Antiviral drug virtual screening method using tobacco mosaic virus RNA helicase as target
A technology of tobacco mosaic virus and RNA helicase, which is applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electronic digital data processing, etc., can solve the problem of no TMV helicase, and achieve the effect of improving the screening speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1: Homology modeling of the three-dimensional structure of TMV RNA helicase
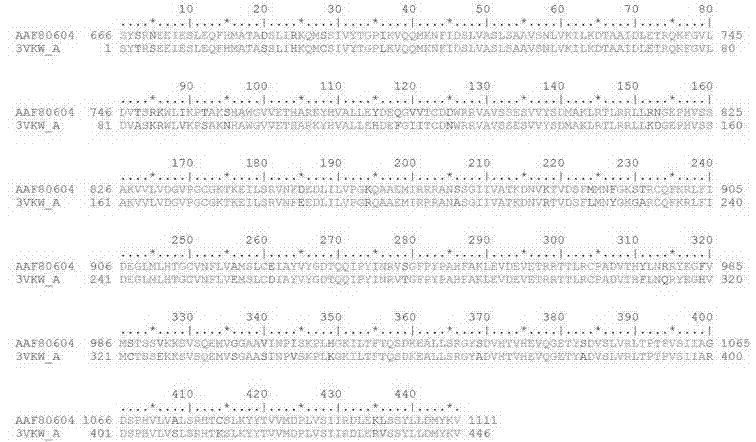
[0038] Taking the 183 kDa replica protein amino acid sequence of TMV (GenBank: AAF80604.1) as the query sequence, using the Protein BLAST program in the NCBI BLAST basic sequence alignment search tool, and using the blastp algorithm to search for known proteins in the Protein Data Bank proteins (pdb) database. Three-dimensional structures of homologous proteins. According to the degree of homology and the nature of the protein, tomato mosaic virus superfamily 1 helicase (PDB: 3VKW) was selected as the template for structural modeling. The template protein sequence length is 446, the fragment coverage rate is 27%, and the coverage corresponds to the 183 kDa protein S666-V1111, which completely contains the viral helicase domain (V829-T1085), and the sequence identity is 90%. The sequence comparison results of the two are as follows: picture 1 shown.
[0039] Using the SWISS-MODEL o...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2: Molecular dynamics optimization of modeled proteins
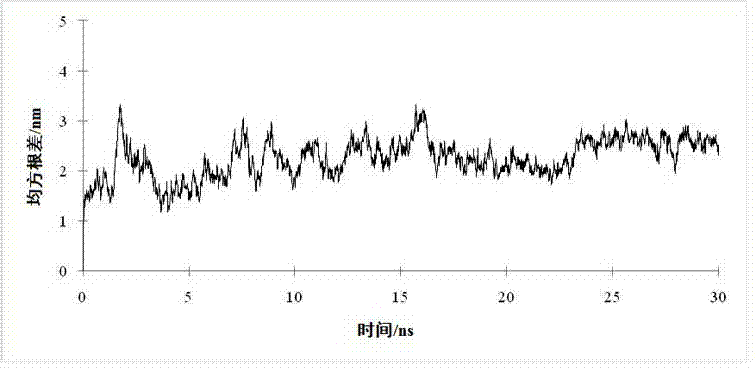
[0042] The structure of TMV-HEL obtained in Example 1 was modified in Amber12 software. Under the FF12SB force field, the explicit water model was first optimized for the entire system until the RMS value of the energy gradient was less than 0.5 kcal / mol / L, and then the model was optimized by molecular dynamics simulation to test whether it had a stable conformation. Runs totaled 30 ns with a time step of 2 fs at a constant temperature of 300K. The relationship between the RMSD value of the TMV-HEL skeleton structure and time in the 30 ns time is shown in the figure 4As shown, the results show that the protein backbone structure changes less after 23 ns than before, so the average structure at 30 ns is taken as the initial structure for subsequent studies.
Embodiment 3
[0043] Example 3: The initial conformation of the RNA helicase of TMV bound to ATP
[0044] After the dynamic optimization structure obtained in embodiment 2, compare this structure with the three-dimensional structure in the PDB database by Dali online server (http: / / ekhidna.biocenter.helsinki.fi / dali_server), find that it is consistent with The hUpf1 protein (PDB: 2GJK) has a similar three-dimensional structure, and the corresponding relationship between the key residues of the ATP hydrolysis site is shown in the table 1 shown.
[0045] Table 1 Alignment of key residues at ATP hydrolysis sites
[0046]
[0047] Through the Fit Monomers function in the Biopolymer module of the SYBYL-X software, TMV-HEL and hUpf1 were superimposed through key residues to obtain the initial structure of the TMV helicase and ATP complex. The local enlarged map of the ATP hydrolysis site after superimposition is shown in the figure 4 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com