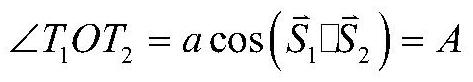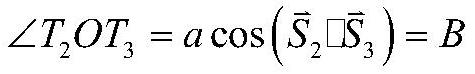Starlight positioning navigation method based on artificial satellite
A positioning navigation and artificial satellite technology, applied in the field of navigation, can solve problems such as the inability to measure carrier position information, and achieve the effects of improving the accuracy of autonomous navigation, high reliability, and high economy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0055] The present invention will be further elaborated below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
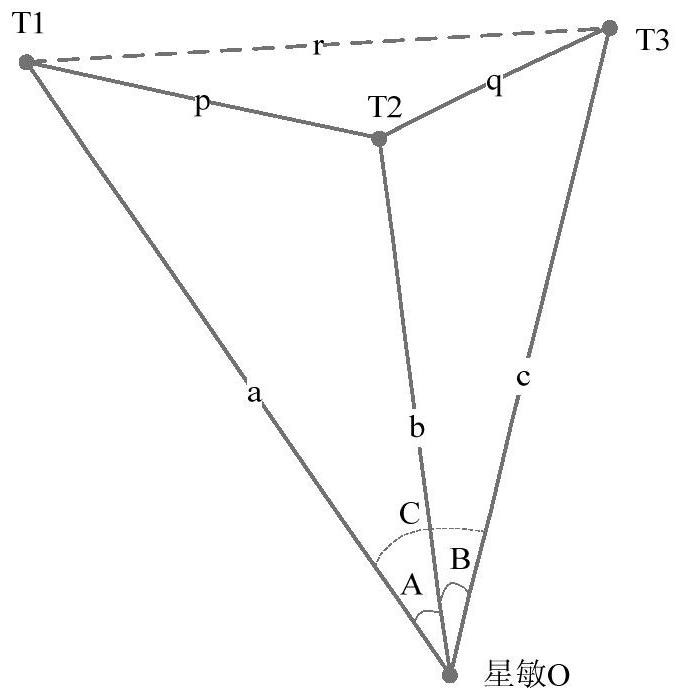
[0056]The present invention uses the star sensor to observe multiple satellites, and combines the satellite orbit data provided by the satellite ephemeris to calculate the relative distance between the satellites; uses the star sensor to measure the unit direction vector of each satellite relative to the star sensor, and calculates the distance between the satellites. Vector included angle; calculate the relative distance between the star sensor and multiple satellites; calculate the position of the star sensor itself according to the satellite orbit data and the relative satellite distance, so as to realize autonomous positioning.
[0057] Such as figure 1 Shown is a schematic diagram of starlight positioning and navigation based on artificial satellites. The satellite-based starlight positioning and navigation method realizes high-precision autonomous ranging throu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com