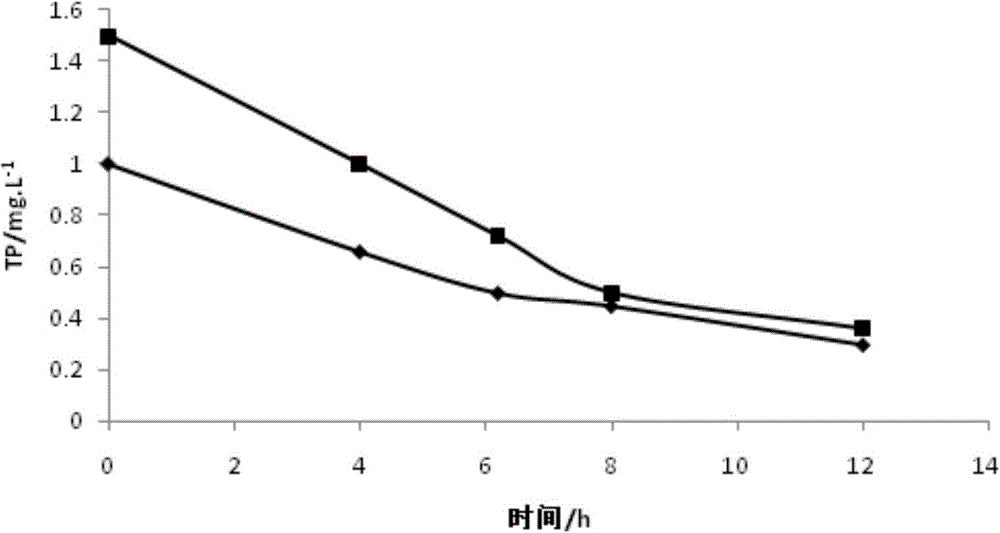
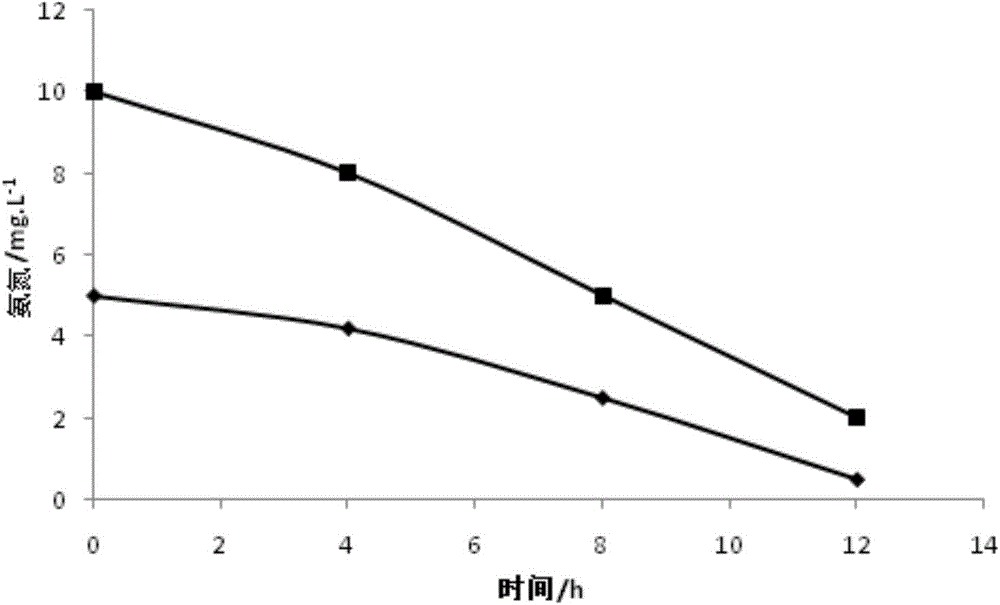
Patents
Literature
66 results about "Blastochloris viridis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Blastochloris viridis is a bacterium from the genus of Blastochloris which was isolated from water of the Clarke reservation lake in New York in the United States...
Green Algal Extract Containing Astaxanthin Having High Storage Stability
InactiveUS20070196383A1Good storage stabilityEasy to operateBiocideOrganic active ingredientsBetaxanthinsAstaxanthin
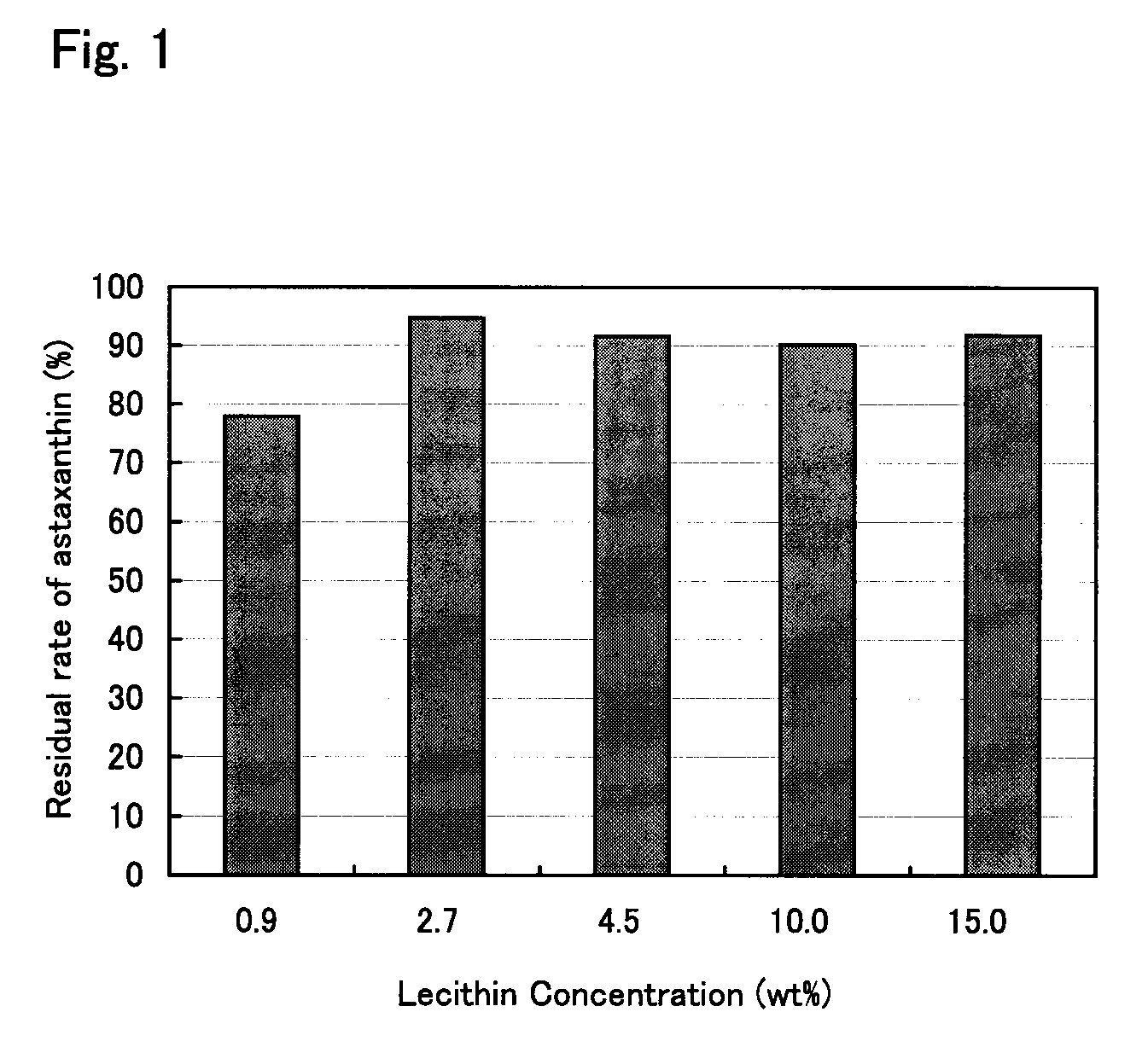
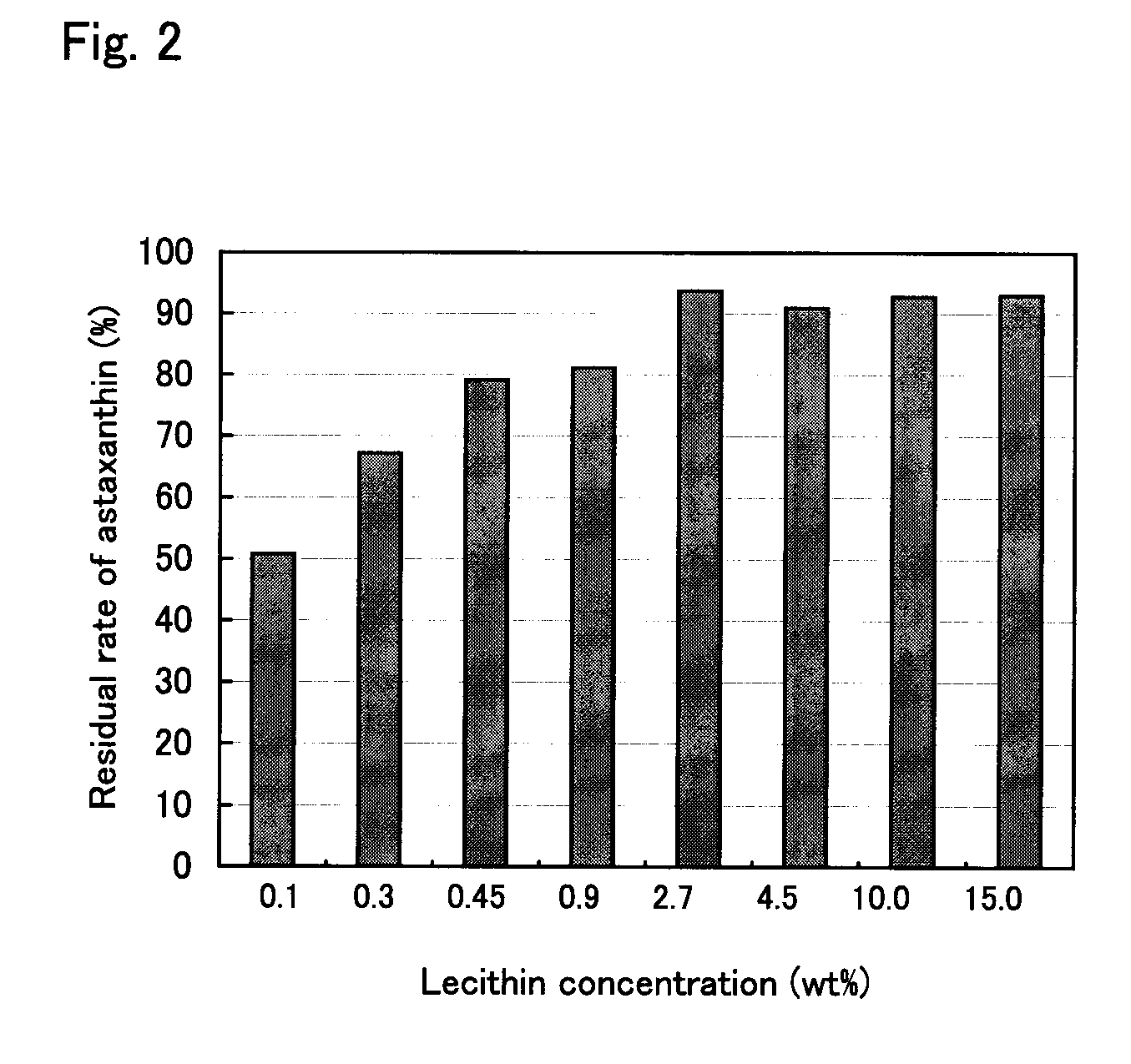
The present invention provides means for increasing the storage stability of astaxanthin in a green algal extract, and a green algal extract containing astaxanthin having high storage stability. The present invention provides a green algal extract comprising astaxanthin at a concentration of 0.5 to 20 wt % expressed in terms of free astaxanthin, and at least one phospholipid at a phospholipid concentration of 0.1 to 15 wt %. This green algal extract has an excellent ability to store stably astaxanthin, and even after storage for one week at 60° C. it is possible to retain approximately 80% or more of the astaxanthin.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Microorganism bacterium agent for straw and excrement mixed composting
ActiveCN103232944AWell mixedPromote the process of mixed aerobic compostingFungiBio-organic fraction processingFecesPseudomonas putida
The invention discloses a microorganism bacterium agent for straw and excrement mixed composting. The microorganism bacterium agent is composed of the following strains: (2-6)*10<10>cfu of hair mould per gram, (2-6)*10<10>cfu of trichoderma virens per gram, (2-6)*10<10>cfu of geotrichum candidum per gram, (2-8)*10<9>cfu of saccharomyces cerevisiae per gram, (3-5)*10<11>cfu of bacillus thermophilus per gram, (2-6)*10<11>cfu of lactobacillus thermophilus per gram, (2-8)*10<10>cfu of white rot fungi per gram, (2-8)*10<10>cfu of monilinia fructicola per gram, (3-7)*10<8>cfu of pseudomonas putida per gram, (2-6)*10<11>cfu of nitrosococcus per gram, (1-4)*10<6>cfu of green algae per gram and (2-5)*10<7>cfu of blue-green algae per gram. The microorganism bacterium agent can promote a straw and excrement mixed aerobatic composting progress, shorten a composting period, improve a composting rotten degree, accelerate biodegradation of organic matters, alleviate ozone generation and diffusion during composting and reduce loss of nutrient substances such as nitrogen, can be applied to composting of different straw and excrement raw materials for composting enterprises and is used for producing bio-organic fertilizers.
Owner:山东土木启生物科技有限公司
Chlorella sorokiniana CS-01 and culture method thereof for producing grease
InactiveCN101705190AWide adaptability to the environmentStrong alkali resistanceUnicellular algaeBiofuelsDry weightBiodiesel
The invention discloses chlorella sorokiniana CS-01 and a culture method thereof for producing grease. The preservation number of the chlorella is CCTCC M209220. The culture method for producing the grease comprises the following steps: inoculating index-cultured strains to BG11 sterilized culture solution, adding 0.3 to 1.5 g / L of sodium nitrate or urea and 1*10-5 mol / L to 1*10-3 mol / L of EDTA-Fe (III) into the culture solution, culturing the strains by ventilating or without ventilating at the temperature of between 25 and 35 DEG C, pH of 6 to 11, 6,600 to 10,000 Lx and lighting ratio of 14:10, and harvesting the grease, wherein the dry weight of the harvested cells is as high as 970 mg / L, and the content of the grease can reach 57 percent. The strain is fresh-water unicellular chlorella, has the advantages of strong environmental adaptation, high growing speed and higher grease yield, and has potential serving as a biodiesel preparation raw material to be cultured in a large scale in interior regions.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for extracting algae glycoproteins
The invention discloses a method for extracting algae glycoproteins. The method for extracting the algae glycoproteins comprises the following step: mixing a certain amount of the mixture of algae, blue-green algae or the mixture of alga powder and water with the water solution with specific fungi. The algae glycoproteins extracted by the method have the functions of preventing and treating the respiratory diseases, and also have functions on broad-spectrum antiviral, anti-inflammatory, anticoagulin, bacteriostasis, refrigeration and immune adjustment.
Owner:徐宝贞
Green alga poly-saccharification nano-selenium and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106539092AEasy to useUse, but these drugs are easy to use in large quantities over a long period of timeOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticDiseaseNanometer size
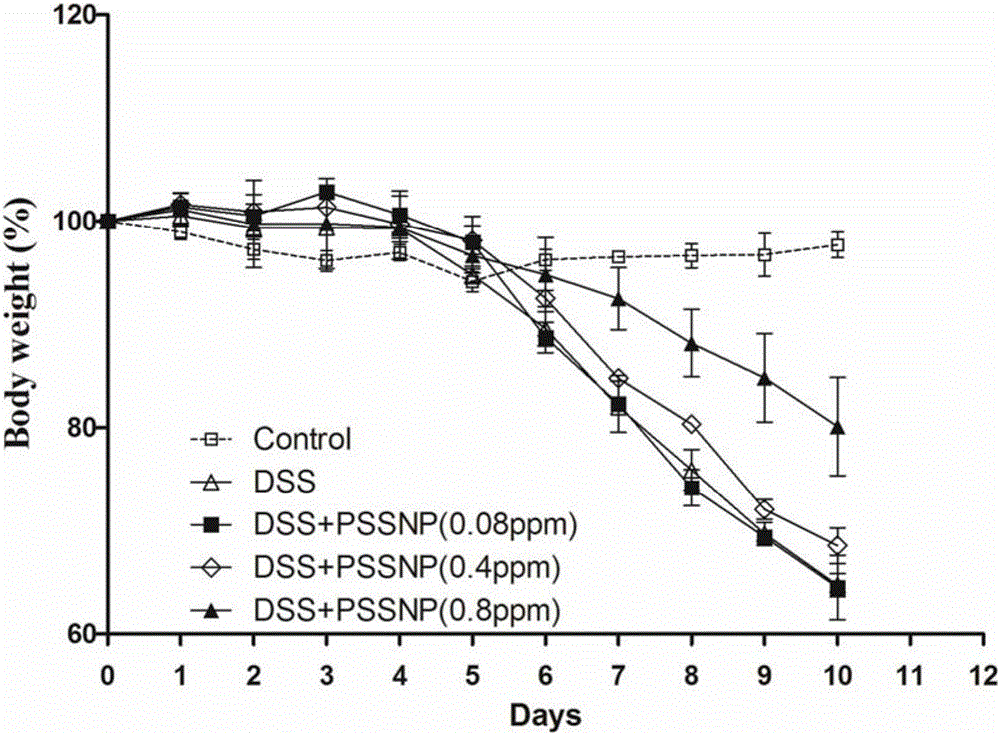
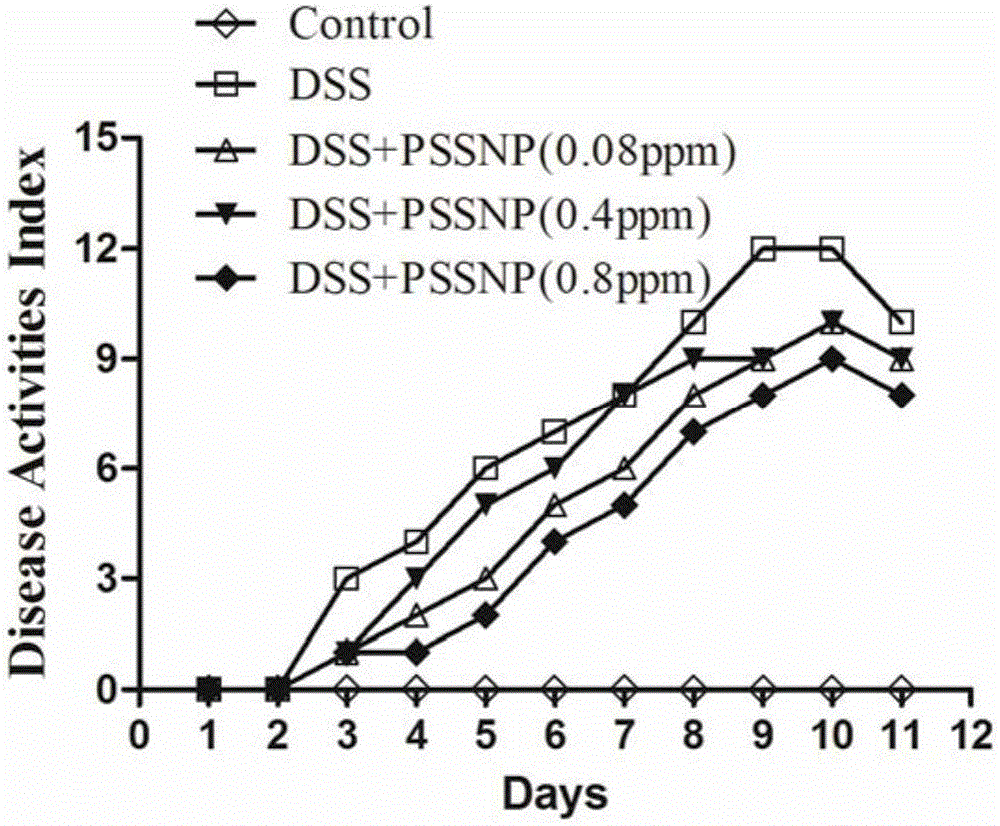
The invention discloses green alga poly-saccharification nano-selenium and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of the food biotechnology. The natural green alga poly-saccharification nano-selenium (PSSNP) prepared by the preparation method easily and conveniently is a necessary micronutrient for a human body, and polysaccharide has an immune regulation effect on an organism. The novel safe effective poly-saccharification nano-selenium is developed, and homogeneity of the nanometer size, stability of liquid-phase conservation and high efficiency of poly-saccharification are achieved. Green alga poly-saccharification nano-selenium (PSSNP) products are mainly suitable for auxiliary treating of enteritis and inflammatory bowel diseases and can also be applied to auxiliary preventing and treating of hyperlipidaemia, atherosclerosis, diabetes and other inflammation-related diseases; and the green alga poly-saccharification nano-selenium is convenient to use, green, safe and low in price and can alleviate patient pains and greatly reduce economical burden.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Heavy metal ions absorbent prepared by straw stalks and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107159167AHigh porosityUniform voidOther chemical processesWater contaminantsSodium BentoniteSorbent
The invention discloses a heavy metal ions absorbent prepared by straw stalks. The heavy metal ions absorbent prepared by straw stalks is mainly prepared from, by weight, 50-100 parts of straw stalks, 15-30 parts of corncob, 20-30 parts of modified bentonite, 15-25 parts of modified diatomite, 5-10 parts of green alga, 1-2 parts of blue-green algae, 0.5-1 part of bacillus, 5-10 parts of fruit enzymes, 5-10 parts of soybean protein powder, 5-10 parts of tartaric acid, and so on. By taking the straw stalks as the main raw material of absorbent and performing cellulose and alkali water treatment, the prepared straw stalk powder is synergistic with modified bentonite and modified diatomite, thus the absorbent has significant absorption to heavy metal ions; the straw stalk powder is chelated with soybean protein powder, tartaric acid, oligosaccharide and chitosan to form macromolecule, and the macromolecule is tightly absorbed by silica gel and resin; thus the effect of effectively removing heavy metal ion is reached.
Owner:韦卓林
Method for quick rooting of divaricate velvetplant root and rhizome by water culture and cutting
InactiveCN104381105APromote growthAuxin ratio can promote plant rootingCalcareous fertilisersMagnesium fertilisersPANAX NOTOGINSENG ROOTInorganic salts
The invention discloses a method for quick rooting of divaricate velvetplant root and rhizome by water culture and cutting and belongs to the technical field of rooting of the divaricate velvetplant root and rhizome. The method mainly comprises a basic formula of quick rooting culture solution, preparation for the quick rooting culture solution and a method for quick rooting by the water culture and cutting. According to the method disclosed by the invention, with simplicity, practicality, economy and high efficiency as the rule, and with the principle that the rooting of plants can be promoted according to the mixture ratio of auxin with proper concentration and the growth of the plants can be promoted according to the mixture ratio of inorganic salts with proper concentration, the divaricate velvetplant root and rhizome is rooted by the water culture and the cutting through adopting a water culture mode of nutrient solution with cold boiled water (river water or tap water placed for over 1-2 days) and the like as mediums; meanwhile, the growth of green alga is suppressed by means of blacking a container and other paths, quick rooting of the divaricate velvetplant root and rhizome by the water culture and the cutting is realized, the rooting speed, root amount, survival rate, plant robustness and the like of the divaricate velvetplant root and rhizome by the water culture and the cutting are greatly improved. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the survival rate of the divaricate velvetplant root and rhizome by the water culture can reach over 98 percent, the divaricate velvetplant root and rhizome can be rooted in 6-7 days, the root amount is abundant, and cuttings are quick in growth.
Owner:DEZHOU UNIV
Algicidal pollution-free fuming agent
InactiveCN101564053AEffective controlGood effect of controlling moss and cyanobacteriaBiocideAnimal repellantsCoriariaMoss
The invention provides an algicidal pollution-free fuming agent, which is a medicament synthesized by natural plants such as coriaria sinica, pelargonium graveolens, southernwood, malt, ginger and the like. The fuming agent is characterized in that 100 to 500 portions of the coriaria sinica, 100 to 500 portions of the pelargonium graveolens, 100 to 500 portions of the southernwood, 100 to 500 portions of the malt and 100 to 500 portions of the ginger are prepared in portion by weight; various materials are mixed and then added with 200 to 1,000 portions of water, the mixture is decocted to form a water agent with the components, and the water agent is filtered and clarified for use; and various materials are mixed and then added with 200 to 1,000 portions of sulfur powder, and the mixture is grinded to form a powder agent with the components. The formulation generally treats the area of every 5 square meters for 1 to 2 seconds, green mosses are dead in 1 day after the treatment, the green mosses in water lose green and become white in 3 days after the treatment, and piled algae are broken and dead. The fuming agent not only can effectively eliminate blue algae, but also can eliminate water hyacinth and float grass. The fuming agent is safe to the water body and aquatic organism, accords with the pollution-free preventing and eliminating requirements, and provides a novel pollution-free preventing and eliminating technique for preventing and eliminating blue-green algae in fresh water areas such as rivers, lakes and the like. The technique has wide application prospect.
Owner:沈阳鸟王旅游发展有限公司
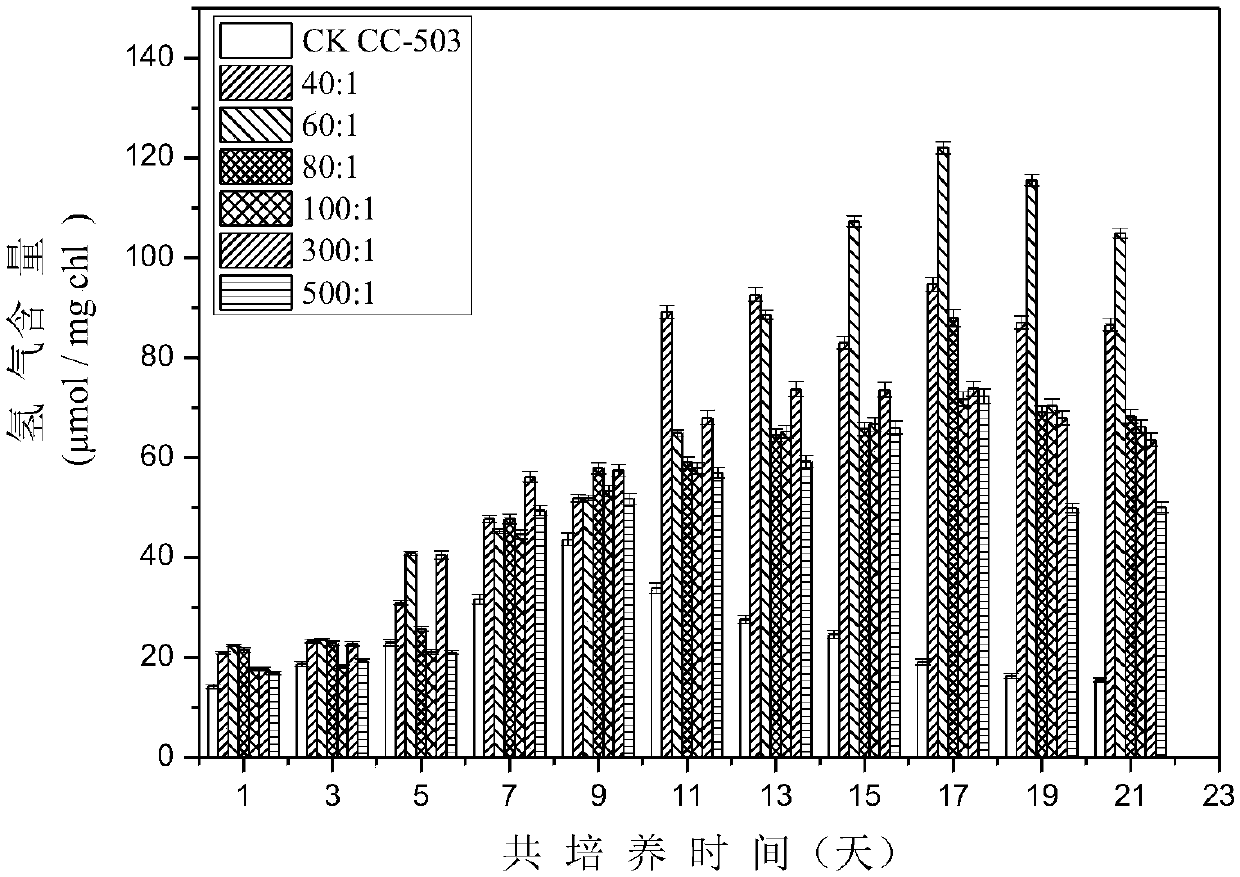
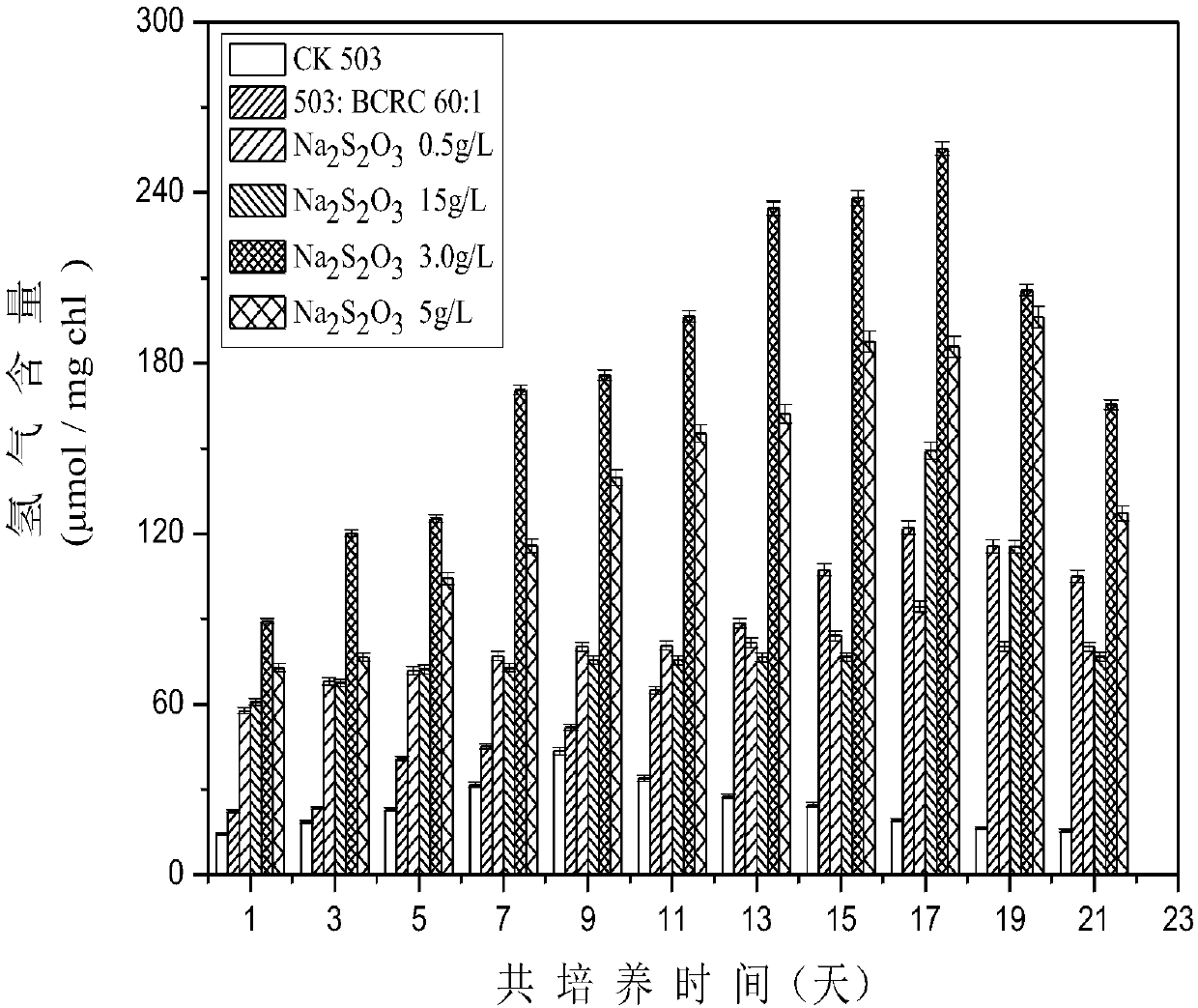
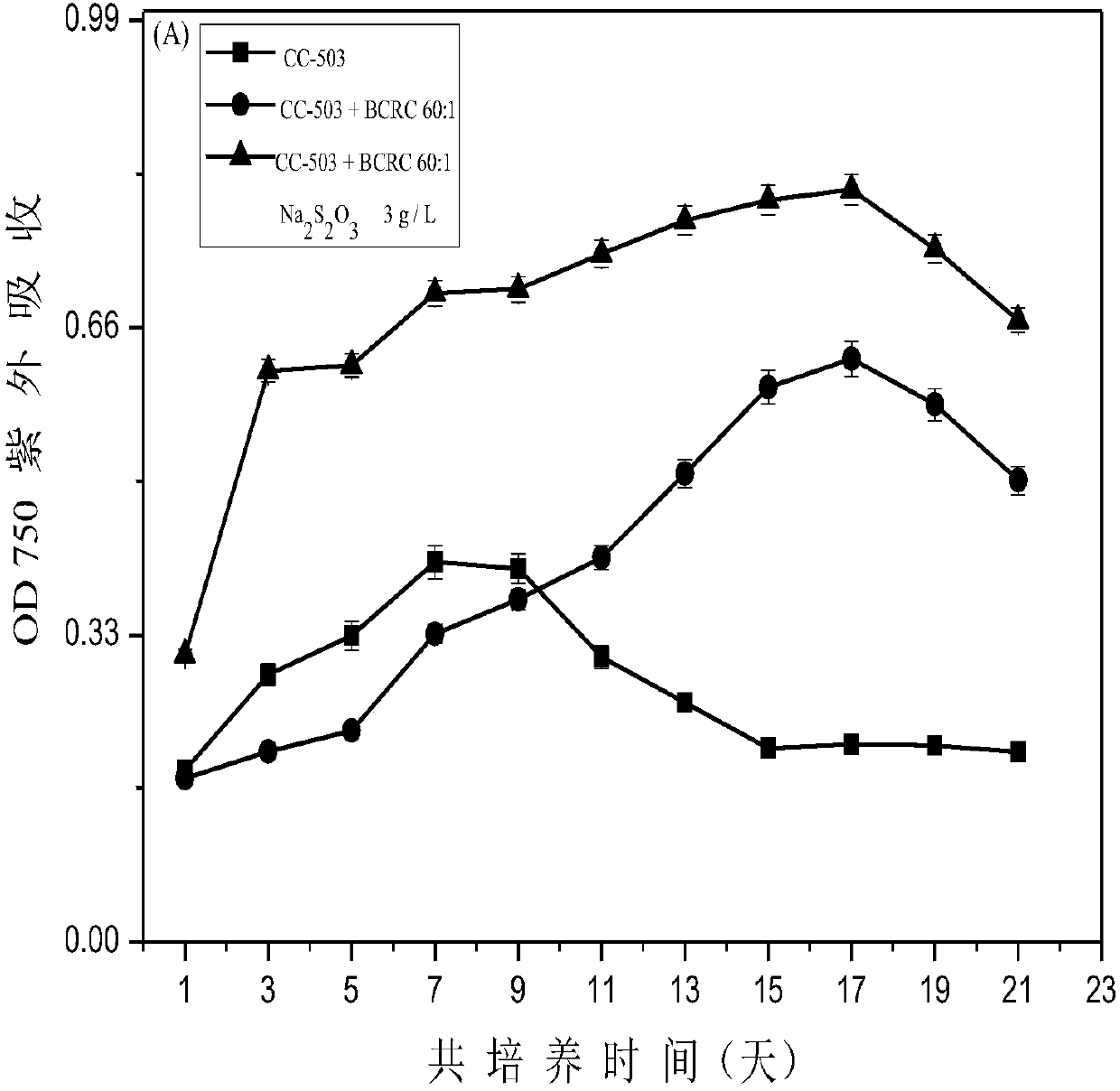
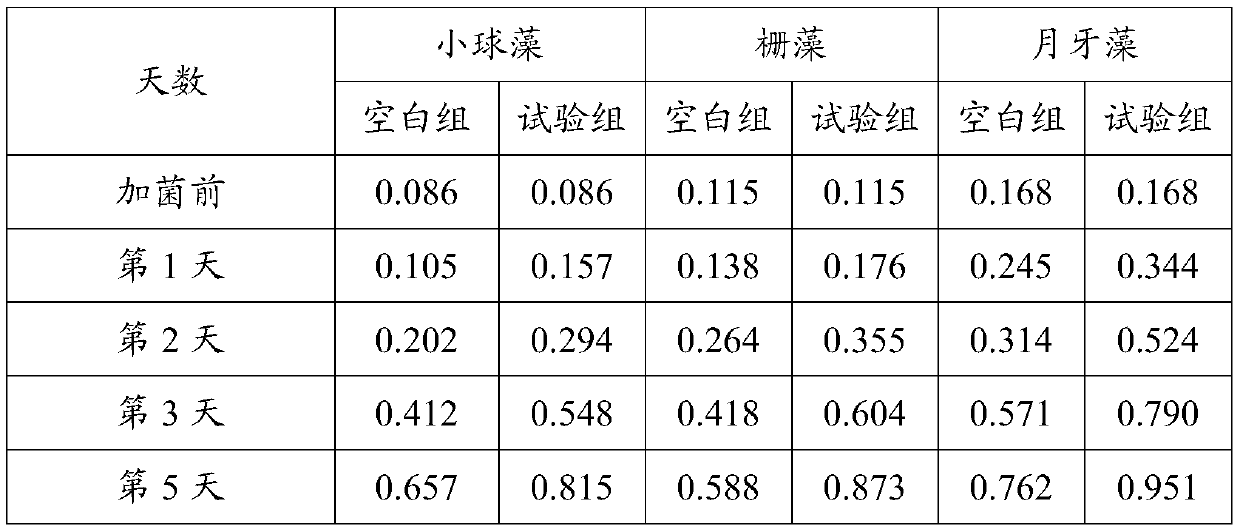
Method for improving hydrogen production quantity of photosynthetic microalgae through phycomycetes co-culture
ActiveCN107663529ASolve \"photosynthetic oxygen production\"Solve the contradiction between \"anaerobic hydrogen production\"Microorganism based processesFermentationPhycomycetesSulfur
The invention discloses a method for improving the hydrogen production quantity of photosynthetic microalgae through phycomycetes co-culture. Particularly, green alga and one kind of facultative anaerobic / facultative chemoautotrophic thiomonas intermedia are proportionally mixed for culture; oxygen released by green alga photosynthesis can be consumed by the bacterium respiration effect; the carbon dioxide released through the bacterium respiration effect can be supplied to the green alga for better performing photosynthesis effect, so that the anaerobic characteristics of the whole culture environment can be well maintained. In addition, the balance catalysis capability of the thiomonas intermedia on the sulfur element is utilized; the limited supply of the sulfur element can be realized,so that the normal growth of the green alga can be ensured; the efficient durable hydrogen production can be realized.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Aquatic-product compound amino acid bacterial fertilizer containing triacontanol and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104016805AGrowth inhibitionStable survivalFertilizer mixturesSodium sulfateZINC SULFATE HEPTAHYDRATE
The invention provides an aquatic-product compound amino acid bacterial fertilizer containing triacontanol and a preparation method thereof, and in particular provides an aquatic-product compound amino acid bacterial fertilizer containing triacontanol which can quickly cultivate algae at a low temperature, and can quickly form excellent water color within 2-3 days after sudden death of algae. Materials for preparing the compound amino acid bacterial fertilizer comprise triacontanol raw powder, alcohol, compound amino acid primary liquid, peregal, lauryl sodium sulfate, sodium silicate, zinc sulphate heptahydrate, ferrous sulfate, sodium molybdate, cobalt chloride, boric acid, manganese chloride and spore bacteria liquor. Free amino acid and each trace element in the aquatic-product compound amino acid bacterial fertilizer can be directly utilized by algae after being applied to a pond, so that conversion is quick and the algae photosynthesis is promoted; the low-concentration triacontanol can promote quick growth of beneficial algae such as diatom, green algae, and the like, at a low temperature, strengthen activity of the algae, so that fertilizer can quickly cultivate algae at a low temperature, and excellent water color can be quickly formed within 2-3 days after sudden death of algae.
Owner:南通聚益成广生物科技有限公司
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Y1711, and culture method and application thereof
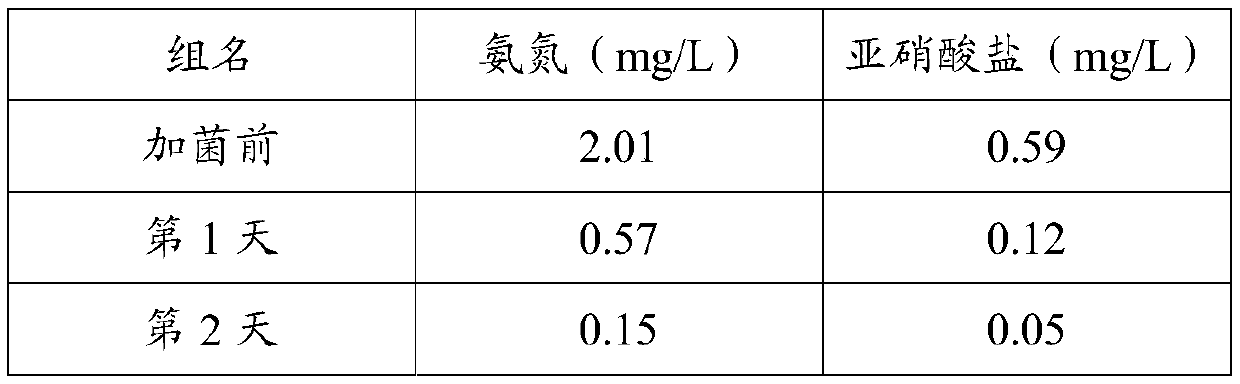
ActiveCN109837230AReduce ammonia nitrogenReduce nitriteBacteriaUnicellular algaeMicroorganismBacillus amyloliquefaciens
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms, and particularly relates to bacillus amyloliquefaciens Y1711, and a culture method and application thereof. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens Y1711 is Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Y1711, the preservation number of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens Y1711 in the China Center for Type Culture Collection is CCTCC NO:M 2018356, and the preservation date is June, 11, 2018. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens Y1711 disclosed by the invention can enable ammonia nitrogen and nitrite in breeding water bodies to be obviously reduced and enable the growthrate of beneficial green alga to be obviously increased, so that a benign circulation is formed, and besides, the bacillus amyloliquefaciens Y1711 is harmless to men and cattle, and can be in large-scale production for improving aquaculture environment.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
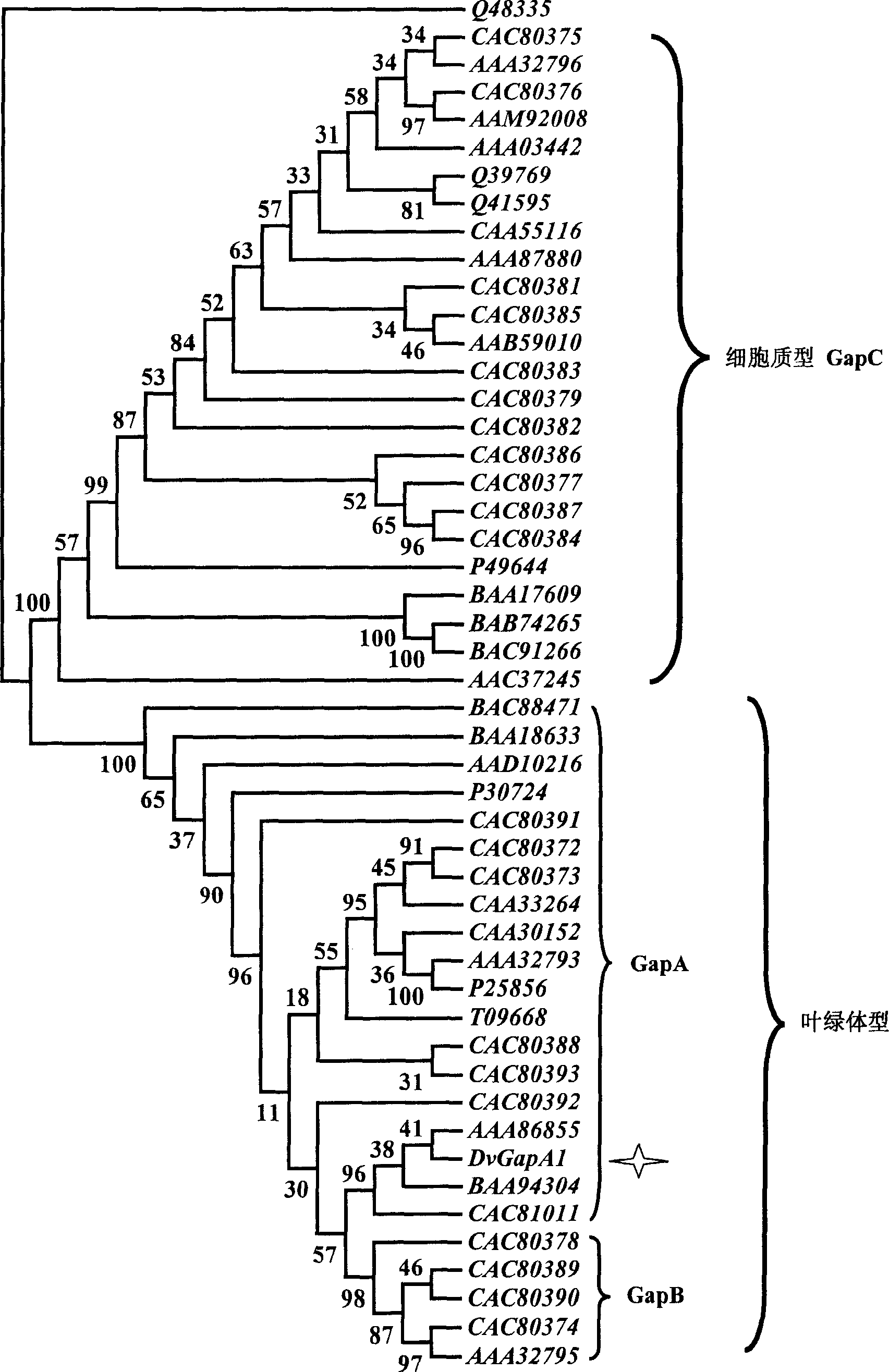
Salt algae NADP glyceral dehyde-3-phosdehydrogenase gene clone and protein expression method
The present invention relates to a kind of saline alga photosynthetic metabolic pathway key enzyme NADP-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene, coded protein and its clone and protein expression method. The invented saline alga photosynthetic metabolic pathway key enzyme NADP-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene has the base sequence showed by SEQ NO 5, and its coded protein has the amino acid sequence showed by SEQ NO 6. Said invention uses homologous fragment of glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene originated from chlamydomonas as probe and firstly clones a glyceraldehydes-3 phosphate dehydrogenase specialized by saline alga. Besides, said invention makes primary analysis for its sequence and coded protein sequence, at the same time makes primary function analysis for said gene.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Moss prevention method for sea cucumber pond based on construction of alga floating bed
PendingCN109197705AGrowth inhibitionSolve the problem of WangfaClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaMacrocystis pyriferaAquaculture of sea cucumbers
The invention discloses a moss prevention method for a sea cucumber pond based on a construction of alga floating bed. According to characteristics of the living history of moss in the pond, the algafloating bed with a vinylon net screen as a matrix and green alga in the ulva family is constructed in the surface layer of a water body of the sea cucumber pond in the larva phase of moss in the midmonth of March to the midmonth of April, a natural sunlight barrier layer is established with growth of alga, the intensity of incident light to the pond bottom is reduced, growth of moss is inhibited,and biological prevention against moss in the sea cucumber pond is realized.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
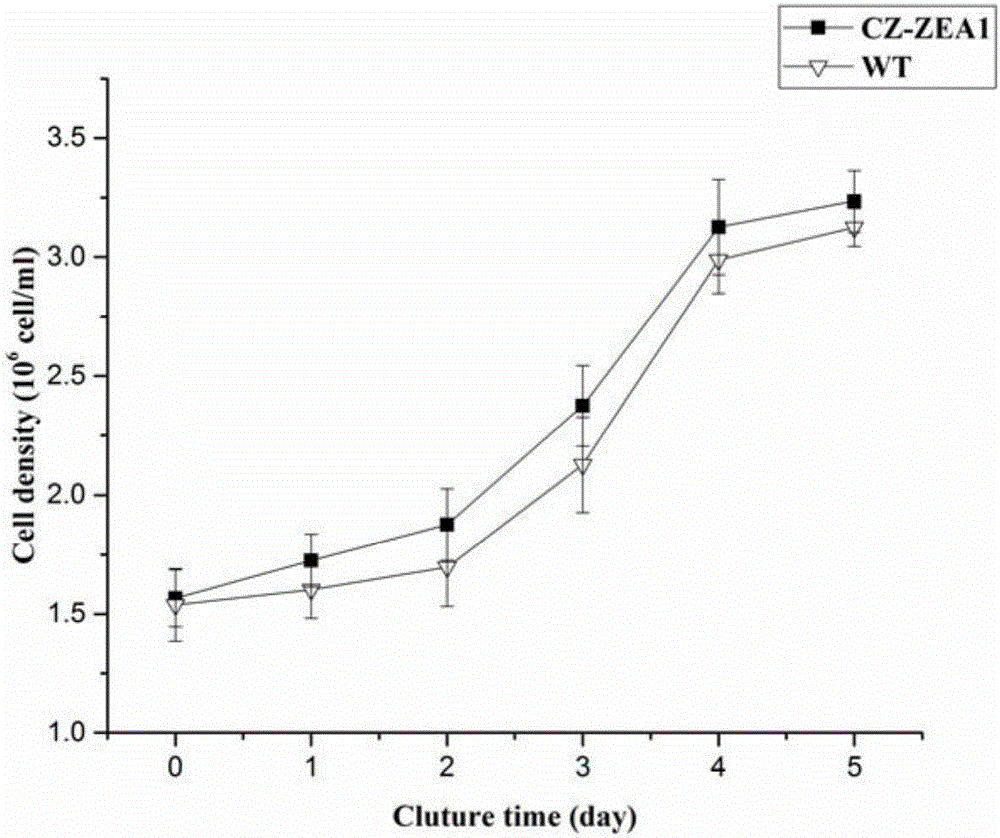
Mutant chlorella strain capable of producing zeaxanthine and beta-carotene and culturing method thereof
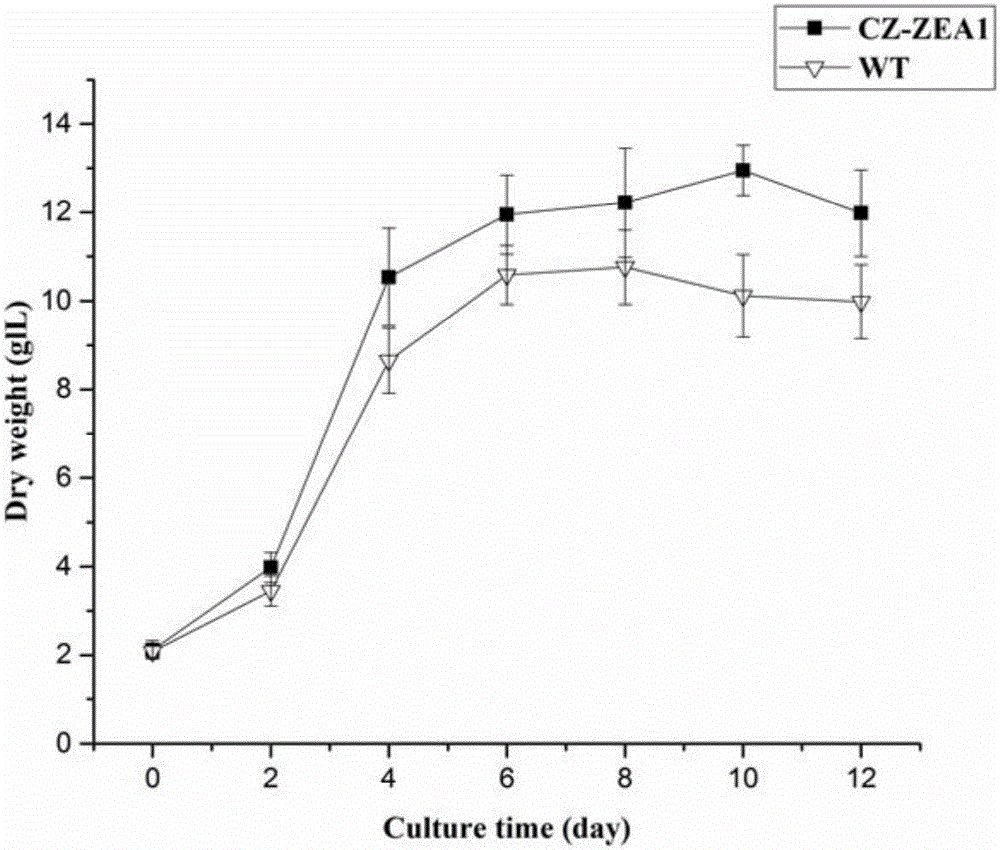
The invention provides a mutant chlorella strain capable of realizing high yield of zeaxanthine and other carotenoids essential to the human body, and a culturing method thereof. The culturing method comprises the following steps: subjecting Chlorella zofingiensis ATCC 30412 to nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis; then coating a Kuhl solid medium containing DPA with treated chlorella cells for culture; selecting a single chlorella colony from the Kuhl solid medium and culturing the single chlorella colony on a Kuhl liquid medium; adding glucose in the middle and later periods of logarithm for induction of carotenoid synthesis; and detecting the variety changes and content of carotenoids in the obtained chlorella body so as to obtain the strain which can realize high yield of zeaxanthine, xanthophyll and beta-carotene and is named as CZ-ZEA1. Under the induction condition that the concentration of glucose is 30 g / L, the biomass of the CZ-ZEA1 is 12.95 g / L, and the contents of zeaxanthine, xanthophyll and beta-carotene reach 2.176 mg / g, 1.10 mg / g and 1.211 mg / g, respecitively. The mutant chlorella strain is an edible alga species and contains high-content optimally-proportioned carotenoids essential to the human body, especially zeaxanthine rare in nature; so the mutant chlorella strain is an ideal new-resource functional foodstuff for preventing deterioration and lesion of the eyes of middle aged and old people and has good development and application prospects.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
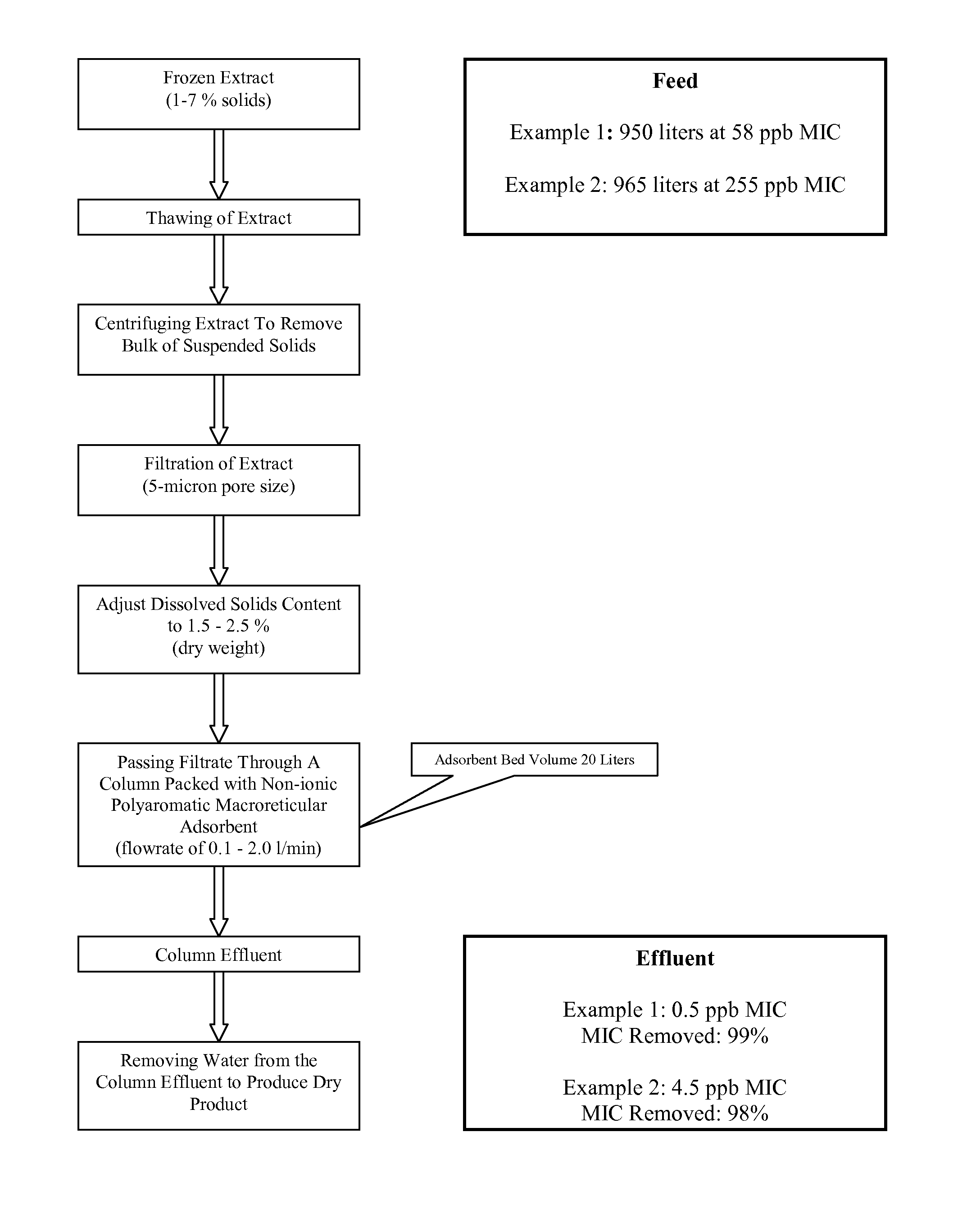
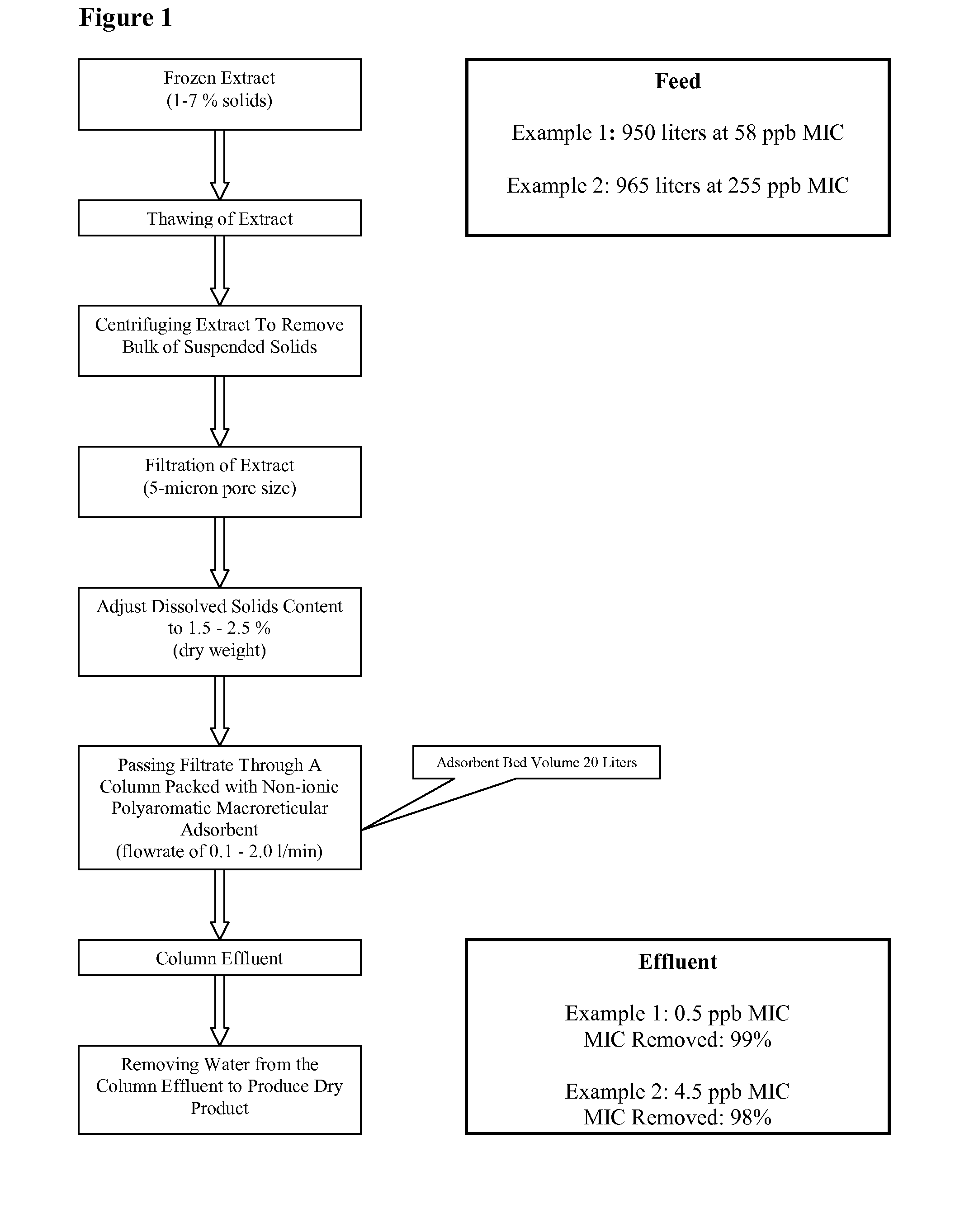
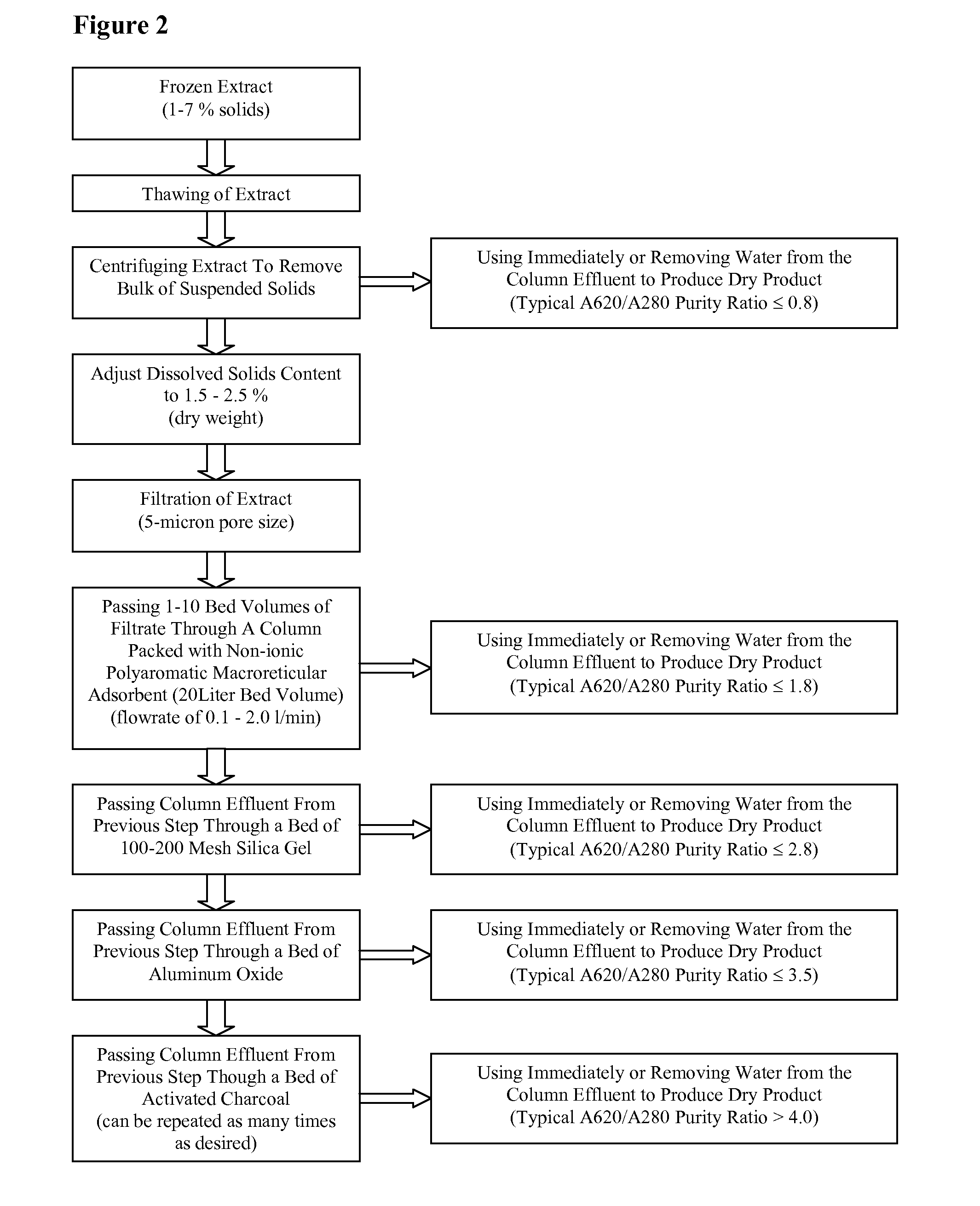
Methods for removal of microcystins and isolation of phycocyanin from cyanobacteria
This disclosure relates to methods of removing contaminating microcystins toxins from preparations of blue-green algae. It also relates to methods of purifying phycocyanin from blue-green algae extracts.
Owner:DESERT LAKE TECH
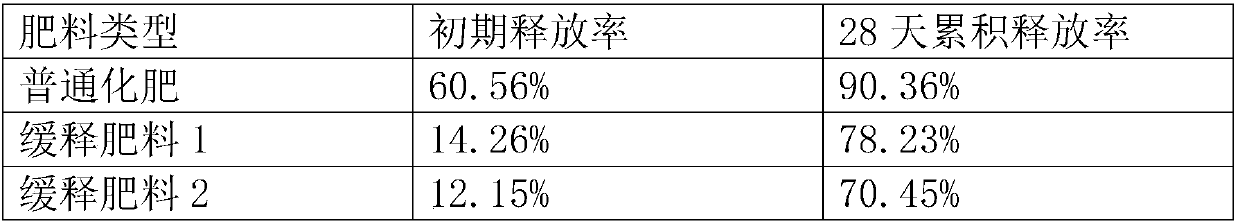
Novel algae polysaccharide derivative coated slow-release fertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107673849AGood sustained release effectReduce solubilityLayered/coated fertilisersFertilizer mixturesWater immersionAlgae
The invention discloses preparation of novel algae polysaccharide derivative coated slow-release fertilizer. A coating material of the slow-release fertilizer comprises an algae polysaccharide fatty acyl derivative and algae dreg powder generated in a production process of algae gel, wherein the algae polysaccharide fatty acyl derivative is derived from C12 to C18 fatty acyl derivatives of polysaccharides extracted from ocean brown alga, red alga and green alga. The slow-release fertilizer disclosed by the invention takes fertilizer as a core; the core is firstly covered with one layer of algae polysaccharide fatty acyl derivative thin film and the film is covered with the algae dreg powder. According to the slow-release fertilizer provided by the invention, the releasing rate of nutrientsis determined through a water immersion method; the slow-release fertilizer has good slow-release performance and the utilization rate of nutrients can be improved; the coated slow-release fertilizeris mainly applied to economic crops, fruit and vegetable crops, grain crops and the like. The coating material disclosed by the invention is mainly prepared from ocean biological polysaccharides andis easy to degrade, so that the coating material has no pollution to environment; the algae polysaccharide fatty acyl derivative also has hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties and can realize the effect of slowly releasing the fertilizer.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
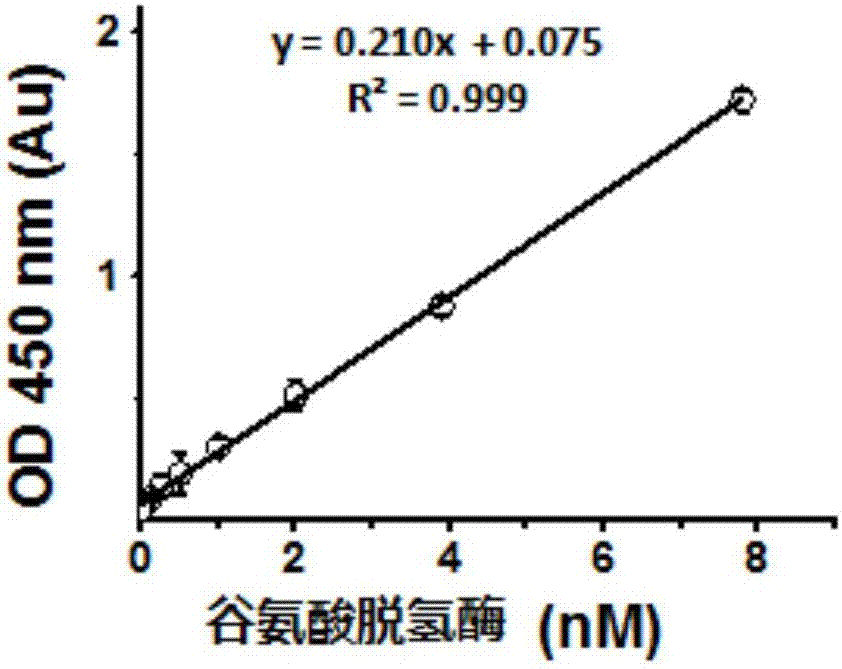
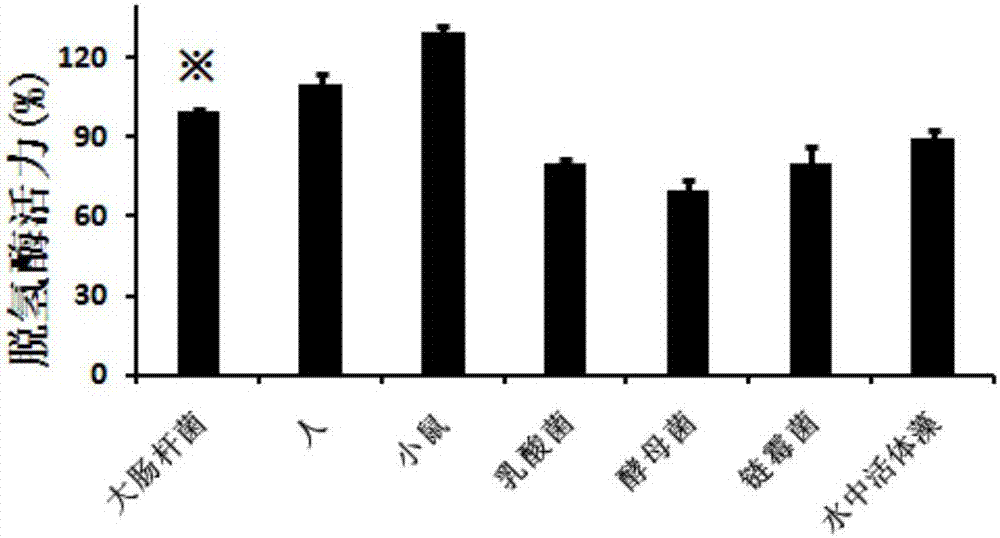
Oxidoreductase activity testing method
The invention relates to the technical field of medicine biological detection, and provides a dehydrogenase activity detection method which can monitor oxidoreductase activity in real time in accordance with color change of a novel tetrazole monosulfonate detection reagent. A tetrazole monosulfonate detection system is adopted, and a good linear dose relationship is presented in detection of dehydrogenase activity; and an EC50 curve is obtained in accordance with an absorbance value of a reactant at 450nm, and dehydrogenase activity evaluation is implemented. The dehydrogenase activity detection method provided by the invention is highly sensitive and is convenient to operate; and the detection method is broad in application range, covering dehydrogenase of various organisms, including archaebacteria (extreme thermophilic bacteria and extreme halophilic bacteria), bacteria (lactobacillus, nitrifying bacteria, escherichia coli, diplococcus pneumoniae and the like), various cellular structure bio-actinomycetes, cyanobacteria (oscillatoria, chroococcus, nostoc and the like), most unicellular algae (chlamydomonas, green algae and the like), fungi (edible fungi, saccharomycetes, mould and the like) as well as animals and plants.
Owner:HANGZHOU JENNIFER BIOTECH CO LTD
Feed additive containing compound algae and preparation process of feed additive
ActiveCN107439795AGrowth inhibitionInhibition formationAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsDiseaseNormal growth
The invention discloses a feed additive containing compound algae. The product contains brown alga saccharides, green alga saccharides as well as active substances such as yeast cell walls and chitosan. After compounding, the feed additive can effectively remove pollution of multiple mycotoxins such as aflatoxin, zearalenone, T2 toxins, vomitoxin and fumonisin in feed raw materials such as corns and grains as well as feed, thereby preventing various diseases caused by the fact that livestock and poultry eat the mycotoxin polluted feed, ensuring the animal health and improving the production benefit. The product has the advantages that (1) the harm of the mycotoxins can be comprehensively prevented; (2) all components have synergistic effects and strong detoxication effects, the desorption is difficult after detoxication, and toxins can be more thoroughly removed; (3) the detoxication efficiency is high, and the dosage is less; (4) the feed additive has strong specificity, only acts on the mycotoxins, does not adsorb nutrient elements and does not affect the normal growth of the livestock and poultry; and (5) the immune system can be enhanced, the immune functions of the livestock and poultry can be improved, and the disease resistance of the body can be enhanced.
Owner:青岛海瓴生物科技有限公司
Photosynthetic hydrogen production from the green alga chlamydomonas reinhardtii
The present invention relates generally to hydrogen production for use in fuel cells, foodstuffs and chemical production, and more particularly, to biologically and photosynthetically produced hydrogen. Specifically, disclosed is a method for producing bacteria and green alga that can produce hydrogen in quantities that exceed four hundred percent of the hydrogen produced by green alga in nature; thus, producing organisms which can serve as hydrogen generators for fuel cells, chemical production and numerous other applications.
Owner:H2OPE BIOFUELS LLC
Special puffed feed for penaeus vannamei
InactiveCN107439844AImprove stabilityIncrease feed intakeFood processingClimate change adaptationAnti stressWater quality
The present invention provides a special puffed feed for penaeus vannamei. The special puffed feed for the penaeus vannamei comprises the following components in parts by weight: 15-35 parts of fish meal, 13-24 parts of wheat flour, 3-5 parts of soybean lecithin, 16-23 parts of fermented soybean meal, 10-20 parts of green alga powder, 2-4 parts of lactic acid bacteria, 2-4 parts of mineral flour, 4-9 parts of fish dissolved pulp proteins, 1.2-2.5 parts of monocalcium phosphate, 11-24 parts of peanut meal, 8-13 parts of cottonseed proteins, 4-10 parts of shrimp shell flour, 4-8 parts of soybean oil, 0.3-0.8 part of non-starch polysaccharide enzyme and 1-3 parts of an attractant. The feed is reasonable in nutrition proportions, can effectively promote growth of the penaeus vannamei, improves immunity and anti-stress ability of the penaeus vannamei, improves a survival rate, reduces a cost of feeding, is also high in stability in water and low in feed coefficients, and can also maintain good algal facies in water body, remove ammonia nitrogen content in water and purify water quality.
Owner:兰溪市酉泽饲料技术服务有限公司
Mutagenic breeding method of high temperature resistant pasteur Du algae
InactiveCN1757707AIncrease productivityExtend the time of outdoor cultivationMicrobiological testing/measurementUnicellular algaeUltravioletCulture mediums
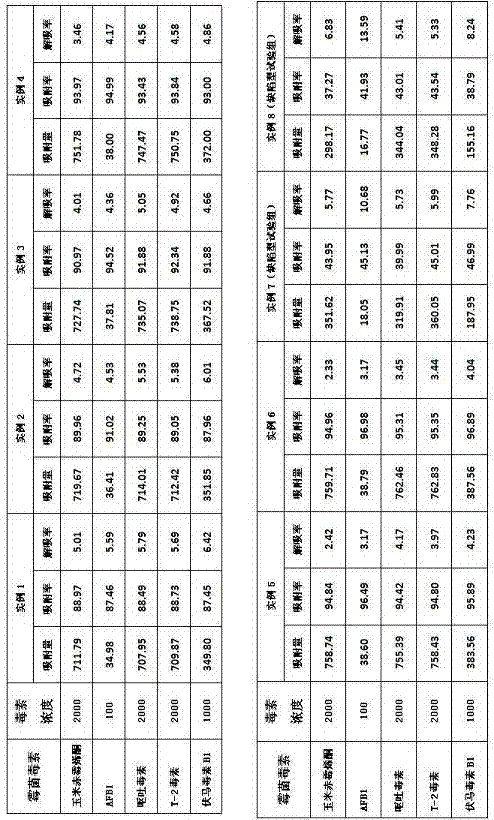
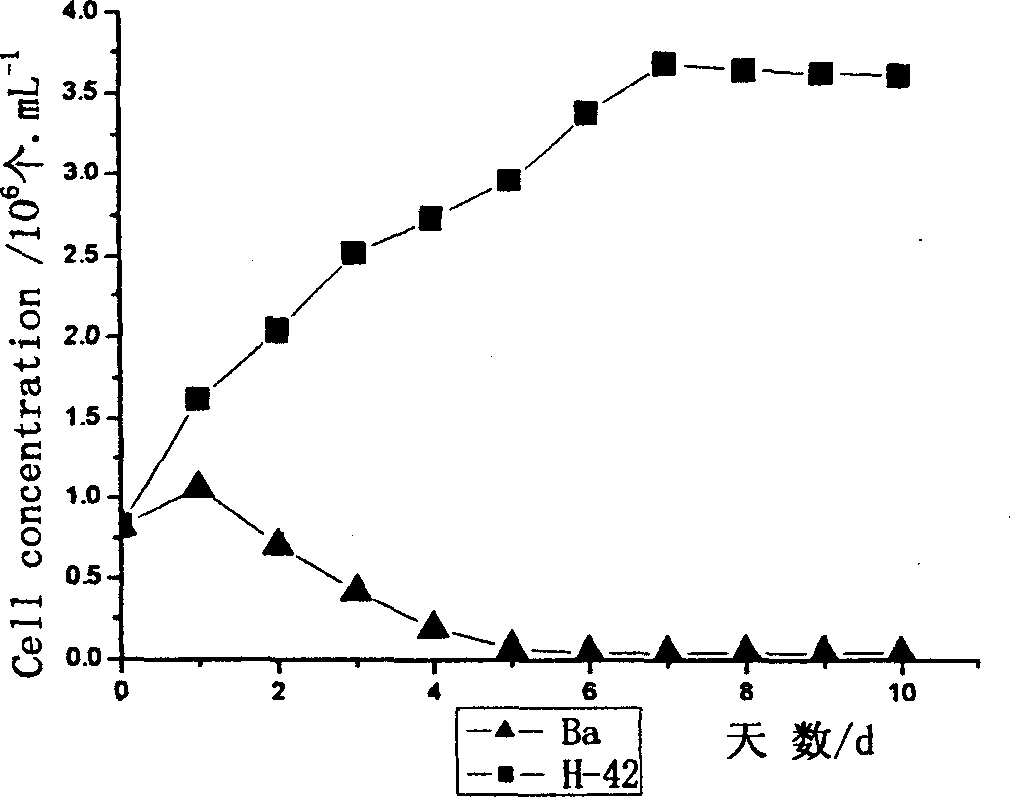
A method for mutagenizing and selectively culturing a refractory single-cell green alga includes such steps as sterilizing and cooling culture medium, inoculating alga liquid, culturing, mixing with iodine solution or bromophenol blue, deactivating, calculating alga density in alga liquid, ultraviolet mutagenizing, dark culturing, mixing the cultured alga liquid with fresh culture medium, culturing, high-temp screening, amplifying culture of living alga cells, culturing under light radiation, inoculating yellow alga, culturing, testing its mutagenized effect, measuring the long and short diameters of cell, extracting DNA, random amplifying of polymorphic DNA, calculating genetic similarity coefficient, extracting H-42 and general protein, electrophoresis, dyeing with Coomassic brilliant blue, recording result and observing the electropherogram to obtain result.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for Producing Biopterins Using Tetrahydrobiopterin Biosynthesis Enzyme
InactiveUS20090104668A1Efficient productionIncrease productionSugar derivativesBacteriaEscherichia coliBiopterin
Biopterins are useful compounds utilized in pharmaceutical agents or functional foods. The presence of sepiapterin reductase (SPR) involved in the biosynthesis of biopterins has not been confirmed so far in microorganisms except for a few microorganisms such as blue-green algae. For efficiently producing biopterins using microorganisms, it has been demanded to obtain and use SPR genes derived from microorganisms. The present inventors have found that when Saccharomyces cerevisiae or Escherichia coli is transformed with a YIR035C gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae or a yueD gene from Bacillus subtilis, the transformed microorganism secretes biopterins into a culture solution. Based on this finding, the present invention provides a polypeptide, DNA encoding the polypeptide, a recombinant vector comprising the DNA, and a transformant obtained by transformation with the vector, which are useful in biopterin production using microorganisms. Moreover, the present invention provides a method for efficiently producing biopterins using the transformant.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Method of using high-concentration organic wastewater of milk factories to cultivate green alga A. dimorphus to prepare lipids and polysaccharides
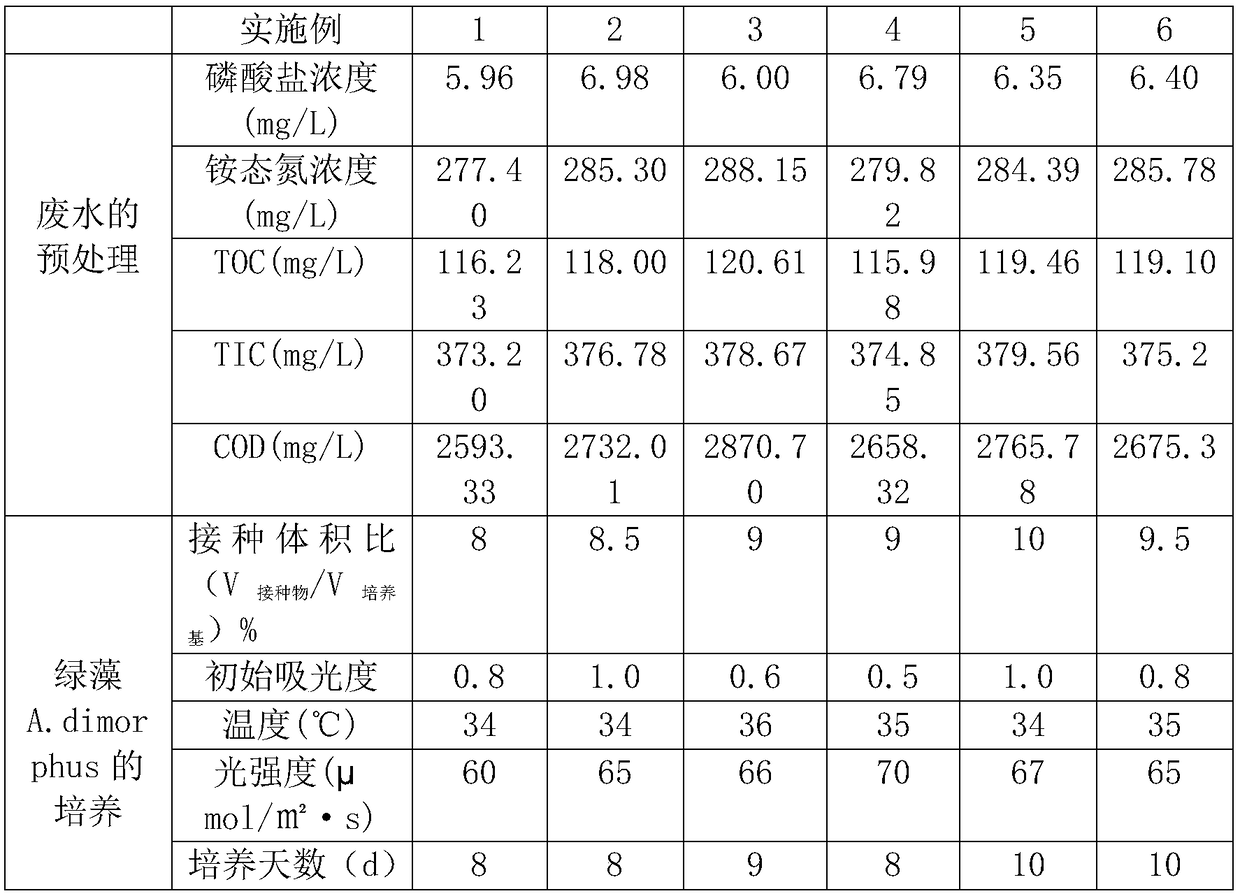
InactiveCN108624631AEliminate distractionsSimple cultivation conditionsBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesLipid formationHigh concentration
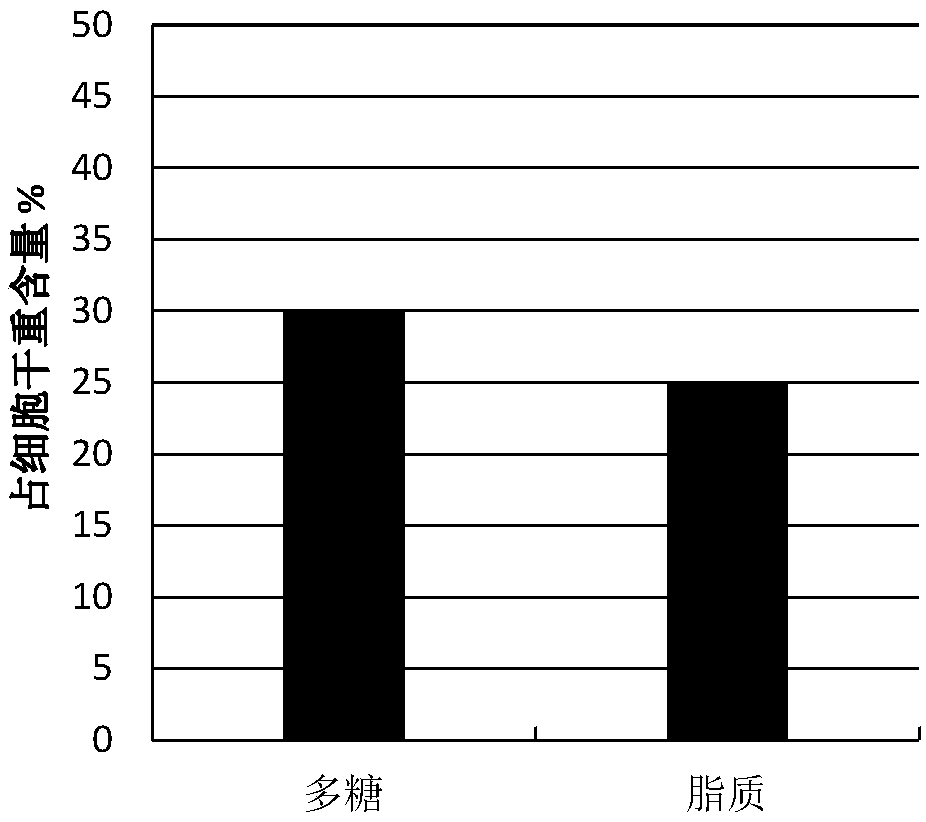
The invention discloses a method of using high-concentration organic wastewater of milk factories to cultivate the green alga A. dimorphus to prepare lipids and polysaccharides. The method comprises the main steps of 1) pretreating wastewater; 2) cultivating the green alga A. dimorphus; 3) measuring lipid content in the green alga A. dimorphus; 4) measuring polysaccharide content in A. dimorphus.The method herein helps reduce the treatment cost of DWW (dairy wastewater) and produce high-value chemicals. The green alga A. dimorphus cultivated herein has about 25% of lipids and about 30% of polysaccharides, which may be further converted into biodiesel and bio-alcohol.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Seaweed flavor enhancer and making method thereof
InactiveCN105231152ARich tasteGood for healthFood ingredient as taste affecting agentFood preparationMushroomYeast extract
The invention belongs to a seaweed flavor enhancer. The seaweed flavor enhancer is characterized by comprising the following components in parts by weight: 15-40 parts of edible salt, 5-15 parts of soft white sugar, 15-40 parts of gourmet powder, 5-10 parts of glucose, 5-10 parts of lactose, 5-10 parts of corn starch, 5-10 parts of maltodextrin, 1-5 parts of I+G, 1-3 parts of a yeast extract, 0.5-2 parts of skipjack powder, 1-3 parts of mushroom powder, 0.5-3 parts of green alga powder and 5-15 parts of water. The seaweed flavor enhancer disclosed by the invention is compound in mouth feel, mainly consists of three taste systems of palatable taste, seaweed taste and spicy taste, and is high in nutrient value, simple in making technology and rich in raw material resources.
Owner:大连雅特盐业有限公司
Closed zero-emission factory-based aquaculture method for penaeus vannamei
InactiveCN108522381AAvoid Poor Water ColorPromote growthWater treatment parameter controlWater contaminantsDiseaseTurbidity
The invention relates to a closed zero-emission factory-based aquaculture method for penaeus vannamei. Before shrimp seeds are put into a culture water body, the salinity, pH, total alkalinity and total hardness are of the culture water body adjusted to required ranges, denitrification type biological floc specie, and then the shrimp seeds are put into the culture water body for management. Penaeus vannamei cultured by the method grows well, and the culture problems of poor color caused by imbalance of carbon and nitrogen, long-term standard exceeding of ammonia nitrogen and nitrite, a high pHvalue or sharp changes, breeding of blue-green algae, parasitic infestation, long-term turbidity of water bodies, serious pollution, frequent diseases and the like are avoided.
Owner:广州普麟生物制品有限公司 +1
Productivity and Bioproduct Formation in Phototropin Knock/Out Mutants in Microalgae
ActiveUS20180187170A1Reduced PHOT expressionHigh genetic stabilityHydrolasesUnicellular algaeElectron micrographsChlamydomonas reinhardtii
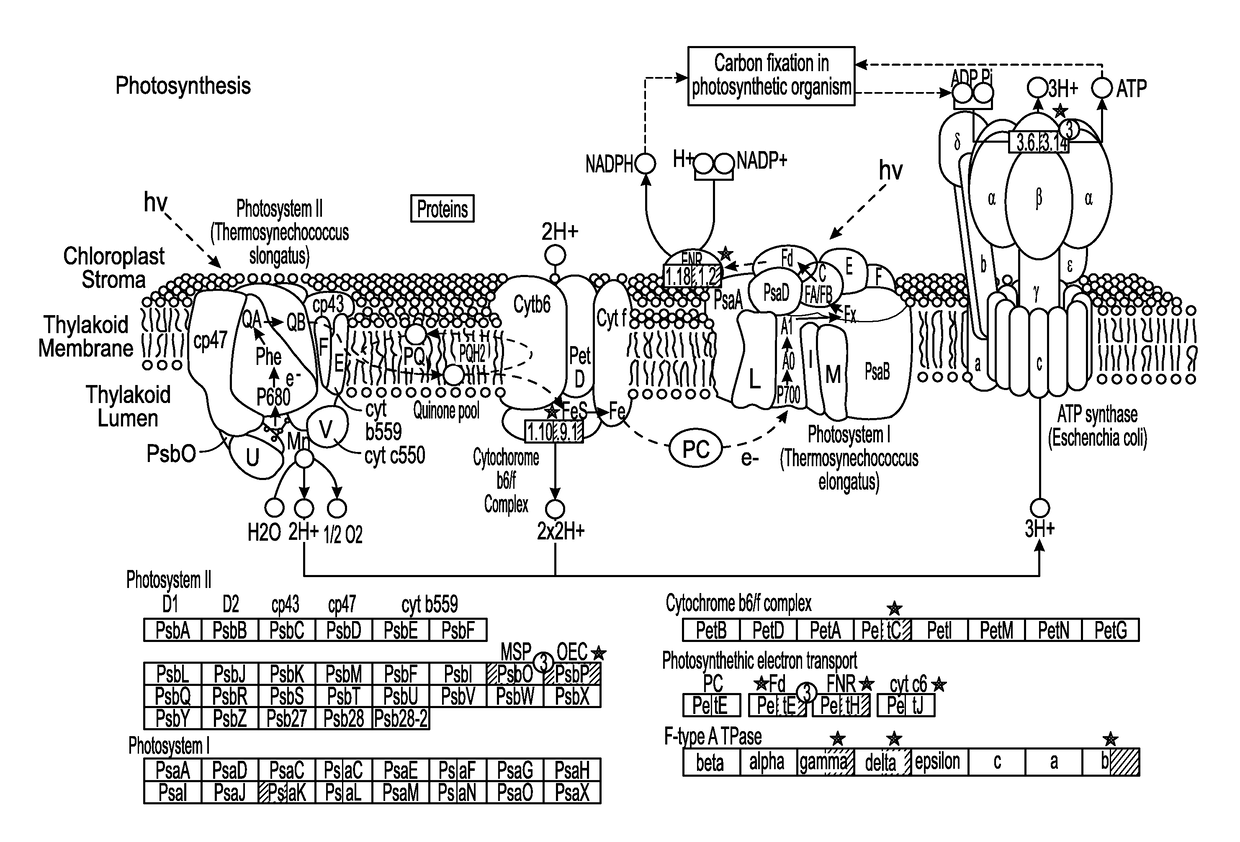
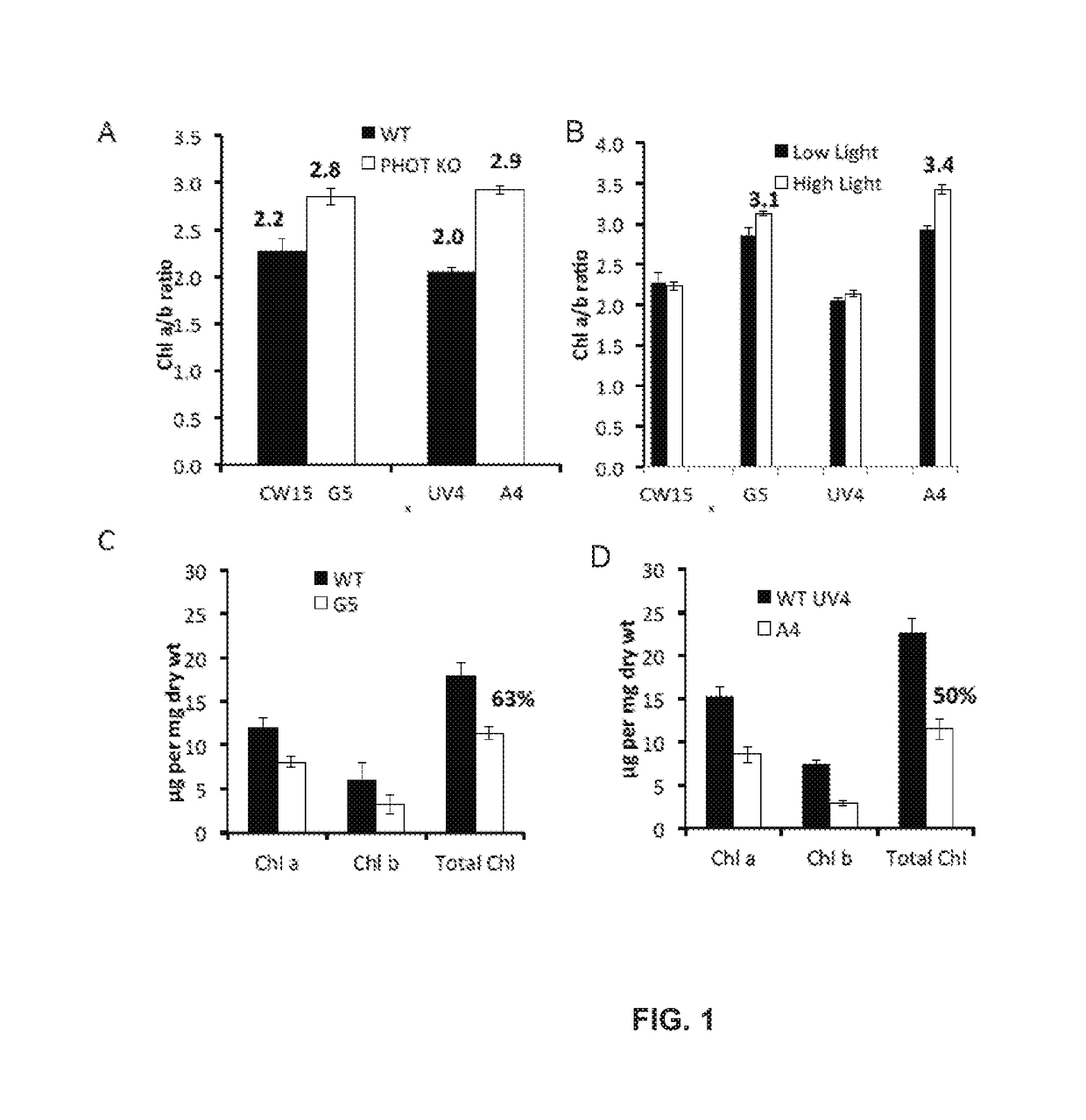
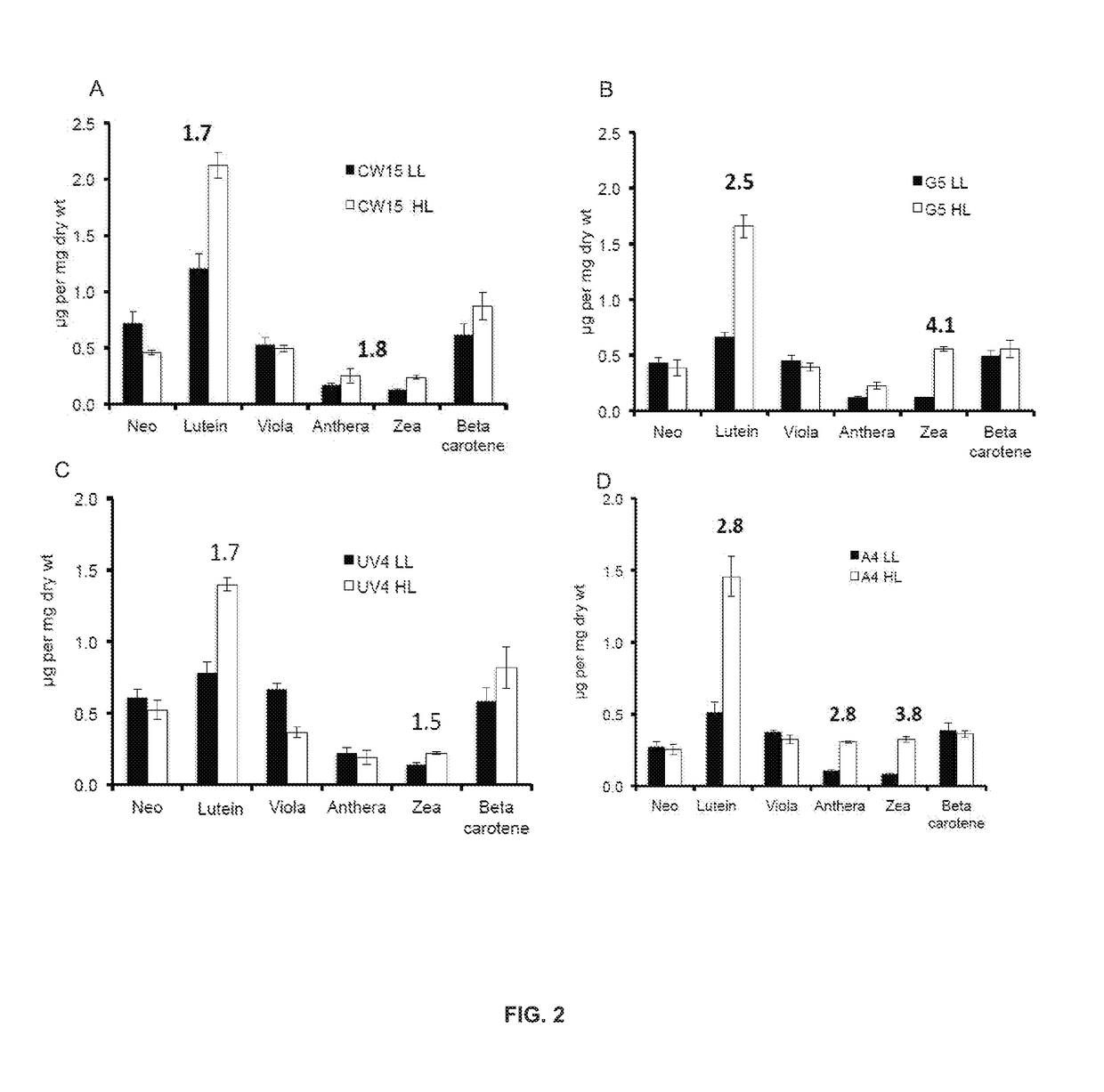
Phototropin is a blue light receptor, which mediates a variety of blue-light elicited physiological processes in plants and algae. In higher plants these processes include phototropism, chloroplast movement and stomatal opening. In the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, phototropin plays a vital role in progression of the sexual life cycle and in the control of the eye spot size and light sensitivity Phototropin is also involved in blue-light mediated changes in the synthesis of chlorophylls, carotenoids, chlorophyll binding proteins. We compared the transcriptome of phototropin knock out (PHOT KO) mutant and wild-type parent to analyze differences in gene expression in high light grown cultures (500 μmol photons m−2 s−1). Our results indicate the up-regulation of genes involved in photosynthetic electron transport chain, carbon fixation pathway, starch, lipid, and cell cycle control genes. With respect to photosynthetic electron transport genes, genes encoding proteins of the cytochrome b6f and ATP synthase complex were up regulated potentially facilitating proton-coupled electron transfer. In addition genes involved in limiting steps in the Calvin cycle Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase / oxygenase (RuBisCO), Sidoheptulose 1,7 bisphosphatase (SBPase), Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (3PGDH) and that mediate cell-cycle control (CDK) were also up regulated along with starch synthase and fatty acid biosynthesis genes involved in starch and lipid synthesis. In addition, transmission electron micrographs show increased accumulation of starch granules in PHOT mutant compared to wild type, which is consistent with the higher expression of starch synthase genes. Collectively, the altered patterns of gene expression in the PHOT mutants were associated with a two-fold increase in growth and biomass accumulation compared to wild type when grown in environmental photobioreactors (Phenometrics) that simulate a pond environment. In conclusion, our studies suggest that phototropin may be a master gene regulator that suppresses rapid cell growth and promotes gametogenesis and sexual recombination in wild type strains.
Owner:NMC INC +1
Chlorella extractive composition and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a chlorella extractive and a preparation method thereof. The chlorella extractive includes an active peptide and an inhibitory nerve transmitter, can effectively inhibit the activity of an angiotension I-converting enzyme and can be further used for developing a composition for adjusting the physiological effect of blood pressure.
Owner:TAIWAN CHLORELLA MFG
An agent for promoting the growth of, and/or suppressing a decrease in, bifidobacterium bacteria and/or lactic acid bacteria
InactiveUS20180369298A1Promote growthSuppressing decreasePowder deliveryBacteriaBacteroidesBifidobacterium
To provide a technology capable of promoting growth of Bifidobacterium bacteria and lactic acid bacteria under an environment causing the growth or no change in cell count while suppressing decrease under an environment causing the decrease. Provided is an agent for promoting the growth of, and / or suppressing a decrease in, Bifidobacterium bacteria and / or lactic acid bacteria containing Arthrospira blue-green algae and / or Spirulina blue-green algae as an active ingredient. Also provided is an oral composition including Arthrospira blue-green algae and / or Spirulina blue-green algae together with at least one type of bacteria selected from the group consisting of Bifidobacterium bacteria and lactic acid bacteria. Furthermore provided is a method for promoting growth of Bifidobacterium bacteria and / or lactic acid bacteria and / or suppressing the decrease including a step for allowing at least one type of bacteria selected from the group consisting of Bifidobacterium bacteria and lactic acid bacteria to coexist with Arthrospira blue-green algae and / or Spirulina blue-green algae.
Owner:MORINAGA MILK IND CO LTD
Method for expressing exogenesis genes by using hainan rubber algae
InactiveCN101139552AIncrease productionImprove economyUnicellular algaeOther foreign material introduction processesOrganismAlgae
The invention discloses a method for representing alien gene, wherein, a single-cell green alga (Heveochlorella hainangensis Zhang) symbiotic with rubber trees is used to represent alien gene, the procedures include pre treating Heveochlorella hainangensis Zhang, heredity transforming, culturing and sieving after transformation. The method provides a technical means for biologically synthesizing relative gene and for synthesizing jasmine acid through representing the jasmine acid by Heveochlorella hainangensis Zhang so as to improve the latex output of rubber trees, and is of high economy value and social development prospect.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Subsurface wetland with effluent N/P suitable for culturing non-toxic green alga
ActiveCN104140161APromote growthPrevent proliferationSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentEutrophicationSlag
The invention relates to a subsurface wetland with effluent N / P suitable for culturing non-toxic green alga. The subsurface wetland comprises a treating pond, wherein a water inlet and a water outlet are respectively formed in front and rear parts of the treating pond; the inside of the treating pond comprises a wetland plant layer, a soil layer and a packing medium layer from top to bottom sequentially; the packing medium layer is divided into a front treatment zone, an intermediate treatment zone and a rear treatment zone according to the water current direction; and the front, intermediate and rear treatment zones respectively contain zeolite and steel slag in different proportions. Compared with the prior art, the subsurface wetland has the advantages that wastewater which is substandard after secondary treatment is subjected to oriented deep treatment; the structure is simple, blockage is prevented and management is convenient; the total nitrogen concentration of effluent is 8-12mg / L, the total phosphorous concentration is 0.4-0.5mg / L, and N / P is 20-30. The water quality of treated water is beneficial to control of eutrophication of receiving water from the source and has a certain economic value by means of ecological reclamation; moreover, after the secondary treated wastewater is further treated by virtue of the subsurface wetland, COD is further reduced.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com