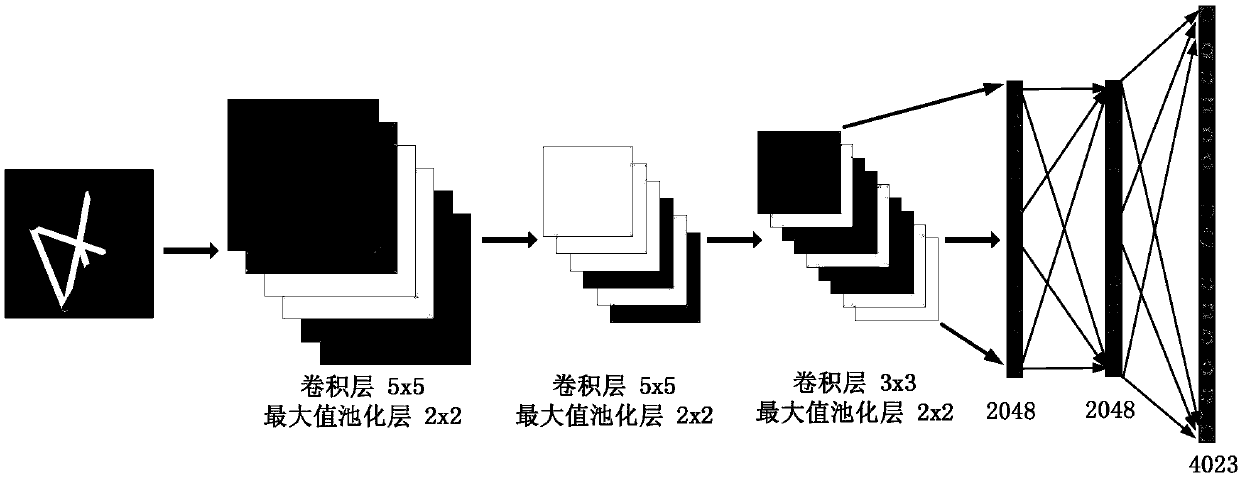
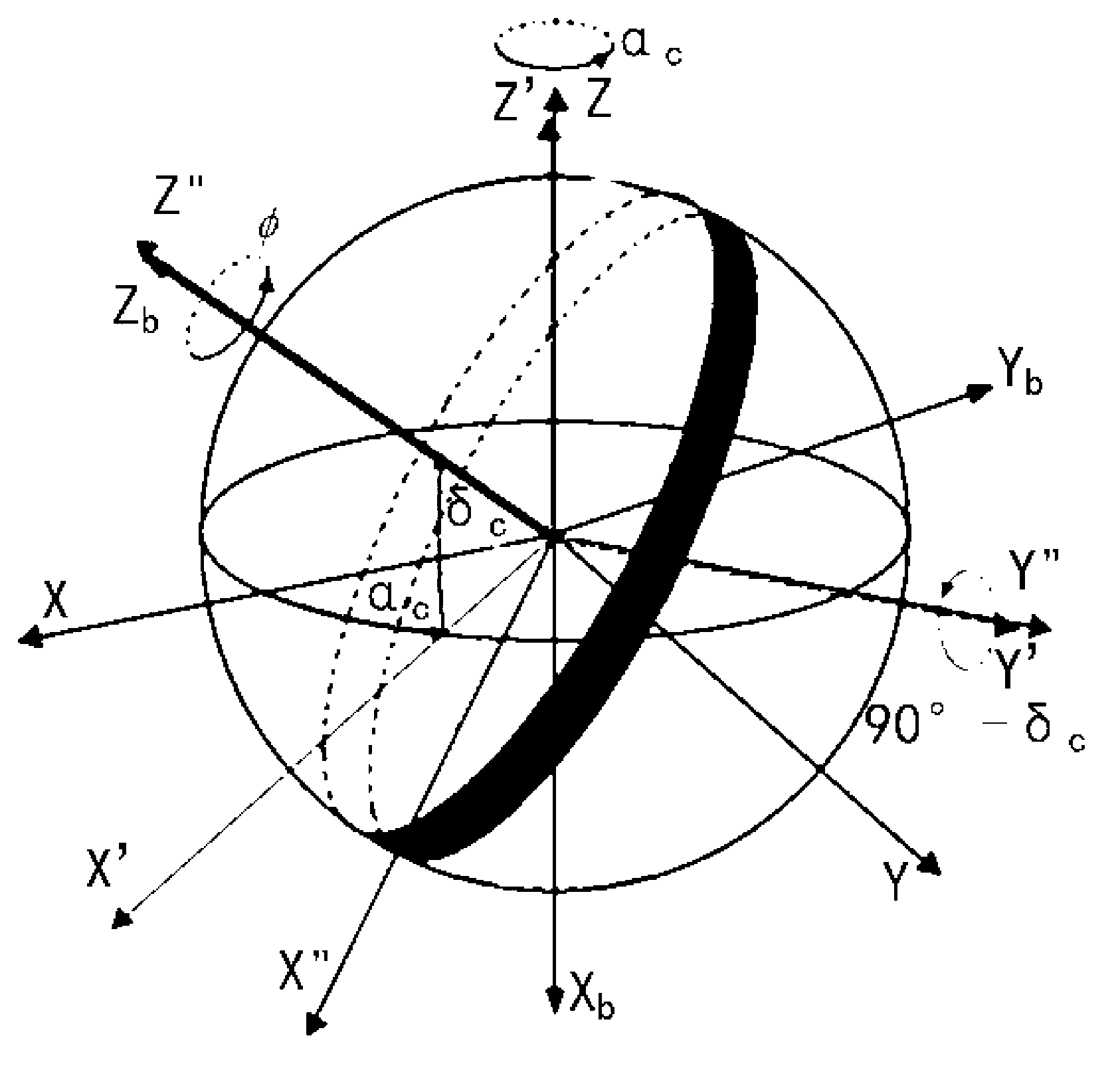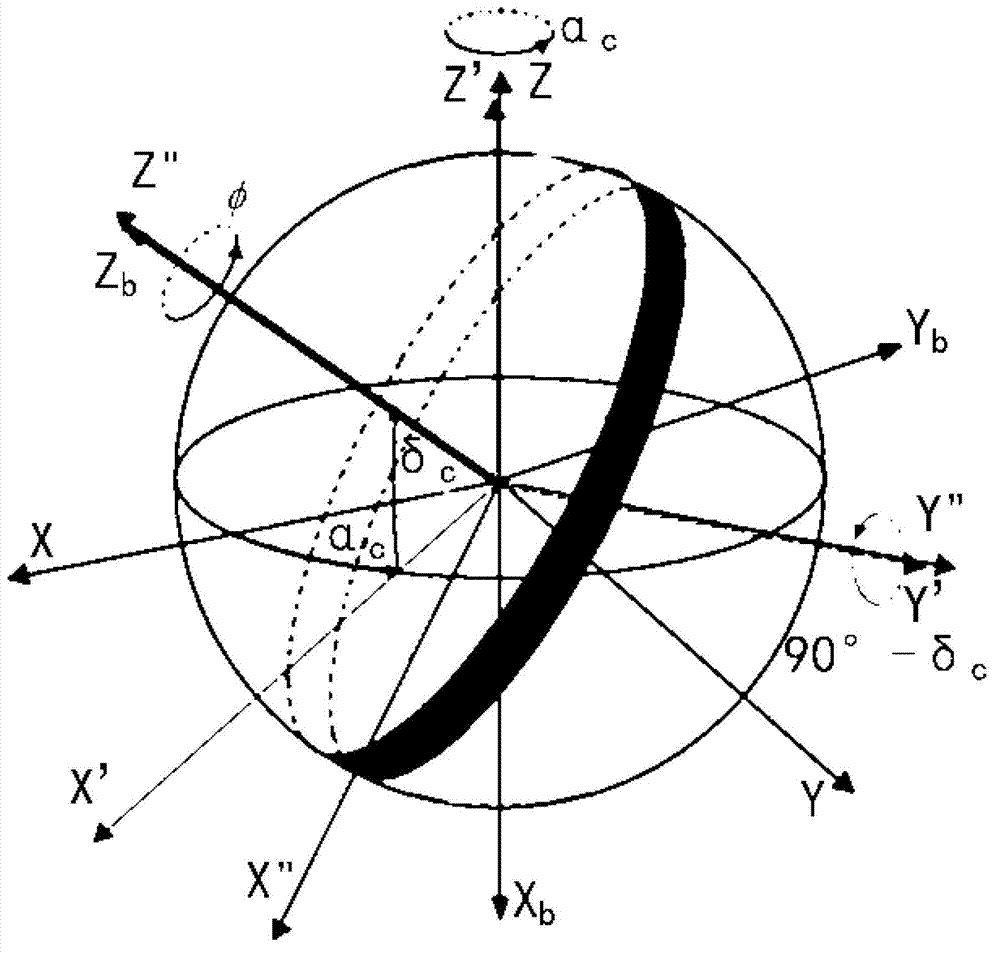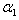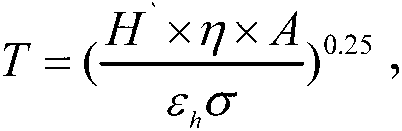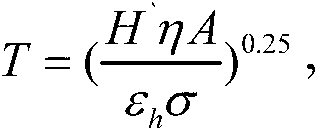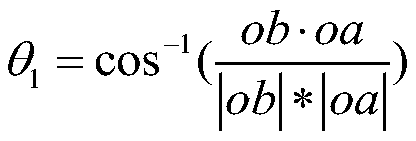Patents
Literature
132 results about "Star catalogue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A star catalogue (Commonwealth English) or star catalog (American English), is an astronomical catalogue that lists stars. In astronomy, many stars are referred to simply by catalogue numbers. There are a great many different star catalogues which have been produced for different purposes over the years, and this article covers only some of the more frequently quoted ones. Star catalogues were compiled by many different ancient people, including the Babylonians, Greeks, Chinese, Persians, and Arabs. They were sometimes accompanied by a star chart for illustration. Most modern catalogues are available in electronic format and can be freely downloaded from space agencies data centres.
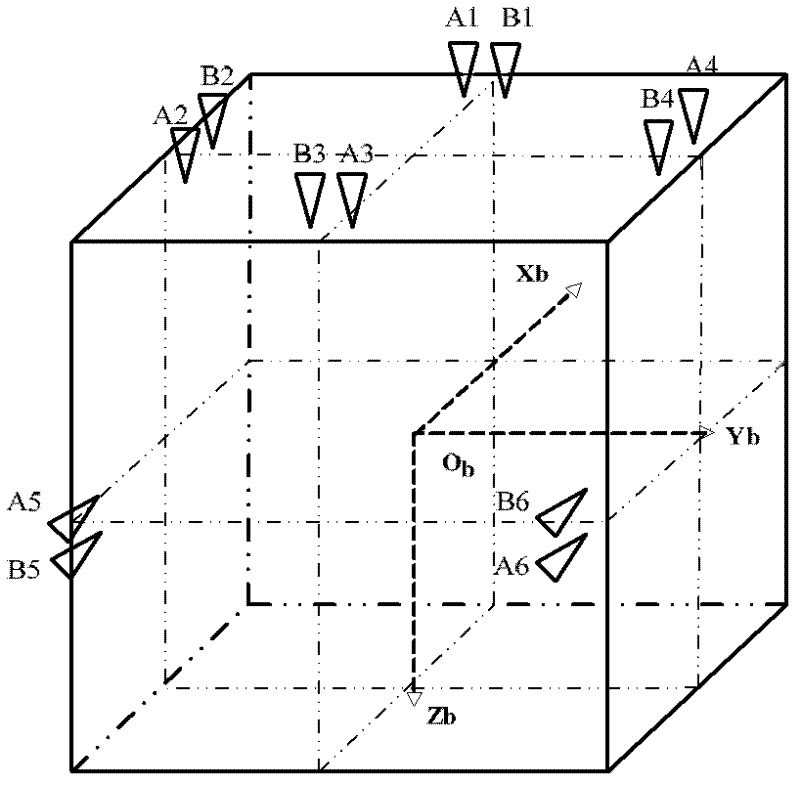
16-thruster layout designing method of omnidirectional orbital transfer spacecraft
ActiveCN102649480AReasonable layoutOptimize layoutCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusStar catalogueComputer module
The invention provides a 16-thruster layout designing method of an omnidirectional orbital transfer spacecraft. The method comprises the following steps: (step A) forming a group of thruster combined modules by using four thrusters according to a method of uprightly mounting three thrusters and obliquely mounting one thruster; (step B) laying four groups of thruster combined modules at four opposite angles of a satellite, wherein any two groups of thruster combined modules are not adjacent to each other; and (step C) configuring two sets of independent branch pipelines, so that eight thrusters in the 16 thrusters share one set of pipeline and the rest eight thrusters share the other pipeline. According to the invention, a thruster layout scheme of a 16-thruster full-orbit motor spacecraft with optimized angle layout is designed; therefore, three-axis and six-direction thrust force can be provided, posture control and orbit control backup functions are obtained, no area center is occupied by angle layout design, and a larger layout space is provided for a star catalogue single machine.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
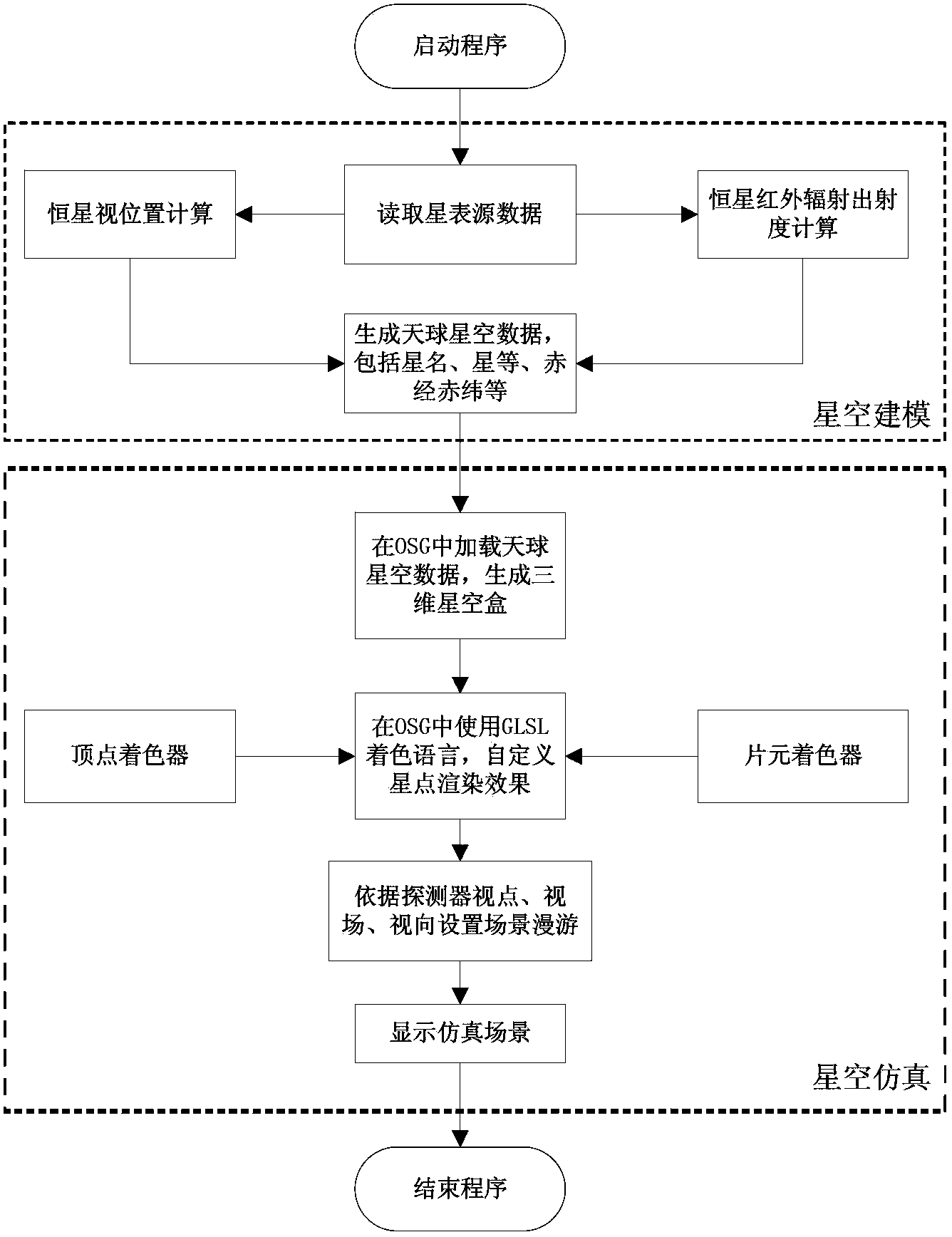
A method for fast generating an optical starry sky background
InactiveCN103679799APrevent size changeIncrease generation speedPlanetaria/globes3D modellingFixed starsNutation
The invention belongs to optical technical field and specifically relates to a method for fast generating an optical starry sky background. The method comprises following steps including: a step 1, modeling a sky background in which star catalogue data of fixed stars is used as a source, by means of transformation of time and a coordinate system and correction of the apparent positions of heavenly bodies, starry sky background models at any observation point any time are constructed and a calculating result is inputted into a base in order to be used for simulation, wherein the calculating result comprises star names, star magnitudes, right ascension, and declination; and a step 2, simulating the established starry sky background model. The step 1 uses Hipparcos Catalogue as a data source of a visible light band. According to the selected Hipparcos Catalogue, the apparent positions of the fixed stars are calculated. Considered factors comprise annual parallax and proper motion caused by revolution of the earth, aberration caused by the self motion of an observer, annual aberration, precession, and nutation caused by earth revolution about the sun. The speed for generating a starry sky background by using the method may reach 50Hz.
Owner:中国航天科工集团第二研究院二〇七所
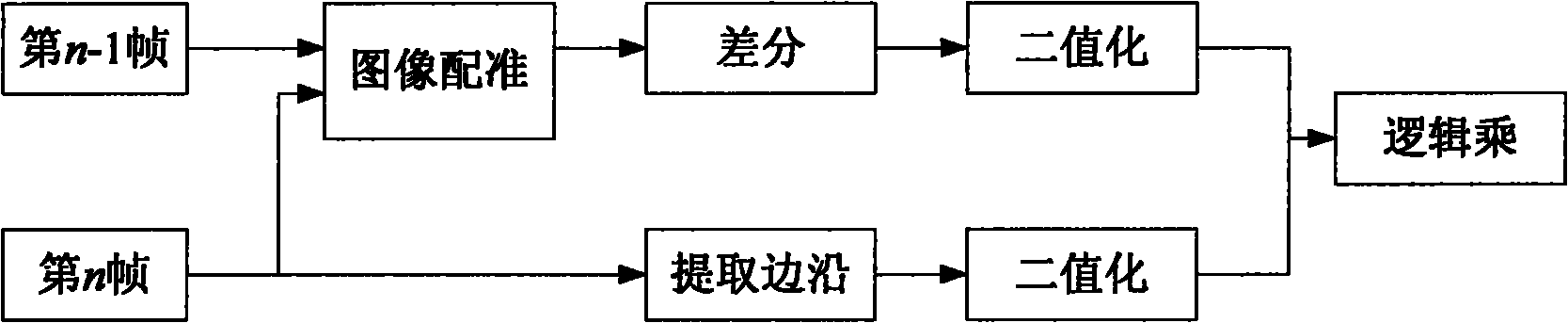
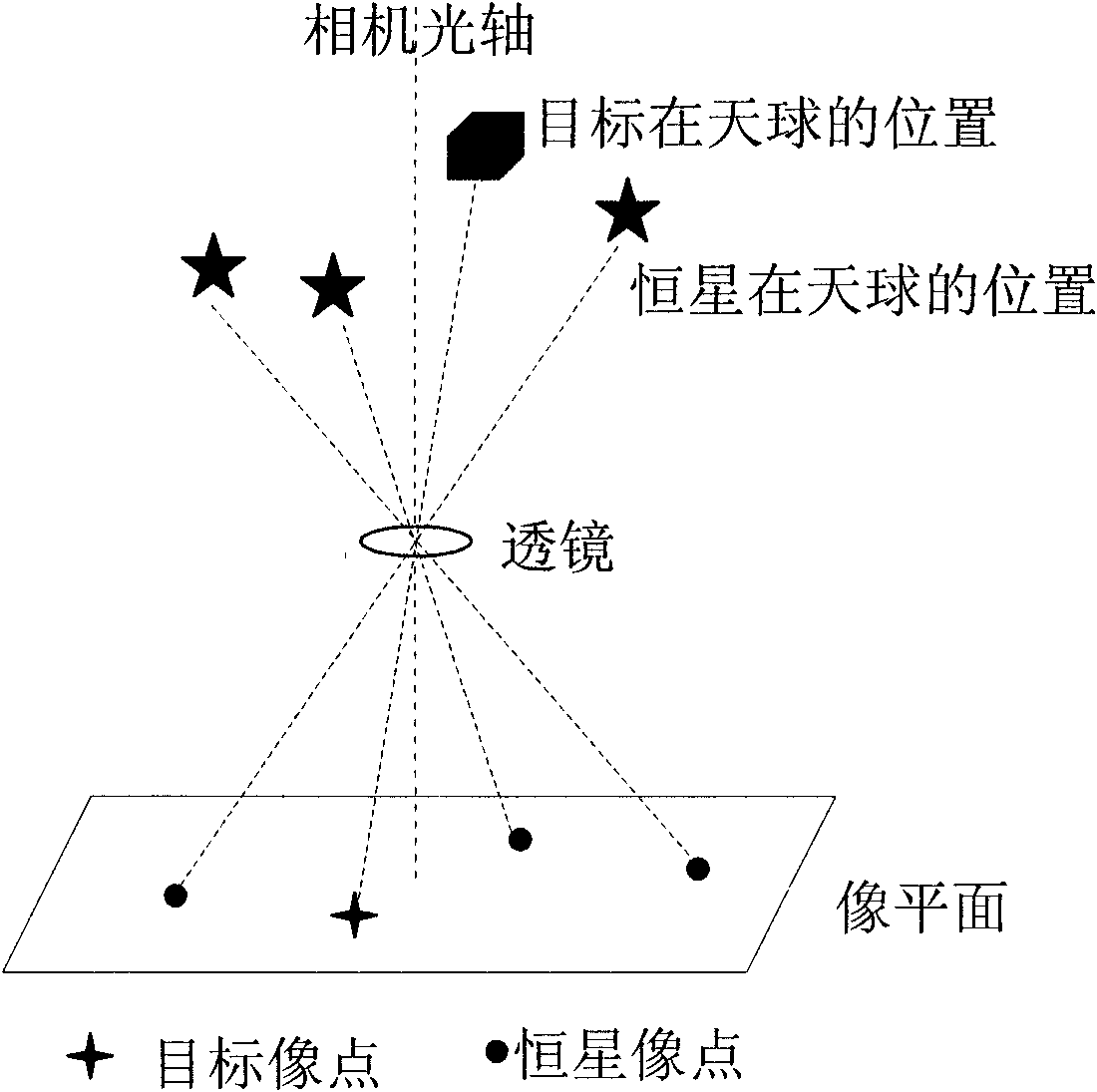
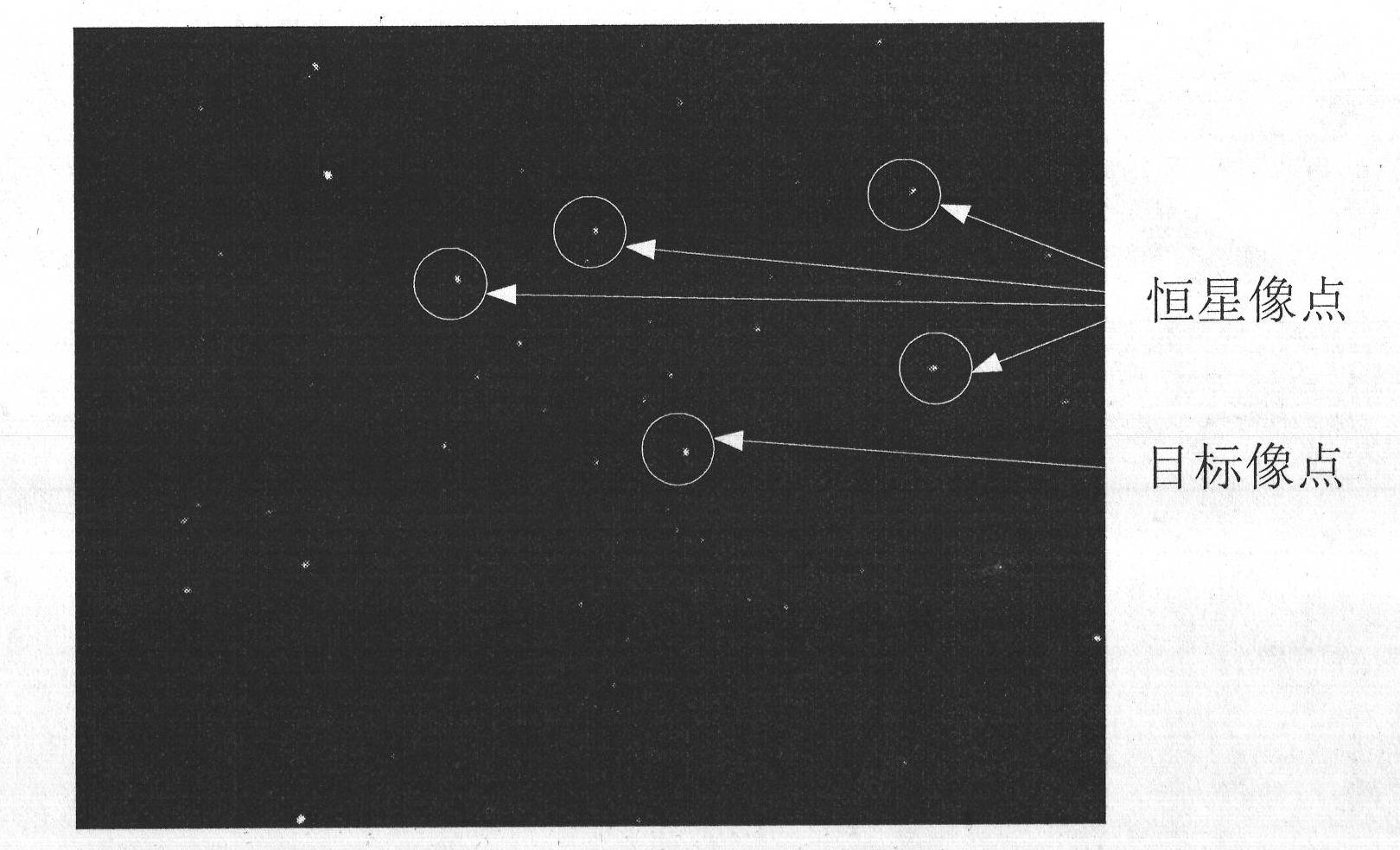
Method for identifying long-distance space motion target based on stellar map matching
InactiveCN102254147AImprove anti-interference abilityEfficient acquisitionImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionFixed starsStar catalogue
The invention provides a method for identifying a long-distance space motion target based on stellar map matching. The method comprises the following steps: extracting coordinates of image points of all original images photographed by a visible light camera of a miniature space detector; composing the arranged image points into triangles in a combination mode; reading a star catalogue in the memory of the visible light camera of the miniature space detector, and identifying all triangles formed by the image points by adopting a triangle identification algorithm; and deleting all the identified image points, and remaining the unidentified image points which are image points of the motion target. In the method, the characteristics of relative motion of the visible light camera of the miniature space detector and the motion target is not required to know in advance, the image points of a fixed star are deleted by adopting a star catalogue identification method, and the star catalogue contains all fixed stars in the starry sky, so that the image points of the target can be effectively acquired by adopting the method, and the star catalogue identification method has the advantage of higher interference resistance.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
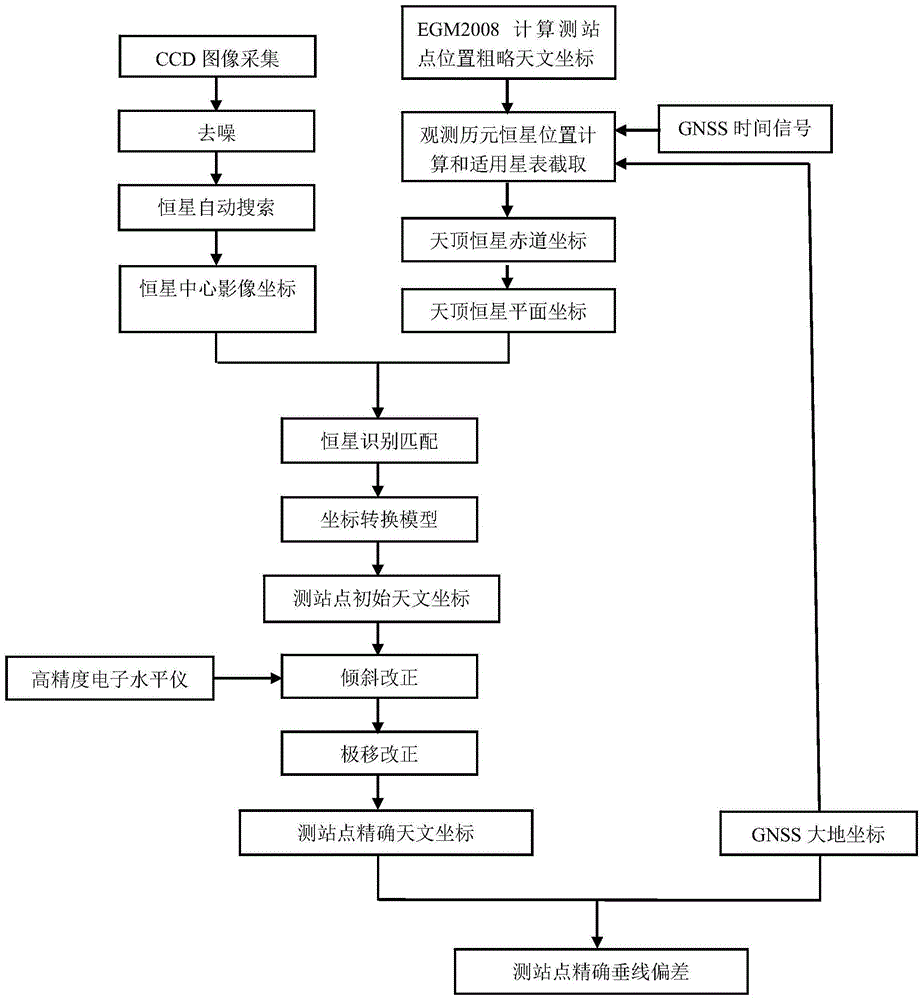
GNSS-CCD-integrated zenith telescope high-precision vertical deflection fast measurement method
ActiveCN104913780AShorten the timeMeasurement accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsInformaticsFixed starsStar catalogue
The invention discloses a GNSS-CCD-integrated zenith telescope high-precision vertical deflection fast measurement method. At a measurement station, the optical axis of a zenith telescope faces to the zenith and takes a picture of a zenith zone so that a CCD fixed star image is obtained, fixed star image coordinates are calculated, exposure epoch is controlled by geodetic coordinates and a GNSS time signal measured by GNSS, fixed star information in the zenith zone is acquired in an appropriate star catalogue according to the measurement station vertical deflection calculated by an EGM2008 geopotential model, coupling identification of fixed stars in a zenith tangent plane zone of a celestial sphere in the star catalogue and in the CCD fixed star image is realized, zenith astronomical coordinates are calculated by least spuare iterative computation, and vertical deflection of the observed point is calculated according to geodetic coordinates. Compared with the prior art, the method provided by the invention has the characteristics of simple operation, time and labor saving and high measurement precision and is suitable for high-precision vertical deflection fast measurement.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
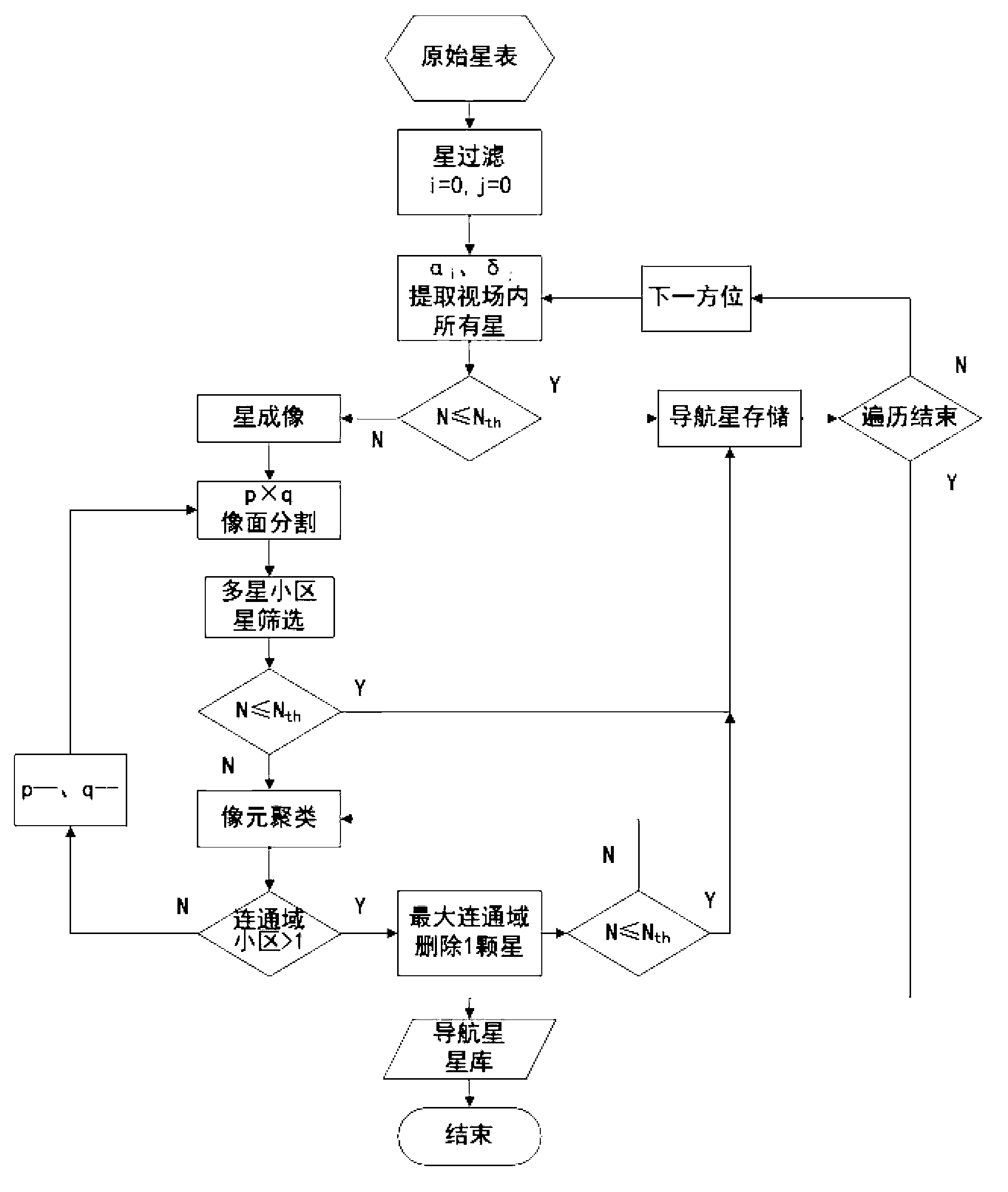
Navigational star screening method for star sensors
InactiveCN102840861AEase of decrementSplit evenlyNavigation by astronomical meansStar catalogueScreening method
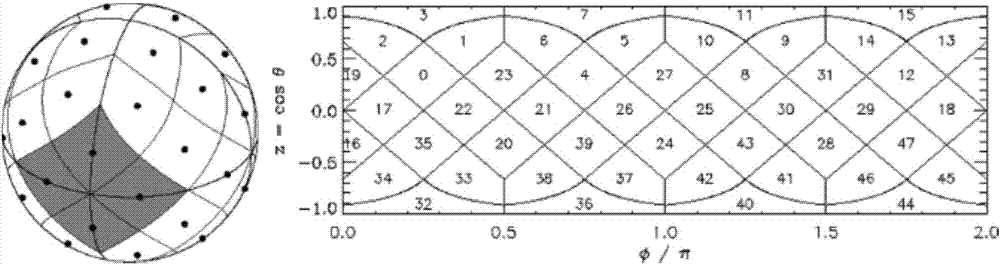
The invention relates to a navigational star screening method for star sensors, which includes the following steps: (1) according to the limiting magnitude of a star sensor, the stars of the original star catalogue of the whole celestial sphere are filtered and a star number threshold Nth is determined; (2) the number of the remaining stars of the star sensor in the field of view of the current sky area is set as N; if N is less than or equal to Nth, then all the remaining stars are chosen as navigational stars, and step 3 is executed; and if N is greater than Nth, then the navigational stars in the field of view of the current sky area are segmented and screened by a multi-scale image plane; (3) after the navigational stars in the field of view of the current sky area are screened, the star sensor turns to the next direction to repeat navigational star screening in step 2 until the whole celestial sphere is traversed. The multi-scale image plane segmentation and screening method adopted in the invention can be adapted to the variation in the star numbers of different sky areas to delete the redundant stars of sky areas with high star distribution density and keep all the stars of low-density sky areas, and moreover, the distribution of the screened navigational stars is even.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF TECH +1
Star sensor navigational star screening method by orthogonal list
InactiveCN102865865AReasonable divisionEvenly find and judgeNavigation by astronomical meansStar catalogueScreening method
The invention relates to a star sensor navigational star screening method by an orthogonal list, comprising the following steps of: 1, carrying out star filtering treatment on the original star catalogue of the whole celestial sphere according to the limit star of a star sensor and the like, and confirming the threshold value Nth of star number; 2, setting the number of the residual stars of the star sensor within a current sky area view field as N, if N is less than or equal to Nth, selecting the residual stars as navigational stars, and carrying out step 3, and if N is larger than Nth, cutting and screening the navigational stars within the current sky area view field by a multi-scale image surface; and 3, after screening of the navigational stars of the current sky area view field is completed, transferring the star sensor to the next position, and repeating the step (2) to screen the navigational stars till going through all the celestial sphere. According to the multi-scale image plane cutting and screening method disclosed by the invention, the redundant stars within a star distribution high intensity sky area can be eliminated along with the star number change of different sky areas, all the stars within a low-intensity sky region can be remained, and the screened navigational stars are evenly distributed.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF TECH +1
Star image distortion detection and estimation method based on star map matching
The invention discloses a star image distortion detection and estimation method based on star map matching. The method is used for solving the technical problem that an existing detection method is low in detection precision under the condition that an image is influenced by distortion. According to the technical scheme, a known star catalogue, a known imaging system parameter and known imaging system orientation are utilized to match star points in an image and star points in the star catalogue, and camera rotation, and camera translation and camera distortion possibly existing in the image are detected and estimated. Due to the fact that the influence caused by the distortion to the star points, the shifting and rotation caused by inaccurate orientation and camera lens translation and rotation to the star points in the image and estimating difficulty caused by the combined action of the translation, the rotation and the distortion are considered, rectification is carried out on the star points in the star image and the star points in the star catalogue by utilizing a longest LCS star point rectification method improved based on a distortion model, wrong matched exterior points possibly existing in a matched point-pair set are removed, the relative rotating translation relation is estimated, and the distortion between a star map and a star target is accordingly estimated. Detection accuracy is improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Optimal selection method of navigational stars of star map simulator based on star density
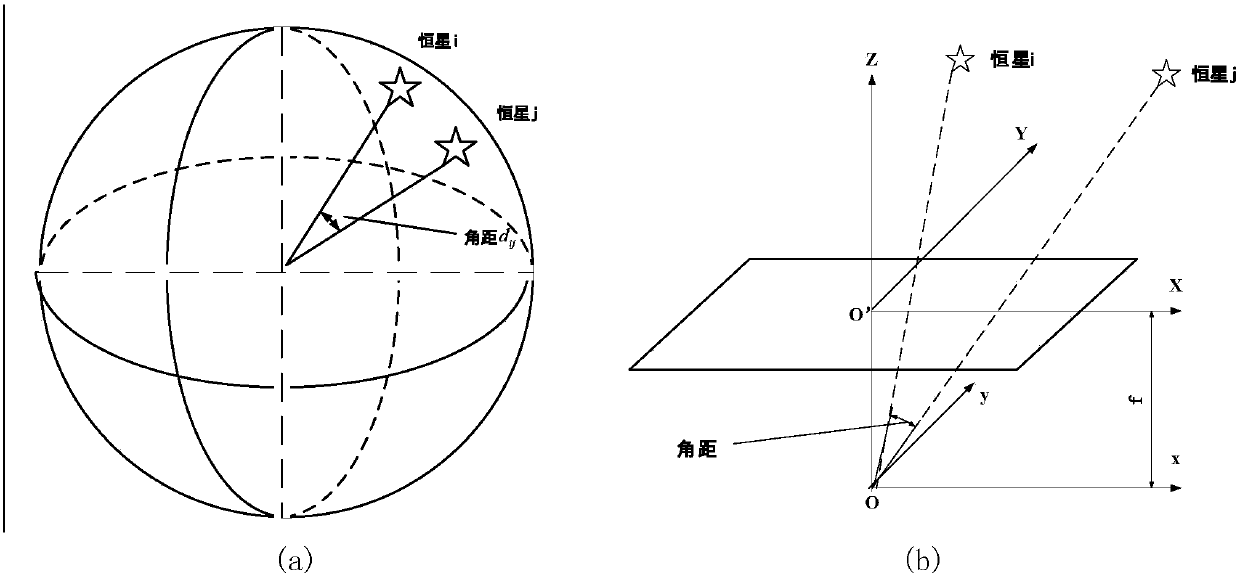
The invention discloses an optimal selection method of navigational stars of a star map simulator based on star density. The optimal selection method comprises the following steps: firstly, processing a star catalogue, extracting effective data fields, carrying out related data processing to obtain six pieces of data corresponding to each fixed star, and then performing proper motion, precession and nutation correction on extracted right ascension and declination values respectively; secondly, according to given optical axis orientation and the size of a field range, extracting fixed stars in the field range and establishing an observational star database; thirdly, on the basis of the observational star database, performing image surface partition and star density calculation respectively by use of an ITSI (Information Technology System Infrastructure) optimal selection method of the navigational stars, and satisfying a set navigational star threshold, and finally realizing the optimal selection of the navigational stars and establishing a navigational star database. The method is relatively simple, but the navigational star database obtained by use of the method is relatively low in standard deviation and relatively even in distribution, and both efficiency and effect are achieved; the established navigational star database is reasonable and significant for smooth implementation of star map matching.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method for rapidly searching navigation star catalogue
ActiveCN101995248AEvenly Overlapped PartitionEasy retrievalInstruments for comonautical navigationVisual field lossStar catalogue
The invention relates to a method for rapidly searching a navigation start catalogue, which comprises the steps of: firstly, dividing a sky region by directly using an original right ascension and declination circle of a celestial sphere; secondly, calculating a right ascension and declination span range of a region covered by a star sensor according to the direction of a visual axis, and searching the navigation star catalogue in the right ascension and declination span range to obtain a navigation star in a visual filed; thirdly, spreading the celestial sphere into a two-dimensional plane with 180*360 to obtain a two-dimensional array of celestial sphere navigation star distribution; and fourthly, compressing the two-dimensional array into a one-dimensional array through two stages of compressions and then indexing the one-dimensional array by using a hash technology. The navigation star is subjected to no redundancy storage by adopting the two stages of compressions and a Hash mapping technology, therefore, the invention realizes that the index time of the navigation star catalogue is 0(1), can be used for rapidly indexing the navigation star in the visual field of the star sensor from the navigation star catalogue when the given visual axis points 8, and has the characteristics of high indexing speed and high efficiency.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Spider web mode and convolutional neural network based star map identification method
ActiveCN107816987AImprove robustnessImprove recognition rateNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by astronomical meansStar catalogueAngular distance
The invention discloses a spider web mode and convolutional neural network based star map identification method. The method comprises the following steps: creating a spider web mode star map in whichthe relative location relation between a main star and companion stars and the angular distance relation of the companion stars are utilized and color information is included; making a training set and a testing set of the spider web mode star map based on a star catalogue; and proposing a convolutional neural network suitable for the spider web mode. According to the method, a high correct identification rate can be obtained under loud noise at star location and star magnitude noise; in addition, a matching star point can be obtained in case of few companion star points within the radius of anavigation star point mode.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
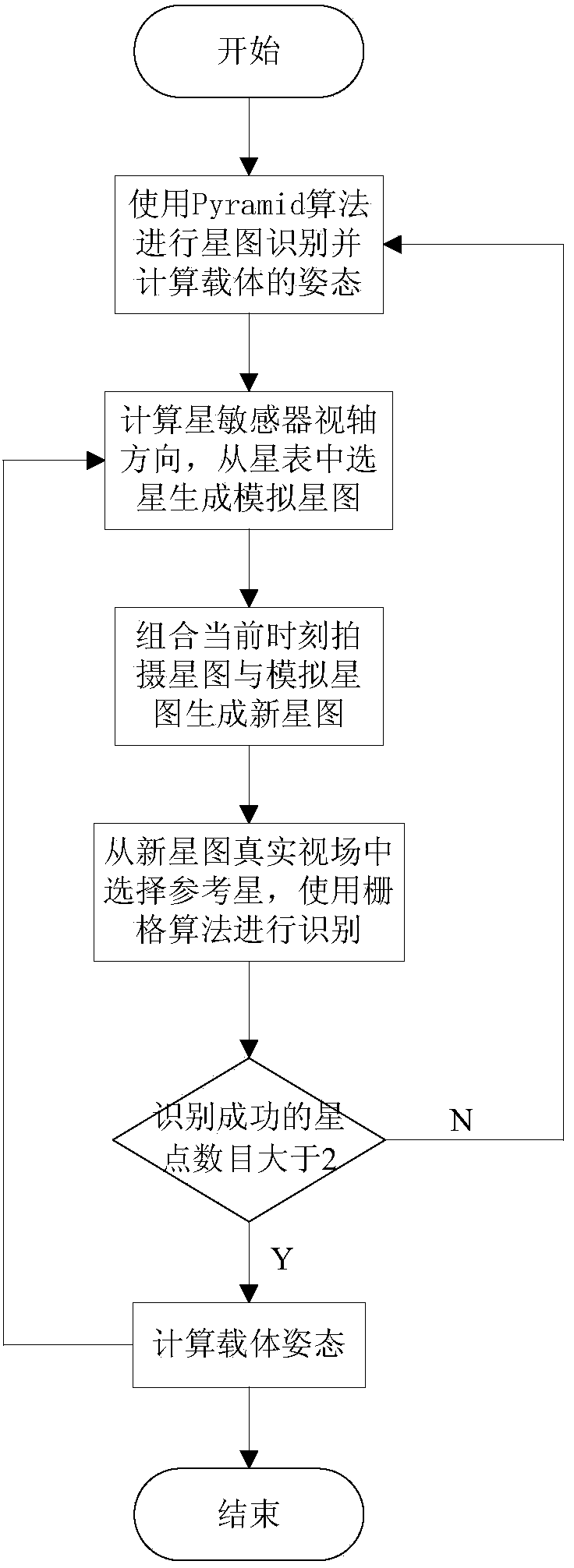
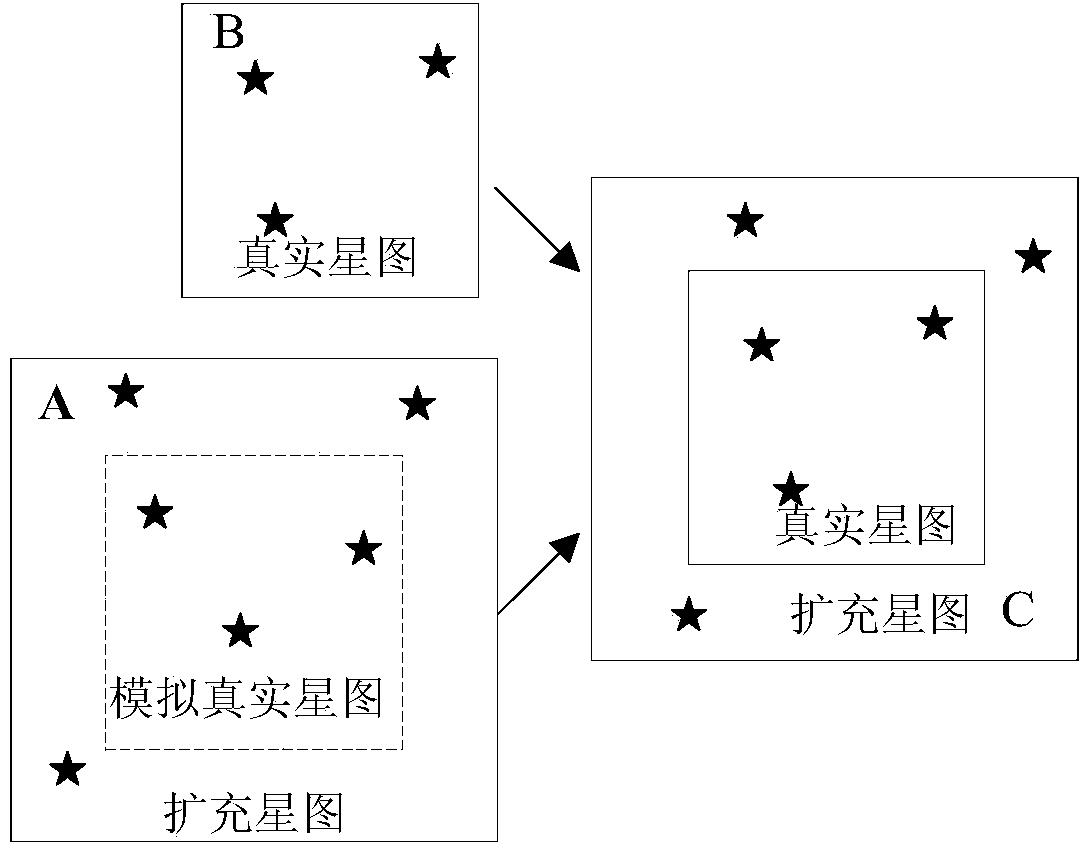
Posture determination method of star sensor
InactiveCN103940432AIncrease in the number of starsImprove recognition rateInstruments for comonautical navigationFixed starsStar catalogue
The invention discloses a posture determination method of a star sensor. The posture determination method of the star sensor comprises the following steps: recognizing a star map at the initial time, and calculating the posture of a carrier; calculating the visual axis direction of the star sensor at the current time by virtue of the posture of the carrier and output information of a gyroscope, and selecting a star from a star catalogue by virtue of the obtained view axis direction so as to generate a simulated star map; combining the simulated star map and a photographed star map of the star sensor at the current time so as to form a novel star map; selecting a reference star from a real view field of the novel star map, and recognizing by a grid algorithm; and recognizing the star map successfully if the number of star points recognized successfully is greater than 2, and calculating the posture of the carrier, or running again. The method for expanding the view field is applied to the grid algorithm, so that the number of fixed stars in the view field increases, and the restriction that the grid algorithm cannot be applied to sensors of small view fields, low stars and the like is broken through, so that the star map recognition process of the star sensor has high recognition rate.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Real-time orbit determination method for drift scanning geosynchronous satellite
InactiveCN104949677AReal-time extractionReal-time identificationInstruments for comonautical navigationStar catalogueGeosynchronous satellite
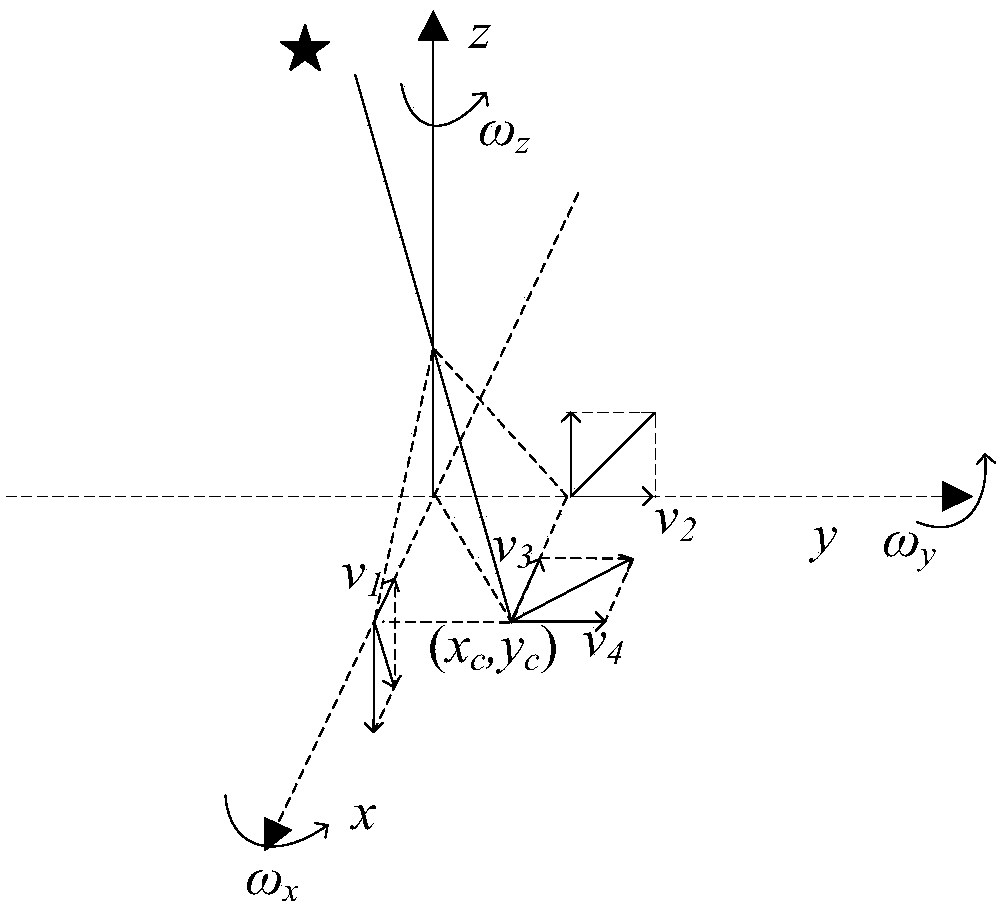
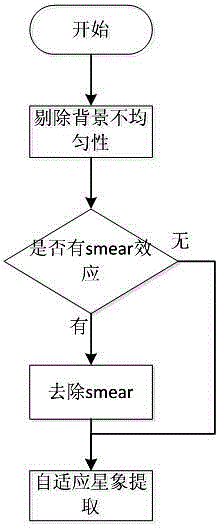
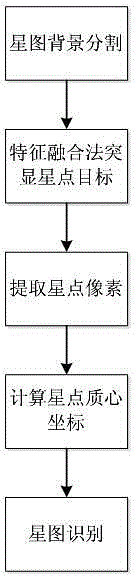
The invention discloses a real-time orbit determination method for a drift scanning geosynchronous satellite. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, processing a star map background to ensure uniform distribution of background pixels, and removing smear if a smear phenomenon occurs; detecting star points in a self-adaptive manner, segmenting an image background, highlighting star images through a feature fusion method, extracting a star image target, and calculating mass center coordinates of the star points; matching and identifying the star images through an improved triangle method, namely, extracting a star image with maximum gray value for triangle matching, performing reduction to obtain CCD negative model parameters according to the matching result, substituting all the star images into a negative model to calculate corresponding celestial coordinates, and matching the celestial coordinates with a star catalogue; and finally, performing reduction on the CCD negative model according to the matching identification result, and substituting geosynchronous satellite coordinates into the CCD negative model to calculate the optical position of the geosynchronous satellite, thereby completing orbit determination of the geosynchronous satellite. The method is high in precision and speed and good in real time property, and is free of bid data calculation and storage.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
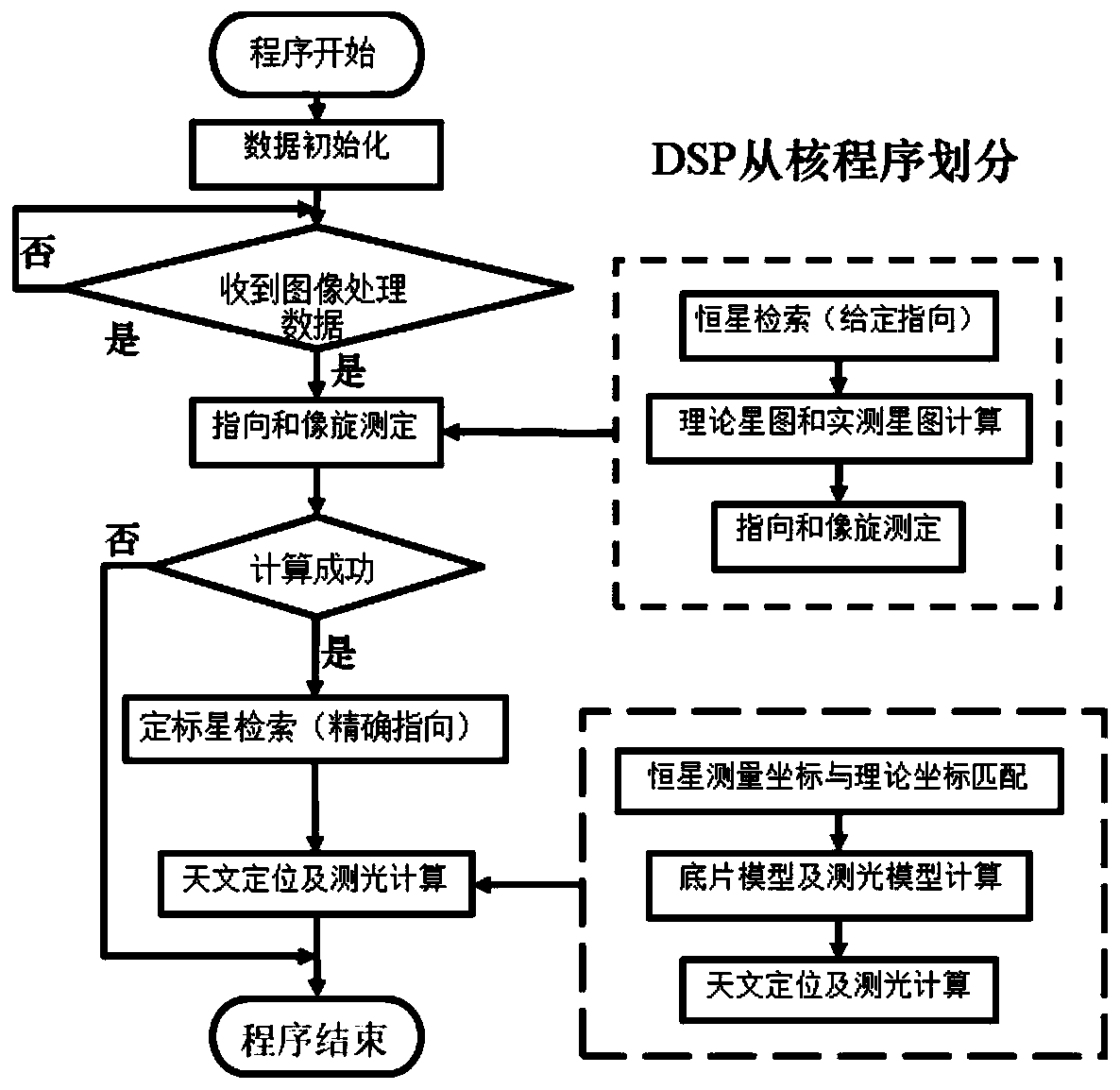
Embedded space target astronomical positioning method
ActiveCN110849353AReduce bandwidth requirementsCharacter and pattern recognitionNavigation by astronomical meansFixed starsStar catalogue
The invention relates to an embedded space target astronomical positioning method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) initializing star catalogue data and star catalogue index data, and setting a focal length, a view field, a camera target surface size and a pixel size according to a telescope used for actual observation; (2) observing by using a telescope, processing an observed image,and reading image processing data into a core processor; (3) carrying out accurate center pointing and image rotation measurement on an actually measured fixed star image by utilizing actually measured astronomical image data; (4) searching N2 theoretical fixed stars in the field of view again by accurate center pointing; and (5) carrying out astronomical positioning and photometry calculation ofthe space target, so as to complete astronomical positioning of the space target. According to the invention, a negative film model is used to calculate the image coordinates and gray scale information of the space target observed in the image so as to obtain the actual astronomical position and luminosity information of the space target, and the bandwidth requirement for data transmission is lowered.
Owner:ZIJINSHAN ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Spark-based sky region coverage generation method for large-scale astronomical data
ActiveCN107491471AImprove access efficiencyImprove processing efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsStar catalogueSky
The invention relates to a Spark-based sky region coverage generation method for large-scale astronomical data. The method is mainly technically characterized in that the data is subjected to block indexing one by one according to right ascension and declination information in combination with an HEALPix layered spherical indexing method by using a map operator of Spark; by using the map operator of the Spark, performing father block number and sub-block number segmentation operation on an HEALPix block number of each piece of the data of a current layer by utilizing bit operation; performing clustering operation on all blocks by using a combineByKey operator of the Spark; and repeatedly iterating the operation until an iterative stop condition is met, thereby obtaining data after sky region coverage generation. The method is reasonable in design, can finish the sky region coverage generation of the large-scale astronomical data in a short time, provides support for realizing quick archiving of massive astronomical data, and improves the data access and processing efficiency; and in addition, the generated result can be used for data visualization, so that a distribution state of the astronomical data, in a star catalogue, in a sky region can be intuitively displayed for a researcher.
Owner:天科大(天津)科技园有限责任公司
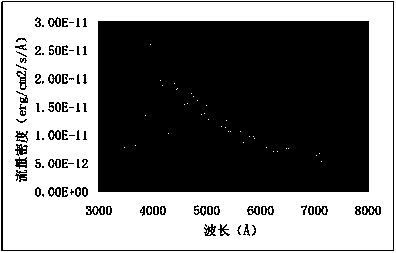
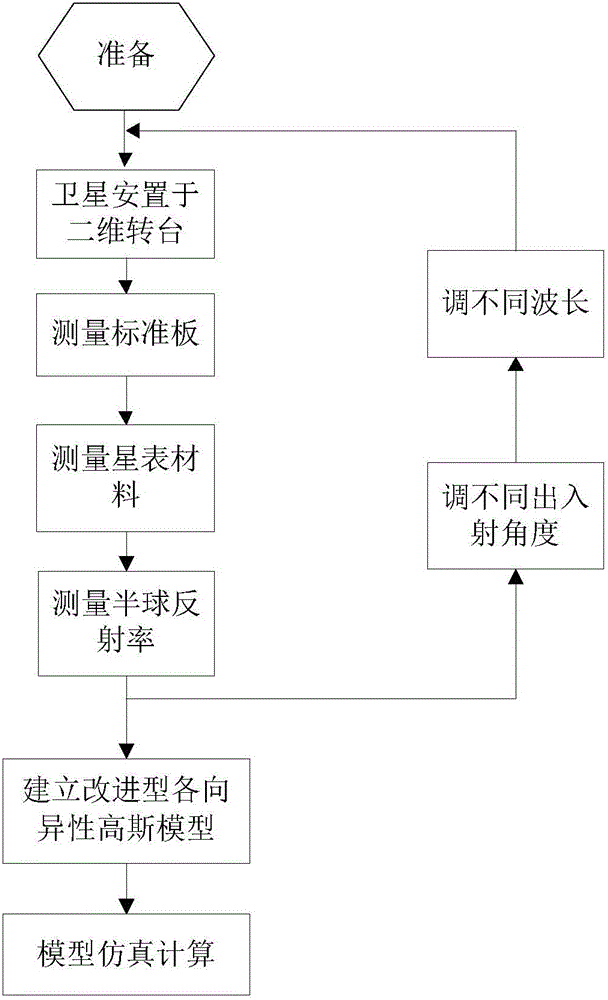
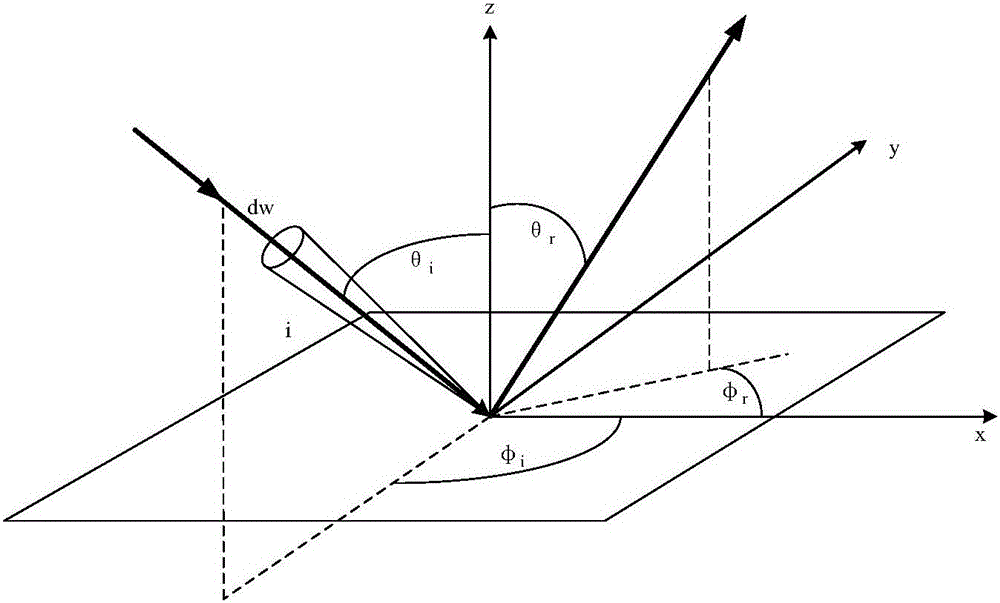
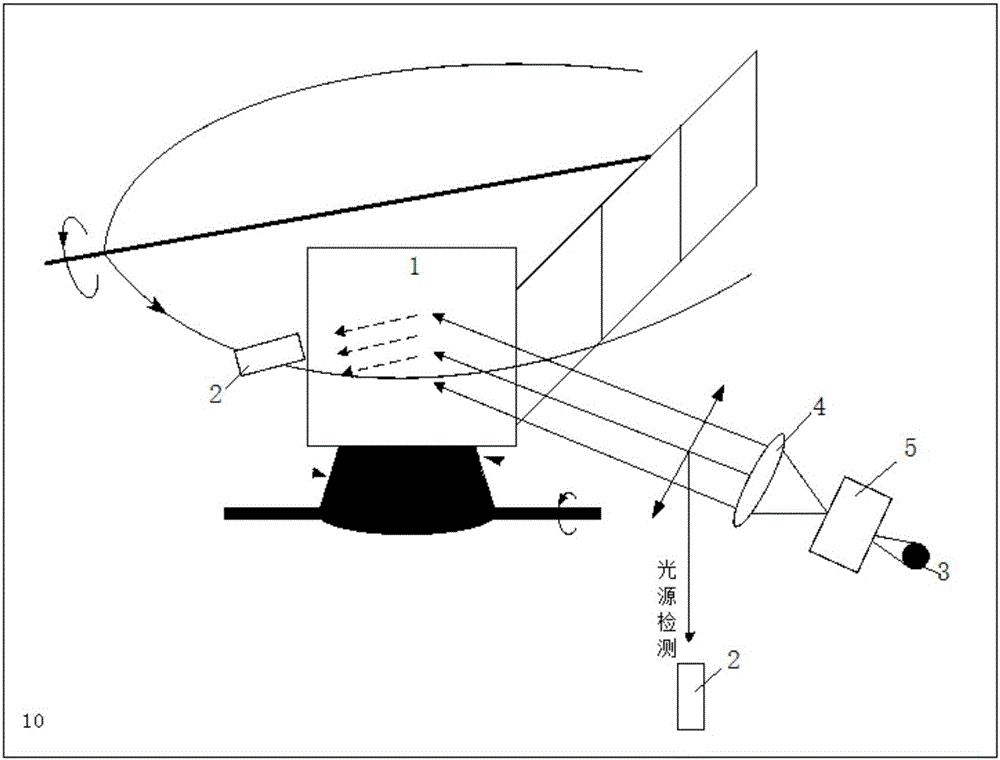
Star catalogue material bidirectional scattering distribution function testing method
ActiveCN105891156AReasonable methodOperableScattering properties measurementsStar catalogueMonochromator
The invention provides a star catalogue material bidirectional scattering distribution function testing method. The method solves the problem that a star catalogue material influences stray light testing under a whole-satellite state and includes the steps that firstly, a xenon lamp spectrum is divided into multiple wavelengths according to requirements by means of a monochromator; secondly, a specific wavelength spectrum and specific light-out and light-in angles are selected for output voltage testing of a standard board and a star catalogue material under the whole-satellite state and hemisphere reflectivity testing of the standard board along with wavelength changes; thirdly, the spectrum wavelengths are changed through the monochromator, a satellite space angle is precisely changed by means of a two-dimensional rotary measuring system, accordingly the light-out and light-in angles of light are changed, and the second step is executed again; fourthly, an improved anisotropic Gaussian model is built; fifthly, the improved Gaussian model based on anisotropy is adopted for BRDF computation. The method has the advantages that the method is reasonable, operation is feasible, quick and efficient, adaptability is high and data is accurate and reliable, and is applicable to stray light testing under the whole-satellite state of an optical satellite.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
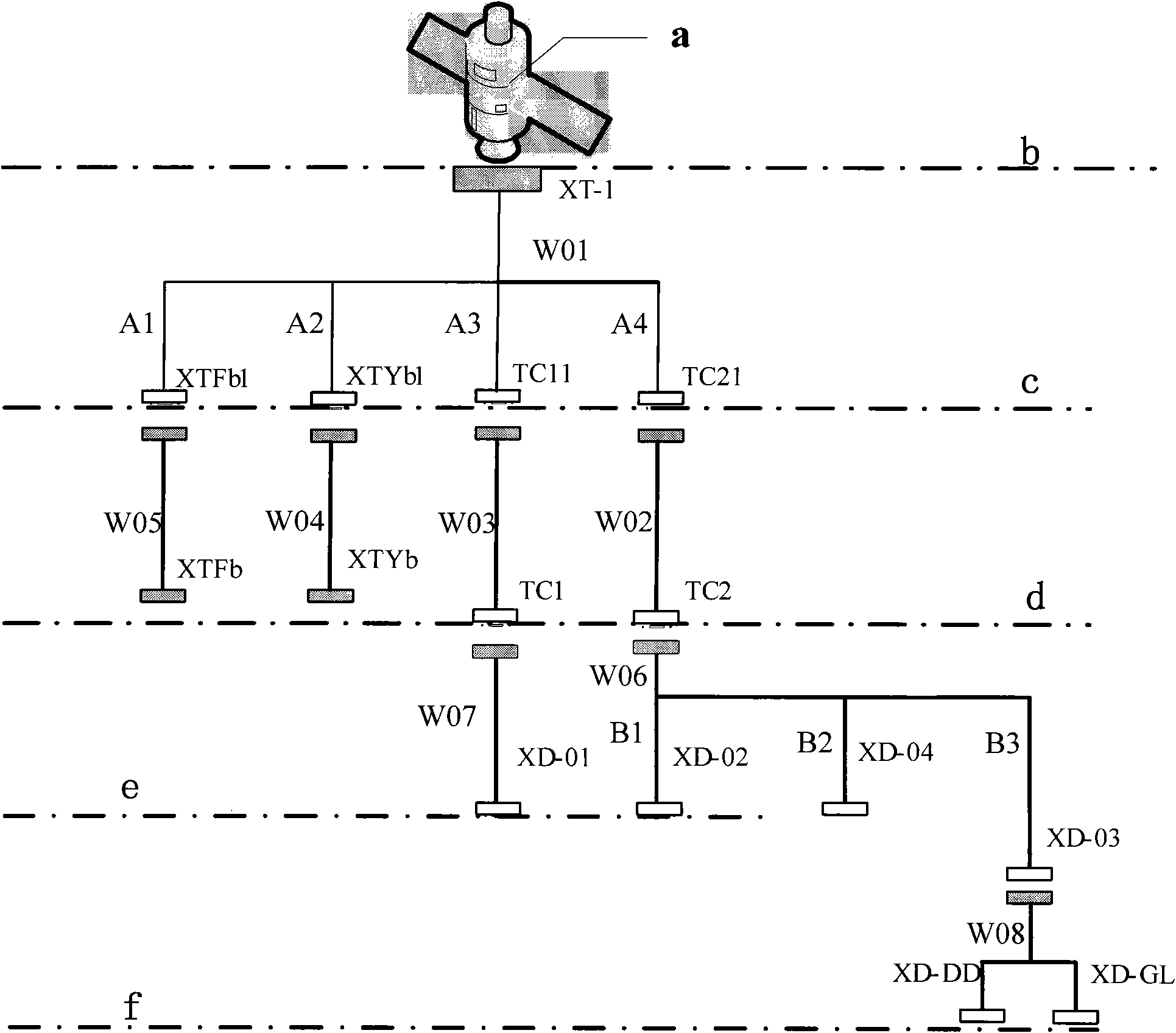
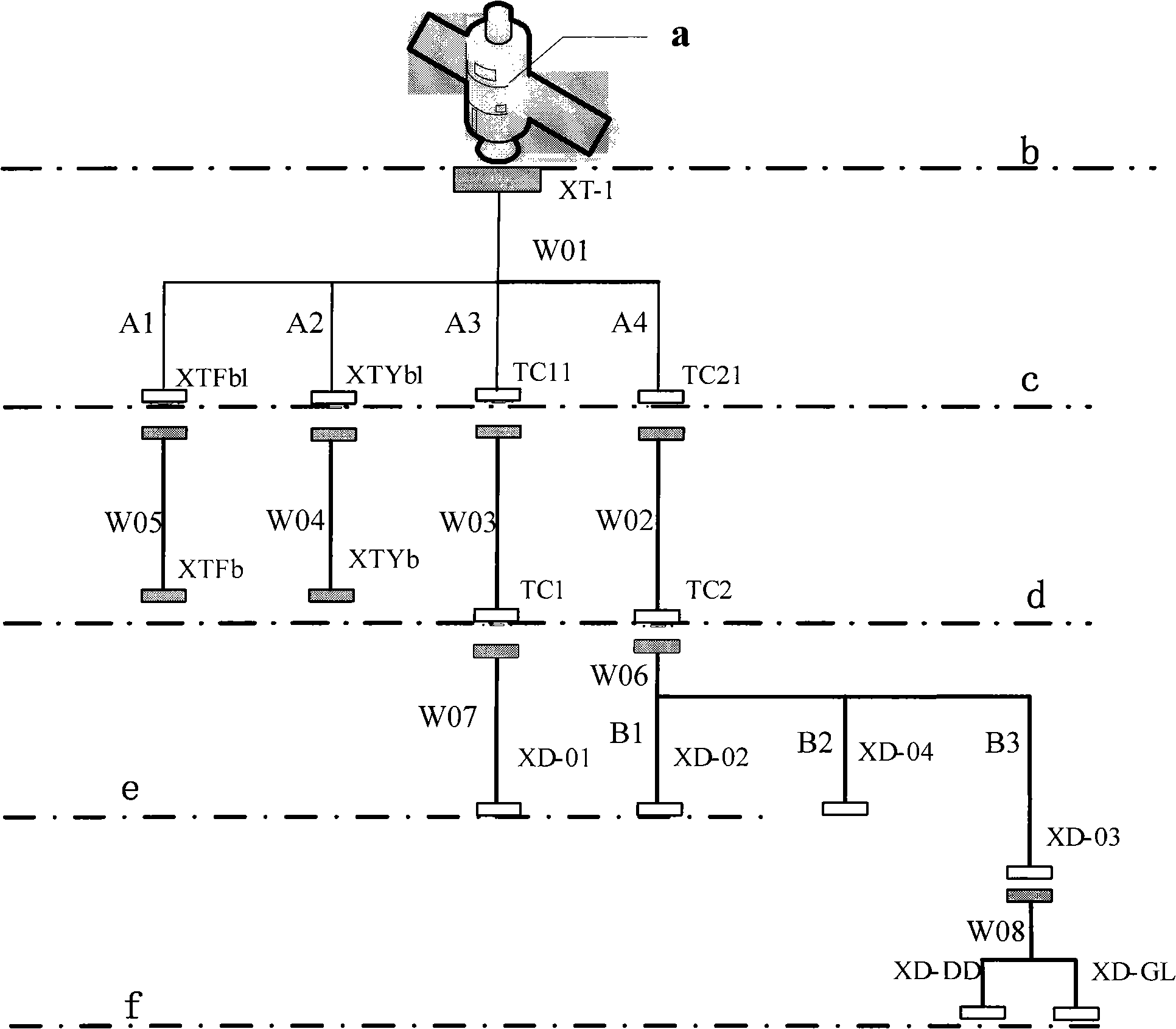
Microsatellite unplugged cable network
ActiveCN101938076ASave structural resourcesSolve problemsCoupling device connectionsArtificial satellitesElectricityMultiplexing
The invention relates to a microsatellite unplugged cable network, which solves the problem that the design of a star catalogue plug is difficult due to structural characteristics of the microsatellite of small volume, body-mounted solar cell array and the like. In the prior art, in order to preserve the star catalogue plug, only a star catalogue plug interface is arranged on the body-mounted solar cell array, which necessarily damages the integral structure of the satellite body-mounted solar cell array. In order to meet the task requirement of the microsatellite and overcome the defects in the prior art, the microsatellite unplugged cable network integrates the satellite star catalogue and the microsatellite unplugged cable, maintains satellite power supply of the traditional unplugged cable, a satellite task test computer interface and controlled quantity, state quantity and analog quantity contacts of a wired station, reasonably utilizes limited pin resources of the unplugged cable, and successfully integrates the traditional star catalogue plug and star catalogue cable into the unplugged cable network according to the electromagnetic compatibility of strong and weak current and pin multiplexing of an electric connector.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
Inertia measurement information-assisted star map matching method
ActiveCN108225307AImprove efficiencyReduce the number of redundant matchesNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsStar catalogueNavigation system
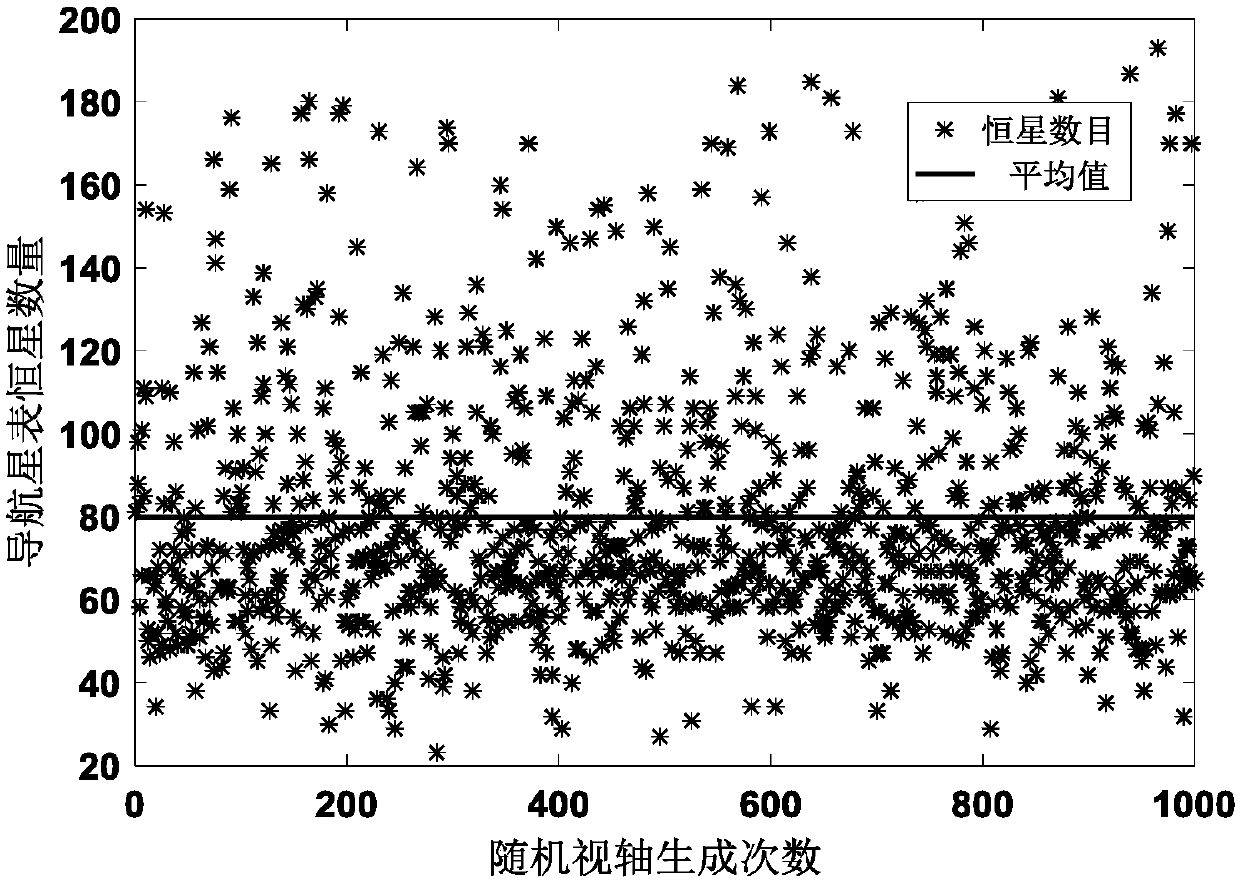
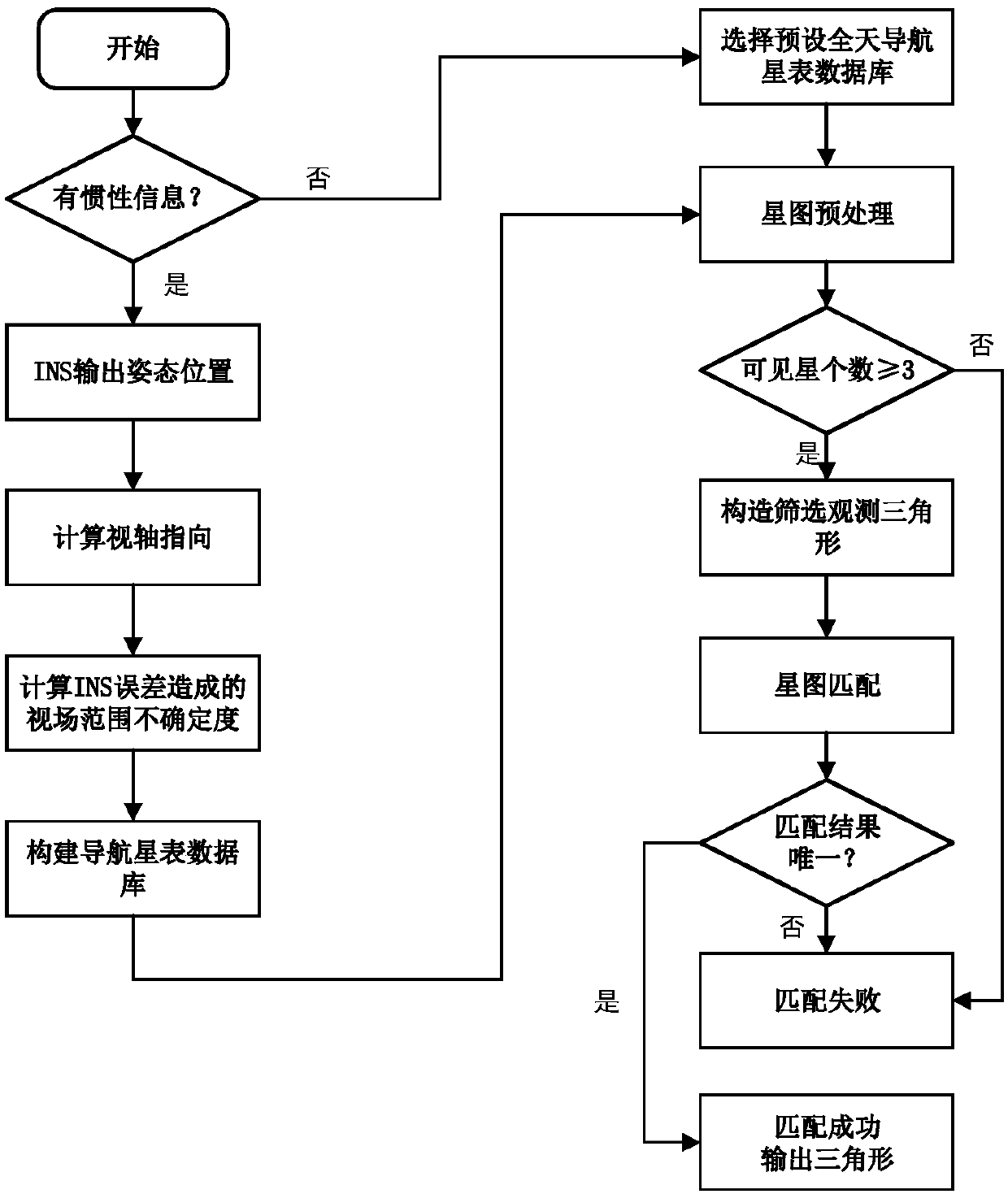
The invention discloses an inertia measurement information-assisted star map matching method, which comprises the steps of utilizing position information and attitude information output by an inertialnavigation system or an integrated navigation system comprising the inertial navigation system for determining a visual axis orientation of a current star sensor; reducing visual axis uncertainty caused by a navigation system error into a view field radius; dynamically screening navigation stars of current moment to form a navigation star catalogue; then utilizing a triangle matching method for carrying out star map matching. Compared with an existing star map matching method, the robustness and the efficiency of the method provided by the invention are improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method and system for detecting inter-satellite angular position error of high-resolution dynamic star simulator
ActiveCN111024127AImprove test accuracyImprove detection efficiencyImage analysisMeasurement devicesEyepieceTheodolite
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method, a device and a system for detecting an inter-satellite angular position error of a high-resolution dynamic star simulator. A star point display device displays a star point image according to star map data generated by a star map generation processor based on a star catalogue database and the position information, light emitted by the display star point is converged through a star simulator optical lens to form parallel light, and the parallel light is projected into a high-precision theodolite eyepiece located at a rear end of the star simulator optical lens to be imaged; a star point image acquisition device is used for acquiring a crosshair displayed by a high-precision theodolite and a to-be-measured star point image in real time, theobtained information is sent to an inter-satellite angular position error detection processor so as to enable the inter-satellite angular position error detection processor to process the received image and calculate a position difference value of the center point positions of the crosshair and the to-be-measured star point image in the same direction, and lastly, an inter-satellite angular position error value is calculated according to a corresponding high-precision theodolite dial display numerical value when each position difference value is 0. The method is advantaged in that test precision and detection efficiency of the inter-satellite angular position error are effectively improved.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Automatic faint star recognition method based on perimeter features
ActiveCN106123891ARapid positioningQuick identificationNavigation by astronomical meansStar catalogueHash function
The invention relates to an automatic faint star recognition method based on perimeter features. The method comprises the following steps that 1, a navigation star catalogue is constructed by adopting a magnitude threshold method according to a fundamental star catalogue, a whole celestial sphere is divided into a plurality of partial overlapped celestial areas by adopting an overlapping ball moment method, two brightest stars in each overlapped celestial area are found to serve as a main star pair, other stars construct a triangular perimeter feature library by serving as auxiliary stars, hash functions are constructed for the generated feature library according to the perimeter size, and fragmentation is conducted; 2, the navigation star catalogue and a navigation feature library are read, star atlas extracting results are sorted in a descending order according to the gray value size, the two brightest stars in each celestial area are taken as the main star pair, the other stars are taken as the auxiliary stars, an observation triangle taking each main star pair as a common side is constructed, and the perimeter of the triangles and the length of the two sides of each triangle taking the corresponding main star pair as the common side are calculated. According to the method, the number of the feature triangles is greatly decreased, and compared with a traditional triangle recognition algorithm based on an angular distance between the stars, the angular distance comparison frequency is decreased, and the recognition speed is increased.
Owner:UNIT 63680 OF PLA
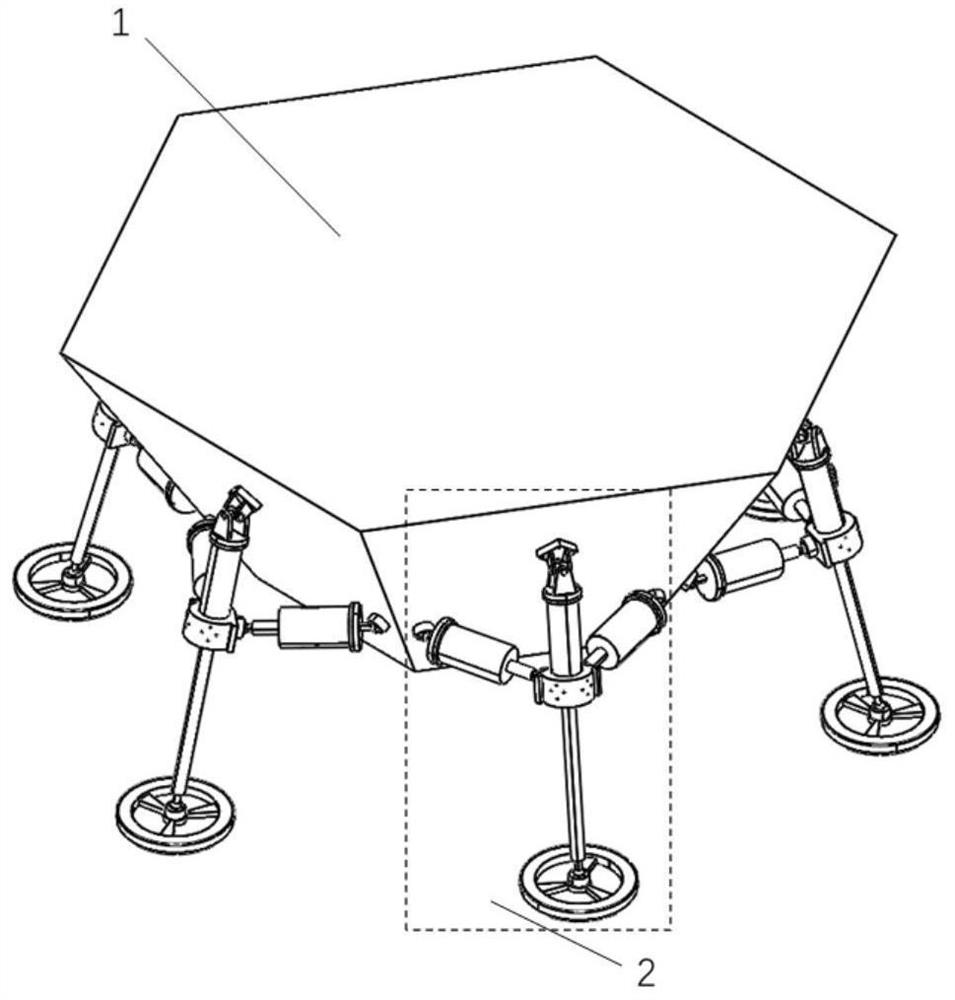
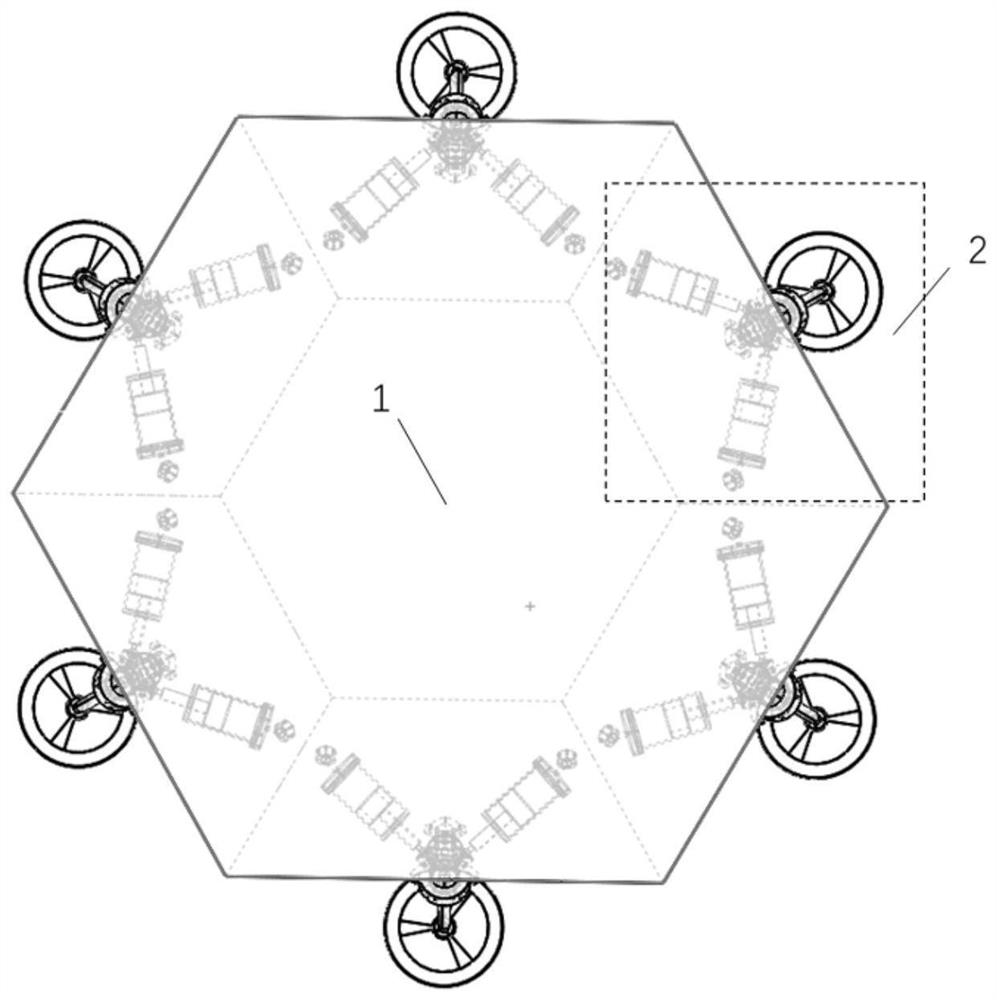
Buffering/walking integrated hexapod lander and gait control method thereof
ActiveCN111746824AAchieving quasi-static walkingHeavy loadArtificial satellitesSystems for re-entry to earthKinematic controllerHexapod
The invention discloses a buffering / walking integrated hexapod lander and a gait control method thereof, belongs to the technical field of deep space star catalogue detection mechanisms, is composed of a mechanical structure, a control system and gait planning, and has two functions of stable landing and flexible roaming. The mechanical structure is composed of a hexagonal frustum type body and six buffering / driving integrated three-degree-of-freedom leg and foot mechanisms which are symmetrically distributed according to the center of a regular hexagon. The control system consists of a main control module and a special motion controller and is used for controlling the position of each driving motor in each buffering / driving integrated three-degree-of-freedom leg-foot mechanism so as to realize quasi-static walking of the lander; the gait planning adopts a stable and efficient 3-3 gait which is more matched with the hexapod configuration, and the smooth fluctuation track of the centroid of the body is realized through the motion control of each buffer / drive integrated three-degree-of-freedom leg and foot mechanism.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Establishment method of daytime star sensor-based infrared star detection navigation star catalogue
ActiveCN103884336ACapable of working day and nightIncrease the probability of observationNavigation by astronomical meansSpecial data processing applicationsFixed starsAviation
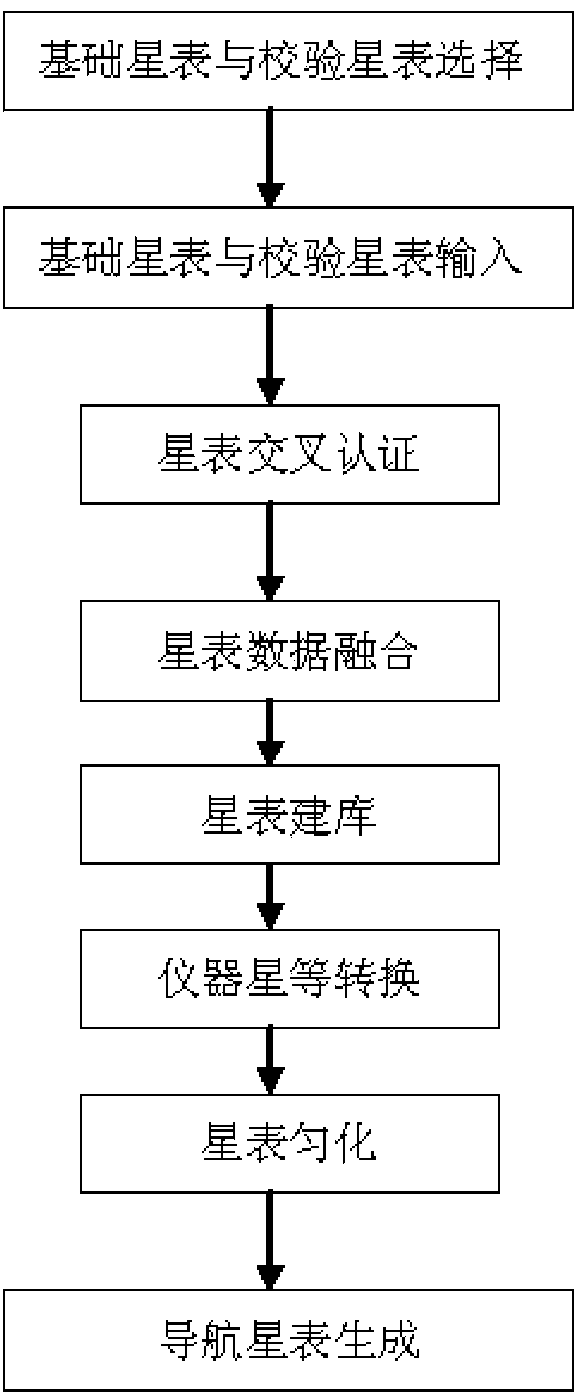
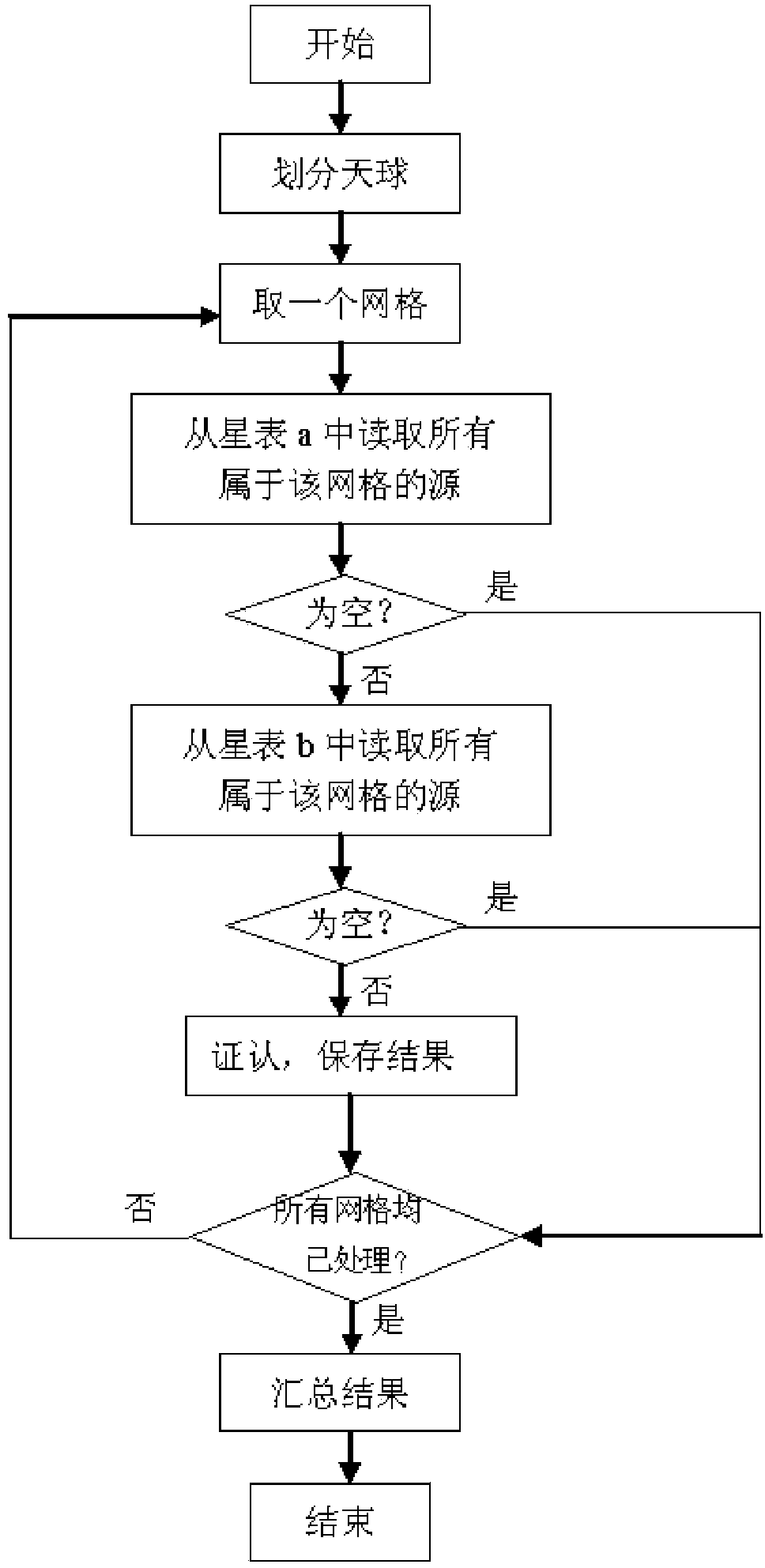
The invention relates to an establishment method of a daytime star sensor-based infrared star detection navigation star catalogue, and belongs to the technical field of design of aerospace attitude sensors. The method comprises the following steps of extracting fixed stars of which any band is higher than or equal to the magnitude 8 from a 2MASS astronomical catalogue, and removing redundant information to form a basic star catalogue for cross certification; performing star catalogue cross certification on data sources of the obtained basic star catalogue and a check star catalogue; performing data fusion on the data sources of the basic star catalogue and the check star catalogue, which pass the star catalogue cross certification, to obtain a star catalogue database; performing file format finishing database establishment on the obtained star catalogue database, wherein the finished star catalogue database comprises a main data file and a data index file; performing instrument star magnitude conversion on the data source of the finished star catalogue database to establish an instrument star magnitude star catalogue; and performing star catalogue homogenizing on the obtained instrument star magnitude star catalogue, and generating a daytime star sensor-based navigation star catalogue by using the homogenized star catalogue database.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Double-star vertex subdivision radian set fuzzy matching based marine celestial navigation method
InactiveCN103852079AOvercome the shortcomings such as error divergenceOvercoming lessNavigation by astronomical meansStar catalogueAngular distance
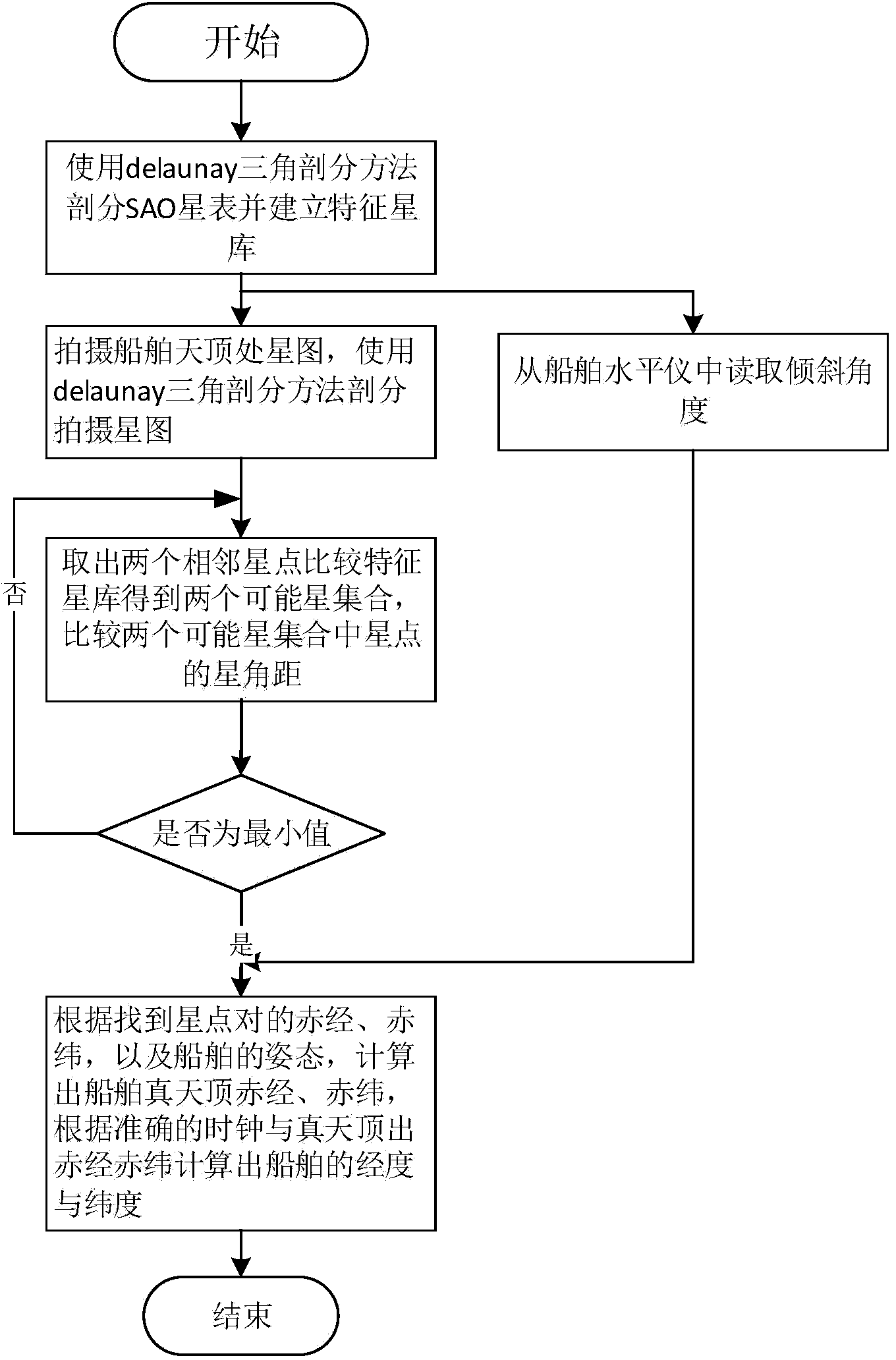
The invention discloses a double-star vertex subdivision radian set fuzzy matching based marine celestial navigation method and relates to a marine celestial navigation method. The invention aims to solve the problems that the conventional navigation method is low in positioning accuracy, the positioning navigation technology in the double-star vertex subdivision radian set fuzzy matching based marine celestial navigation method is influenced by weather and sea conditions, a satellite navigation signal is easily interfered and inertial navigation equipment error is insufficient in divergence along with time. The method comprises the following steps: (1) dividing a Smithsonian star catalogue and establishing a characteristic star database; (2) photographing a star map perpendicular to the right above part of a ship plane; (3) comparing the star angular distance between stars in two possible star sets, wherein the stars with the minimum star angular distance refer to the solved star pair, and realizing star map recognition; and (4) determining the true zenith right ascension and declination according to an inclination angle read by the ship during photographing, combining the exact time, namely the double-star vertex subdivision radian set fuzzy matching-based marine celestial navigation method is finished. The method belongs to the technical field of marine navigation.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF COMMERCE
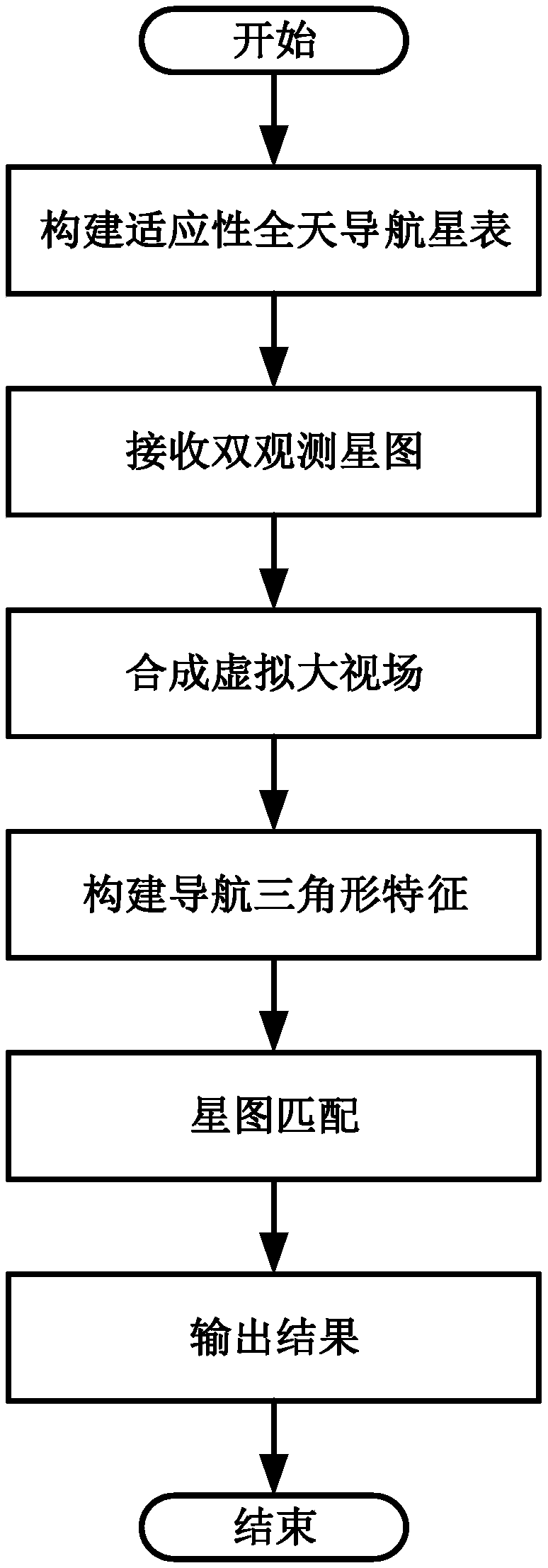
Start atlas matching method of cross-discontinuous field of view fusion
InactiveCN109238269AOvercoming a small numberOvercoming the problem of poor geometryNavigation by astronomical meansFixed starsNavigational triangle
The invention discloses a start atlas matching method of cross-discontinuous field of view fusion. The method comprises the following steps: determining a conversion matrix between a star sensor coordinate systems; determining an angular distance between optical probe visual axis orientations; screening fixed stars in an astronomy fundamental star catalogue by utilizing an apparent magnitude equal-threshold filter method to acquire an alternative fixed star set; computing an annular fixed star screening region based on a dual-visual axis installation relation, traversing and screening all fixed stars in the alternative fixed star set to acquire a navigation fixed star set, and establishing a dual field of view adaptive all-day navigation start catalogue according to grouped storage principle; receiving a dual field of view start atlas processed by the start sensor to acquire a virtual discontinuous field of view star atlas under the same visual axis; traversing all start points in a large field of view star atlas to construct a navigation triangle feature set; performing triangle start atlas matching by using the navigation star catalogue and the navigation triangle feature, and outputting an identification result. Through the method disclosed by the invention, the problems that the visible star is less and the geometric configuration is bad are remedied by utilizing multiple small fields of view synthesis; the navigation star catalogue is constructed in a targeted way, and the efficiency and the robustness of the algorithm are enhanced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method for perceiving star catalogue topography by laser stripe information
ActiveCN102116612AGet rid of complex disadvantagesHigh speedUsing optical meansProfile tracingStar cataloguePattern perception
The invention belongs to the field of visual environment perception for a robot, and particularly discloses a method for perceiving star catalogue topography by laser stripe information. In the method, the topography is designed into three regions so as to evaluate perception results in advance; the defect of complex algorithm in lattice-fitting scene description is eliminated; and the provided results and design weights for the subsequent algorithm are applicable to various path planning algorithms. Compared with the traditional binocular stereo vision technology, the invention has the advantages that the speed is higher; an image pair (1024*1024) is matched with the traditional gray scale; a search window is set into the size of 5*5 and adopts an SAD (sum of absolute differences) matching mode; and the matching recovery runs once on an industrial personal computer (IPC) with a main frequency (p42.4) within about 2 minutes. By utilizing the method, points obtained through calculation are reduced, but the reliability is enhanced and the operation time is less than 1 second.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
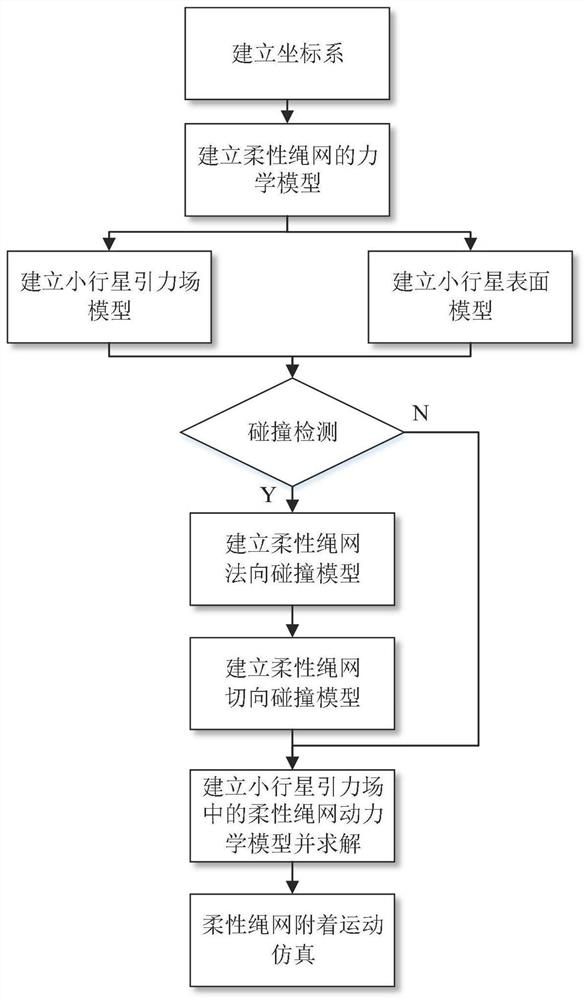
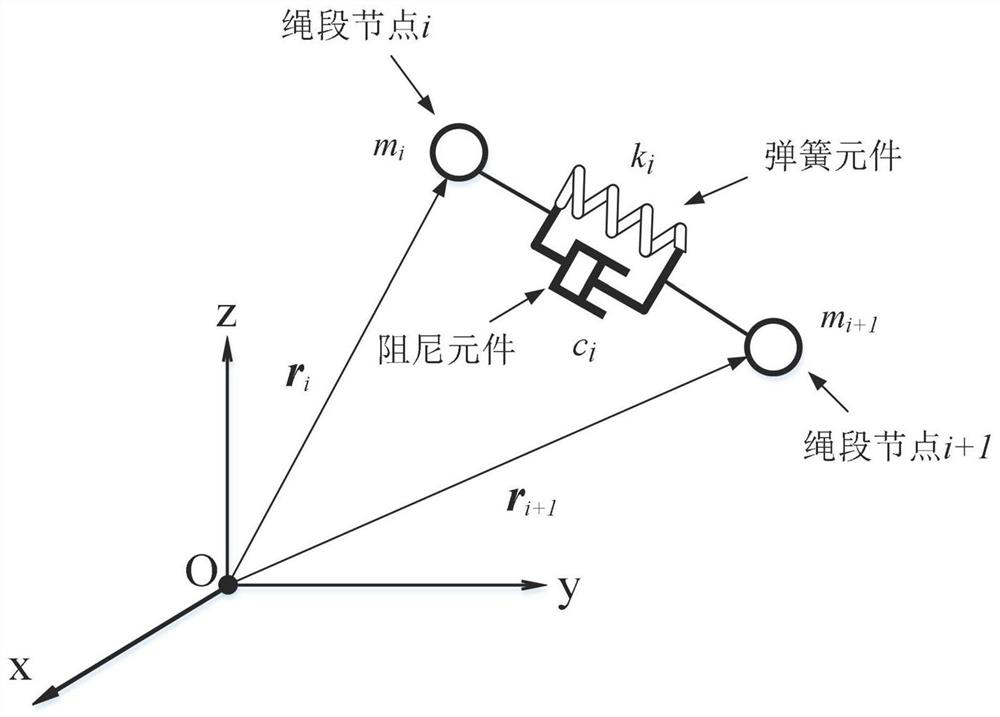
Attachment motion parameter calculation method of flexible rope net in asteroid gravitational field
ActiveCN111881555ASustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationStar catalogueDynamic models
The invention provides an attachment motion parameter calculation method of a flexible rope net in an asteroid gravitational field, and belongs to the field of asteroid detection. The method comprisesthe following steps: firstly, establishing a mechanical model of a flexible rope net in an asteroid body coordinate system; respectively establishing an asteroid gravitational field model and a surface model; performing collision detection on the flexible rope net and the asteroid, calculating normal collision force and friction force of nodes of the flexible rope net, finally establishing a dynamic model of the flexible rope net in an asteroid gravitational field, and calculating to obtain attachment motion parameters of the flexible rope net in the asteroid gravitational field. By utilizingthe method, the problems of rebound escape and overturning out-of-control of the detector caused by the problems of insufficient star catalogue information, complex landing terrain and the like in anasteroid weak gravitational field attachment task can be solved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Autonomous all-weather stellar refraction satellite location method
ActiveCN104236553AImprove navigation accuracyImprove data update rateInstruments for comonautical navigationFixed starsNatural satellite
The invention relates to an autonomous all-weather stellar refraction satellite location method. The method comprises the following steps: observing and acquiring a star map by adopting a CCD (charge coupled device) with a saturation inhibition function, performing the image processing on the acquired star map, and extracting a non-refracted star and a refracted star; matching the star map with a star map of a navigation star catalogue by utilizing a triangular matching algorithm to acquire the right ascension and declination of each star on the star map; searching the star map for a fixed star which is closest to each refracted star to be used as a corresponding star of the refracted star, and calculating a refraction angle gamma of each refracted star; calculating the tangential height h of each refracted star according to an atmosphere model and the refraction angle; and selecting three refracted stars on the observation star map, and calculating the position of a satellite under earth centered inertial system according to the right ascensions, declinations and tangential heights h of the three refracted star. By adopting the method, the all-weather high-precision astronomical autonomous navigation of the satellite is realized; moreover, the data updating rate is high, and the involved equipment is simple, low in cost and low in power consumption.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
Autonomous optical navigation feature comprehensive optimization method for landing of extraterrestrial celestial body
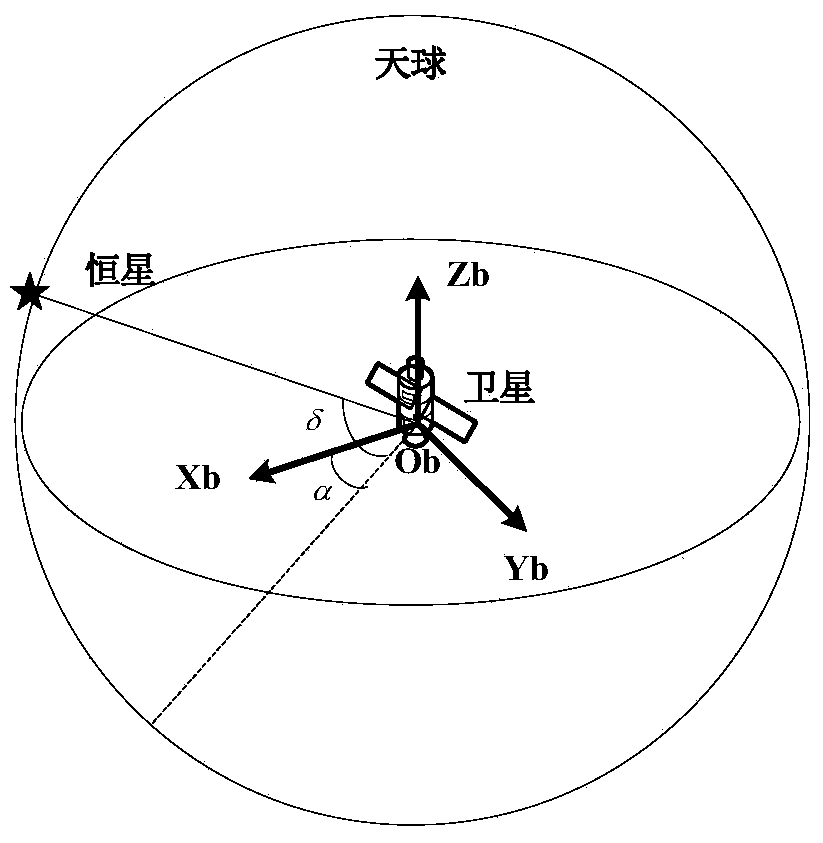
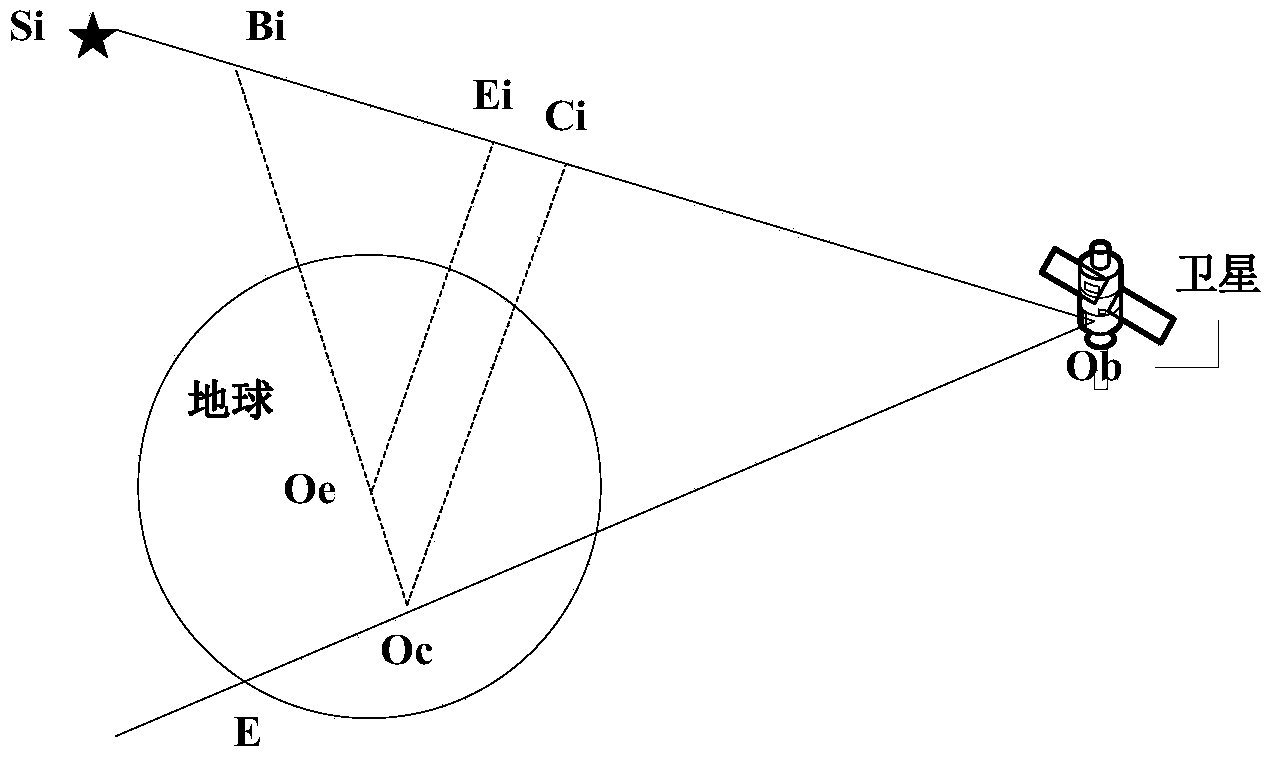
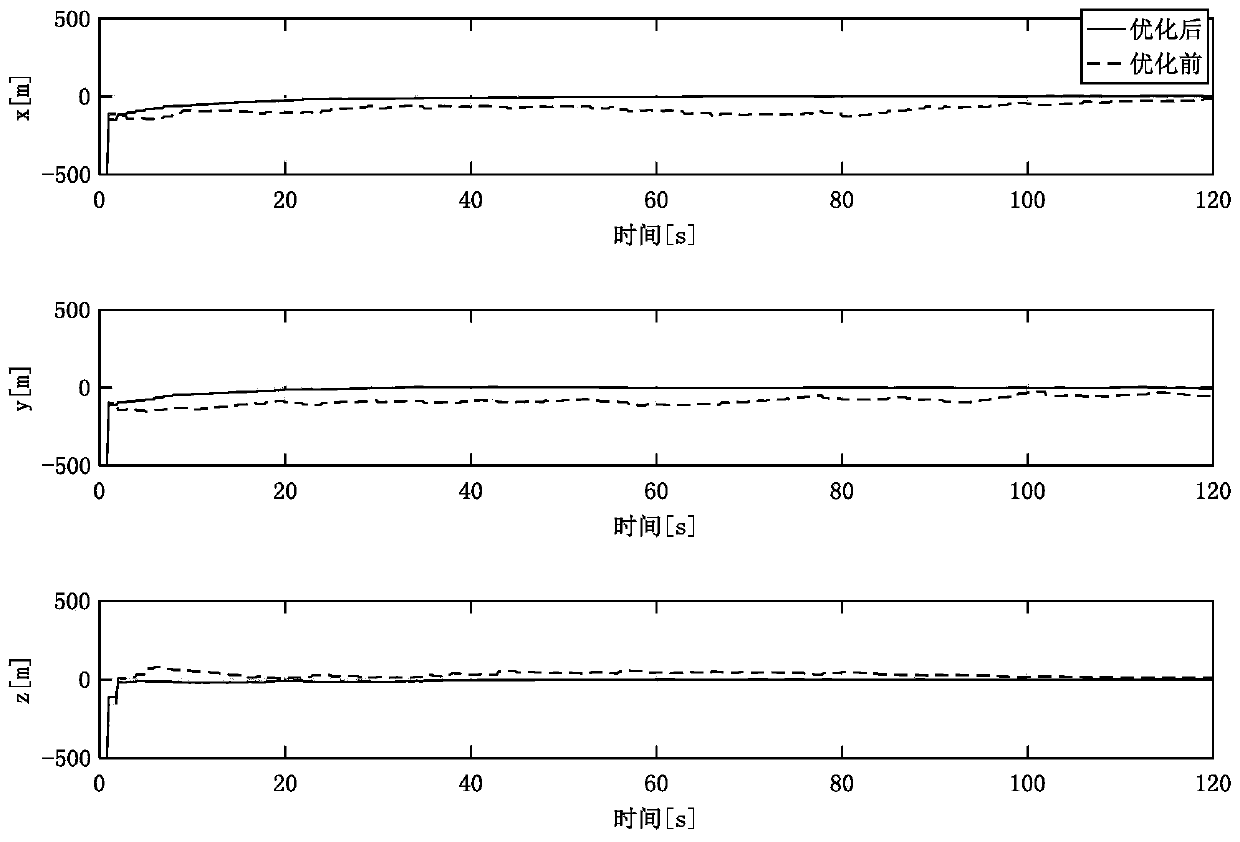
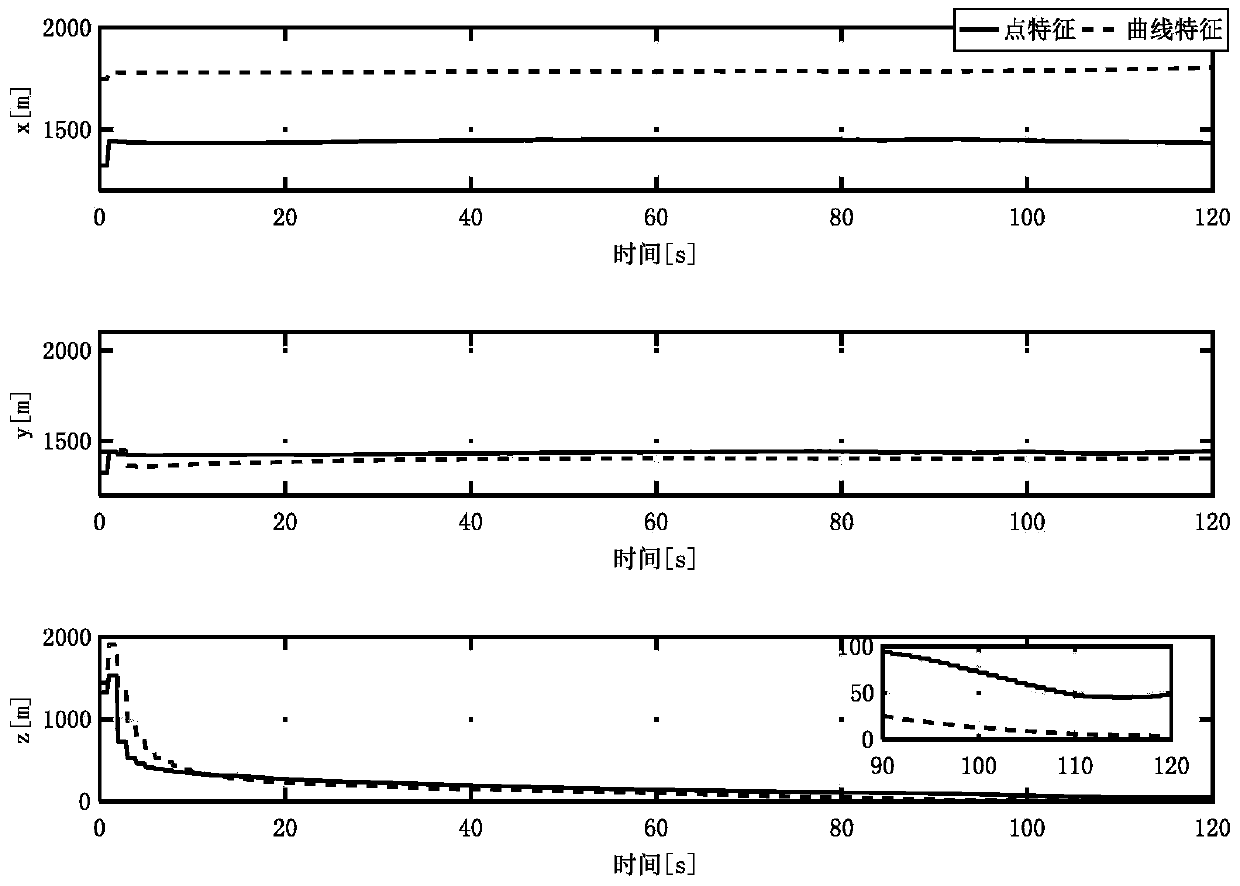
ActiveCN110702122AHigh precisionGuaranteed stabilityInstruments for comonautical navigationPicture interpretationStar catalogueCelestial body
The invention relates to an autonomous optical navigation feature comprehensive optimization method for landing of an extraterrestrial celestial body, and belongs to the technical field of deep spaceexploration. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing observation equations of different geometric feature landmarks by using star catalogue image information; analyzing the observability degree and the estimation error lower limit of a navigation system by using a Fisher information matrix; on the basis, optimizing randomly distributed feature point landmarks by taking theobservability degree and the estimation error lower limit of the navigation system as evaluation indexes; and optimally selecting different navigation landmark feature points and curves, so that the precision of the navigation system is improved, and the stability of the navigation system is ensured. According to the method, the randomly distributed feature point landmarks are optimized by takingthe observability degree and the estimation error lower limit of the navigation system as the evaluation indexes, and the different navigation landmark feature points and curves are optimally selected, so that the precision of the navigation system is improved. The method is suitable for a planet landing task and is also suitable for a small celestial body landing task.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Determination method for influence on star catalogue device by 10-N thruster plume
ActiveCN103217269AAvoid modeling analysis processMany iterationsAerodynamic testingHeat flowStar catalogue
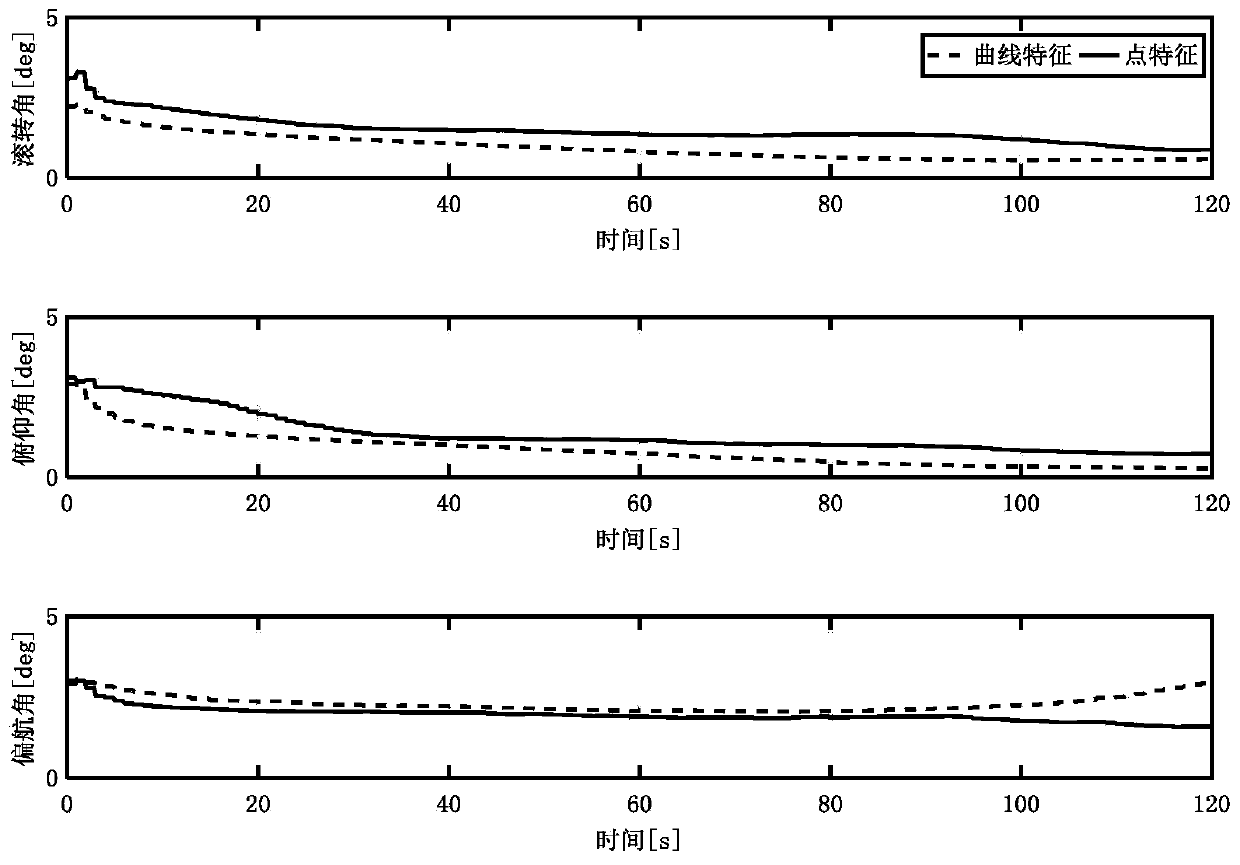
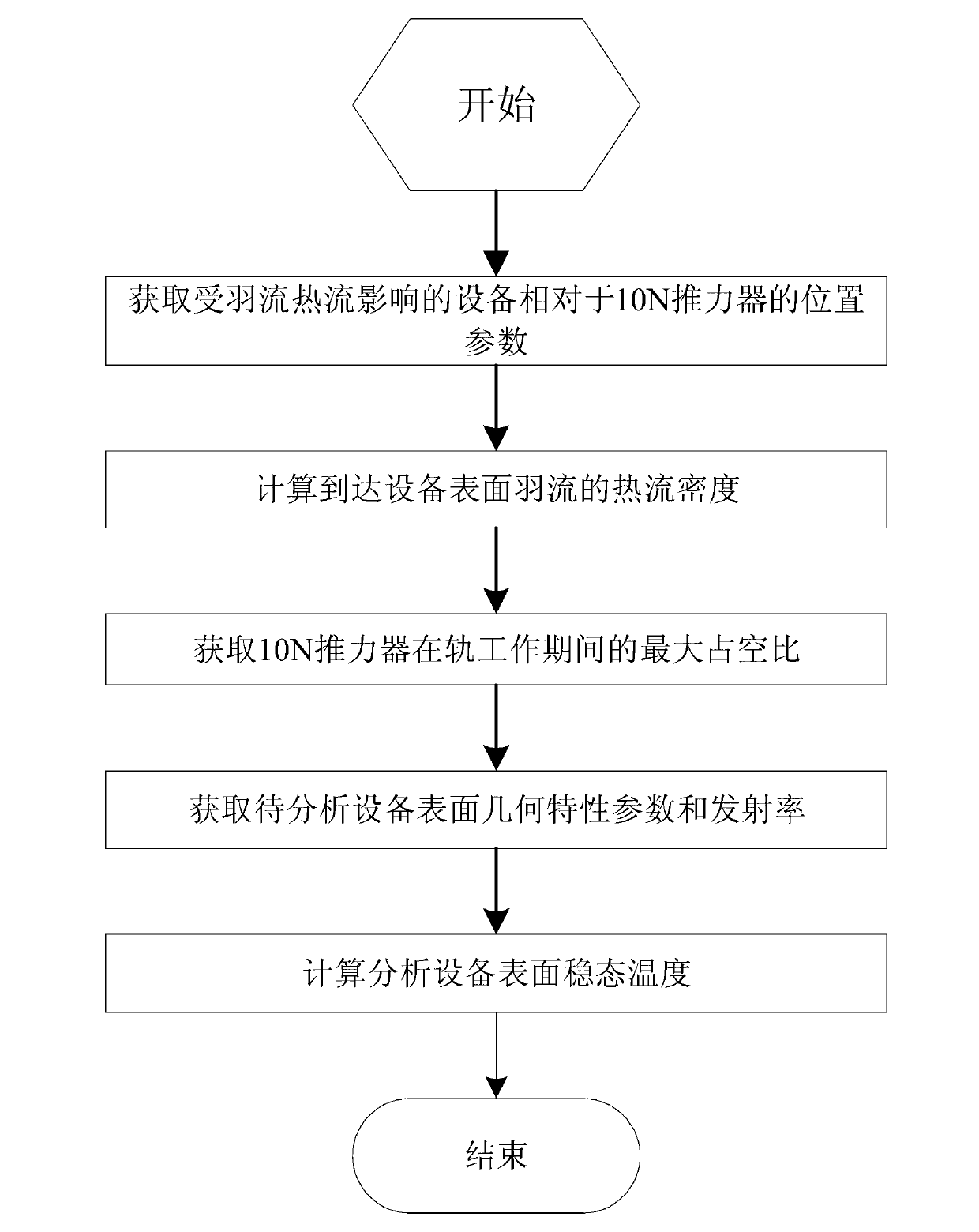
A determination method for influence on a star catalogue device by 10-N thruster plume can rapidly calculate steady state temperature of the influenced device based on the foundation of analyzing thermal flux density of the device influenced by the 10-N thruster plume and combined with a working duty ratio of a 10-N thruster and thermal characteristics and surface geometric characteristics of the influenced device. The determination method for the influence on the star catalogue device by the 10-N thruster plume is specially suitable for a medium and high orbit satellite with the 10-N thruster serving as an actuating mechanism, the influence on the device by the temperature of the plume can be estimated and determined in the process of satellite configuration layout design, and references are offered for layout adjustment or thermal protection design of the influenced device.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
Autonomous star map identification method based on dimensionality reduction star catalogue
ActiveCN110715656AReduce capacityNavigational calculation instrumentsInstruments for comonautical navigationStar catalogueAlgorithm
The invention discloses an autonomous star map identification method based on a dimensionality reduction star catalogue. Eigenvectors of an observation star is established, the star catalogue is established and matched, the eigenvectors of the observation star o are compared with eigenvectors of a navigation star one by one, and features of the navigation star are successfully matched with elements in the eigenvectors when the quantity of the successfully matched elements in the eigenvectors is maximum and is greater than a certain threshold; and if matching fails, a star which is next nearestto the observation star o is selected as an inter-star geometric angle calculation reference, and the eigenvectors of the observation star are obtained again and then are matched with eigenvectors inthe star catalogue.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE AUTOMATIC CONTROL RES INST
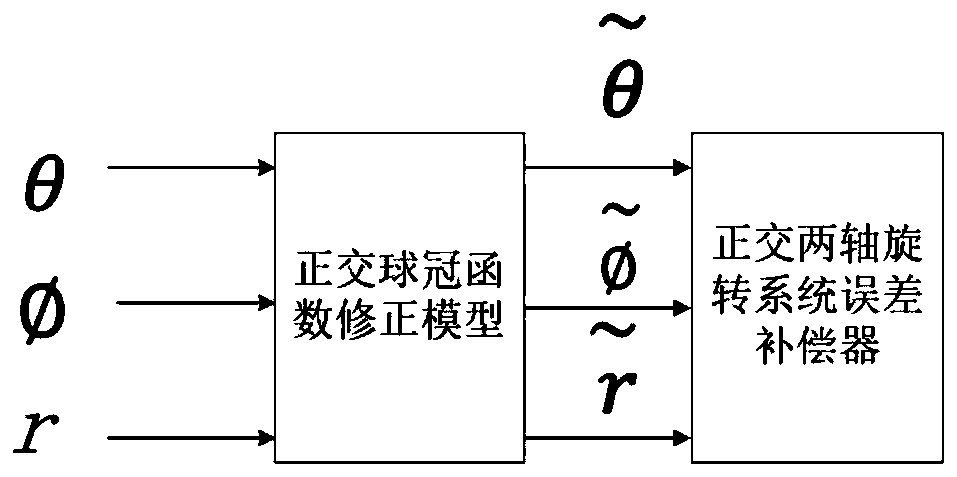
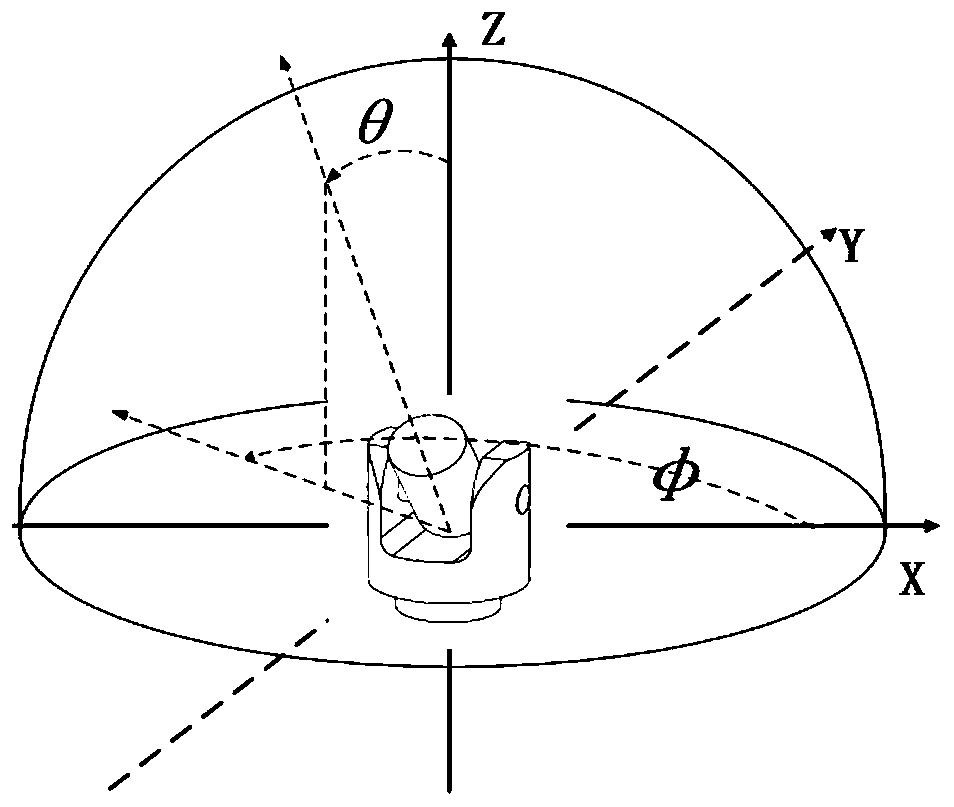
Correction method for pointing error of biaxial rotation system based on spherical crown function
ActiveCN110580060AImprove stabilityLess susceptible to measurement noiseControl using feedbackDirection findersFixed starsStar catalogue
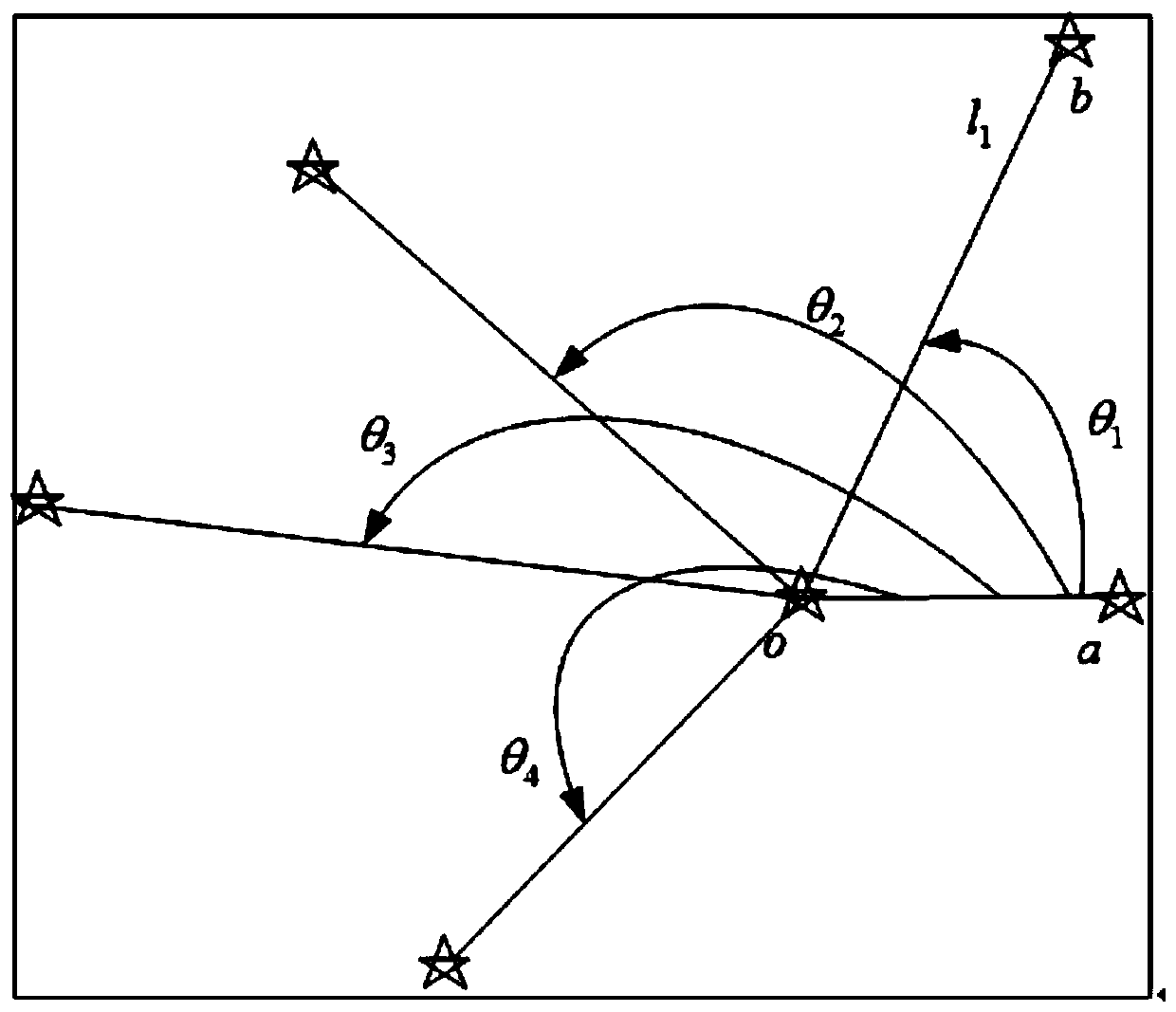
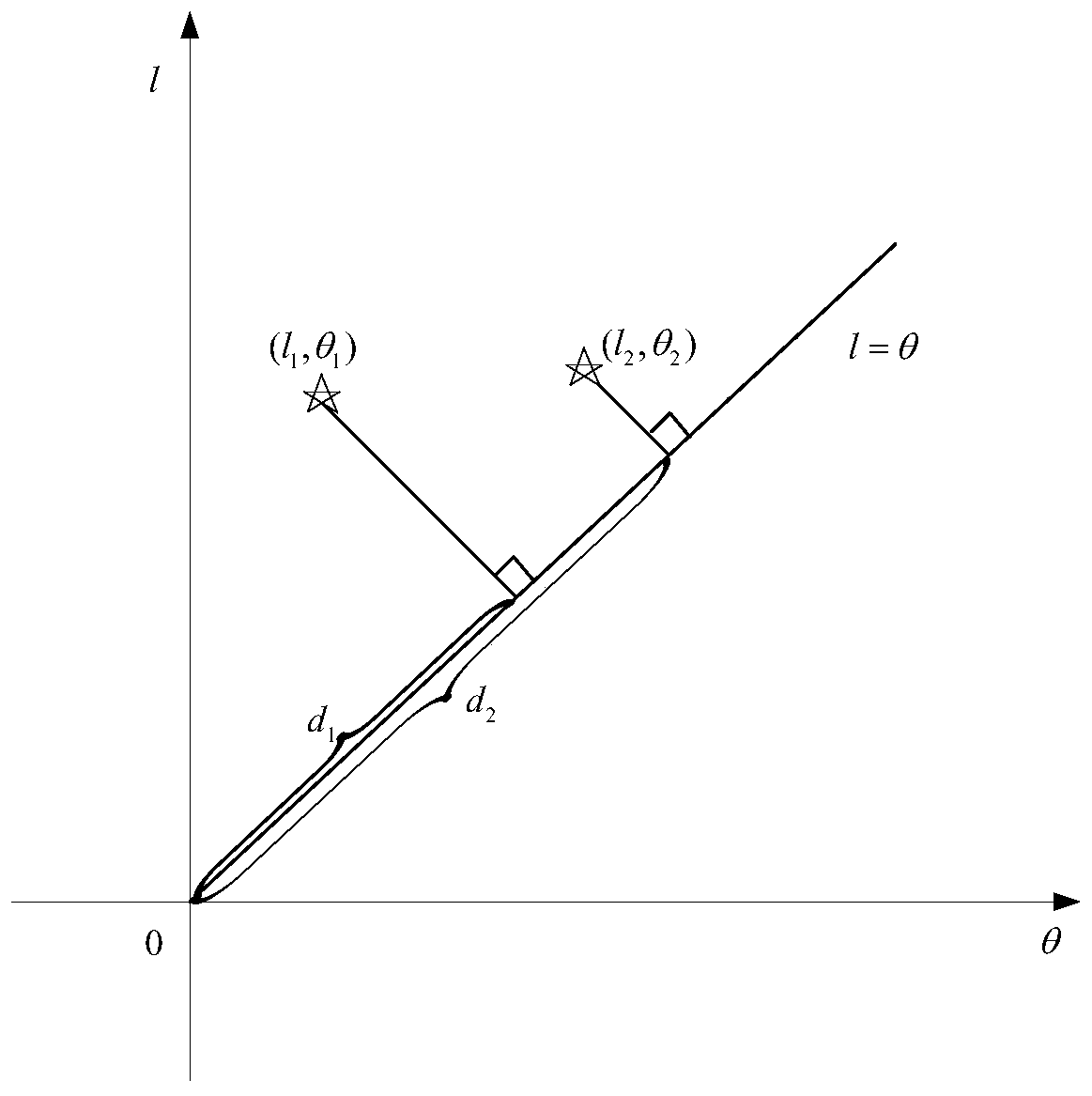
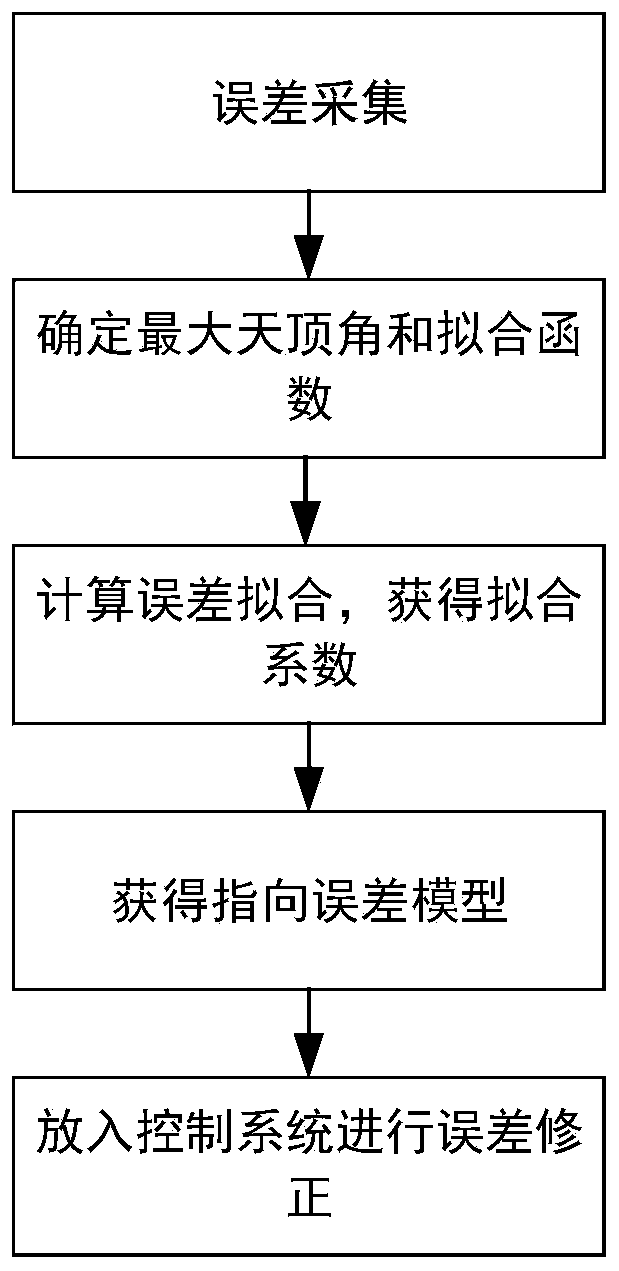
The invention discloses a correction method for a pointing error of a biaxial rotation system based on a spherical crown function. The method comprises the steps: error collection by selecting fixed stars or radio sources which are uniformly distributed all day long from a star catalogue for tracking observation, obtaining the theoretical and measurement positions of the fixed stars, subtracting the theoretical positions from the measurement positions, and obtaining error distribution; error model fitting by selecting an appropriate orthogonal spherical crown function model for the obtained error distribution, performing fitting, and calculating an error fitting coefficient; and error control compensation by putting the error model and a related fitting coefficient into a pointing controlsystem for compensation. The orthogonal spherical crown function model comprises a hemispherical harmonic function HSH, a Zernike spherical crown function ZSF and a longitudinal spherical crown function LSF. By adopting the method, the model is high in stability and is not easily influenced by measurement noise; the form of the model does not need to be determined according to the frame form of the telescope, and the correction precision is high.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ASTRONOMICAL OPTICS & TECH NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSE
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com