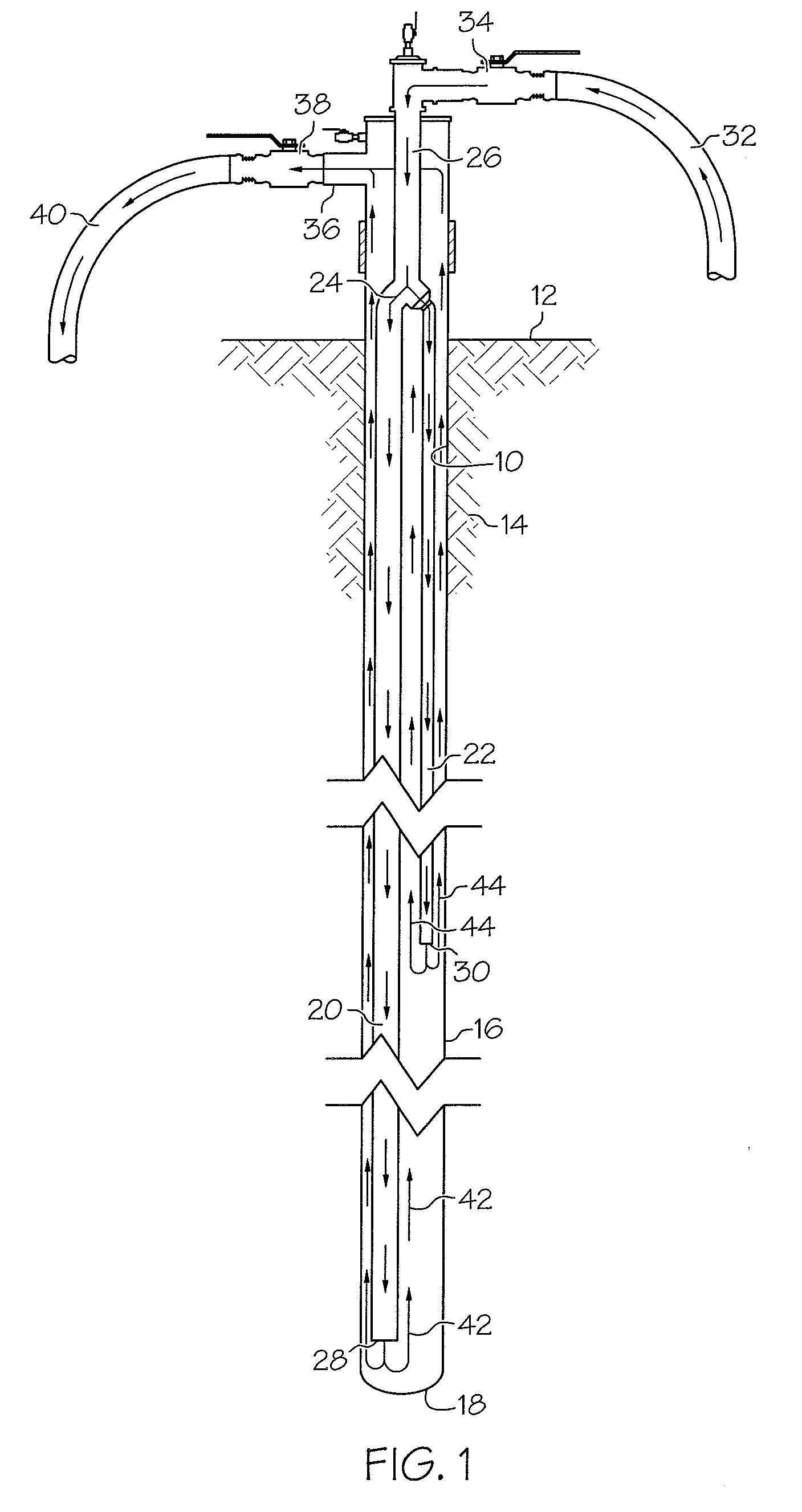
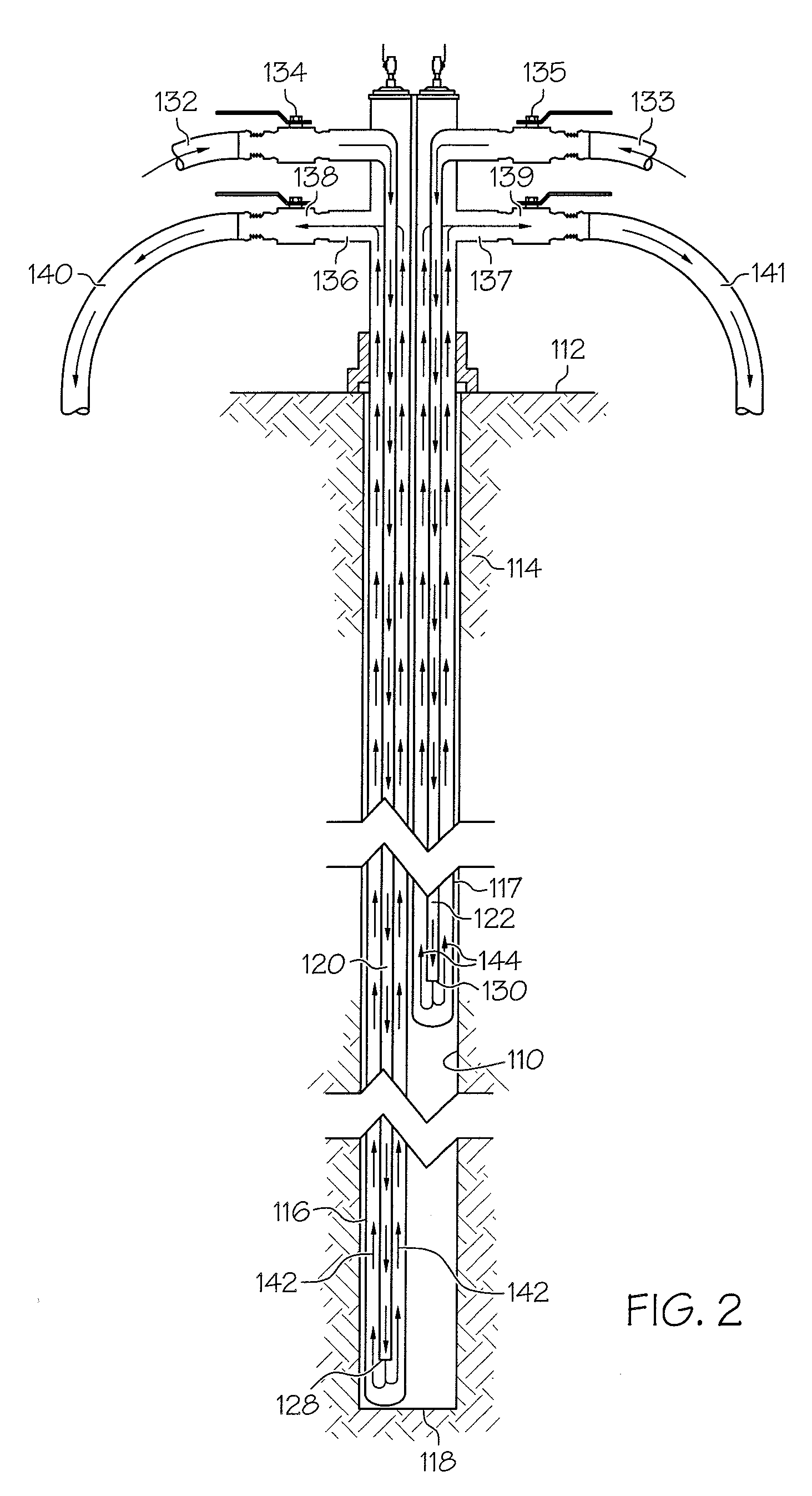
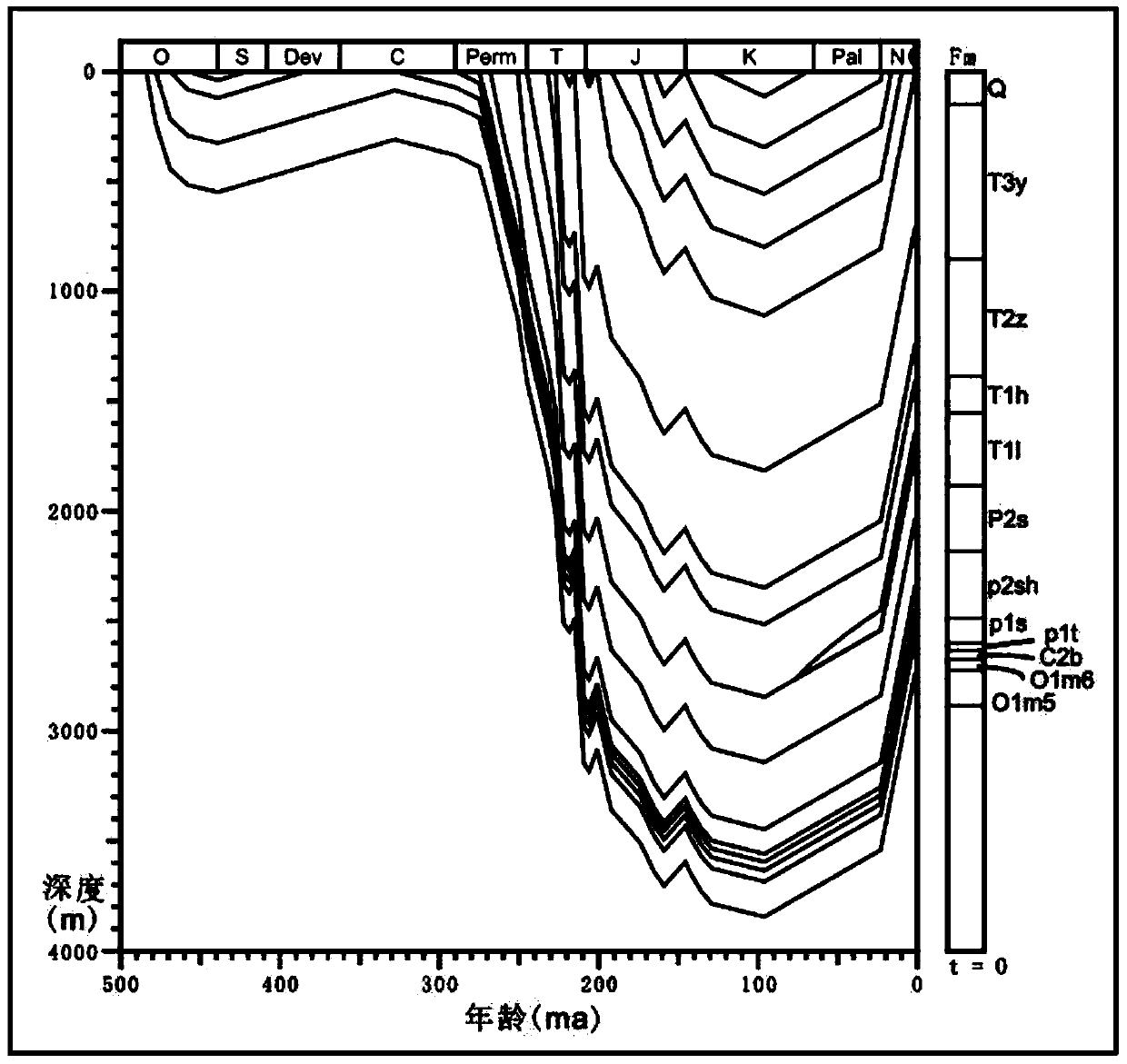
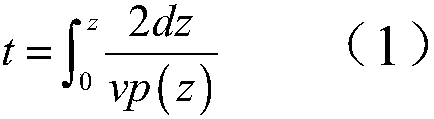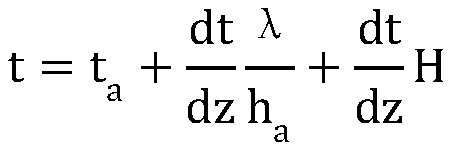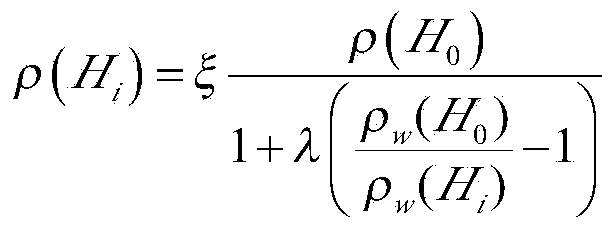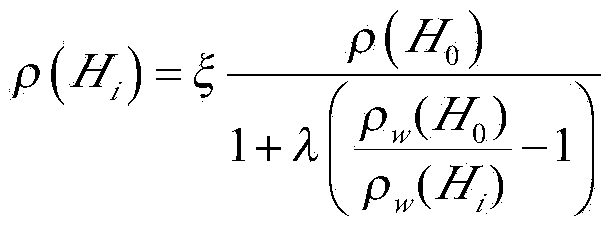Patents
Literature
77 results about "Geothermal gradient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
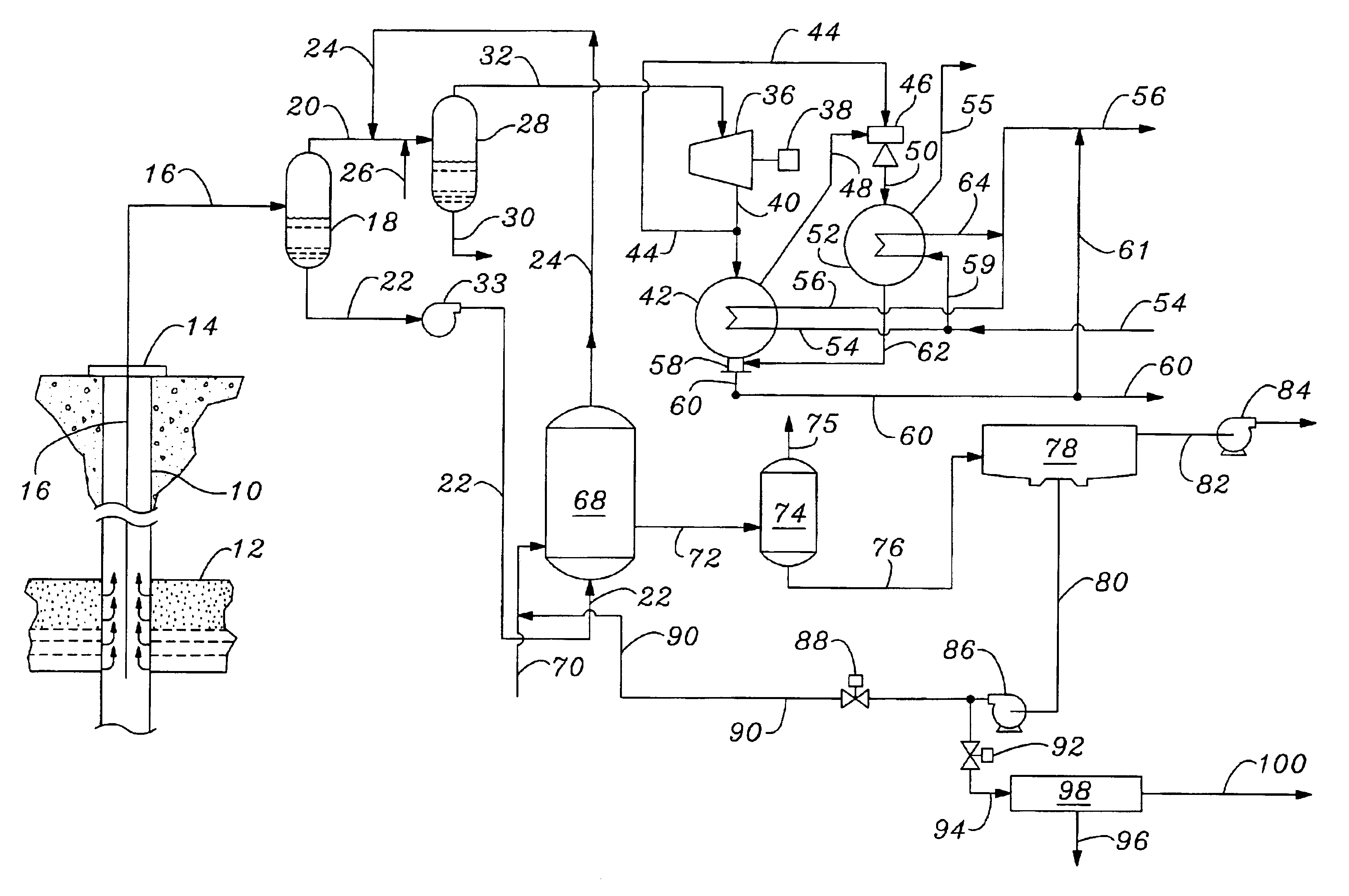
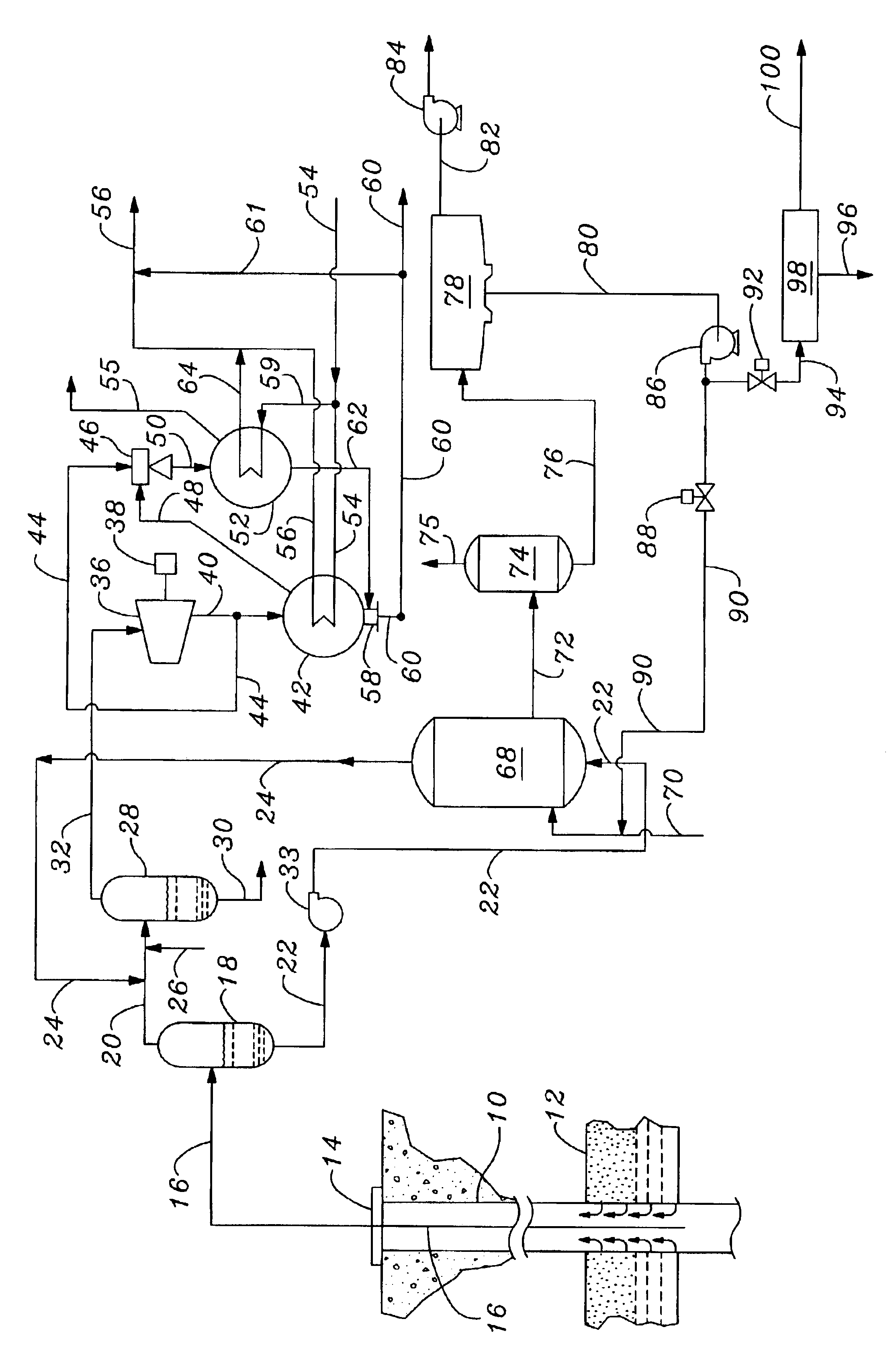
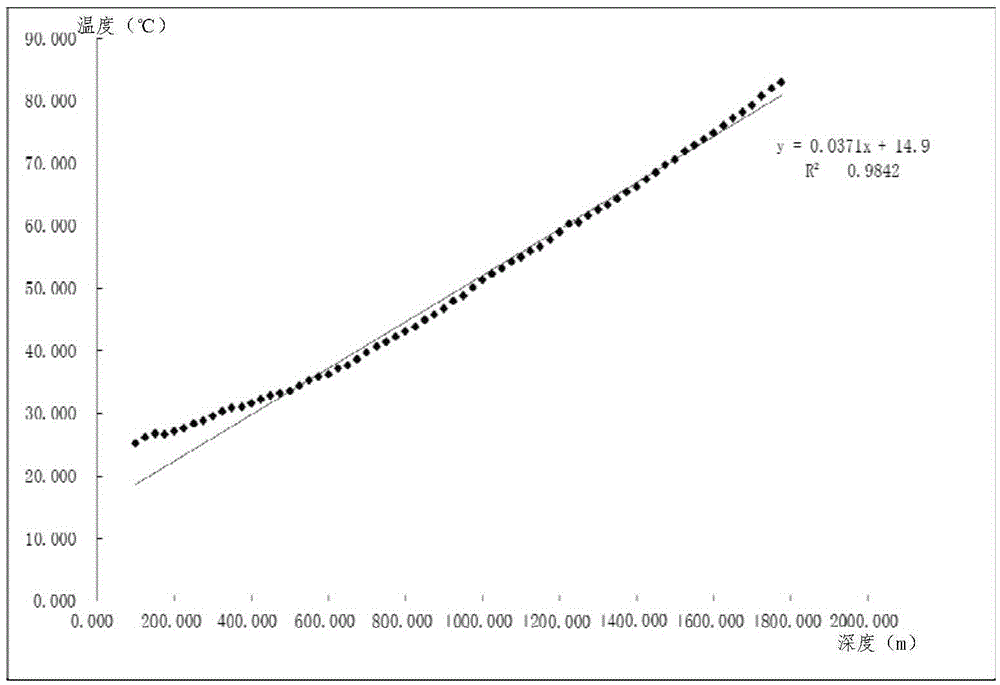
Geothermal gradient is the rate of increasing temperature with respect to increasing depth in the Earth's interior. Away from tectonic plate boundaries, it is about 25–30 °C/km (72-87 °F/mi) of depth near the surface in most of the world. Strictly speaking, geo-thermal necessarily refers to the Earth but the concept may be applied to other planets.
Method for synthesizing crystalline magnesium silicates from geothermal brine
Crystalline magnesium silicates are synthesized from silica-containing brines, preferably spent geothermal brines, by mixing the brine with a magnesium-containing compound, adjusting the pH of the resultant mixture between 8.0 and 14, and crystallizing the magnesium silicate from the mixture at a temperature between 50° C. and 200° C. Kerolite is preferably synthesized from brine by adjusting the pH in a range between 9.5 and 10.5 and heating the mixture to between 100° C. and 170° C. to precipitate the crystalline kerolite. The brine remaining after the crystallization step is depleted in silica and can be further processed without significant problems caused by silica scaling.
Owner:UNION OIL OF CALIFORNIA
Geothermal grout, and methods of preparing and utilizing same
A thermally enhanced, single component, geothermal grout from recycled materials, such as class F fly ash and cement kiln dust. Additional components can include a mid-range water reducer and a dry caustic.
Owner:KONCZAK JEFFREY J
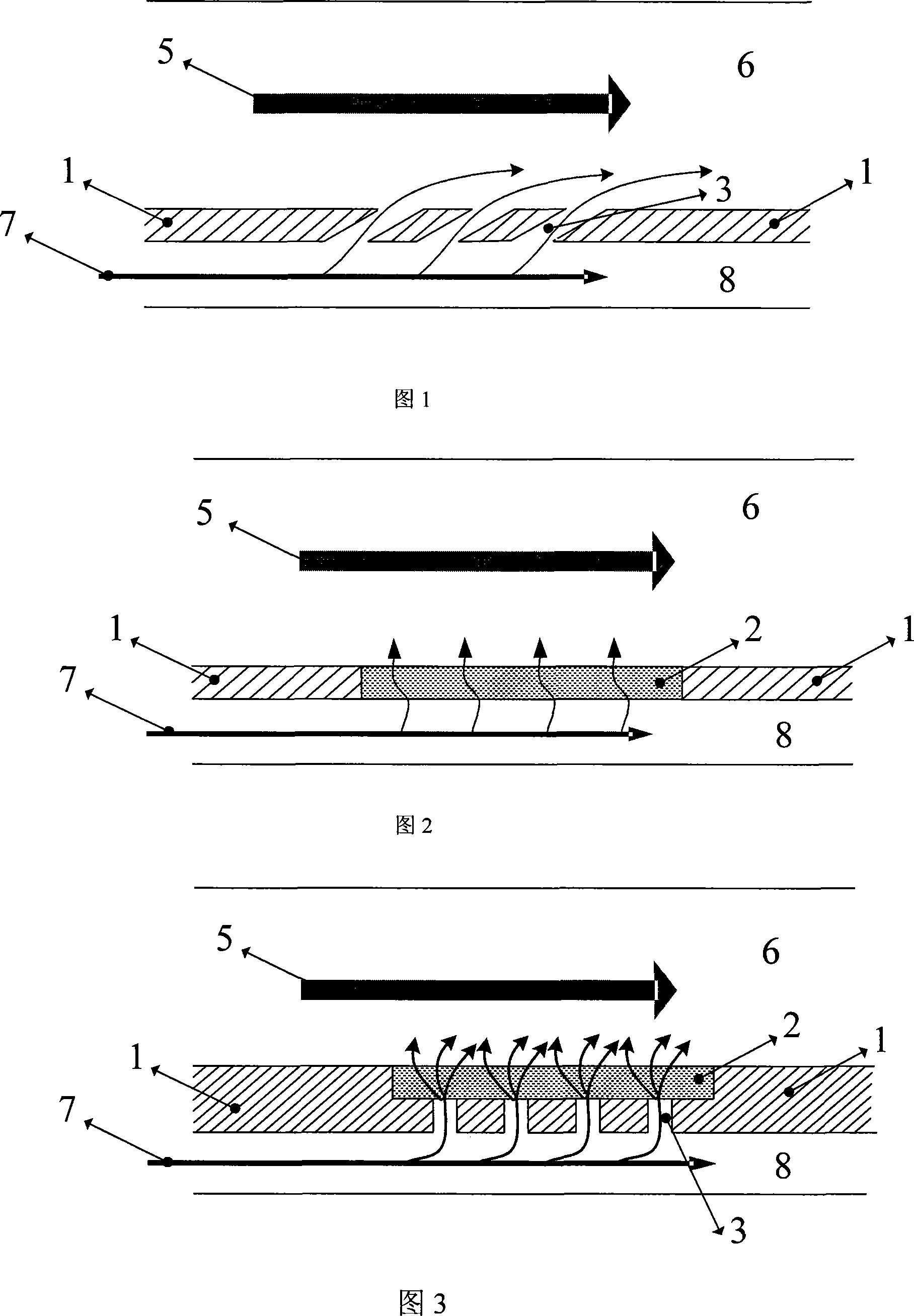
Heated wall surface cooling structure and gas turbine impeller vane with the same
ActiveCN101173610AEffective cooling efficiencyImprove thermal stressBlade accessoriesMachines/enginesPorous mediumEngineering
The invention relates to a cooling structure of the heated wall surface and a gas turbine blade of the cooling structure; wherein, the cooling structure comprises a compact wall surface layer, and a plurality of discrete through holes for the coolant to pass through are arranged on the compact wall surface layer; a porous coating is covered on the heated side of the compact wall surface layer to enable the porous coating and the compact wall surface layer with a plurality of discrete through holes to form a structure of double-layer superimposition, and the outlet of the discrete through hole is communicated with the porous coating. The porous coating can be continuously covered on the compact wall surface layer, and also can be covered on the local areas of the outlet of the discrete through holes. The invention has the advantages of synthesizing the characteristics of gas film cooling and transpiration cooling, fully combining the advantages of two cooling ways, effectively improving the cooling efficiency of the wall surface, reducing the geothermal gradient of the wall surface, and avoiding the continuous increase of the heat stress of materials. Simultaneously, the intensity of the cooling structure of the invention is enough to be used for common impeller machinery.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
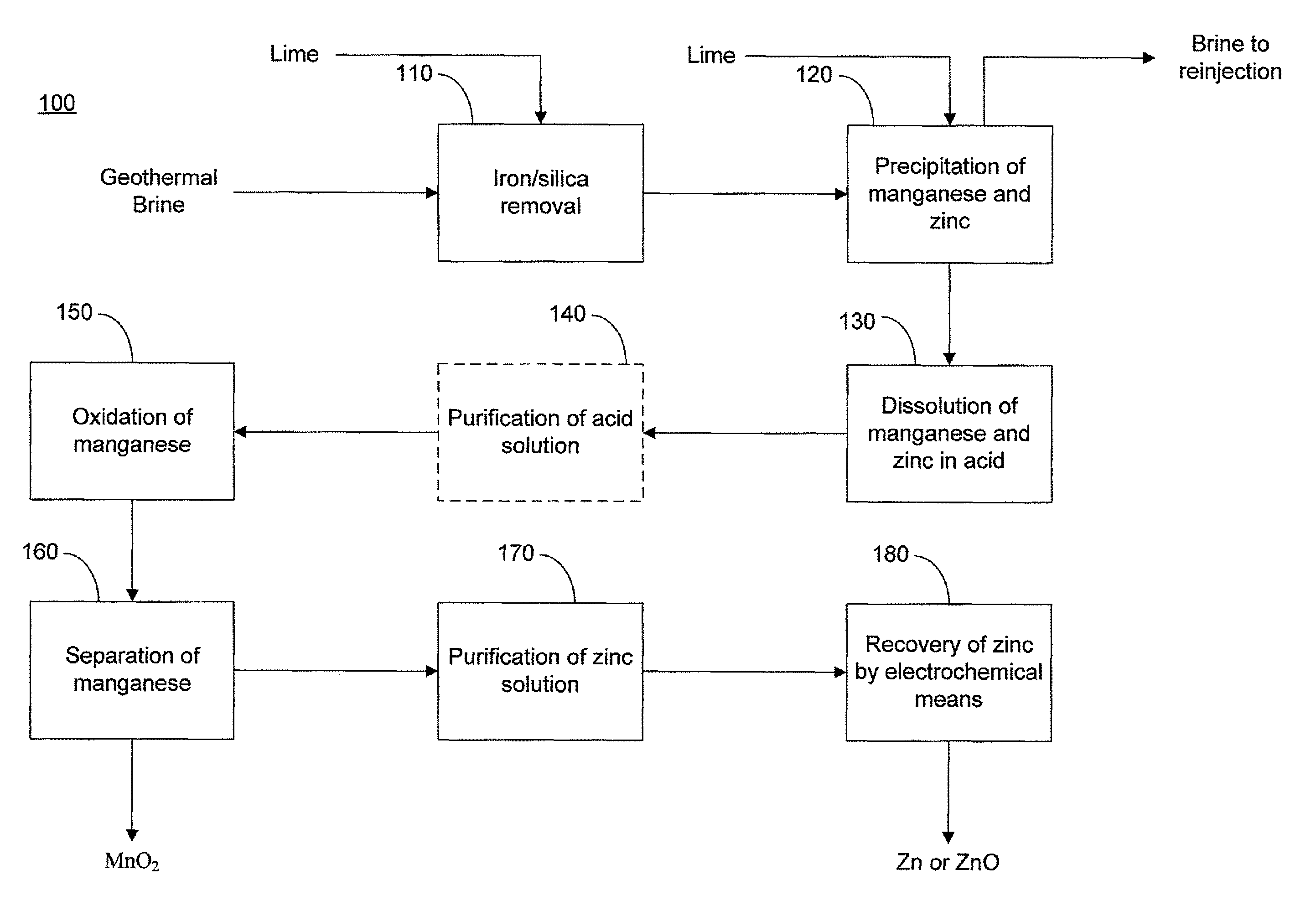
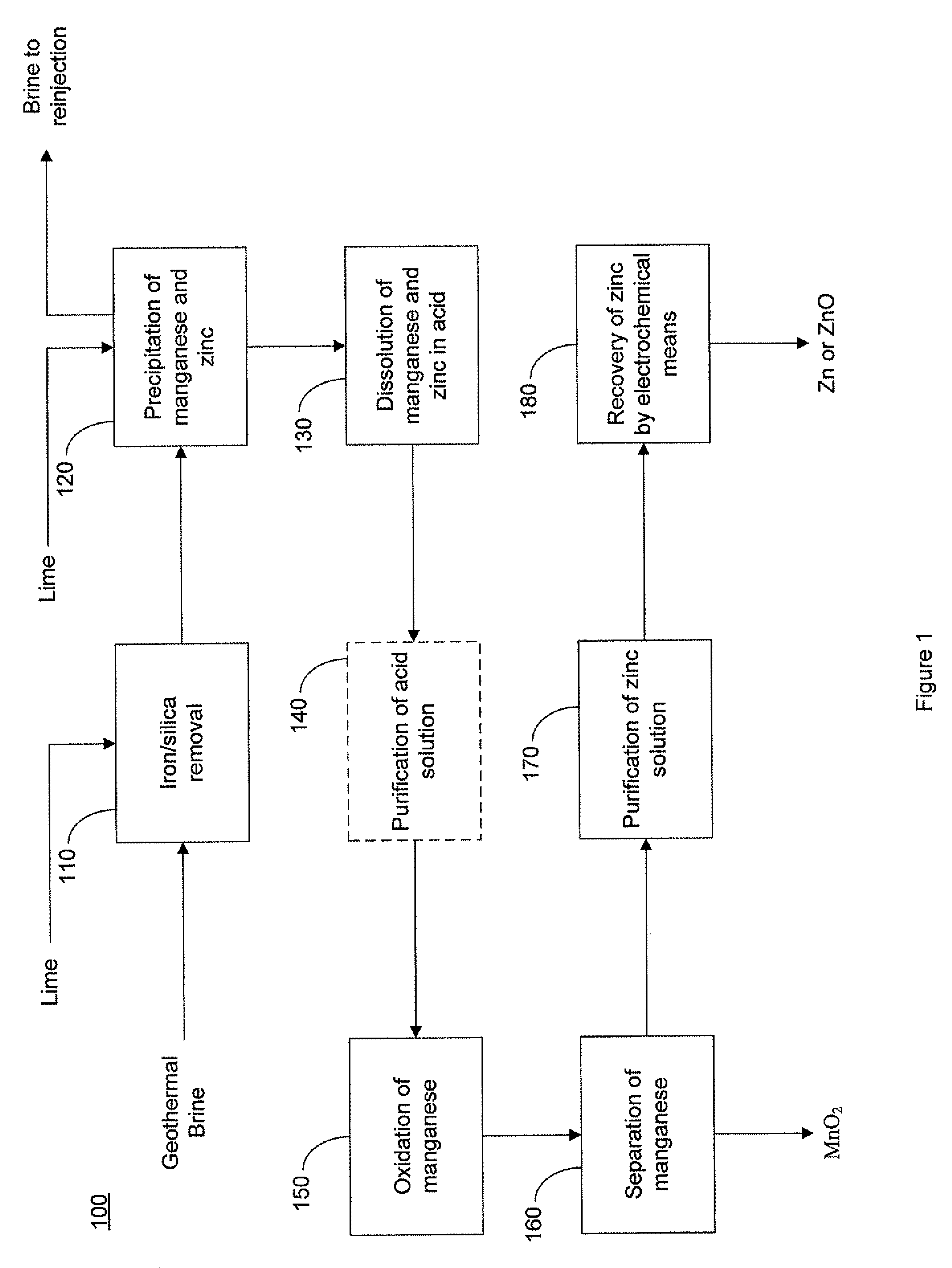
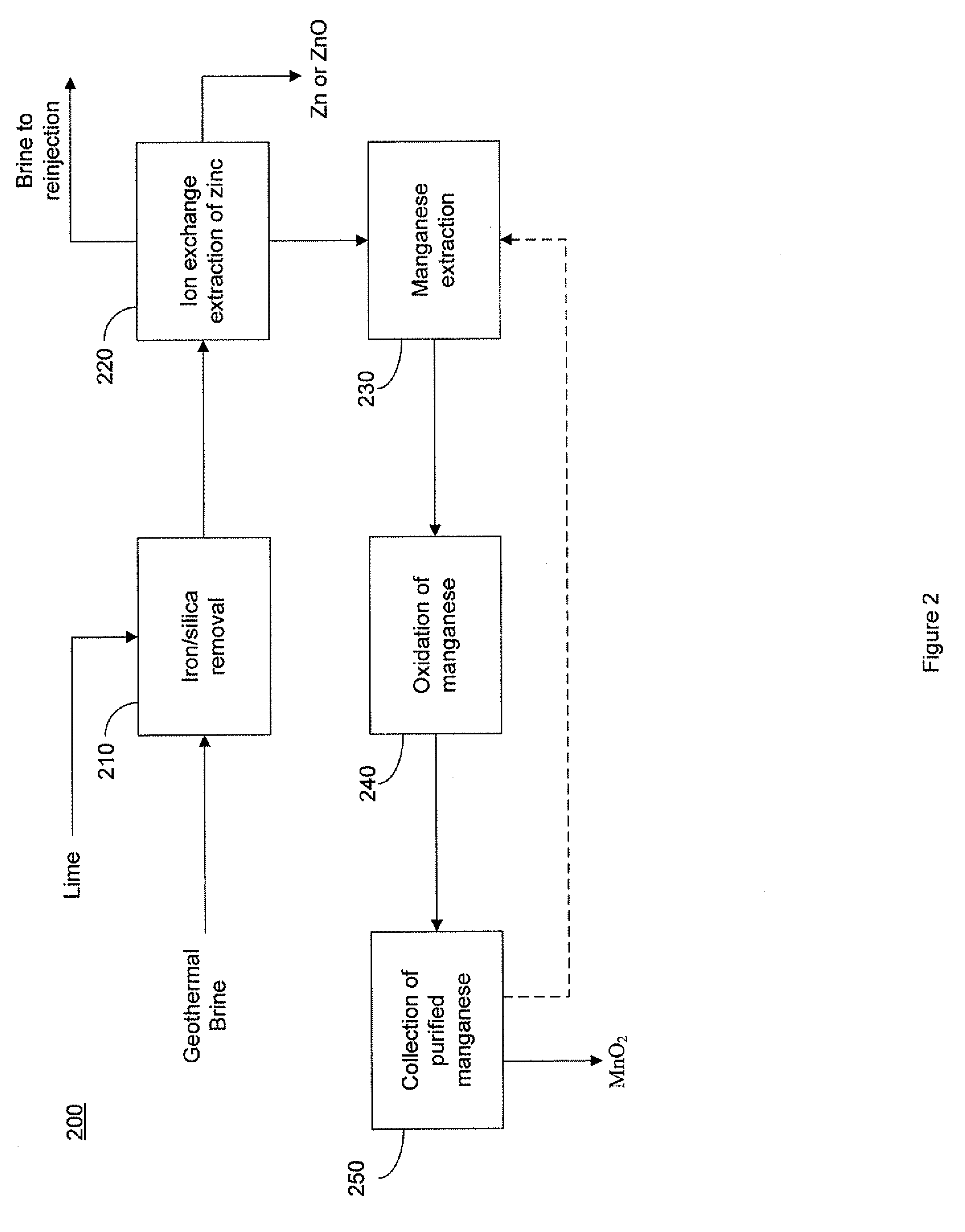
Selective recovery of manganese and zinc from geothermal brines
This invention relates to a method for the selective recovery of manganese and zinc from geothermal brines that includes the steps of removing silica and iron from the brine, oxidizing the manganese and zinc to form precipitates thereof, recovering the manganese and zinc precipitates, solubilizing the manganese and zinc precipitates, purifying the manganese and zinc, and forming a manganese precipitate, and recovering the zinc by electrochemical means.
Owner:TERRALITHIUM LLC
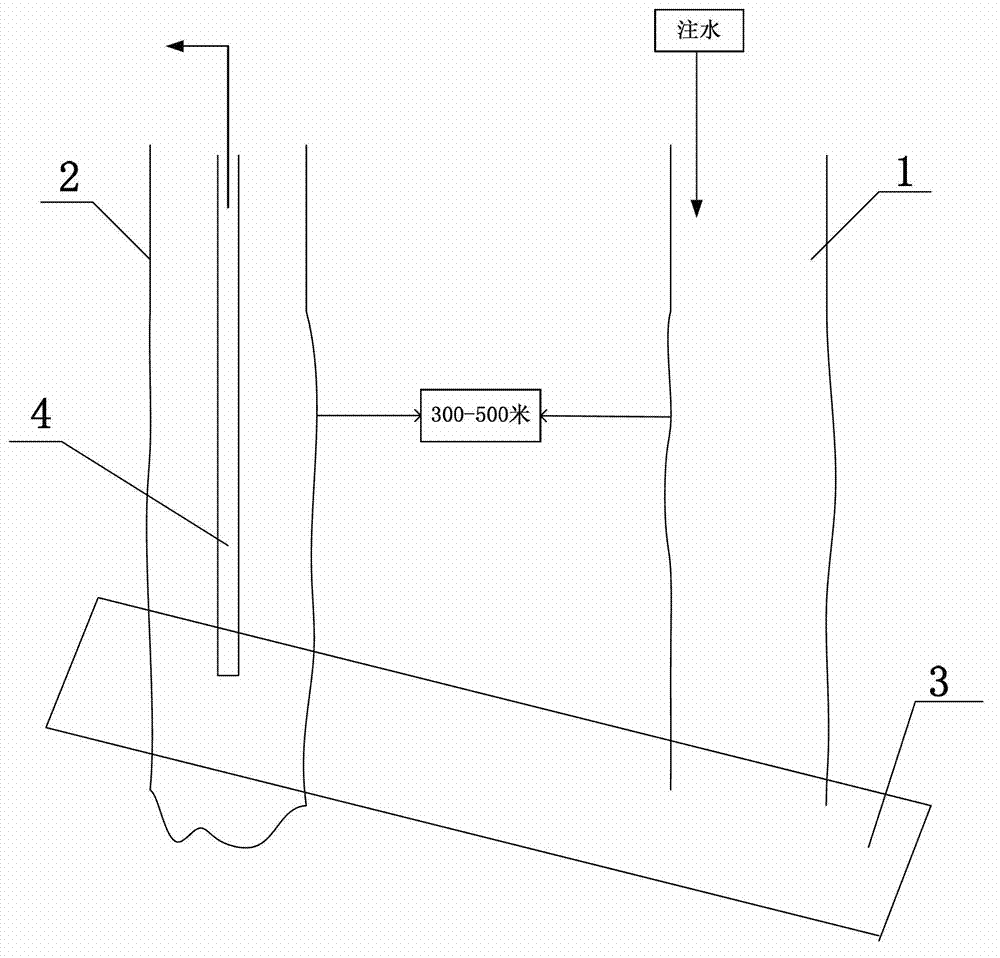
Method of circular mining geothermal resources
ActiveCN103090571ASolve the problem of drilling wellsOther heat production devicesGeothermal energy generationSoil scienceWell drilling
The invention relates to a method of circular mining geothermal resources. The method comprises following steps: (1) an area with a relatively-high geothermal gradient is confirmed; (2) a reservoir stratum in the area with the relatively-high geothermal gradient is confirmed; (3) well positions of two wells are confirmed along a main extending direction of the reservoir stratum, well drilling is conducted, one well is arranged on a relatively-low position of the reservoir stratum and is a water inlet well, and the other well is arranged on a relatively-high position of the reservoir stratum and is a water outlet well; (4) the water inlet well and the water outlet well are all drilled on the reservoir stratum, then perforation is conducted on the same reservoir stratum segment, a reservoir stratum channel is obtained, and the water inlet well is communicated with the water outlet well through the reservoir stratum; (5) on the ground, ground surface fresh water is injected from the water inlet well, the ground surface fresh water passes through the reservoir stratum channel, then hot water after heated is obtained, hot water after heated flows into the water outlet well, and then the hot water is sent to the water outlet well.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIV OF WATER RESOURCES & ELECTRIC POWER
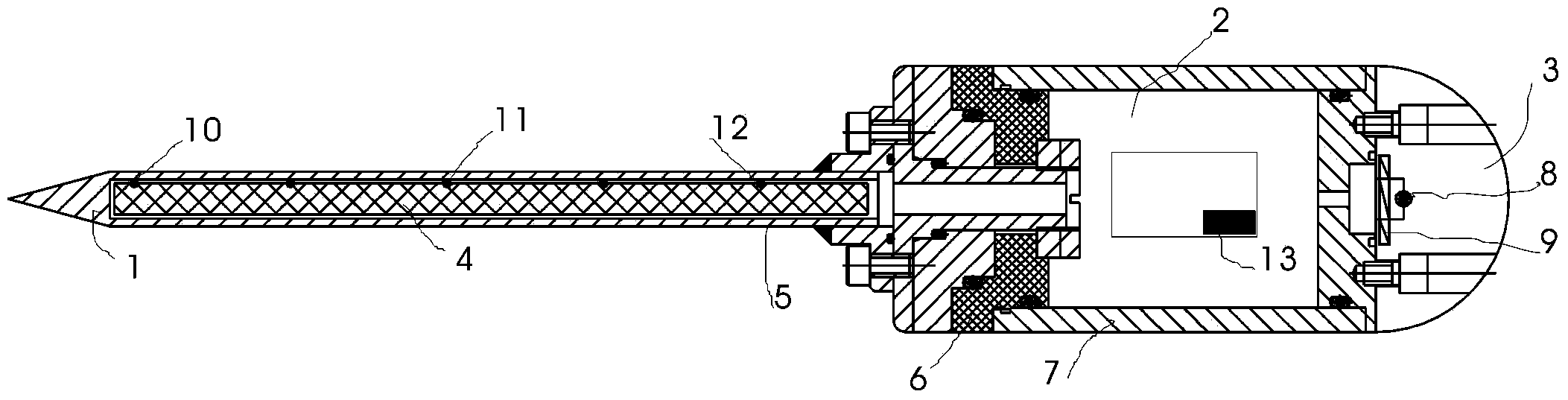
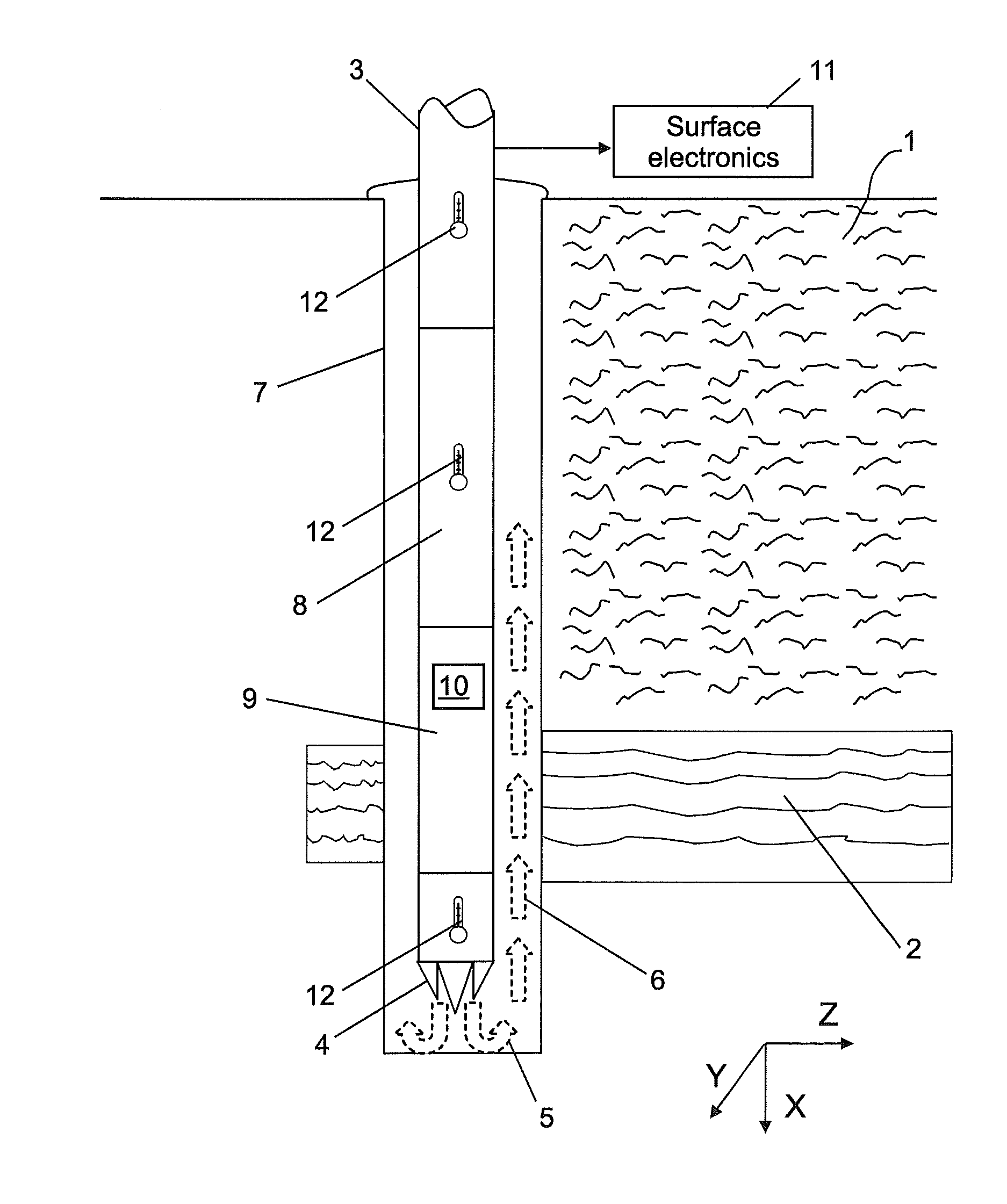
High-precision seabed geothermal gradient detection device
InactiveCN104062691AImprove consistencyImprove response speedThermometer detailsBatteries circuit arrangementsOcean bottomThermal insulation
The invention provides a high-precision seabed geothermal gradient detection device used for detecting seabed surface-layer geotherm parameters. The high-precision seabed geothermal gradient detection device comprises a pressure protection pipe, a thermal insulation rod, an insulator, a two-color LED, an electronic instrument cabin shell, a charging induction coil and a plurality of thermistors, wherein a cavity of the electronic instrument cabin shell is an electronic instrument cabin. The insulator is installed on one side of the electronic instrument cabin, the pressure protection pipe is supported by the insulator, the thermal insulation rod is installed in the pressure protection pipe, and the thermistors are installed on the thermal insulation rod. A three-axis acceleration sensor is installed in the electronic instrument cabin, the two-color LED and the charging induction coil are installed outside the electronic instrument cabin, a transparent protection cover is installed outside the two-color LED and the charging induction coil, and the two-color LED, the charging induction coil, the thermistors and the three-axis acceleration sensor are connected with a control device through conducting wires, wherein the control device is installed in the electronic instrument cabin. Variation of the angle of inclination of the device is indicated through the two-color LED, operation is facilitated, and data acquisition efficiency is improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH +1
Sectional type ground temperature gradient fitting method based on stratigraphic unconformity surface
InactiveCN105652342AAccurate responseOvercoming the problem of insufficient ability to identify ground temperature anomaliesDetection/prospecting using thermal methodsComplex mathematical operationsGround temperatureEngineering
The invention discloses a sectional type ground temperature gradient fitting method based on a stratigraphic unconformity surface. The method comprises the steps of: 1) determining the distribution and burial depth of the stratigraphic unconformity surface, obtaining temperature measurement data, and drawing a ground temperature curve with the temperature and the burial depth respectively serving as a transverse coordinate and a longitudinal coordinate; 2) in the range of 0-100 m downward from the stratigraphic unconformity surface, selecting the most bending part of the ground temperature curve as a ground temperature gradient critical surface, and dividing the ground temperature curve into an upper cure and a lower curve; 3) carrying out linear fitting respectively on temperature measurement data corresponding to the upper curve and the lower curve, and obtaining an upper straight line and a lower straight line, wherein the gradients thereof are respectively the ground temperature gradients of a shallow stratum and a deep stratum and reflect the practical ground temperature field of a temperature measurement well area. The method is characterized in that according to the development characteristics of stratums in different areas, the ground temperature gradients above and below the ground temperature gradient critical surface are independently fitted, so that the ground temperature gradients of upper and lower stratums are obtained, the ground temperature field characteristics of new and old stratums are really reflected, and a reliable basis is provided for oil and gas and geothermal resources exploration, development and utilization.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
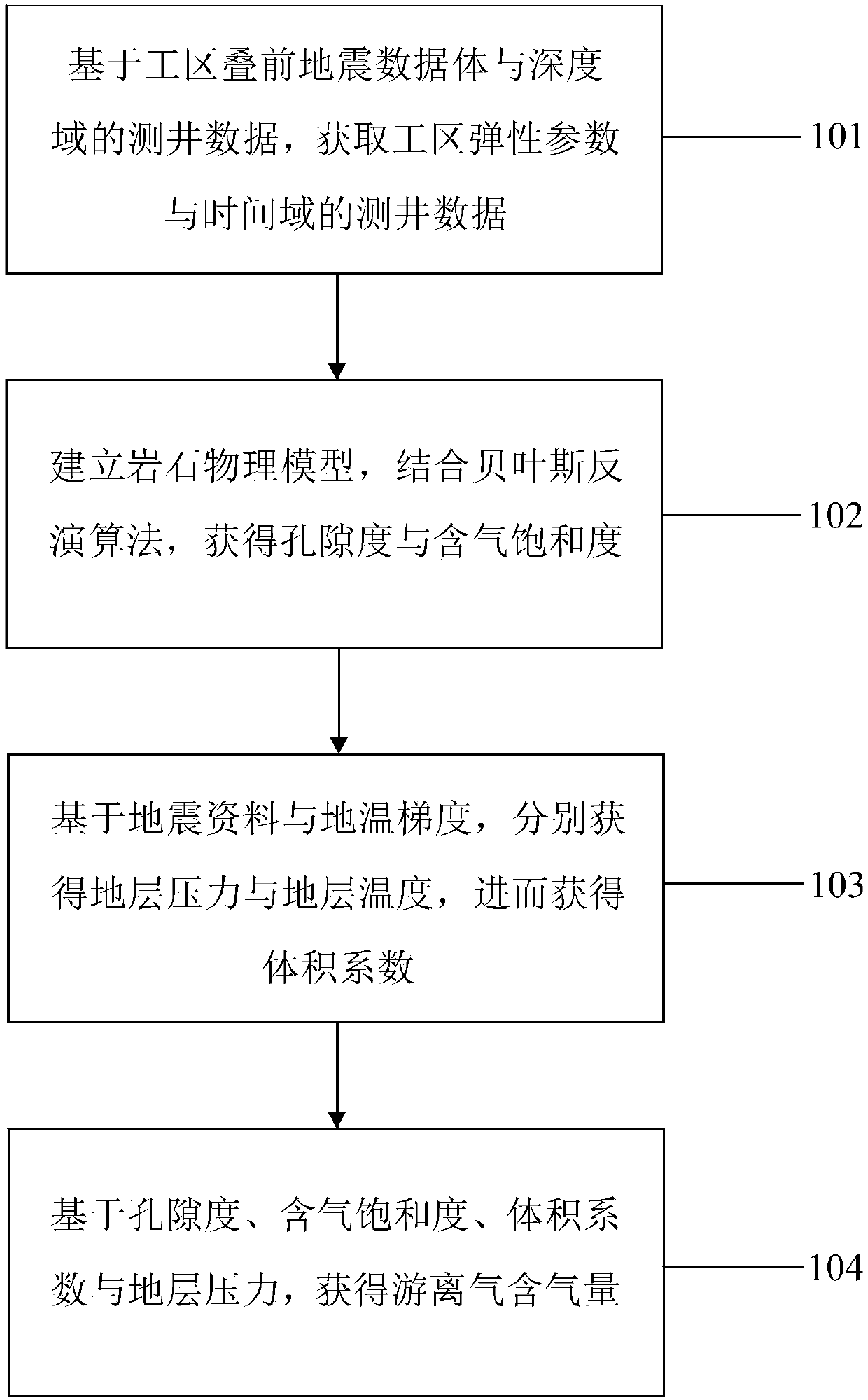
Shale gas reservoir free gas content earthquake predicating method and system thereof
The invention discloses a shale reservoir free gas content earthquake predicating method and a system thereof. The method comprises the steps of respectively acquiring work area elastic parameters andtime domain well logging data based on a work area pre-stack seismic data volume and depth domain well logging data; establishing a rock physical model based on the work area elastic parameters, andobtaining porosity and gas saturation; based on seismic data and ground temperature gradient, respectively acquiring a stratum pressure and a stratum temperature, and furthermore obtaining a volume coefficient; and based on the porosity, the gas saturation, the volume coefficient and the stratum pressure, establishing a calculation model of the free gas content, thereby obtaining the free gas content, wherein the work area elastic parameters comprise longitudinal wave impedance, transverse wave impedance and density. According to the shale reservoir free gas content earthquake predicating method and the system, through restraining the factors such as the stratum temperature, the stratum pressure, porosity and gas saturation, high-precision predication for free gas content of the shale reservoir is realized.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
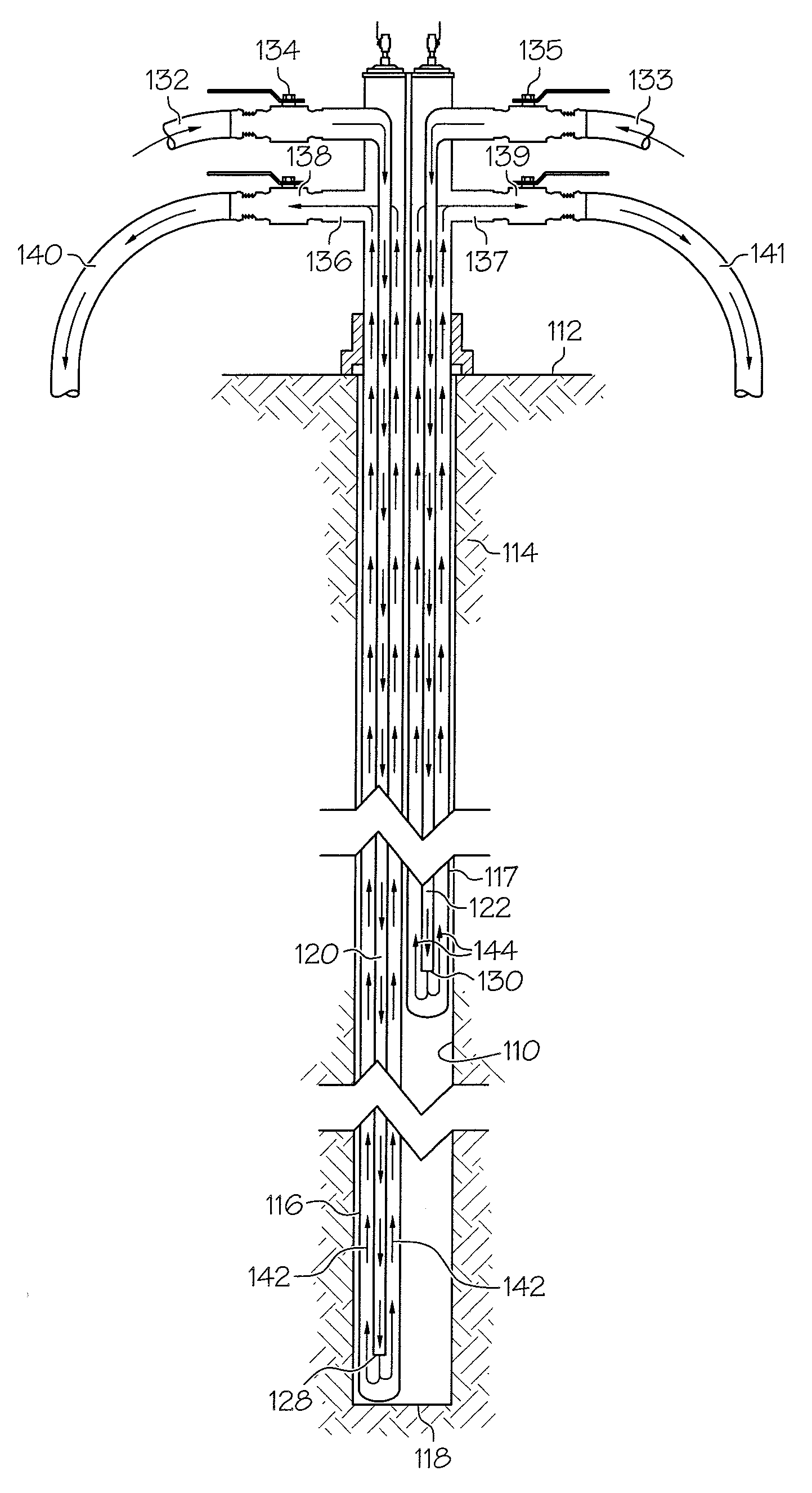
Ground freezing method and apparatus with geothermal gradient compensation
InactiveUS20070266715A1Function increaseUniformly formedDomestic cooling apparatusOther heat production devicesGround freezingProcess engineering
A ground freezing method and apparatus compensates for geothermal gradients by supplying more refrigerant to deeper parts of the earth. One or more metal freeze pipes are installed in a bore and equipped with one or more feed pipes. The feed pipes extend to different depths with the longer feed pipes being larger to supply more refrigerant to greater depths and achieve uniform top to bottom ground freezing despite the effects of geothermal gradients.
Owner:LAYNE CHRISTENSEN COMPANY
Method for establishing burial-thermal evolution history map of shale gas reservoir
InactiveCN110517794AImprove accuracyAccuracy of high thermal evolution historyInformaticsInstrumentsGround temperatureLithology
The invention provides a method for establishing a burial-thermal evolution history map of a shale gas reservoir. The method comprises the steps of acquiring layering data of a current stratum and static temperature measurement data of the current stratum; establishing a stratum lithology model of an interval for research; acquiring various burial history parameters; calculating the paleo-thickness and the buried depth of each stratum in each period; determining the ground temperature gradient, the heat conductivity, the heat generation rate and the ground heat flow value characteristics of the current ground temperature field; analyzing a formation mechanism and an evolution rule of the paleo-geothermal field; determining the maximum paleo-ground temperature experienced by the stratum towhich the sample belongs in the geological evolution process by using vitrinite reflectivity data; moreover, determining the paleo-geothermal gradient at the moment jointly by utilizing the Ro data ofthe multiple samples at different depths; determining a paleo-temperature evolution process of the sample, restoring a paleo-geothermal gradient evolution history, and drawing a burial history map ofthe paleo-geothermal field of the research area; calculating hydrocarbon source rock maturity evolution history; establishing and drawing a burial-thermal evolution history map of a sedimentary basin. According to the invention, high thermal performance history precision can be obtained.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
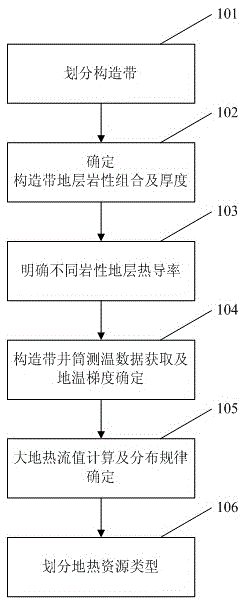
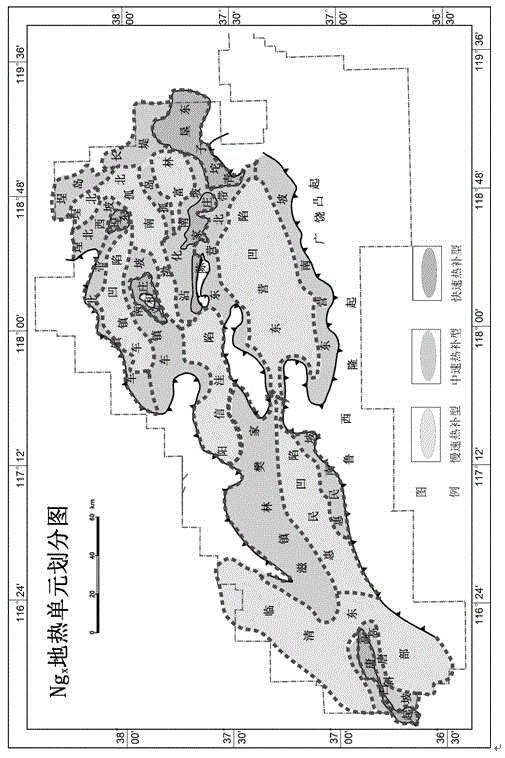
Sedimentary basin type underground heat resource classification method
ActiveCN105487135AOvercoming intractable difficultiesOvercoming the problem of low division accuracySeismologyLithologyGround temperature
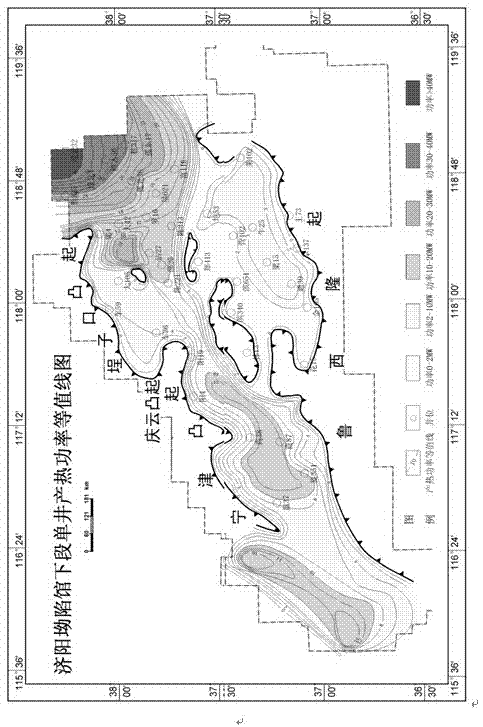
The invention provides a sedimentary basin type underground heat resource classification method. The method comprises the steps that 1) tectonic zones of a sedimentary basin are divided by utilizing well drilling, logging, well logging and earthquake data and the like; 2) lithological combination and thickness of the stratum are determined for different tectonic zones; 3) the thermal conductivities of different lithological stratums are made clear via rock core sampling test; 4) shaft temperature measuring data of the tectonic zones is obtained, and distribution of the ground temperature gradient is determined according to the shaft temperature measuring data; 5) the ground heat flow value is calculated by utilizing the thermal conductivities of different lithological stratums and the ground temperature gradient comprehensively via a geothermic formula, and the planar distribution rule of the ground heat flow value is made clear; and 6) sedimentary basin type underground heat resource is classified according to the planar ground heat flow value. The method is highly operable, and can be used to provide more accurate methods and materials for research on geothermal reservoir reasons, evaluation of underground heat resource amount and research on development and utilization area selection of the underground heat resource.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
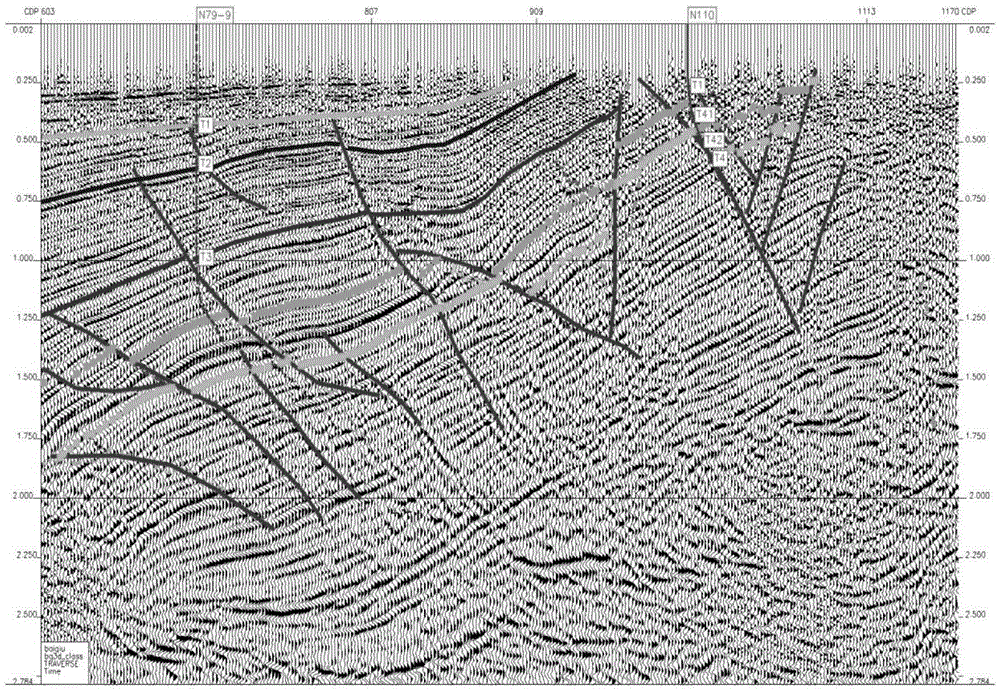
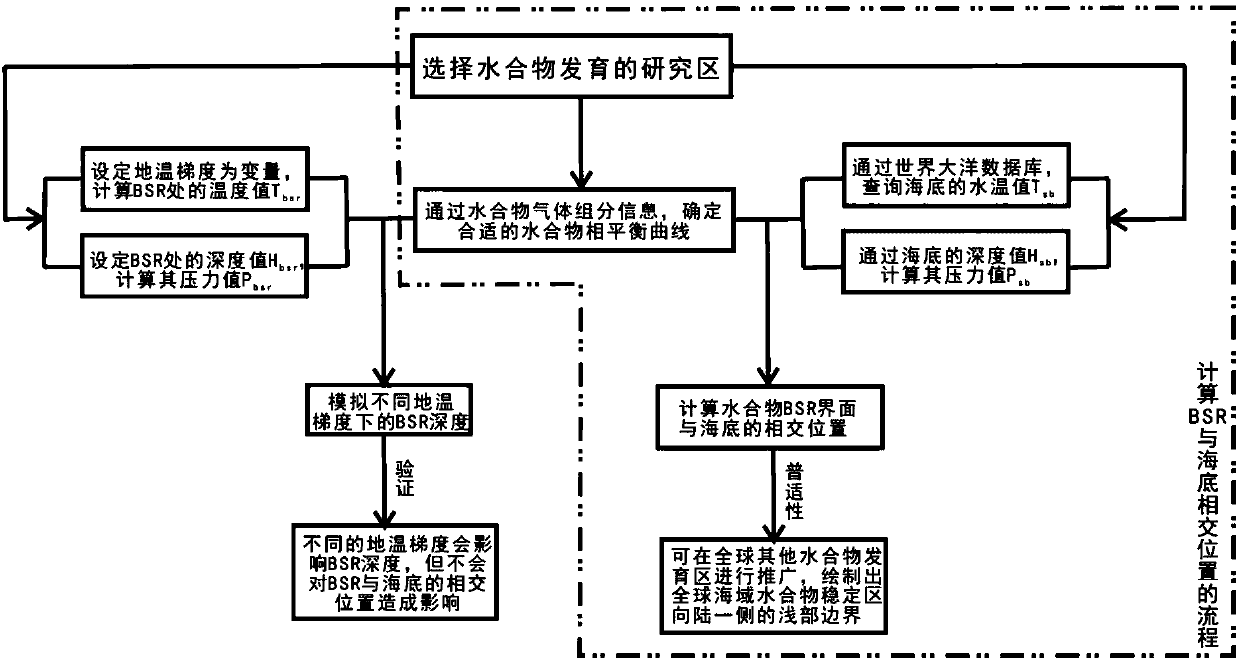
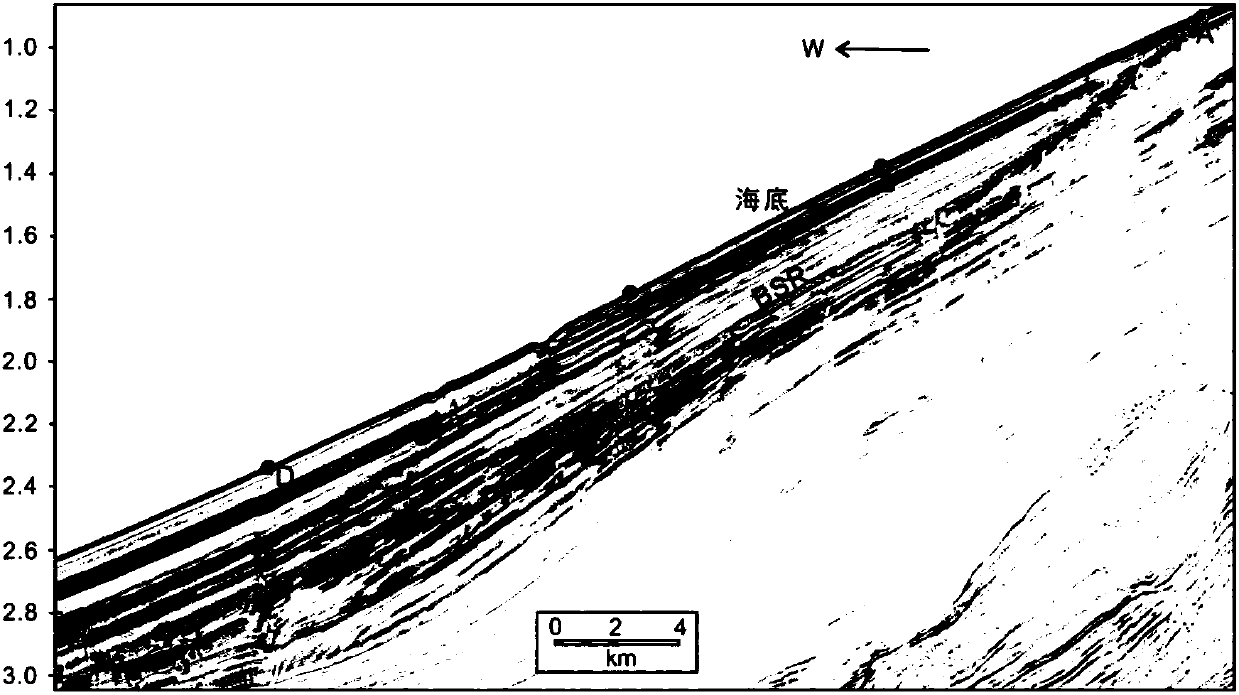
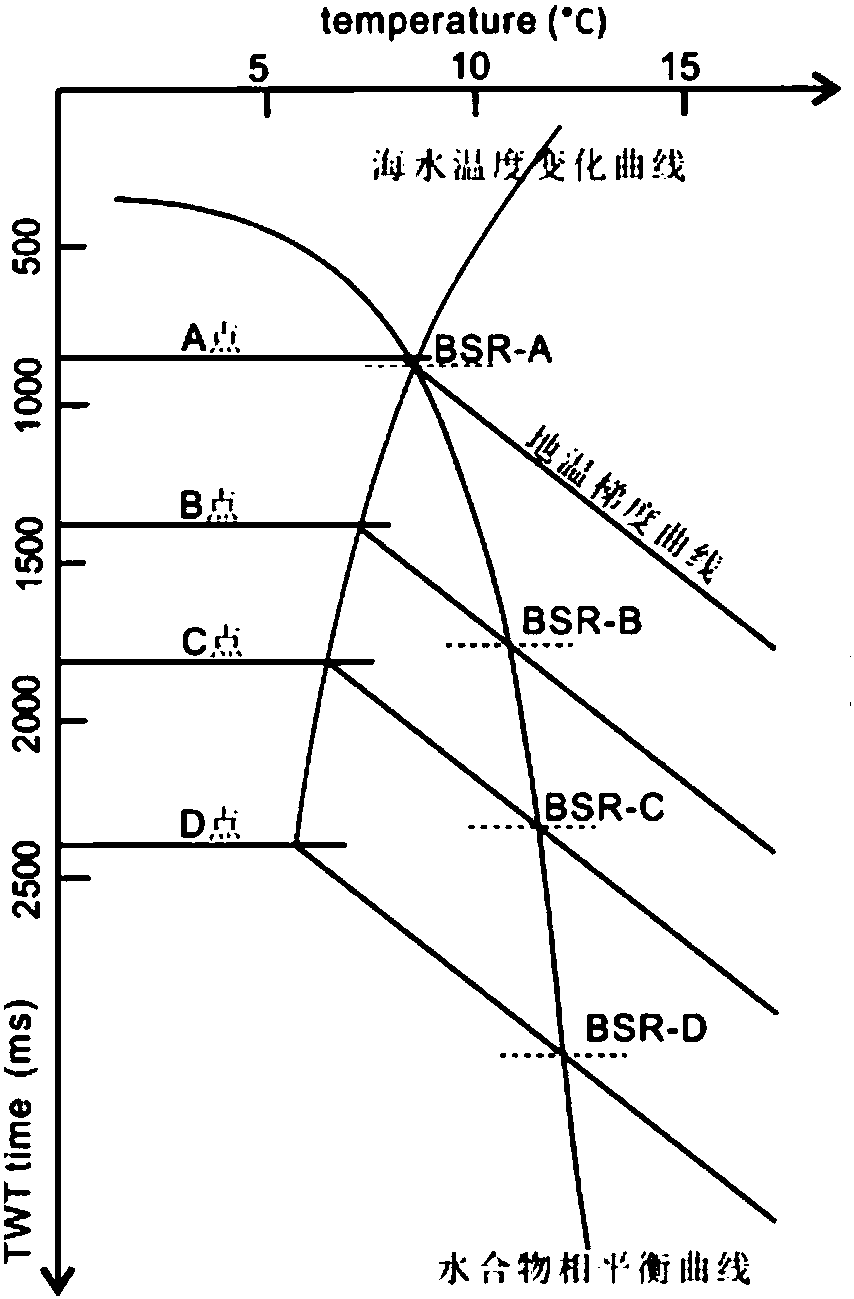
Research method for determining intersecting position of gas hydrate BSR (Bottom Simulating Reflection) interface and sea bottom
InactiveCN107861158ACalculations are reliableEasy to operateSeismology for water-covered areasSurface oceanStudy methods
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
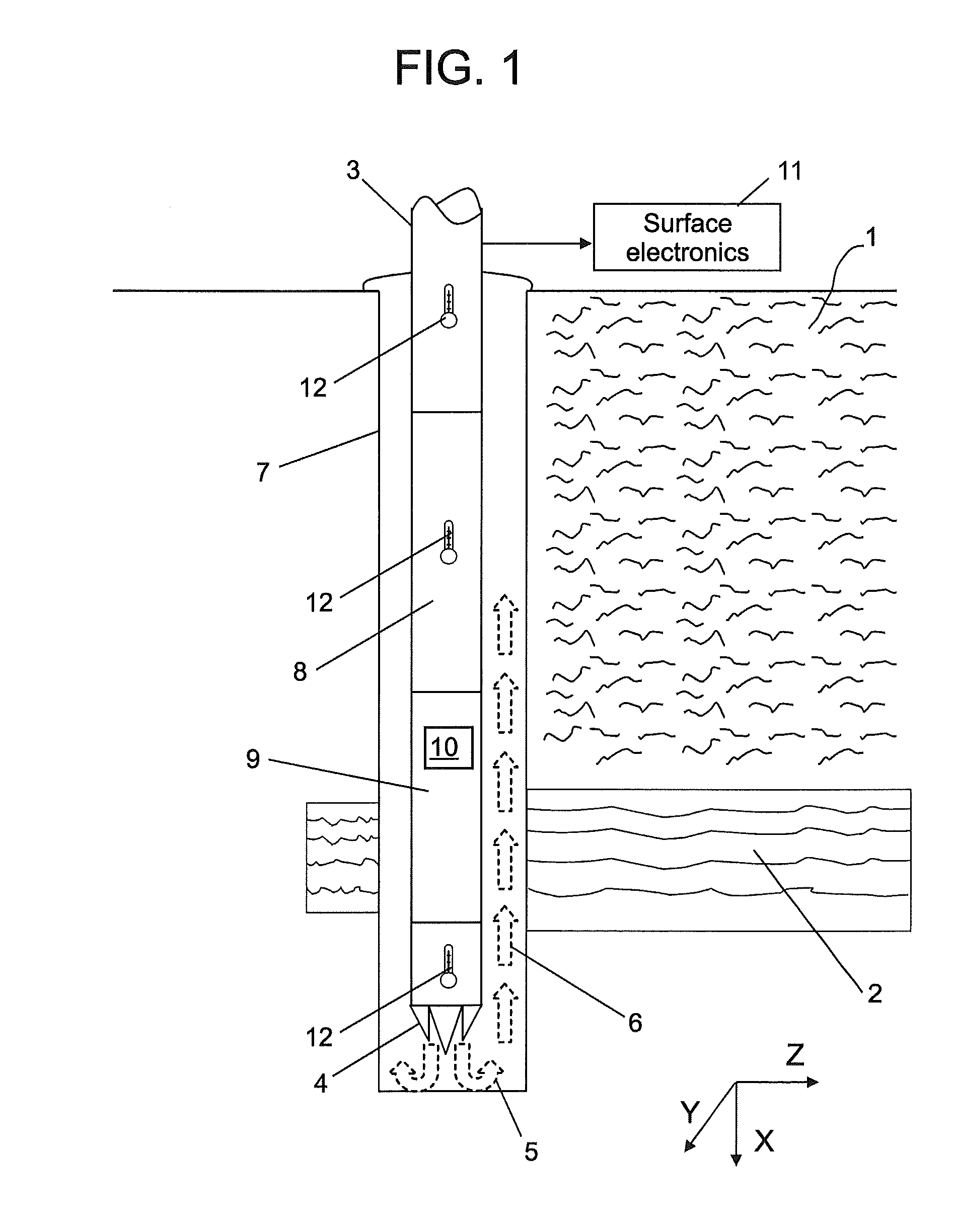
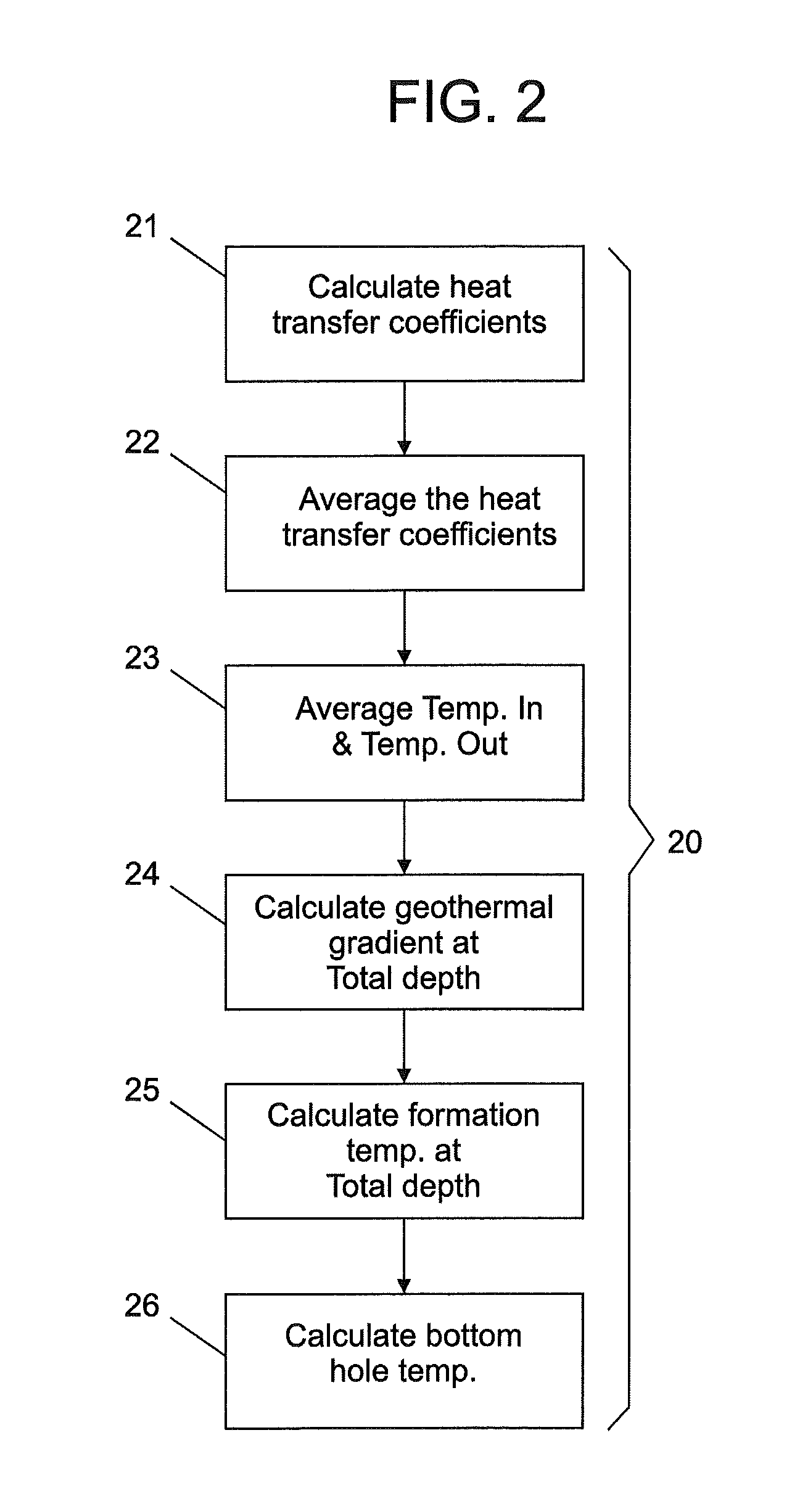
Distributed measurement of mud temperature
ActiveUS20100106421A1Thermometer detailsElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingEngineeringHeat transfer coefficient
A method for estimating a temperature within sub-surface materials traversed by a wellbore includes: obtaining temperature data from a plurality of measurements of temperature taken within the wellbore; calculating an overall heat transfer coefficient from the measurement data; calculating a geothermal gradient from the overall heat transfer coefficient; and using the geothermal gradient to estimate the temperature within the sub-surface materials. A system and a computer program product are provided.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Automobile out star wheel isothermal extrusion preliminary shaping device
InactiveCN101264489AReduce temperature gradientReduce lossExtrusion diesPass rateMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a pre-forming device of automobile external star wheel by isothermal extrusion, which comprises a punch and a female die, the punch and the female die are laterally fixed and vertically movably matched by means of a guide pillar. The female die is provided with a die cavity, and a heating device is arranged at the periphery of the die cavity. The heating unit is arranged at the die cavity of the invention to maintain the outer layer temperature of the mold. The pre-forming device has the advantages of greatly reducing the geothermal gradient of blank and mold, effectively lessening the thermal dispersion of blank in the forming process, achieving the extrusion pre-forming under the isothermal condition, avoiding the situation that the die cavity can not be filled due to excessively fast temperature drop, material deformation and resistance increase, thus improving the pass rate of finished products, and reducing waste.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Marine gas hydrate three-phase dynamic virtual construction method
ActiveCN109488261AOvercome the problem of three-phase changeRealize dynamic simulation effectConstructionsFluid removalLaboratory testGeothermal gradient
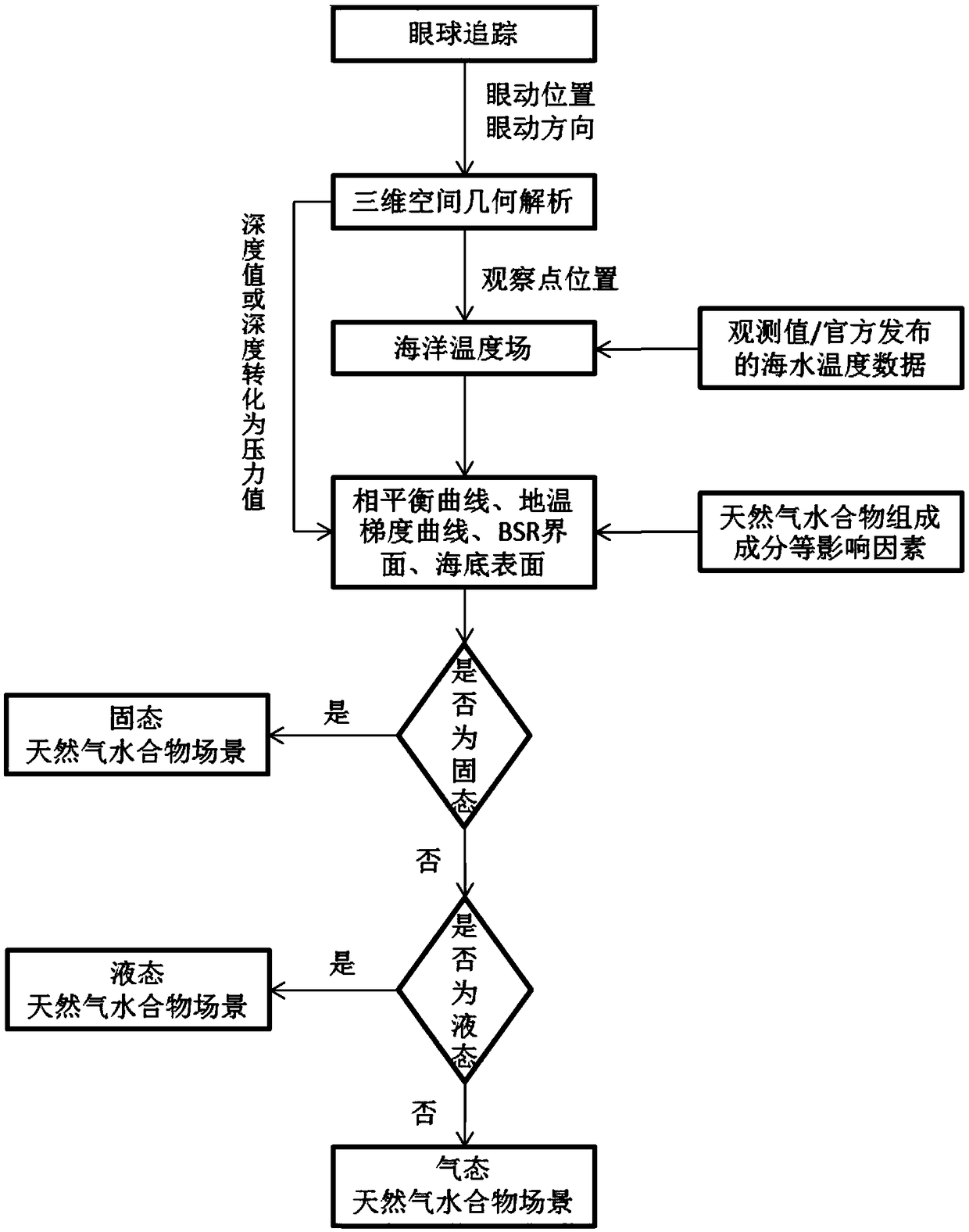
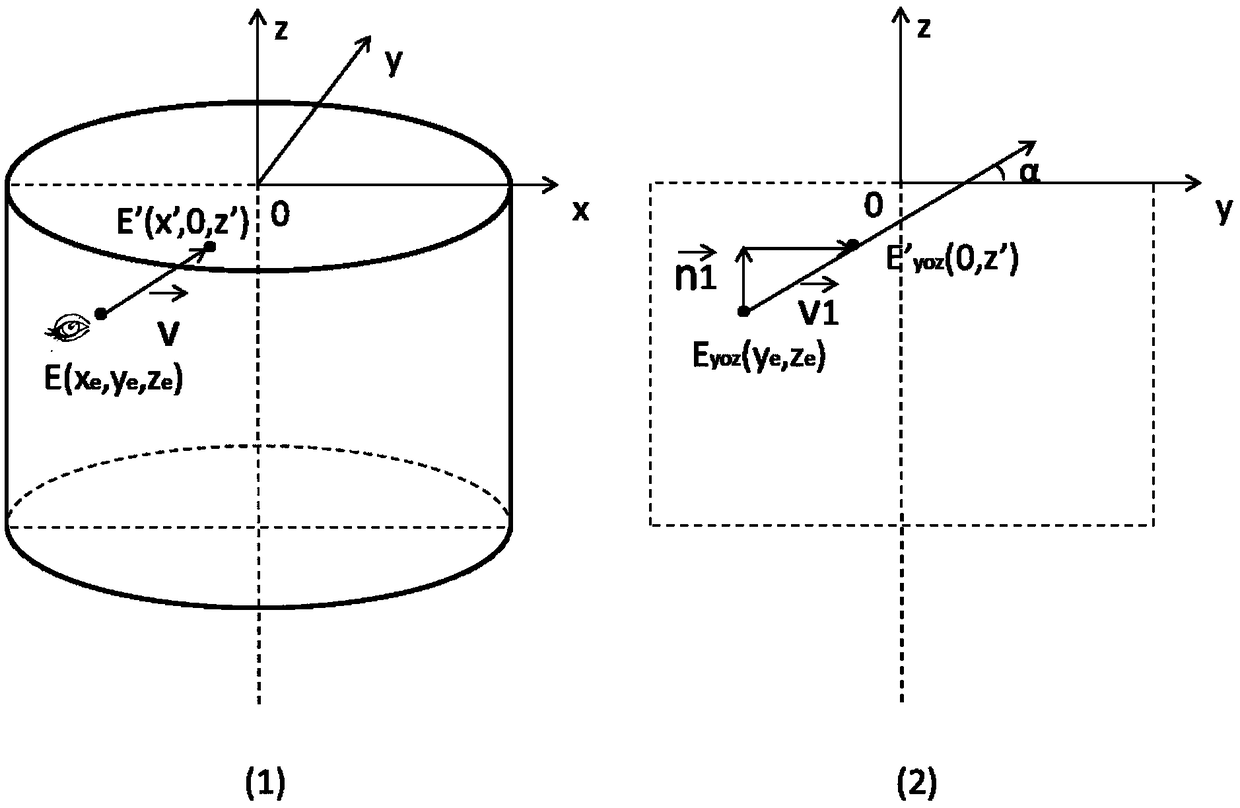
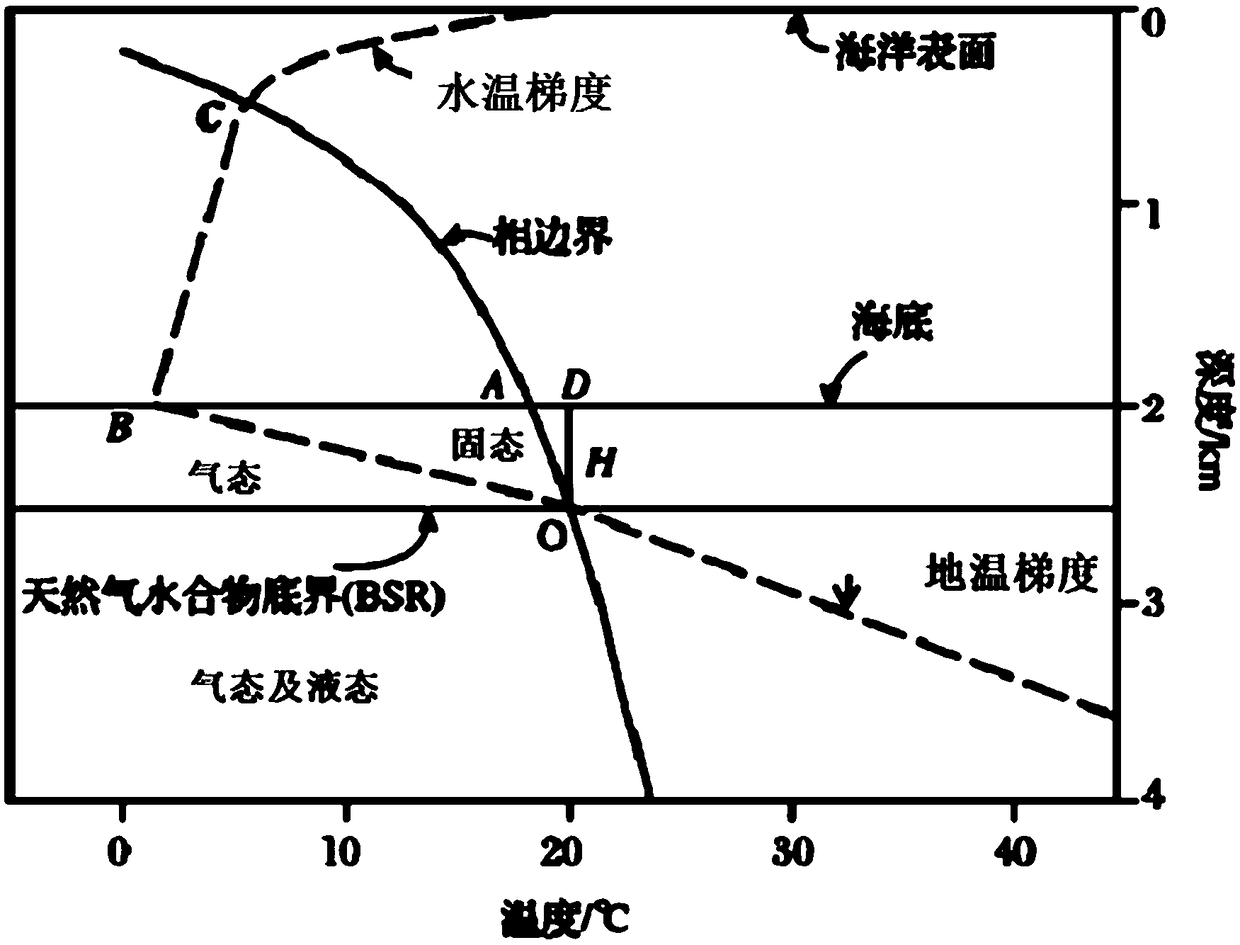
The invention provides a marine gas hydrate three-phase dynamic virtual construction method. According to the method, a view angle is interactively positioned by eyeball tracking, the position of an observation point is acquired by three-dimensional space geometric analysis, the pressure value and the temperature value of the observation point are acquired according to a depth pressure conversionand marine temperature field model, the physical state of a gas hydrate at the position of the observation point is judged according to a gas hydrate three-phase state judgment model built according to geothermal gradient, water temperature gradient, deep sea gas hydrate phase equilibrium curves and the like, the physical state is dynamically displayed in a three-dimensional scene, and eyeball tracking driven gas hydrate three-phase state dynamic simulation effects are achieved. Marine gas hydrate three-phase conversion virtual construction and expression are achieved, so that the stabilizingmechanism of the marine gas hydrate is visually and vividly expressed, gas hydrate three-phase virtual scenes of different sea areas can be built based on the method, and the method is widely used forthe fields of marine gas hydrate laboratory test analysis research, on-site mining simulation, teaching, popularization of science and the like.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF MARINE GEOLOGY
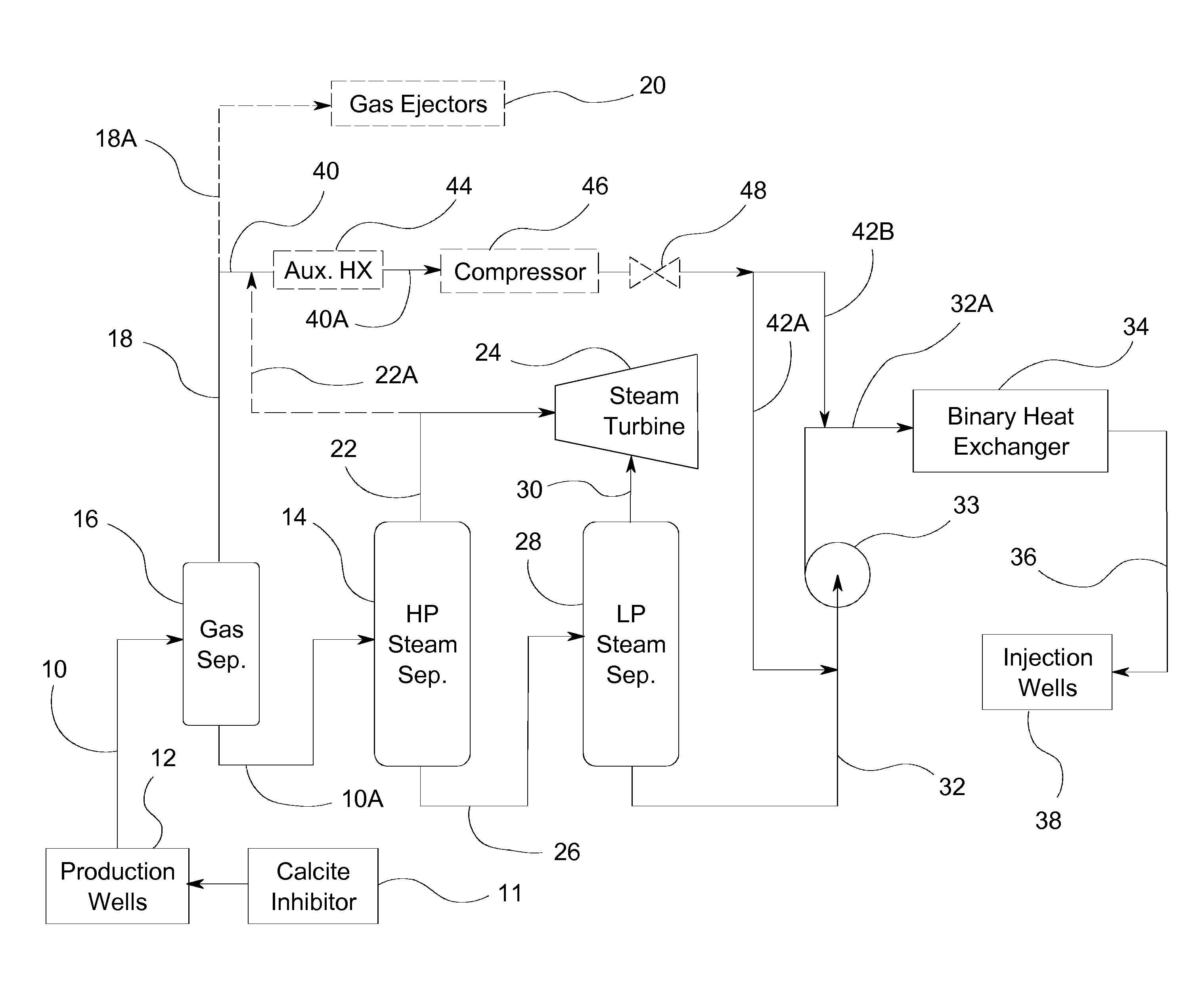
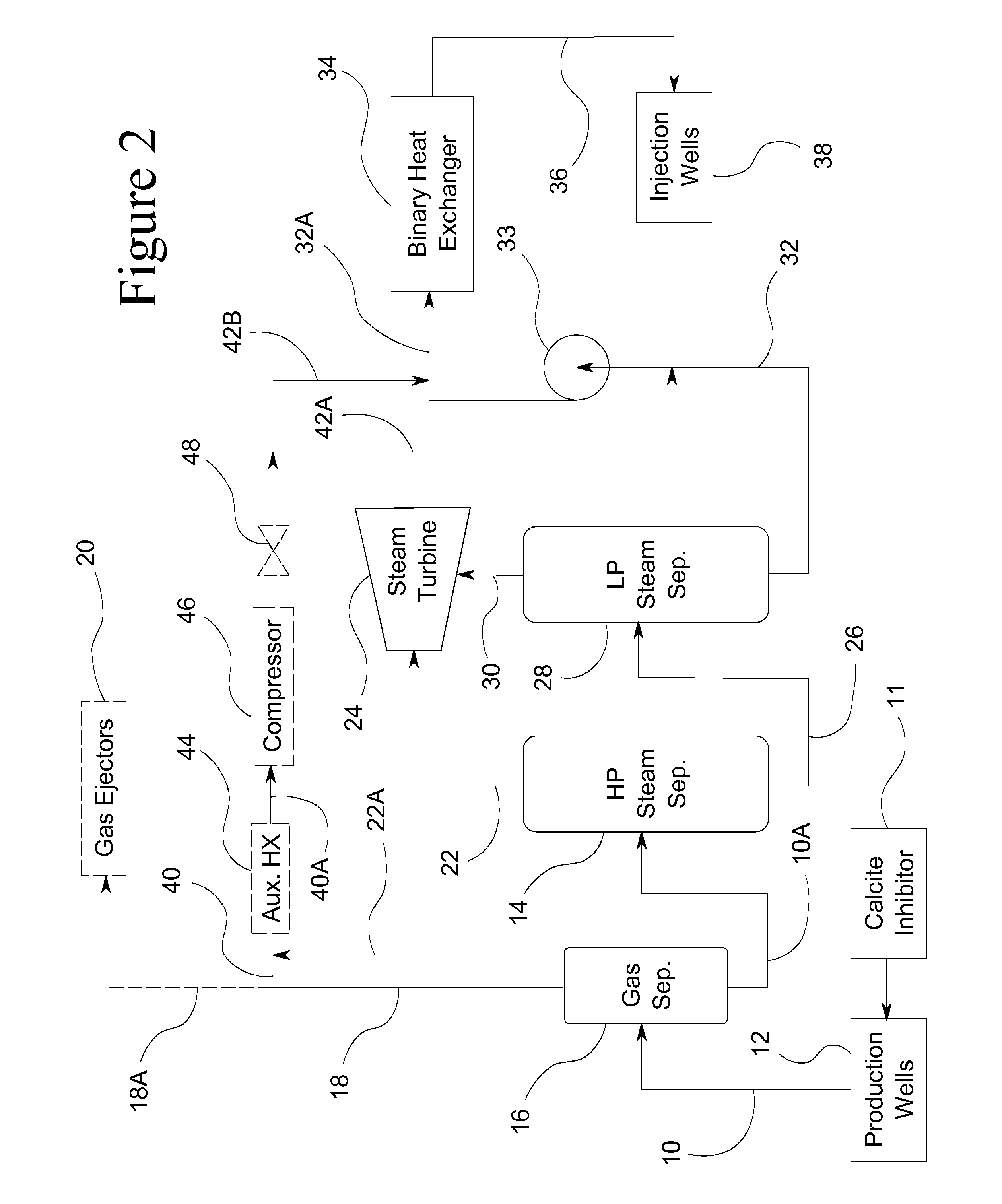
Return carbon dioxide to flashed geothermal brine to control scale deposition in a geothermal power plant
ActiveUS20110219769A1Reduced pHReduce supersaturationGeothermal energy generationScale removal and water softeningMetallic sulfideDecrease ph
Geothermal brine always contains some carbon dioxide in solution. Separating steam from geothermal brine removes the carbon dioxide, sharply increasing the pH of the brine and causing precipitation of pH sensitive minerals, including calcium carbonate, magnesium silicate and other metal silicates, clays, and metal sulfides. The binary heat exchanger in a steam-binary hybrid geothermal power plant is especially sensitive to scale deposition from flashed geothermal brine, and application of expensive scale inhibitors is required.Deposition of scale in the binary heat exchanger can be controlled by separating a small amount of gas-rich vapor from the brine before the main stage of steam separation, and combining this gas rich vapor with the flashed brine before in enters the binary heat exchanger. The carbon dioxide thus added to the brine will decrease pH, decreasing or completely blocking precipitation and deposition of pH sensitive minerals as scale.
Owner:CHEMTREAT
Inverted arc layer buried geothermal anti-freezing heating system of energy tunnel
InactiveCN106437792ALow operating and maintenance costsImprove the heating effectUnderground chambersOther heat production devicesAnti freezingGeothermal heating
Provided is an inverted arc layer buried geothermal anti-freezing heating system of energy tunnel. The system comprises a tunnel heat exchange section and a tunnel heating section. In the tunnel section corresponding to the tunnel heat exchange section, a heat exchange layer is placed between the tunnel inverted arc and a refilled layer. A first inlet water hole is communicated with a first water feeding pipe. A first outlet water hole of the heat exchange layer is communicated with a first return water pipe. The first water feeding pipe and the first return water pipe are both connected with the front end of a heating pump to form heat exchange circulation pipeline. In the tunnel section corresponding to the tunnel heating section, a heating layer is placed both between a tunnel primary liner and a tunnel secondary liner, and between a road surface and the refilled layer. A second inlet water hole of the heating layer is communicated with a second water feeding pipe. A second return water hole is communicated with a second water return pipe. Both the second water feeding pipe and the second water return pipe are connected with the rear end of the heating pump to form a heat circulation pipeline. The system has the advantage of having good adaptability and high efficiency of heat exchange, saving cost and shortening construction cycle.
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY +1
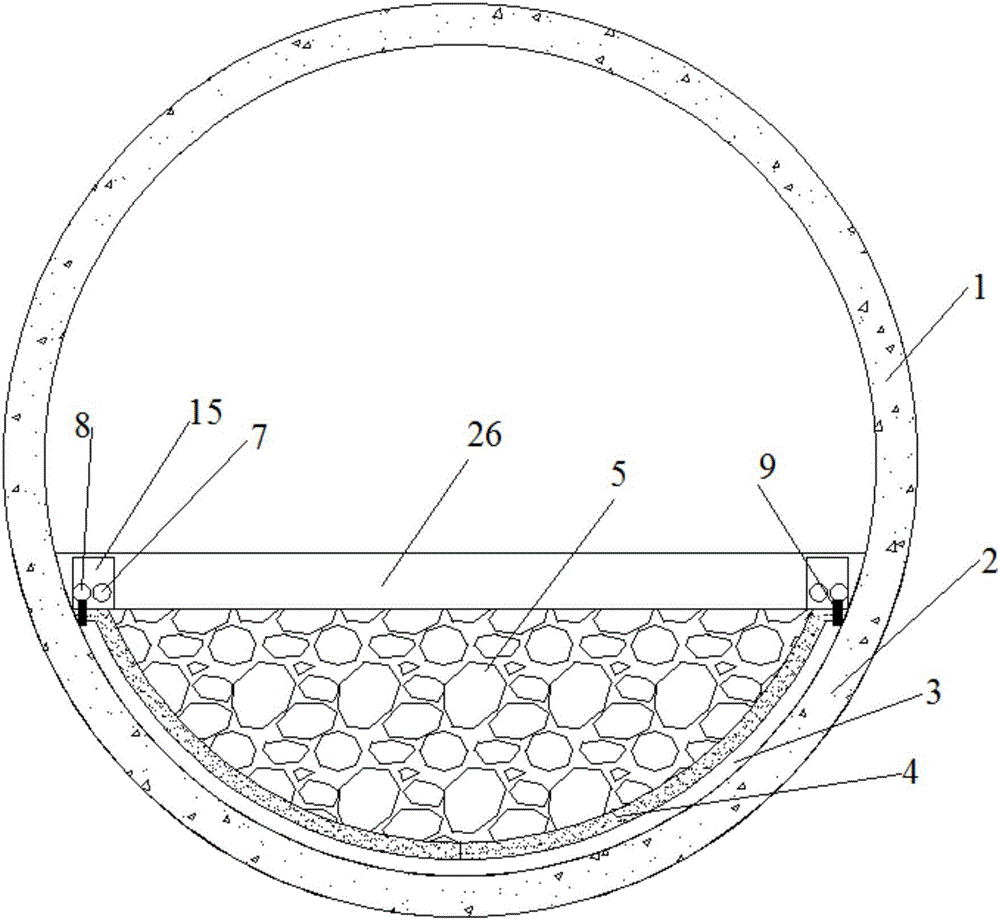
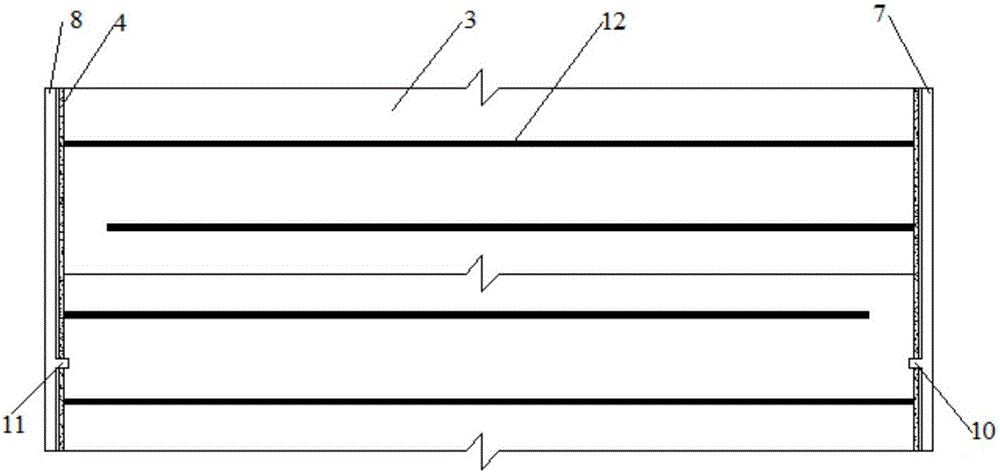
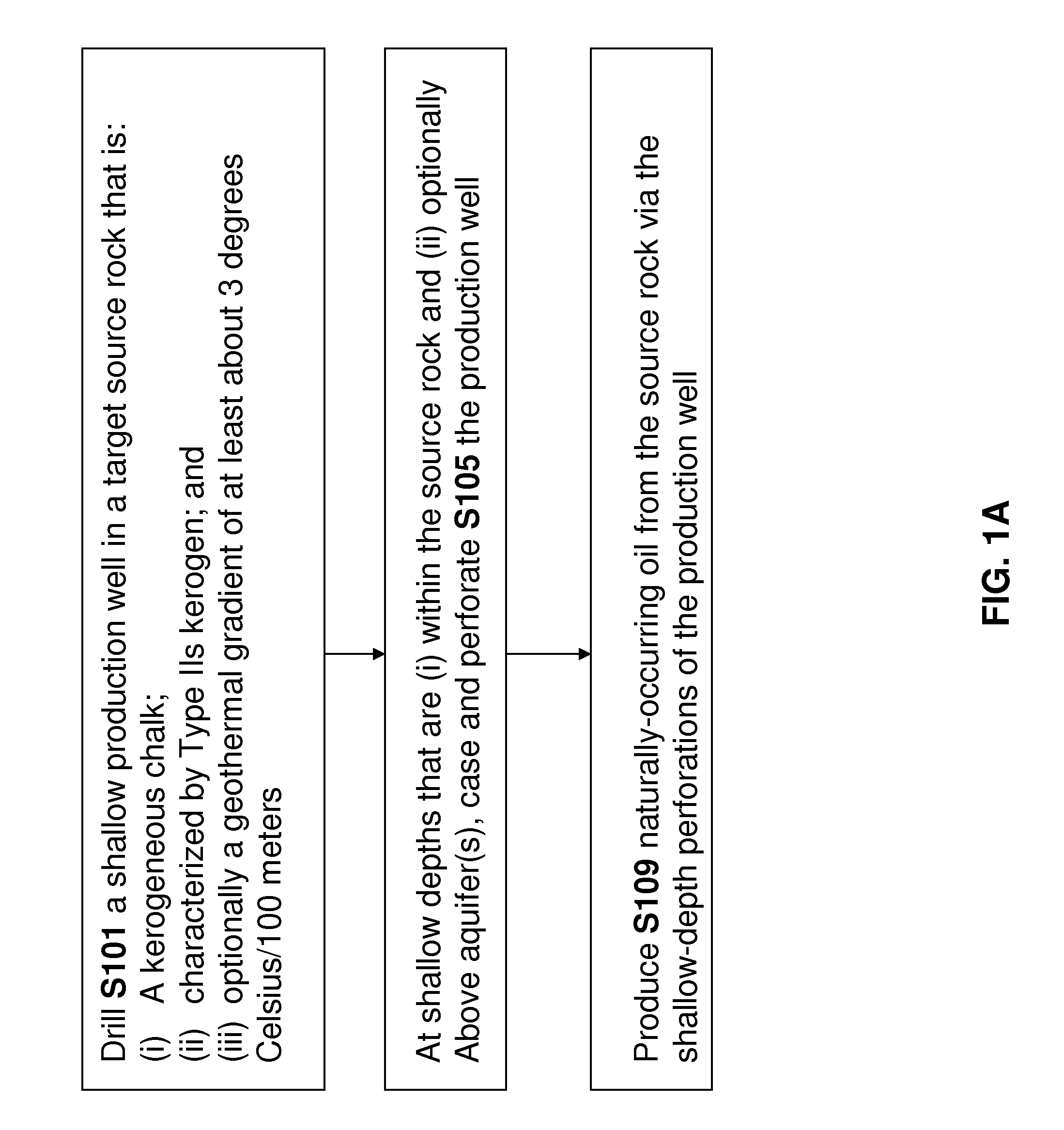
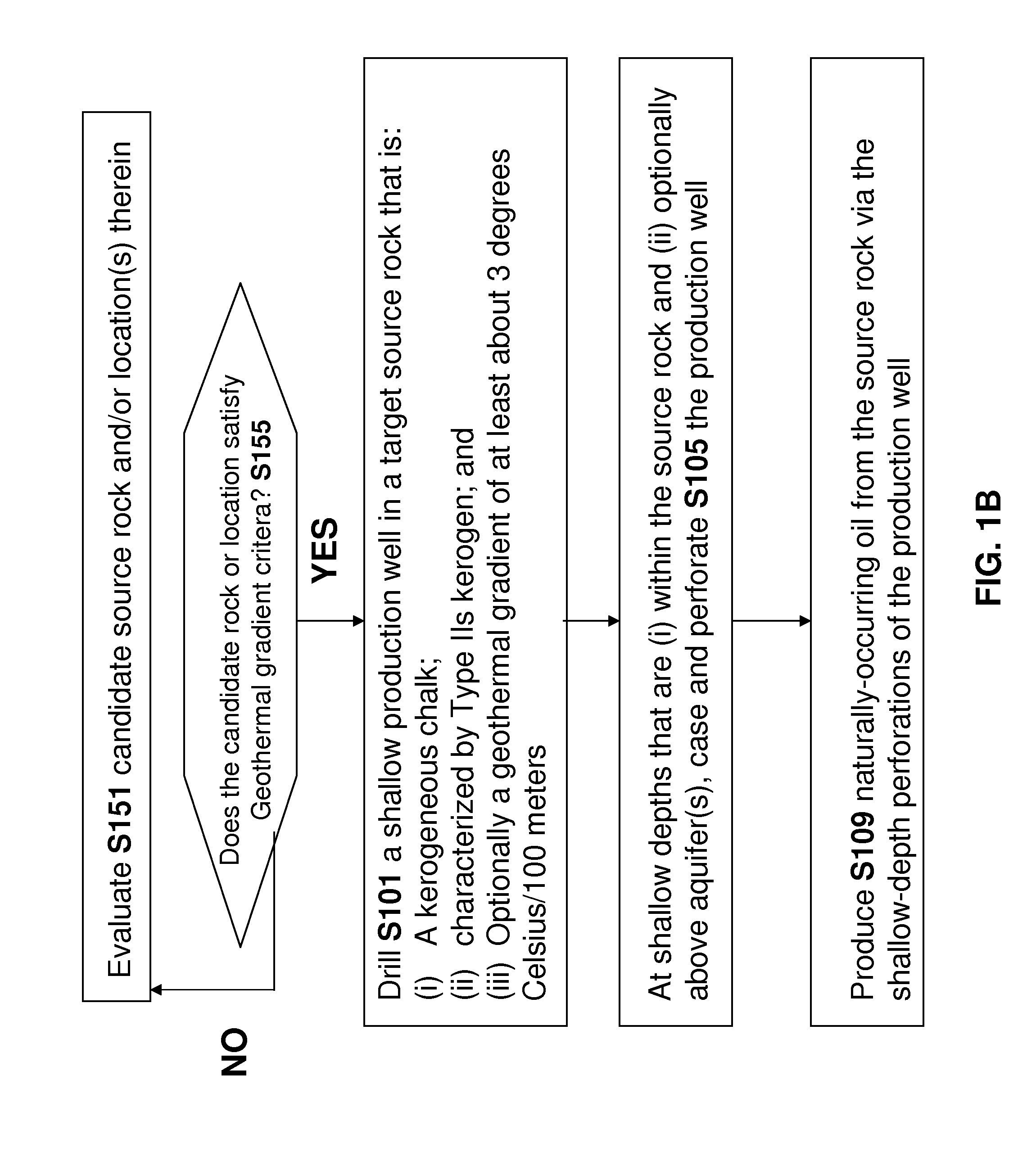
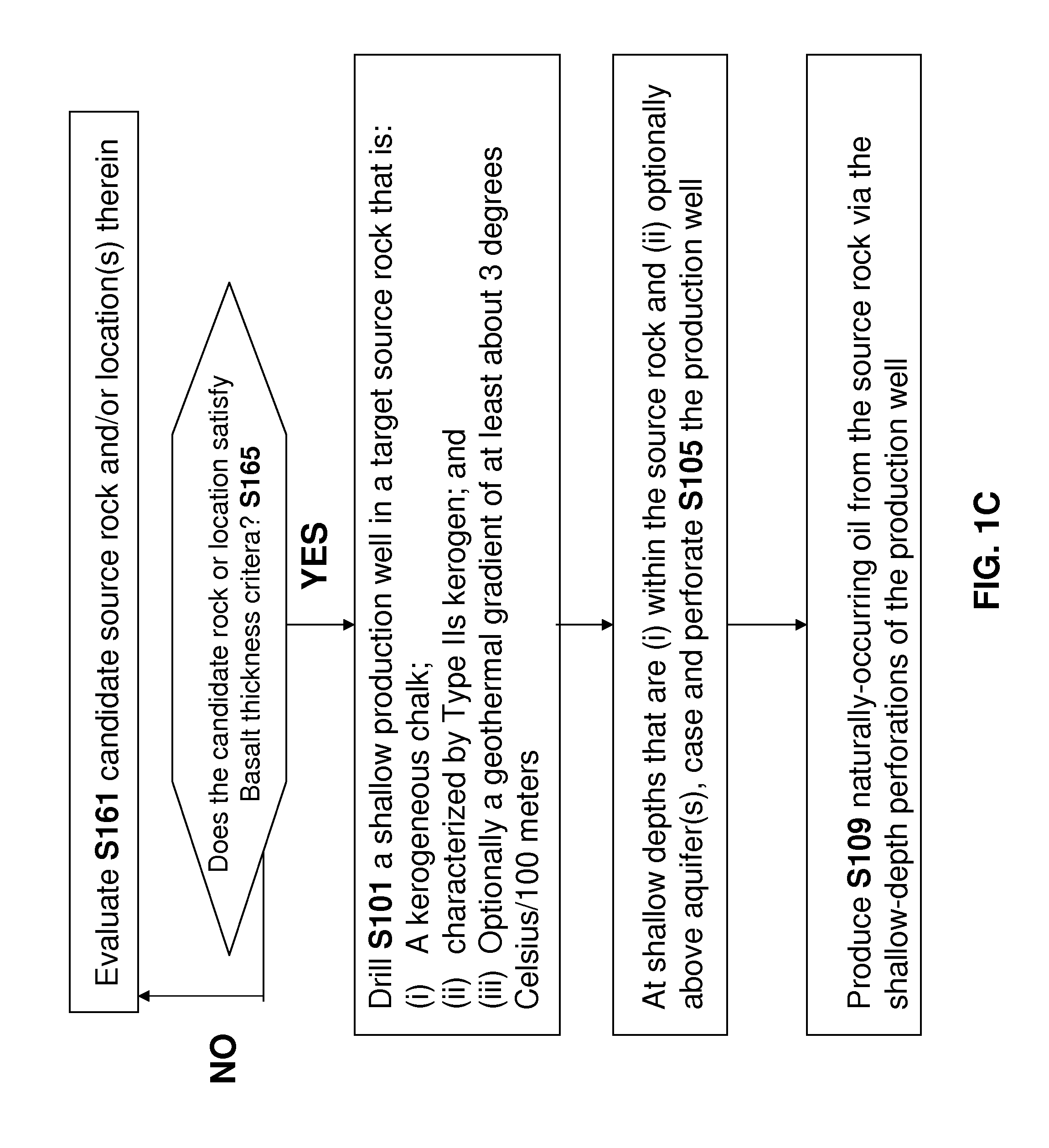
Method and apparatus for producing unconventional oil at shallow depths
InactiveUS20150184500A1Sufficient thermal energyLow costSurveyHydrocarbon distillationKerogenWell drilling
An oil production well is drilled into a kerogenous chalk source rock comprising (i) type IIs kerogen and (ii) shallow naturally-occurring unconventional oil derived from the type IIs kerogen that is resident within pore space of the source rock. In some embodiments, the production well is drilled at a location where the geothermal gradient is at least 3 degrees C. per 100 m is present at or near the production well. It is believed that the presence of this geothermal gradient accelerated maturation of the type IIs kerogen of the source rock to convert a portion of the type IIs kerogen into the unconventional oil. In some embodiments, the shallow production well is non-vertical. In some embodiments, at depths that are shallow and within the source rock, the production well is cased and perforated. Oil from the source rock may be produced via the production well and the shallow-depth perforated locations thereof.
Owner:GENIE IP
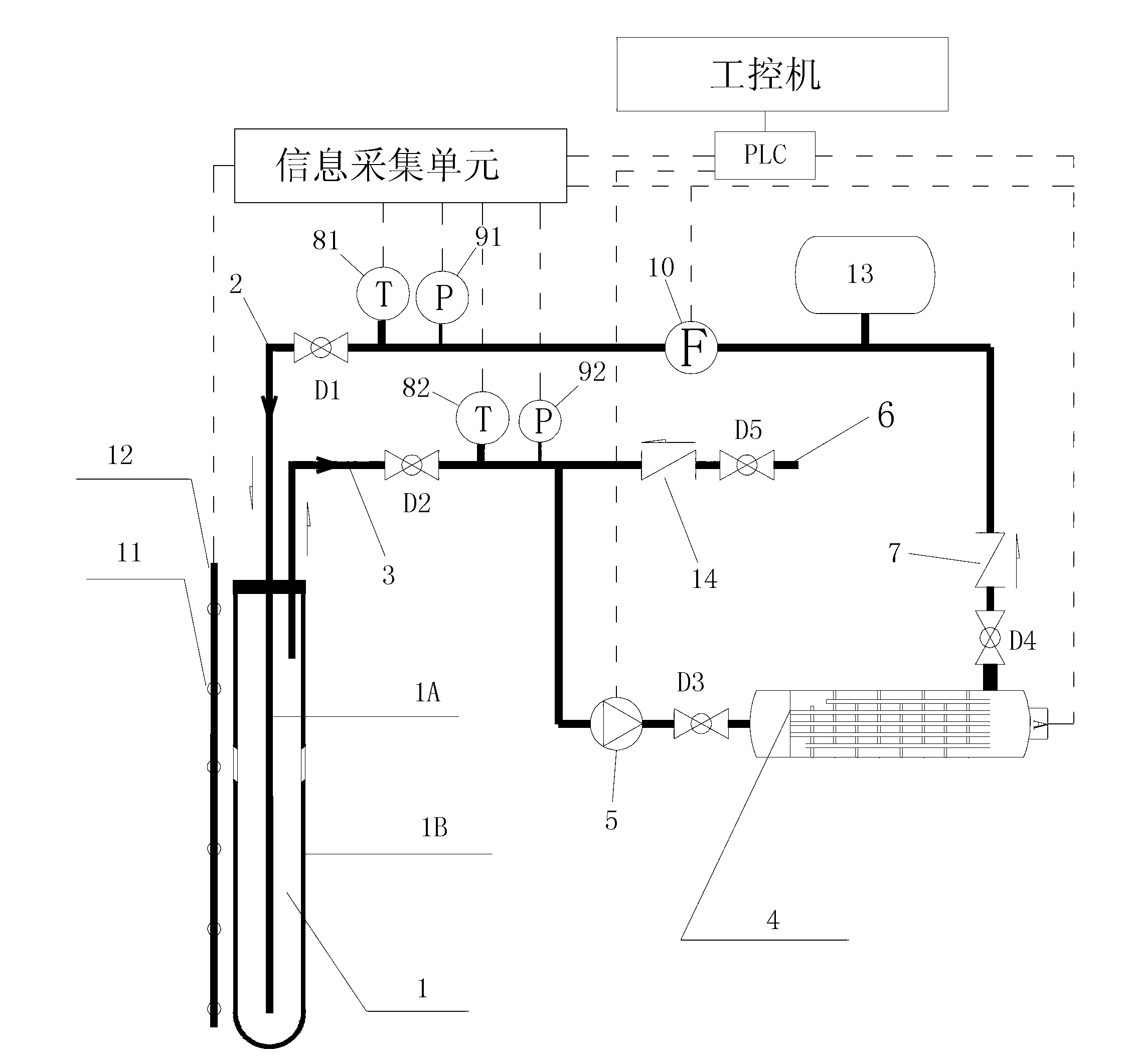
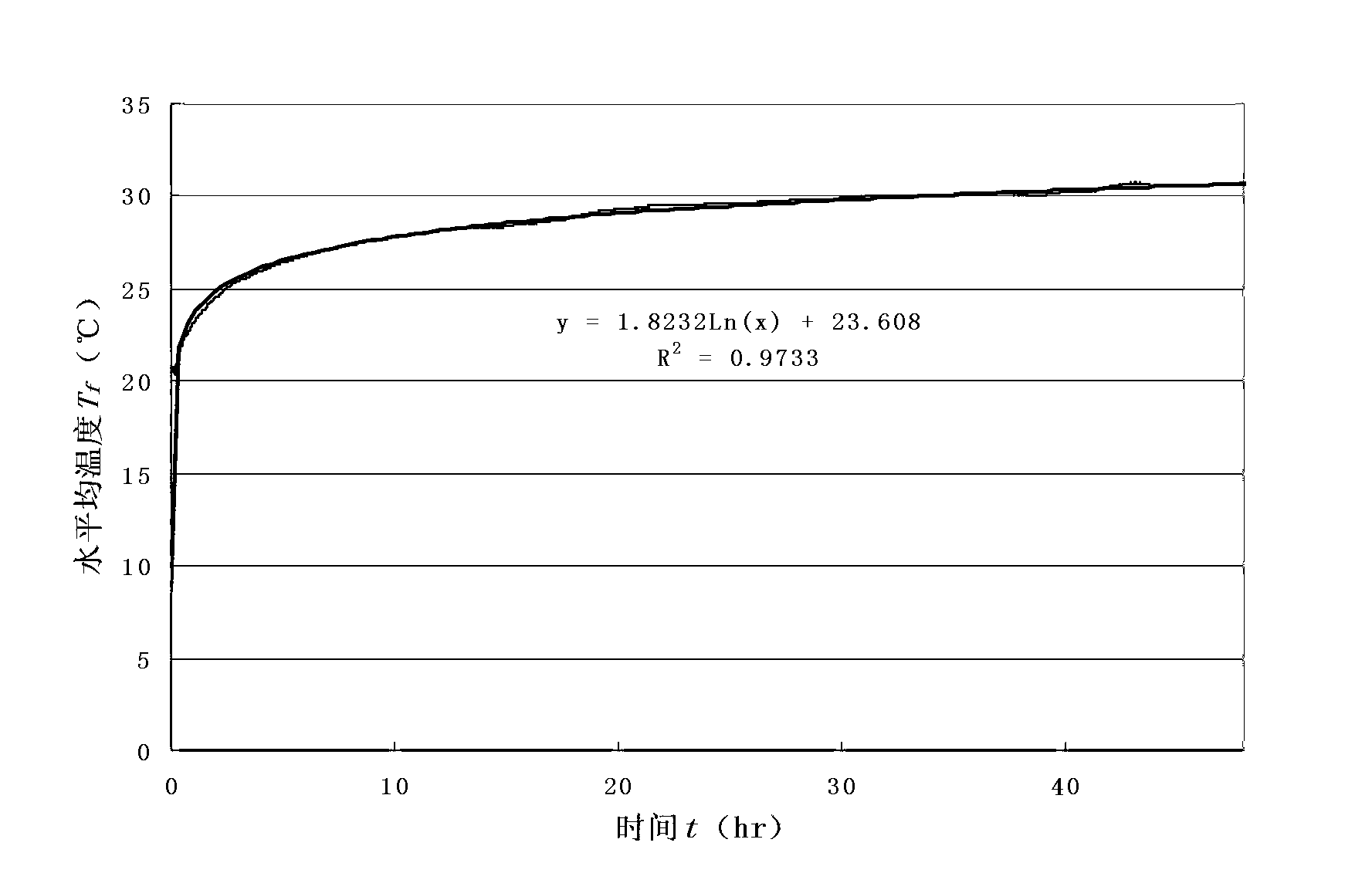
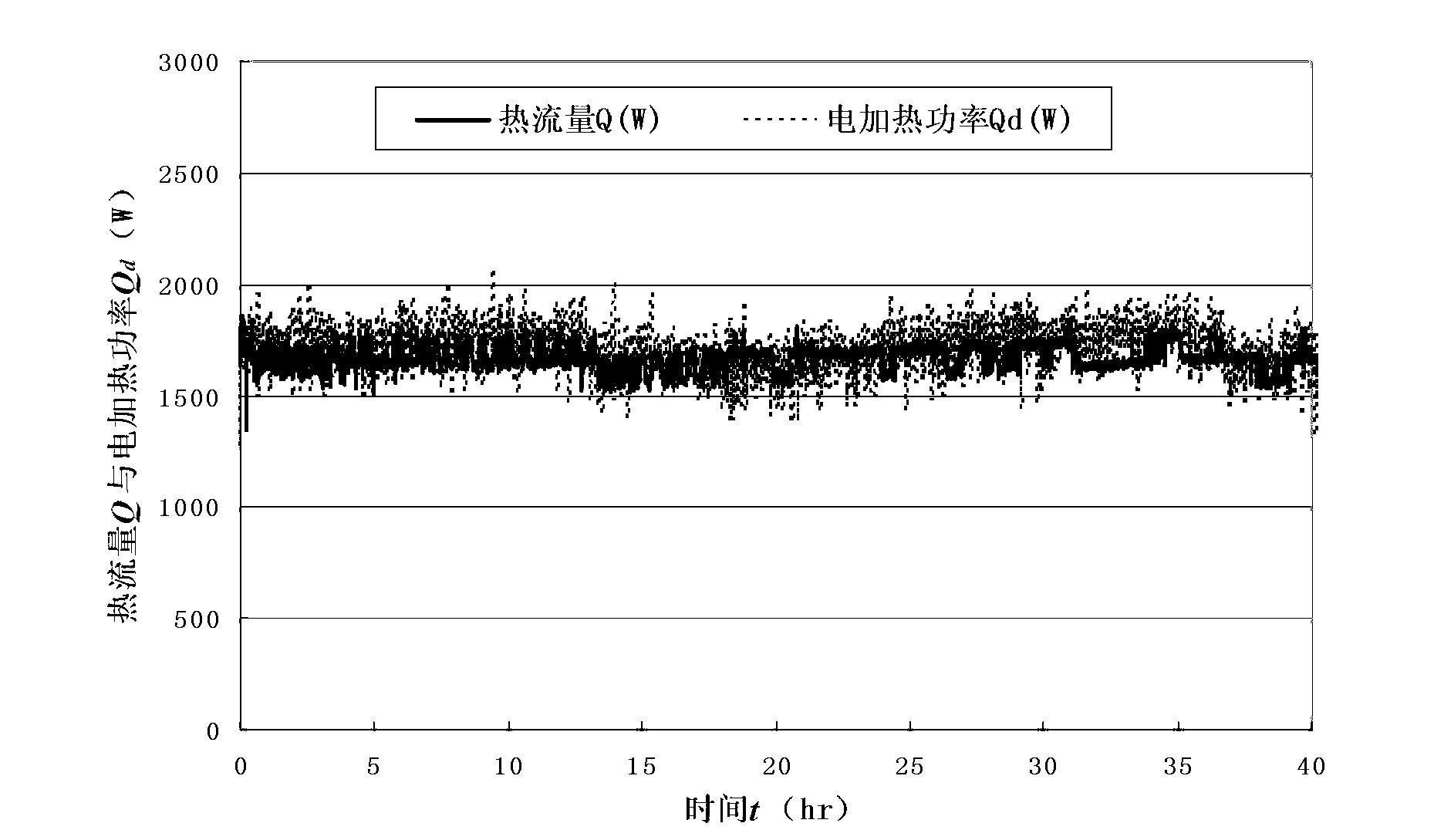
Rock-soil thermophysical property tester
InactiveCN103018274AReasonable application of theoryUniversalMaterial heat developmentGround temperatureHeat transmission
The invention discloses a rock-soil thermophysical property tester, which comprises a heat exchanger, a water inlet pipe, a water outlet pipe, a heater, a centrifugal water pump, a flowmeter, a water inlet pipe thermometer, a water outlet pipe thermometer and a detector. The heat exchanger adopts a sleeve type heat exchanger and consists of an inner pipe and an outer pipe, namely an inner cylinder and an outer cylinder. Theoretically, the rock-soil thermophysical property tester is similar to or even completely meets a physical model presumed by a heat transmission model; the precision of measured rock-soil heat conduction coefficients is effectively improved; furthermore, a plurality of temperature sensors are buried in the ground and are used for monitoring ground temperature gradient in real time; actual temperature of rock-soil can be really reflected; the calculation precision and verification of the heat conduction coefficient can be conveniently improved; the rock-soil thermophysical property tester is compact in structure and portable; on-site running is stable; the test precision meets a standard requirement; the whole test process is automatically executed; and the rock-soil thermophysical property tester is convenient to operate, is stable in performance and is suitable for long-time running test research on a buried heat exchange pipe of a ground source heat pump.
Owner:ZHEJIANG COLLEGE OF CONSTR
Method for compiling top surface temperature contour map of oil region heat reservoir
InactiveCN109751044AAvoid the inconvenience of compilingHigh precisionConstructionsGround temperatureWell drilling
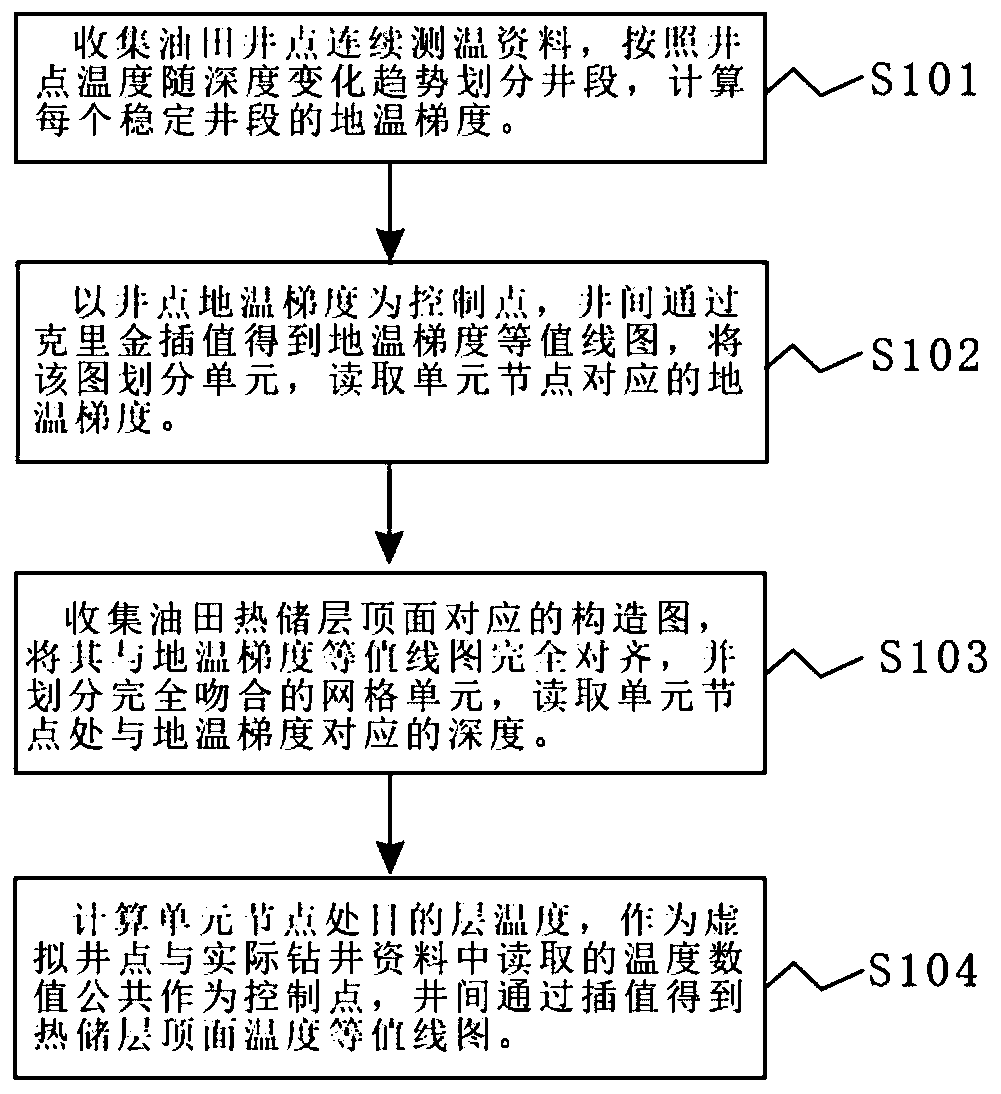
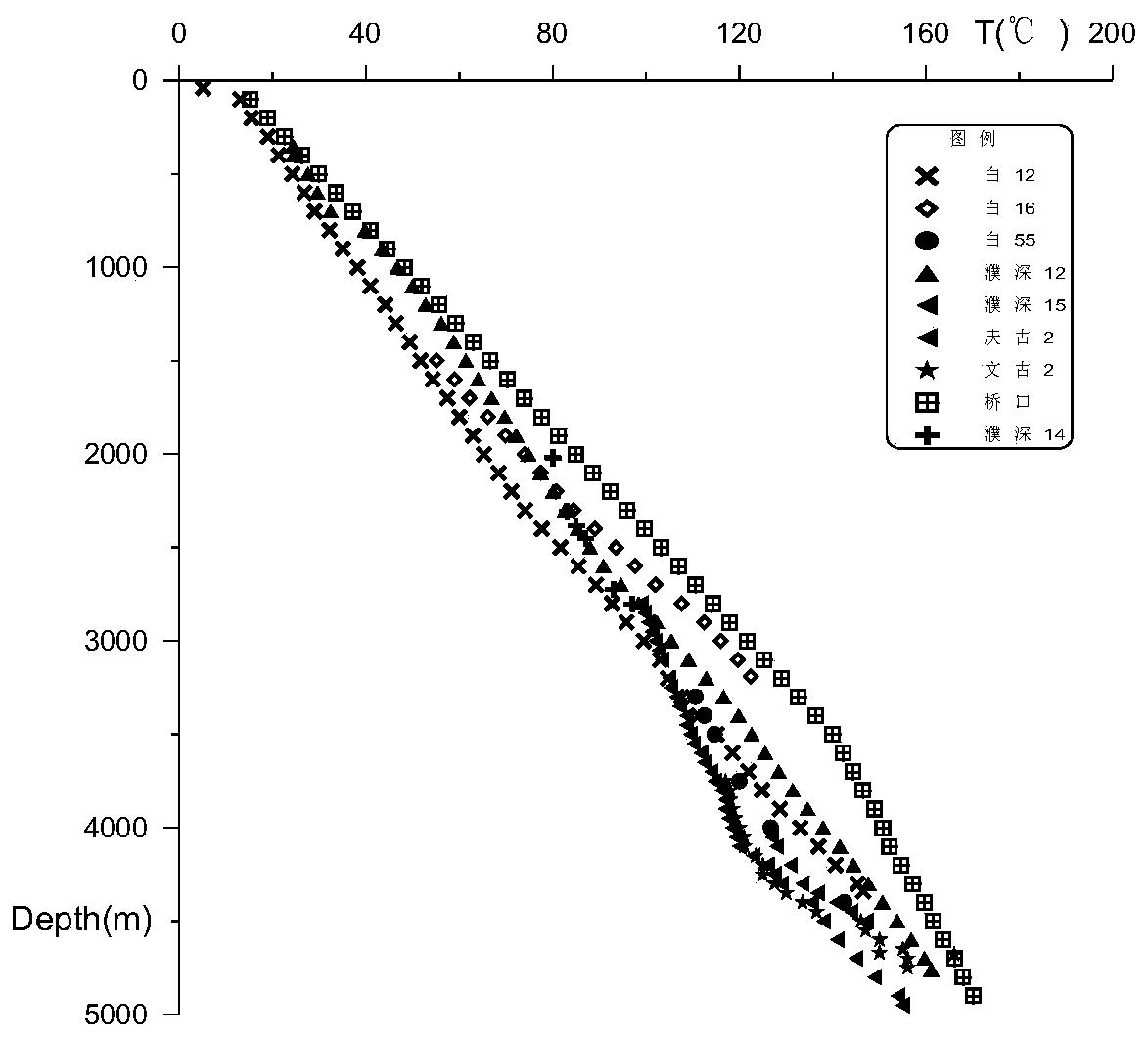
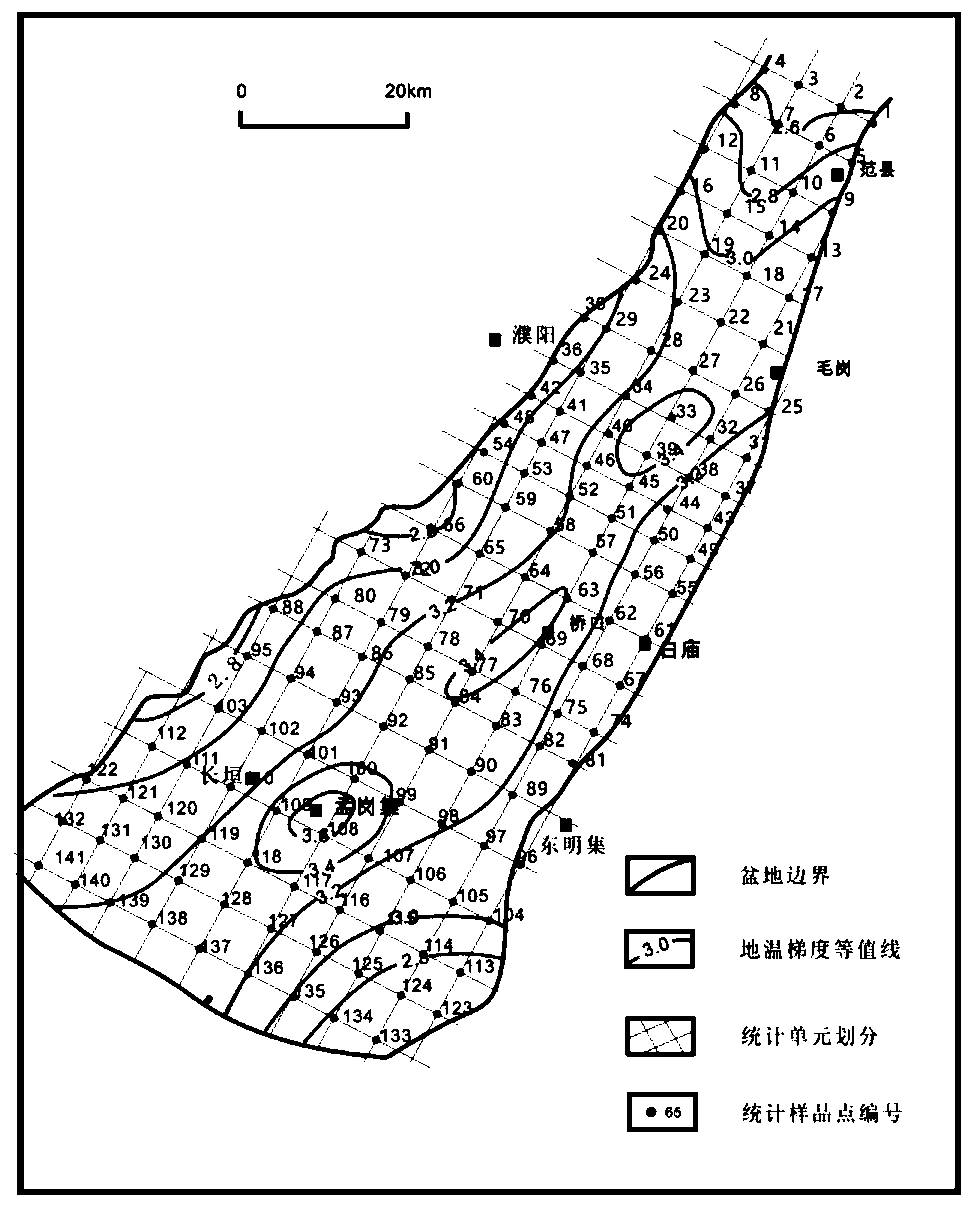
The invention discloses a method for compiling a top surface temperature contour map of an oil region heat reservoir, comprising the following steps of: A, collecting well point continuous temperaturemeasurement data, and calculating a ground temperature gradient in sections; B, with a known well point as a control condition, obtaining a ground temperature gradient contour map corresponding to adepth section of the heat reservoir between wells through a Kriging interpolation method; C, dividing a structure map and the geotherm gradient contour map into geotherm calculation units which are completely matched with each other; and D, taking virtual wells and actual drilling data as control points according to the structure map and a ground temperature gradient distribution map unit, and obtaining a ground temperature contour map of the top surface of the heat reservoir through interpolation between the wells. According to the method, the ground temperature gradient contour map is firstly compiled in a segmented mode, then the temperature of the control point is calculated, and the ground temperature contour map is compiled, so that deviation caused by structural fluctuation during direct interpolation is avoided. Unit nodes serve as virtual wells and are evenly distributed in a whole basin, and inconvenience brought to temperature contour map compiling due to the fact that oil and gas drilling wells are mainly concentrated at a high construction position is avoided.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
New hydro-thermal enclosed type underground heat resource quality classification evaluation method
InactiveCN105447639AOvercome the problem of low accuracy of quality classification evaluationHigh precisionResourcesGround temperatureHeat flow
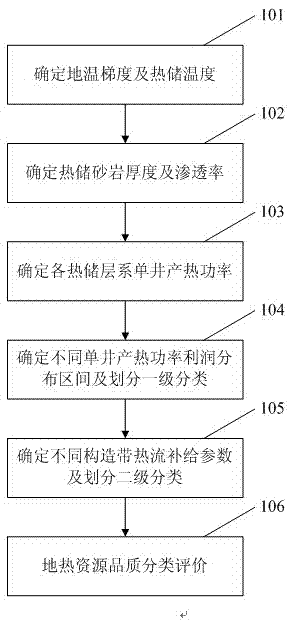
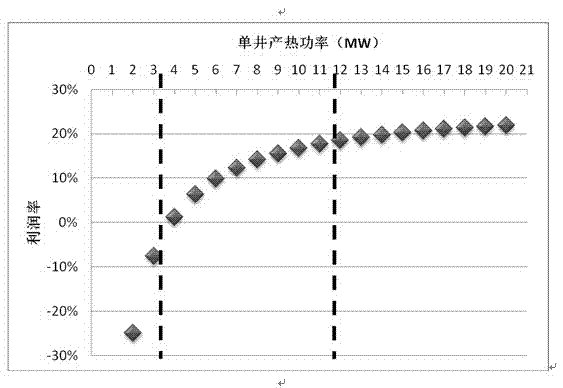
The invention provides a new hydro-thermal enclosed type underground heat resource quality classification evaluation method, comprising steps of calculating and determining distribution characteristics of ground temperature gradient and heat storage temperature according to temperature test materials obtained during the oil gas exploration process, determining thickness and permeability of heat storage sandstone through well logging, logging and test data which are obtained through the oil gas exploration process, determining heat generation power of a single well of each heat storage system, determining profit distribution intervals of heat generation power profit of various single wells and performing first-level classification dividing, determining heat flow supply parameter of various structures and performing second level classification dividing, and performing geothermal resource classification evaluation by integrating the first level and the second level classification dividing. The new hydro-thermal enclosed type underground heat resource quality classification evaluation method can realize quality classification evaluation of hydro-thermal enclosed type underground heat resource and provides a prerequisite condition for the following underground heat resource exploitation utilization and area selection.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
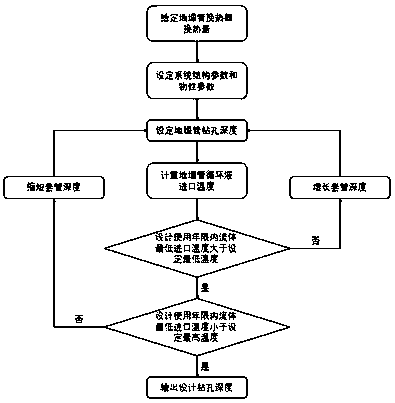
Method for designing and calculating drilling depth of medium-deep buried pipe geothermal heat exchanger
ActiveCN111539130AReduce the temperatureLow energy efficiencyGeothermal energy generationDesign optimisation/simulationPipeWater temperature
The invention discloses a method for designing and calculating the drilling depth of a medium-deep buried pipe heat exchanger, and the method comprises the steps: building a numerical heat exchange model on the basis of considering the ground temperature gradient, simulating the heat transfer process of a buried pipe, and carrying out the design and calculation of the drilling depth of the buriedpipe. Structural parameters of the buried pipe and physical property parameters of all parts of the system are known, the design and calculation of the drilling depth of the buried pipe according to the design thermal load are met, and the inlet water temperature of the buried pipe should be within a certain temperature range in the service life cycle of a building. According to the method, on thebasis that the designed thermal load is met, the designed drilling depth value is accurately calculated, and it is avoided that due to the fact that the designed drilling depth is small, the temperature of circulating liquid in the buried pipe is reduced, and the energy efficiency ratio of the heat pump unit is reduced; meanwhile, drilling cost waste caused by the fact that the drilling depth ofthe buried pipe is too large is avoided, data reference is provided for drilling design calculation of actual engineering, and in the actual engineering design process, the drilling design depth valuecan be obtained through calculation only by adjusting various parameters.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
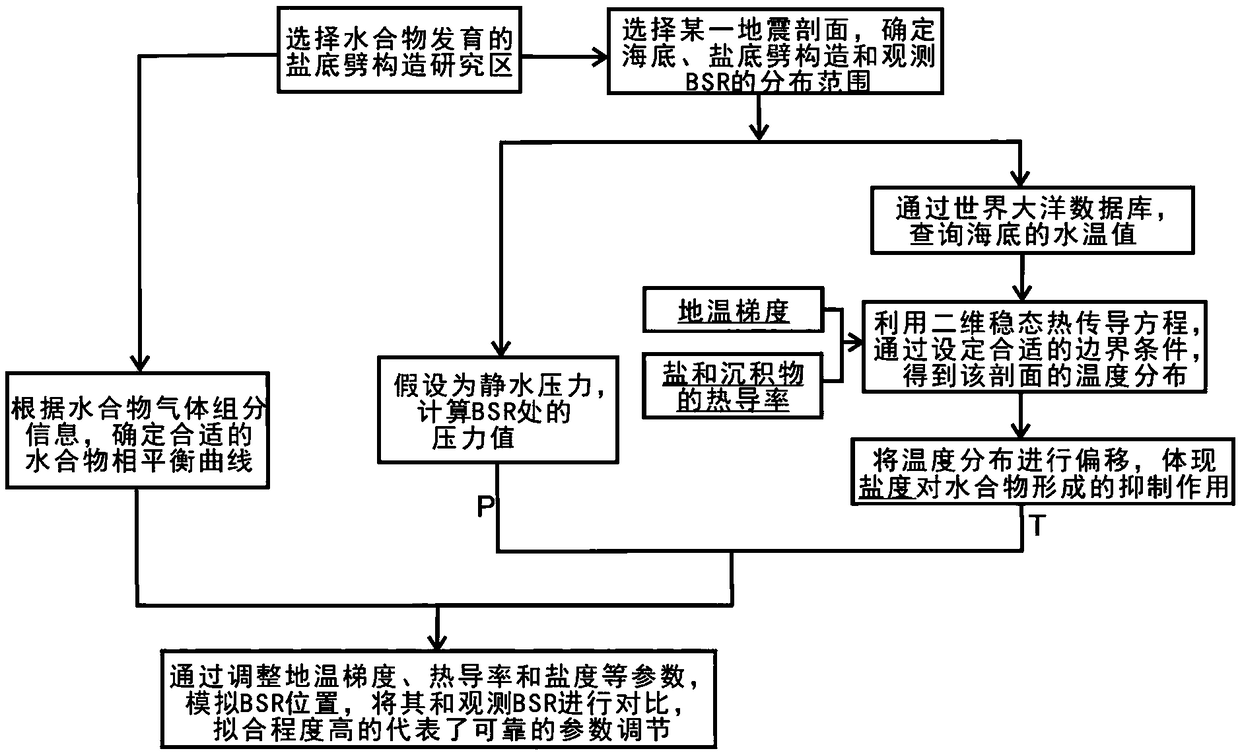
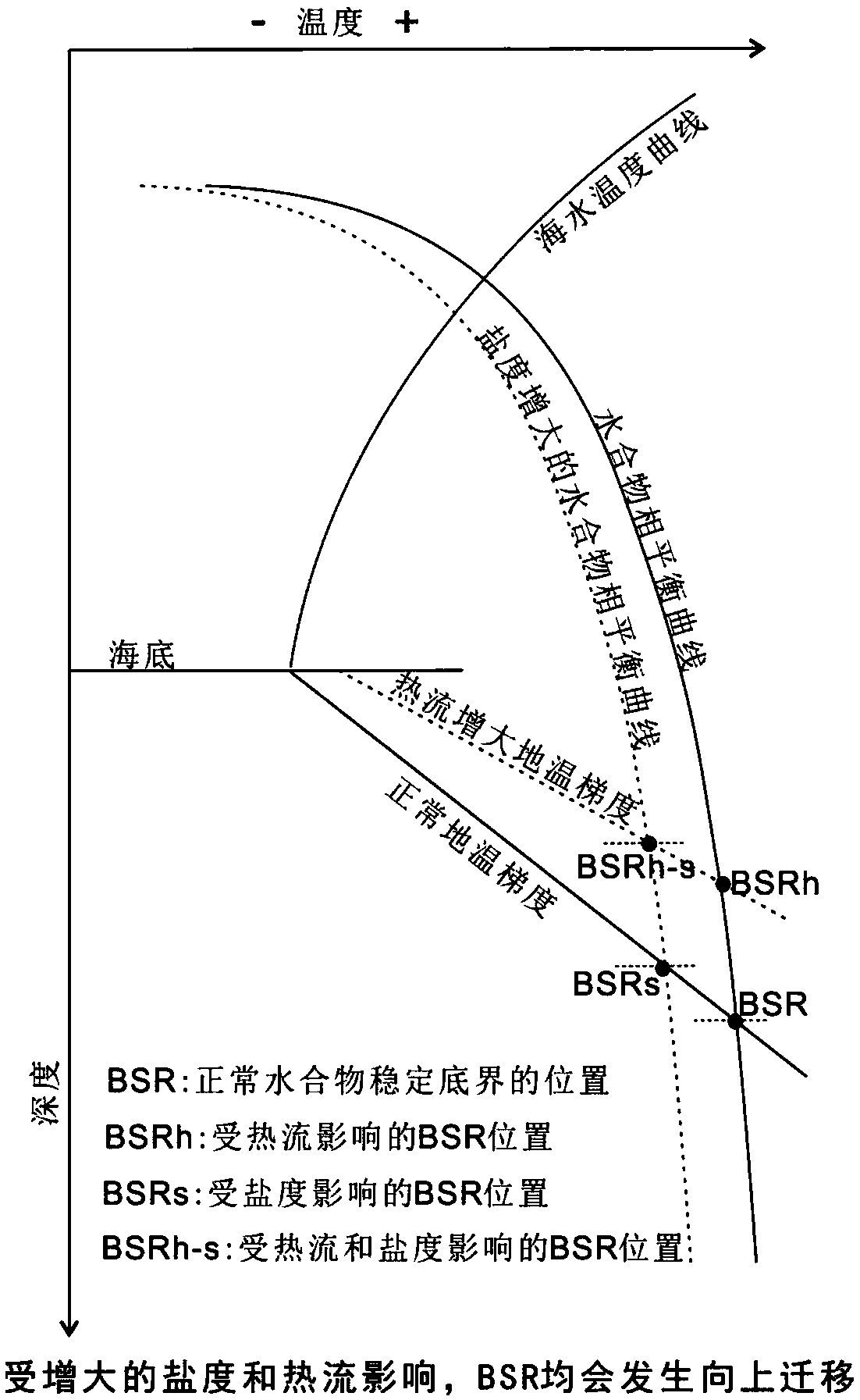
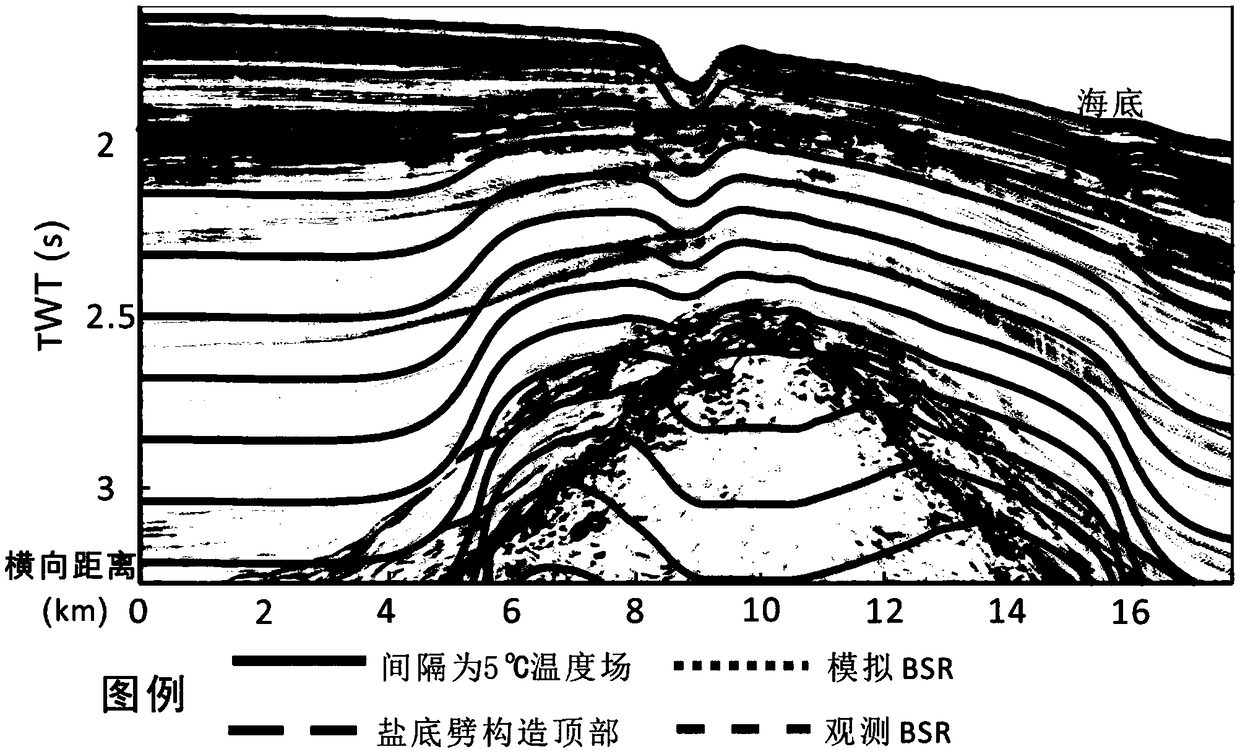
Two-dimensional numerical simulation method and system of hydrate stability bottom boundary of salt diapirism structure belt
ActiveCN108647461AIn line with the geothermal gradientDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSalinitySediment
The invention belongs to the technical field of natural gas hydrate exploration, and discloses a two-dimensional numerical simulation method and system of a hydrate stability bottom boundary of a saltdiapirism structure belt. Influences of geothermal gradients, different thermal conductivity of salt and sediment and high salinity abnormalities of the salt diapirism structure belt on the hydrate stability bottom boundary (shown as BSR on seismic data) are analyzed, and are reflected in a hydrate phase equilibrium condition for numerical simulation on the BSR. The system includes a BSR featureselection module, a double-pass travel time determination module, a phase equilibrium stability curve selection module of natural gas hydrate, a pressure value determination module of BSR developmentdepth, a depth value calculation module of the BSR, a temperature value determination module of all points of a seabed on a seismic section, a temperature field distribution calculation module of theseismic section, a hydrate stability bottom boundary moving module and a comparing and analysis module. The method and the system can be used for any salt diapirism structure belt with obvious boundaries to predict a position of a hydrate stability bottom boundary thereof.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
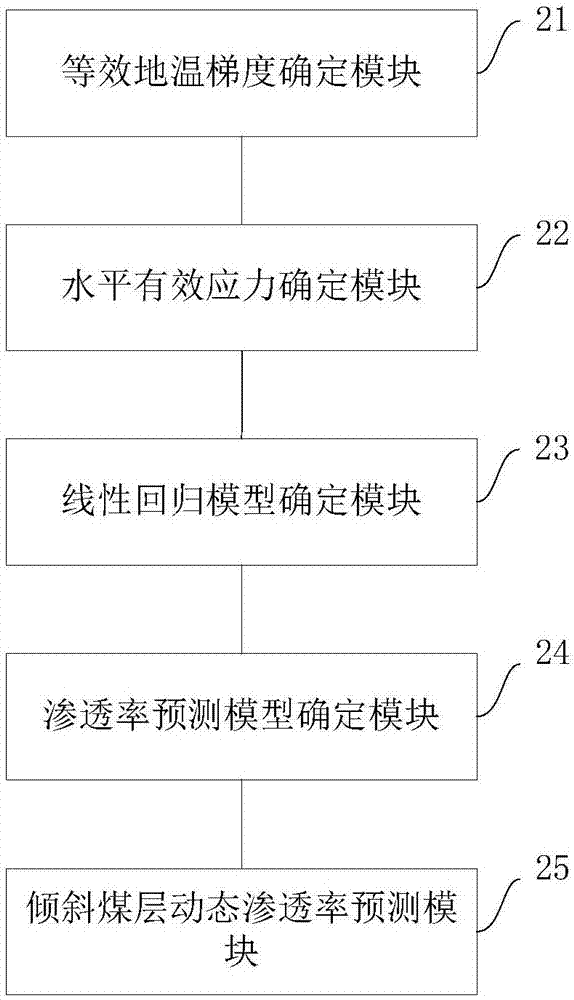
Dynamic permeability predicting method and device of inclined coal seam
ActiveCN108005644APermeability is accurateAccurate and reliable reservoir physical parametersBorehole/well accessoriesLinear regressionMethane gas
An embodiment of the application provides a dynamic permeability predicting method of an inclined coal seam and a dynamic permeability predicting device of the inclined coal seam. The method includessteps of confirming an equivalent geothermal gradient of a coal seam according to the coal seam buried depth and the coal seam temperature; confirming reservoir gap pressure of the coal seam under thedevelopment stage, and confirming the effective stress of the coal seam according to the reservoir gap pressure and the coal seam confining pressure; confirming function without dimension relation offactors of methane gas testing coal seam permeability, and confirming a linear regressive model of the coal seam permeability according to the function without dimension relation and the coal seam permeability data under different temperature and stress load conditions; substituting the equivalent geothermal gradient of the coal seam and the horizontal effective stress of the coal seam to the linear regressive model, and acquiring a dynamic permeability predicting model of the inclined coal seam; predicting the dynamic permeability of the coal seam according to the dynamic permeability predicting model of the inclined coal seam. According to the embodiment of the application, the method and the device can improve the accuracy predicting dynamic permeability of the inclined coal seam.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
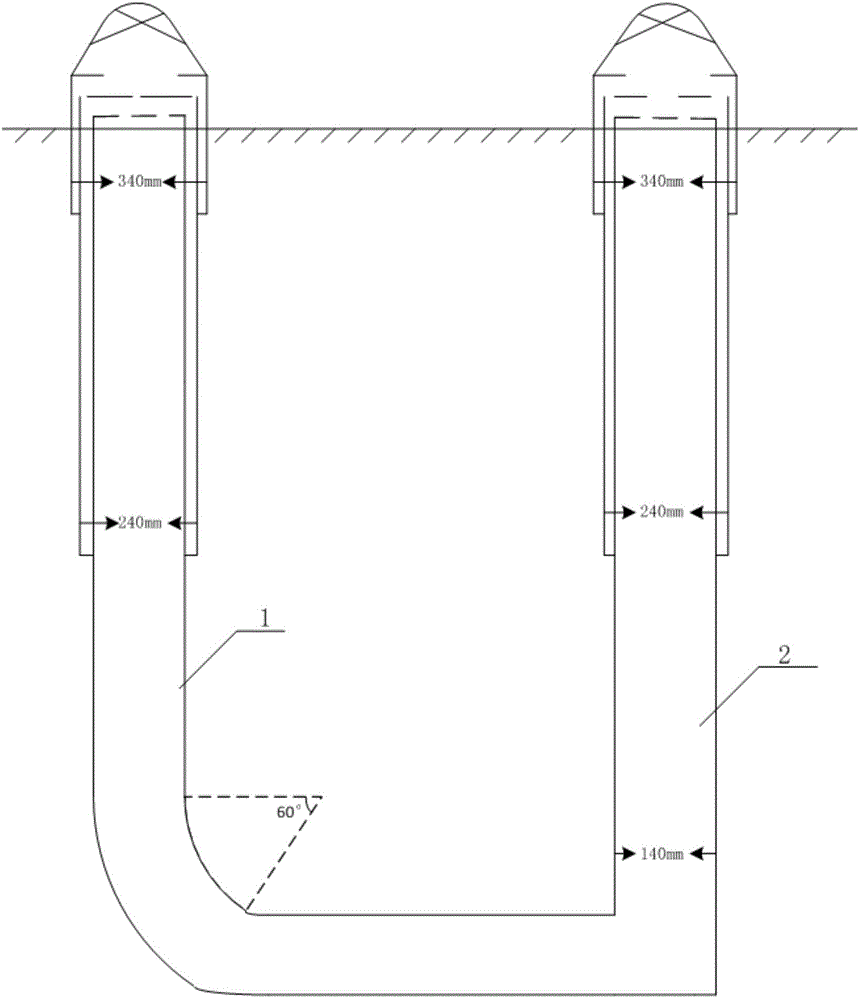
Method for heating surface water by using natural heating furnace of the Earth
ActiveCN104654641ASave resourcesEmission reductionOther heat production devicesGeothermal energy generationWell drillingWater flow
The invention relates to a method for heating surface water by using a natural heating furnace of the Earth. The method comprises the following steps of (1) determining a sedimentary rock region; (2) determining a region with relatively high geothermal gradient in the sedimentary rock region; (3) determining well positions of two wells in the region with relatively high geothermal gradient so as to perform well drilling, wherein one well is a water-inlet well, the other well is a water-outlet well, and the two wells are in abutting joint; (4) on the ground, filing surface fresh water from a straight well section of the water-inlet well, wherein the surface fresh water flows through a horizontal well section to form heated hot water, and the heater hot water flows into the water-outlet well and then is delivered to the water-outlet well. According to the method, energy sources, such as coal and natural gas are not used, so that the method is very environment-friendly and sustainable, and substantial coal sources are saved.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIV OF WATER RESOURCES & ELECTRIC POWER
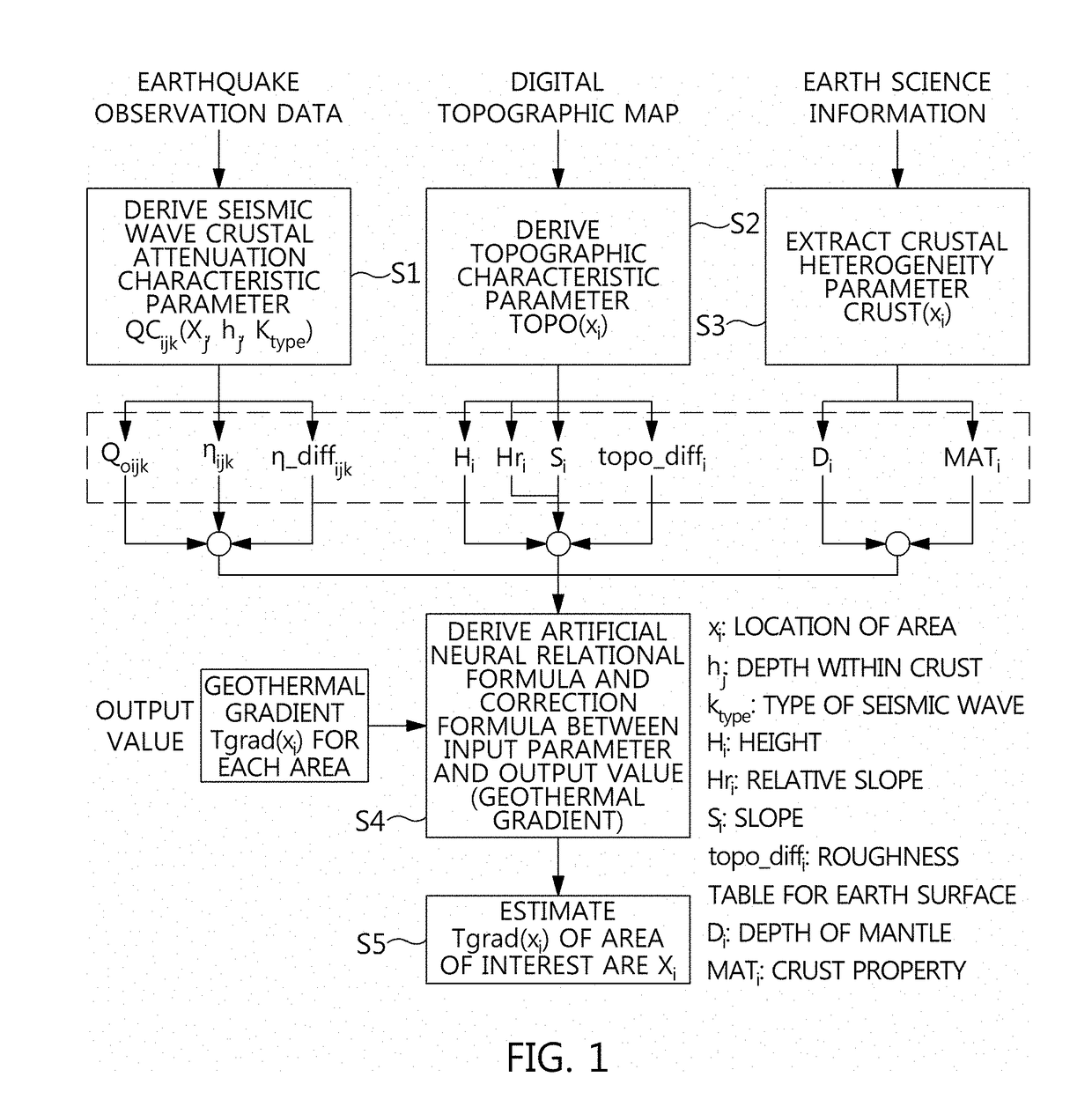
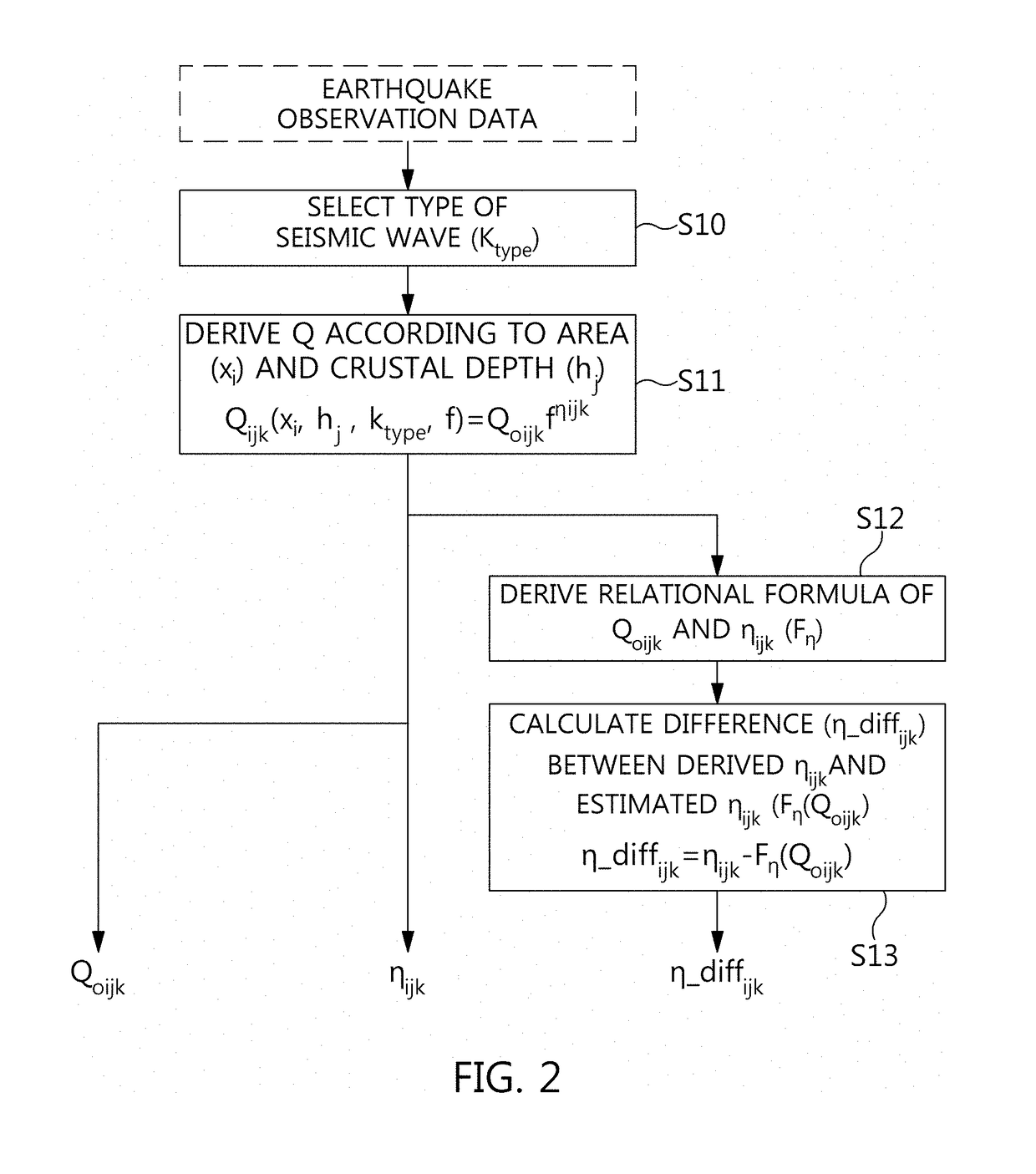
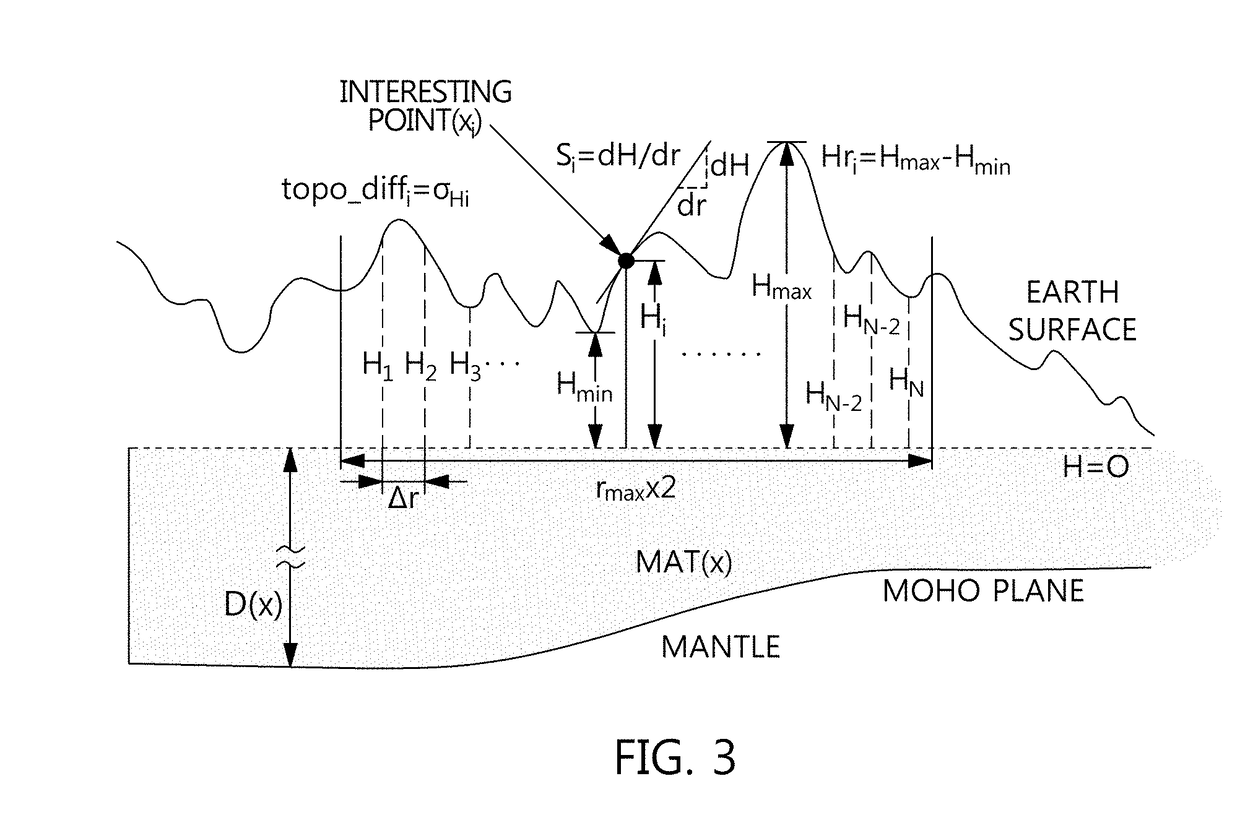
Method for estimating geothermal gradient and device for estimating geothermal gradient
The present invention relates to a method for estimating a geothermal gradient and an apparatus for estimating a geothermal gradient, and provides a method for estimating a geothermal gradient, the method comprising the steps of: calculating, at each of a plurality of points, a seismic wave crustal attenuation characteristic parameter of a seismic wave measured on the basis of the measured seismic wave information, with respect to the plurality of points; deriving an artificial neural network relational formula on the basis of the seismic wave crustal attenuation characteristic parameter; and calculating a geothermal gradient of an area of interest excluding the plurality of points on the basis of the artificial neural network relational formula, such that the geothermal gradient is estimated at a low cost by using a highly reliable method.
Owner:KOREA ELECTRIC POWER CORP
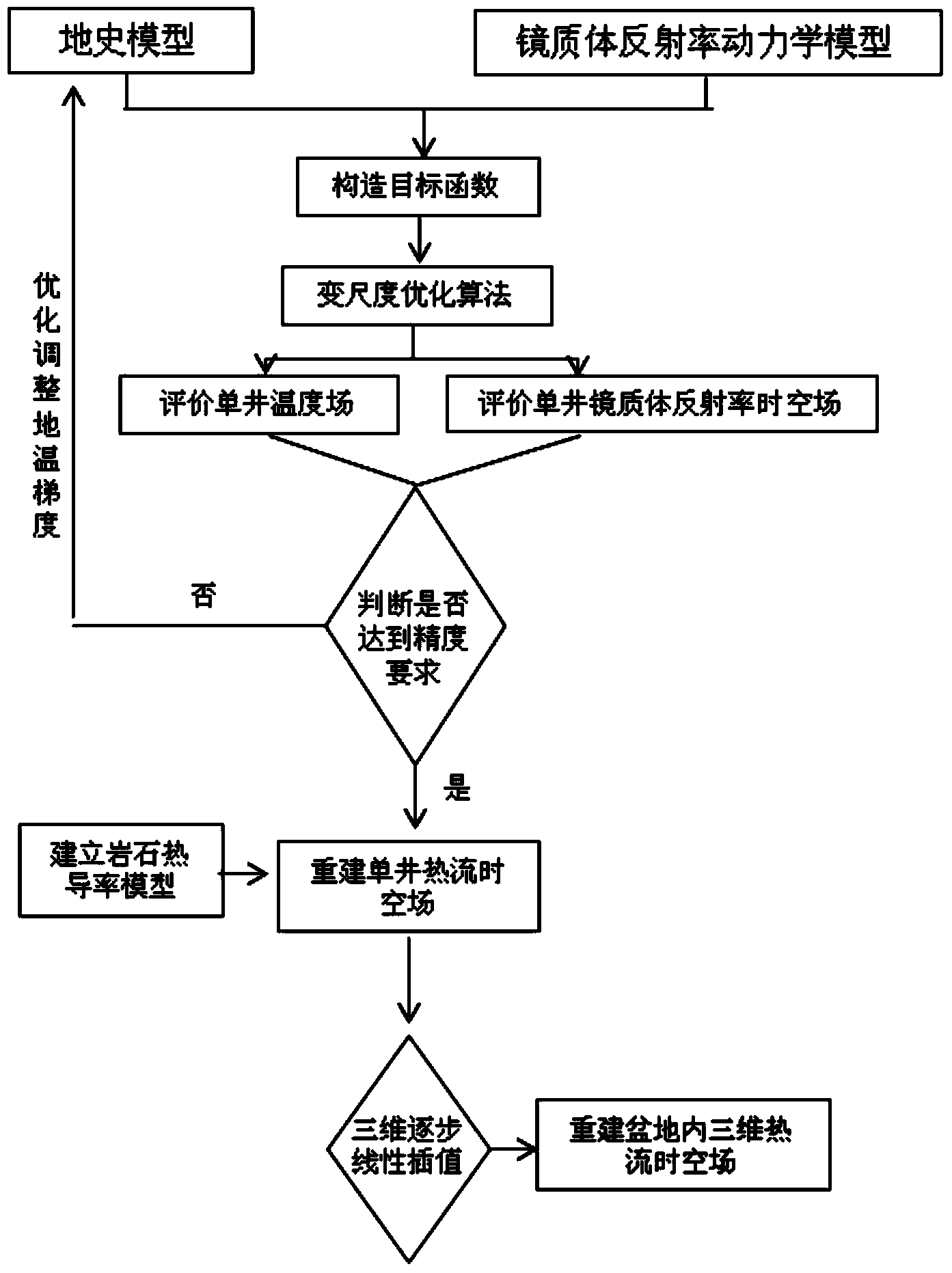
Reconstruction method for three-dimensional heat flow space-time field in petroliferous basin
InactiveCN104239673AFast convergenceThe calculation process is simple and not cumbersomeSpecial data processing applicationsHeat flowReconstruction method
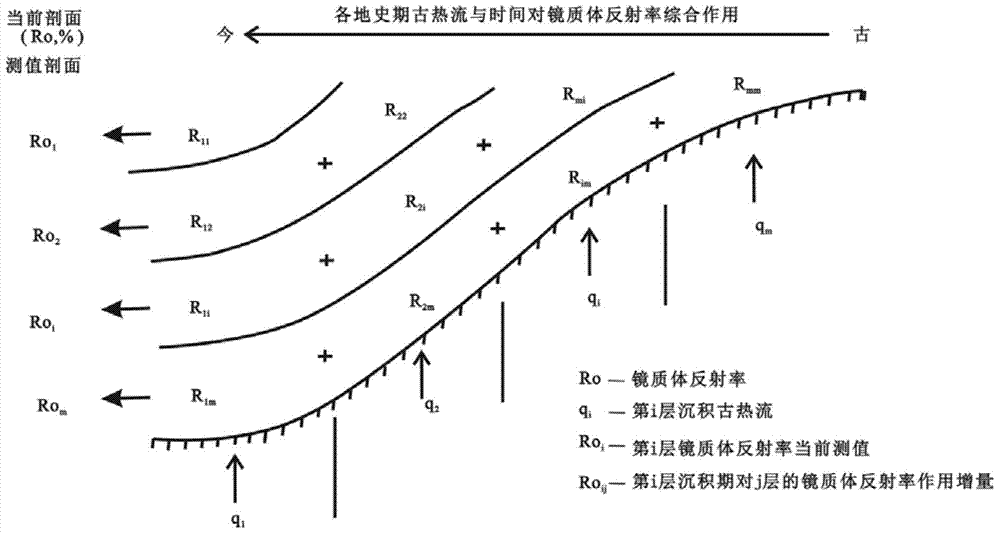
The invention relates to a reconstruction method for a three-dimensional heat flow space-time field in a petroliferous basin. The reconstruction method includes following steps: 1), collecting and tidying basic data in the basin; 2), establishing a geologic history model in the basin; 3), establishing a vitrinite hydrocarbon dynamics calibration model; 4), constructing an objective function of ancient geothermal gradient and ancient ground surface temperature during various layer deposition periods; 5), solving the objective function; 6), evaluating a vitrinite reflectance space-time field in a basin inner well; 7), judging whether or not, analogue values and measured values of a single well vitrinite reflectance space-time field and a temperature field meet accuracy requirement; 8), establishing a rock thermal conductivity model; 9), reconstruct the three-dimensional heat flow space-time field of a single well; and 10), reconstructing the three-dimensional heat flow space-time field in the basin. The reconstruction method can be widely used for reconstruction of three-dimensional heat flow space-time fields in the petroliferous basin, and provides technical support for exploration and development of oil gas in the basin.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Paleo-heat flow change recovering method and device
InactiveCN103577711AImprove applicabilityImprove effectivenessSpecial data processing applicationsMathematical modelComputational model
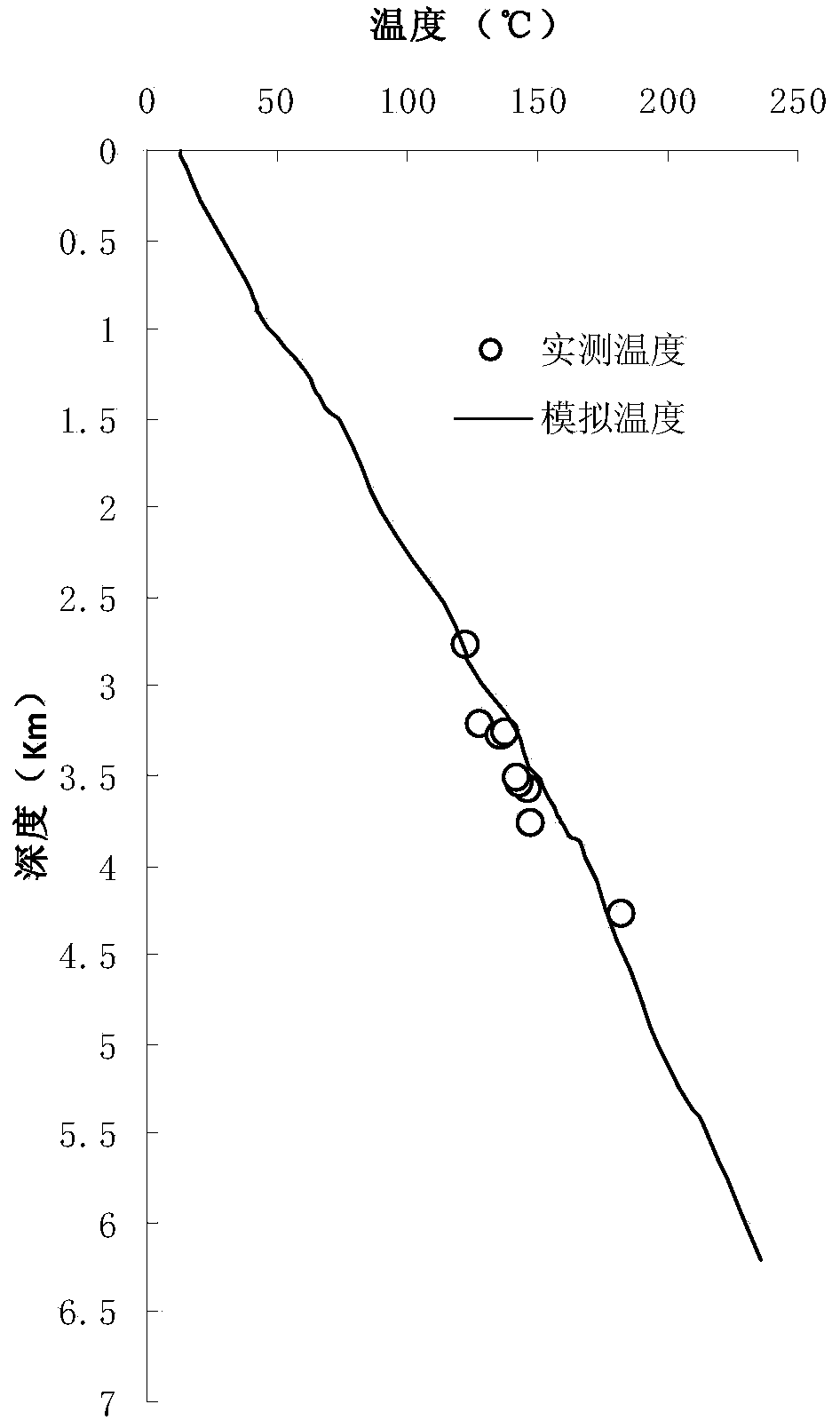
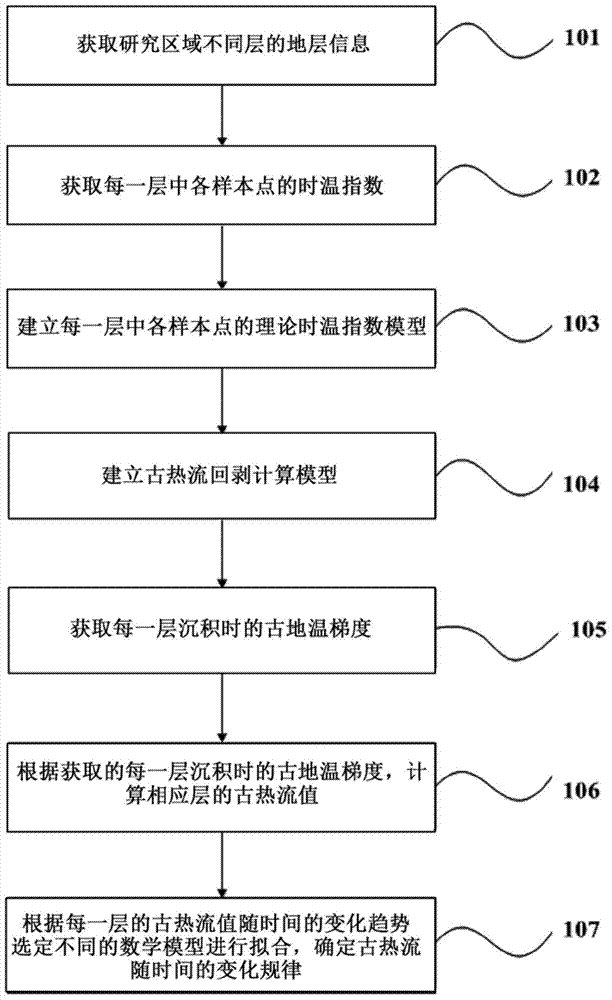
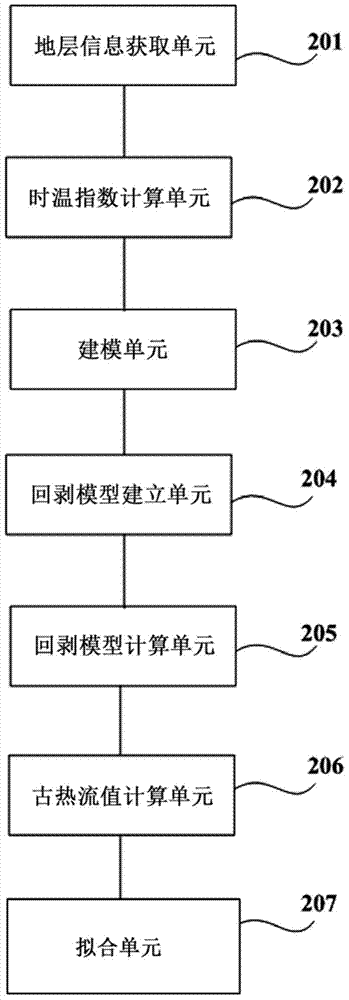
The invention provides a paleo-heat flow change recovering method and device. The method comprises the following steps: stratum information of different strata in a survey region is obtained, wherein the stratum information comprises sample depths of all sample points in all the strata, geologic history times, vitrinite reflectance, a current earth surface temperature, a current geothermal gradient, paleogeotemperature of initial sediment, the maximal burial depth of a sediment base, thermal conductivity of all the strata and geologic history times which the sediment goes through; a time-temperature index of all the sample points in each stratum is obtained; a theoretical time-temperature index model of all the sample points in each stratum is established; a paleo-heat flow back-stripping calculation model is established; a palaeogeothermal gradient of each stratum at the time of sedimentation is obtained; according to the obtained palaeogeothermal gradient of each stratum at the time of sedimentation, the paleo-heat flow value of the corresponding stratum is calculated; according to the change trend of the paleo-heat flow value of each stratum over time, different mathematic models are selected for fitting, and a change rule of paleo-heat flow over time is determined. The paleo-heat flow change recovering method can be applied to complicated geological conditions, thereby being better in adaptability and effectiveness.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
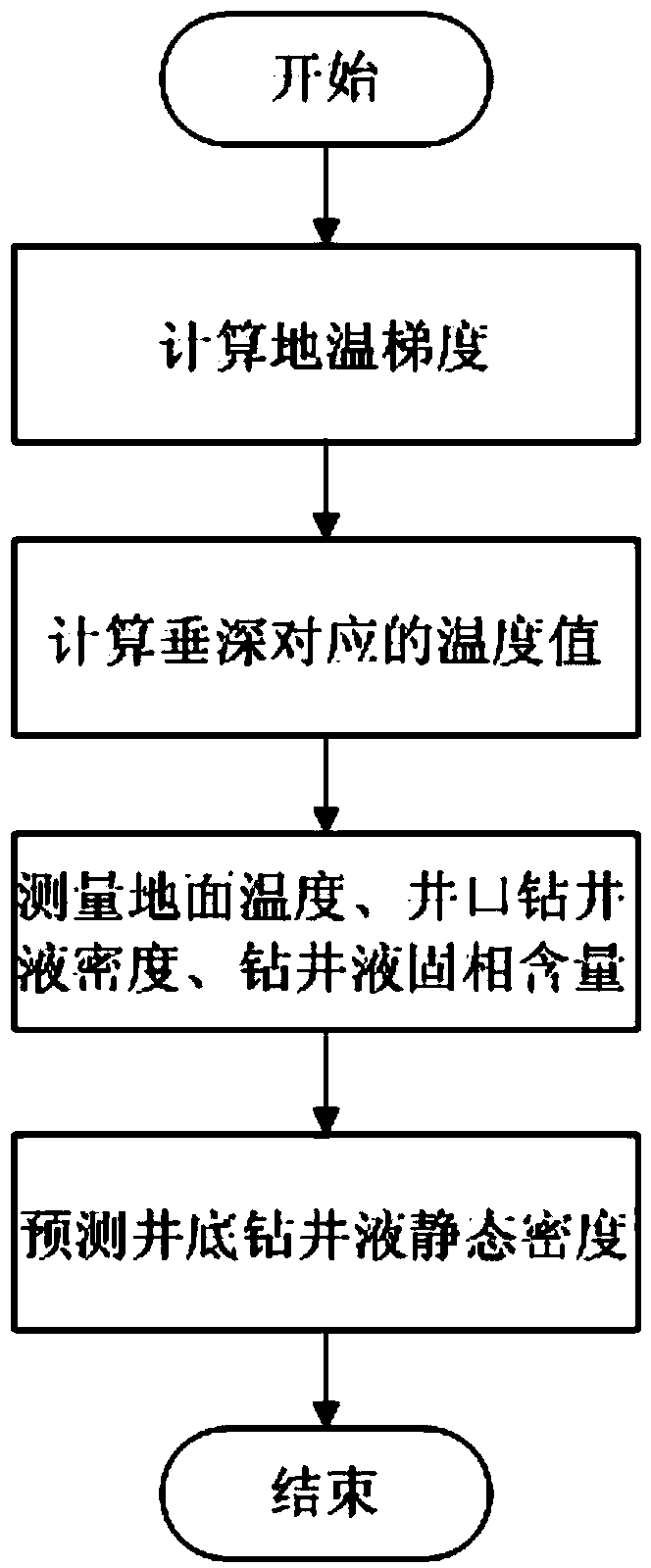
Method for predicting static density of water-based drilling fluid at bottom of well
ActiveCN104111208AAchieve protectionAchieve forecastSpecific gravity measurementGround temperatureWater based
The invention relates to a method or for predicting the static density of a water-based drilling fluid at the bottom of a well. The method based on a same ground temperature gradient of two adjacent wells comprises the following steps: obtaining the ground temperature gradient of an adjacent well according to the measured data of the adjacent well as the ground temperature gradient of a predicated well, obtaining the temperatures corresponding to all vertical depths of the predicated well, respectively measuring the ground temperature, the density of the drilling fluid and the solid phase content of the drilling fluid, and recursively obtaining the static density of the drilling fluid at the bottom of the well according to a relationship among the temperature, the pressure and the density of the drilling fluid between adjacent vertical depths in order to predicate the density of the drilling fluid at the bottom of the well. The method uses a common thermometer, a drilling fluid density meter and a solid phase content measuring instrument to predicate the density of the drilling fluid at the bottom of the well, can be very easily realized and popularized in the field, and is of great significance of realizing near-balanced drilling and reservoir protection and improving the mechanical drilling speed.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for quantitatively calculating hot compaction strength
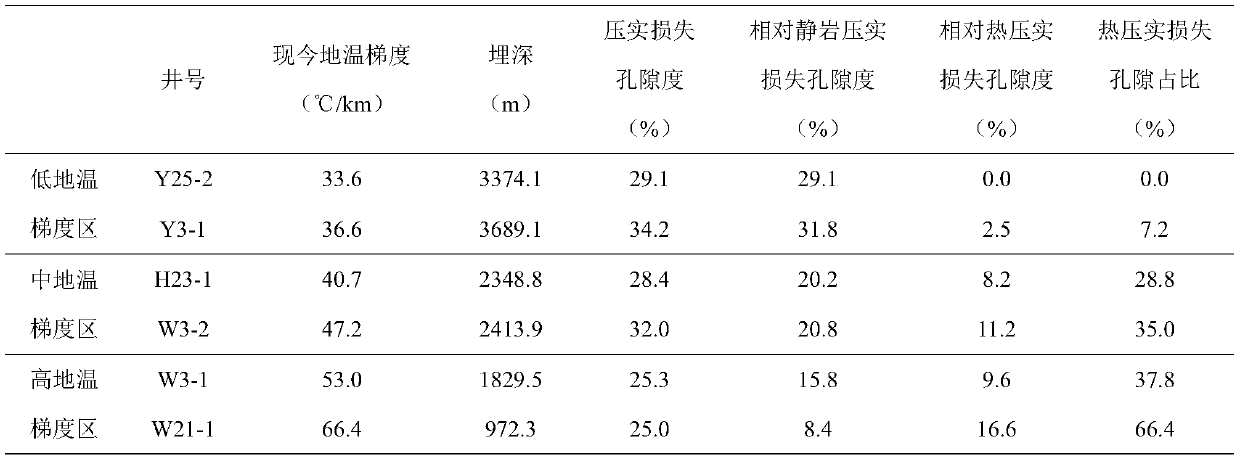
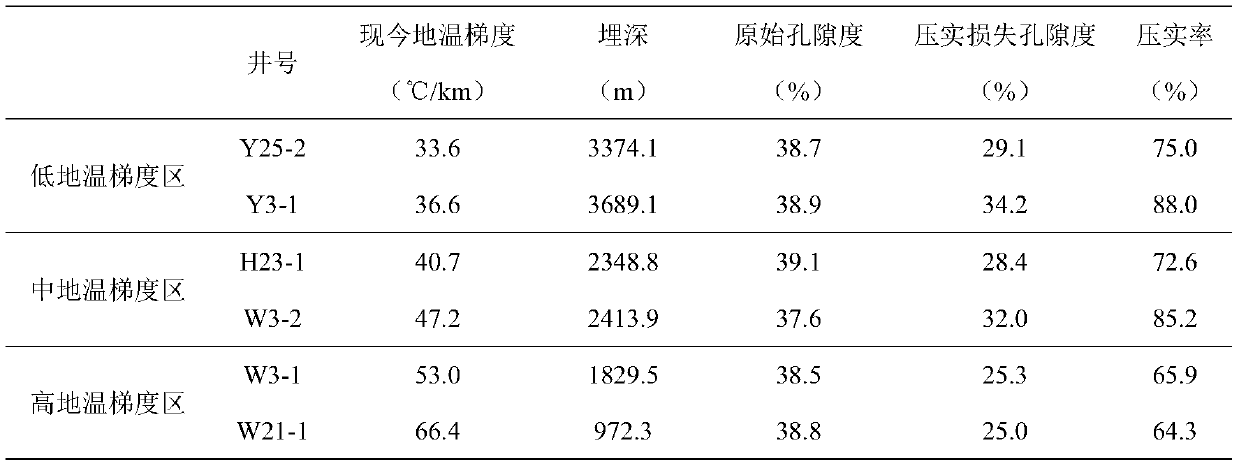
PendingCN110096839AImprove reliabilityIncreased compaction rateDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsPorosityGround temperature
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively calculating the hot compaction action strength. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the steps that representative nearby typicalgeological landforms are screened and found out for experiments; the selected research area is divided into a plurality of ground temperature gradient areas; compaction effect characteristics and mechanism differences of different ground temperature gradient areas are researched and compared; quantitative relations among different ground temperature gradient areas, buried depths and sandstone porosities are calculated; calculating results of different single wells are compared to judge the original porosity difference of different single wells and the change of the compaction loss porosity ofdifferent wells along with the current ground temperature gradient; and finally obtaining a quantitative calculation method for a hot compaction pore reduction mechanism and hot compaction loss porosity. The method assists to study and analyze a sedimentary basin lithofacies formation mechanism, an evolution process, influence on reservoir physical properties and influence on oil gas geology, provides a powerful guiding effect for prediction of multiple types of high-quality reservoirs, and facilitates oil field exploration and mineral exploration deployment.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN) +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com