Methods for removal of microcystins and isolation of phycocyanin from cyanobacteria
a technology of phycocyanin and microcystin, which is applied in the direction of peptides, chemical/physical processes, water/sewage treatment by ion exchange, etc., can solve the problems of inability to produce large-scale quantities of this beneficial protein, and the method does not remove any microcystins that may already be present in the water
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Removal of Microcystins Contamination from a Blue-Green Algae Preparation
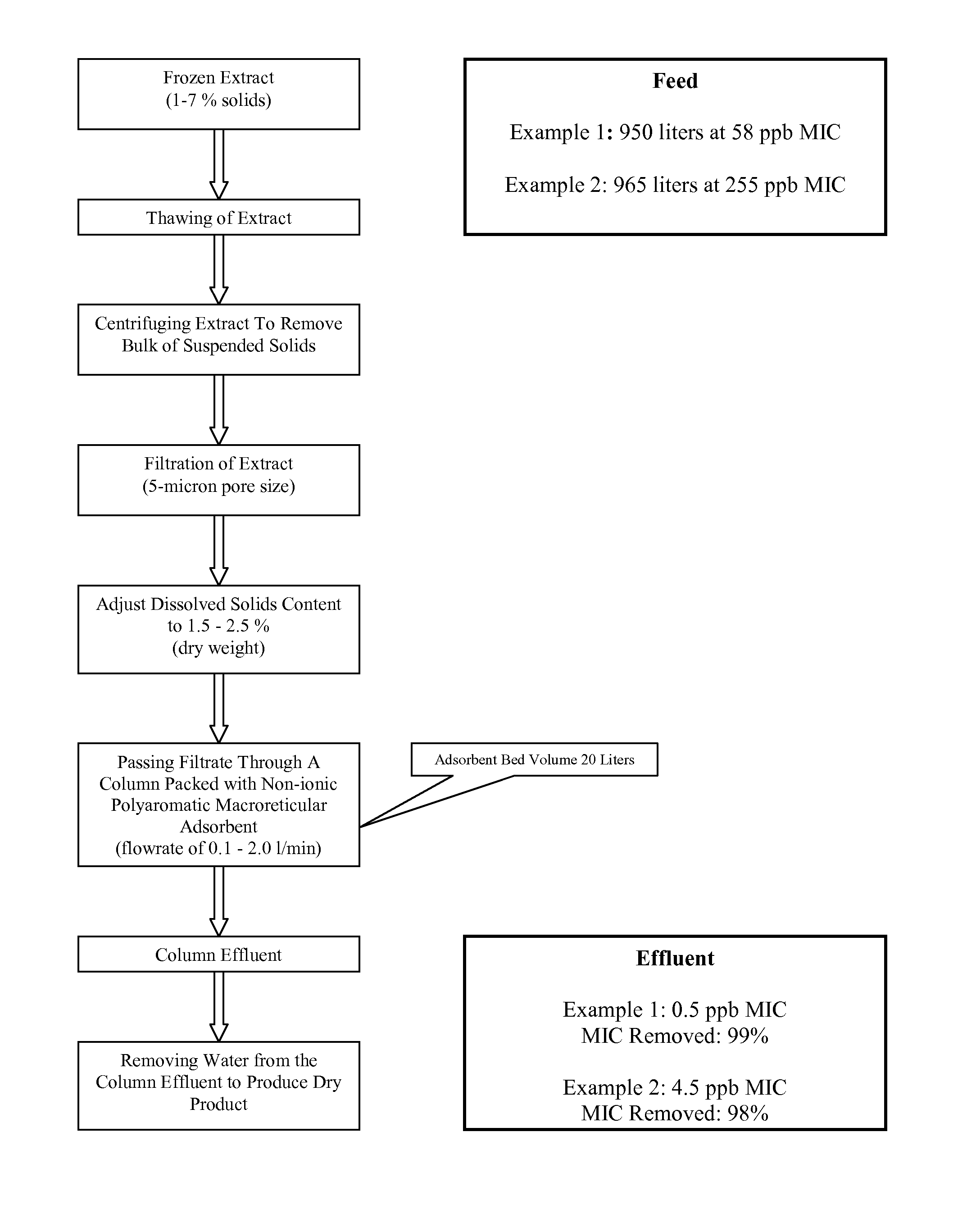
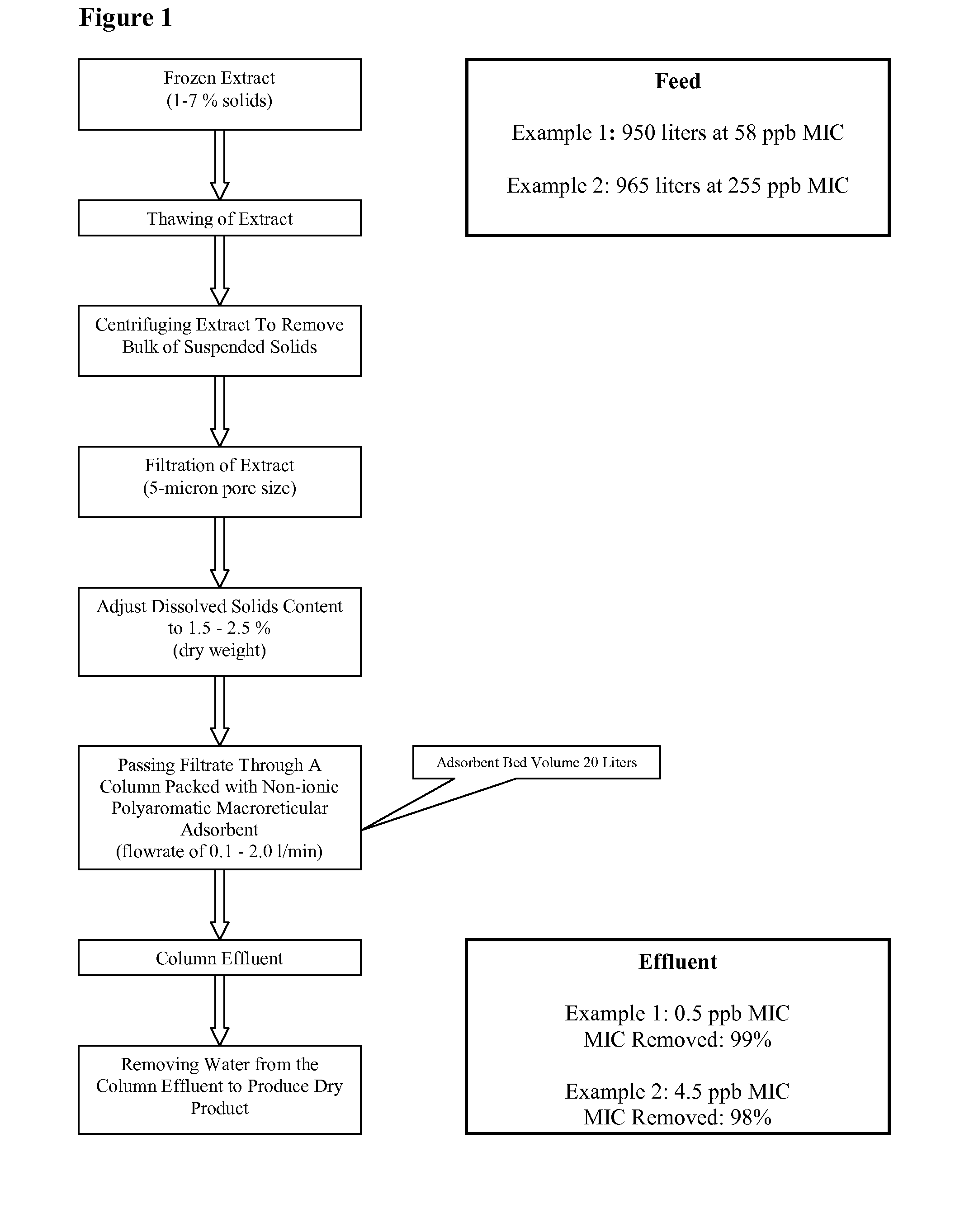
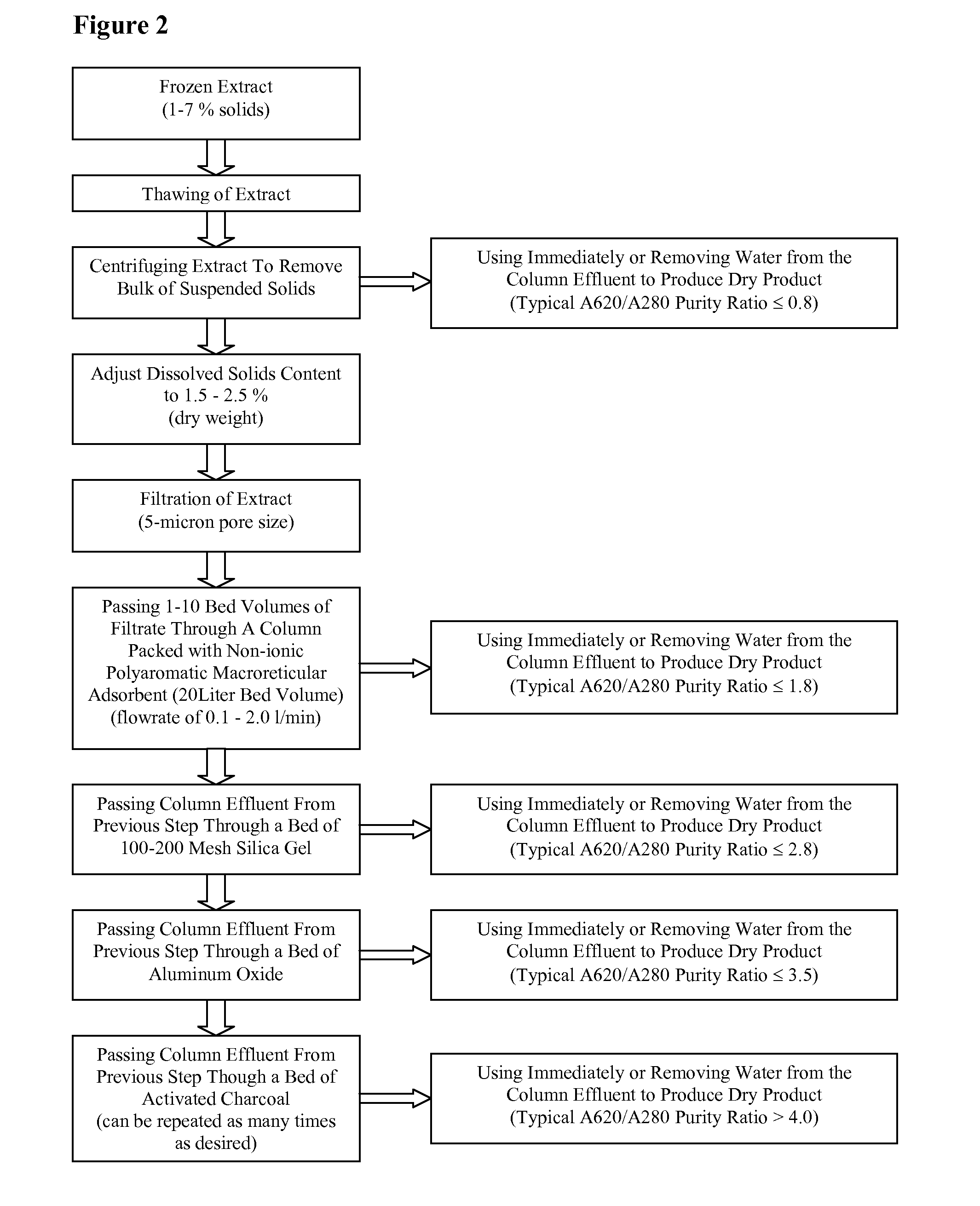
[0093]This example demonstrates the method of removing microcystins contamination from freshly-harvested AFA. This embodiment of the method is illustrated in FIG. 1.
1) AFA Preparation.
[0094]Freshly harvested AFA was collected in a 250 gallon plastic tote and frozen. The amount of algae collected was 1-5% dry weight, and was visibly contaminated with Microcystis aeruginosa. The contents of the tote were thawed to lyse the algal cells and release the water-soluble cellular constituents (such as phycocyanin and microcystin LR) into the aqueous extract. The suspended solids in the lysed cell mixture were removed by centrifugation, and the dissolved solid content of the supernatant was adjusted to 1.5-2.5% (dry weight) by either adding water or removing water by reverse osmosis.
2) Microcystin Removal.
[0095]AMBERLITE® FPX66 food grade adsorbent resin (Rohm and Hass) was packed into a column with a 20 liter bed volu...
example 2
Scaled-Up Removal of Microcystins Contamination from a Blue-Green Algae Preparation
[0097]This example illustrates a scaled-up method of removing microcystins contamination from a preparation of blue-green algae.
[0098]Removal of microcystins contamination from AFA can be scaled up to increase the amount of harvested cells that can be processed through a single column packed with a resin such as AMBERLITE FPX66. Cells are processed as in Example 1, except multiple plastic totes (for example, three) are processed simultaneously. Following removal of cellular debris, the supernatant of three totes is channeled into the column for microcystin removal. The post-column concentration of microcystins in the AFA preparation is measured by ELISA as in Example 2.
example 3
Removal of Microcystins Contamination from Water
[0099]The presence of Microcystis algae in sources of drinking water, and the resultant contamination of those sources with microcystins, is a global public health problem. The methods disclosed herein of removing microcystins from a blue-green algae preparation can also be applied in the context of removing microcystins contamination from any contaminated aqueous solution, including sources of drinking water. This example illustrates the removal of microcystins contamination from any water sample.
[0100]Removal of microcystins from contaminated water was achieved by the same method described in Example 1, except that the water does not need to be frozen prior to processing. In examples where the water contains few suspended solids, it is also not necessary to centrifuge the sample to be purified. Using the method described in Example 1, two liters of microcystins-contaminated water containing 0.25 ppm microcystin LR were passed through...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com