Depth based foveated rendering for display systems
A technology for display devices and users, applied in stereoscopic systems, 3D image processing, data processing input/output processes, etc., can solve problems such as complex visual perception systems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
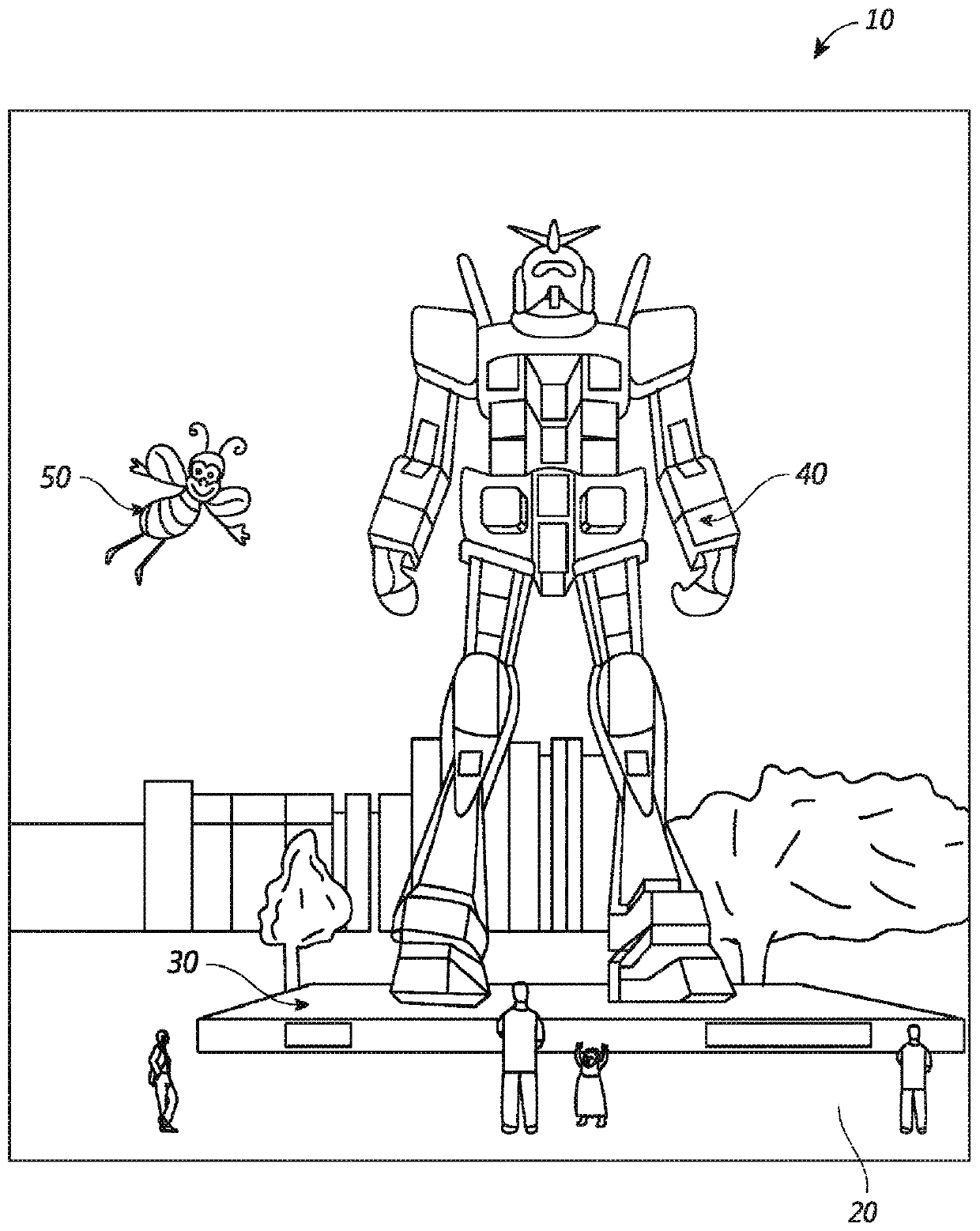
[0107] Rendering virtual content for augmented and virtual display systems is computationally intensive. Among other things, computational intensity may use undesirably large amounts of memory, result in high latency, and / or may require the use of powerful processing units, which may have high cost and / or high energy consumption.
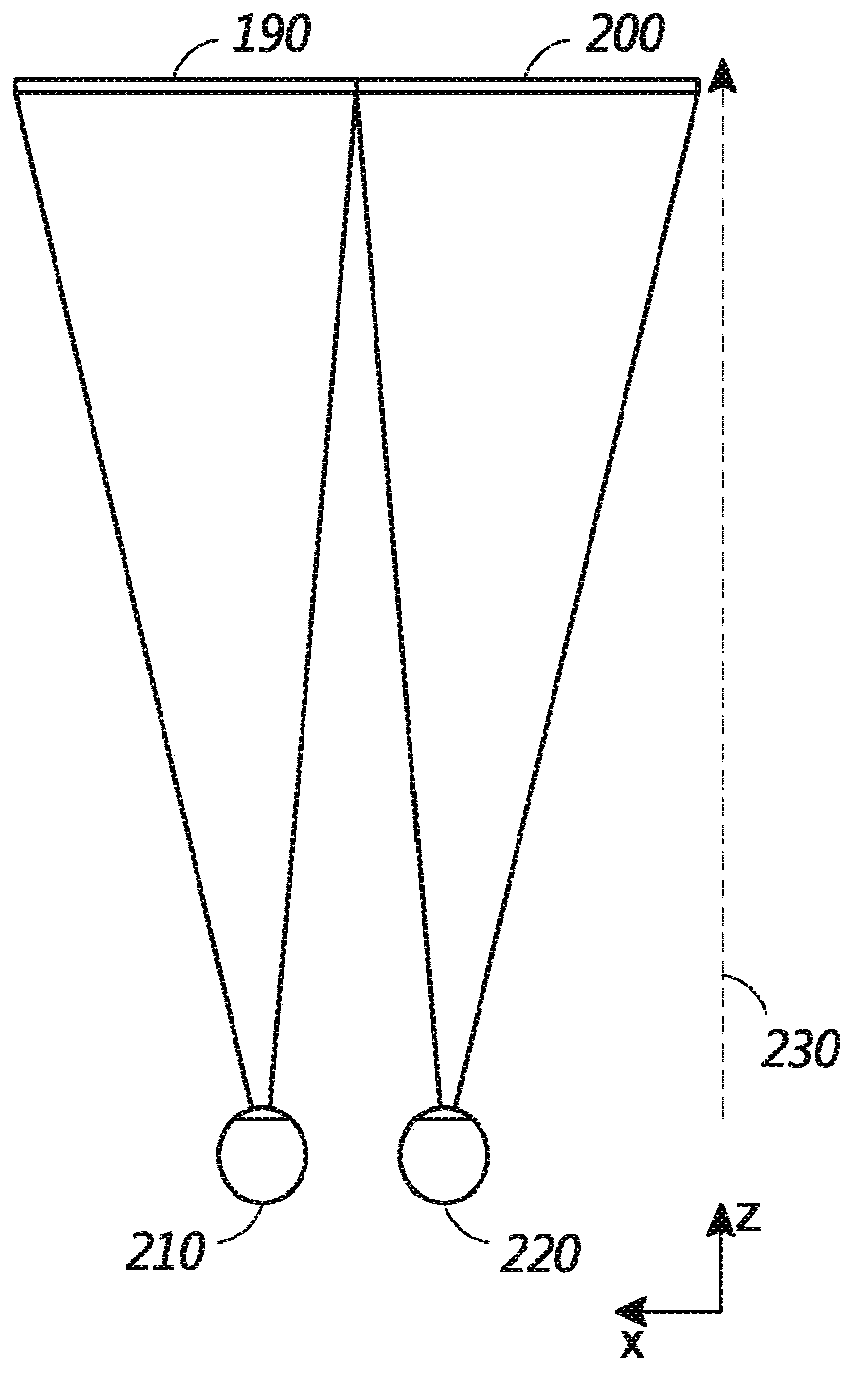
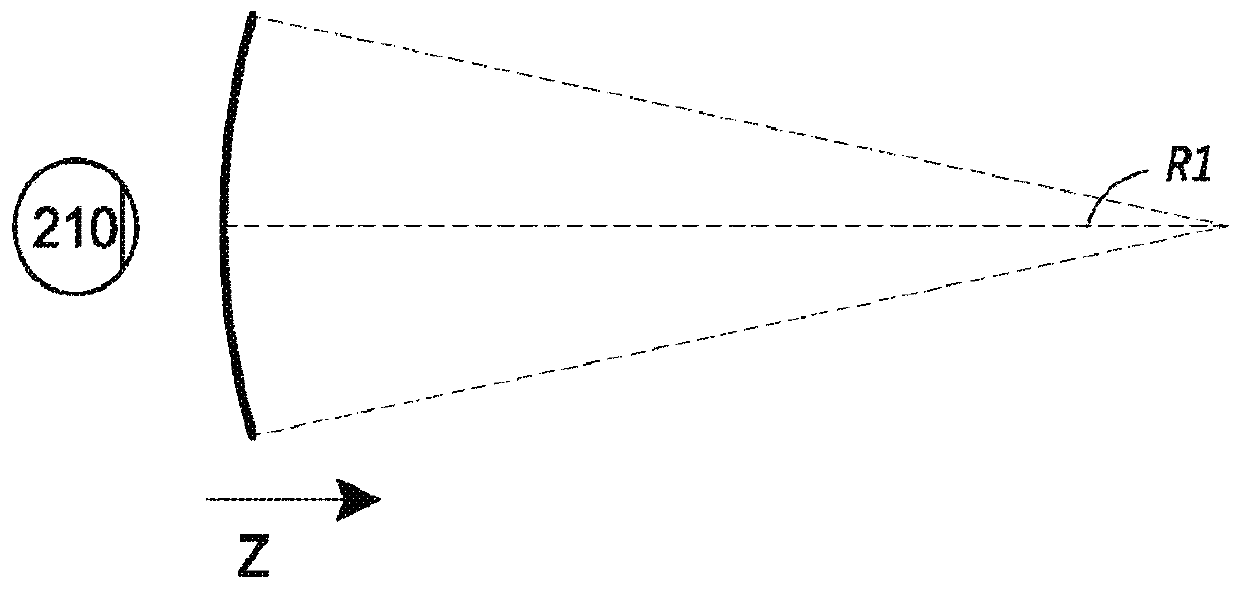
[0108] In some embodiments, methods and systems conserve computing resources, such as memory and processing time, by reducing the resolution of virtual content located at locations away from the gaze point of the user's eyes. For example, the system may render virtual content at a relatively high resolution (e.g., the highest resolution) at or near the gaze point of the user's eyes, while utilizing one or more lower resolutions for virtual content further away from the gaze point. . The virtual content is presented by a display system that can display the virtual content at multiple different depths (e.g., multiple different depth planes, such as t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com