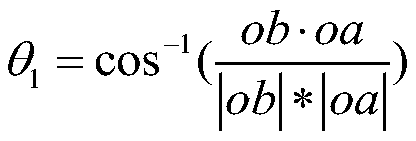Autonomous star map identification method based on dimensionality reduction star catalogue
An identification method and star map identification technology, applied in the field of astronomical navigation, can solve the problems of large storage space, long operation time, and complicated calculation of the navigation star database, and achieve the goal of reducing the capacity of star catalogues, small capacity of star catalogues, and high recognition rate. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
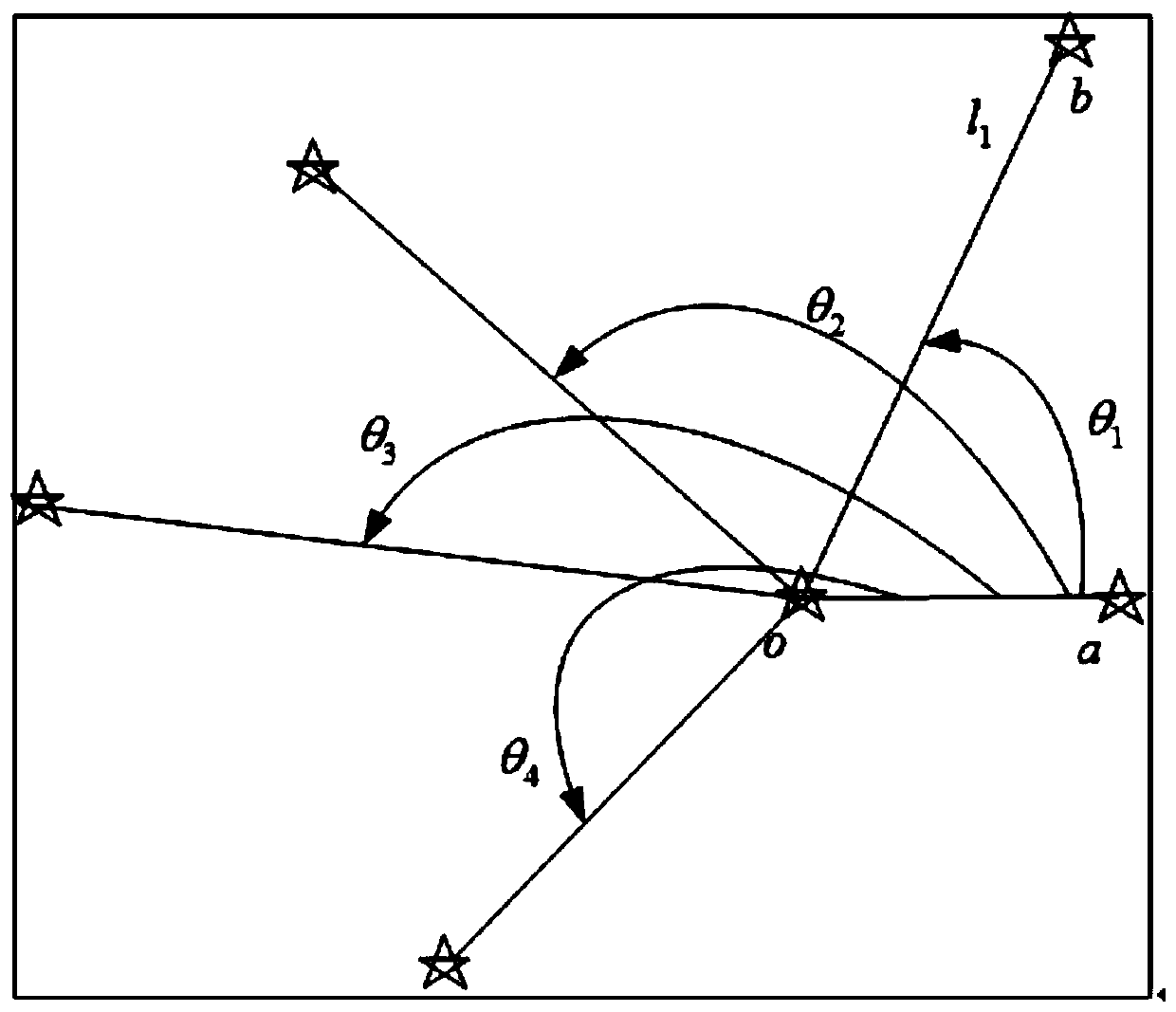
[0031] 1. Establish the observation star feature vector
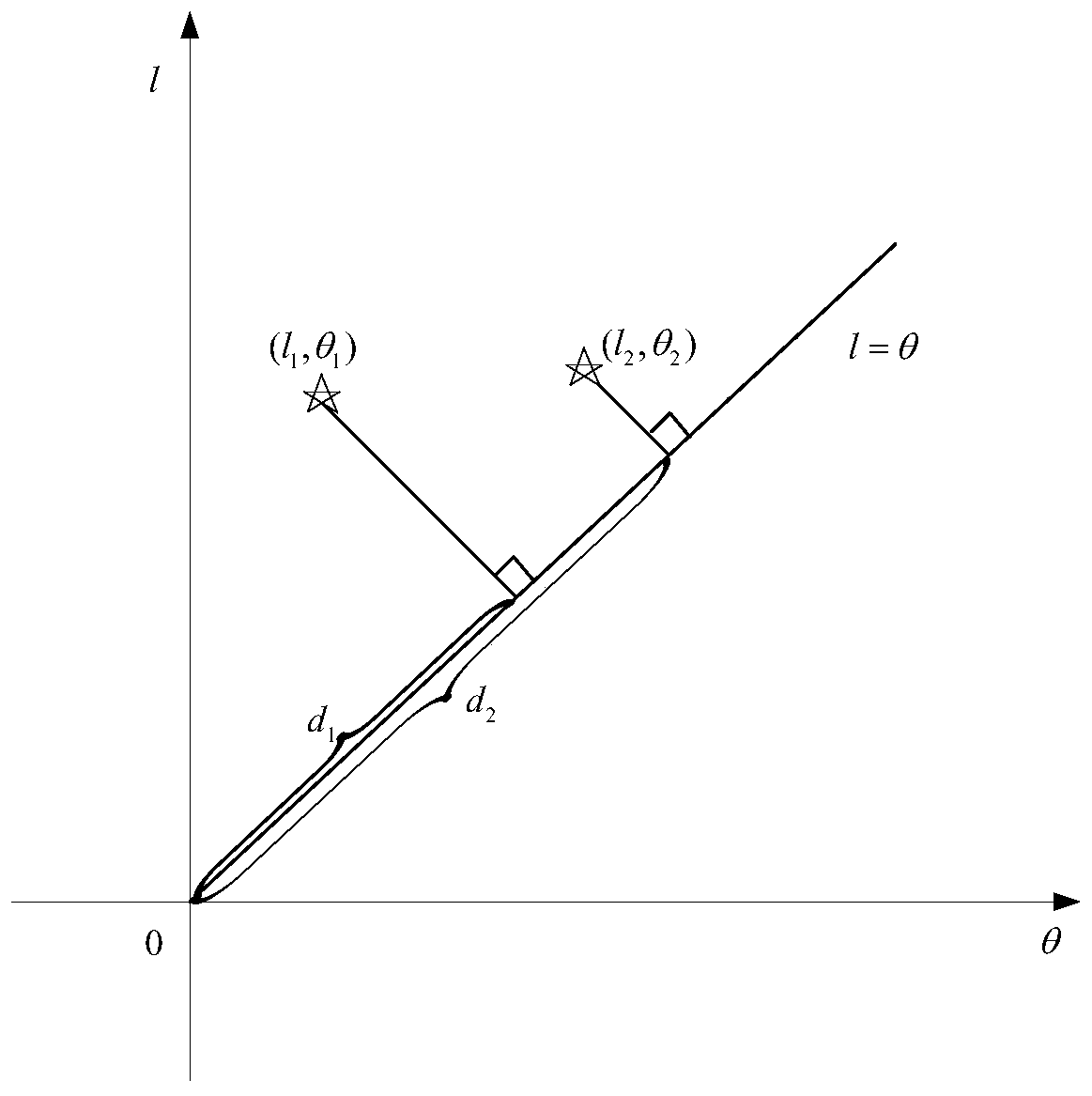
[0032] Select the observation star o closest to the center of the field of view, and the nearest neighbor star a to the observation star o. Calculate the distance from other observed stars to the observed star o, take the observed star oa as the starting edge, calculate the geometric angle between other observed stars and oa with the star o as the vertex (according to the same rotation direction). Obtain the angular distance of each observation star from the observation star o and the angle of the distance oa to form a set of vectors (l 1 ,θ 1 ),(l 2 ,θ 2 ),…(l n ,θ n ). Calculate (l 1 ,θ 1 ),(l 2 ,θ 2 ),…(l n ,θ n ) projection distance d on l=θ 1 , d 2 ,... d n .
[0033] star distance l 1 and θ 1 For example, the calculation method is as follows:
[0034]
[0035]
[0036] and,
[0037]
[0038] (l 1 ,θ 1 ) projection distance d on l=θ 1 The calculation method is
[0039]
[0040] 2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com