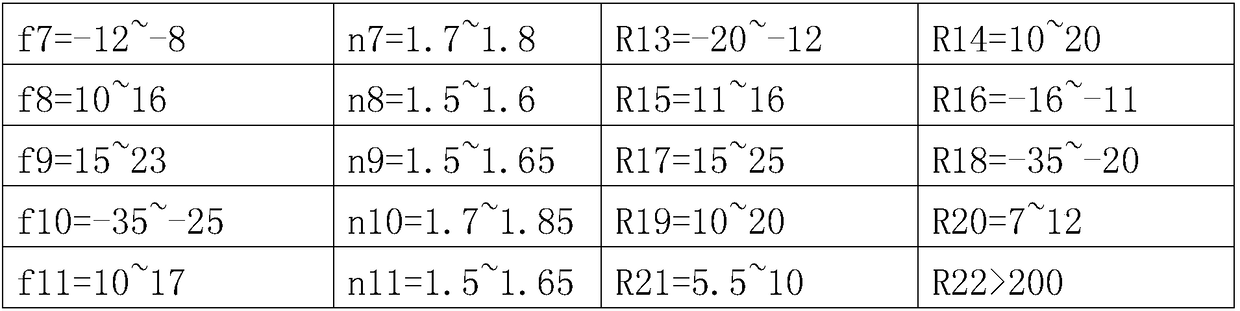
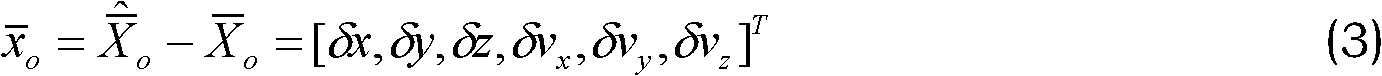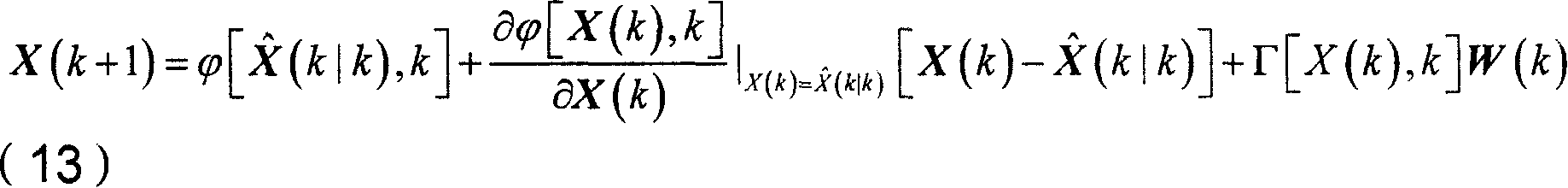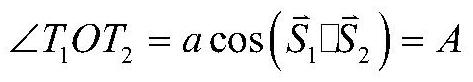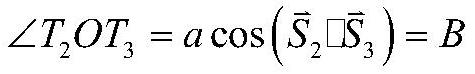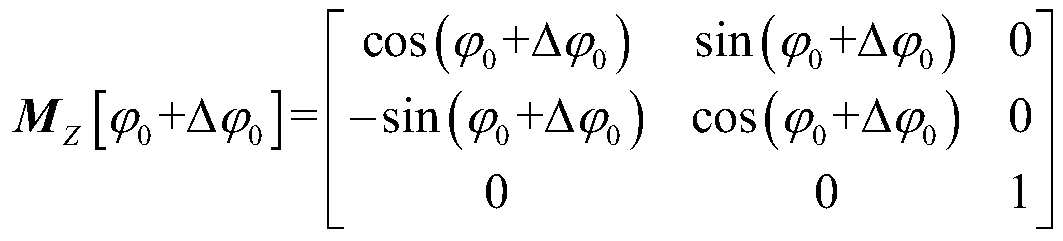Patents
Literature
223 results about "Starlight" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Starlight is the light emitted by stars. It typically refers to visible electromagnetic radiation from stars other than the Sun observable from Earth during the night time although a component of starlight is observable from the Earth during the daytime.
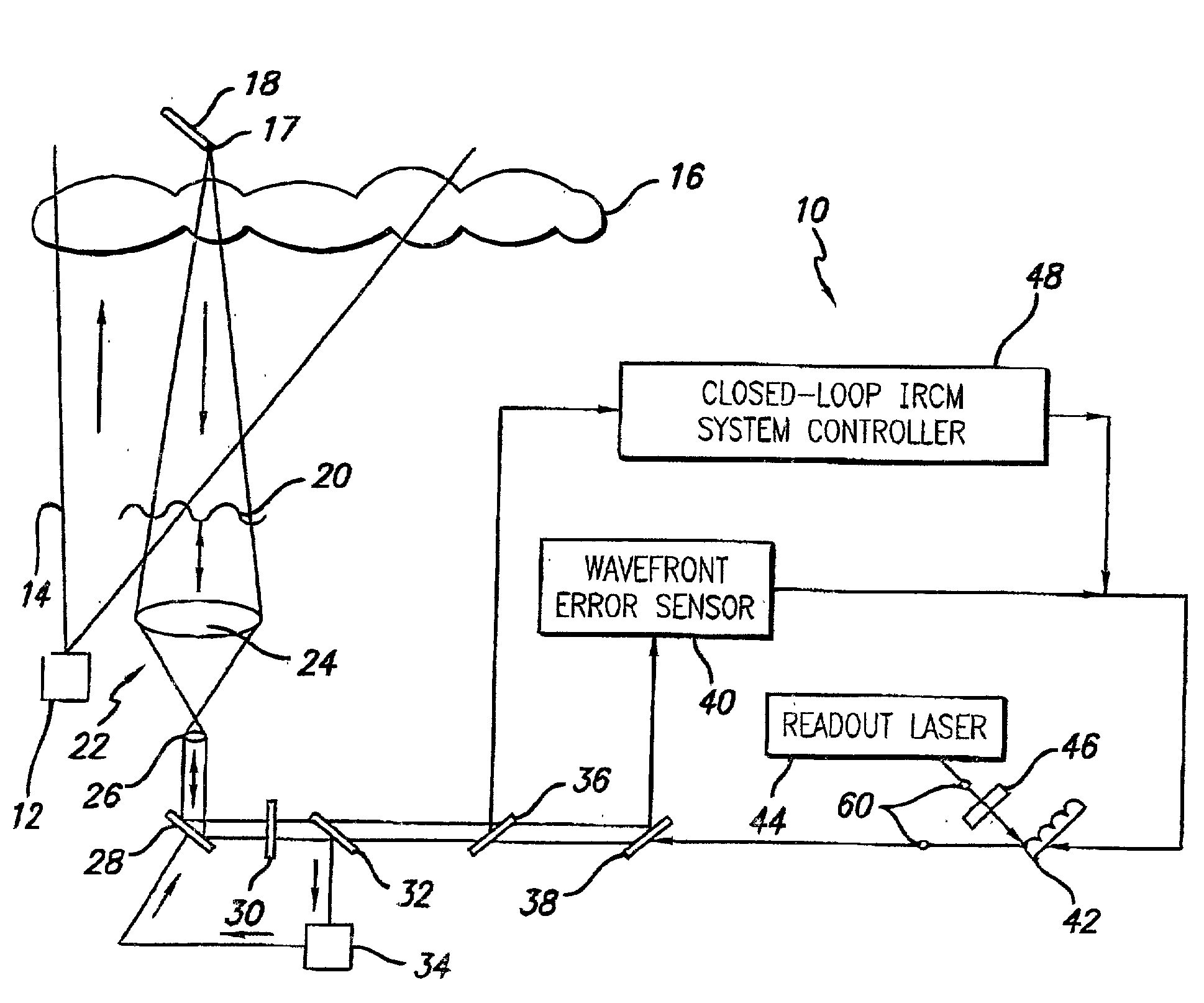
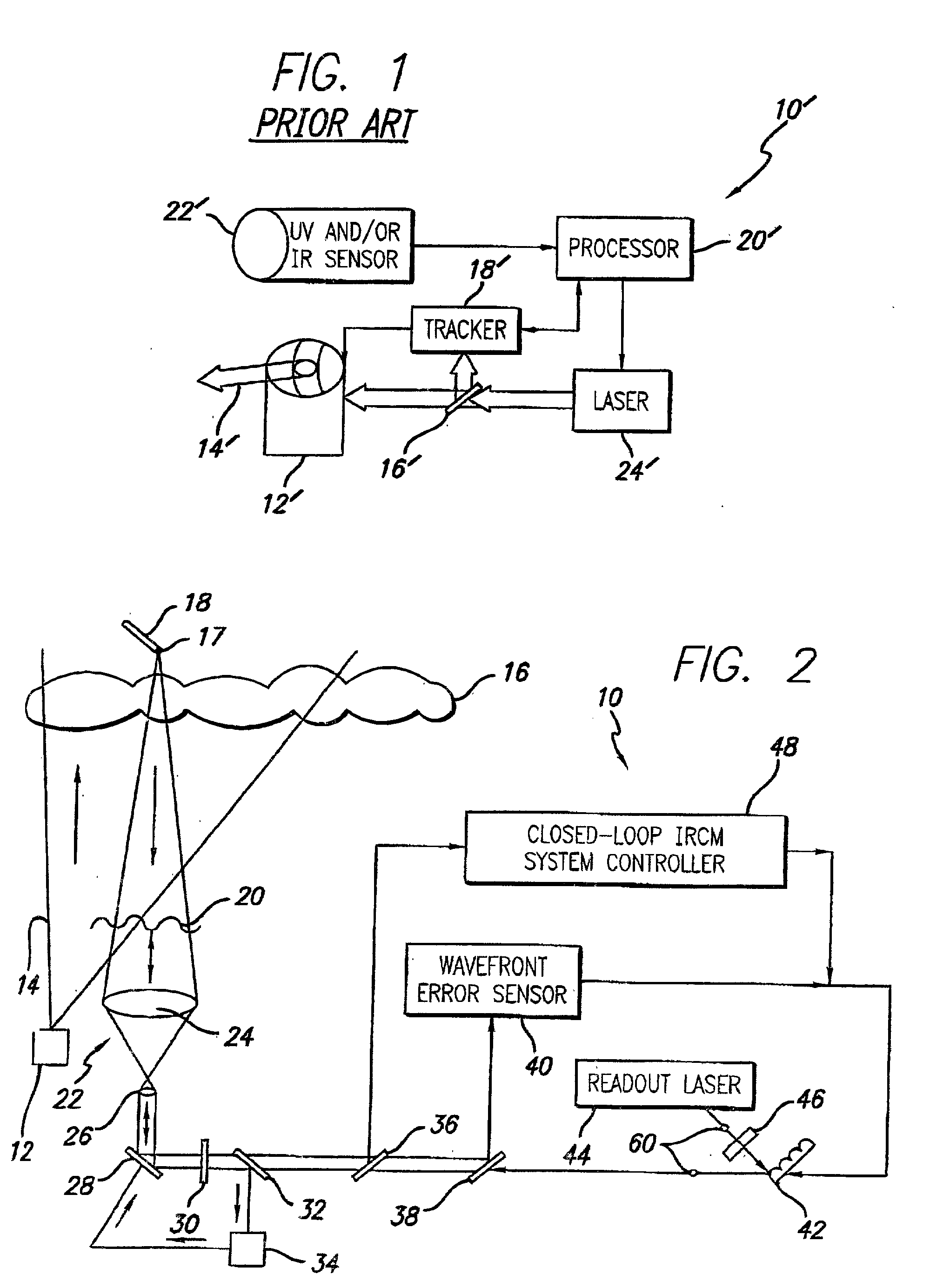
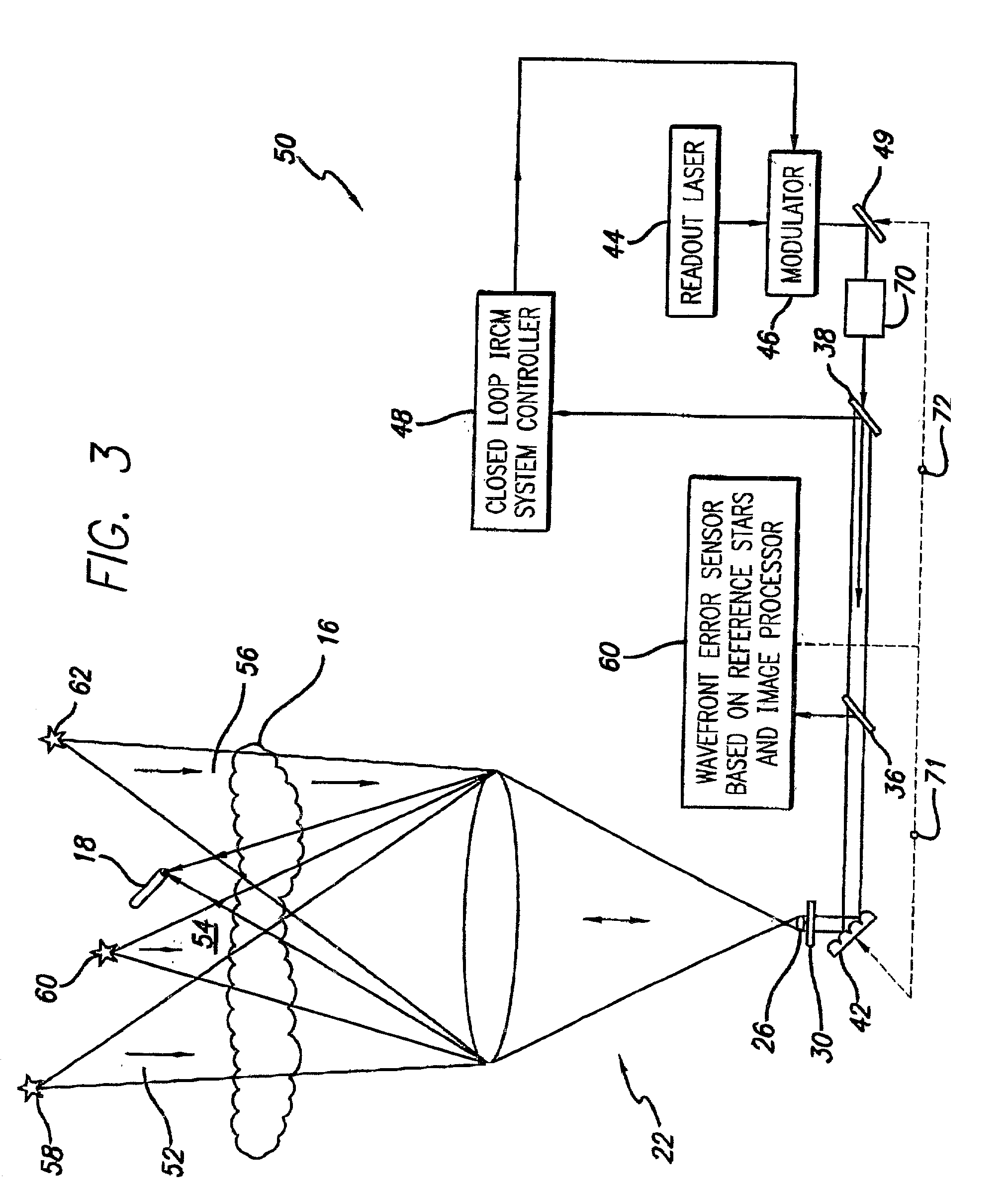
Robust infrared countermeasure system and method
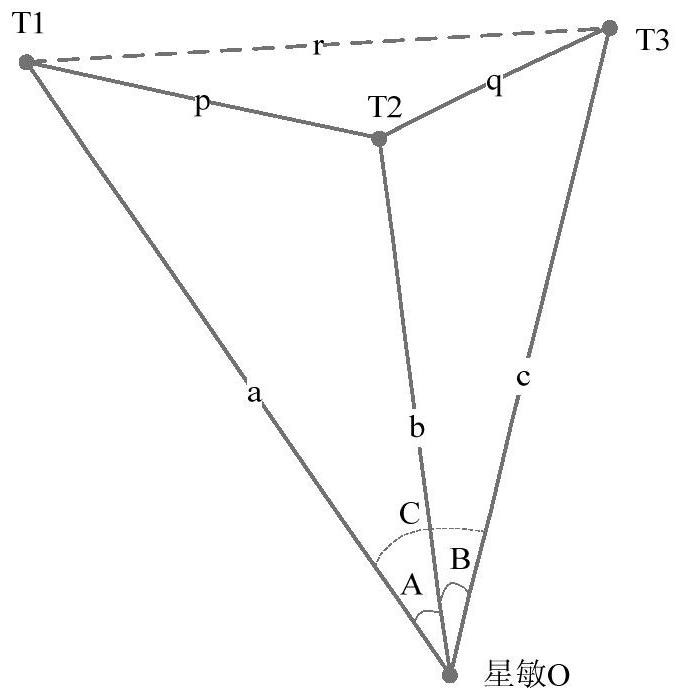
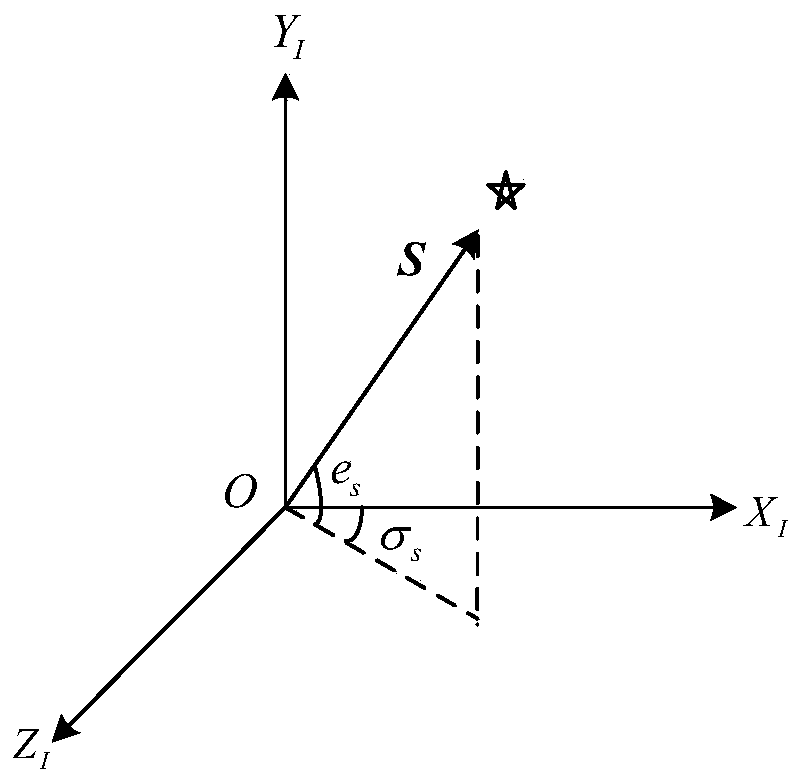
InactiveUS20020153497A1Photometry using reference valueWave based measurement systemsCountermeasureOptical phase conjugation
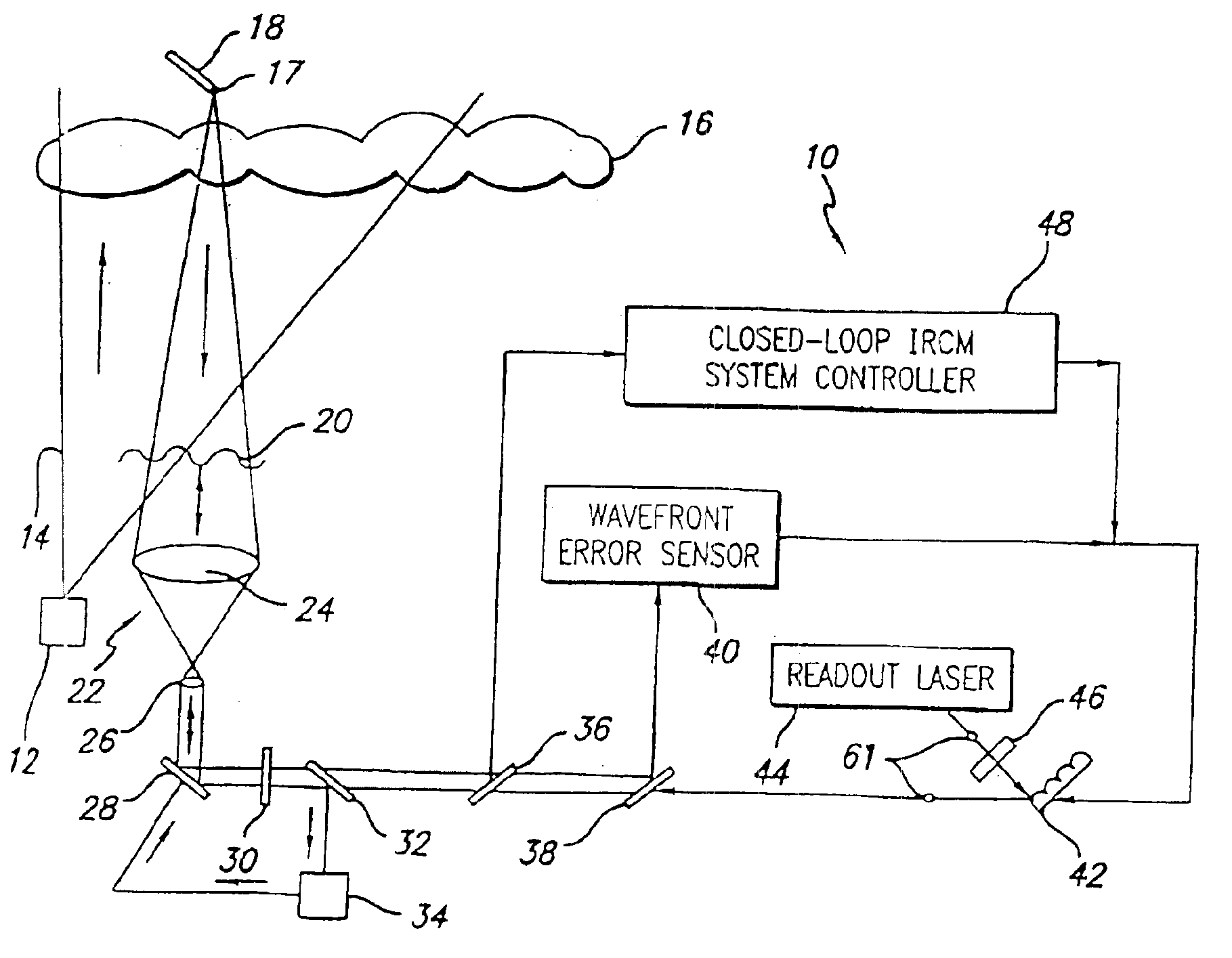
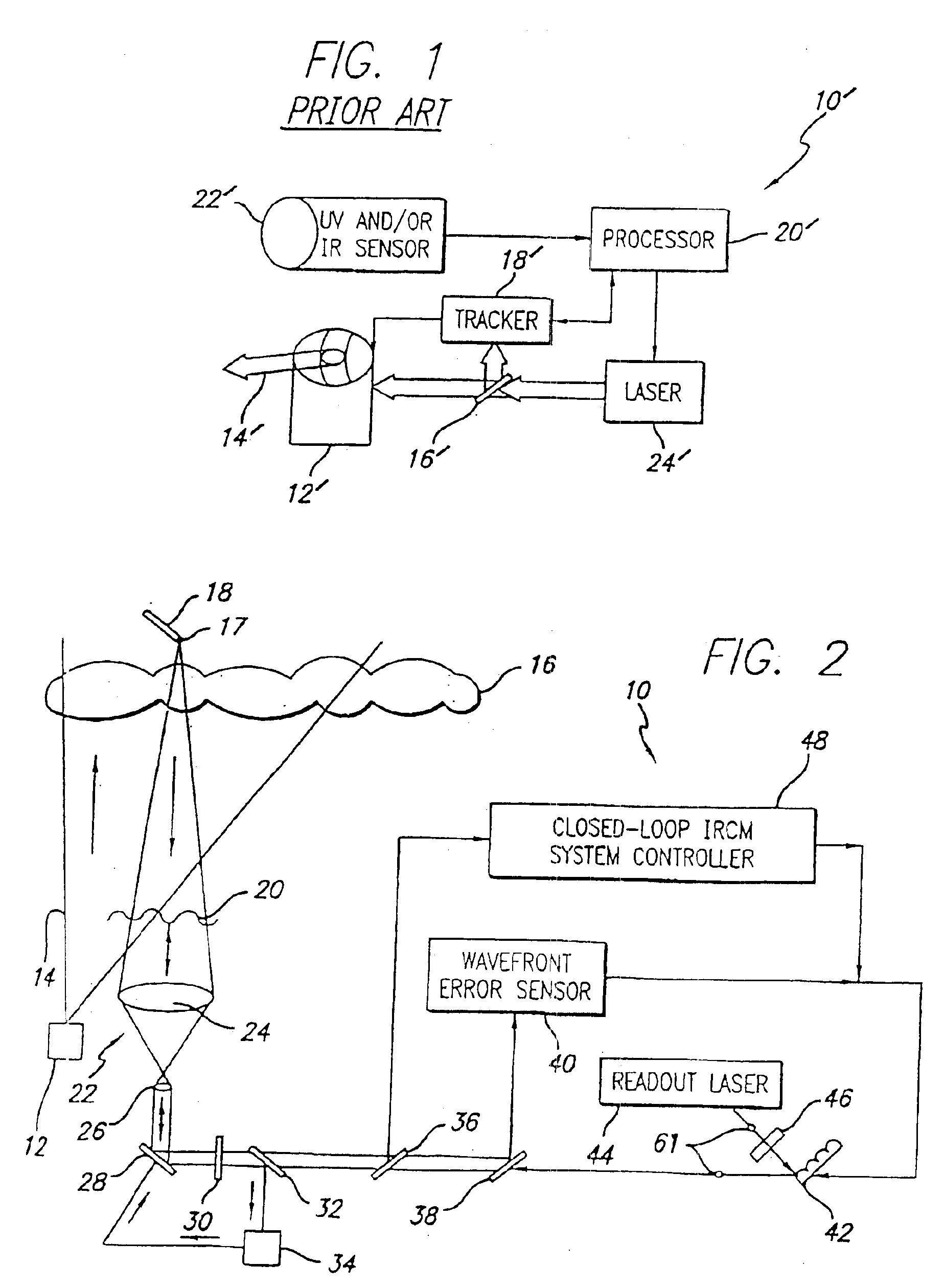
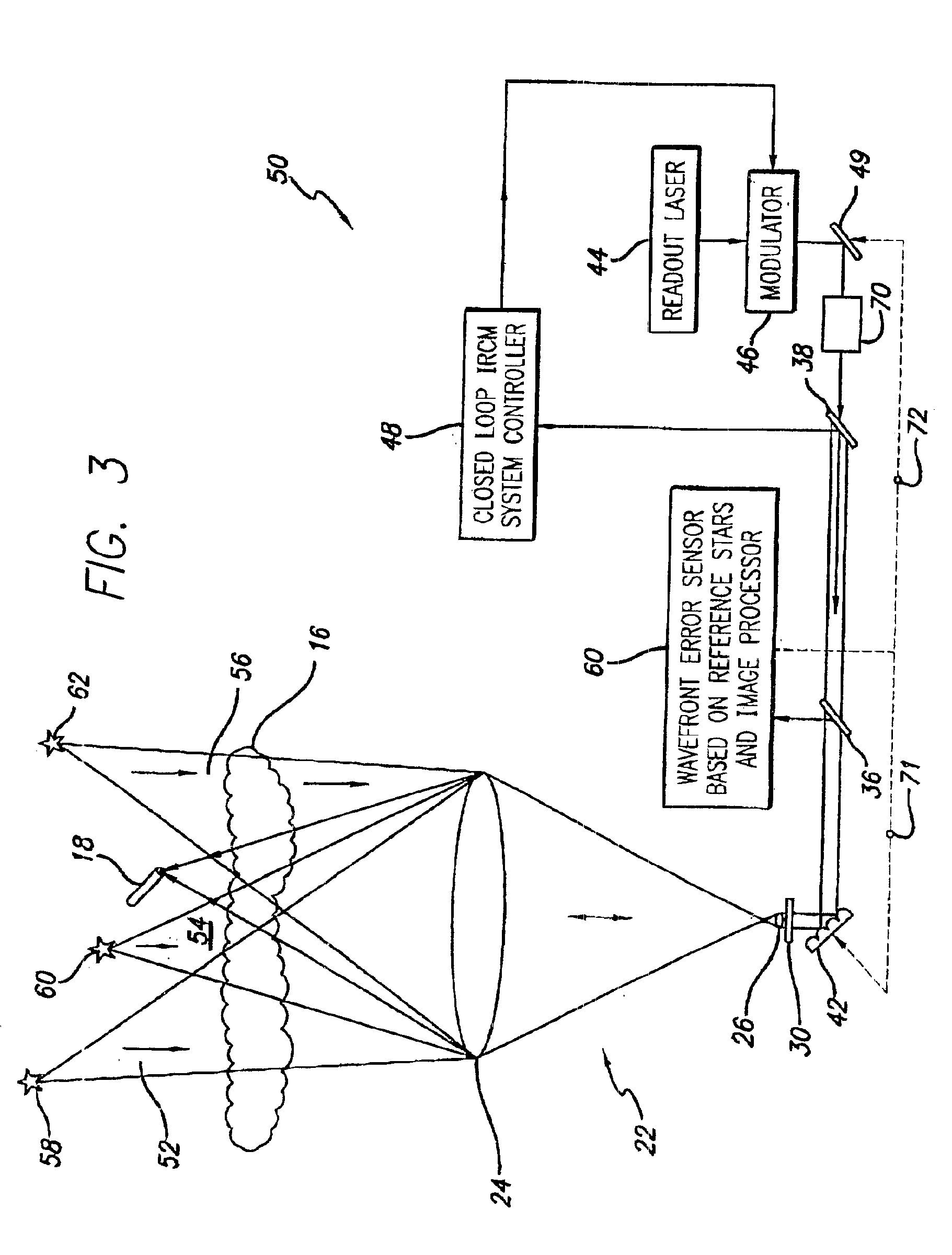
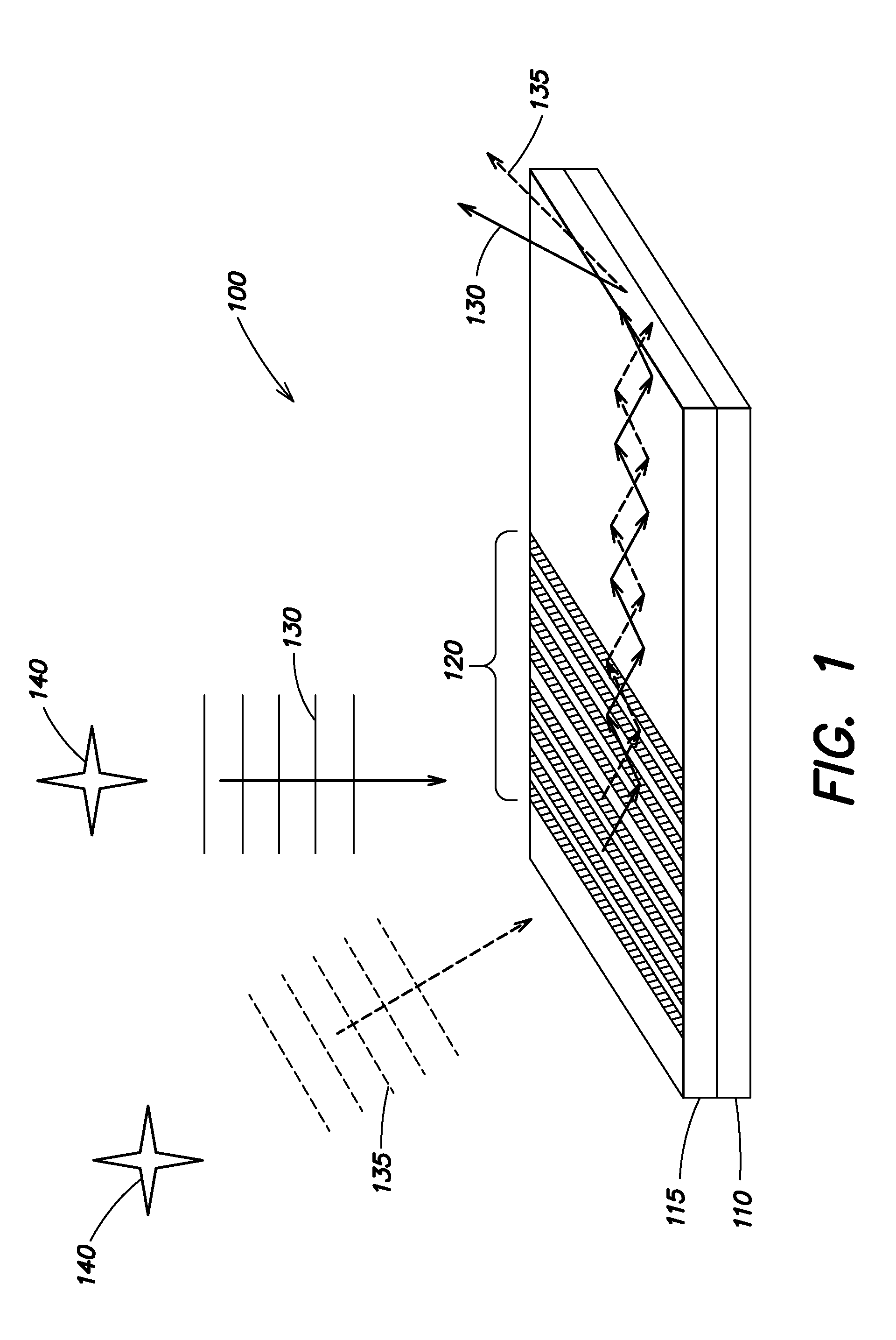
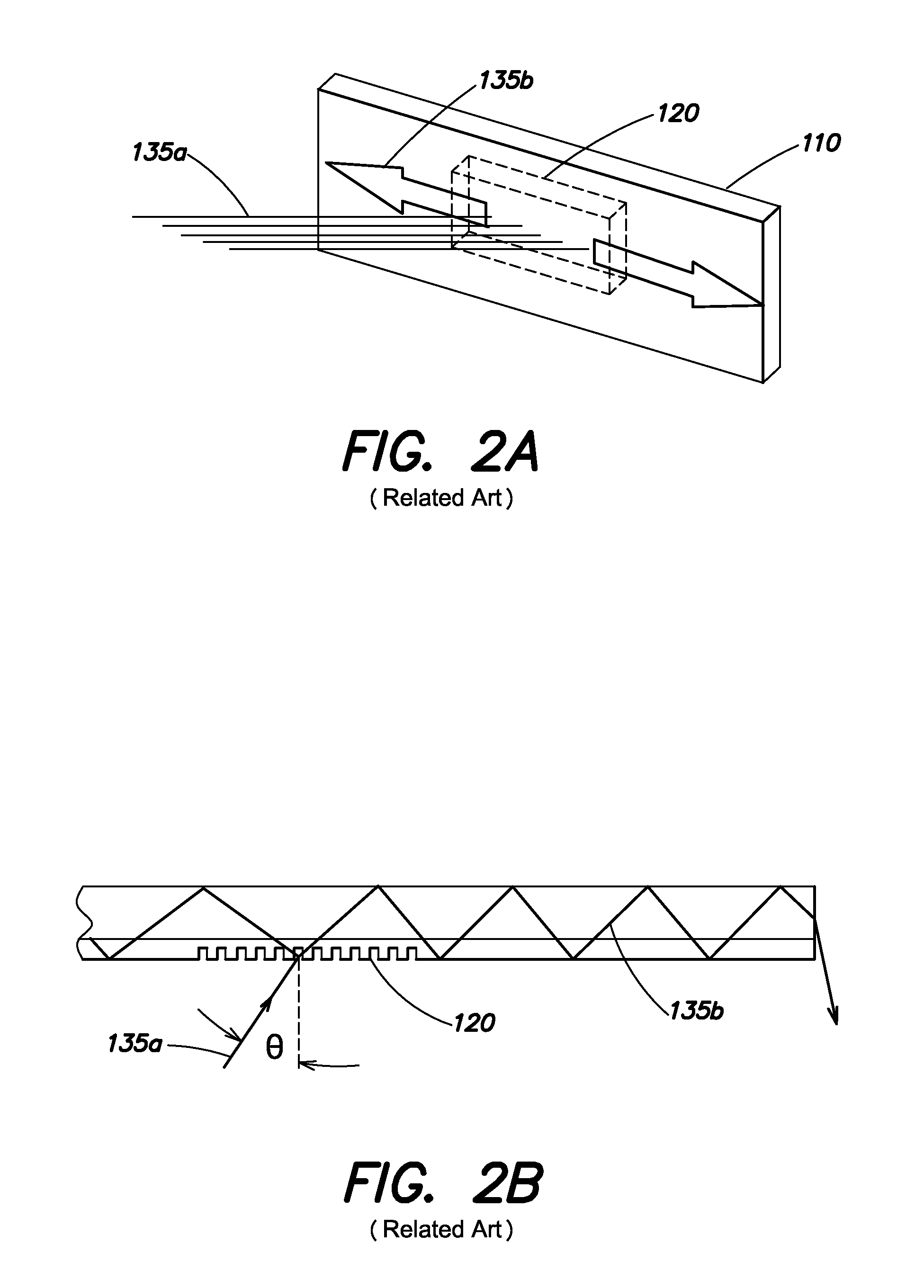
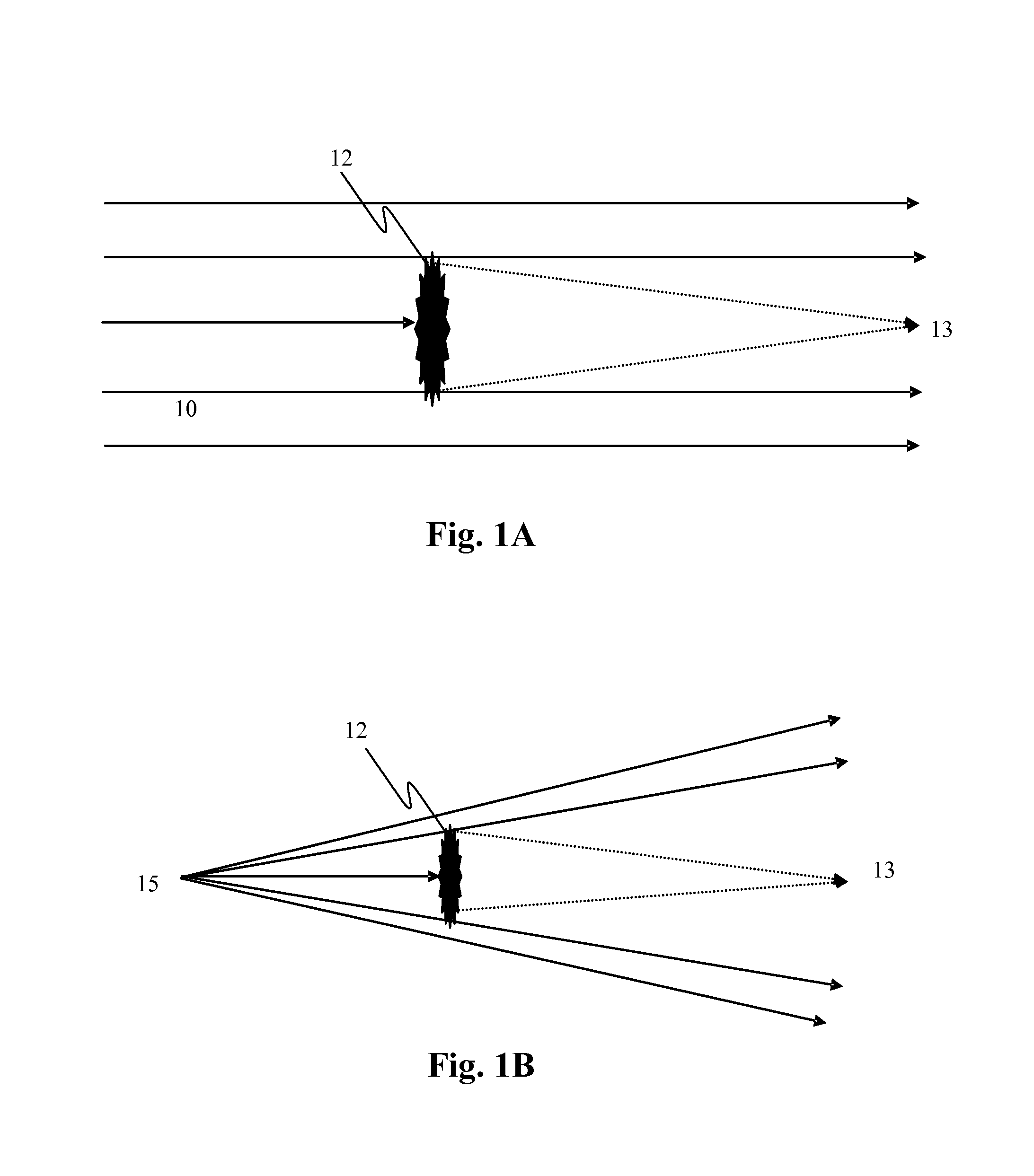
A system and method for focusing electromagnetic energy on a moving target. Generally, the inventive system sends a pilot beam to a target and analyzes a return wavefront to ascertain data with respect to any distortions and other phase and / or amplitude information in the wavefront. This information is then used to pre-distort an output beam by so that it is focused on the target by the intervening distortions. In an illustrative embodiment, the pilot beam is provided by a beacon laser mounted off-axis with respect to the output beam. The reflected wavefront is received through a gimbaled telescope. Energy received by the telescope is detected and processed to ascertain wavefront aberrations therein. This data is used to predistort a deformable mirror to create an output beam which is the phase conjugate of the received wavefront. In a first alternative embodiment, a nonlinear optical phase-conjugate mirror is employed to generate the required wavefront-reversed replica of the received wavefront. The system further includes an arrangement for modulating the output beam to confuse the target. In a second alternative embodiment, the system is adapted to examine atmospheric distortions of starlight to predistort the output beam. The alternative embodiment offers a faster response time and a lower susceptibility to detection.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
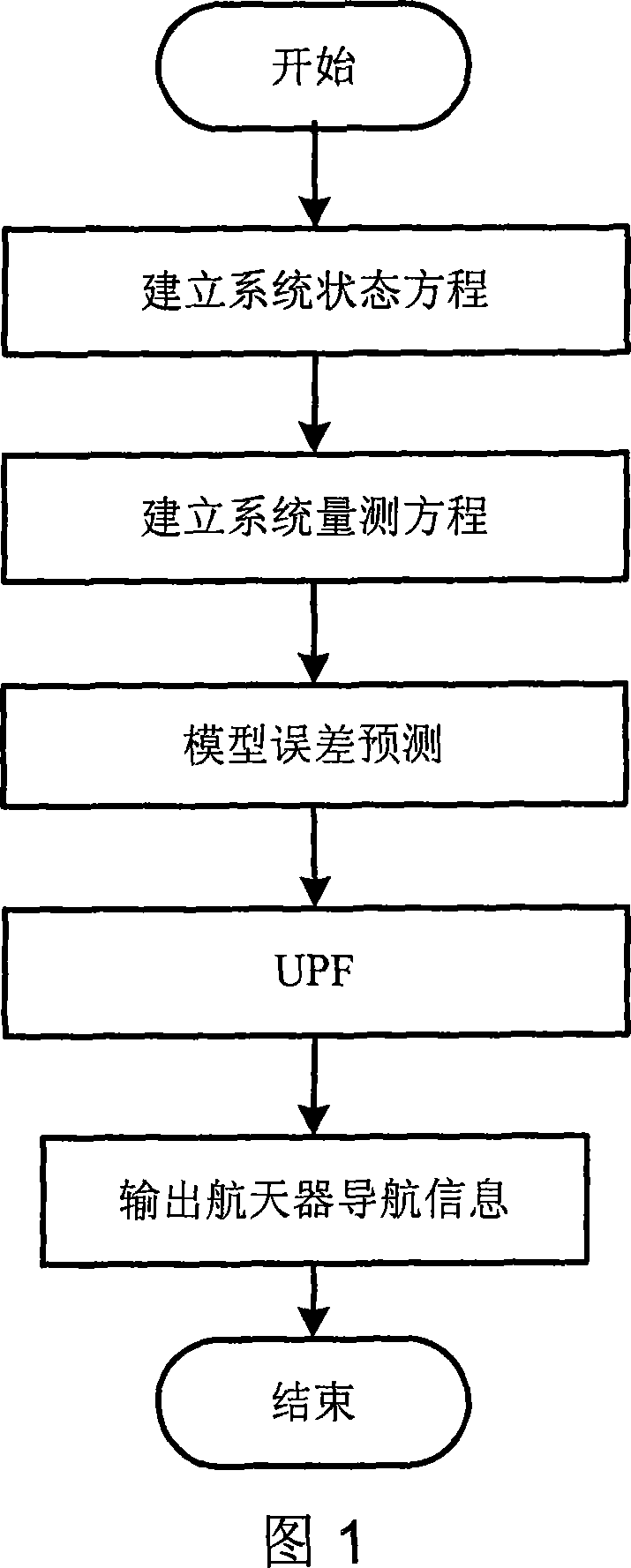
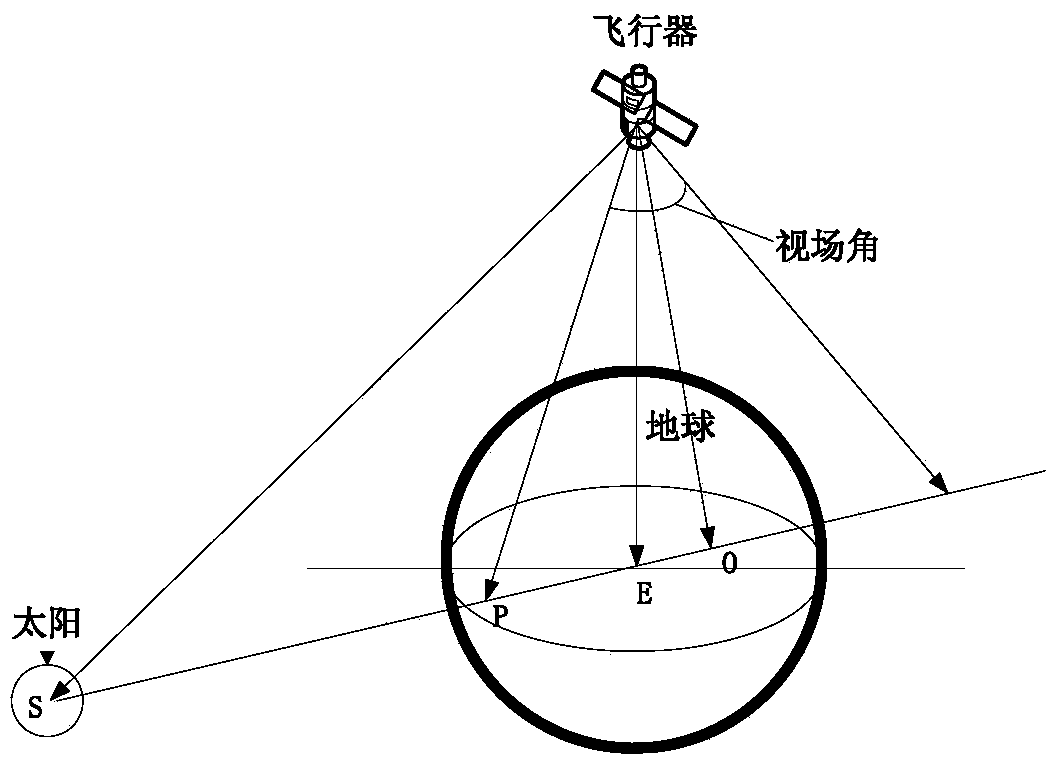
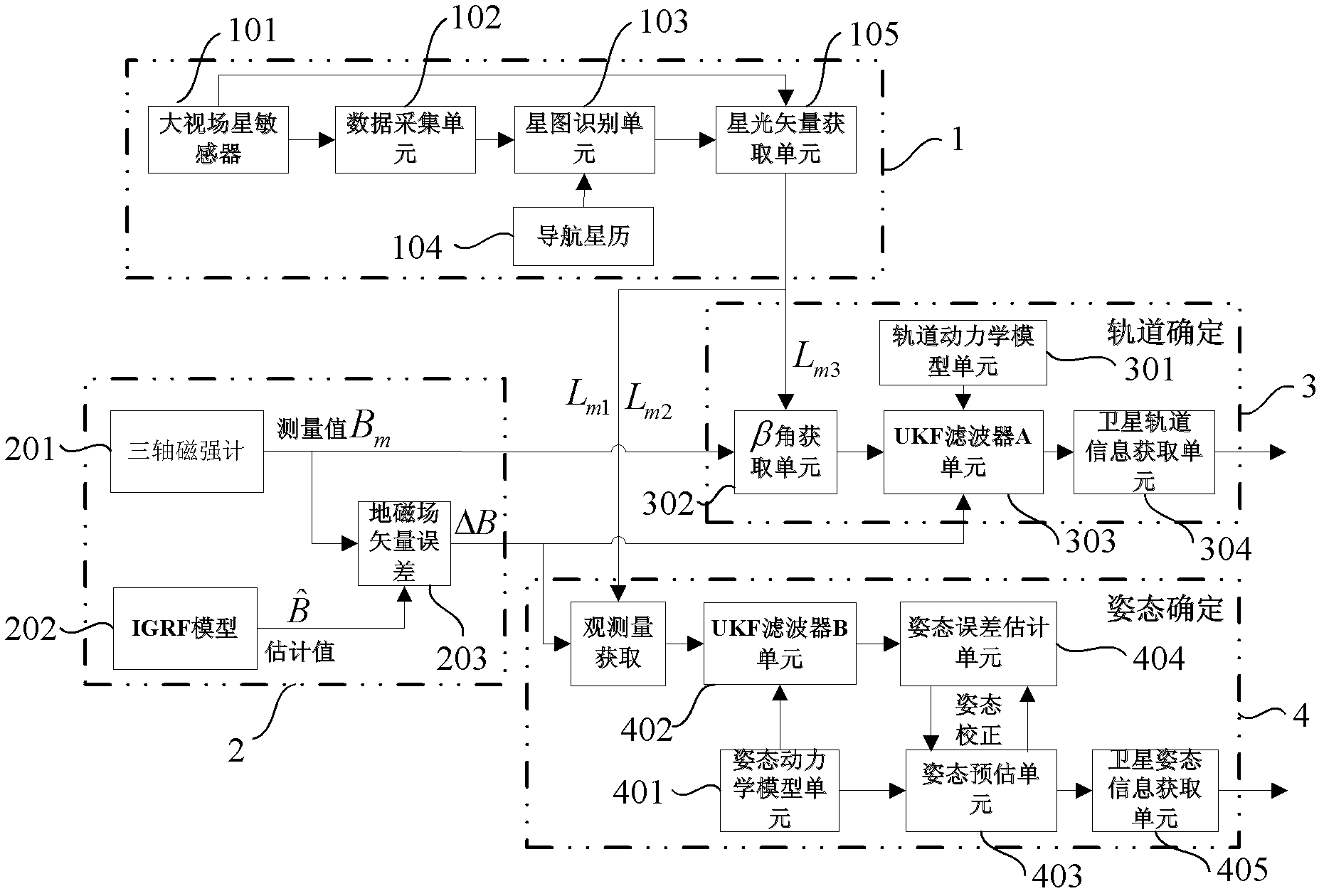
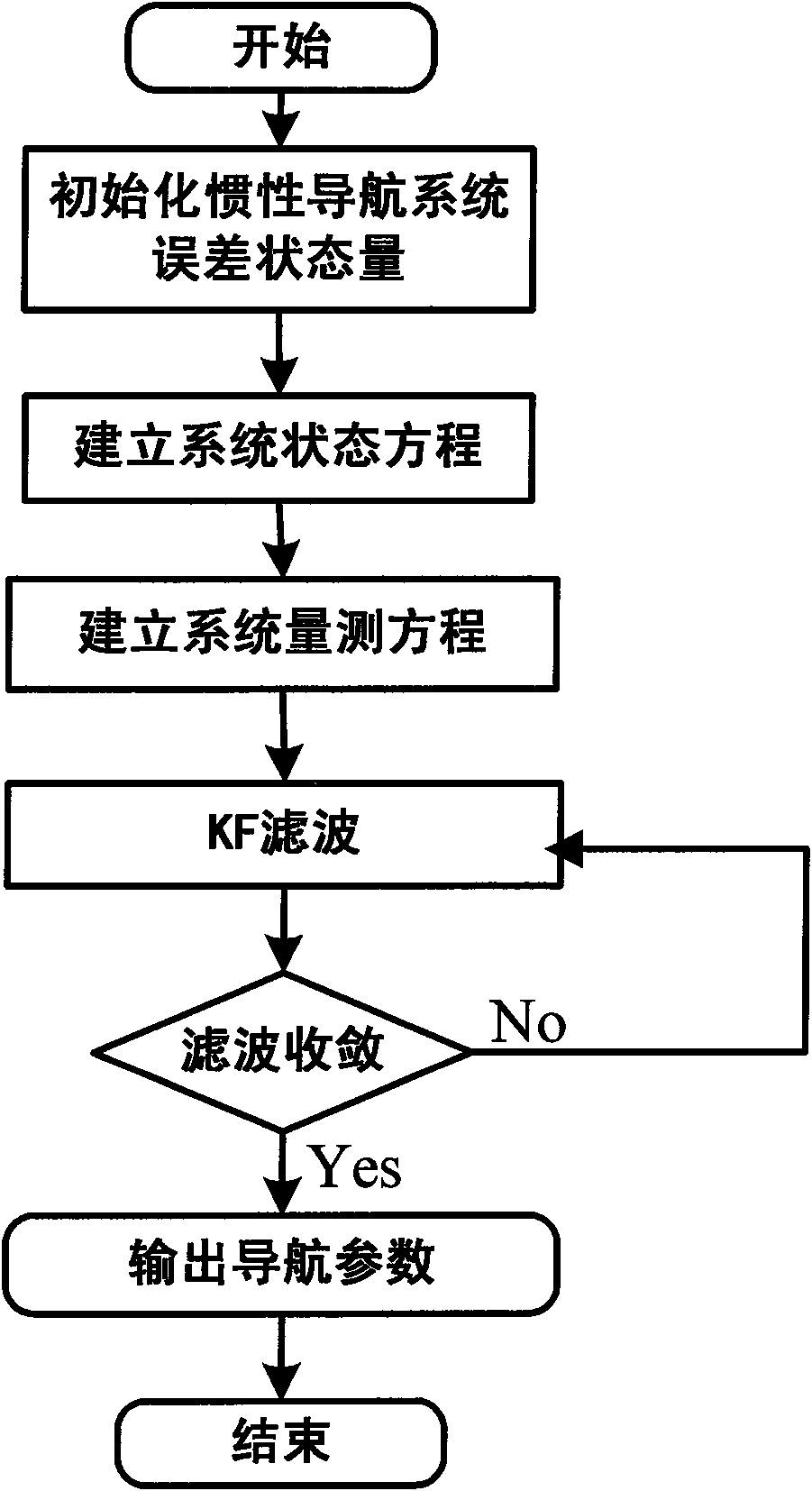
Self boundary marking method based on forecast filtering and UPF spacecraft shading device
ActiveCN101082494AOvercoming inaccuracyImprove filtering accuracyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsNavigation by astronomical meansSpaceflightInformation integration
There are a sort of predictive filtering and the self-demarcation of the UPF spaceflight, it relates to the spaceflight airmanship field. It applies to the self-demarcation of the spaceflight peg-top, especially it relates to a sort of spaceflight self-demarcation method of the inertia / starlight which bases the predictive filtering and the UPF (Unscented Particle Filter) information coalescence, thereby it applies to the navigation determining gesture of the spaceflight. First it establishes the self-demarcation state equations of the spaceflight, and then it makes the gesture information which is observed by the star sensing device to become the measuring equations, finally it adopts the self-demarcation arithmetic which bases the predictive filtering and the UPF spaceflight to estimate and amend the drift error of the peg-top, thereby it obtain the high exact gesture of the spaceflight.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
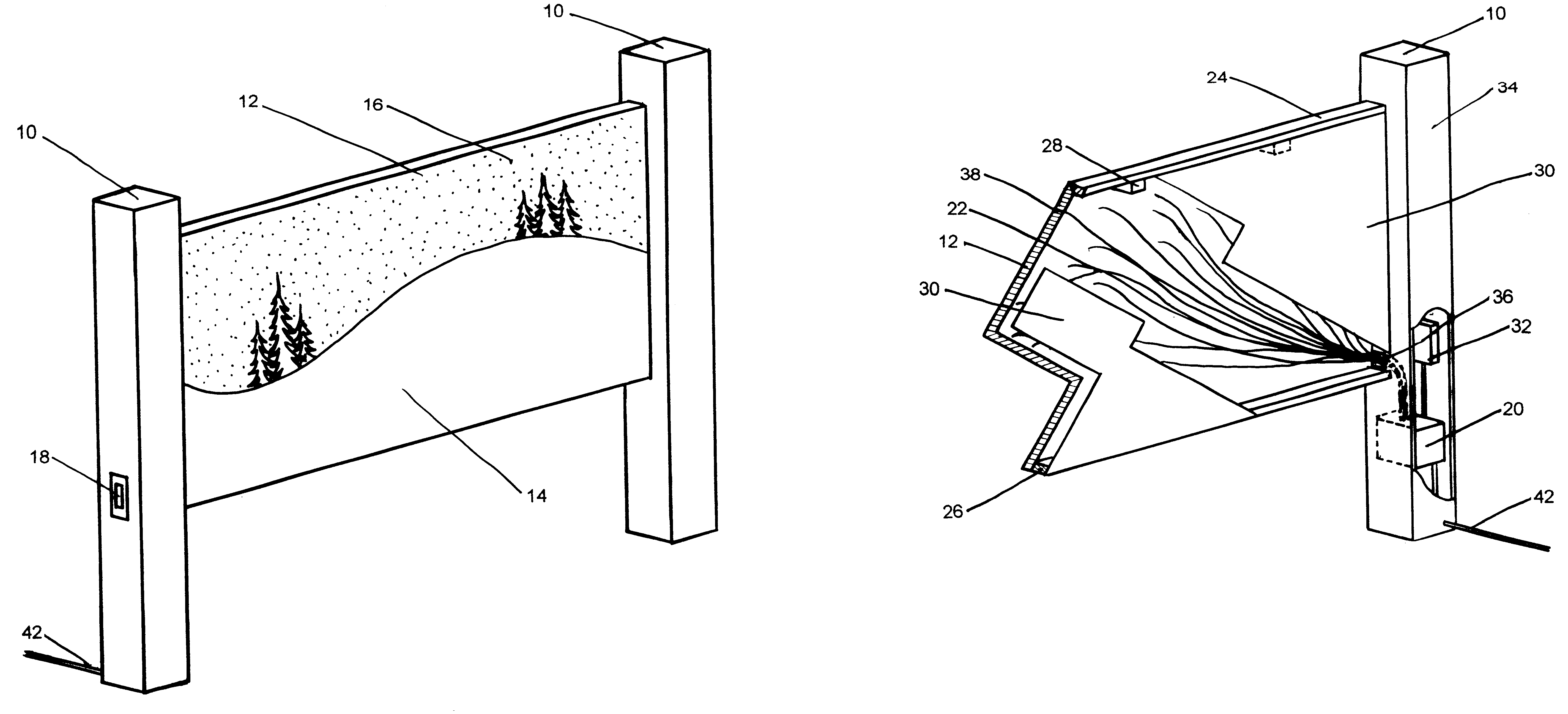
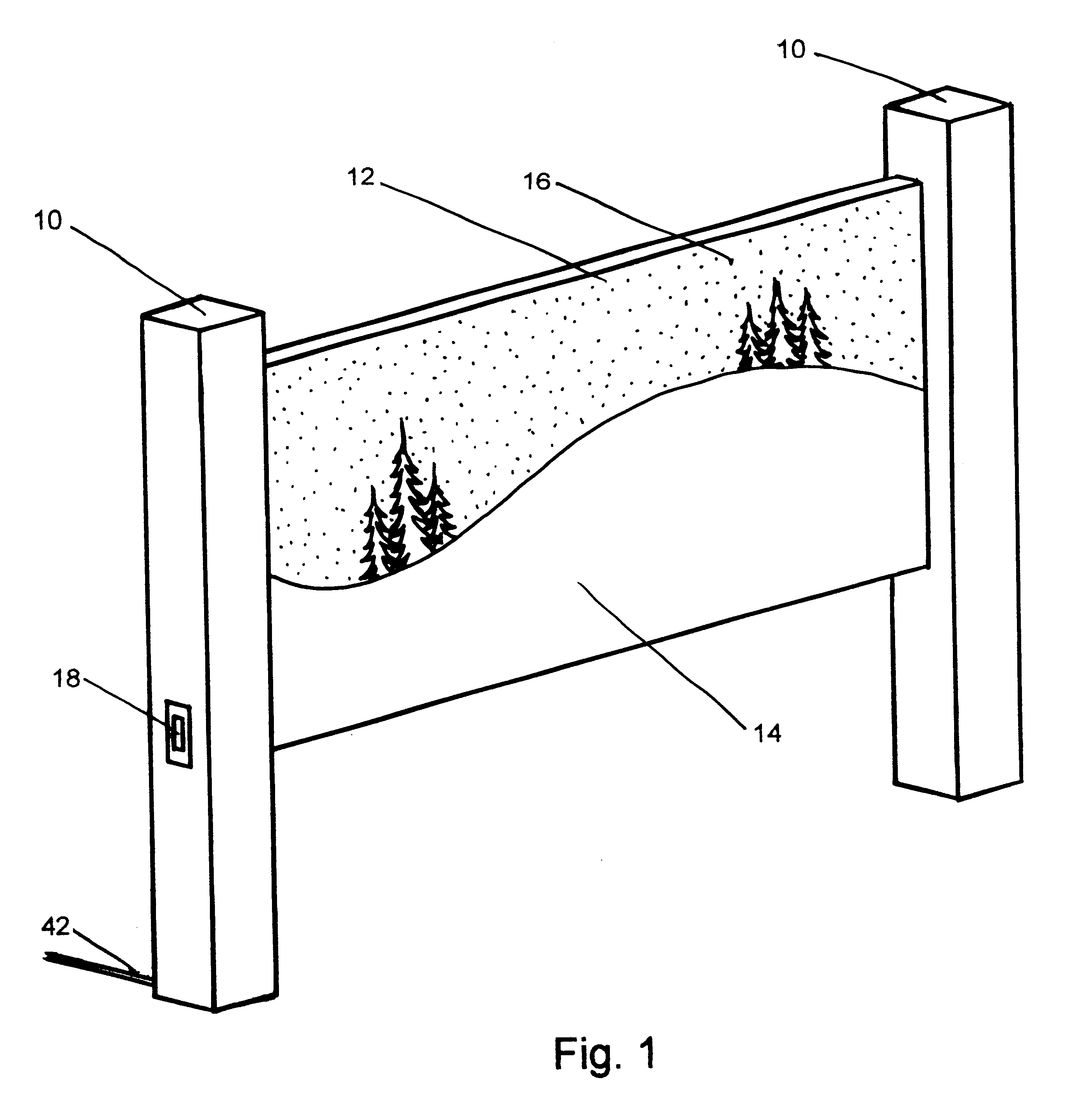
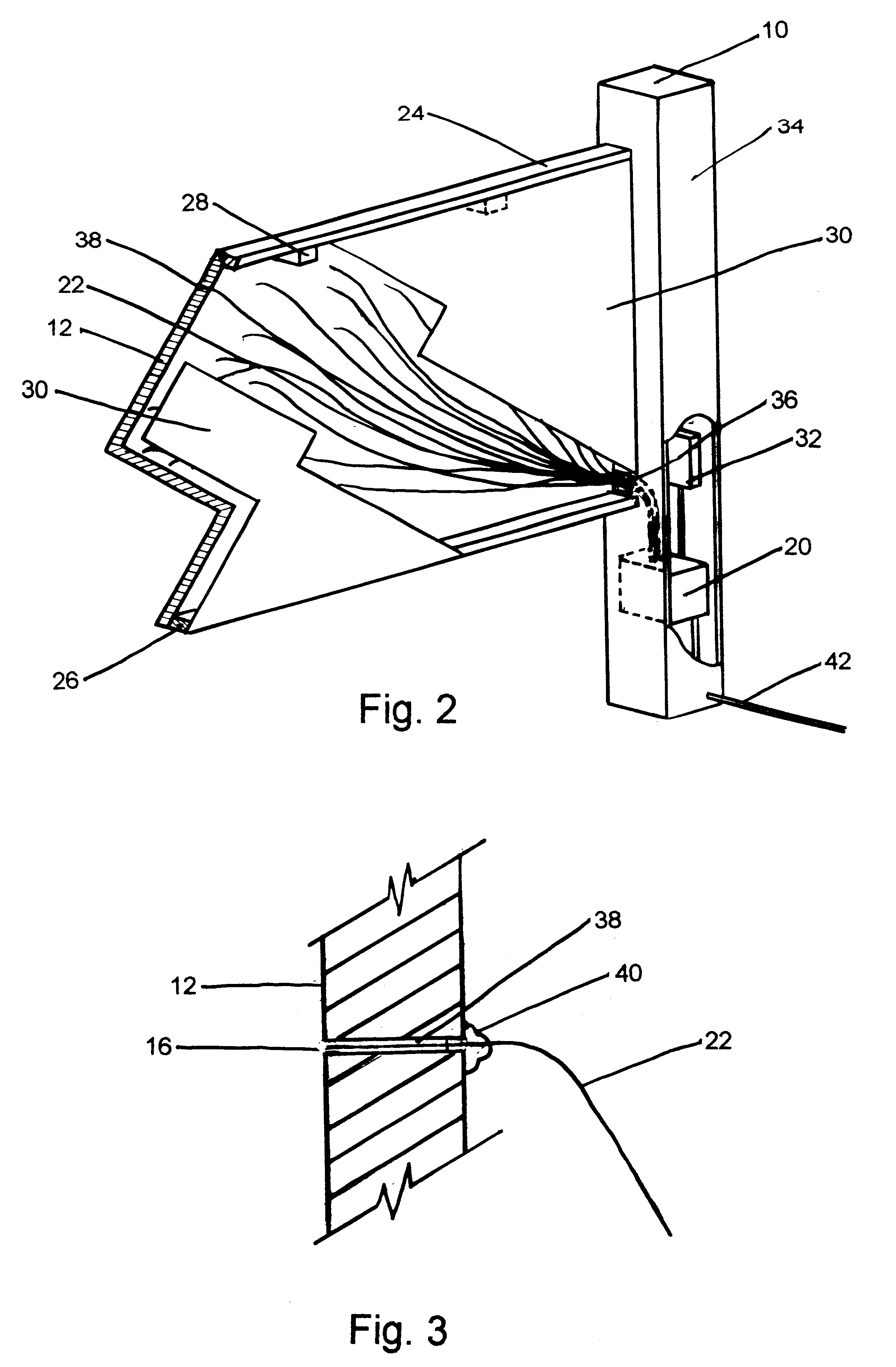
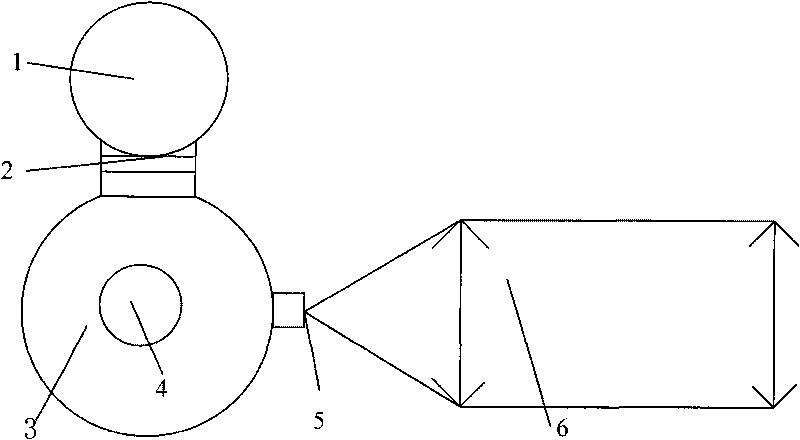
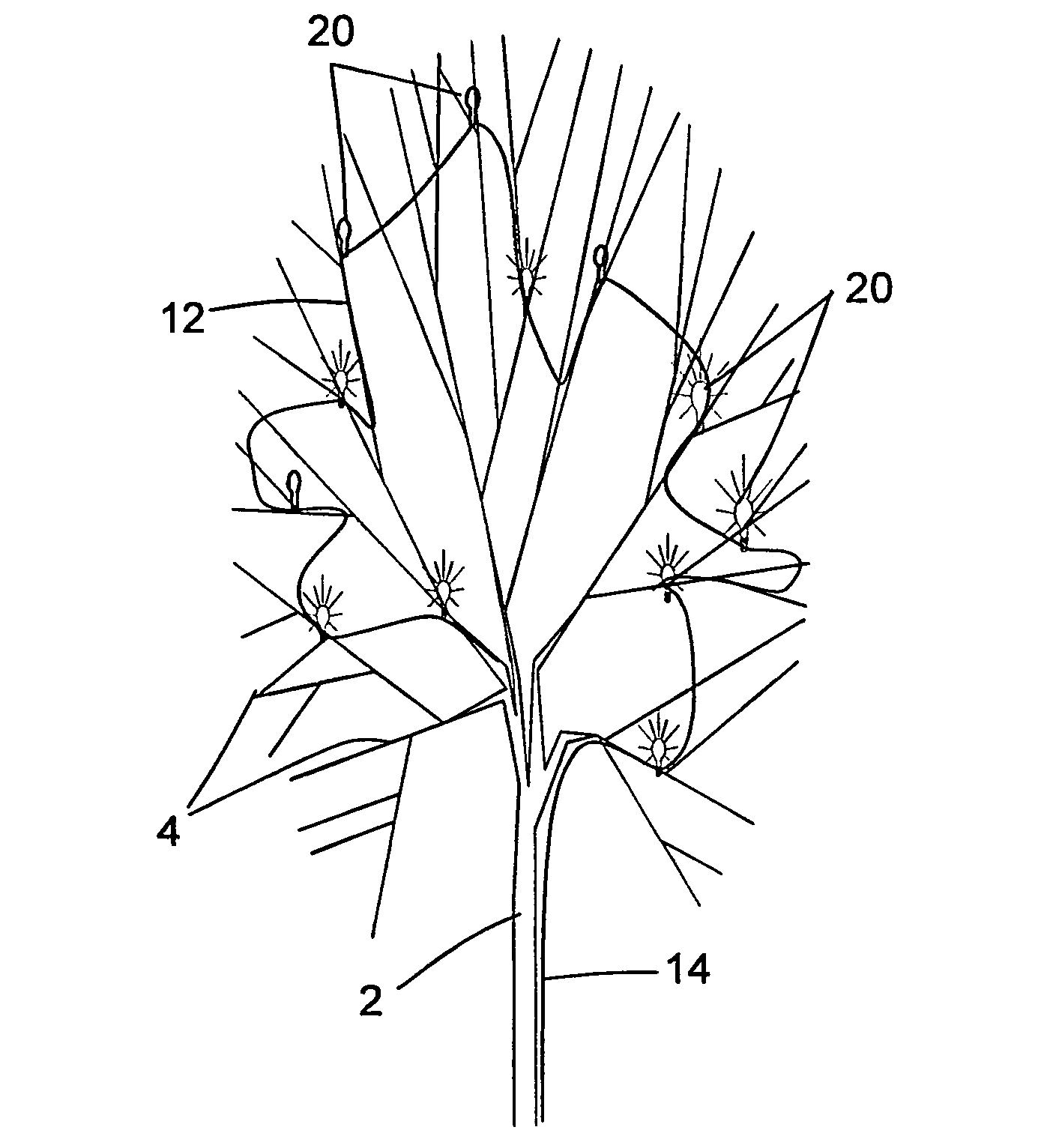
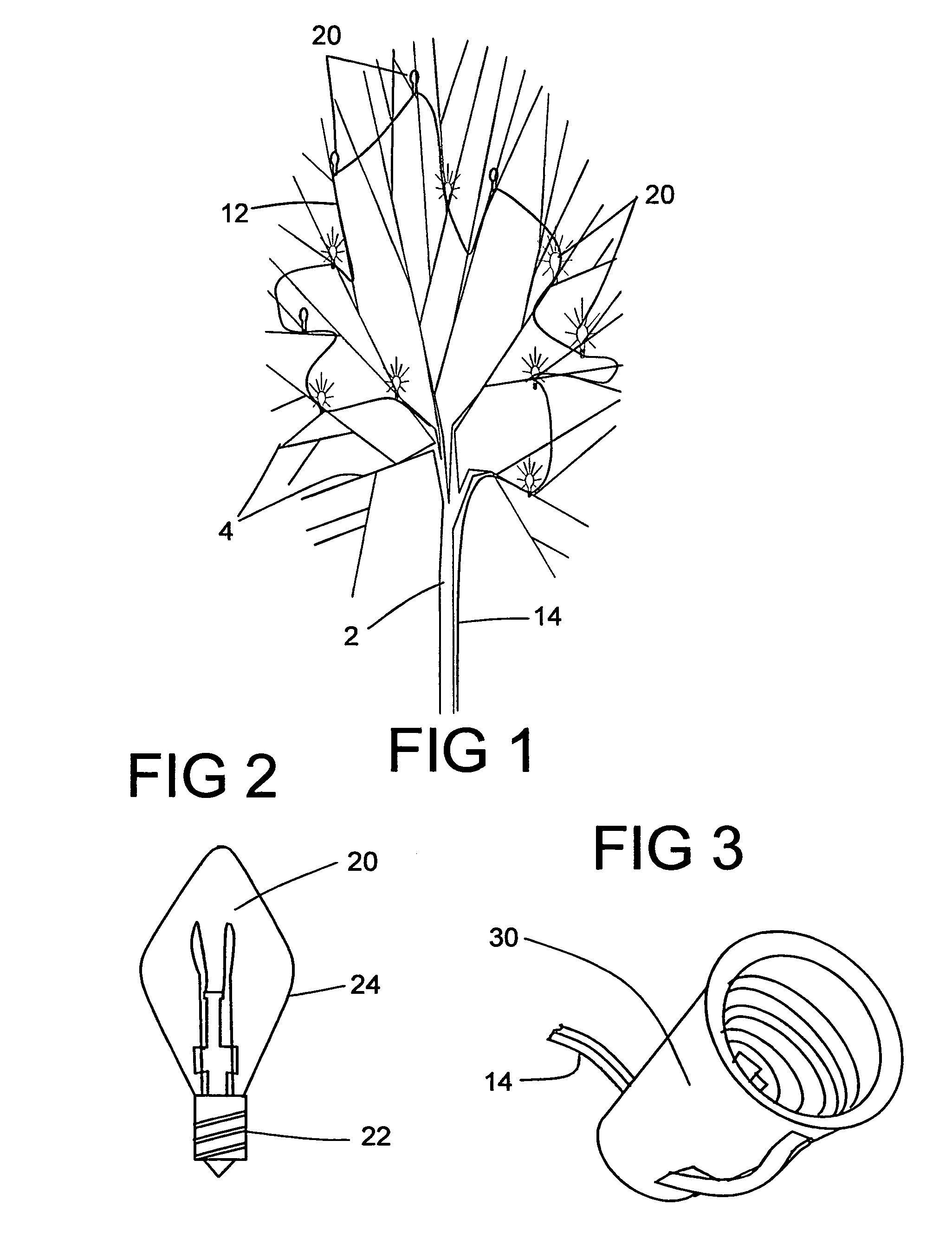
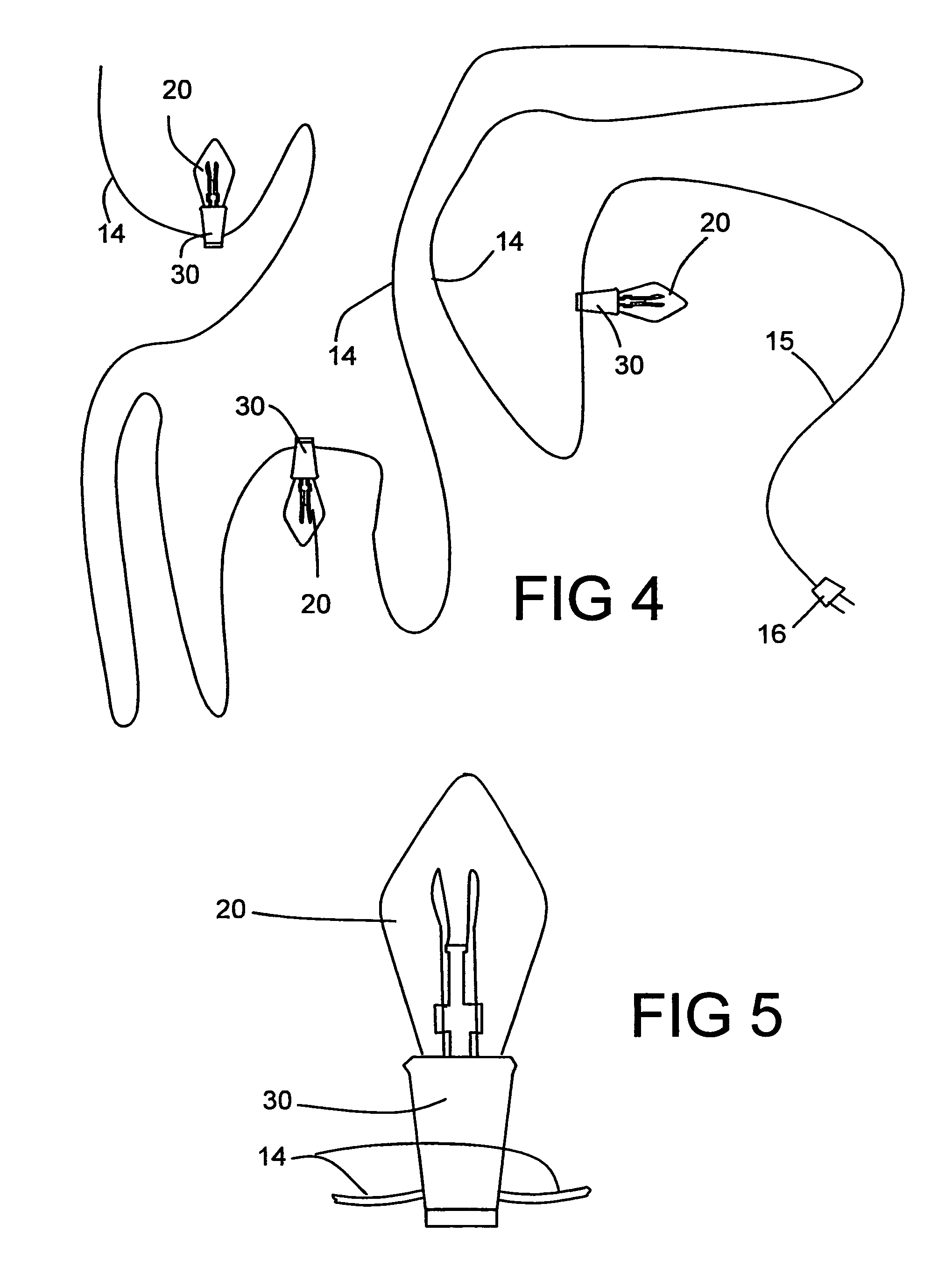
Fiber optic starlight furniture
A fiber optic illuminated starlight scene on a headboard. By using a plurality of optical fibers (22) lighted by an illuminator (20) and the optical fiber / visible end (16) are positioned flush with front panel (12) decorative scene (14) a realistic rendition of a starlight scene is created. The optical fibers / visible ends (16) placement and dispersion in the decorative scene (14) along with the distance and angle of the optical fibers (22) to the illuminator makes each individual optical fiber / visible end (16) appear as starlight.
Owner:NELSON ERIC S
Satellite starlight refraction navigation error determination and compensation method
ActiveCN104236546AHigh positioning accuracyNavigation by astronomical meansRefraction angleAtmospheric models
The invention relates to a satellite starlight refraction navigation error determination and compensation method. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, generating data of a satellite orbit by virtue of STK software; establishing a satellite attitude planning model; determining an actual observation visual field, and simulating an observation star map comprising refraction stars and non-refraction stars; calculating to obtain the tangential height h of the refraction stars; calculating to obtain the tangential height h'' of the refraction stars with errors of refraction angles and errors of an atmospheric model, wherein tangential height errors are mainly caused by the measurement precision errors of the refraction angles and the errors of the atmospheric model; calculating to obtain the position of a satellite under a geocentric inertial coordinate system; and performing filtration by an extended Kalman filtration method, and outputting a starlight refraction navigation estimated position and position errors. The method provided by the invention can realize accurate prediction of navigation precision of a satellite starlight refraction navigation system, and is comprehensive in error analysis and accurate and reliable in results.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
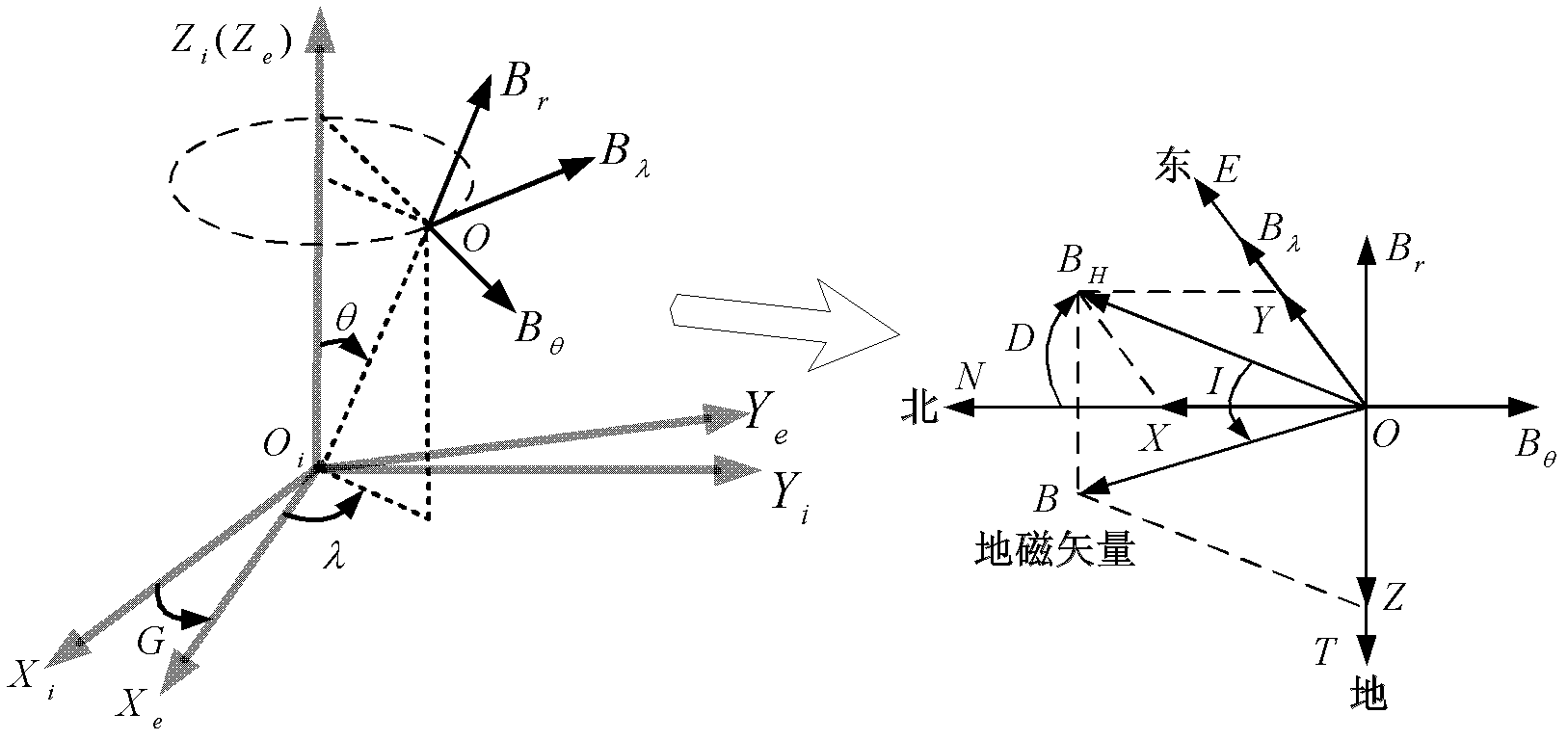
Small satellite autonomous navigation system based on starlight/ geomagnetism integrated information and navigation method thereof
InactiveCN102607564AImprove navigation accuracyImprove adaptabilityInstruments for comonautical navigationSatellite radio beaconingAutonomous Navigation SystemMarine navigation
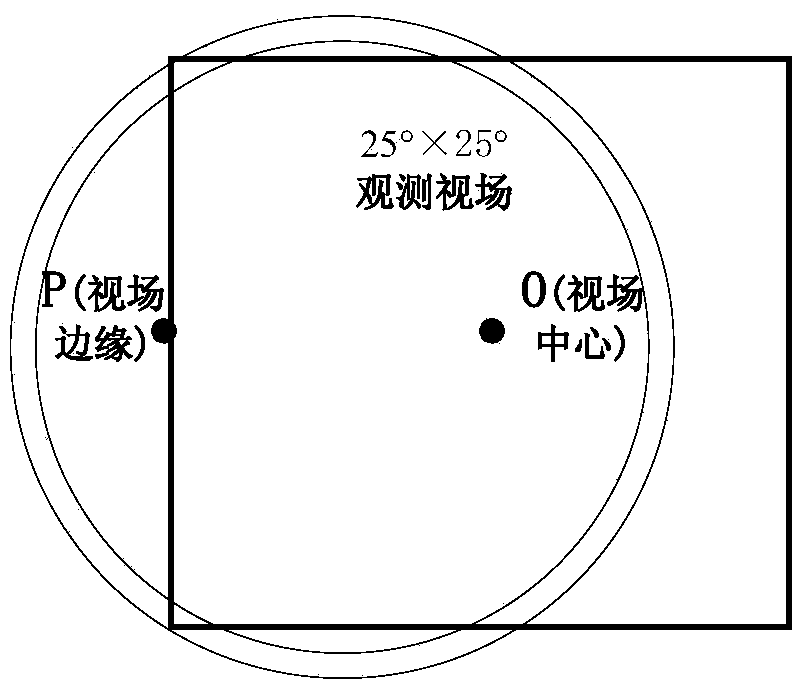
The invention provides a small satellite autonomous navigation system based on starlight / geomagnetism integrated information and a navigation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of integrated navigation. The autonomous navigation system comprises a star sensor measuring system, an earth magnetic field measuring system, an orbit determination system and an attitude determination system. The navigation method comprises the following steps of: the establishment of a navigation system state equation, the measurement equation establishment of the navigation system and integrated navigation system information fusion based on UKF(unscented kalman filter). According to the method, a large view filed star sensor is utilized to simultaneously observe starlight vector information of multiple navigational stars, thereby making up the defect caused by overlarge measurement noise of a magnetometer and obtaining high navigation accuracy; based on track and attitude information contained in the measured values of a magnetometer and the star sensor and in comprehensive consideration of influences of various factors, a measurement equation of the system is established, the adaptability and the stability of a filter to measurement noise are improved; therefore, the method is suitable for navigation of a low earth rail small satellite adopting a cheap small autonomous navigation system.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
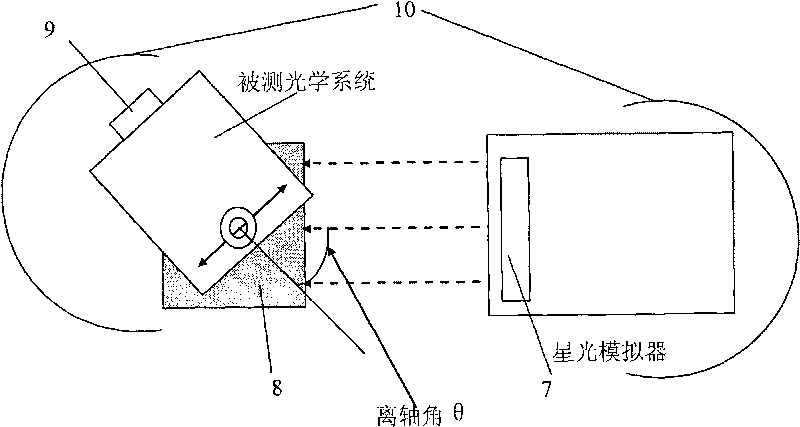
Zero deflection band based star sensor ground surface calibration method
InactiveCN101013033ARemove estimated effectsSmall amount of calculationPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryCosmonautic vehicle trackingSingle starEngineering
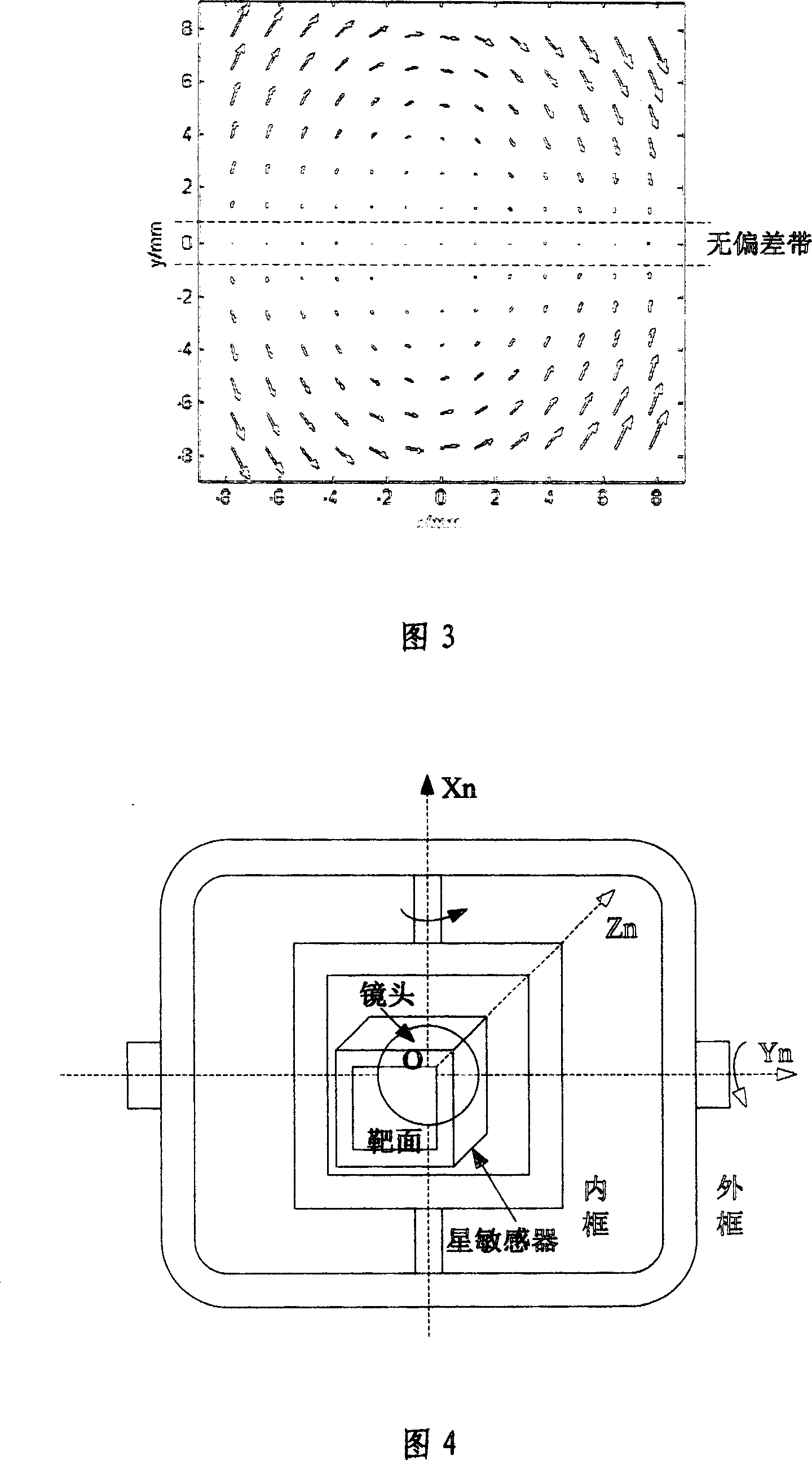
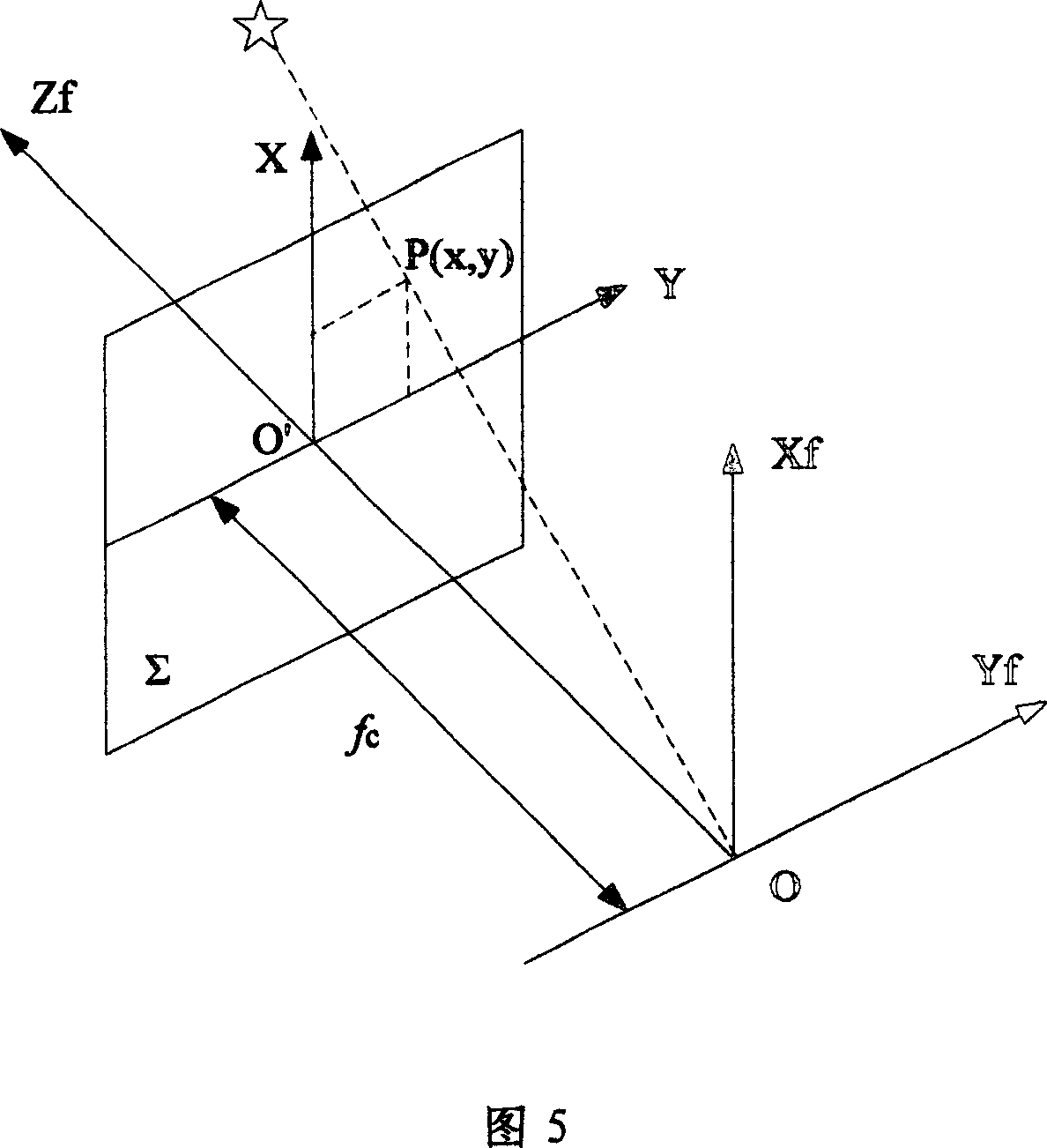
The invention is a space measurement technology, involving the improvement to the star sensor calibration method. The invention uses the calibration system which comprising the air cushion platform, single star starlight simulator, star sensor, two-dimensional axial turntable and data processing computer, and its steps are: 1. establish the star sensor imaging model; 2. parameters calibrating. The invention uses no deviation strip to calibration focus and radial distortion coefficient, eliminating the internal parameter estimation effect by the external installation error; the method has simple model and small computing volume, particularly applied to the star sensor calibration based on radial distortion.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
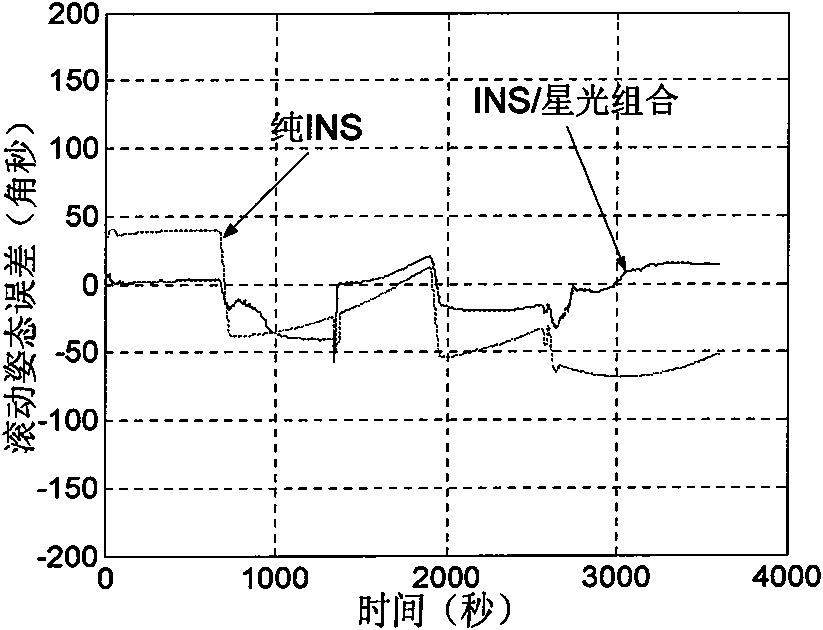
Airborne starlight of coupling inertial position error and independent navigation method of inertial composition
InactiveCN101660914AGive full play to the role of attitude observationAvoid the need to independently maintain the attitude combination algorithm in the geographic systemInstruments for comonautical navigationAviationMathematical model
The invention discloses airborne starlight of a coupling inertial position error and an independent navigation method of inertial composition. In the method, firstly theoretical analysis is carried out on an attitude integrated observation principle in navigation under an aviation airborne geography department, an attitude observation linearization measurement equation under a geography departmentis established, inter-conversion relation between the attitudes from an inertial system to the geography department measured and output by a star sensor (star light) is analyzed, a coupling error model between the attitudes under the inertial system measured and output by the star sensor and the attitudes under the geography department calculated and output by the inertial navigation is established through introducing an inertial navigation position error conversion matrix, and finally aviation airborne starlight based on the modeling thoughts of the coupling inertial position error and a mathematical model of an inertial integrated navigation system are designed, and a KF filtering method is adopted to optimally estimate the error state of the inertial navigation. The invention has high-accuracy in navigation, and can give full play to the estimation function of the attitude measurement equation under the geography department on error state amount of the aviation airborne inertial navigation system.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
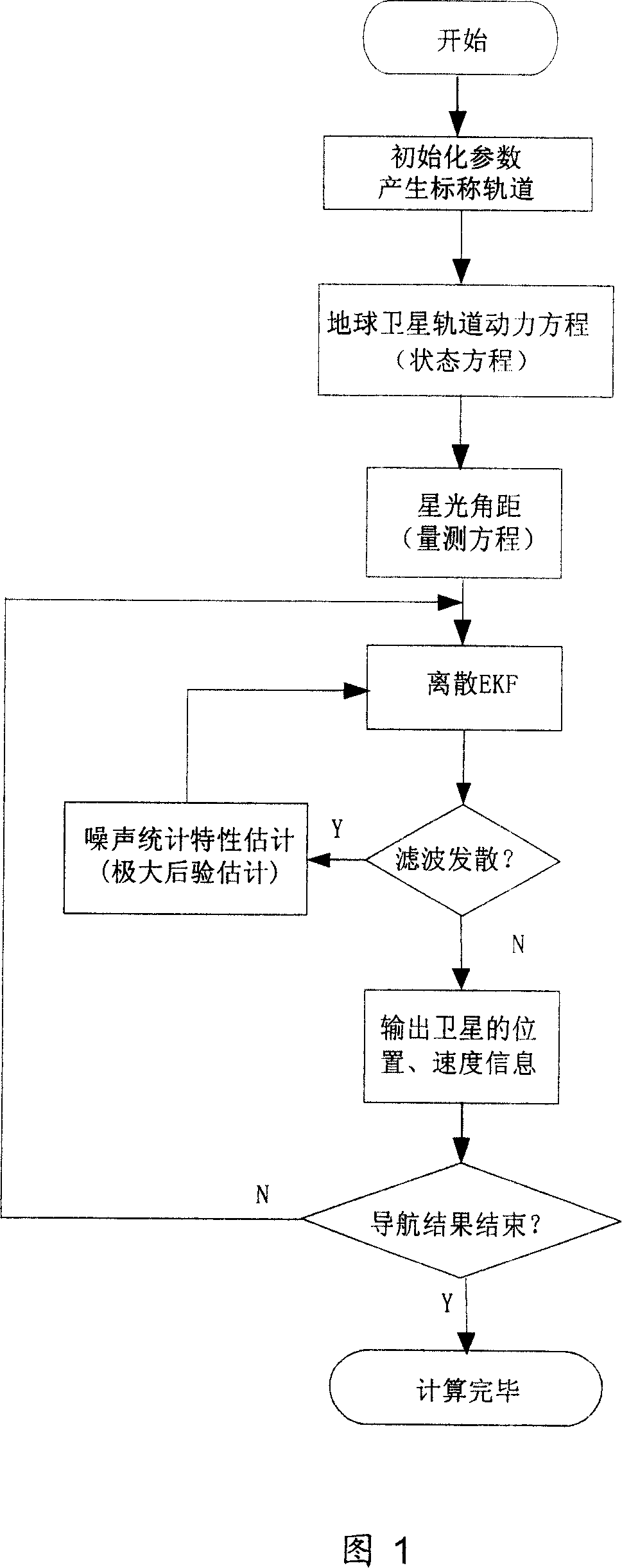
Earth satellite self astronomical navigation method based on self adaptive expansion kalman filtering
InactiveCN1987355AImprove navigation accuracyOvercome the problem of divergenceNavigational calculation instrumentsInstruments for comonautical navigationEarth satelliteKinematics equations
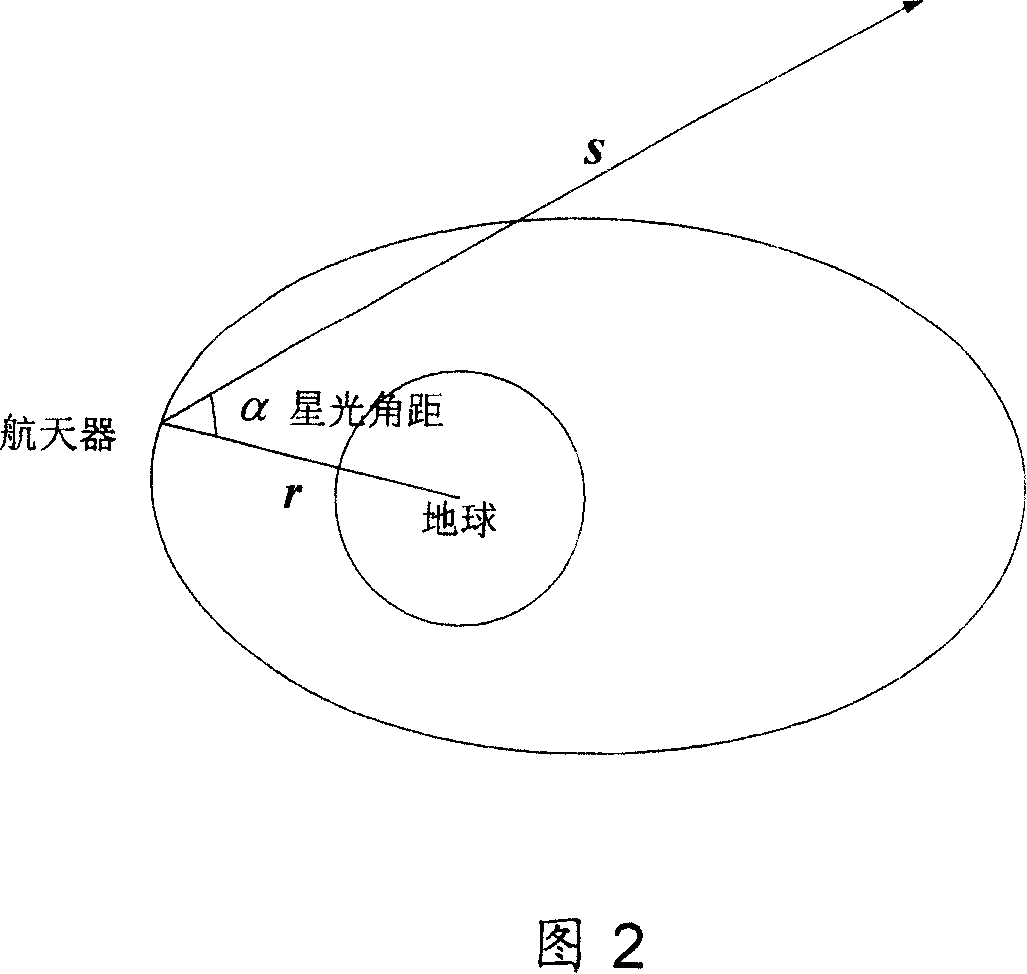
The method includes steps: building up kinematical equation of earth satellite orbit based on rectangular coordinate system; building up measurement equation based on angular distance of starlight as measuring quantity; building up discrete type extended Kalman filtering equation to determine whether extended Kalman filtering is divergent; using prognostic filtering residual to determine whether extended Kalman filter is divergent; if yes, then the method carries out estimating statistic characteristics of noise; otherwise, carrying out calculation according to standard extended Kalman filtering program. The invention solves issue that divergence of noise filter caused by inaccurate determination of statistic characteristics of noise influences on navigation accuracy. Advantages are: independent, flexible and simple, and high precision. The invention is especially suitable to earth application satellite needed high navigation accuracy in resource, weather areas etc.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Static multi- light path star simulator
InactiveCN101236087AFlexible adjustmentGuaranteed test accuracyInstruments for comonautical navigationNavigation by astronomical meansOptical axisAstronomy
A static multi-optical-path star simulator comprises a flange and at least four starlight pipes, wherein each starlight pipe can produce a simulation star, optical spectrum and brightness of each starlight pipe can be separately adjusted, the starlight pipes are installed on the flange by an angular adjustment mechanism, optical axles of two arbitrary star pipes are not parallel, relative angle between two arbitrary star pipes can be adjusted in a range not smaller than 10 degrees, a large amount of simulation constellations with different constructions can be produced, brightness and spectral characteristic of all asterions can be different, geometrical similarity between two arbitrary simulation constellations is relatively low, and physical characteristics of actual star field can be well simulated.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
In-orbit calibration method of star sensor lens distortion and satellite attitude determination method based on starlight vector correction
InactiveCN103234556ARealize CalibrationEliminate errors in satellite attitude determinationMeasurement devicesFixed starsOptical axis
The invention relates to an in-orbit calibration method of star sensor lens distortion and a satellite attitude determination method based on starlight vector correction. The invention relates to an in-orbit calibration method of star sensor lens distortion and a satellite attitude determination method. The invention aims at solving a problem of incapability of calibrating a temperature distortion term of an existing calibration method, and a problem of low precision of an existing satellite attitude determination. The star sensor lens distortion in-orbit calibration method comprises the steps that: an included angle between fixed star incident light and a lens optical axis is obtained by calculation according to target fixed star imaging point coordinates and a star sensor lens distortion formula; a light vector direction of the target fixed light is obtained according to the included angle of the incident light and the lens optical axis; and in-orbit calibration of star sensor lens distortion is carried out according to a principle that the included angles of light vector directions of a plurality of target fixed stars are fixed. The attitude determination method comprises the steps that: a target fixed star starlight vector is obtained by calculation according to the target fixed star imaging point coordinates and the star sensor lens distortion formula obtained by calibration; and satellite attitude is determined through star map matching. The methods provided by the invention are applied in the technical field of satellite attitude determination.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Robust infrared countermeasure system and method
InactiveUS6872960B2Susceptibility to detectionFast response timePhotometry using reference valueInstruments for comonautical navigationCountermeasureOptical phase conjugation
A system and method for focusing electromagnetic energy on a moving target. Generally, the inventive system sends a pilot beam to a target and analyzes a return wavefront to ascertain data with respect to any distortions and other phase and / or amplitude information in the wavefront. This information is then used to pre-distort an output beam by so that it is focused on the target by the intervening distortions. In an illustrative embodiment, the pilot beam is provided by a beacon laser mounted off-axis with respect to the output beam. The reflected wavefront is received through a gimbaled telescope. Energy received by the telescope is detected and processed to ascertain wavefront aberrations therein. This data is used to predistort a deformable mirror to create an output beam which is the phase conjugate of the received wavefront. In a first alternative embodiment, a nonlinear optical phase-conjugate mirror is employed to generate the required wavefront-reversed replica of the received wavefront. The system further includes an arrangement for modulating the output beam to confuse the target. In a second alternative embodiment, the system is adapted to examine atmospheric distortions of starlight to predistort the output beam. The alternative embodiment offers a faster response time and a lower susceptibility to detection.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
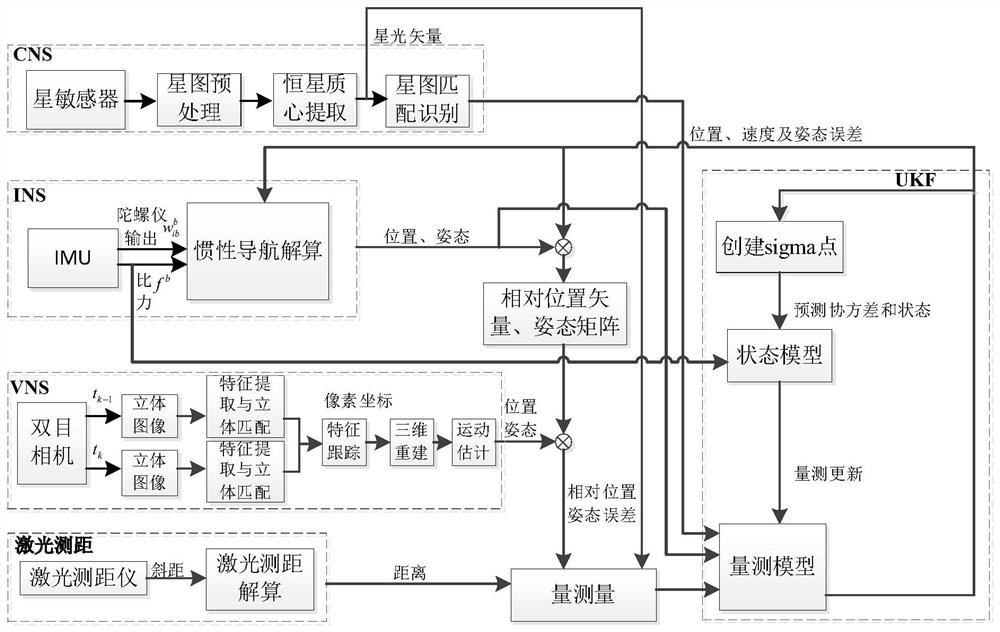
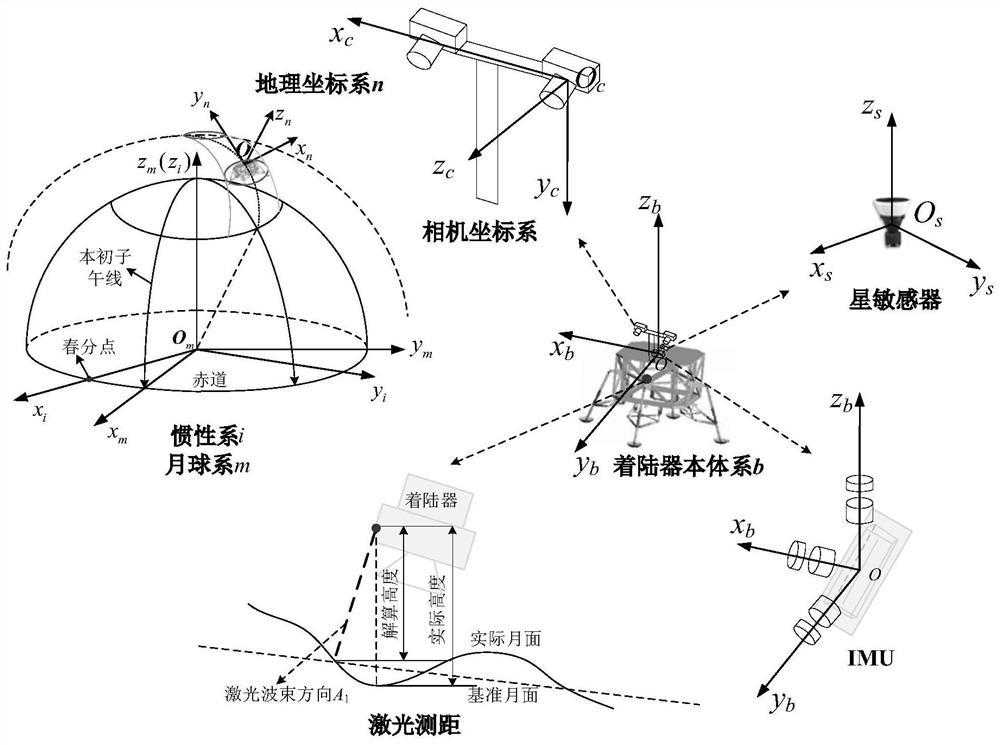
Inertia/vision/astronomy/laser ranging integrated navigation method suitable for lunar lander
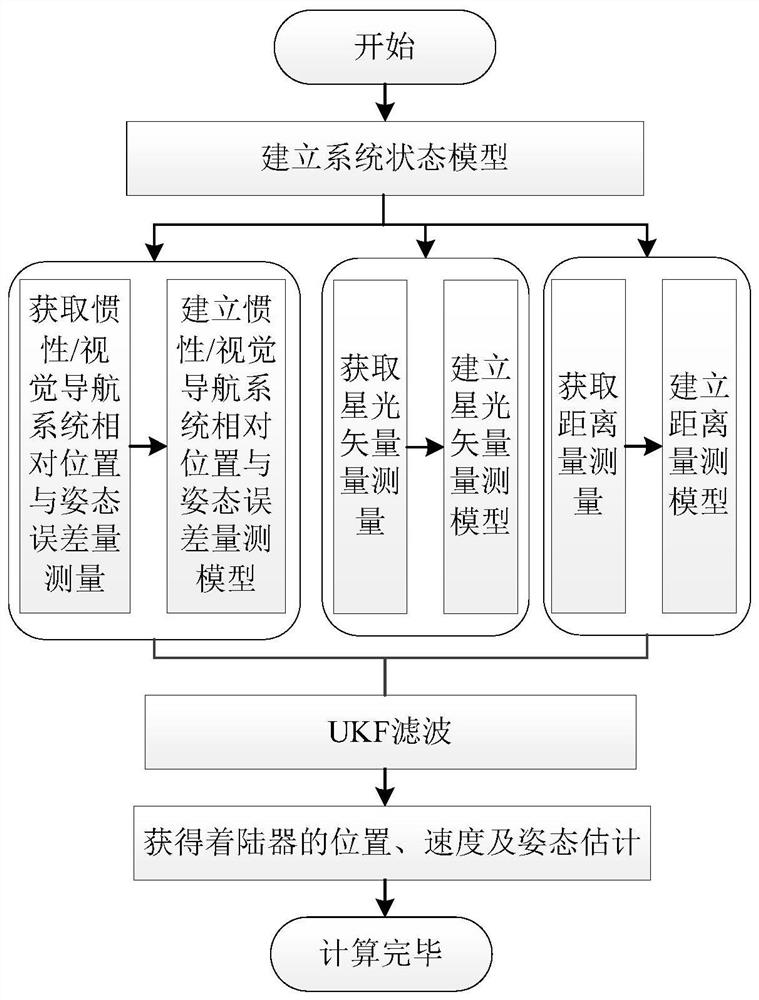
ActiveCN111947652AHigh precisionImprove reliabilityNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsNavigation by astronomical meansLaser rangingSpace probe
The invention relates to an inertia / vision / astronomy / laser ranging combined navigation method suitable for a lunar lander. The method includes: firstly, according to mechanical arrangement of inertialnavigation under a lunar fixed connection coordinate system, taking an inertial navigation error equation as a state model, and then taking the relative position and attitude error obtained by an inertial / visual navigation system, the starlight vector obtained by an astronomical navigation system and the distance obtained by a laser range finder as measurement quantities; then respectively establishing measurement models of relative position and attitude errors, starlight vectors and laser ranging of the inertial / visual navigation system according to the measurements; and finally, estimatingthe position, the speed and the attitude of the lander by using UKF filtering, and correcting the attitude error and the inertial device error of the lunar lander. The invention belongs to the field of deep space probe autonomous navigation, can provide high-precision position, speed and attitude information for a lunar lander, and has important practical significance for deep space detection.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Standard starlight simulator and stray light PST (point source transmittance) optical detection system containing same
InactiveCN101750097ALarge continuous dimming dynamic rangeSmall caliberNavigation by astronomical meansTransmittanceStray light
The invention relates to a standard starlight simulator and a stray light PST (point source transmittance) optical detection system containing the same. The standard starlight simulator comprises a light source, an iris diaphragm, a dodging instrument, a star point plate and a collimation system; the iris diaphragm is arranged on the incident optical path of the light source; the dodging instrument is arranged on the output optical path of the iris diaphragm; the star point plate is arranged above the dodging instrument; and the collimation system is arranged on the output optical path of the star point plate. The invention provides the standard starlight simulator which can greatly enlarge the range of the simulated stellar magnitude and realize accurate measuring and calibrating under pianissimo light environment and has high measurement accuracy, and the stray light PST (point source transmittance) optical detection system containing the simulator.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
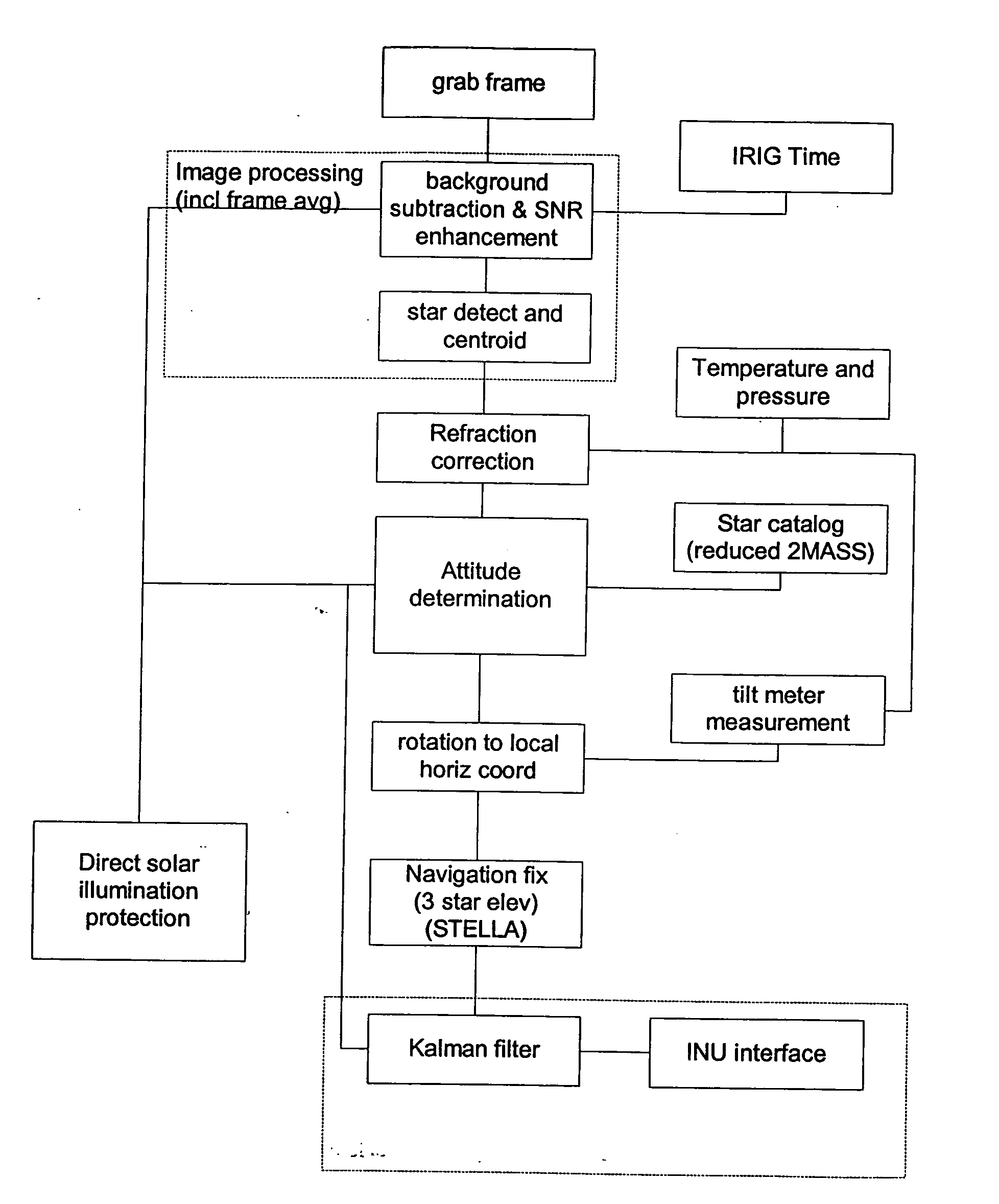
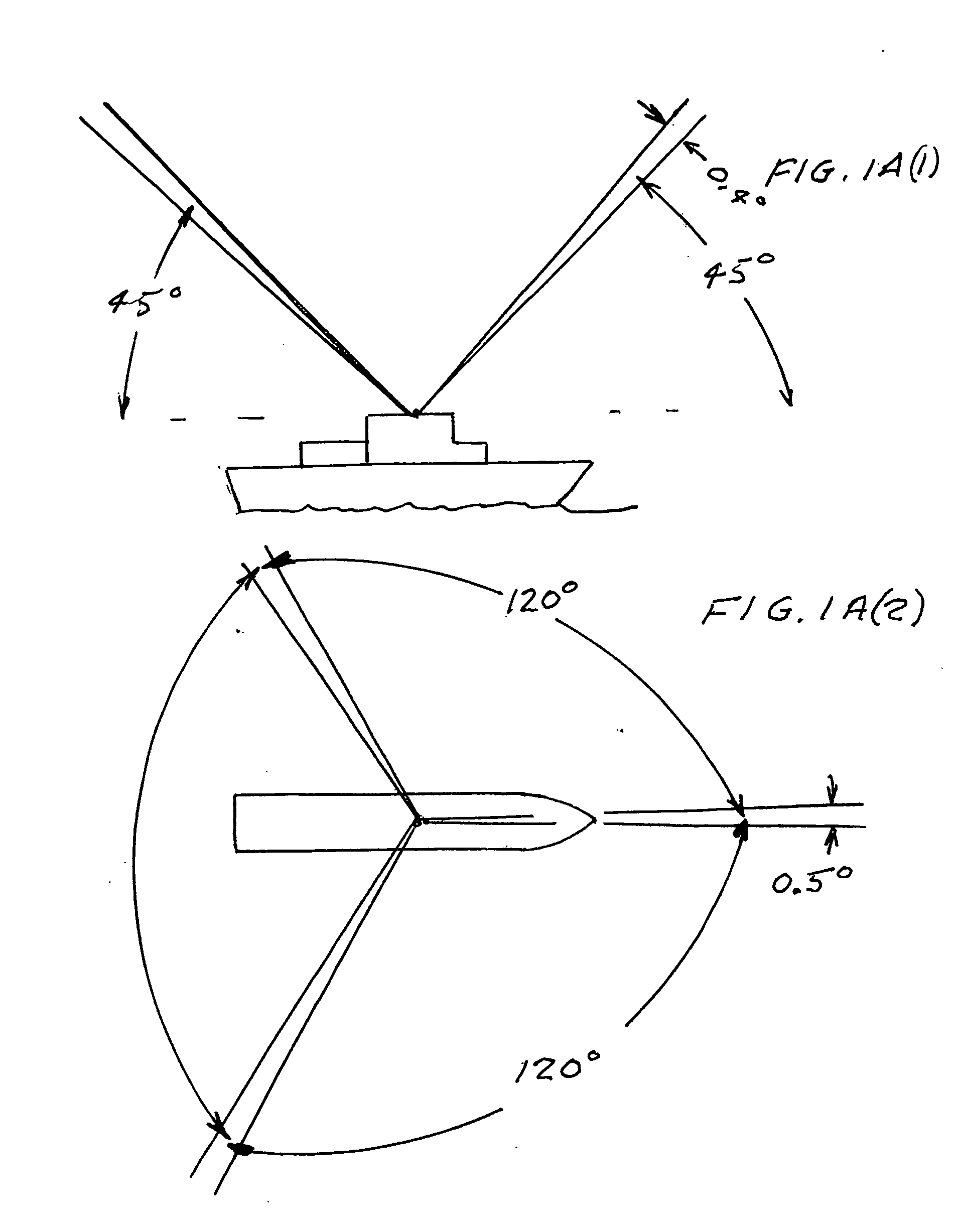
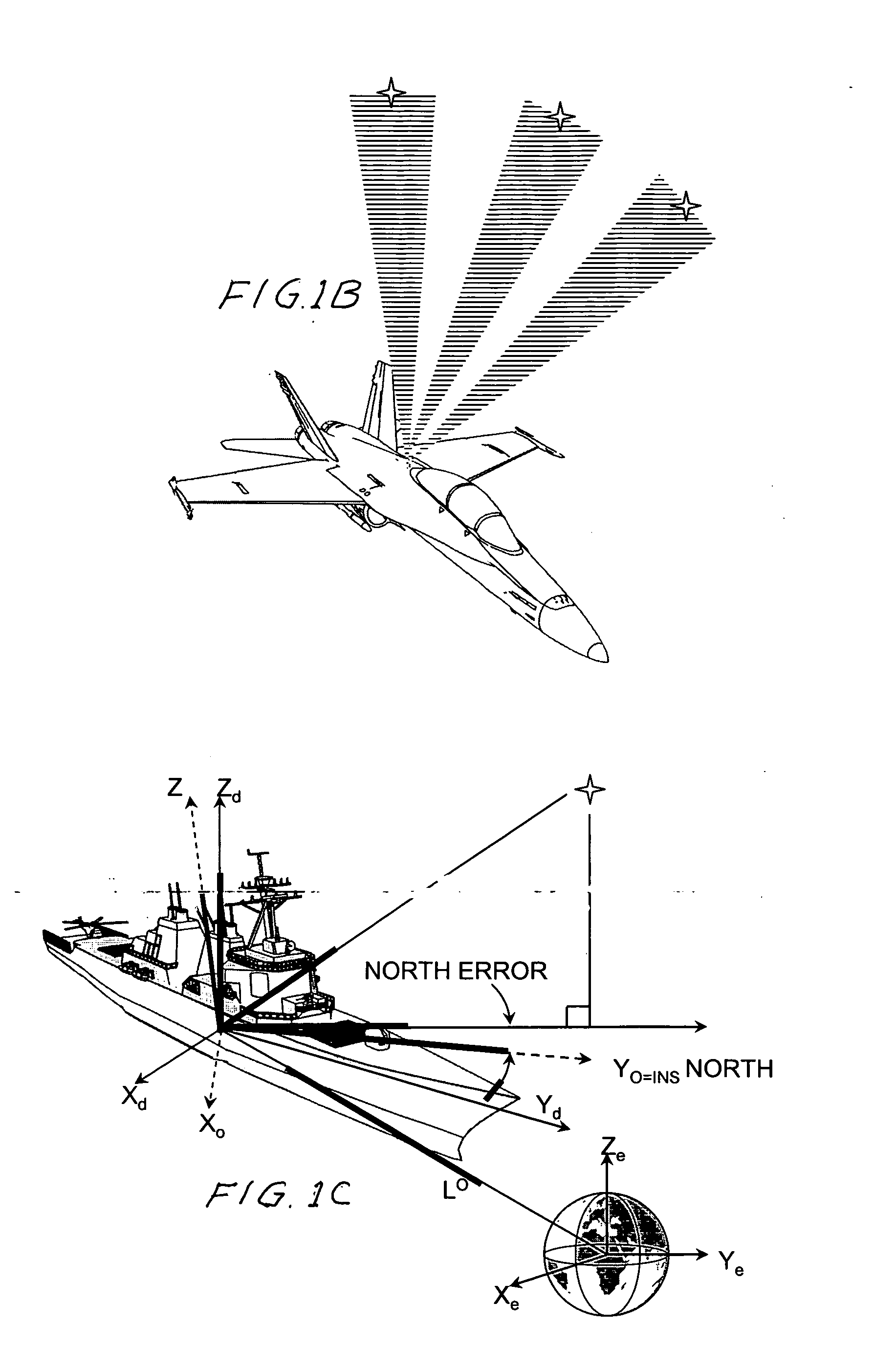
Daytime stellar imager
InactiveUS20060085129A1Turbulence effectIncrease probabilityNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsNavigation by astronomical meansDisplay deviceLongitude
An automatic celestial navigation system for navigating both night and day by observation of K-band or H-band infrared light from multiple stars. A preferred embodiment uses three telescopes with each of the three telescopes rigidly mounted with respect to each other and rigidly mounted on a movable platform such as a ship or airplane with each telescope being directed at a substantially different portion of sky. Telescope optics focuses, onto the pixel array of a sensor, H-band or K-band light from stars in the field of view of each telescope. The system also includes an inclinometer, an accurate timing device and a computer processor having access to cataloged infrared star charts. The processor is programmed with special algorithms to use image data from the infrared sensors, inclination information from the inclinometer, time information from the timing device and the cataloged star charts information to determine positions of the platform. At least two telescopes pointed far enough from the sun detect stars. Direction information from two stars is needed for locating the platform with respect to the celestial sphere. The computer is also preferably programmed to use this celestial position information to calculate latitude, longitude and absolute azimuth, all of which may be displayed on a display device such as a monitor. In a preferred embodiment each of the three telescopes are fixed on a moving ship and views a 0.5×0.4 degree region of the sky for H-band starlight from stars with brightness greater than 6.4 H-band magnitude. Located stars are then compared with star positions from the star catalog within a selected 5×5 degree region of the sky. A correlation of the data from the three telescopic measurements determines the position of the ship to a precision of 30 meters.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
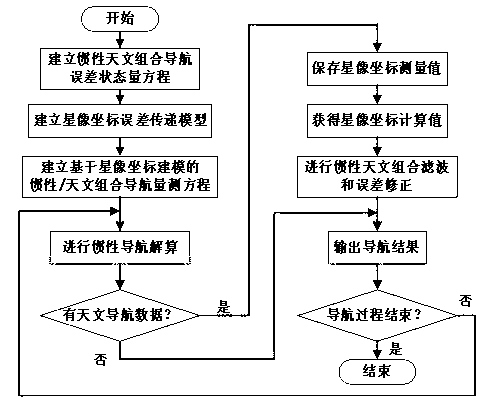
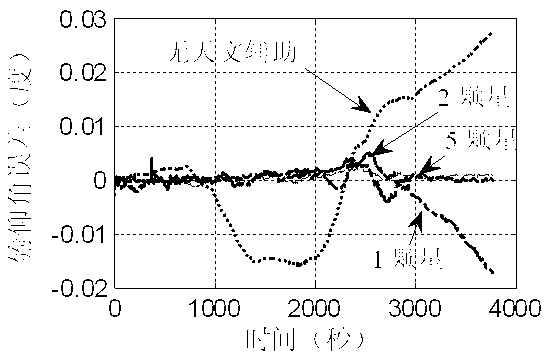
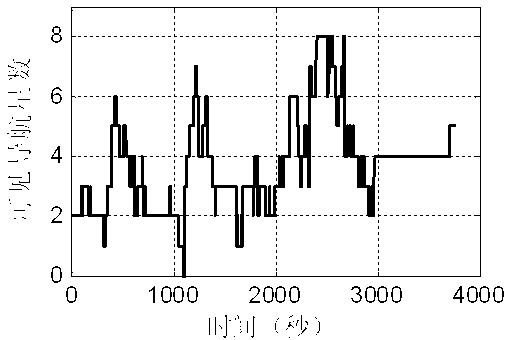
Inertial and celestial combined navigation method based on star coordinate modeling
ActiveCN103063216AIncrease flexibilityImprove navigation performanceNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsNavigation by astronomical meansStar numberComputer science
The invention provides an inertial and celestial combined navigation method based on star coordinate modeling. With the method, according to the difference in observed number of stars, inertial and celestial combination during multi-star observation is automatically realized, and star starlight measurement information application flexibility is improved. When star configurations are substantially deteriorated, characteristics of observation noises inputted into a Kalman filter are maintained stable, such that navigation performance under a situation with substantially reduced available navigation star number during high dynamic flight is improved. Compared with conventional inertial and celestial combined systems without the technology provided by the invention, the method provided by the invention has better adaptability to situation with deteriorated star configurations. Therefore, the method provided by the invention is suitable for engineering applications.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method of processing stone surface
The invention discloses a method for processing a stone surface, which comprises the following processes: the natural stone with a pore is first smoothly milled by a mill. The milled stone is cleanly washed and is dried by a drier or natural wind. A part of the pores is then sealed by a gummed paper according to the needs. The rest pores are filled by the milled powder and then is smoothly milled by the mill. The next process is to tear off the gummed paper in the pore and then a glue solution is coated on the pores. A gold powder or silver powder or other luminous substance is filled on the glue solution. After the glue solution is dried, the surface of the stone is coated by a layer of paint with an ability of butter resistance; finally, a layer of resin is coated on the painted stone surface. After a levigation using the mill, the stone surface is polished and waxed, then the stone with a golden flickering or silver flickering or starlight flicking surface is obtained. The stone manufactured by the process method in the invention has the advantages of simple process, being able to retain the nature characteristic of the natural stone and add the flickering effect.
Owner:DONGGUAN DIANYA FURNITUR
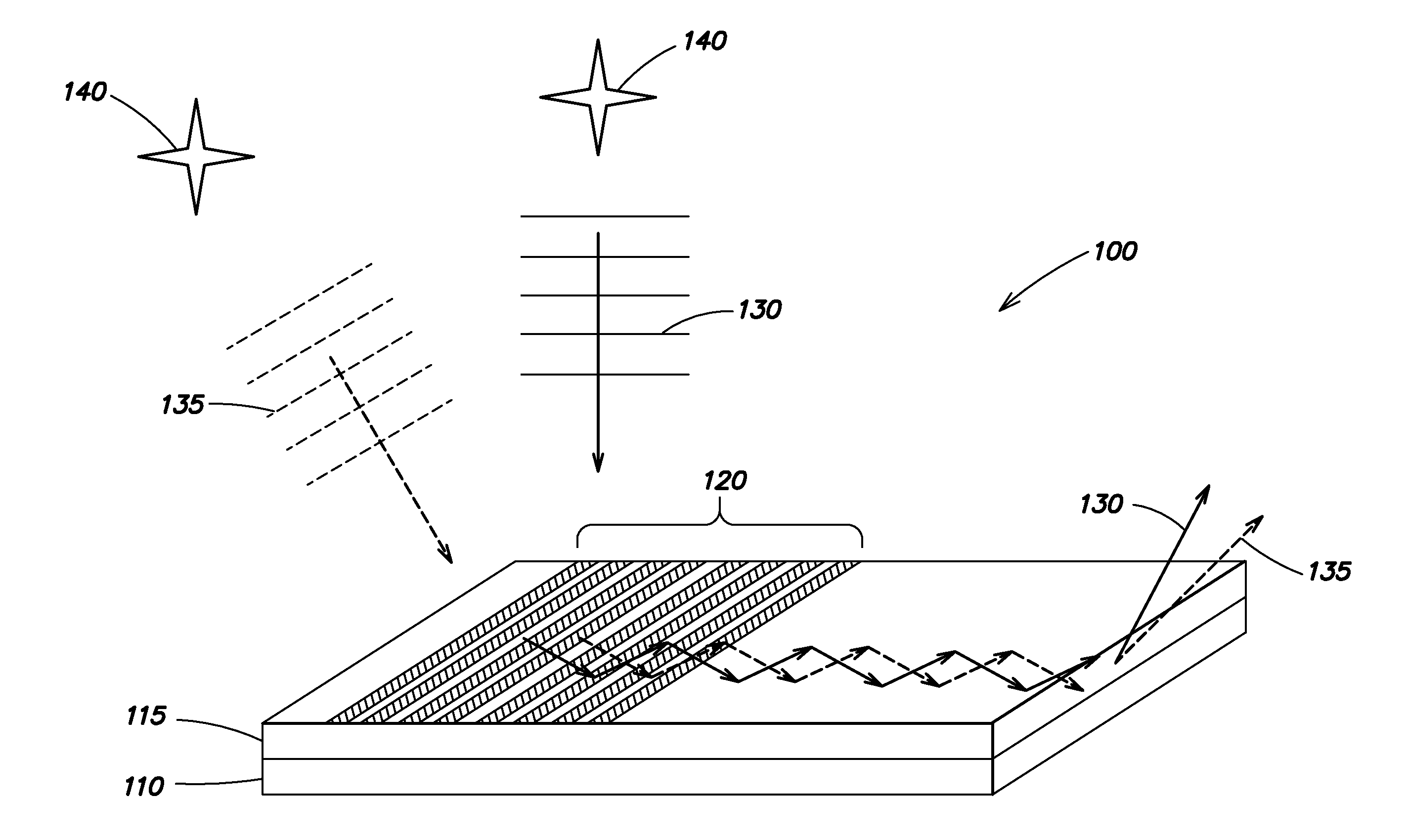
Chip-scale star tracker
ActiveUS20150002854A1Large light collection aperturePhotometry using reference valueInstruments for comonautical navigationStar trackerBroadband
A chip scale star tracker that captures plane-wave starlight propagating in free space with a wafer-thin angle-sensitive broadband filter-aperture, and directs the light into a waveguide structure for readout. Angular information about the star source is determined from characteristics of the starlight propagating in the waveguide. Certain examples include internal propagation-constant-based baffling to elimination stray light from extreme angles.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
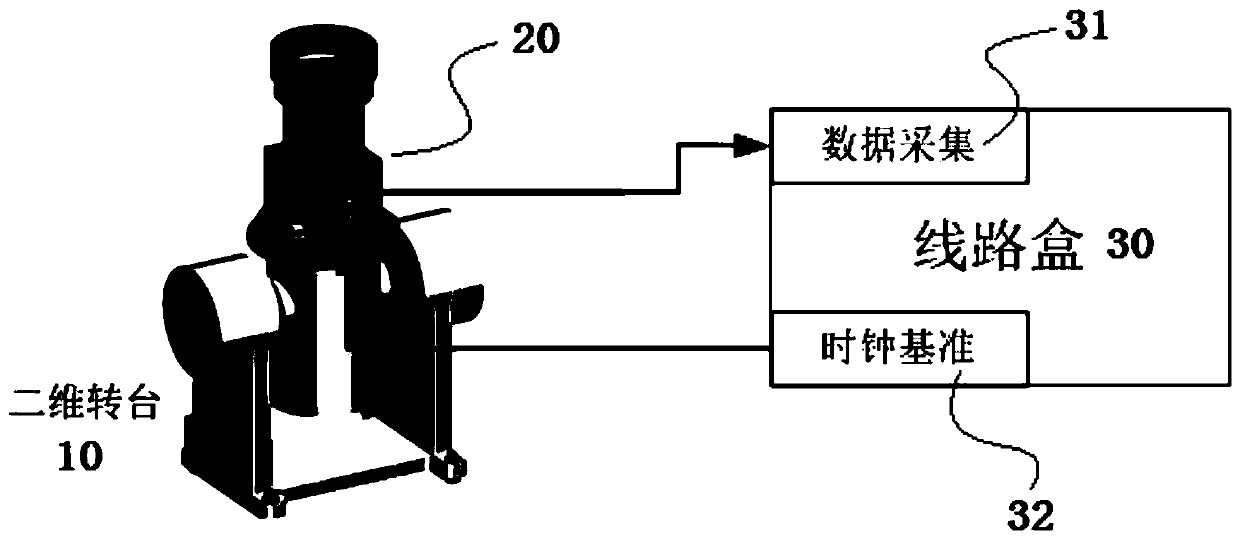
Star sensor calibration device based on external field star observation and star observation calibration method
The invention discloses a star sensor calibration device based on external field star observation and a star observation calibration method thereof. The calibration device comprises a medium-precisionturntable capable of rotating around a zenith, a star sensor arranged on the turntable, and a circuit box connected with the star sensor. The circuit box comprises a data acquisition module and a clock reference module. The calibration method comprises the following steps: step 1, replacing a single-star simulator with starlight, replacing a high-precision turntable with the earth, driving a starsensor through a turntable, simulating a laboratory calibration system, and carrying out a star observation experiment; and step 2, applying a parameter method in laboratory calibration to star observation calibration for data processing; to be specific, constructing an initial alignment error model, compensating an initial alignment error, carrying out nonlinear optimization solution, constructing a distortion correction model, and carrying out least square solution. According to the method provided by the invention, a parameter method in laboratory calibration is applied to star observationcalibration; and especially for a large-field star sensor, the calibration precision is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
Starlight glazed ceramic tile and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a starlight glazed ceramic tile which comprises a green body layer, a ground glaze layer, a chromophoric glaze layer and a dry granular glaze layer from bottom to top. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) pressing powder into a green body, and drying the green body at 145-160 DEG C for 1-1.5 hours; (2) cleaning the surface of the green body, and spraying water to the surface of the green body to wet the surface of the green body; (3) applying ground glaze to the surface of the green body; (4) carrying out silk-screen printing to form the chromophoric glaze; (5) performing ink-jet printing of patterns; (6) applying transparent bright dry granules to the brick surface; (7) putting the green body obtained in the step (5) into a kiln, and firing thegreen body for 40-60 minutes at the temperature of 1150-1200 DEG C; and (8) performing soft polishing on the transparent bright dry granules protruding out of the surface of the fired ceramic tile toobtain the starlight glaze ceramic tile. The protruding surface of the ceramic tile is in a fine and soft matte feeling, but the whole ceramic tile is in a flashing spot starlight effect, the patterndefinition is good, the product is extremely attractive, and the blank of the product on the market is filled up.
Owner:GUANGDONG XINRUNCHENG CERAMICS
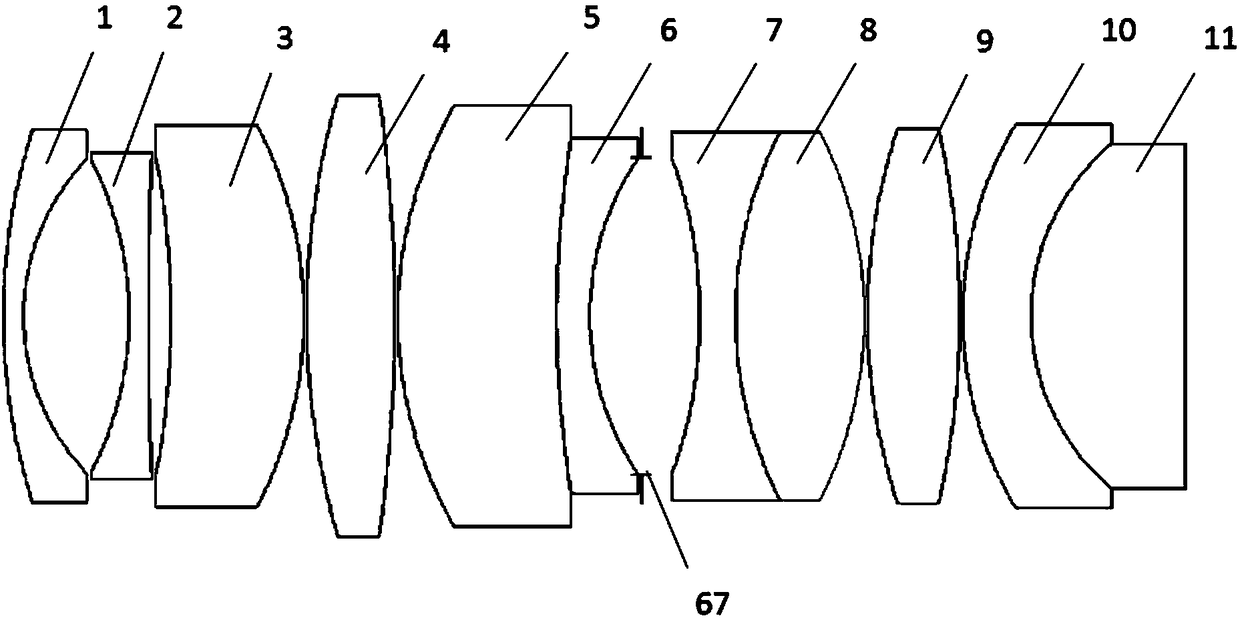
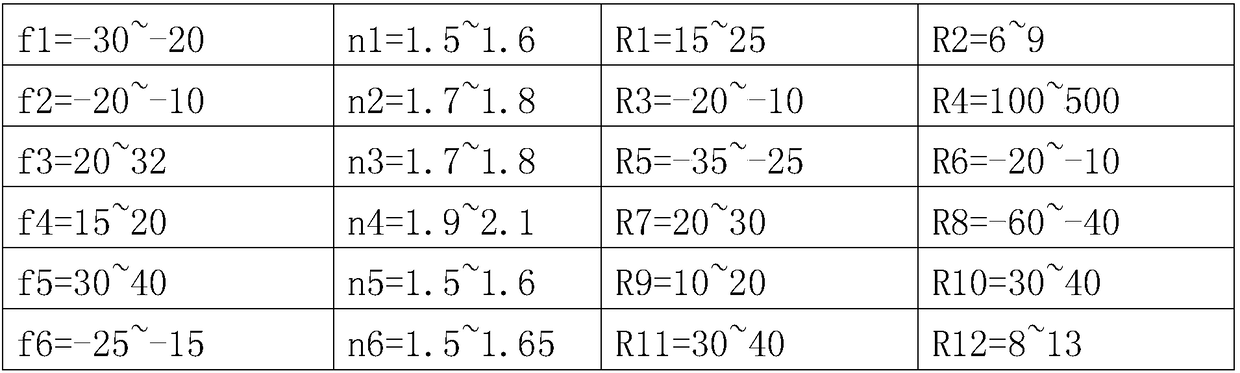
Super star-light-level high-resolution fixed focus lens
PendingCN108563000ASuitable for monitoring needsImprove image qualityOptical elementsCamera lensPrime lens
The present invention provides a super star-light-level high-resolution fixed focus lens which comprises a first lens with convex-concave negative focal power, a second lens with biconcave negative focal power, a third lens with concave-convex positive focal power, a fourth lens with biconvex positive focal power, a fifth lens with convex-concave positive focal power, a sixth lens with convex-concave negative focal power, a seventh lens with biconcave negative focal power, an eighth lens with biconvex positive focal power, a ninth lens with biconvex positive focal power, a tenth lens with convex-concave negative focal power and an eleventh lens with biconvex positive focal power which are orderly arranged from an object side to an image side along an optical axis. 11 specially arranged lenses are adopted, the super star-light-level high-resolution fixed focus lens has a characteristic of ultra large amount of light pass, a wide angle 110 degrees of the field of view angle is supported,and at the same time, the requirements of resolution and imaging can be ensured when the lens is used in an environment of -40 DEG C to 70 DEG C.
Owner:DONGGUAN YUTONG OPTICAL TECH
Wear-resistant antifouling ceramic tile with starlight diamond effect and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111646776ADelicate colorImprove wear resistanceNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesMacromolecular adhesive additivesGlazeMullite
The invention belongs to the technical field of ceramic materials, and particularly relates to a wear-resistant antifouling ceramic tile with a starlight diamond effect and a preparation method of thewear-resistant antifouling ceramic tile. The ceramic tile comprises a green body, ground glaze, surface glaze, an ink jet layer, a starlight glaze layer and a glue layer which are sequentially compounded from bottom to top, wherein the starlight glaze layer is prepared from starlight glaze particles; the starlight glaze particles are prepared from, by mass, 10-15 parts of carborundum, 5-10 partsof mullite, 3-6 parts of aluminum oxide, 20-30 parts of potassium feldspar, 10-20 parts of quartz sand, 3-5 parts of zinc oxide, 3-7 parts of barium carbonate and 8-12 parts of calcined talc. According to the wear-resistant antifouling ceramic tile with the starlight diamond effect, the glaze layer is fine and smooth in color, natural and vivid, good in wear resistance, high in antifouling property, high in strength and excellent in mechanical property, and the surface of the wear-resistant antifouling ceramic tile flashes like diamonds.
Owner:山东狮子王新材料科技有限公司
Decorative light string with blinking lights
A decorative lighting string including blinking or twinkling lights spaced apart by at least three feet and preferably approximately six feet on a light string will create the effect of twinkling starlight or flickering firelight when used as part of a decorative scheme, such as Christmas decorations. This decorative lighting display is especially suited for outdoor use and can be effectively used in deciduous trees after they have lost their leaves. Twinkling lights that emit an illuminate of at least 40 lumens are especially suited for outdoor use. A random, irregular lighting pattern in which the lights do not appear to be connected by a light string provides the illusion of twinkling lights suspended in mid-air in a dark or darkening sky.
Owner:BRILES ROGER DANIEL
Deep Shadow Occulter
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for occulting light. The occulter shape suppresses diffraction at any given size or angle and is practical to build because it can be made binary to avoid scatter. Binary structures may be fully opaque or fully transmitting at specific points. The diffraction suppression is spectrally broad so that it may be used with incoherent white light. An occulter may also include substantially opaque inner portion and an at least partially transparent outer portion. Such occulters may be used on the ground to create a deep shadow in a short distance, or may be used in space to suppress starlight and reveal exoplanets.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO FOUND
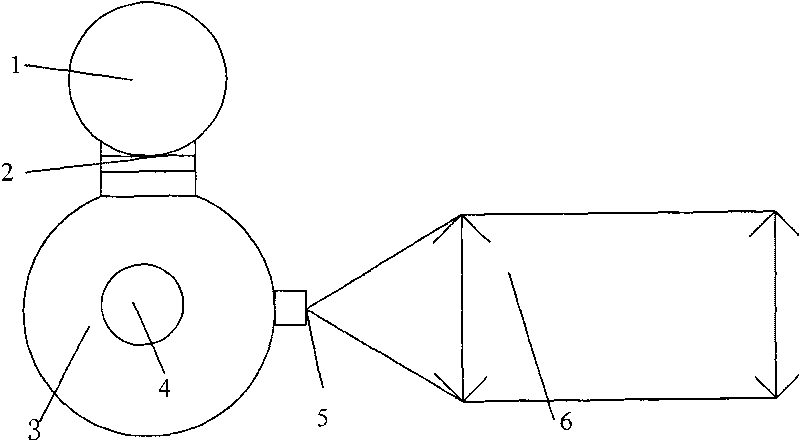
Optical system of small dynamic starlight analog device
InactiveCN1896797ASimple structureReduce weightCosmonautic condition simulationsStructural/machines measurementOptical axisOptic system
A kind of optical system of the minitype dynamic starlight simulator belongs to the space detecting technique field. It includes a lamp-house, a illuminating optical lens, a digital minicrystal and a collimating objective group. The digital minicrystal and the collimating objective group are set at the ray axis of the horizontal beam path. The reflecting surface of the digital minicrystal is towards the collimating objective group and on the focal surface of it. The beam path axis composed of the lamp-house and the illuminating optical lens forms certain angle with the horizontal beam path axis and its extension line goes through the center of the digital minicrystal. The lamp-house emits uniform light through the illuminating optical lens and the light is reflected by the digital minicrystal and is sent out by the collimating objective group along the horizontal ray axis. The structure of the optical system is simple; the volume is small; the weight is light. And it is applied conveniently.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Adaptive satellite selection method and system with celestial body interference
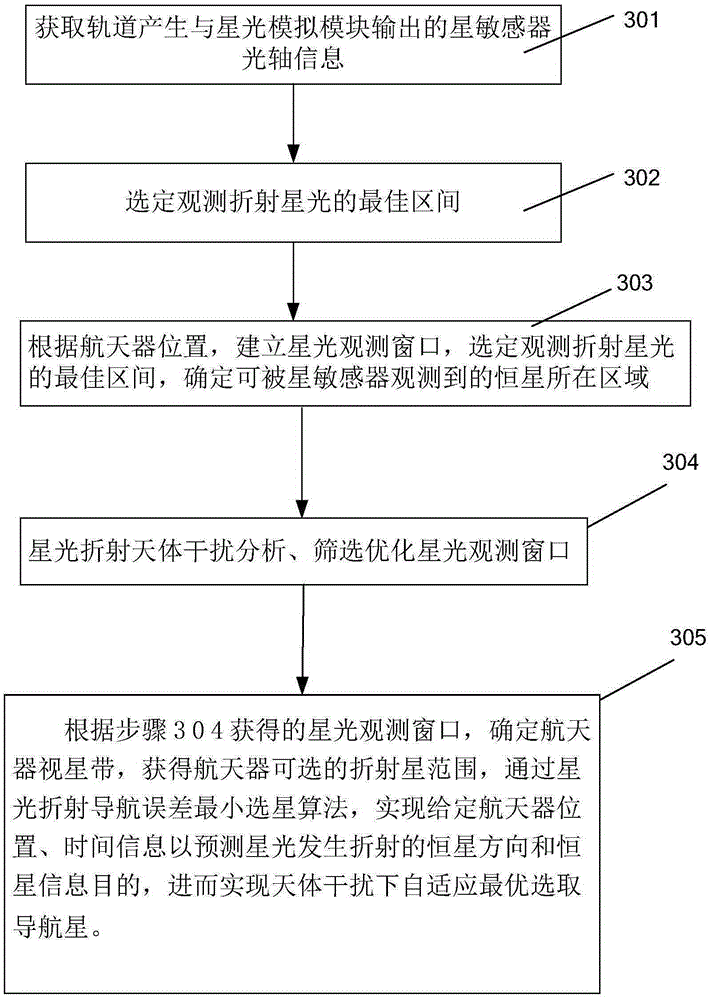
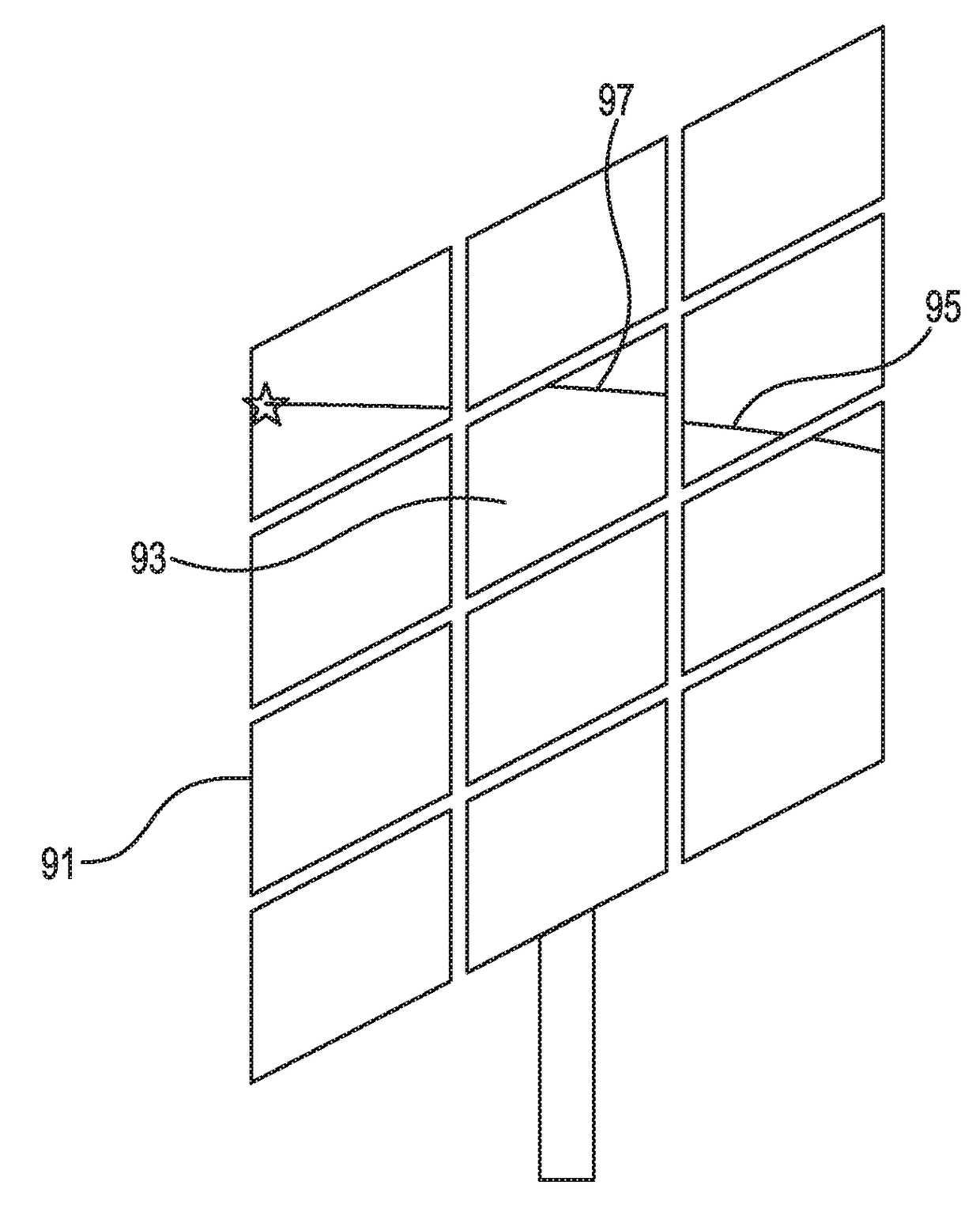
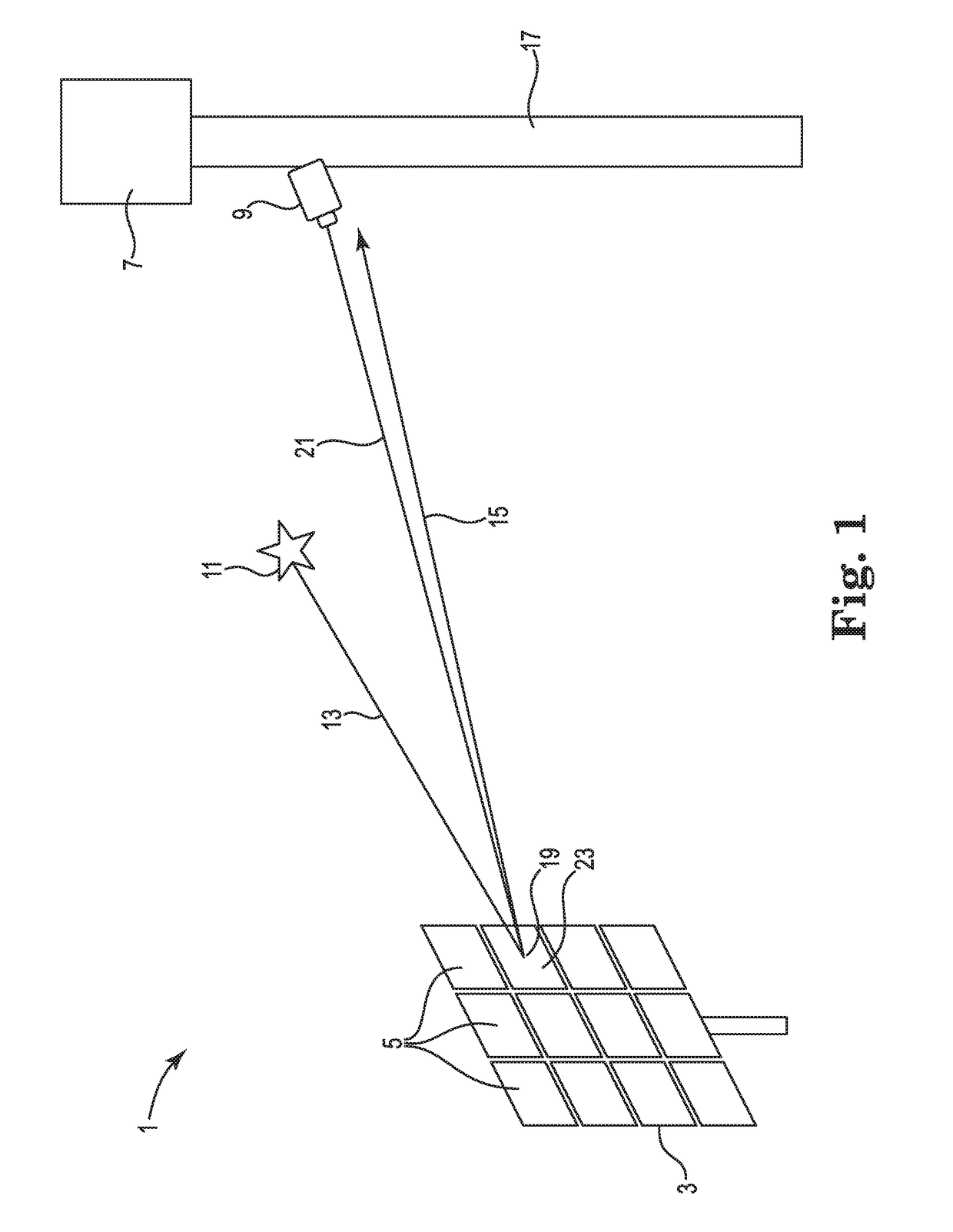
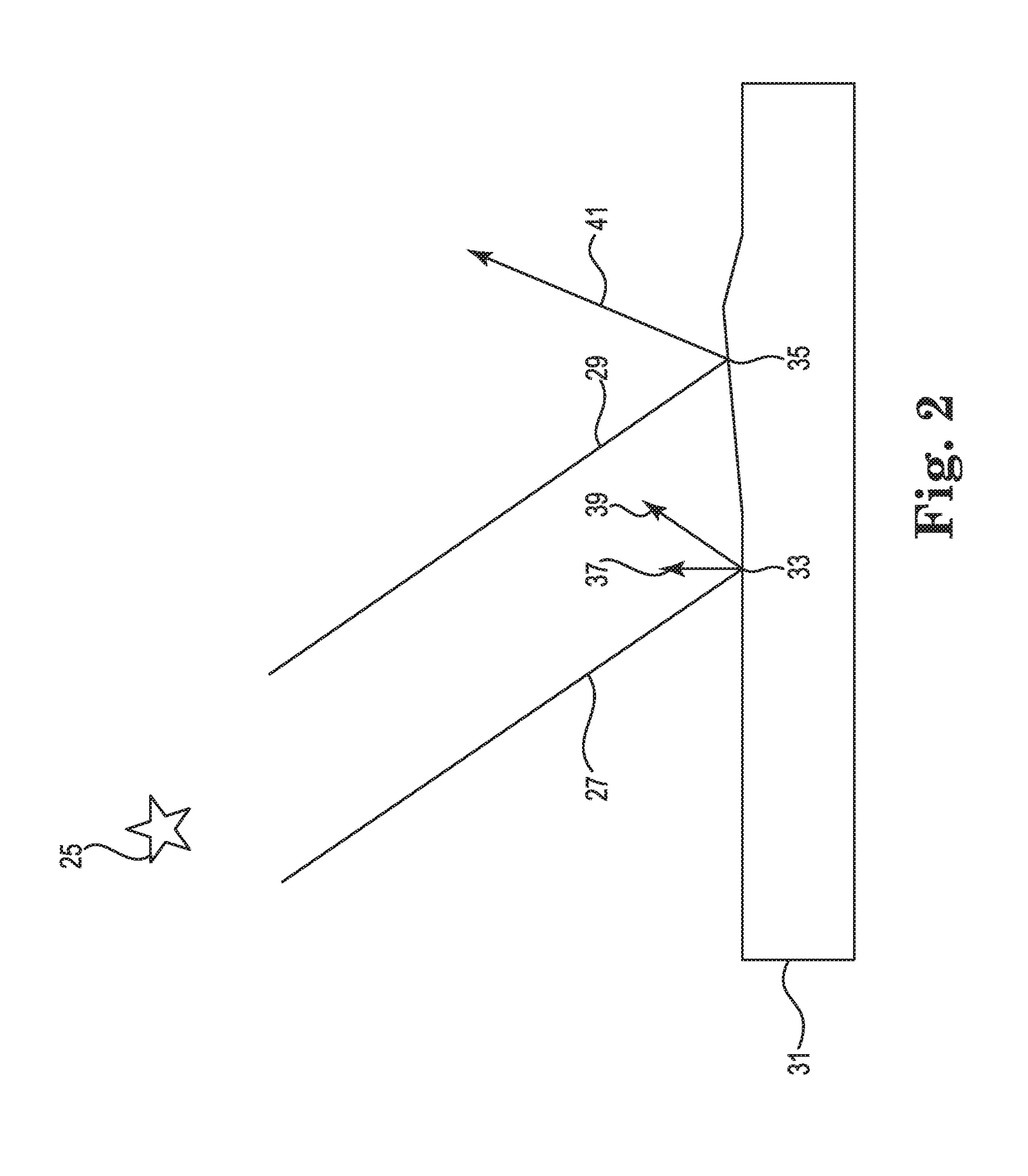
InactiveCN105352500ARealize the function of adaptively selecting navigation starsNavigation by astronomical meansFixed starsTime information
The invention discloses an adaptive satellite selection method and system with celestial body interference. The method comprises: obtaining the optical axis information of a star sensor sent by a starlight analog module and formed by an orbit; selecting a optimum interval of observing the refractive starlight; establishing a starlight observation window according to the position of a spacecraft, determining the area of the fixed star observed by the star sensor; analyzing the starlight refraction celestial body interference to select and optimize the starlight observation window; determining an observing star area of the spacecraft according to the obtained starlight observation window to obtain a selectable refraction star range of the spacecraft, predicting the direction and information of the fixed star of which starlight occurs refraction according to the given position and time information of the spacecraft by using a starlight refraction navigation error minimum satellite selection method, and selecting the adaptive navigational star. The adaptive satellite selection method and system with celestial body interference can exclude the celestial body interference according to the given position and time information of the spacecraft, and can predict the direction and information of the fixed star of which starlight refracting accurately, so that the function of selecting the adaptive navigational star is realized.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Heliostat characterization using starlight
InactiveUS20180299264A1Easy constructionQuickly takenSolar heating energySolar heat collector controllersHeliostatNight sky
The present invention offers an improvement to existing canting, slope error, and / or pointing measurement approaches, by using one or more cameras to observe the reflections of points of light in the firmament, such as the reflections of stars and / or planets as visible within the night sky in the heliostat facets. An illustrative heliostat measurement system comprises a plurality of heliostats, and at least one camera that observes at least one heliostat. The heliostats reflect an image of the firmament that can be observed by the at least one camera. The system further comprises (i) at least one captured image of the firmament reflected from at least one of the heliostats; and (ii) a computer comprising programming that determines a heliostat imperfection from the captured image, wherein the heliostat imperfection is selected from at least one of a slope error, a canting error, and a pointing error.
Owner:SOLARRESERVE TECH
Starlight positioning navigation method based on artificial satellite
ActiveCN113984069AImprove autonomous navigation accuracyAchieving autonomous attitude determinationInstruments for comonautical navigationHigh level techniquesFlight vehicleEphemeris
Owner:BEIJING LINJIN SPACE AIRCRAFT SYST ENG INST
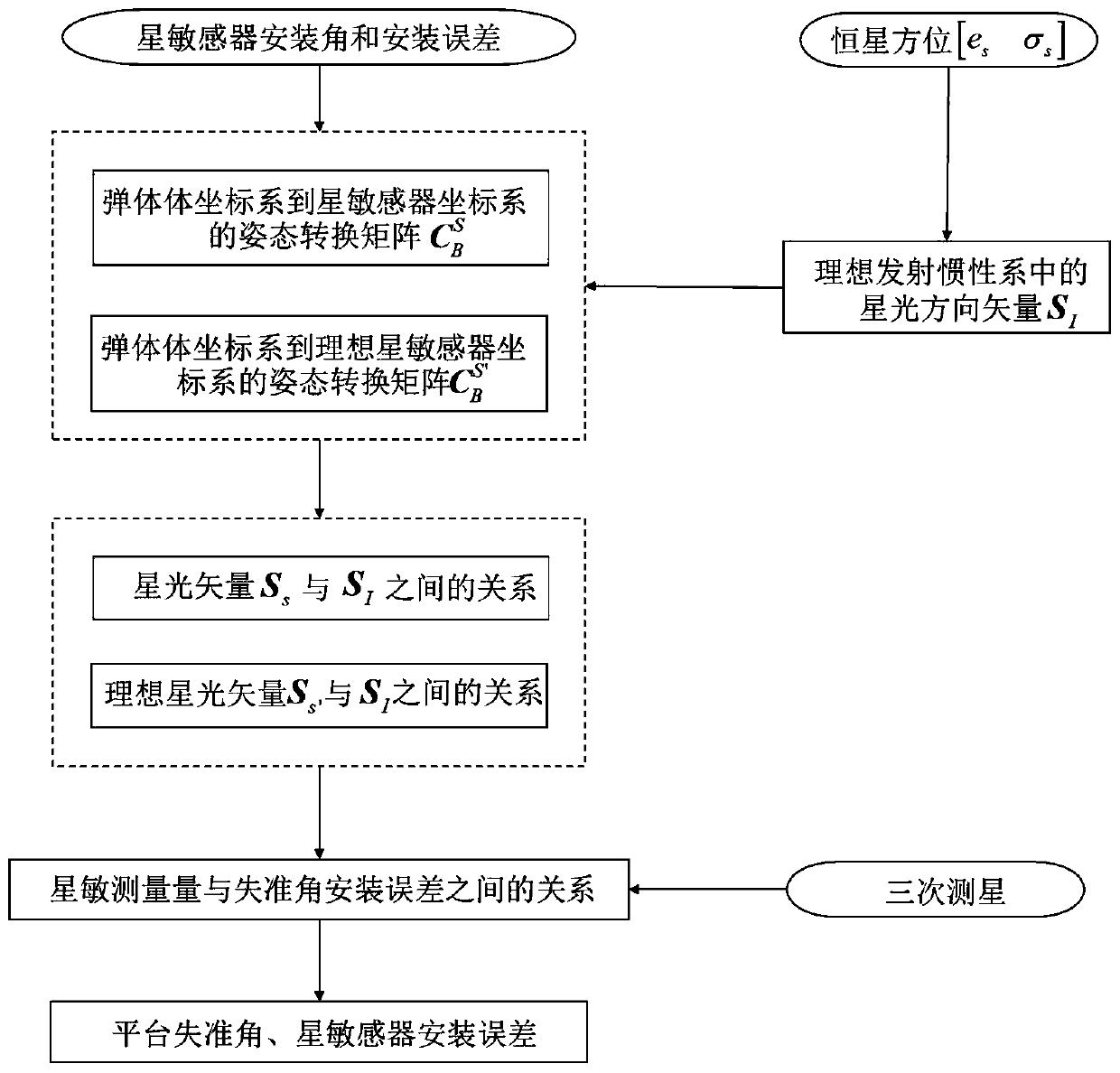
Starlight/inertia integrated navigation and error online calibration method
ActiveCN110672128AImprove navigation accuracyImprove correction accuracyMeasurement devicesFixed starsClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a starlight / inertia integrated navigation and error online calibration method. The method comprises the steps: based on a three-time missile-turning star measurement result ofa star sensor, estimating a platform misalignment angle and a star sensor installation error by utilizing a least square method according to starlight direction unit vectors of three fixed stars in alaunching inertial coordinate system, so that the starlight / inertial integrated navigation precision is improved. According to the method, the misalignment angle of the platform and the installation error of the star sensor are calibrated simultaneously on line, and the correction precision of the star sensor to the inertial navigation system is improved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
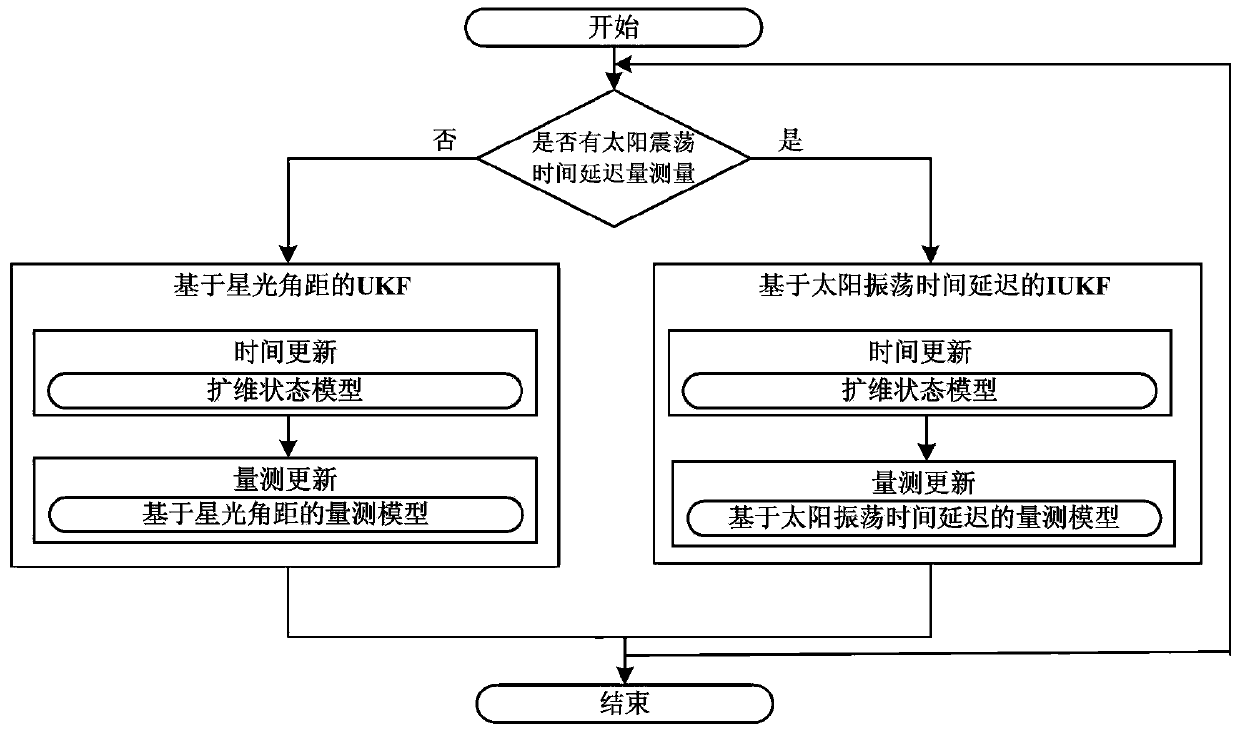
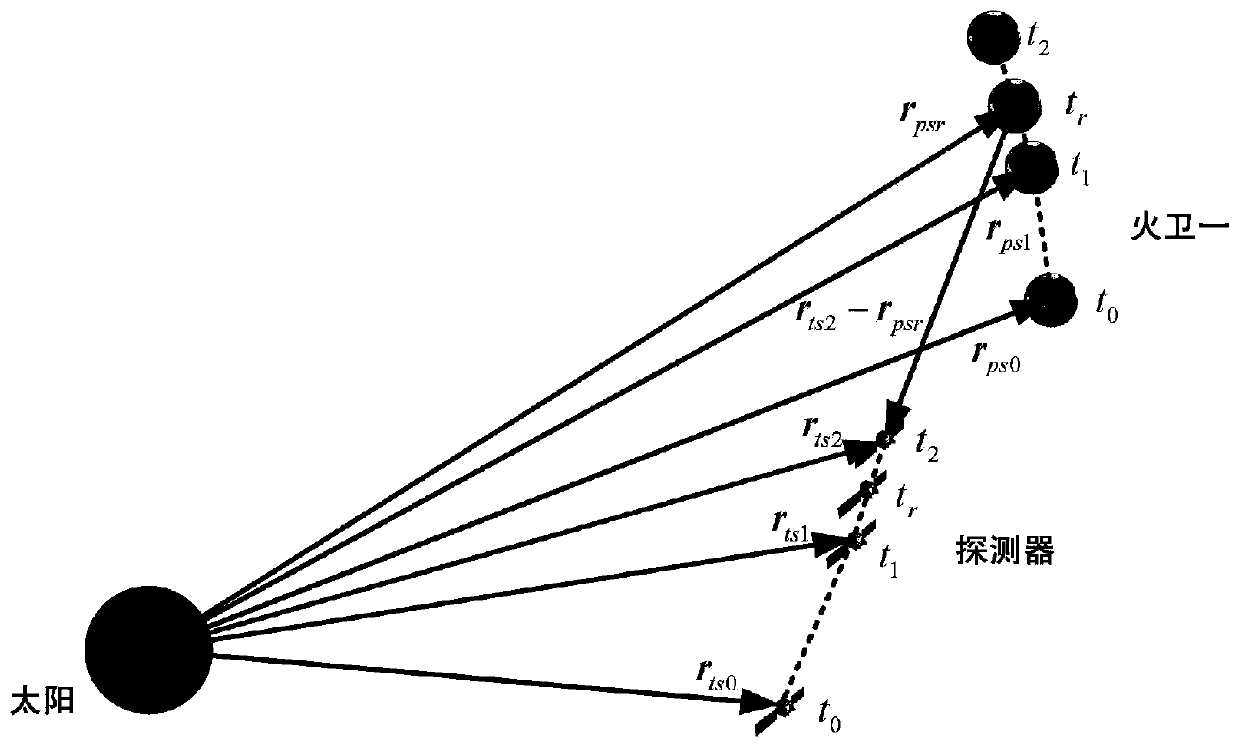
Deep space probe angle measurement and time delay integrated navigation method based on on-line estimation
ActiveCN110940333ARealize online estimationImprove estimation accuracyInstruments for comonautical navigationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsFixed starsCelestial body
The invention provides a deep space probe angle measurement and time delay integrated navigation method based on on-line estimation, and the method comprises the steps: estimating the current positionand speed information of a probe and a reflection celestial body according to the orbit dynamics, and building a system state model through employing the current position and speed information as a system state quantity; obtaining starlight angular distance measurement between the detector and the reflection celestial body as well as between the detector and the background fixed star by using anangle measurement sensor, and establishing a starlight angular distance measurement model; respectively observing the direct sunlight and the reflected sunlight reflected by the reflection celestial body by using two atom frequency discriminators so as to obtain time delay measurement, and establishing a time delay measurement model; obtaining state estimation and error covariance estimation through implicit unscented Kalman filtering, correcting the actual position and speed information of the reflection celestial body, then obtaining the actual position and speed information of the detector,and achieving detector navigation. The influence of the ephemeris error of the reflection celestial body on the navigation precision is inhibited, and the autonomous navigation precision of the detector is improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for artificially breeding spathiphyllum
ActiveCN102326510AEnsure consistencyGuaranteed stabilityPlant genotype modificationSeedlingTissue culture
The invention relates to a method for artificially breeding spathiphyllum. The method comprises the following steps of: hybridizing Jesus No.2 and spathiphyllum starlight which are used as parents to obtain seeds in a generation F1; sowing the seeds in the generation F1; comparing and eliminating the produced seedlings in the whole growth process, screening excellent individual plants suitable for market prospect, wherein the individual plant has hybridizing advantages of the parents; carrying out tissue culture rapid clonal propagation on the selected excellent individual plants, finally obtaining seedlings with consistent characteristics, and carrying out batch trial planting to obtain a variety with characteristics consistent with these of the optimized individual plants, same with these of the optimized mother plant of the generation F1, thus the selected variety is confirmed to form a new variety, and consistence and stability of all plant lines are ensured through the vegetativepropagation of the individual plant.
Owner:SUNSHINE HORTICULTURE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com