Method for treating glucosamine processing wastewater by utilizing fungus and microalgae symbiotic system
A technology for processing wastewater and algae-bacteria symbiosis, applied in microorganism-based methods, methods using spores, biological water/sewage treatment, etc. The effect of secondary pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
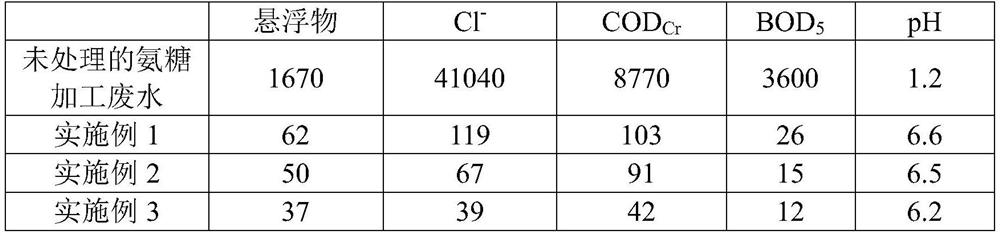
[0041] A method for utilizing a fungal-microalgae symbiotic system to process wastewater from glucosamine processing, comprising the following steps:
[0042] (1) Microalgae pre-culture: Euglena gracilis var. saccharophila was cultured in a 2000ml shake flask with 200ml of Hunter medium three months before use, so that the total number of Euglena gracilis var. saccharophila cells was 1×10 9 100ml of glucosamine processing wastewater was added to the culture system every two weeks. When the volume of the culture solution reached 600ml, all the culture solution was transferred to 10L In the large-mouth glass jar container, add ammonia sugar processing wastewater to the mark, and culture it for 3 days in an outdoor sealed and ventilated container to obtain algal cells;
[0043] (2) Fungal pre-culture: Aspergillus niger and Mucor hiemalis were inoculated into G-YPD medium three months before use, cultured at room temperature for 8 days, and then transferred to a new G-YPD culture ...
Embodiment 2
[0048] A method for utilizing a fungal-microalgae symbiotic system to process wastewater from glucosamine processing, comprising the following steps:
[0049] (1) microalgae pre-cultivation: with embodiment 1;
[0050] (2) Fungal pre-culture: Aspergillus niger and Mucor hiemalis were inoculated into G-YPD medium three months before use, cultured at room temperature for 9 days, and then transferred to a new G-YPD culture In the base, the nutrient components of the original YPD medium are reduced by 20% for each transfer, until the final plate medium contains only two components of glucosamine processing wastewater and agar, and finally the two fungi are collected using sterile 0.05% Tween solution. spore;
[0051] (3) Construct algae-bacteria symbiosis system: inject the slagging and primary precipitation ammonia sugar processing wastewater into the open reaction tank, put the two kinds of fungal spores obtained in step (2) into the ammonia sugar processing wastewater, and thr...
Embodiment 3
[0055] A method for utilizing a fungal-microalgae symbiotic system to process wastewater from glucosamine processing, comprising the following steps:
[0056] (1) microalgae pre-cultivation: with embodiment 1;
[0057](2) Fungal pre-culture: Aspergillus niger and Mucor hiemalis were inoculated into G-YPD medium three months before use, cultured at room temperature for 7 days, and then transferred to a new G-YPD culture In the base, the nutrient components of the original YPD medium are reduced by 20% for each transfer, until the final plate medium contains only two components of glucosamine processing wastewater and agar, and finally the two fungi are collected by using sterile 0.05% Tween solution. spore;
[0058] (3) Construct an algae-bacteria symbiosis system: inject the slagging and primary precipitation ammonia sugar processing wastewater into the open reaction tank, and put the two kinds of fungal spores obtained in step (2) into the ammonia sugar processing wastewater...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com