Satellite starlight refraction navigation error determination and compensation method
A technology of starlight refraction and compensation method, which is applied in the field of astronomical navigation, and can solve the problems of not comprehensively considering the influence of navigation accuracy and failing to meet the needs of satellite starlight refraction navigation system for accurate prediction of navigation accuracy, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
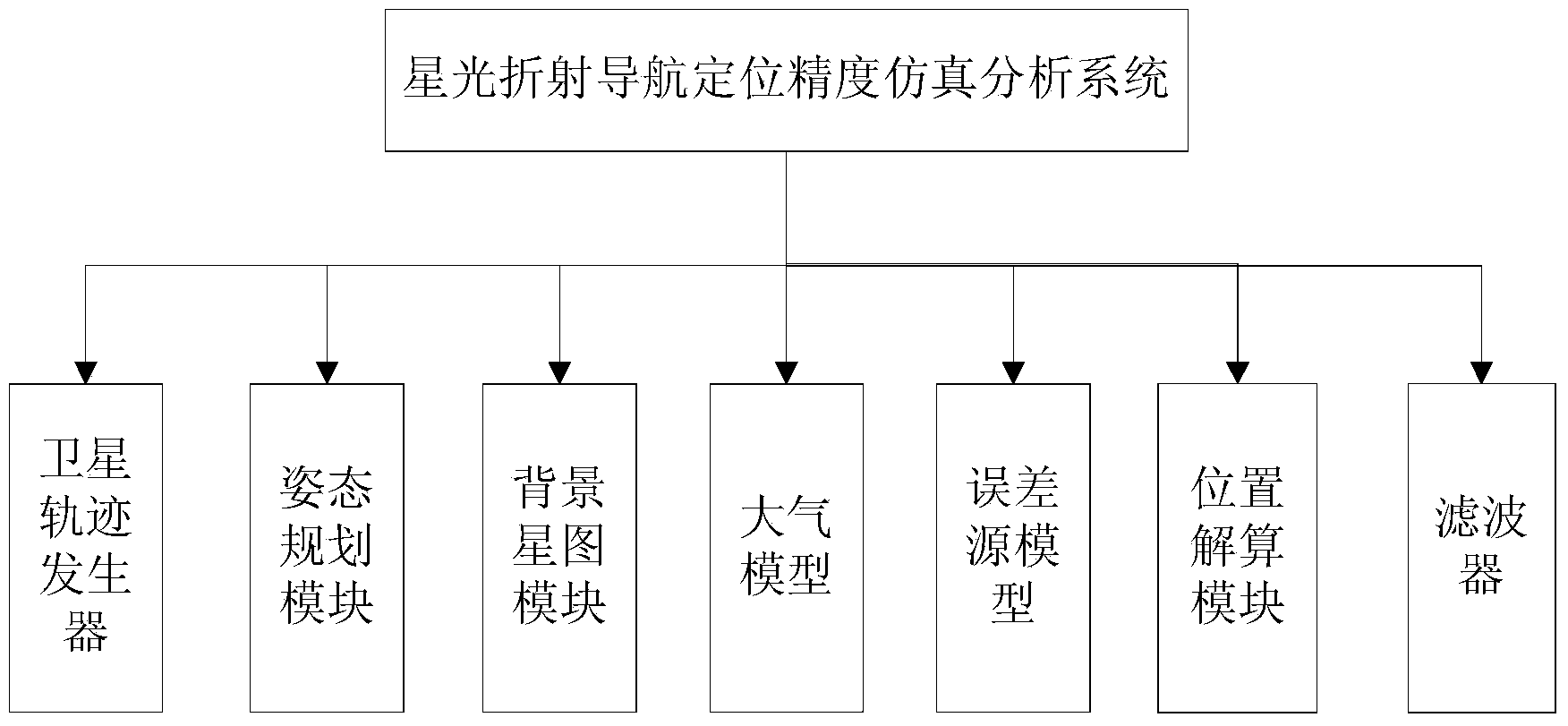
[0121] In order to explain the positioning error of star light refraction navigation, the influence of three main factors on the positioning accuracy, namely, the measurement accuracy of refraction angle, the error of atmospheric model, the number of refraction stars and the uniformity of distribution, are analyzed through simulation.
[0122] The input conditions of the simulation system are as follows:
[0123] 1) The simulation orbit is the GTO orbit of the satellite, the altitude ranges from 20000km to 36000km, and the orbit parameters are: a=24421.2km, e=0.726543, i=28.5°, Ω=139.3°, ω=75°;
[0124] 2) Technical indicators of starlight refraction sensor system:
[0125]
[0126] 3) Atmospheric model:
[0127] γ=2350.1074e -0.10326788h , where h is the atmospheric height in km; γ is the atmospheric refraction angle in ".
[0128] 4) Atmospheric model error 1%.
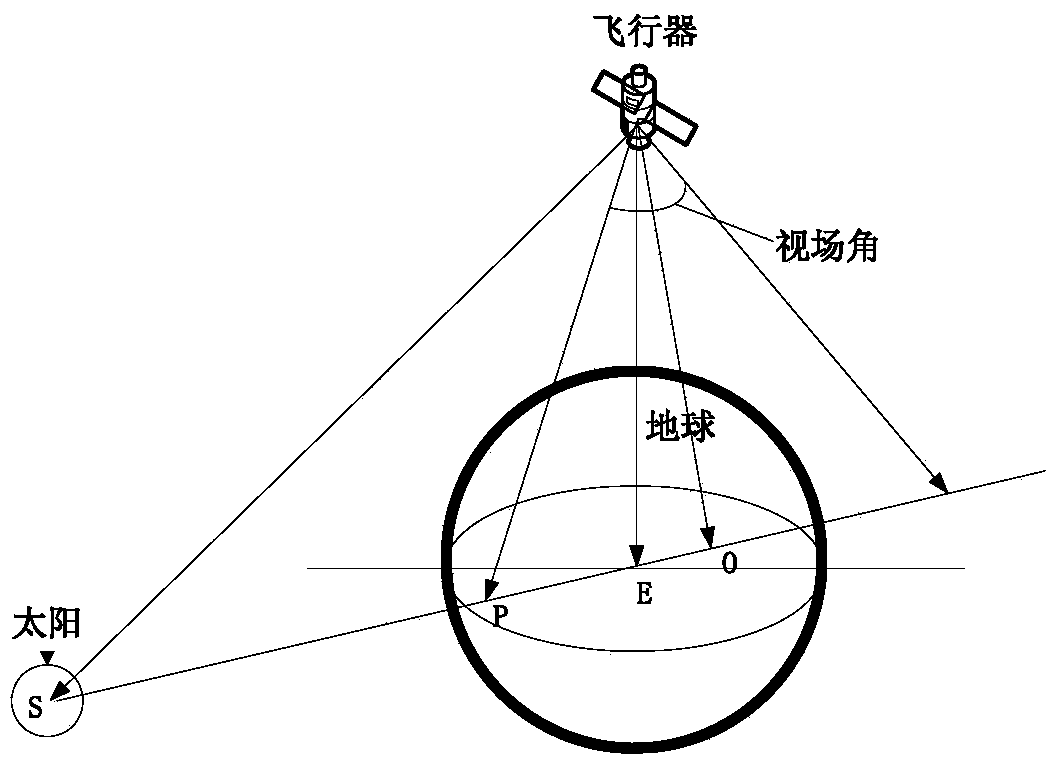
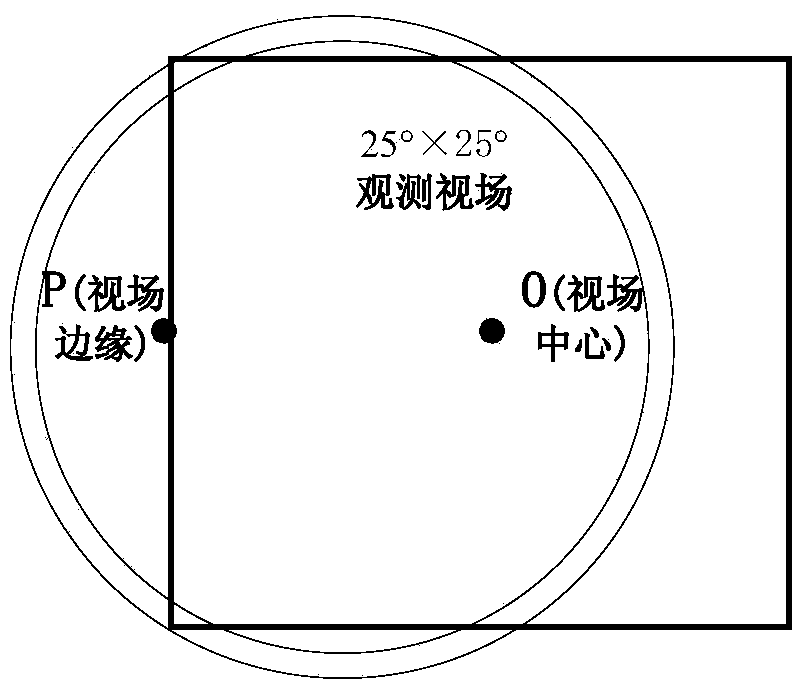
[0129] Figure 10 According to the above input conditions, and choose the refraction star behind the atmo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com