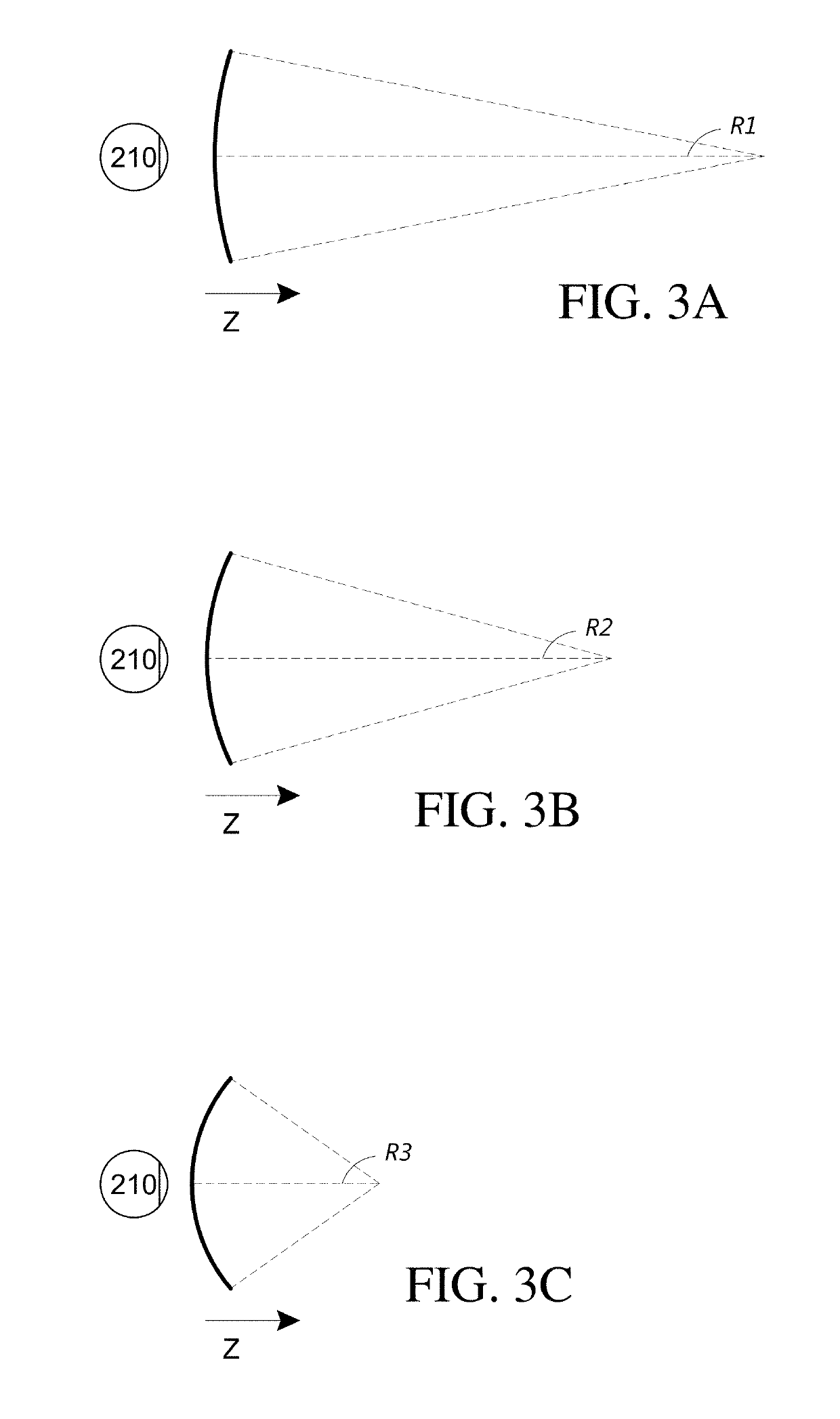
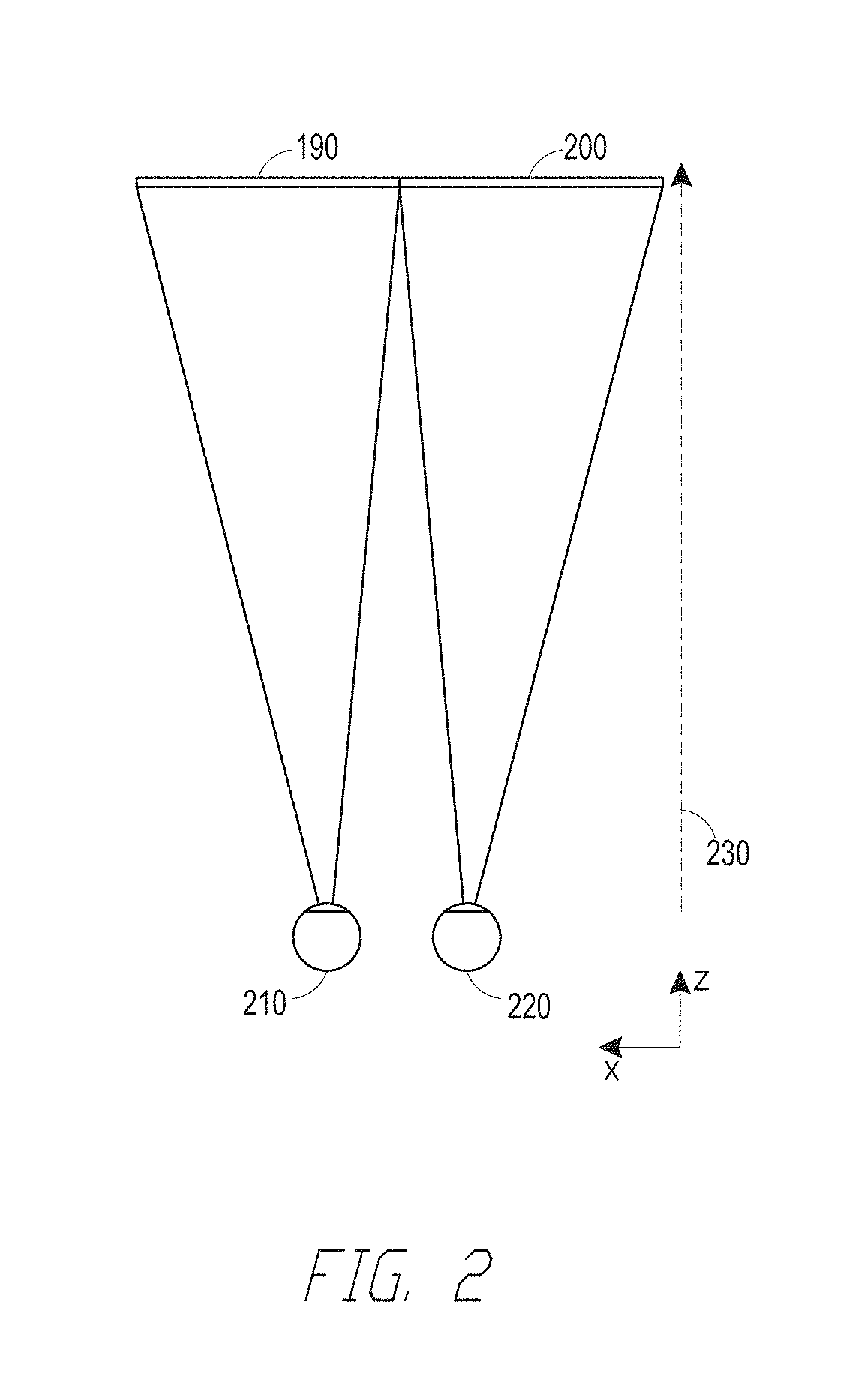
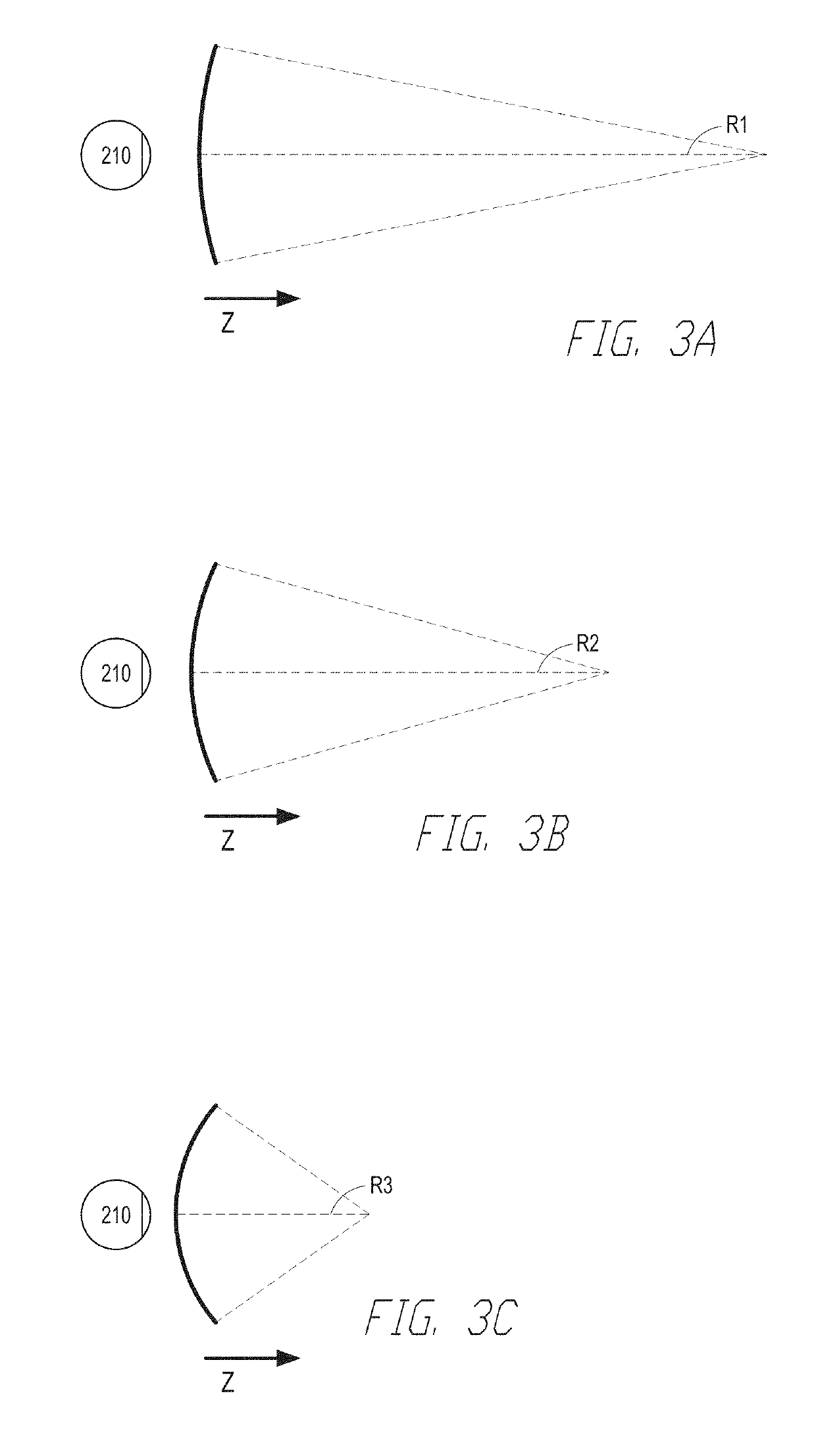
Patents
Literature
113 results about "Depth plane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
At normal subject sizes, depth of field extends roughly one third in front of your plane of focus and two thirds behind it, but at macro sizes, it becomes closer to fifty-fifty, making your actual plane of focus in the middle of the perceived depth of field.
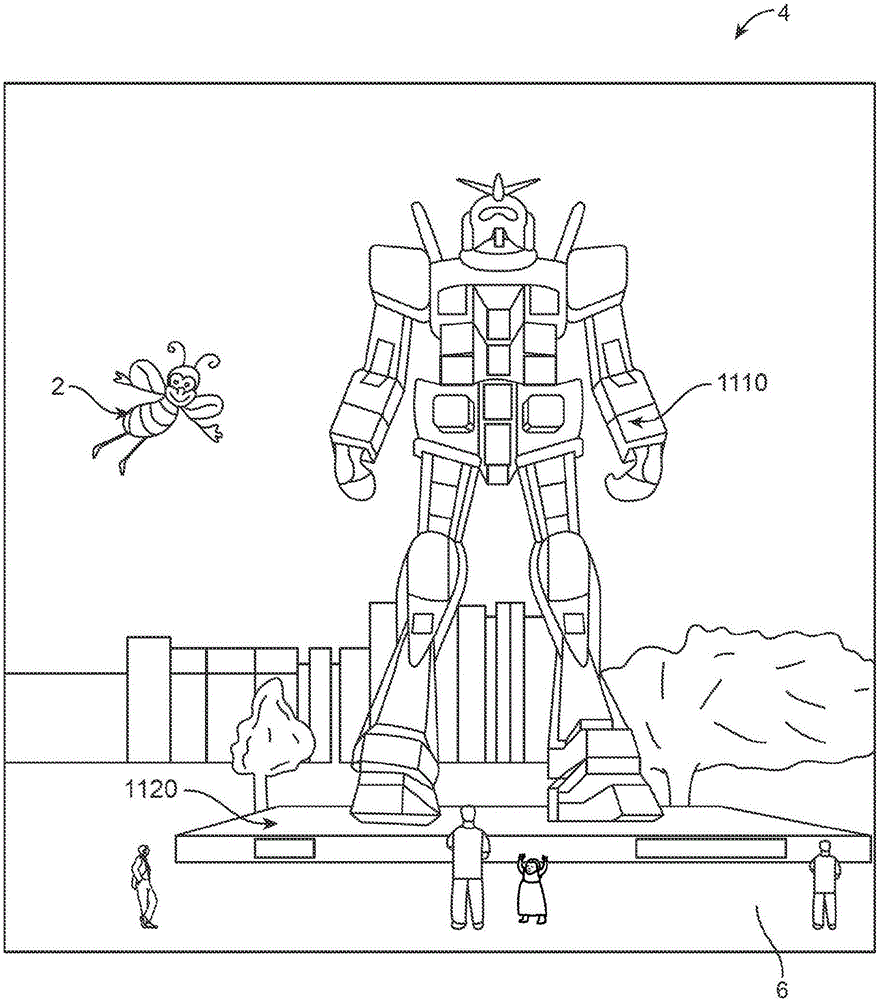
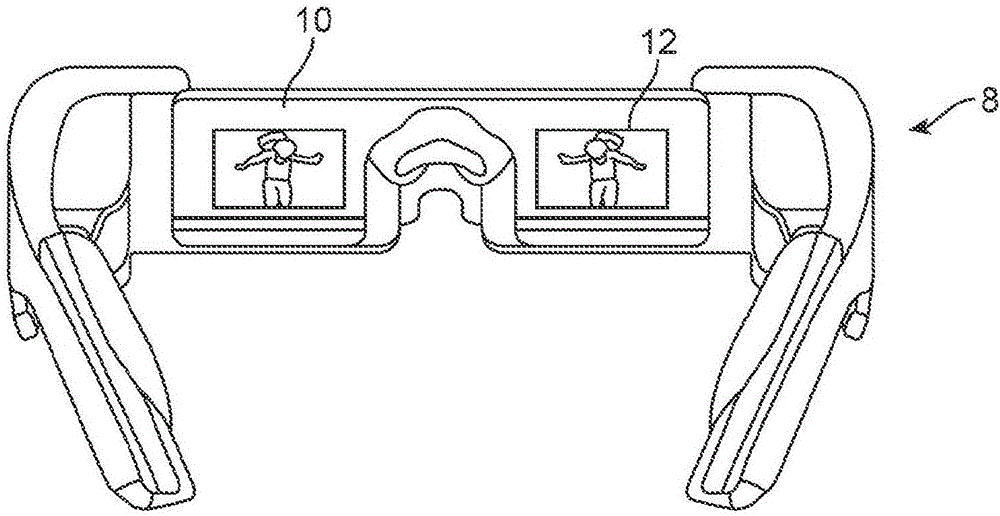
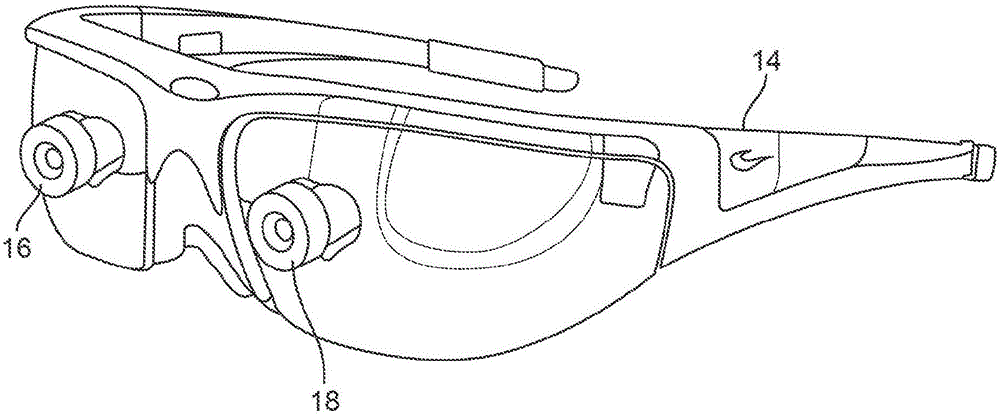
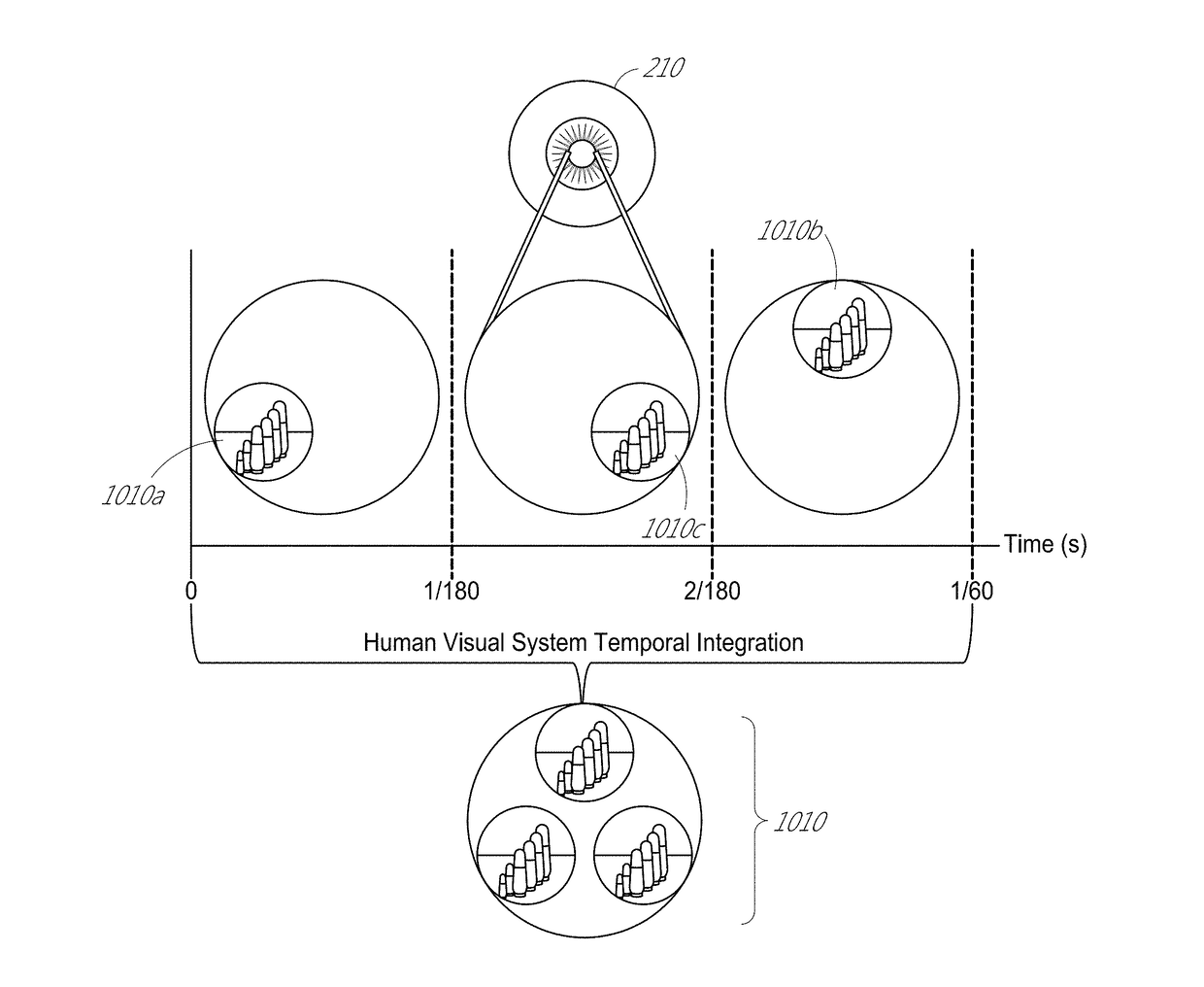
Depth based foveated rendering for display systems
Methods and systems for depth-based foveated rendering in the display system are disclosed. The display system may be an augmented reality display system configured to provide virtual content on a plurality of depth planes using different wavefront divergence. Some embodiments include monitoring eye orientations of a user of a display system based on detected sensor information. A fixation point is determined based on the eye orientations, the fixation point representing a three-dimensional location with respect to a field of view. Location information of virtual objects to present is obtained, with the location information indicating three-dimensional positions of the virtual objects. Resolutions of at least one virtual object is adjusted based on a proximity of the at least one virtual object to the fixation point. The virtual objects are presented to a user by display system with the at least one virtual object being rendered according to the adjusted resolution.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
Compound camera and methods for implementing auto-focus, depth-of-field and high-resolution functions
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
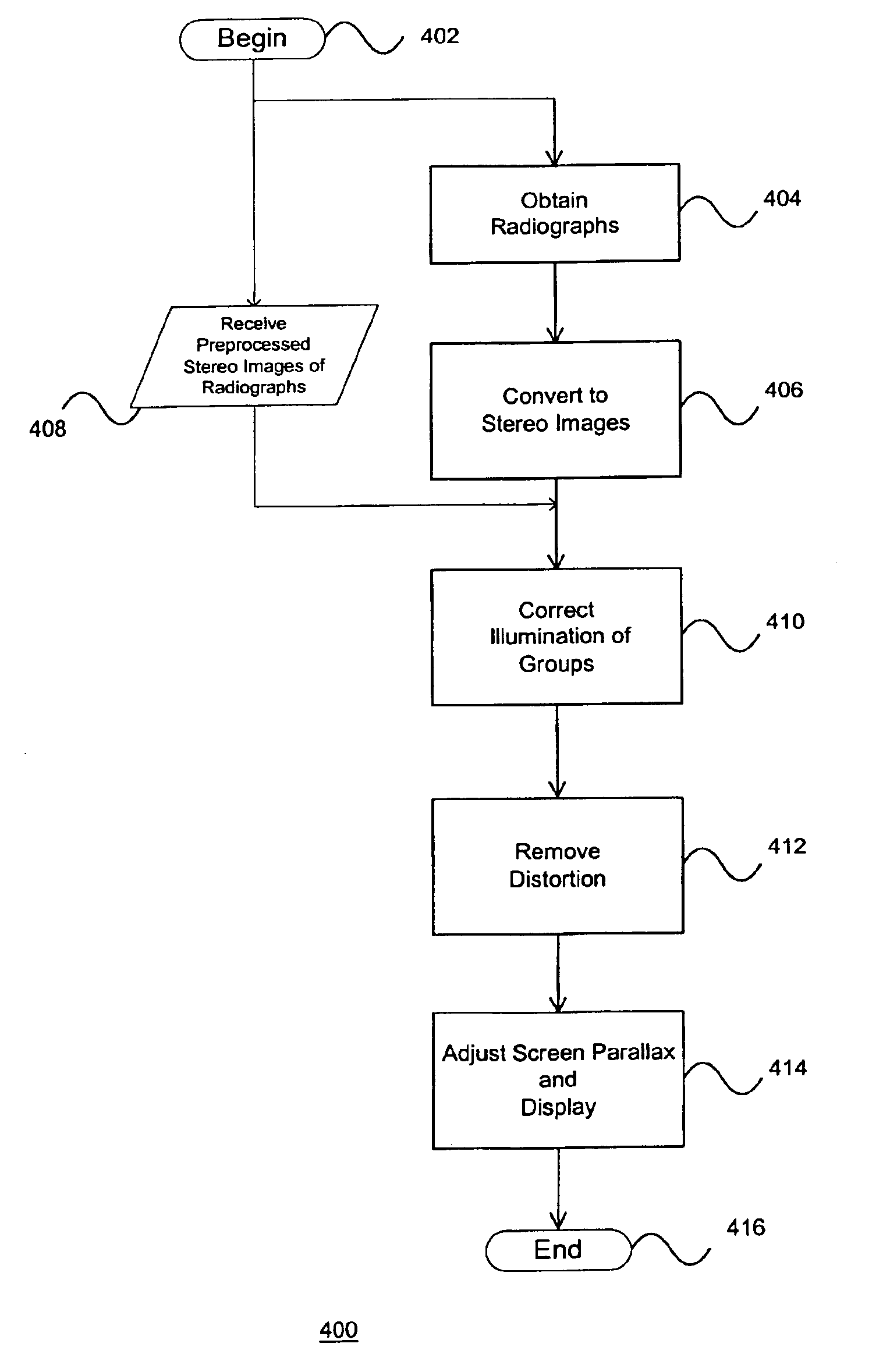
Stereo image processing for radiography
InactiveUS6862364B1Reduce and eliminate illumination errorConvenient lightingImage enhancementImage analysisParallaxX-ray
Pairs of stereo Xray radiographs are obtained from an X-ray imaging system and are digitized to form corresponding pairs of stereo images (602, 604). The pairs of stereo images (602, 604) are adjusted (410) to compensate for gray-scale illumination differences by grouping and processing pixel groups in each pair of images. Distortion in the nature of depth plane curvature and Keystone distortion due to the toed-in configuration of the X-ray imaging system are eliminated (412). A screen parallax for the pair of stereo images is adjusted (414) to minimize depth range so as to enable a maximum number of users to view the stereoscopic image, and particular features of interest.
Owner:CANON KK
Systems and methods for augmented reality
Methods and systems for triggering presentation of virtual content based on sensor information. The display system may be an augmented reality display system configured to provide virtual content on a plurality of depth planes using different wavefront divergences. The system may monitor information detected via the sensors, and based on the monitored information, trigger access to virtual content identified in the sensor information. Virtual content can be obtained, and presented as augmented reality content via the display system. The system may monitor information detected via the sensors to identify a QR code, or a presence of a wireless beacon. The QR code or wireless beacon can trigger the display system to obtain virtual content for presentation.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
Method for the microscopic three-dimensional reproduction of a sample
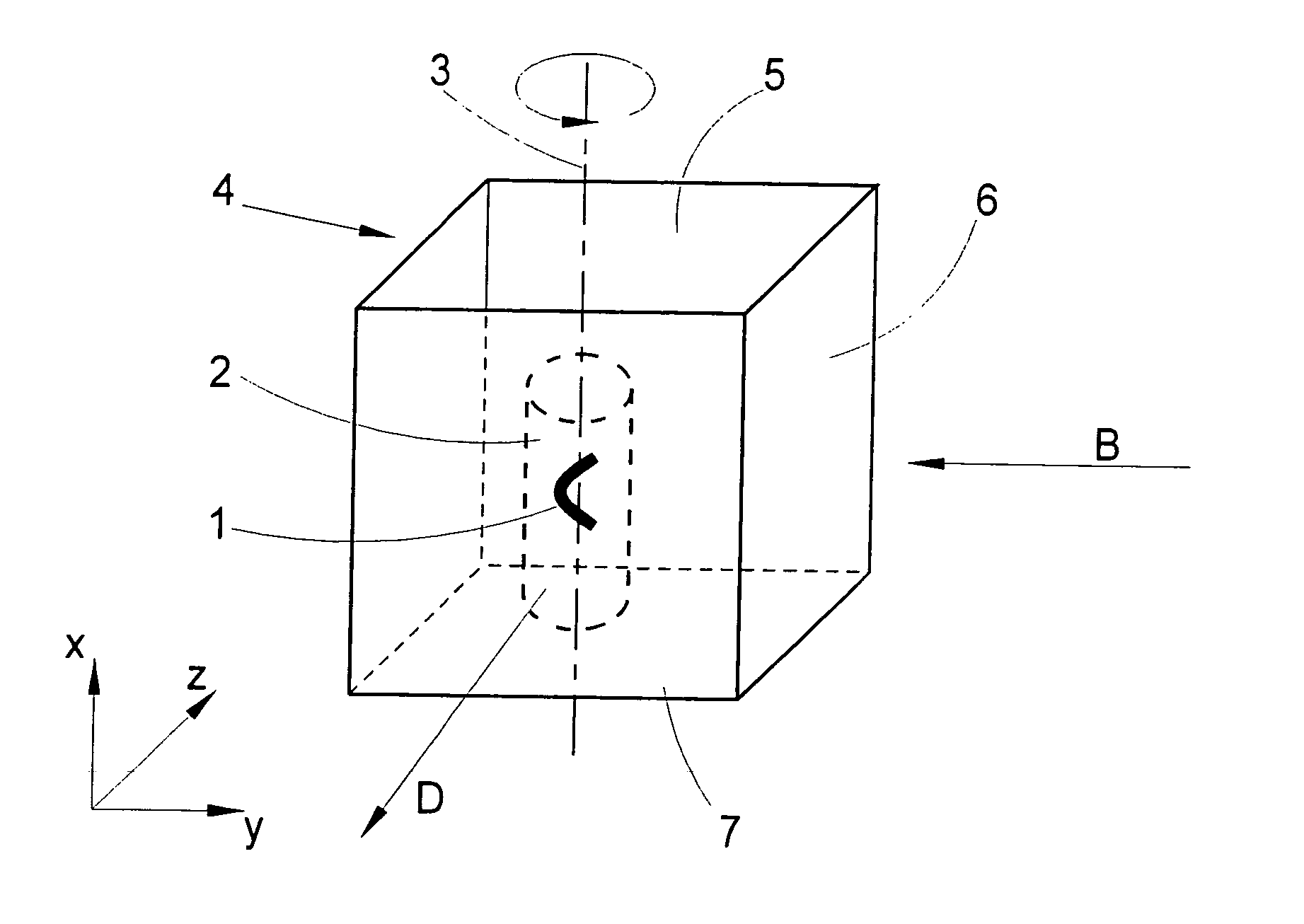
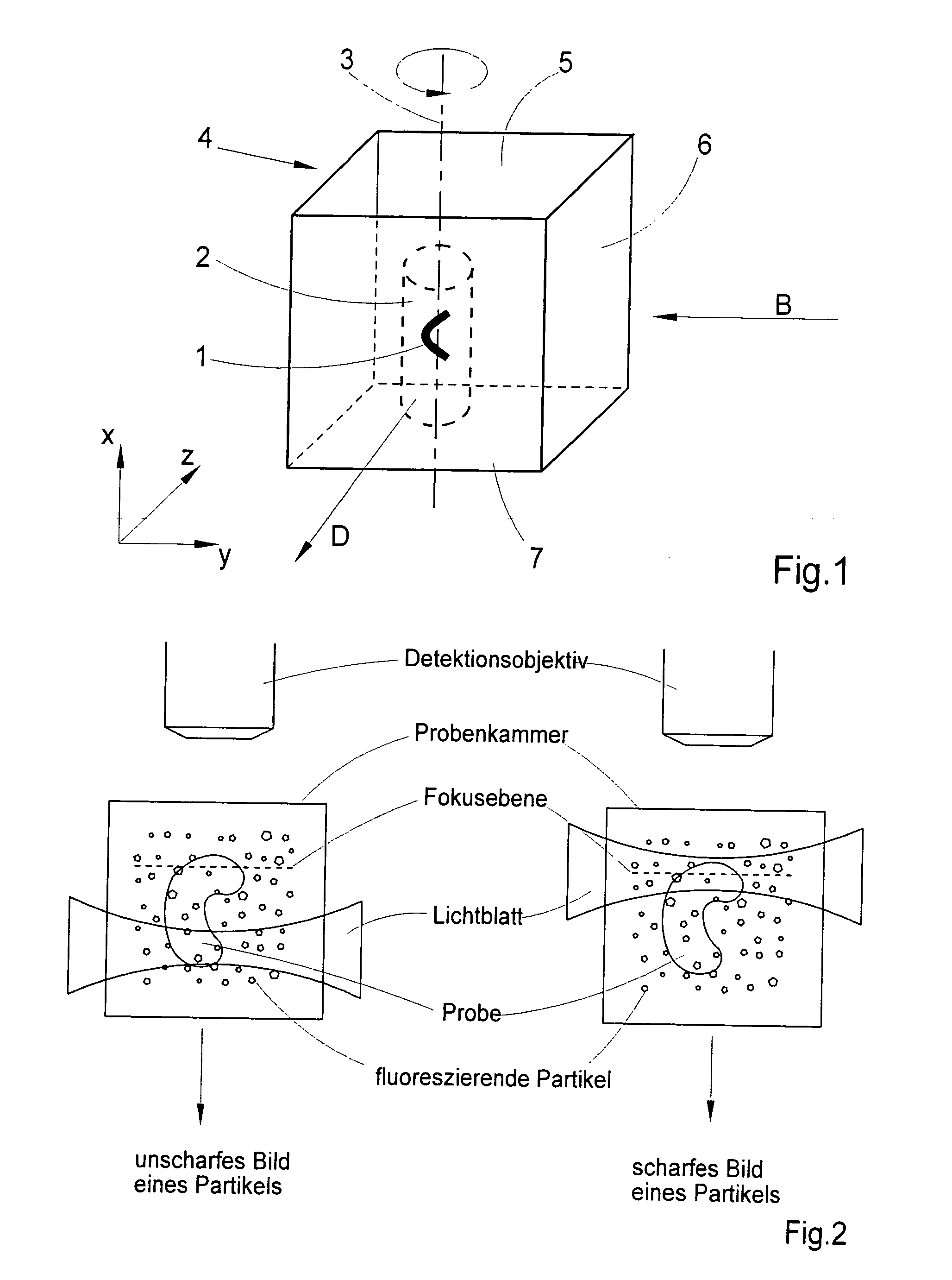
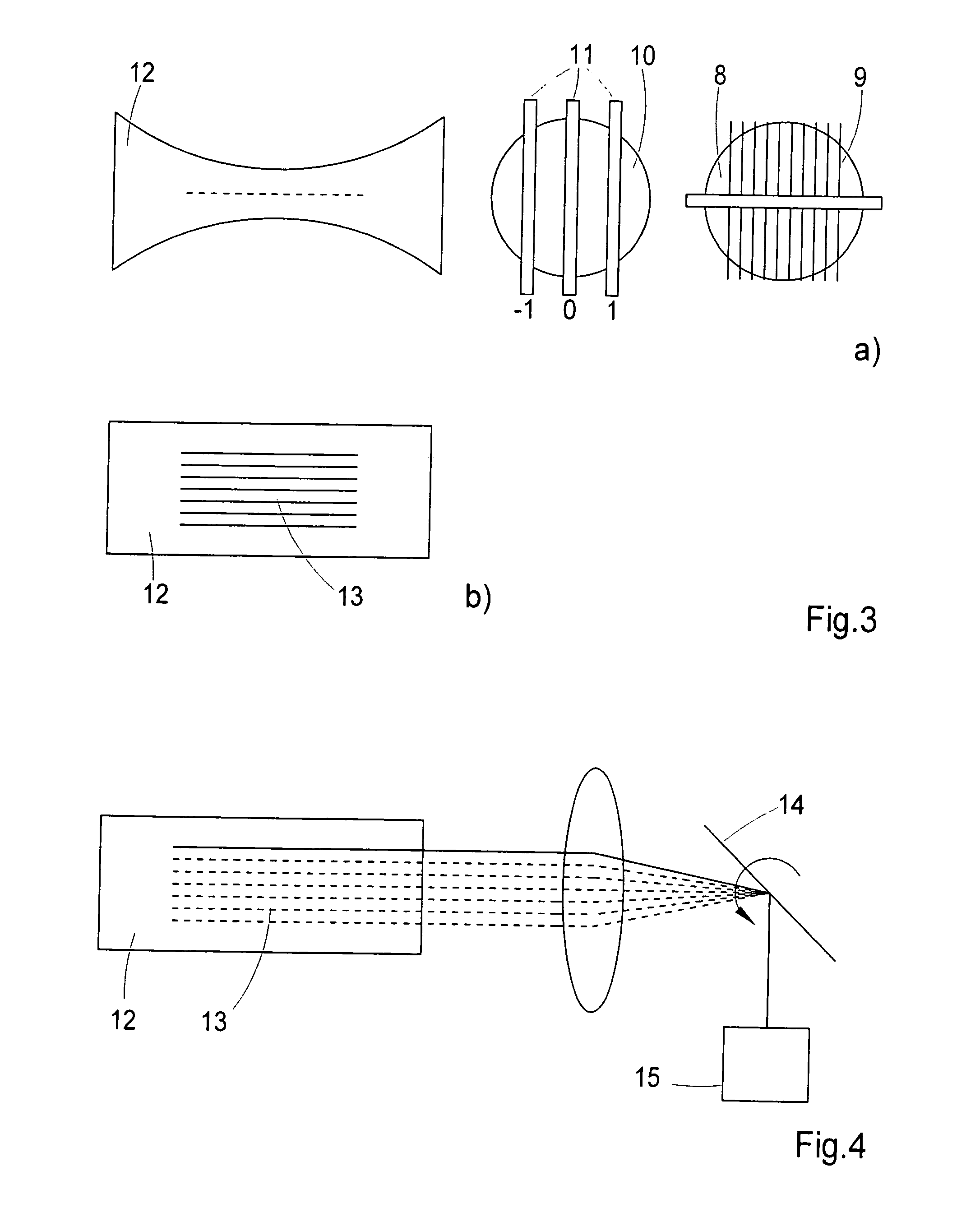
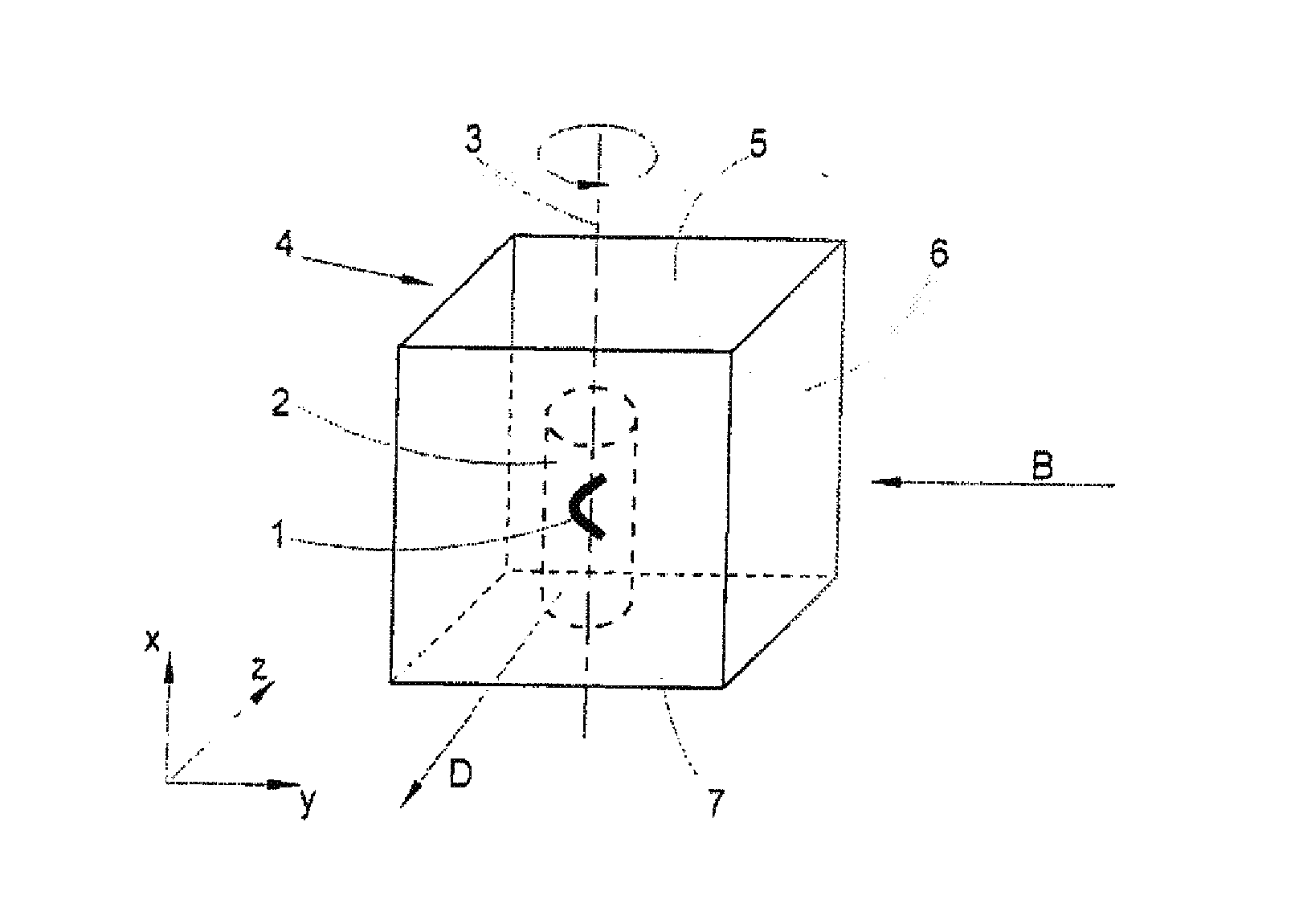
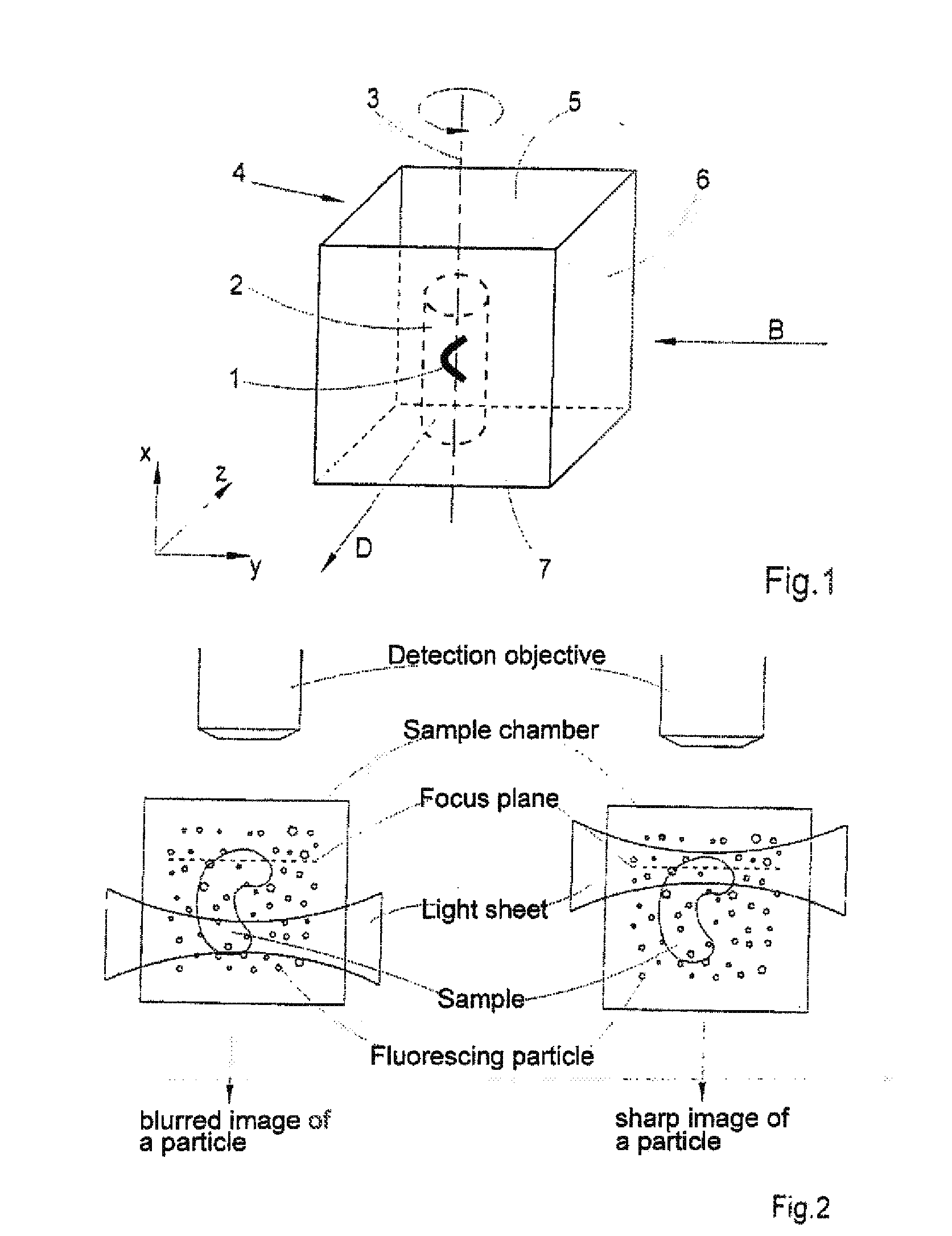
InactiveUS20100201784A1Avoid shadow effectMore resolutionImage analysisMicroscopesSpatially resolvedFluorescence
A method for the three-dimensional imaging of a sample in which image information from different depth planes of the sample is stored in a spatially resolved manner, and the three-dimensional image of the sample is subsequently reconstructed from this stored image information is provided. A reference structure is applied to the illumination light, at least one fluorescing reference object is positioned next to or in the sample, images of the reference structure of the illumination light, of the reference object are recorded from at least one detection direction and evaluated. The light sheet is brought into an optimal position based on the results and image information of the reference object and of the sample from a plurality of detection directions is stored. Transformation operators are obtained on the basis of the stored image information and the reconstruction of the three-dimensional image of the is based on these transformation operators.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Virtual and augmented reality systems and methods
ActiveUS20170276948A1Mechanical apparatusPicture reproducers using projection devicesDepth planeAugmented reality systems
Methods and systems are disclosed for presenting virtual objects on a limited number of depth planes using, e.g., an augmented reality display system. A farthest one of the depth planes is within a mismatch tolerance of optical infinity. The display system may switch the depth plane on which content is actively displayed, so that the content is displayed on the depth plane on which a user is fixating. The impact of errors in fixation tracking is addressed using partially overlapping depth planes. A fixation depth at which a user is fixating is determined and the display system determines whether to adjust selection of a selected depth plane at which a virtual object is presented. The determination may be based on whether the fixation depth falls within a depth overlap region of adjacent depth planes. The display system may switch the active depth plane depending upon whether the fixation depth falls outside the overlap region.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
Dual depth exit pupil expander
An optical device includes a waveguide including an in-coupling optical element configured to in-couple light into the waveguide, a light distributing element configured to receive light from the in-coupling optical element and distribute light at a selected wavelength, and an out-coupling optical element configured to receive light from the light distributing element and out-couple light out of the waveguide. The out-coupling optical element includes a first region configured to out-couple light at a first depth plane based on a lens function of the first region and a second region configured to out-couple light at a second depth plane based on a different lens function of the second region.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
Depth based foveated rendering for display systems
ActiveUS20190287495A1Change in amountInput/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementFixation pointWavefront
Methods and systems for depth-based foveated rendering in the display system are disclosed. The display system may be an augmented reality display system configured to provide virtual content on a plurality of depth planes using different wavefront divergence. Some embodiments include determining a fixation point of a user's eyes. Location information associated with a first virtual object to be presented to the user via a display device is obtained. A resolution-modifying parameter of the first virtual object is obtained. A particular resolution at which to render the first virtual object is identified based on the location information and the resolution-modifying parameter of the first virtual object. The particular resolution is based on a resolution distribution specifying resolutions for corresponding distances from the fixation point. The first virtual object rendered at the identified resolution is presented to the user via the display system.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
Gaze-contingent Display Technique
ActiveUS20160191910A1Increase speedImprove viewing experienceSteroscopic systemsInput/output processes for data processingProgram instructionSpatial perception
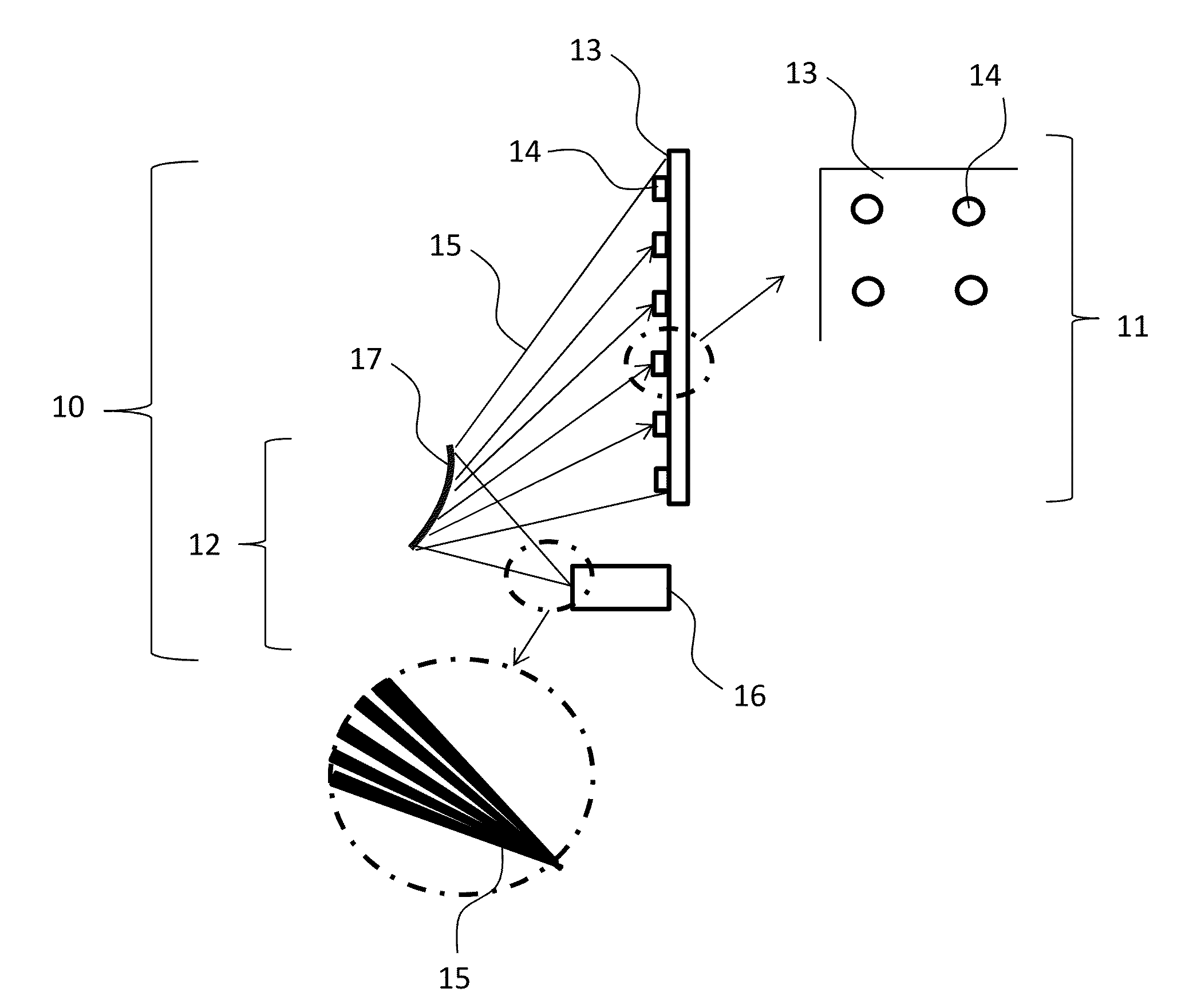
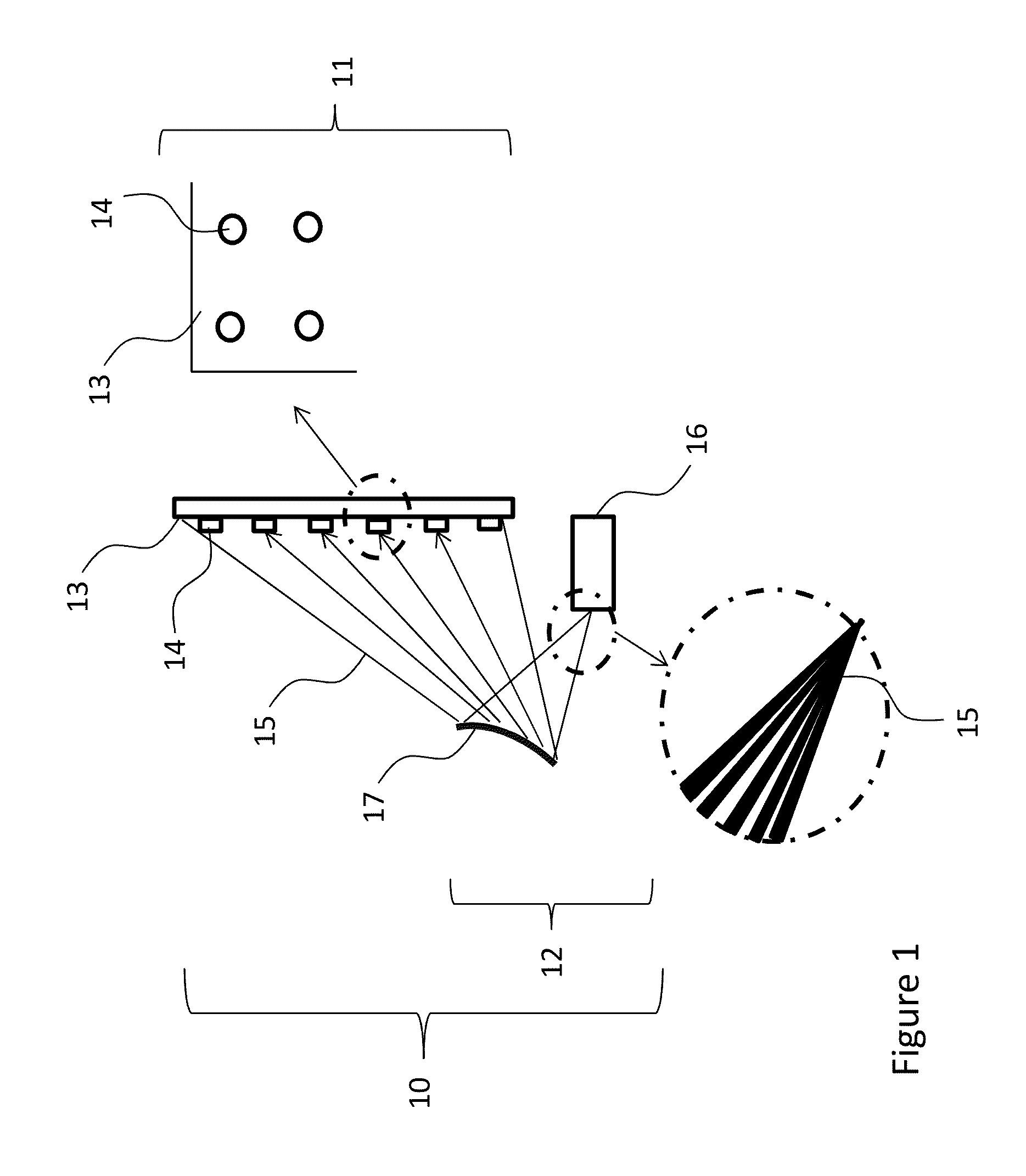
A gaze contingent display technique for providing a human viewer with an enhanced three-dimensional experience not requiring stereoscopic viewing aids. Methods are shown which allow users to view plenoptic still images or plenoptic videos incorporating gaze-contingent refocusing operations in order to enhance spatial perception. Methods are also shown which allow the use of embedded markers in a plenoptic video feed signifying a change of scene incorporating initial depth plane settings for each such scene. Methods are also introduced which allow a novel mode of transitioning between different depth planes wherein the user's experience is optimized in such a way that these transitions trick the human eye into perceiving enhanced depth. This disclosure also introduces a system of a display device which comprises gaze-contingent refocusing capability in such a way that depth perception by the user is significantly enhanced compared to prior art. This disclosure comprises a nontransitory computer-readable medium on which are stored program instructions that, when executed by a processor, cause the processor to perform operations relating to timing the duration the user's gaze is fixated on each of a plurality of depth planes and making a refocusing operation contingent of a number of parameters.
Owner:VON & ZU LIECHTENSTEIN MAXIMILIAN RALPH PETER
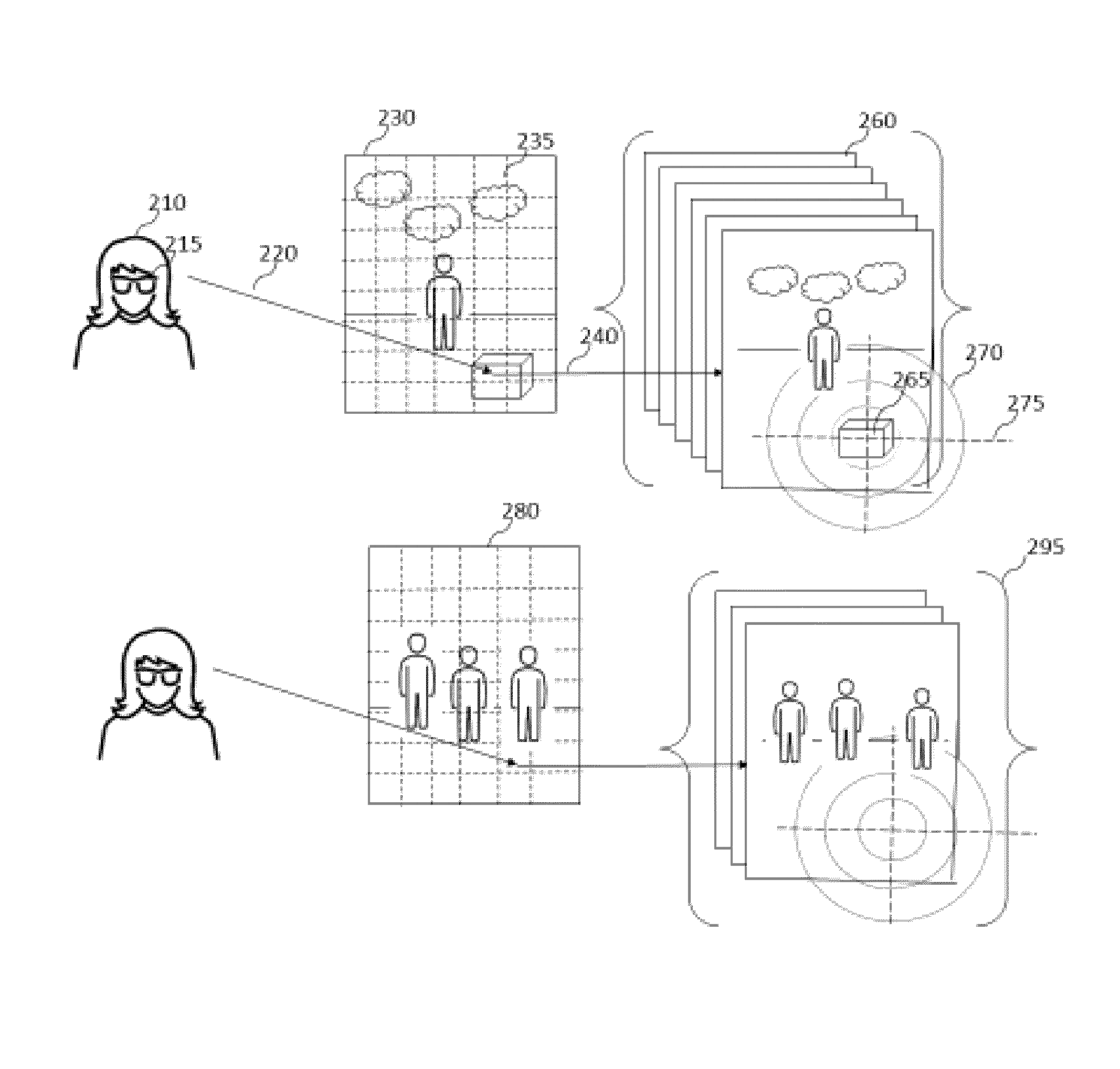
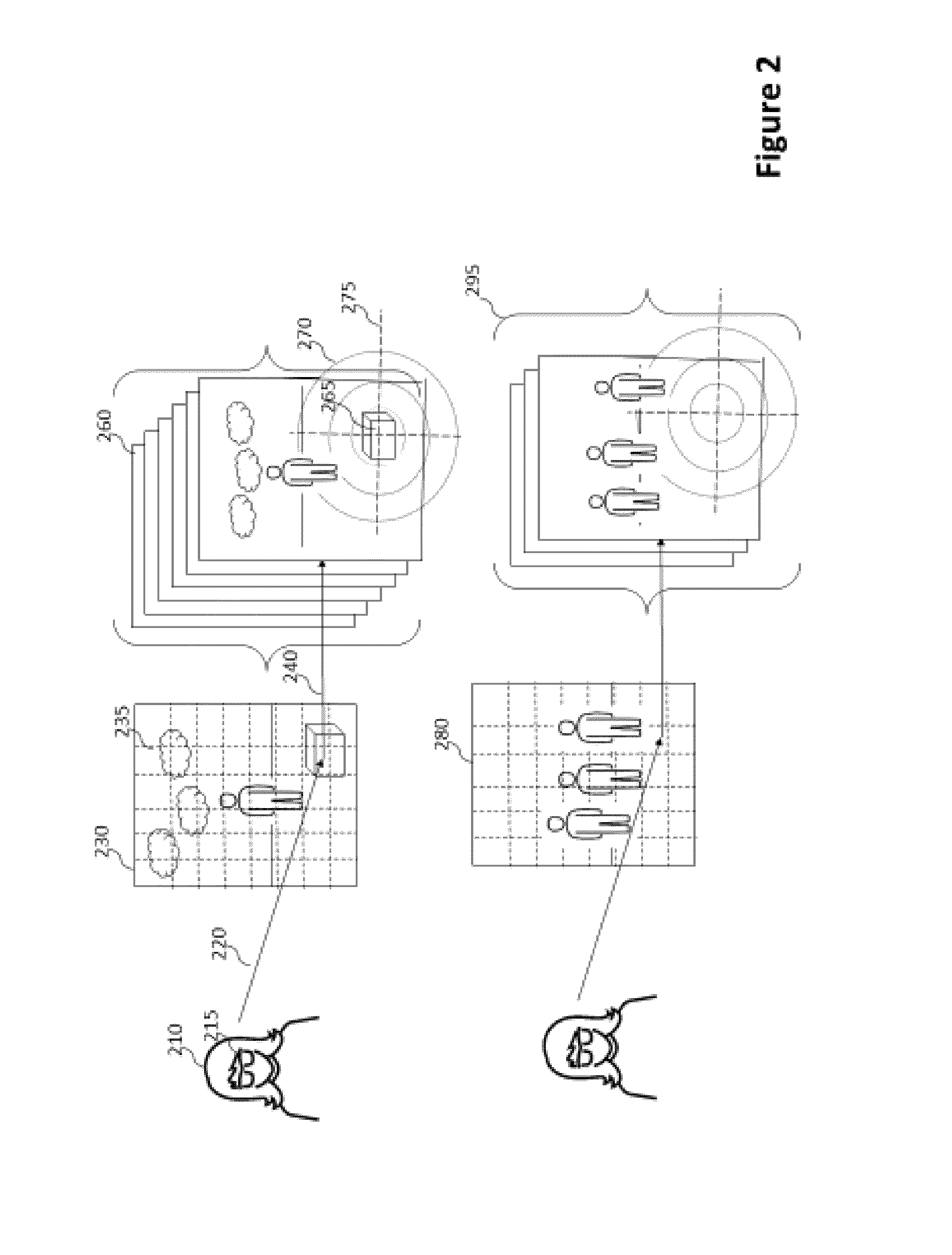
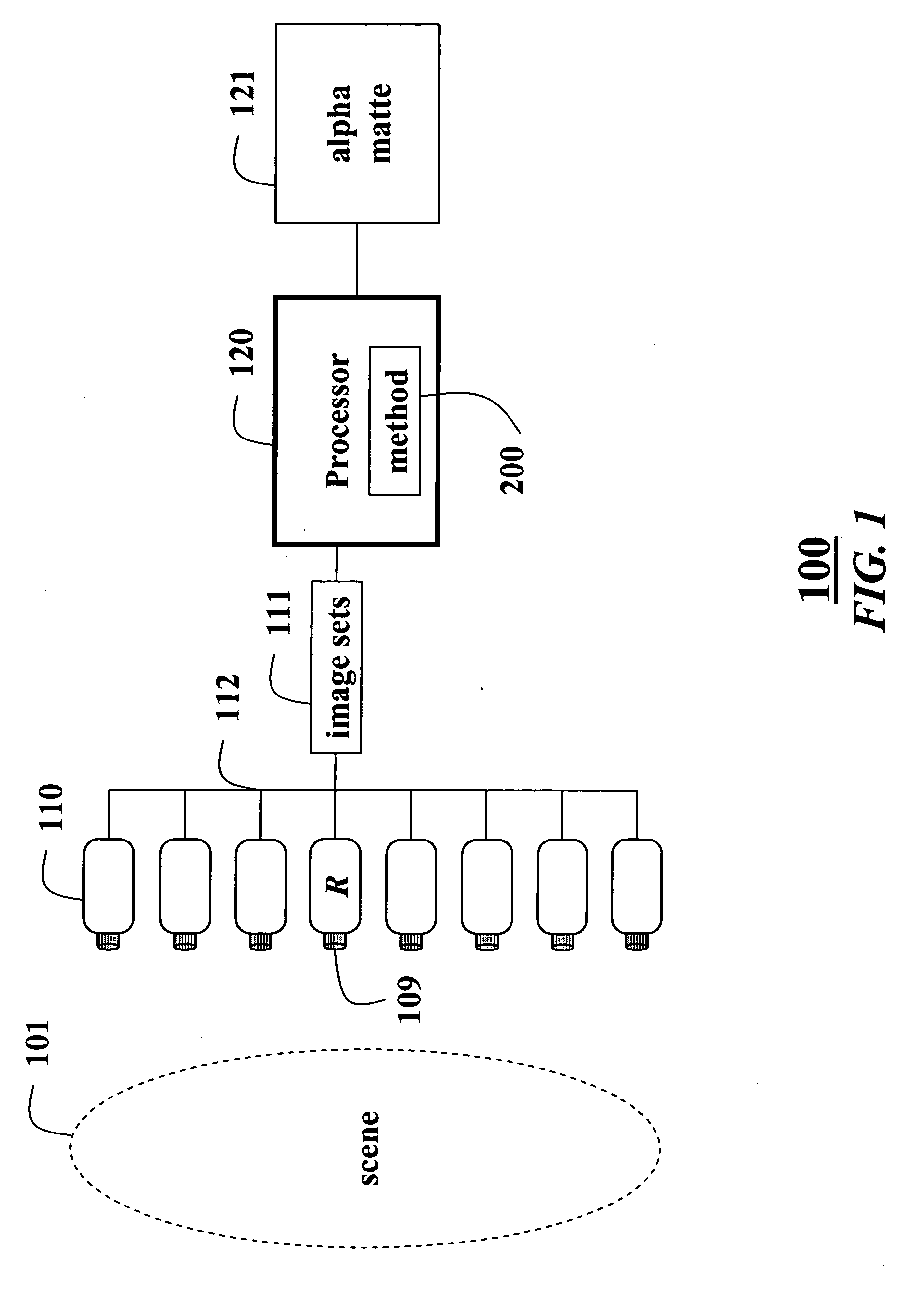
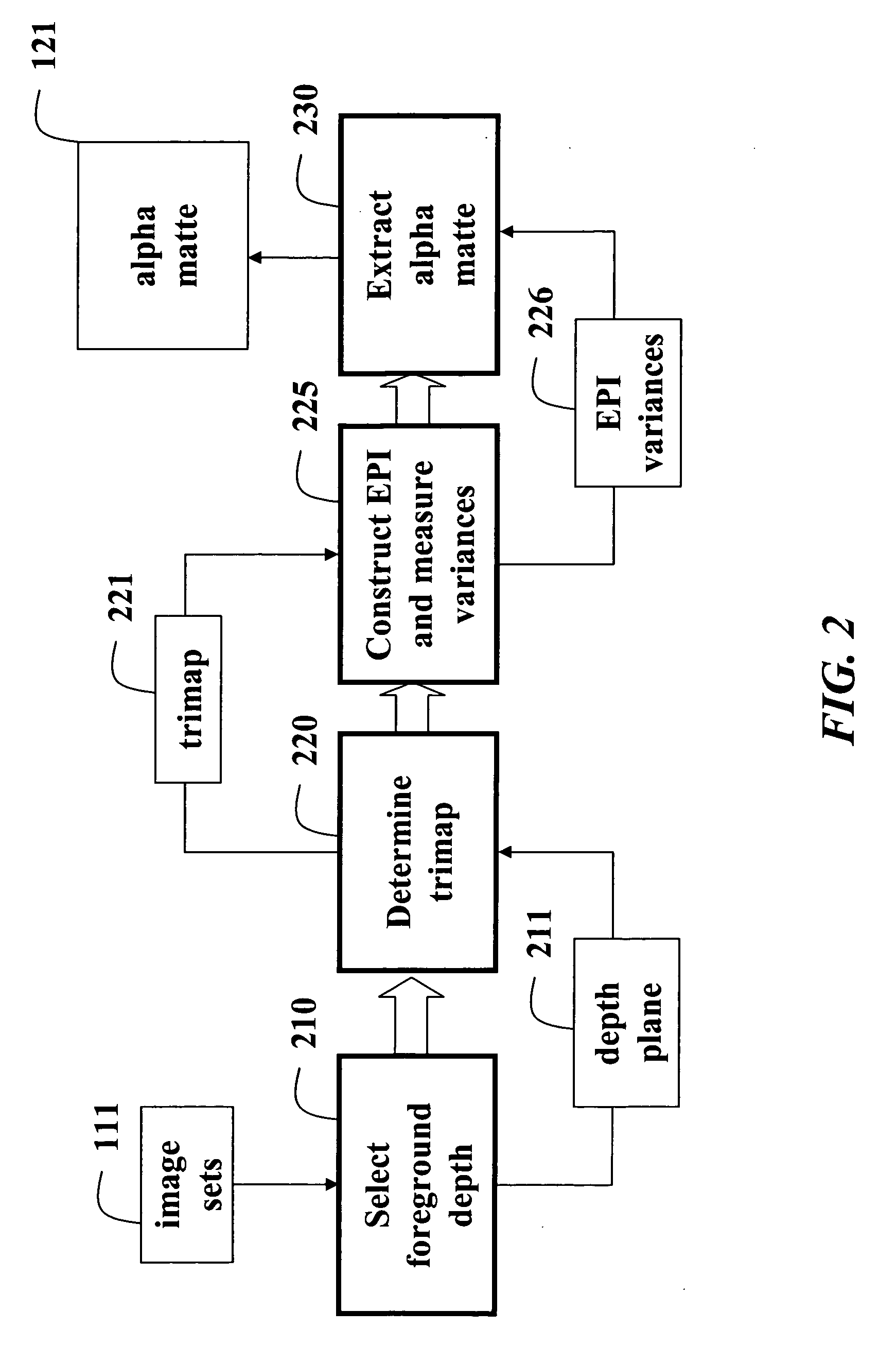
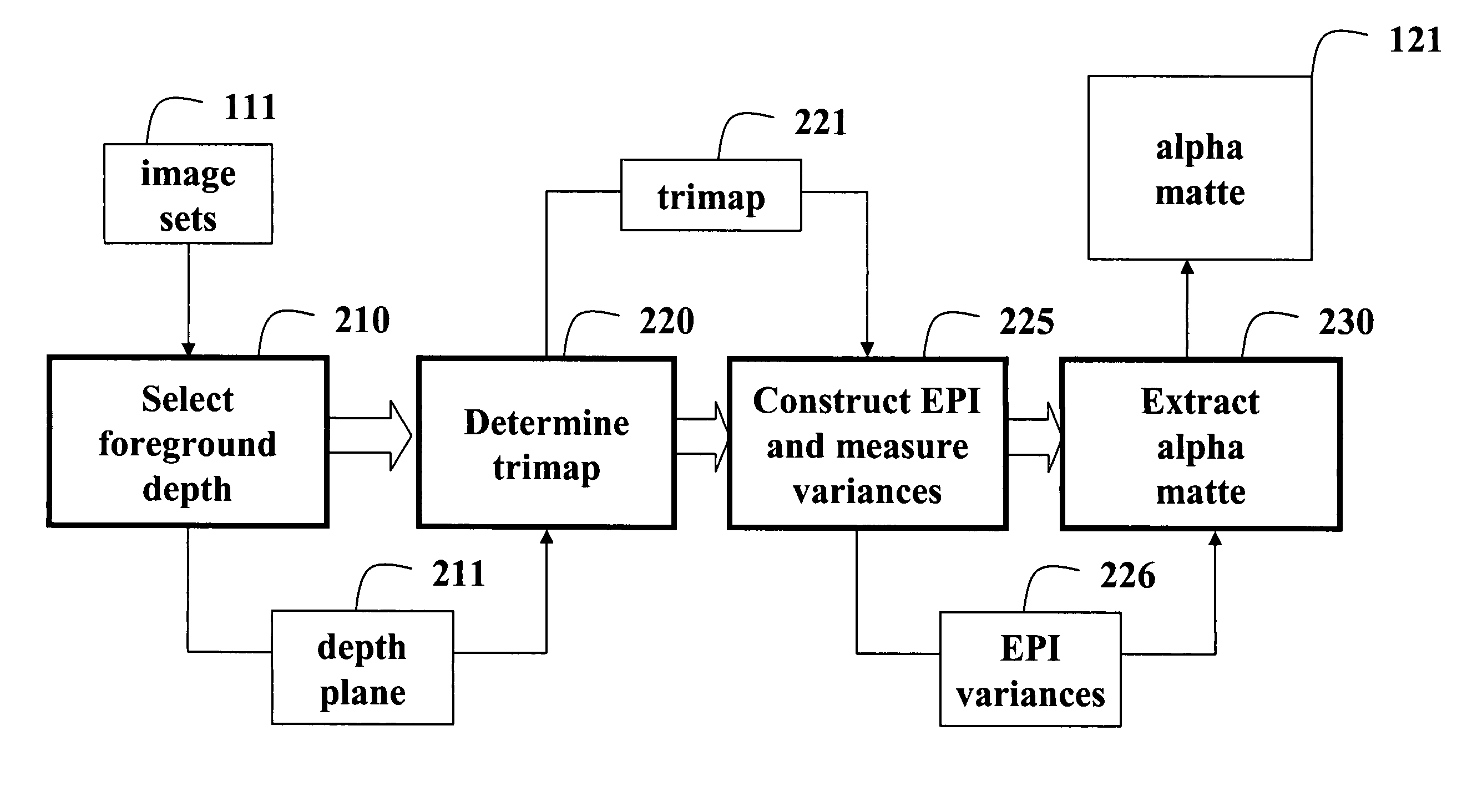
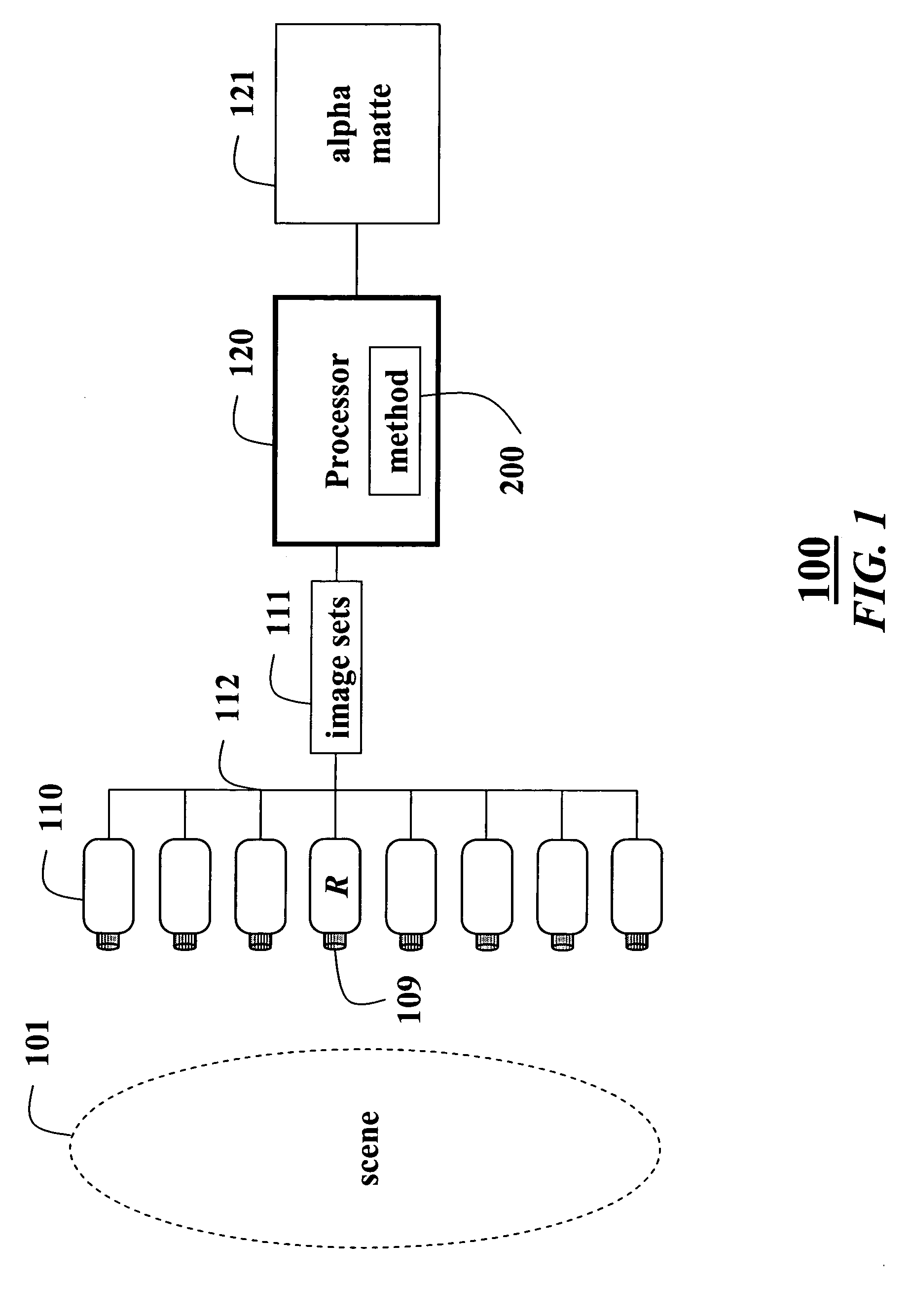
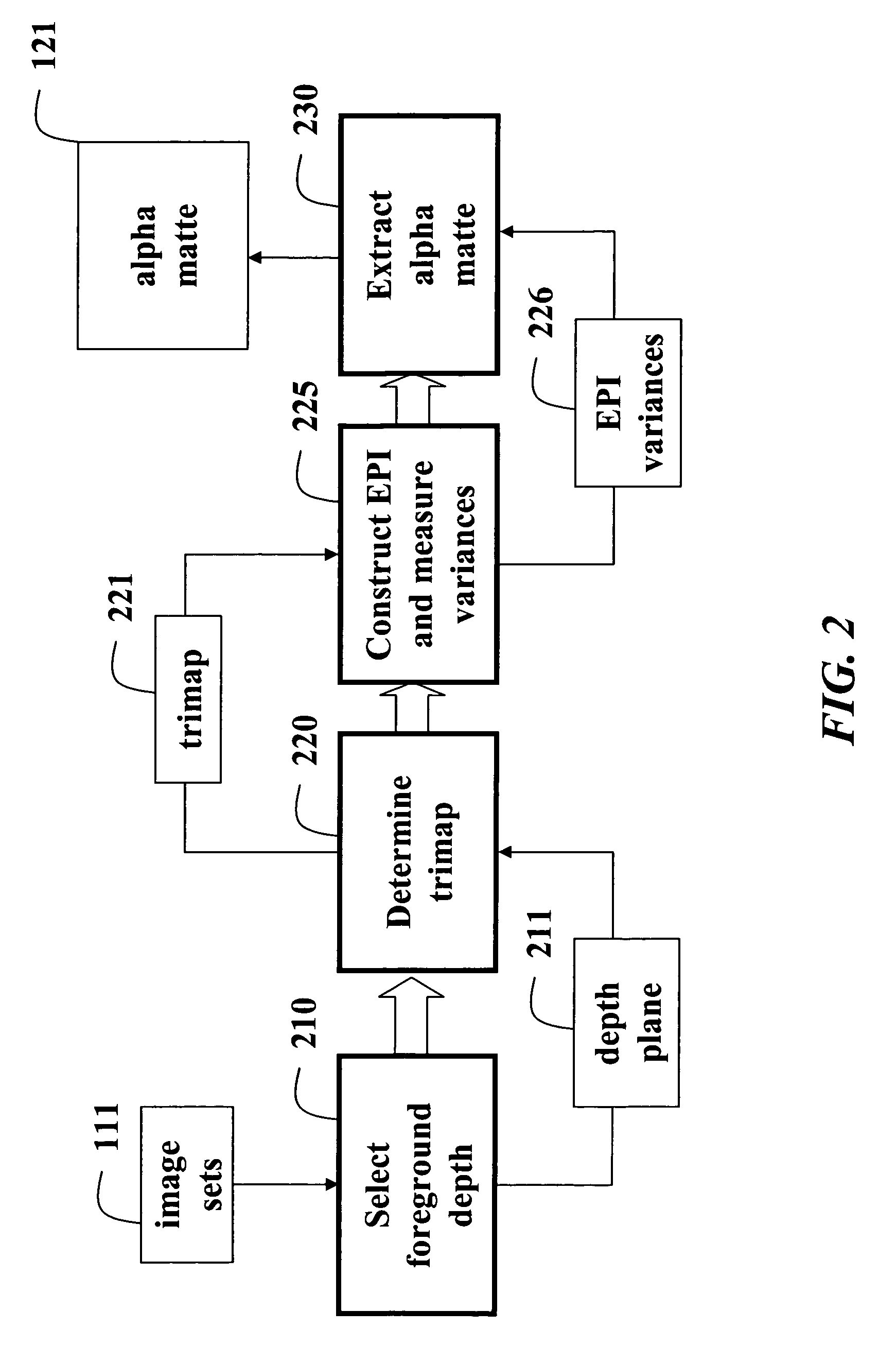
Matting using camera arrays
InactiveUS20070070226A1Quality improvementTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsScan lineDepth plane
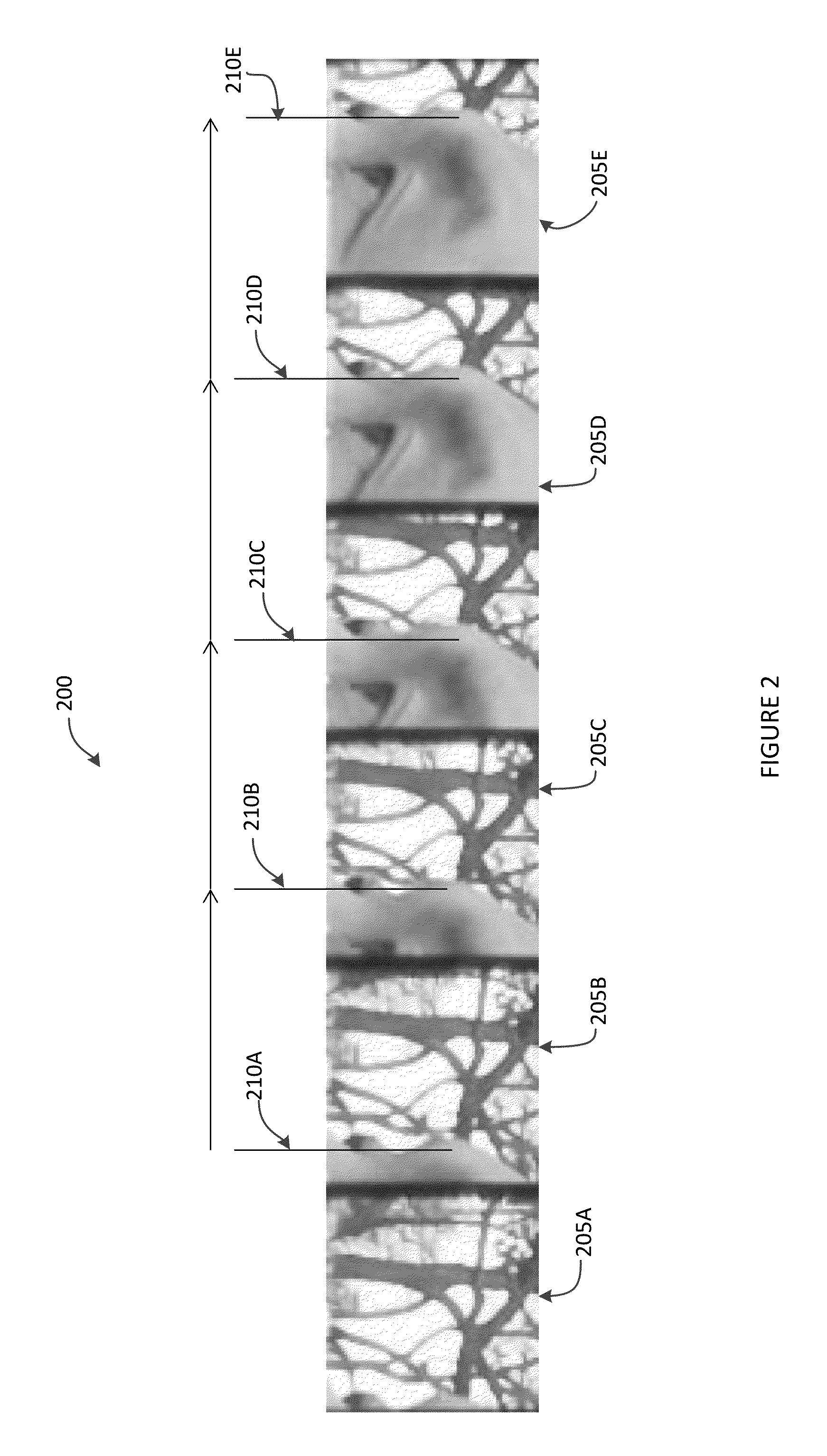
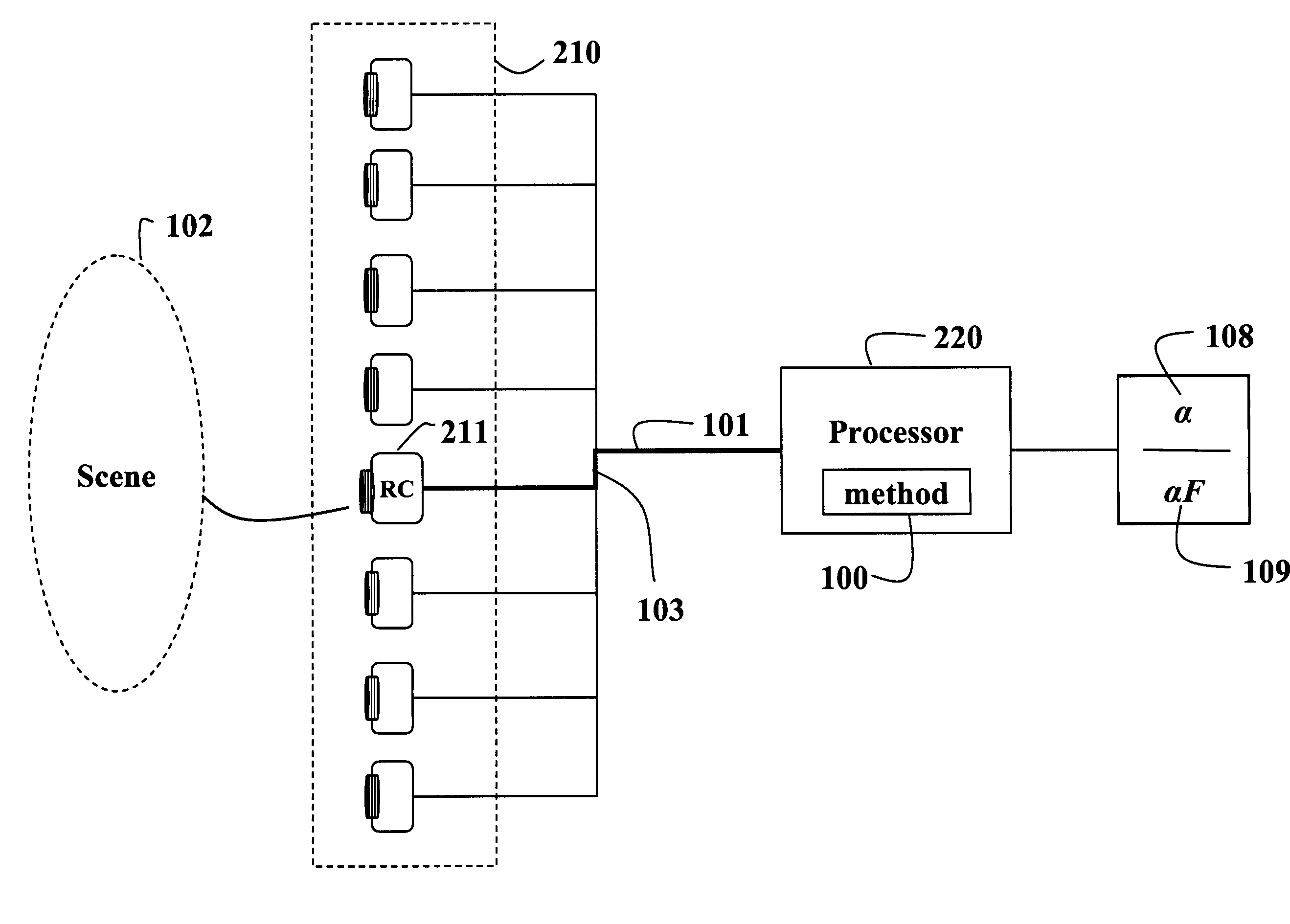
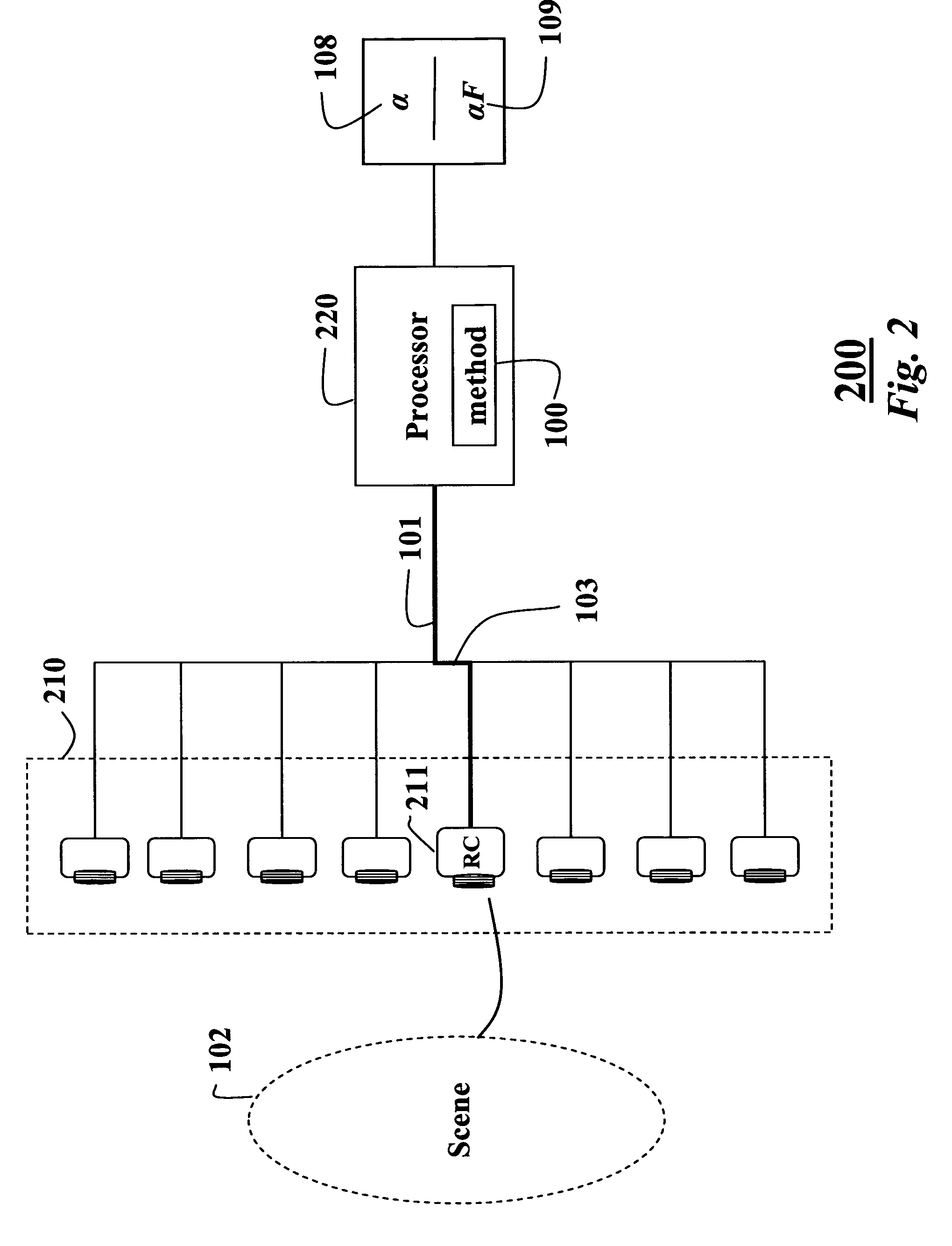
A method extracts an alpha matte from images acquired of a scene by cameras. A depth plane is selected for a foreground in the scene. A trimap is determined from a set of images acquired of the scene. An epipolar plane image is constructed from the set of images and the trimap, the epipolar plane image including scan lines. Variances of intensities are measured along the scan lines in the epipolar image, and an alpha matte is extracted according to the variances.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Virtual and augmented reality systems and methods
ActiveUS20170053450A1Reduce power consumptionReduce redundant informationImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionDisplay deviceDepth plane
A virtual or augmented reality display system that controls a display using control information included with the virtual or augmented reality imagery that is intended to be shown on the display. The control information can be used to specify one of multiple possible display depth planes. The control information can also specify pixel shifts within a given depth plane or between depth planes. The system can also enhance head pose measurements from a sensor by using gain factors which vary based upon the user's head pose position within a physiological range of movement.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
Augmented reality display having multi-element adaptive lens for changing depth planes
In some embodiments, an augmented reality system includes at least one waveguide that is configured to receive and redirect light toward a user, and is further configured to allow ambient light from an environment of the user to pass therethrough toward the user. The augmented reality system also includes a first adaptive lens assembly positioned between the at least one waveguide and the environment, a second adaptive lens assembly positioned between the at least one waveguide and the user, and at least one processor operatively coupled to the first and second adaptive lens assemblies. Each lens assembly of the augmented reality system is selectively switchable between at least two different states in which the respective lens assembly is configured to impart at least two different optical powers to light passing therethrough, respectively. The at least one processor is configured to cause the first and second adaptive lens assemblies to synchronously switch between different states in a manner such that the first and second adaptive lens assemblies impart a substantially constant net optical power to ambient light from the environment passing therethrough.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
Transparent display including a screen with patterned light deflective elements
ActiveUS20160124295A1Limit reliability and lifetimeEasy to scaleBuilt-on/built-in screen projectorsAdvertisingOptical powerDisplay device
A transparent display device includes a screen that has a plurality of light deflecting elements that are separated by transparent areas, and a projector device. The projector device is configured to direct light onto the light deflecting elements and not onto the transparent areas. The display device may include a first screen and a second screen separated longitudinally relative to the projector, wherein each screen respectively has a plurality of light deflecting elements. The projector is configured to direct light onto the light deflecting elements and not onto the transparent areas of the two screens such that light from the first and second light deflecting elements appear in different virtual depth planes. Alternatively, a single screen may have first and second pluralities of light deflecting elements of different optical powers, such that light from the first and second light deflecting elements appear in different virtual depth planes.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method and apparatus for generating plenoptic depth maps
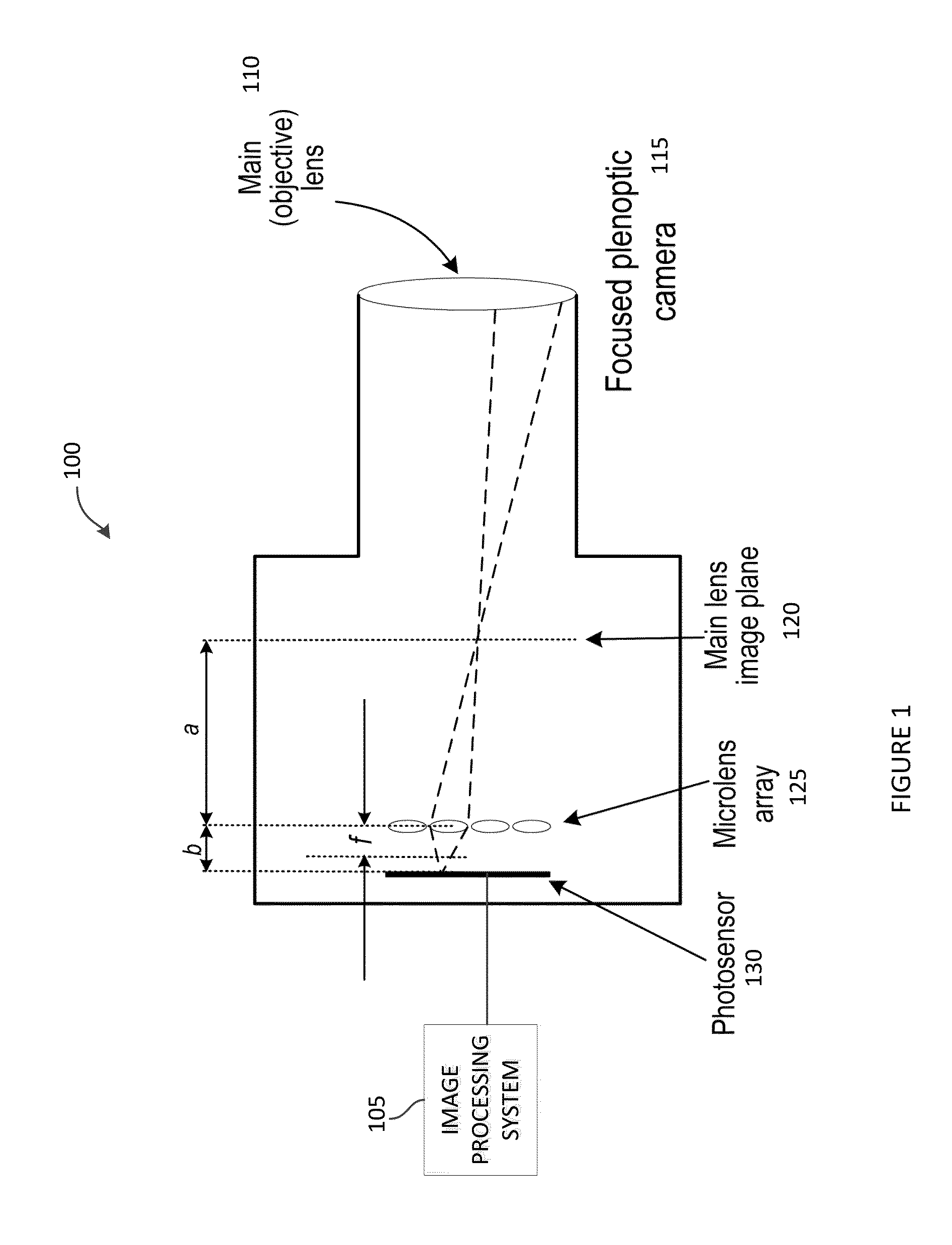
Described is systems and methods for determining the depth of pixels captured in a plenoptic image. The systems and methods may provide a plurality of views of each pixel location in the plenoptic image. One way of providing the plurality of views is to obtaining pixel intensities from the views for each pixel location in the plenoptic image. A variance can then be calculated of the distribution of pixel intensities for each pixel position. If the variance is below a predetermined threshold, the systems may mask out at least one depth plane and then recalculate the variance in the distribution of pixel intensities to determine if the variance is below the threshold.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Video matting using camera arrays
InactiveUS7420590B2Reduce varianceAdditional varianceTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionDepth planeAlpha matting
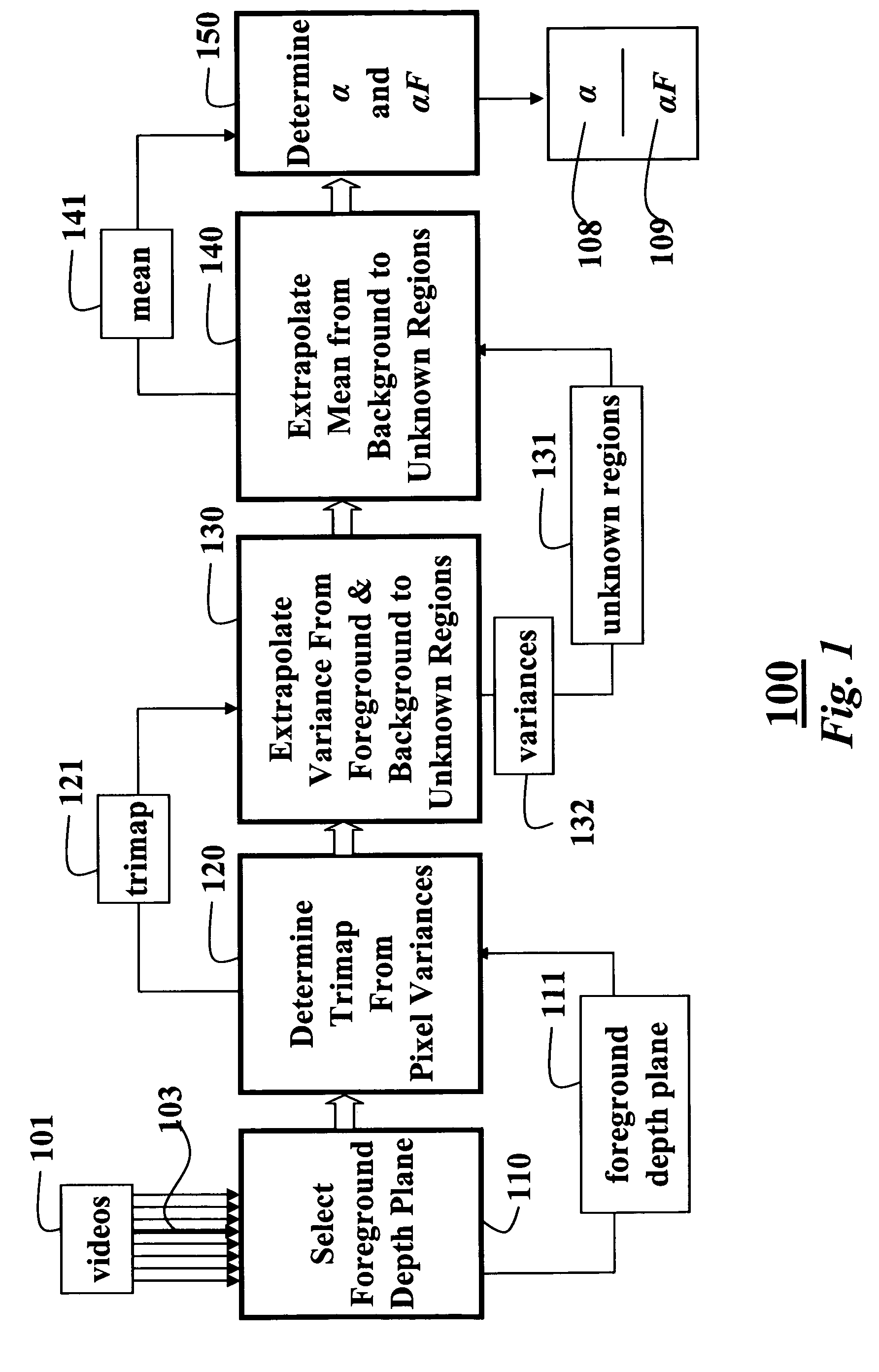
A method and system for determining an alpha matte for a video is presented. A set of videos is acquired by an array of cameras. A centrally located camera in the array is designated as a reference camera and acquires a reference video. A foreground depth plane is selected from the set of videos. A trimap is determined from variances of pixel intensities in each image. Variances of the intensities of pixels labeled as background and pixels labeled as foreground are extrapolated to the pixels labeled as unknown in the trimap. Means of the intensities of the pixels labeled as background are extrapolated to the pixels labeled as unknown to determine an alpha matte for the reference video.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Method for the microscopic three-dimensional reproduction of a sample
ActiveUS20130094755A1Improve image qualityLess subjectImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionSpatially resolvedFluorescence
A method for the three-dimensional imaging of a sample in which image information from different depth planes of the sample is stored in a spatially resolved manner, and the three-dimensional image of the sample is subsequently reconstructed from this stored image information is provided. A reference structure is applied to the illumination light, at least one fluorescing reference object is positioned next to or in the sample, images of the reference structure of the illumination light, of the reference object are recorded from at least one detection direction and evaluated. The light sheet is brought into an optimal position based on the results and image information of the reference object and of the sample from a plurality of detection directions is stored. Transformation operators are obtained on the basis of the stored image information and the reconstruction of the three-dimensional image of the is based on these transformation operators.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Matting using camera arrays
A method extracts an alpha matte from images acquired of a scene by cameras. A depth plane is selected for a foreground in the scene. A trimap is determined from a set of images acquired of the scene. An epipolar plane image is constructed from the set of images and the trimap, the epipolar plane image including scan lines. Variances of intensities are measured along the scan lines in the epipolar image, and an alpha matte is extracted according to the variances.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Systems and methods for operating a display system based on user perceptibility
Systems and methods are disclosed for operating a head-mounted display system based on user perceptibility. The display system may be an augmented reality display system configured to provide virtual content on a plurality of depth planes by presenting the content with different amounts of wavefront divergence. Some embodiments include obtaining an image captured by an imaging device of the display system. Whether a threshold measure or more of motion blur is determined to be exhibited in one or more regions of the image. Based on a determination that the threshold measure or more of motion blur is exhibited in one or more regions of the image, one or more operating parameters of the wearable display are adjusted. Example operating parameter adjustments comprise adjusting the depth plane on which content is presented (e.g., by switching from a first depth plane to a second depth plane), adjusting a rendering quality, and adjusting power characteristics of the system.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
Augmented reality display comprising eyepiece having a transparent emissive display
PendingUS20190107719A1Reduce the effect of refractionStatic indicating devicesImage data processingEyepieceDisplay device
An augmented reality head mounted display system an eyepiece having a transparent emissive display. The eyepiece and transparent emissive display are positioned in an optical path of a user's eye in order to transmit light into the user's eye to form images. Due to the transparent nature of the display, the user can see an outside environment through the transparent emissive display. The transmissive emissive display comprising a plurality of emitters configured to emit light into the eye of the user. A first variable focus optical element is positioned between the transparent emissive display and the user's eye and is configured to modify emitted light to provide the appropriate amount of divergence for image information to be interpreted by the user as being on a particular depth plane. A second variable focus optical element is positioned between the transparent emissive display and the environment and is configured to offset effects of the first variable focus optical element on the view of the environment.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
Methods and system for creating focal planes in virtual and augmented reality
Configurations are disclosed for presenting virtual reality and augmented reality experiences to users. The system may comprise a spatial light modulator operatively coupled to an image source for projecting light associated with one or more frames of image data, and a variable focus element (VFE) for varying a focus of the projected light such that a first frame of image data is focused at a first depth plane, and a second frame of image data is focused at a second depth plane, and wherein a distance between the first depth plane and the second depth plane is fixed.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
System and method for presenting image content on multiple depth planes by providing multiple intra-pupil parallax views
ActiveUS20180113311A1Change in positionImage data processingSteroscopic systemsParallaxOphthalmology
An augmented reality display system is configured to direct a plurality of parallactically-disparate intra-pupil images into a viewer's eye. The parallactically-disparate intra-pupil images provide different parallax views of a virtual object, and impinge on the pupil from different angles. In the aggregate, the wavefronts of light forming the images approximate a continuous divergent wavefront and provide selectable accommodation cues for the user, depending on the amount of parallax disparity between the intra-pupil images. The amount of parallax disparity is selected using a light source that outputs light for different images from different locations, with spatial differences in the locations of the light output providing differences in the paths that the light takes to the eye, which in turn provide different amounts of parallax disparity. Advantageously, the wavefront divergence, and the accommodation cue provided to the eye of the user, may be varied by appropriate selection of parallax disparity, which may be set by selecting the amount of spatial separation between the locations of light output.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
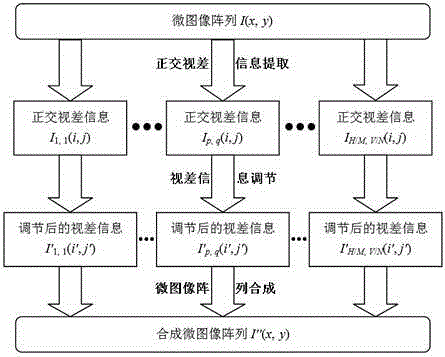
Integral imaging three-dimensional display center depth plane adjusting method
ActiveCN104954779AIncrease profitReduce shooting costsSteroscopic systemsParallaxThree dimensionality
The invention provides an integral imaging three-dimensional display center depth plane adjusting method. According to the method, a micro image array with a center depth plane z0 is acquired through integral imaging shooting, integral imaging three-dimensional display of a center depth plane z1 is realized, and z0 is not equal to z1. The method comprises three processes, namely, extraction of orthogonal parallax information, adjustment of parallax information and synthesis of the micro image array. Integral imaging three-dimensional display of different center depth planes can be realized without reshooting of three-dimensional scenes, so that the utilization rate of three-dimensional information is increased, and the shooting cost is saved.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Stereoscopic display device and display method thereof
InactiveCN107357047AOptical path changeNon-linear opticsOptical elementsSpatial light modulatorDisplay device
The invention provides a stereoscopic display device and a display method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of display. The stereoscopic display device comprises a display screen and a lens array arranged at the light output side of the display screen. The stereoscopic display device also comprises a spatial light modulator arranged between the display screen and the lens array. The spatial light modulator can be switched between different states; and under different states, light paths of light emitted from the display screen in the spatial light modulator are different. According to the technical scheme, the stereoscopic display device and the display method thereof can provide a plurality of imaging center depth planes.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Three-dimensional object rapid reconstruction method based on camera array
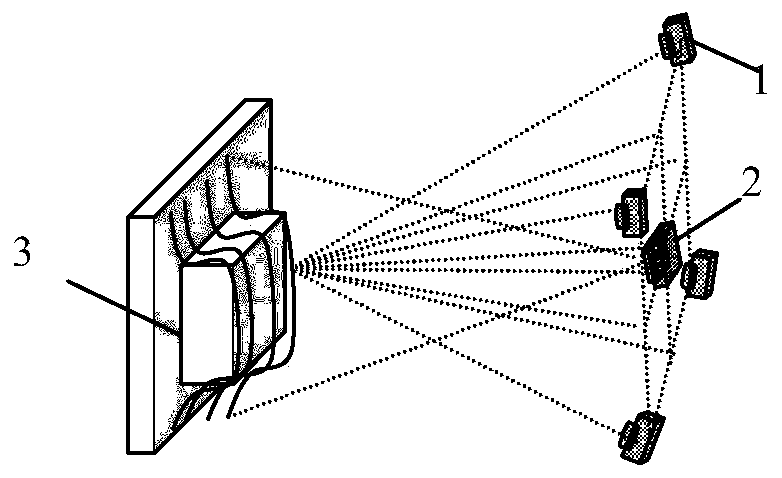
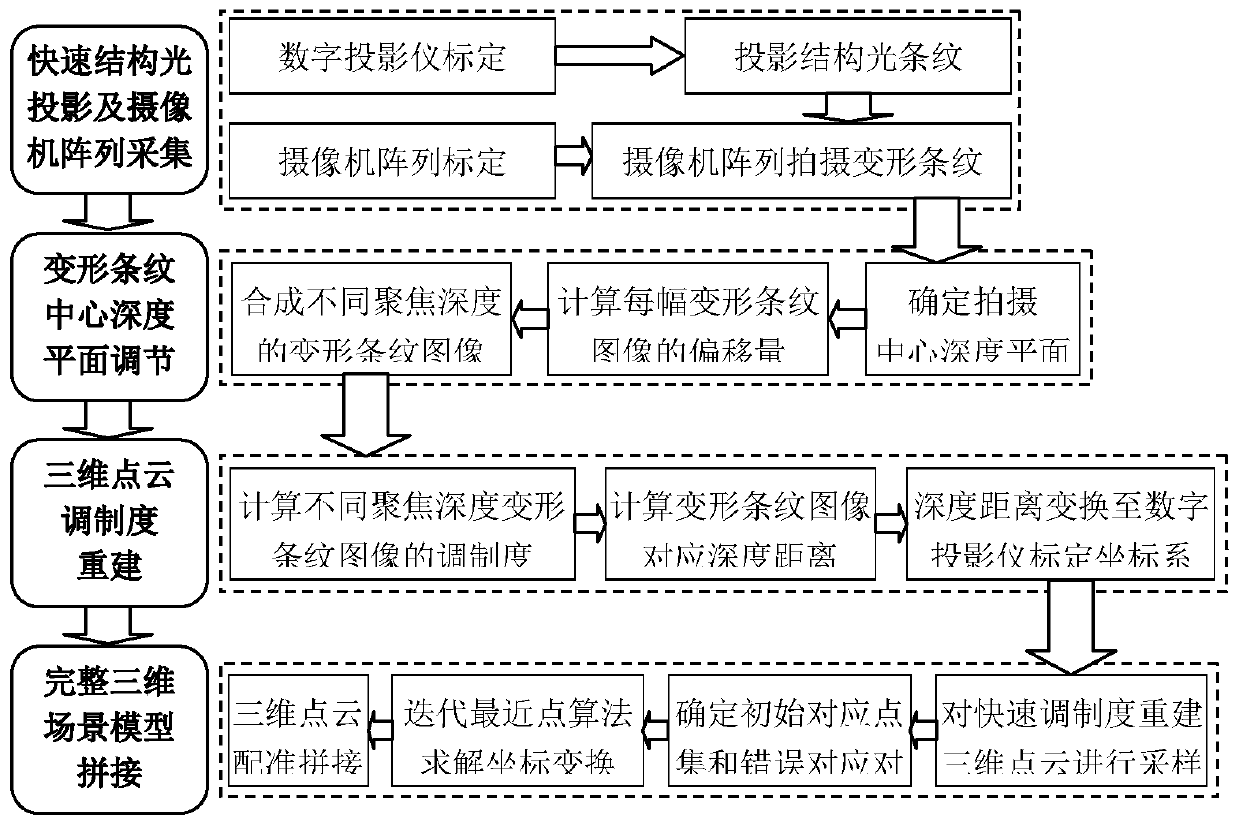
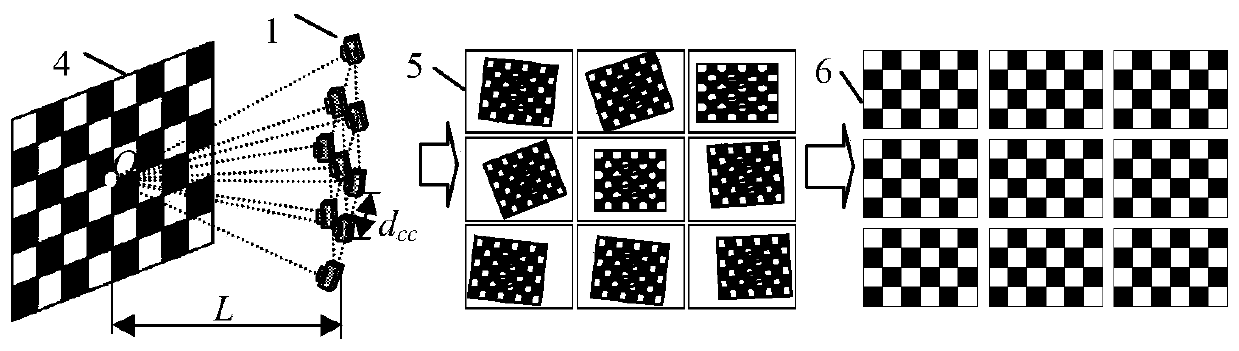
ActiveCN110288642AEasy to operateFast rebuildImage enhancementImage analysisCamera auto-calibrationReconstruction method
The invention discloses a three-dimensional object rapid reconstruction method based on a camera array, amd aims to provide a rapid reconstruction method which is high in acquisition precision and can rapidly reconstruct the three-dimensional point cloud of a tested object. The method is realized through the following technical schemes of during the structured light projection and the camera array acquisition, firstly, carrying out digital projector and camera array calibration, collecting a measured three-dimensional scene by utilizing a camera array, obtaining the projection result light stripes and the light stripe images shot by the camera array, and establishing a corresponding relation of the same point in the space on different images; according to the determined shooting center depth plane, calculating the offset of each deformation stripe; carrying out three-dimensional point cloud modulation degree reconstruction according to the deformation stripe center depth plane adjustment, and calculating the modulation degrees of the deformation stripe images with corresponding depth distances and different focusing depths of the deformation stripe images; and registering and reconstructing the three-dimensional point cloud, and iterating a nearest point algorithm to solve the coordinate transformation so as to obtain a complete three-dimensional scene reconstruction model.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
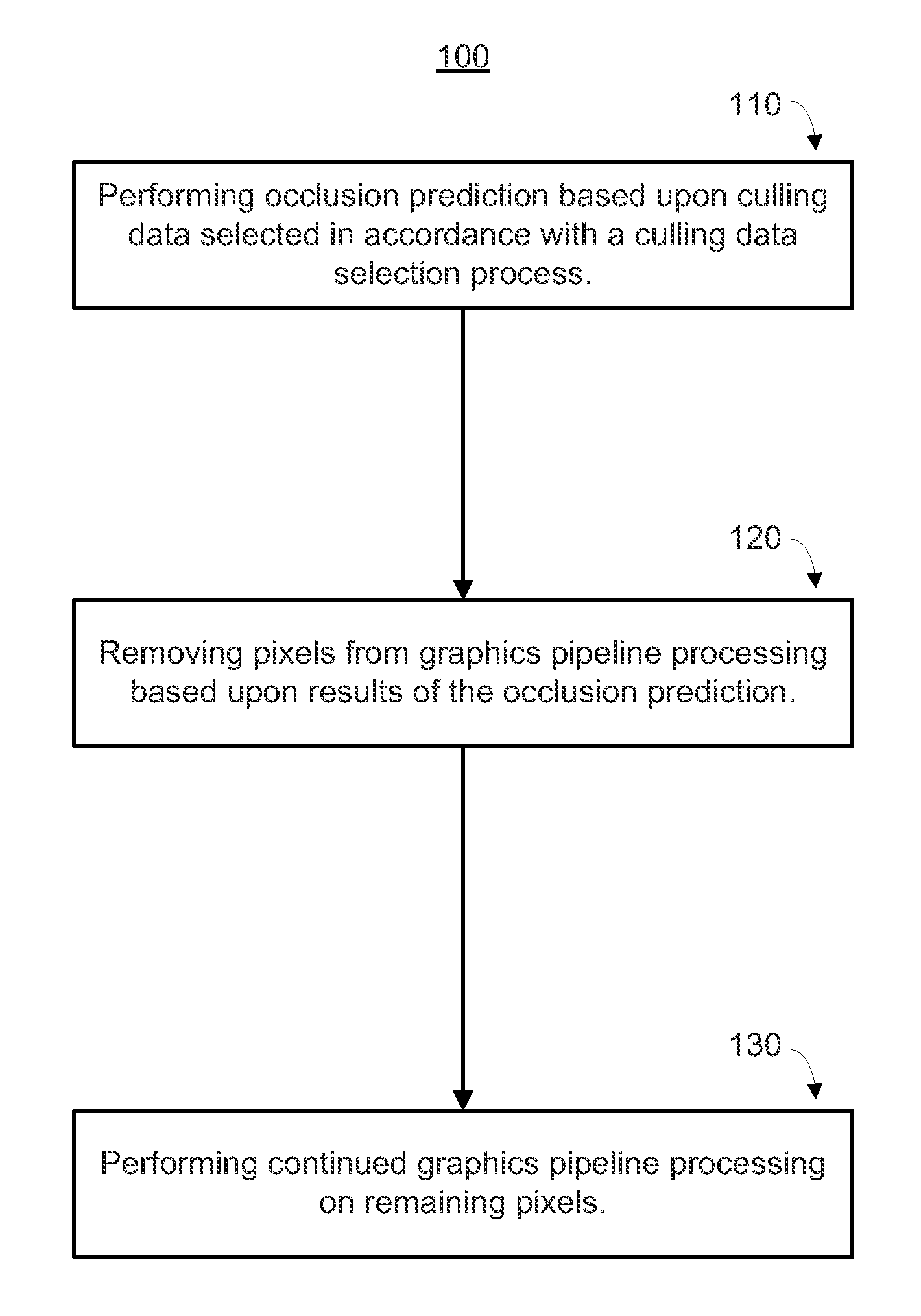
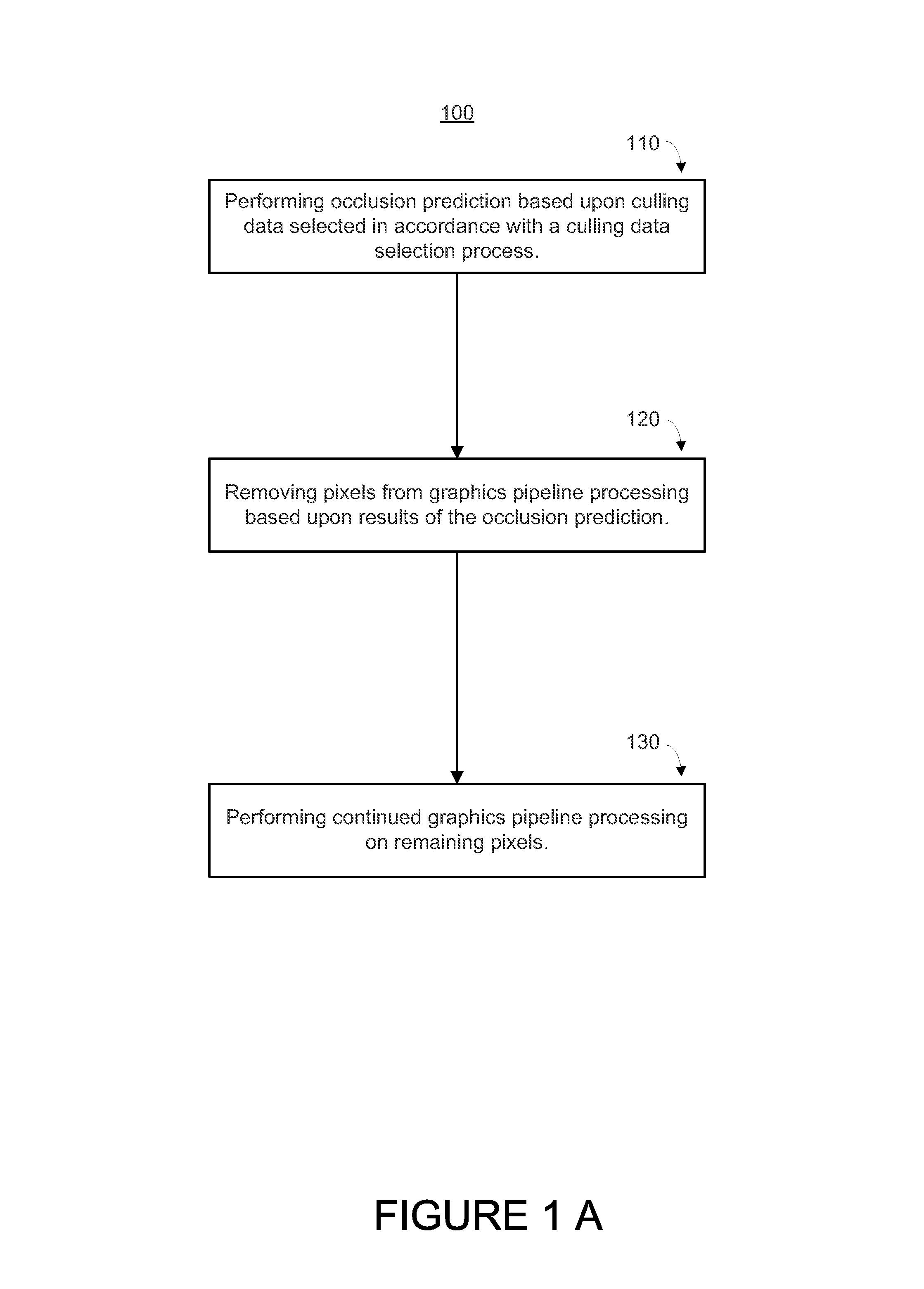
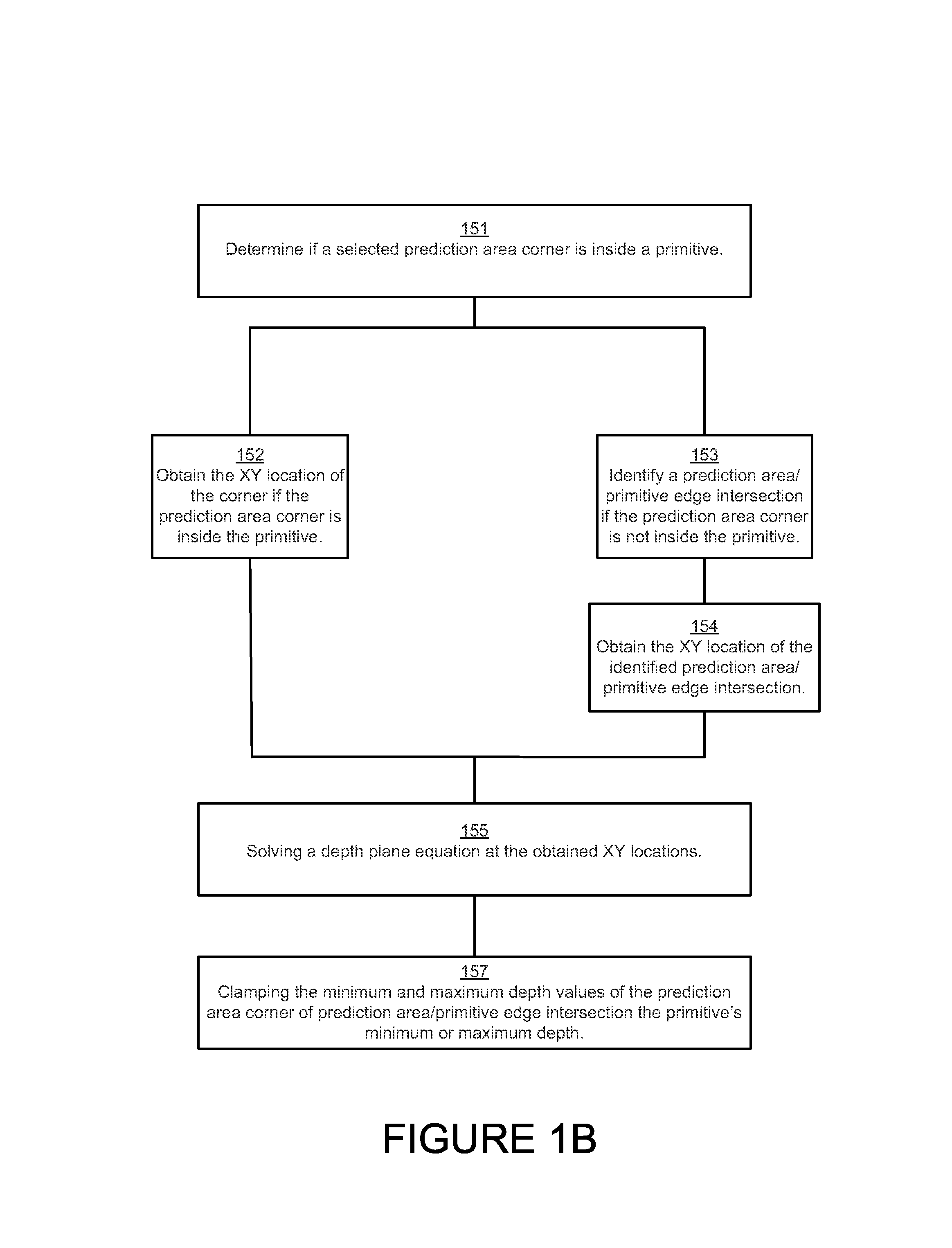
Tight depth range occlusion prediction system and method
ActiveUS8854364B1Work lessImprove performanceCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingComputational scienceMaximum depth
The range of depth values within the overlap of a convex polygon and a square or rectangular rasterization area can be determined by identifying whether the minimum and maximum depth values occur at the corners of the rasterization area or at intersections of the polygon's edges with the area's sides. By choosing between the corner and intersection for both the minimum and maximum depth limit, solving the depth plane equation at the chosen location, and clamping against the polygon's vertex depth range, a tight depth range describing the depth values within that overlap are obtained. That tight depth range is utilized to cull pixel values early in the pipeline, improving performance and power consumption.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Virtual and augmented reality systems and methods
ActiveUS20180061139A1Reduce redundant informationReduce power consumptionImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)Radiology
A virtual or augmented reality display system that controls a display using control information included with the virtual or augmented reality imagery that is intended to be shown on the display. The control information can be used to specify one of multiple possible display depth planes. The control information can also specify pixel shifts within a given depth plane or between depth planes. The system can also enhance head pose measurements from a sensor by using gain factors which vary based upon the user's head pose position within a physiological range of movement.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
Augmented reality systems and methods with variable focus lens elements
ActiveUS10459231B2Input/output for user-computer interactionNon-optical adjunctsRefractive errorVergence movement
An augmented reality display system includes a pair of variable focus lens elements that sandwich a waveguide stack. One of the lens elements is positioned between the waveguide stack and a user's eye to correct for refractive errors in the focusing of light projected from the waveguide stack to that eye. The lens elements may also be configured to provide appropriate optical power to place displayed virtual content on a desired depth plane. The other lens element is between the ambient environment and the waveguide stack, and is configured to provide optical power to compensate for aberrations in the transmission of ambient light through the waveguide stack and the lens element closest to the eye. In addition, an eye-tracking system monitors the vergence of the user's eyes and automatically and continuously adjusts the optical powers of the pair of lens elements based on the determined vergence of those eyes.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
Method and system for utilizing image sensor pipeline (ISP) for scaling 3D images based on z-depth information
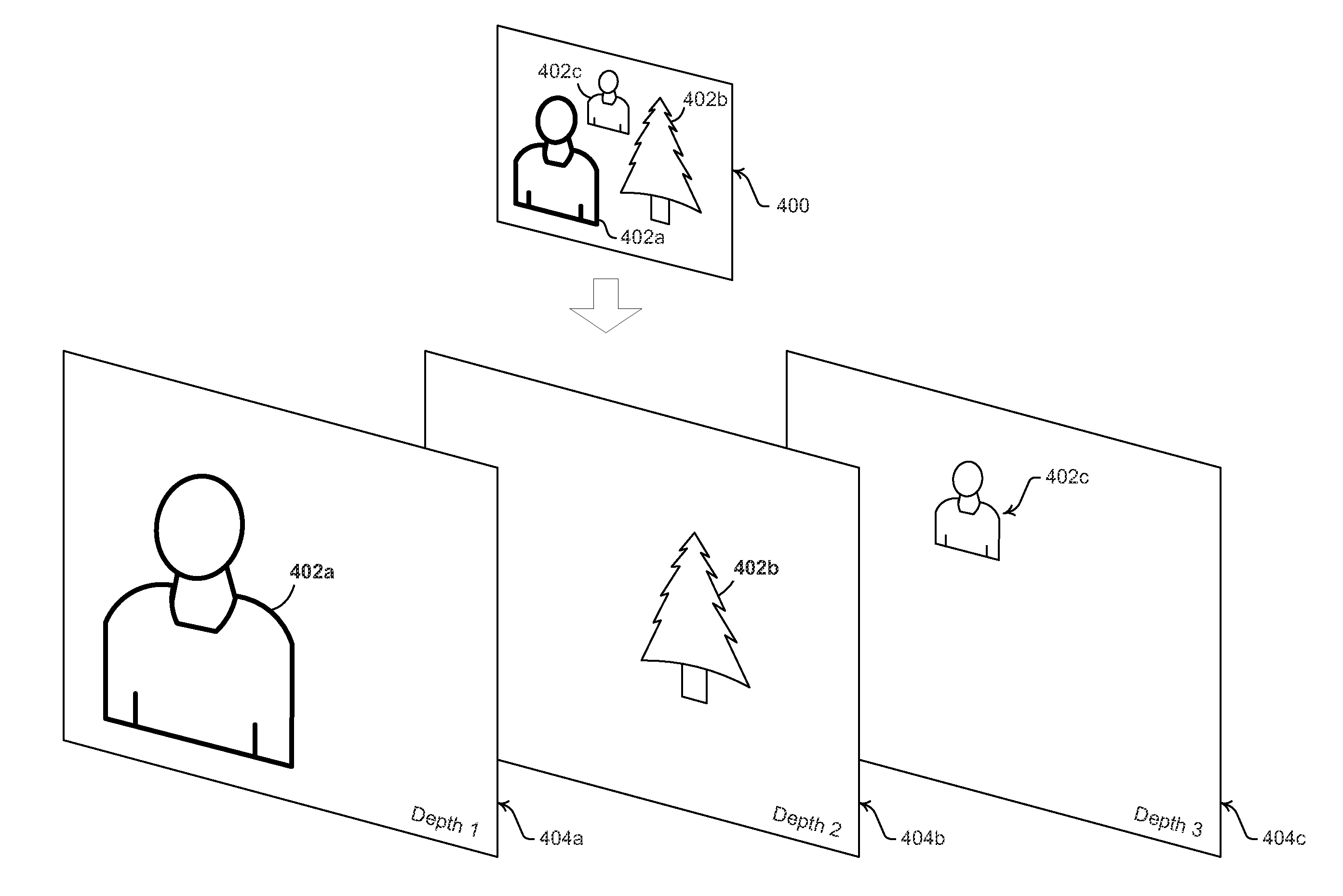
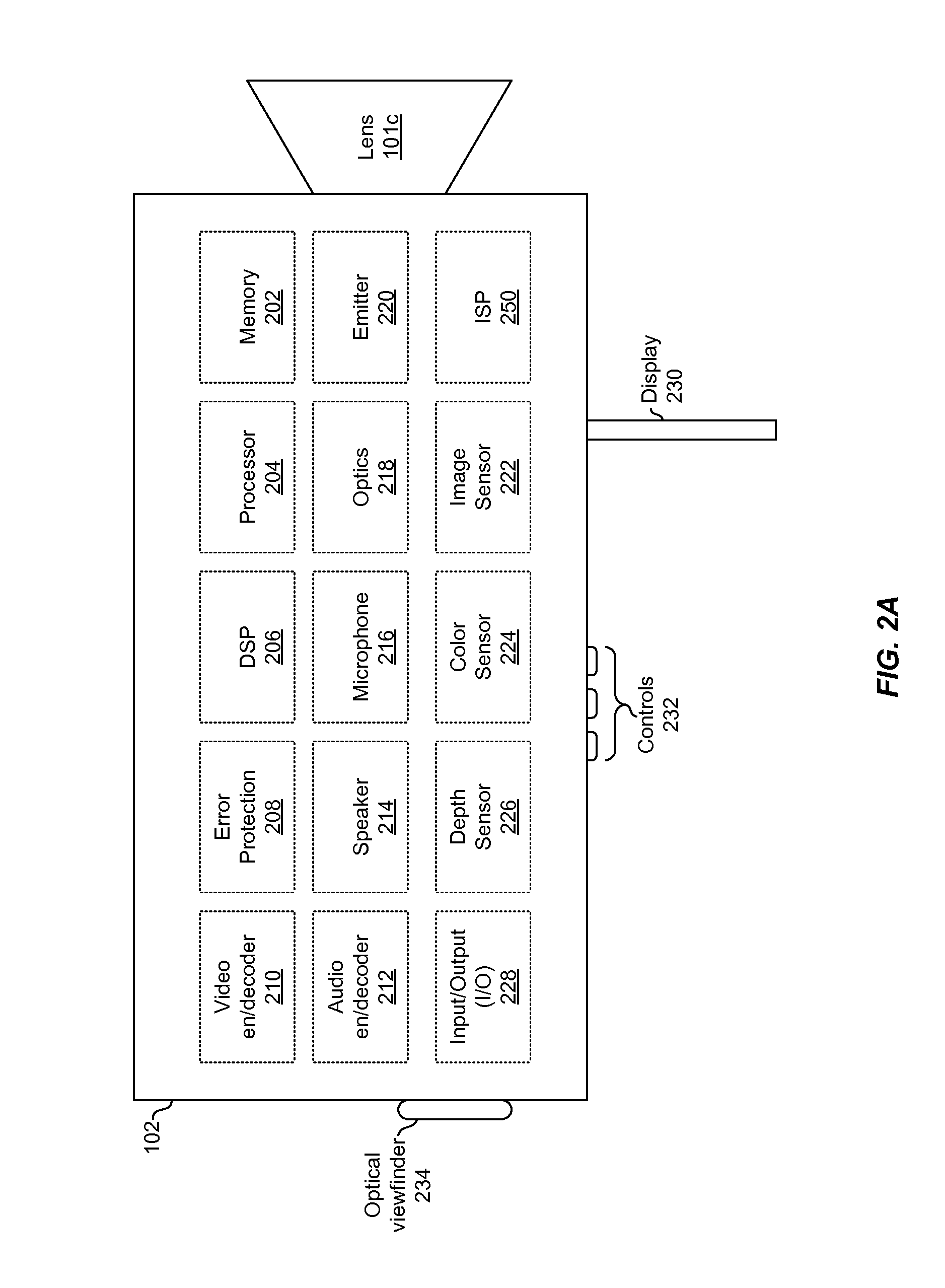
A monoscopic video camera may capture, via at least one image sensor, two-dimensional video, and may capture, via at least one depth sensor, corresponding depth information for the captured two-dimensional video. The monoscopic video camera may then adaptively configure scaling operations applicable to the captured two-dimensional video based on the depth information, which may comprise variably scaling different portions of the two-dimensional video. In this regard, the monoscopic video camera may determine, based on the depth information, a plurality of depth planes. The different portions of the two-dimensional video that are subjected to variable scaling may be determined based on the plurality of depth planes. Configuration of scaling operations may be performed in response to user input, which may comprise a zoom command. In this regard, scaling operations may be configured to focus on one or more of the different portions of the two-dimensional video based on zoom commands.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Depth based foveated rendering for display systems
Methods and systems for depth-based foveated rendering in the display system are disclosed. The display system may be an augmented reality display system configured to provide virtual content on a plurality of depth planes using different wavefront divergence. Some embodiments include monitoring eye orientations of a user of a display system based on detected sensor information. A fixation point is determined based on the eye orientations, the fixation point representing a three-dimensional location with respect to a field of view. Location information of virtual objects to present is obtained, with the location information indicating three-dimensional positions of the virtual objects. Resolutions of at least one virtual object is adjusted based on a proximity of the at least one virtual object to the fixation point. The virtual objects are presented to a user by display system with the at least one virtual object being rendered according to the adjusted resolution.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
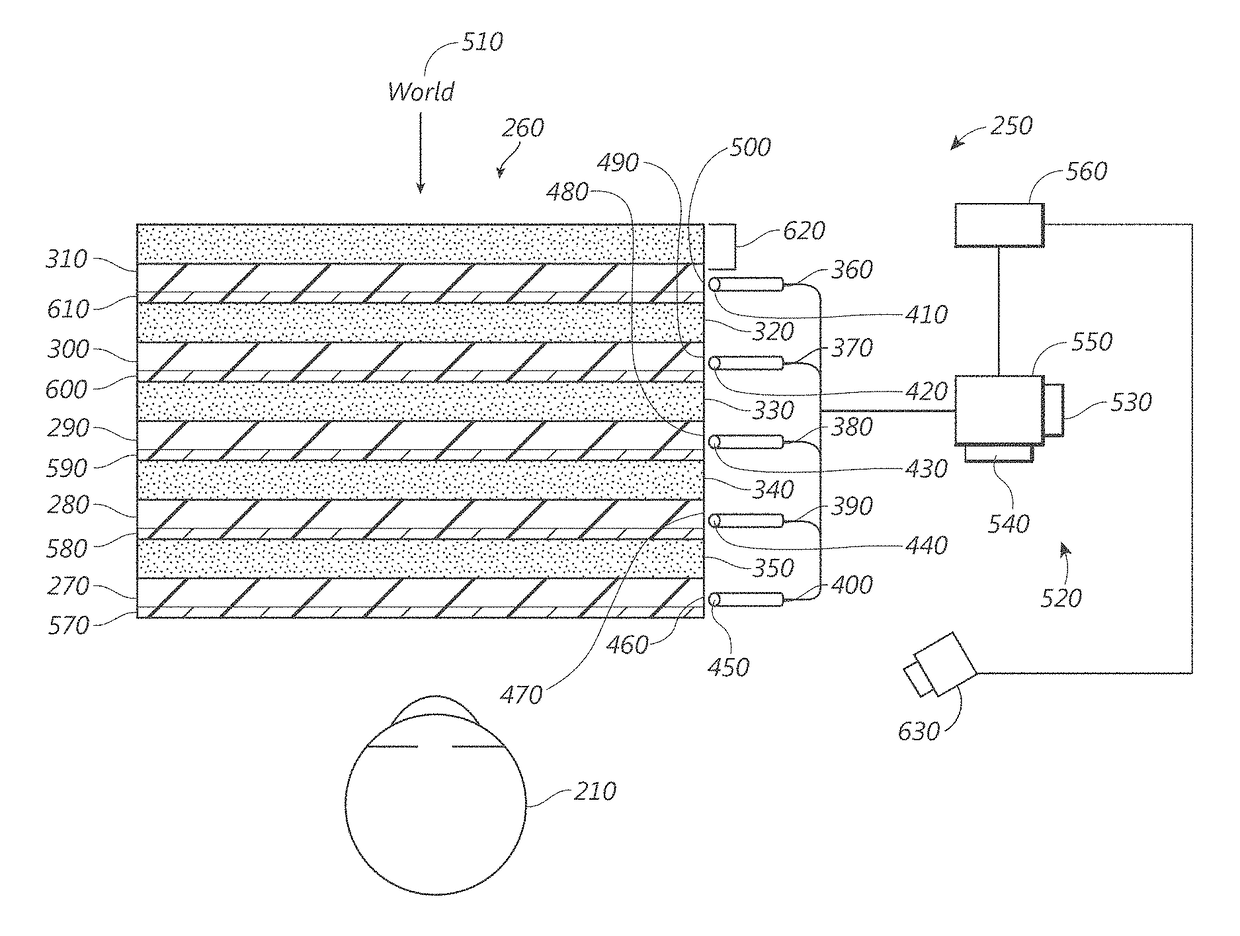
Virtual and augmented reality systems and methods having unequal numbers of component color images distributed across depth planes
Images perceived to be substantially full color or multi-colored may be formed using component color images that are distributed in unequal numbers across a plurality of depth planes. The distribution of component color images across the depth planes may vary based on color. In some embodiments, a display system includes a stack of waveguides that each output light of a particular color, with some colors having fewer numbers of associated waveguides than other colors. The stack of waveguides may include by multiple pluralities (e.g., first and second pluralities) of waveguides, each configured to produce an image by outputting light corresponding to a particular color. The total number of waveguides in the second plurality of waveguides is less than the total number of waveguides in the first plurality of waveguides, and may be more than the total number of waveguides in a third plurality of waveguides, in embodiments where three component colors are utilized.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com