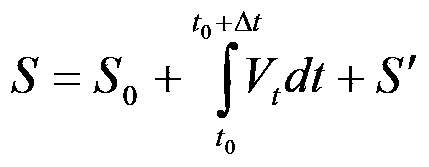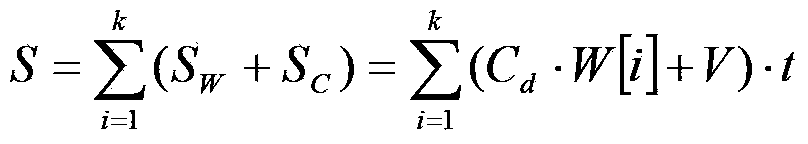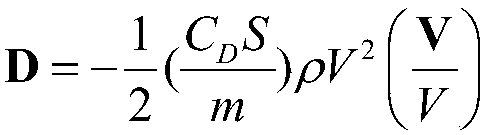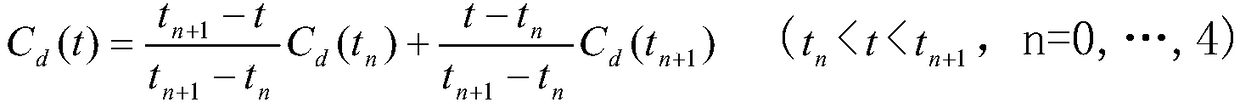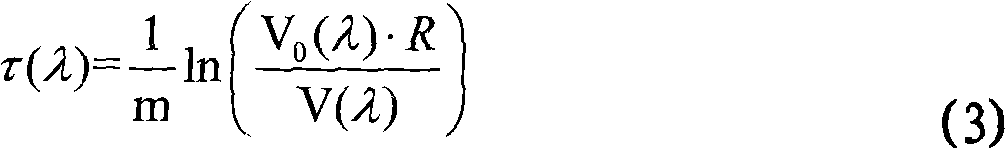Patents
Literature
84 results about "Atmospheric model" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An atmospheric model is a mathematical model constructed around the full set of primitive dynamical equations which govern atmospheric motions. It can supplement these equations with parameterizations for turbulent diffusion, radiation, moist processes (clouds and precipitation), heat exchange, soil, vegetation, surface water, the kinematic effects of terrain, and convection. Most atmospheric models are numerical, i.e. they discretize equations of motion. They can predict microscale phenomena such as tornadoes and boundary layer eddies, sub-microscale turbulent flow over buildings, as well as synoptic and global flows. The horizontal domain of a model is either global, covering the entire Earth, or regional (limited-area), covering only part of the Earth. The different types of models run are thermotropic, barotropic, hydrostatic, and nonhydrostatic. Some of the model types make assumptions about the atmosphere which lengthens the time steps used and increases computational speed.
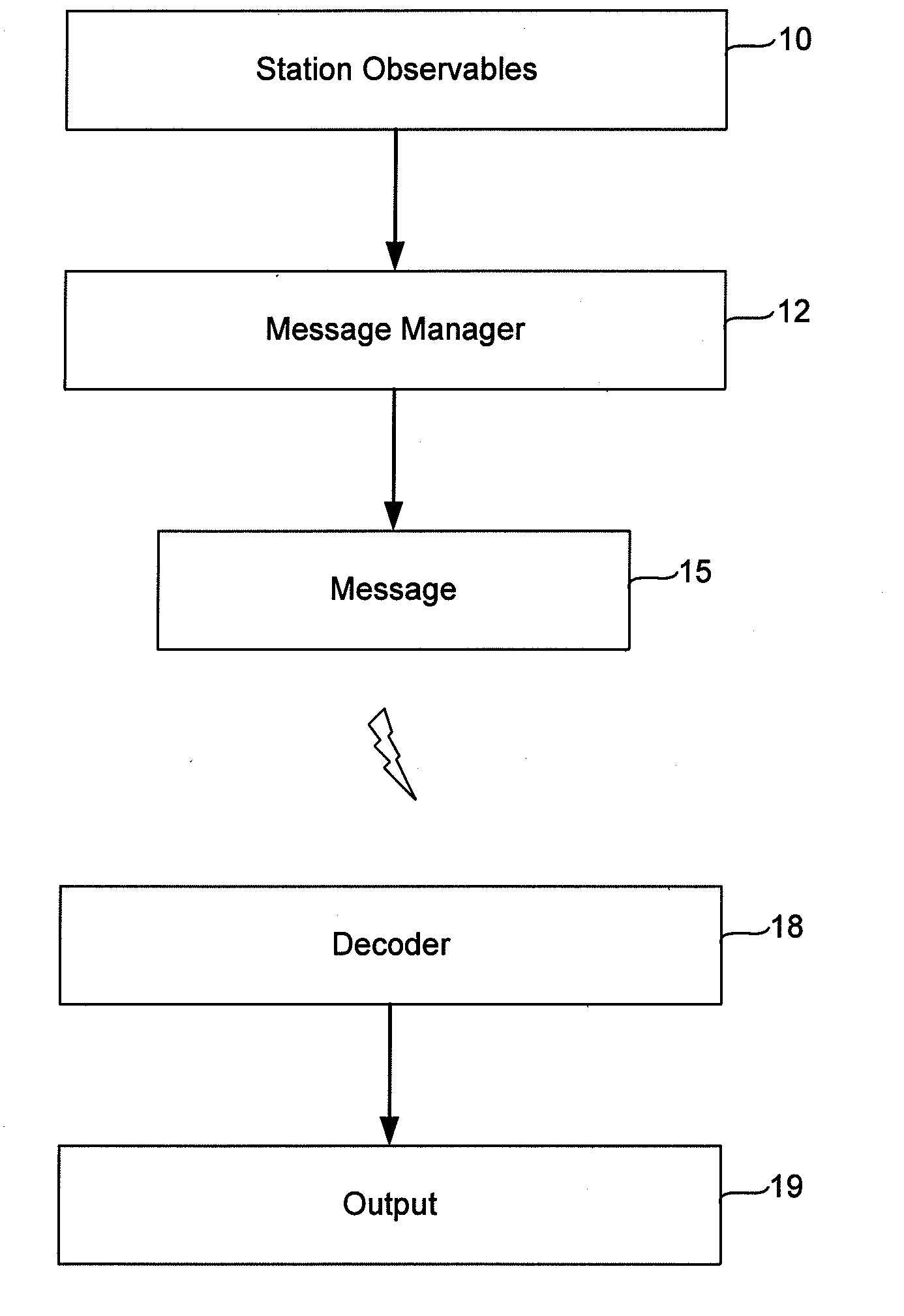
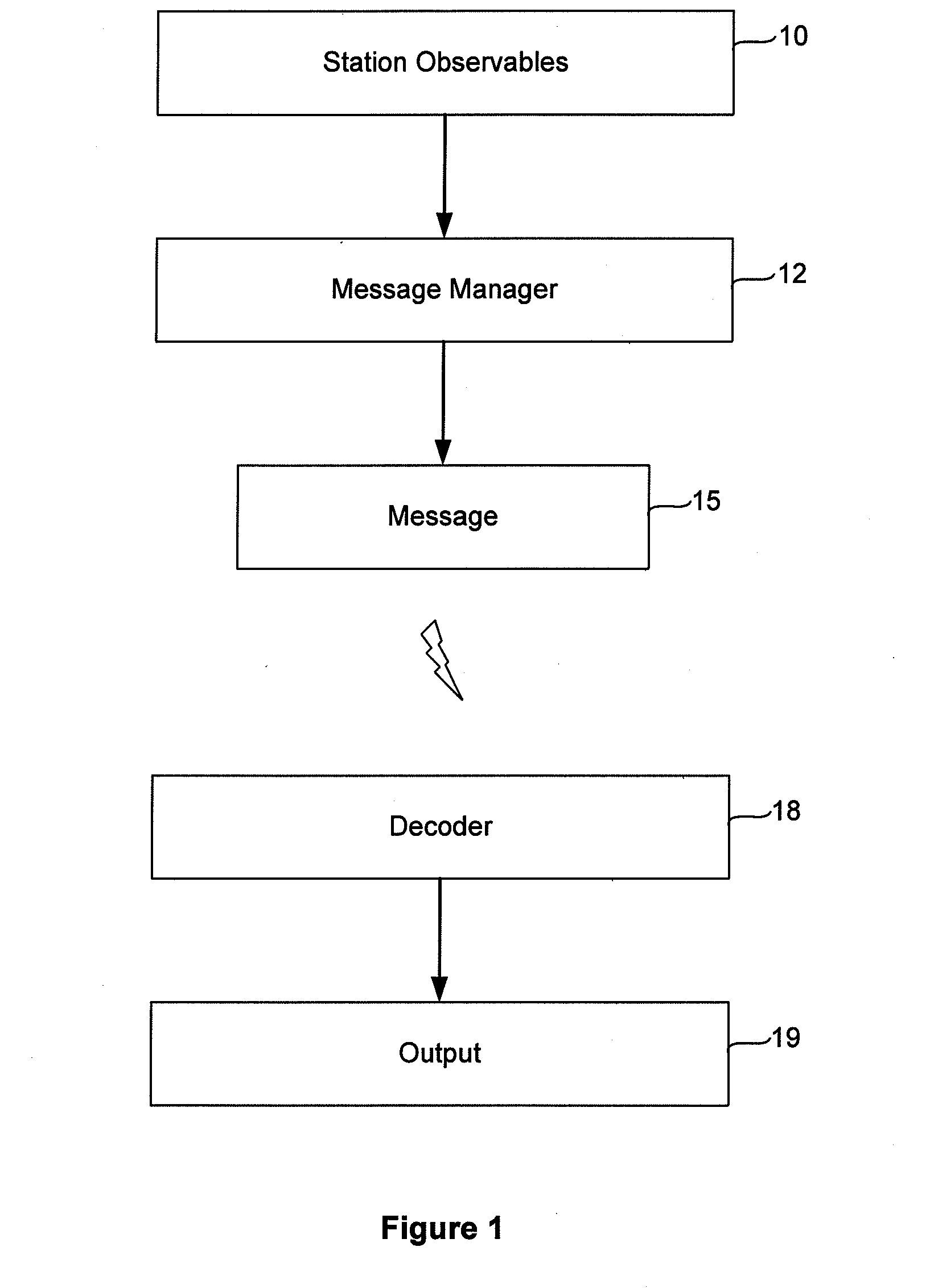
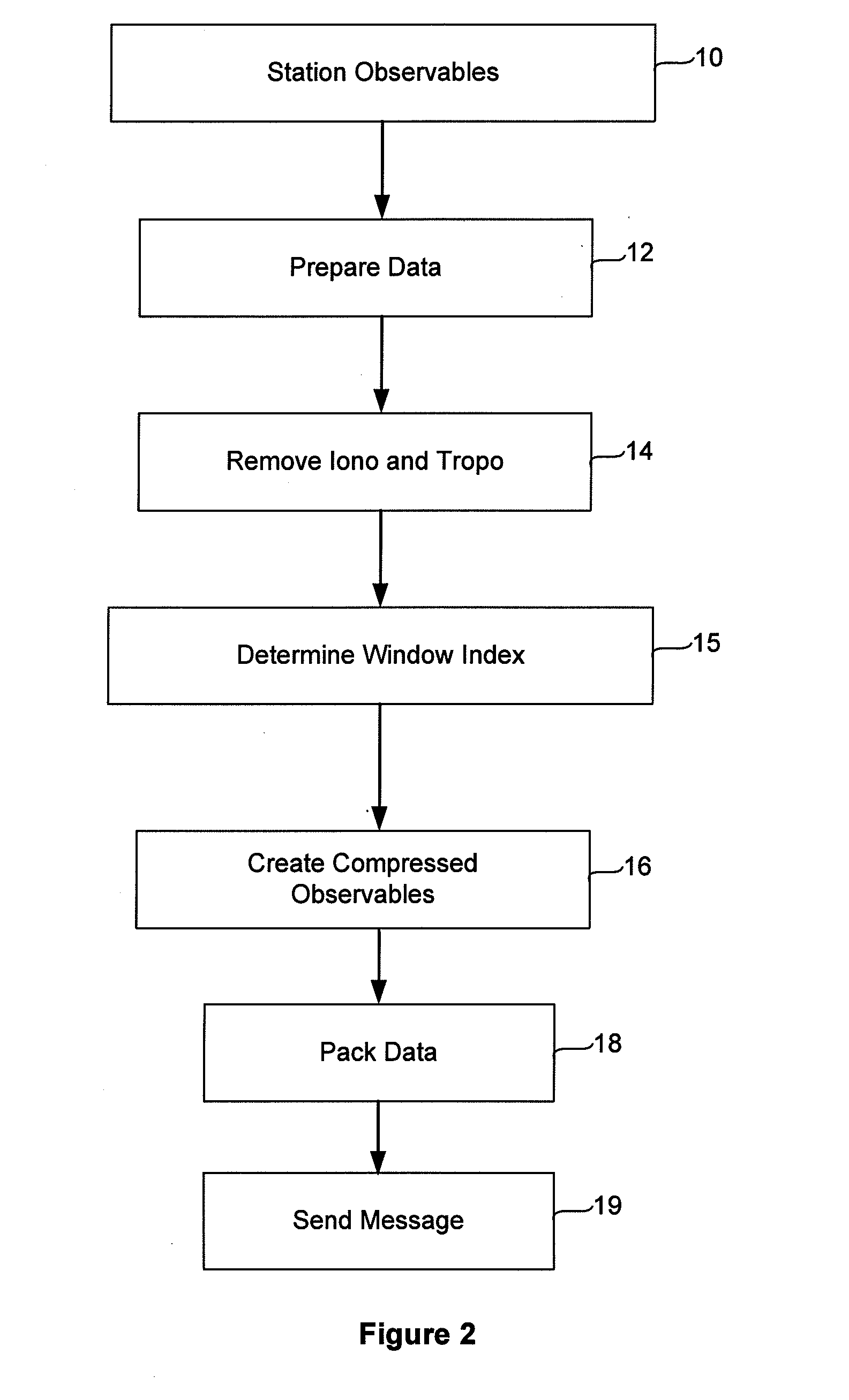
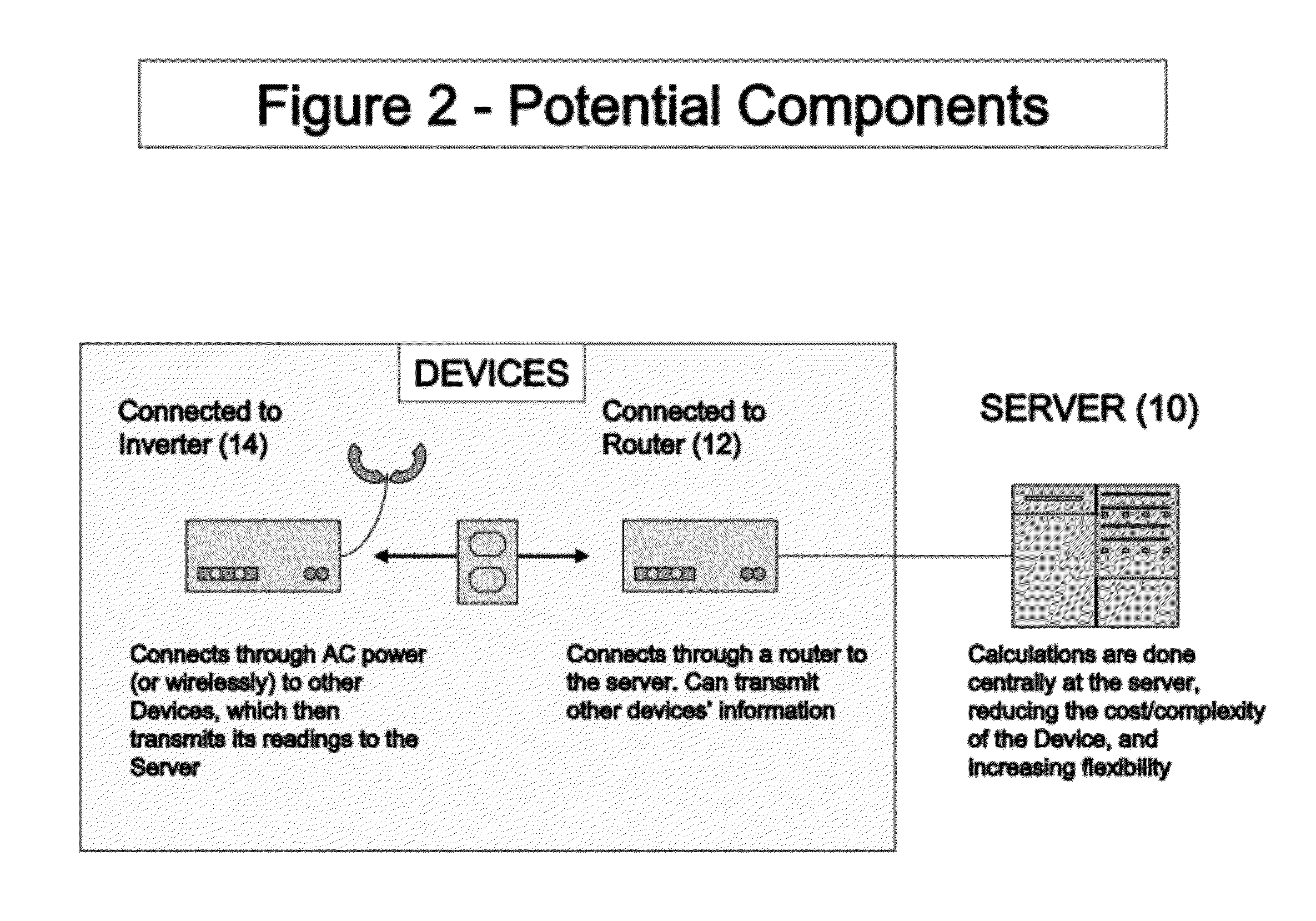
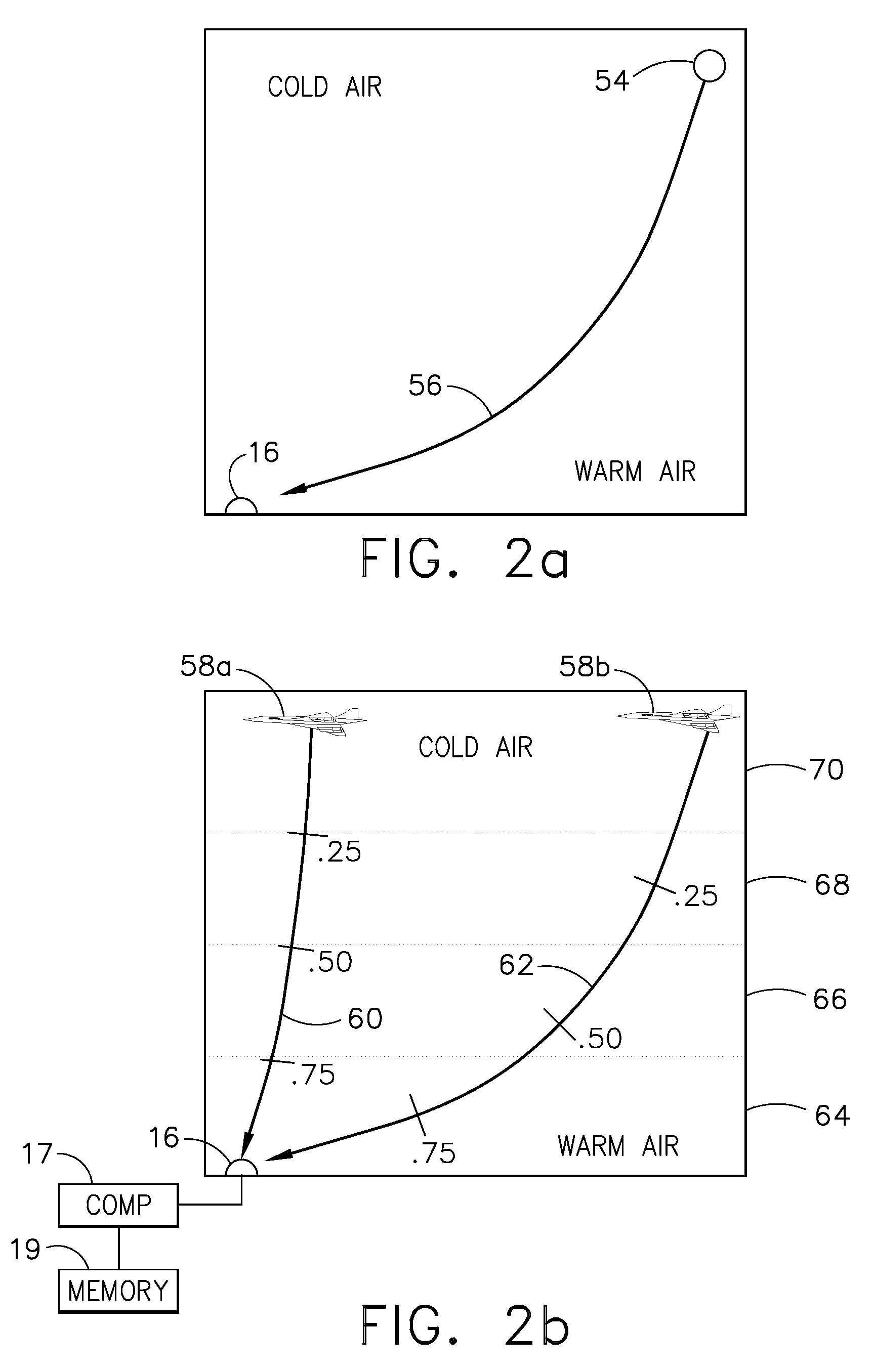
Compact Transmission of GPS Information Using Compressed Measurement Record Format
ActiveUS20100085249A1Smooth bandwidth utilizationGuaranteed usageCode conversionTime-division multiplexMessage lengthObservation data
A format for providing messages among GNSS apparatus includes providing a message identification block and a message body. The message identification block includes information specifying a message length and a message type block specifying a message type. Rather than sending all data from one apparatus to another, ambiguous observation data is sent to conserve bandwidth. At the sender a deconstruction of GNSS code and carrier observations using knowledge of the signal structure and constellation geometry, together with simplifications of atmospheric models, allows removal from the observation data of that information which can be implicitly understood or recreated by the recipient. This enables only the necessary information to be packed for transmission to the recipient.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
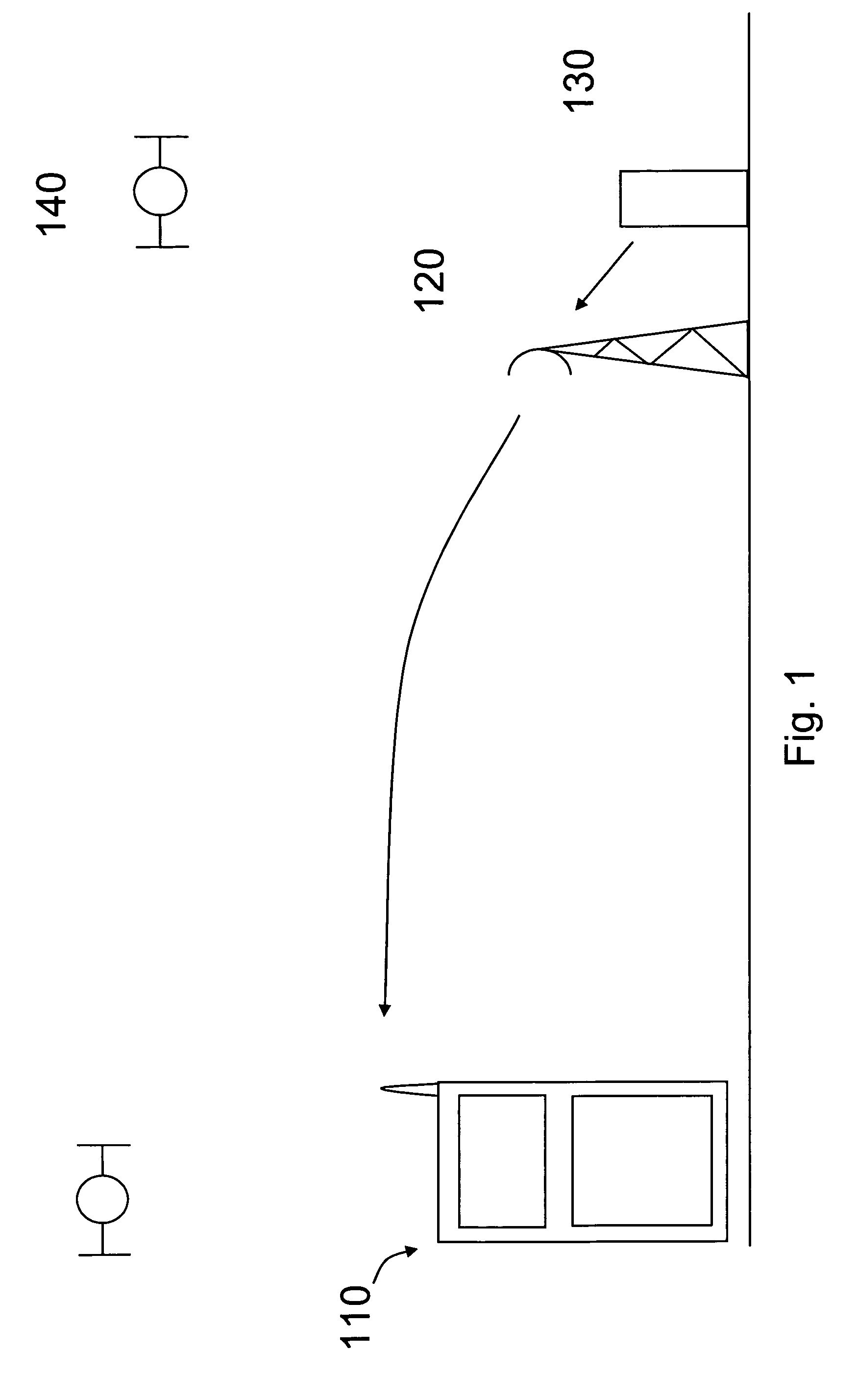
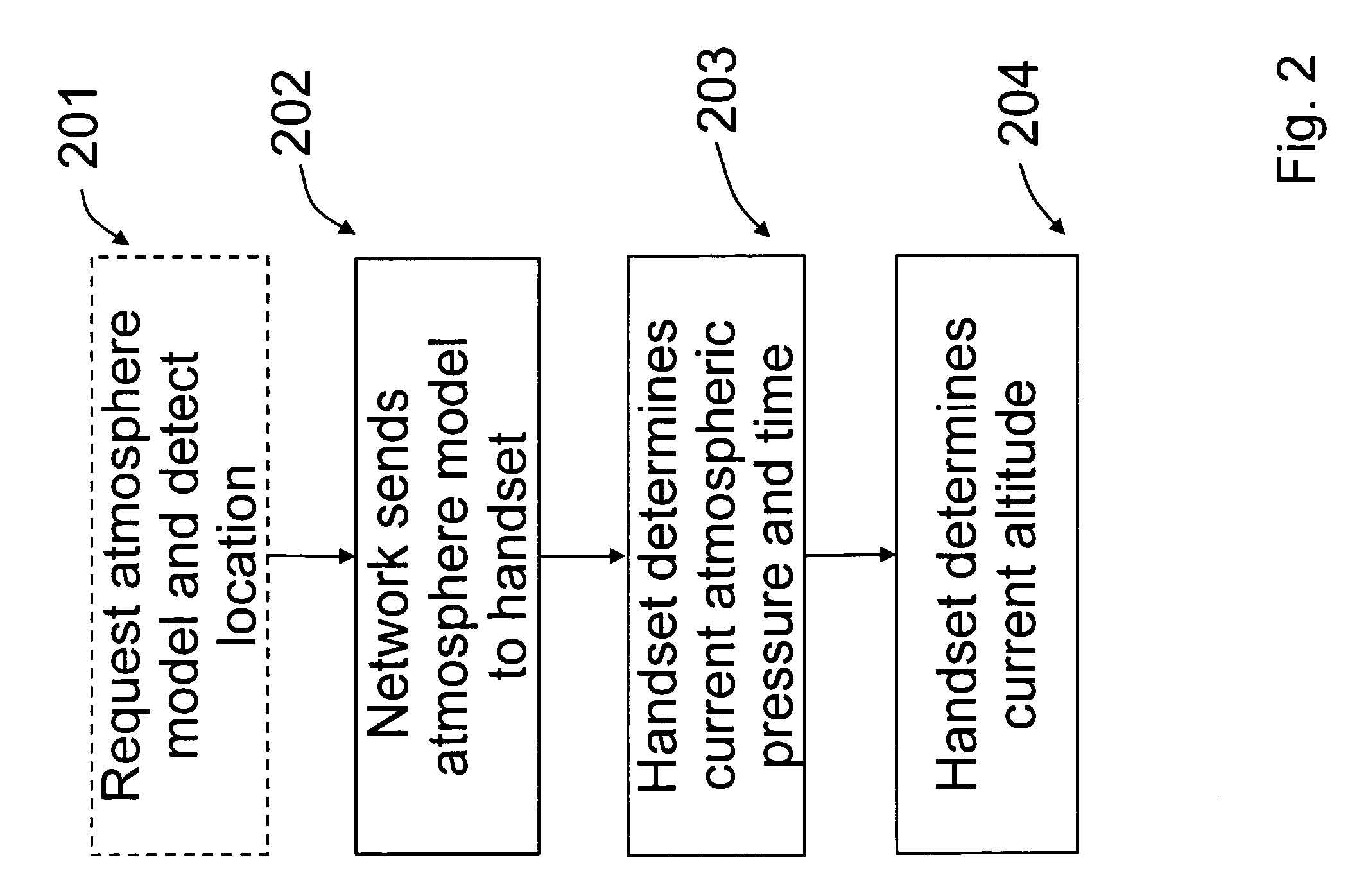
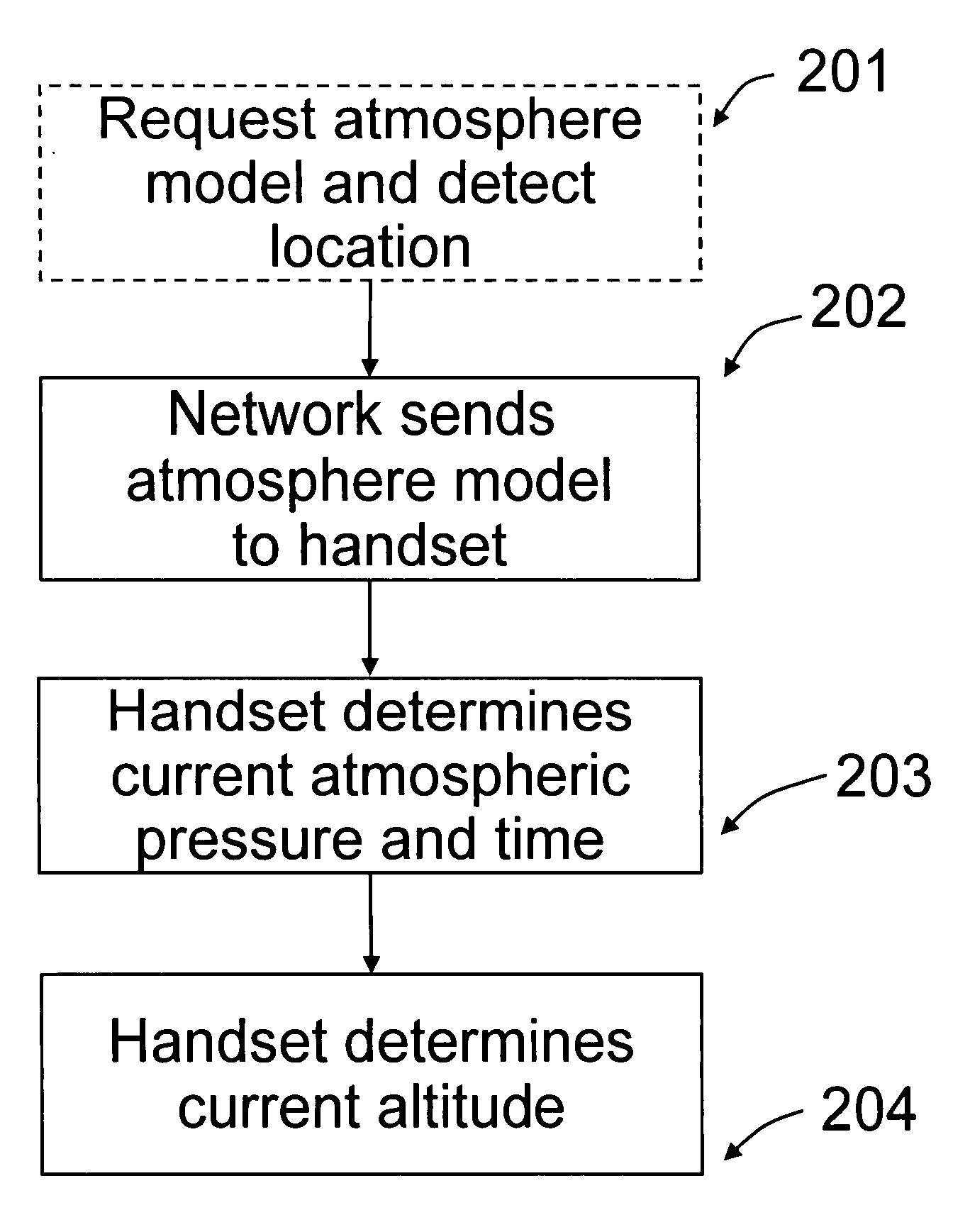
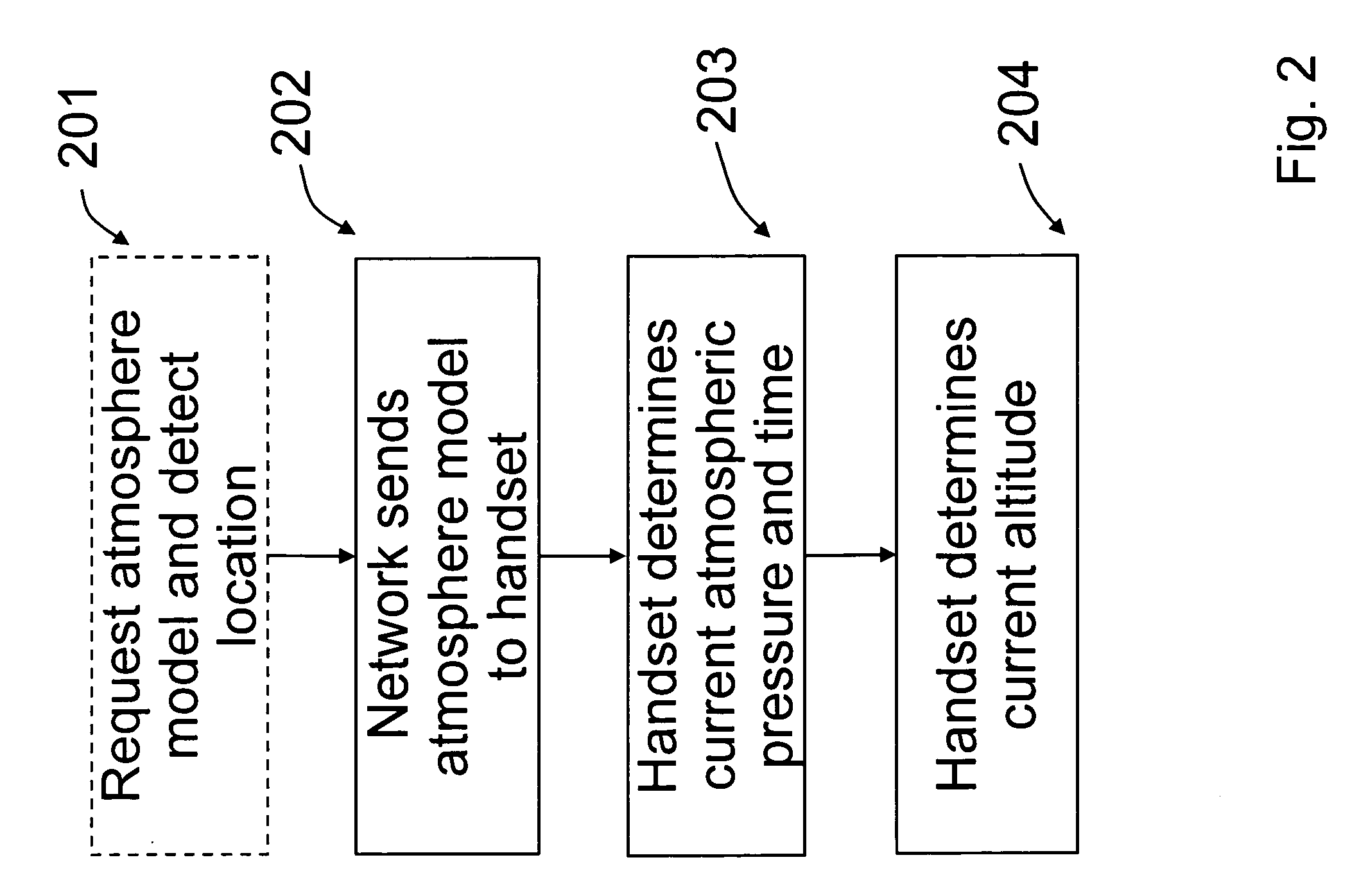
Atmosphere model
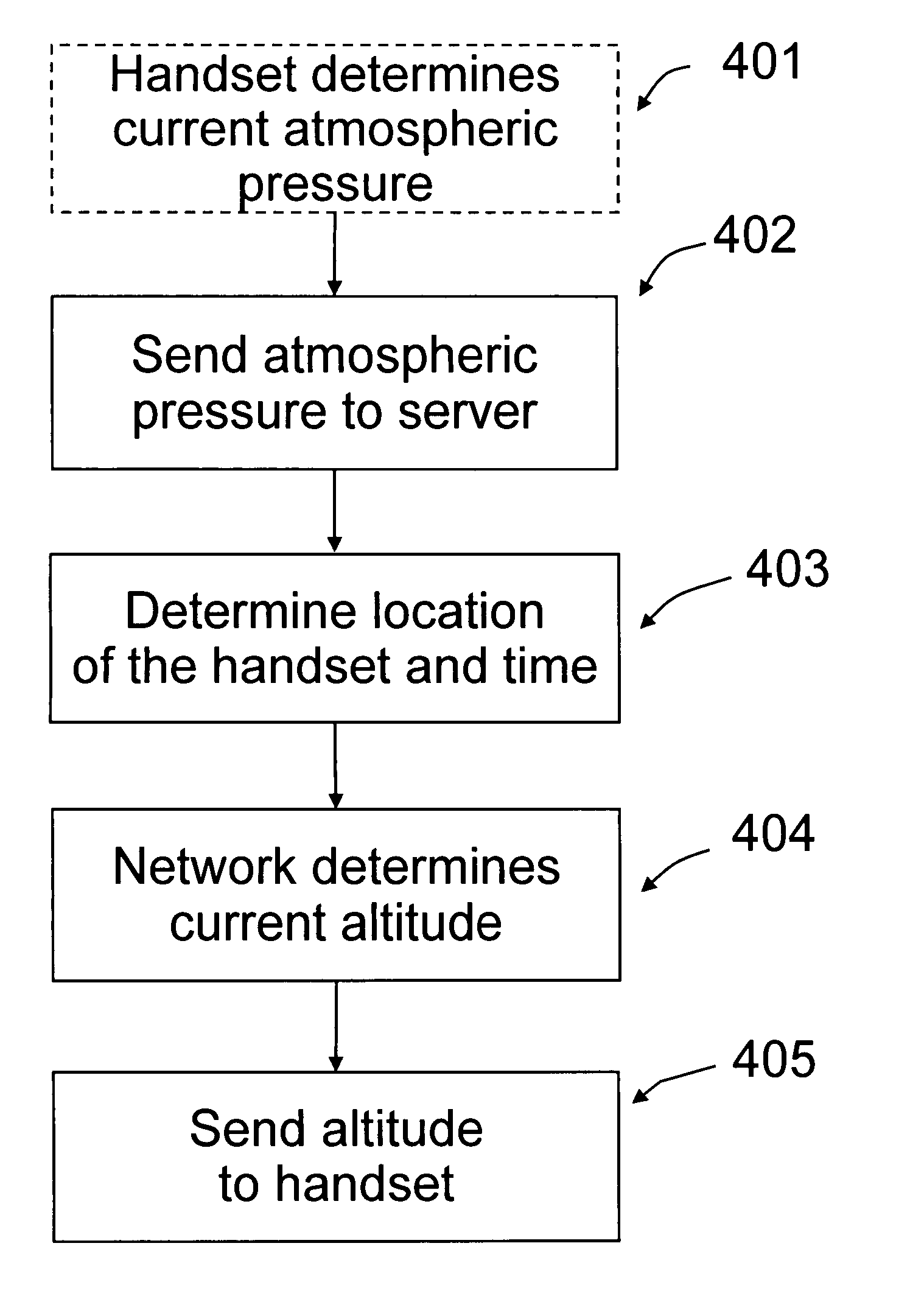
ActiveUS7751949B2Fluid pressure measurement using pressure-sensitive liquidDigital data processing detailsAtmospheric modelAtmospheric models
The invention relates to a time and location dependent atmosphere model and especially determining the altitude of a mobile terminal based on this model and the measured barometric pressure at the location of the terminal. The atmosphere model provides a long term, wide area barometric pressure model estimate.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Estimating solar irradiance components from plane of array irradiance and global horizontal irradiance
ActiveUS20120191351A1Reduce model biasImprove accuracySunshine duration recordersGeneration forecast in ac networkDirect normal irradianceAtmospheric model
A computer implemented method of estimating at least one solar irradiance component, the method comprising: obtaining a sensor measurement from an instrument to provide a measured global horizontal irradiance (GHImeasured), wherein the measured global horizontal irradiance (GHImeasured) consists of at least an estimated diffuse horizontal irradiance (DHIestimated) and an estimated direct normal irradiance (DNIestimated); providing at least one modeled component, wherein at least one of the modeled components is a modeled global horizontal irradiance based on an atmospheric model (GHImodel); calculating an irradiance estimate modifier (IMOD) in a computing device according to the measured global horizontal irradiance (GHImeasured) and the modeled global horizontal irradiance (GHImodel); and providing at least one estimated solar irradiance component by a computing device according to the irradiance estimate modifier (IMOD) and at least one modeled component.
Owner:LOCUS ENERGY
Atmosphere model
ActiveUS20070016346A1Take advantage ofFluid pressure measurement using pressure-sensitive liquidDigital data processing detailsAtmospheric modelAtmospheric models
The invention relates to a time and location dependent atmosphere model and especially determining the altitude of a mobile terminal based on this model and the measured barometric pressure at the location of the terminal. The atmosphere model provides a long term, wide area barometric pressure model estimate.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
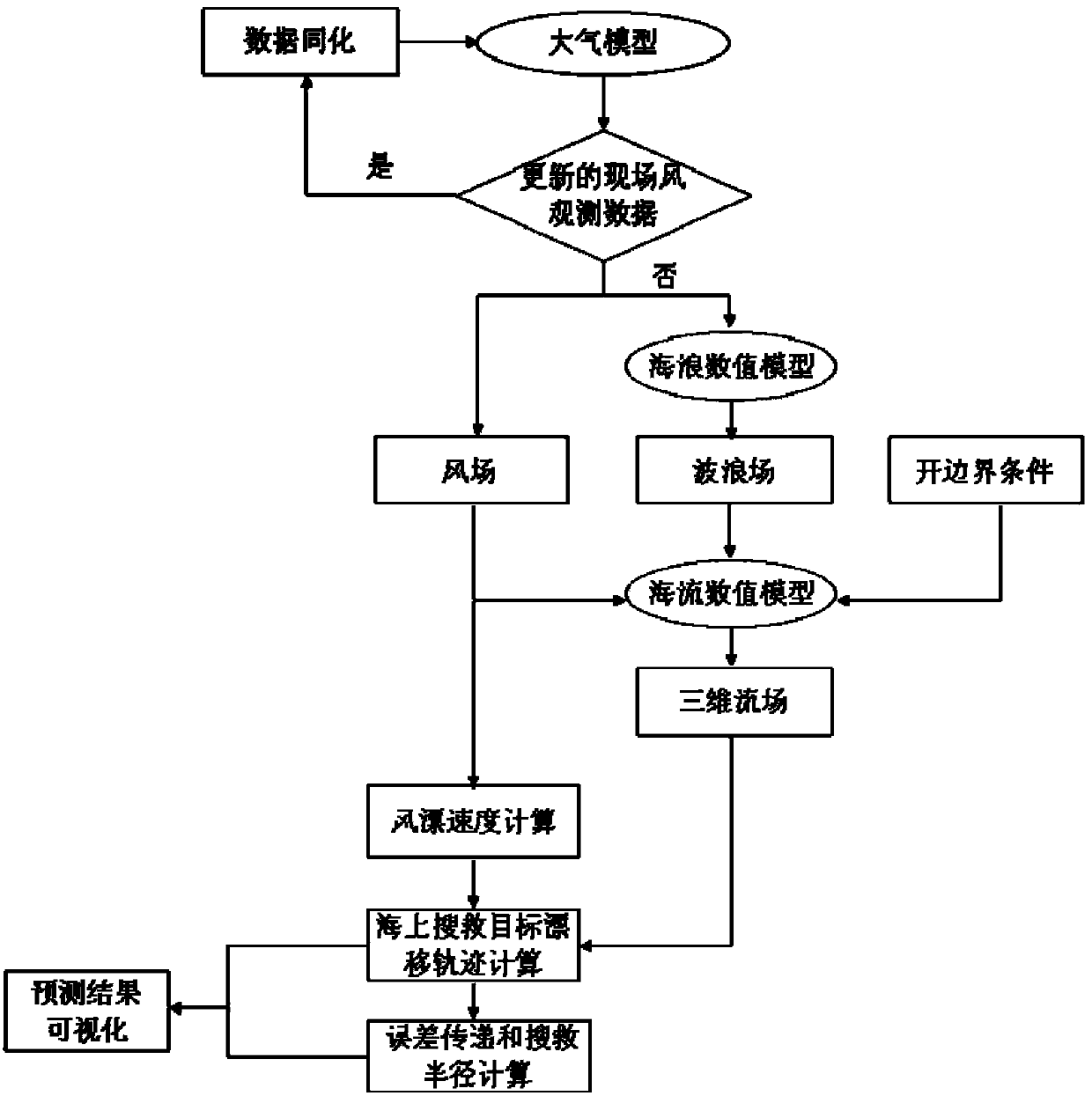
Predication method of maritime searching and rescuing target drifting path
ActiveCN103366227APrecise and Efficient ForecastingAccurate predictionForecastingICT adaptationWind drivenPredictive methods
Owner:中国地质大学深圳研究院
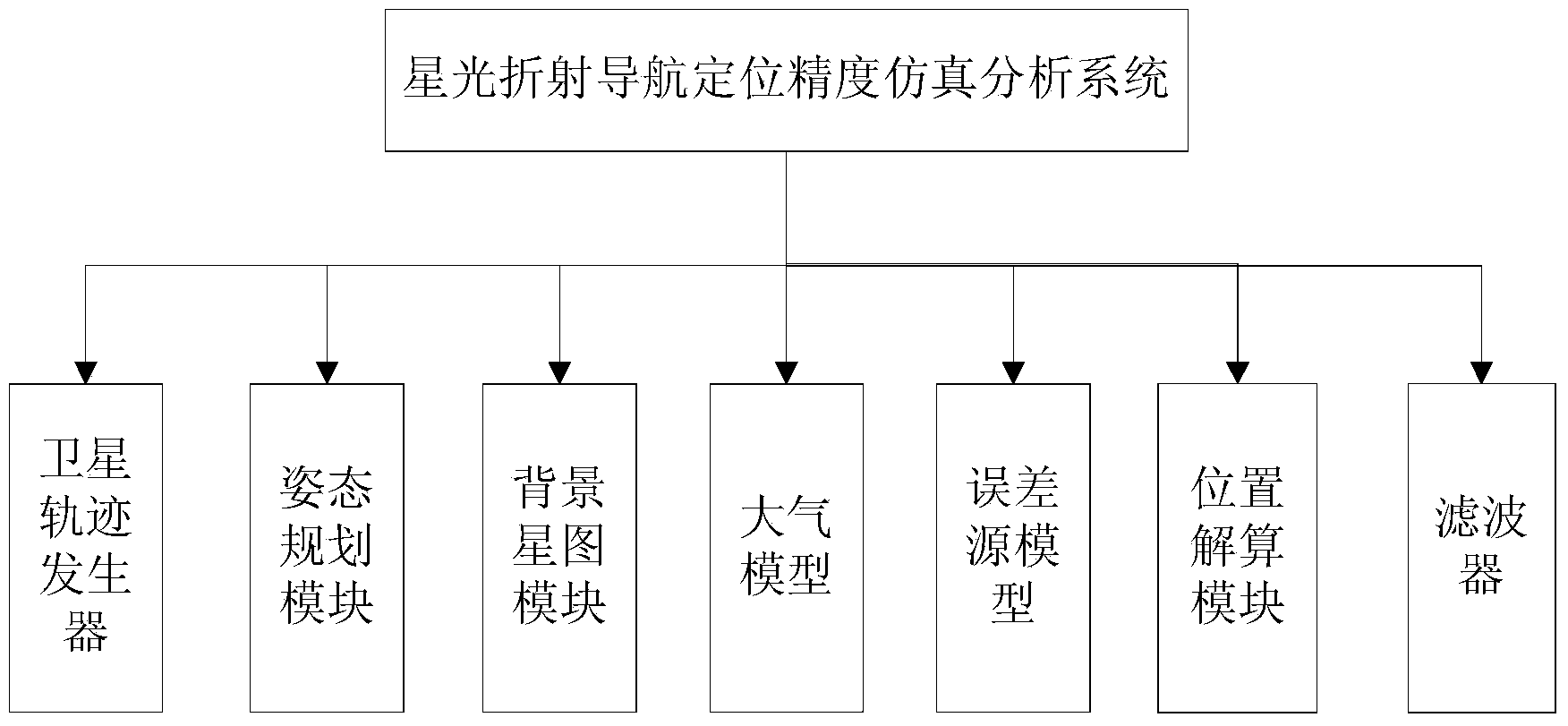
Satellite starlight refraction navigation error determination and compensation method
ActiveCN104236546AHigh positioning accuracyNavigation by astronomical meansRefraction angleAtmospheric models
The invention relates to a satellite starlight refraction navigation error determination and compensation method. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, generating data of a satellite orbit by virtue of STK software; establishing a satellite attitude planning model; determining an actual observation visual field, and simulating an observation star map comprising refraction stars and non-refraction stars; calculating to obtain the tangential height h of the refraction stars; calculating to obtain the tangential height h'' of the refraction stars with errors of refraction angles and errors of an atmospheric model, wherein tangential height errors are mainly caused by the measurement precision errors of the refraction angles and the errors of the atmospheric model; calculating to obtain the position of a satellite under a geocentric inertial coordinate system; and performing filtration by an extended Kalman filtration method, and outputting a starlight refraction navigation estimated position and position errors. The method provided by the invention can realize accurate prediction of navigation precision of a satellite starlight refraction navigation system, and is comprehensive in error analysis and accurate and reliable in results.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
Acoustic profiler for wind, temperature, and turbulence
InactiveUS7343793B2Facilitate data analysisDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesVolume measurement and fluid deliverySound sourcesMeasurement point
Characterizing atmospheric conditions is accomplished by measuring at least one varying spectral characteristic of sound at a plurality of intervals from a sound source with the point of measurement and the sound source in relative motion and separated by altitude. The spectral characteristic of the sound at each interval is attributed to a path traveled by the sound and a plurality of simultaneous equations is created for the plurality of paths using a second plurality of altitude segments for each path, each segment having a particular vector as a variable on the spectral characteristic, the initial coefficients in each vector assumed based on predetermined atmospheric models for each altitude segment. The resulting calculated vector and the predetermined atmospheric model are iterated for a minimized cost function in a variational analysis to determine the vector for each altitude segment, the vector providing atmospheric properties for the associated altitude segment.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
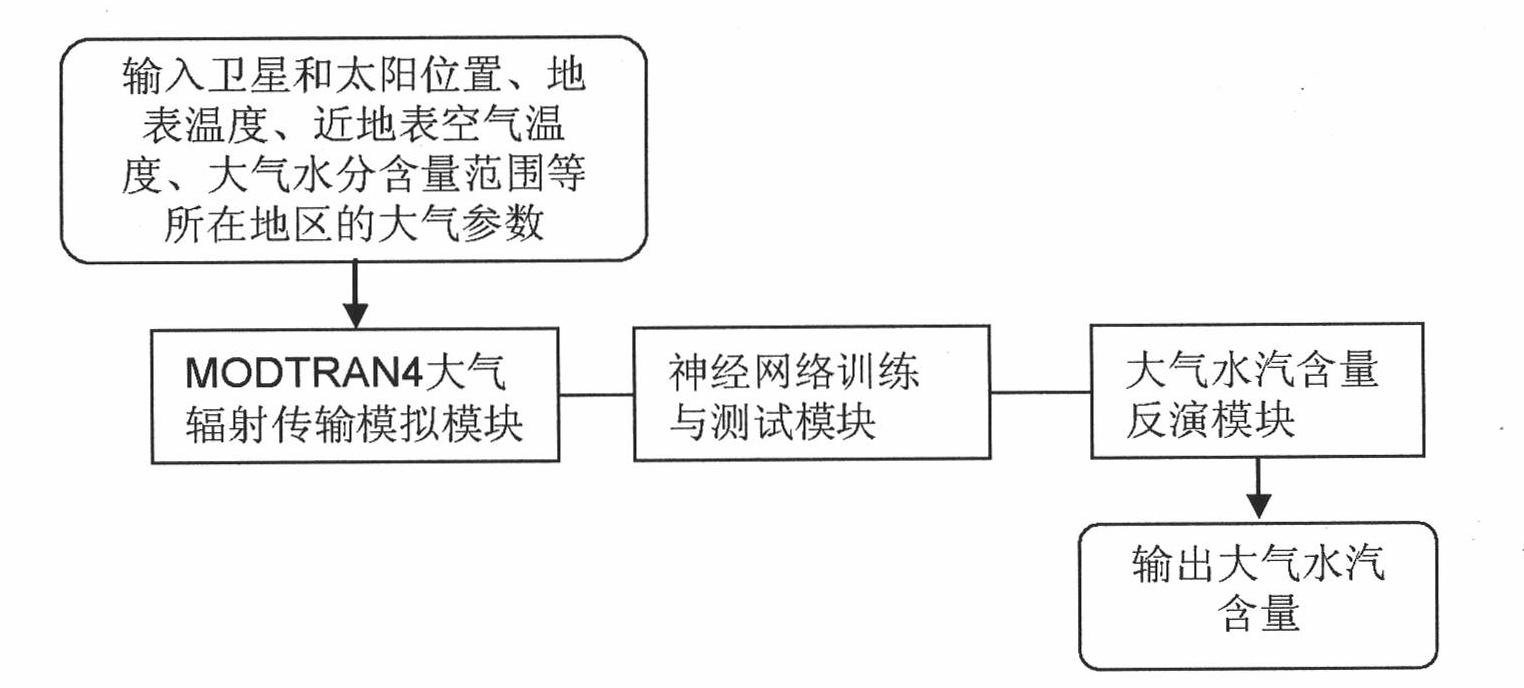
Method for inverting atmospheric water vapor content from MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) data
InactiveCN101936877AReduce unknownsReduce computing timeMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological neural network modelsData setDisaster monitoring
The invention relates to a method for inverting atmospheric water vapor content from MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) data, which can be applied to the remote sensing application departments, such as meteorology, environment monitoring, land management, crop condition monitoring, disaster monitoring and the like. The method comprises the following three steps of: (1) performing forward simulation to the second, fifth, seventeenth, eighteenth and nineteenth near-infrared bands of acquired remote sensing MODIS data in given areas and seasons and an atmospheric model by using atmospheric radiation transmission simulation software MODTRAN, and establishing a training and test database; (2) repeatedly training and testing the training and test data set by using a neural network; and (3) performing inversion calculation to the MODIS actual image data, and performing actual earth surface verification and application analysis. The atmospheric water vapor inversed product has high precision, strong practicability and relatively simple operation. The method can be applied to the departments of weather forecast, environment monitoring, crop condition monitoring, disaster monitoring and the like.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
Space target falling multi-model tracking guiding technology
ActiveCN109323698AImprove accuracyReduce mistakesInstruments for comonautical navigationTraffic control systemsDamping factorAtmospheric model
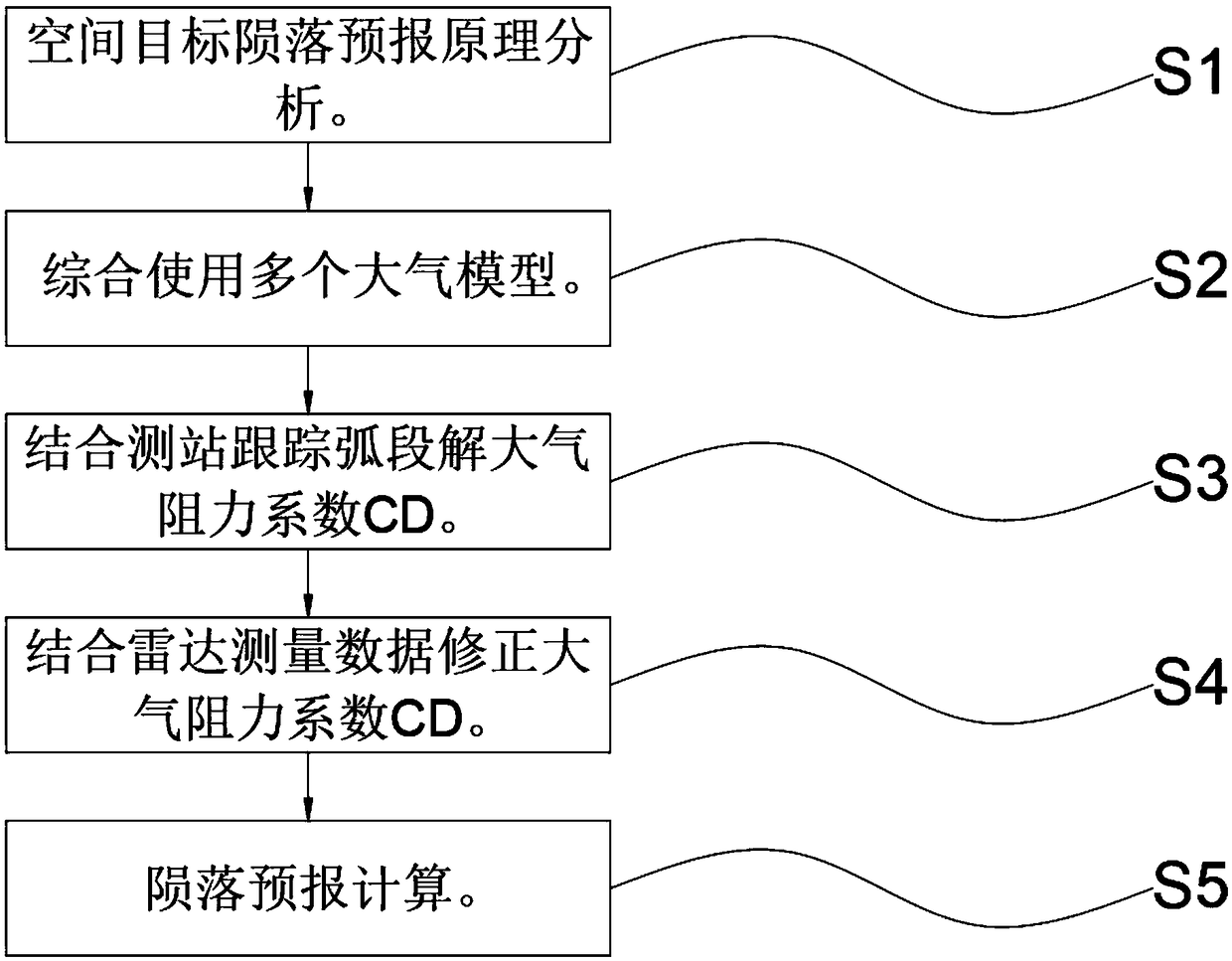
The invention discloses a space target falling multi-model tracking guiding technology. The space target falling multi-model tracking guiding technology comprises the steps of analyzing a space targetfalling forecast principle, syntheticallyusing a plurality of atmosphere models, combining an observation station tracking arc segment to calculate an atmosphere coefficient of drag CD, and combiningradar measuring data to correct the atmosphere coefficient of drag CD and a falling forecast calculation. The space target falling multi-model tracking guiding technology is scientific and reasonable, is safe and convenient in utilization, combines orbit dynamicscharacteristics of a falling target and adaptive ranges of the various atmosphere models, adopts methods of atmosphere model switching and damping factor discrete solution to perform falling forecasts, improves the accuracy of the falling forecasts and can be further adapted to calculation and forecast of a super-low orbit, and combines a tracking arc segment to perform CD value estimation.A discrete variation of a CD value accords with a variation trend of measured atmosphere as far as possible, the multiple atmosphere models aresynthetically used in the quick guiding process, the atmosphere models are replaced along with the change of heights, and according to the space target falling multi-model tracking guiding technology, errors of the space target falling forecastsare reduced to less than 10%.
Owner:中科星图测控技术股份有限公司
Accoustic profiler for wind, temperature, and turbulence
InactiveUS20070256491A1Facilitate data analysisDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesVolume measurement and fluid deliveryFrequency spectrumSound sources
Characterizing atmospheric conditions is accomplished by measuring at least one varying spectral characteristic of sound at a plurality of intervals from a sound source with the point of measurement and the sound source in relative motion and separated by altitude. The spectral characteristic of the sound at each interval is attributed to a path traveled by the sound and a plurality of simultaneous equations is created for the plurality of paths using a second plurality of altitude segments for each path, each segment having a particular vector as a variable on the spectral characteristic, the initial coefficients in each vector assumed based on predetermined atmospheric models for each altitude segment. The resulting calculated vector and the predetermined atmospheric model are iterated for a minimized cost function in a variational analysis to determine the vector for each altitude segment, the vector providing atmospheric properties for the associated altitude segment.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Method for controlling glide flying ballistic curve damping
ActiveCN104176268AAchieve stabilizationSuppression of ballistic long-period oscillationsSpecial data processing applicationsGround installationsLow speedLongitudinal plane
The invention discloses a method for controlling glide flying ballistic curve damping. The method comprises the following three major steps: step 1: taking into consideration influence of earth curvature, ignoring influence of earth rotation, studying three degree-of-freedom kinematical equation of gliding of an aircraft, and acquiring condition of furthest distance of powerless gliding of the aircraft; step 2: based on the atmosphere model and the aircraft aerodynamic force model already known, performing force analysis on the longitudinal plane of the aircraft under stable gliding condition, and acquiring stable gliding ballistic curve angle of inclination gamma*; step 3: adding feedback to the control instruction, introducing ballistic curve damping control. The method is a guidance method enabling stable gliding of the aircraft, and is applicable to aircrafts having a glide ballistic curve, including a cannonball of a low speed and a short range as well as a long-distance, reentry, and hypersonic-velocity aircraft.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Atmospheric correction method during INSAR measurement
InactiveCN105842692AReal-time effective meteorological parametersReliable resultsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImage resolutionAtmospheric models
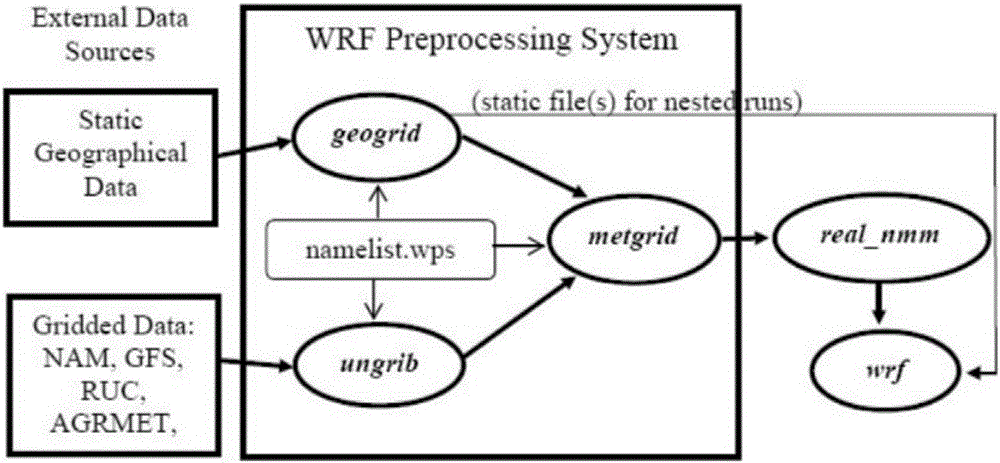
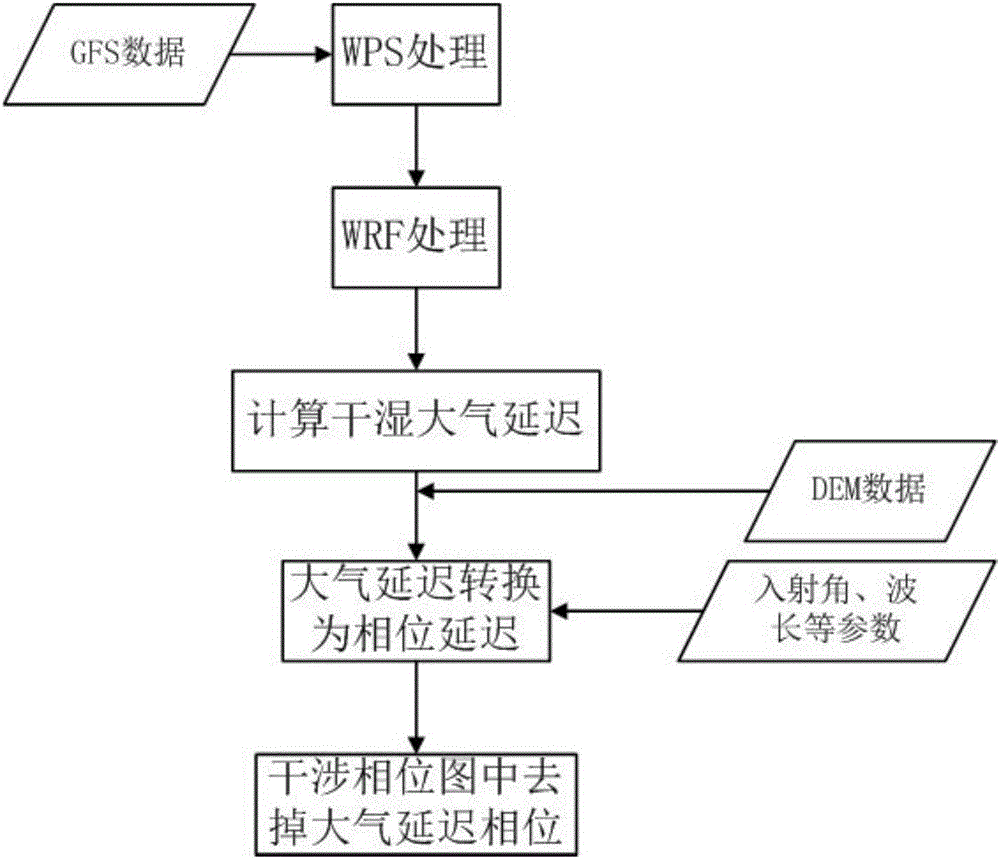
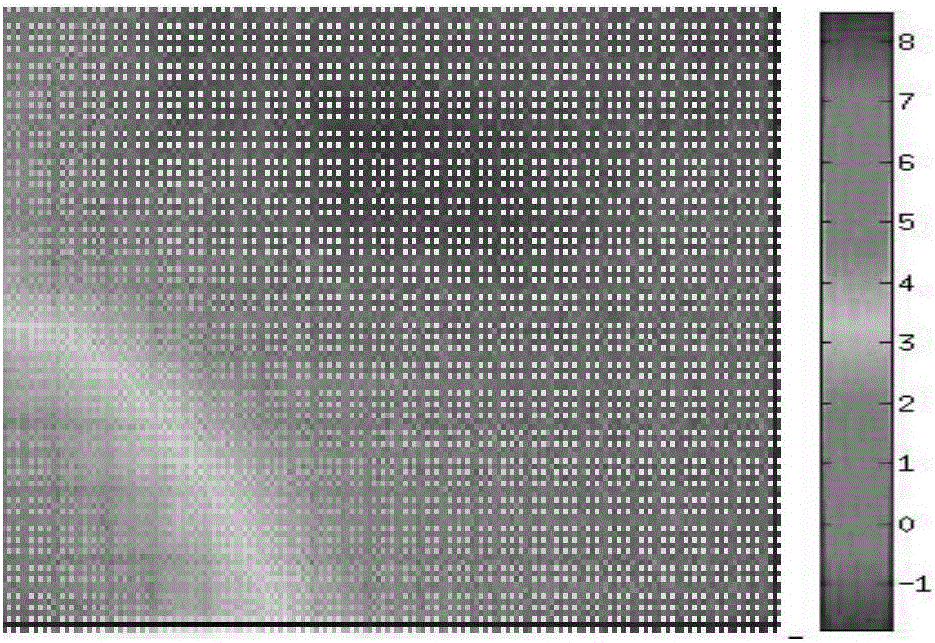
The invention discloses an atmospheric correction method during INSAR measurement. The method comprises the following steps of (1) using a WRF model to simulate a parameter needed during calculation of atmospheric delay, wherein the WRF model adopts GFS data as meteorological data; (2) calculating dry and wet atmospheric delay; (3) converting the atmospheric delay into phase delay; and (4) removing an atmospheric delay phase in an INSAR interference phase diagram. In the method, a mesoscale atmospheric model WRF is used to carry out atmospheric correction and the model can predict a weather condition and can reach a 1km resolution level, which is better than a prediction condition through using a method based on MERIS, MODIS and GPS data. By using the GFS meteorological data, a prediction data time interval is 3 hours and the data is updated for every 6b hours so that timeliness is high. A measurement result is accurate and the method is suitable for popularization and application.
Owner:中科卫星应用德清研究院 +1
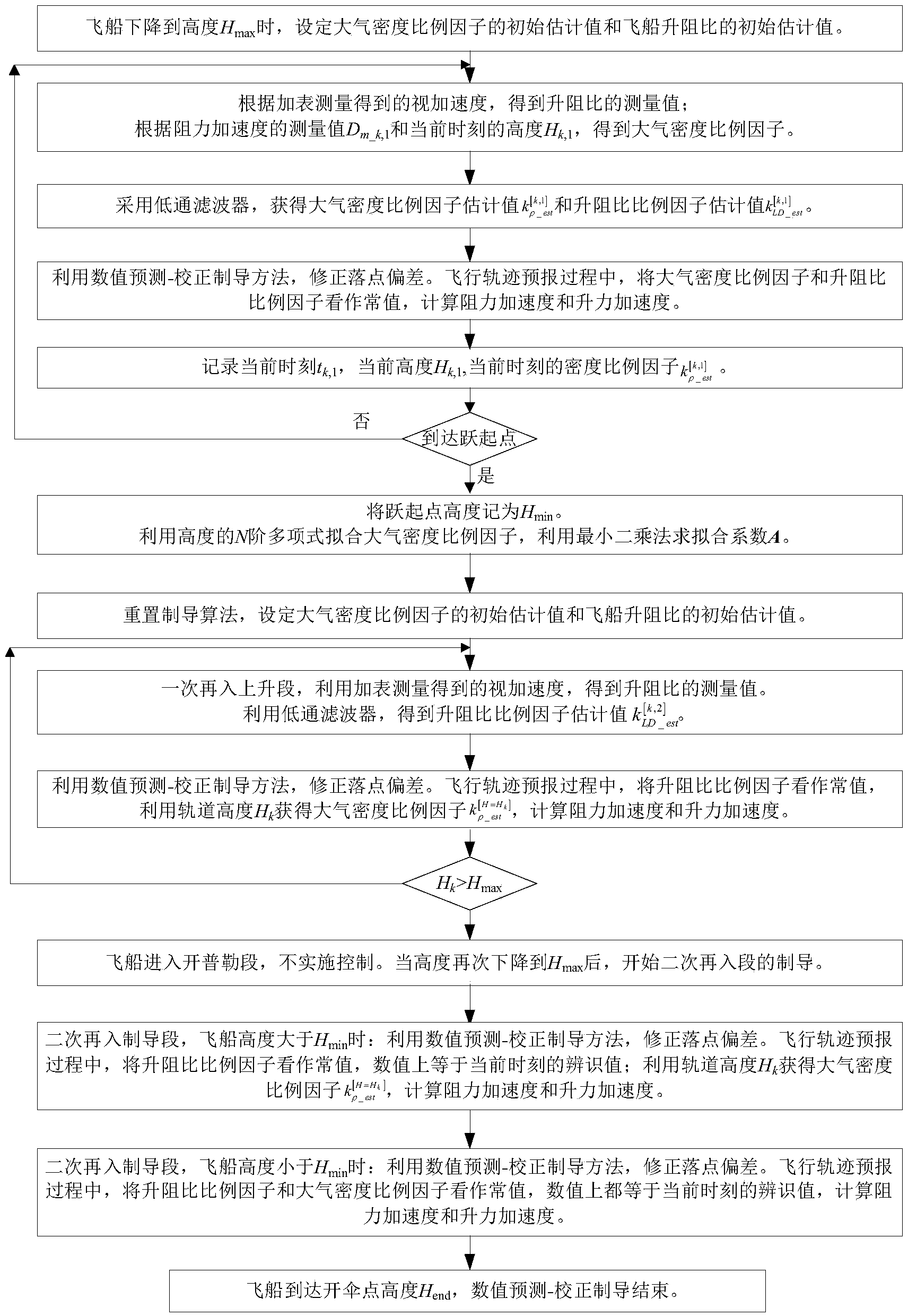
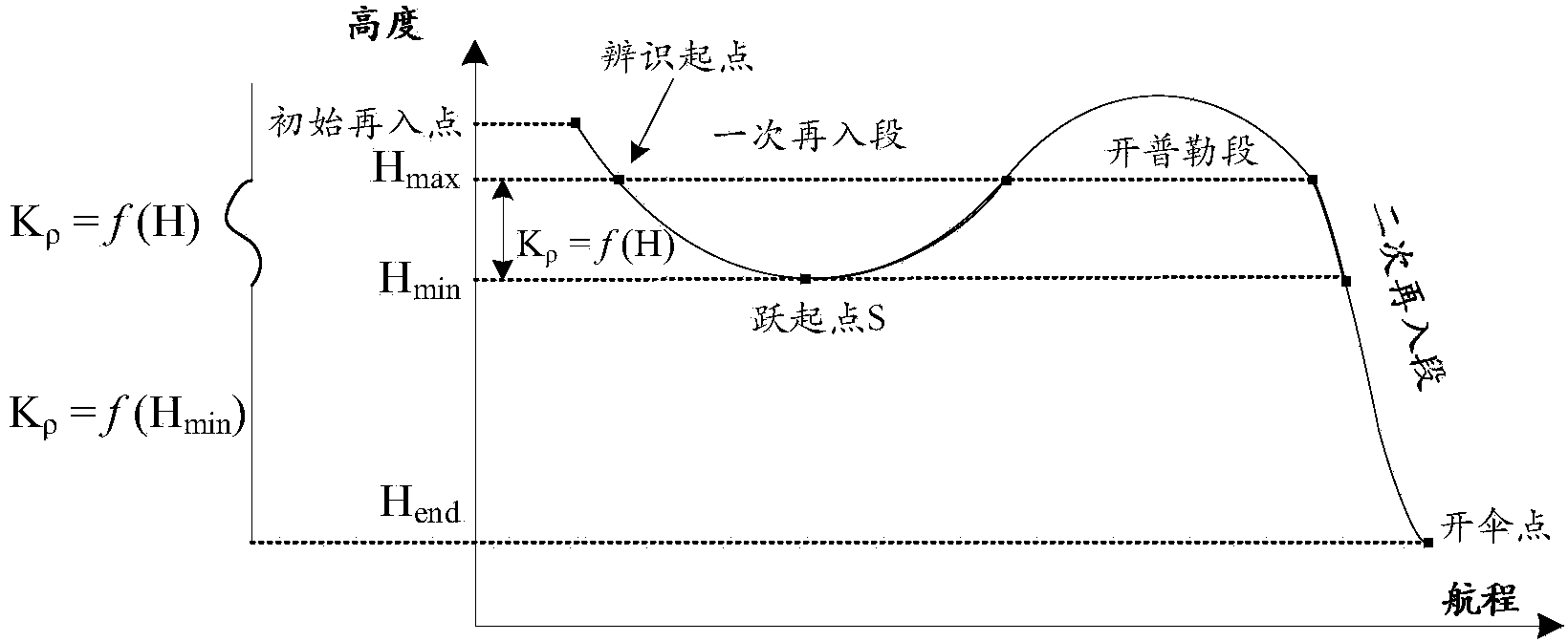
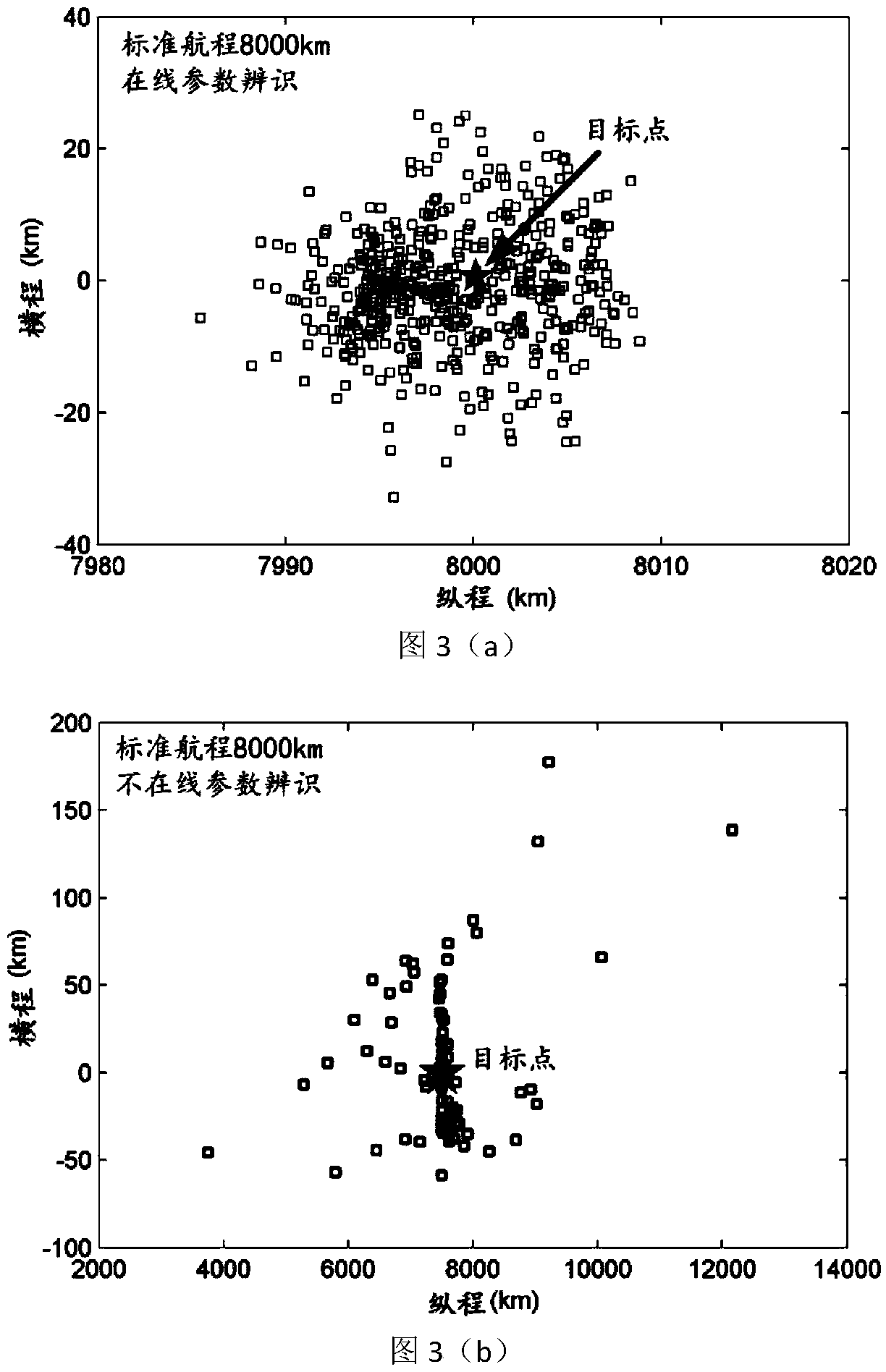
On-line parameter identification method for jumping type reentry of lunar spacecraft
ActiveCN103708045AImprove robustnessHigh precisionSystems for re-entry to earthCosmonautic landing devicesLow-pass filterAtmospheric model
The invention discloses an on-line parameter identification method for jumping type reentry of a lunar spacecraft. The on-line parameter identification method comprises the steps of obtaining on-line estimation values of an atmospheric density scaling factor and a lift-drag ratio scaling factor through a low-pass filter at a primary reentry descending branch, executing track forecasting, correcting the deflection of a drop point, and constructing a fitting function relation between the atmospheric density scaling factor and the height; obtaining an atmospheric density scaling factor at a primary reentry ascending branch and in the initial stage of a secondary reentry branch via a constructed fitting function, estimating a lift-drag ratio scaling factor of the lunar spacecraft on line, executing track forecasting, and correcting the deflection of the drop point; estimating an atmospheric density scaling factor and a lift-drag ratio scaling factor in the later stage of the secondary reentry branch, executing track forecasting, and correcting the deflection of the drop point. According to the on-line parameter identification method, the robustness and the precision of a guidance algorithm are improved; the adaptability to a real atmosphere model is high.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
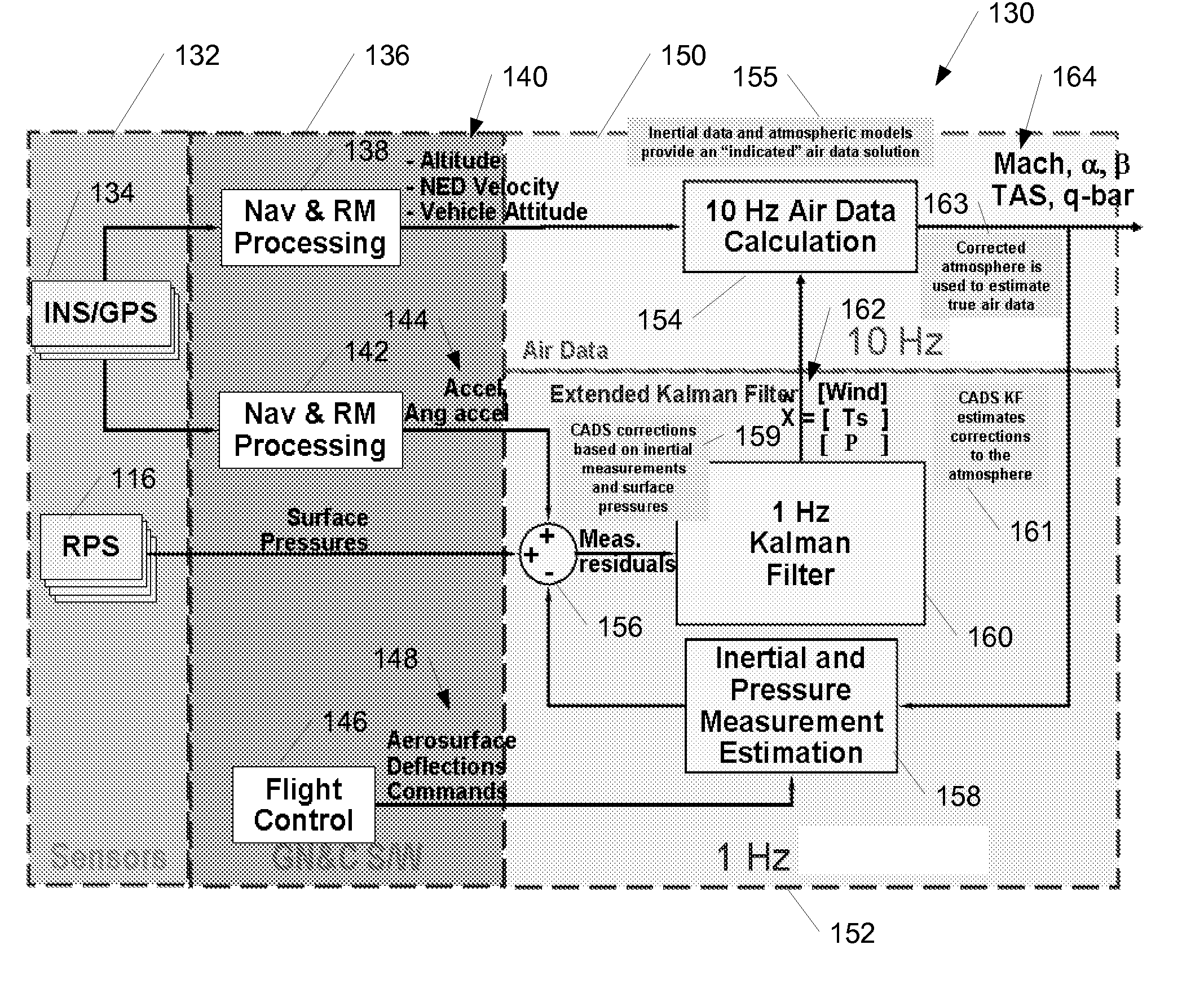
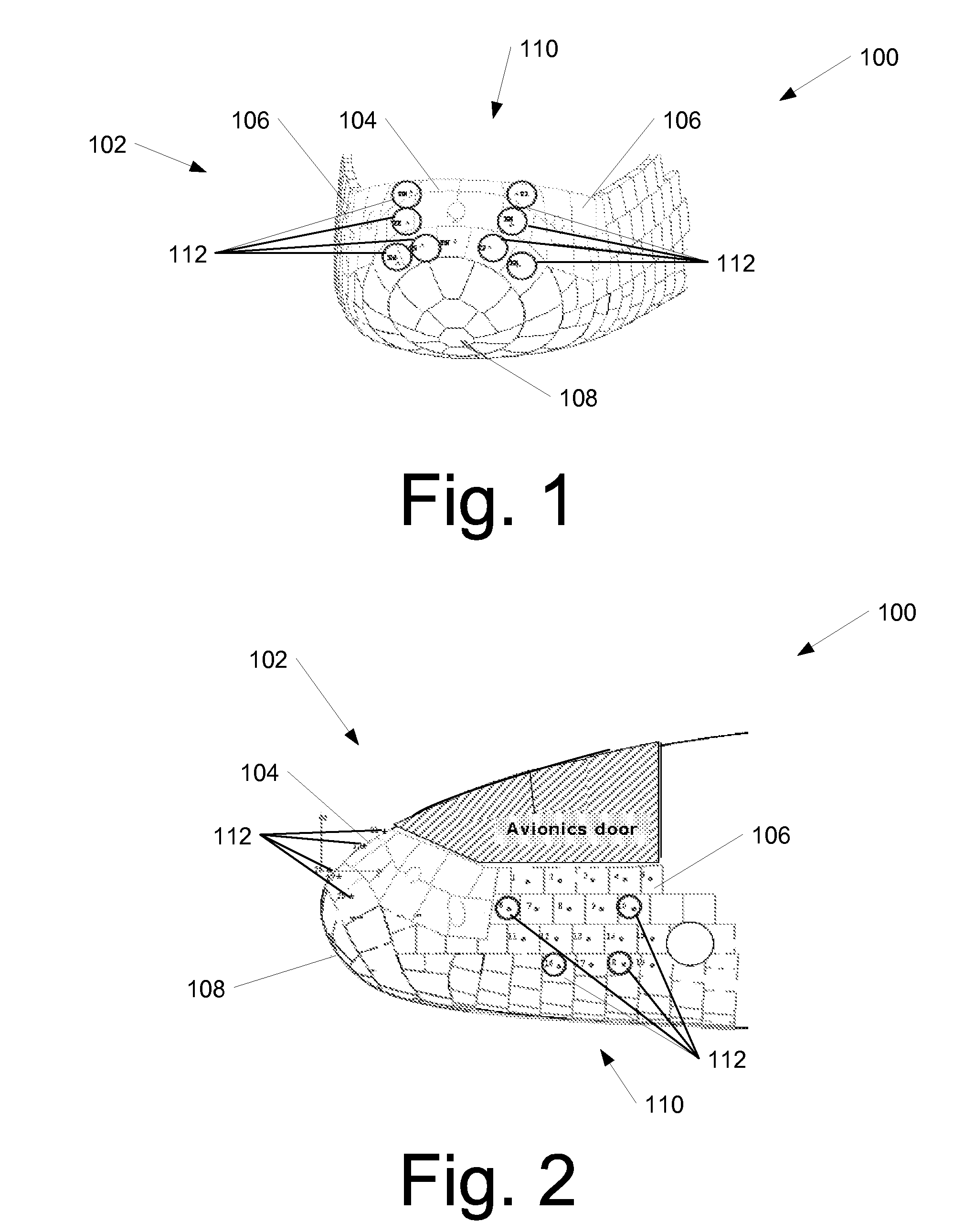
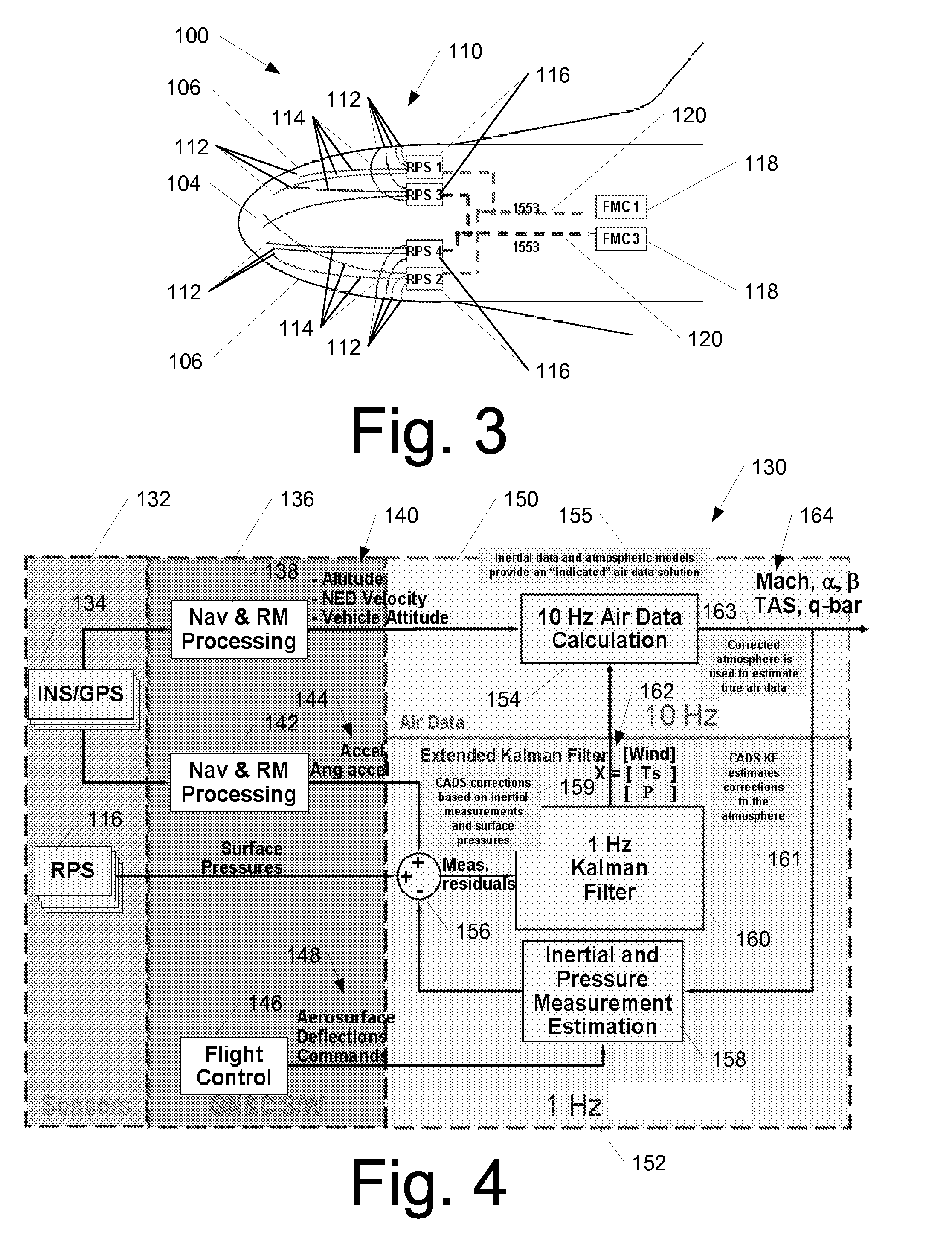
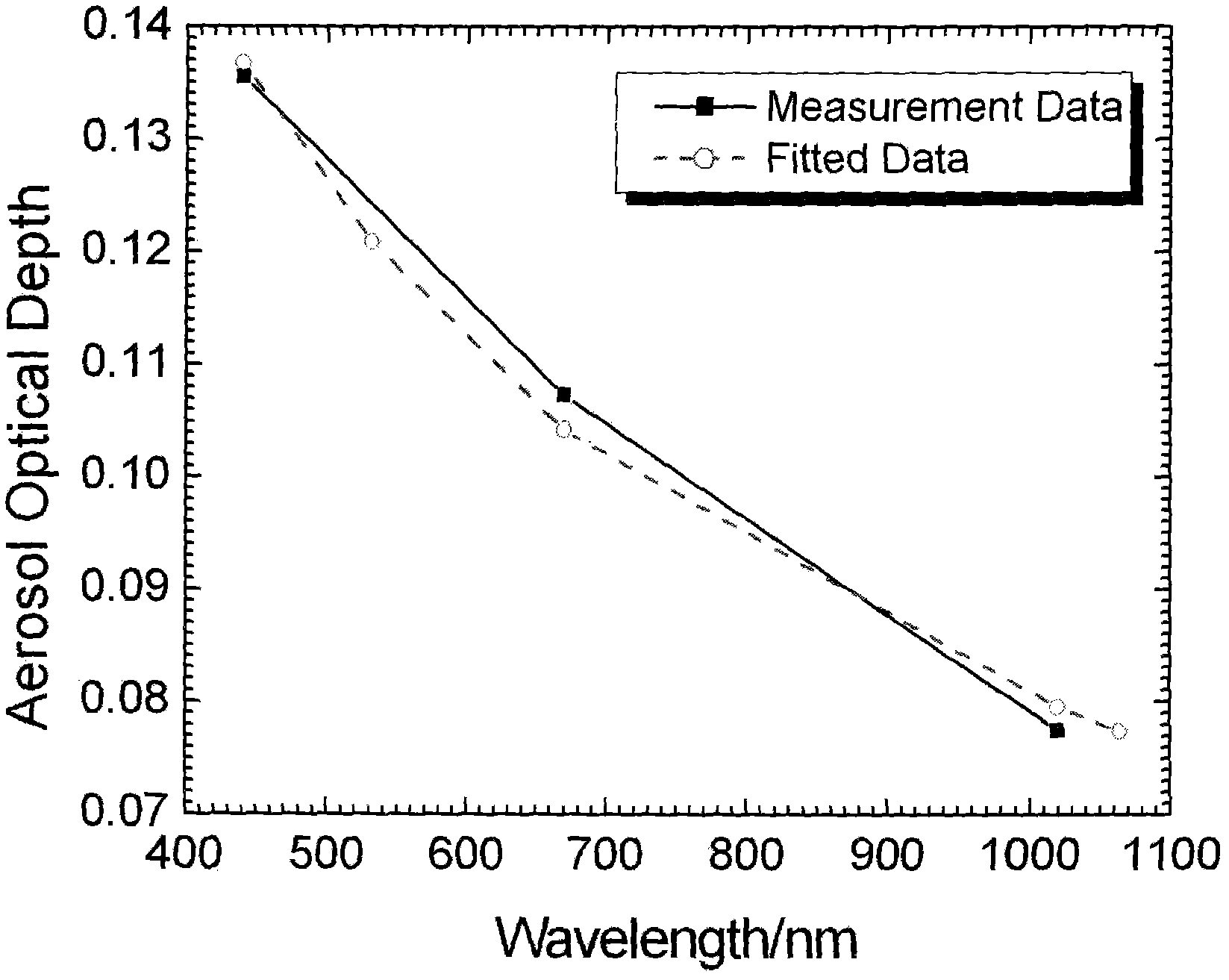
Methods and systems for calculating atmospheric vehicle air data
ActiveUS20080066540A1Eliminate needDigital data processing detailsFluid speed measurement using pressure differenceAtmospheric modelsAtmospheric model
Methods and systems for calculating atmospheric vehicle air data are disclosed. In one embodiment, a method of calculating air data includes acquiring one or more pressure measurements at locations on an outer surface of the aircraft; acquiring one or more measurements using an alternate navigation device; computing an indicated air data solution using the one or more measurements obtained using the alternate navigation device and an atmospheric model; computing corrections to the indicated air data solution using one or more other measured parameters, wherein the one or more other measured parameters include at least one of the one or more pressure measurements and the one or more measurements obtained using the alternate navigation device; determining a corrected air data solution using the indicated air data solution and the corrections; and providing the corrected air data solution for use in controlling the aircraft.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
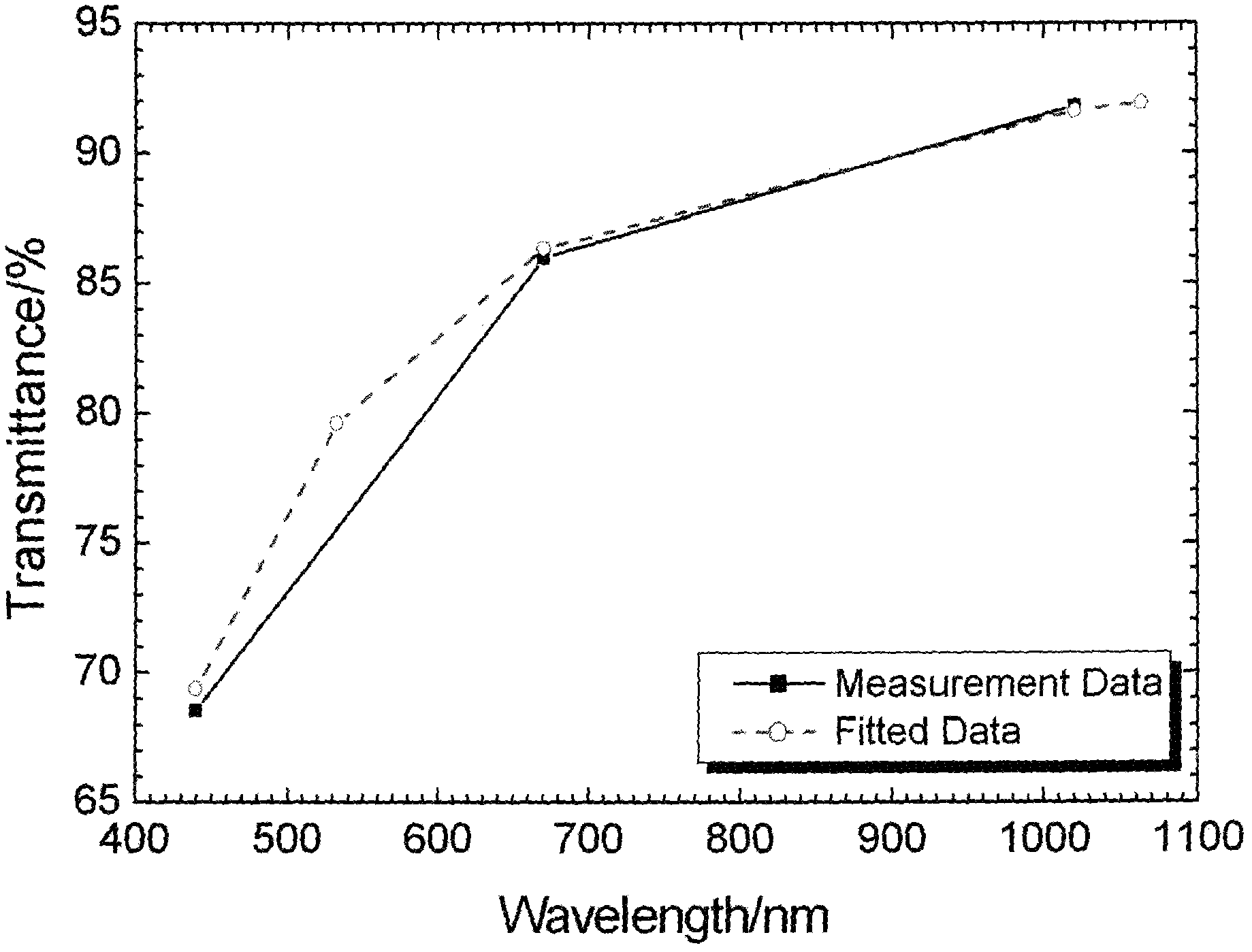
Inversion method for transmittance of whole atmosphere
InactiveCN102565007ASolve the problem of atmospheric transmittanceTransmissivity measurementsMulti bandRadiometer
The invention discloses an inversion method for the laser transmittance of the whole atmosphere. The method comprises the following steps of: measuring an aerosol optical depth of the whole atmosphere by selecting a specific wavelength, and performing inversion to obtain the aerosol optical depth of the whole atmosphere of other wavelengths; and inverting the transmittance of the whole atmosphere. The method has the advantages that: inversion of the transmittance of the whole atmosphere in ultraviolet, visible and infrared bands is realized by using a multi-band solar radiometer and atmospheric model or local atmospheric measured data and high-resolution atmospheric absorption optical depth computation software; and the problem about measurement of the laser transmittance of the whole atmosphere in a broad spectrum is solved.
Owner:NO 63655 TROOPS OF THE CHINESE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
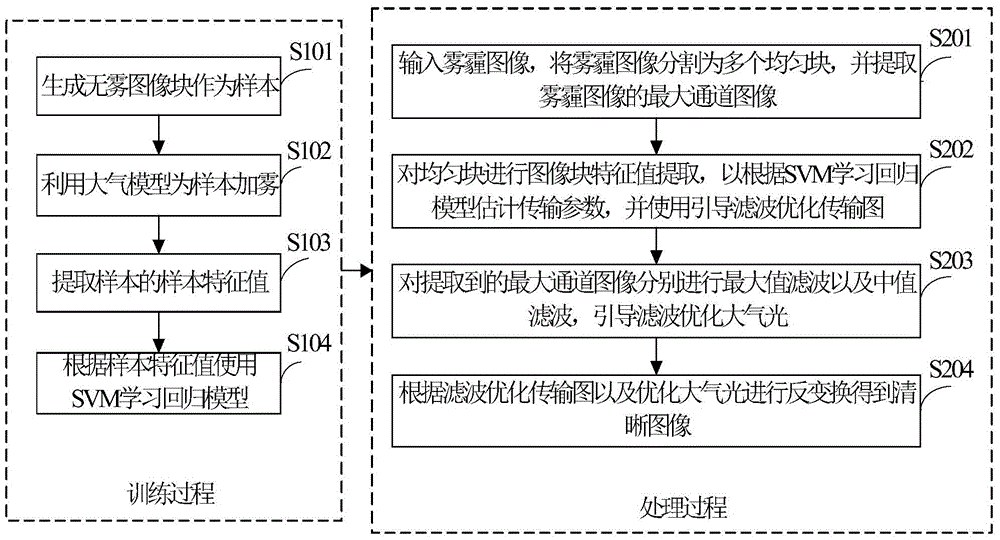
Regression model-based fast single-image defogging algorithm and system
ActiveCN105654440AImprove image qualitySolve technical problemsImage enhancementImage analysisFeature extractionImaging processing
The invention discloses a regression model-based fast single-image defogging algorithm and system. The algorithm includes a training process of a regression model and a processing process of a foggy image. The training process includes the following steps that: a fog-free image block is generated and is adopted as a sample; an atmospheric model is utilized to add fog to the sample; the sample feature value of the sample is extracted; and an SVM learning regression model is utilized according to the sample feature value. The processing process includes the following steps that: a foggy image is inputted, the foggy image is divided into a plurality of uniform blocks, and the maximum channel image of the foggy image is extracted; image block feature extraction is performed on the uniform blocks, and transmission parameters are estimated according to the SVM learning regression model, and guided filtering is adopted to optimize a transmission diagram; maximum value filtering and median filtering are performed on the extracted maximum channel image, guided filtering is adopted to optimize atmospheric light; and inverse transformation is carried out according to the filtering optimized transmission diagram and the optimized atmospheric light, so that a clear image can be obtained. With the algorithm adopted, fog removing processing can be performed on an image fast and accurately, and image processing quality can be effectively improved.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
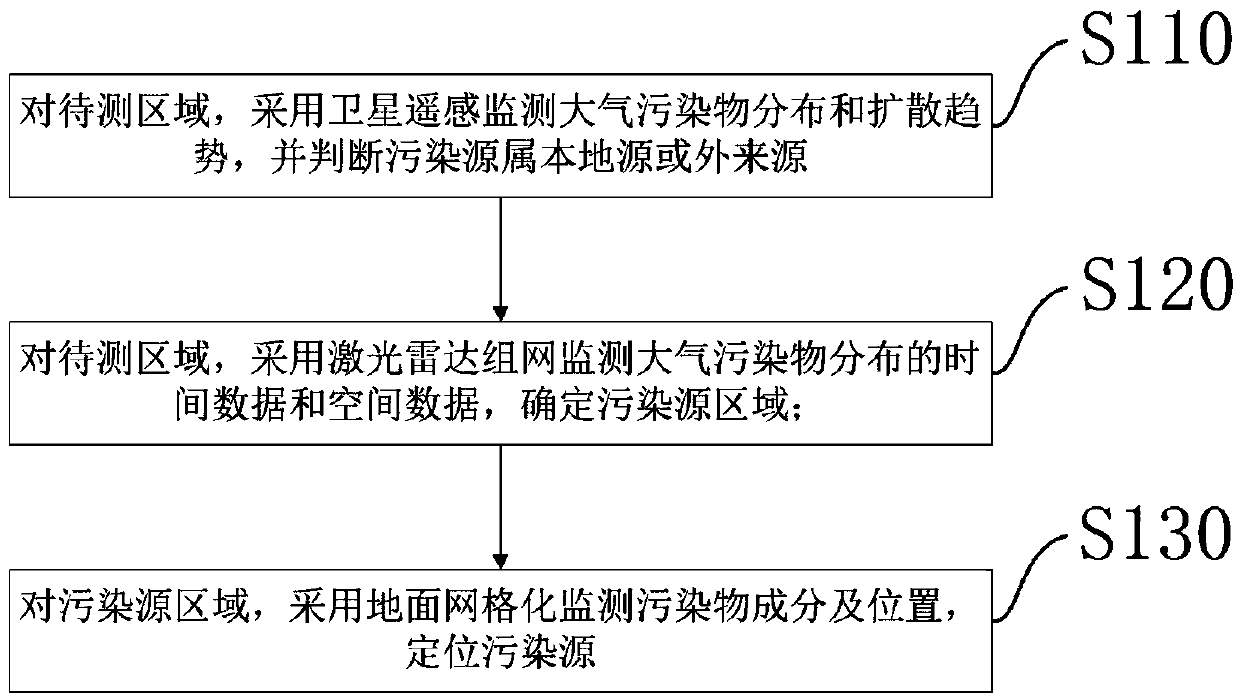
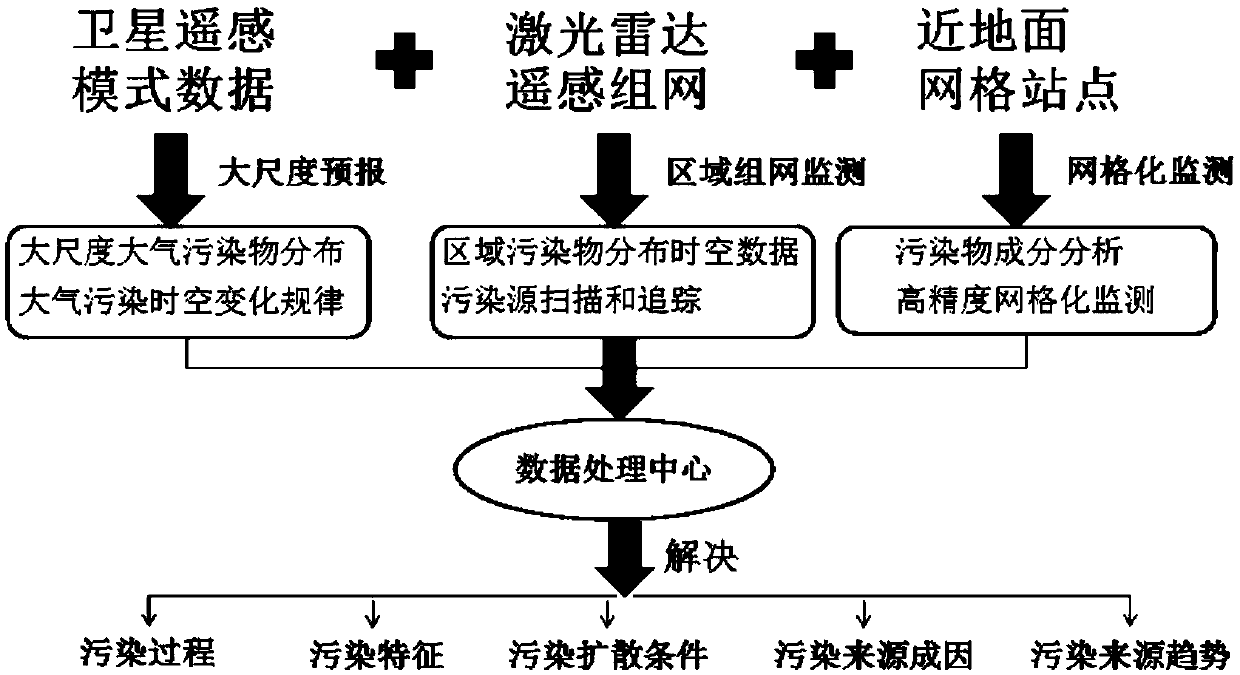
Integrated space and terrestrial information based stereoscopic monitoring method for air pollution and monitoring system
InactiveCN109541628ARealize high-precision real-time monitoringParticle suspension analysisElectromagnetic wave reradiationGrid siteThree level
The invention discloses an integrated space and terrestrial information based stereoscopic monitoring method for air pollution and a monitoring system. The method comprises the following steps: establishing satellite remote sensing and atmospheric model monitoring to monitor the distribution and diffusion trends of large-scale dyes in a region to initially determine local and external sources; establishing a laser radar network monitoring system to locate and track air pollution sources at the same time; and establishing a densely distributed ground monitoring grid site for accurate analysis of the causes of atmospheric pollution sources. Through the three-level monitoring system, the detection of air pollution in the monitoring area can be completed, and serious areas of air pollution, sources of pollutants, and the distribution and diffusion situation of key pollution sources can be clarified. And then the processing, statistics, and analysis of massive data can be completed based ona software platform to obtain monitoring results. The invention can realize effective monitoring of atmospheric pollutants, which has high distance resolution and time resolution.
Owner:天津珞雍空间信息研究院有限公司
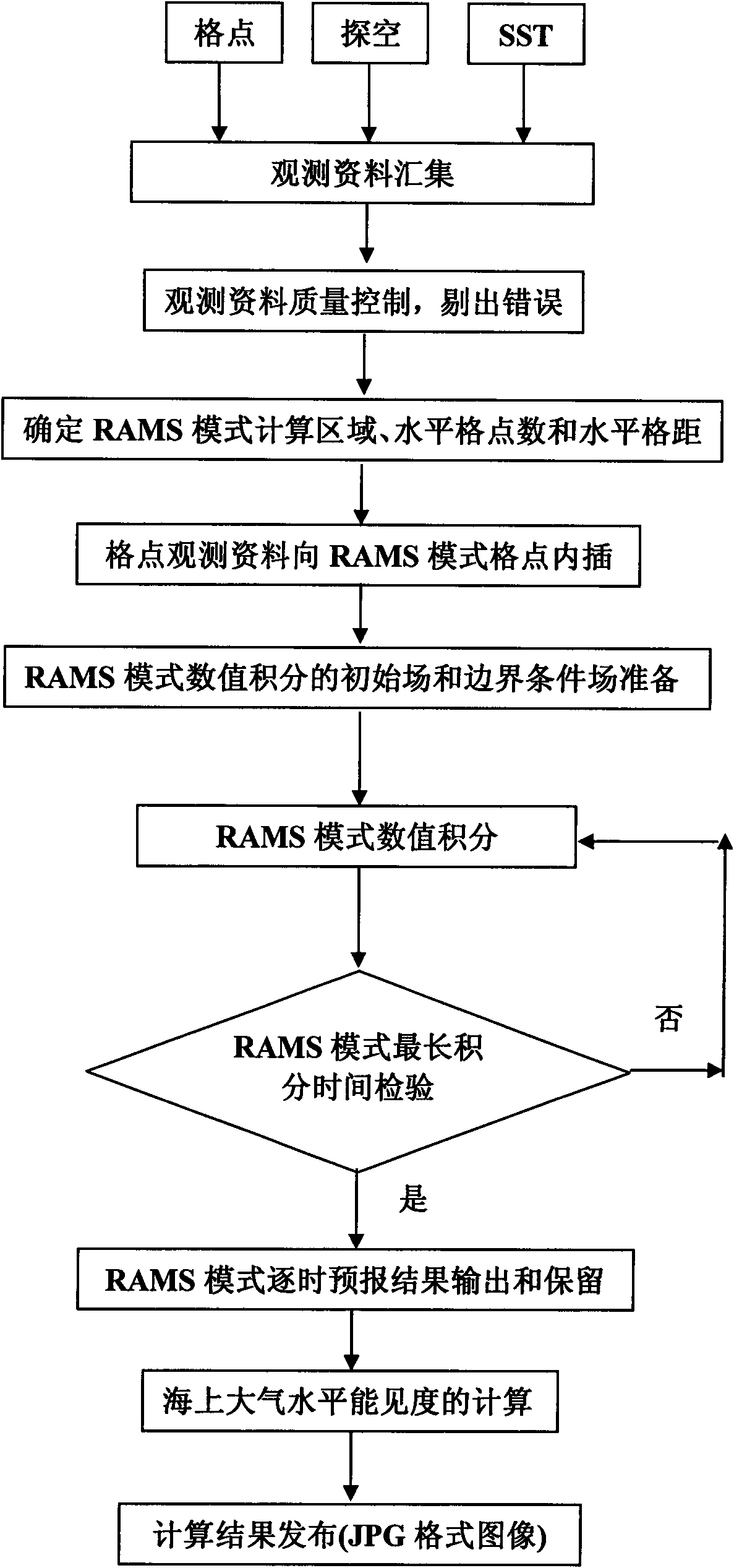
Method for acquiring atmospheric horizontal visibility field under maritime dense fog condition
The invention relates to a method for acquiring an atmospheric horizontal visibility field under a maritime dense fog condition, which comprises the following steps: collecting survey station soundingdata and the like of grid point meteorology and a related sea region, and performing quality control for the survey station sounding data to remove errors; determining a calculation region, a horizontal grid point number and a horizontal grid interval of a regional atmospheric model system RAMS model, interpolating the grid point meteorology data to all horizontal grid points of the RAMS model, preparing an initial condition and boundary condition field, and performing numerical integration for the RAMS model; and outputting and reserving forecast result data files, performing quantitative calculation by using an atmospheric horizontal visibility calculation formula, finally drawing the calculation result into a chromatic atmospheric visibility distribution graph, and outputting images interms of a JPG format. The method can effectively overcome the defects that the maritime atmospheric visibility observation station data is rare, the satellite remote sensing method cannot judge whether the cloud is grounded and the like in the prior art, provides quick and quantitative maritime atmospheric horizontal visibility field for various maritime activities, and has broad application prospect.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
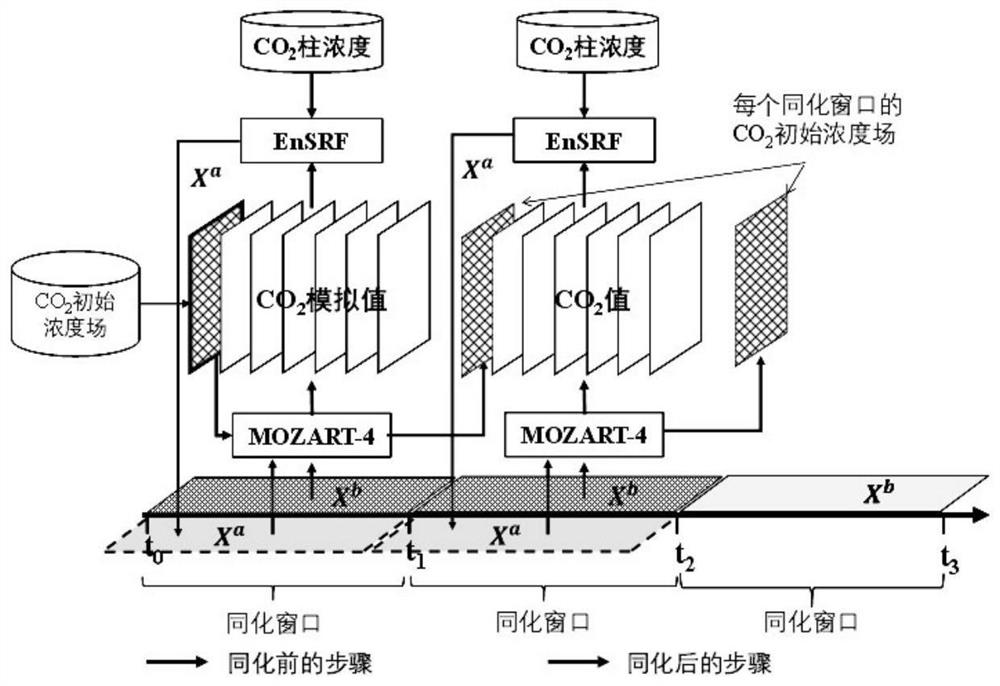
Method for observing and inverting surface carbon flux based on satellite CO2 column concentration
PendingCN111723482ACorrection errorDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsCarbon assimilationObservation data
The invention discloses a method for observing and inverting surface carbon flux based on satellite CO2 column concentration. The method comprises the following steps: constructing an EnKF carbon fluxinversion system and coupling the EnKF carbon flux inversion system to an MOZART-4 global atmospheric chemical transmission model; performing Gaussian random disturbance on the priori CO2 flux to obtain a set sample, inputting the set sample into an atmospheric model MOZART-4 to simulate CO2 concentration, assimilating observation data of corresponding positions and time, and obtaining optimizedCO2 flux; inputting the optimized flux into the MOZART-4 model again for operation, and generating a new initial field for flux optimization of the next assimilation window; and repeating the step 2 for cyclic assimilation. The high-resolution carbon assimilation inversion system constructed through a new algorithm and a new program can directly assimilate satellite column concentration data, andglobal and regional carbon flux errors and simulation precision are effectively corrected.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
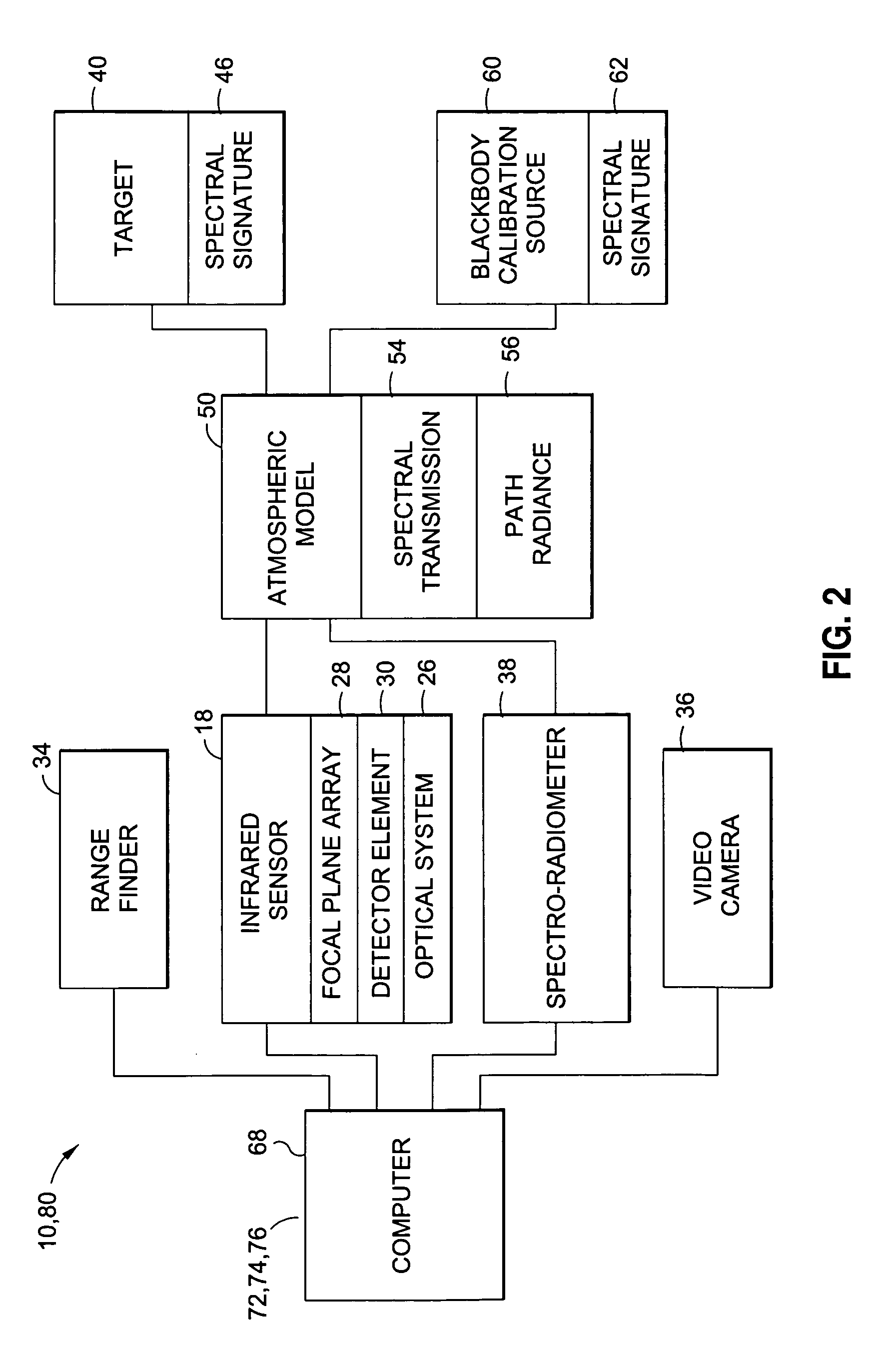
Infrared sensor calibration system and method
ActiveUS20100051794A1High quality imagingReduce riskMaterial analysis by optical meansCalibration apparatusAtmospheric modelAtmospheric models
A calibration system for an infrared imaging system includes an infrared sensor having a sensor model for imaging a target having a target spectral signature. The infrared imaging system includes an atmospheric model having atmospheric spectral values. The calibration system comprises a blackbody calibration source having a calibration source spectral signature and a computer for receiving the sensor model, the target spectral signature, the calibration source spectral signature and the atmospheric spectral values. The computer predicts a target spectral signature propagation at the infrared sensor and matches the target spectral signature propagation with the calibration source spectral signature propagation to determine a blackbody calibration source temperature for radiometric calibration of the infrared sensor.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Estimating solar irradiance components from plane of array irradiance and global horizontal irradiance
ActiveUS8972221B2Reduce model biasImprove accuracySunshine duration recordersGeneration forecast in ac networkIlluminanceDirect normal irradiance
Owner:LOCUS ENERGY
Design and execution of a target system that includes a component model
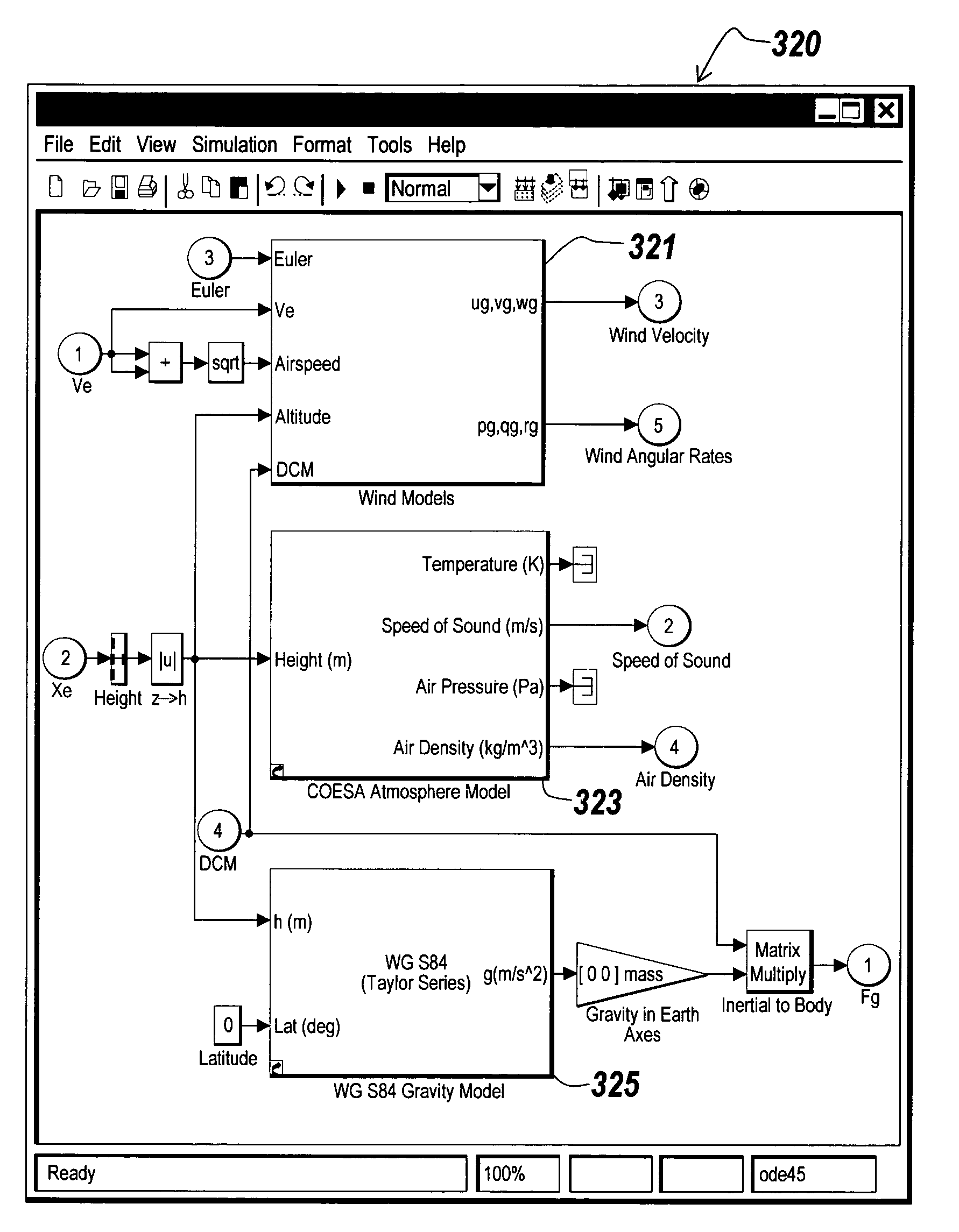
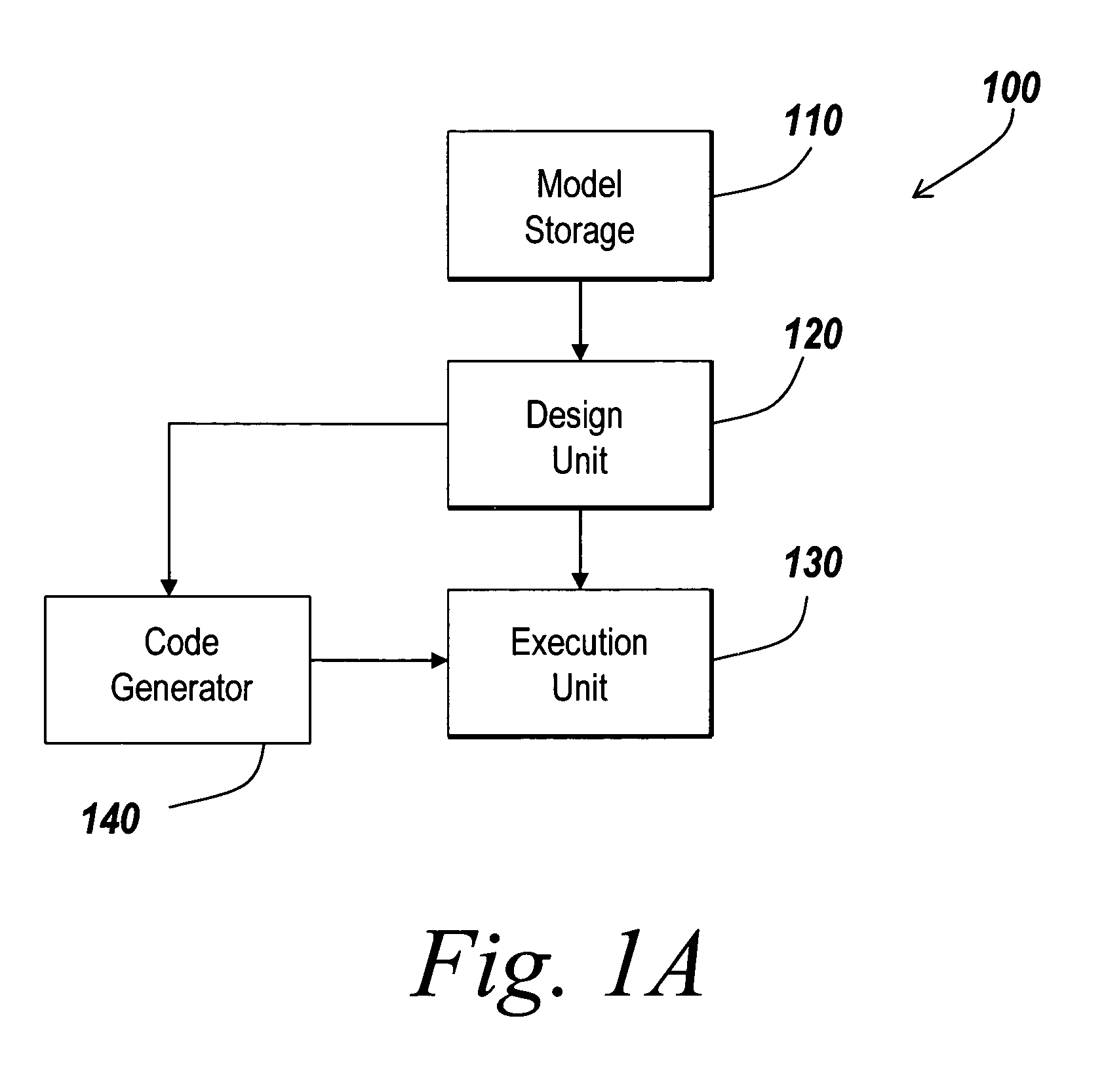
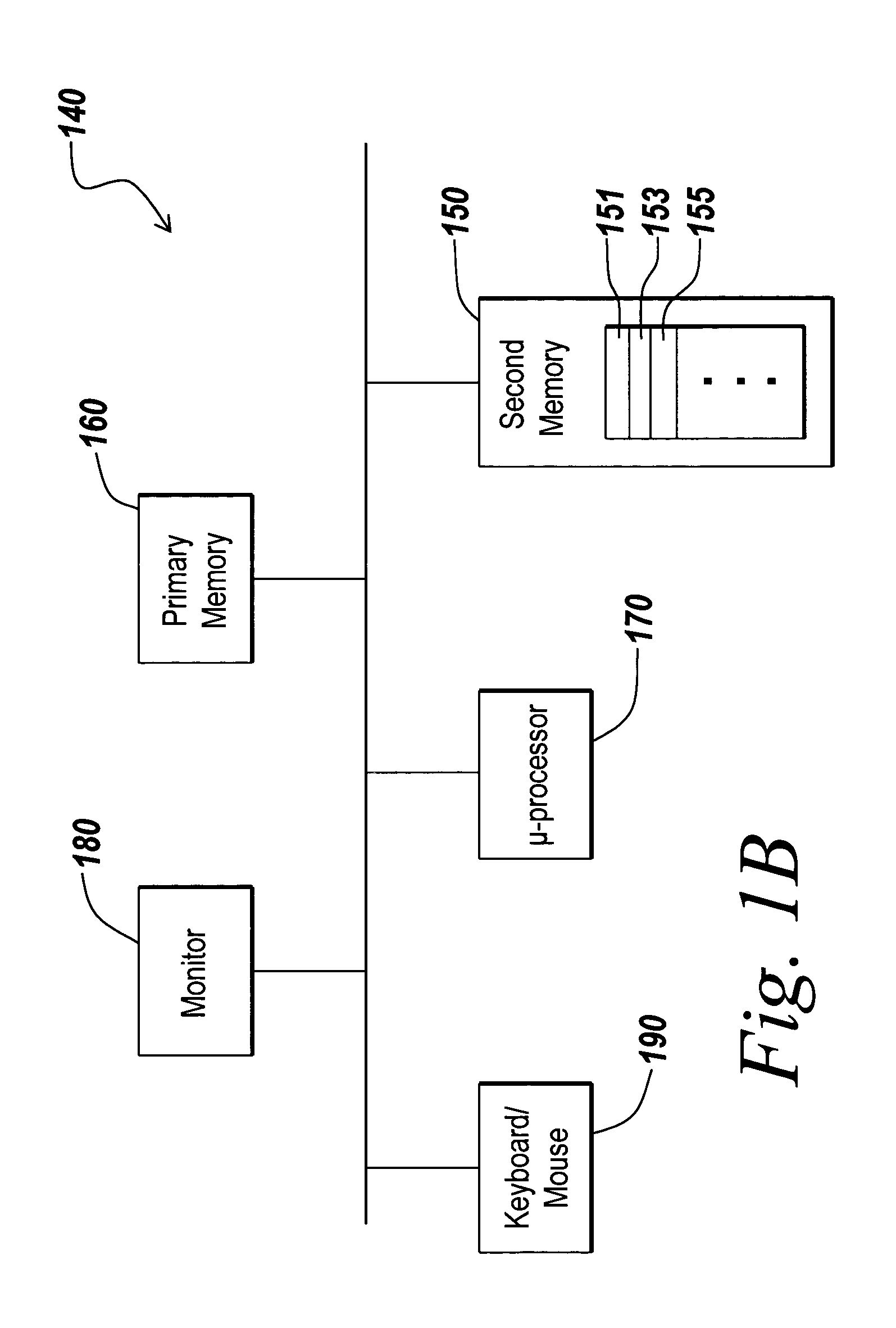
ActiveUS7720657B1Good choiceDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsComponent Object ModelAviation
Methods and systems for the design and execution of an aerospace or aeronautic system are provided. The aerospace or aeronautic system may incorporate planetary environment models and models of equations of motion. The planetary environment models mathematically represent planetary environment specifications, such as atmosphere and wind. Atmosphere models include standard day atmosphere models and non-standard day atmosphere models, and wind models include continuous wind turbulence models and discrete wind turbulence models. The models of equations of motion include models of three-degree-of-freedom equations of motion with variable mass and models for six-degree-of-freedom equations of motion with variable mass. As a result, the present invention can design and execute a target system more accurately than the conventional system that provides only standard day planetary environment models, continuous wind turbulence models, or fixed mass equations of motion models.
Owner:THE MATHWORKS INC
Water resource scheduling method based on land-atmosphere coupling
ActiveCN106204333ATake advantage ofJudging the storage and discharge volumeClimate change adaptationForecastingWater storageSufficient time
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
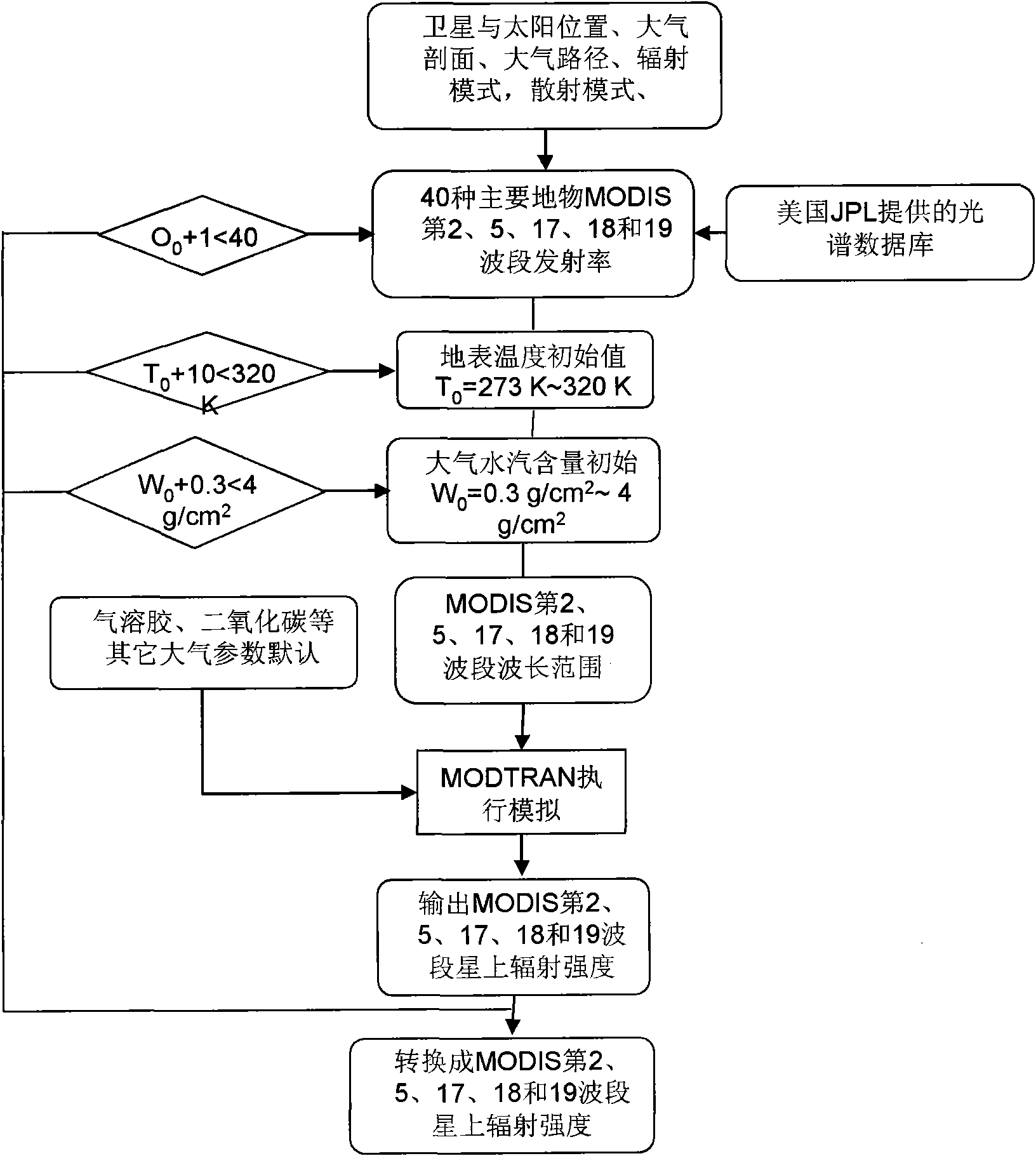
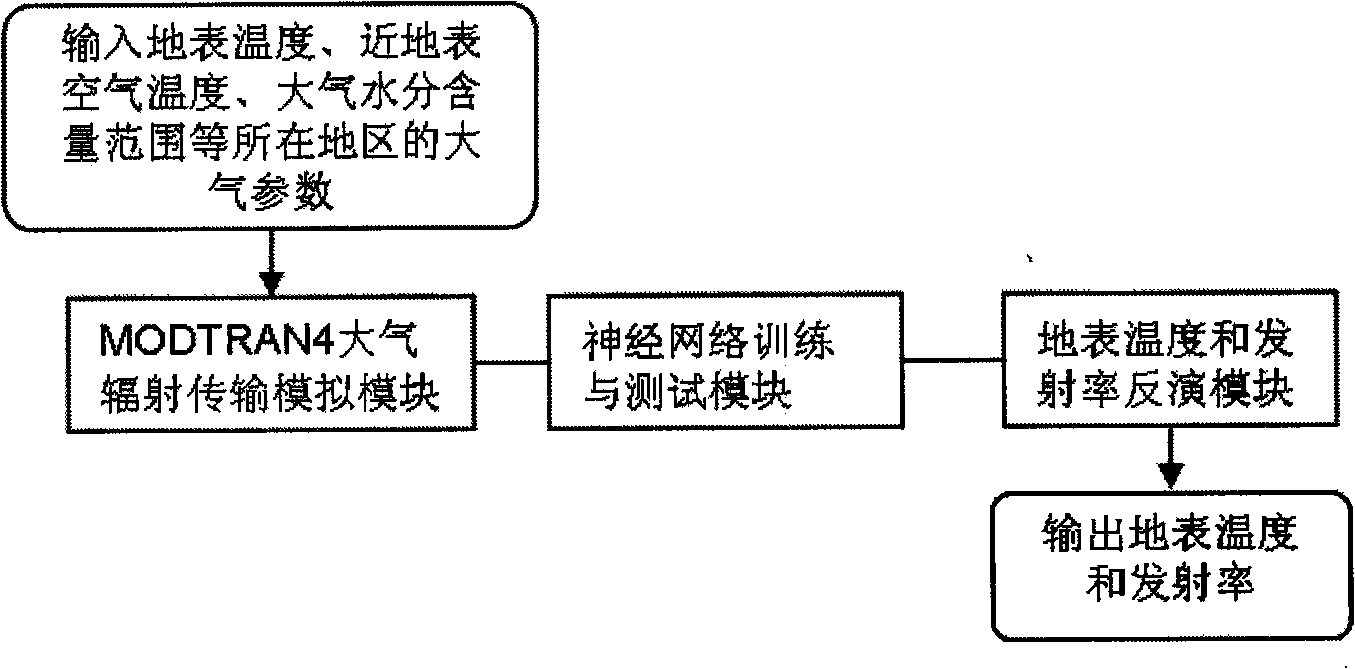
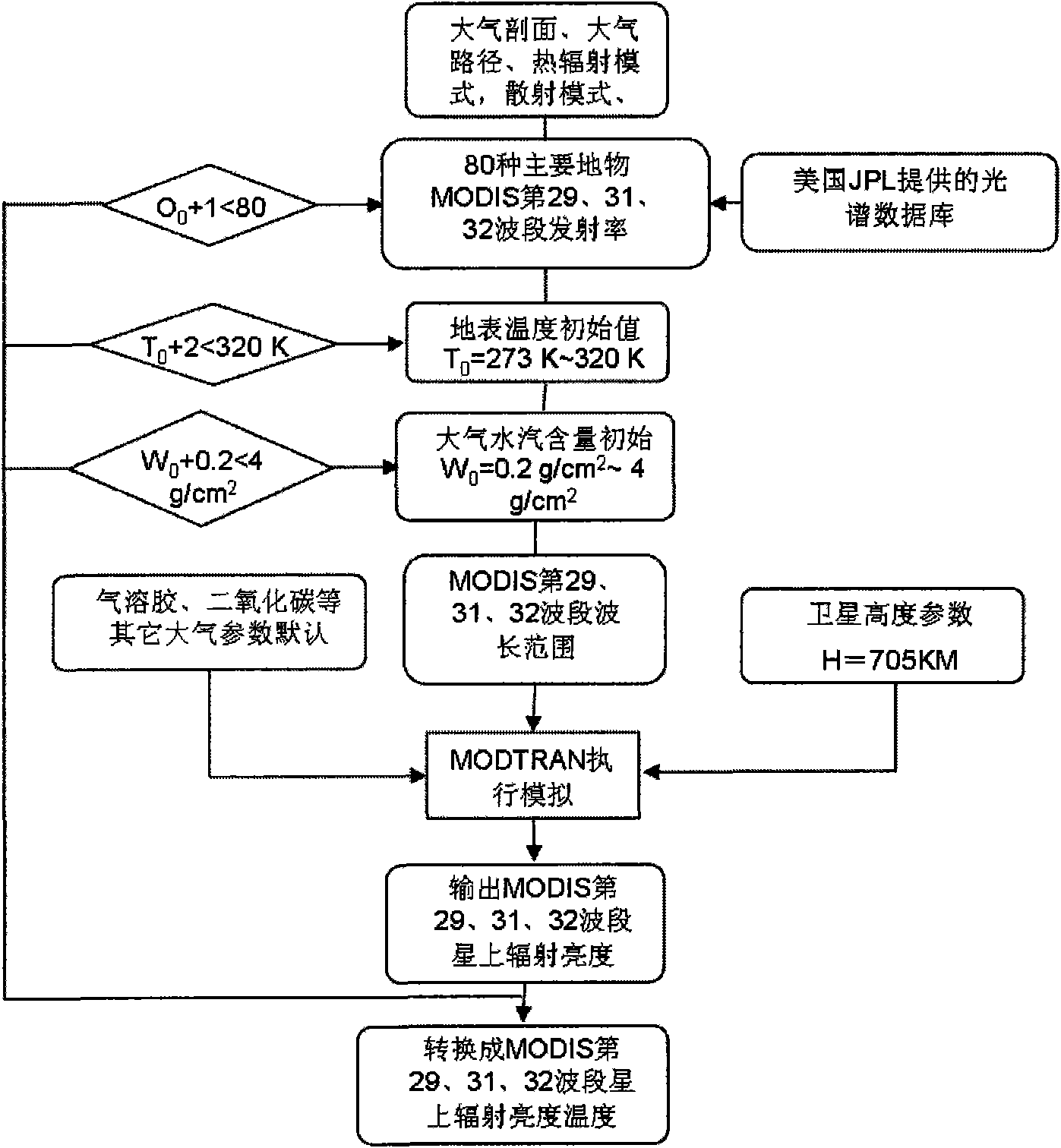
Method for inversing surface temperature and emissivity from MODIS data
InactiveCN101655564AReduce unknownsReduce computing timeBiological neural network modelsElectromagnetic wave reradiationData setEmissivity
A method for inversing surface temperature and emissivity from a remote sensing MODIS data comprises the steps of forward simulating by utilizing an atmospheric radiation transferring simulation software MODTRAN4 aiming at the atmospheric model, the region and the season of the 29th, 31st and 32nd thermal infrared bands of the received remote sensing MODIS data to create a training and testing database, retraining and retesting the training and testing database by using a neural network, back calculating an actual MODIS image data, verifying the actual ground surface and analyzing the application. The surface temperature and the emissivity received by the invention have the advantages of high precision, wide application range and simple operation.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +2
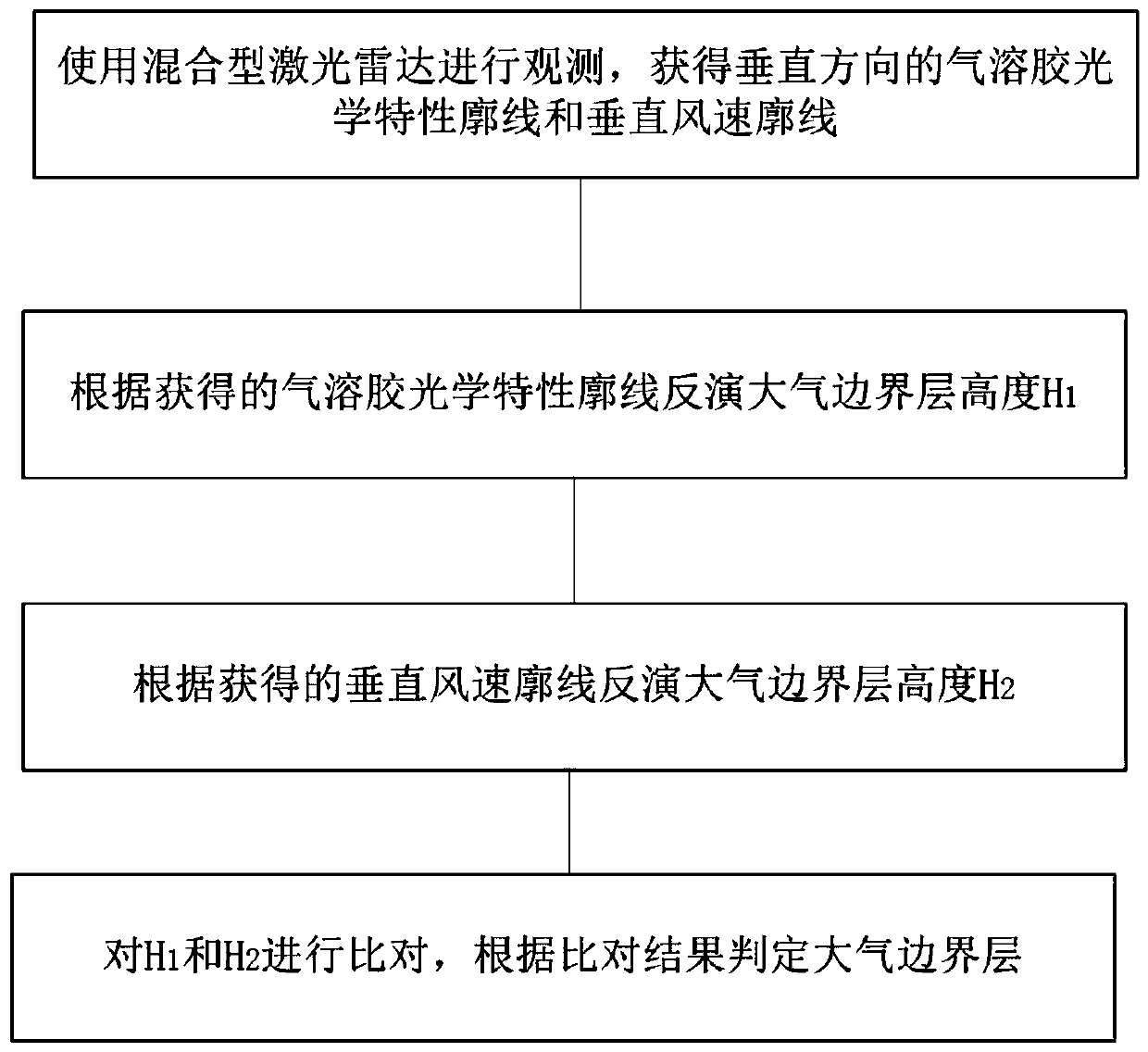
Atmospheric boundary layer detection method based on hybrid laser radar
The invention discloses an atmospheric boundary layer detection method based on a hybrid laser radar. The basic principle is that the hybrid laser radar is used, a direct detection aerosol laser radarsystem and a coherent wind-measuring laser radar system are integrated, the vertical profiles of aerosol optical characteristics and turbulence intensity are simultaneously detected the atmospheric boundary layer heights are separately inverted, and various types of atmospheric boundary layers are judged by comparing the difference between the heights with a selected threshold value. The atmospheric boundary layers can be quantitatively classified with only one device, and various types of boundary layers can be quantitatively parameterized, the atmospheric boundary layer detection method based on the hybrid laser radar is helpful to further improve the accuracy of atmospheric models such as climate models, weather forecast models and atmospheric pollution diffusion models.
Owner:山东国耀量子雷达科技有限公司
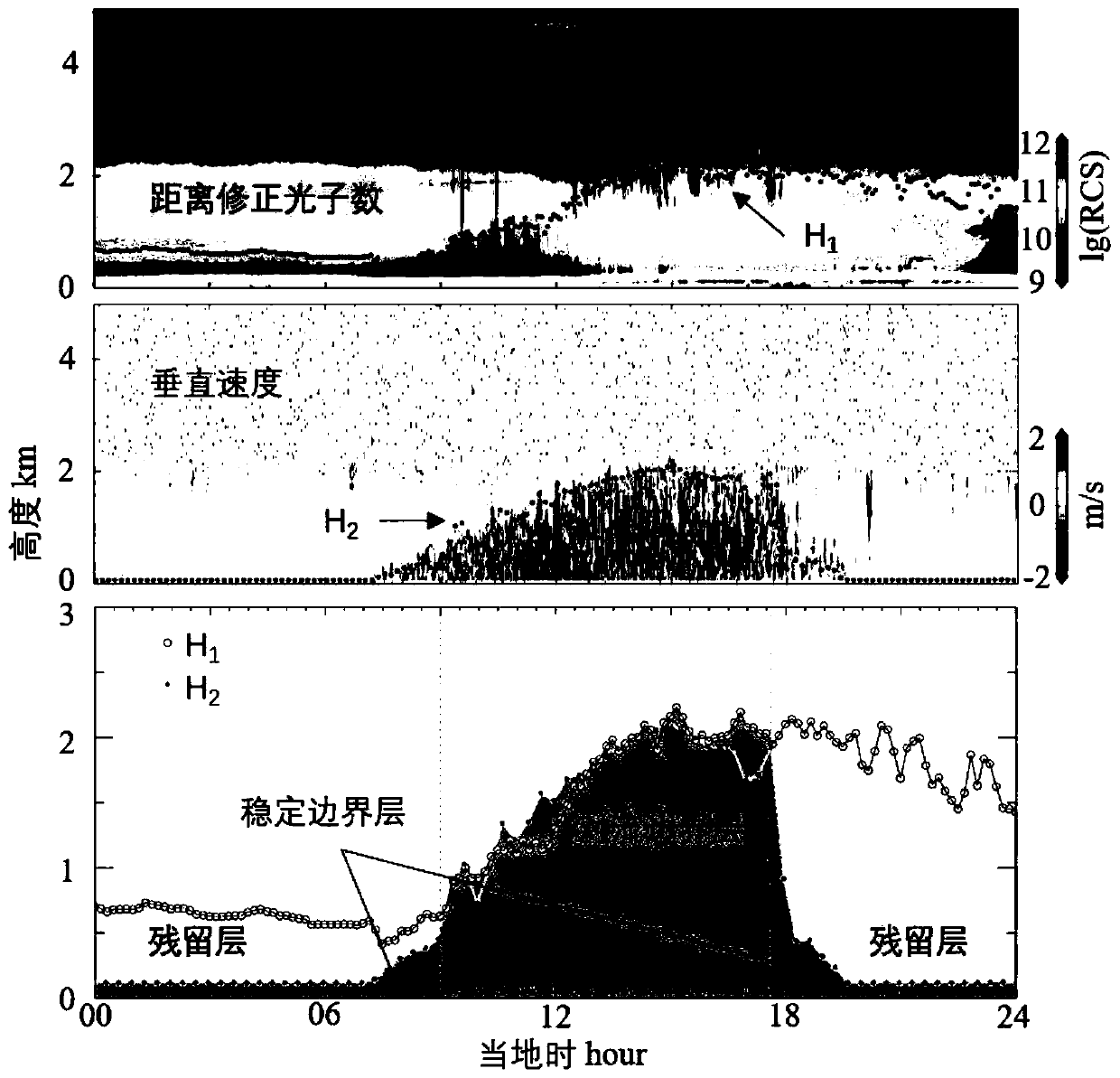
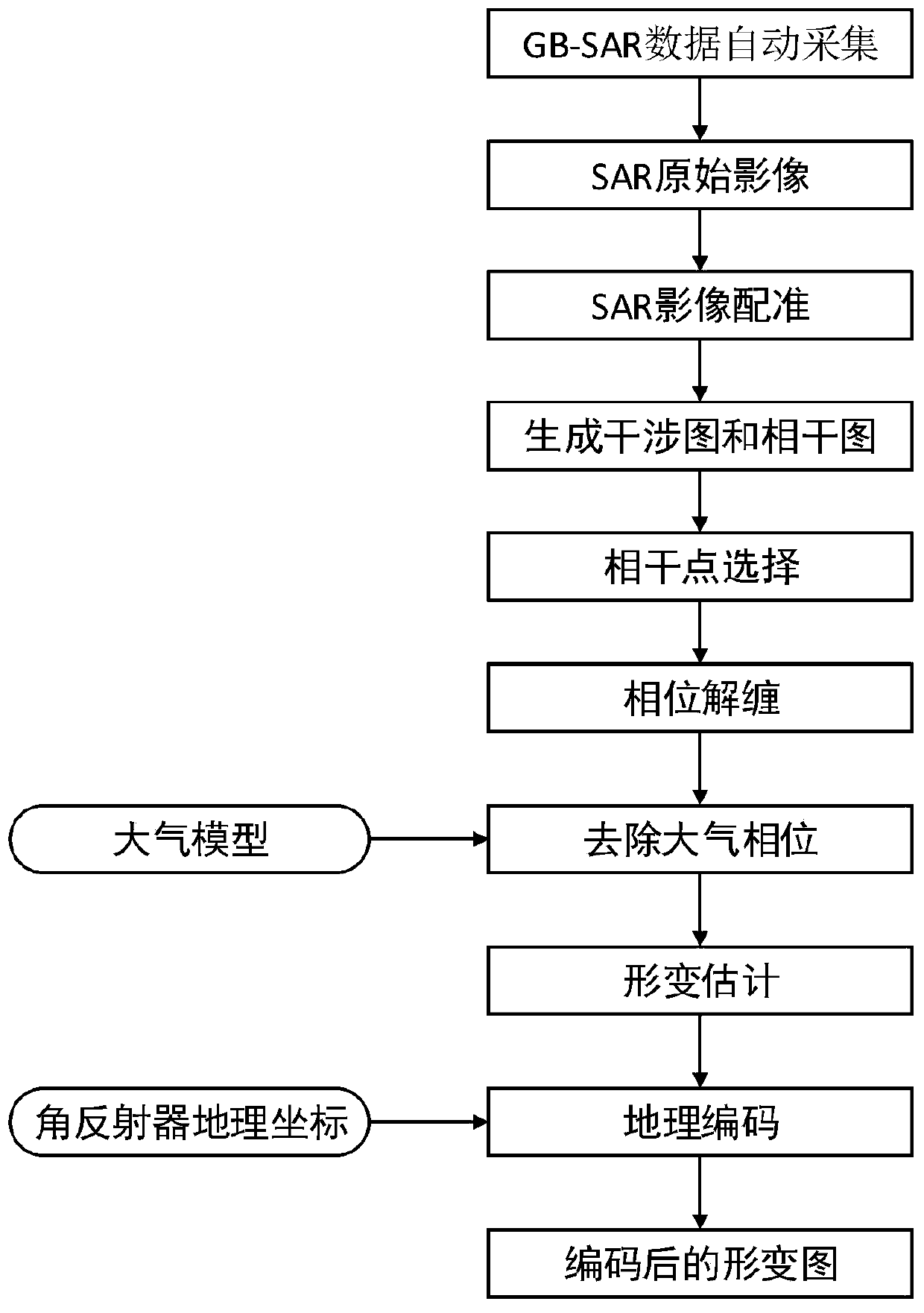
River reservoir bank deformation data automatic collection and processing method based on ground stable platform SAR
InactiveCN110471062AGet it directlyEasy accessUsing wave/particle radiation meansRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDeformation monitoringEngineering
The invention provides a river reservoir bank deformation data automatic collection and processing method based on a ground stable platform SAR, and belongs to the field of deformation monitoring. Themethod can be applied to the deformation monitoring of a river reservoir bank under the condition of complicated topography and landforms. According to the method, firstly, a GB-SAR is used for continuous observation to obtain monitoring data and to obtain an SAR original image; then, multiple images are subjected to a series of processing to obtain an interference pattern and a coherence pattern; next, an algorithm is used for extracting a coherence point; next, each pixel in the coherence pattern is subjected to phase unwrapping; next, an atmosphere phase is removed by using an atmosphere model; next, a deformation value is calculated according to the real phase of the deformation; and finally, the geocoding is performed according to the corner reflector geographical coordinate, and a coded deformation pattern is obtained. The river reservoir bank high-slope deformation monitoring technology is finally realized. The technology can be used for fast and accurately obtaining the slopedeformation information; the detection precision on the slope is improved; and the correct evaluation is made on the slope stability.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Typical rainfall event selection method for numerical atmospheric model
ActiveCN105954821AUniversally applicableWeather condition predictionModel selectionClassification methods
The present invention relates to a typical rainfall event selection method for a numerical atmospheric model. The method comprises: a typical rainfall event classification method based on individual rainfall amount; a rainfall time inhomogeneity calculation method; a rainfall spatial inhomogeneity calculation method; and a typical rainfall event selection method based on a rainfall spatial-temporal inhomogeneity coefficient. In the invention, the standardized typical rainfall event selection method is provided for selection and adjustment of a numerical atmospheric model from the perspective of rainfall amount and spatial-temporal distribution, the rainfall type is quantitatively described, and the simulation accuracy of the numerical atmospheric model for different types of rainfall in a certain research area is measured, which can not only provide the basis for model setting in the research area, but also shows that the model is more suitable for which type of rainfall, provides the basis for model selection and provides reasonable numerical atmospheric model simulation plans with respect to different types of rainfall for relevant departments such as meteorology, water conservancy and the like. The typical rainfall event selection method of the invention can be widely applied.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
Short-time atmosphere model modification method based on measured atmospheric density
InactiveCN107132155AImproving Orbit Forecast AccuracySpecific gravity measurementModel modificationDensity model
The invention provides a short-time atmosphere model modification method based on measured atmospheric density. The method comprises the following steps: selecting an atmosphere density model, and collecting and calculating measured atmospheric density in a set duration; respectively performing linear fitting on the density value of the atmosphere model and the measured density value so as to obtain a measured atmospheric density fitted curve and a model density fitted curve; calculating an included angle between the measured atmospheric density fitted curve and the model density fitted curve; and rotating the model density fitted curve point by point, thereby obtaining a time value t' after rotation and a selected atmosphere model density value after rotation. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the measured atmospheric density value is introduced into orbit calculation, and the spacecraft orbit forecast accuracy is well improved.
Owner:CHINA XIAN SATELLITE CONTROL CENT
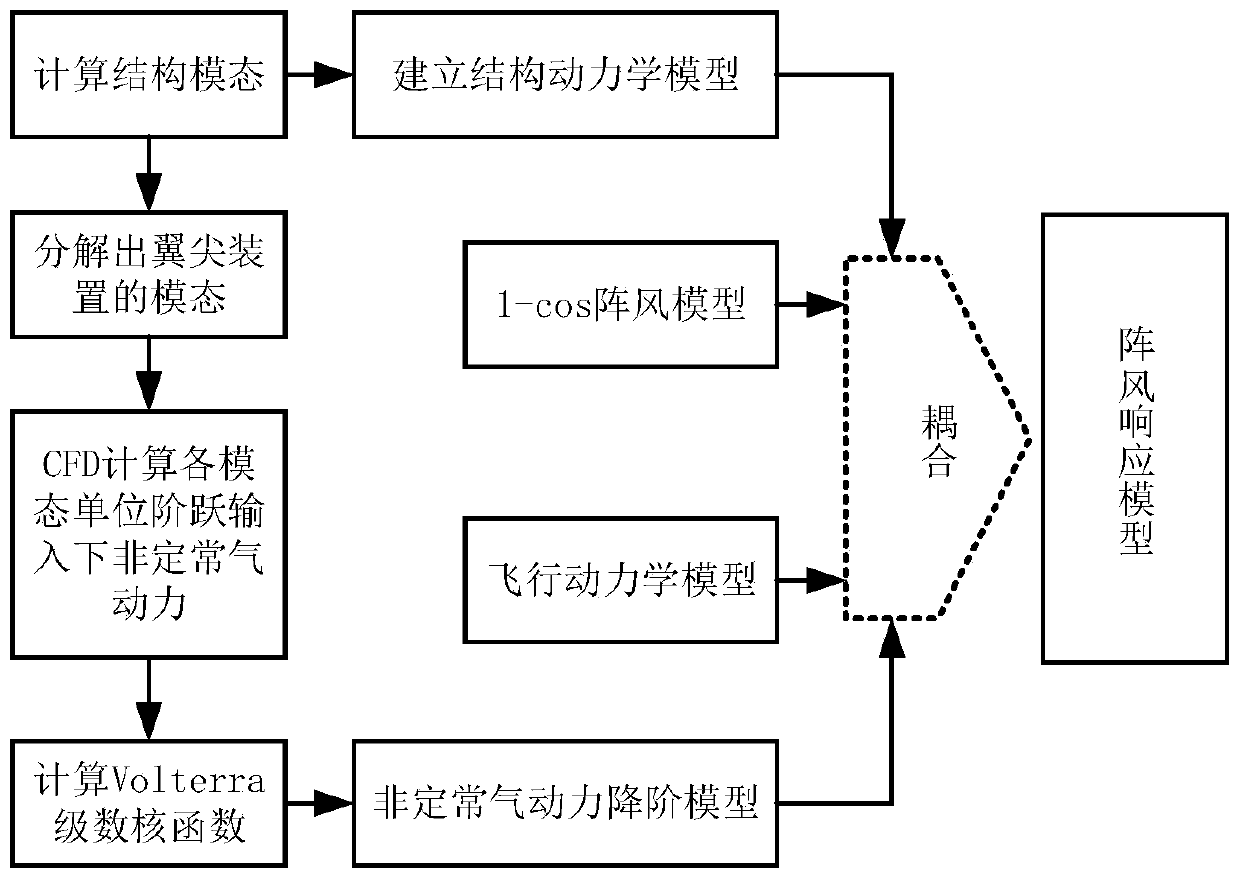
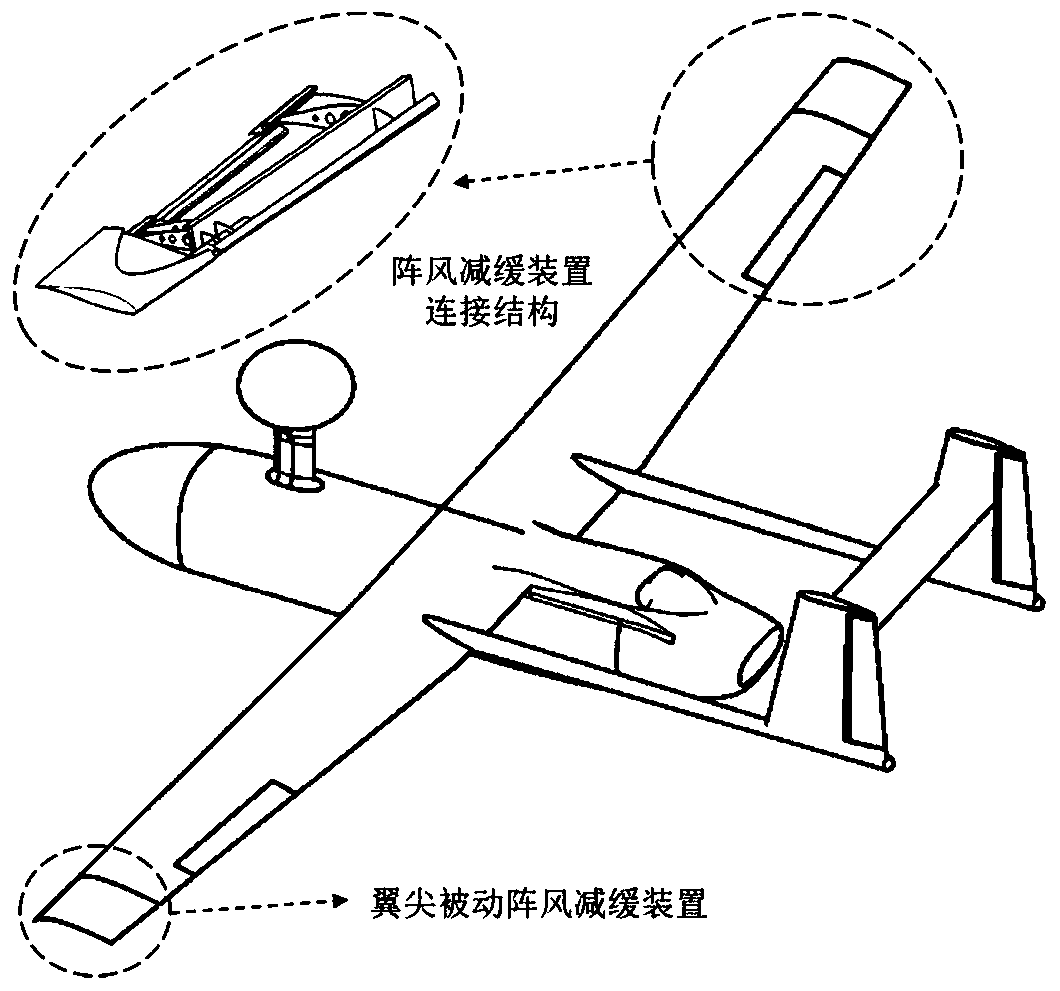
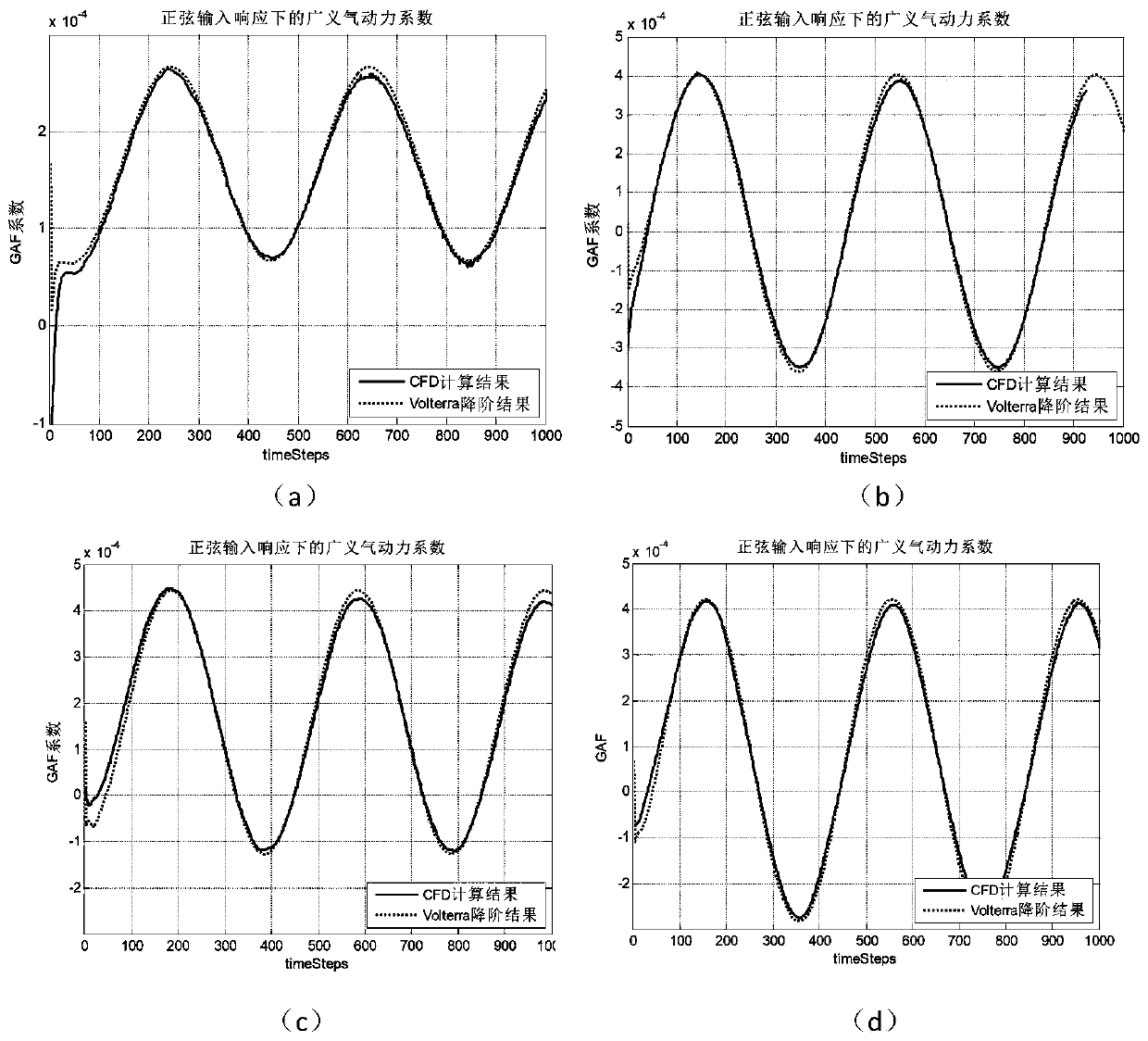
A modeling analysis method for gust response of a fixed-wing aircraft
ActiveCN109840349AReduce orderHigh precisionSustainable transportationComplex mathematical operationsAtmospheric modelModelling analysis
The invention discloses a modeling analysis method for gust response of a fixed-wing aircraft, which reduces the order of a model by reducing the order of an aerodynamic model, has higher precision and small calculated amount compared with the traditional method, and is suitable for engineering analysis. After the model is coupled with an aircraft structure model, an atmosphere model, a steering engine model and the like, a gust response model with low order is obtained, and gust response analysis and gust slowing control design are facilitated.
Owner:XIAN AISHENG TECH GRP +1
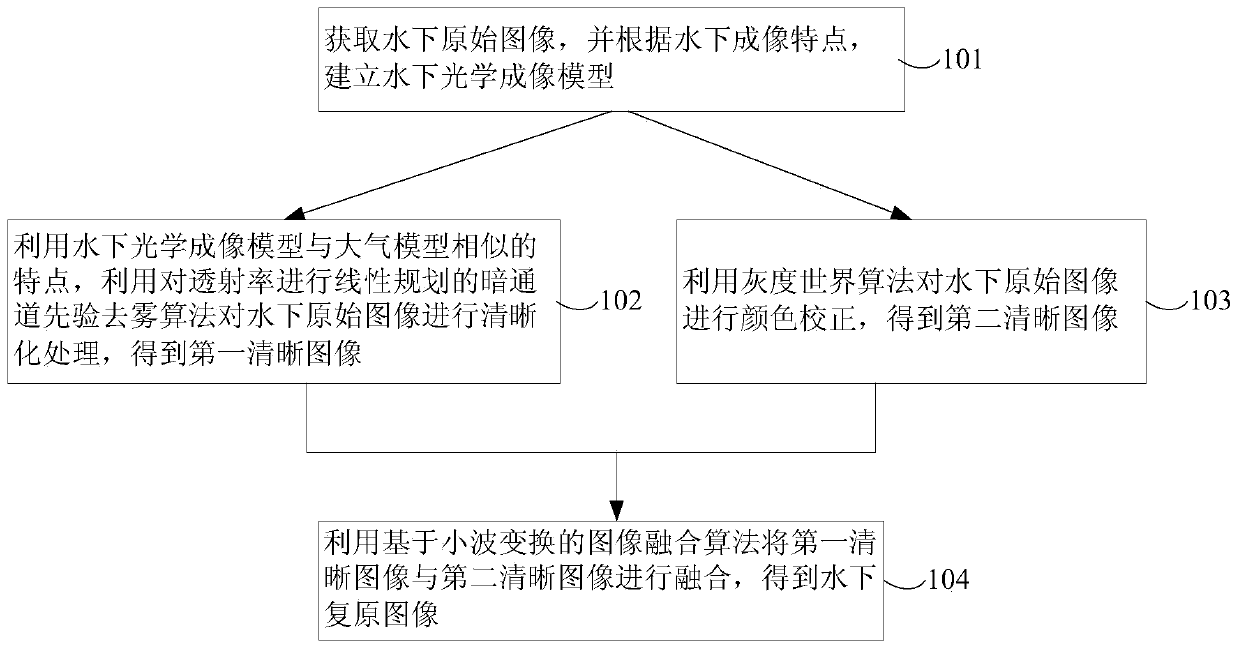
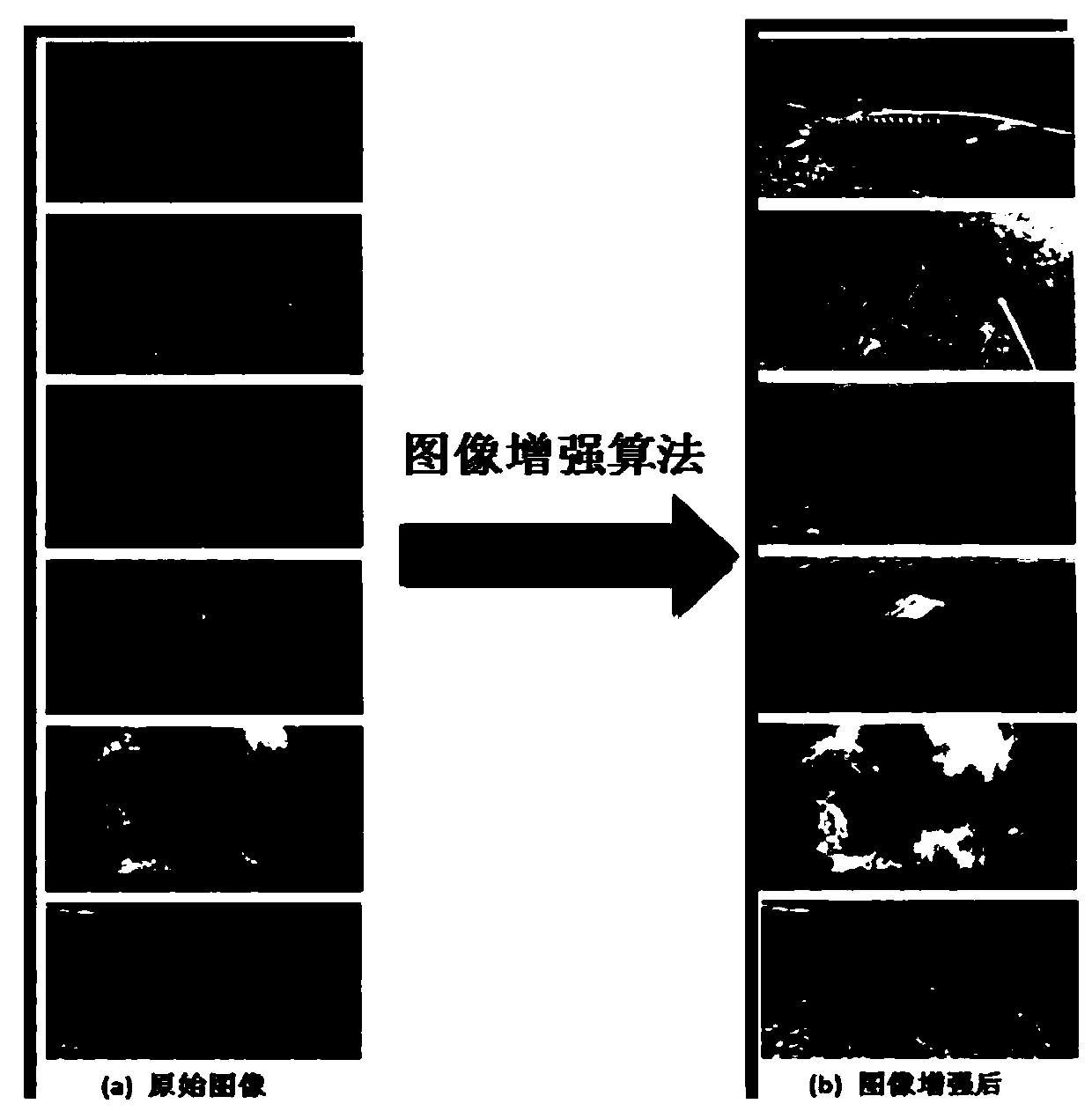
Underwater image enhancement method and enhancement device
ActiveCN110148095AImprove visual effectsImprove clarityImage enhancementImage analysisImage fusion algorithmColor correction
The invention provides an underwater image enhancement method and an underwater image enhancement device, which can improve the restoration accuracy and efficiency of an underwater image. The method comprises the steps that an underwater original image is acquired, and an underwater optical imaging model is established according to underwater imaging characteristics; a characteristic that an underwater optical imaging model is similar to an atmosphere model is utilized, a dark channel prior defogging algorithm for performing linear programming on transmissivity is utilized to perform clearnessprocessing on an underwater original image to obtain a first clear image, and the clearness processing comprises contrast enhancement; performing color correction on the underwater original image byusing a gray world algorithm to obtain a second clear image; and fusing the first clear image and the second clear image by using an image fusion algorithm based on wavelet transform to obtain an underwater restored image. The invention relates to the technical field of image enhancement and restoration.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com