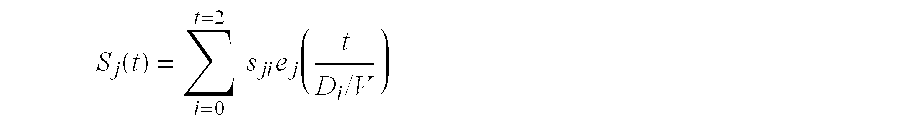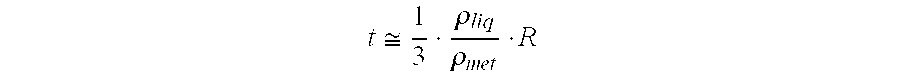Patents
Literature
90 results about "Displacement velocity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
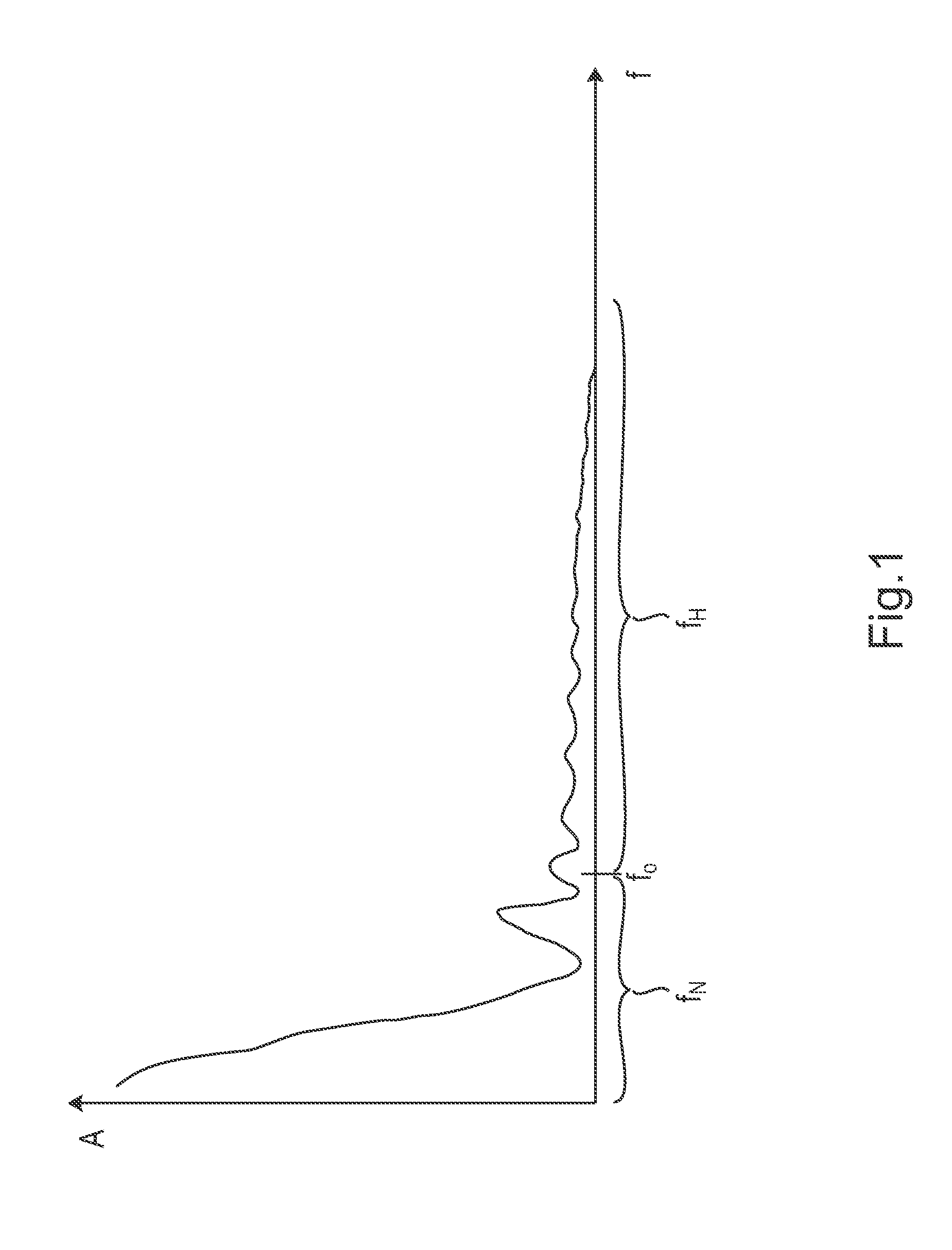
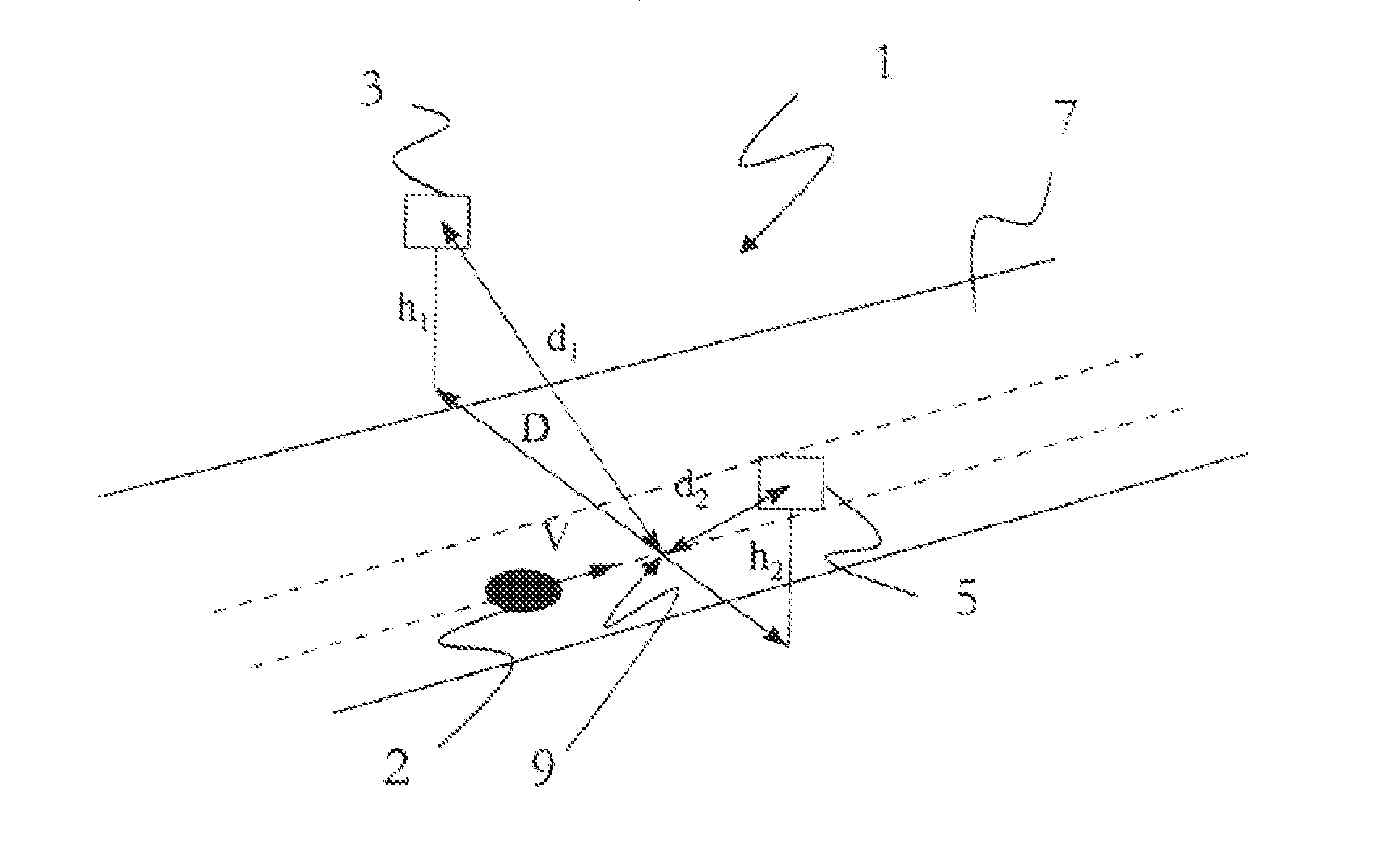
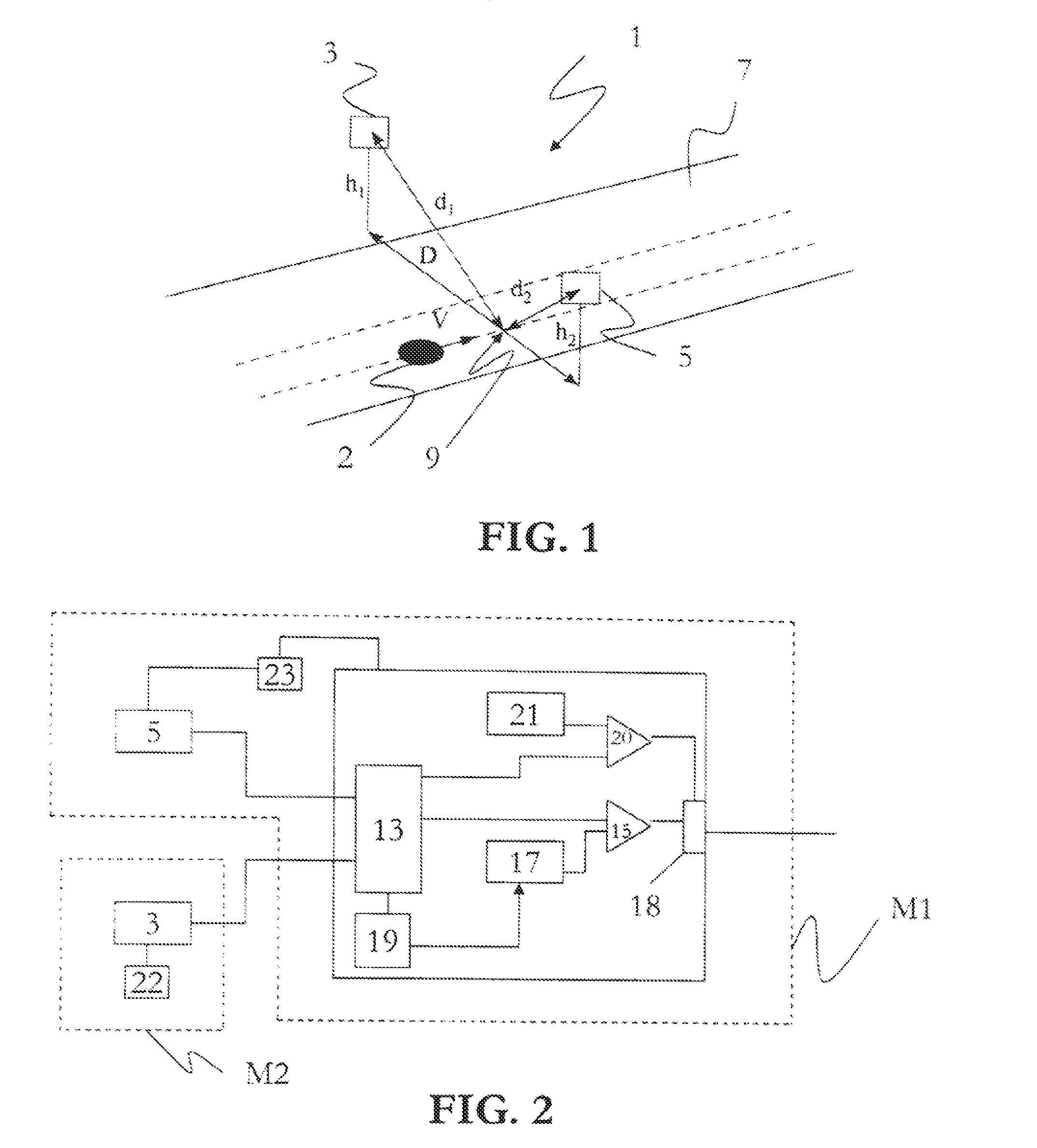
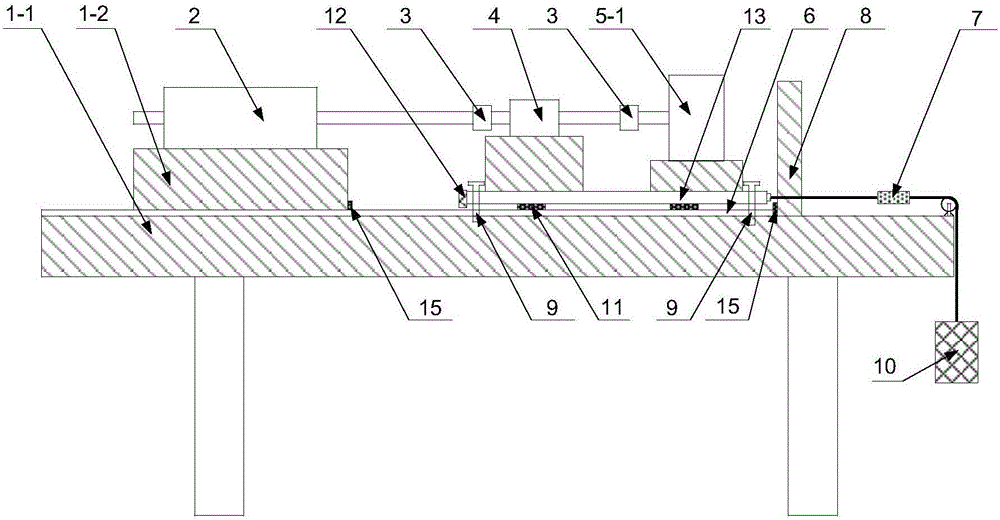
Displacement and Velocity Displacement is the vector difference between the ending and starting positions of an object. Velocity is the rate at which displacement changes with time. The average velocity over some interval is the total displacement during that interval, divided by the time.
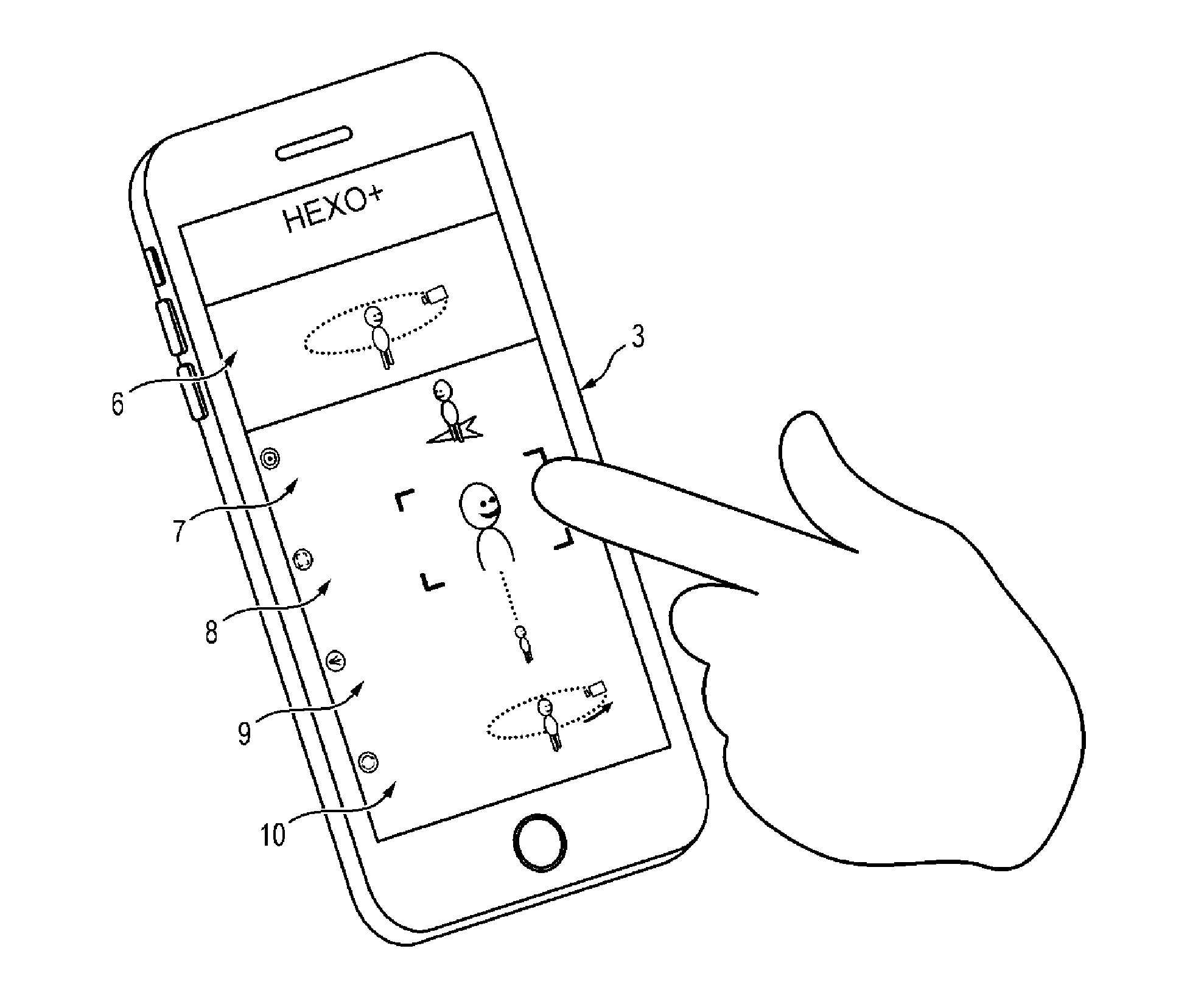
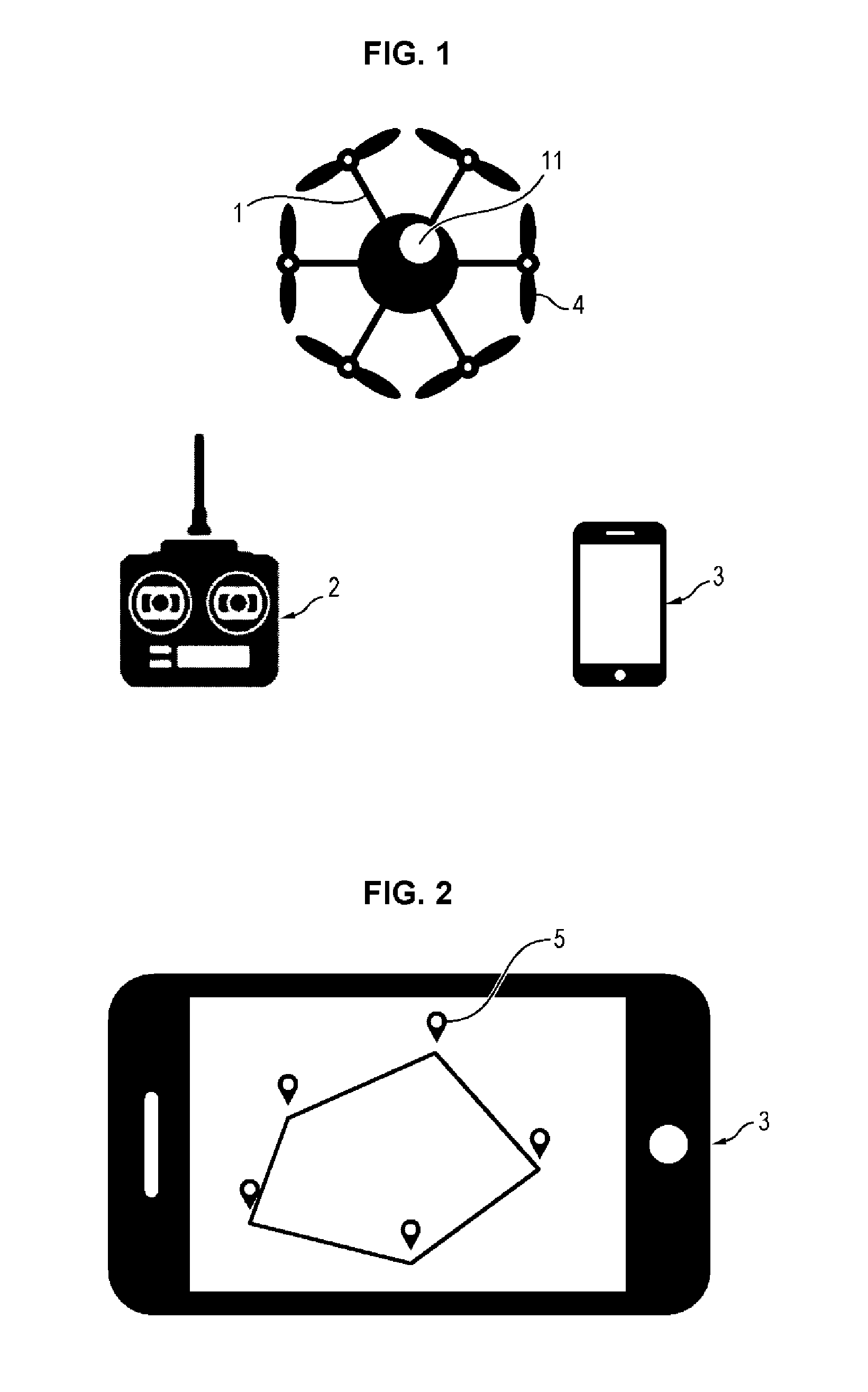
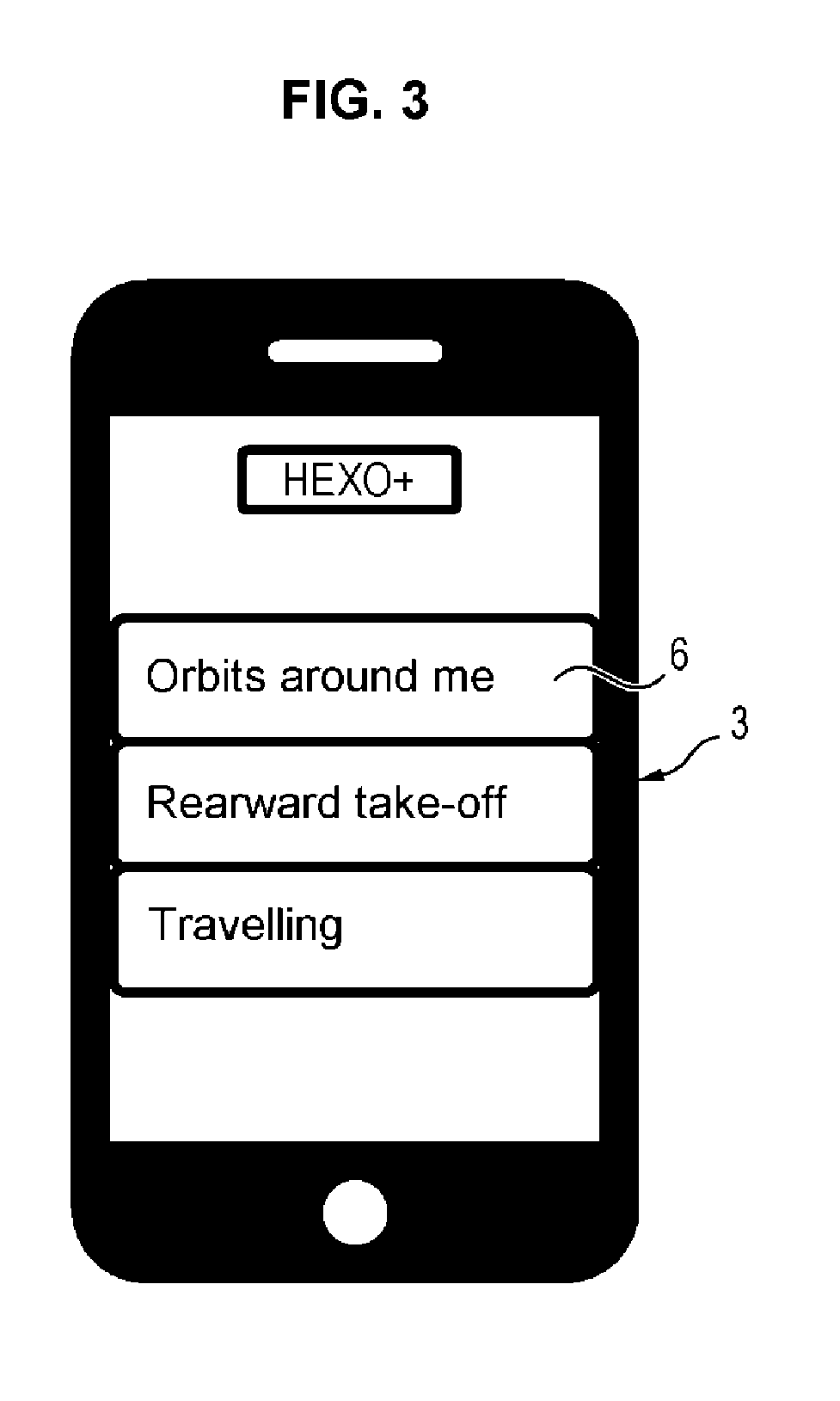
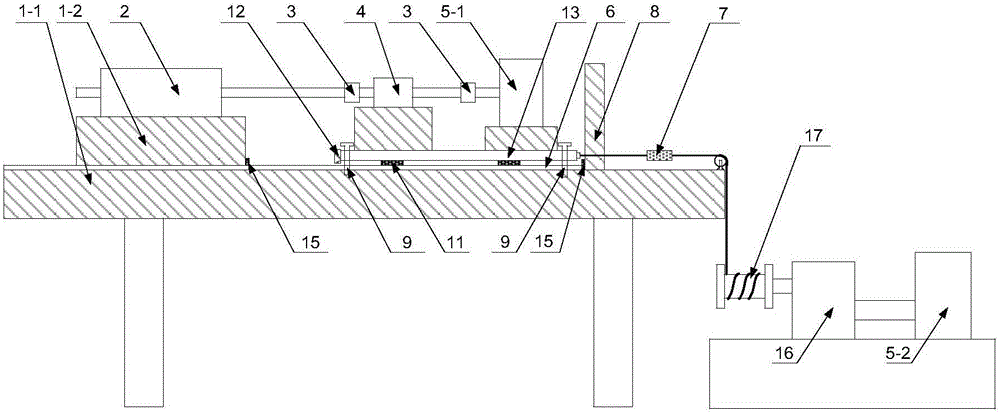
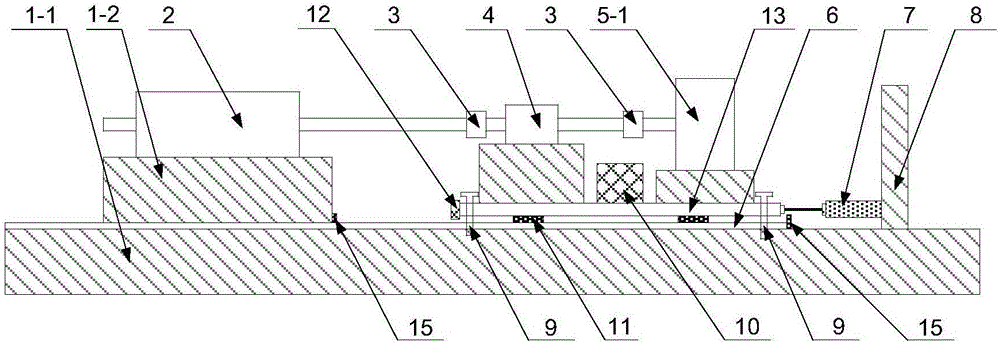
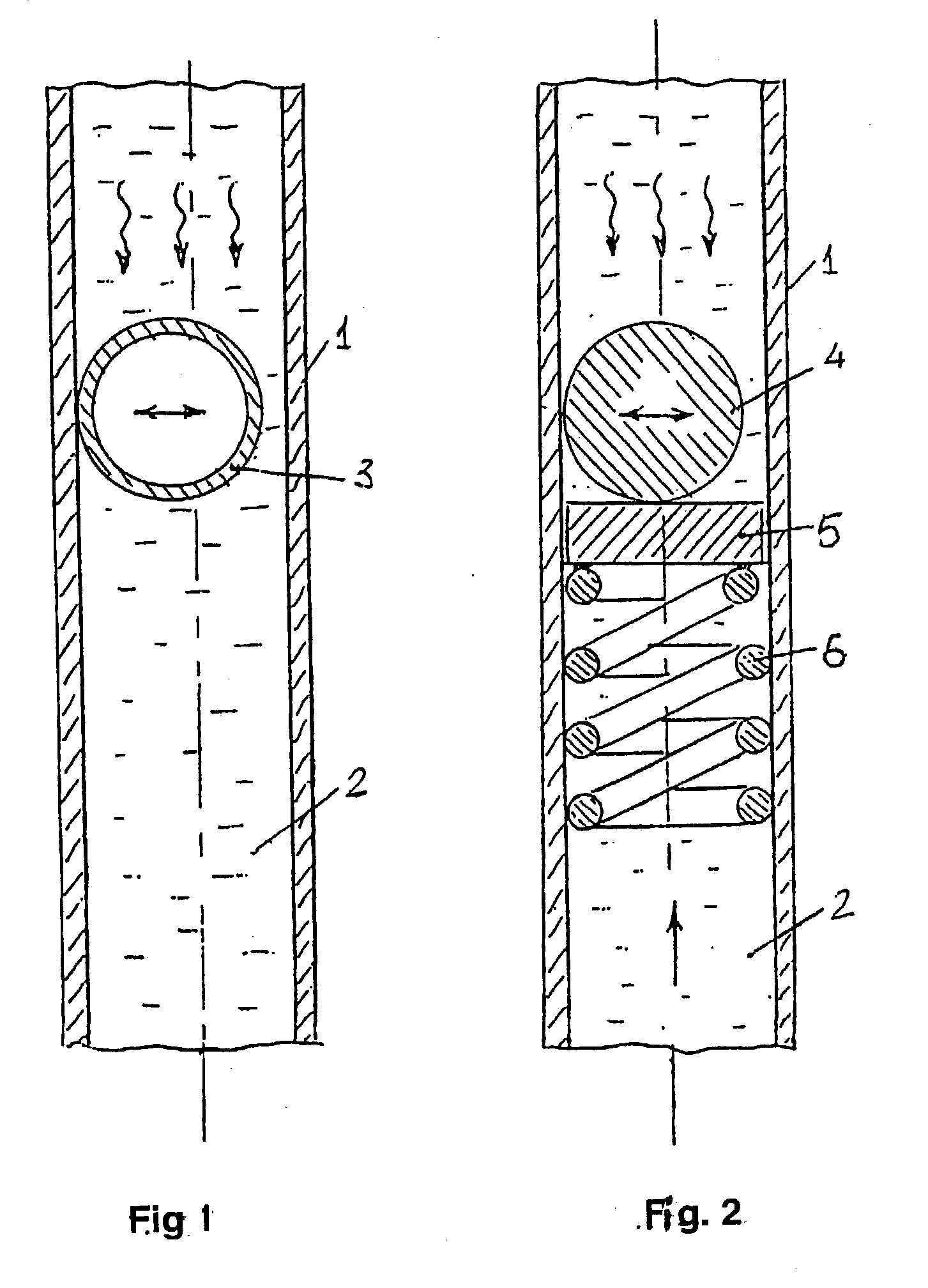
Method of automatically piloting a rotary-wing drone for performing camera movements with an onboard camera
The object of the invention is an autonomous piloting method, by means of a base station, for a rotary-wing drone with multiple rotors, for controlling the drone in attitude and in velocity following a selected camera movement and a position of the subject to be filmed. The method comprises the following steps:1. Selection by the user of a camera movement (6) defined by a set of parameters comprising: image shooting mode in a fixed or moving point (7); type of a movement in attitudes relative to the subject to be filmed (8); displacement velocity; displacement directions or axes; direction of the displacement (10); image shooting altitudes (9);2. Generation of commands for positions (15) through which the drone will have to pass, from the said set of parameters (12) and from the instantaneous position of the subject to be filmed (13) as well as from its recent trajectory (14);3. Activation of the image shooting by the video camera once the drone is launched on the positions sent by the onboard base station on the subject.The device according to the invention is particularly intended for the taking of aerial views.
Owner:SQUADRONE SYST
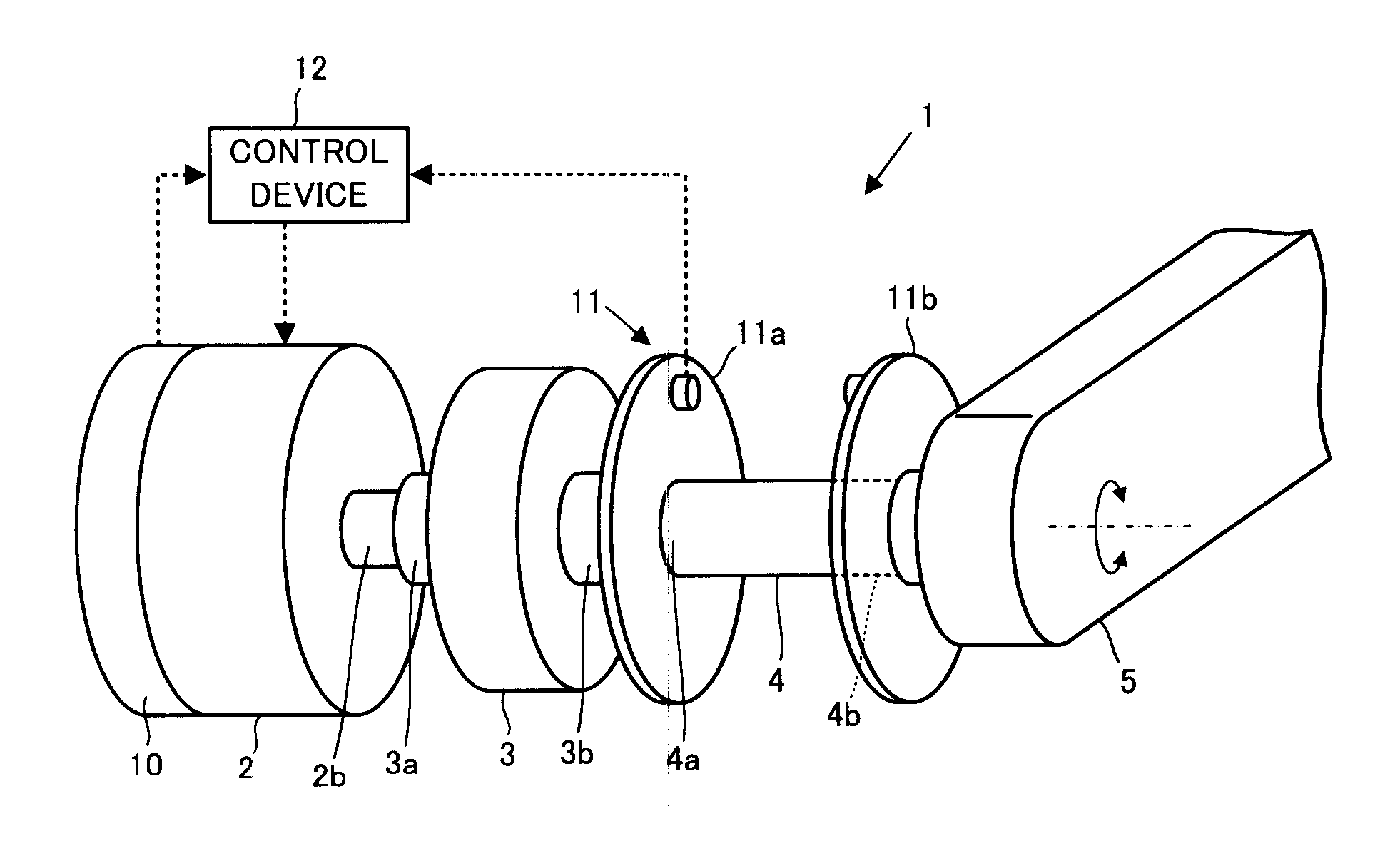
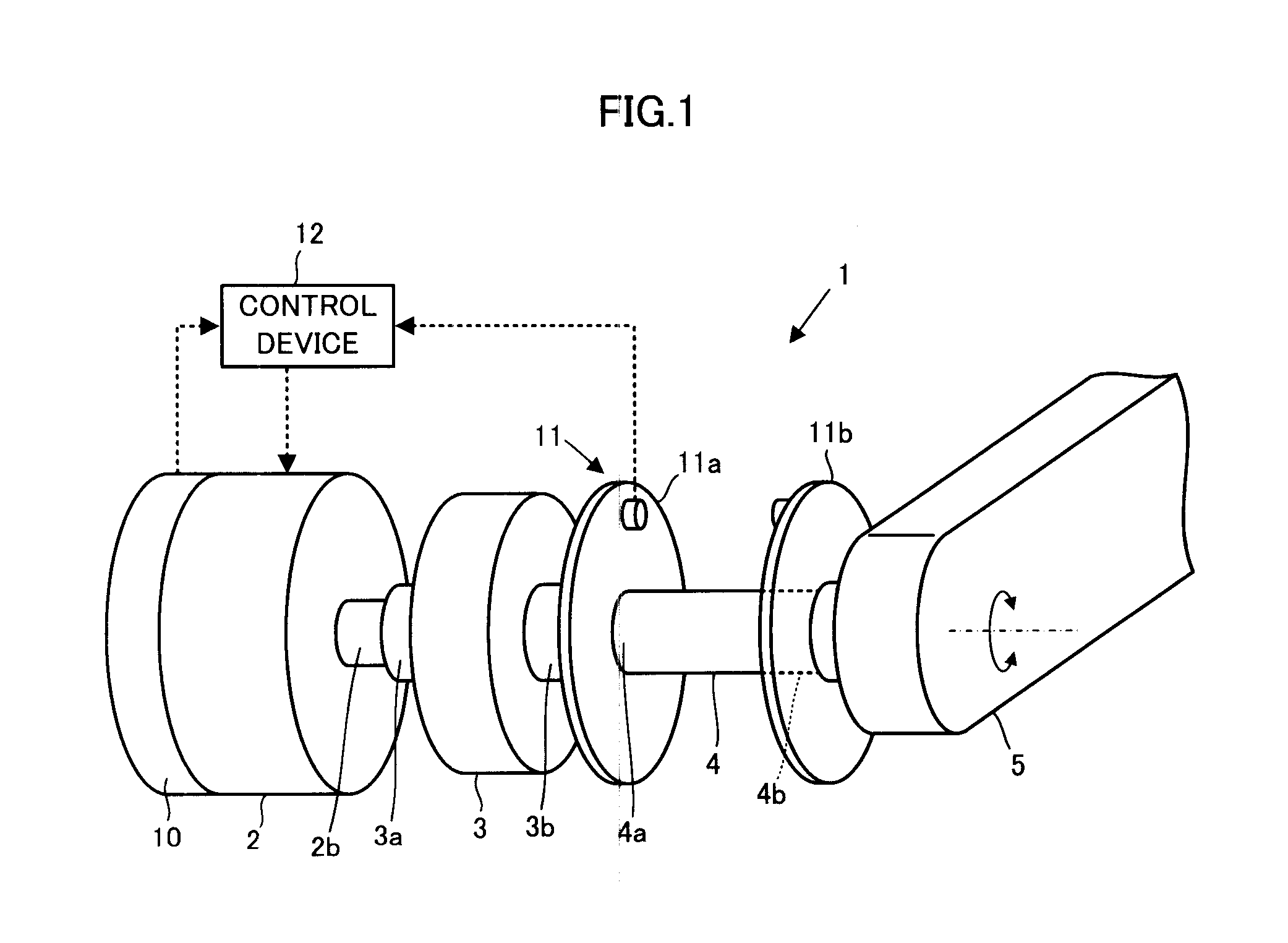
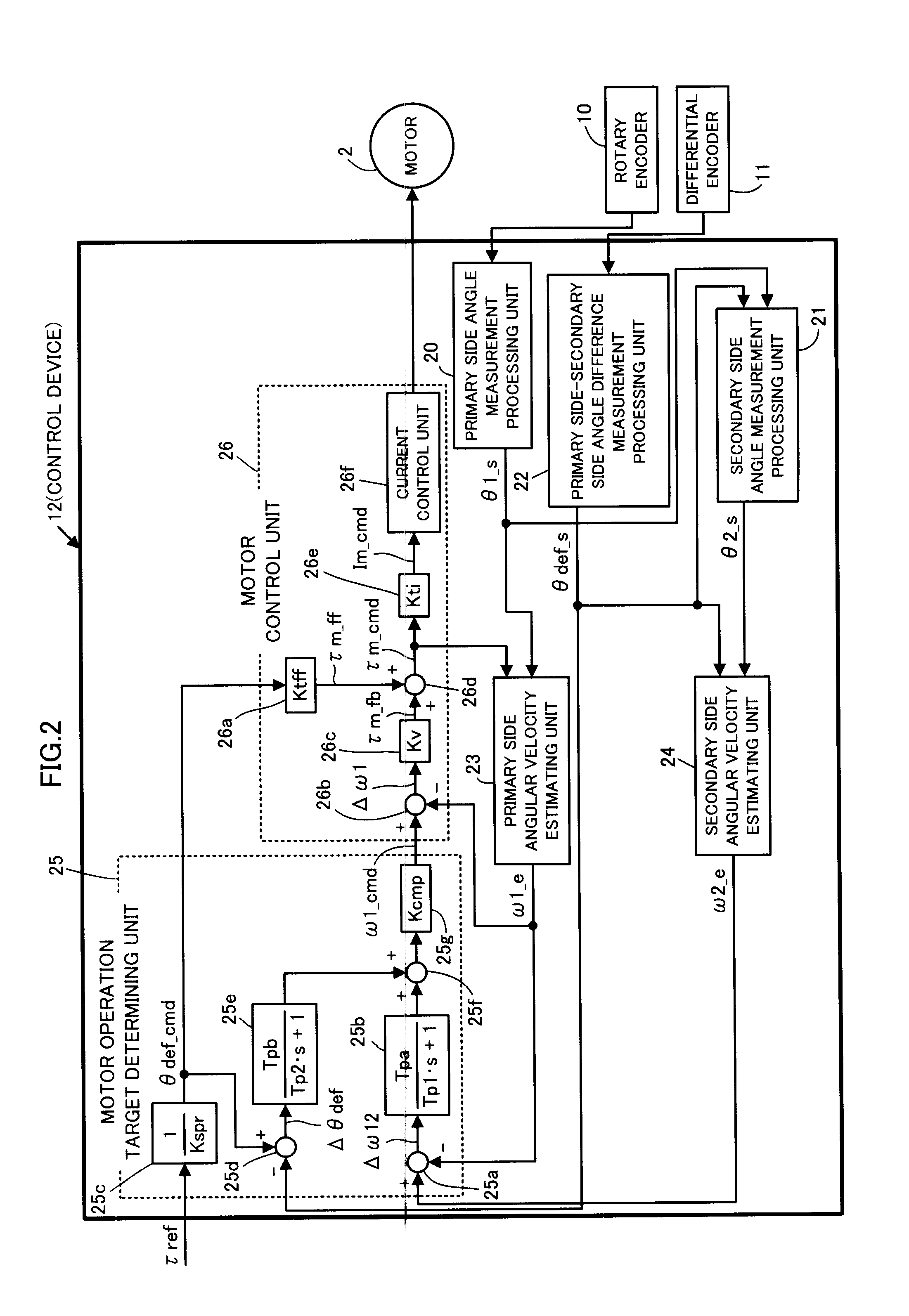
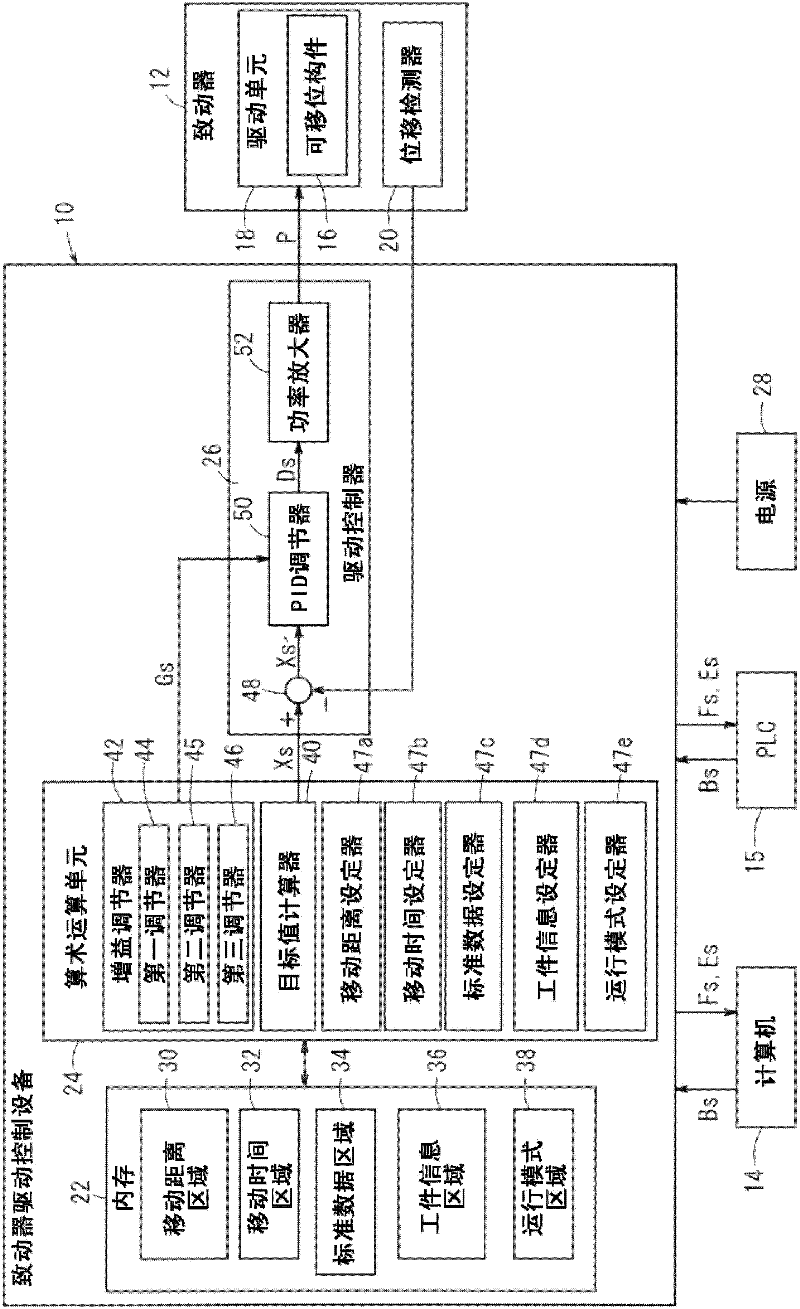
Control device for power device
ActiveUS20120239198A1Reduce vibrationImprove vibrationProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorLow-pass filterReducer
In a power device 1 having a speed reducer 3 and a spring member 4 having elastic characteristics to a power transmission system between an actuator 2 and a driven element 5, an operation target of the actuator 2 is determined according to a linear coupling value of values that are obtained by passing through low-pass filters, a deviation Δω12 between an estimated value ω1_e of a displacement velocity of an input unit 4a of the spring member 4 and an estimated value ω2_e of a displacement velocity of the driven element 5, and a deviation Δθdef between a measured value θdef_s of a deviation difference between the input unit 4a of the spring member 4 and the driven element 5, and a target value θdef_cmd of the displacement difference corresponding to a target driving force τref of the driven element 5.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Control method for moving speed of cursor of air mouse
InactiveCN101398721AEasy to operateImprove the ability of precise positioningInput/output processes for data processingComputer scienceDisplacement velocity
The invention discloses a method for controlling the displacement velocity of an air mouse cursor. In the method, a horizontal obliquity value is measured by an obliquity sensor embedded in an air mouse, and the displacement velocity of a cursor is calculated according to the horizontal obliquity value. When the horizontal obliquity value is less than a preset stopping angle, and the horizontal obliquity value is not changed within certain time, the air mouse is considered as being static, and the cursor is stopped moving even if a slight amount of obliquity angle exists. Contrarily, if the horizontal obliquity value is changed, the cursor is processed for single-point movement by the form of a slight amount of movement or a screen pixel point moving at a time. The method can overcome the problem that the cursor is not easy for positioning exactly when the air mouse is operated.
Owner:KYE SYST CORP
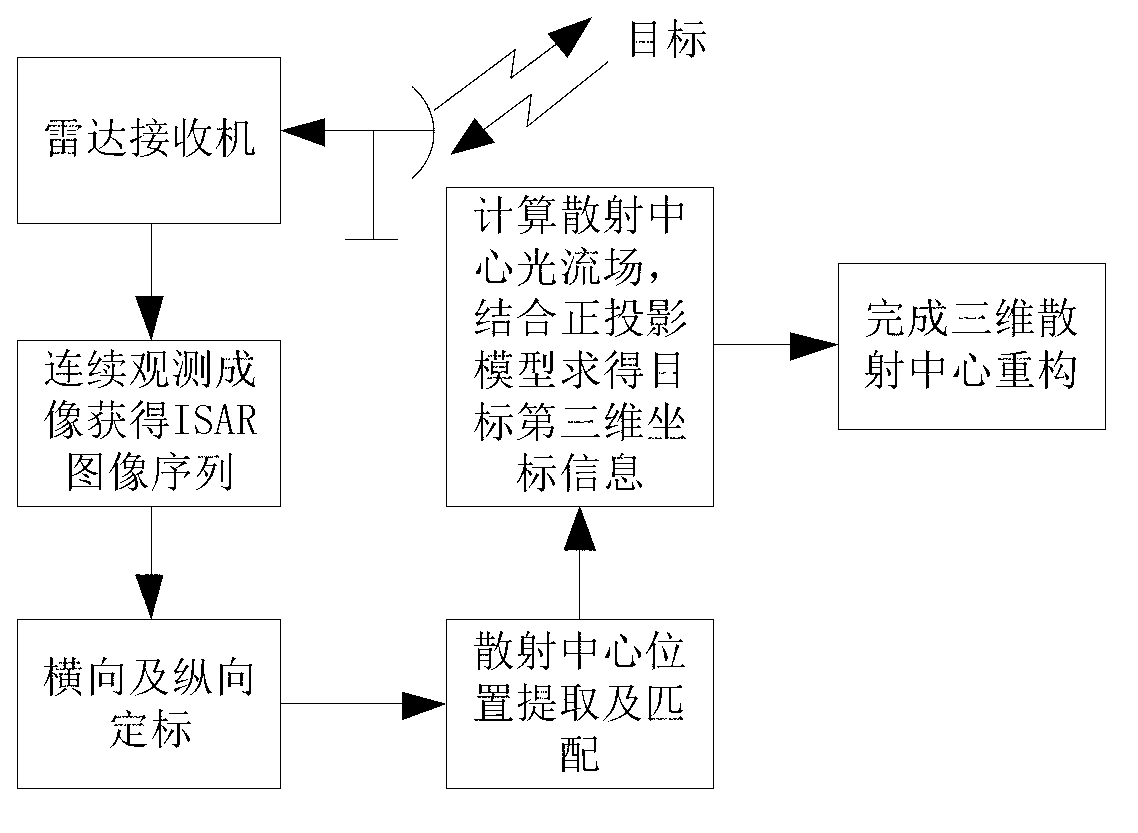
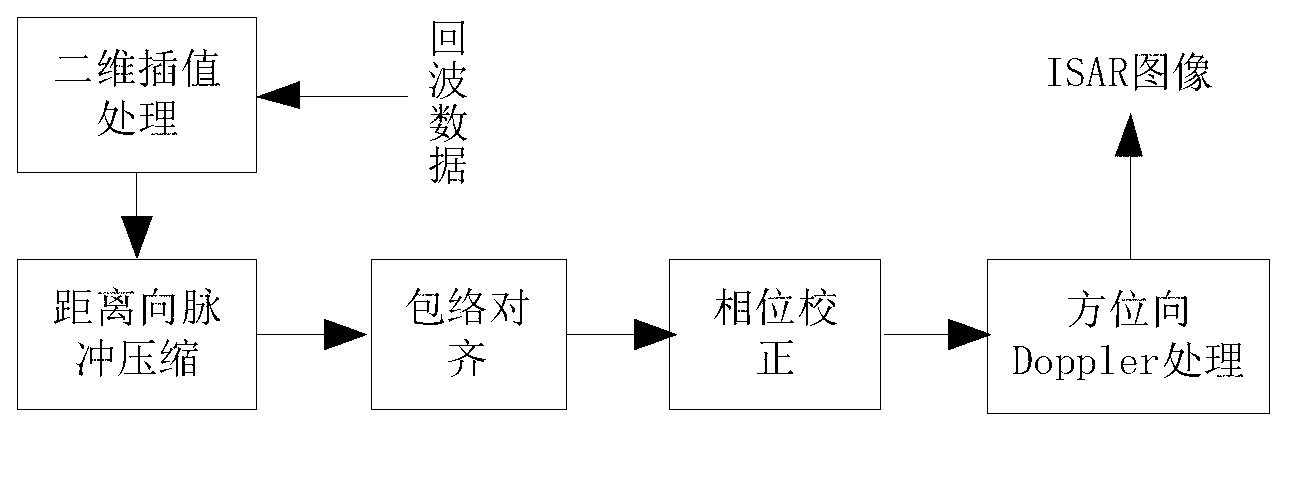
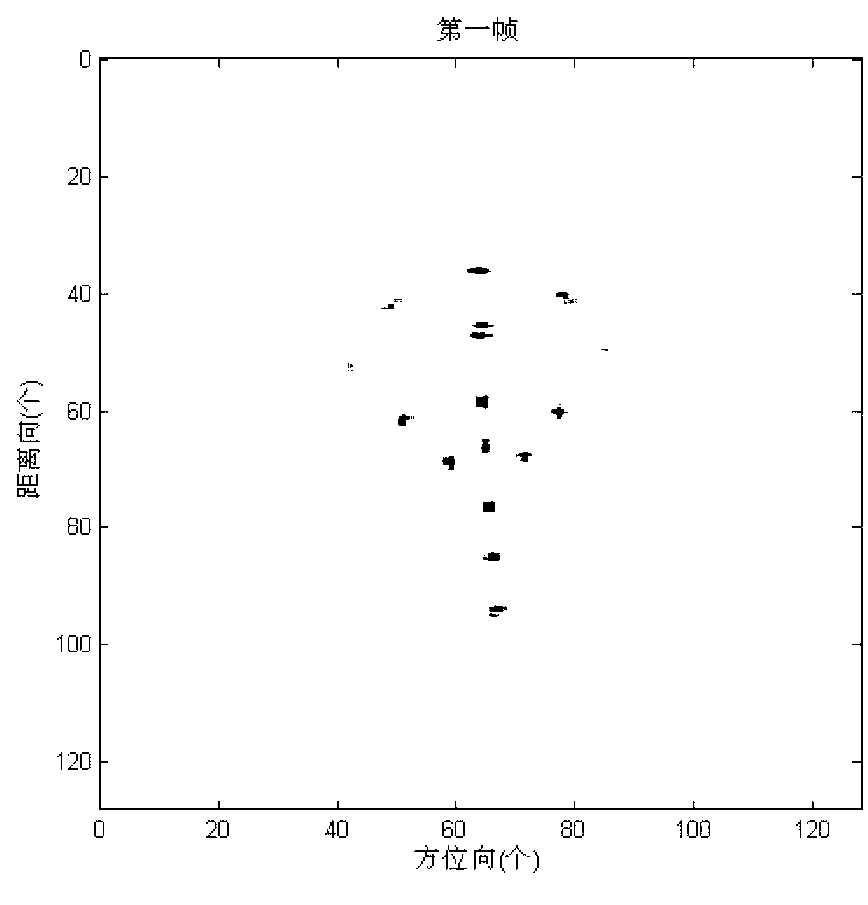
Method for reconstructing target three-dimensional scattering center of inverse synthetic aperture radar
InactiveCN103217674AResolve mismatchSmall amount of calculationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterferometric synthetic aperture radarInverse synthetic aperture radar
The invention provides a method for reconstructing target three-dimensional scattering center inverse synthetic aperture radar. The method for reconstructing the target three-dimensional scattering center of the inverse synthetic aperture radar comprises the following steps: conducting continuous image formation on echo data after motion compensation so as to obtain an ISAR two-dimensional image sequence; respectively conducting horizontal scaling and vertical scaling on the information storage and retrieval (ISAR) two-dimensional image sequence so as to obtain a position coordinate of the scattering center; and respectively extracting a position coordinate of the scattering center in an ISAR two-dimensional image of each frame, calculating a displacement velocity field of every two adjacent frames of the scattering center of the ISAR two-dimensional image, combining projection equation and target motion equation of an orthographic projection model so as to obtain estimated values of a third dimension coordinate by combining a projection equation and a target motion equation of an orthographic projection model, and averaging multiple estimated values to obtain the final third dimension coordinate. Therefore, reconstruction of the target three-dimensional scattering center is completed directly. The method for reconstructing the target three-dimensional scattering center of the inverse synthetic aperture radar does not need cost of extra system hardware, can distinguish scattering centers with different heights in the same distance and position resolution unit, does not need to utilize prior information such as observation perspective of the radar, and has relatively small calculating amount.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Multi-parameter shaft analyzer (MPSA)
Methods and apparatus are provided for measuring multiple operating parameters of a rotating shaft with a sensor. One embodiment of the apparatus comprises a sensor in close proximity to a matched pair of thumbnail depressions on the surface of a rotating shaft body. The thumbnail depressions enable the sensor to detect axial displacement and rotational speed of the shaft in addition to detecting radial displacement of the shaft body. Signal processing circuitry analyzes the sensor output data and computes separate values for the axial displacement, speed and radial displacement parameters. Additional filtering and signal processing techniques can be used to ascertain peak axial displacement, to reduce noise, and to compute other parameters, such as acceleration and power spectral density.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
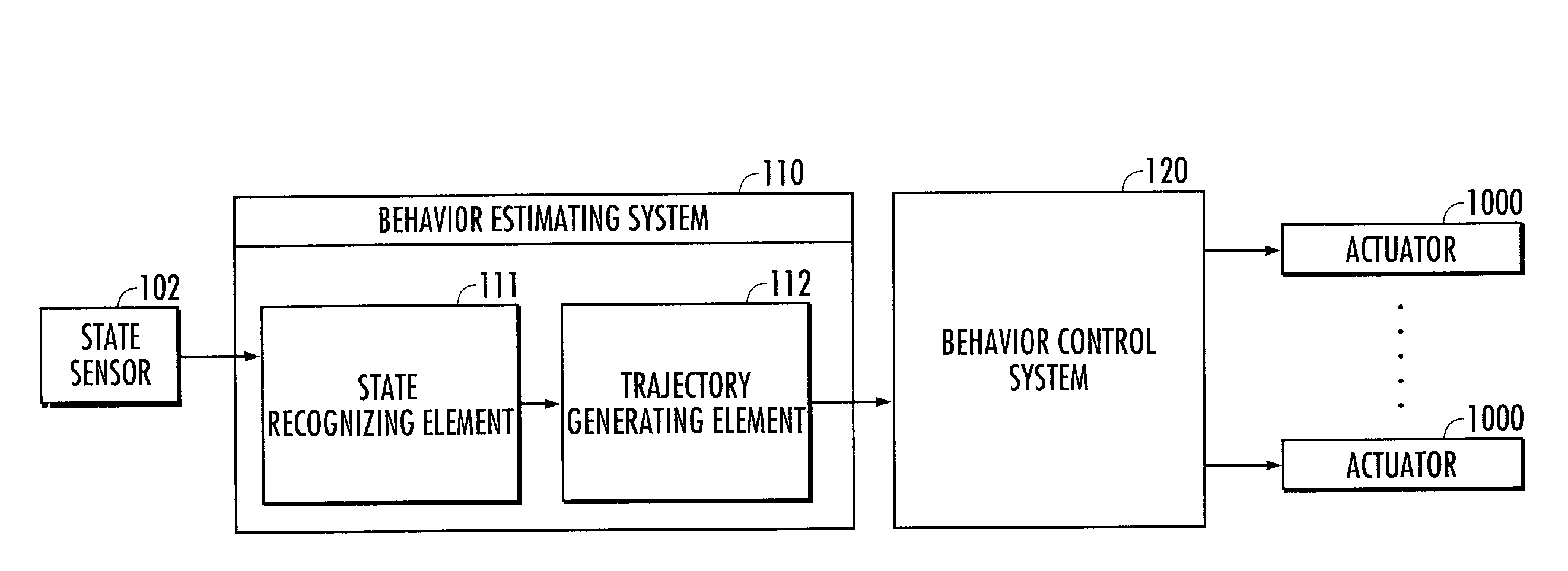
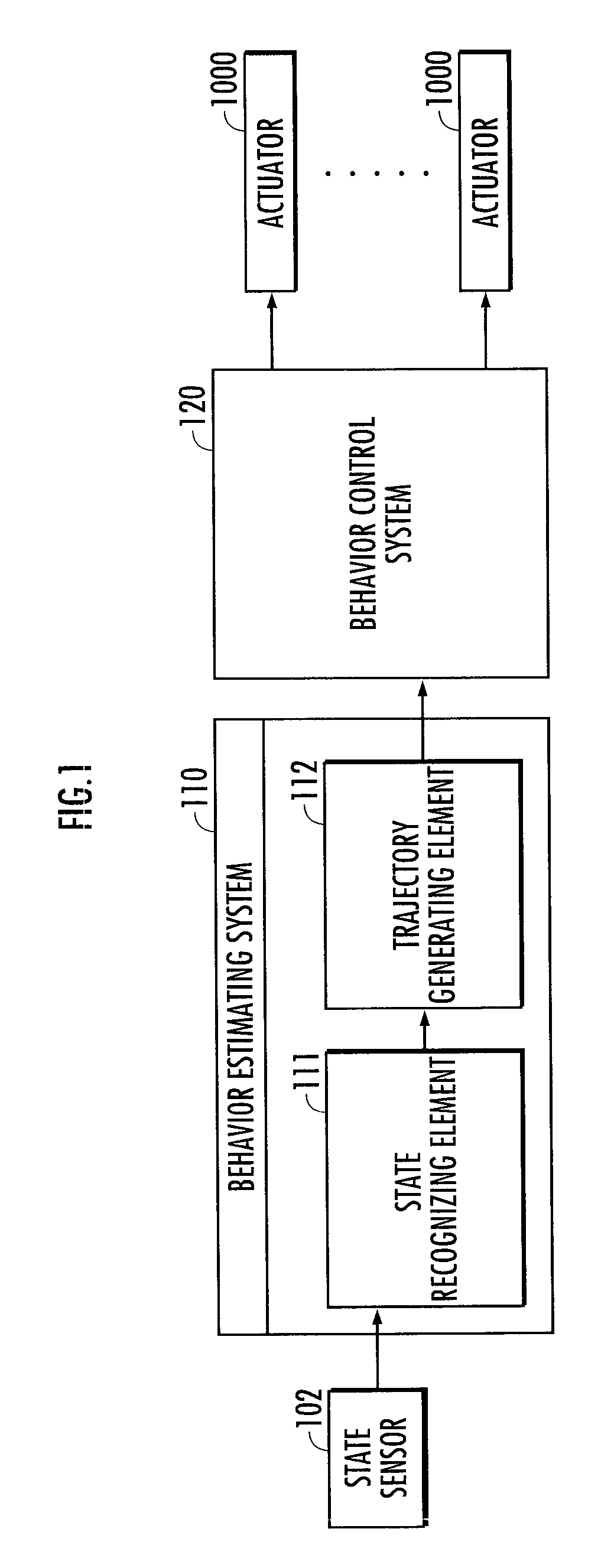
Behavior estimating system
ActiveUS20090326679A1Improve accuracyImprove stabilityComputer controlSimulator controlState variableComputer science
A behavior estimating system is provided. According to the system, an estimated trajectory which provides the basis on which the behavior of an agent is controlled is generated according to a second model which represents a motion of an instructor in which the position and the displacing velocity of the position of a state variable and the time differential values thereof continuously change, in addition to the position of a characteristic point of a reference trajectory which represents a motion of the instructor and a plurality of first models which represent a plurality of shape characteristics of reference trajectories. A behavior manner corresponding to a first model whose fluctuation, which is allowed under a condition that an estimated trajectory passes a characteristic state variable or a range in the vicinity thereof, is the smallest and whose stability is the highest is estimated as the behavior manner of the instructor.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Pump
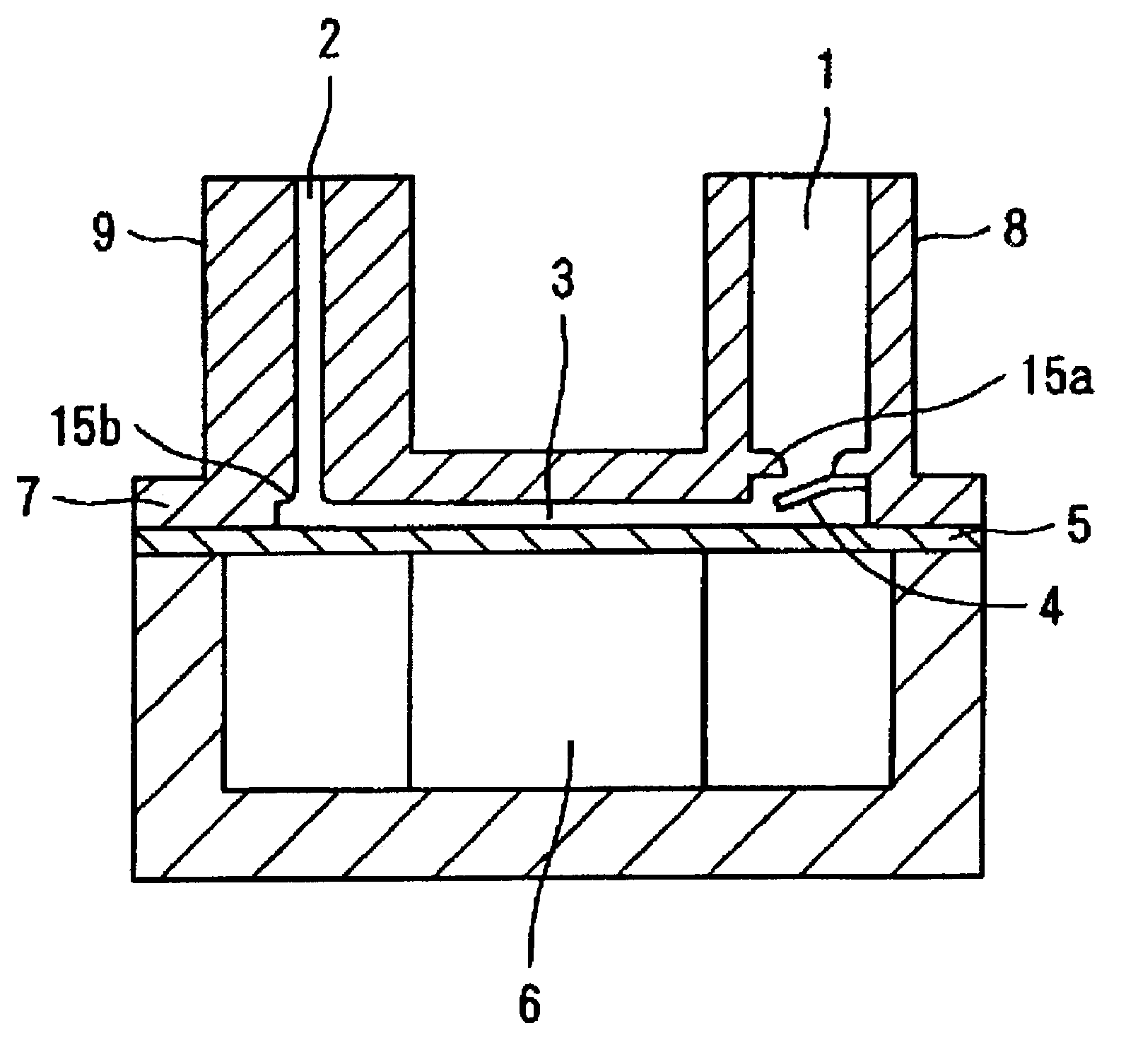
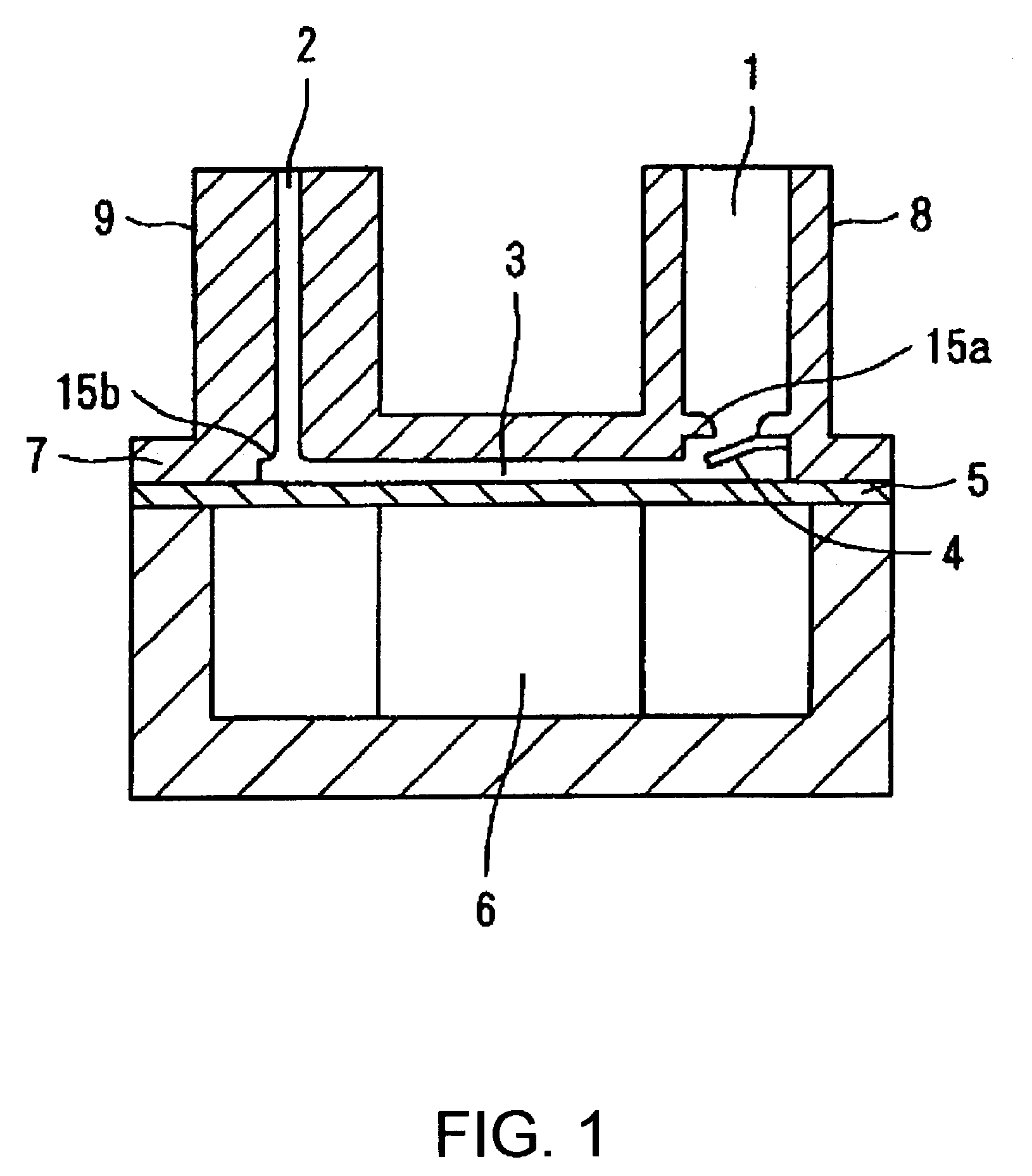
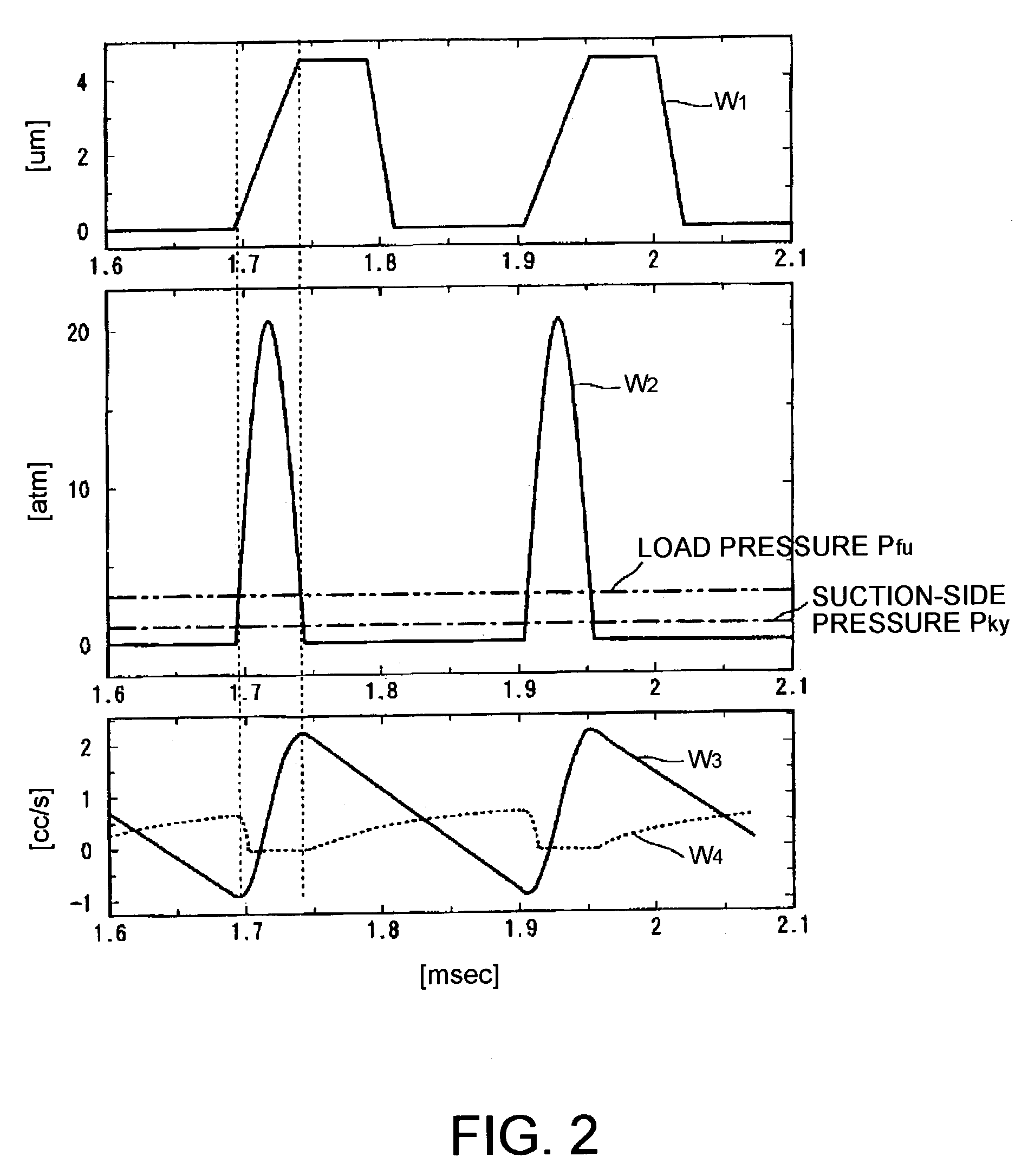
ActiveUS7059836B2Little resistanceA large amountPositive displacement pump componentsPump controlElectricityPump chamber
The invention provides a pump which has reduced pressure loss by using fewer mechanical on-off valves, which has increased reliability, which can be used under a high load pressure, which can be driven at a high frequency, and which has good drive efficiency by increasing discharge fluid volume per pumping period. A circular diaphragm, disposed at the bottom portion of a case, has its outer peripheral edge secured to and supported by the case. A piezoelectric device to move the diaphragm is disposed at the bottom surface of the diaphragm. A space between the diaphragm and the top wall of the case is a pump chamber. An inlet flow path, having a check valve serving as a fluid resistor disposed thereat, and an outlet flow path, which opens to the pump chamber during operation of the pump, open towards the pump chamber. In the pump, driving of the piezoelectric device is controlled so that an average displacement velocity in a pump chamber volume reducing step of the diaphragm becomes a velocity at which the diaphragm reaches the reached-displacement-position in a time equal to or less than ½ and equal to or greater than 1 / 10 of a natural vibration period T of fluid inside the pump chamber and the outlet flow path.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method for controlling parking consistency of train set of multi-agent system
ActiveCN108628169AWith processing powerImprove robustnessAdaptive controlAnti jammingControl objective
The invention provides a method for controlling parking consistency of a train set of a multi-agent system. The method includes the steps of establishing a multi-agent system model of a distributed train set, designing a PID controller according to the control target to track a displacement speed curve of a virtual navigator, and designing a composite tracking controller which comprises a slidingmode variable structure observer to feed disturbance information back to the controller. The tracking precision is improved, and the anti-jamming capability is high. The tracking controller designed by the invention can track the consistency of the braking speed of the train set. The adjacent carriages are always in a safe vehicle distance.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF TECH
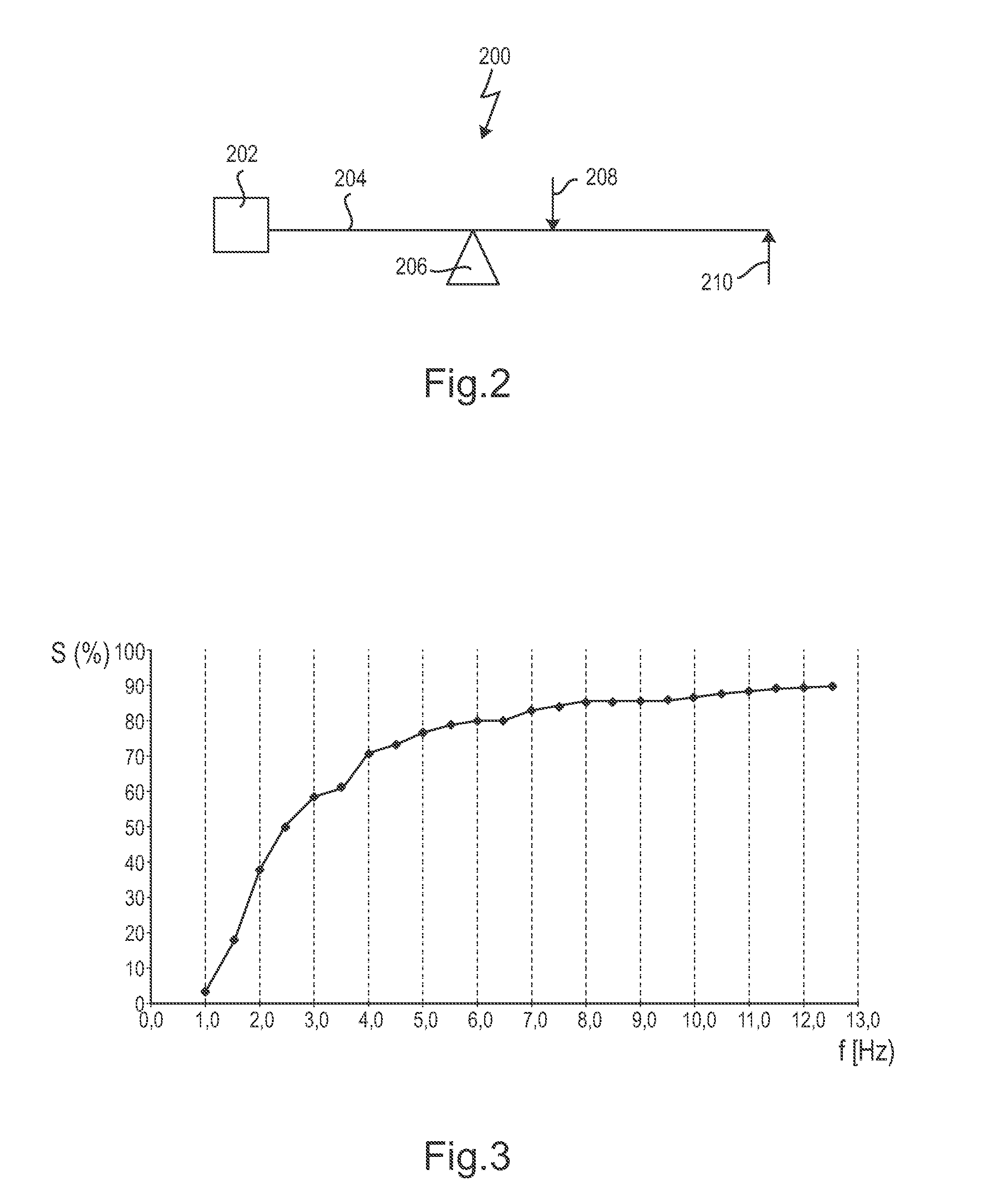
Long-range optical device having image stabilization
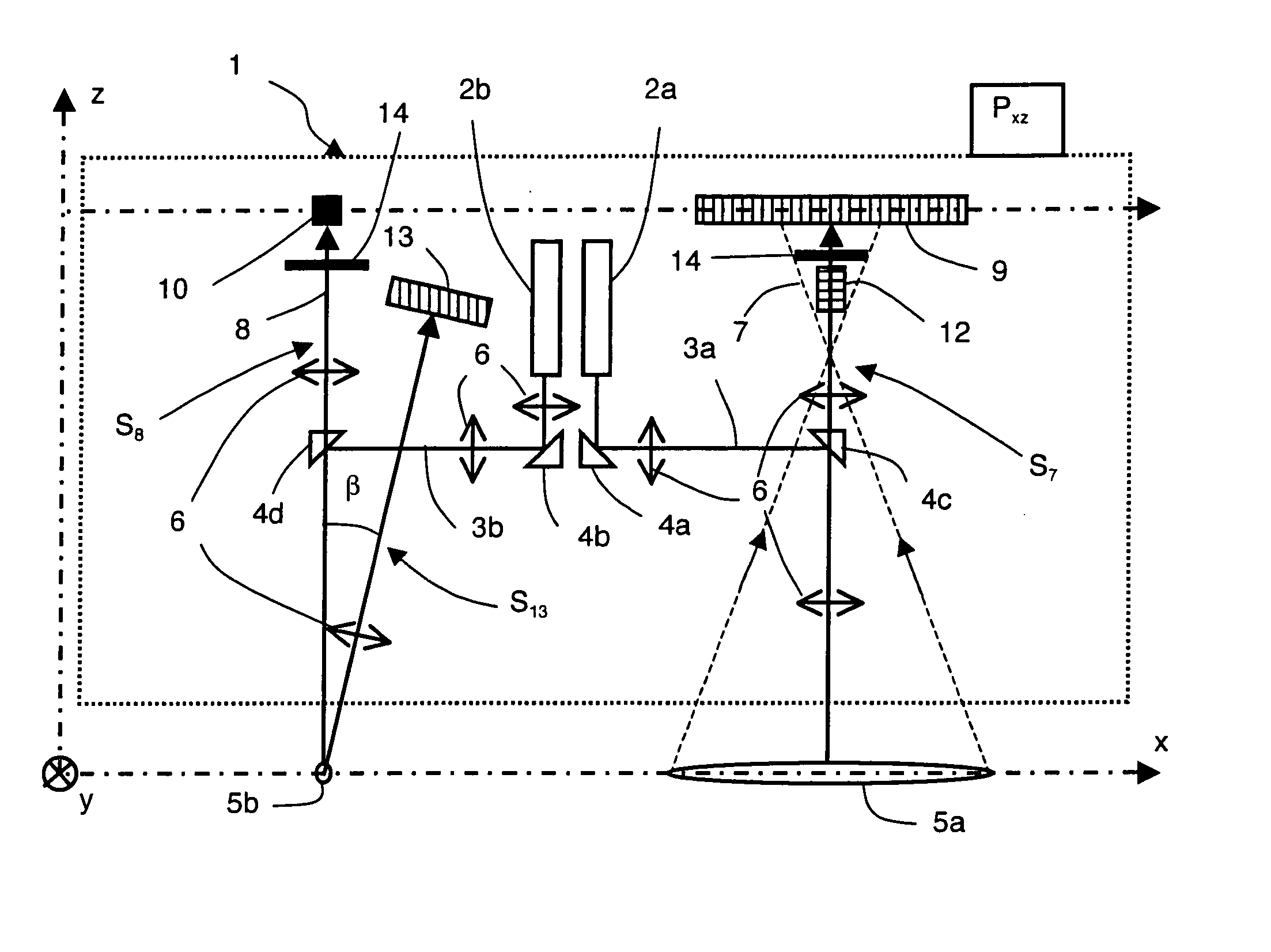
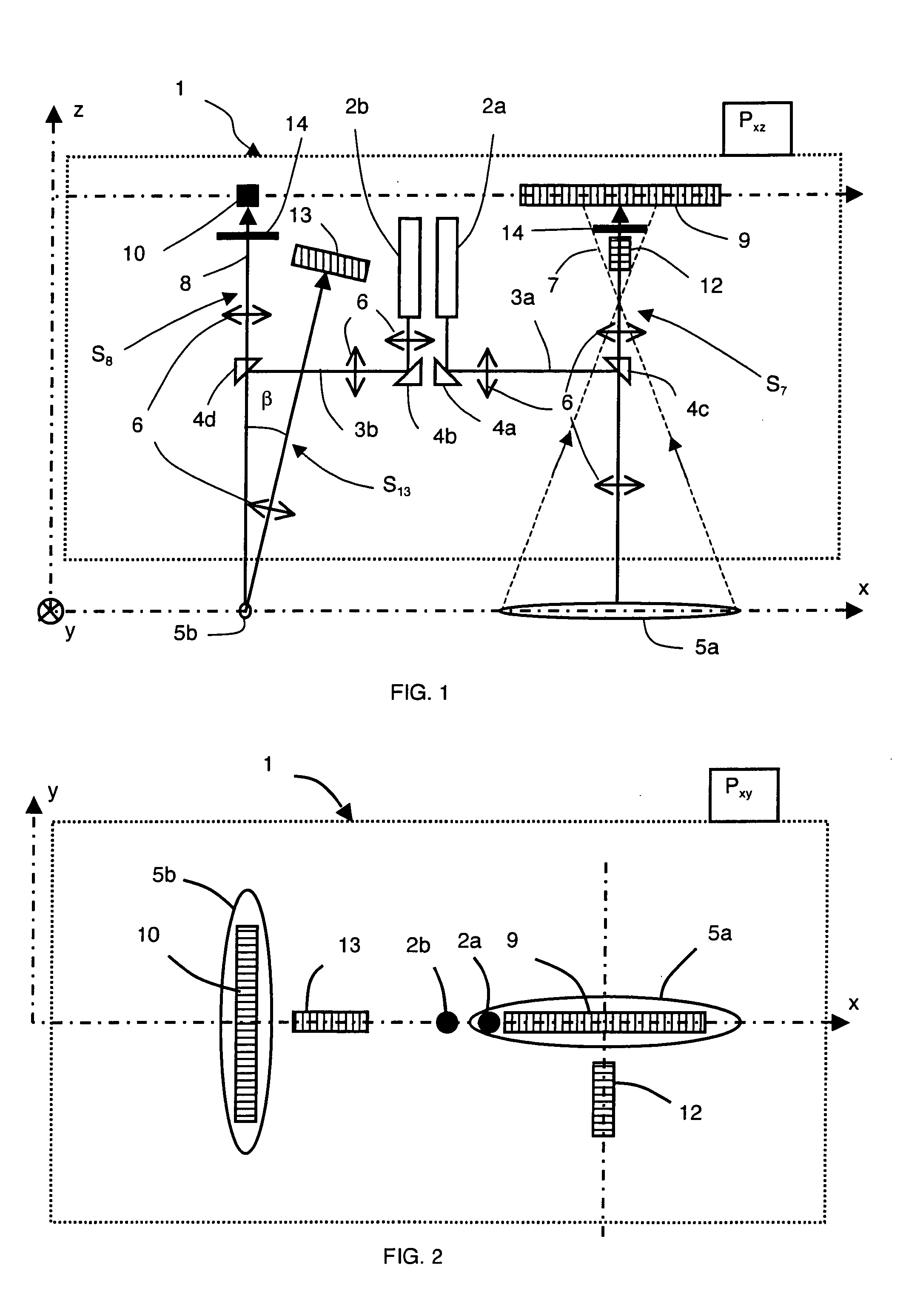
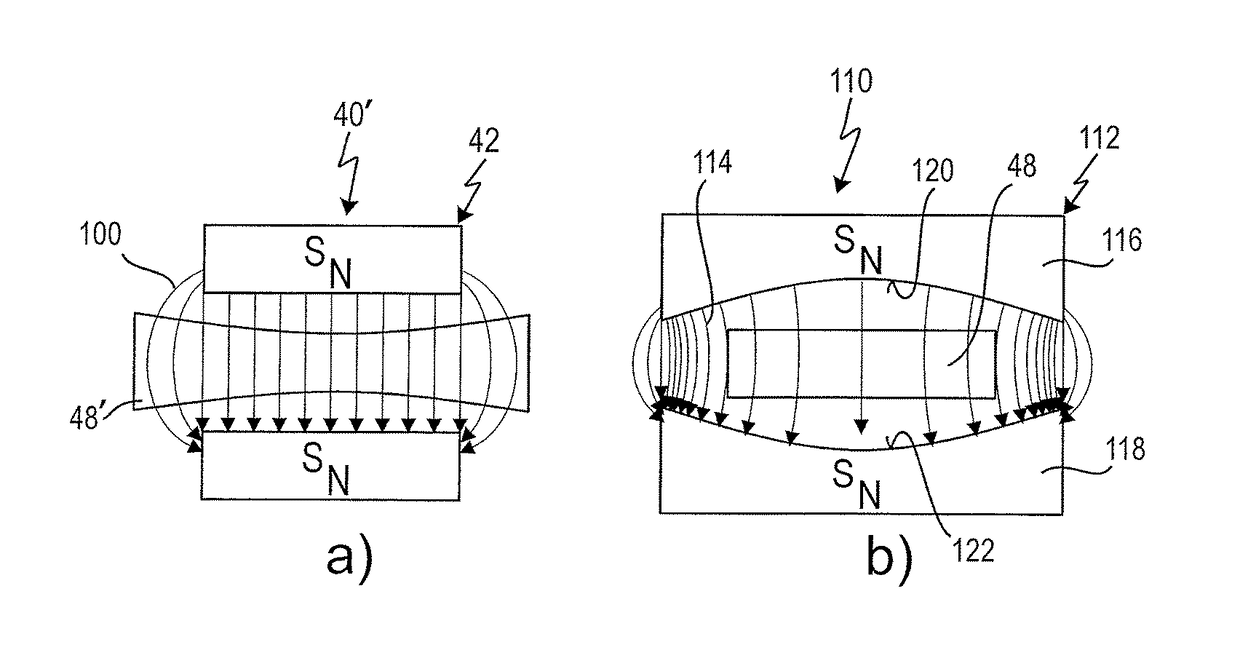
A long-range optical device has at least one optical channel, which has a housing and an arrangement of optical elements, wherein at least one of the optical elements is movable relative to the housing for image stabilization in the event of perturbing movements of the housing. The device further has a first passive stabilization system based on mass inertia for the at least one movable optical element, which, in the event of displacement of the at least one optical element relative to the housing, generates a first restoring force proportional to the displacement and a second restoring force proportional to the displacement velocity. The first stabilization system is designed for image stabilization in the event of perturbing movements in a first frequency range. The long-range optical device has at least one second stabilization system, which is coupled to the first stabilization system and is designed for image stabilization against perturbing movements in at least one second frequency range, wherein the first and the at least one second frequency ranges are at least partially different.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Experimental method for simulating fault slip
InactiveCN104949890AEasy to operatePracticalMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesPre stressingRock sample
The invention discloses an experimental method for simulating fault slip. The experimental method comprises the following specific steps: I, processing a rock sample; II, setting a sound emission probe on each of a rock A and a rock C, and setting four sound emission probes on a rock B; III, placing the rock C in a pressure chamber of a micro-control rock servo pressure tester, placing the rock B on the rock C, placing the rock A on the rock B, and laying quartz powder with identical particle size on contact surfaces of the rocks to form quartz powder layers; IV, applying axial pre-stress; and V, performing experimental record and analysis, wherein horizontal shear force is applied to a combination at a constant displacement speed, a sound emission system starts working, the sound emission probes are used for acquiring data in real time, waveforms generated by the data are recorded in the sound emission system and then are converted into digital signals through a built-in AD conversion card, and the digital signals are stored in a computer hard dick. The experimental method is simple in operation and convenient in use, and is capable of simulating fault slip so as to improve the accuracy of data detection.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
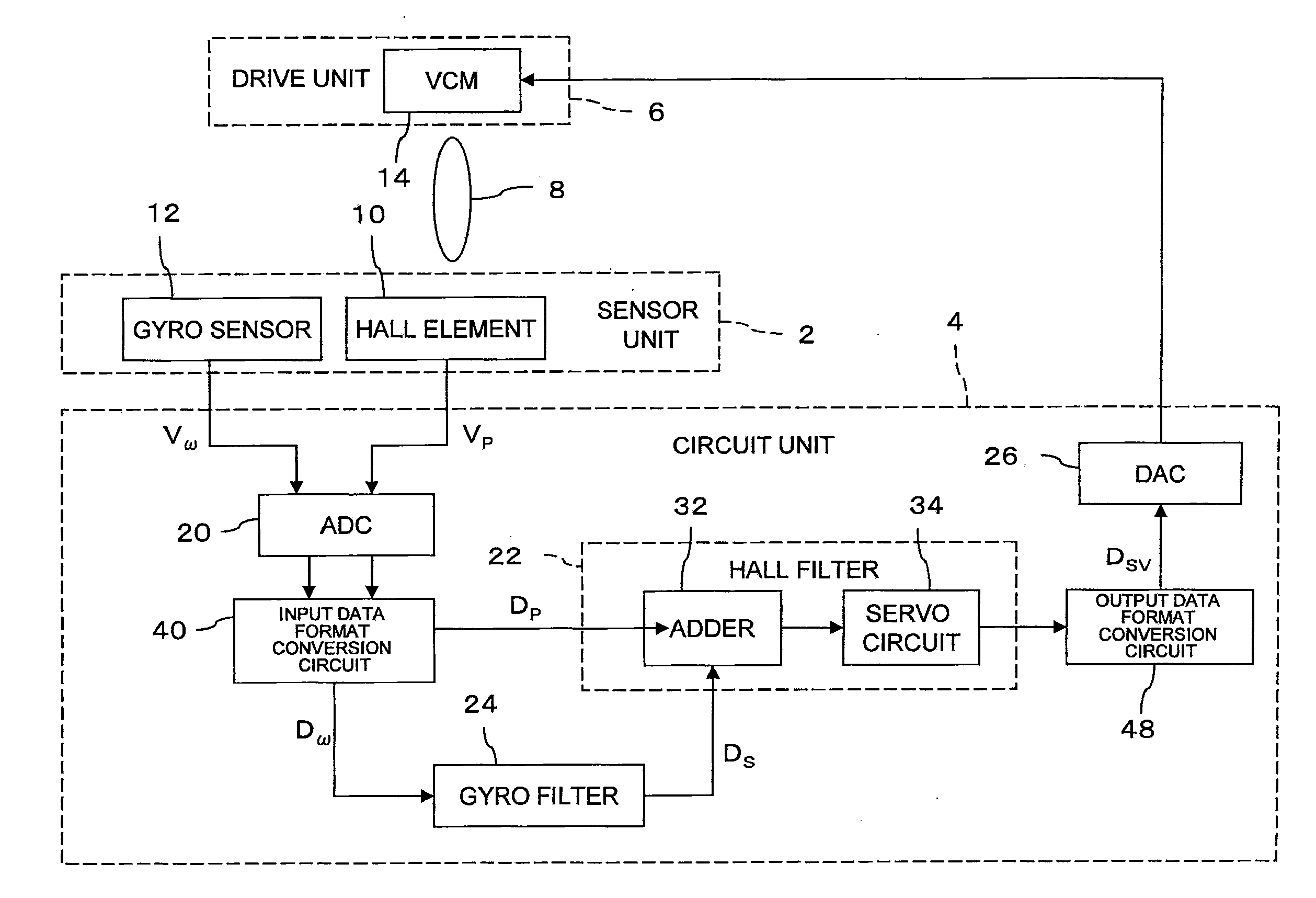
Control circuit for image-capturing device
InactiveUS20110279692A1Efficient data processingEfficient executionTelevision system detailsPrintersClassical mechanicsFloating point
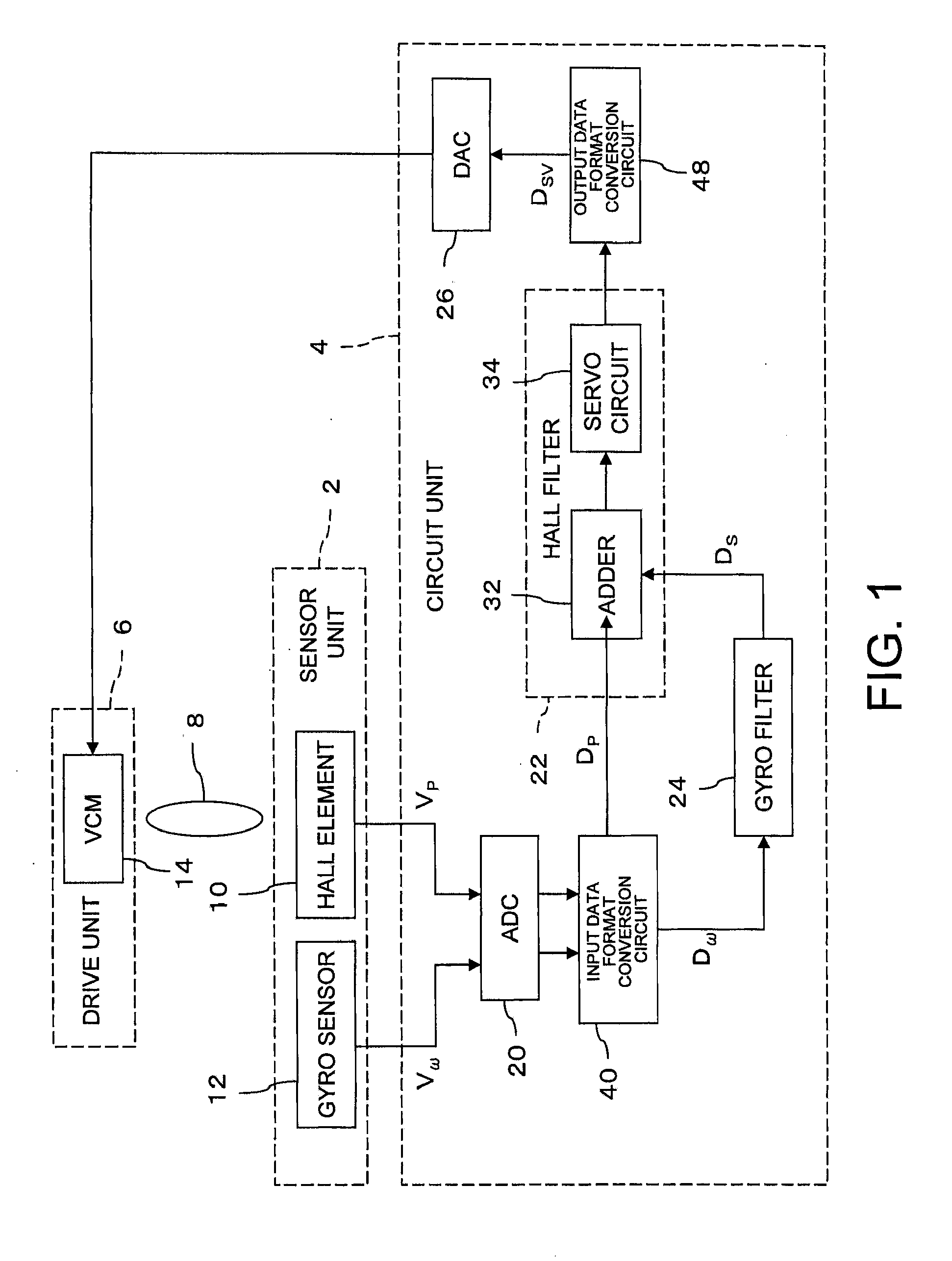
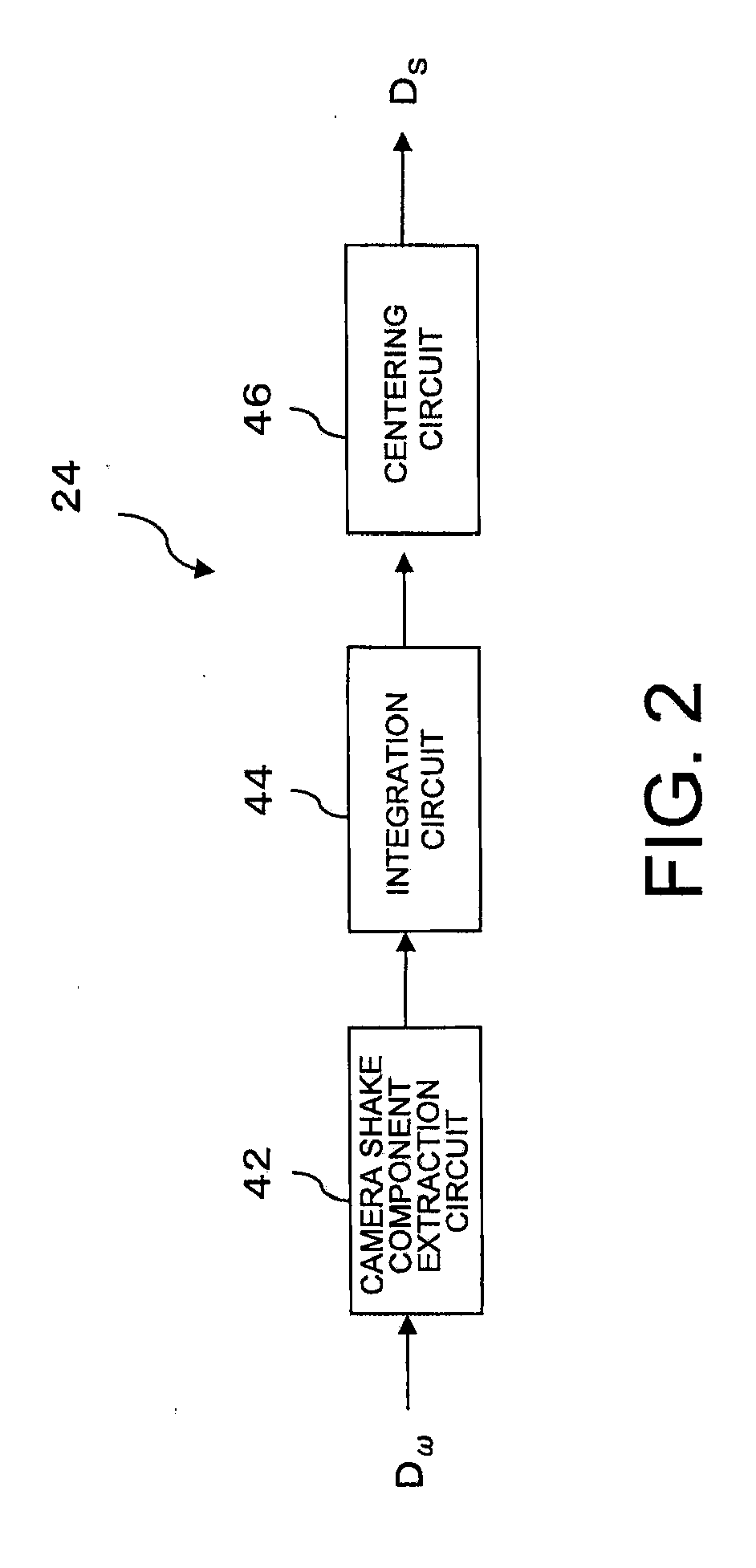
Performing data processing more effectively for camera shake correction is desirable. Movement of an image-capturing device is compensated on the basis of displacement velocity of the image-capturing device detected by a displacement velocity detector and position regarding a focus adjustment member of the image-capturing device detected by a position detector. An input data format converter converts the displacement velocity detected at the displacement velocity detector from fixed-point format to floating-point format and converts the detected position of the focus member to floating-point data. Furthermore, a gyro filter uses data processing in floating-point format to calculate displacement data for a required amount the image-capturing device is to be displaced and a Hall filter uses data processing in floating-point format to generate drive data for the focus adjustment member. Then, the drive data in floating-point format from the Hall filter is converted to drive data in fixed-point format.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Displacement detecting method, correction table making method, motor control apparatus, and processing machine
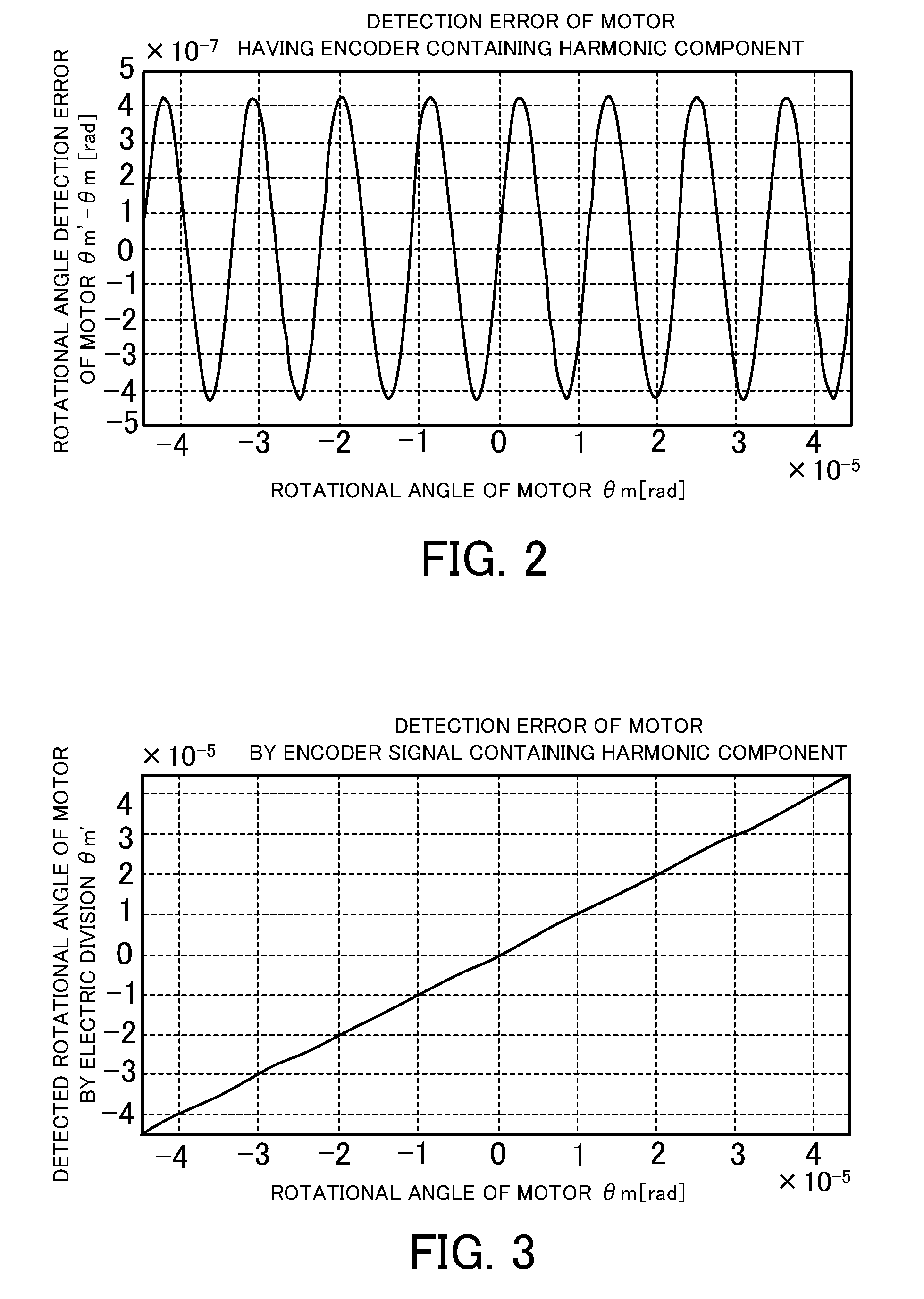
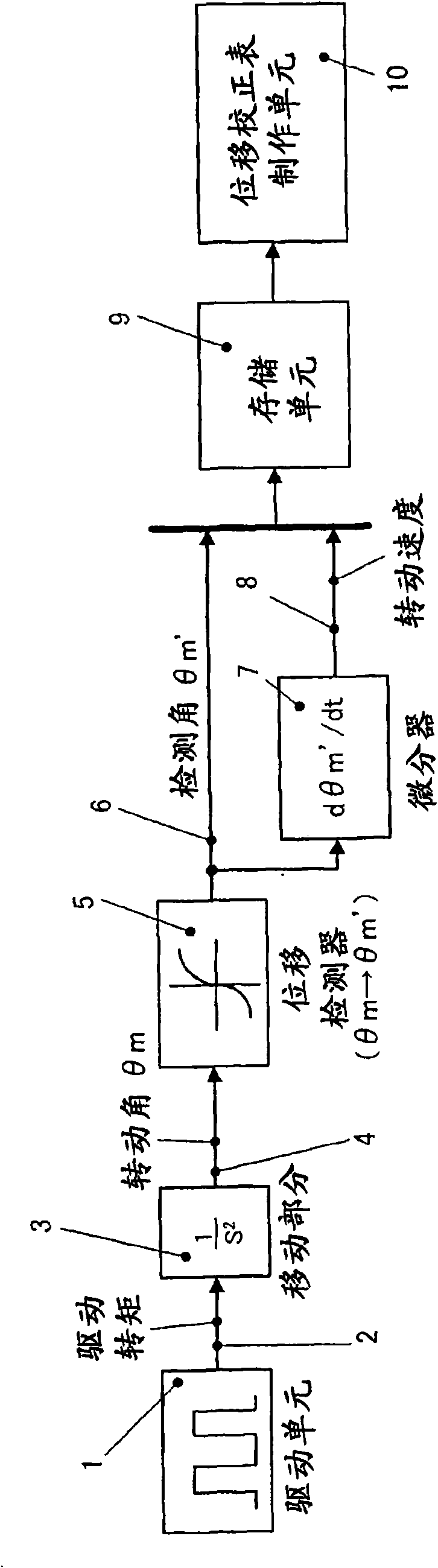
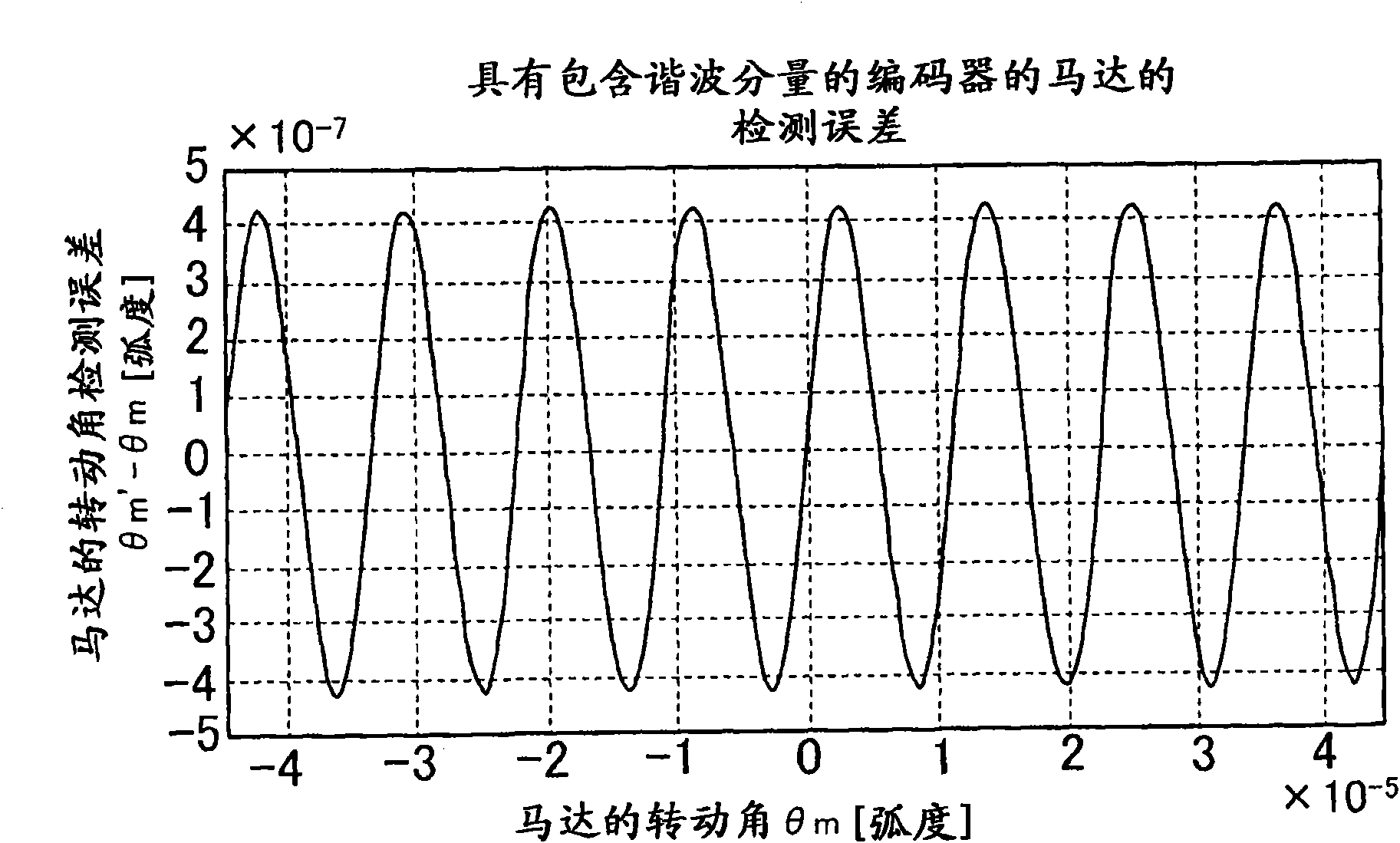
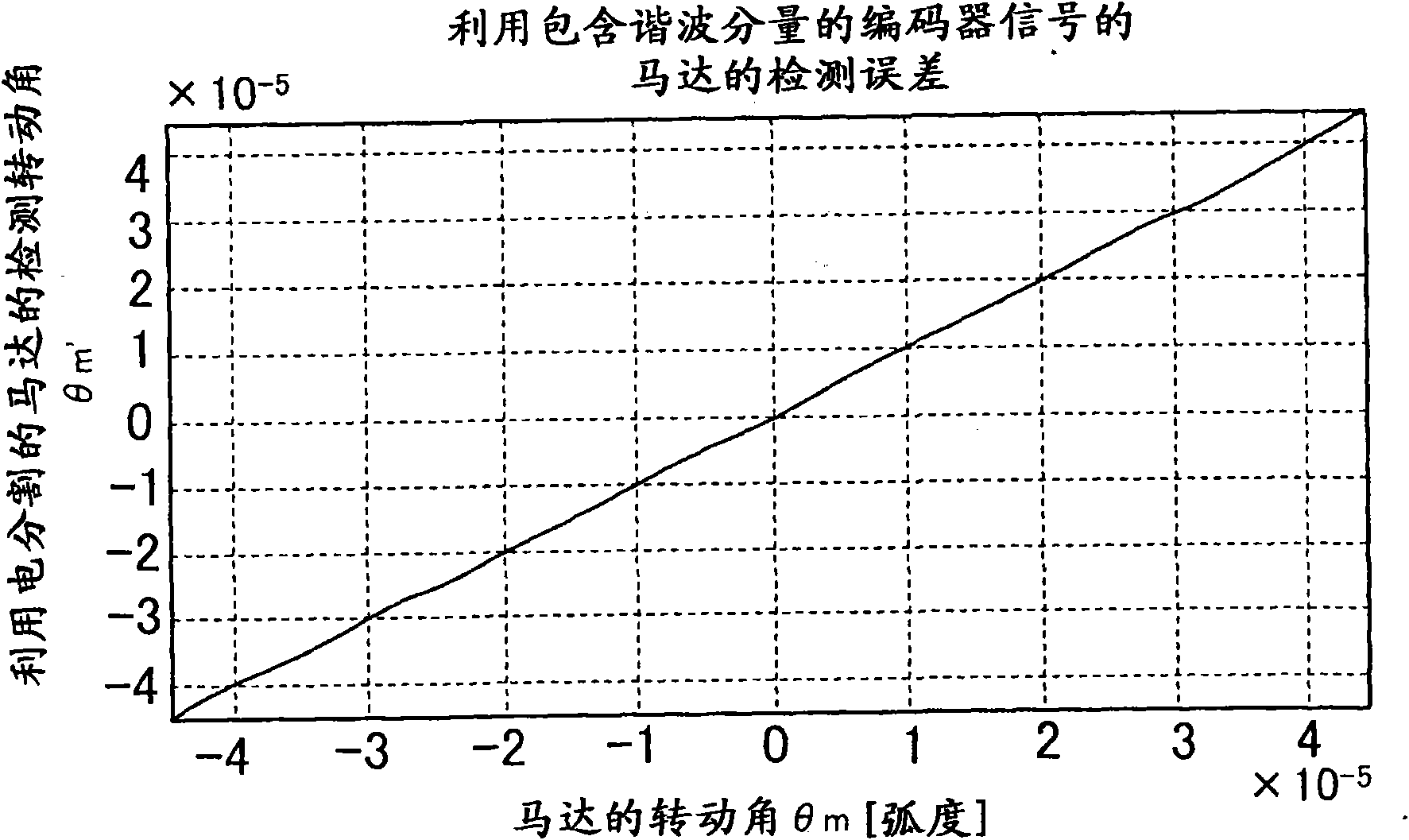
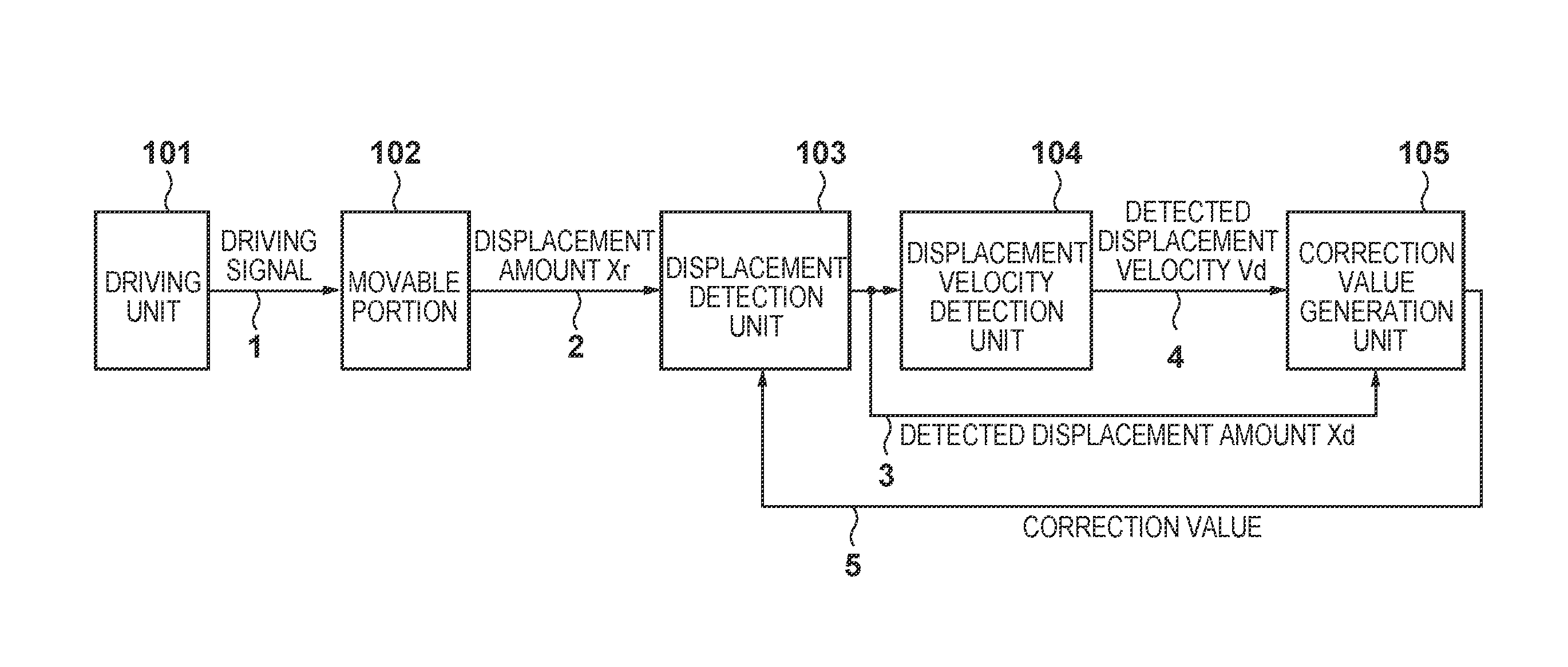
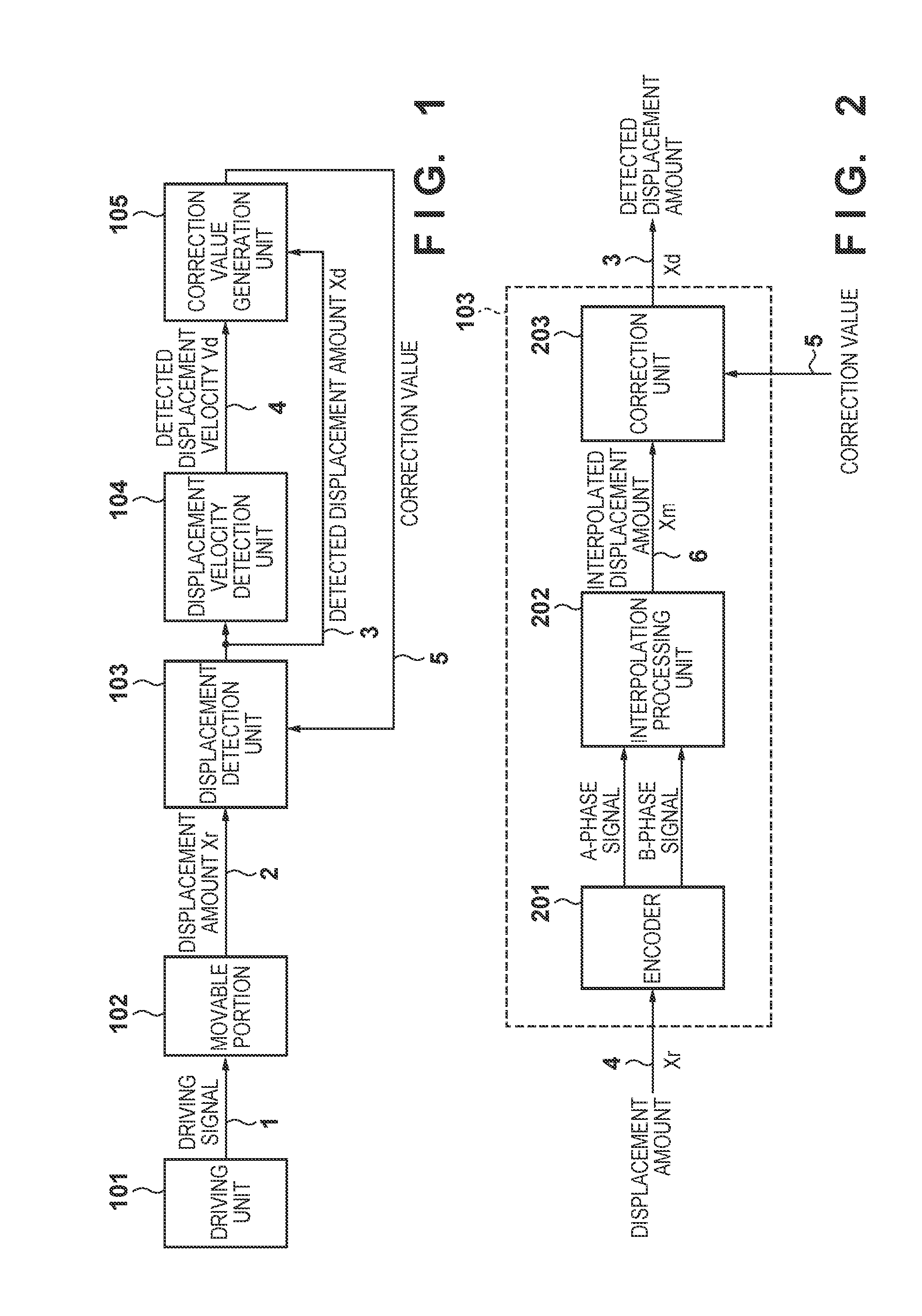
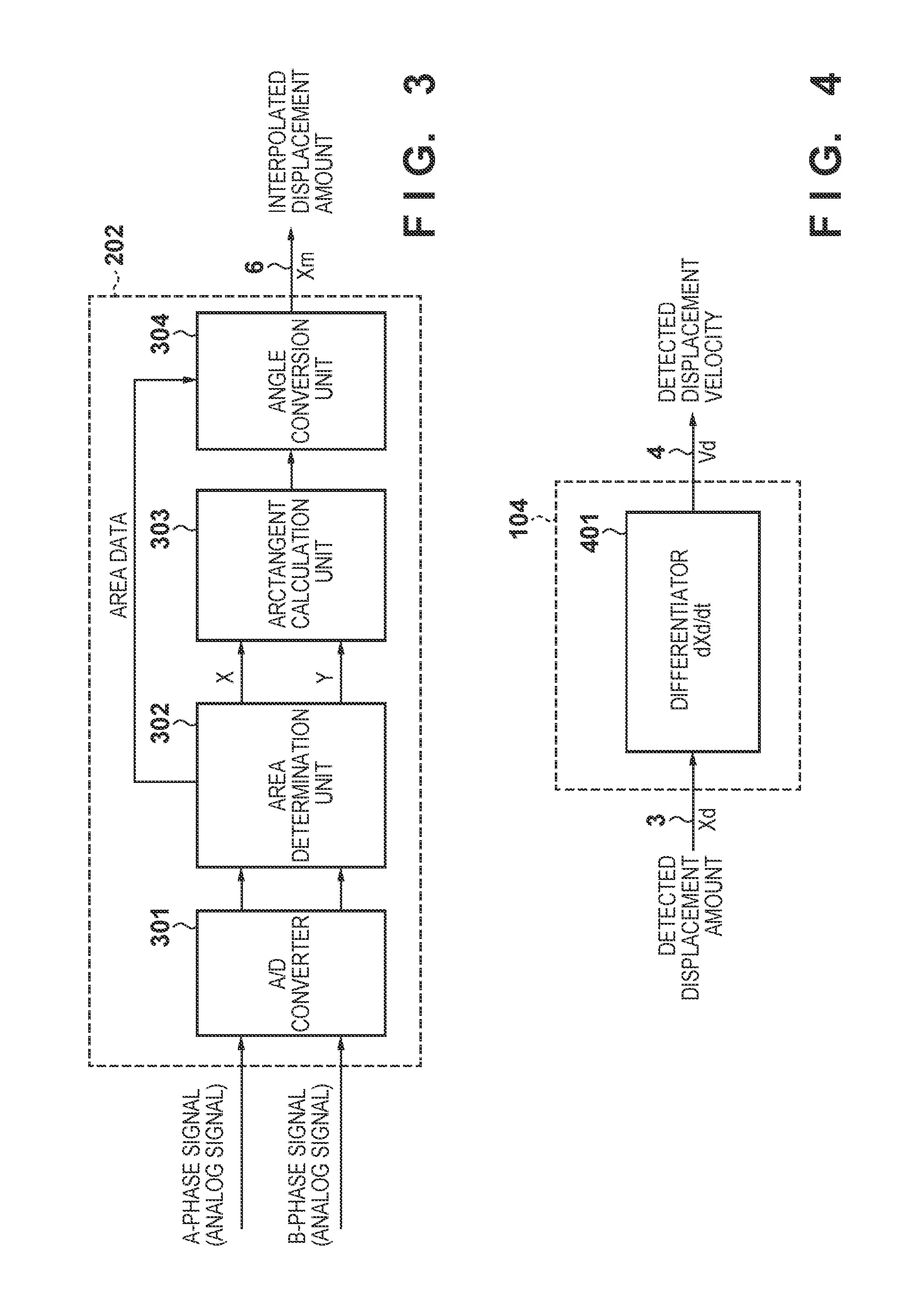
InactiveUS20090309532A1Improve detection accuracyDetection errorElement comparisonIncline measurementMotor controlDisplacement velocity
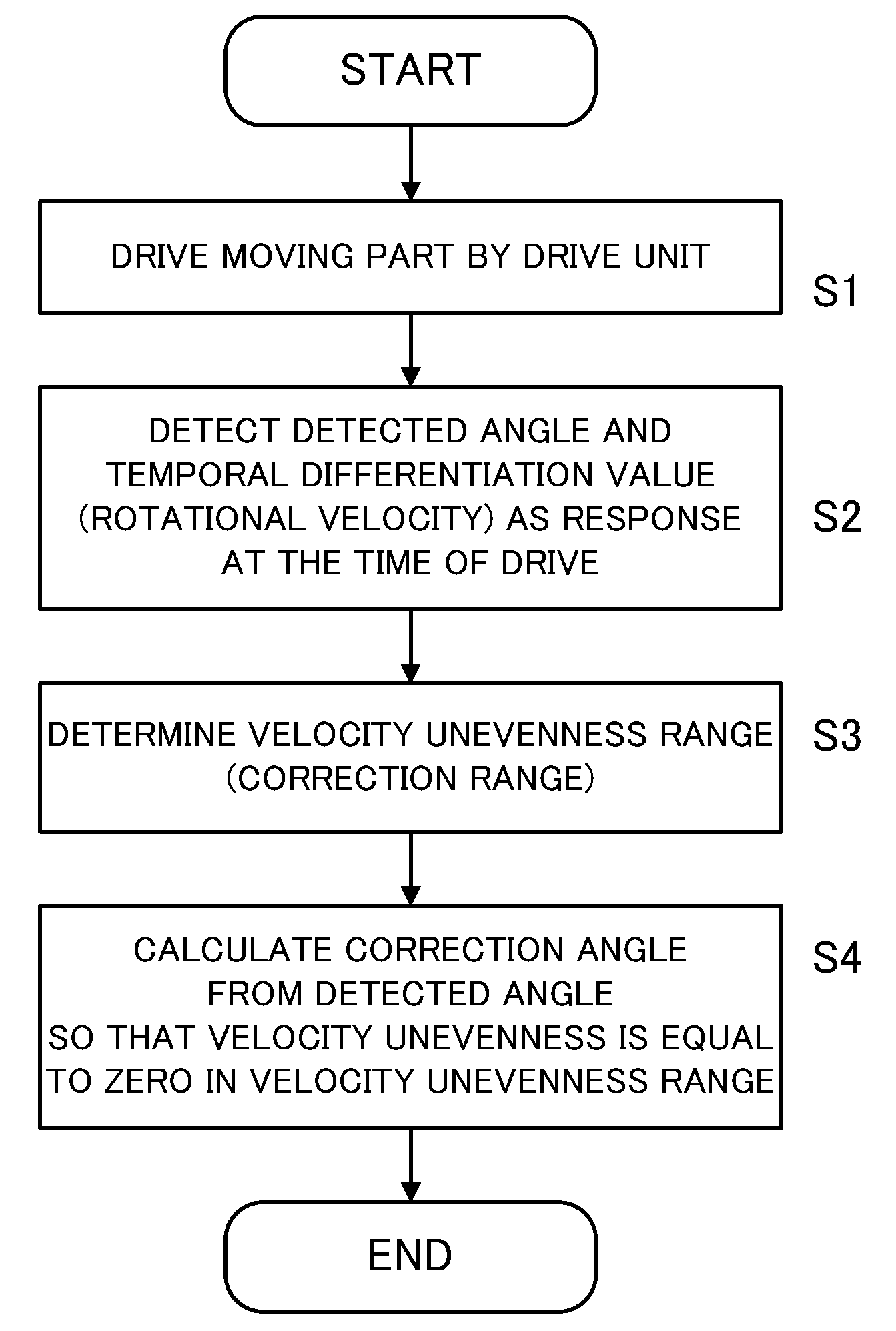
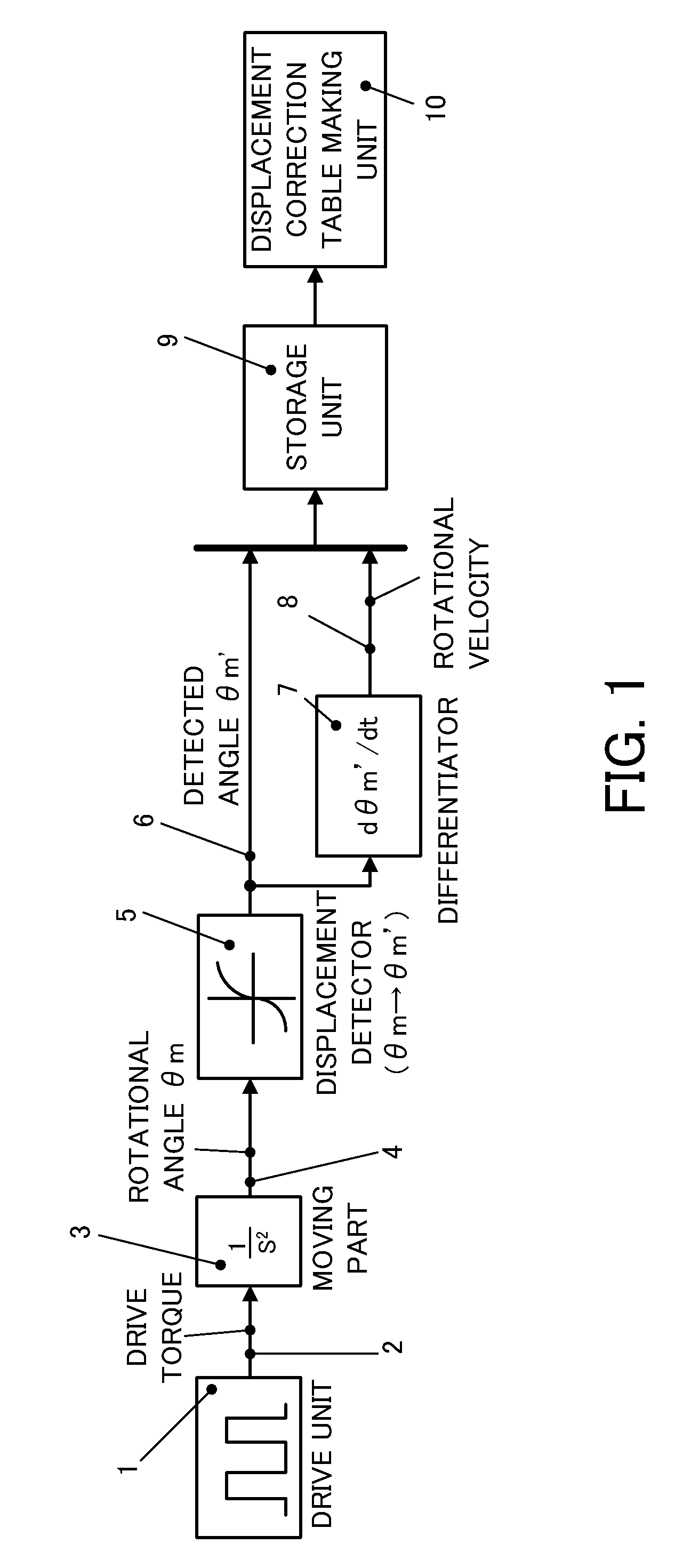
A displacement detecting method of the present invention includes the steps of driving a moving part 3 using a drive unit 1, detecting a displacement amount 6 (detected angle θm′) of the moving part 3 using a displacement detector 5, correcting the displacement amount 6 (detected angle θm′) using a displacement correction table so that a displacement velocity (dθm′ / dt) of the displacement amount 6 (detected angle θm′) detected by the displacement detector 5 is constant, and detecting a displacement amount (detected angle θm″) corrected by the displacement correction table as the displacement amount of the moving part 3.
Owner:CANON KK
Displacement detecting method, correction table making method, motor control apparatus, and processing machine
The invention relates to a displacement detecting method, a correction table making method, a motor control apparatus, and a processing machine. The displacement detecting method of the present invention includes the steps of driving a moving part (3) using a drive unit (1), detecting a displacement amount (6) (detected angle m') of the moving part (3) using a displacement detector (5), correcting the displacement amount (6) (detected angle theta m') using a displacement correction table so that a displacement velocity (d m' / dt) of the displacement amount (6) (detected angle theta m') detected by the displacement detector (5) is constant, and detecting a displacement amount (detected angle theta m'') corrected by the displacement correction table as the displacement amount of the moving part (3).
Owner:CANON KK
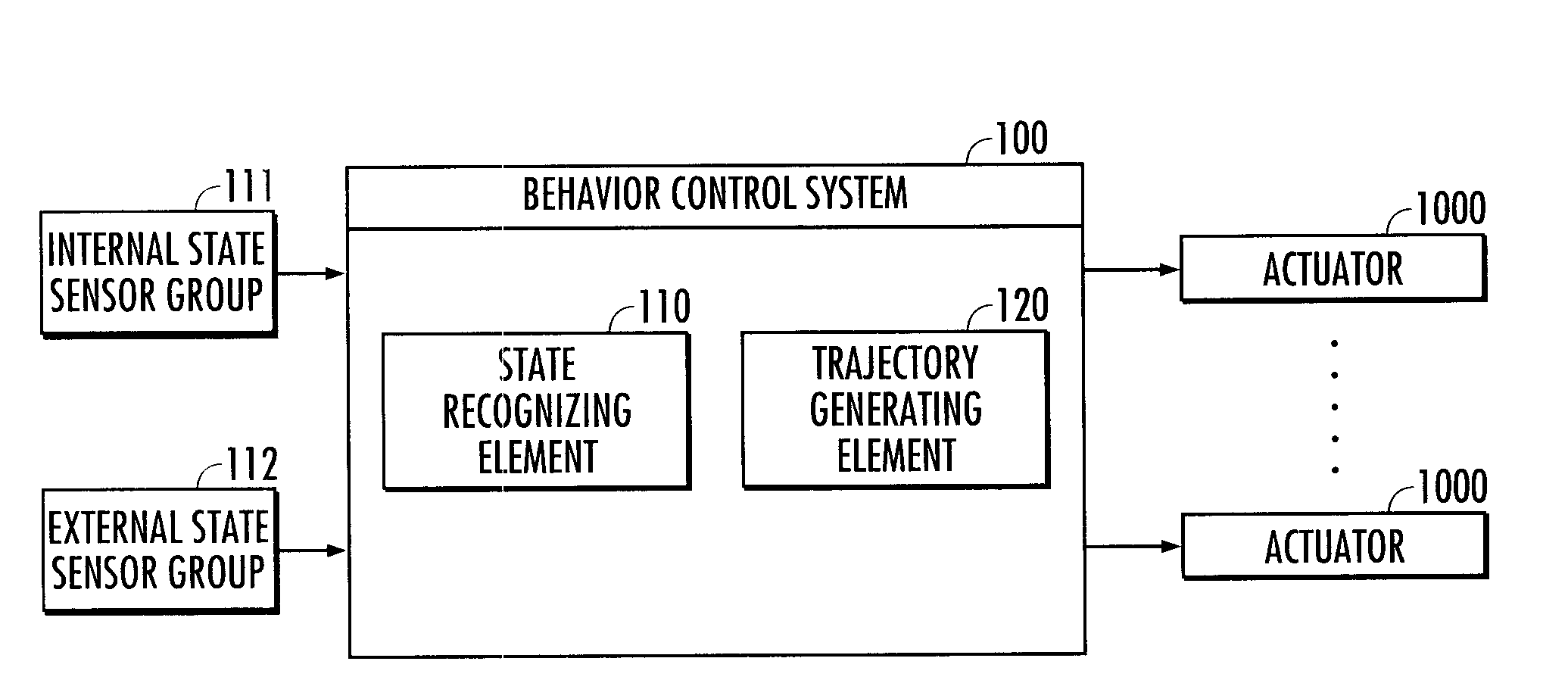
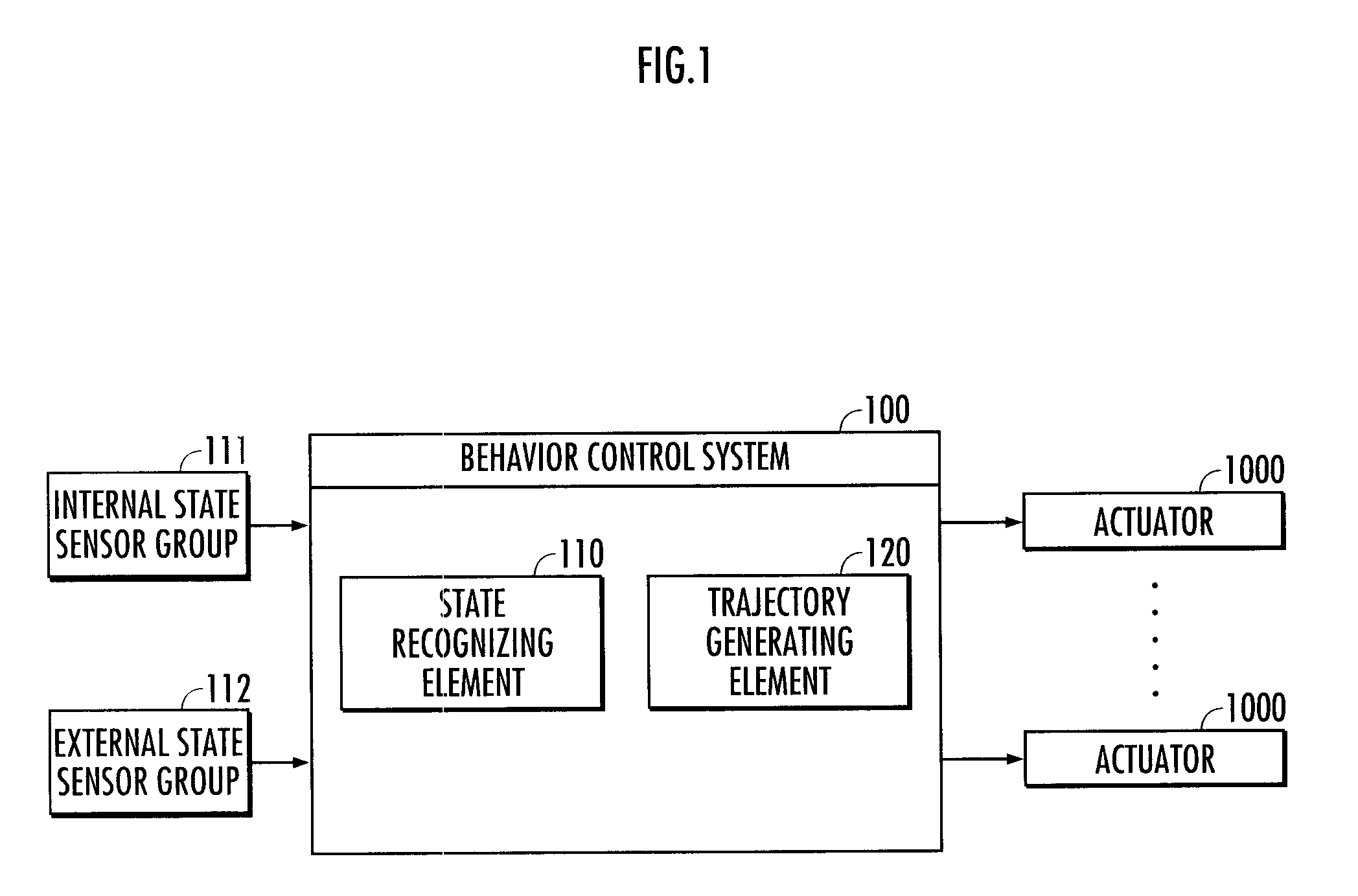
Behavior control system
A behavior control system is capable of causing an agent carry out a task by smooth motions. The behavior control system makes it possible to reproduce a typical shape characteristic of a reference trajectory, i.e., the characteristic of a motion of an instructor carrying out a task, by using a first model defined on the basis of a plurality of reference trajectories representing the position of a first state variable in a time-series manner. Further, a learning trajectory representing the position of a second state variable in a time-series manner is generated on the basis of a second model, which represents an agent's motion in which the position of the second state variable corresponding to the first state variable and one or a plurality of time differential values (a displacing velocity and acceleration) thereof continuously change, in addition to the first model.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
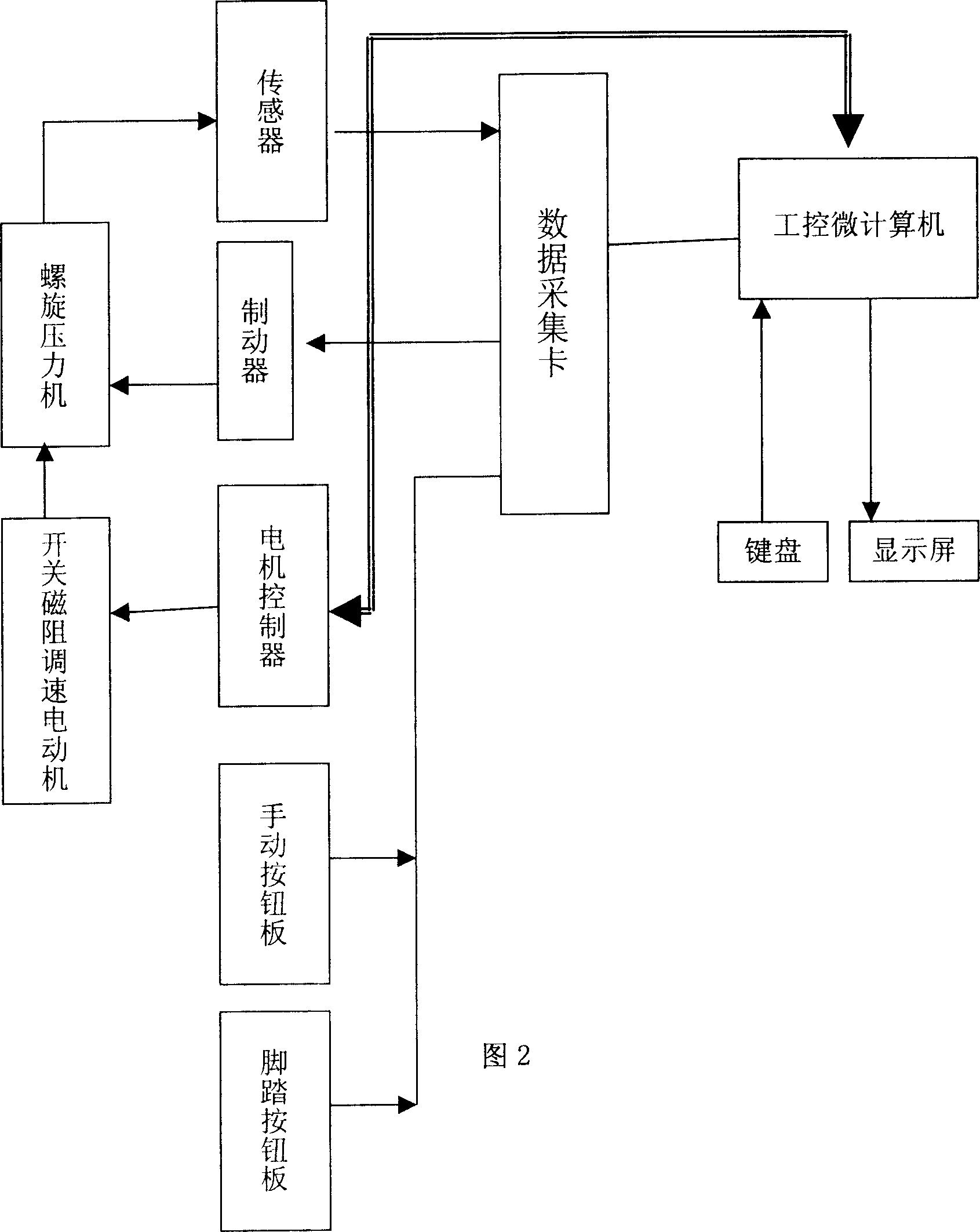
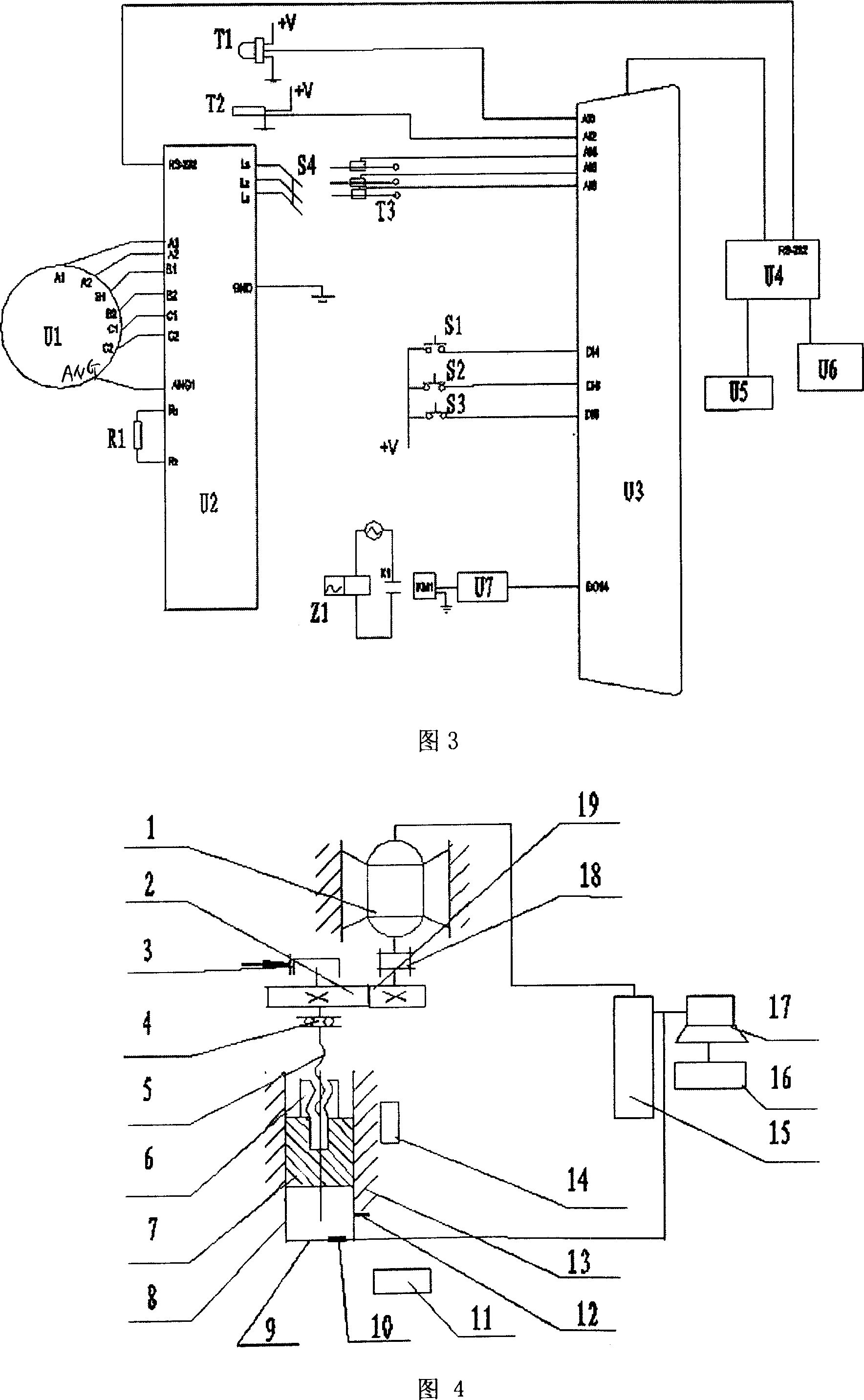
Digital control method for spiral pressure machine transmission and digital control spiral pressure machine
InactiveCN1970285ASimple structureExtend your lifeComputer controlPress ramMotor driveMagnetic reluctance
The screw extruder drive digital control comprises inputting running data by the operator and work station control computer control motor running, with the motor using switch magnetic resistance speed regulating motor, based on the input data, through the calculation of the work station control computer control motor, switch magnetic resistance speed regulating motor driving the extrusion of the screw. Switch magnetic speed regulating motor provides power to spiral compressor, through regulating angular displacement and velocity of the speed regulating motro to control the displacement and speed change of the slide of the compressor, realizing digital control fo the spiral compressor with simple structure, free from speed regulation, easy control of the slide displacement velocity.
Owner:SHANDONG KEHUI POWER AUTOMATION
Single-Particle LIDAR Anemometry Method and System
ActiveUS20110181863A1Reduce power/sensitivity requirementGood bijectionDevices using optical meansFluid speed measurementFrequency modulationDisplacement velocity
The present invention concerns a single-particle LIDAR anemometry method and system comprising the continuous emission of one or more light beams through a gas containing particles, said beam being focused onto a measurement volume, a step of detecting a signal backscattered by particles passing through said volume, the method being characterized in that it comprises at least the following phases:determining in a time period Δt the frequency of each of the pulses included in the backscattered signal;distinguishing pulses based on duration and / or intensity and / or frequency-modulation criteria; andestimating the displacement velocity of said beam relative to the gas from several of the frequencies determined over the time period Δt excluding those corresponding to the pulses distinguished during the preceding stepA notable application of the invention is for the measurement of the airspeed of an aircraft
Owner:THALES SA
Ultrasound measurement apparatus and ultrasound measurement method
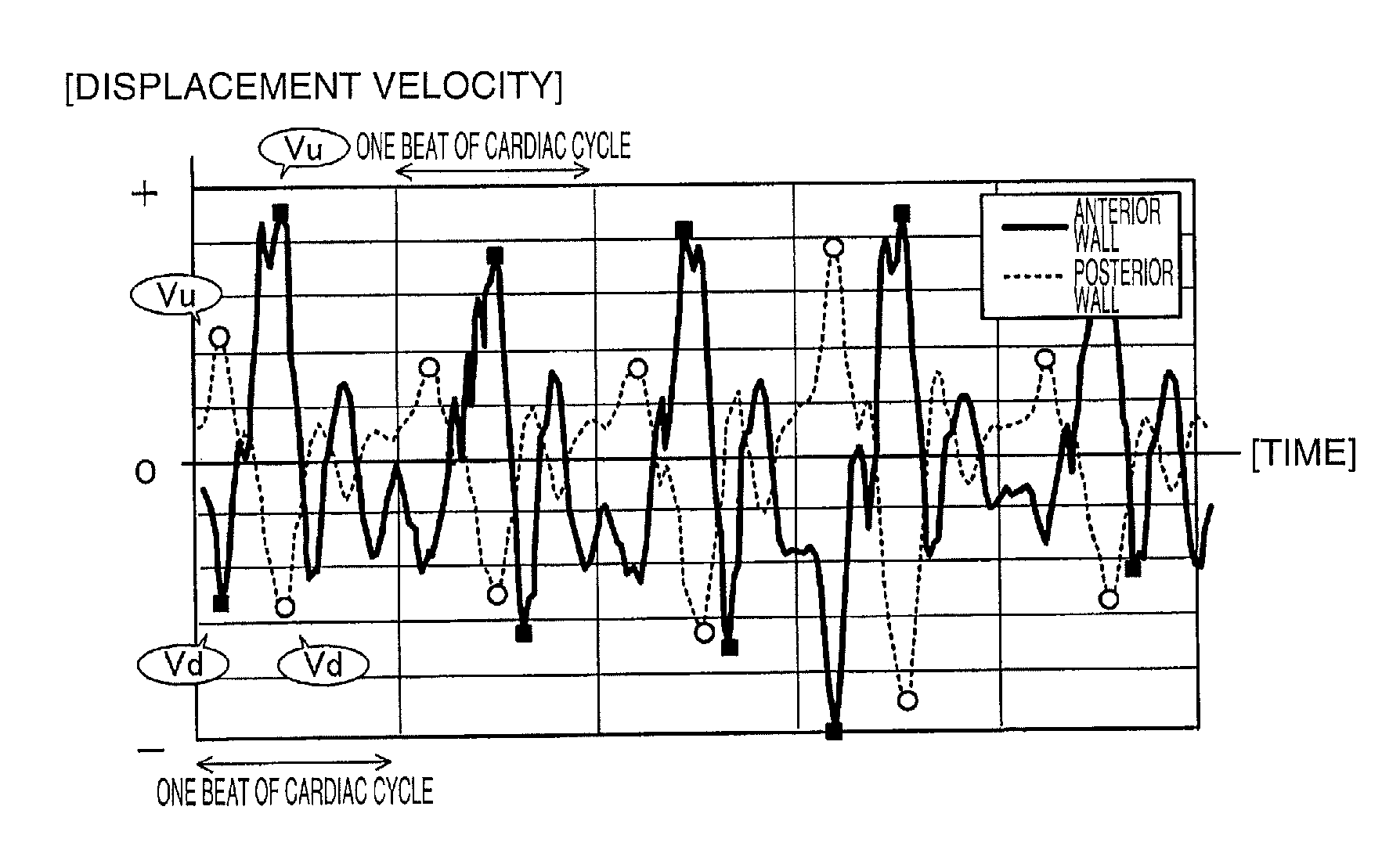
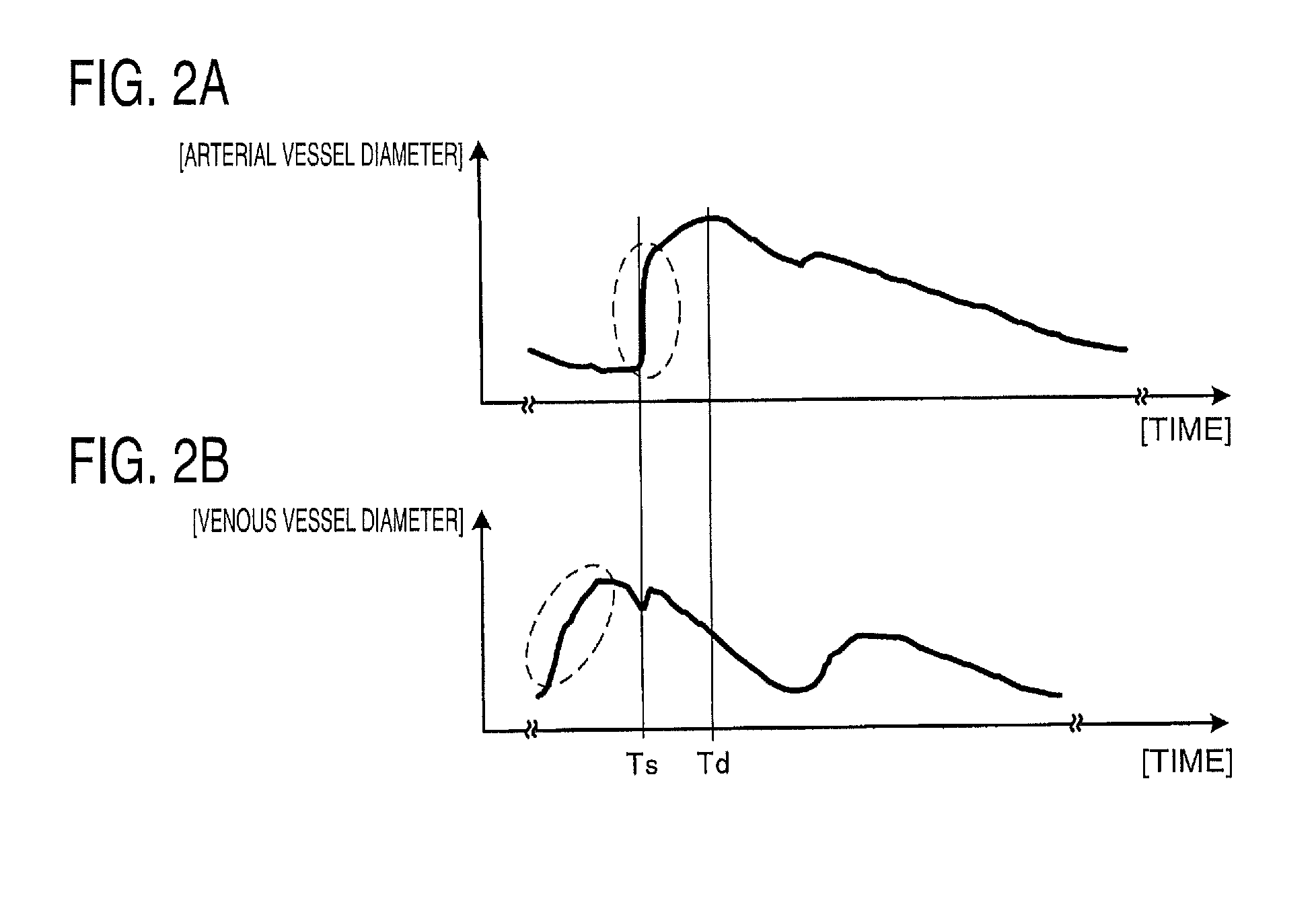
A region of interest which is considered to be a vascular wall of an artery is set in a B-mode image, and tracking processing is performed for each region of interest. A maximum displacement velocity Vu in a positive direction and a maximum displacement velocity Vd in a negative direction are obtained as a peak value of a displacement velocity of the vascular wall. If a first peak ratio (Vu / Vd) of a region of interest corresponding to an anterior wall is equal to or greater than a predetermined first feature threshold value (for example, 2.0) using the obtained maximum displacement velocity Vu in the positive direction and maximum displacement velocity Vd in the negative direction, it is determined that the region of interest is an artery.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Device for measuring the speed of displacement of an object deforming the lines of the terrestrial magnetic field
InactiveUS20130057264A1Road vehicles traffic controlUsing electrical meansMagnetic tension forceClassical mechanics
An apparatus for measuring speed of movement of an object deforming lines of Earth's magnetic field includes a first and second magnetometer disposed on either side of a traffic roadway for the object and substantially perpendicular to the object. The magnetometers are configured for measuring deformation of Earth's magnetic field by the object travelling over the roadway. The apparatus also includes a processing unit configured for extracting, from each of the magnetometers, a measurement value corresponding to a quotient defined by a distance of the object with respect to the magnetometer divided by a speed of movement of the object, and for calculating a speed of the object from the measurement values and a geometrical disposition of the magnetometers with respect to one another and with respect to the traffic roadway.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Dynamic performance test device for linear rotating motor and testing method
ActiveCN106324499AImprove test efficiencyImplement load performance testingDynamo-electric machine testingTest efficiencyElectric machine
The present invention provides a dynamic performance test device for linear rotating motor. The device comprises a measured linear rotating electric machine, a motor base, a test platform base, a first bottom plate, a second bottom plate, a rotating speed and torque tester, a rotary load, a slider and a slide rail, a stop plate, a limit switch, a thrust sensor, a displacement speed sensor and a linearly rotating load. The measured linear rotating electric machine is connected to the motor base and fixed to the first base plate, and the first base plate is fixed on the test platform base. The output shaft of the measured linear rotating electrical machine is connected with the rotating speed and torque tester and connected with the first rotating load. The rotating speed and torque tester and the first rotating load are fixed on the second bottom plate provided with the slider. The device realizes the same platform measurement of linear, rotating and spiral motion of the linear rotating machine and enables the dynamic performance test under each motion modes, improves the testing efficiency. The test device is simple in structure, high in precision, and simple and convenient in operation.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Optical Device for Measuring the Displacement Velocity of a First Moving Element with Respect to a Second Element
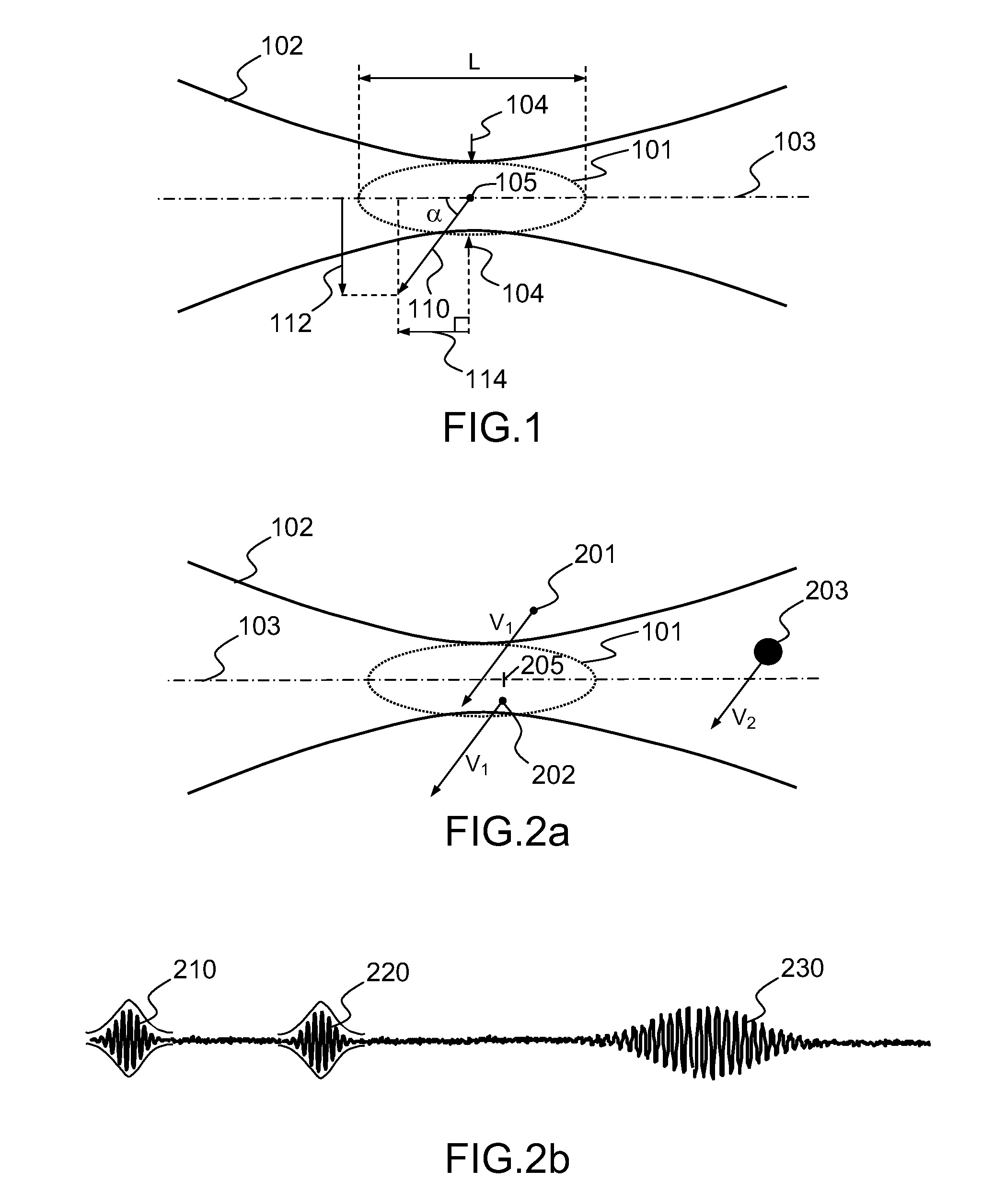
InactiveUS20070229798A1Accurately determineOptical rangefindersUsing optical meansOptical triangulationLight beam
An optical device for measuring the displacement velocity of a first movable element in relation to a second element which is fixed to one of said elements and comprises two lasers transmitting two incident beams towards the other elements. The device including photosensitive linear arrays for front and rear detection which are substantially perpendicular to each other. Additional front and rear photosensitive linear arrays are disposed at a distance from the photosensitive front and rear linear arrays. A processing circuit is connected to the photosensitive linear arrays and determines the longitudinal and / or transversal displacement velocity of the movable element. The circuit also determines the distance between the device and the other element by means of optical triangulation and corrects the longitudinal and / or transversal displacement velocity value according of the said distance.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Material testing method
InactiveUS20050097964A1Guaranteed accuracyAccurate assessmentAcceleration measurement using interia forcesForce measurementMaterials testingEngineering
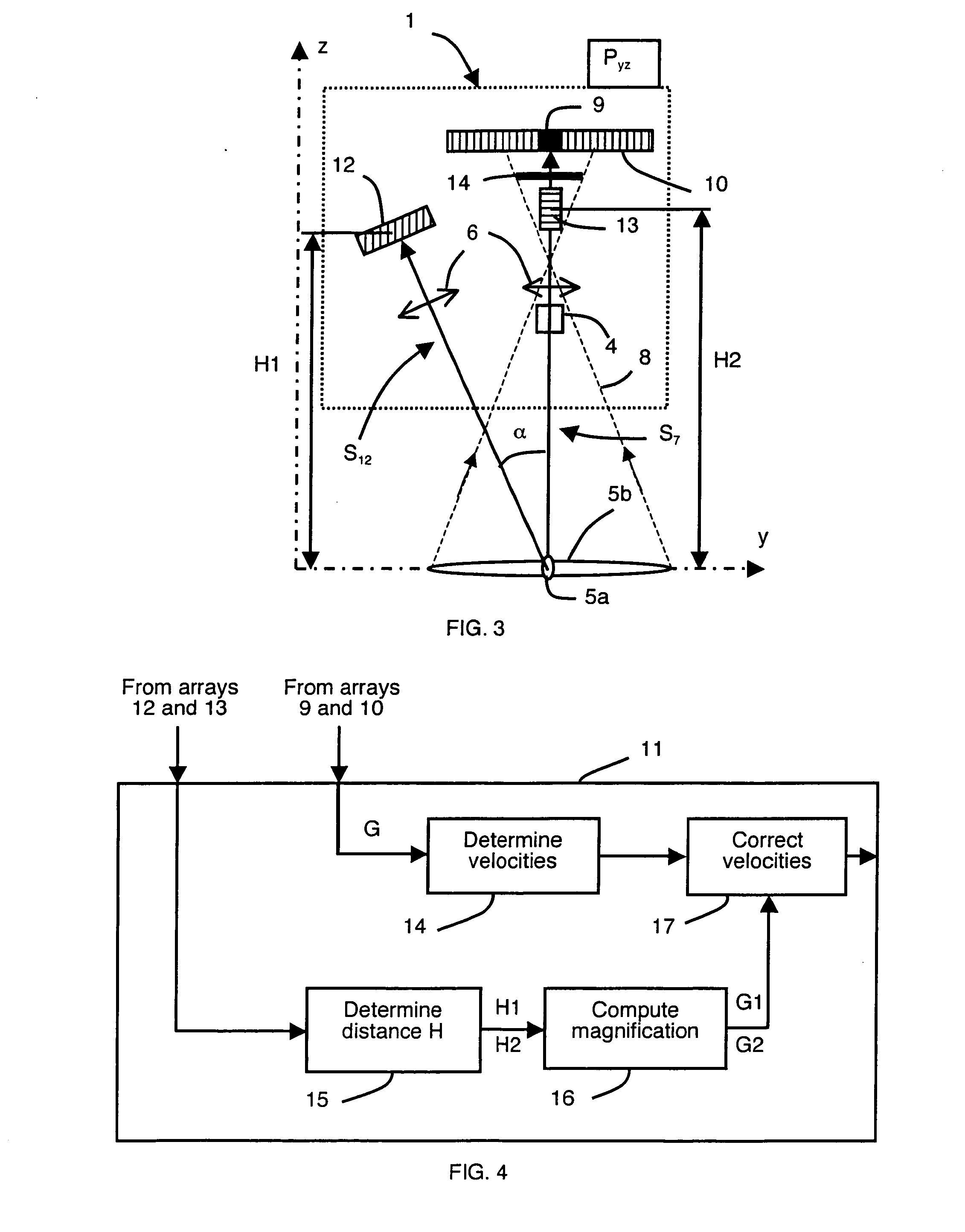
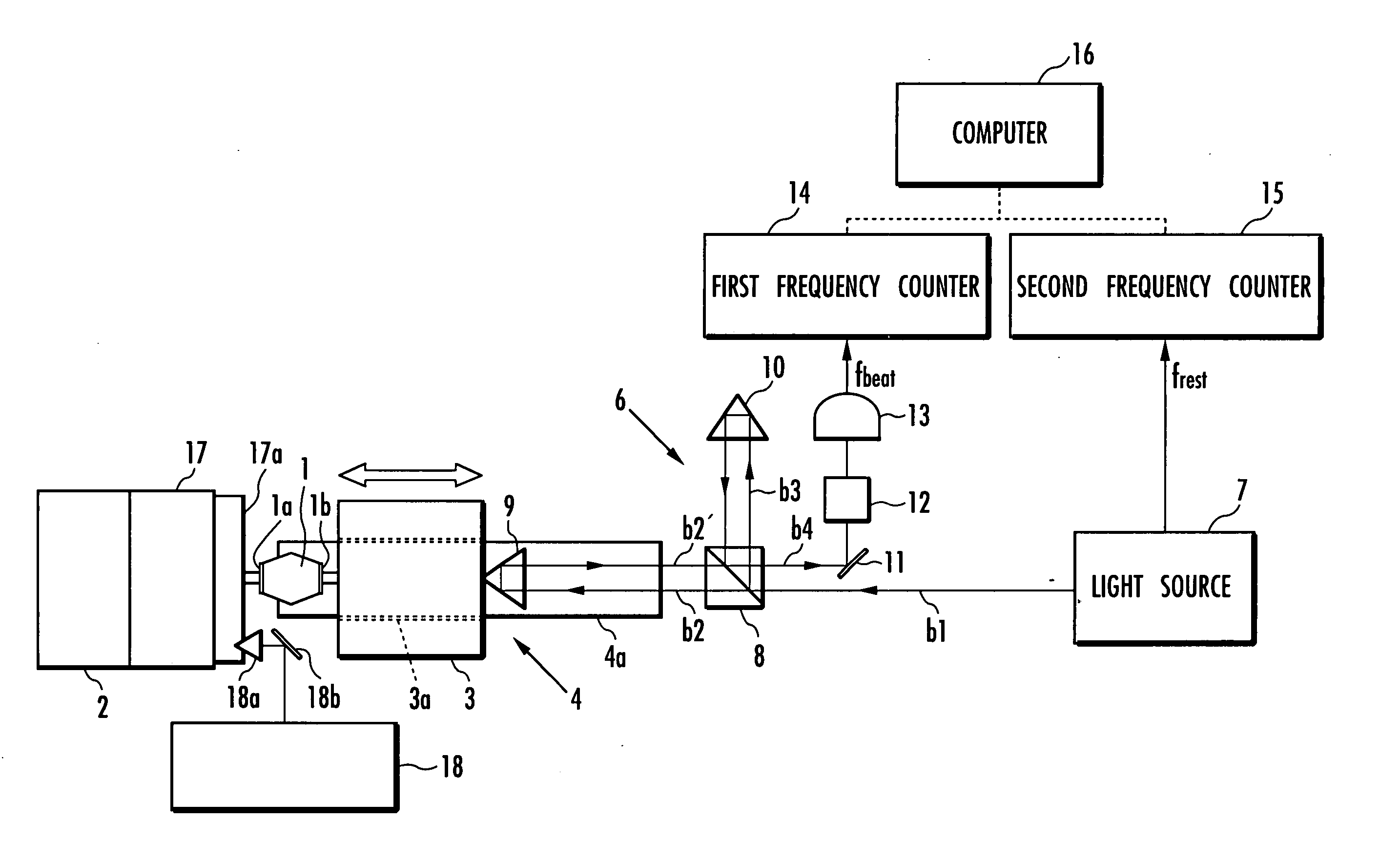
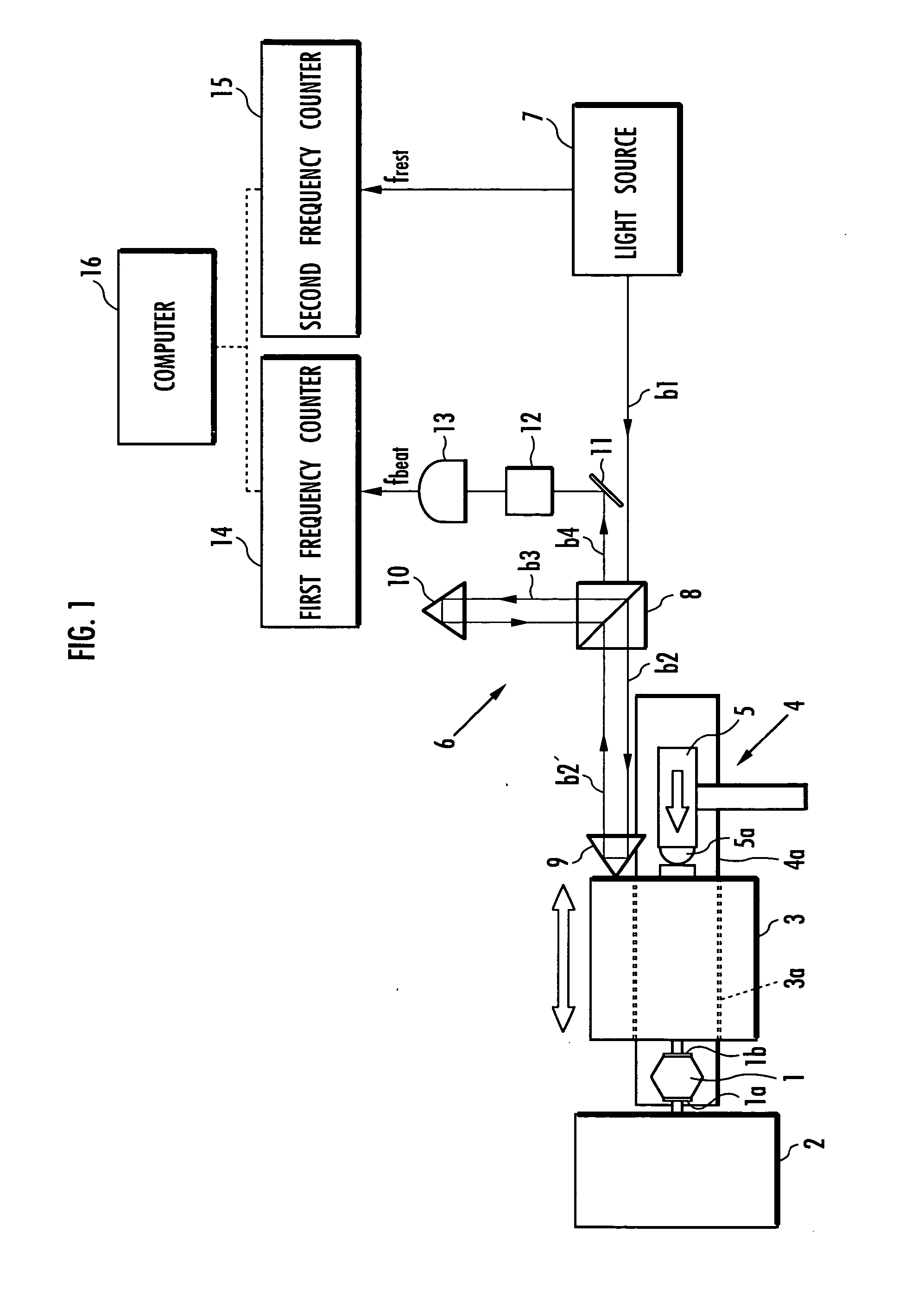
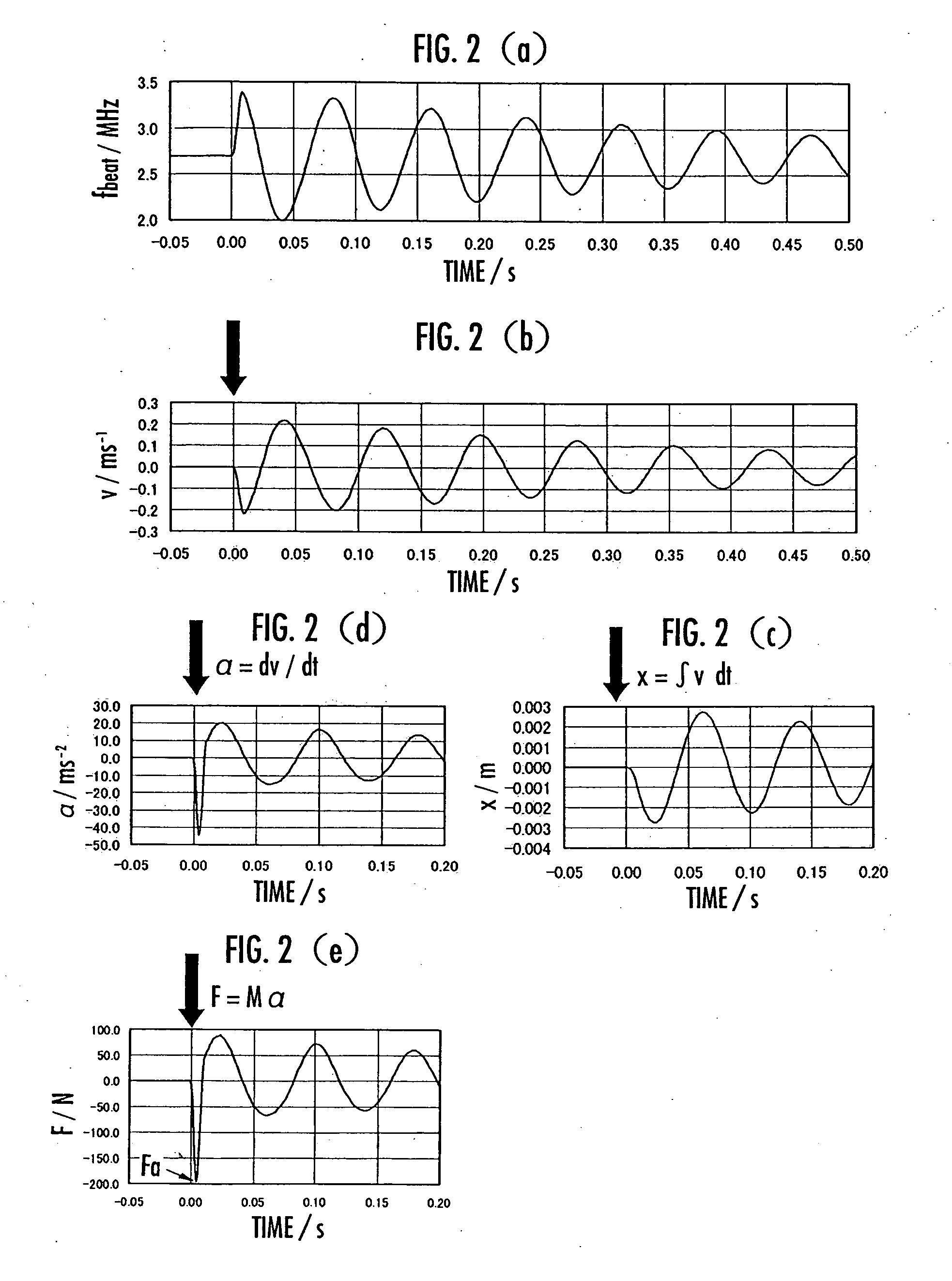
The present invention aims to achieve accurate measurement and evaluation of mechanical properties of an object to be measured 1 without use of a force sensor. A weight 3 is attached to the object to be measured 1 to form a mass-spring system in which the object to be measured 1 serves as a spring element. Then vibration is applied to the mass-spring system to measure the inertial force acting on the weight 3 and the displacement of the weight 3 so that the mechanical properties of the object to be measured 1 will be evaluated based on the inertial force and displacement. A light wave interferometer 6 measures the displacement velocity of the weight 3 to calculate the inertial force from the acceleration determined by differentiating measured values of the displacement velocity of the weight 3 and calculate the displacement of the weight 3 by integrating the measured values of the displacement velocity of the weight 3.
Owner:GUNMA UNIVERSITY
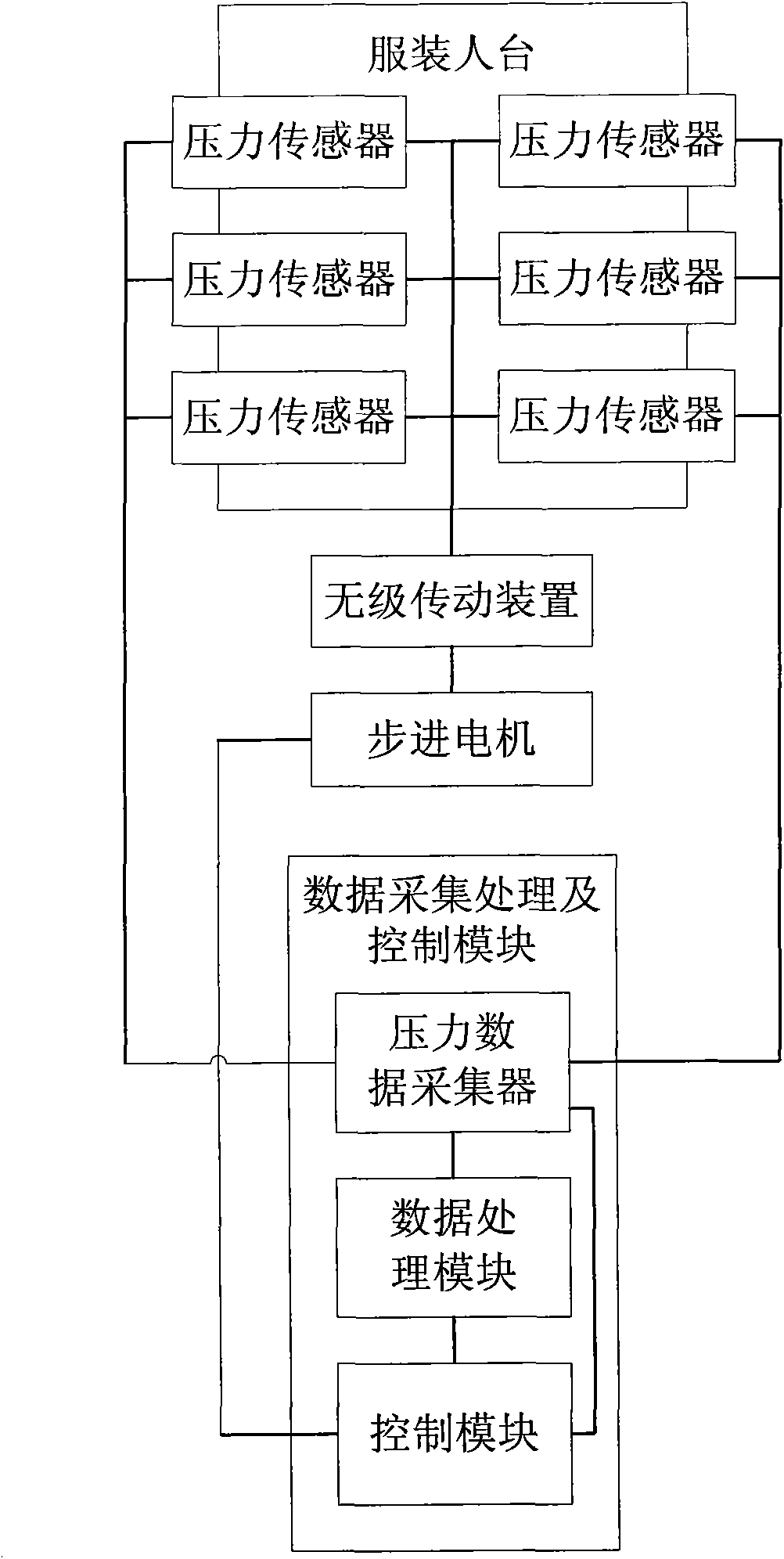
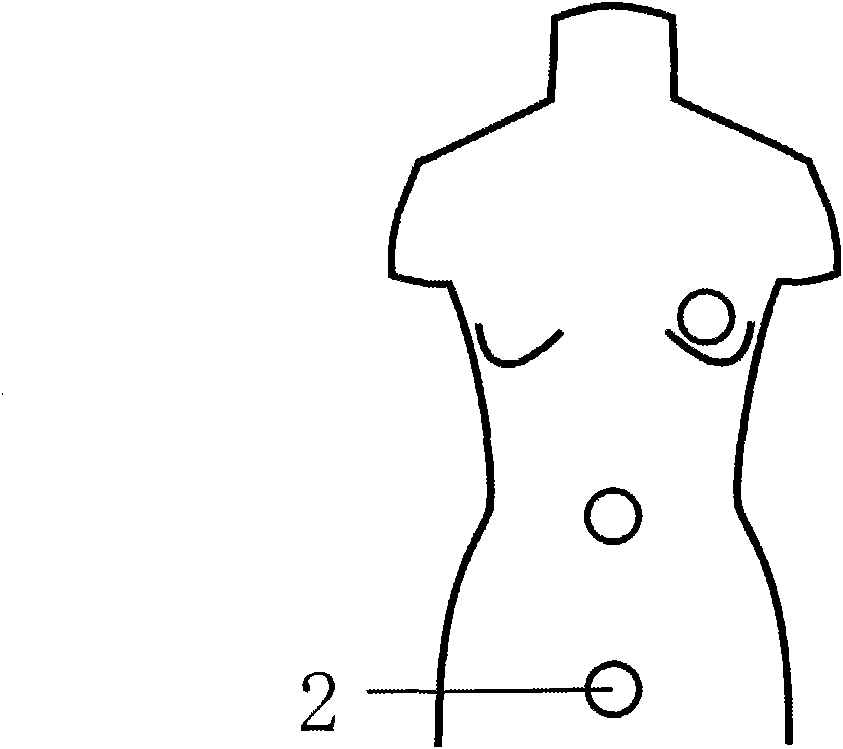
Service mannequin pressure test system
InactiveCN101839787ASimple organizationEasy to operateMultiple fluid pressure valves simultaneous measurementData connectionEngineering
The invention relates to a service mannequin pressure test system comprising a service mannequin, a pressure sensor, a stageless transmission device, a stepping motor and a data collecting, processing and control module, wherein the pressure sensor is buried in the surface of the service mannequin, the stageless transmission device is connected with the pressure sensor to control the protruded height and the protruding speed on the service mannequin, the stageless transmission device is in control connection with the stepping motor, and the data collecting, processing and control module is connected with the pressure sensor. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the advantages that the pressure sensor, a data connecting wire and the like are hidden in the mannequin without causing the additional deformation of clothing; and the protruded height on the surface of a human body and the displacement speed of the pressure sensor preburied in the mannequin through multipoints can be regulated through the stageless transmission device so that the simultaneous measurement of multipoint clothing pressure can be realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF ENG SCI
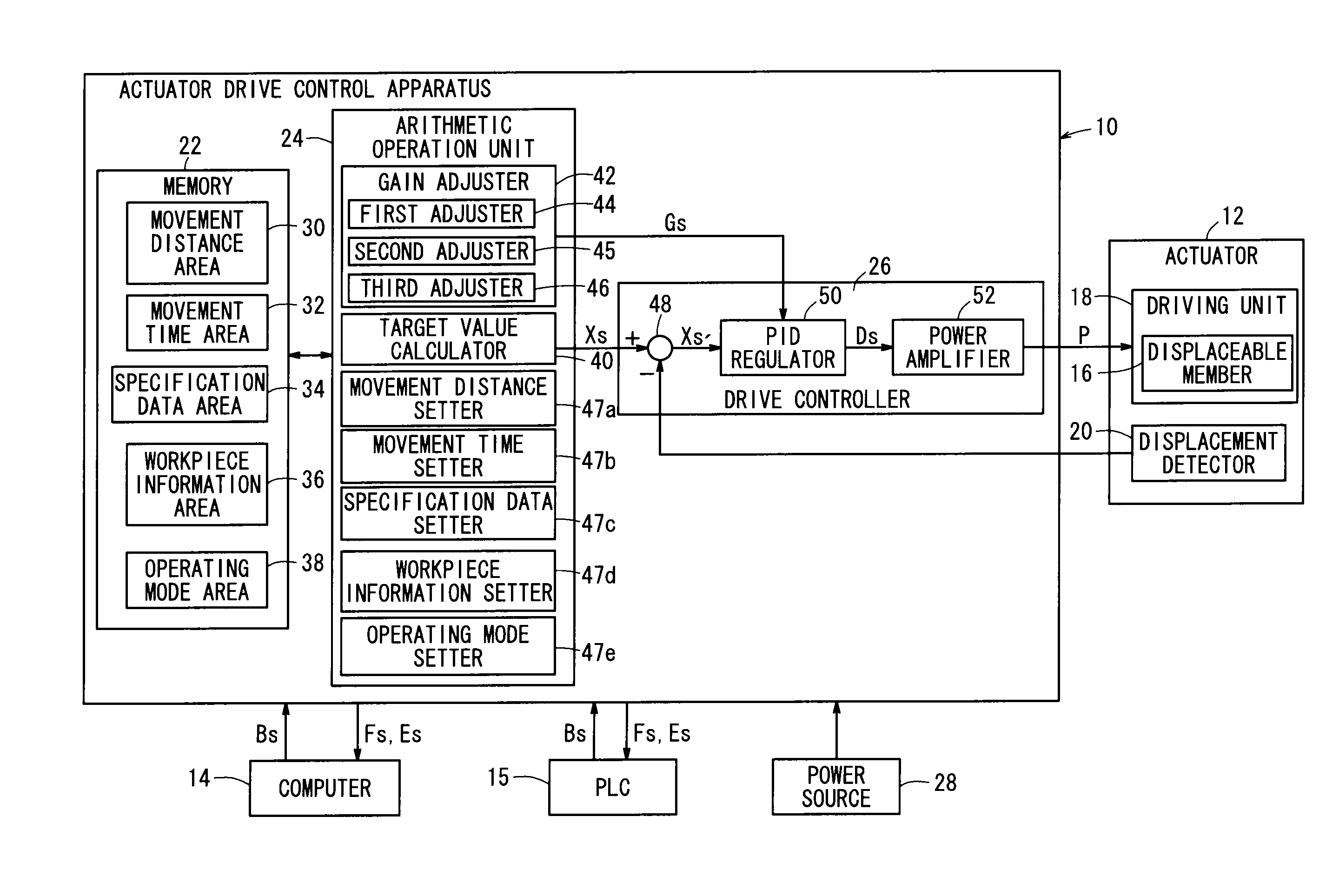
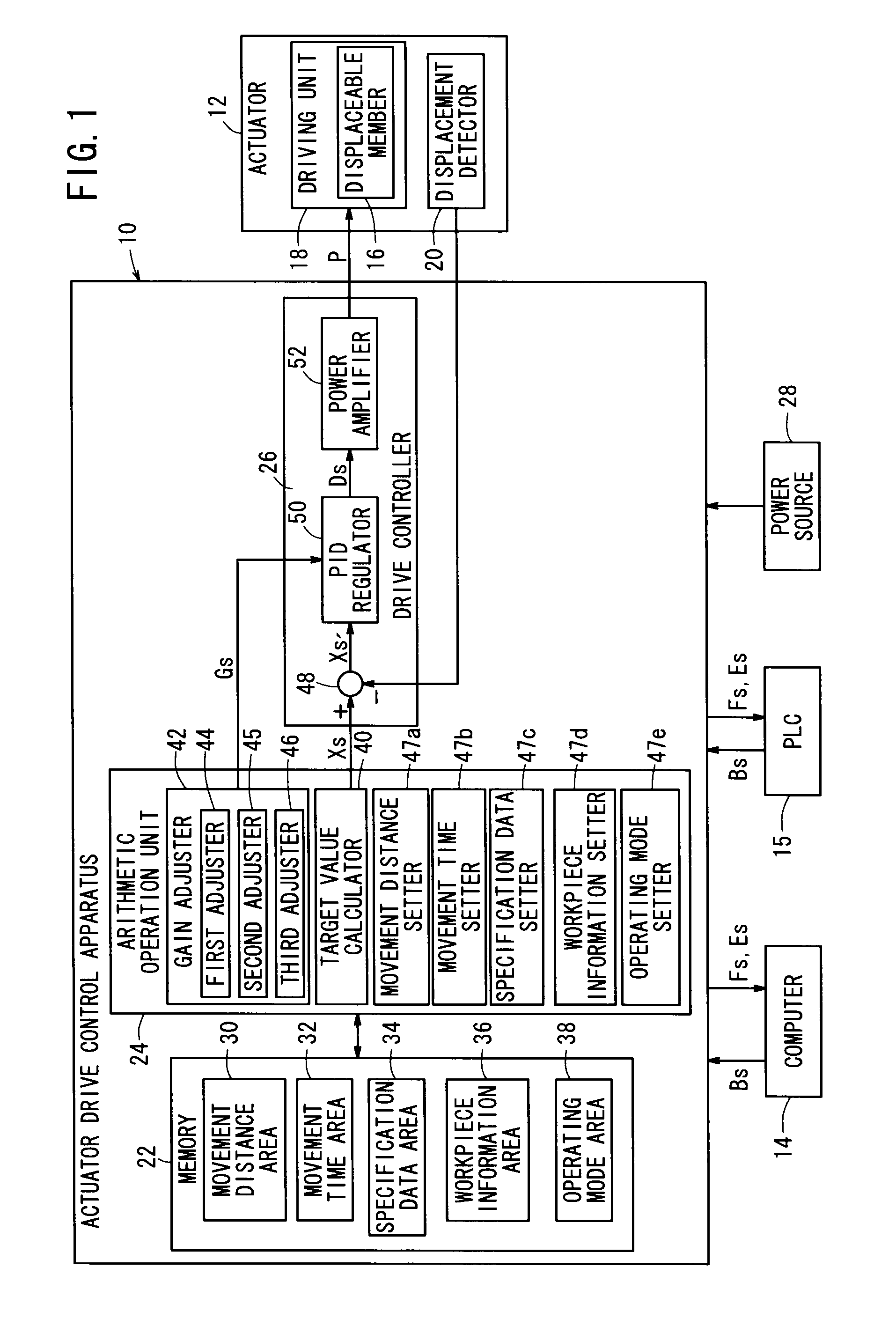
Drive control apparatus and drive control method for actuator
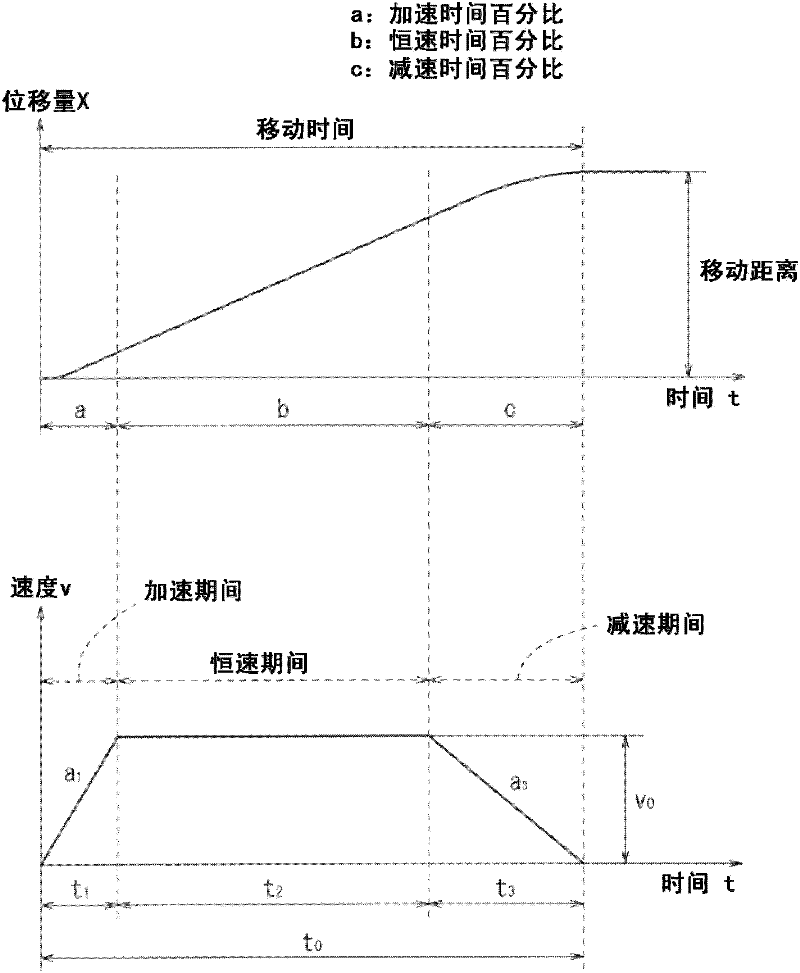
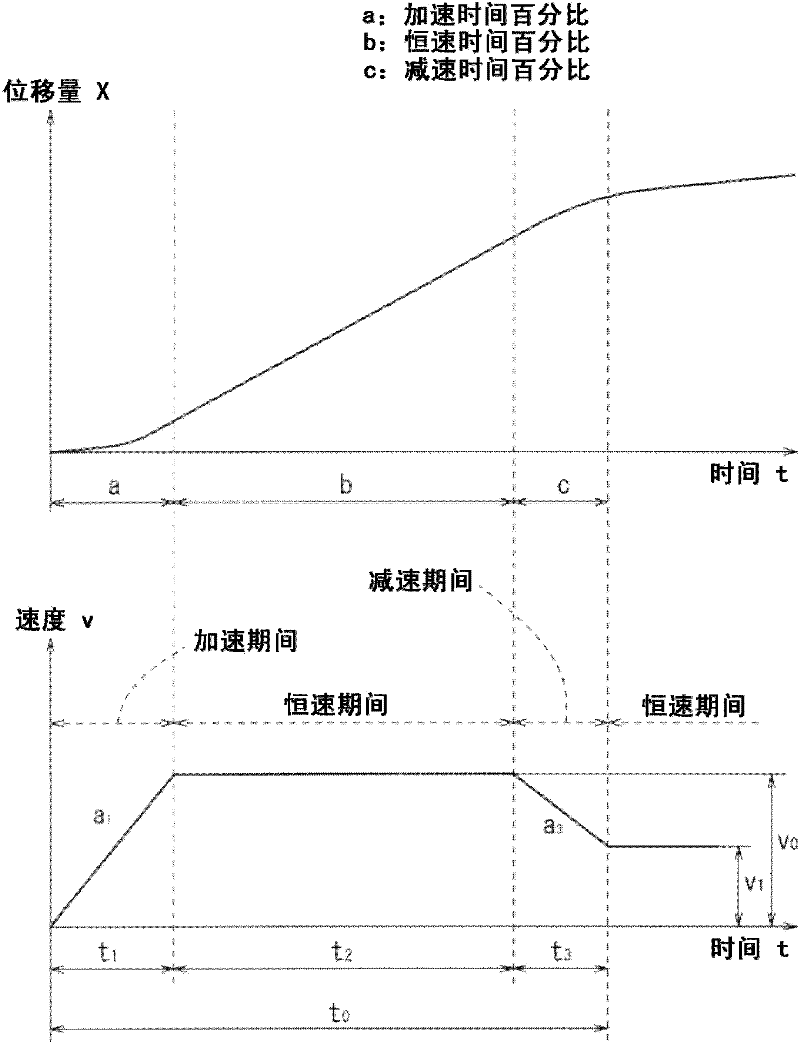
InactiveUS20120123564A1Reduce workloadAvoid it happening againElectric controllersControl using feedbackActuatorControl theory
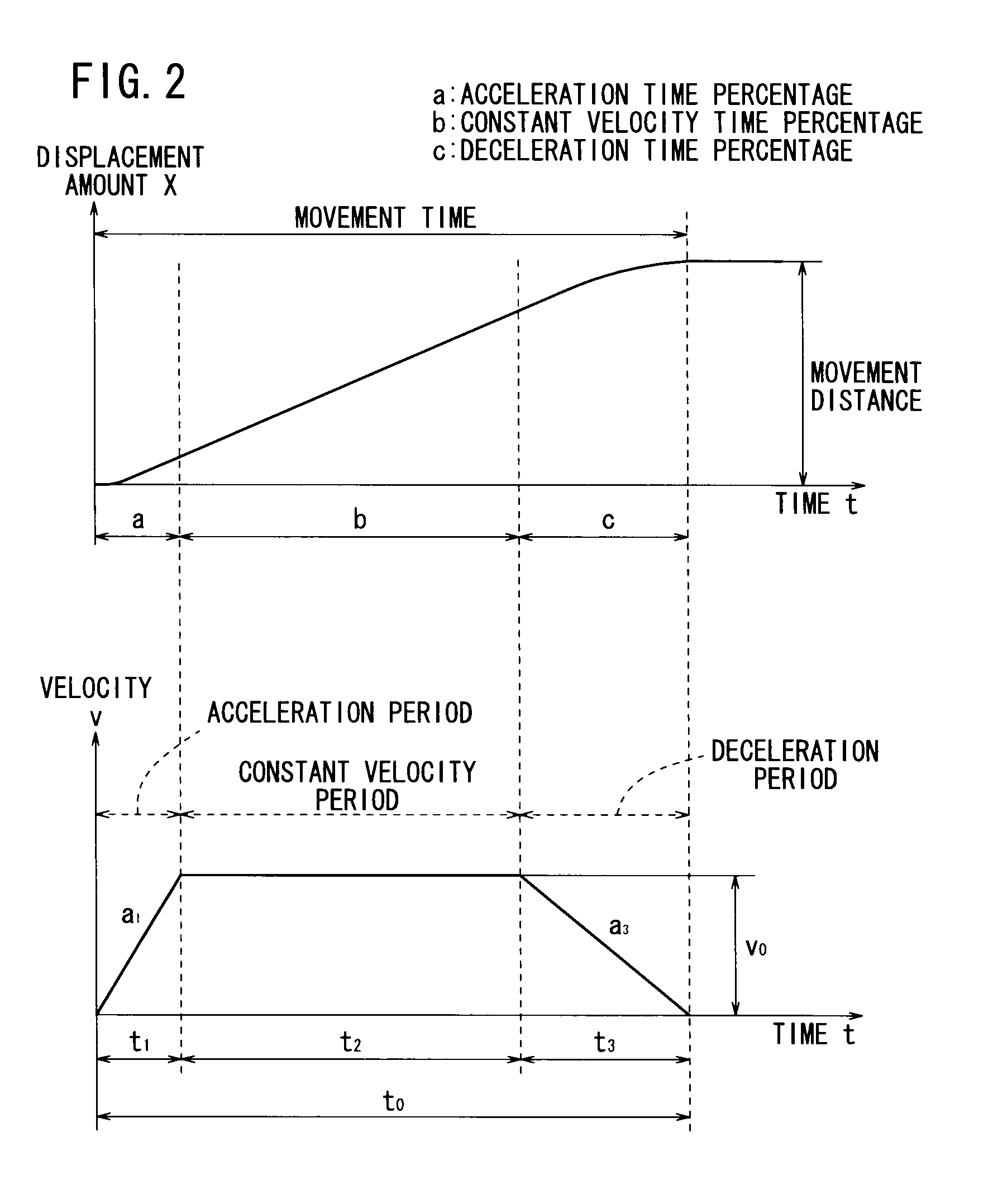
An actuator drive control apparatus is equipped with a movement distance setting means for setting a movement distance of a displaceable member, a movement time setting means for setting a movement time, a target value calculating means for calculating a target value of a displacement amount or a displacement velocity of the displaceable member at an arbitrary timing based on the movement distance and the movement time, and a drive controller for generating driving power based on the displacement amount or the displacement velocity target value of the displaceable member and sending the drive power to an actuator.
Owner:SMC CORP
Correction value derivation apparatus, displacement amount derivation apparatus, control apparatus, and correction value derivation method
InactiveUS20140028478A1Detection precision can be improvedReduce detection errorElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersErrors and residualsComputer science
This invention improves detection precision by reducing a detection error of a change in position of a target. A correction value derivation apparatus for deriving a correction value used in correction of a displacement amount derived based on an encoder signal indicating a change in position of a movable portion as a target, comprises: a displacement amount derivation unit configured to derive a detected displacement amount of the movable portion based on the encoder signal; a displacement velocity derivation unit configured to derive a detected displacement velocity based on the detected displacement amount derived by the displacement amount derivation unit; an average displacement velocity calculation unit configured to calculate an average displacement velocity over a predetermined displacement range; and a correction value derivation unit configured to derive the correction value based on the detected displacement velocity and the average displacement velocity.
Owner:CANON KK
Drive control apparatus and drive control method for actuator
ActiveCN102467101APrecise shiftReduce workloadElectric controllersControl using feedbackActuatorControl theory
Owner:SMC CORP
Method for vibrational impact on a pipe string in a borehole and devices for carrying out said method
The invention relates to well construction and is directed at an oscillation excitation in a pipe string. According to the inventive method, an operating fluid is circulated in the pipe string. An autonomous mechanism for vibrational impact embodied in the form of an element, for instance a hollow ball having a rigid envelop and filled with gas, possessing a positive floatability, covering from 0.85 to 0.95 of a cross-sectional flow area of the pipe string and having an unrestricted degree of freedom. In the second variant, the inventive device comprises a ball support embodied in the form of a transverse beam or a crossbar rigidly connected to a spiral cylindrical spring arranged inside a tube under the ball with the aid of an easy-push fit. The spring force is selected with respect to a calculated axleload dependence on the mass of the ball and on flow strength with a basic flow rate of the operating fluid. A lateral oscillation is actuated simultaneously with a displacement of the mechanism for vibrational impact inside the pipe string. A direction of displacement of the mechanism for vibrational impact, verboten frequency and amplitude, and a time of action of the vibrational impact in a determined part of the pipe string are fixed with respect to the flow rate of the operating fluid. The speed of the displacement of the mechanism for vibrational impact is fixed with respect to the basic flow rate which is defined at zero speed. When the flow rate of the operating fluid exceeds the basic flow rate, the mechanism for vibrational impact is displaced towards the bottom of the well and when flow rate of the operating fluid decreases with respect to the basic flow rate, the mechanism for vibrational impact is displaced towards the well cellar. The invention reduces a friction force during displacement inside the well, precludes sticking and performs vibration impact on the fluid medium filling the well.
Owner:BIP TECH
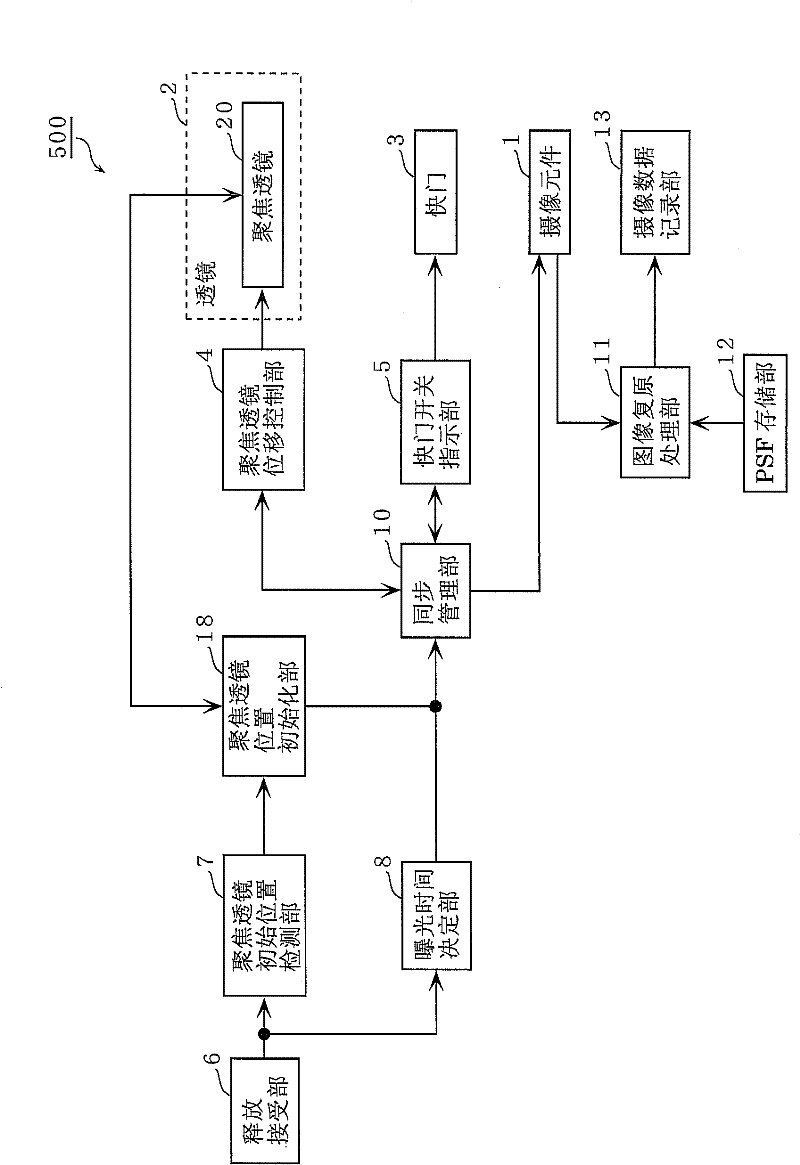
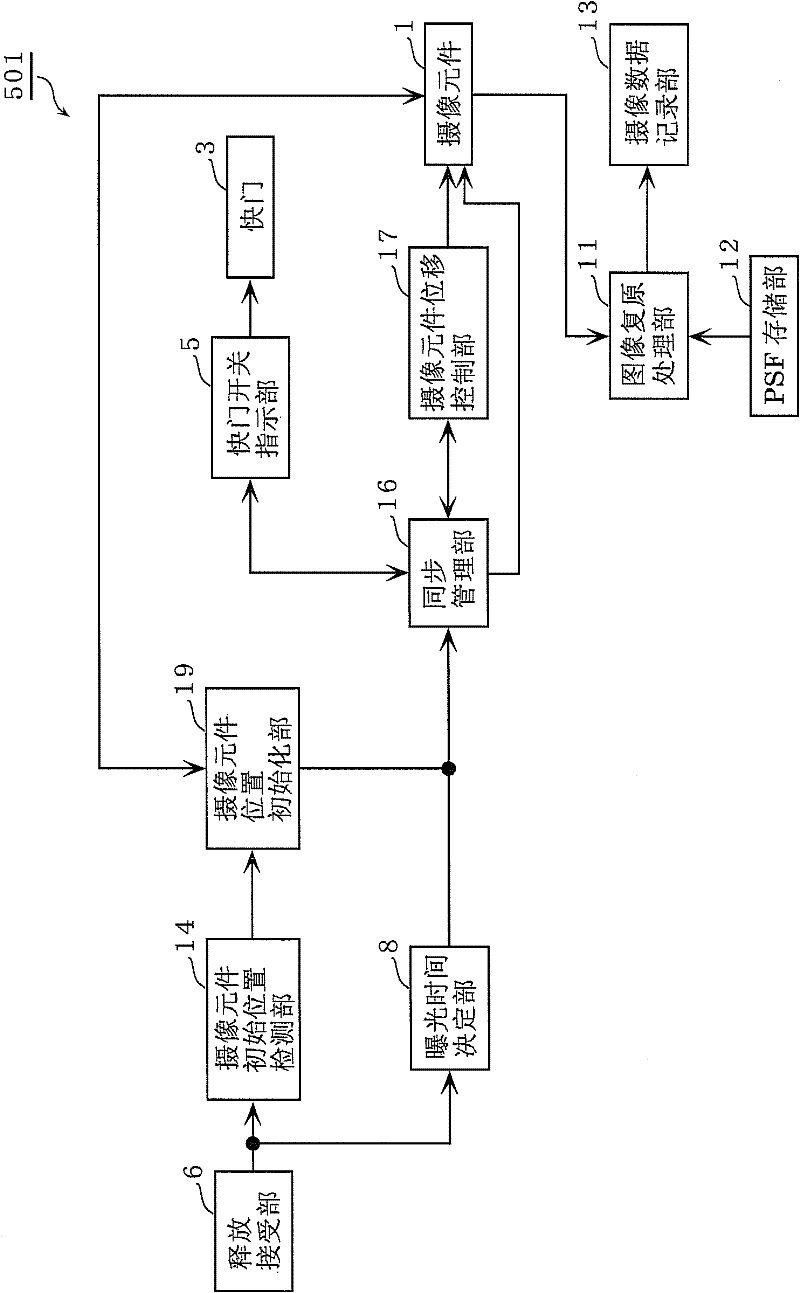
Imaging device and control method for same
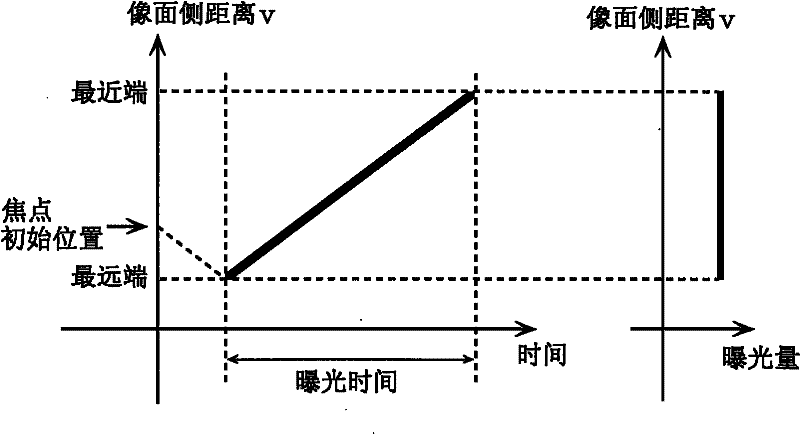
InactiveCN102308569AInhibit deteriorationTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementEngineeringDisplacement control
The disclosed imaging device (100) is provided with a displacement control unit (22) which displaces the focus position of the imaging device (100) on the side towards the subject to be imaged by changing the imaging surface distance, and a displacement pattern setting unit (21) which sets a displacement pattern in a frame period to be implemented by the displacement control unit (22). The displacement pattern setting unit (21) sets the displacement pattern of the focus position so that: during the acceleration period of the frame period, the displacement rate of the imaging surface distance increases from zero; during the constant velocity period, the imaging surface distance is displaced at a constant rate; and during the deceleration period, the displacement rate of the imaging surface distance decreases to zero. The acceleration period and the deceleration period are each at least 1 / 10 of the length of the frame period.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Linear array CCD on-road vehicle speed measuring method based on instant hardware technology
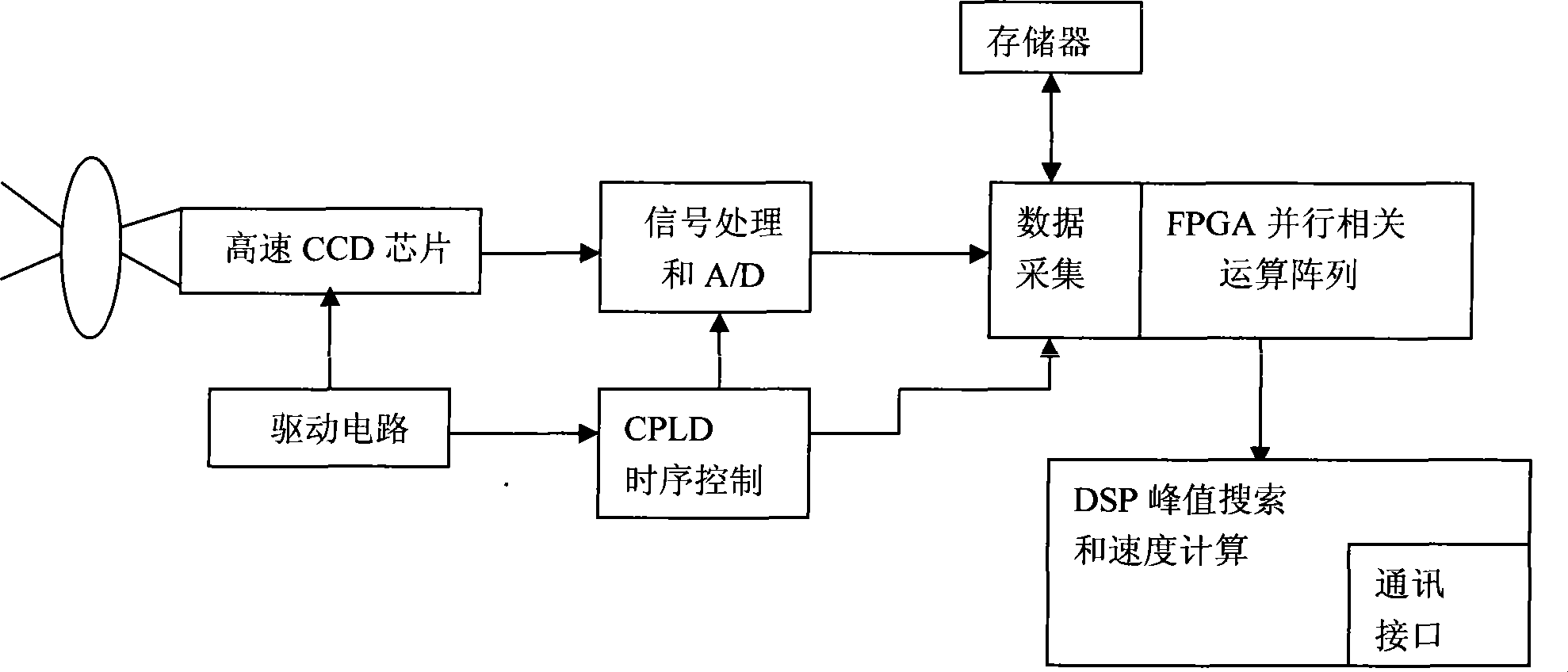
InactiveCN101383098AImprove performanceHigh precisionRoad vehicles traffic controlDevices using time traversedTerrainRadar
The invention discloses a velocity testing method for road vehicles, which is based on a linear array CCD (Charge Coupled Device) of instantaneous hardware. A linear array CCD video camera is erected on road. Aiming at a vehicle running on the road, photos are taken at a certain interval of time so as to obtain two groups of image signal sequences of the vehicle at different moments, and the displacement distances of the two groups of image signal sequences on the linear array CCD are calculated; based on the time difference of the two known moments, an image displacement velocity is calculated, and the movement velocity of the vehicle can be finally calculated according to the distance between the linear array CCD video camera and the vehicle and the parameters of the linear array CCD video camera. The invention has stable performance, higher accuracy and lower cost without being influenced by terrain and externally transmitting radar waves, thereby being hard to be detected by an electronic dog and having a favorable hidden velocity testing capability.
Owner:ANHUI HONGSHI OPTOELECTRONICS HIGH TECH CO LTD
Image-stabilized long-range optical device
ActiveUS9625734B2Reduce frictionNon-rotating vibration suppressionTelescopesImage stabilizationEddy current
A long-range optical device has at least one optical channel which comprises a housing and an arrangement of optical elements. At least one of the optical elements is movable relative to the housing for image stabilization in the event of perturbing movements of the housing. The device further comprises a stabilization system for the at least one movable optical element, which has an eddy current damper for damping movements of the at least one movable element. The stabilization system, in the event of a displacement of the at least one movable optical element, generates a restoring force proportional to the displacement velocity of the at least one movable optical element. The eddy current damper comprises a magnet system and an eddy current carrier interacting therewith. The restoring force generated by the eddy current damper is dependent on the amplitude of the displacement of the at least one movable optical element.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Planning system and method for maintaining a cycle time in an automobile factory
ActiveUS20180284738A1Easy to disassembleEasy to useTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlConveyor beltCycle time
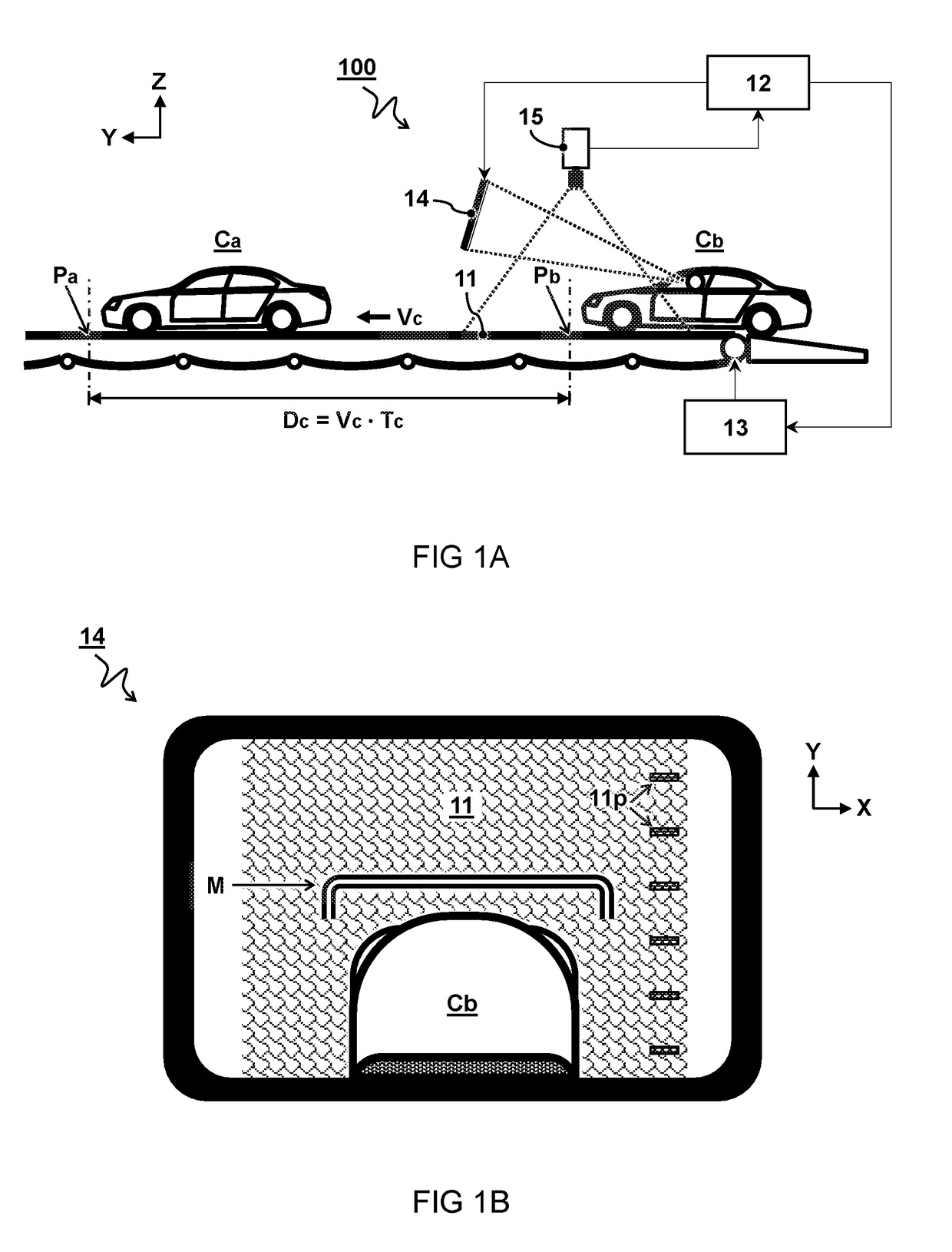
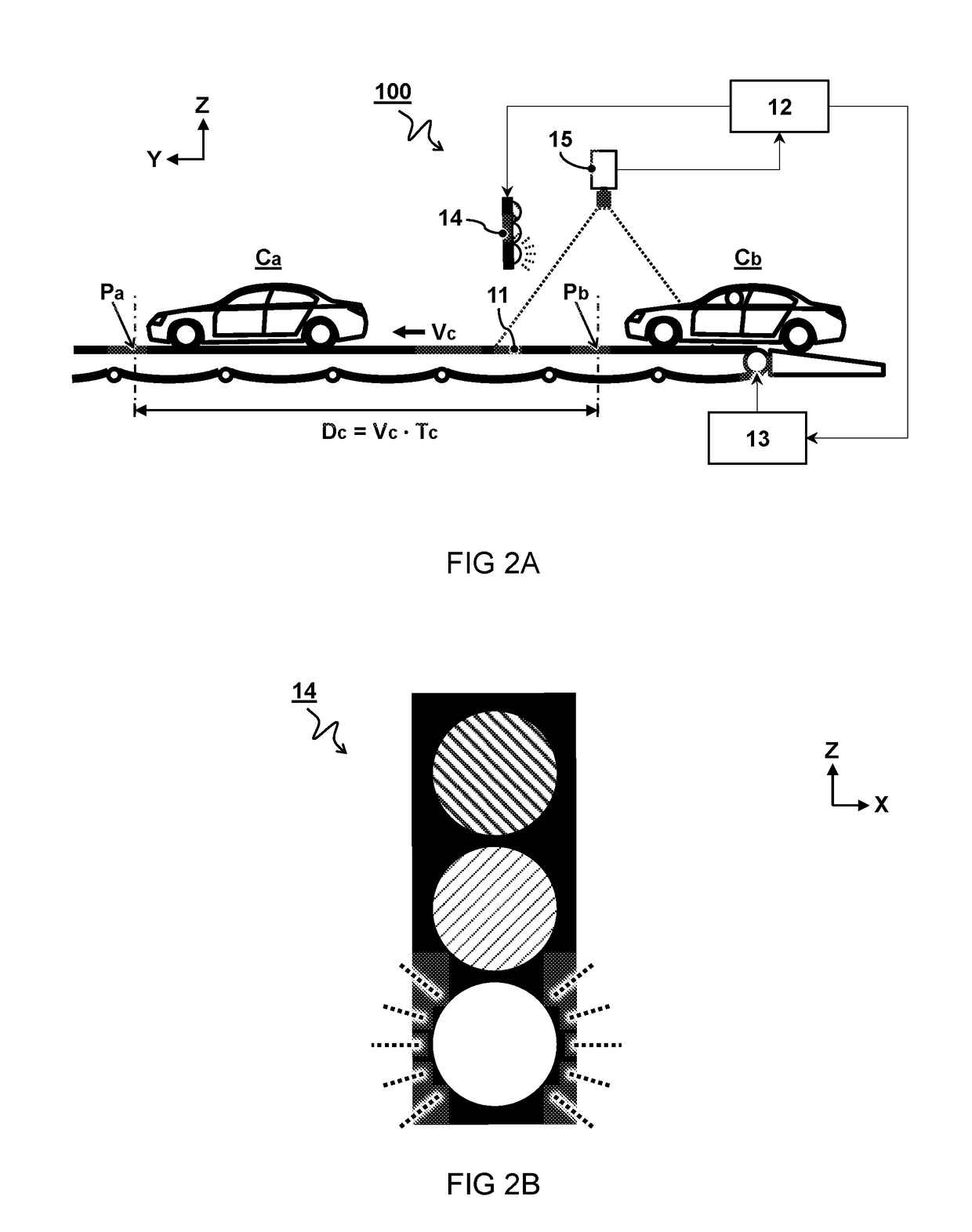
An automobile factory planning system and method for controlling a cycle time. The system comprises a conveyor belt configured to transport a plurality of automobiles at a controlled displacement velocity along a manufacturing path through the automobile factory. A feedback device is configured to provide a visual indicator of a designated position at which a next automobile is to be placed on the conveyor belt relative to the position of a previous automobile. The designated position is calculated as a function of the cycle time and the displacement velocity of the conveyor belt.
Owner:REXNORD FLATTOP EURO BV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com