Embedded space target astronomical positioning method
A space target, astronomical positioning technology, applied in astronomical navigation, character and pattern recognition, structured data retrieval, etc., can solve the problems of low efficiency, long time-consuming space target monitoring, complex data processing process, etc., to reduce bandwidth requirements. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] The technical solutions of the present invention will be clearly and completely described below through specific embodiments.
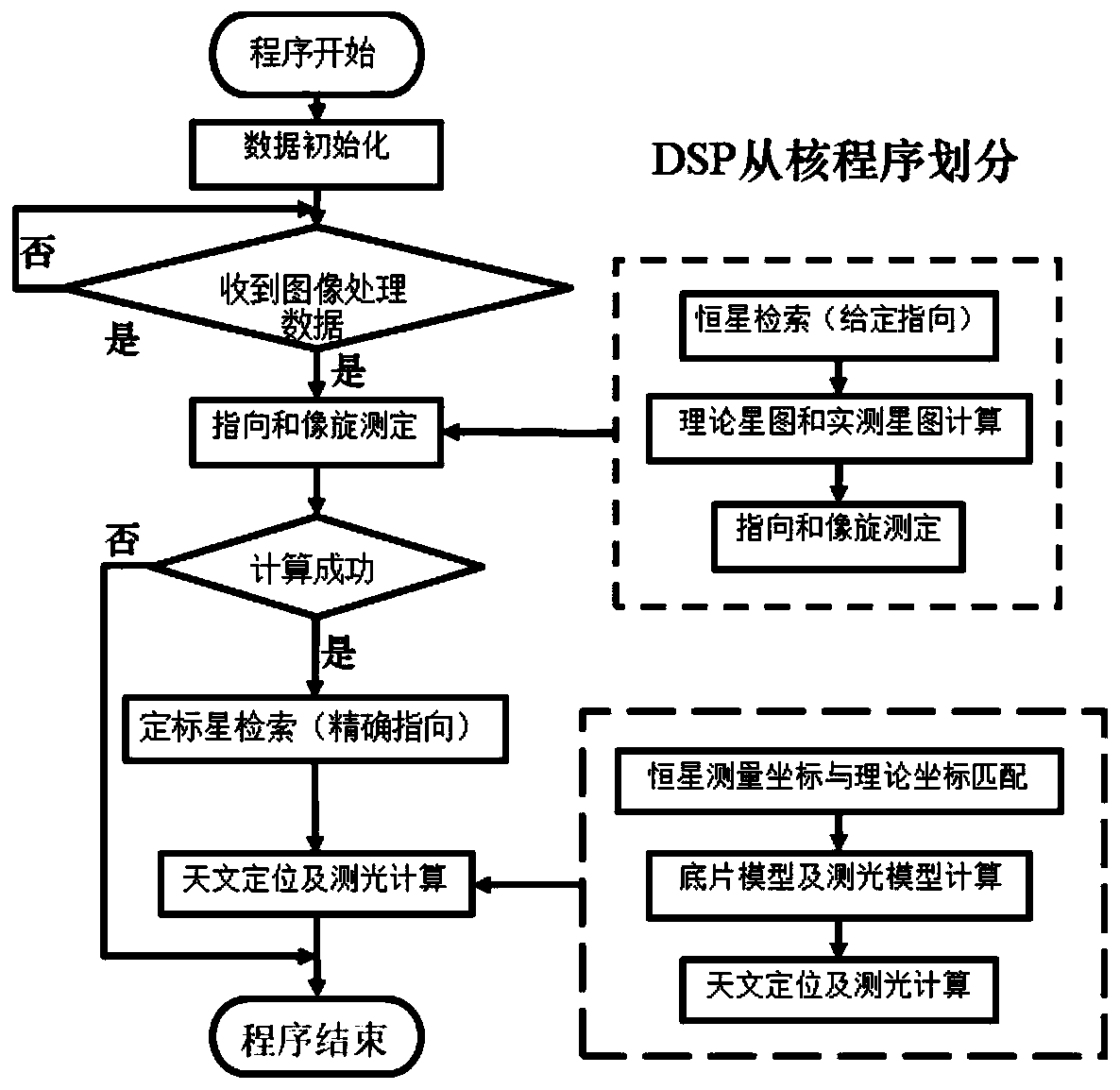
[0035] The present invention provides an embedded space target astronomical positioning method, the specific process of which is as follows figure 1 As shown, it specifically includes the following steps:
[0036] (1) Initialize the star catalog data and star catalog index data. The initialized star catalog includes standard stars that have been accurately measured in practice, that is, theoretical stars. The position and photometric information of the theoretical stars are used as standard values in astronomical measurements; according to The telescope used for actual observation sets the focal length and field of view and the size of the camera target surface and the pixel size, wherein the star catalog used by the astronomical positioning method of the present invention is the GAIA star catalog.
[0037](2) Use a telescope to observe, and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com