Method for improving hydrogen production quantity of photosynthetic microalgae through phycomycetes co-culture
A technology of co-cultivation and algal bacteria, which is applied in the field of new energy and biological hydrogen production, can solve the problems of high cultivation cost, multiple equipment, and high equipment cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] 1. Cultivation of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
[0047] A. Select Chlamydomonas reinhardtii species, from the Yellow Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences;
[0048] B. Cultivate Chlamydomonas reinhardtii:
[0049] (a) Liquid culture conditions of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: using Tris-Acetate-Phosphate medium (hereinafter referred to as TAP, the formula is shown in Table 1), initial pH 7.2, light intensity level four, and culture temperature 25±1℃, When in liquid culture, it can be cultured statically or placed on a horizontal shaking shaker at 100-120 rpm, and passaged every 5 days.
[0050] (b) Chlamydomonas reinhardtii solid TAP medium: Pour the TAP medium containing 1.5% to 2% agar powder to the plate, streak the plate with an inoculation needle for cultivation, and subculture once every 2 weeks;
[0051] C. Chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production medium: Chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production medium uses TAP-S (TAP sulfur-deficient m...
Embodiment 2
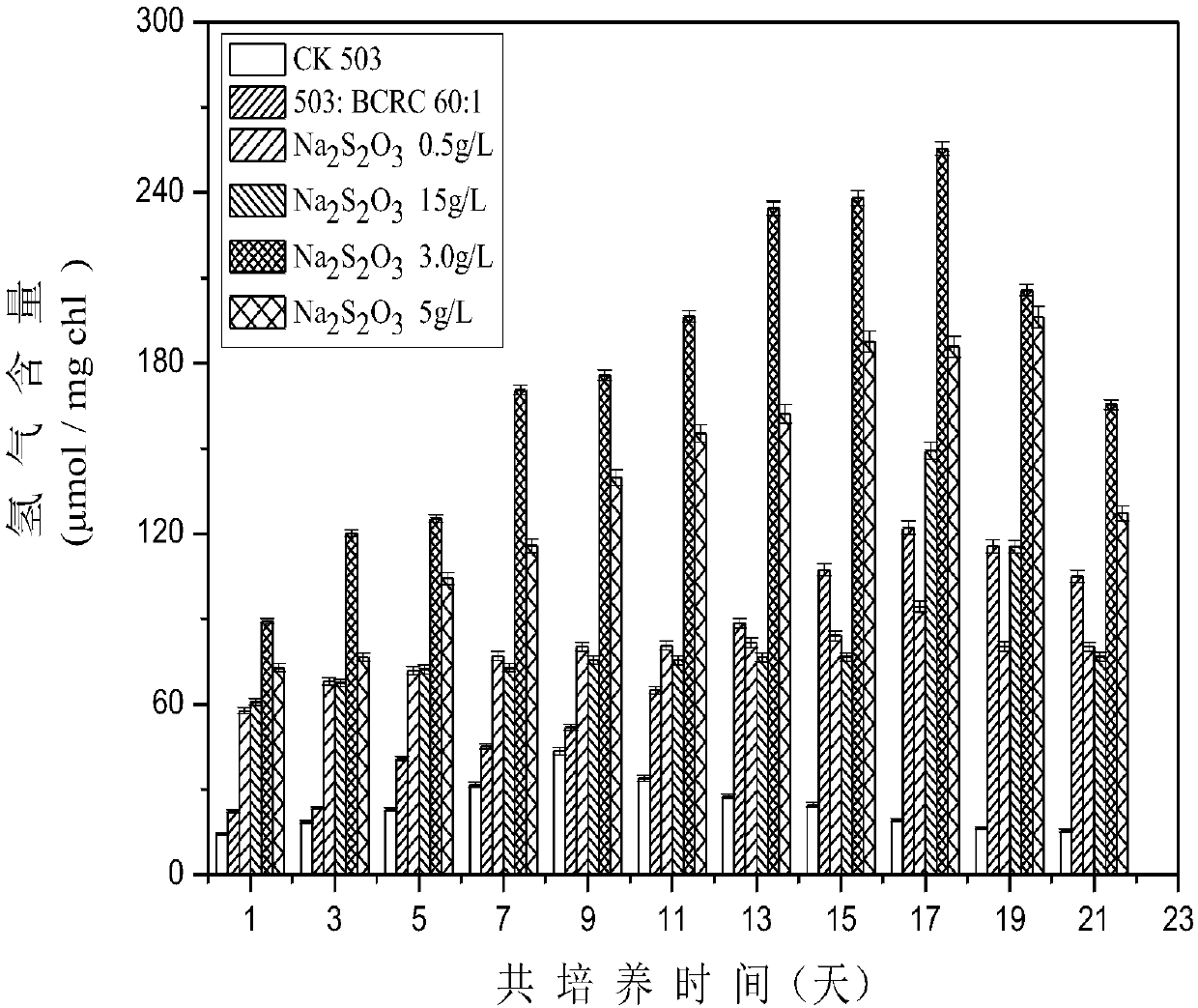
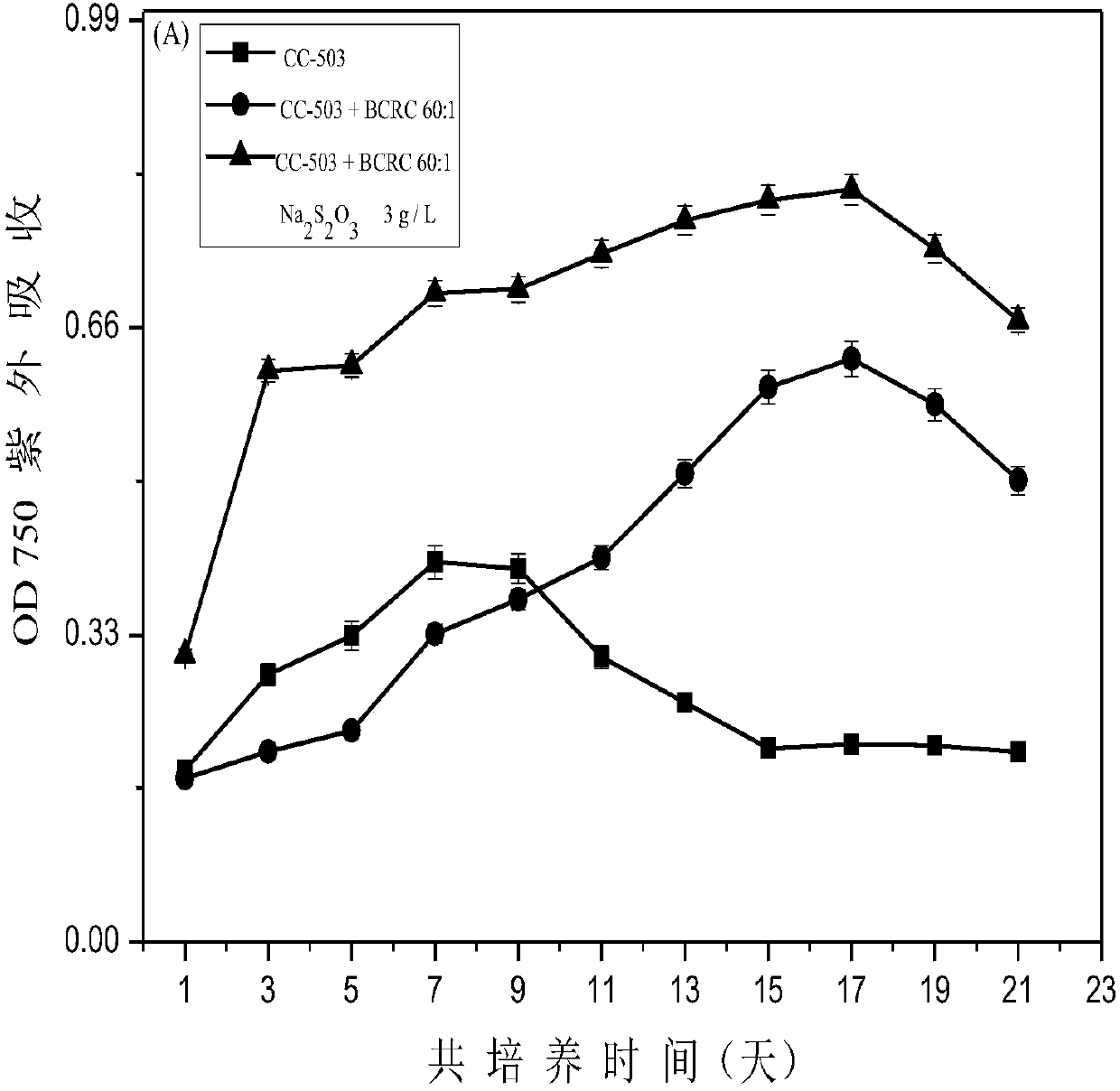
[0115] Method for co-cultivating sulfur oxidizing bacteria and chlorella
[0116] A. Co-cultivation method in TAP medium
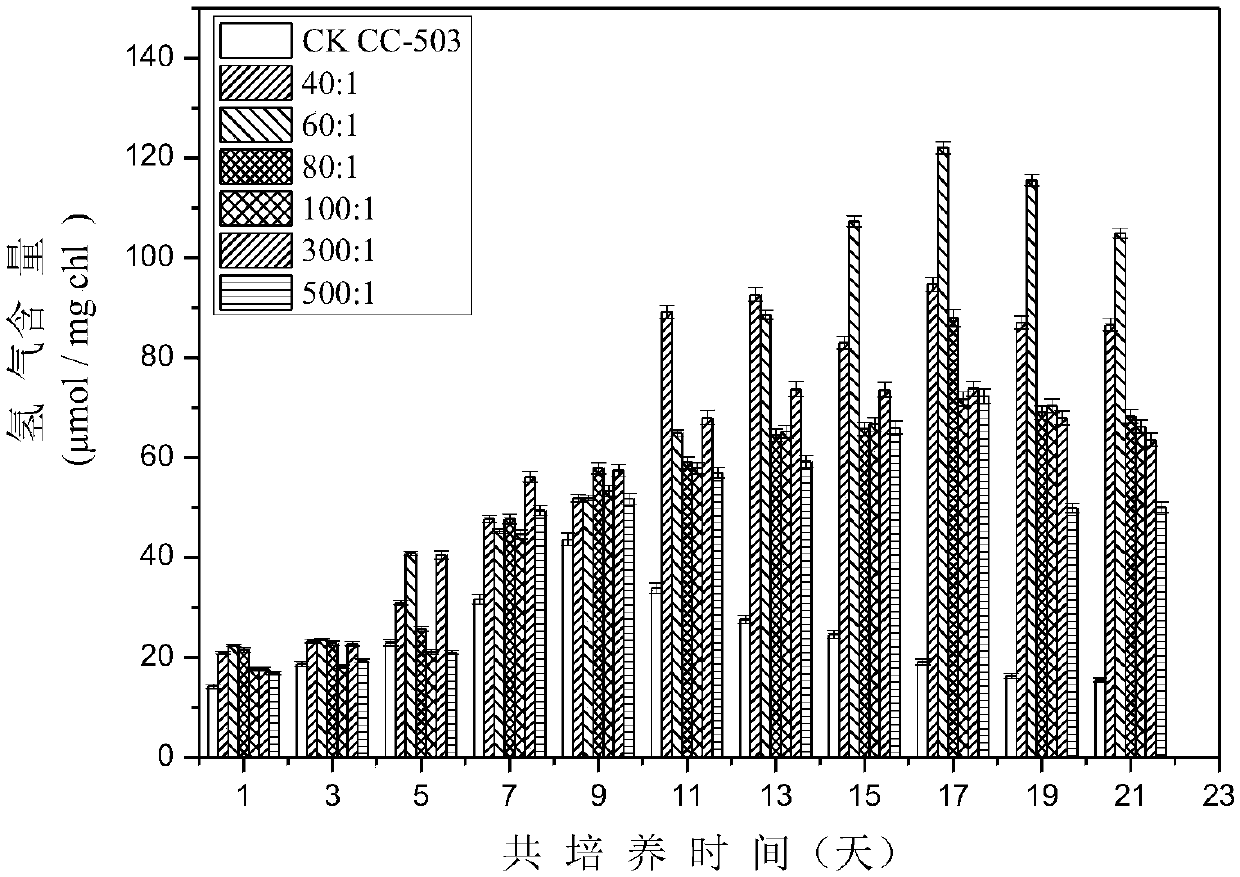
[0117] Firstly, the chlorella was cultured in the TAP medium to the mid to late log phase, and then the algae was centrifuged at 5000 rpm for 5 min in a centrifuge, and washed with fresh medium for 3 times. The sulfur oxidizing bacteria that grow to the logarithmic phase are first washed three times with TAP medium, and the original medium 688 is removed, and then resuspended in TAP medium to adjust the OD 600 = 1.0. Chlorella (chlorophyll = 0.5mg / L) and sulfur oxidizing bacteria were transferred to hydrogen-producing culture flasks according to 20:1, 40:1, 60:1, 80:1, and 100:1. Each group was set with 3 controls. In addition, sulfur oxidizing bacteria and chlorella were separately set as controls. Finally, put all hydrogen production bottles at 25±1℃, dark treatment for 24h to deplete the original sulfur element, after dark treatment, set the light incubato...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com