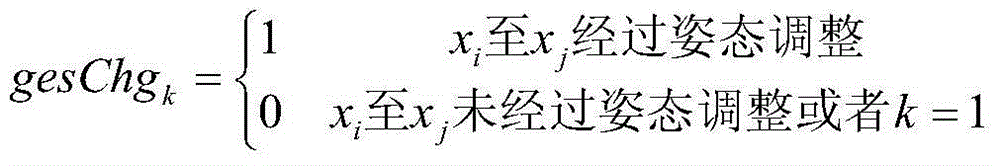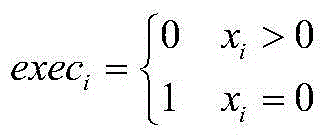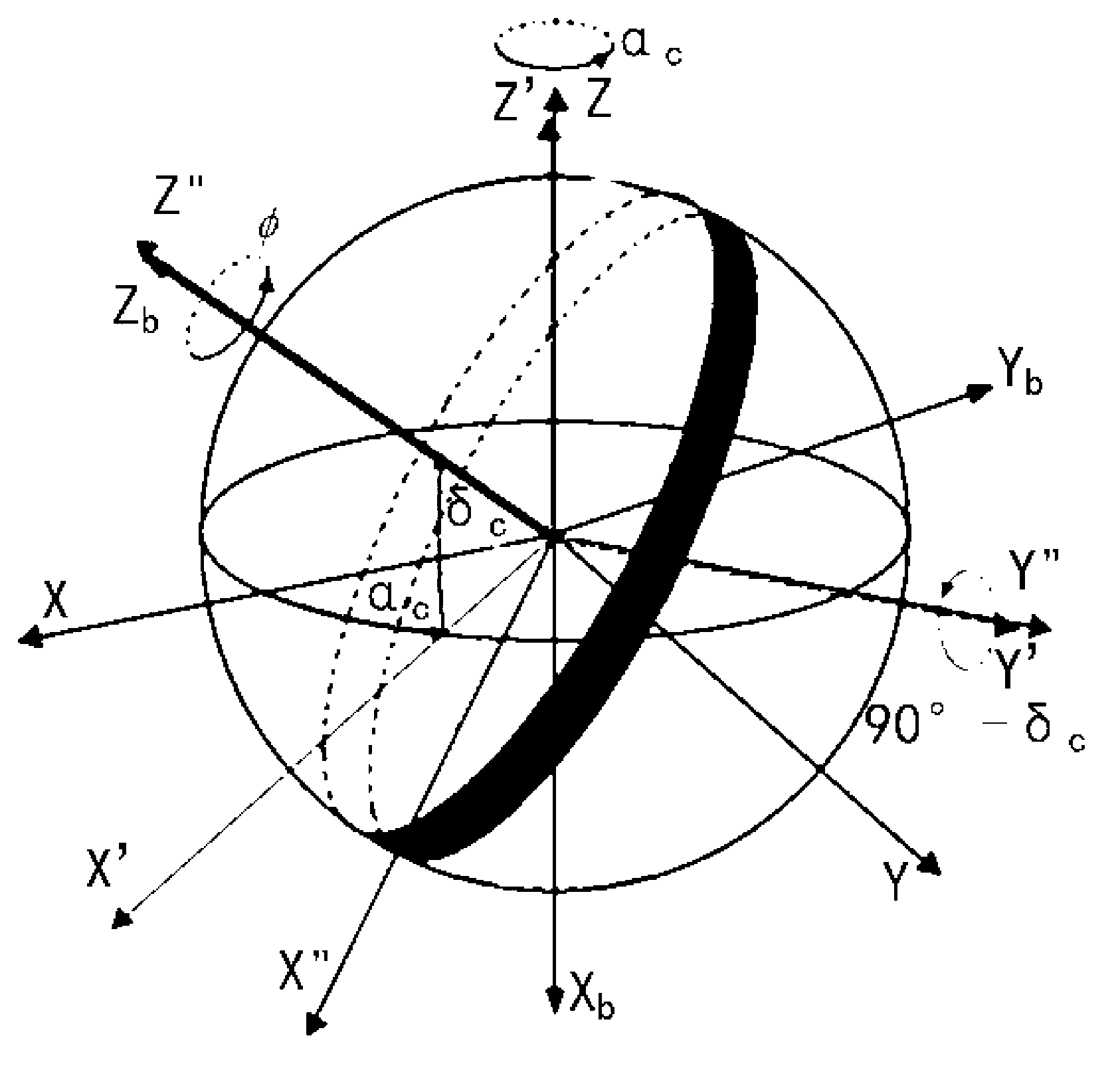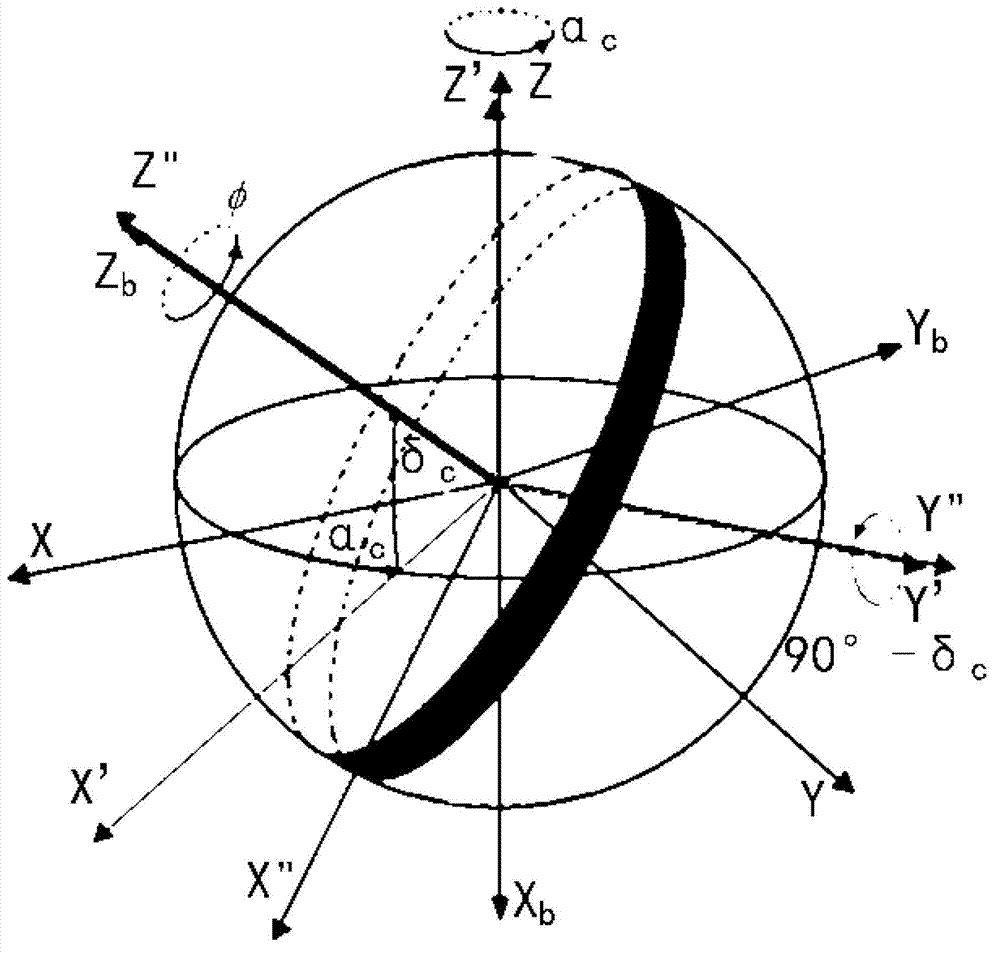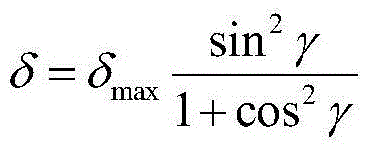Patents
Literature
147 results about "Celestial sphere" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
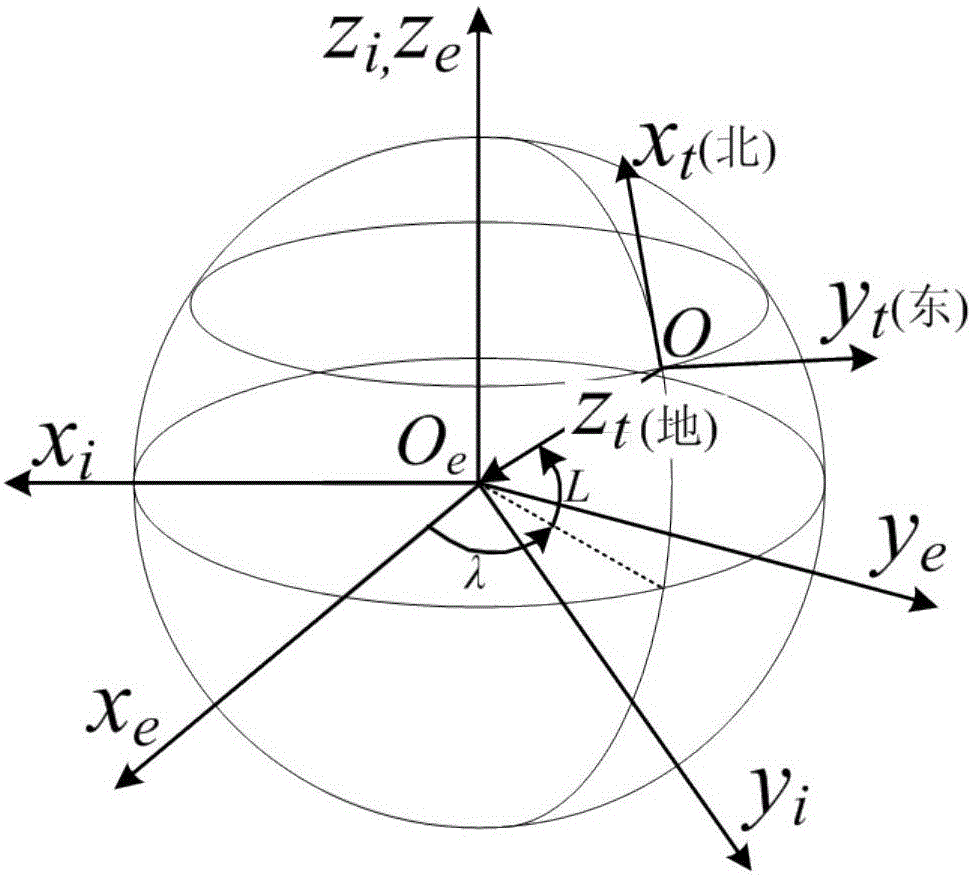
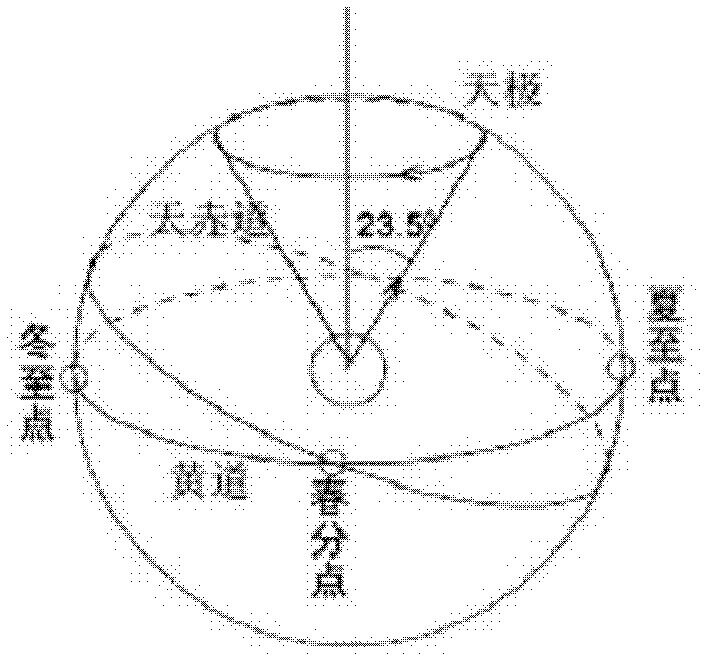
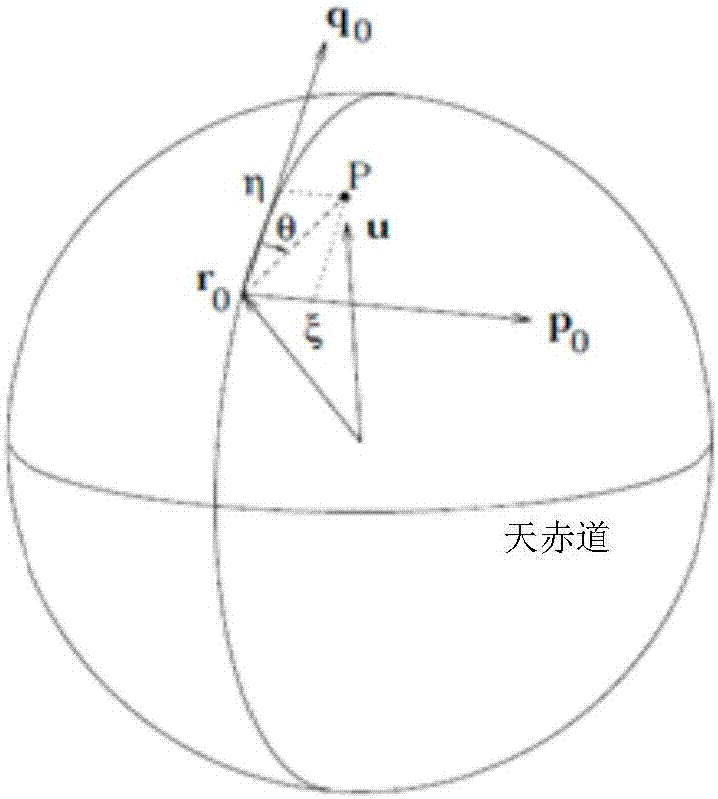
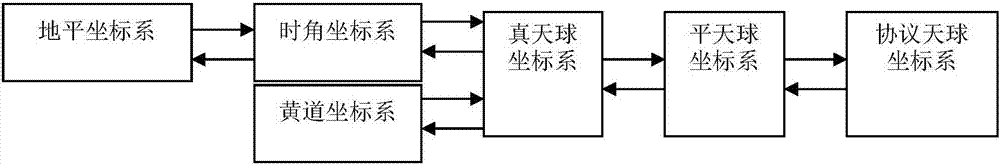
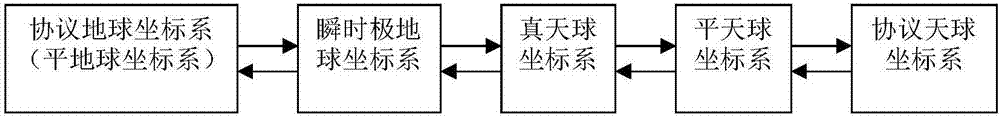
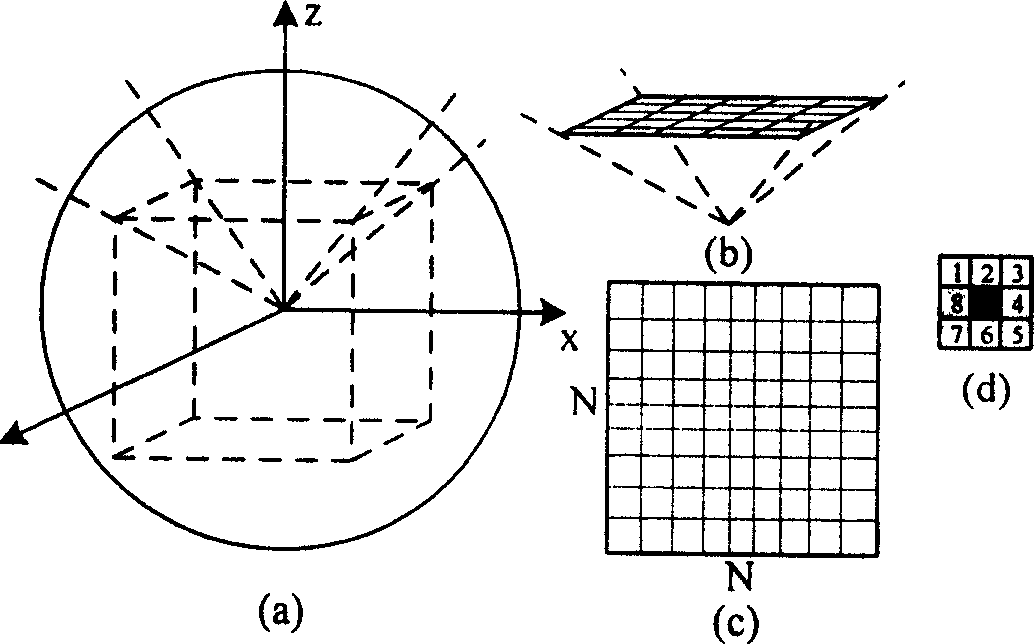
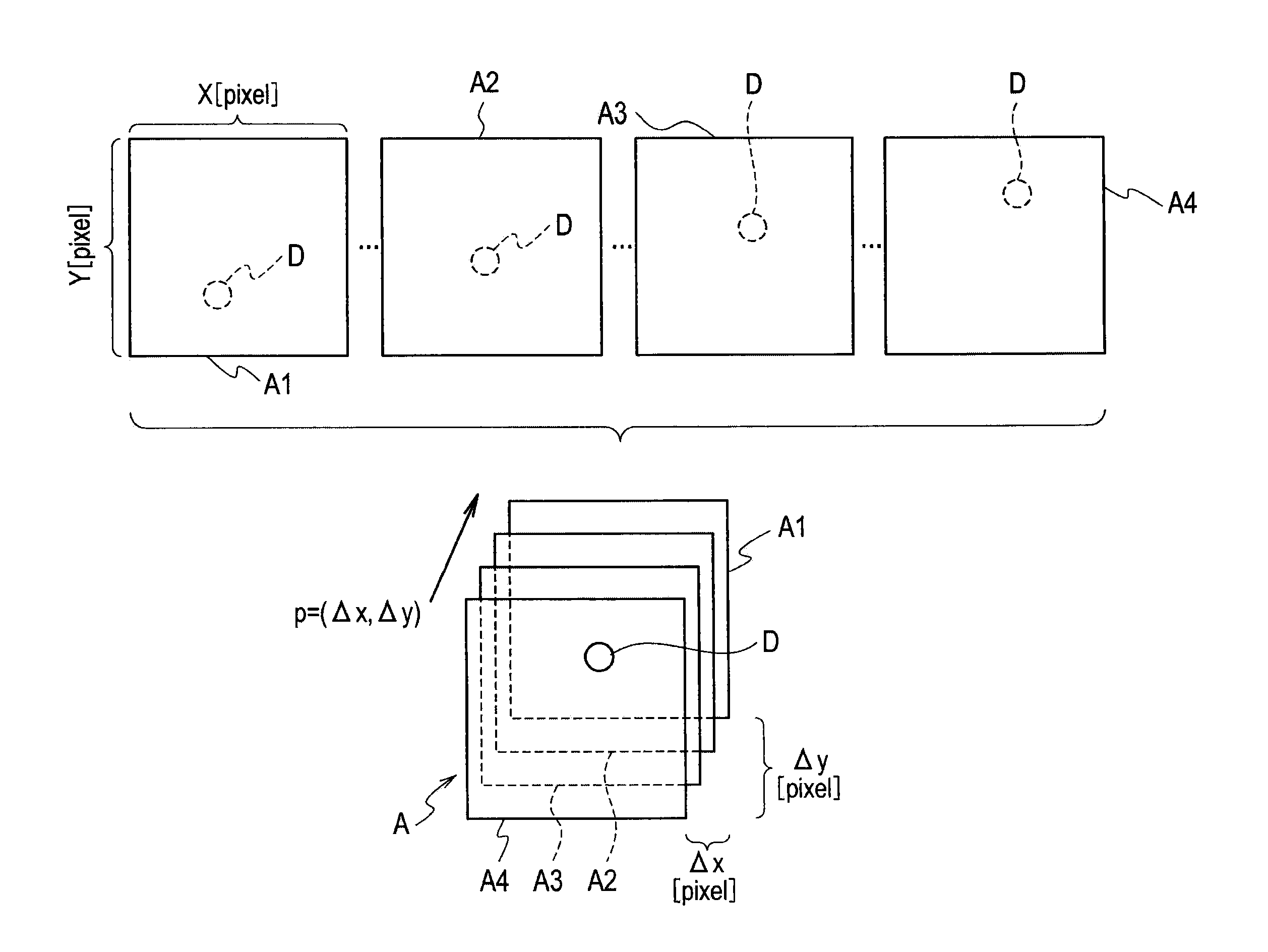
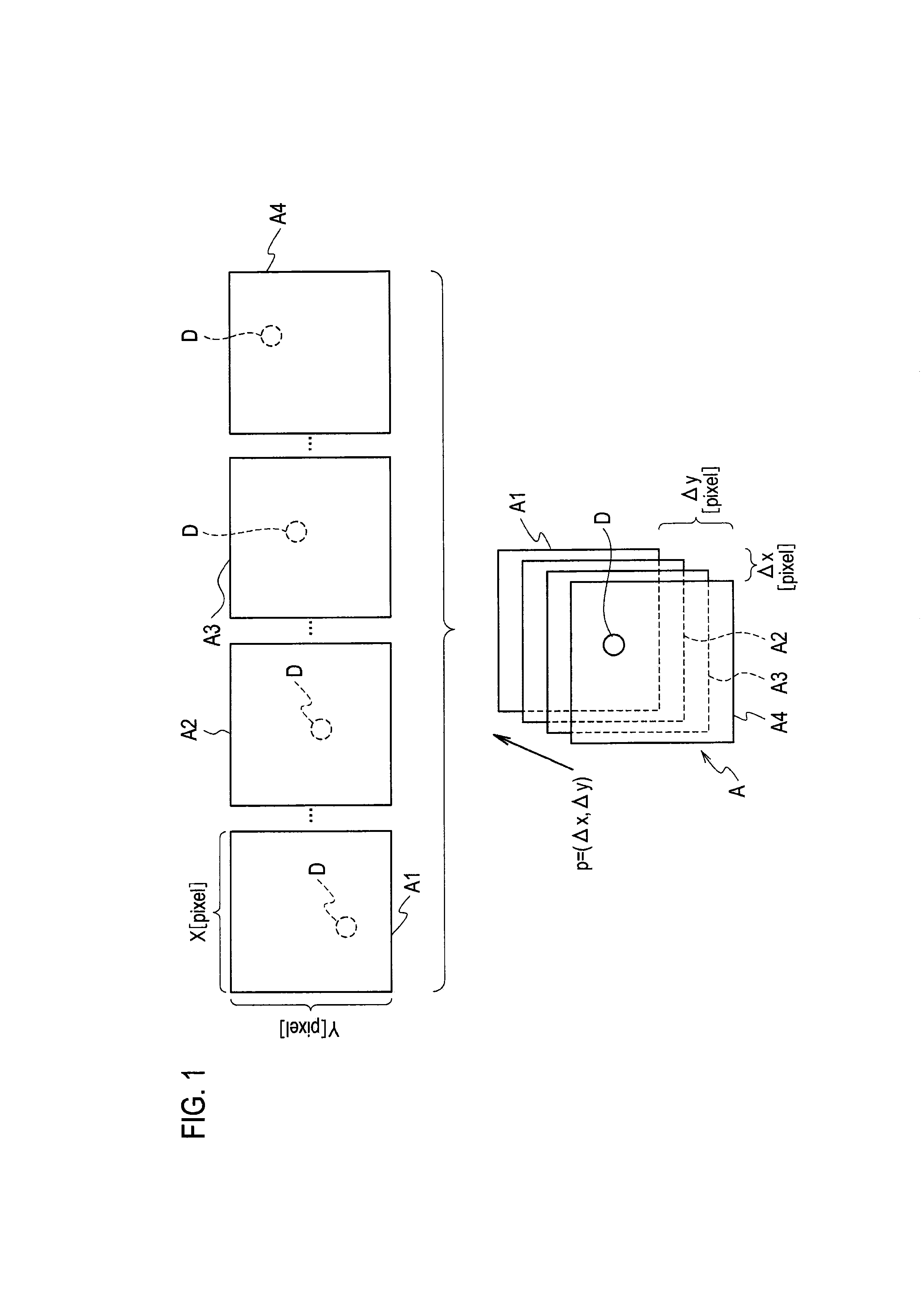
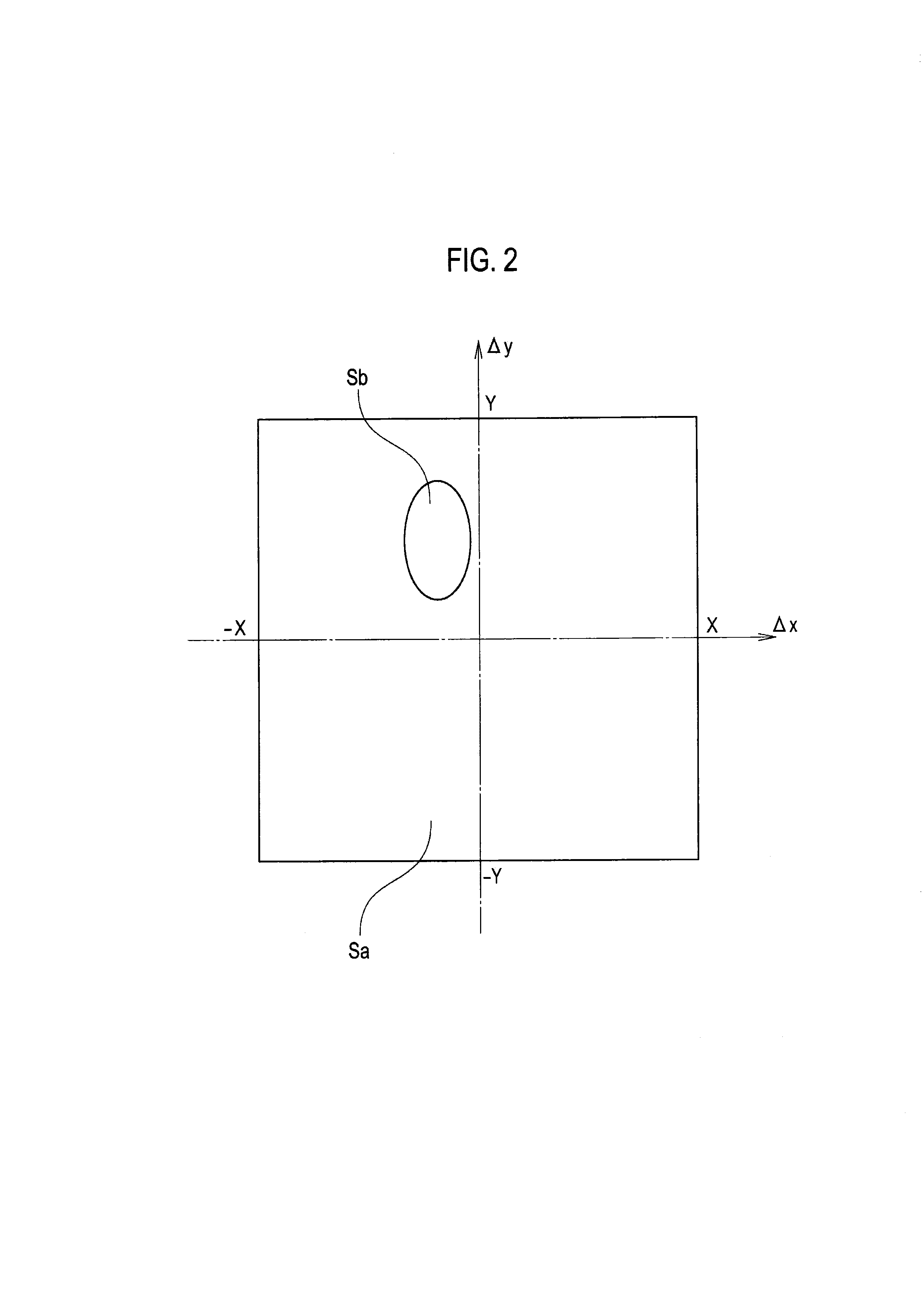
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, which may be centered on Earth or the observer. If centered on the observer, half of the sphere would resemble a hemispherical screen over the observing location.
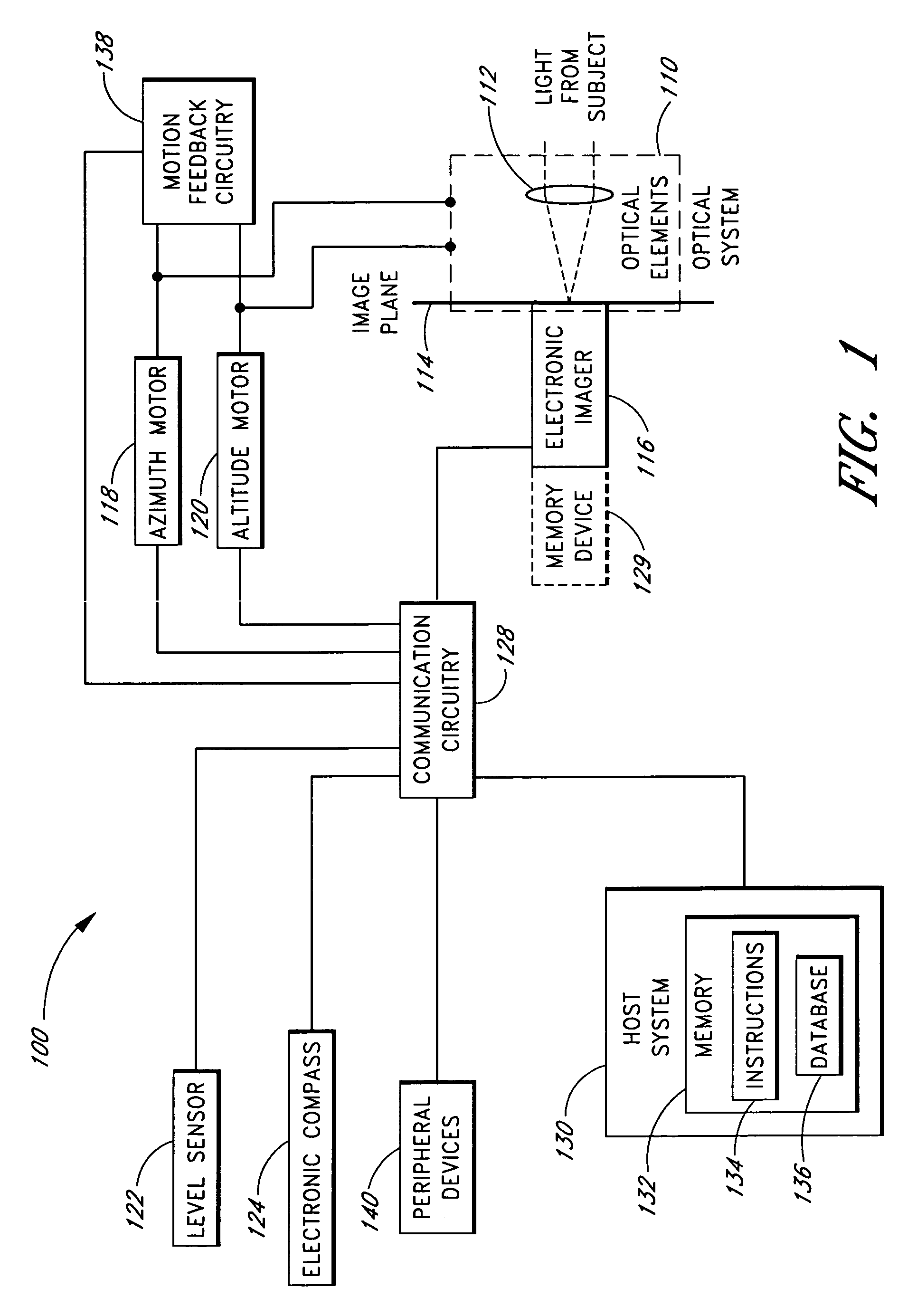
Daytime stellar imager
InactiveUS7349804B2Increase probabilityHighly preventive effectReactors manufactureNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsDisplay deviceLongitude
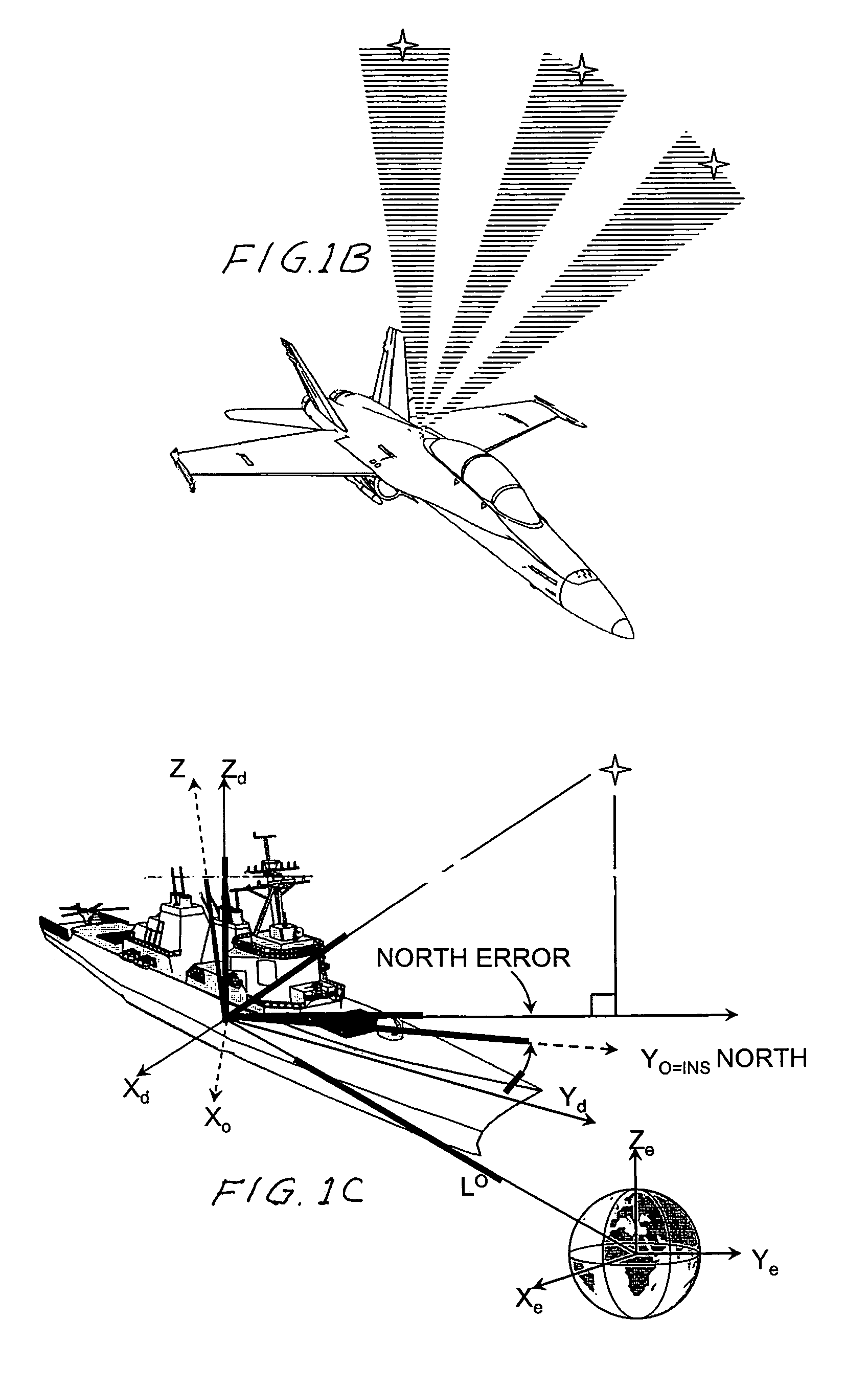
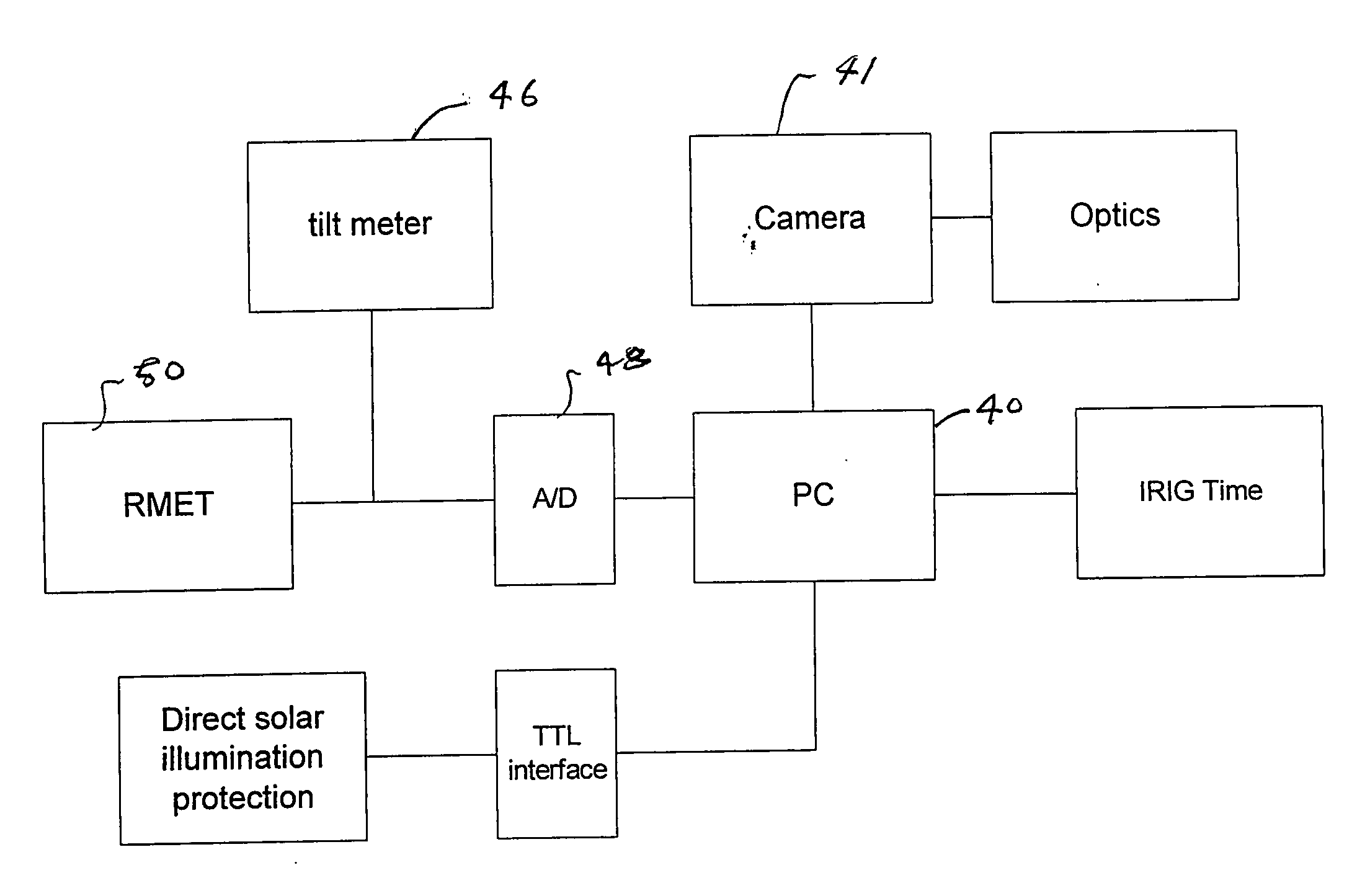
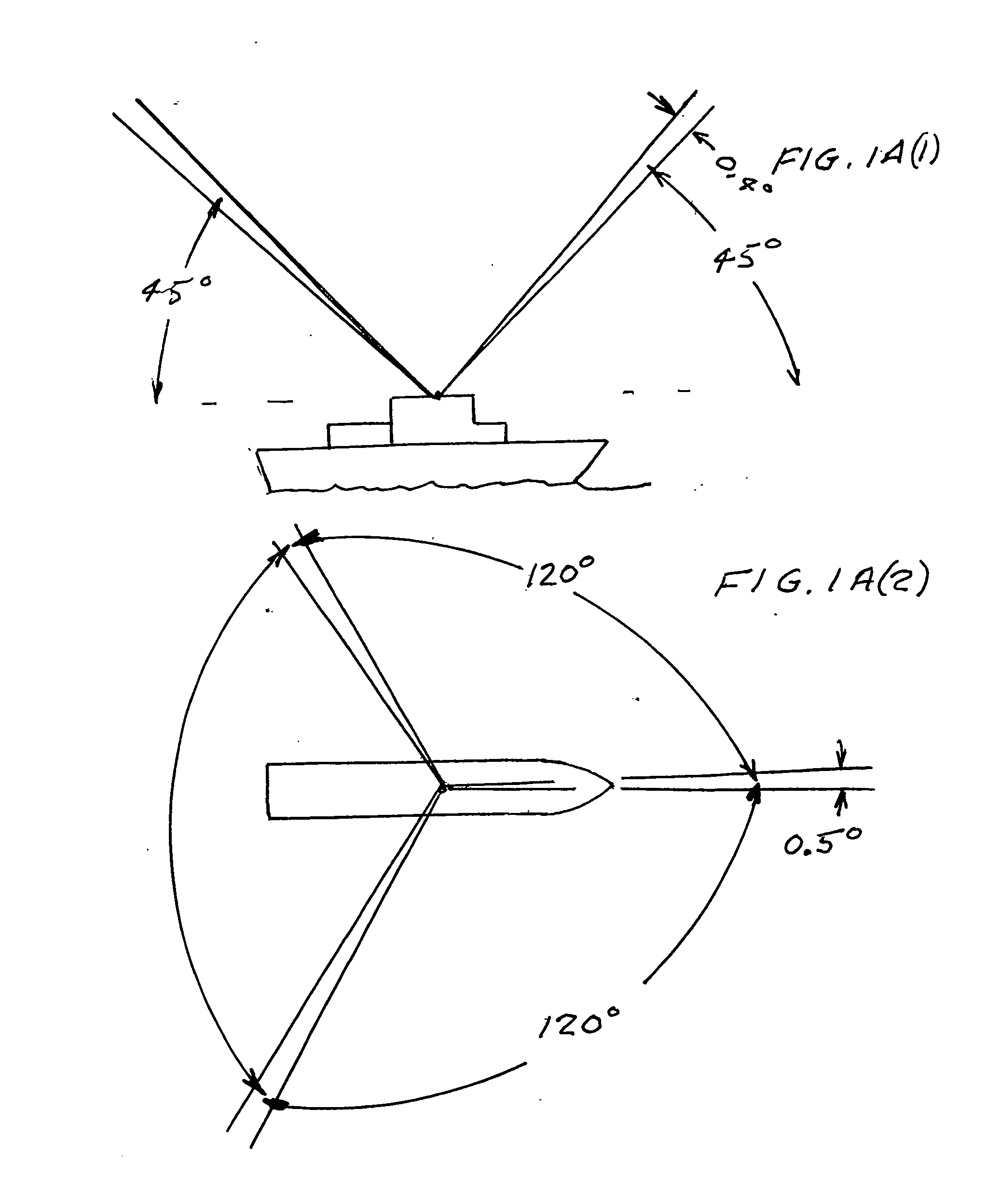
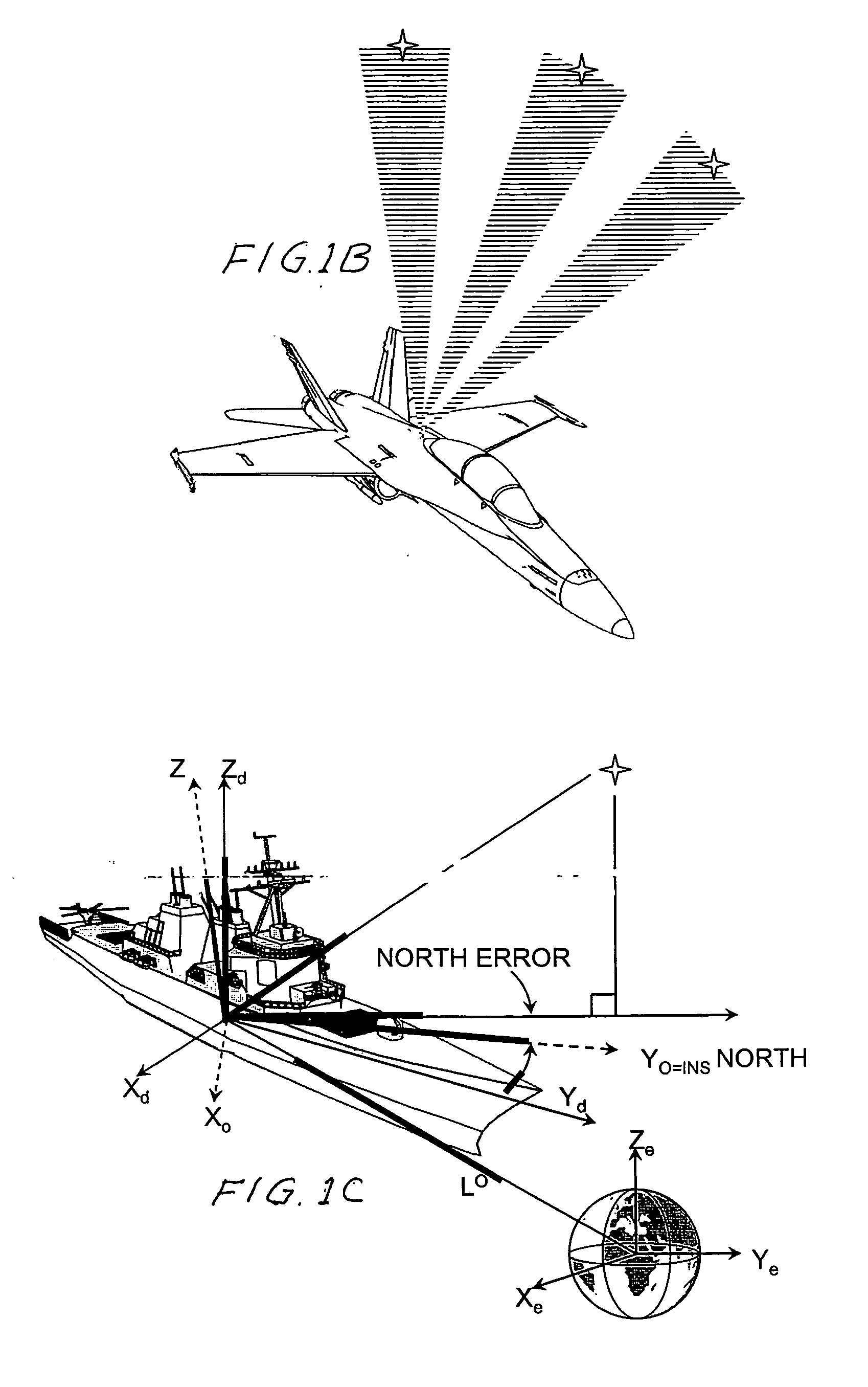
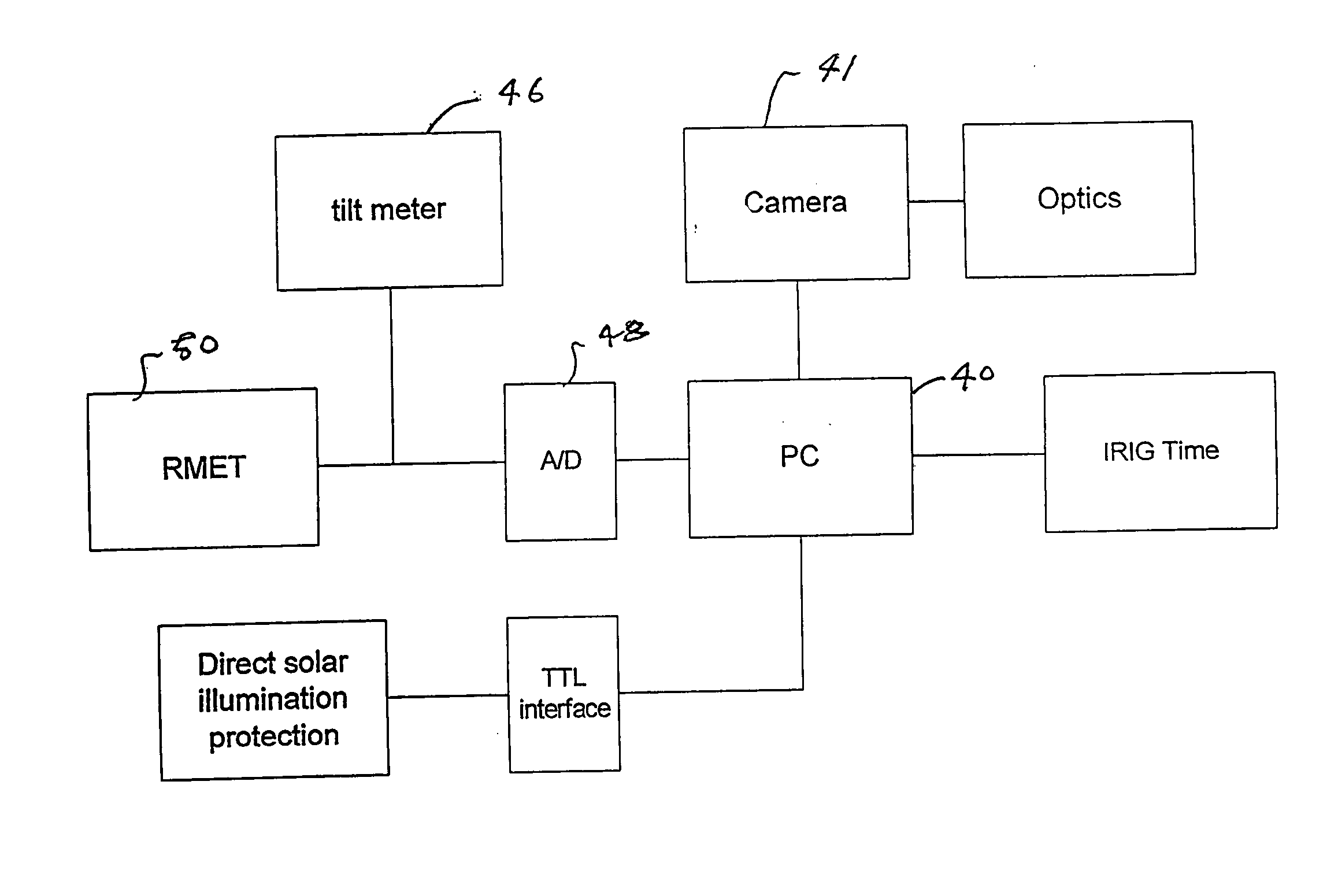
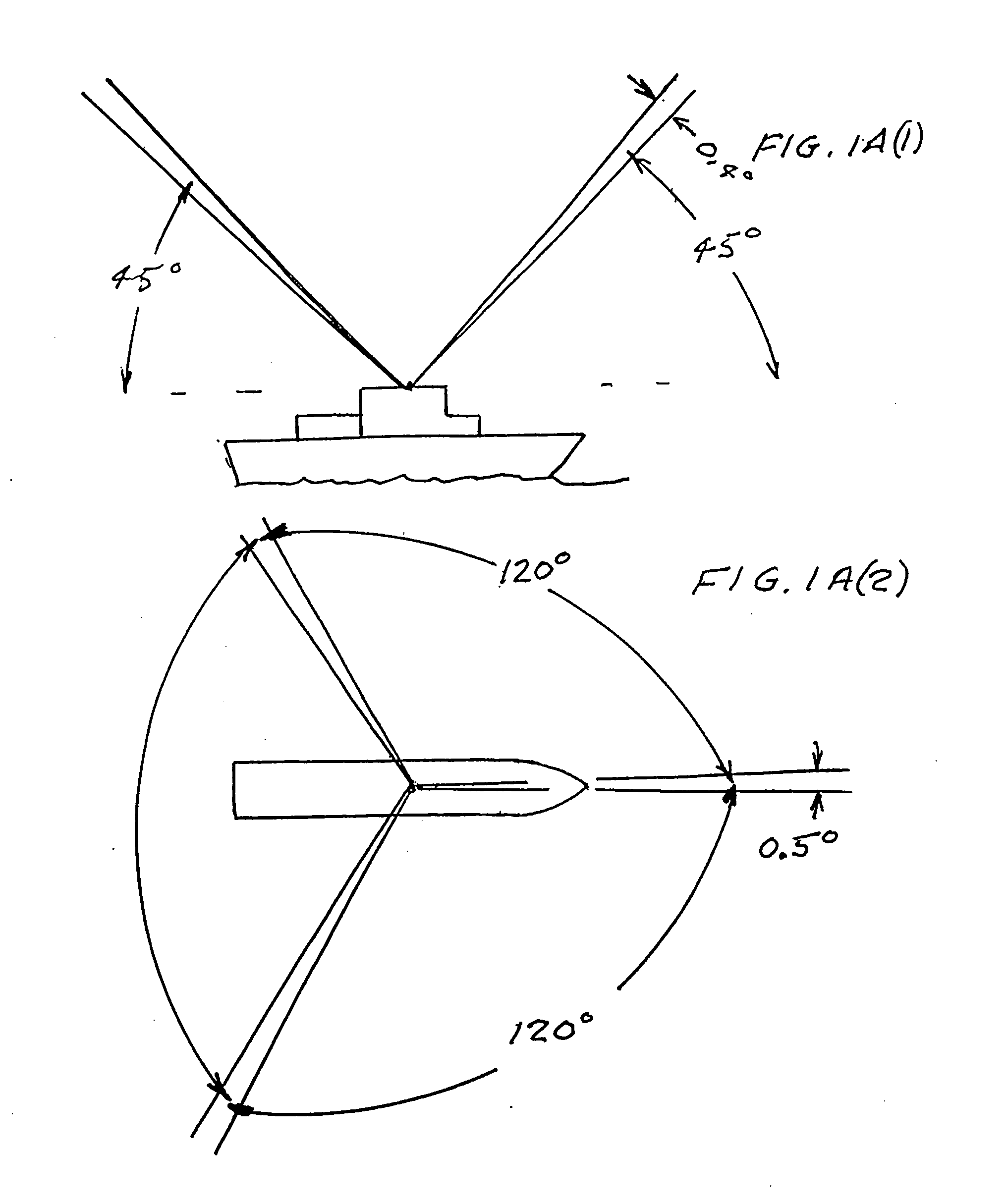
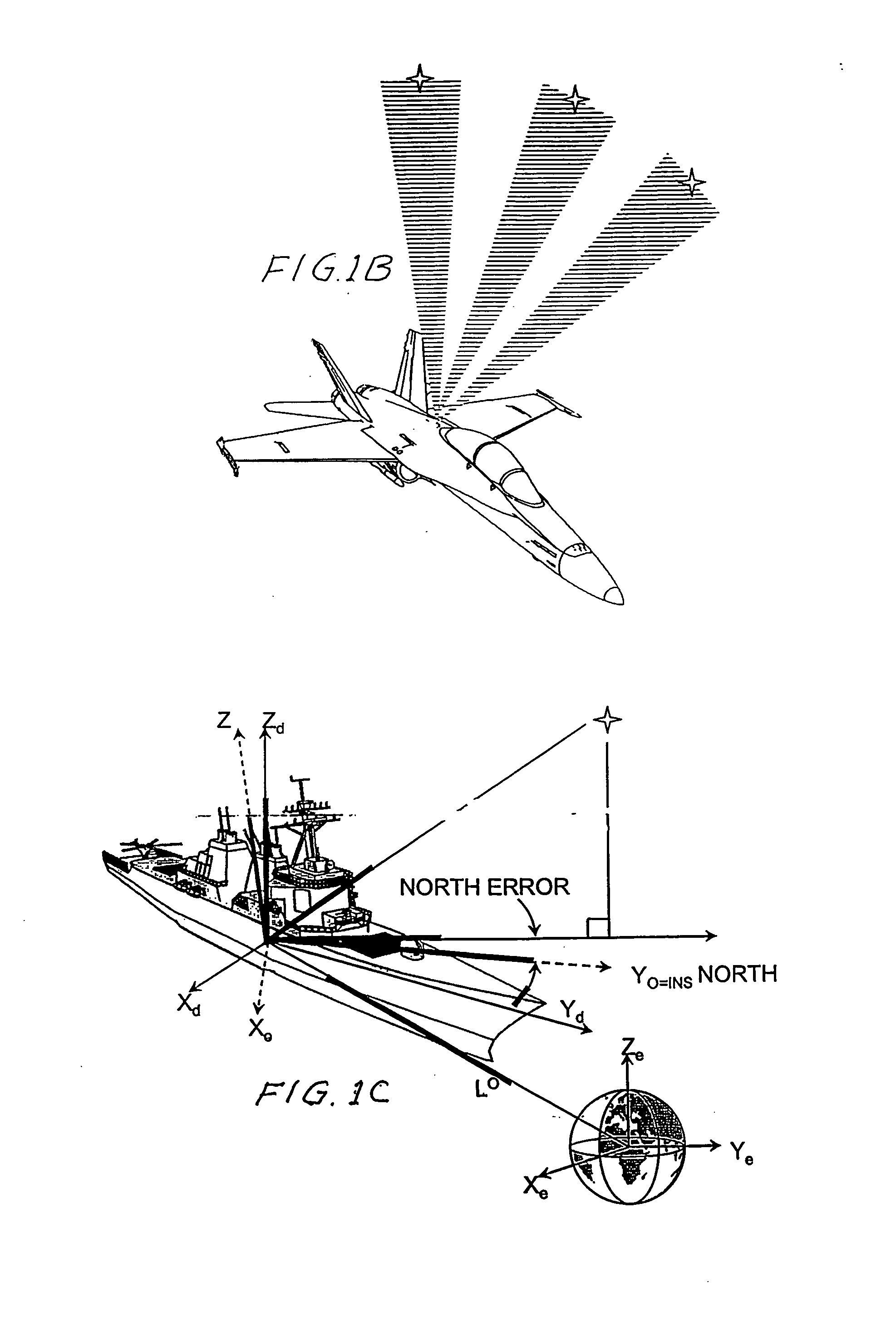
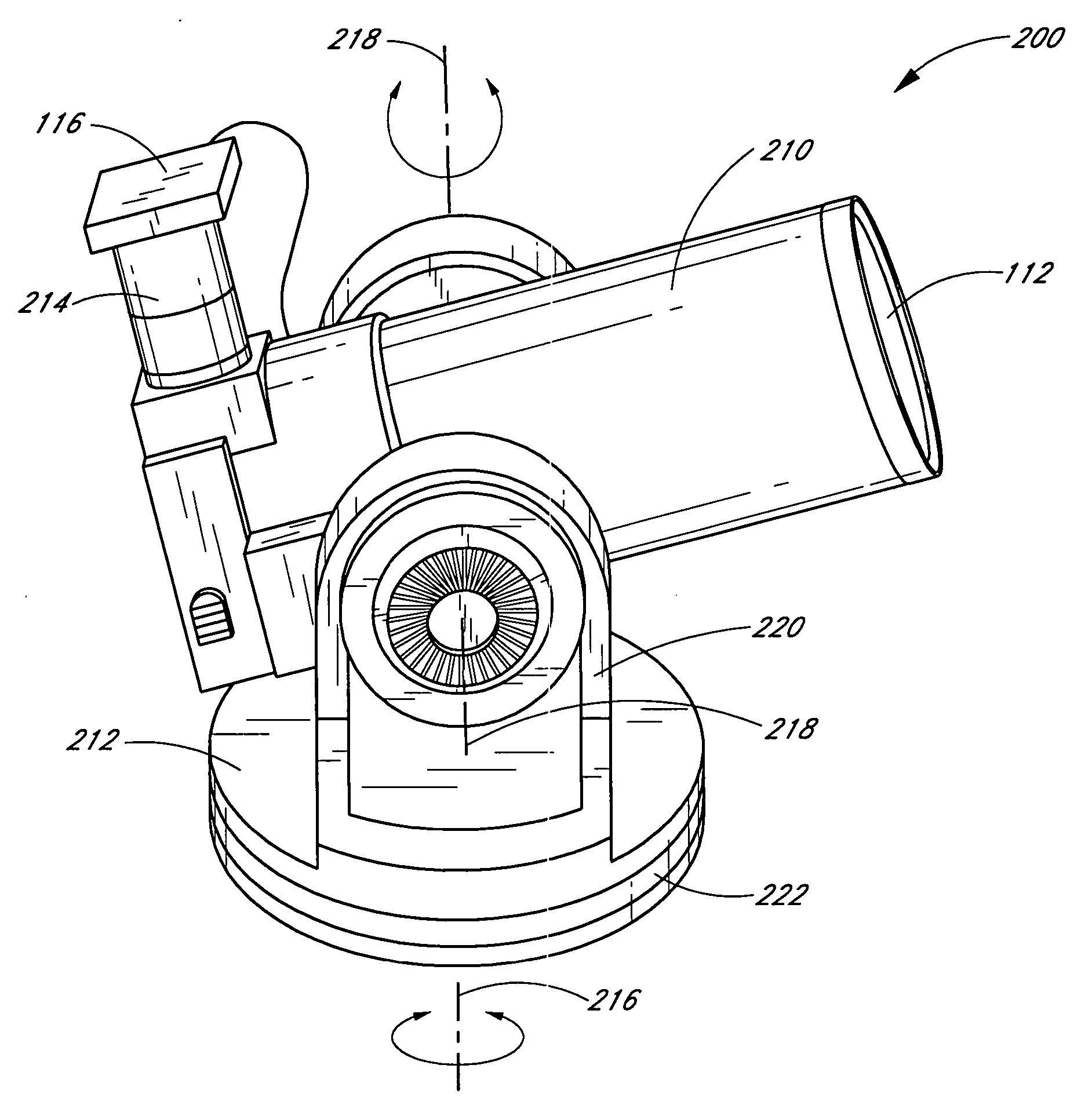
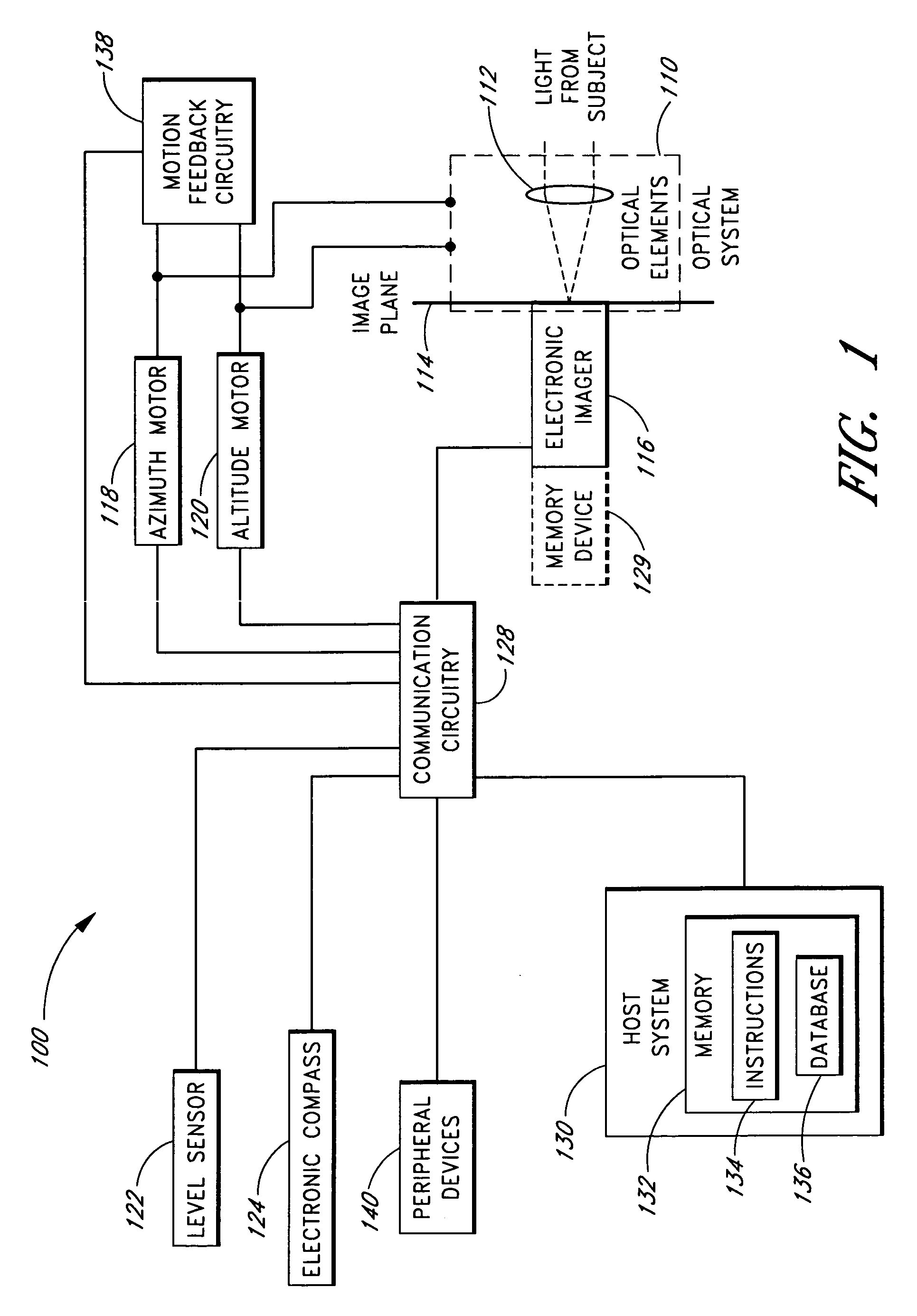
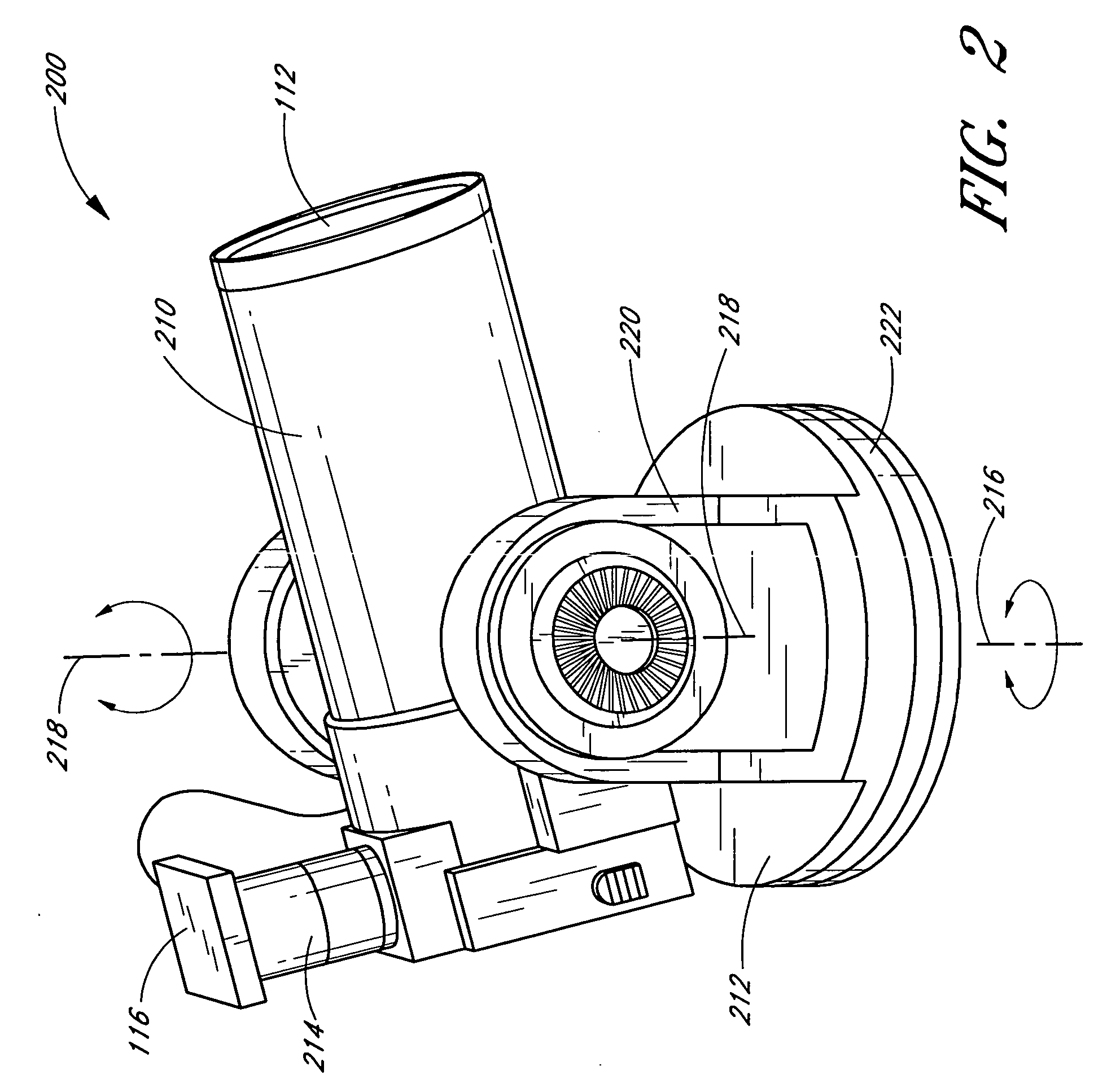
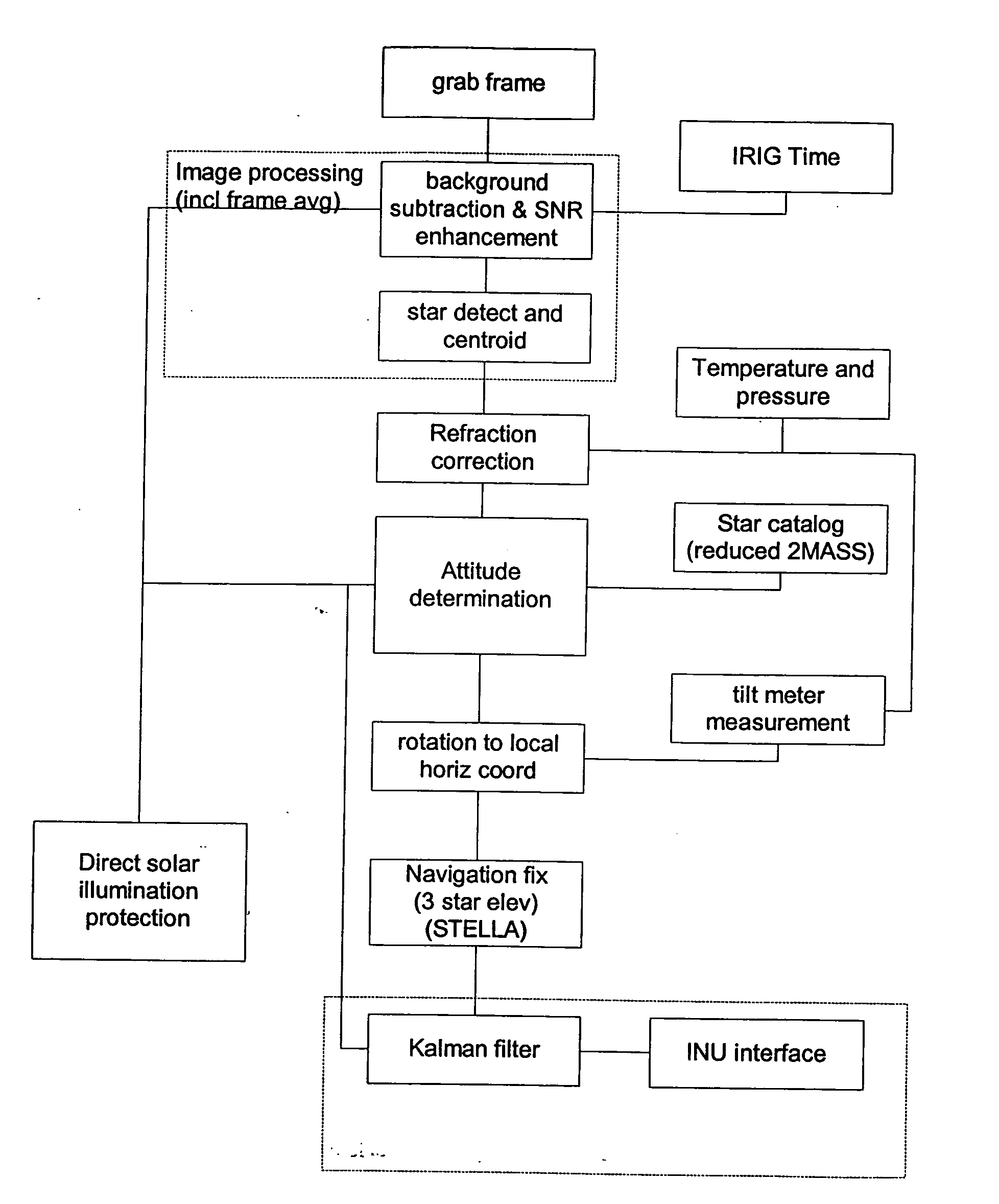
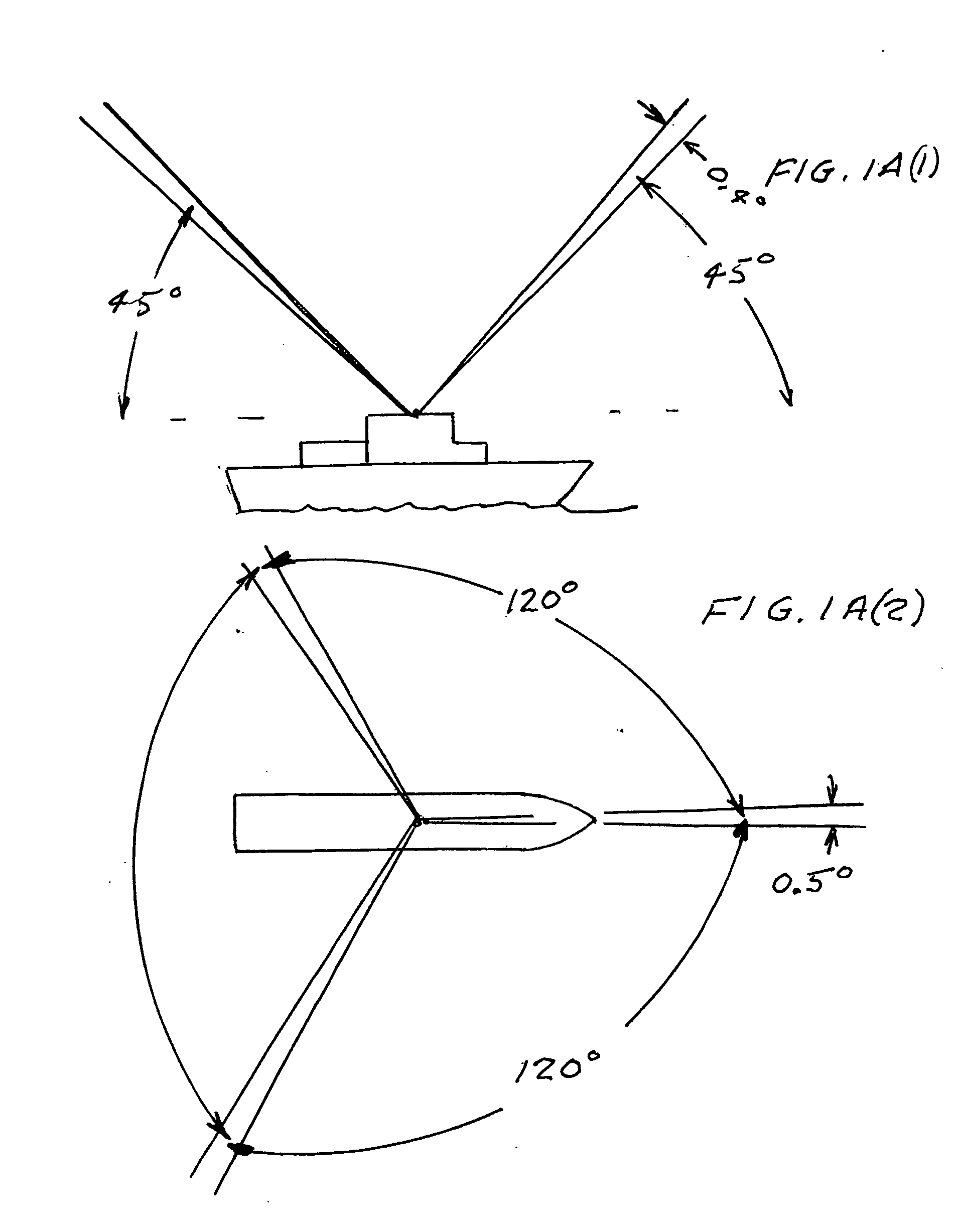
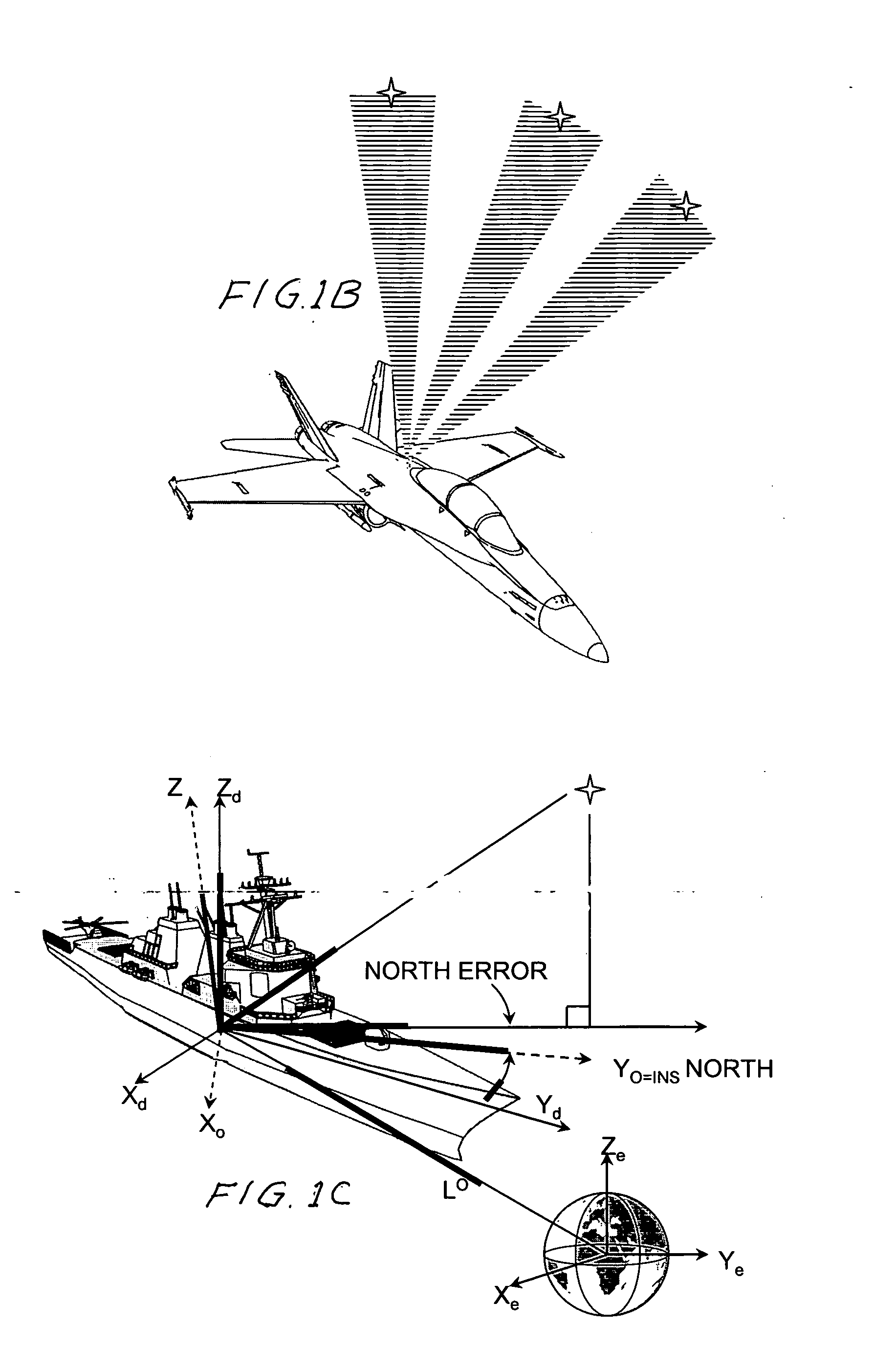
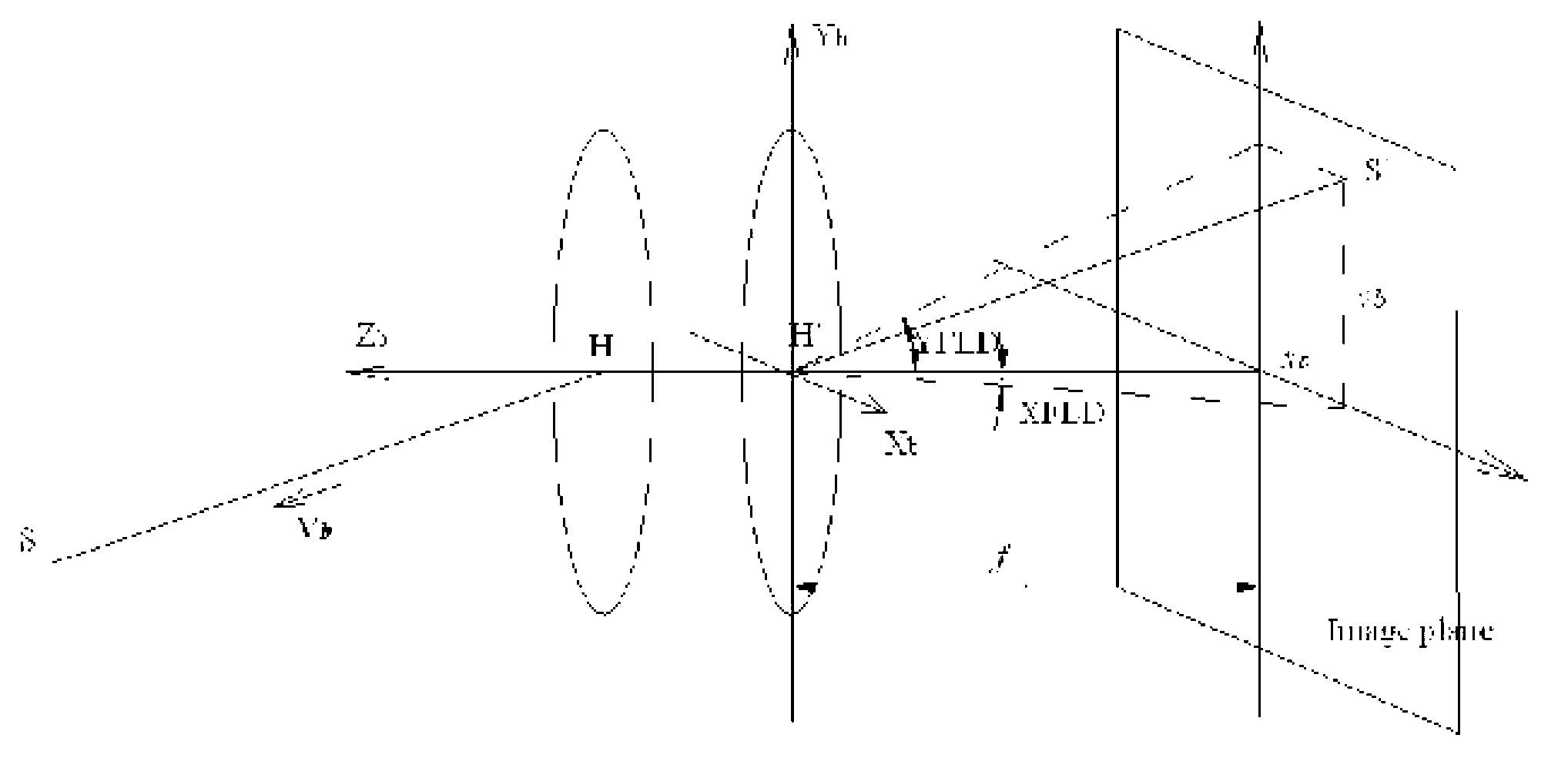
An automatic celestial navigation system for navigating both night and day by observation of K-band or H-band infrared light from multiple stars. In a first set of preferred embodiments three relatively large aperture telescopes are rigidly mounted on a movable platform such as a ship or airplane with each telescope being directed at a substantially different portion of sky. Embodiments in this first set tend to be relatively large and heavy, such as about one cubic meter and about 60 pounds. In a second set of preferred embodiments one or more smaller aperture telescopes are pivotably mounted on a movable platform such as a ship, airplane or missile so that the telescope or telescopes can be pivoted to point toward specific regions of the sky. Embodiments of this second set are mechanically more complicated than those of the first set, but are much smaller and lighter and are especially useful for guidance of aircraft and missiles. Telescope optics focus (on to a pixel array of a sensor) H-band or K-band light from one or more stars in the field of view of each telescope. Each system also includes an inclinometer, an accurate timing device and a computer processor having access to catalogued infrared star charts. The processor for each system is programmed with special algorithms to use image data from the infrared sensors, inclination information from the inclinometer, time information from the timing device and the catalogued star charts information to determine positions of the platform. Direction information from two stars is needed for locating the platform with respect to the celestial sphere. The computer is also preferably programmed to use this celestial position information to calculate latitude and longitude which may be displayed on a display device such as a monitor or used by a guidance control system. These embodiments are jam proof and insensitive to radio frequency interference. These systems provide efficient alternatives to GPS when GPS is unavailable and can be used for periodic augmentation of inertial navigation systems.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Daytime stellar imager
InactiveUS20070038374A1Small and light systemAvoid star image blurCosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsDisplay deviceLongitude
An automatic celestial navigation system for navigating both night and day by observation of K-band or H-band infrared light from multiple stars. In a first set of preferred embodiments three relatively large aperture telescopes are rigidly mounted on a movable platform such as a ship or airplane with each telescope being directed at a substantially different portion of sky. Embodiments in this first set tend to be relatively large and heavy, such as about one cubic meter and about 60 pounds. In a second set of preferred embodiments one or more smaller aperture telescopes are pivotably mounted on a movable platform such as a ship, airplane or missile so that the telescope or telescopes can be pivoted to point toward specific regions of the sky. Embodiments of this second set are mechanically more complicated than those of the first set, but are much smaller and lighter and are especially useful for guidance of aircraft and missiles. Telescope optics focus (on to a pixel array of a sensor) H-band or K-band light from one or more stars in the field of view of each telescope. Each system also includes an inclinometer, an accurate timing device and a computer processor having access to catalogued infrared star charts. The processor for each system is programmed with special algorithms to use image data from the infrared sensors, inclination information from the inclinometer, time information from the timing device and the catalogued star charts information to determine positions of the platform. Direction information from two stars is needed for locating the platform with respect to the celestial sphere. The computer is also preferably programmed to use this celestial position information to calculate latitude and longitude which may be displayed on a display device such as a monitor or used by a guidance control system. These embodiments are jam proof and insensitive to radio frequency interference. These systems provide efficient alternatives to GPS when GPS is unavailable and can be used for periodic augmentation of inertial navigation systems.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Daytime stellar imager for attitude determination
InactiveUS20060085130A1Small and light systemAvoid star image blurInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationJet aeroplaneGuidance control
An automatic celestial navigation system for navigating both night and day by observation of K-band or H-band infrared light from multiple stars. In a first set of preferred embodiments three relatively large aperture telescopes are rigidly mounted on a movable platform such as a ship or airplane with each telescope being directed at a substantially different portion of sky. Embodiments in this first set tend to be relatively large and heavy, such as about one cubic meter and about 60 pounds. In a second set of preferred embodiments one or more smaller aperture telescopes are pivotably mounted on a movable platform such as a ship, airplane or missile so that the telescope or telescopes can be pivoted to point toward specific regions of the sky. Embodiments of this second set are mechanically more complicated than those of the first set, but are much smaller and lighter and are especially useful for guidance of aircraft and missiles. Telescope optics focus (on to a pixel array of a sensor) H-band or K-band light from one or more stars in the field of view of each telescope. Each system also includes a GPS sensor and a computer processor having access to catalogued infrared star charts. The processor for each system is programmed with special algorithms to use image data from the infrared sensors, position and timing information from the GPS sensor, and the catalogued star charts information to determine orientation (attitude) of the platform. Direction information from two stars is needed for locating the platform with respect to the celestial sphere. The computer is also preferably programmed to calculate further information which may be used by a guidance control system. These systems provide efficient alternatives to inertial navigation systems when such systems are too expensive and can be used for periodic augmentation and calibration of inertial navigation systems.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
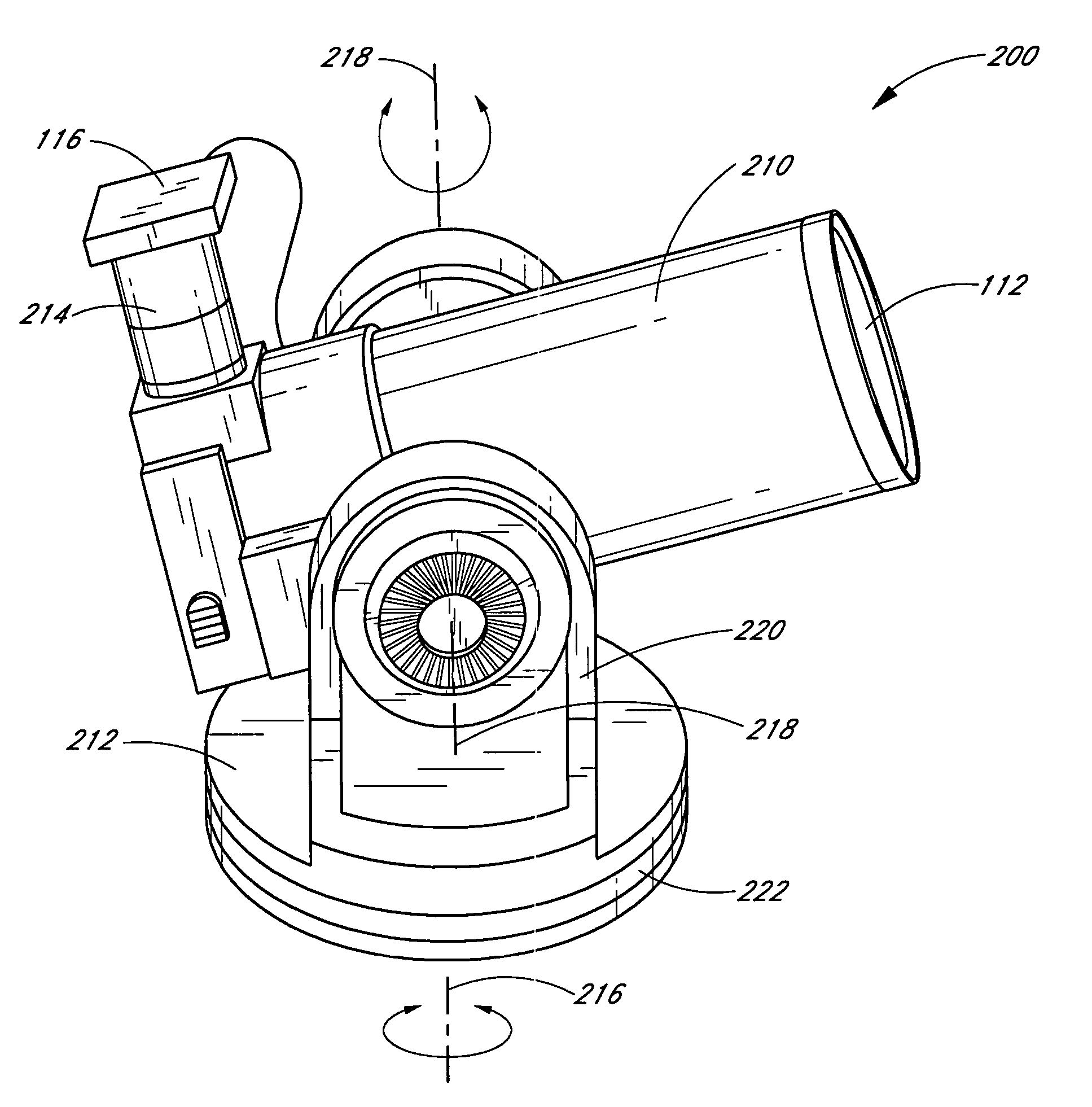
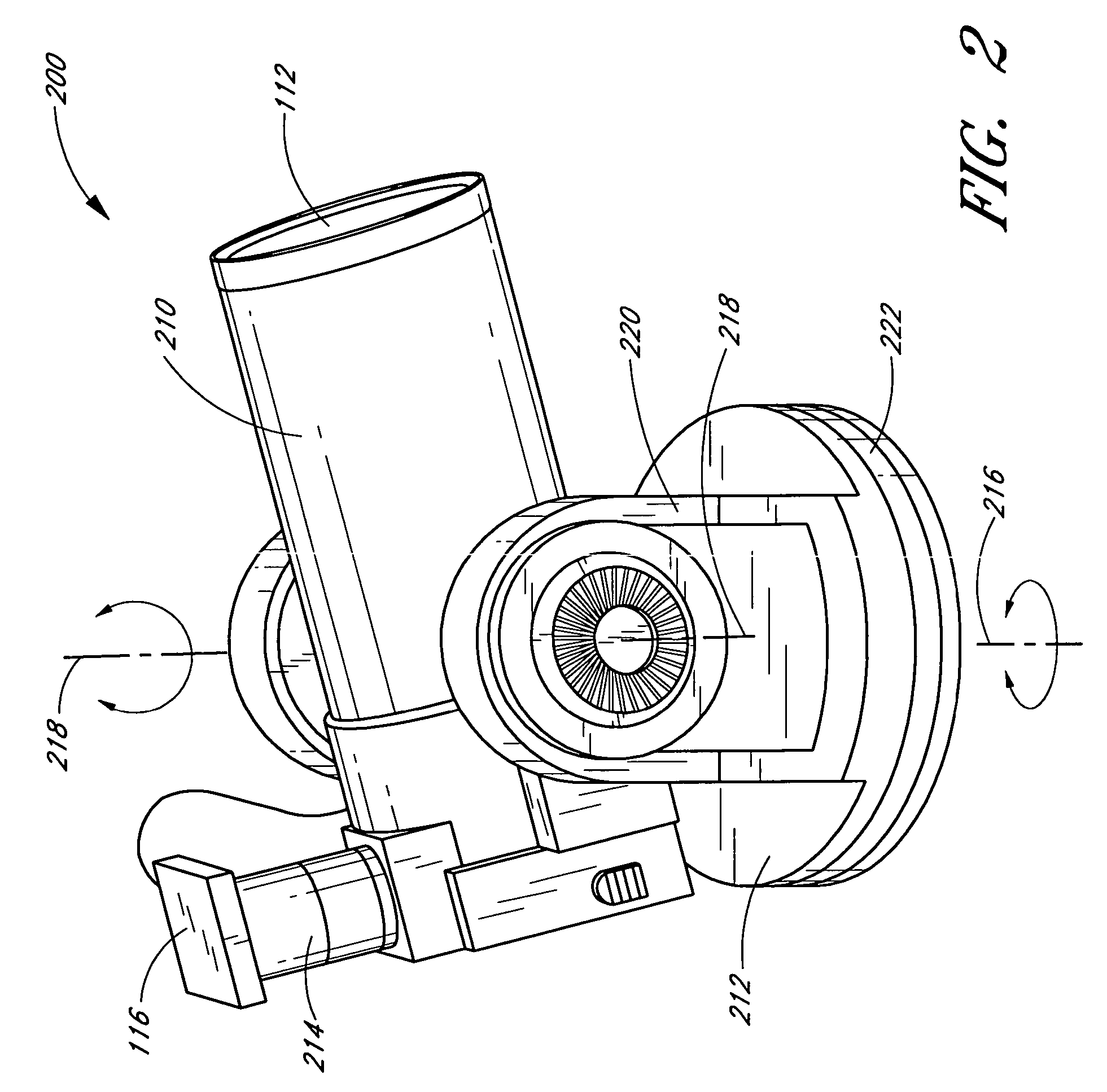
Self-aligning telescope
ActiveUS20060238860A1Quickly and accurately orientImprove accuracyPhotometry using reference valueInstruments for comonautical navigationSkyCelestial body
Embodiments of the present disclosure include self-aligning telescope control systems and self-alignment methods. In an embodiment, a telescope control system orients a telescope with respect to the celestial sphere by pointing the telescope in the direction of an alignment star or alignment area of the sky. The telescope control system images a field of view in the alignment area, and processes the images to determine the celestial coordinates of a center of the filed a field of view the alignment area. The telescope control system then maps the telescope's coordinate system to the celestial coordinate system. Once mapped, the telescope control system can advantageously slew the telescope to any desired celestial object in the viewable sky based on, for example, user selection, system recommendations, combinations of the same, or the like.
Owner:MEADE INSTRUMENTS
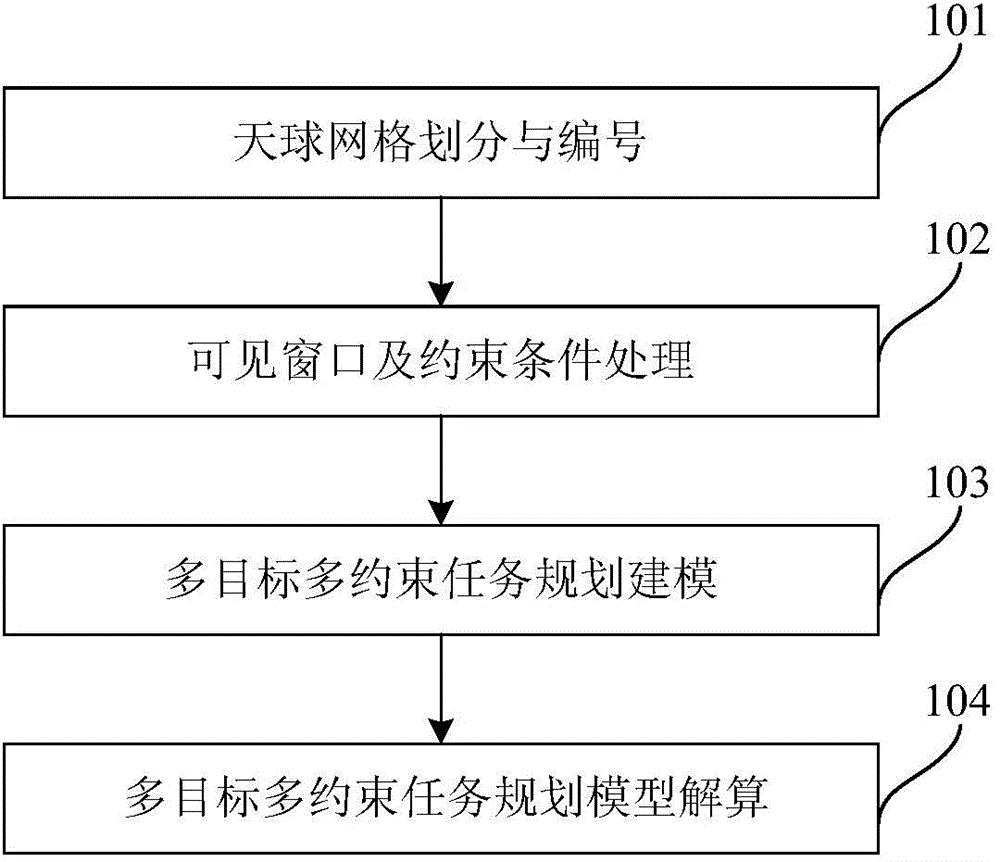
Sky scanning multiple-objective task programming method for space astronomical satellite
ActiveCN104090819AReduce time complexityReduce space complexityMultiprogramming arrangementsSkyCelestial sphere
The invention relates to a sky scanning multiple-objective task programming method for a space astronomical satellite. The method comprises the first step of grid division and numbering of a celestial sphere, the second step of processing of a visible window and constraint conditions, the third step of programming and modeling of multiple-objective tasks, the fourth step of resolving processing of a multiple-objective and multiple-constraint-condition programming model. According to the sky scanning multiple-objective task programming method for the space astronomical satellite, planet energy, storage and ground data transmission constraints are comprehensively considered, multiple-objective programming problem modeling is conducted from the aspects of the scientific detection requirement and the project implementation requirement, and a solution algorithm is provided to lower the time of conflict resolution and space complexity.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
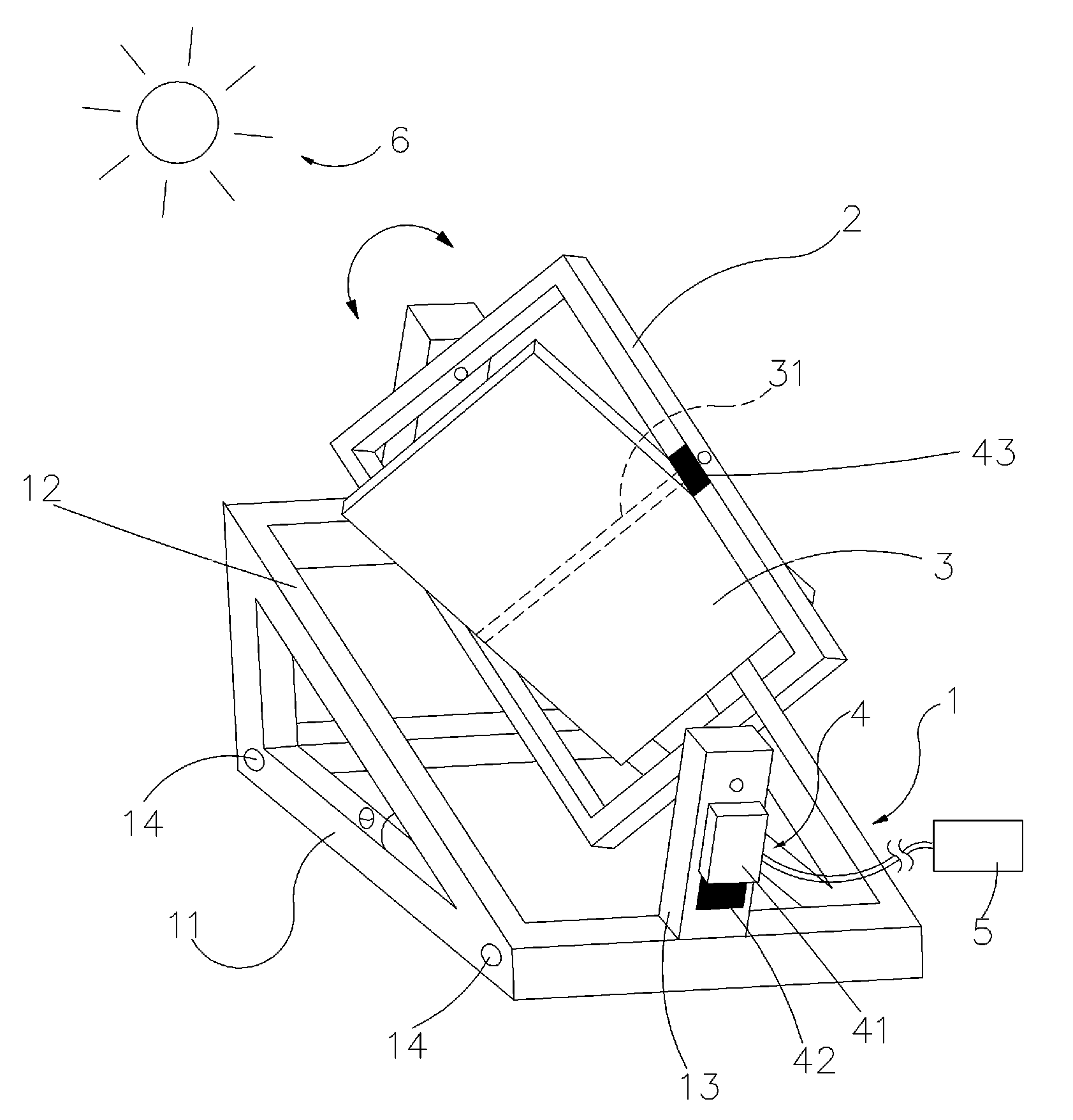
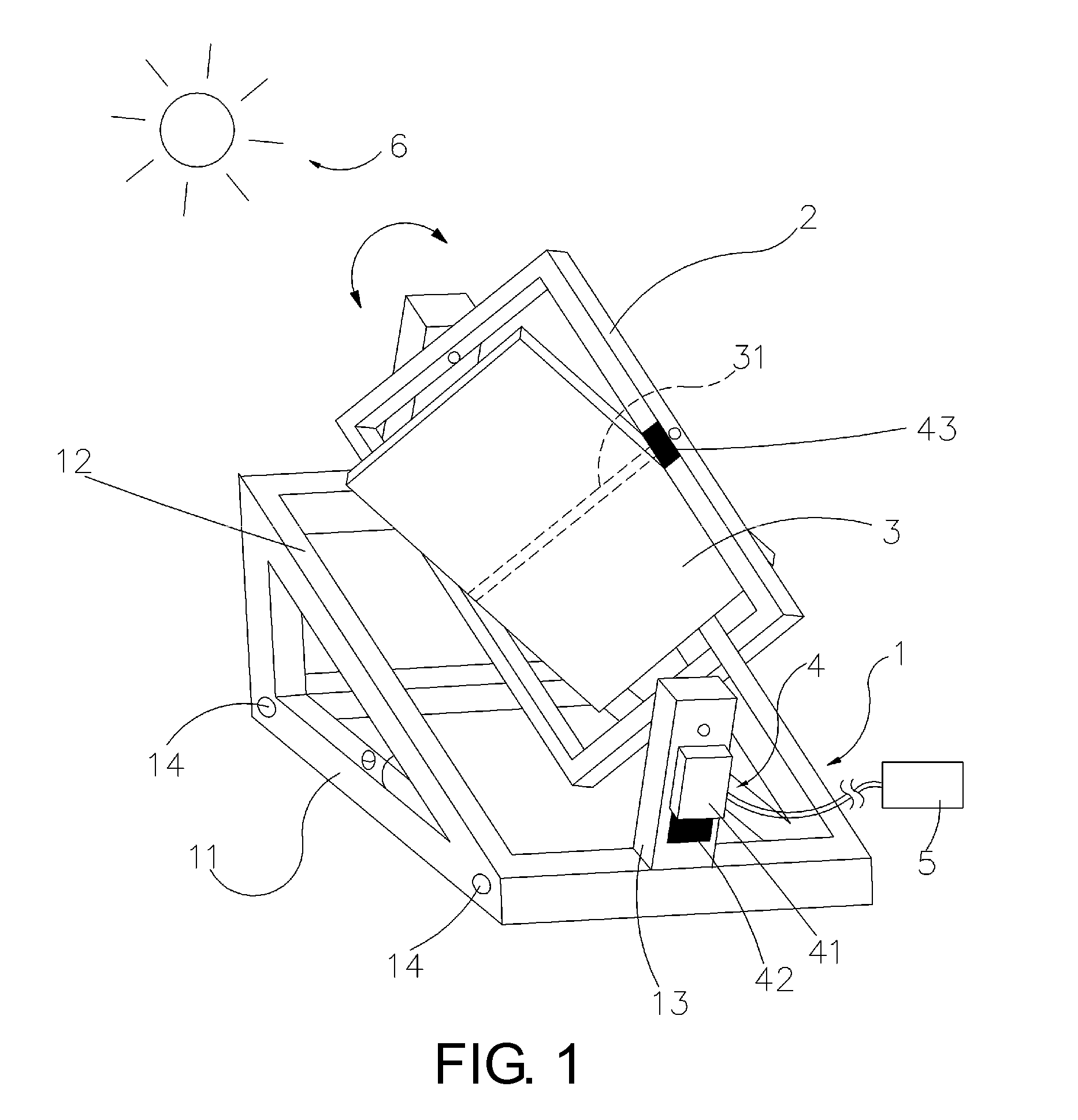
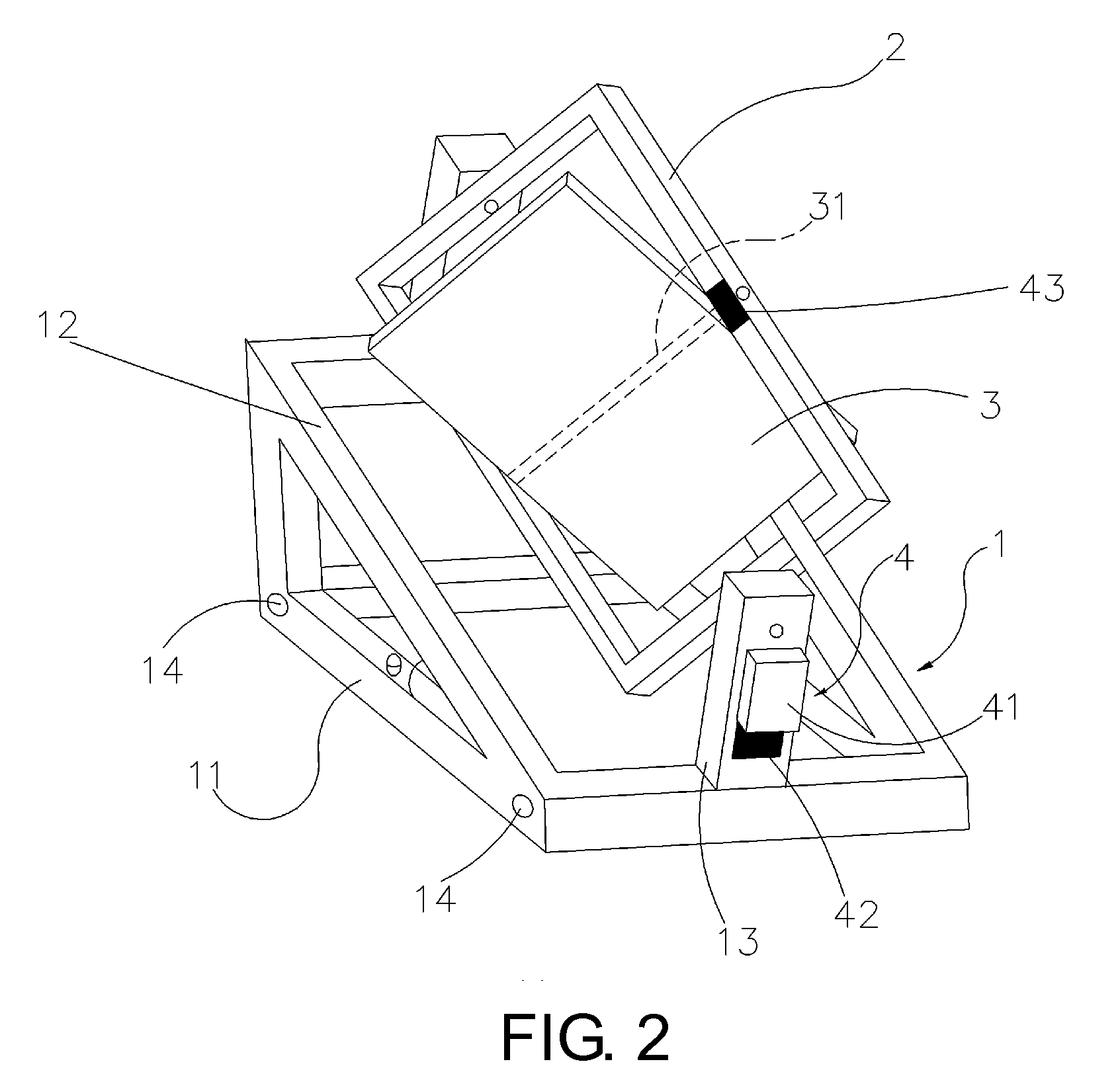
Control Method and Device for Quasi-Uniaxial Sun Chase of Solar Panels
InactiveUS20090301467A1High incident solar energySimple processPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyPresent methodLongitude
The present invention relates to a control method and device for quasi-uniaxial sun chase of solar panels. The present method uses uniaxial driving to perform real-time tracking of the zodiacal longitude position of solar “daily periodic change”, then abiding by seasonal “annual periodic change” to perform tracking fine tuning of less 0.25 degrees per day on celestial sphere declination. The present device includes a supporting unit with two corresponding holders on the end face, a frame body for solar panel installation configured between the said two holders, and a control mechanism including a setting unit as well as an enable unit connected to the frame body. Thereby, in addition to real-time correction to the corresponding position of the solar panel to Sun by setting the control mechanism to allow the solar panel to acquire higher incident solar energy. The present invention provides a simple device structure with lower operation power consumption.
Owner:CHENG HONG WEN
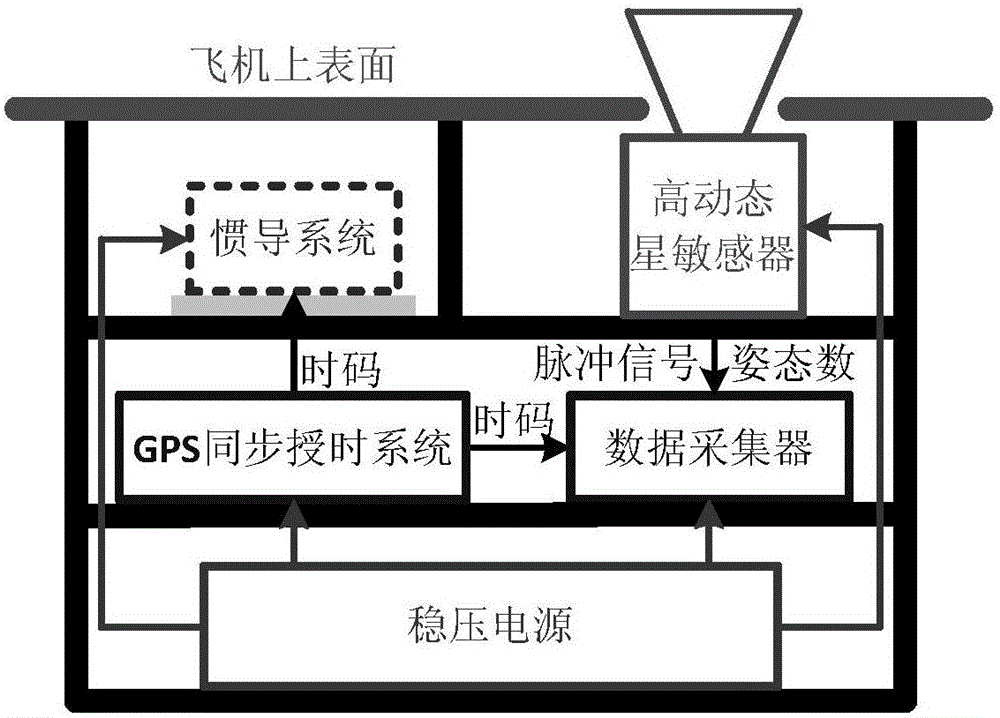
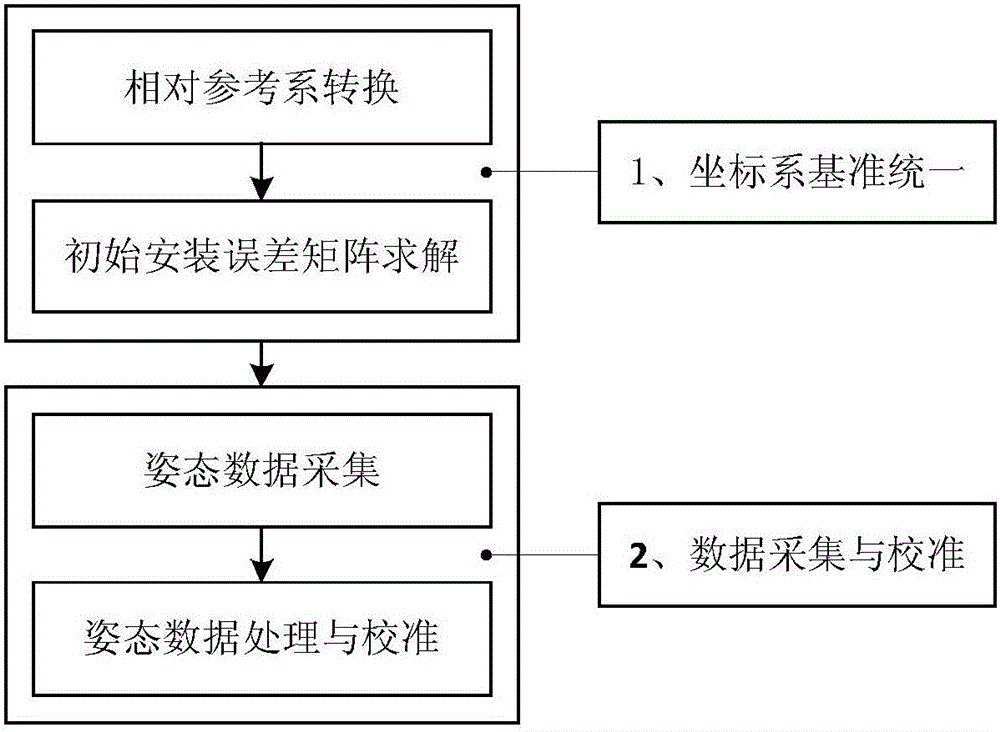
Attitude parameter calibration method and attitude parameter calibration device of airborne inertial navigation system
ActiveCN105737858ARealize dynamic online calibrationImprove reliabilityMeasurement devicesBaseline dataFixed stars
The invention discloses an attitude parameter calibration method and an attitude parameter calibration device of an airborne inertial navigation system. A high-dynamic star sensor is used as a data acquisition method and fixed stars are used as measuring objects; the plurality of fixed stars on a celestial sphere are detected, and start point positioning, star map identification and attitude calculation are carried out to provide attitudes of the star sensor relative to an inertial reference system; then, airplane attitude standard data under an inertial navigation coordinate system is obtained according to a conversion relation between a star sensor coordinate system and the inertial navigation coordinate system; finally, the standard data is used as reference and is compared with the attitude data of the inertial navigation system, so that the dynamic online calibration of the attitude precision of the inertial navigation system is realized under an airborne environment.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for making guide star database based on output accuracy of star sensors
InactiveCN106595645AGuaranteed completenessGuaranteed even distributionNavigation by astronomical meansFixed starsSky
The invention provides a method for making a guide star database based on output accuracy of star sensors. The method comprises the following steps: S1, subjecting a basic star database to screening of fixed stars; S2, generating the direction of an optical axis of a test sky area covering the whole celestial sphere; S3, converting the celestial system of coordinates of all the fixed stars in a field of view under the direction of the optical axis into a planar system of image plane projection; S4, dividing an image plane into n regions and arraying fixed stars in each region according to m combination modes; S5, carrying out attitude solution on each combination mode of the fixed stars and removing combination modes with great errors in an accuracy index; S6, searching for fixed stars in the whole view field of the image plane and combination modes of the fixed stars forming polygons with great errors in a mismatching accuracy index; and S7, carrying out steps S2 to S6 on each optical axis direction and combining overlapped fixed star points in each sky area so as to obtain the guide star database. According to the invention, the selection process of guide stars in each field range is optimized, so a fixed star combination eventually chosen is guaranteed to meet requirements of average distribution, and attitude calculation precision is guaranteed to be optimal.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
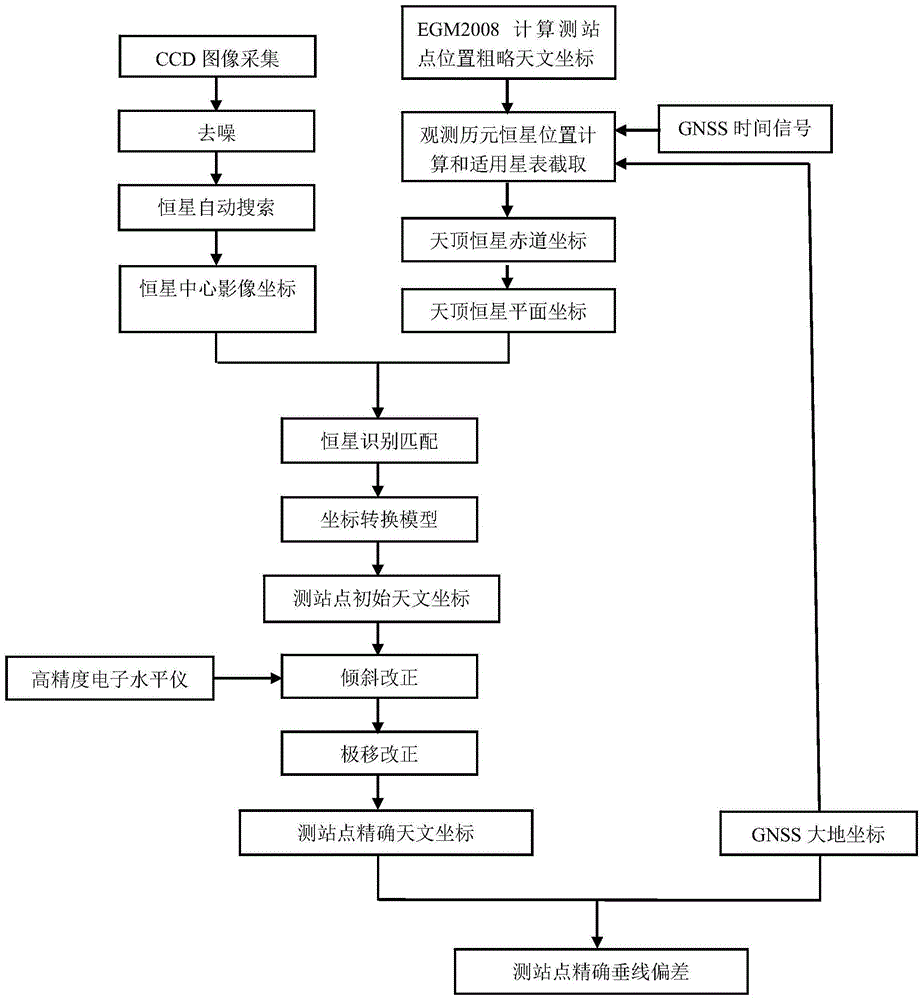
GNSS-CCD-integrated zenith telescope high-precision vertical deflection fast measurement method
ActiveCN104913780AShorten the timeMeasurement accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsInformaticsFixed starsStar catalogue
The invention discloses a GNSS-CCD-integrated zenith telescope high-precision vertical deflection fast measurement method. At a measurement station, the optical axis of a zenith telescope faces to the zenith and takes a picture of a zenith zone so that a CCD fixed star image is obtained, fixed star image coordinates are calculated, exposure epoch is controlled by geodetic coordinates and a GNSS time signal measured by GNSS, fixed star information in the zenith zone is acquired in an appropriate star catalogue according to the measurement station vertical deflection calculated by an EGM2008 geopotential model, coupling identification of fixed stars in a zenith tangent plane zone of a celestial sphere in the star catalogue and in the CCD fixed star image is realized, zenith astronomical coordinates are calculated by least spuare iterative computation, and vertical deflection of the observed point is calculated according to geodetic coordinates. Compared with the prior art, the method provided by the invention has the characteristics of simple operation, time and labor saving and high measurement precision and is suitable for high-precision vertical deflection fast measurement.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
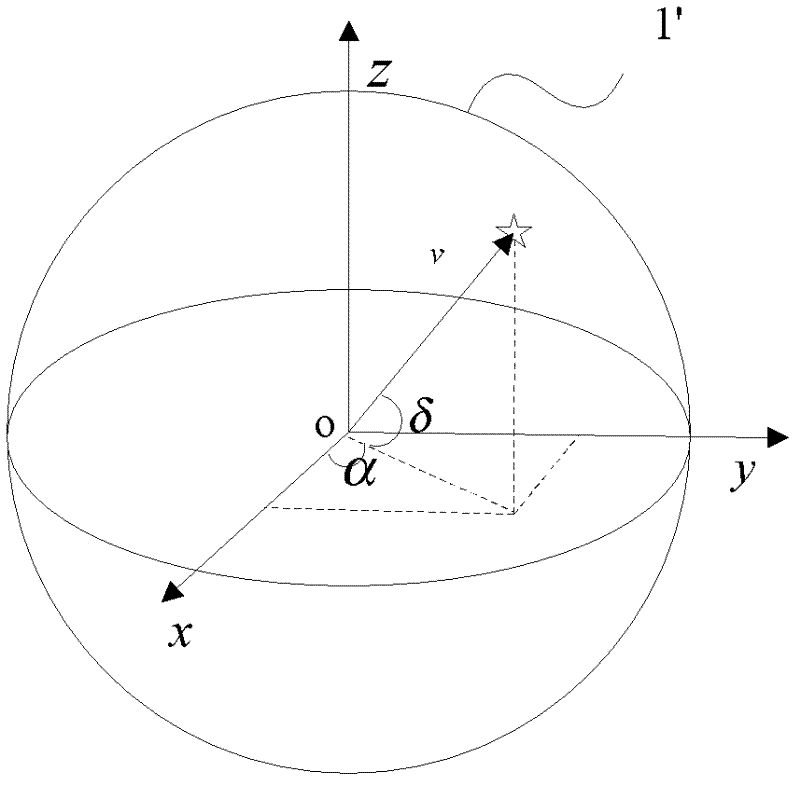
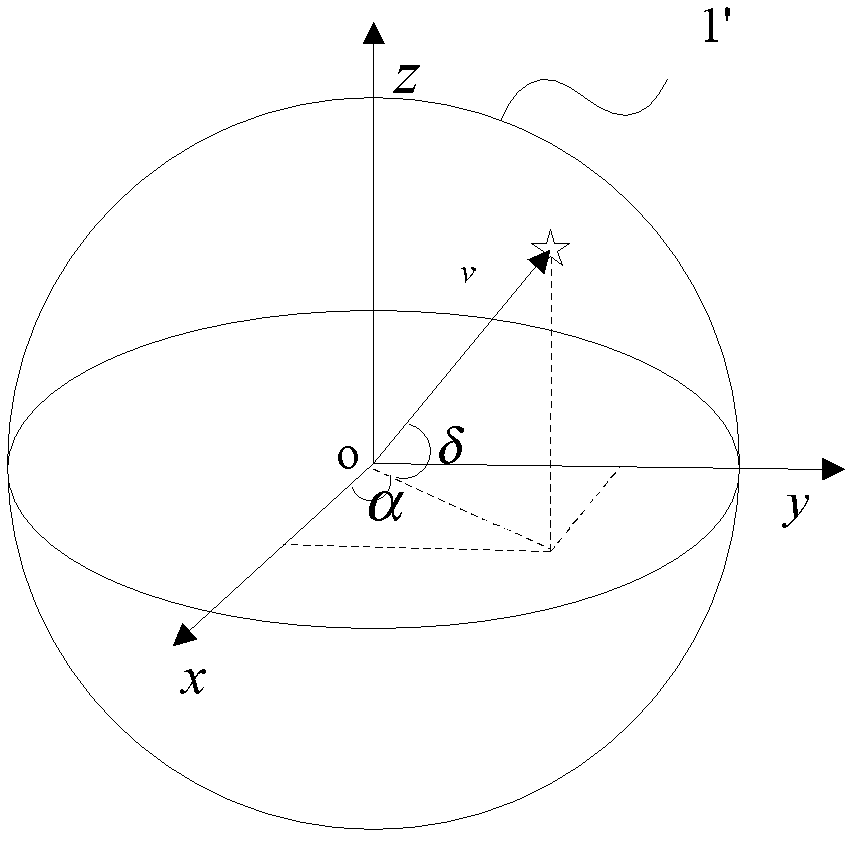
Accuracy measurement method for star sensor
The invention discloses a precision measurement method for a star sensor, which comprises the following steps of: 1) fixing the star sensor on the earth; 2) inputting time T of measurement starting time relative to J2000.0 into the star sensor; 3) determining the direction vector of J2000.0 right angle coordinate system according to the declination and right ascension as well as apparent motion parameter (alpha', delta') of a navigator star under the J2000.0 coordinate system; 4) converting the direction vector of the navigation star under the J2000.0 right angle coordinate system into the direction vector under an epoch ecliptic coordinate system; 5) converting the direction vector under the epoch ecliptic coordinate system into the direction vector (v CRFT) under a spherical coordinate system; and 6) changing the direction vector of the navigation star under the spherical coordinate system into the direction vector (v TRF) under a fixed ground coordinate system, on the basis of the direction vector (v TRF) under the fixed ground coordinate system, obtaining the precision of the star sensor. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the precision measurement of the starsensor can be easily realized.
Owner:北京天银星际科技有限责任公司
Double-spectrum autonomous navigation sensor and design method of double-spectrum autonomous navigation sensor
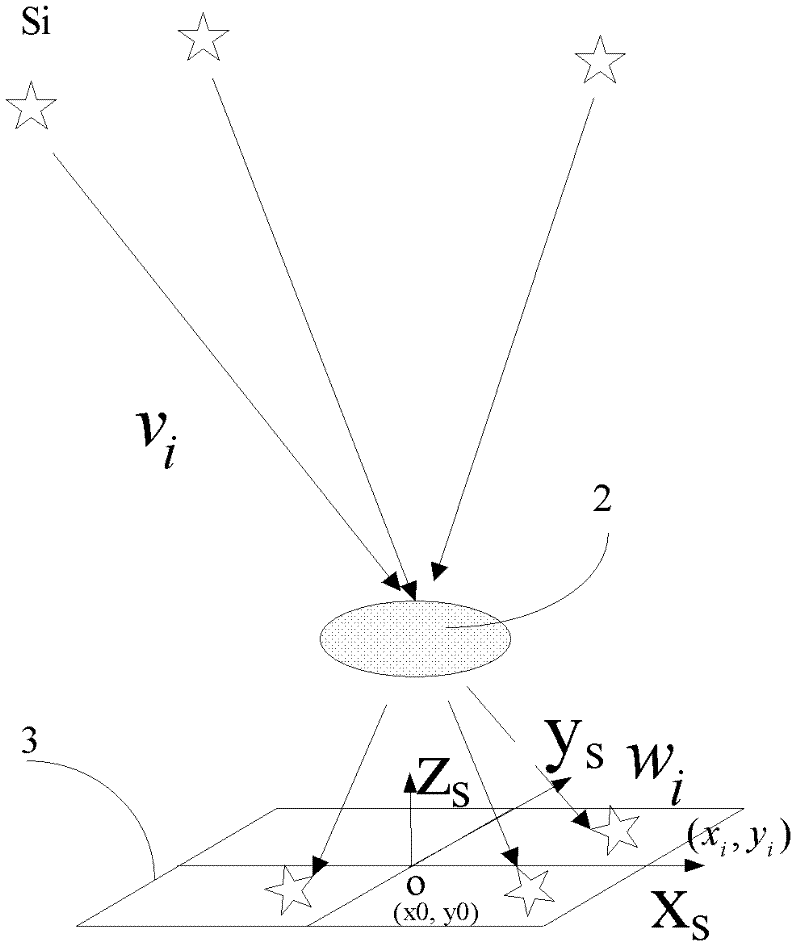
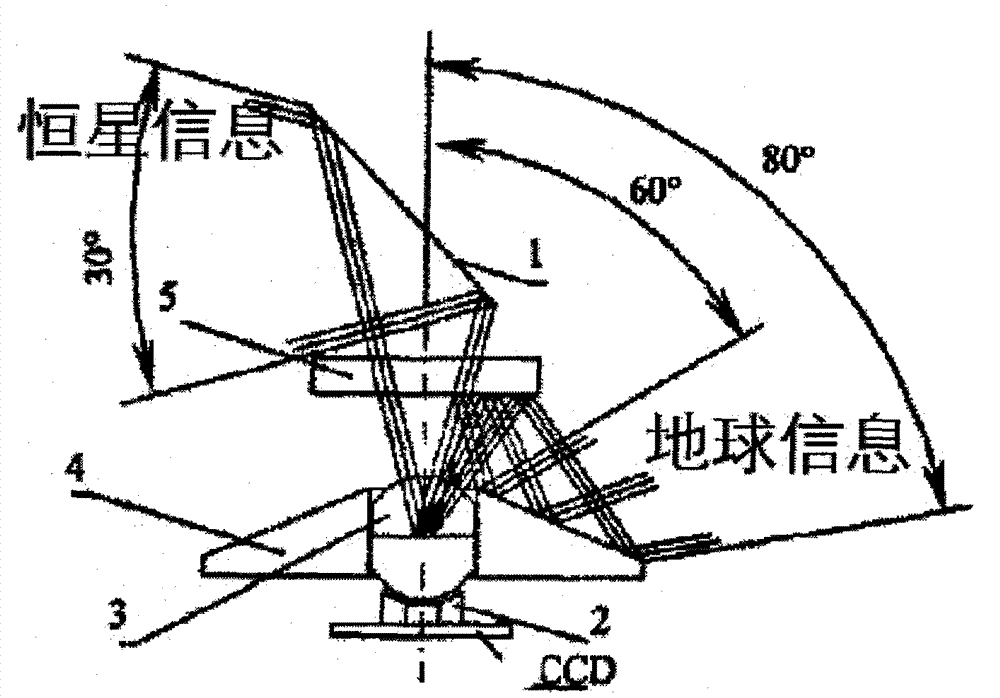
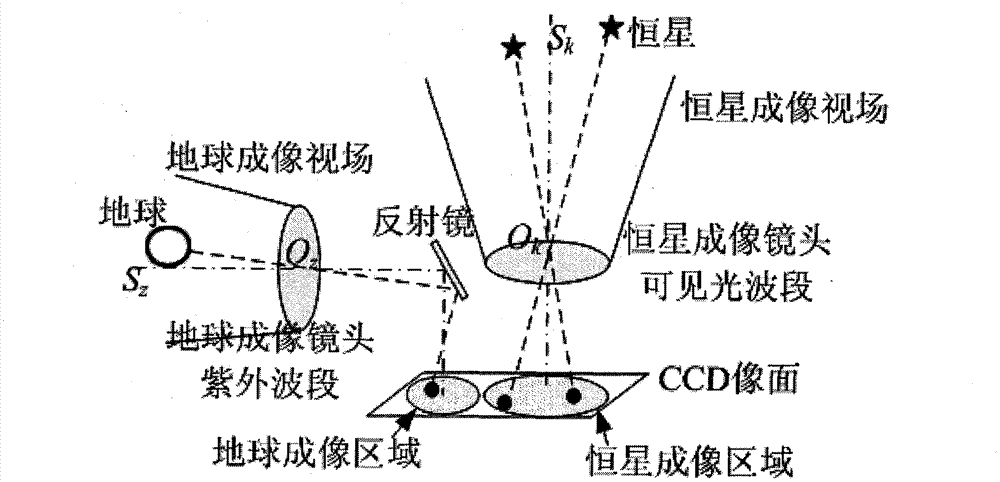
ActiveCN102927982AFull Coverage GuaranteedAvoid UV Band InformationNavigation by astronomical meansCamera lensUltraviolet
The invention relates to a double-spectrum autonomous navigation sensor and a design method of the double-spectrum autonomous navigation sensor. The sensor comprises a stellar visible light band lens, an earth ultraviolet band imaging lens and a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) sensor, wherein the stellar visible light band lens can only image stellar visible light band information, the earth ultraviolet band imaging lens can image earth ultraviolet band information, and the center of an optical axis of the earth ultraviolet band imaging lens is perpendicular to the center of an optical axis of the stellar visible light band imaging lens; and an image formed by the ultraviolet band imaging lens is reflected to the CCD sensor by a 45-degree reflector, and the two lenses can image in the same CCD sensor. The design method comprises the steps of designing the visible light band lens and selecting the earth ultraviolet band imaging lens and the CCD sensor. The double-spectrum autonomous navigation sensor has advantages of low power consumption, high navigation accuracy and low error, and also has the advantage of utilizing stars for covering the whole heavenly body.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for automatically aligning telescope
A manual controller commands a telescope mount to automatically track a specific bright star after the image of the star is located to center of an electronic eyepiece and a timer is started. The average moving speed of the bright star is calculated after a predetermined elapsed time to acquire the right ascension (RA) and the declination (DEC) coordinates of this bright star. Subsequently, the RA and DEC coordinates are compared with pre-stored data contained within a database used to identify the bright star. The celestial sphere coordinates of the telescope can be determined after a minimum of one bright star is identified. In the auto-tracking procedure, the manual controller controls movement of telescope by feedbacks of the drifting speed and direction of the specific bright star in an electronic eyepiece for the purpose of keeping the specific bright star in the center of the electronic eyepiece.
Owner:NANTONG SCHMIDT OPTO ELECTRICAL TECH CO LTD
Image processing device and image processing method
ActiveUS20180007387A1Not limitedDigital video signal modificationSelective content distributionOmnidirectional antennaImaging processing
The present disclosure relates to an image processing device and an image processing method for instantaneously displaying an image of a user's field of view.An encoder encodes a celestial sphere image of a cube formed by images of multiple planes generated from omnidirectional images, the encoding being performed plane by plane at a high resolution, to generate a high-resolution encoded stream corresponding to each of the planes. The encoder further encodes, at a low resolution, the celestial sphere image to generate a low-resolution encoded stream. The present disclosure may be applied, for example, to image display systems that generate a celestial sphere image so as to display an image of the user's field of view derived therefrom.
Owner:SONY CORP
Accuracy Measurement System for Star Sensor
ActiveCN102288200AImprove pointing accuracyGuaranteed accuracyMeasurement devicesStar trackerRectangular coordinates
The invention discloses an accuracy measurement system for a star sensor. The accuracy measurement system comprises a fixer and a star sensor accuracy measurement unit, wherein the fixer is used for fixing the star sensor to make a main shaft of the star sensor aligned with a zenith; the star sensor accuracy measurement unit is used for measuring the accuracy of a navigation star; a test startingmoment T is input into the star sensor; a direction vector under a J2000.0 rectangular coordinate system is determined according to declination, right ascension and apparent motion parameters of the navigation star under a J2000.0 coordinate system; the direction vector is converted into the direction vector under an epoch ecliptic coordinate system and then converted into a direction vector (VCRFT) under a celestial sphere coordinate system; the direction vector of the navigation star under the celestial sphere coordinate system is changed into a direction vector (VTRF) under an earth-fixed coordinate system; and based on the direction vector (VTRF) under the earth-fixed coordinate system, the accuracy of the star sensor is obtained. According to the accuracy measurement system provided by the invention, the star sensor is fixedly connected to the earth by using the accuracy of rotation of the earth, and the main shaft of the star sensor is aligned with the zenith for observation.
Owner:北京天银星际科技有限责任公司
Self-aligning telescope
ActiveUS7339731B2Quickly and accurately orientImprove accuracyPhotometry using reference valueInstruments for comonautical navigationSkyCelestial body
Embodiments of the present disclosure include self-aligning telescope control systems and self-alignment methods. In an embodiment, a telescope control system orients a telescope with respect to the celestial sphere by pointing the telescope in the direction of an alignment star or alignment area of the sky. The telescope control system images a field of view in the alignment area, and processes the images to determine the celestial coordinates of a center of the filed a field of view the alignment area. The telescope control system then maps the telescope's coordinate system to the celestial coordinate system. Once mapped, the telescope control system can advantageously slew the telescope to any desired celestial object in the viewable sky based on, for example, user selection, system recommendations, combinations of the same, or the like.
Owner:MEADE INSTRUMENTS
Daytime stellar imager
InactiveUS20060085129A1Turbulence effectIncrease probabilityNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsNavigation by astronomical meansDisplay deviceLongitude
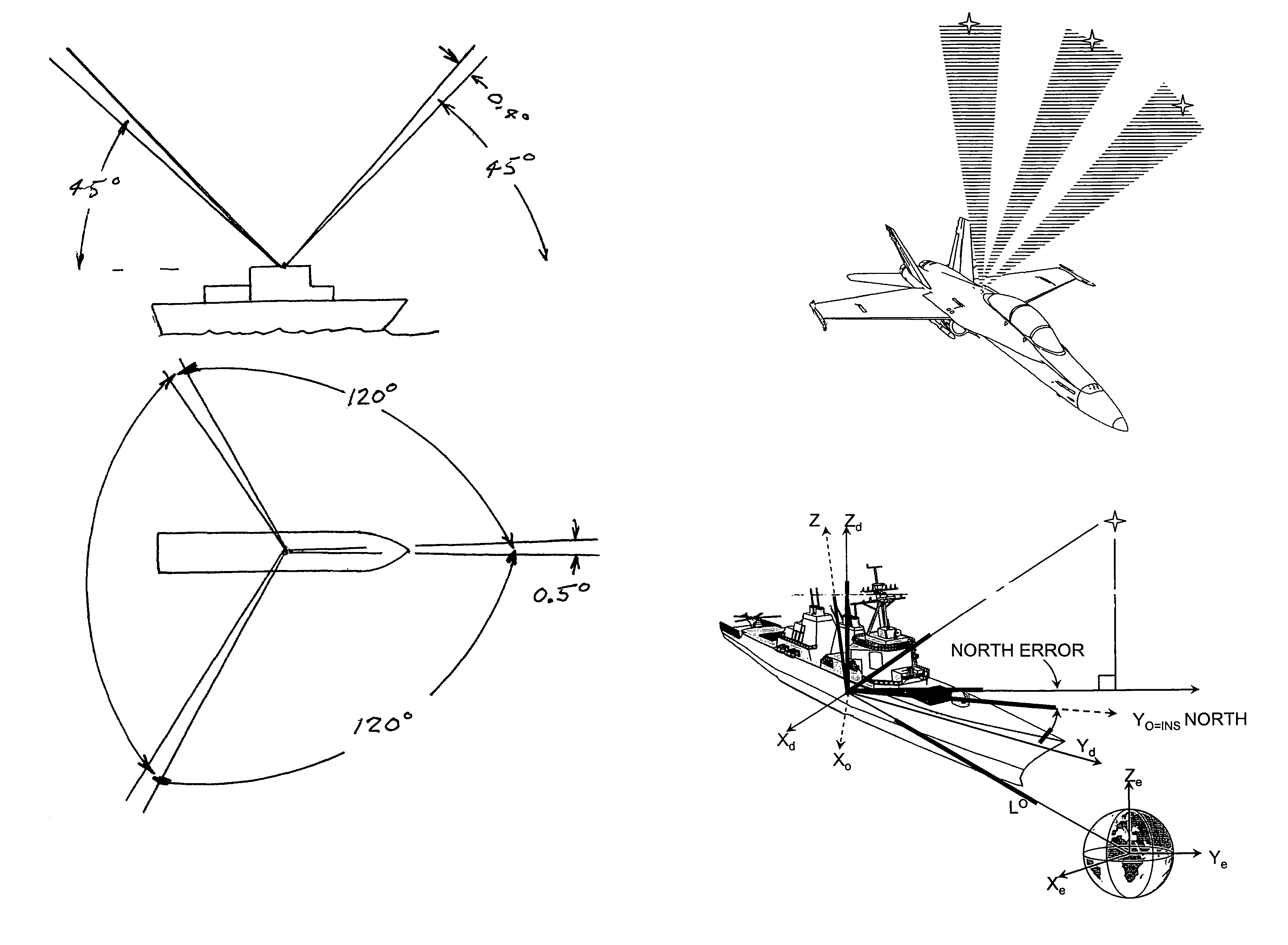
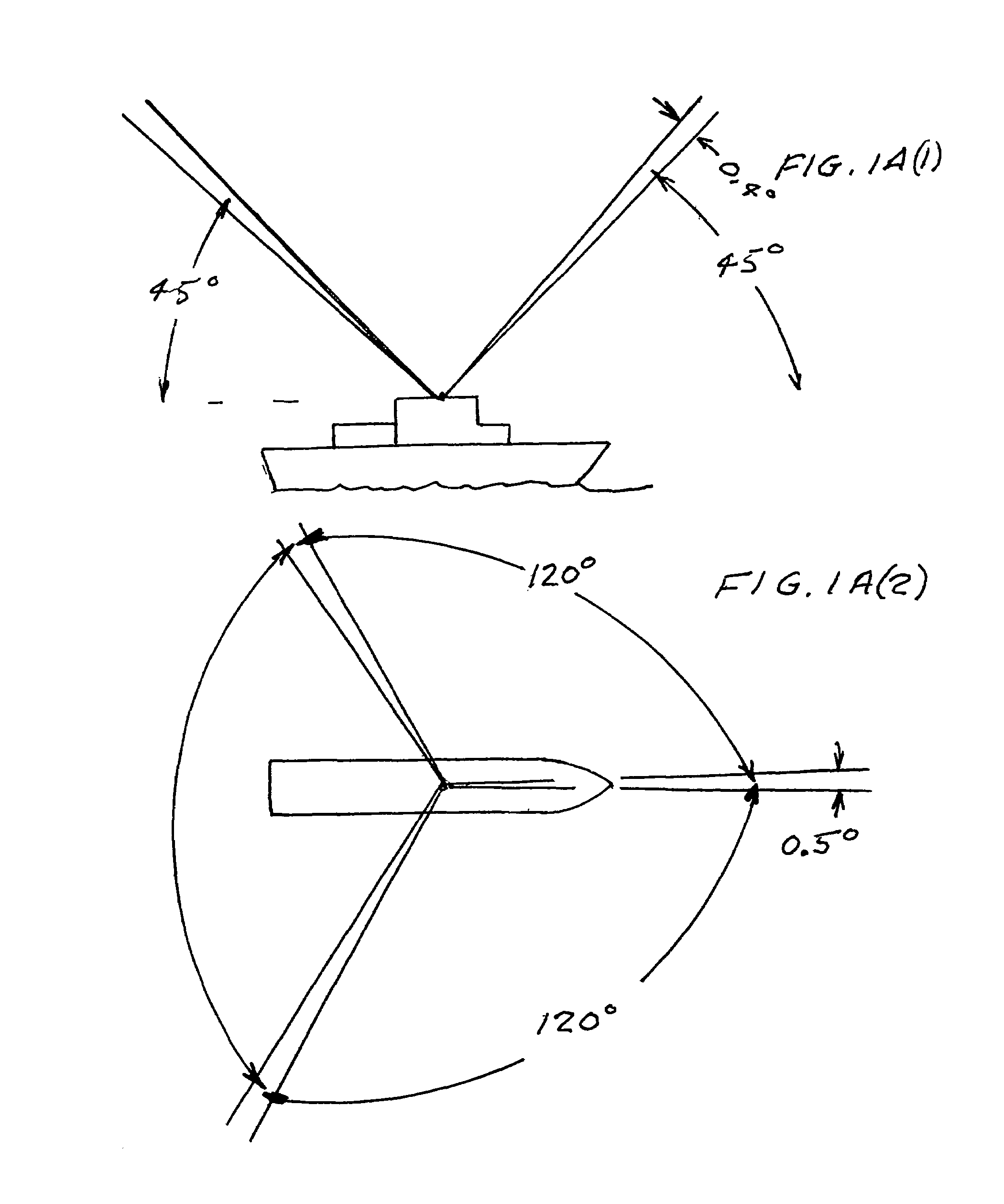
An automatic celestial navigation system for navigating both night and day by observation of K-band or H-band infrared light from multiple stars. A preferred embodiment uses three telescopes with each of the three telescopes rigidly mounted with respect to each other and rigidly mounted on a movable platform such as a ship or airplane with each telescope being directed at a substantially different portion of sky. Telescope optics focuses, onto the pixel array of a sensor, H-band or K-band light from stars in the field of view of each telescope. The system also includes an inclinometer, an accurate timing device and a computer processor having access to cataloged infrared star charts. The processor is programmed with special algorithms to use image data from the infrared sensors, inclination information from the inclinometer, time information from the timing device and the cataloged star charts information to determine positions of the platform. At least two telescopes pointed far enough from the sun detect stars. Direction information from two stars is needed for locating the platform with respect to the celestial sphere. The computer is also preferably programmed to use this celestial position information to calculate latitude, longitude and absolute azimuth, all of which may be displayed on a display device such as a monitor. In a preferred embodiment each of the three telescopes are fixed on a moving ship and views a 0.5×0.4 degree region of the sky for H-band starlight from stars with brightness greater than 6.4 H-band magnitude. Located stars are then compared with star positions from the star catalog within a selected 5×5 degree region of the sky. A correlation of the data from the three telescopic measurements determines the position of the ship to a precision of 30 meters.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Navigational star screening method for star sensors
InactiveCN102840861AEase of decrementSplit evenlyNavigation by astronomical meansStar catalogueScreening method
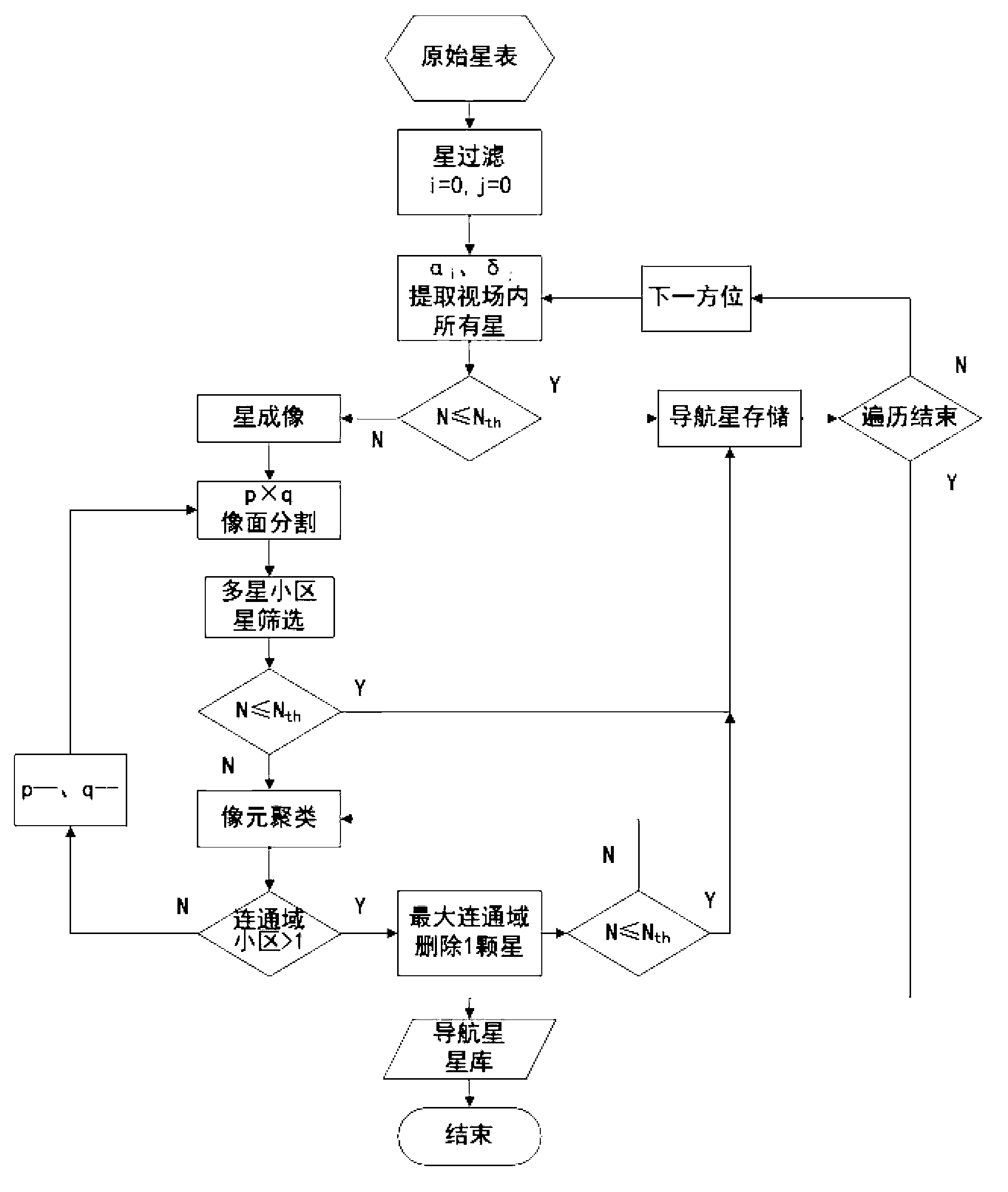
The invention relates to a navigational star screening method for star sensors, which includes the following steps: (1) according to the limiting magnitude of a star sensor, the stars of the original star catalogue of the whole celestial sphere are filtered and a star number threshold Nth is determined; (2) the number of the remaining stars of the star sensor in the field of view of the current sky area is set as N; if N is less than or equal to Nth, then all the remaining stars are chosen as navigational stars, and step 3 is executed; and if N is greater than Nth, then the navigational stars in the field of view of the current sky area are segmented and screened by a multi-scale image plane; (3) after the navigational stars in the field of view of the current sky area are screened, the star sensor turns to the next direction to repeat navigational star screening in step 2 until the whole celestial sphere is traversed. The multi-scale image plane segmentation and screening method adopted in the invention can be adapted to the variation in the star numbers of different sky areas to delete the redundant stars of sky areas with high star distribution density and keep all the stars of low-density sky areas, and moreover, the distribution of the screened navigational stars is even.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF TECH +1
Star sensor navigational star screening method by orthogonal list
InactiveCN102865865AReasonable divisionEvenly find and judgeNavigation by astronomical meansStar catalogueScreening method
The invention relates to a star sensor navigational star screening method by an orthogonal list, comprising the following steps of: 1, carrying out star filtering treatment on the original star catalogue of the whole celestial sphere according to the limit star of a star sensor and the like, and confirming the threshold value Nth of star number; 2, setting the number of the residual stars of the star sensor within a current sky area view field as N, if N is less than or equal to Nth, selecting the residual stars as navigational stars, and carrying out step 3, and if N is larger than Nth, cutting and screening the navigational stars within the current sky area view field by a multi-scale image surface; and 3, after screening of the navigational stars of the current sky area view field is completed, transferring the star sensor to the next position, and repeating the step (2) to screen the navigational stars till going through all the celestial sphere. According to the multi-scale image plane cutting and screening method disclosed by the invention, the redundant stars within a star distribution high intensity sky area can be eliminated along with the star number change of different sky areas, all the stars within a low-intensity sky region can be remained, and the screened navigational stars are evenly distributed.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF TECH +1
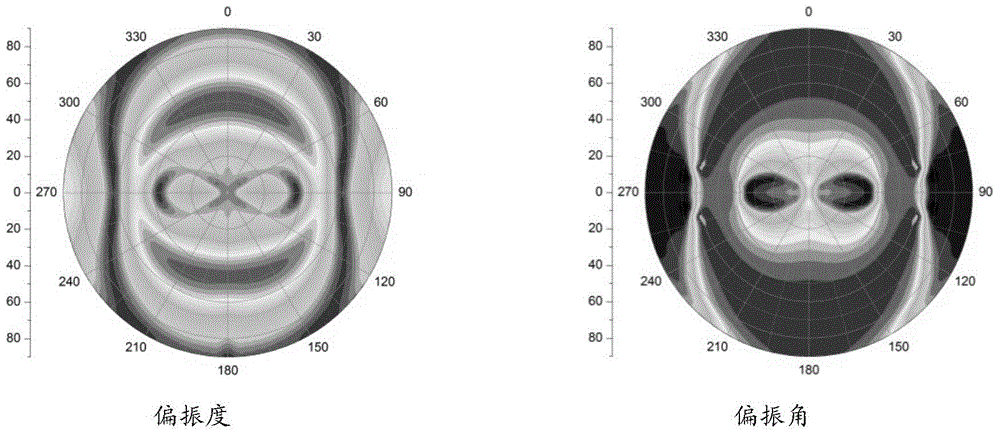
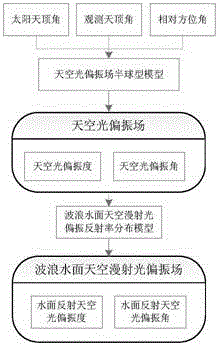
Wave water surface sky diffuse reflection light polarization field simulation method
InactiveCN103940515AIn line with the actual situation of natureImprove universalityLight polarisation measurementRayleigh scatteringDiffuse reflection
The invention relates to a wave water surface sky diffuse reflection light polarization field simulation method. The method has the following steps: a celestial coordinate system describing a sky light polarization field is established; sun point location and observation point location are designed in the celestial coordinate system; a sky light scattering angle is calculated in spherical geometry; degree of polarization of sky light at any point is calculated according to a semi-analytical Rayleigh scattering model; a polarization angle of sky light is calculated according to the sun point location and sky observation point coordinates via a vector mode; the polarized reflectance and the degree of polarization of wave water surface sky diffused light are calculated; and the polarization angle of water surface reflected sky light is obtained according to information of sky light degree of polarization in combination with an STOKES vector and a trigonometric function relationship so that calculation of the polarization state of water surface reflected sky light is realized. Sky light can be incident at any polarization state, and the polarization state of the reflected light of a static water surface and the wave water surface can be realized so that polarization characteristics of a natural water surface can be really described.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Sun vector resolving method based on underwater polarization distribution mode
ActiveCN111220150AAngle measurementNavigation by astronomical meansRayleigh scatteringRayleigh Light Scattering
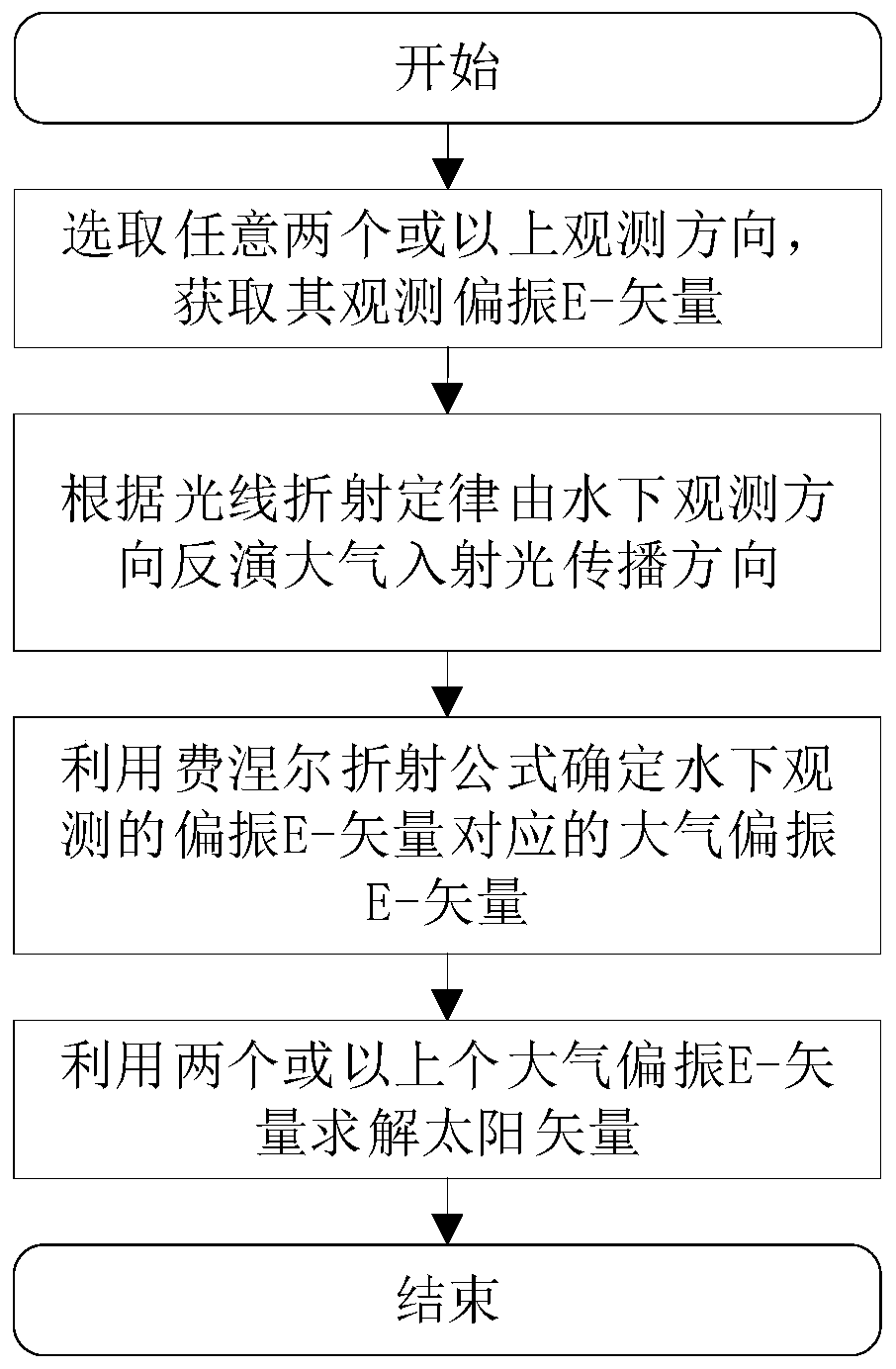
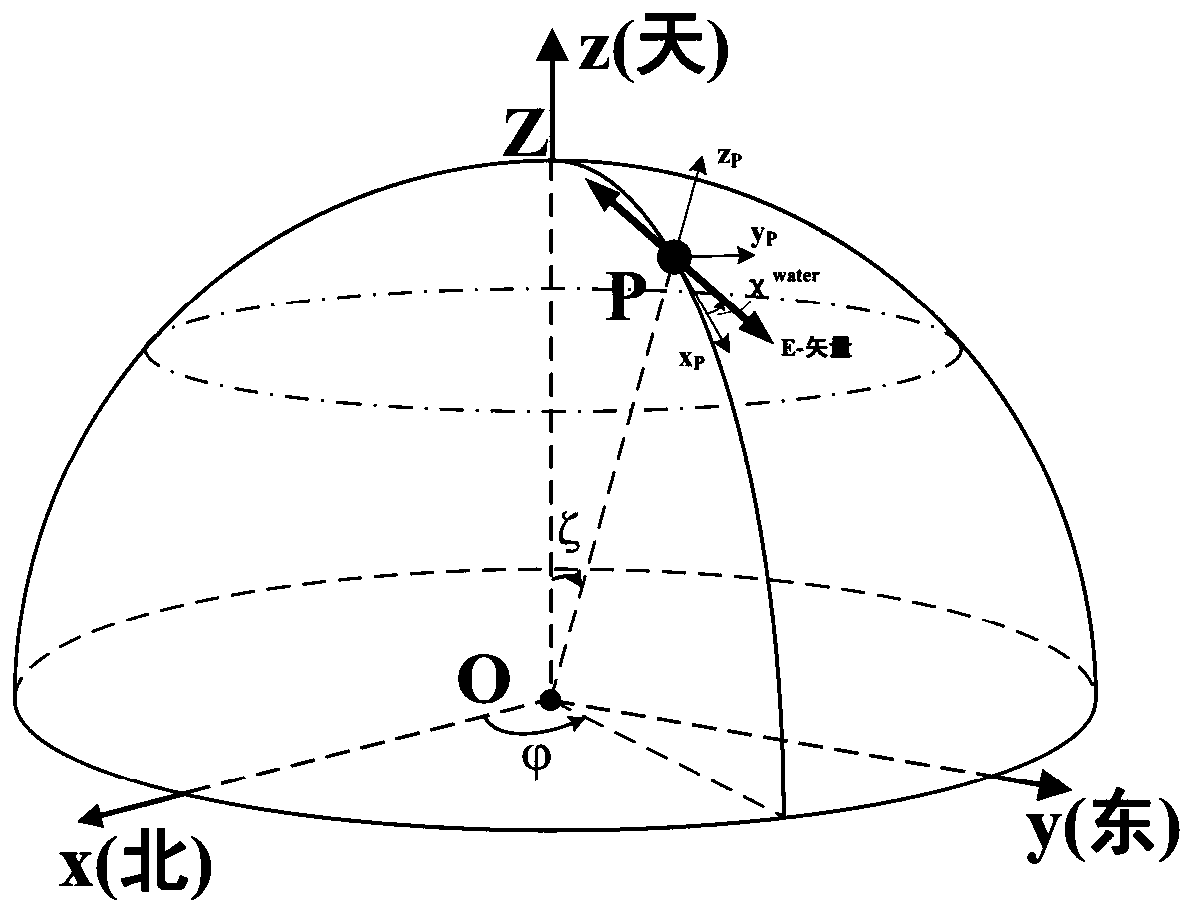
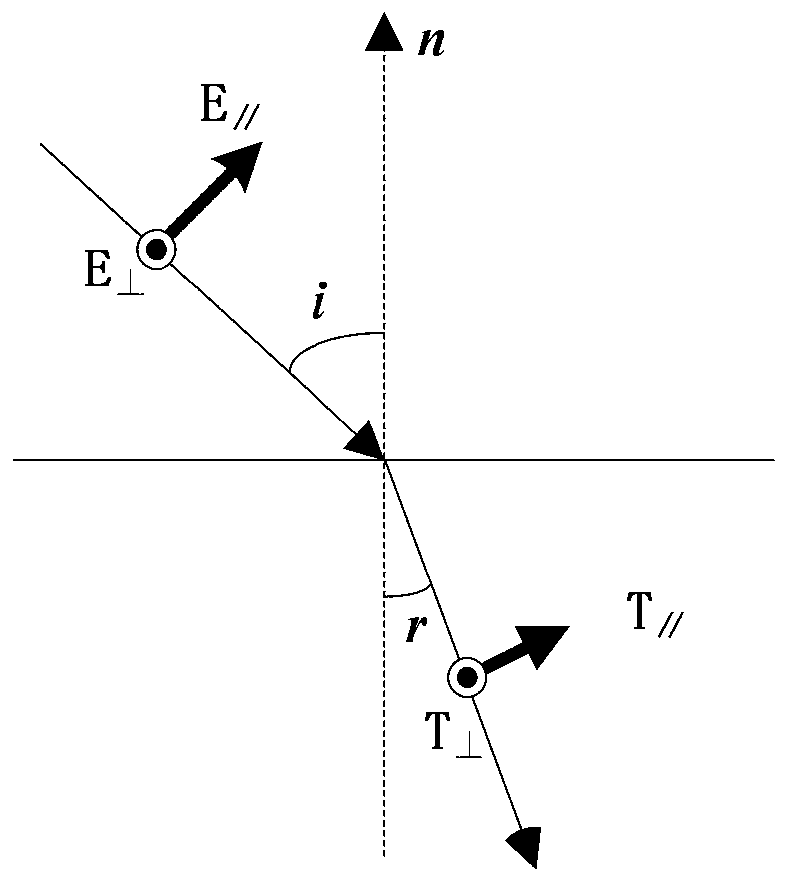
The invention relates to a sun vector resolving method based on an underwater polarization distribution mode. The method comprises the steps of firstly, obtaining the underwater polarization azimuth angle information in at least two arbitrary observation directions under an underwater celestial coordinate system; then, inverting the propagation direction of the atmospheric incident light in the underwater observation direction based on the law of light refraction; determining an atmospheric polarization E-vector corresponding to a polarization E-vector observed underwater by using a Fresnel refraction formula; and finally, according to a Rayleigh scattering model, obtaining a solar vector by utilizing the vertical relationship between the atmospheric polarization E-vector and the solar vector. According to the invention, the sun vector calculation basic model based on the polarization distribution mode in an underwater Snell window under the horizontal attitude is established, and themethod can be popularized and applied to the underwater application scenes of point source type and image type polarization sensors.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Construction method of star database of triangle matching-type star sensor
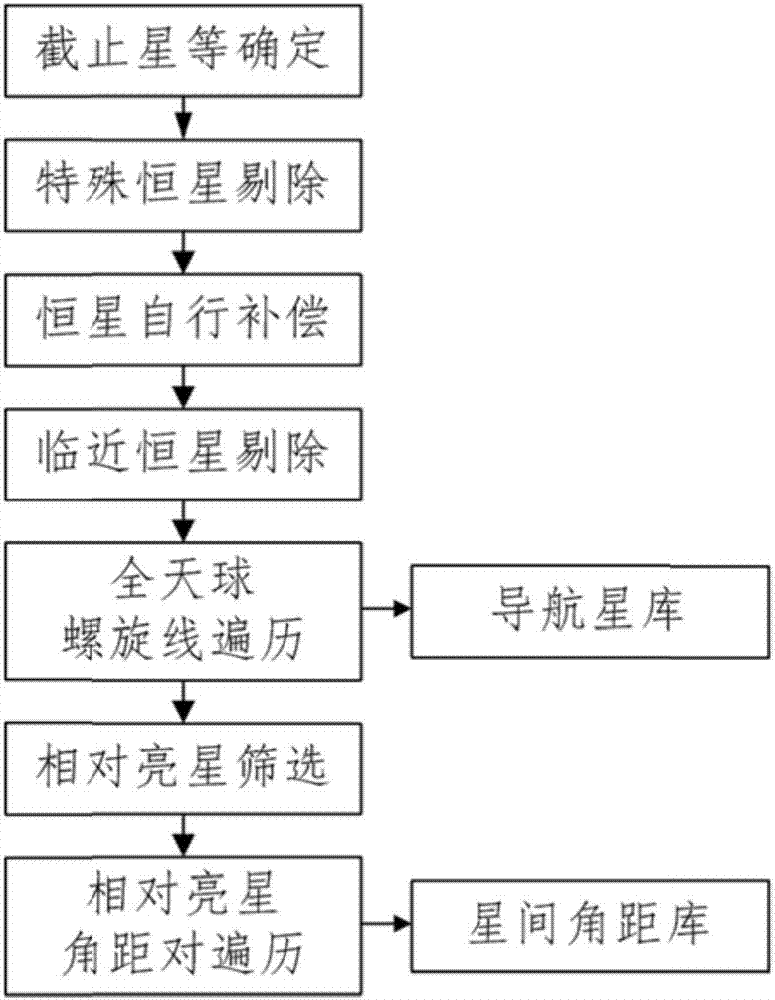
ActiveCN107883946AReduce false recognition rateGuaranteed recognition effectNavigation by astronomical meansHelical lineFixed stars
A construction method of a star database of a triangle matching-type star sensor includes steps of: S1) determining basic cut-off magnitude and candidate cut-off magnitude; S2) rejecting peculiar stars; S3) performing fixed star proper motion compensation algorithm; S4) determining threshold of angular distances of neighboring fixed stars; S5) performing whole-celestial sphere helical line traversal; S6) determining relative bright stars; and S7) generating database of angular distances between stars.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE INST FOR METROLOGY & MEASUREMENT TECH +1
Video display system, video display device, and video display method
ActiveUS20170018217A1Improve dynamic rangeIncrease awarenessTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesComputer graphics (images)Display device
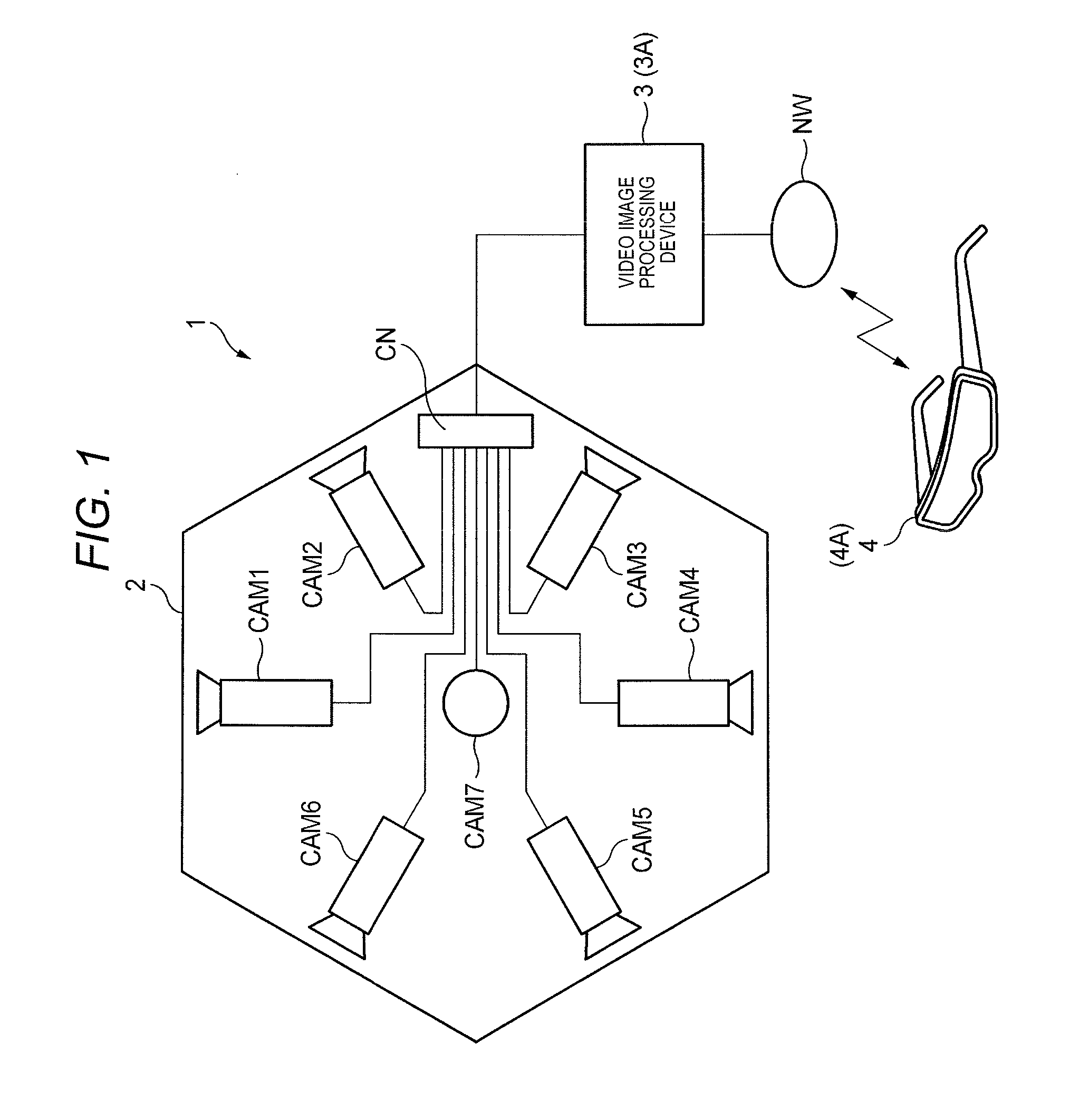
A video image processing device uses a plurality of video data captured by a plurality of cameras to generate a wide range video data of the entire celestial sphere having a 360-degree range around an area where the plurality of cameras is installed and to transmit the generated wide range video data of the entire celestial sphere to a video display device. The video display device detects a direction of the video display device as a direction of a sight line of the user, receives the transmitted wide range video data of the entire celestial sphere, segments a predetermined area of video data including a detection result of a sensor from the wide range video data of the entire celestial sphere, adjusts a luminosity of the extracted predetermined area of video data to fall in a certain range of luminosity, and displays the adjusted predetermined area of video data.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
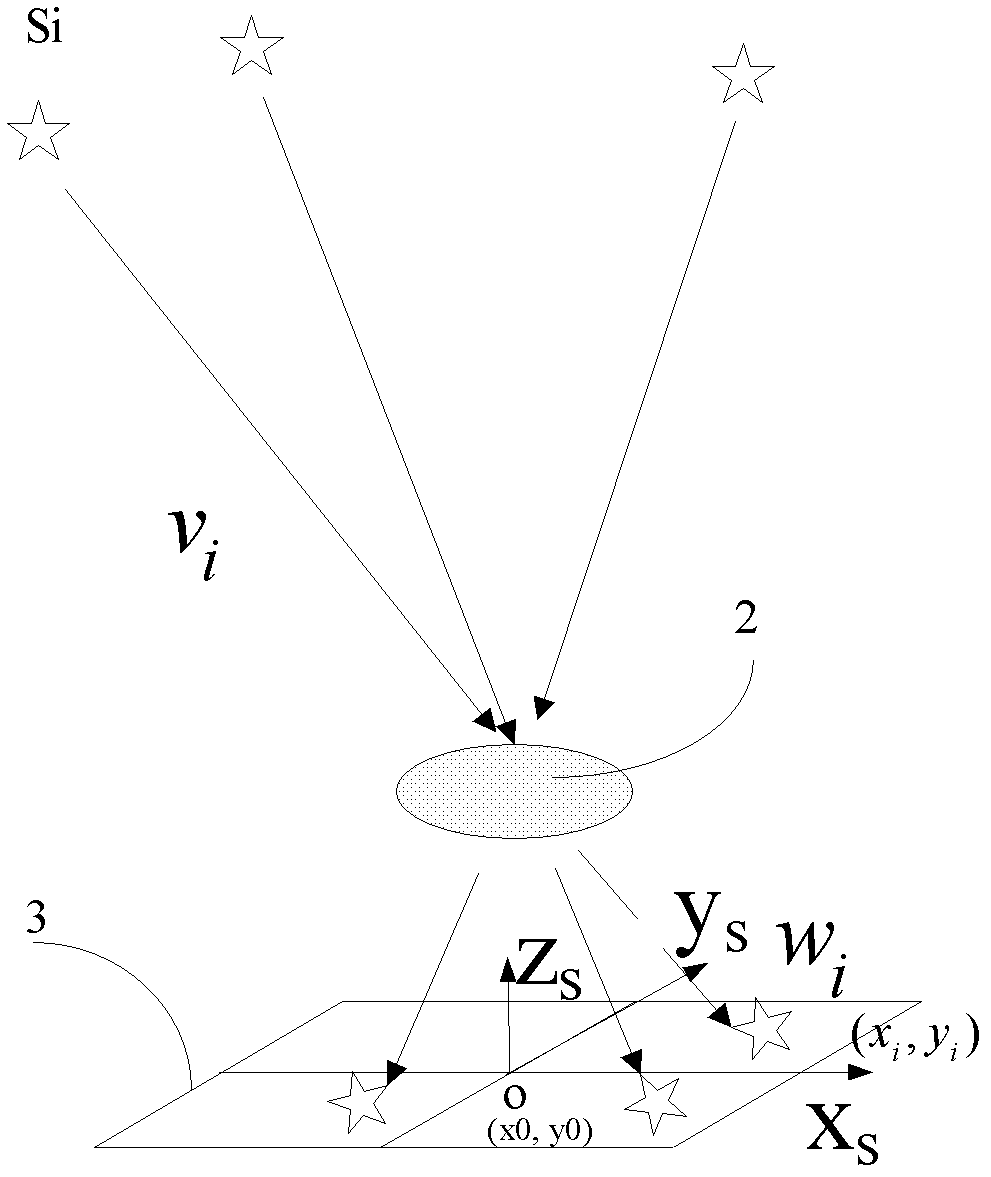
Method for rapidly searching navigation star catalogue
ActiveCN101995248AEvenly Overlapped PartitionEasy retrievalInstruments for comonautical navigationVisual field lossStar catalogue
The invention relates to a method for rapidly searching a navigation start catalogue, which comprises the steps of: firstly, dividing a sky region by directly using an original right ascension and declination circle of a celestial sphere; secondly, calculating a right ascension and declination span range of a region covered by a star sensor according to the direction of a visual axis, and searching the navigation star catalogue in the right ascension and declination span range to obtain a navigation star in a visual filed; thirdly, spreading the celestial sphere into a two-dimensional plane with 180*360 to obtain a two-dimensional array of celestial sphere navigation star distribution; and fourthly, compressing the two-dimensional array into a one-dimensional array through two stages of compressions and then indexing the one-dimensional array by using a hash technology. The navigation star is subjected to no redundancy storage by adopting the two stages of compressions and a Hash mapping technology, therefore, the invention realizes that the index time of the navigation star catalogue is 0(1), can be used for rapidly indexing the navigation star in the visual field of the star sensor from the navigation star catalogue when the given visual axis points 8, and has the characteristics of high indexing speed and high efficiency.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Bionic celestial structure type sun angle sensing device
ActiveCN102385392AMeasurement data directlyHigh precisionControl using feedbackCelestial sphereLight hole
The invention discloses a bionic celestial structure type sun angle sensing device comprising a celestial sphere and a sea urchin pipe structure, wherein the sea urchin pipe structure comprises a plurality of speculum pipes; an optical sensor is arranged on the outer end of each speculum pipe; a compound eye structure is arranged on one semispherical surface of the celestial sphere; the compound eye structure comprises a plurality of light leak holes are formed on the housing of the celestial sphere; a plurality of light holes allowing light to pass through are formed on the other semispherical surface of the celestial sphere; each light hole is communicated with and fixedly mounted on the inner end of one speculum pipe; the plurality of light leak holes are arranged symmetrically one to one with the plurality of light holes; and the center connection line of a pair of mutually symmetrical light leak hole and the light hole is coincident with the central axis of the speculum pipe arranged on the light hole, and further coincident with one diameter of the body of the celestial sphere. The sun angle sensing device is more direct in measuring data and relatively high in accuracy, andhas certain adaptability to cloudy and overcast weathers; and the device is capable of effectively realizing the sun tracking function.
Owner:北京绿贝区块链科技有限公司
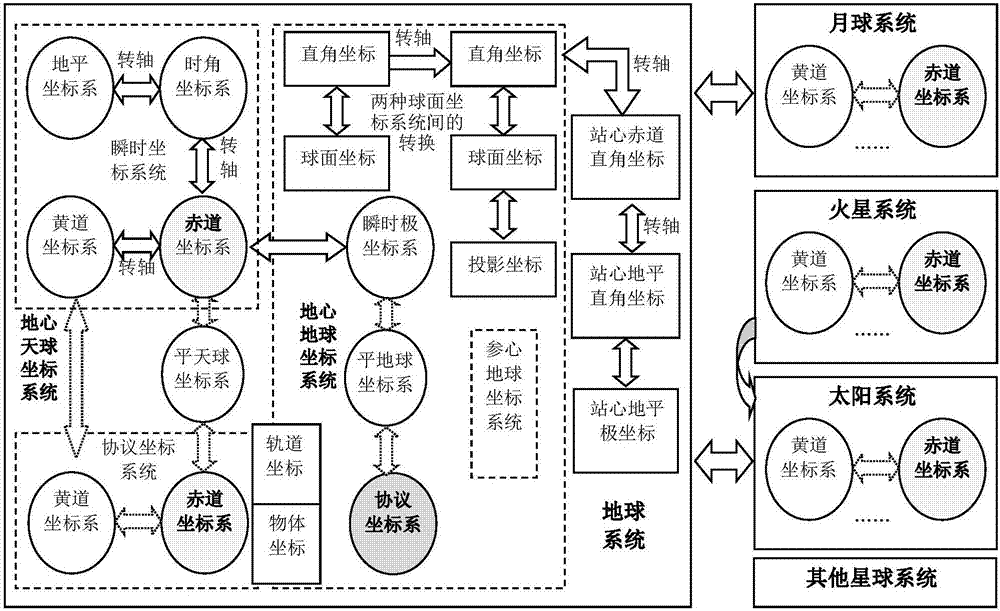
Whole-space information system-oriented coordinate system conversion method
InactiveCN107885546AImprove accuracyImprove reliabilityProgram loading/initiatingGeographical information databasesPhysical spaceSpatial information systems
The invention provides a whole-space information system-oriented coordinate system conversion method, and belongs to the field of geospatial information visualization. A space conversion framework ofa whole-space information system is established, and description of WKT on a space reference system is extended to enable the same to support definition of planets and coordinate systems of celestial-sphere coordinate systems, orbit coordinate systems and the like; and a space reference memory model based on a nine-degree-of-freedom space reference tree is designed, and thus maintenance of the space reference tree, calculation of relative status and plug-in realization of the coordinate system conversion method are realized. The method can effectively solve continuous whole-space-time modelingand simulation of the whole-space information system from macroscopic worlds (such as stars and planets in a solar system) to microcosmic worlds (such as indoor environments), from static status to dynamic status and from physical space-time to logical space-time, has good scalability and realization efficiency, and can be widely applied to many fields of satellite positioning and navigation, aerospace remote-sensing, smart cities, territorial planning, military application and the like.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU NORMAL UNIV
Method of dividing navigational star table
InactiveCN1808524AImprove retrieval efficiencyQuick searchPlanetaria/globesRectangular coordinatesCelestial sphere
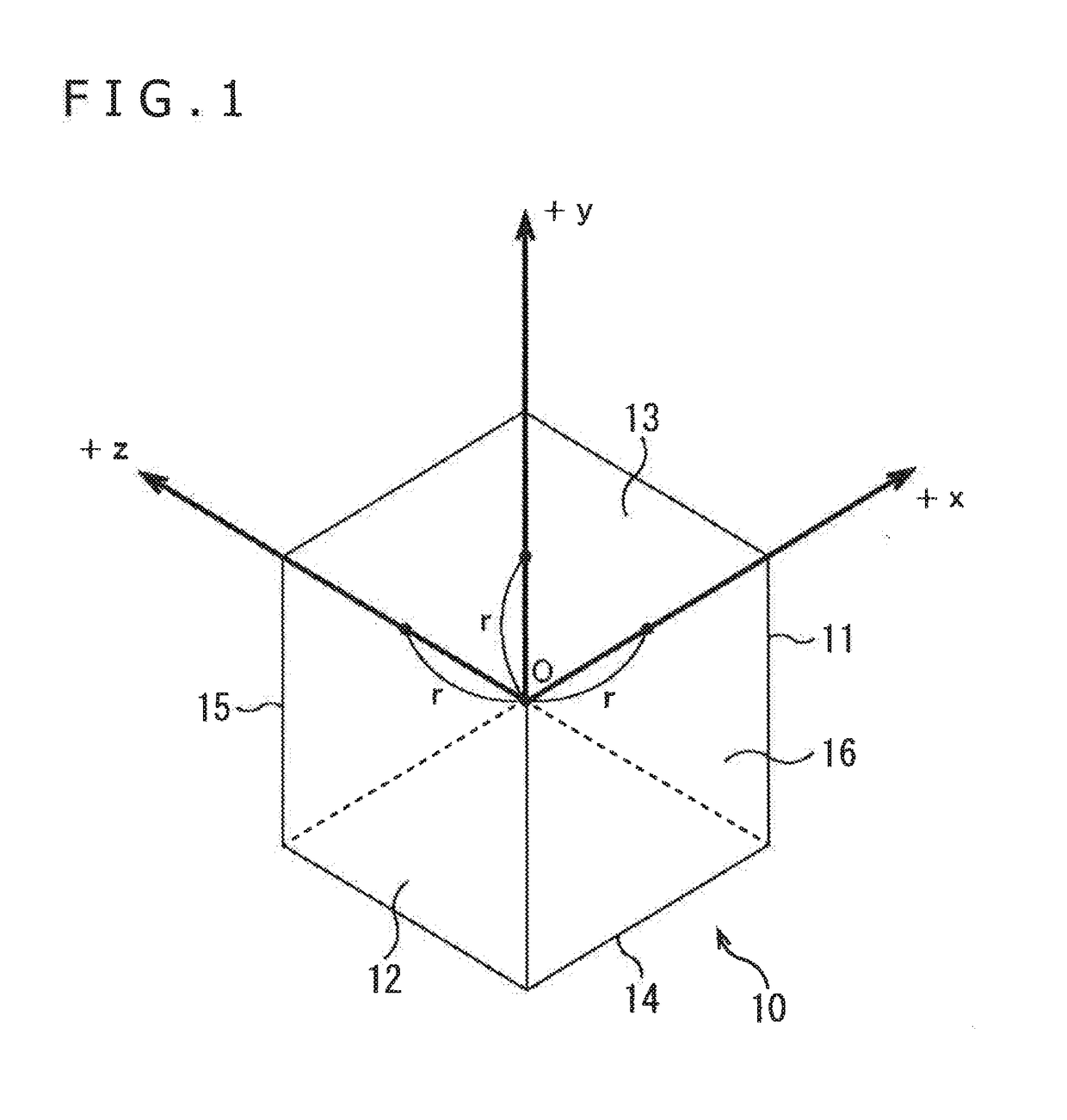
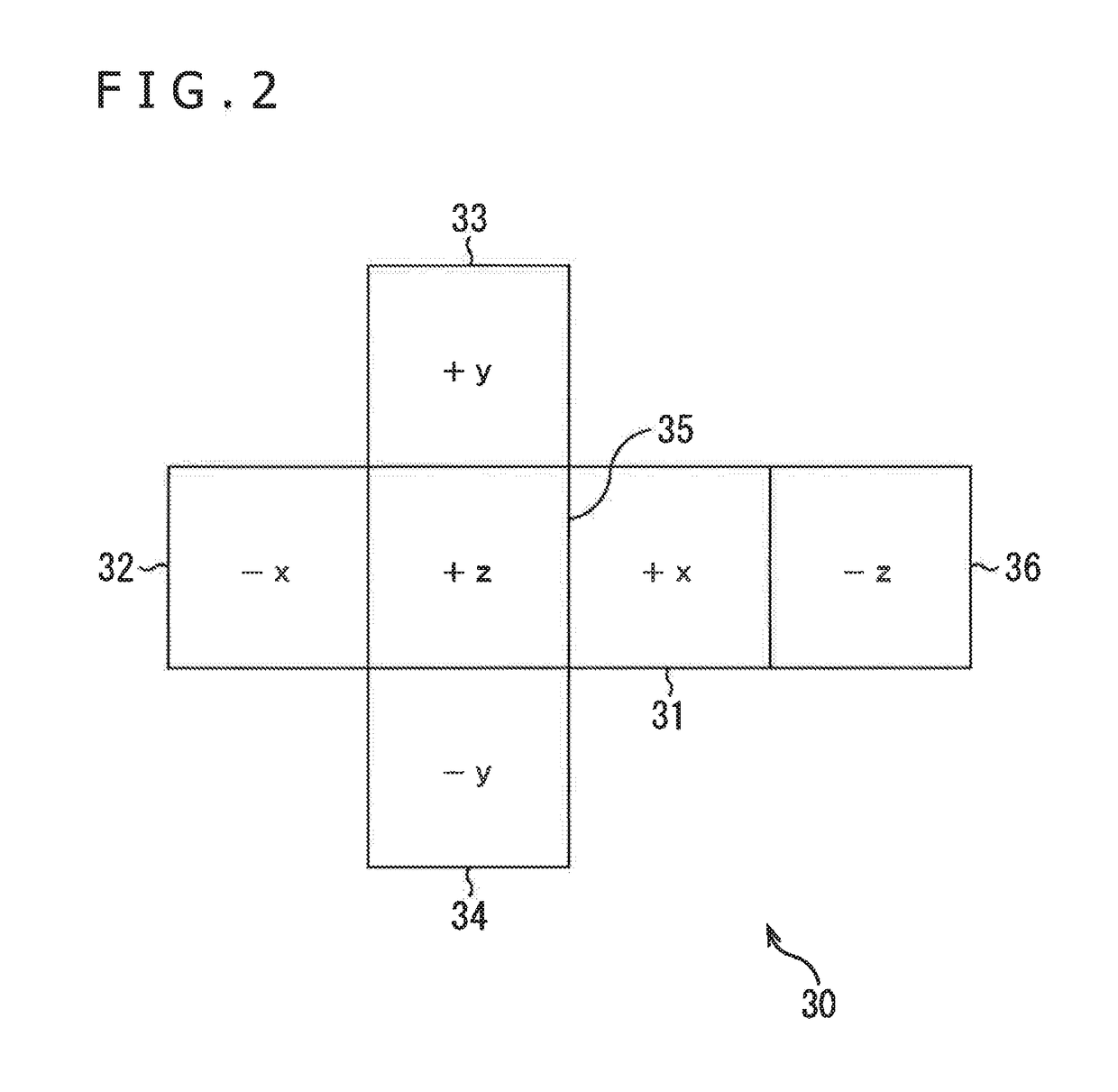
The improved method for NSTR catalogue division method comprises: dividing equally the celestial sphere into six areas with its inscribed cube then for Ní‡N sub-blocks for every area; calculating directional vector opposite to the central axis and boundary point of every sub-block to scan NSTR catalogue and ascribe every NSTR into opposite sub-block; building the partition table to store the opposite stored sub-block SN. This invention realizes the homogeneous division in rectangular coordinates system with high search efficiency.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Large target surface low illumination level all-celestial shooting system
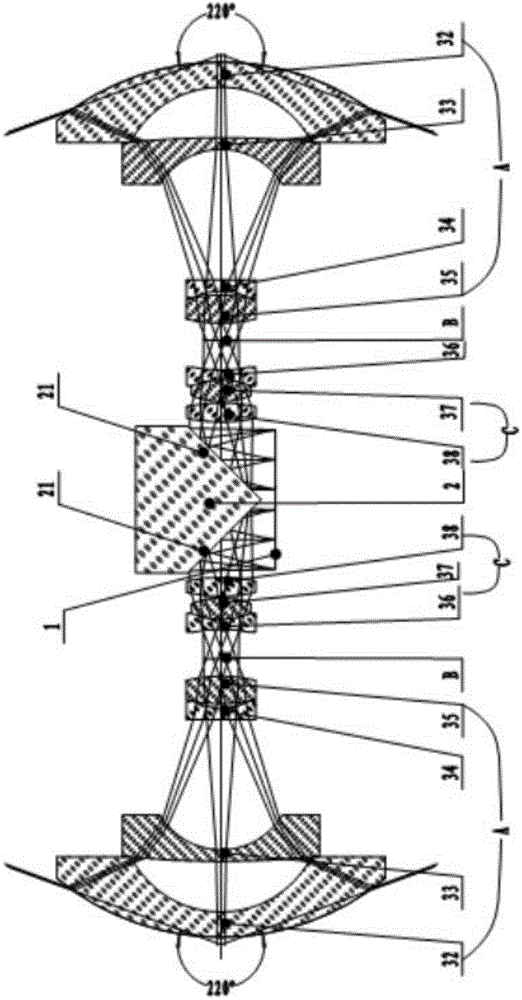
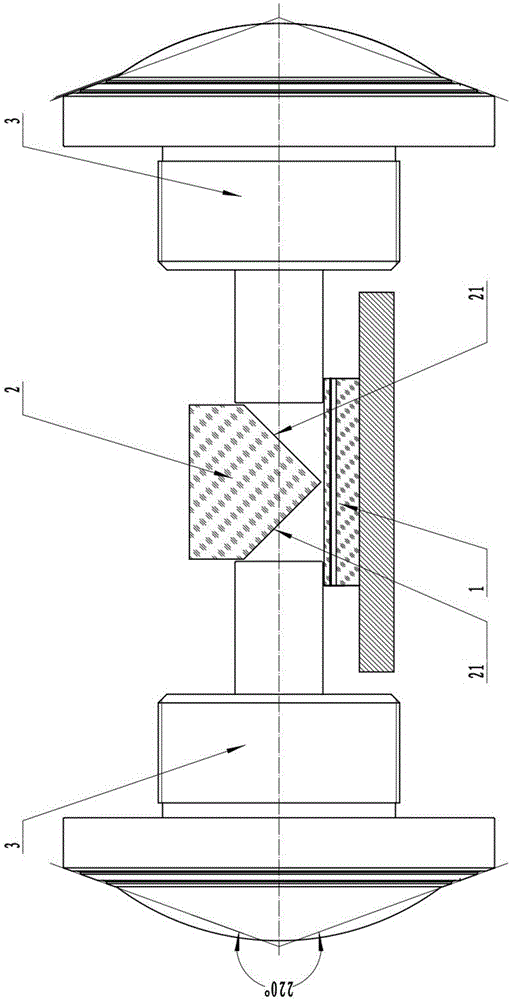
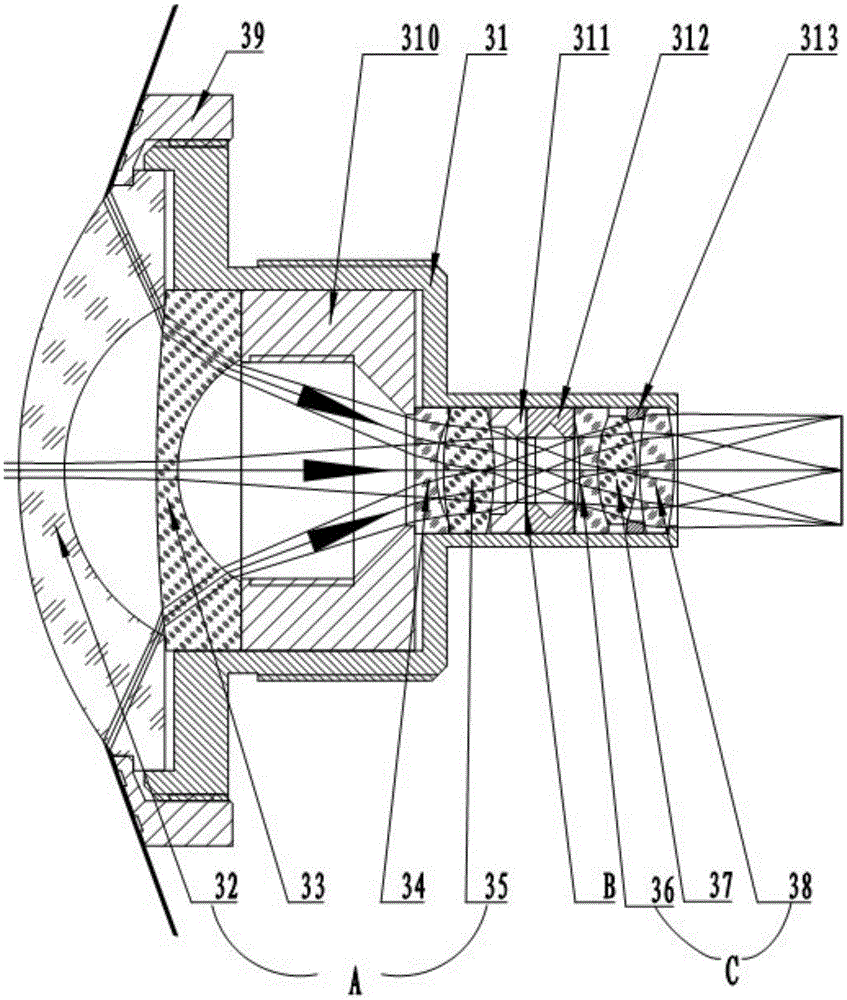
ActiveCN105530415AIncrease the effective apertureReduce edge distortionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsVisual field lossIlluminance
The invention discloses a large target surface low illumination level all-celestial shooting system, comprising a sensing chip, a rectangular prism and two wide-angle lenses. The rectangular prism is provided with two reflection surfaces; the two wide-angle lenses are symmetrically arranged on two sides of the rectangular prism and a 45-degree included angle is formed between the incident light axis of each wide-angle lens and the reflection surface of the corresponding side; the 45-degree included angles are formed between the sensing chip and the two reflection surfaces; the visual field angle of the wide angle lens is more than 220 degrees and F-Theta distortion is smaller than 15%; the effective rear intercept of the wide angle lens is greater than 5.6mm; the system utilizes two wide angle lenses with visual field angles greater than 220 degree to converge the light rays which are then imaged on the same sensor chip after refraction by the rectangular prism; two wide angle lens commonly use one sensor chip to constitute a large target low illumination level all-celestial shooting system, which increases the effective aperture of the system, reduces the distortion of the edge of the system, greatly improves the resolution ratio of the integral system and enables the system effect to achieve the all dimension 720 degree visual effect.
Owner:FOCTEK PHOTONICS LNC
Method of detecting space debris
ActiveUS20130170707A1Efficient detectionSimple processImage analysisCosmonautic vehiclesVirtual spaceMotion vector
A method of detecting space debris includes: generating a virtual space debris in accordance with the law of conservation of mass by applying a debris breakup model to an object of breakup origin; calculating an orbit of each virtual space debris based on a debris orbit propagation model; and generating appearance frequency distribution of a motion vector of each virtual space debris on the celestial sphere based on the orbit calculation. The above operations are executed multiple times. The method further includes setting a search range vector based on a motion vector having a high level of the appearance frequency distribution of the motion vector, and applying a stacking method to regions in images captured at time intervals during the fixed point observation, the regions being shifted along the search range vector sequentially in the order of capture, thereby detecting space debris appearing on the images.
Owner:IHI CORP +1
Navigation database building method applicable to high level background star pattern recognition
InactiveCN104298667ASolve the distribution in the pole densitySolve the situationNavigation by astronomical meansSpecial data processing applicationsFixed starsNavigational triangle
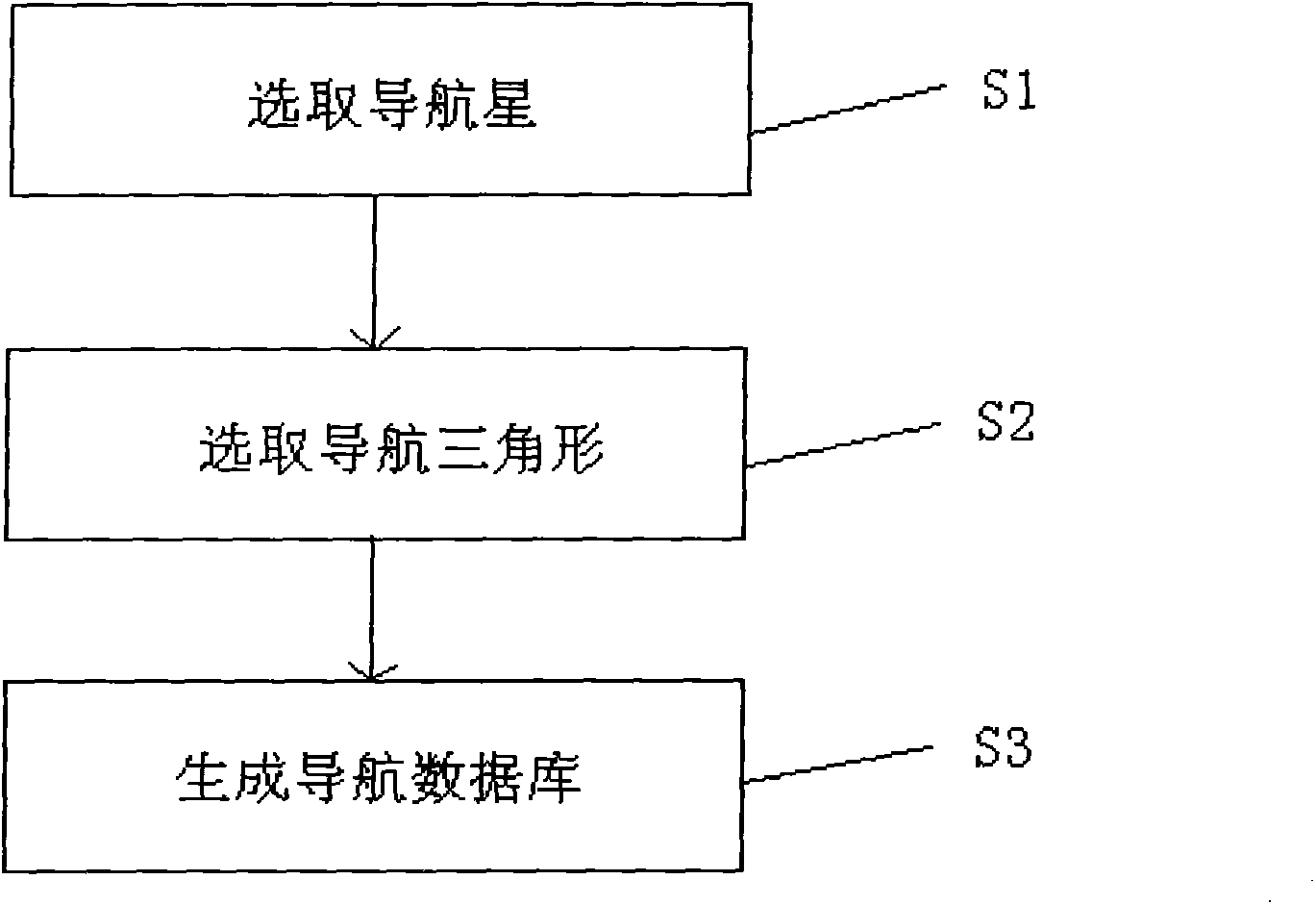
The invention relates to a navigation database building method applicable to high level background star pattern recognition, and belongs to the technical field of navigation database building. According to the method, on the basis of obtaining a visual axis realizing uniform unit spherical surface distribution, navigation stars and navigation triangles are selected, so that the navigation stars and the navigation triangles distributed as uniformly as possible in aspects of positions and energy in a celestial sphere can be obtained; each navigation star is enabled to have a chance to construct the navigation triangles; the data redundancy and the regional hollowness caused by energy instability, nonuniform distribution and a huge number of fixed stars and triangles are avoided; and the effectiveness of a star pattern recognition algorithm is ensured.
Owner:THE 3RD ACAD 8358TH RES INST OF CASC
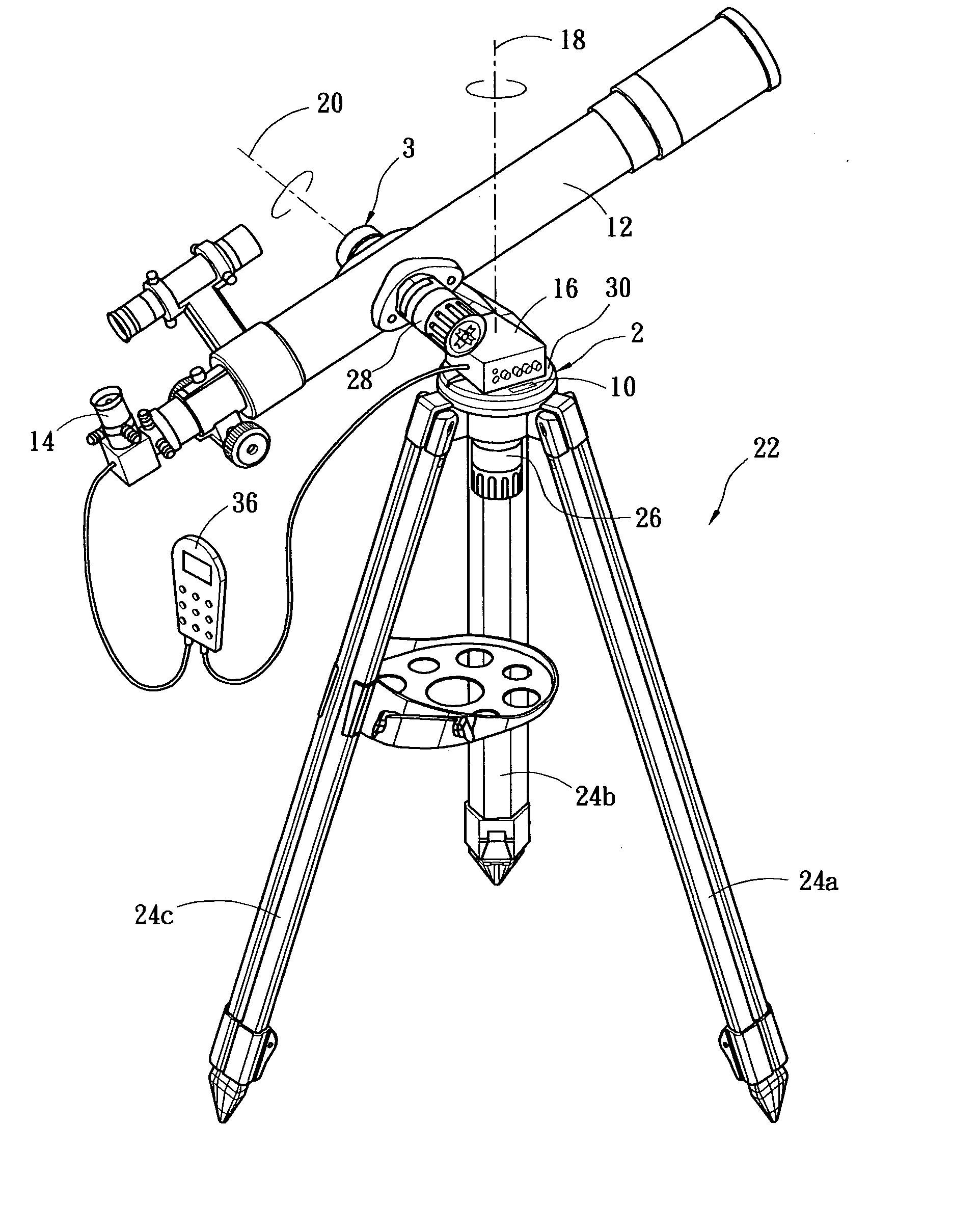
Polar axis auxiliary adjusting system for equatorial type astronomical telescope and realizing method thereof
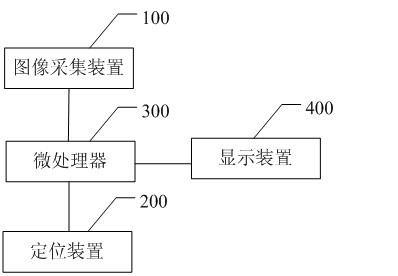
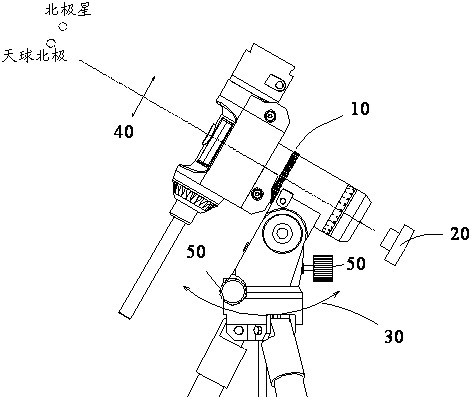
The invention relates to a polar axis auxiliary adjusting system for an equatorial type astronomical telescope and a realizing method thereof, wherein the polar axis auxiliary adjusting system comprises an image acquisition device coaxial with a polar axis, a positioning device, a microprocessor and a display device. The microprocessor is respectively connected with the image acquisition device, the positioning device and the display device. Thus, the polar axis auxiliary adjusting system can assist a user in accurately adjusting the polar axis of the equatorial type astronomical telescope, so as to cause the polar axis to accurately point at the position of the polaris of the northern hemisphere. Meanwhile, an adjusting method is very simple, and the polar axis of the equatorial type astronomical telescope can be easily adjusted in real time without utilizing excessive astronomical knowledge and data.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BOSMA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com