (b) identifying corresponding objects within the reference image and the other images; (c) computing a disparity between the identified corresponding objects; and (d) generating the relative depth map from the disparities.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
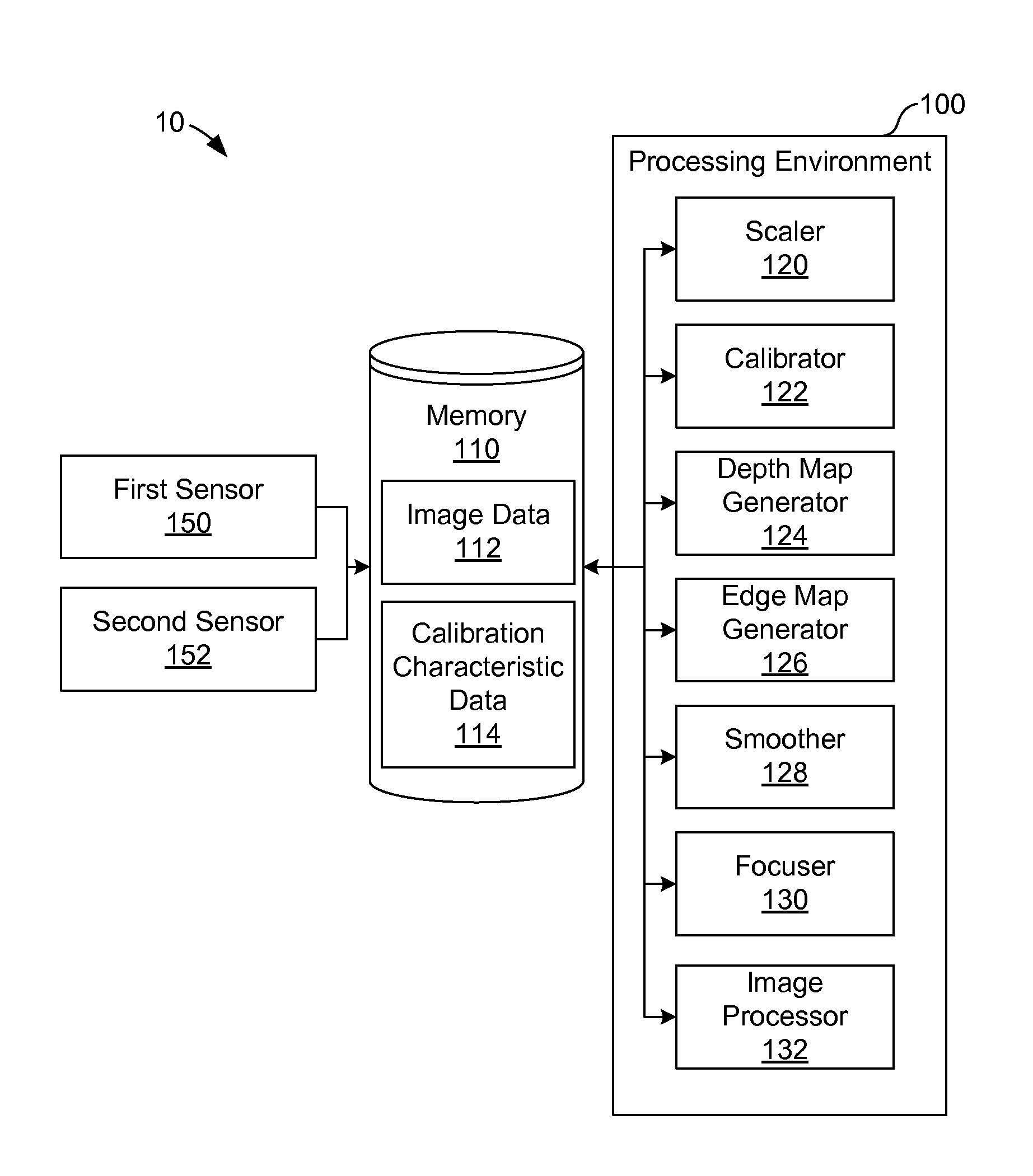
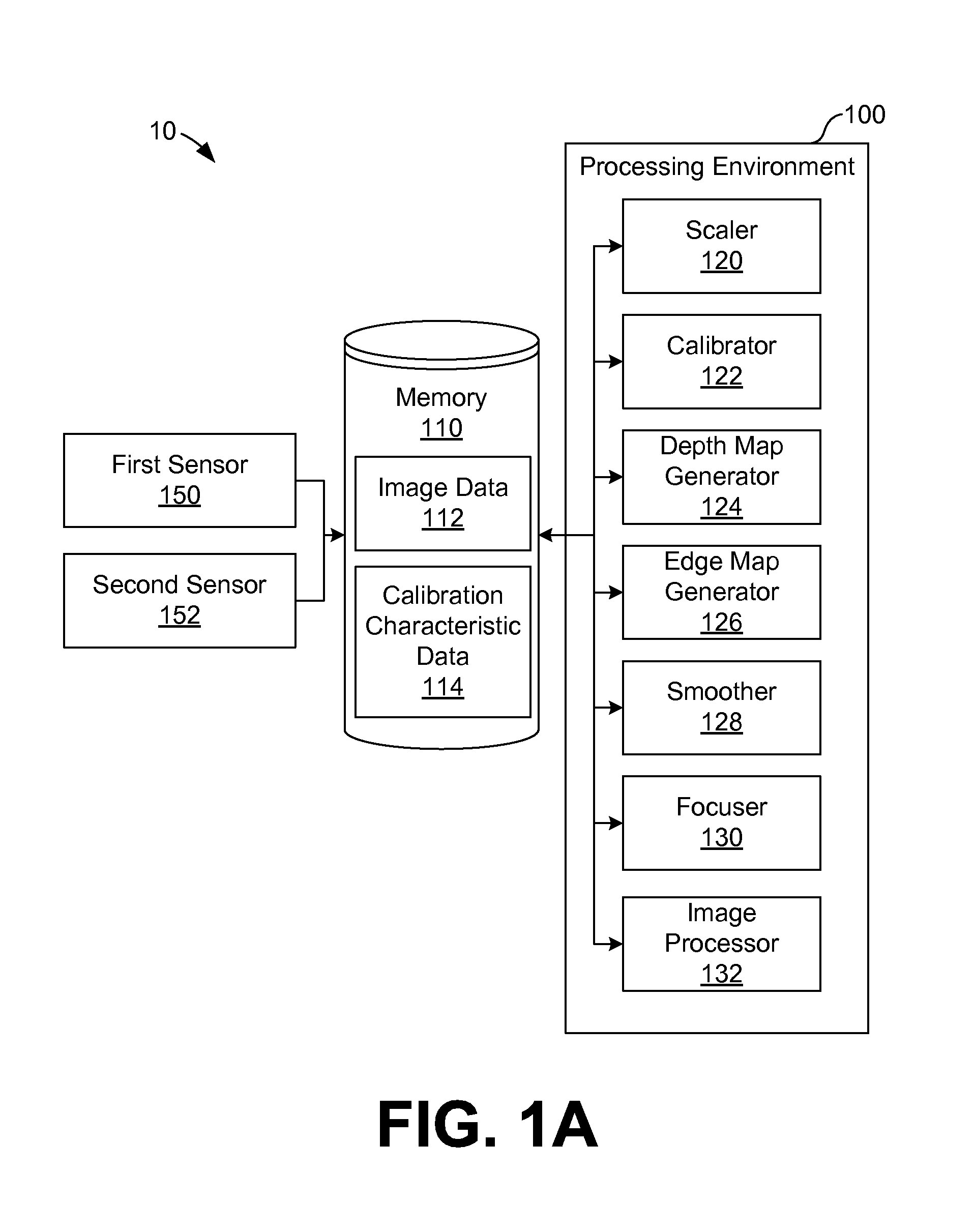
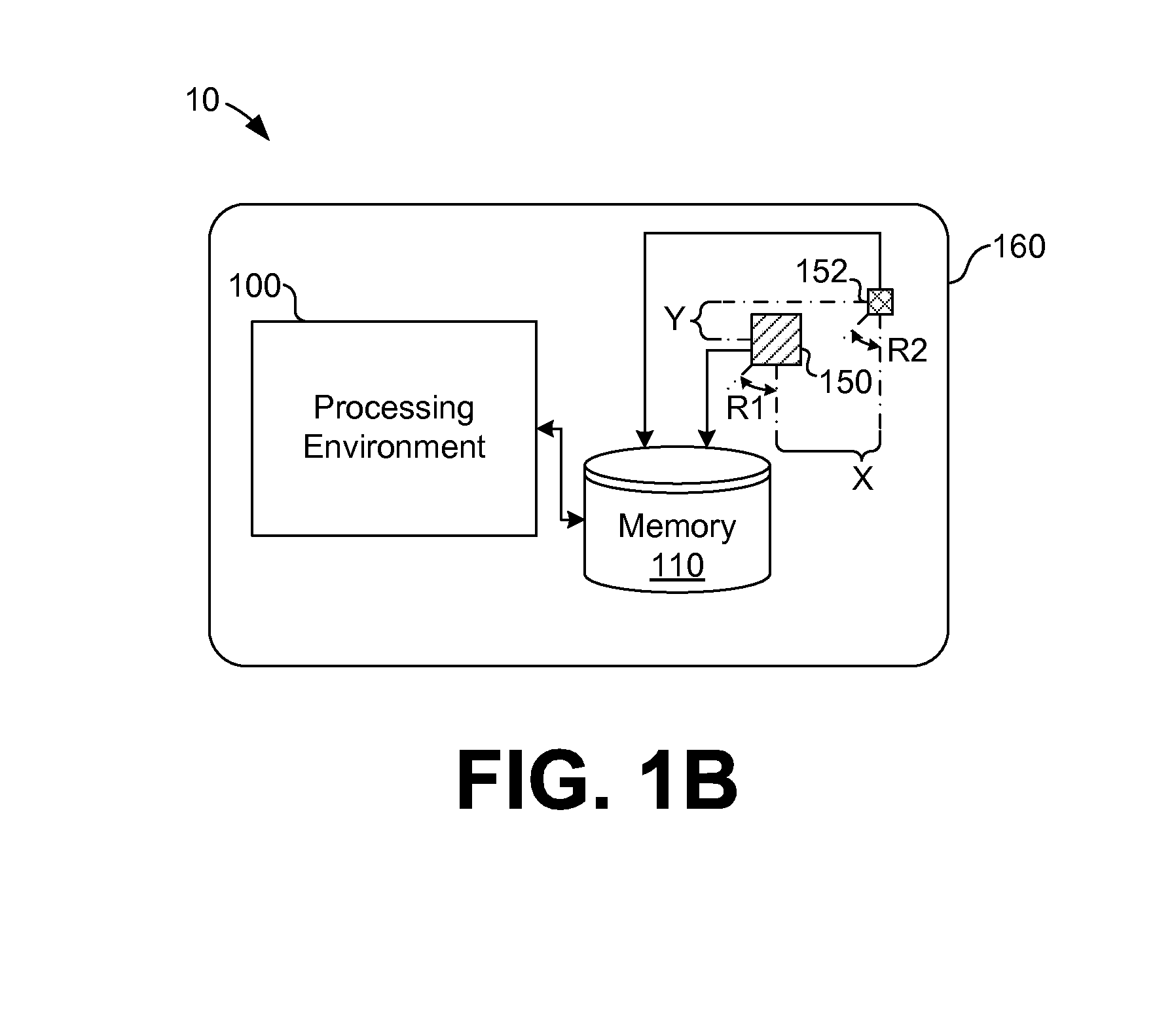
Depth map generation and post-capture focusing
Aspects of depth map generation and post capture focusing and re-focusing are described. According to one embodiment, a depth map is generated. The depth map may include a mapping among relative depth values in a field of view of an image based on a difference between pixels of a first image and pixels of a second image. An edge map may also be generated by identifying edges in at least one of the first image or the second image. Using the depth map and the edge map, the relative depth values in the depth map may be smoothed using the edge map. In this manner, certain discontinuities in depth values may be smoothed within edge-bounded regions defined by the edge map. The depth map may be used for focusing and re-focusing, for example, or for object extraction, scene understanding, or gesture recognition, among other imaging processes.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
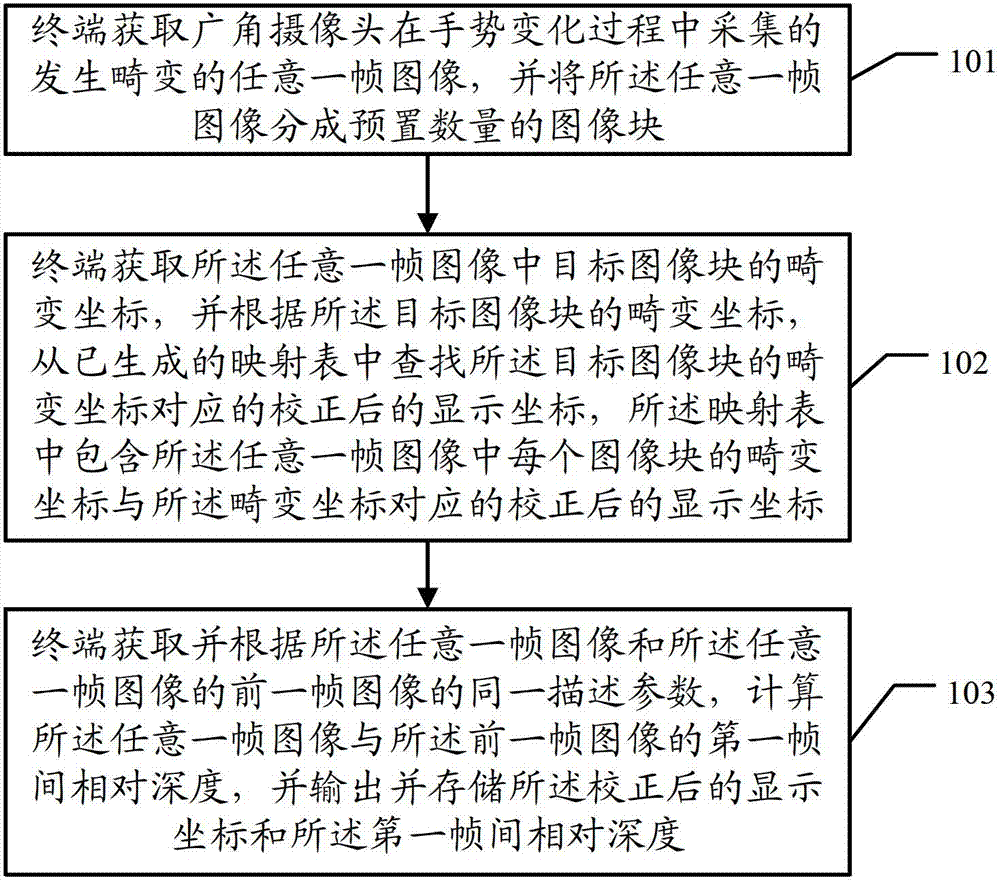
Method, terminal and system for correcting aberrant image
The invention discloses a method for correcting an aberrant image, which comprises the following steps: obtaining an aberrant image at a random frame collected by a wide angle camera in the gesture variation process, and dividing the aberrant image at the random frame into image blocks with preset quantity; obtaining aberrant coordinates of target image blocks in the random-frame image; according to the aberrant coordinates of the target image blocks, looking up corrected display coordinates corresponding to the aberrant coordinates of the target image blocks from a generated mapping table which comprises the aberrant coordinate of each image block of the random-frame image and the corresponding corrected display coordinate; obtaining the same description parameter of the random-frame image and a former-frame image of the random-frame image; computing a first inter-frame relative depth of the random-frame image and the former-frame image according to the same description parameter; and outputting and storing the corrected display coordinates and the first inter-frame relative depth. The technical scheme provided by the invention can improve the precision of close range gesture identification.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method for calibrating three-dimensional imaging system
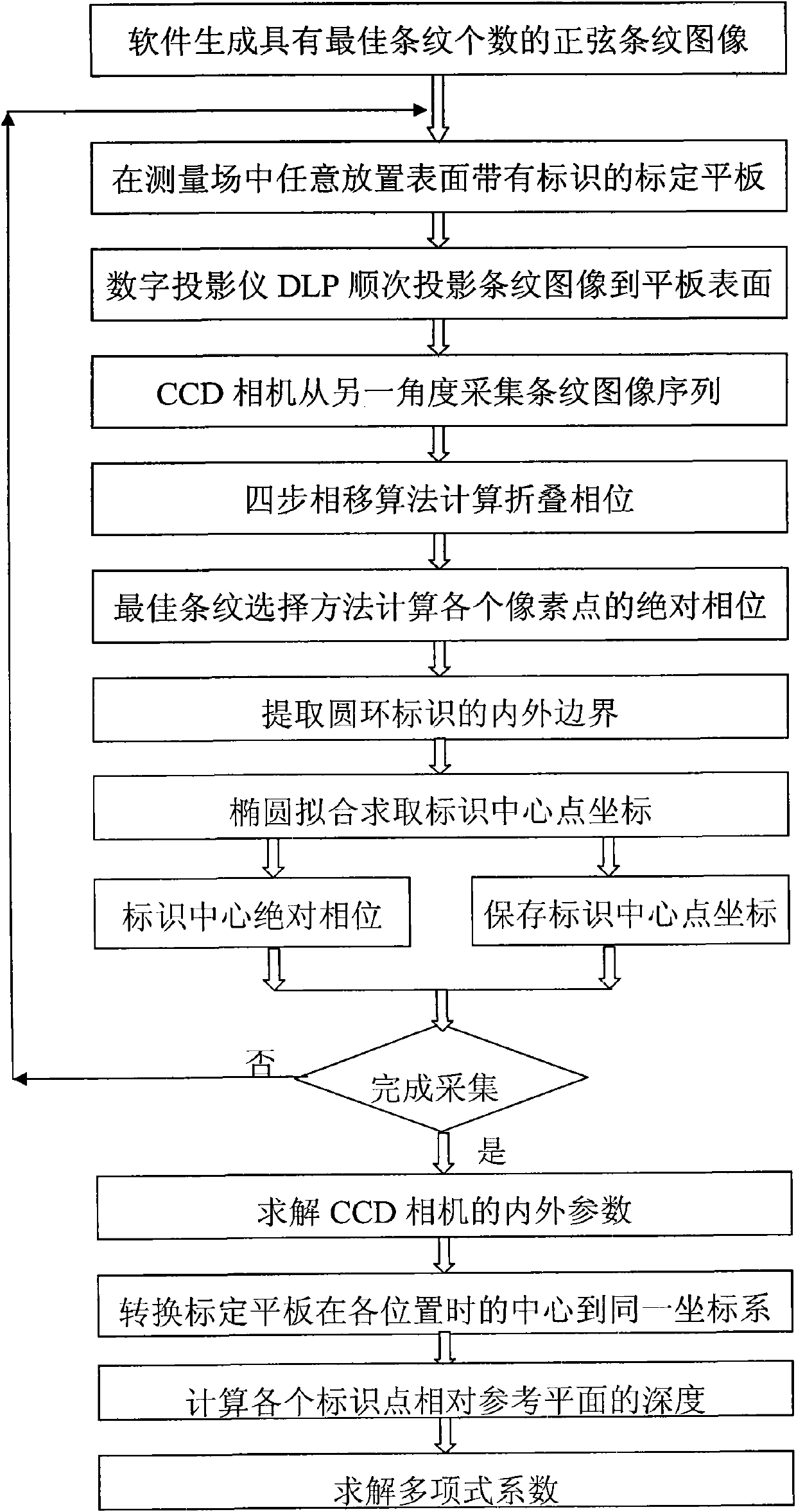
InactiveCN101949693AEasy CalibrationEasy Calibration TasksUsing optical meansSinusoidal gratingDiffuse reflection
The invention discloses a method for calibrating a three-dimensional imaging system, which comprises the following steps of: 1, designing a calibration flat plate to be white and have a diffuse reflection surface and designing black annular identifiers in a square matrix arrangement mode on the calibration flat plate simultaneously, wherein the center distance between adjacent identifiers is equal; 2, placing the calibration flat plate at different positions in a measurement field, projecting non-uniform sinusoidal grating stripes with the optimal number of stripes at each placement position onto the surface of the calibration flat plate, and acquiring and calculating the absolute phase of each white pixel point inside the black annular identifiers; 3, extracting the central point position of each identifier from a corresponding absolute phase diagram to solve the relative depths of the identifiers when the calibration flat plate is at each placement position; 4, establishing a high-order polynomial (A) to express the relationship between the absolute phases and the relative depths; and 5, converting the absolute phases into actual depth data by using the calibrated polynomial coefficients so as to finish the calibration of the three-dimensional imaging system.
Owner:众趣(北京)科技有限公司
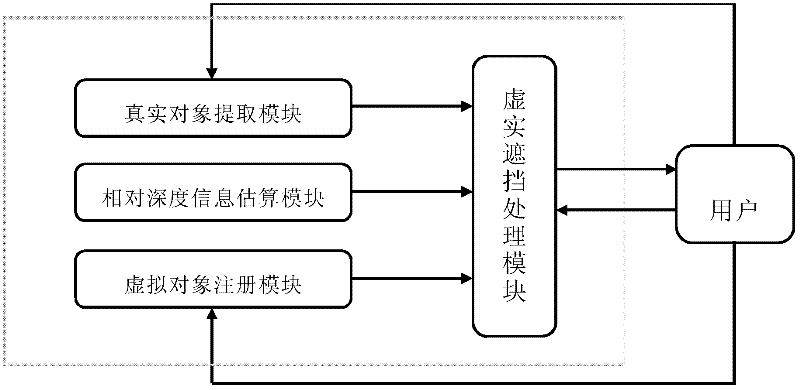
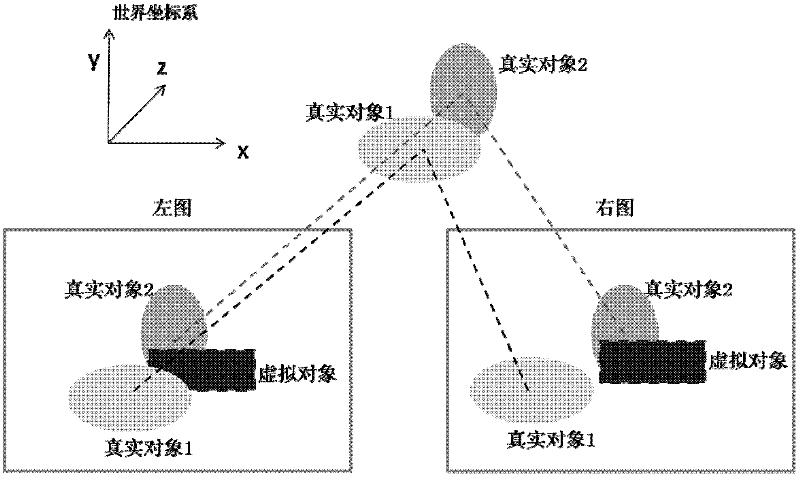
Binocular image and object contour-based virtual and actual sheltering treatment method
ActiveCN102509343AHigh speedReduce complexityImage analysis3D-image renderingParallaxImage segmentation algorithm
The invention relates to a binocular image and object contour-based virtual and actual sheltering treatment method, which comprises the following steps of: accurately calculating the regional contour of a real object by an interactive image segmentation algorithm, and taking the regional contour as the geometrical information of the real object; and according to the negatively-correlated relation between parallax and depth, estimating the parallax of a virtual object under a current visual angle, determining the relative depth information between the virtual object and the real object in a current scene, and hierarchically dividing the scene. The front-and-back sheltering relation between the virtual object and the real object is estimated and determined by using the relative depth information, the depth information is not required to be calculated in a pixel-by-pixel manner; and the virtual and actual sheltering treatment is achieved in a two-dimensional image space, whether the sheltering between the virtual object and the real object exists or not is judged, and corresponding treatment is carried out, so that the binocular image and object contour-based virtual and actual sheltering treatment method can be applicable to most sheltering circumstances and a better virtual and actual sheltering treatment effect is achieved. The binocular image and object contour-based virtual and actual sheltering treatment method can be widely applied to the spatial sheltering treatment of virtual reality systems, such as interactive digital entertainment, sports research and training simulation, distance education and training and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Measuring apparatus for three-dimensional profilometry and method thereof
ActiveUS20150070472A1Image analysisPicture reproducers using projection devicesRelative phaseLight beam
The present invention provides measuring apparatus and method for three-dimensional profilometry of an object, wherein a random-speckle beam and a structured fringe beam are projected onto the object and reflected therefrom for forming deformed random-speckle beam and structured fringe beams that are separately acquired by an image acquiring device thereby obtaining a random-speckle image utilized to determine an absolute phase information of each position on the surface of the object, and a structured fringe image utilized to determine a relative phase information for each position of the surface of the object. Each absolute phase information and each relative phase information corresponding to each position are converted into an absolute depth and a relative depth, respectively. Finally, the depth information of each position on the surface of the object is calculated by combining the corresponding absolute depth and the relative depth whereby the surface profile of the object can be established.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
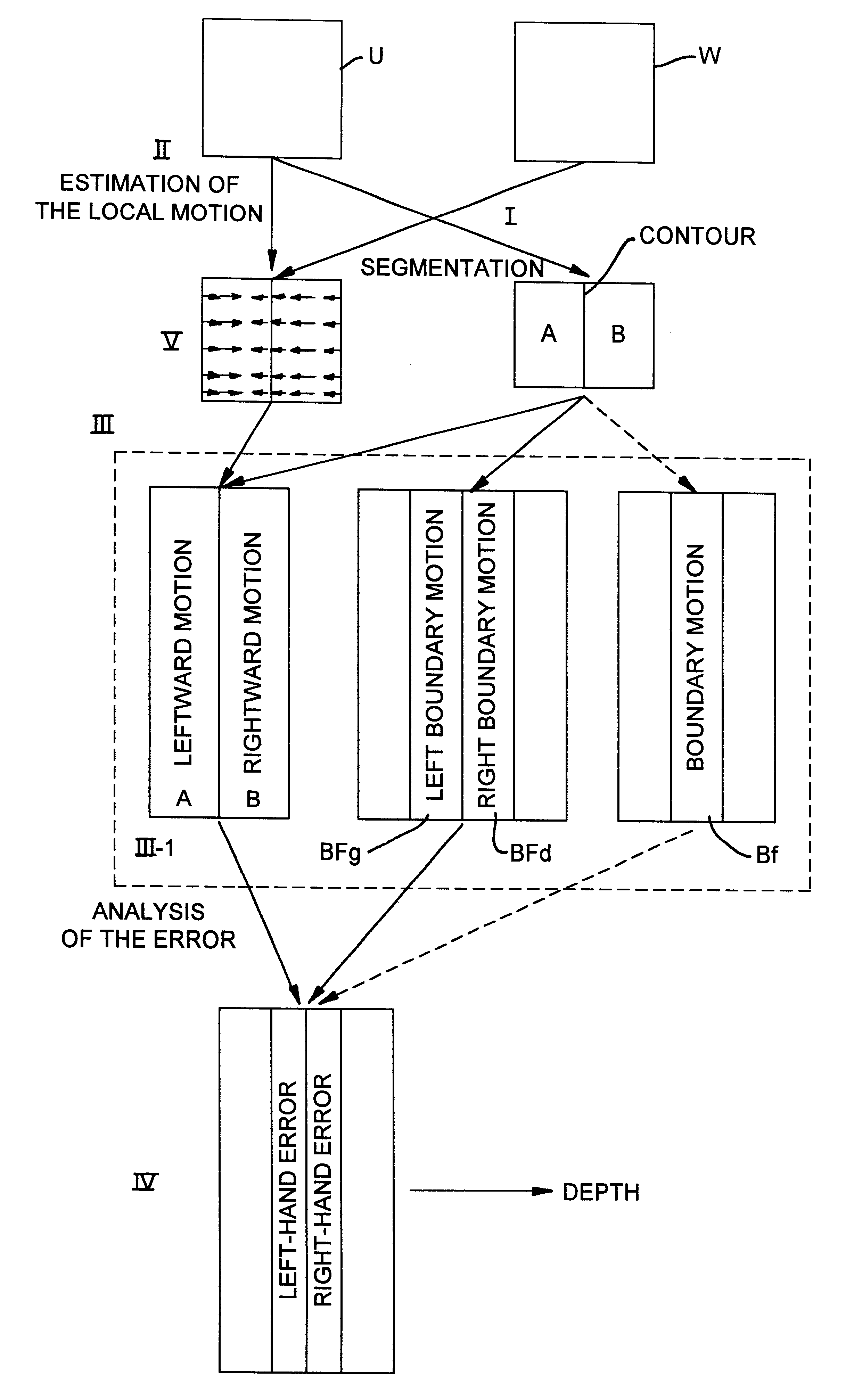
Method for the detection of the relative depth of objects in an image from a pair of images
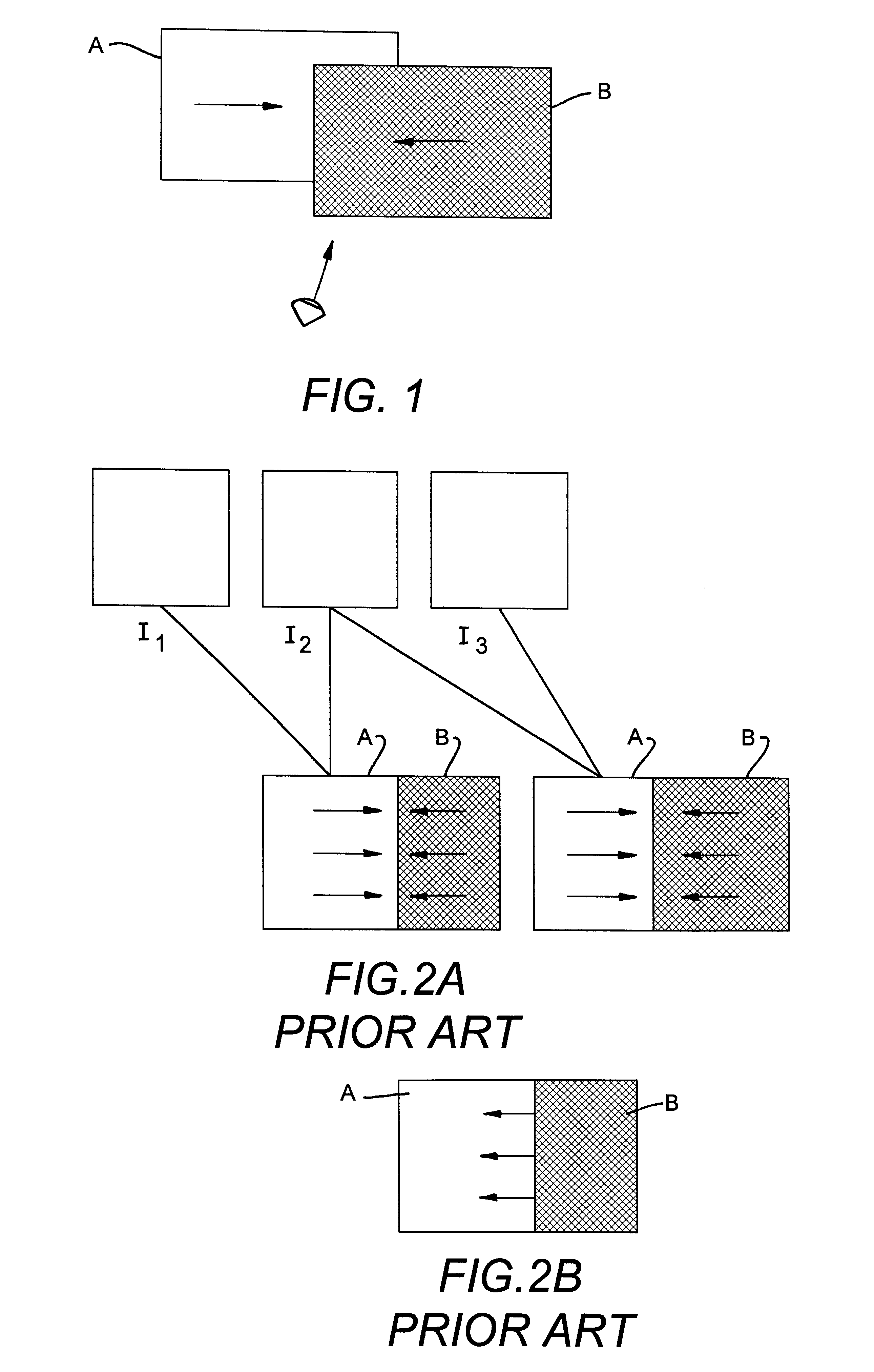
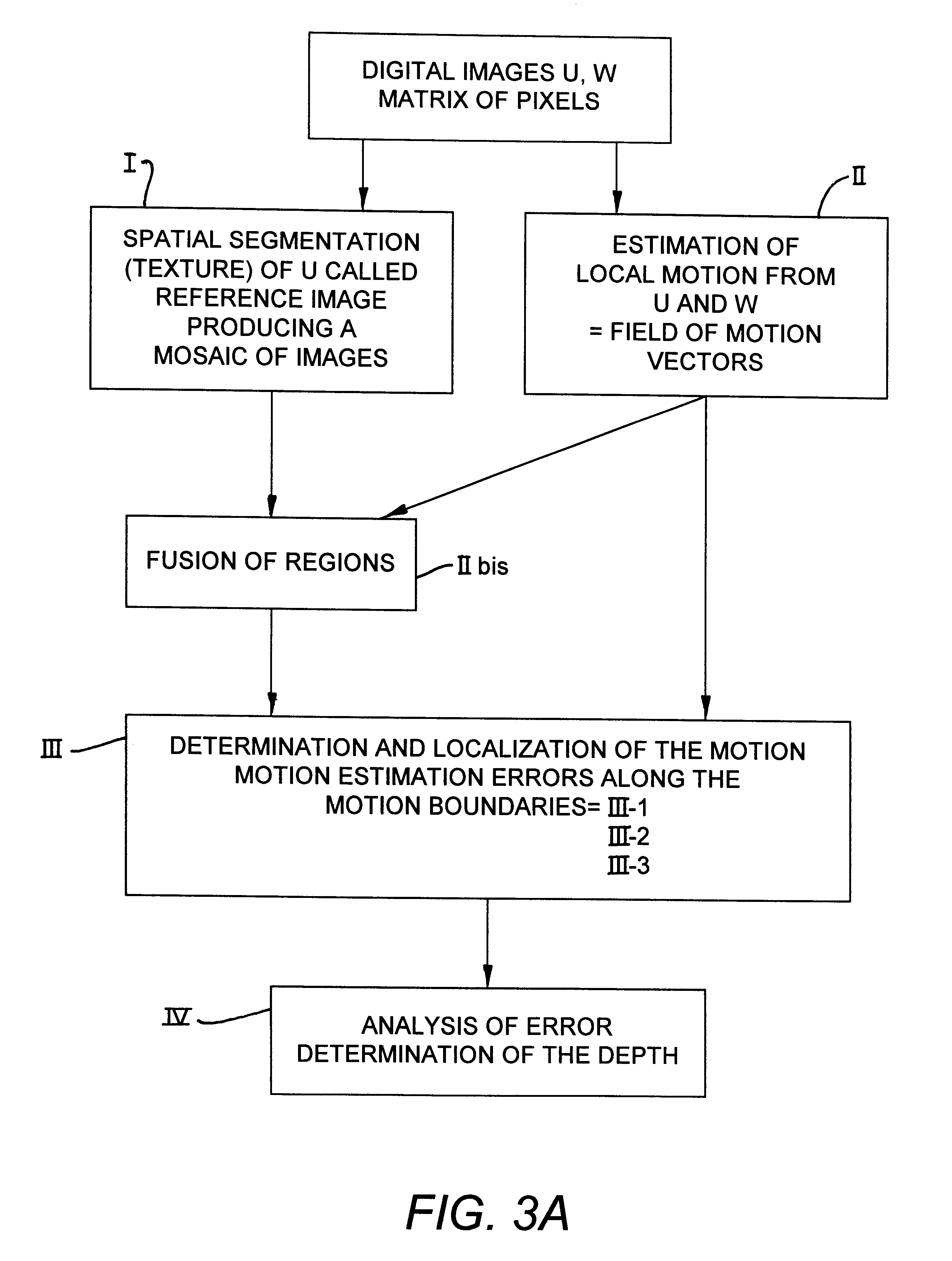
Disclosed is a method for the detection of the relative depth of two neighboring regions in relative motion with respect to each other in two images obtained from different shots of a scene, in order to know the composition of the scene. The method consists in carrying out a spatial segmentation of one of the images, called a reference image; a local estimation of the motion between the two images, the resultant vector field of which is called local motion; a determining of the motion estimation errors along the motion boundaries; and an analysis of the localization of the motion estimation errors along the motion boundaries to conclude that a region A is in front of a region B when the motion estimation error along the boundary is chiefly localized on the side B of this boundary.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC
Extraction method of visual saliency area based on monocular depth map
InactiveCN104574366AReduce noise interferenceTest results are obviousImage enhancementImage analysisFeature vectorVisual saliency
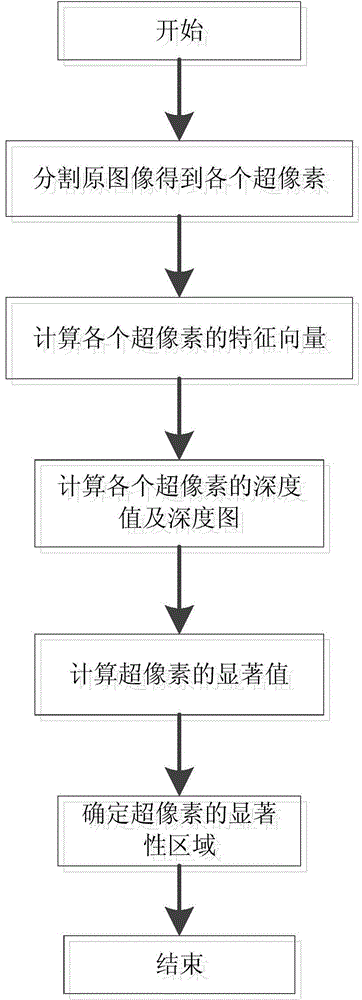
The invention discloses an extraction method of a visual saliency area based on a monocular depth map. The extraction method of the visual saliency area comprises the following sequential steps: dividing an original image to obtain super pixels; building a characteristic vector of each super pixel to estimate an absolute depth characteristic of absolute depth in a scene in the image; building a probability model by using a Gaussian-Markov random field model, calculating a distance relation between the super pixel characteristic vector and an adjacent super pixel characteristic vector by virtue of the probability model to obtain a relative depth characteristic on the basis of the absolute depth characteristic and obtain depth values and depth maps of the super pixels simultaneously; calculating saliency values of the super pixels; calculating a gain coefficient according to the depth values and correcting the saliency values by using the gain coefficient. The extraction method can be used for quickly and automatically identifying the saliency objects in the image without any prior knowledge, is high in universality and can also be used for accurately detecting the saliency area.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Pedestrian counting method based on multiple features
ActiveCN103279791AFast executionLow costCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionLight spot
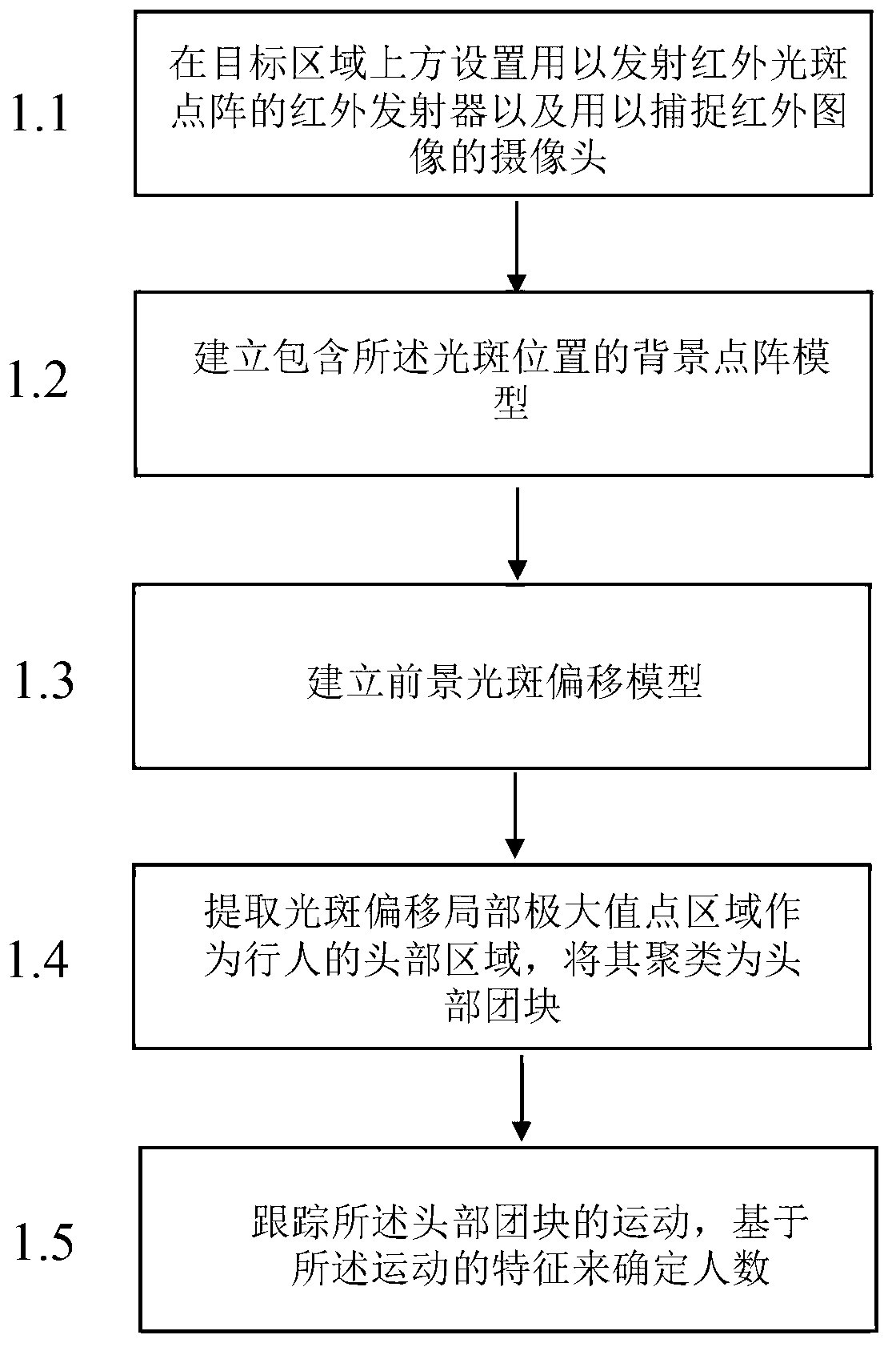
The invention discloses a pedestrian counting method based on multiple features. A background lattice model and a capture prospect lattice are set, so the position of the light spot of the background lattice model and the position of the light spot of the capture prospect lattice are compared, a prospect light spot offset model is set, then a light spot offset local maximum value point area in the prospect light spot offset model is extracted to serve as a head area of a pedestrian and is clustered to a head block mass, a motion trail is traced finally, and the number of people is determined and recorded based on motion features. The pedestrian counting method is based on light stream computing, renewal of a pedestrian individual track is achieved by means of intra-frame block mass bilateral matching, and statistics of the number of people is accurate and reliable. The pedestrian counting method is further based on sparse depth data, and improves the execution speed of an algorithm compared with a method based on a dense depth. At last, relative depth acquisition equipment adopted in the pedestrian counting method is low in cost, so the pedestrian counting method has a greater advantage in cost.
Owner:WINNER TECH CO INC
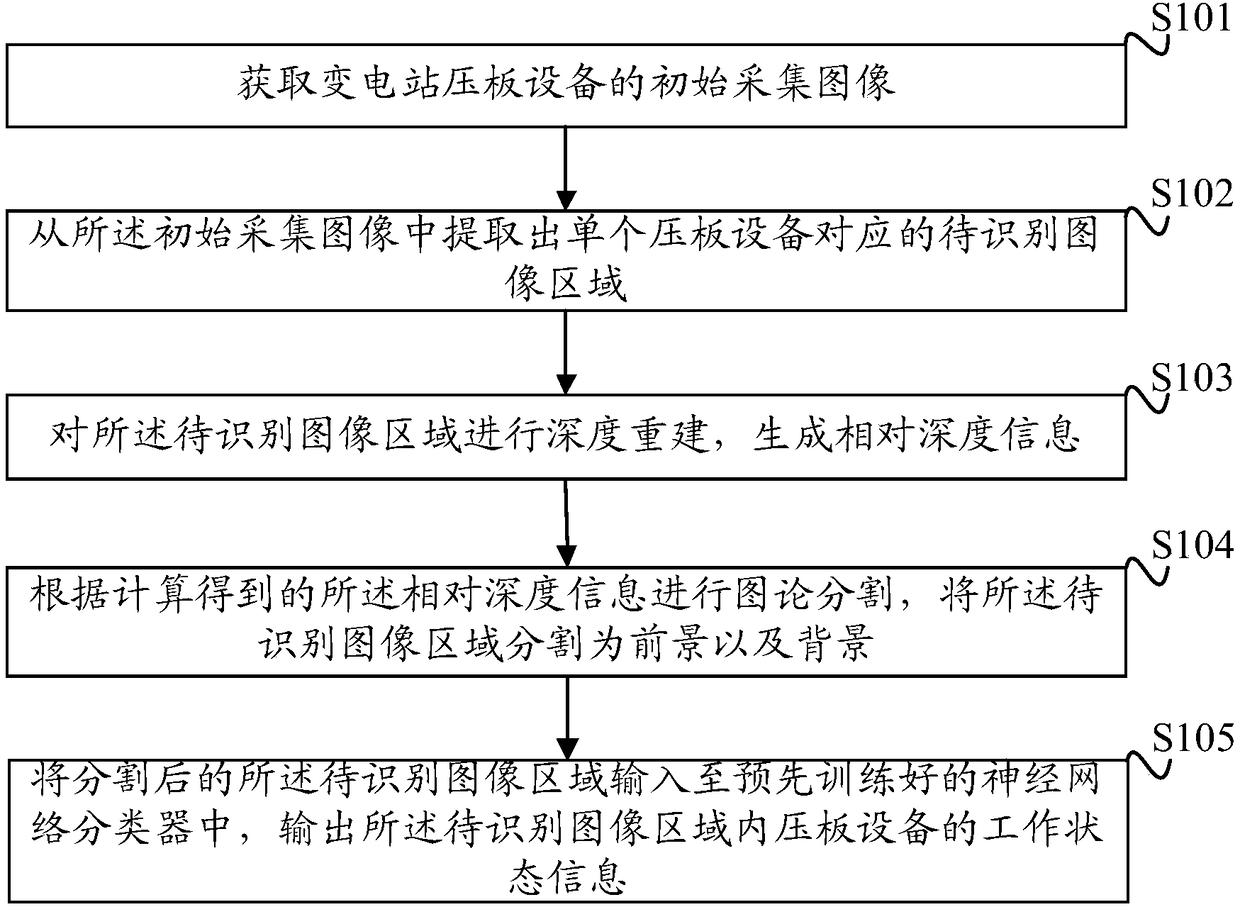
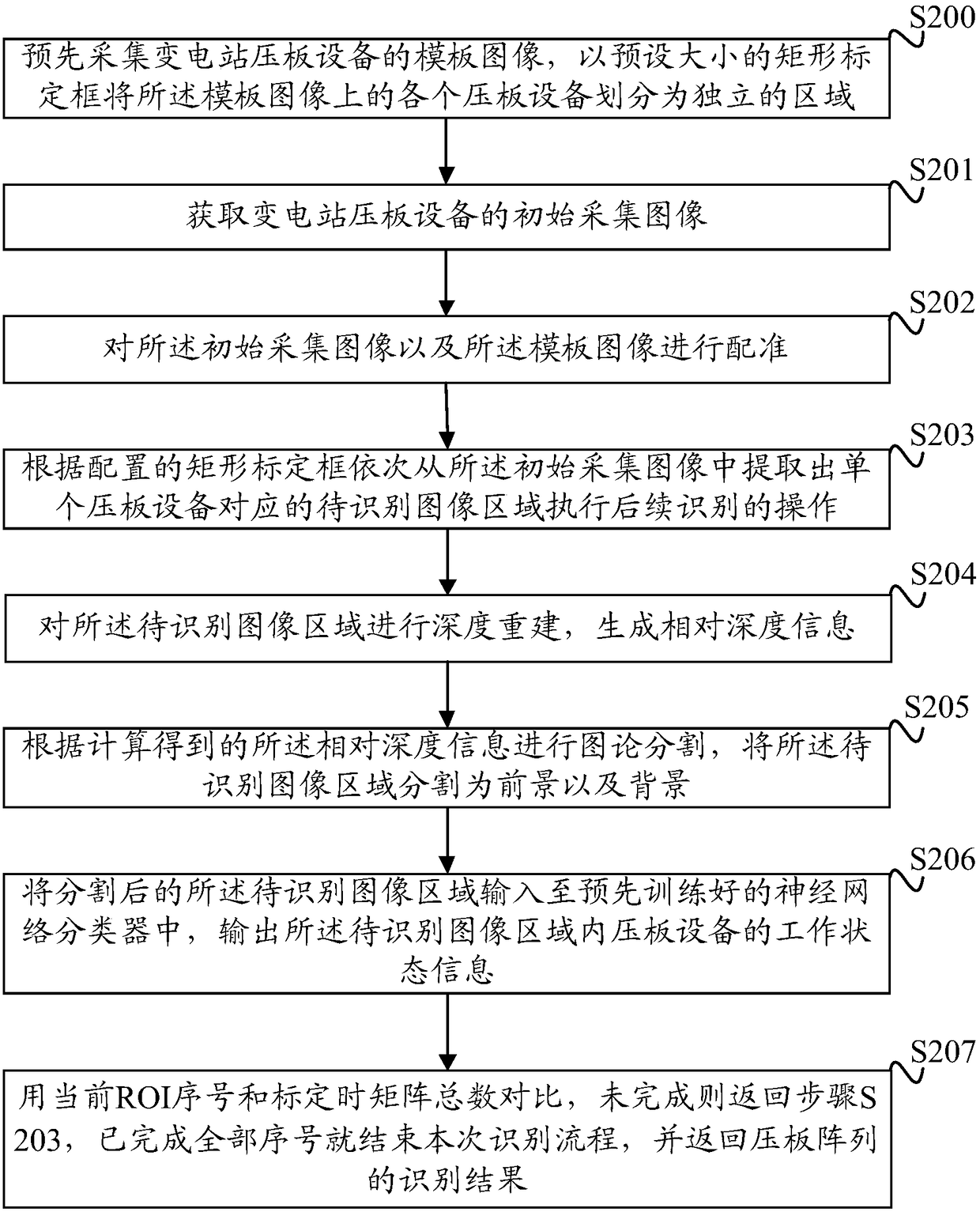
Identification method and device of states of pressing plate devices of transformer station
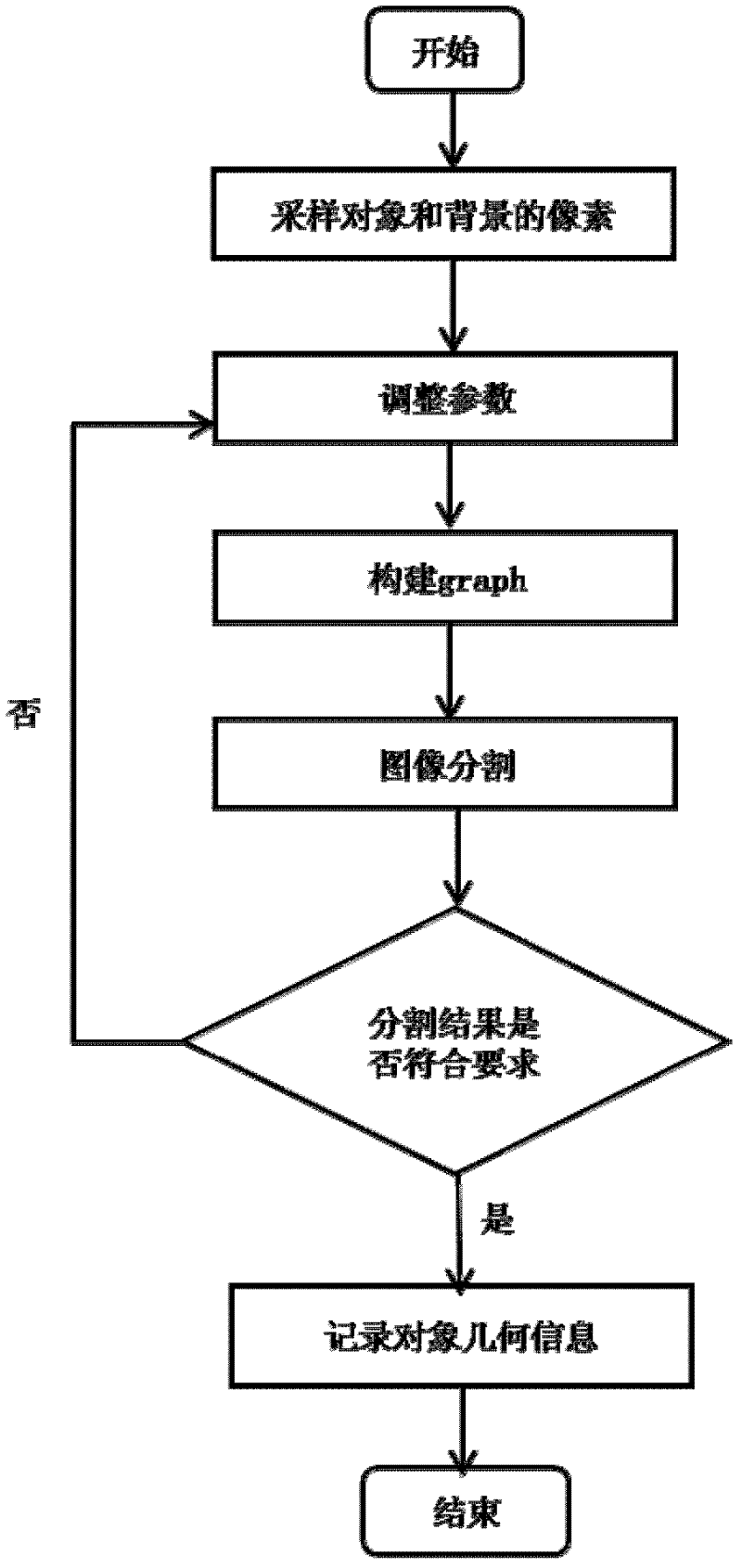
InactiveCN108573256ALower quality requirementsImprove robustnessCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionTransformer
The invention discloses an identification method and device of device states of pressing plates of a transformer station. The method comprises steps of acquiring initial acquisition images of pressingdevices of a transformer station; extracting a to-be-identified image region corresponding to a signal pressing plate device from the initial acquisition images; carrying out depth reconstruction onthe to-be-identified image region so as to generate relative depth information; according to the relative depth information obtained through calculation, carrying out graph theory segmentation; segmenting the to-be-identified image region into foregrounds and backgrounds; and inputting the segmented to-be-identified image region into a pre-trained neural network classifier, and outputting workingstate information of the pressing plate devices in the to-be-identified image region. According to the invention, in a way of depth information reconstruction, the foregrounds and the backgrounds of the graph theory segmentation are determined; by use of the graph theory segmentation, images are segmented; by use of the trained neural network, the segmented images are identified; requirements on quality of illumination and images are quite low; quite high robustness is achieved in onsite light ray interference; and identification accuracy is quite high.
Owner:STATE GRID INTELLIGENCE TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for generating stereoscopic image from two-dimensional image by using mesh map
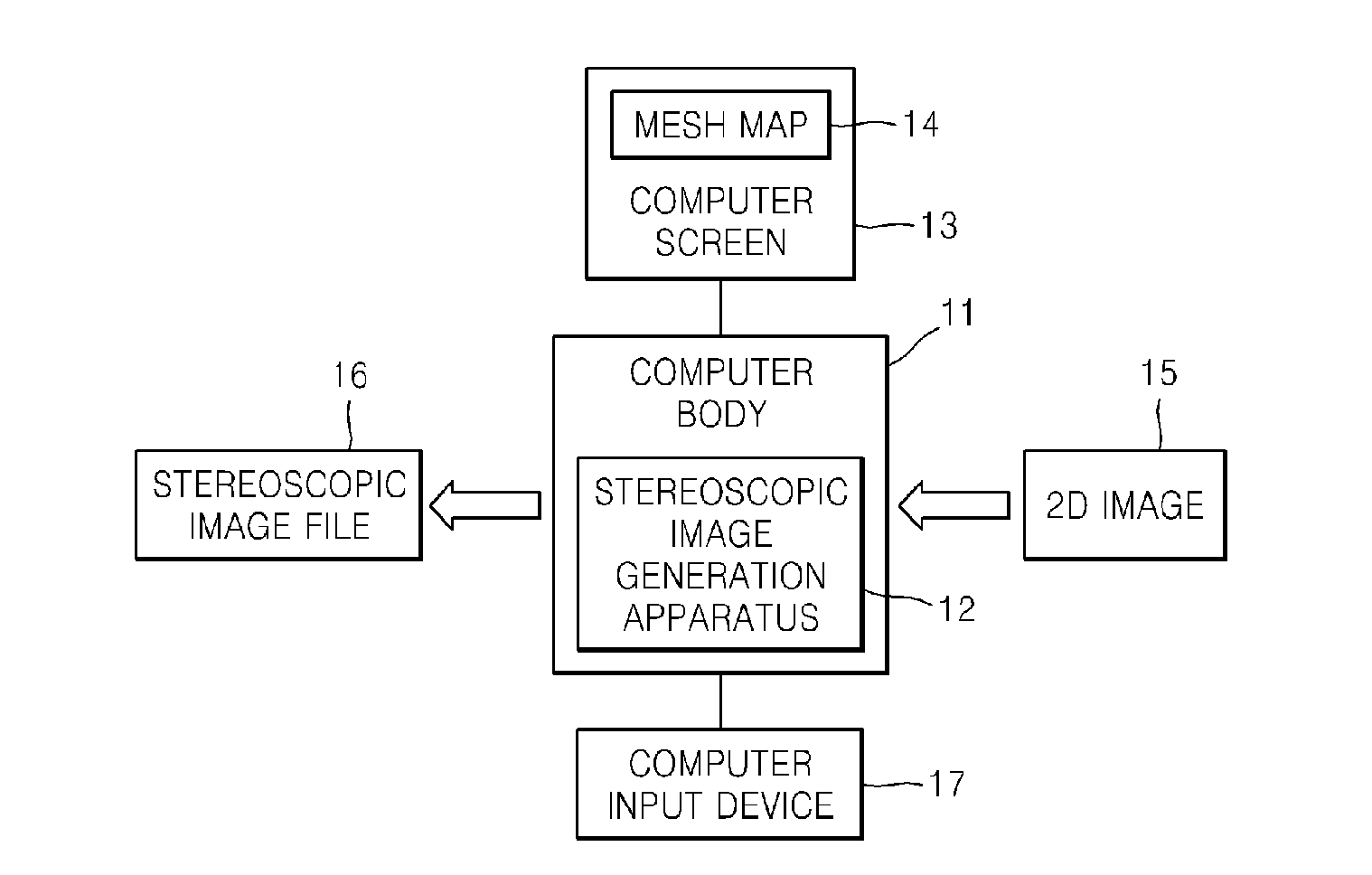
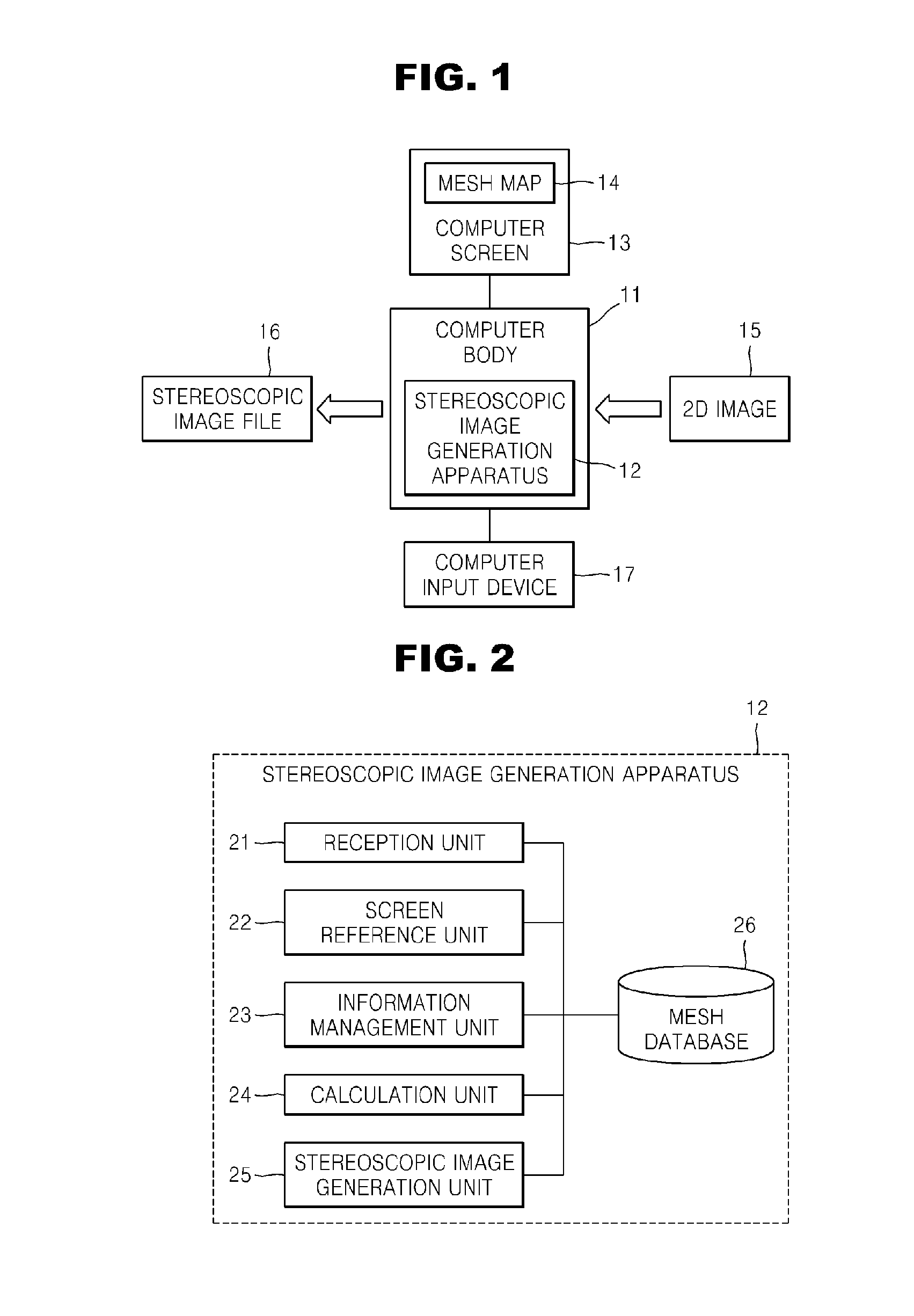
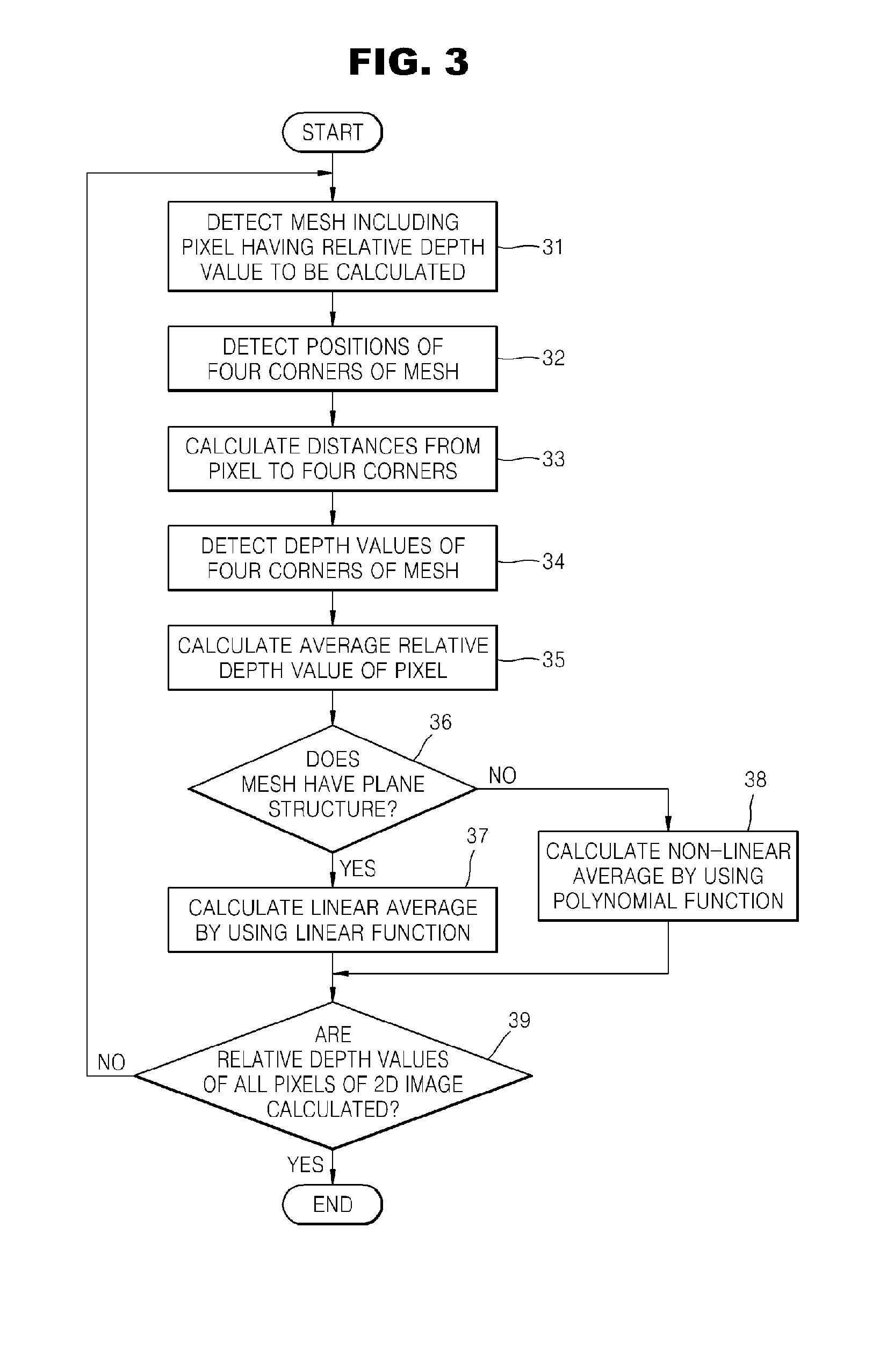
InactiveUS20100086199A1Low costShort timeCharacter and pattern recognitionSteroscopic systemsComputer graphics (images)Image generation
Provided are a method and apparatus for generating a stereoscopic image from a two-dimensional (2D) image by using a mesh map and a computer readable recording medium having recorded thereon a computer program for executing the method. Also provided are a method and apparatus for generating a stereoscopic image by reading a 2D image, displaying the 2D image and a mesh map by overlapping the 2D image and the mesh map, and editing mesh shapes and depth information (depth values) of the mesh map by a user, and a computer readable recording medium having recorded thereon a computer program for executing the method. The method of generating a stereoscopic image includes receiving a 2D image; displaying the 2D image and a mesh map by overlapping the 2D image and the mesh map; editing mesh shapes and depth information (depth values) of the mesh map by a user in accordance with shapes of a displayed image; calculating relative depth information of pixels included in the 2D image in accordance with the mesh shapes and the depth information of the edited mesh map; and generating a stereoscopic image file by using the calculated relative depth information of the 2D image. The present invention may be used in a system for generating a stereoscopic image from a 2D image including a general still image or moving picture.
Owner:VENTURE 3D INC +1
Apparatus and method for obtaining and providing imaging information associated with at least one portion of a sample, and effecting such portion(s)
ActiveUS20130066215A1Treatment safetySmall sizeDiagnostics using lightDiagnostics using spectroscopyRelative phaseLength wave
Exemplary apparatus and process can be provided for imaging information associated with at least one portion of a sample. For example, (i) first different wavelengths of at least one first electro-magnetic radiation can be provided within a first wavelength range provided on the portion of the sample so as to determine at least one first transverse location of the portion, and (ii) second different wavelengths of at least one second electro-magnetic radiation within a second wavelength range can be provided on the portion so as to determine at least one second transverse location of the portion. The first and second ranges can east partially overlap on the portion. Further, a relative phase between at least one third electro-magnetic radiation electro-magnetic radiation being returned from the sample and at least one fourth electro-magnetic radiation returned from a reference can be obtained to determine a relative depth location of the portion.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
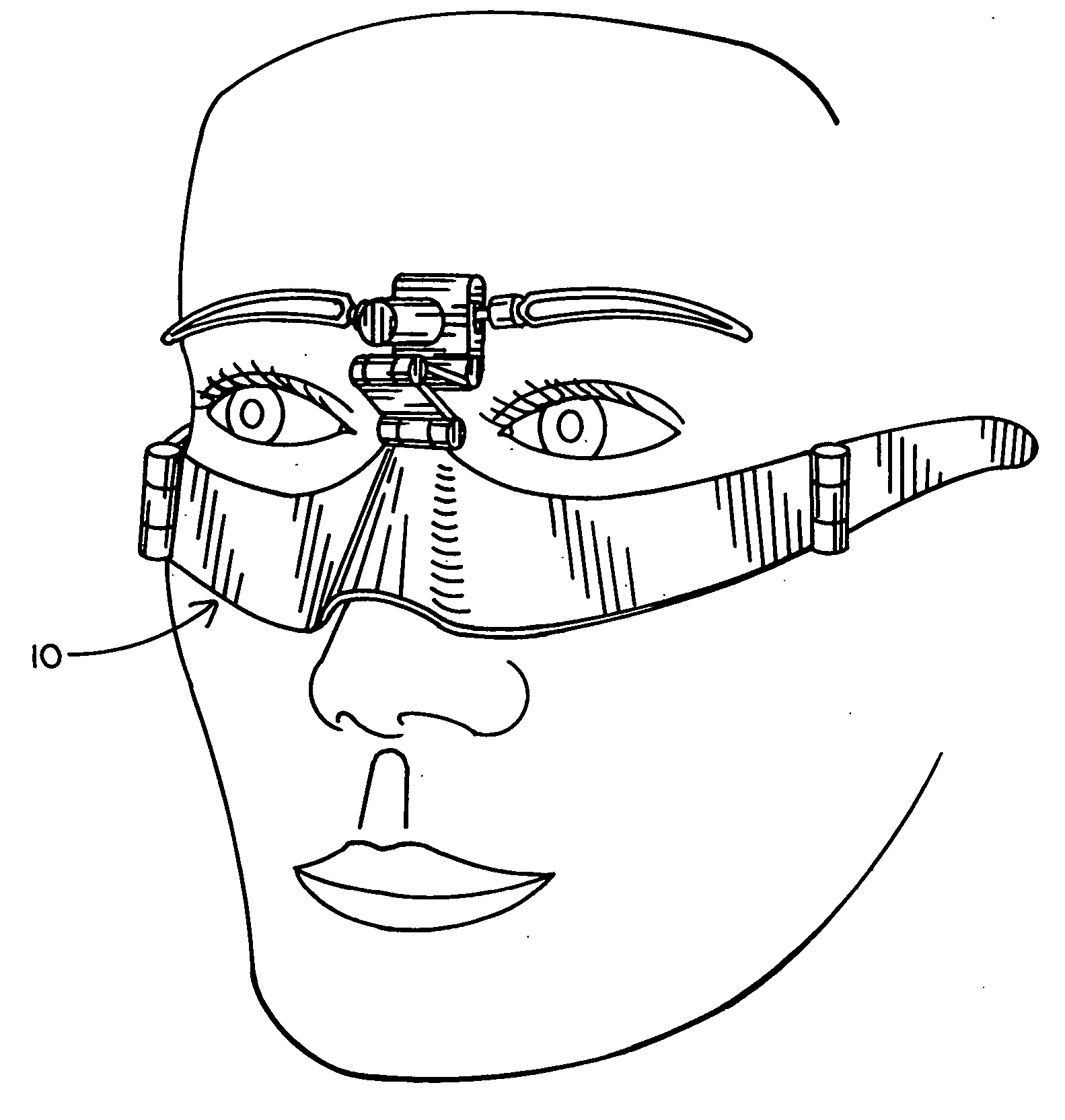
Eyebrow guide
An eyebrow guide configured as an adjustable facial frame designed to be centered over the nose and having a pair of selectively shaped and positioned eyebrow templates for use in guiding the appliance used to shape, color, shave, cut or otherwise cosmetically treat the user's eyebrows. The frame comprises a nosepiece designed to overly the nose to both center and stabilize the guide. The frame also has a pair of opposed side members which extend from the nosepiece toward and over the ears in a manner similar to conventional eyeglass frames to further stabilize and support the guide. Intermediate of the eyebrow templates and the nose piece is a three-piece, double hinged member designed to provide adjustment for virtually any facial dimensions in regard to distance between the eyebrows and the nose as well as their relative depth. In addition, the upper portion of this double-hinged member provides a dial for eyebrow angle adjustment for the templates.
Owner:LAM PHILLIP L
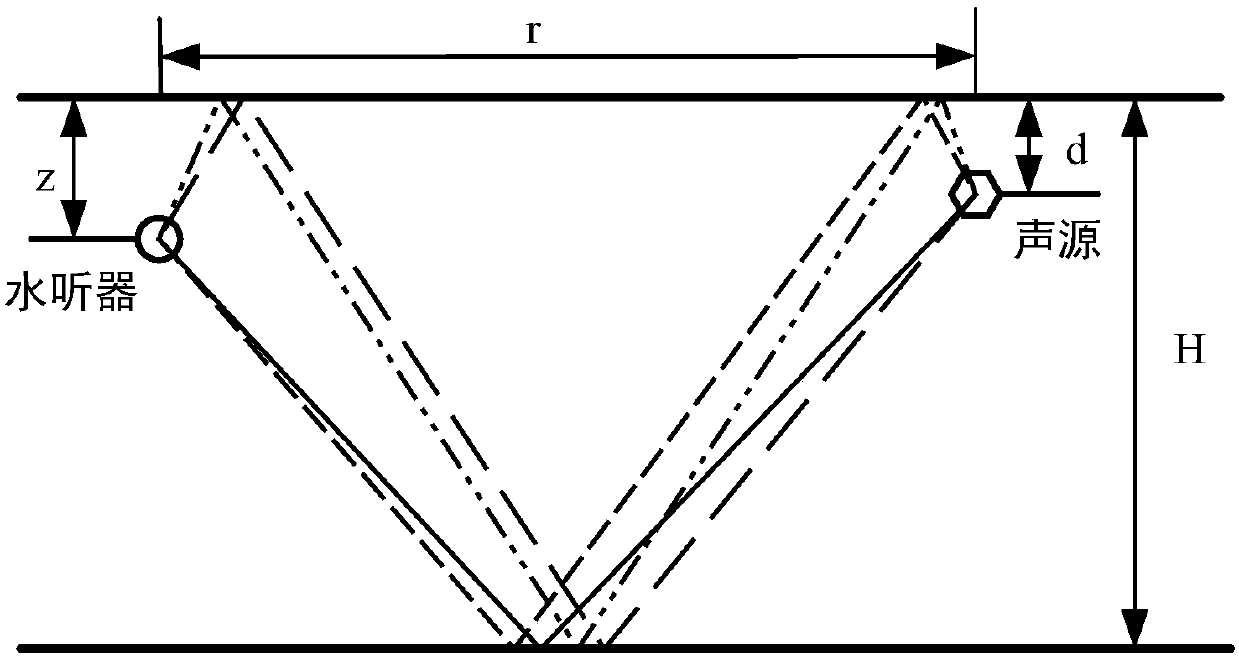
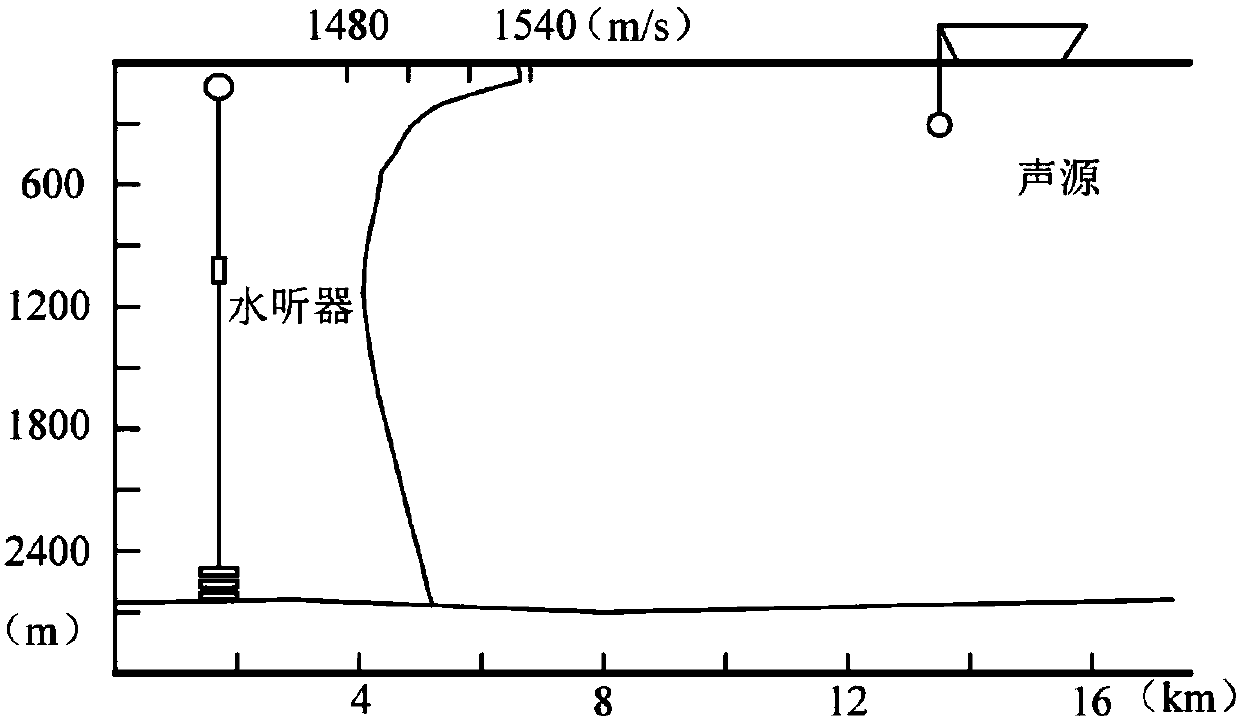
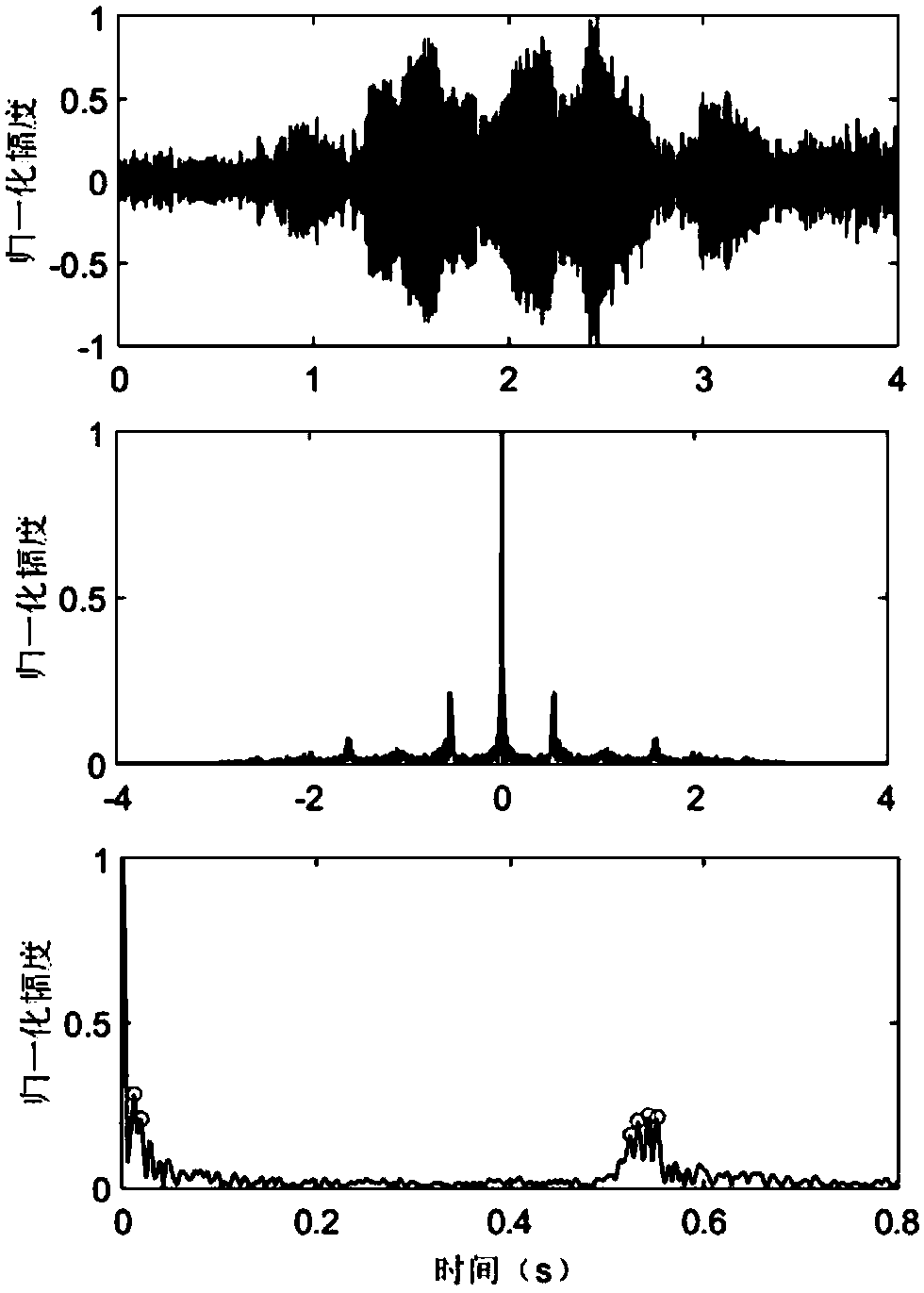
Single-hydrophone sound source passive positioning method in deep sea environment
The invention relates to a single-hydrophone sound source passive positioning method in a deep sea environment. A wide-band signal received by a single hydrophone is used. A large-aperture array composed of a number of hydrophones is not needed. Signal synchronization between hydrophones is not needed. Sound source positioning in the deep sea environment can be realized without exposing the position in a passive receiving mode. According to the invention, six indiscernible relative time delays are arranged in ascending order to form a relative time delay vector for sound source positioning; anerror vector is acquired by subtracting the measured time delay vector from a predicted time delay vector, and the 1-norm and the reciprocal of the error vector is acquired for sound source positioning; the method is used in the South China Sea at a sea depth of 2680 meters in summer; a sound source is a linear chirp signal with a bandwidth of 2.9kHz to 3.1kHz; the sound source distance is 13.8 kilometers, and the depth is 49 meters; the positioning of the sound source is completed; the relative distance error is 2.9%; and the relative depth error is 22.5%.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
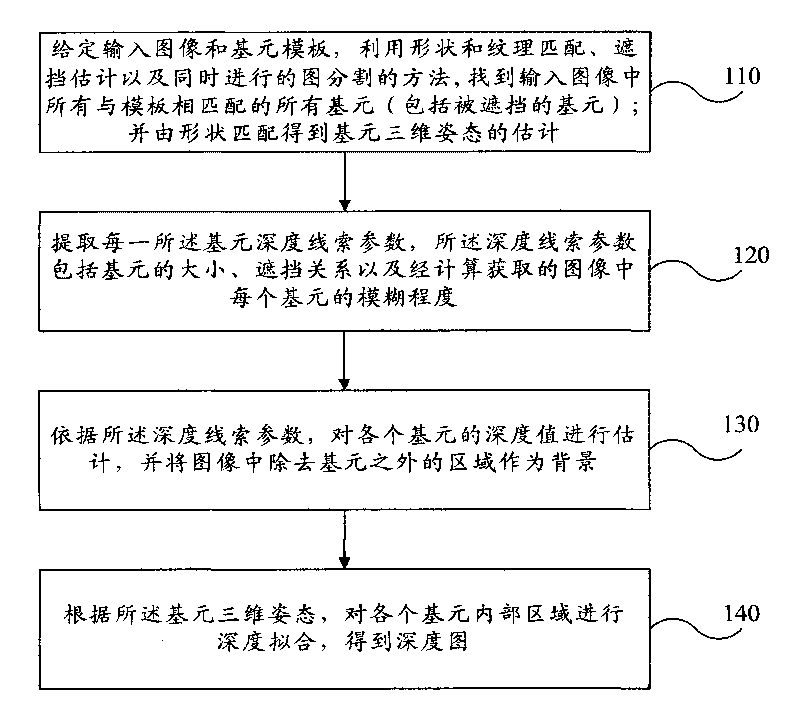
Image segmentation and multithread fusion-based method and system for evaluating depth of single image
The invention discloses an image segmentation and multithread fusion-based method and an image segmentation and multithread fusion-based system for evaluating depth of a single image. The method comprises the following steps: setting an input image and an element template, and finding all elements matched with the template in the input image by using the match of shape and texture, shielding evaluation and an image segmentation method which is simultaneously performed on the basis of an image model; extracting depth cue parameters of each element, wherein the depth cue parameters comprise the size of the element, a shielding relationship and the blur length of each element in the image obtained by the computation; according to the depth cue parameters, evaluating a depth value of each element and using an area in the image except the elements as a background; performing depth fitting on an inner area of each element according to a three-dimensional pose of the element obtained by matching the shape; and finally obtaining an optimized depth map. By comprehensively utilizing the depth cue parameters such as the imaging sizes of objects, the shielding relationship and the blur length, the relative depth map of the single image is obtained.
Owner:BEIJING SHENRUI BOLIAN TECH CO LTD
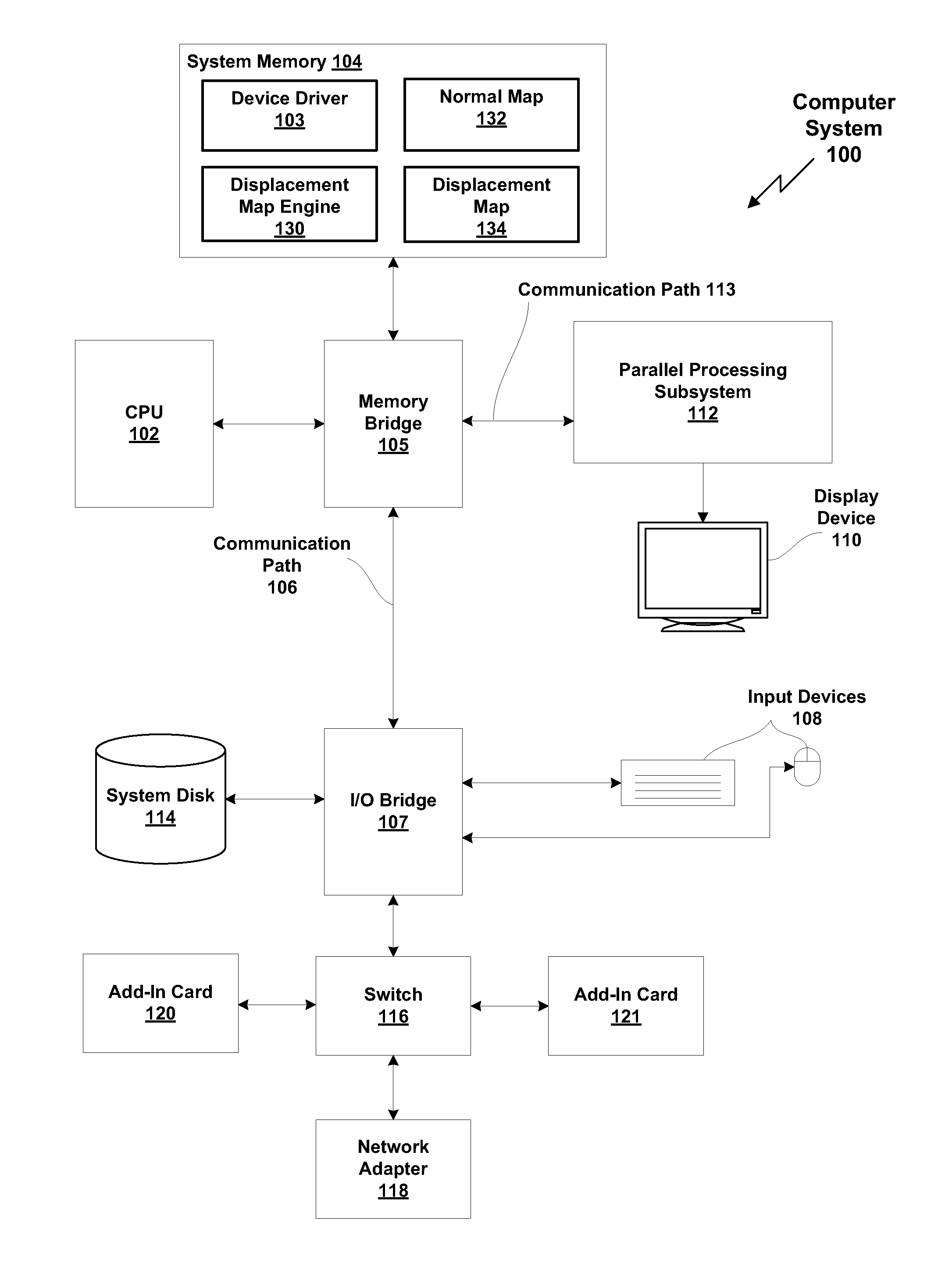
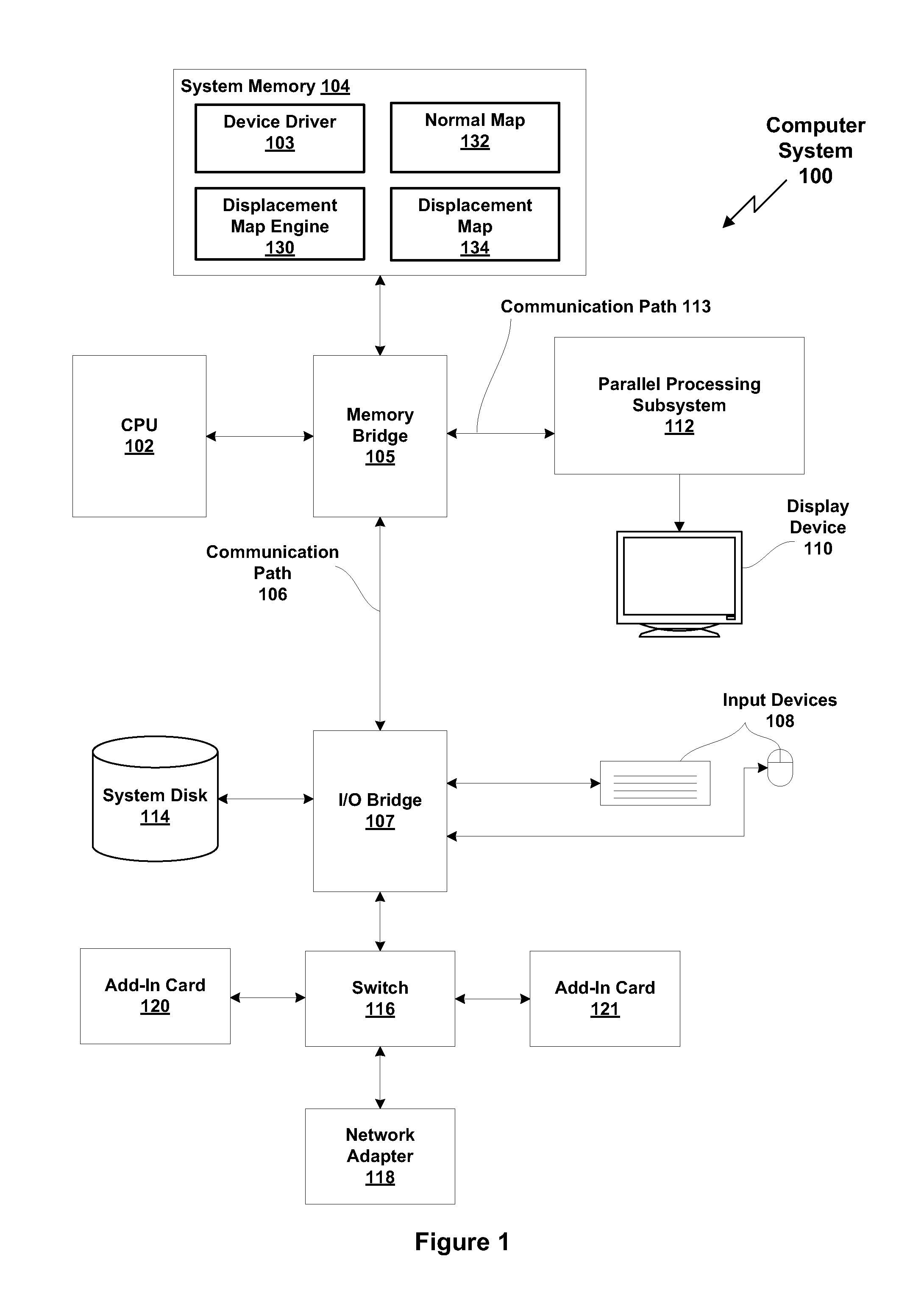
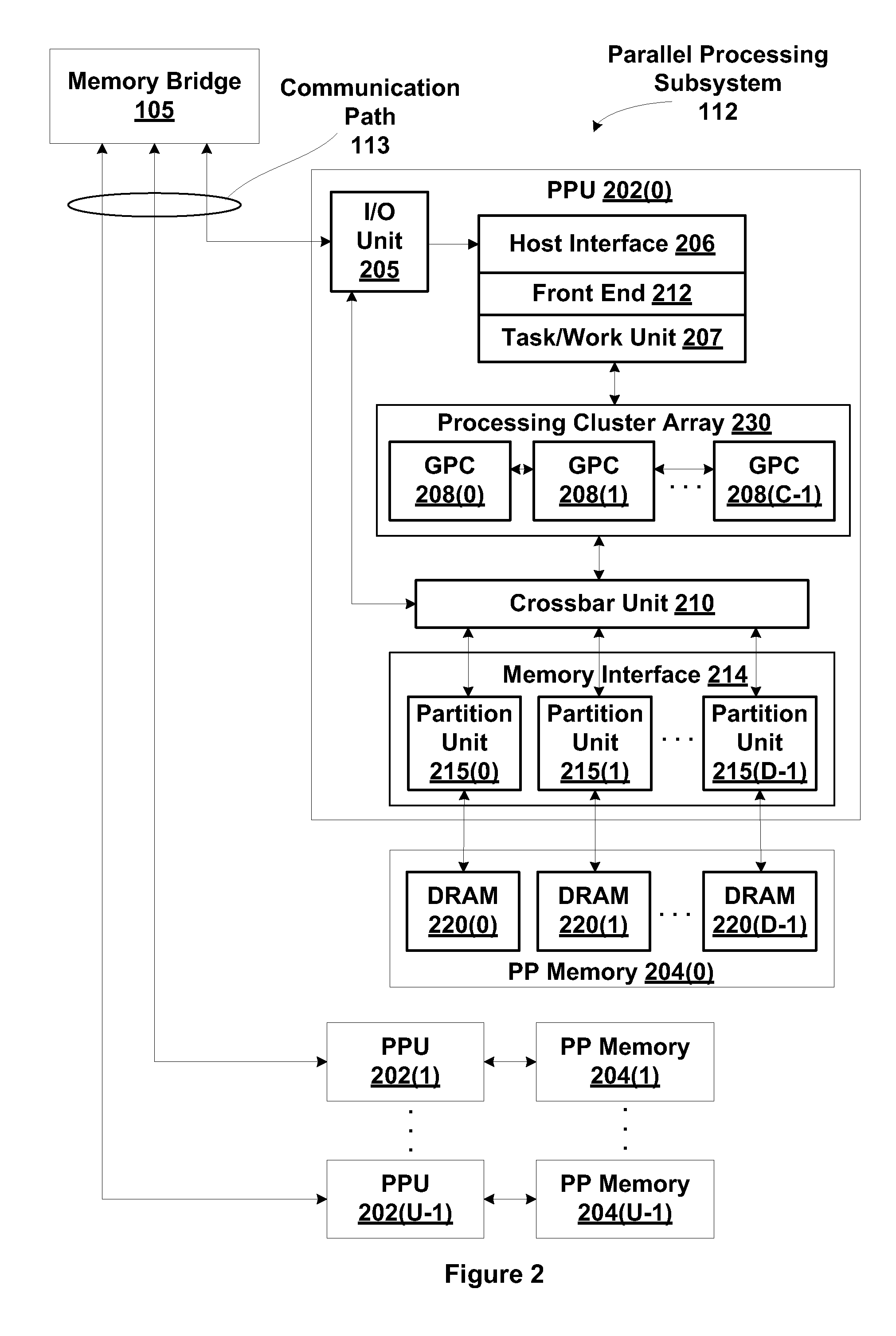
Method and system for generating a displacement map from a normal map
ActiveUS20140035940A1Quickly and inexpensively convertedMore geometric featureCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingPattern recognitionDisplacement mapping
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth a technique for generating a displacement map. The technique involves receiving a normal map which includes one or more normal vectors associated with a texture map, processing the one or more normal vectors to a calculate one or more depth difference vectors associated with the texture map, and generating one or more rays associated with a first texel of the texture map, where each of the one or more rays associated with the first texel traverses one or more other texels of the texture map. The technique further involves calculating, for each of the one or more rays associated with the first texel, relative depths of each of the one or more other texels traversed by the ray based on each of the depth difference vectors that correspond with the one or more other texels traversed by the ray, determining a displacement value associated with the first texel based on the relative depths calculated for the one or more rays, and storing the displacement value in a displacement map.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
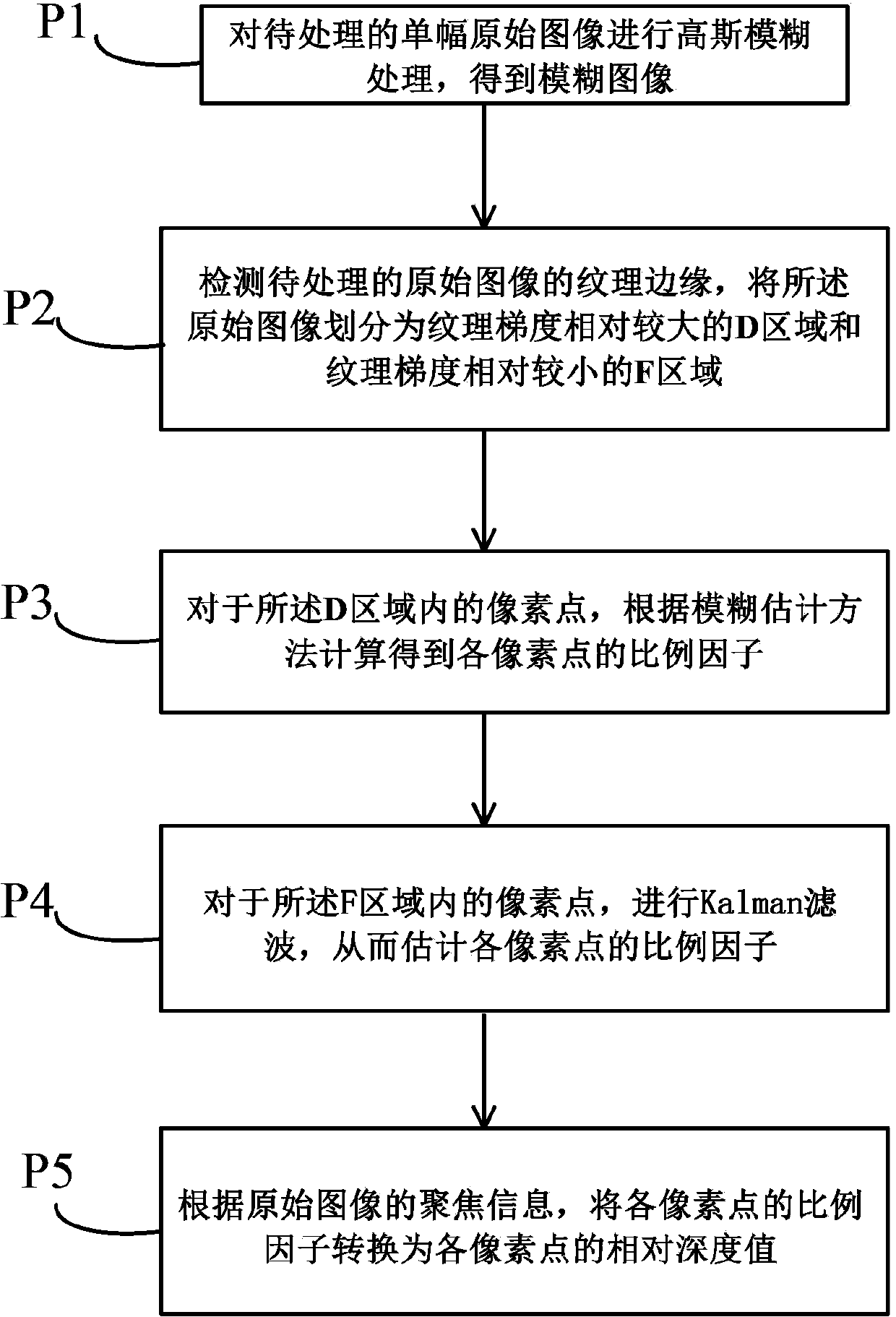
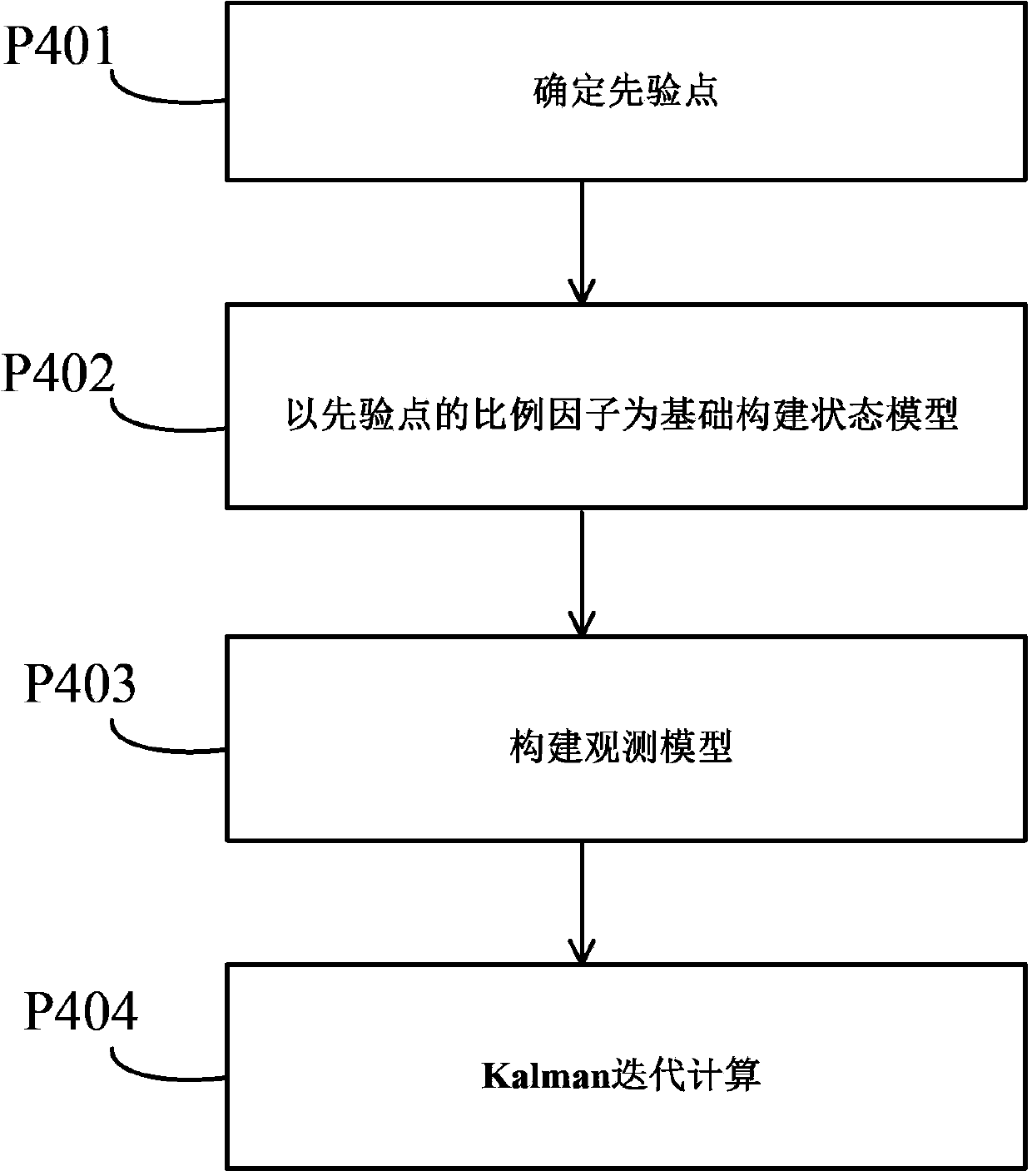
Method for obtaining image depth information
ActiveCN103473743AHigh precisionCompatible discontinuityImage enhancementImage analysisEstimation methodsRelative depth
The invention discloses a method for obtaining image depth information. The method for obtaining the image depth information includes the following steps that firstly, a single-width primitive image to be processed undergoes Gaussian Blur processing to obtain a blurred image; secondly, a grain rim of the primitive image to be processed is detected, the primitive image is divided into a zone with the large grain gradient which is defined as a D zone and a zone with the large grain gradient which is defined as an F zone; thirdly, in terms of pixel points in the D zone, scale factors of all the pixel points are obtained by calculation with a blurred estimation method; fourthly, in terms of all the pixel points in the F zone, Kalman filtering is carried out and scale factors of all the pixel points are estimated; fifthly, according to focusing information of the primitive image, the scale factors of all the pixel points are converted into relative depth values of all the pixel points. According to the method for obtaining the image depth information, the idea of Kalman filtering is introduced, noise generated when depth values are obtained with a regular defocusing method can be hindered, the precision of the final depth image is improved and extra information supplementing is not needed.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
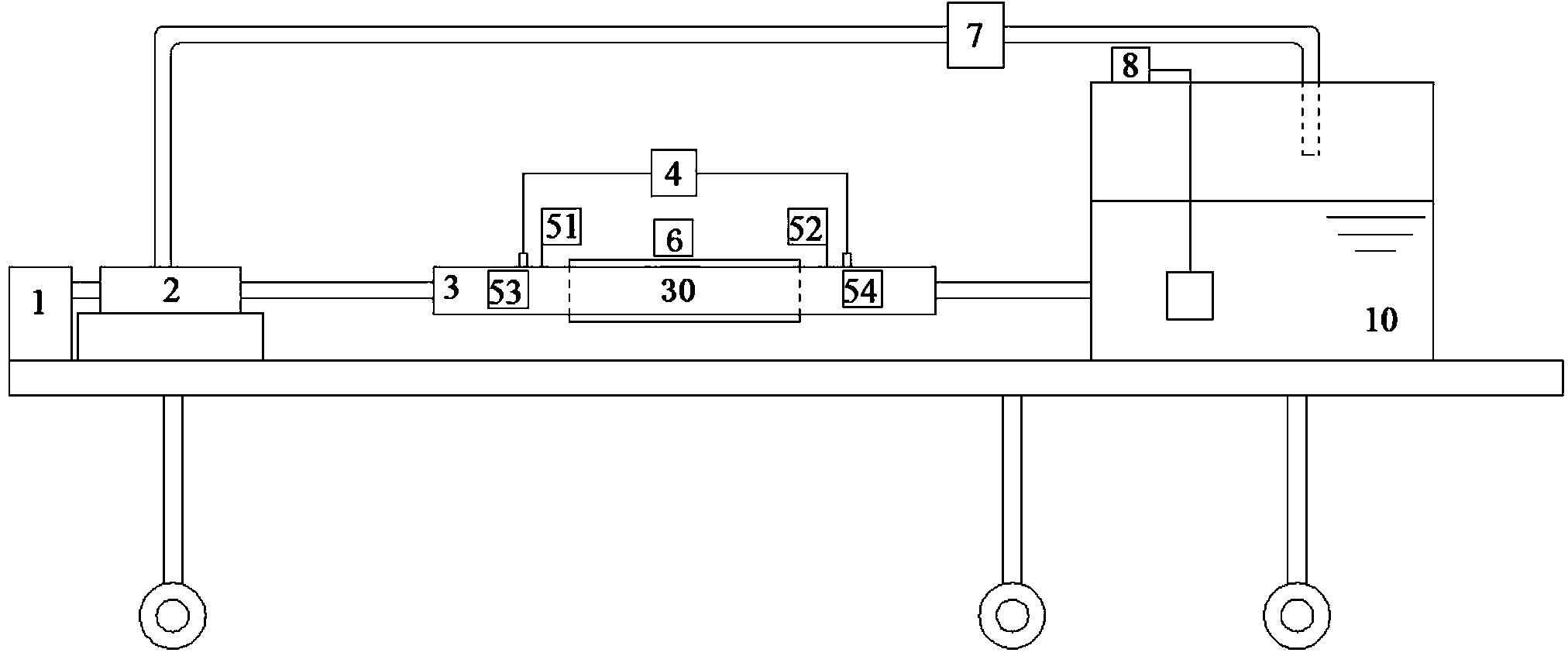
Fluid flow heat-exchanging experimental device with ball socket/ball bulge flow control structure
ActiveCN103616404AChange relative depthChange spanwise spacingMaterial heat developmentTemperature controlEngineering
The invention discloses a fluid flow heat-exchanging experimental device with a ball socket / ball bulge flow control structure. The fluid flow heat-exchanging experimental device comprises a speed adjusting motor, a centrifugal pump, a testing section, an electric heating system, a flow meter, a water tank temperature control system and a water tank, wherein the speed adjusting motor is connected with the centrifugal pump; a water outlet of the water tank is communicated with an inlet of the testing section and an outlet of the testing section is communicated with the inlet of the centrifugal pump; the outlet of the centrifugal pump is communicated with the water tank; the testing section comprises an experimental channel upper cover plate and an experimental channel lower cover plate which are buckled with each other; a concave region is arranged in the middle of the experimental channel lower cover plate; the concave region is internally filled with a building block type ball socket / ball bulge flow control structure. According to the fluid flow heat-exchanging experimental device, a relative depth, a spanwise spacing and a streamwise spacing of a ball socket / ball bulge in a channel and the manner of combining the ball socket with the ball bulge are changed by replacing the ball socket / ball bulge, a spanwise filling block, a streamwise filling block and the like; a whole molding design method of the testing channel is improved by the design; building block type blocked structural design is adopted and the change of geometrical parameters of the channel can be finished conveniently and rapidly in a time-saving and labor-saving manner.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
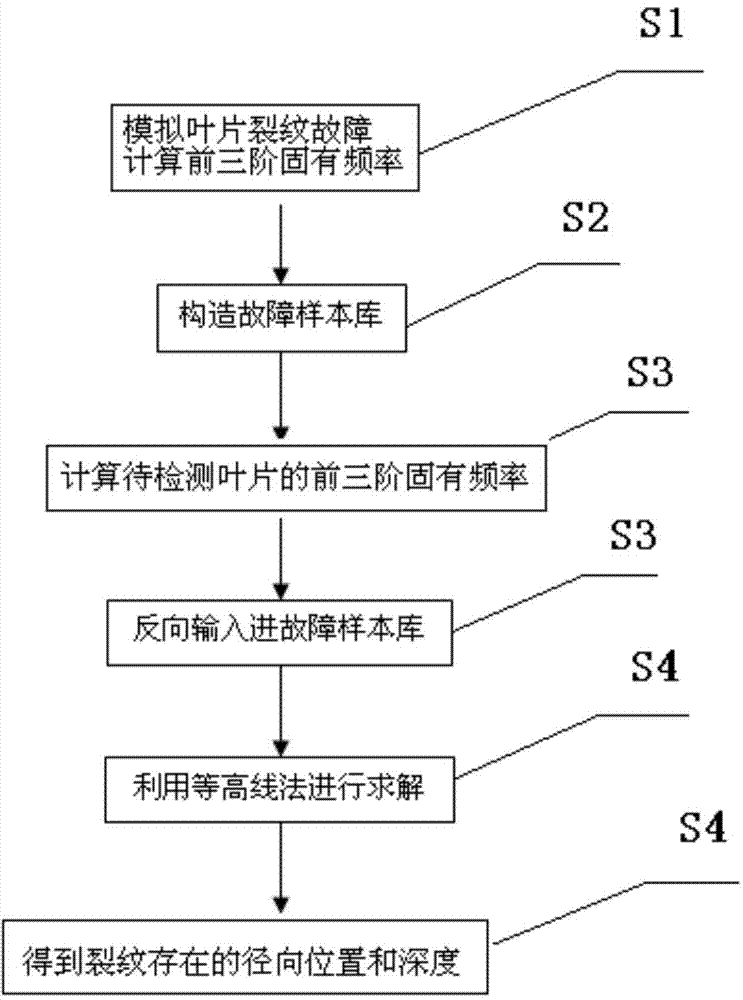
Determination method of fan blade crack position
InactiveCN104267097ATimely diagnosisRealize quantitative analysisAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSpecial data processing applicationsRadial positionEngineering
The invention discloses a determination method of a fan blade crack position. The determination method comprises the following steps: S1. simulating crack faults at different positions of a blade and calculating front three-order inherent frequency; S2. drawing an inherent frequency resolving surface diagram by taking the inherent frequency of each order, the relative depth of a crack and the relative radial position of the crack as coordinate axes, and constructing a fault sample library; S3. calculating the front three-order inherent frequency of the blade when the blade is subjected to fault diagnosis, and reversely inputting into the fault sample library; and S4. solving by a contouring method to obtain the depth and the radial position of the crack. According to the method, the position of the crack of the blade can be solved by the contouring method, the fan blade crack can be timely diagnosed, the position of the fan blade crack can be quantitatively analyzed, the diagnosis speed is high and the result is reliable, and therefore, a powerful guarantee is provided for equipment maintenance.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com