Method for identifying long-distance space motion target based on stellar map matching
A space motion and target recognition technology, applied in the aerospace field, can solve the problems of missing moving targets, small amount of calculation, and difficult space background recognition of moving targets, and achieve high anti-interference, efficient acquisition, complexity and noise reduction. sensitive effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
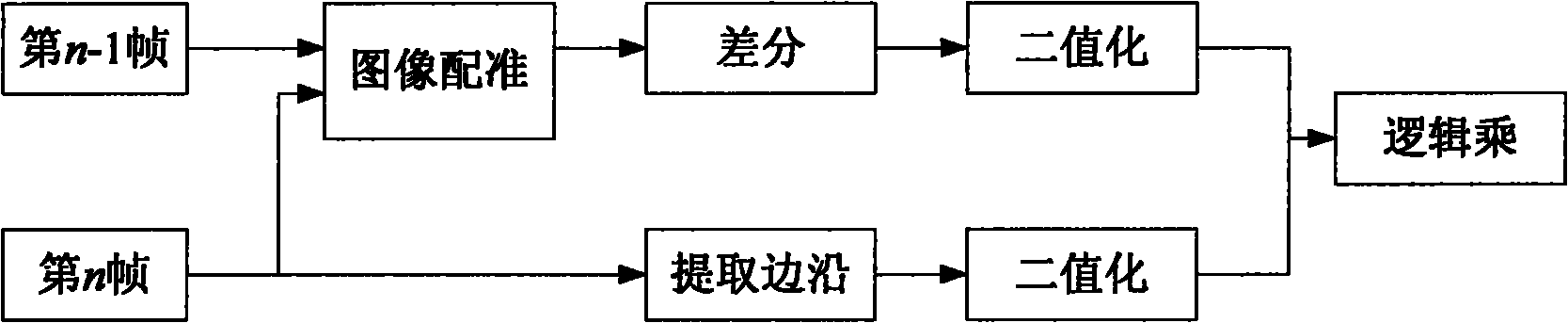
[0022] Example 1: Combining Figure 6 , the present invention is based on a star map matching long-distance space moving target recognition method, the steps are as follows:
[0023] Step 1: Extract the image point coordinates of the original images captured by the visible light cameras of all miniature space probes, and save all image point energy;
[0024] Step 2: sort all the image points in descending order of energy;
[0025] Step 3: Form all triangles by combining the sorted image points;
[0026] Step 4: Read the star catalog in the memory of the visible light camera of the miniature space probe;
[0027] Step 5: Use a triangle recognition algorithm to recognize all triangles formed by the image points;
[0028] Step 6: Eliminate all identified image points;
[0029] Step 7: Keep the unrecognized image point, which is the moving target image point.
Embodiment 2
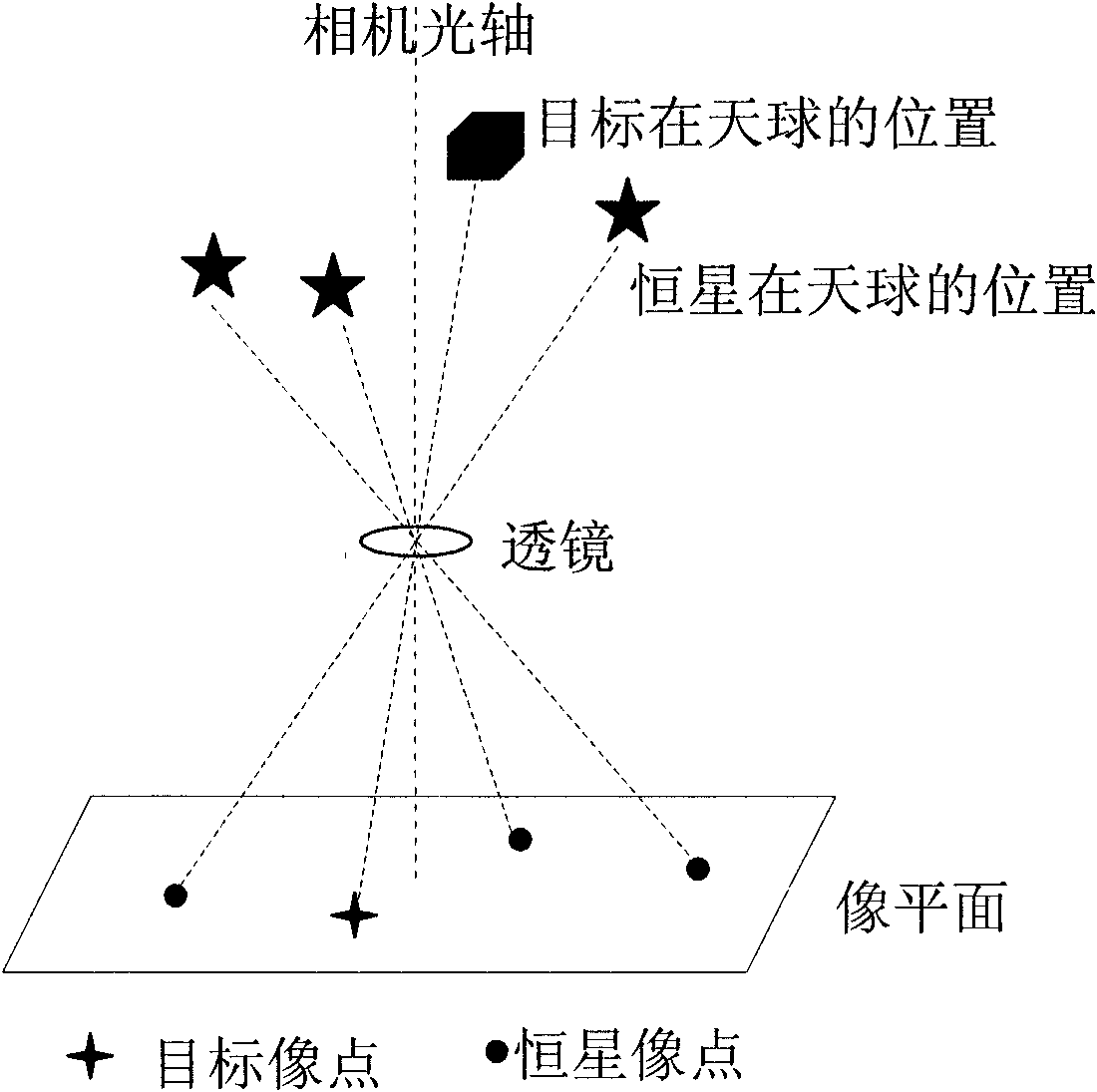
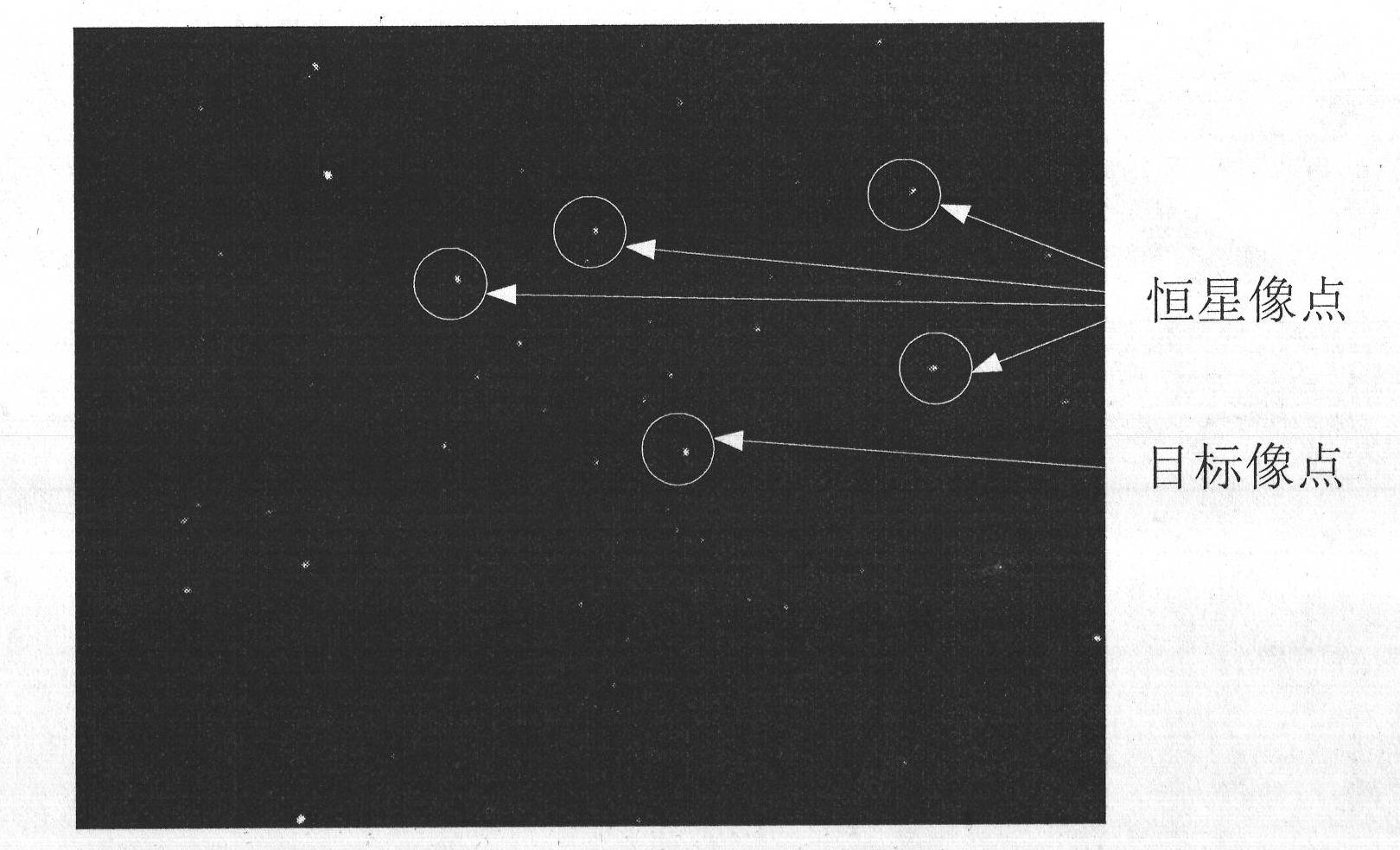
[0030] Example 2: Combining Figure 2-Figure 4 , the working principle of the visible light camera of the miniature space probe of the present invention is as follows figure 2 As shown, the image points in the captured images are almost all stellar image points (such as image 3 ), star image points cannot be connected into a line or any other conventional graphics, which makes it difficult to find a registration basis for common registration methods. The star catalog contains all the stars in the celestial sphere, so the star map recognition algorithm can be used to find out the corresponding stars from the star catalog for all the star images in the images taken by the visible light camera of the miniature space probe, and pick out the identified star images. The next one is the image point of the moving target. According to the original image captured by the visible light camera of the miniature space probe, the coordinates of all the image points are extracted from it (...
Embodiment 3
[0032]Embodiment 3: The main performance index of the present invention: the main observation surface of the moving target is about 2m×2m. In the long-distance section of 15km to 30km, the illumination is provided by sunlight and earth reflection, and the magnitude of the moving target is equivalent to 2nd to 6th magnitude. The visible light camera resolution of the miniature aerospace probe that shoots the target is 1024×1024, the field of view is 14°×14°, and it can detect stars above magnitude 6. The imaging of the moving target is specially defocused into multiple pixels, and the miniature aerospace The visible light camera of the detector has a certain disturbance. When oriented to the ground or to inertial orientation, the attitude pointing error is 0.1°, and the attitude stability is 0.05° / s; 0.1° / s. The navigation star library in the visible light camera of the miniature space probe comes from the SKY2000 star catalog, using all the stars whose visible magnitude is ab...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com