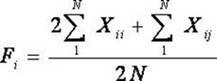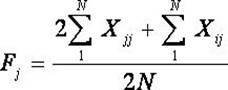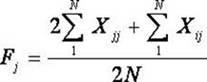Patents
Literature
57 results about "Electropherogram" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
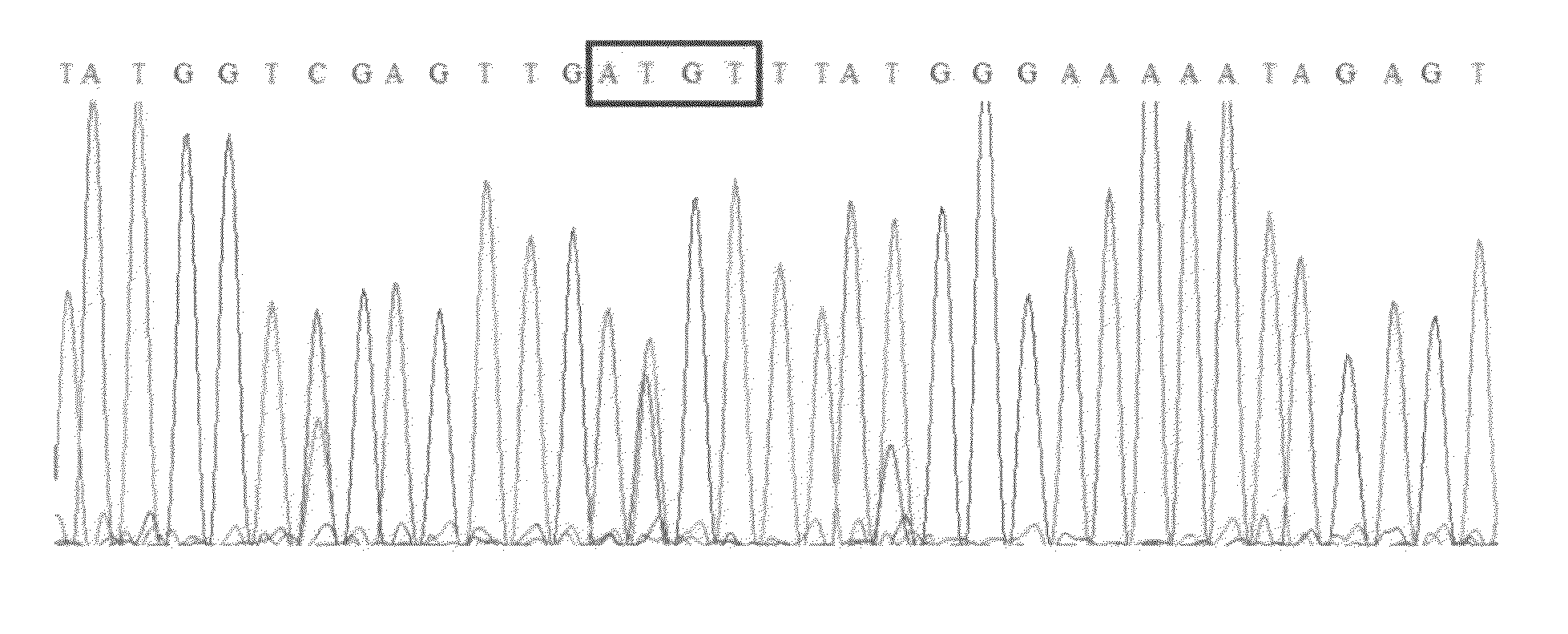
An electropherogram (or electrophorogram) is a record or chart produced when electrophoresis is used in an analytical technique, primarily in the fields of molecular biology or biochemistry. In the field of genetics, an electropherogram is a plot of DNA fragment sizes, typically used for genotyping such as DNA sequencing. Such plots are often achieved using an instrument such as an automated DNA sequencer. Such electropherograms may be used to determine DNA sequence genotypes, or genotypes that are based on the length of specific DNA fragments.
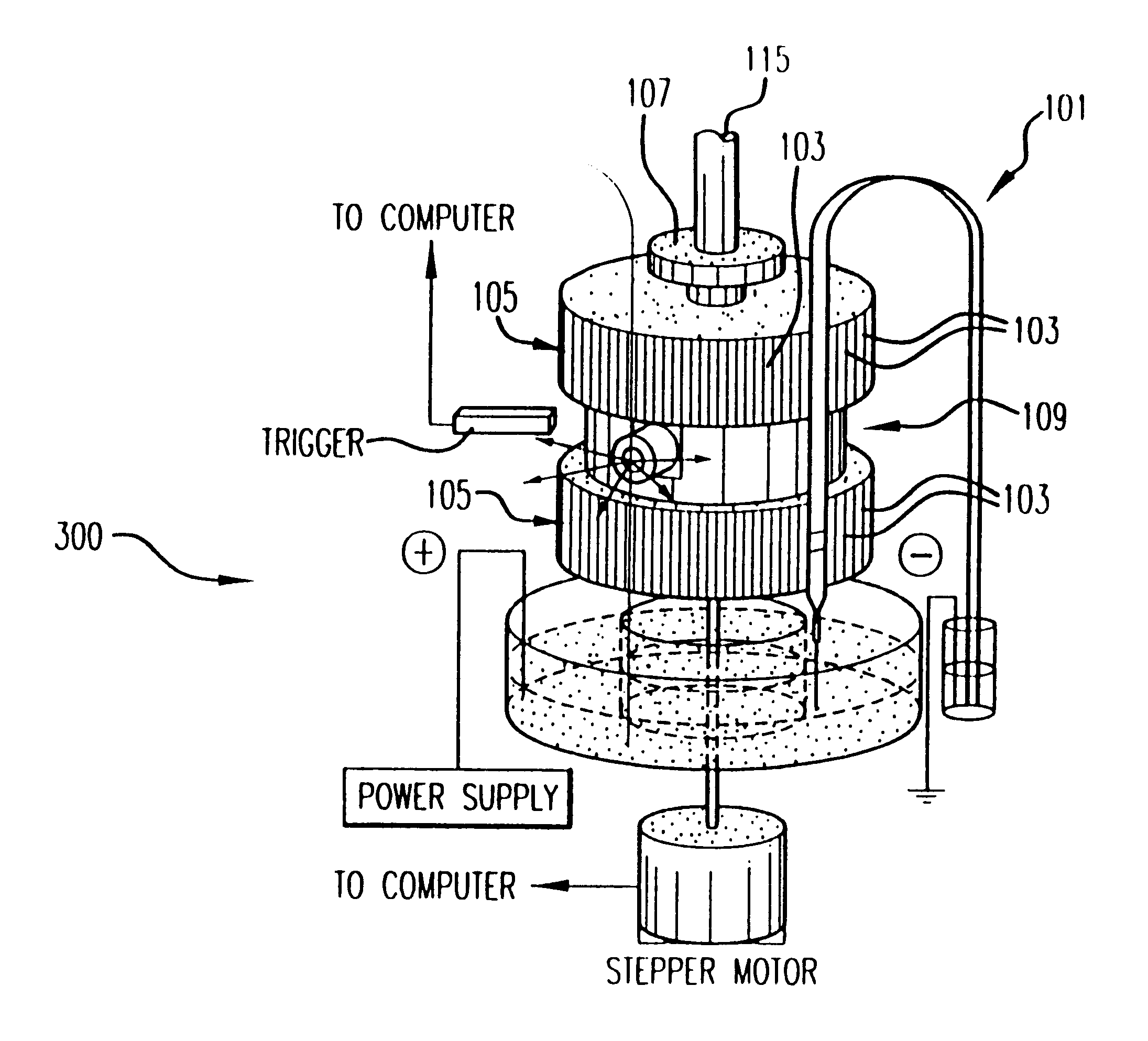
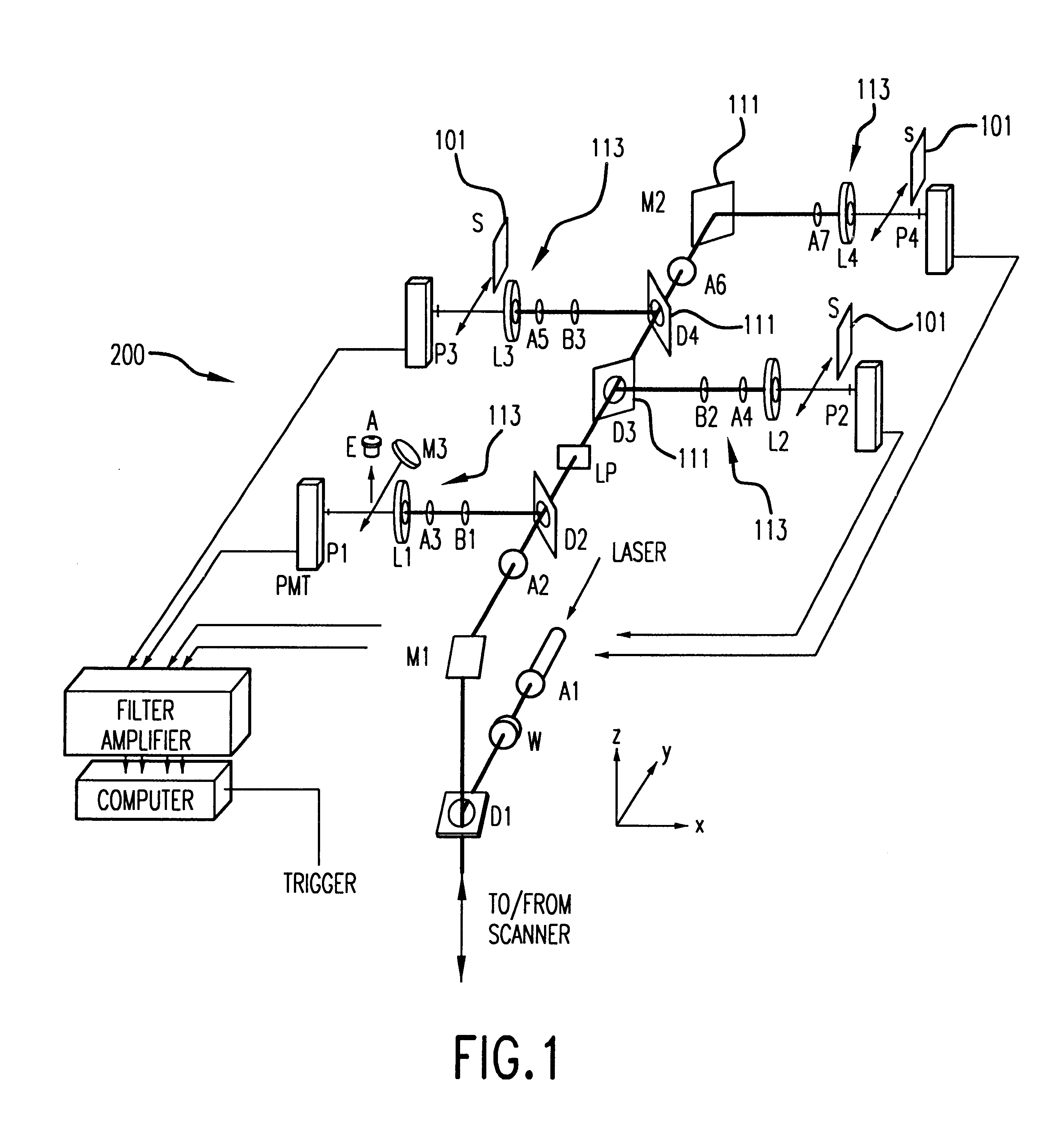
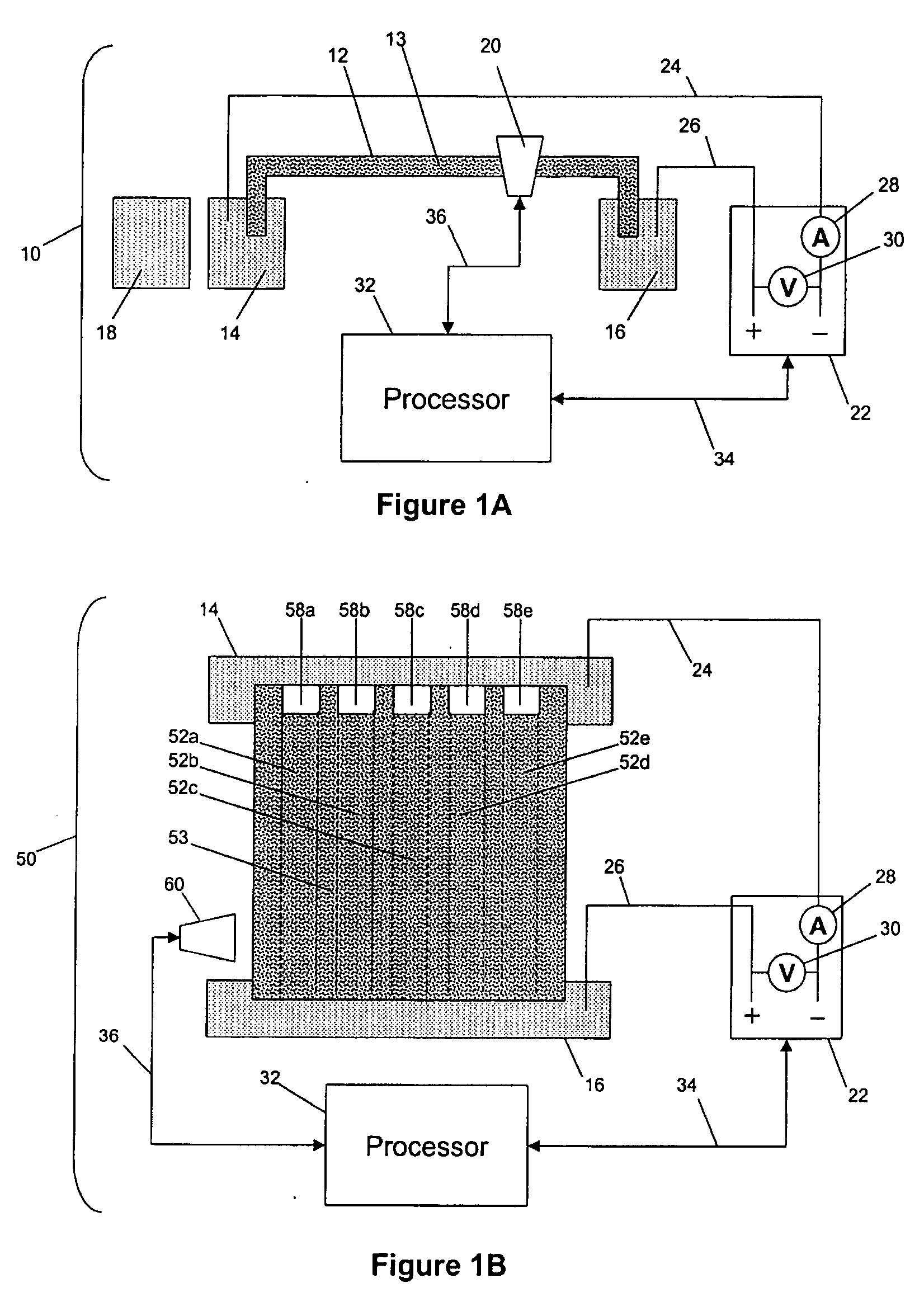
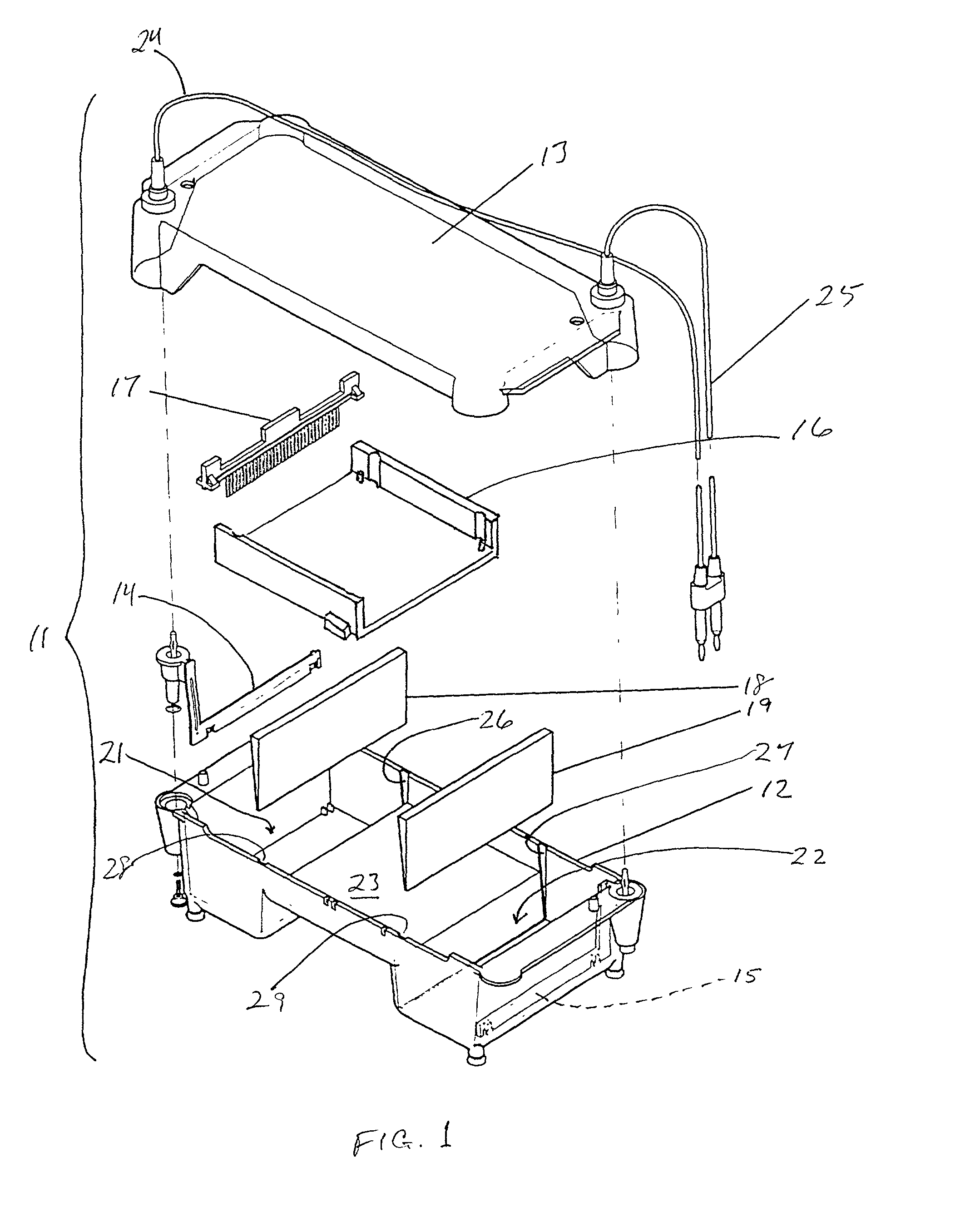
Capillary array electrophoresis scanner
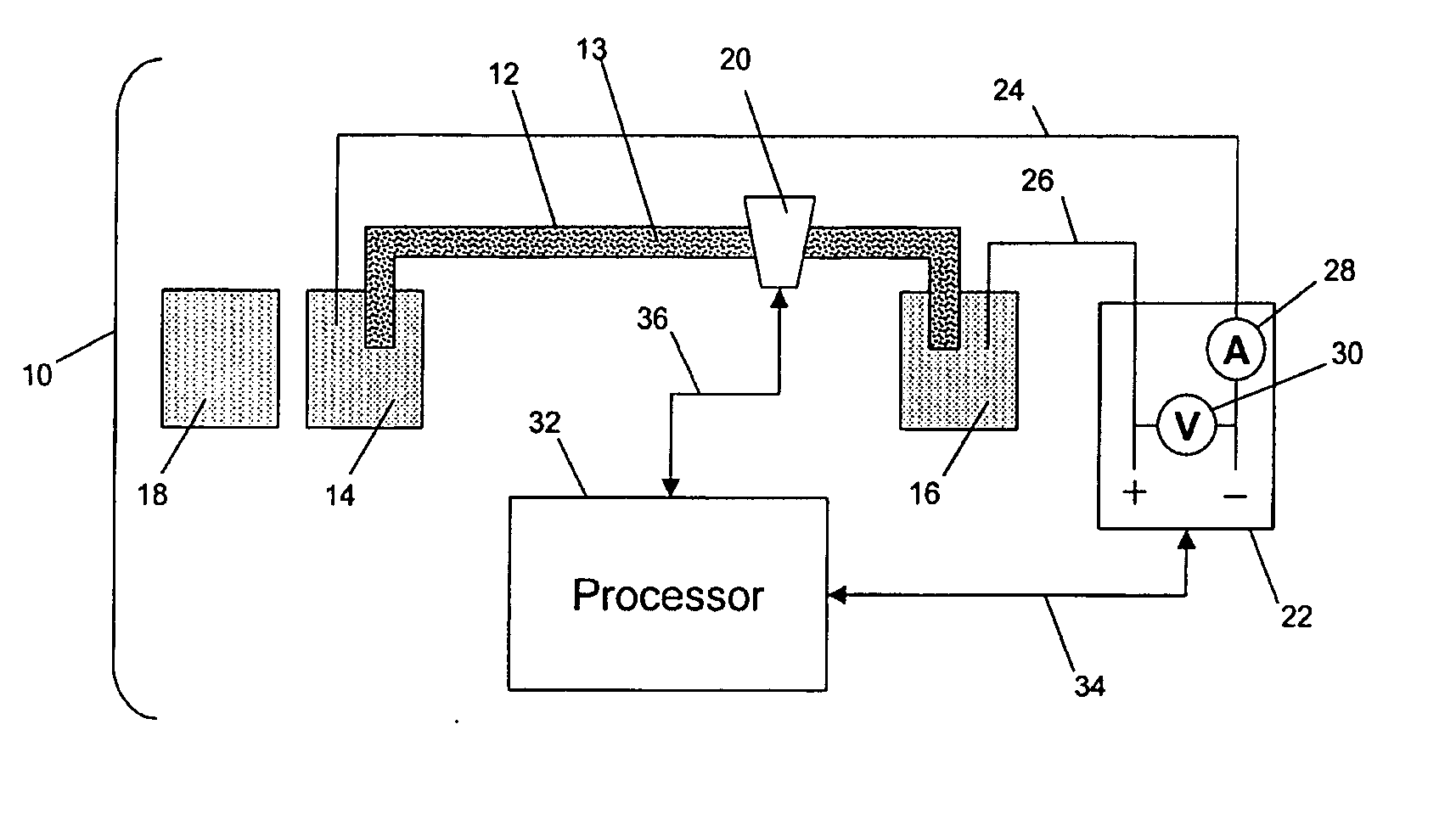
InactiveUS6270644B1Apparatus is enlargedCellsFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesPhysicsElectropherogram
A Monster Capillary Array Electrophoresis scanner measures four-color electropherograms from over a thousand capillary electrophoretic separations in parallel. The system consists of a two-dimensional confocal rotary scanner and a four-color detection unit.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Methods for sanger sequencing using particle associated clonal amplicons and highly parallel electrophoretic size-based separation
InactiveUS20100112588A1Low accuracyLarge amount of sampleMicrobiological testing/measurementSanger sequencingComputational biology
Methods for highly parallel Sanger sequencing are discussed. In particular, provided herein are methods using particles to clonally amplify templates and to introduce the amplified nucleic acids into many parallel channels with a single template per channel. Once in the channels, the nucleic acids are separated by size using electrophoresis to produce long read length sequencing information. Methods involving optical detection of the size-separated nucleic acids and analysis of the resulting electropherograms to yield the sequences are disclosed.
Owner:CAERUS MOLECULAR DIAGNOSTICS
Molecular marker method for identifying indica type rice and japonica rice by using rice grain
InactiveCN102031253AHigh speedSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationAgricultural scienceAgarose electrophoresis
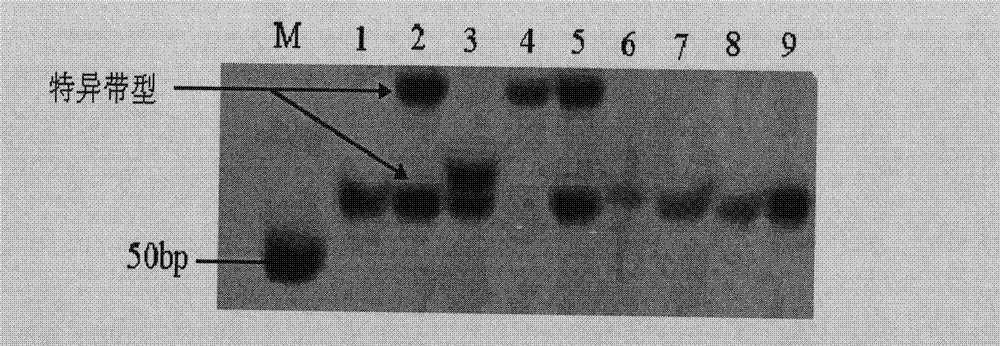
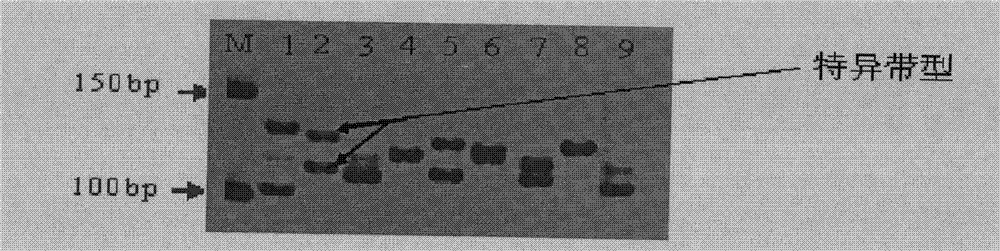
The invention belongs to the technical field of biotype identification, in particular to a method for identifying indica type rice and japonica rice using rice grain by using a rice grain (rice) and inserting or deleting (InDel) a molecular marker. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting DNA from the rice grain, and comparing full-genome DNA sequences of indica type rice 93-11 andjaponica rice Nipponbare to obtain 40 pairs of specific InDel primers; and performing fragment amplification, electrophoretic separation and electrophoresis pattern analysis on the extracted DNA the in rice seed to identify the characteristics of the indica type rice and japonica rice of a rice sample. The method concretely comprises the following steps of: taking the DNA extracted from the rice grain as a template, and analyzing and counting molecular fingerprint patterns obtained on the basis of a polymerase chain reaction and agarose electrophoresis by using combination of the 40 pairs of specific InDel primers; and determining the characteristics of the indica type rice and japonica rice of the tested rice seed (sample) according to gene frequency (Fi or Fj) calculated by 93-11 genotype and japonica rice Nipponbare genotype molecular fingerprint on 40 InDel loci of the sample. The result can be obtained by only detecting the sample of one grain of seed, and the method is convenient and rapid, accurate in identification, and has good popularization and application prospect.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
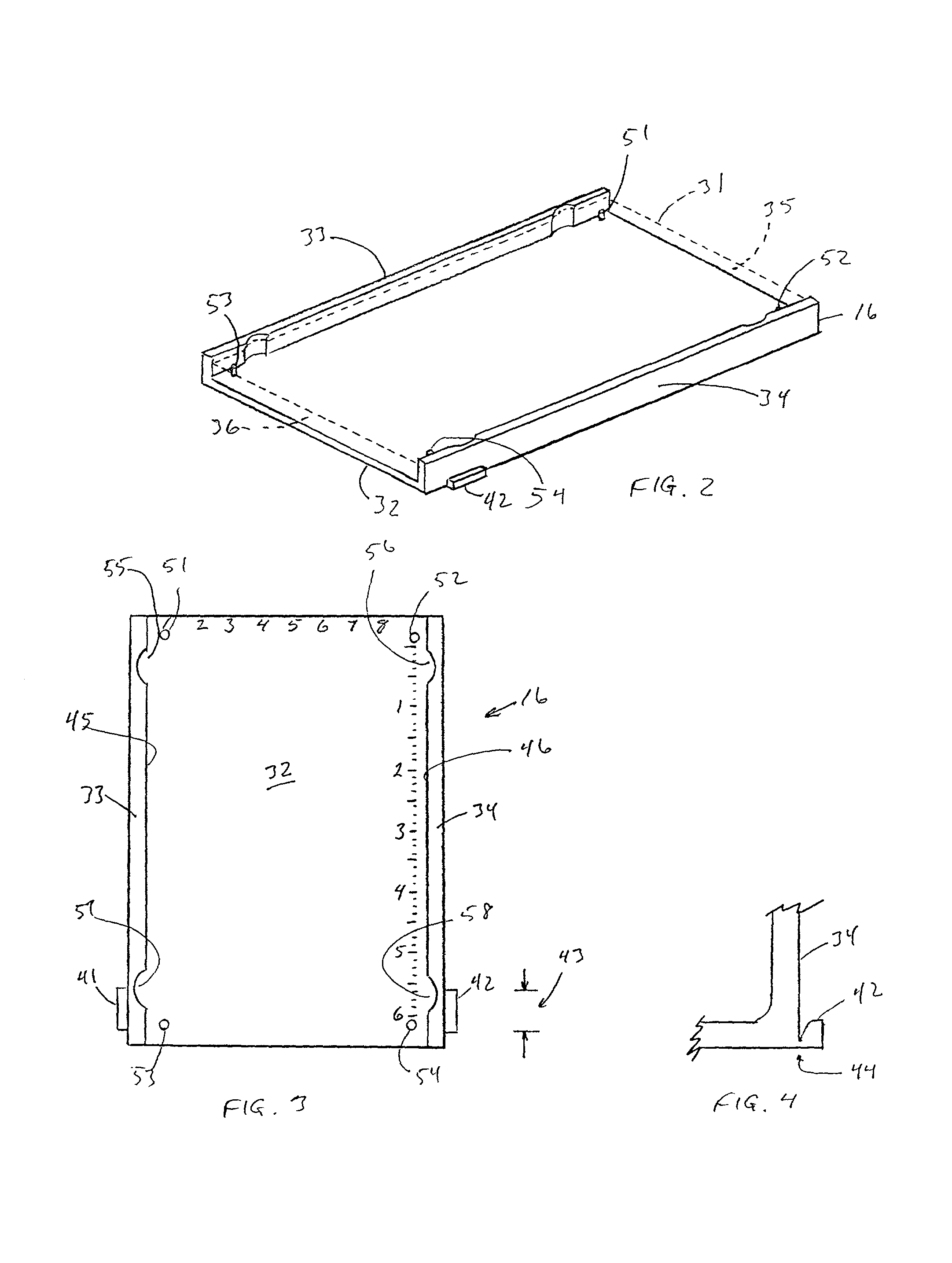
Precast gel and tray combination for submerged gel electrophoresis
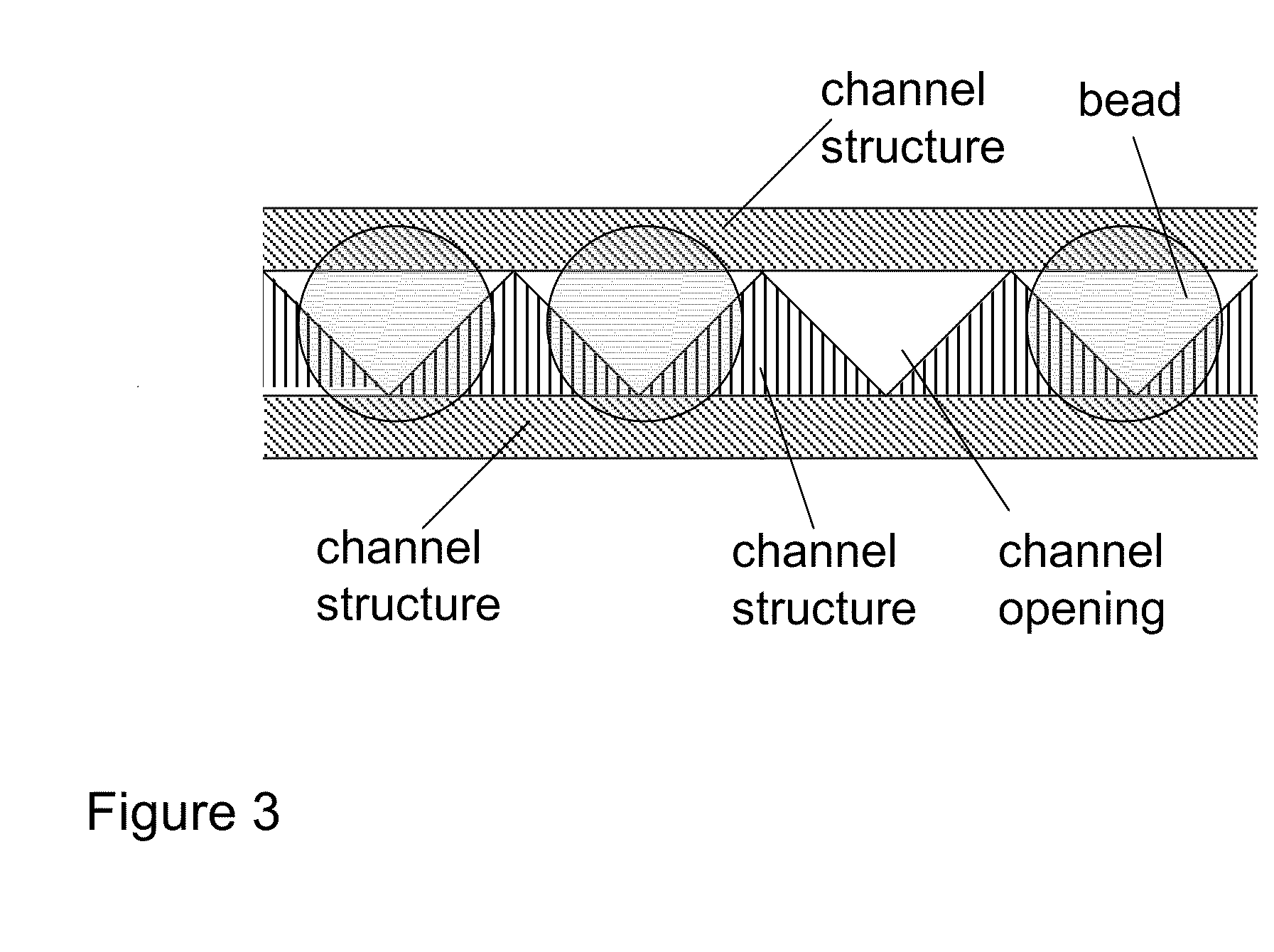
A precast slab gel for use in submerged ("submarine") horizontal electrophoresis is formed in a tray that includes a flat base and two raised walls on opposing sides of the base, the walls containing one or more tabs on their outer surfaces, the tabs mating with grooves in the interior walls of the tank. The mating of the tabs with the grooves prevents movement and floating of the tray within to the electrophoresis cell during use. The tabs are designed to mate with grooves that are present in the tank for other purposes, which adds to the versatility of the design. Further versatility is achieved by joining the tabs to the tray walls by thin webs, which make the tabs readily removable, thereby rendering the tray usable in cell tanks that do not contain grooves. Further aspects of the invention include pins or posts extending upward from the tray base to anchor the gel, and the printing of indicia on the tray base by hot foil stamping, with the discovery that indicia printed in this manner are capable of producing a fluorescent image as part of the image produced by fluorescent-dyed protein spots in the electropherogram.< / PTEXT>
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Microfluidic chip for detecting heavy metal ions in water and detection method
InactiveCN105424784AReduce volumeLight in massMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCrossed electrophoresisBuffer solution
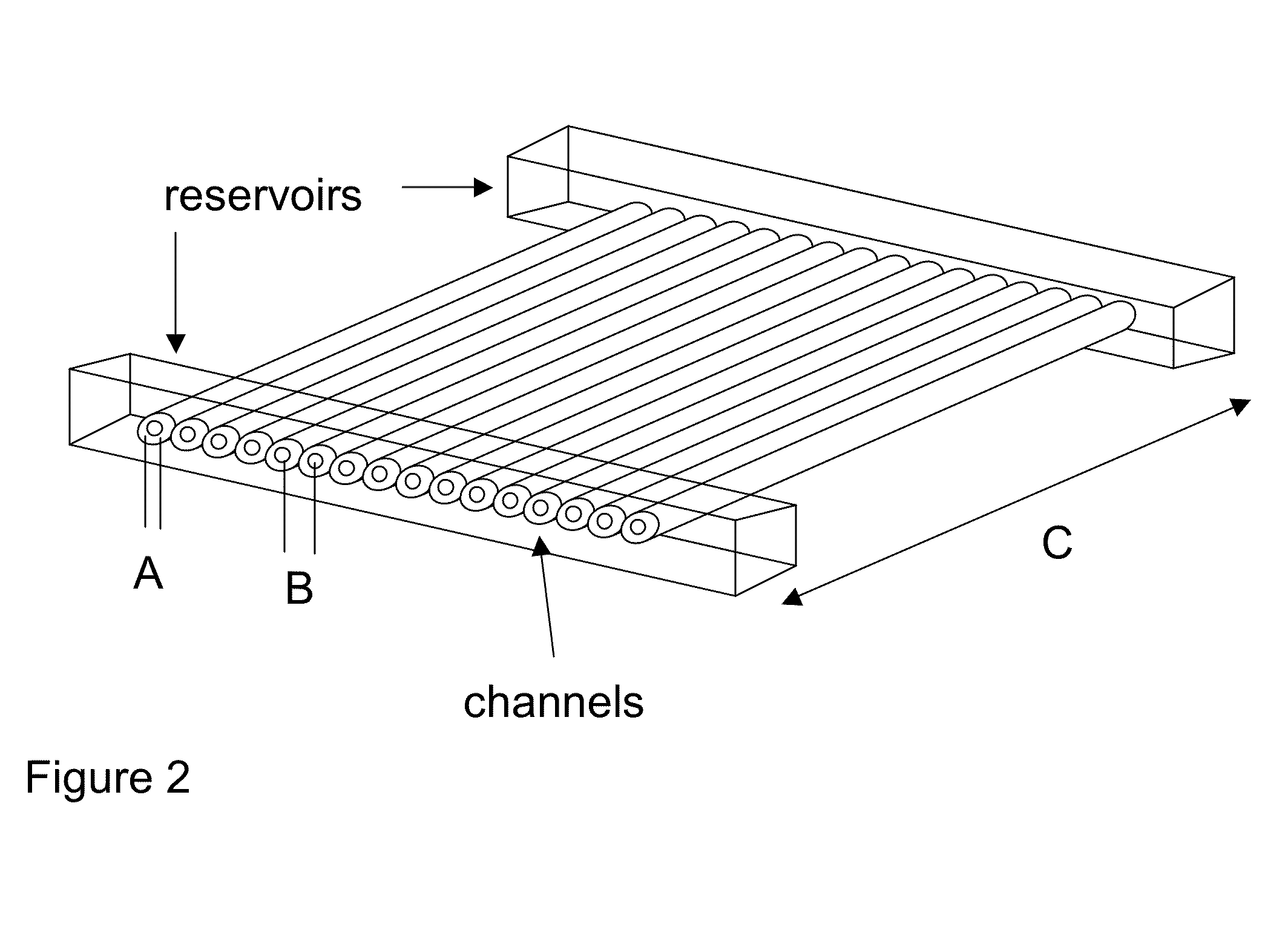
The invention belongs to the field of environmental protection, and particularly relates to a microfluidic chip for detecting heavy metal ions in water and a detection method. The microfluidic chip comprises micro-channels and micro-valves, wherein the micro-channels comprise a reference micro-channel, an ion imprint micro-channel, an electrophoresis sample introduction micro-channel, an electrophoresis separation micro-channel, a connection micro-channel, a waste liquor exhaustion micro-channel and a buffer solution exhaustion micro-channel; the micro-valves comprise a reference end outlet micro-valve, an ion imprint exit micro-valve, a waste liquor exit micro-valve, a buffer solution cut-off micro-valve and a sampling cut-off micro-valve. The detection method comprises the following steps: acquiring a first electropherogram of cross electrophoresis before heavy metal ion adsorption; then, acquiring a second electropherogram of cross electrophoresis after heavy metal ion adsorption; finally, recognizing specific heavy metal ions according to the difference between the two electropherograms, and calculating heavy metal contents. The microfluidic chip and the detection method have the advantages that not only are the production cost and the use cost very low, but also the anti-interference ability is very high; moreover, the detection process is simple, and the detection time is short.
Owner:HIT YIXING ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION +1
Analyte Identification in Transformed Electropherograms
InactiveUS20070158193A1Accurate detection and quantificationMaintain good propertiesSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementAnalyteElectric power
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
Rapid identification method for genetic purity of cabbage seed
InactiveCN101017152AAccurate identificationNot affectedMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrophoresisDNA fragmentation
This invention discloses one cabbage seed heritage purification rapid test method in biological technique field, which comprises the following steps: extracting cabbage gene set DNA and using filtered property lead production of NAUISR1034 and NAUSSR1011 for PCR extending ; processing extended DNA section for agarose gel and non-variable polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for 0.8 to 1 and 2 to 2.2 to catch electrophoresis spectrum; through comparing and analyzing the DNA section difference to process new summer 50 mixture heritage purification identification.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Molecule detection method of Fusarium graminearum to medium resistance level bacterial strain of carbendazim
InactiveCN101985653ATimely guidanceReasonable guidanceMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrophoresisBacterial strain
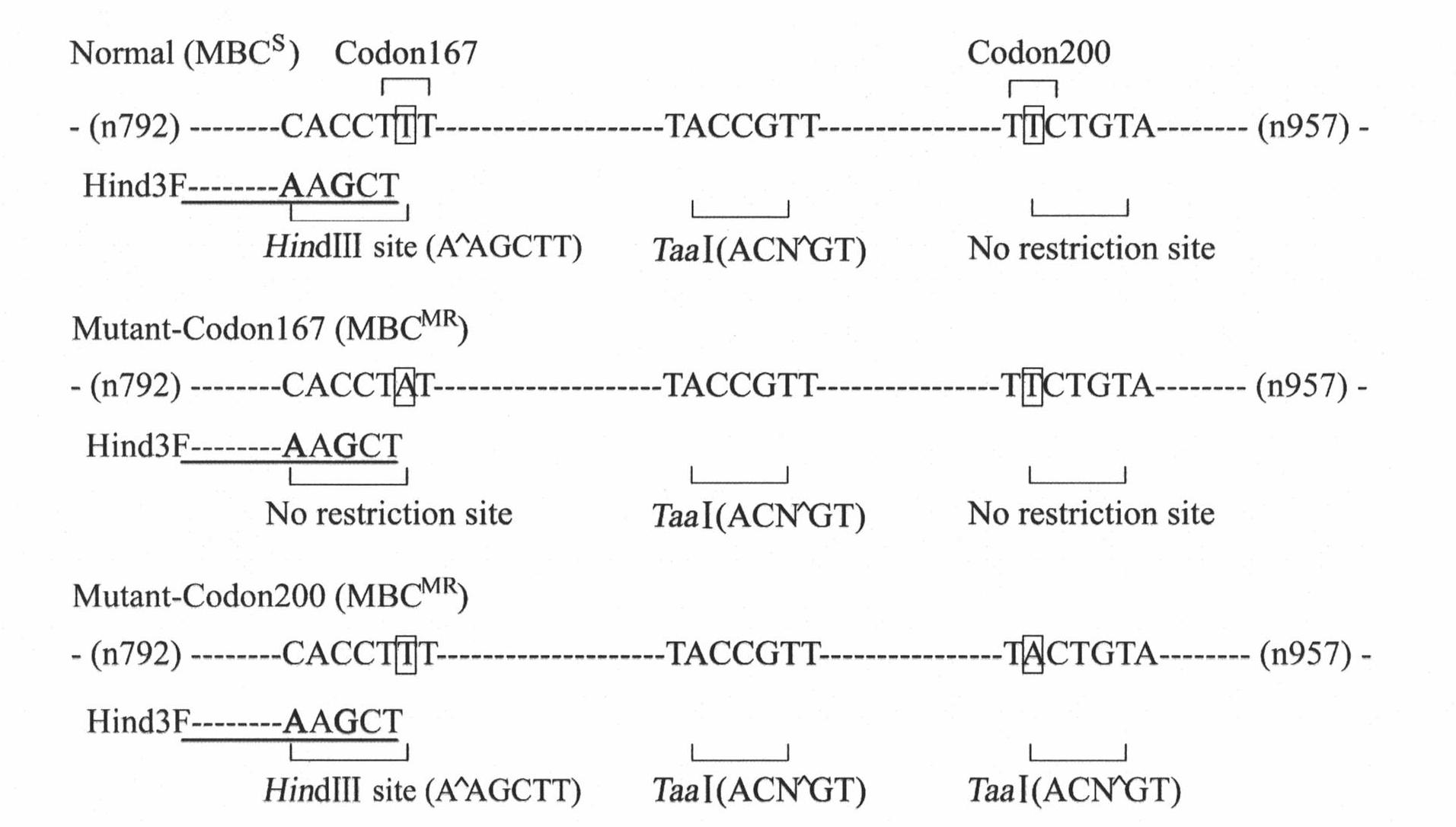
The invention belongs to a molecule detection method of Fusarium graminearum to medium resistance level bacterial strain of carbendazim. The method can be used for monitoring drug resistance of Fusarium graminearum to carbendazim and prevalence warning, wherein Fusarium graminearum can cause wheat scab. The detection method includes the following three main steps: (1) nuclear genome DNA of bacterial strain to be detected is respectively extracted: (2) internal and external primer pairs are utilized to carry out nested PCR, thus obtaining a target segment; (3) the target segment is respectively restricted by restriction enzymes HindIII and TaaI (Tsp4CI), and genotype of medium resistance level bacterial strain can be accurately identified by virtue of a restriction product electrophoresis spectrum. By adopting PIRA-PCR (primer-introduced restriction analysis PCR) technology, quantity of Fusarium graminearum with medium drug resistance in field and ratio thereof in group can be rapidly and accurately detected. Detection accuracy reaches more than 95%.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Quick qualitative and quantitative measuring method of fermented lactobacillus in probiotic milk products
InactiveCN101649352AQualitatively accurateSimplify testing proceduresMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyLactobacillus fermentum
The invention relates to a quick qualitative and quantitative measuring method of fermented lactobacillus in probiotic milk products. Aiming at fermented lactobacillus in probiotic milk products, themethod designs a species specific primer of a 16S rRNA gene sequence of fermented lactobacillus by self, the species specific primer PCR reaction and real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR reaction ofthe primer is carried out to establish the simple, convenient, quick and accurate qualitative and quantitative measuring method of fermented lactobacillus in probiotic milk products by agarose gel electrophoresis pattern analysis and real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR pattern analysis.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
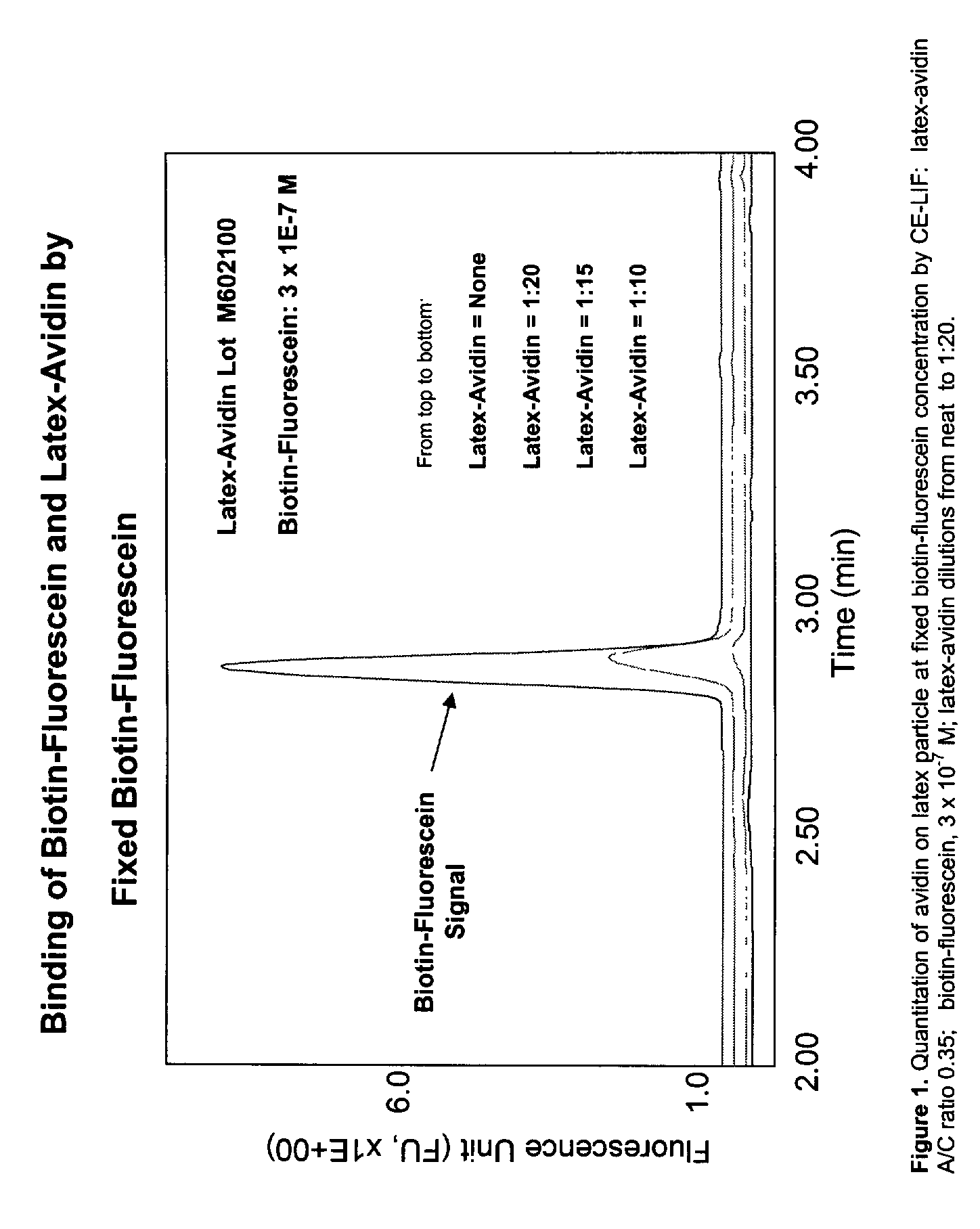
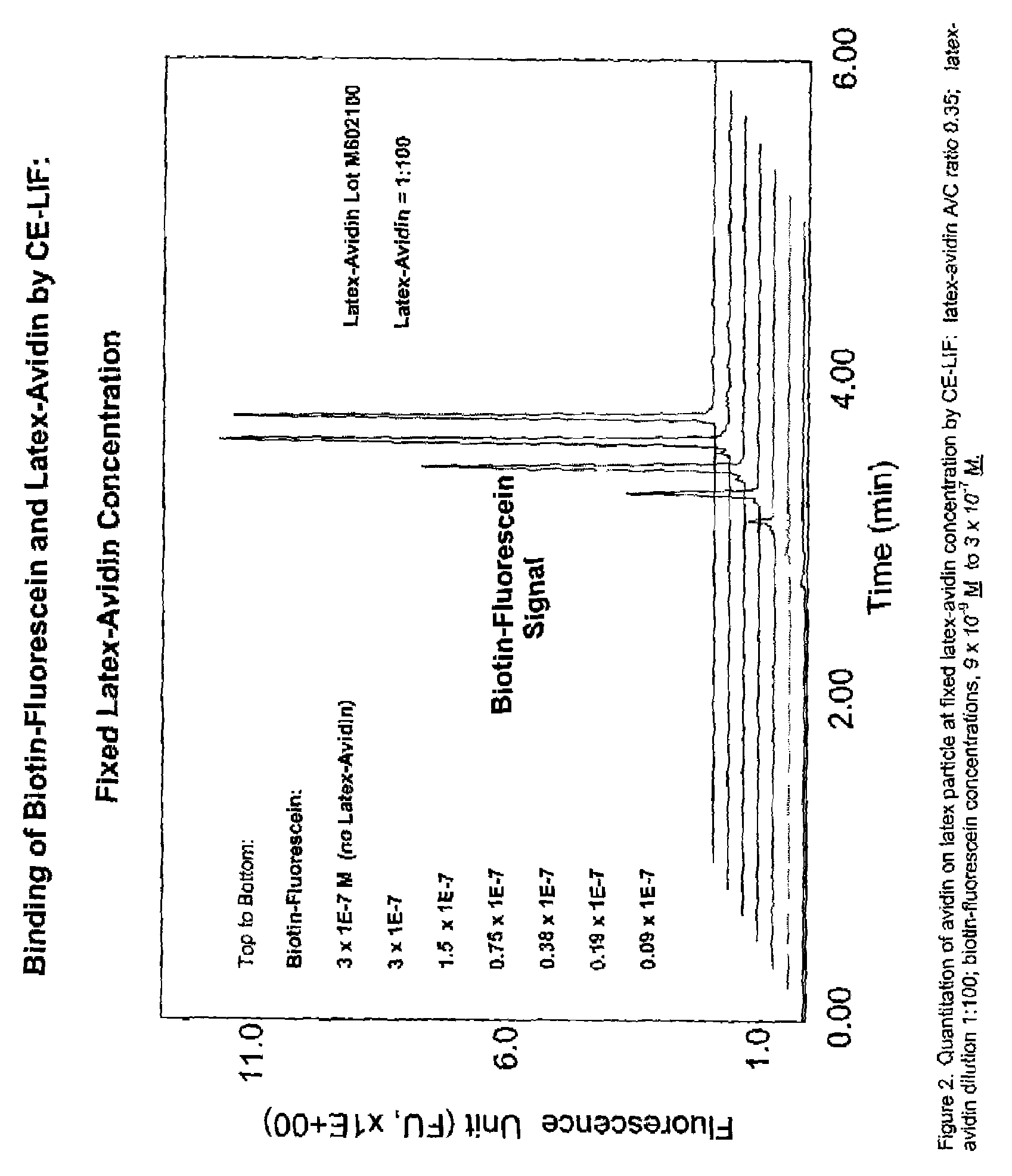
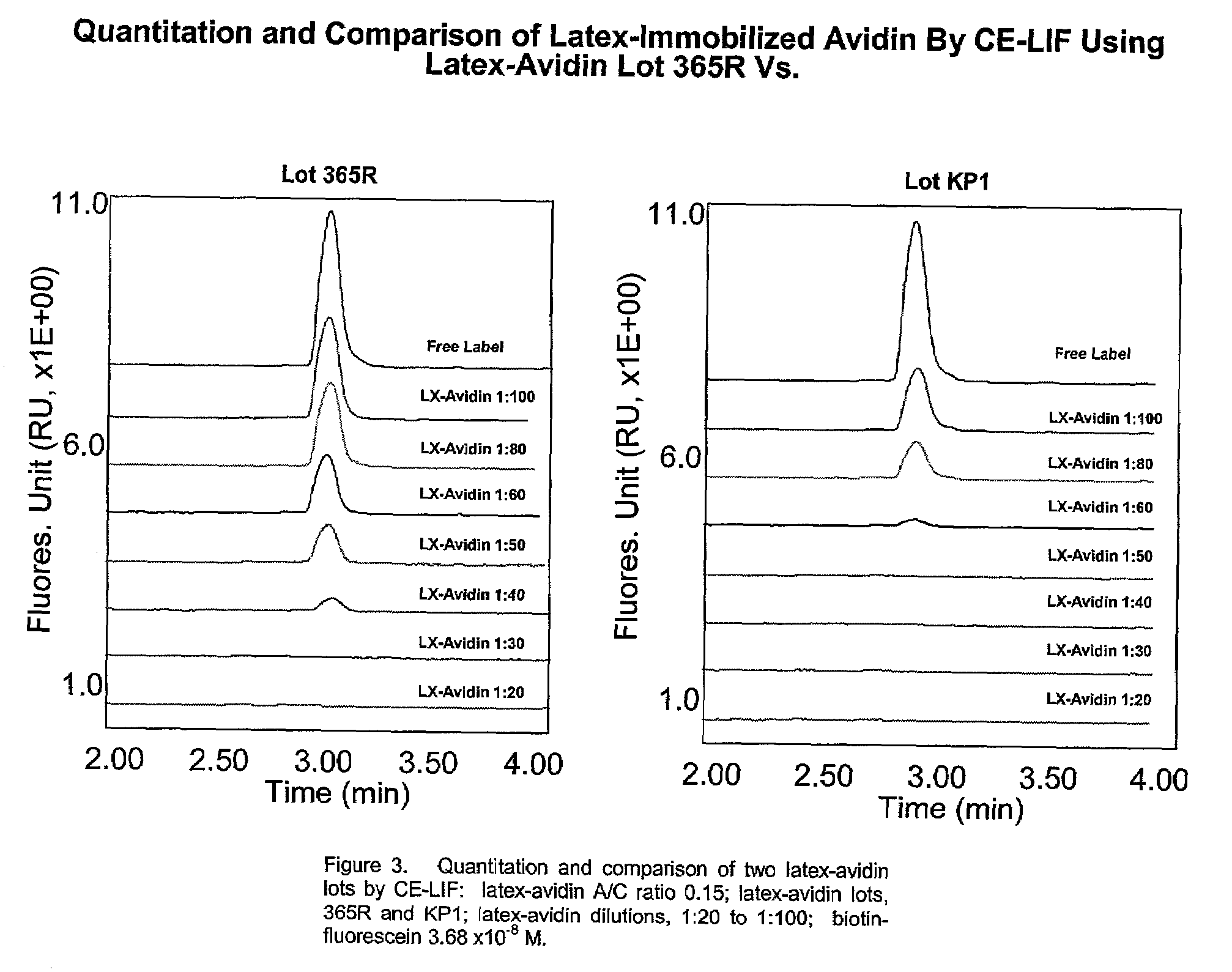
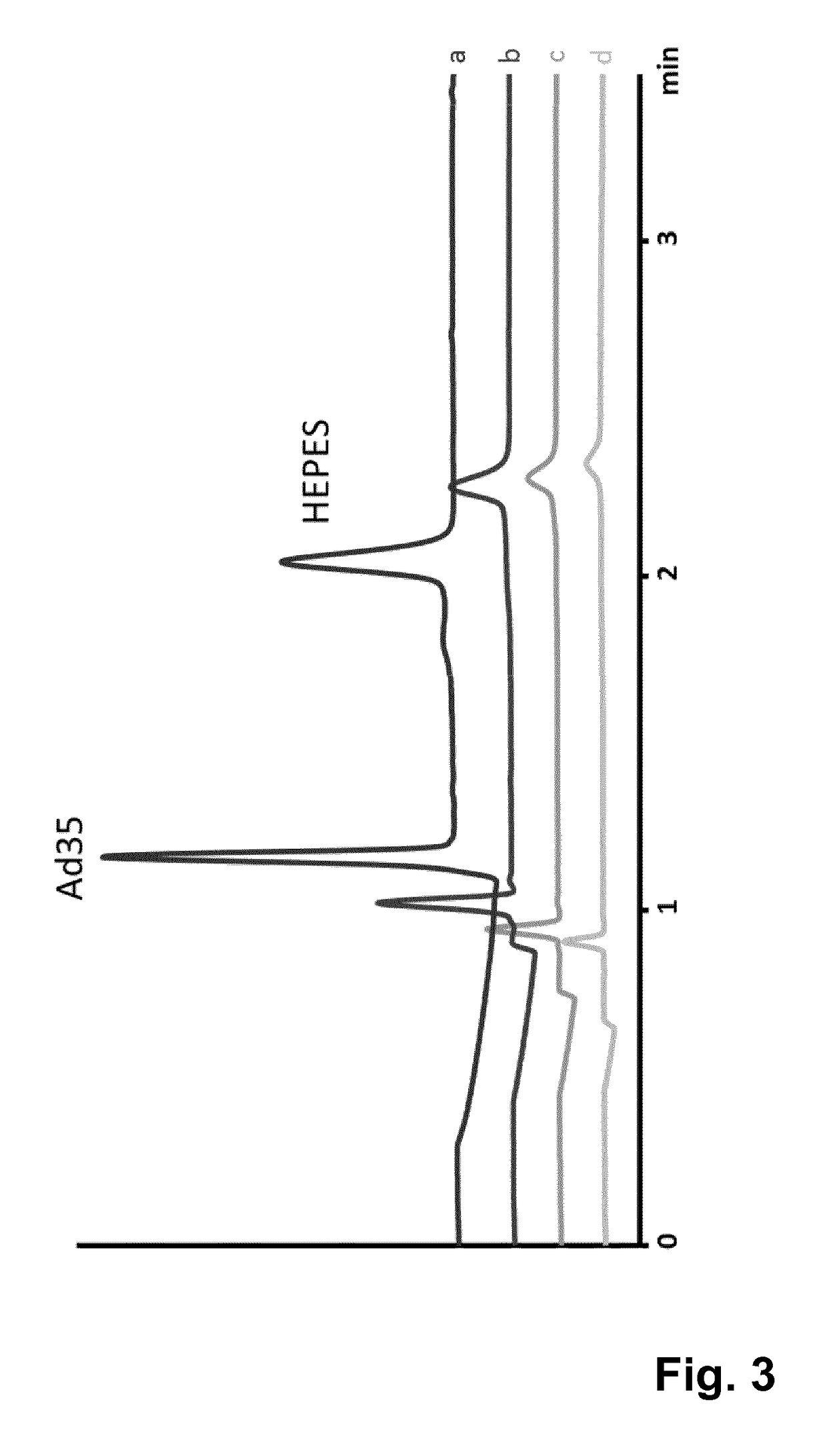
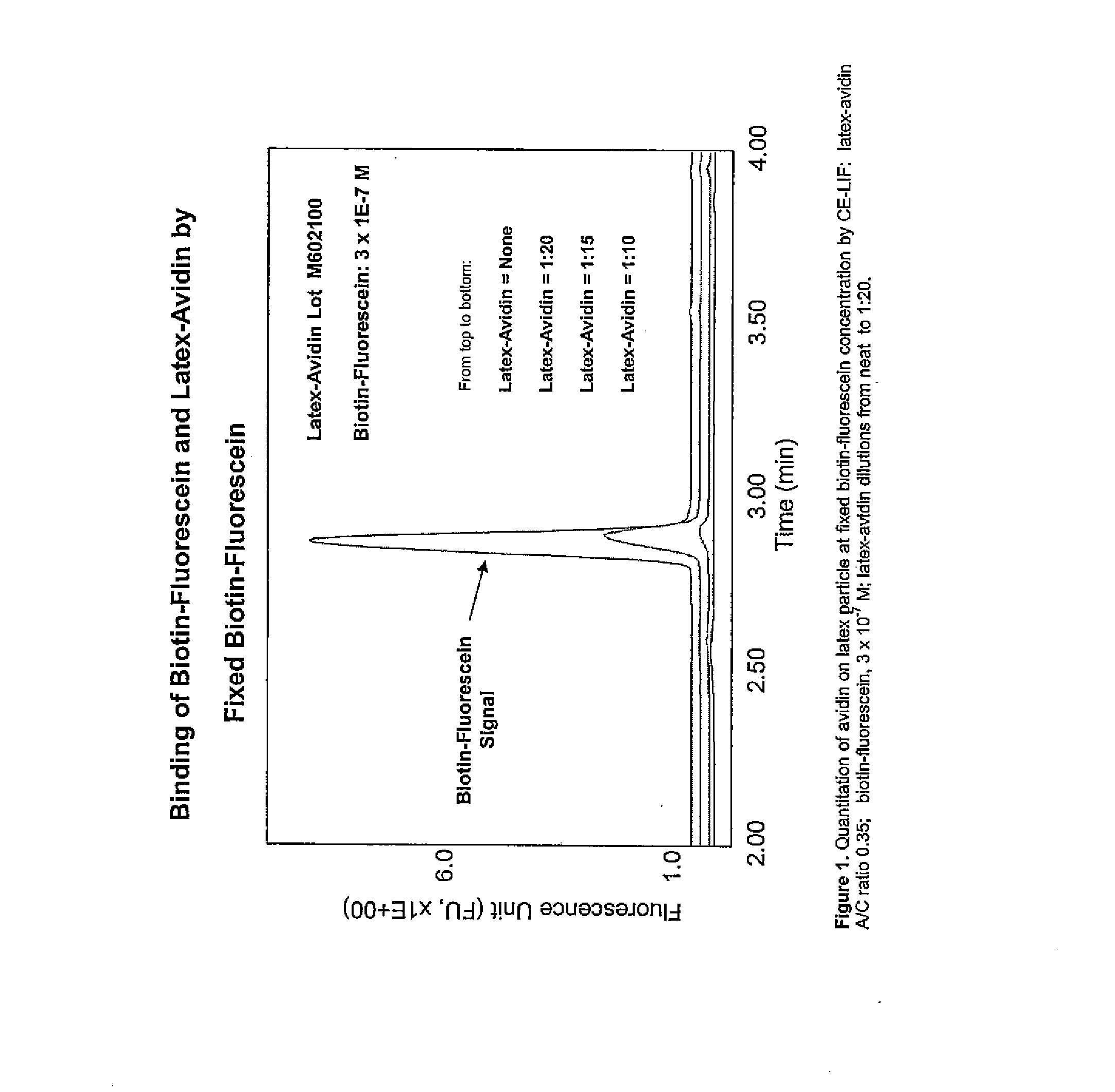
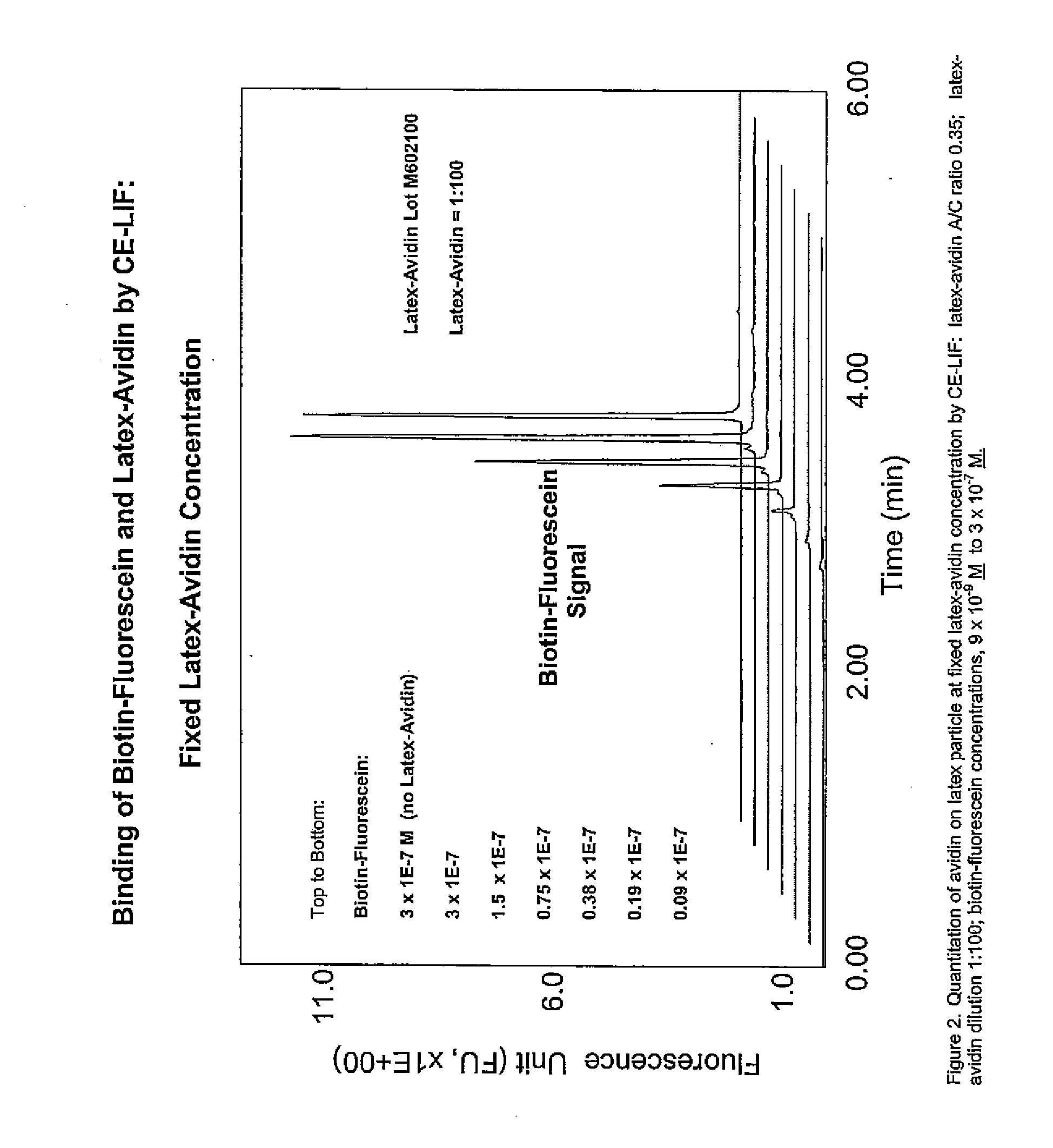
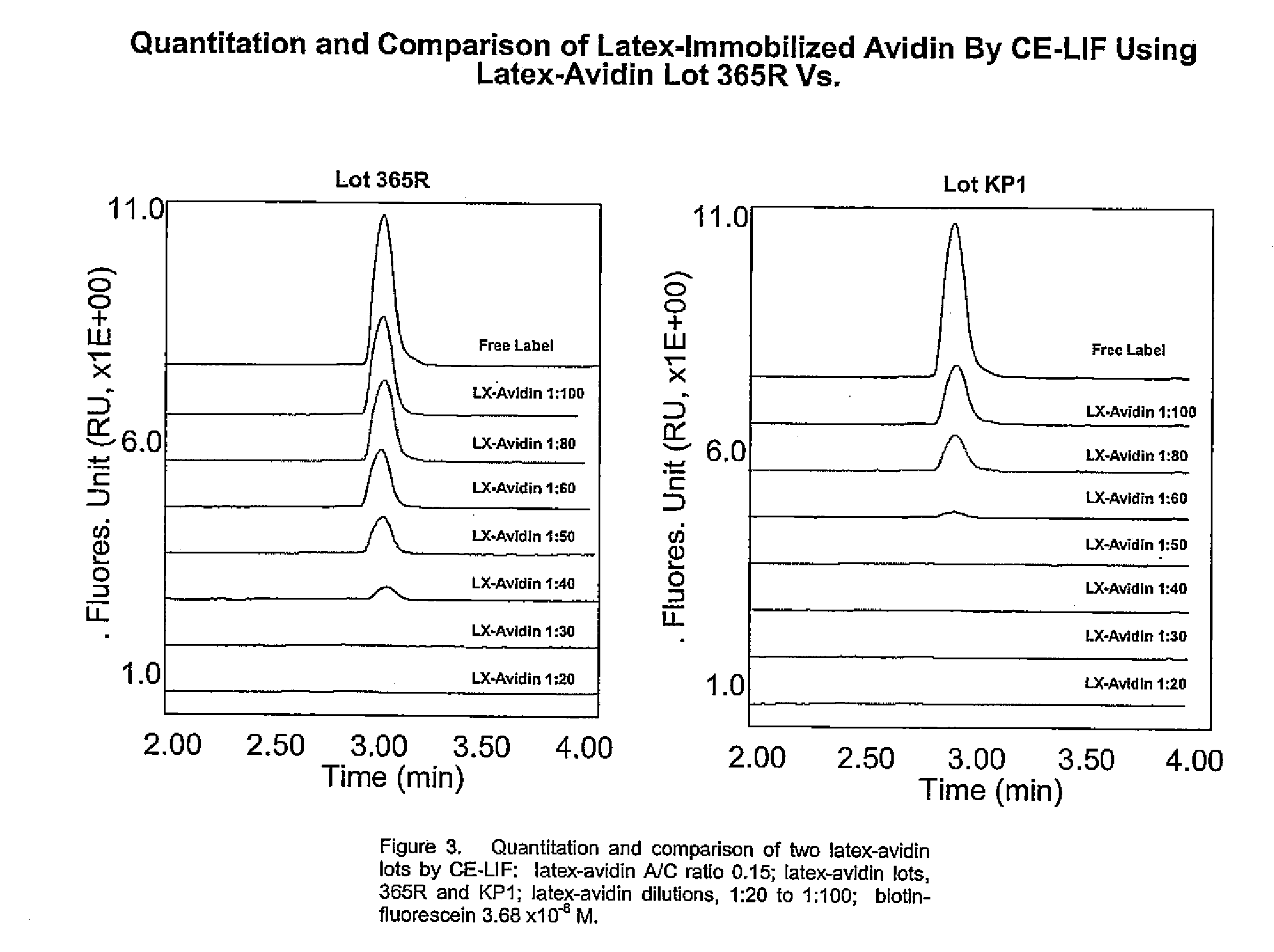
Particle based homogeneous assays using capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence detection
InactiveUS7179658B2Simplified electropherogramsEasy to detectElectrolysis componentsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorTarget analysisAnalyte
The invention provides highly sensitive and rapid homogeneous assays which employ particle-enhanced assay formats in concert with capillary electrophoresis and laser-induced fluorescence (LIF) detection to determine the concentration of an analyte of interest in a sample. Such a determination is made by measuring fluorescent signal(s) (i.e., an electropherogram) produced upon LIF of species present in the reaction mixture that are capable of producing such signals. The method of this invention produces simplified electropherograms by reducing the number of signals that must be separated and subsequently measured, and therefore increases the accuracy of the detection and / or quantification of target analyte concentration in a sample.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
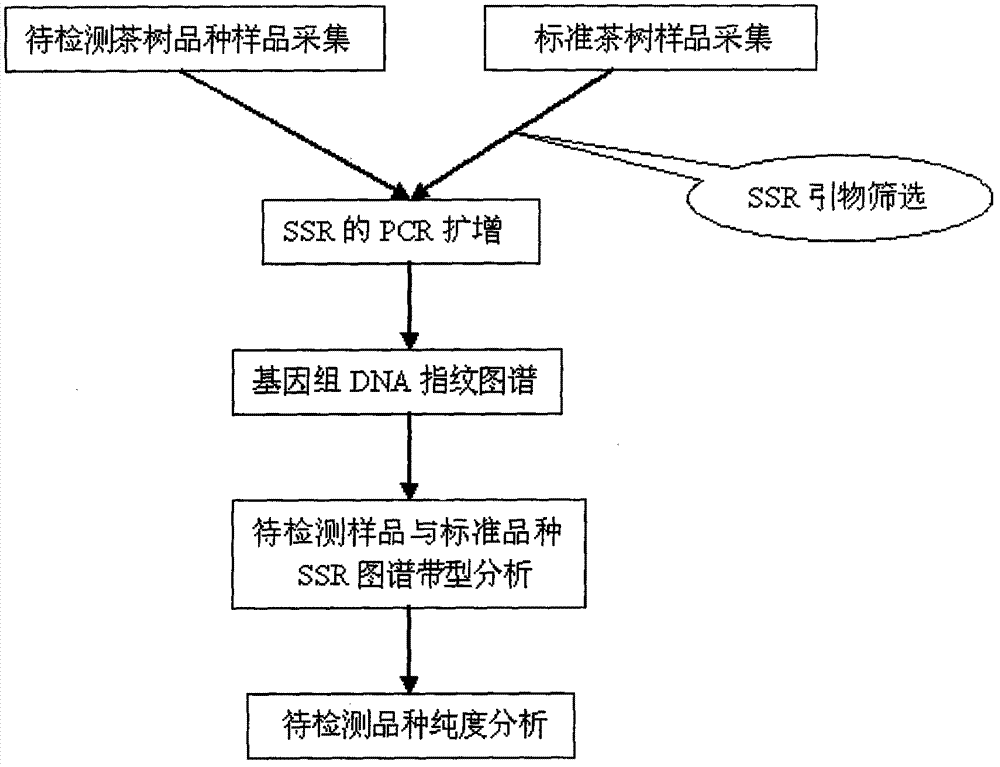
Molecular marking method for identifying tea clonal variety of tea trees
InactiveCN102776271ASimplified extraction procedureOmit purificationMicrobiological testing/measurementA-DNABud
Belonging to the field of biotechnologies, the invention provides a molecular marking method for identifying a tea clonal variety of tea trees. The method includes the following steps of: 1) putting 1.0g of fresh and tender buds and leaves of a variety to be tested into a mortar, adding liquid nitrogen and grinding the mixture into powder, adding a CTAB buffer solution, conducting water bathing at a temperature of 65DEG C for 30-60 minutes, then adding a DNA extracting solution to obtain the genome DNA of the tea tree variety to be tested; 2) taking the genome DNA extracted in step 1) as a template, using SSR (simple sequence repeat) primers for PCR amplification, and subjecting the amplification product to 10% native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, thus obtaining an electropherogram of the variety to be tested; and 3) comparing the electropherogram of the variety to be tested with a standard tea tree variety electropherogram obtained according to the step 1) and step 2), and if the variety to be tested and the standard variety are consistent in band composition, determining the variety to be tested and the standard variety as an identical variety, thus obtaining the purity of the variety to be tested. Compared with other methods, the invention can reflect the genetic background and genetic relationship of tea tree varieties more truly. And the technology provided in the invention can be used as a scientific basis for identifying the authenticity of the tea tree varieties.
Owner:刘本英
Precast gel and tray combination for submerged gel electrophoresis
A precast slab gel for use in submerged ("submarine") horizontal electrophoresis is formed in a tray that includes a flat base and two raised walls on opposing sides of the base, the walls containing one or more tabs on their outer surfaces, the tabs mating with grooves in the interior walls of the tank. The mating of the tabs with the grooves prevents movement and floating of the tray within to the electrophoresis cell during use. The tabs are designed to mate with grooves that are present in the tank for other purposes, which adds to the versatility of the design. Further versatility is achieved by joining the tabs to the tray walls by thin webs, which make the tabs readily removable, thereby rendering the tray usable in cell tanks that do not contain grooves. Further aspects of the invention include pins or posts extending upward from the tray base to anchor the gel, and the printing of indicia on the tray base by hot foil stamping, with the discovery that indicia printed in this manner are capable of producing a fluorescent image as part of the image produced by fluorescent-dyed protein spots in the electropherogram.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
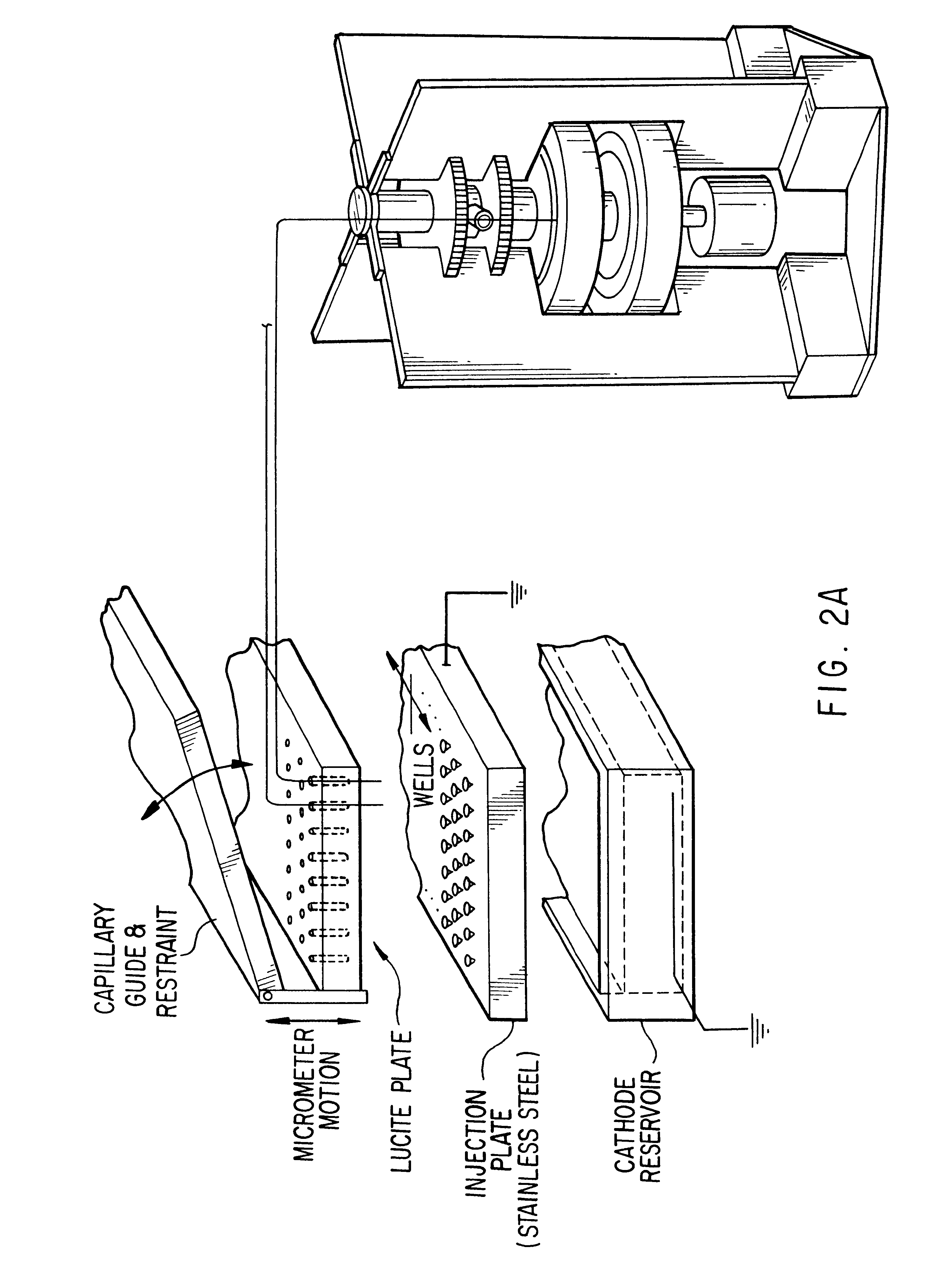
Preparation of defect-free polyacrylamide electrophoresis gels in plastic cassettes
InactiveUS20050059761A1Uniform pore sizeMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPolyacrylamideGel Forming Solution
Irregularities in the pore structures of polyacrylamide gels that are formed in cassettes against plastic walls are reduced or eliminated by the inclusion of an oxygen scavenger in the gel-forming solution. Avoidance of the irregularities results in electropherograms with fewer distortions in the solute bands.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Method for quickly identifying genetic purity of glutinous corn hybrid
InactiveCN102505044AAccurate identificationImprove the efficiency of genetic purity identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrophoresisDNA fragmentation
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and relates to a method for quickly identifying the genetic purity of a glutinous corn hybrid. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting genomic deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) from glutinous corn, performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification by using the screened sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) effective primer combination NAUSRem7 / NAUSRpm1 and random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) effective primers NAUSR709 and NAUSR712, respectively performing non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and agarose gel electrophoresis on a PCR product obtained through amplification, and shooting a DNA electrophoresis pattern; and comparing and analyzing the size and position difference of polymorphism amplified fragments formed due to the difference of DNA fragment sequences in the electrophoresis pattern, and identifying the genetic purity of the glutinous corn F1 hybrid, namely a Suyunuo 2 seed. The detection method has the advantages of marking stability, high accuracy, no influence of the growth stage and environment of a sample to be detected, low cost, capability of being performed in thewhole growth season, and the like.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
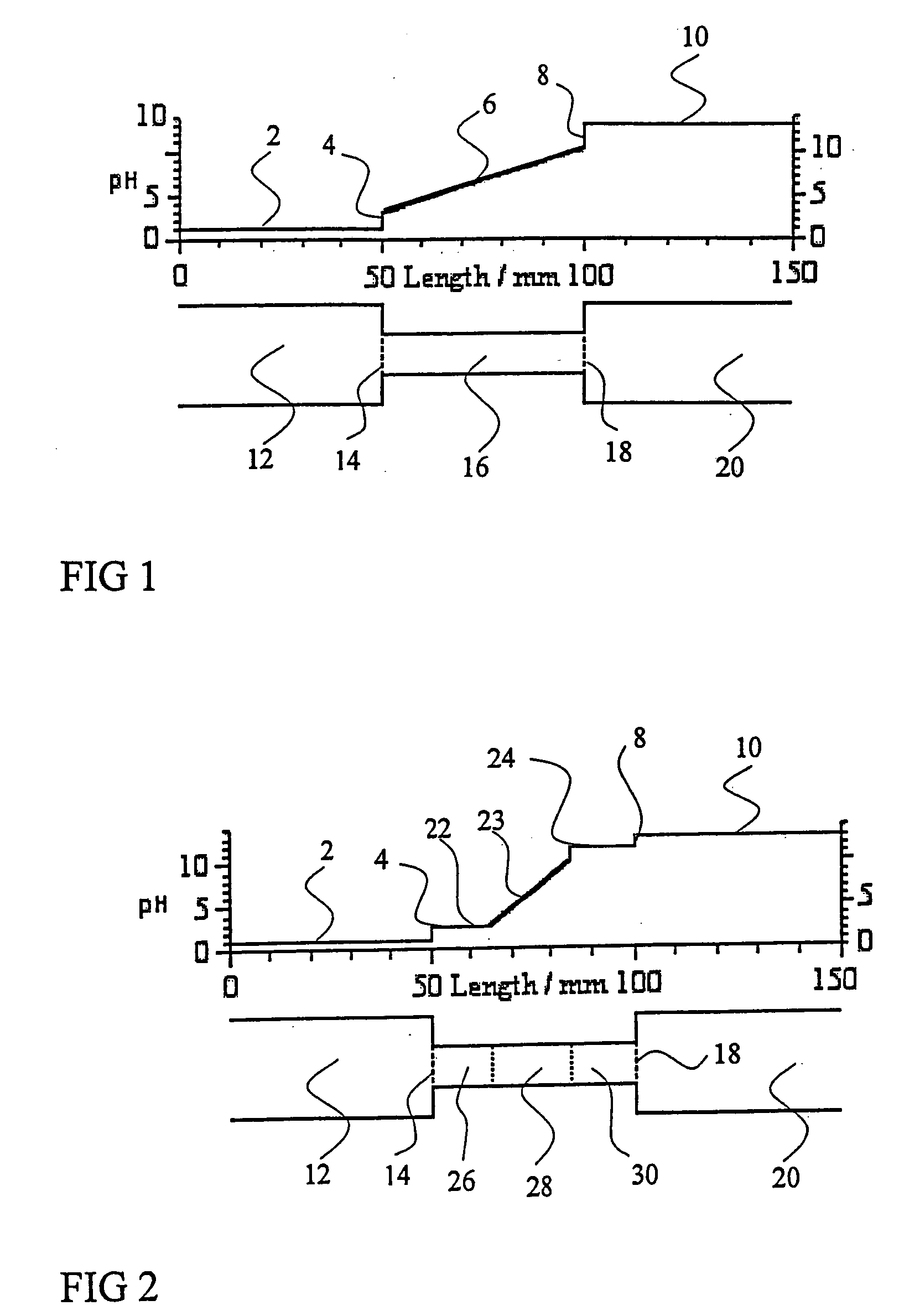
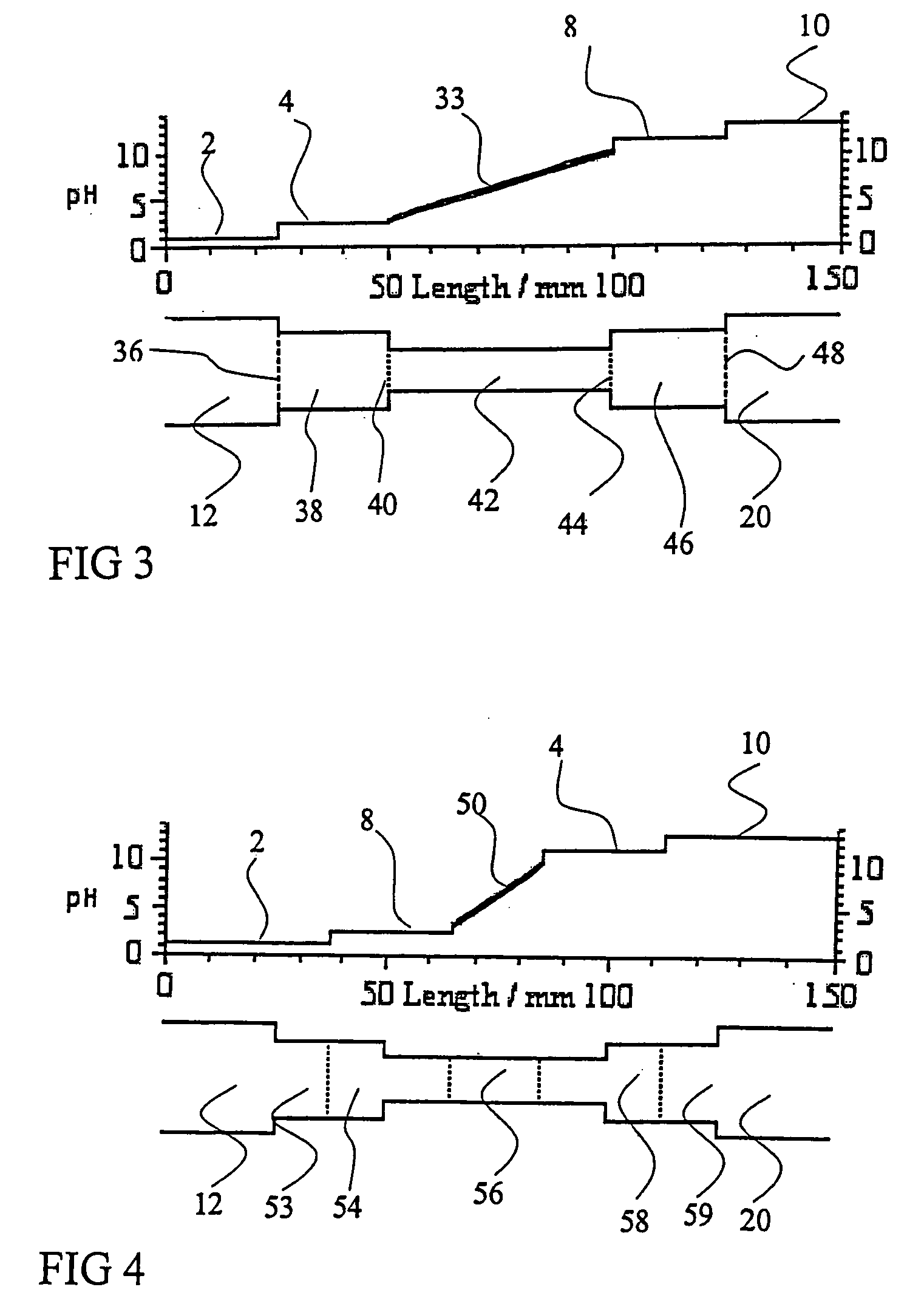
Method and apparatus to improve the concentration detection sensitivity in isoelectric focusing systems
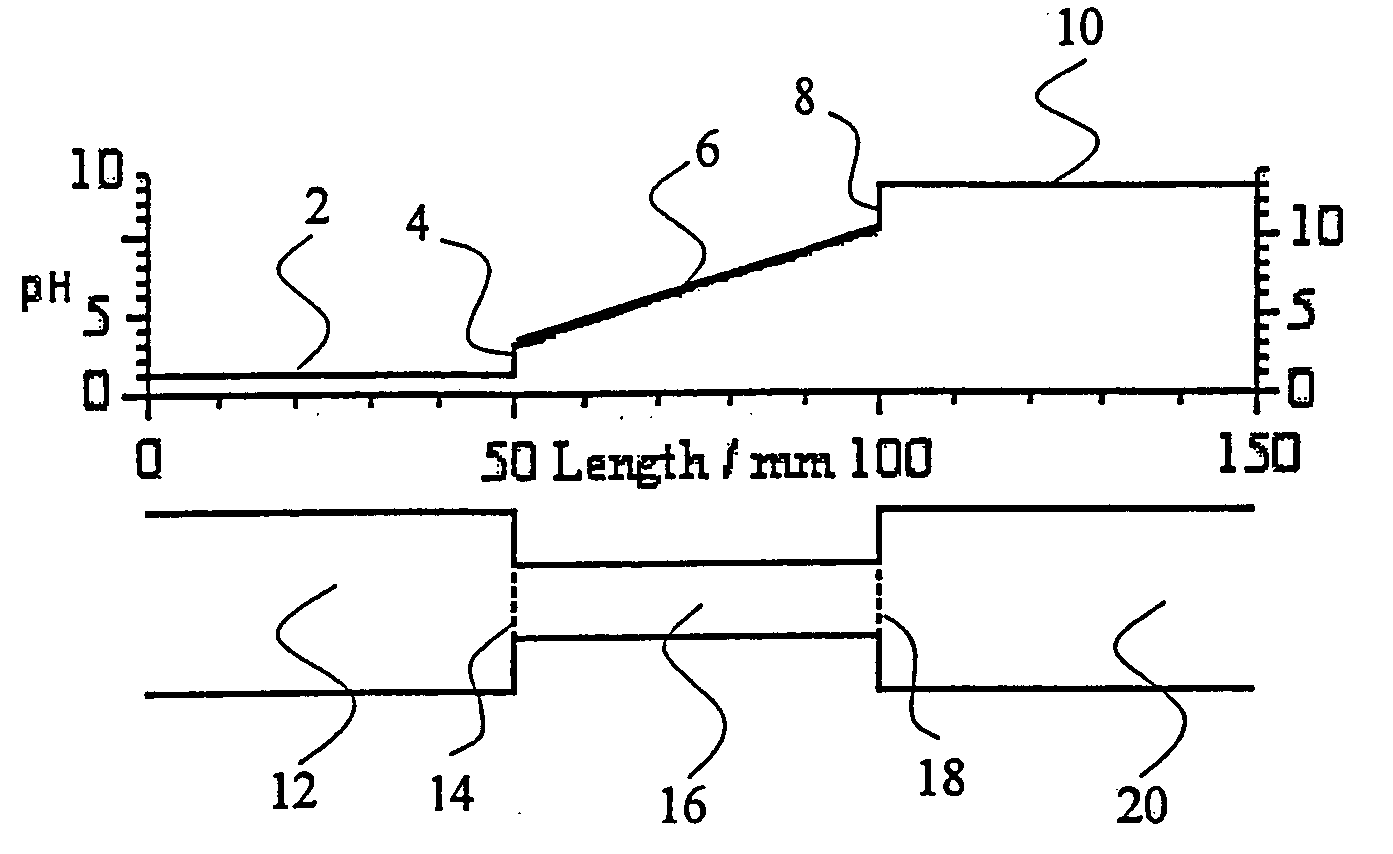
InactiveUS20050161332A1Simplified determinationImproves concentration detection limitElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementElectricityAnalyte
Isoelectric focusing systems are used to analyze ampholytic analytes in a sample. These systems use an electrophoretically generated pH gradient to separate components according to their isoelectric points. This invention overcomes two shortcomings associated with these systems. First, the invention enables the detection of ampholytic analytes whose original concentration in a sample is so low that their concentration after focusing is below their respective detection limit. Auxiliary agents are added to the sample and auxiliary compartments are connected to the separation compartment to increase the final concentration of the focused ampholytic analytes in the separation compartment above their respective detection limit. The second limitation the invention overcomes is the detrimental effects of salt in a sample. Salt alters the pH gradient developed in the separation compartment during focusing compared to the pH gradient obtained for a salt-free sample, thus skewing the electropherogram obtained in the isoelectric focusing separation. This invention eliminates the problems caused by salt-induced shift of the pH gradient by accumulating, during isoelectric focusing, components of salt in the sample and the added auxiliary agents in an auxiliary compartment connected to the separation compartment. By adjusting the amount of auxiliary agent so that at the end of the focusing step no salt or auxiliary agent is located in the separation compartment, one can maintain the correct shape of the pH gradient in the separation compartment, increase the concentration of the focused ampholytic analyte above its respective detection limit and avoid the unwanted effects of salt in the sample.
Owner:VIGH GYULA
Mutagenesis, selective breeding and identification method of cold tolerant Danaliella
InactiveCN1888047AExtend the time of outdoor cultivationLong breeding cycleUnicellular algaeElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentUltravioletWild type
The ultraviolet ray mutagenesis, selective breeding and identification method of cold tolerant Dunaliella includes: inoculating Dunaliella to culture medium; lighting and dark inducing for synchronized growth; mixing Dunaliella liquid with iodine solution or bromophenol blue solution to deactivate Dunaliella, injecting Dunaliella liquid to culture dish, mutagenesis under ultraviolet lamp before dark culturing, mixing with fresh culture liquid and painting the mixture to Dunaliella culture medium for low temperature lighting culture; inoculating single Dunaliella colony to the culture liquid and low temperature lighting culturing; sampling detection to comparing the low temperature lighting growth curves of cold tolerant Dunaliella mutant and wild prototype strain; extracting total DNA for RAPD comparison; calculating genetic similarity coefficient; extracting total protein and post-electrophoresis staining while record results; comparing protein electropherogram; and confirming the obtained cold tolerant Dunaliella mutant.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Preparation of defect-free polyacrylamide electrophoresis gels in plastic cassettes
InactiveUS6846881B2Uniform pore sizeMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGel Forming SolutionPolyacrylamide
Irregularities in the pore structures of polyacrylamide gels that are formed in cassettes against plastic walls are reduced or eliminated by the inclusion of an oxygen scavenger in the gel-forming solution. Avoidance of the irregularities results in electropherograms with fewer distortions in the solute bands.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Method for finger-printing heparins
InactiveUS20110048946A1Guaranteed to be accurate and consistentHigh resolutionOrganic active ingredientsElectrolysis componentsPolyaminePolyamine metabolism
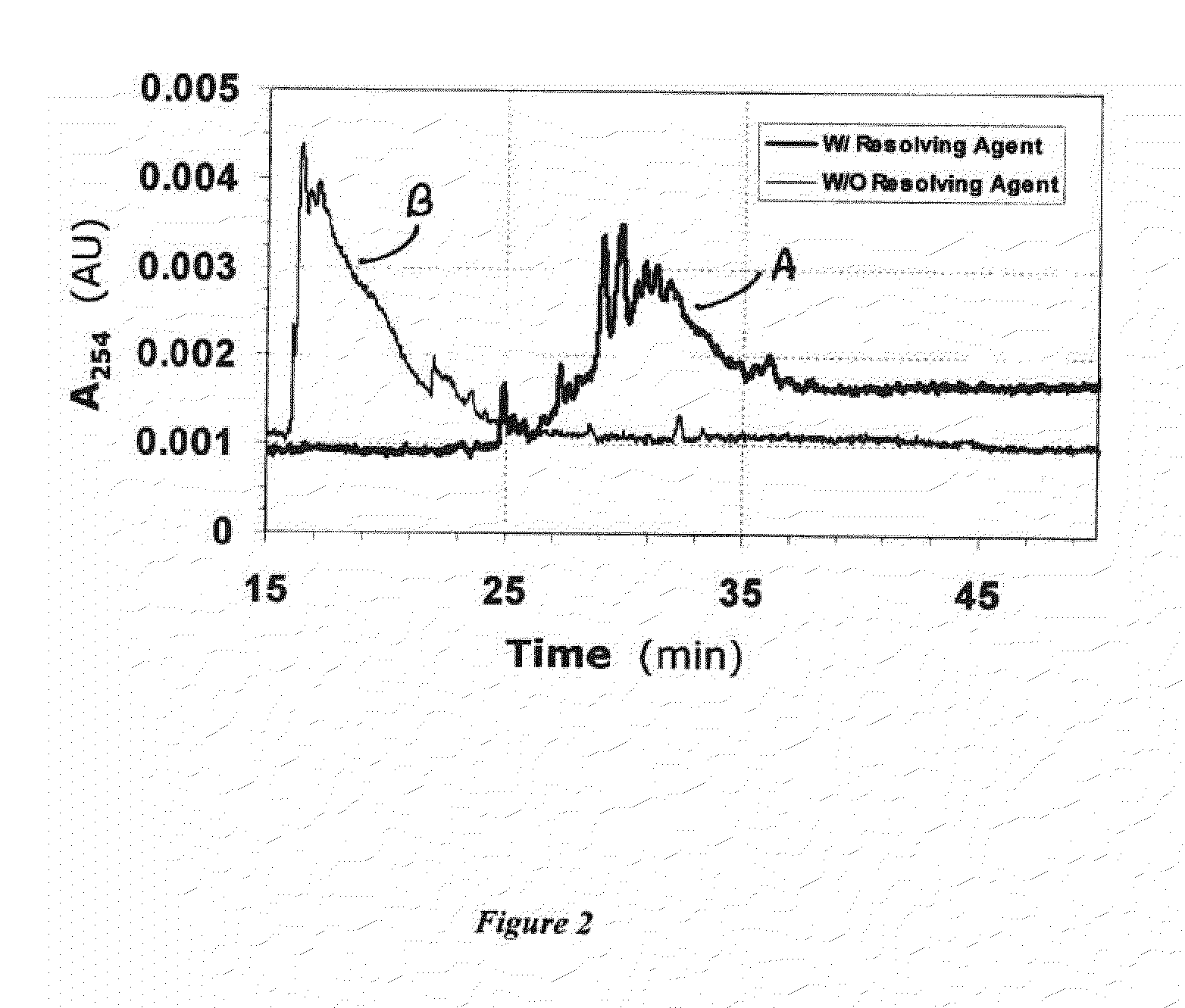
Methods to generate a distinctive fingerprint (pattern of migration) for a sample of complex, polydisperse heparins are provided. The methods involve adding resolving agents such as polyamines to a heparin sample and then analyzing the sample with a technique that separates macromolecules according to charge to mass ratio (e.g. capillary electrophoresis). The resulting electropherogram is unique to and characteristic of the heparin sample. The methods may be used, for example, to monitor the quality and consistency of various heparin preparations.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
Mutagenic breeding method of high temperature resistant pasteur Du algae
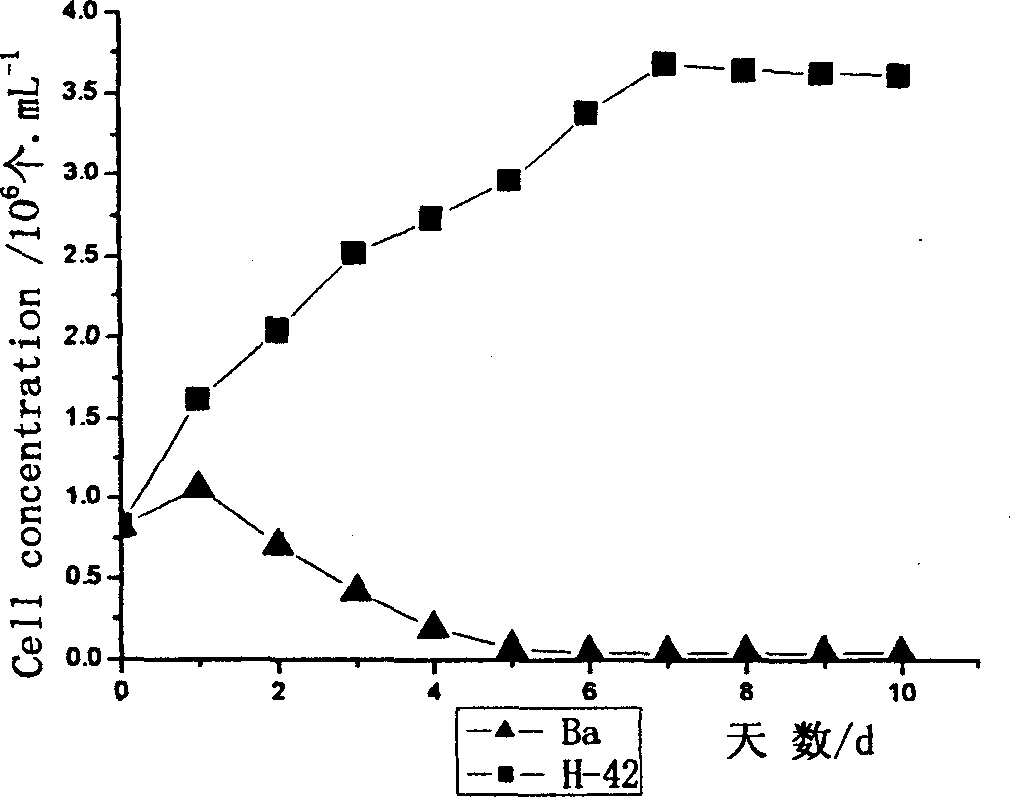
InactiveCN1757707AIncrease productivityExtend the time of outdoor cultivationMicrobiological testing/measurementUnicellular algaeUltravioletCulture mediums
A method for mutagenizing and selectively culturing a refractory single-cell green alga includes such steps as sterilizing and cooling culture medium, inoculating alga liquid, culturing, mixing with iodine solution or bromophenol blue, deactivating, calculating alga density in alga liquid, ultraviolet mutagenizing, dark culturing, mixing the cultured alga liquid with fresh culture medium, culturing, high-temp screening, amplifying culture of living alga cells, culturing under light radiation, inoculating yellow alga, culturing, testing its mutagenized effect, measuring the long and short diameters of cell, extracting DNA, random amplifying of polymorphic DNA, calculating genetic similarity coefficient, extracting H-42 and general protein, electrophoresis, dyeing with Coomassic brilliant blue, recording result and observing the electropherogram to obtain result.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
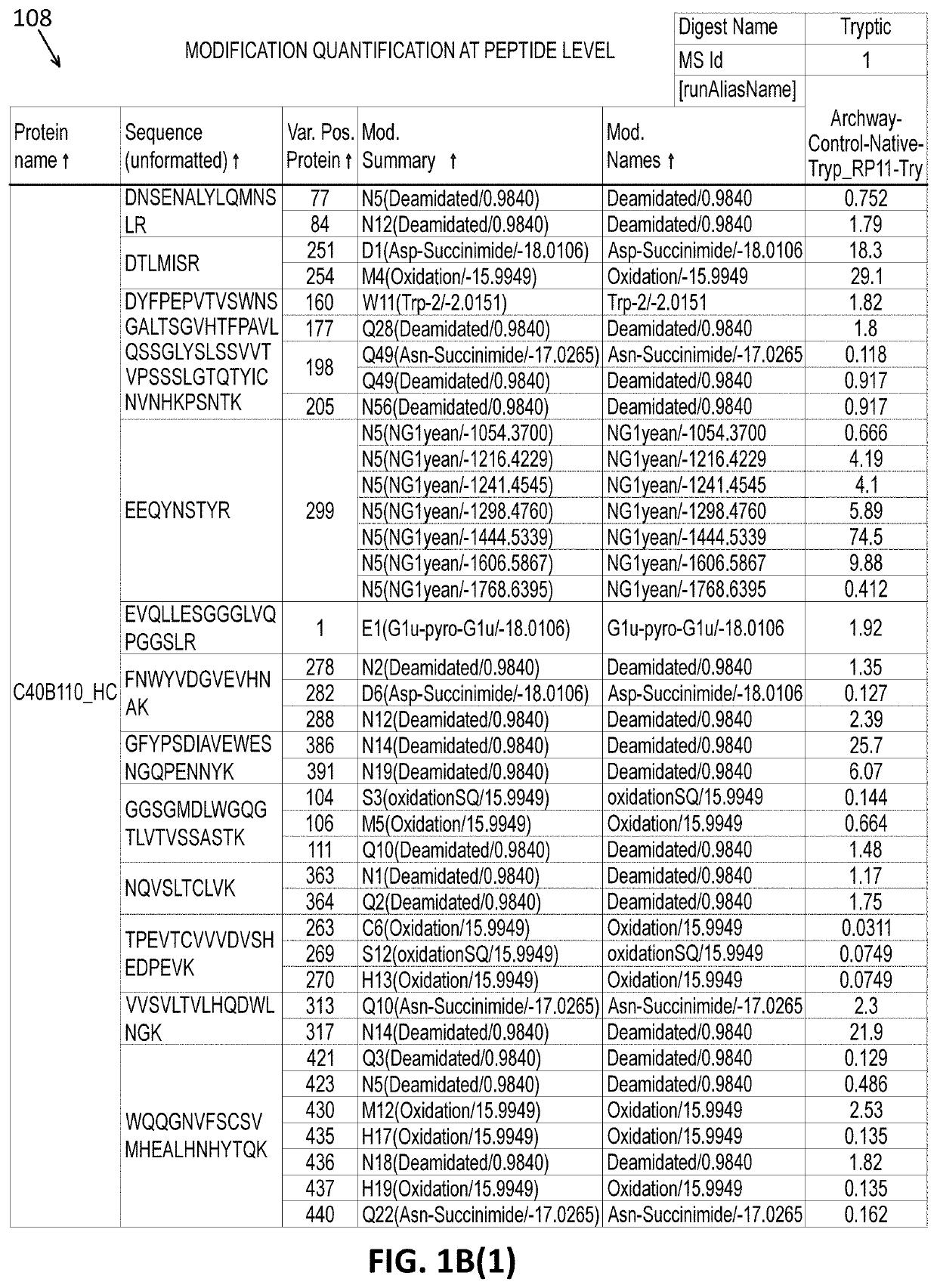
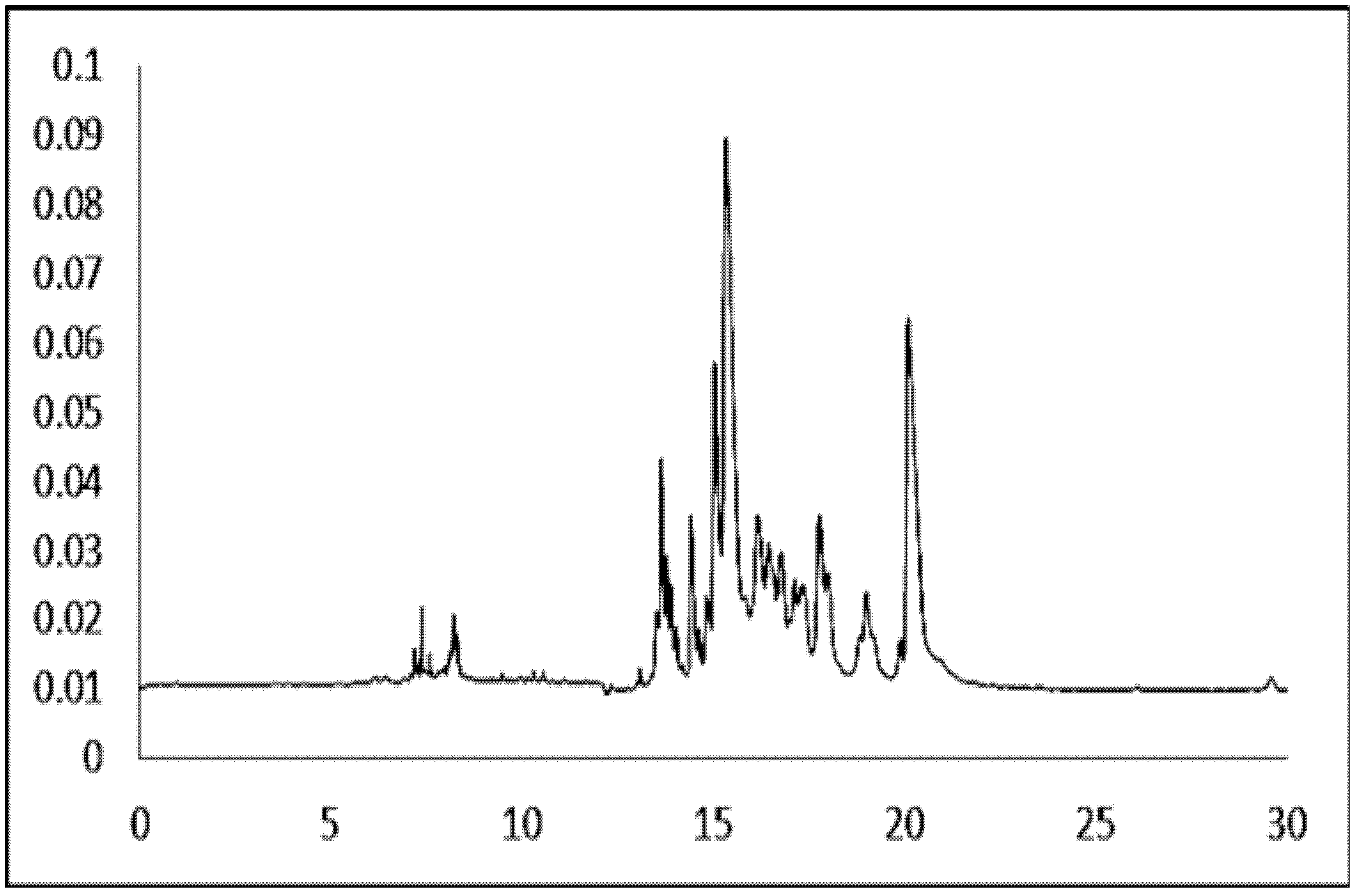
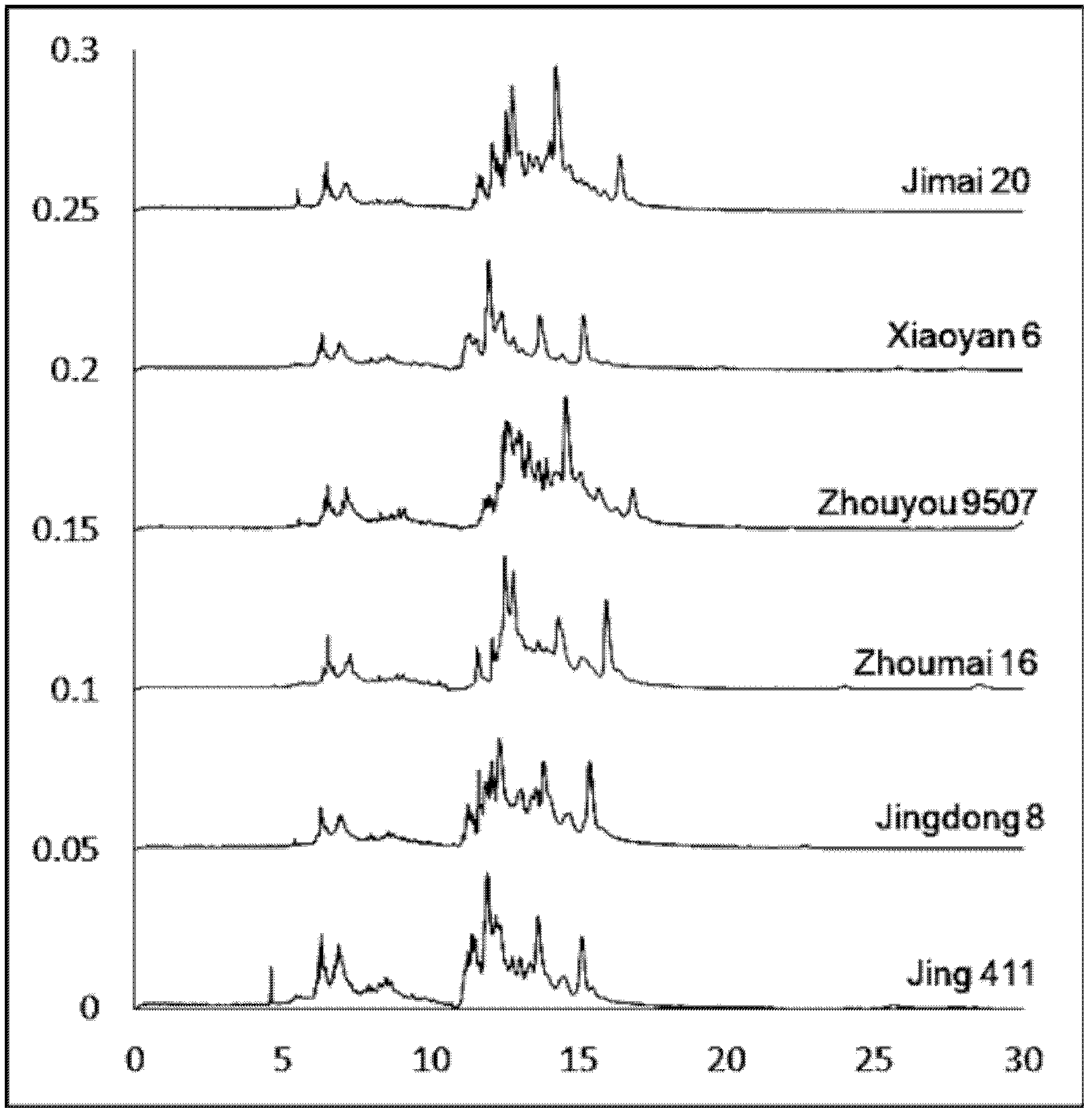
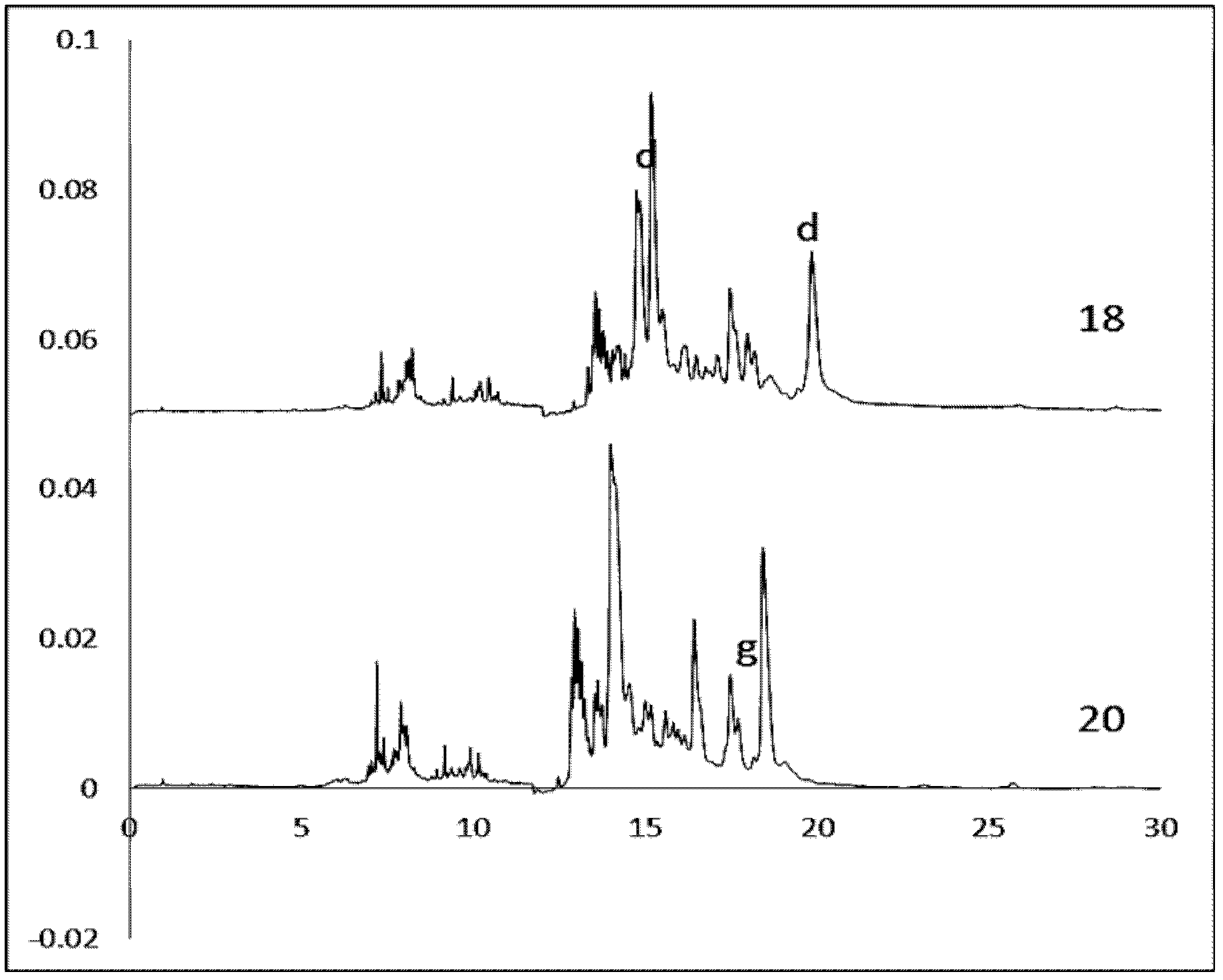
Intact mass reconstruction from peptide level data and facilitated comparison with experimental intact observation
ActiveUS20210048440A1Biological testingSpectrometer combinationsMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryProtein-protein complex
Methods and apparatuses for the identification and / or characterization of properties of a macromolecule based on mass spectrometry data. Specifically, described herein are methods and apparatuses for converting peptide-level data into a pseudo-intact mass spectra. Also described herein are methods and apparatuses for converting peptide-level data into a pseudo-electropherogram. The methods may be well suited for analyzing proteins and protein complexes, including estimating properties of post-translational modifications of the proteins and protein complexes. Methods may include generating a theoretical graph or spectrum based on peptide-level mass spectrometry data. In some embodiments, the theoretical graph may be a theoretical intact mass spectrum or a theoretical charge distribution spectrum.
Owner:PROTEIN METRICS LLC
Capillary electrophoresis method for identifying low molecular weight glutelin subunit of wheat and application thereof
InactiveCN102323320AReduce dosageHigh speedPreparing sample for investigationHollow article cleaningBiotechnologyCapillary electrophoresis
The invention discloses a capillary electrophoresis method for identifying a low molecular weight glutelin subunit of wheat. Through the method, a standard capillary electrophoresis pattern of the low molecular weight glutelin subunit of the wheat can be established, and further, a set of complete technical systems for identifying the high-quality subunit of the wheat is formed. According to protein peak migration time and peak area identified variety and germplasm, screened high-quality subunits and allelic genes, the rapid improvement on the quality of the wheat is realized.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
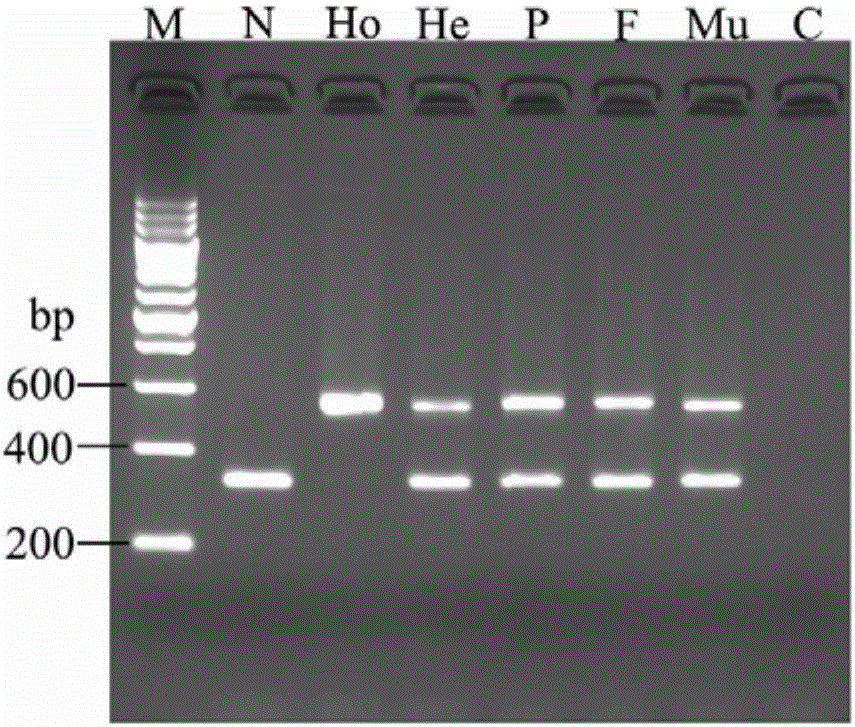
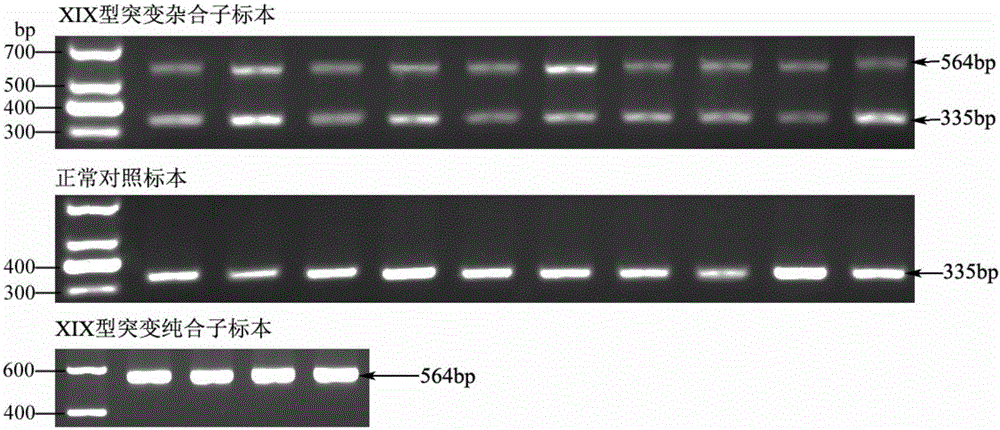
High-frequency XIX type mutation screening primer and high-frequency XIX type mutation screening kit for disease-causing gene SLC25A13 of Citrin deficiency (CD)
InactiveCN105695592AEasy to detectQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyMutation screening
The invention discloses a Citrin deficiency disease-causing gene SLC25A13 high-frequency type XIX mutation screening primer and a kit, which belong to the field of biotechnology. The present invention provides three newly designed primers, establishes a multiplex PCR system relying on common Taq enzymes, and can identify whether a sample is XIX mutation negative, positive or heterozygous through one PCR and analysis of the electrophoretic pattern, which is accurate, simple, fast and low cost. The screening primers and kits of the present invention do not require DNA sequencing, are simple, fast, and low-cost, and the detection results are direct and reliable. The detection time and cost are significantly better than existing methods, and can be completed with simple and common equipment, suitable for Rapid detection and large-scale population screening of high-frequency XIX mutations of the SLC25A13 gene by medical and testing institutions around the world.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Method for fast detecting fish collagen by means of capillary electrophoresis
InactiveCN105675695AFast analysisImprove reliabilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAquatic productPeak area
The invention discloses a method for rapidly detecting fish collagen by capillary electrophoresis, which comprises the following steps: (1) extracting the whole protein in fish skin and dissolving it in an equilibrium buffer solution with a pH of 7-8, and then adding anion exchange In the chromatographic column, the eluent is eluted, and the solution corresponding to the breakthrough peak is collected as the sample; (2) The obtained sample is subjected to capillary zone electrophoresis to obtain an electrophoretic spectrum, and the peak area obtained in the electrophoretic spectrum is substituted into the fish collagen The concentration of fish collagen in the sample solution was calculated from the standard curve regression equation of the protein. The present invention uses capillary electrophoresis to rapidly, qualitatively and quantitatively detect a new type of fish allergen, aquatic product allergen fish collagen. The invention uses the established method to qualitatively and quantitatively analyze fish collagen, which has no literature report, and provides new basis for fast and accurate detection of fish collagen.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
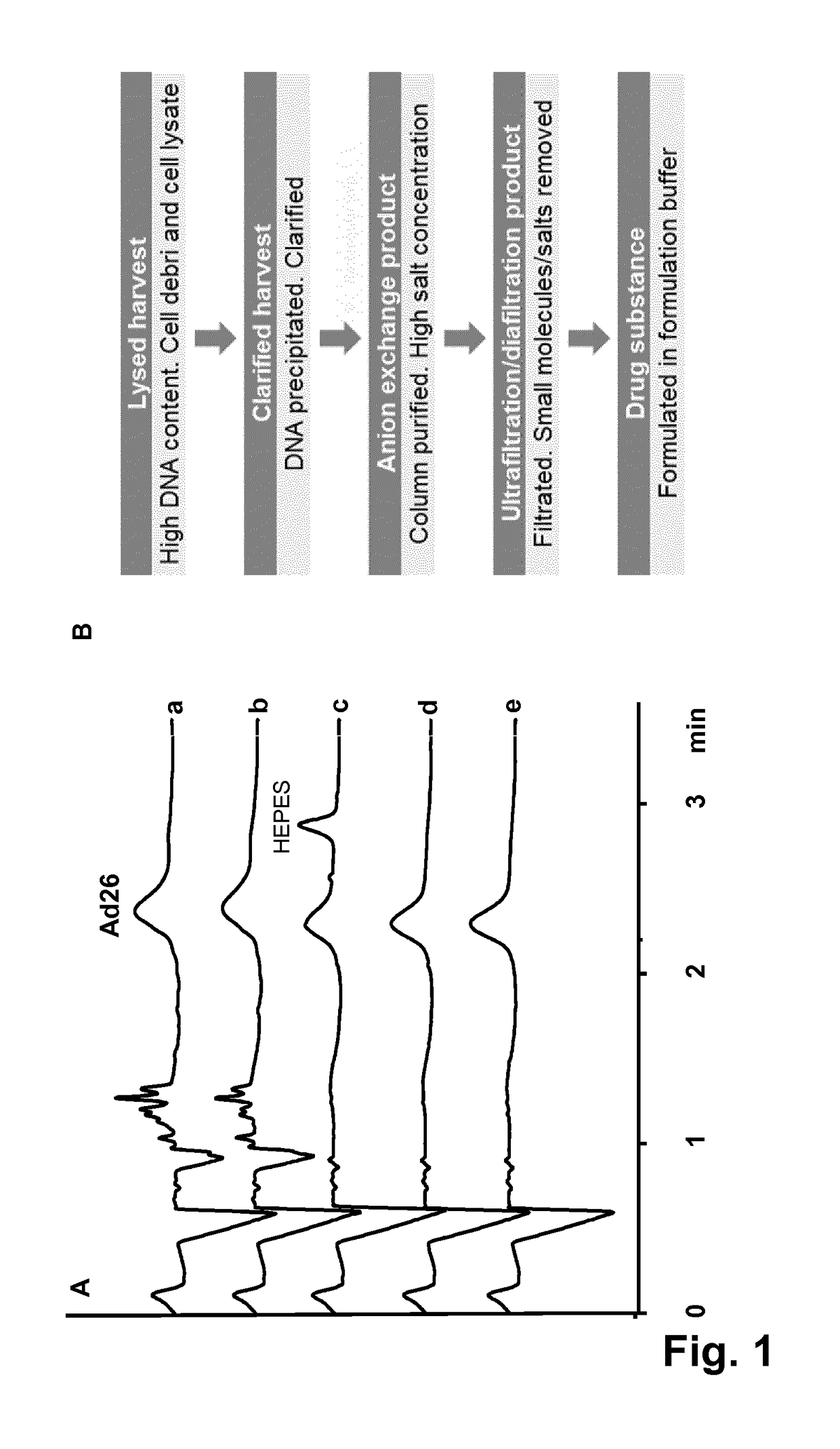
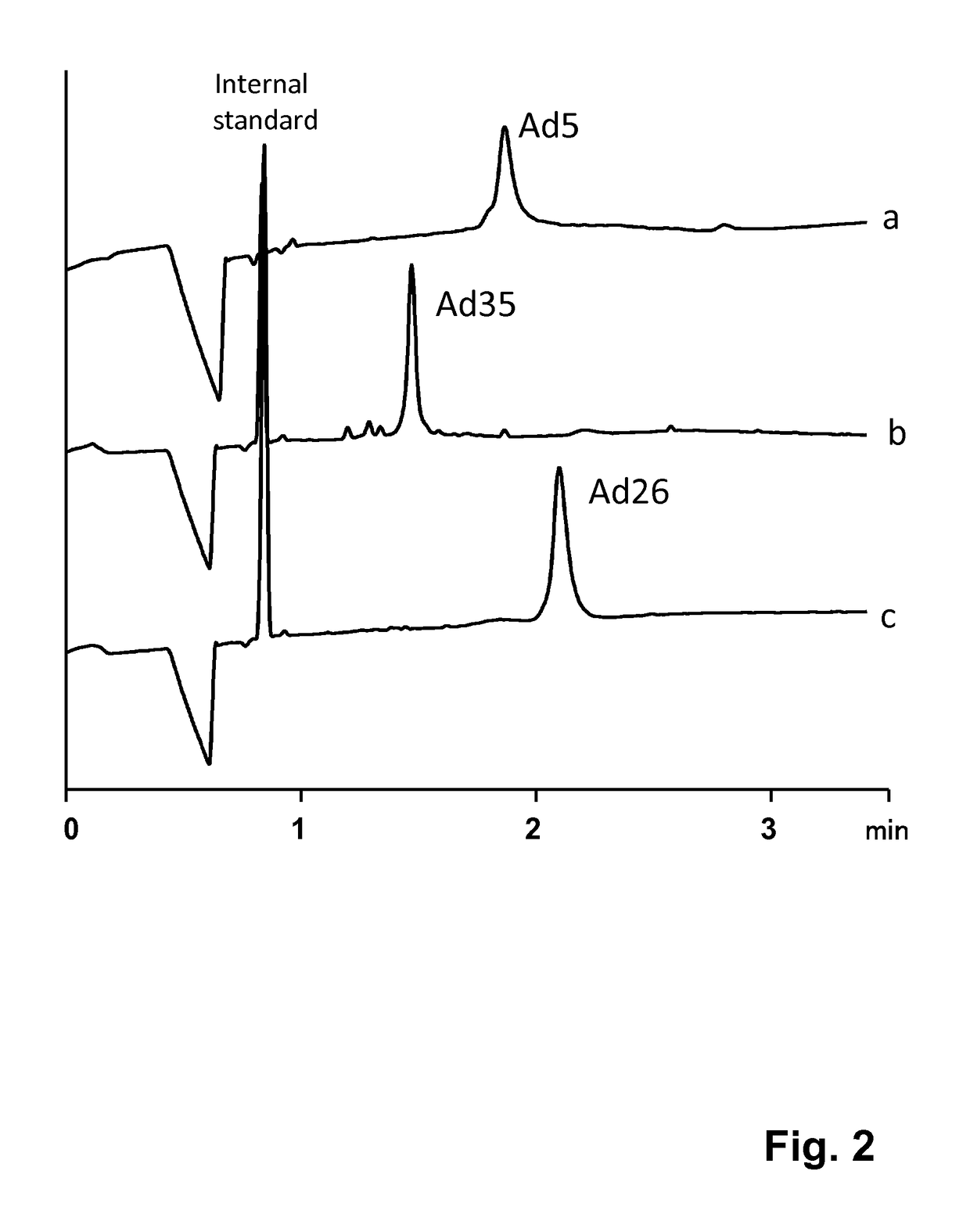
Method for quantification of virus particles using capillary zone electrophoresis
ActiveUS20180011056A1Robust and accurate and reliable and fastPoor recoveryMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansReference sampleBuffer solution
The present invention provides a method for the quantification of virus particles in a biological sample, comprising the steps of: (a) introducing said biological sample comprising virus particles into a capillary tube containing a buffer solution; (b) applying an electrical field to said capillary tube of sufficient voltage to allow for the separation of the virus particles from additional constituents in said sample, to obtain electrophoretical fractions; (c) generating an electropherogram associated with the electrophoretical fractions; and (d) determining the concentration of virus particles in said sample by comparing the electropherogram with an electropherogram generated from a reference sample containing a known concentration of said virus particles.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
Particle based homogeneous assays using capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence detection
InactiveUS20070259338A1Sensitive highSimplified electropherogramsElectrolysis componentsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorTarget analysisAnalyte
The invention provides highly sensitive and rapid homogeneous assays which employ particle-enhanced assay formats in concert with capillary electrophoresis and laser-induced fluorescence (LIF) detection to determine the concentration of an analyte of interest in a sample. Such a determination is made by measuring fluorescent signal(s) (i.e., an electropherogram) produced upon LIF of species present in the reaction mixture that are capable of producing such signals. The method of this invention produces simplified electropherograms by reducing the number of signals that must be separated and subsequently measured, and therefore increases the accuracy of the detection and / or quantification of target analyte concentration in a sample.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
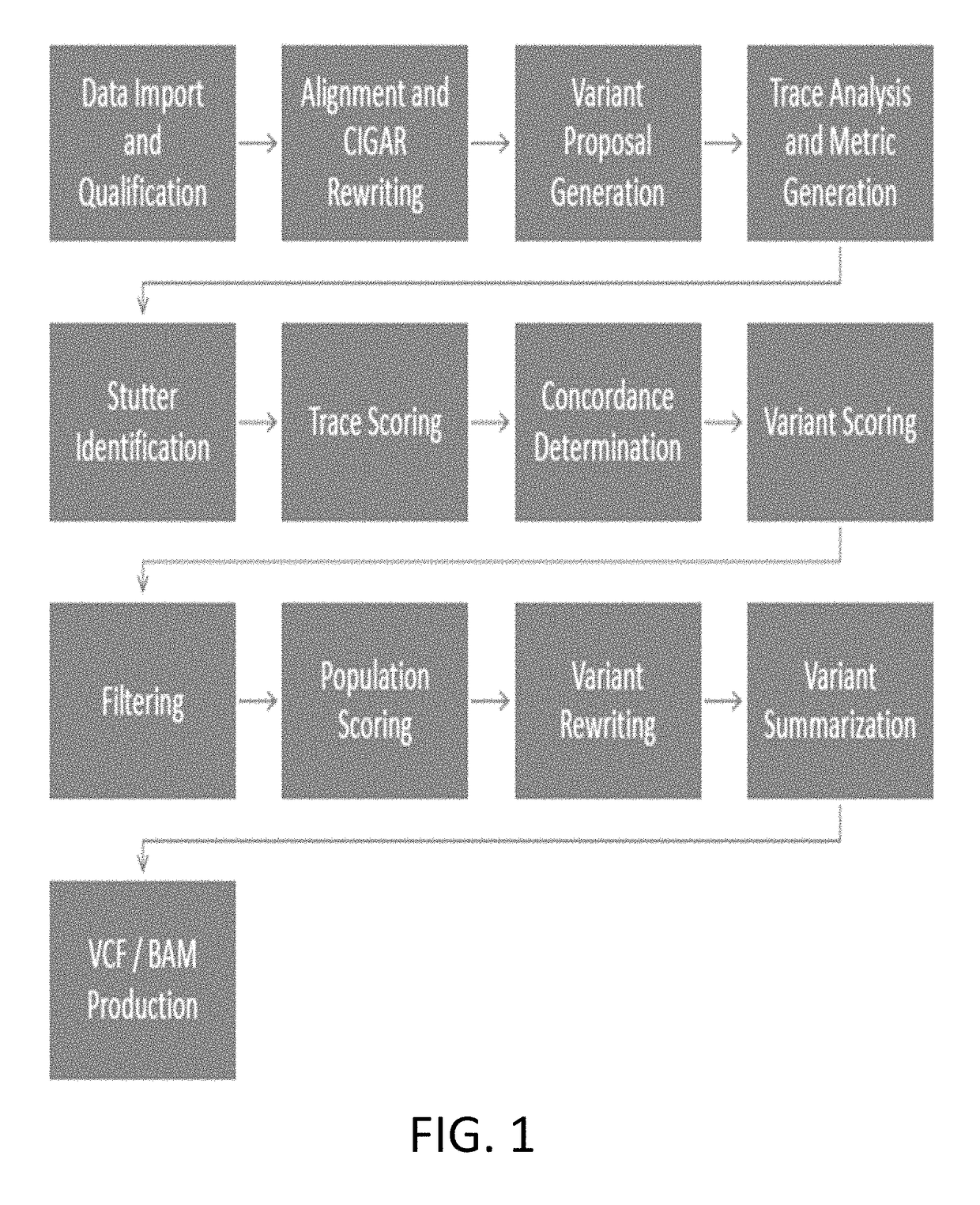
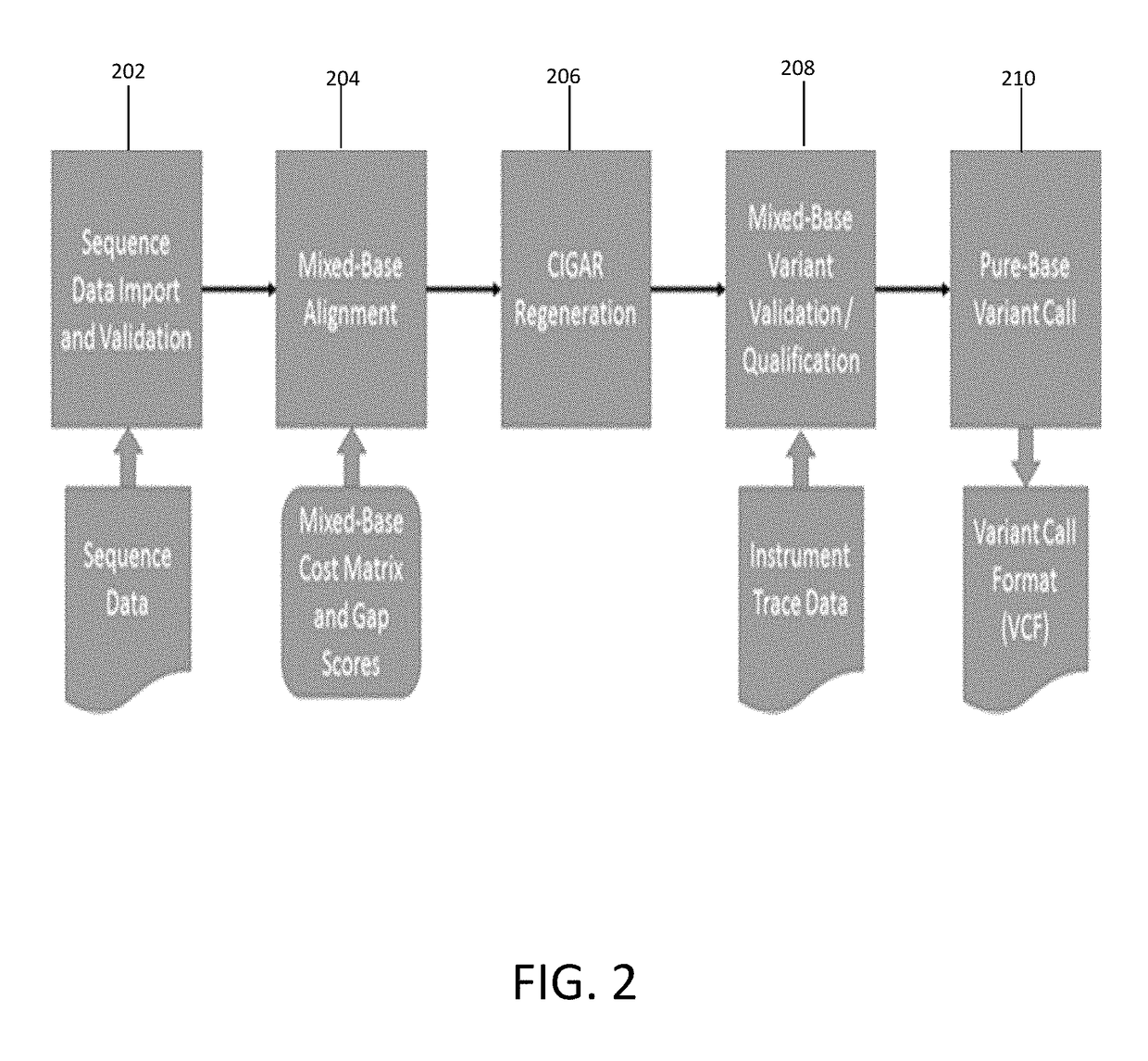
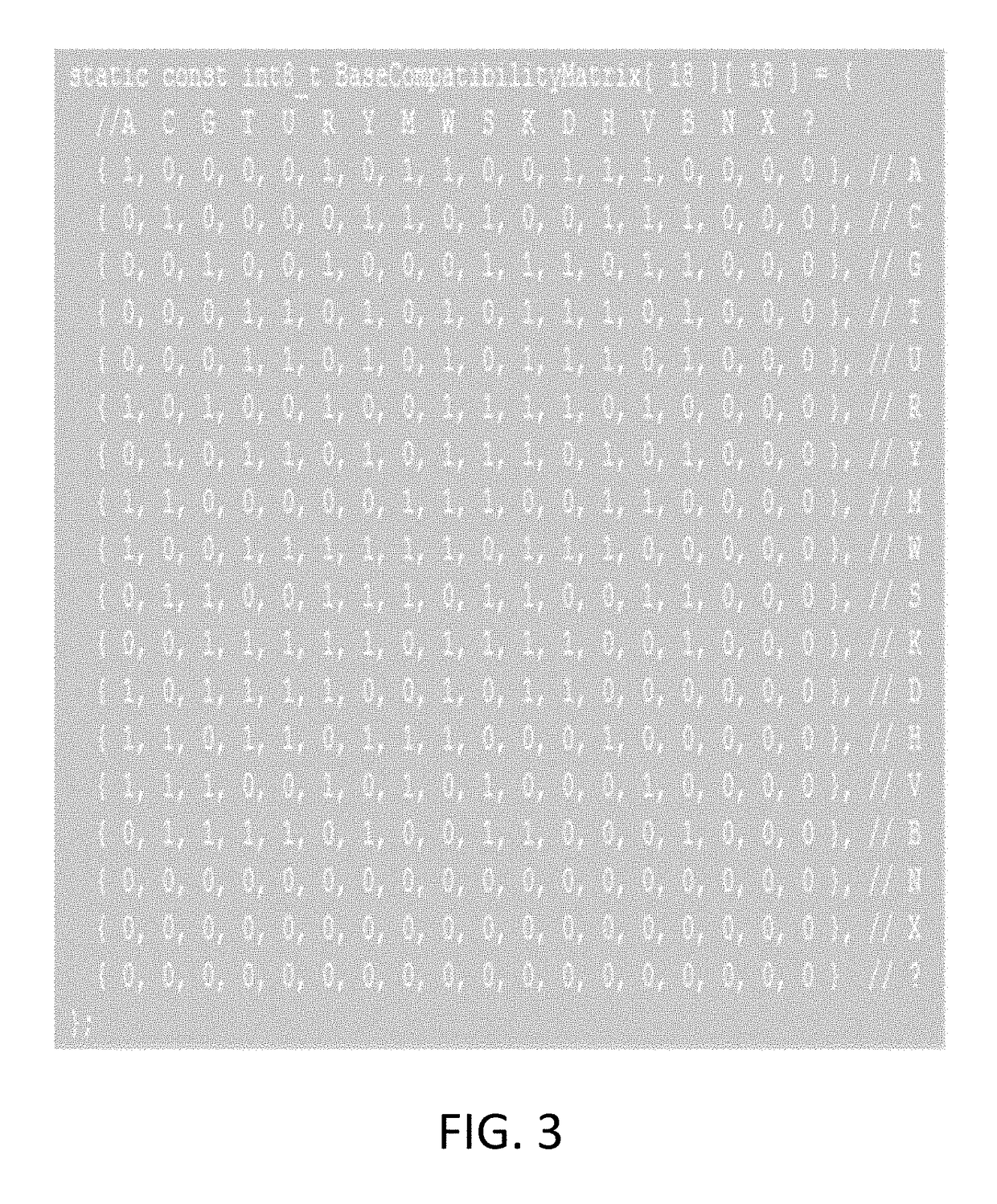
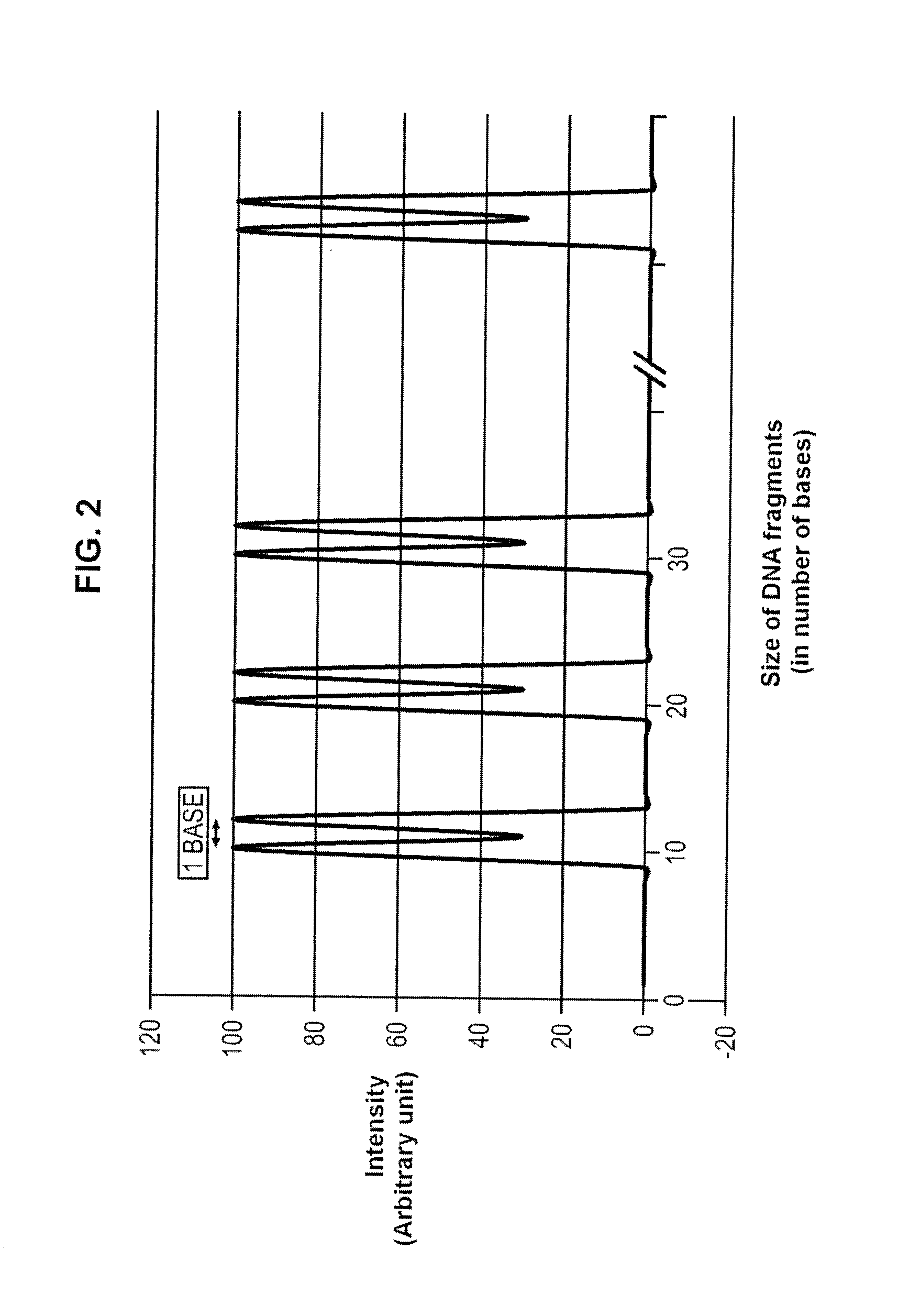
Methods and systems for variant detection
ActiveUS10197529B2Material analysis by electric/magnetic meansSequence analysisElectropherogramInstrumentation
In one exemplary embodiment, a method for detecting variants in electropherogram data is provided. The method includes receiving electropherogram data from an instrument and analyzing the electropherogram data to identify mixed bases in the electropherogram data. The method further includes identifying features within the electropherogram data indicative of errors and validating the identified mixed bases. Then the method includes determining variants in the electropherogram data based on the validated mixed bases.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Simple algorithm for quantifying polymorphisms in electropherograms
InactiveUS20110238318A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingGenomic sequencingSequence analysis
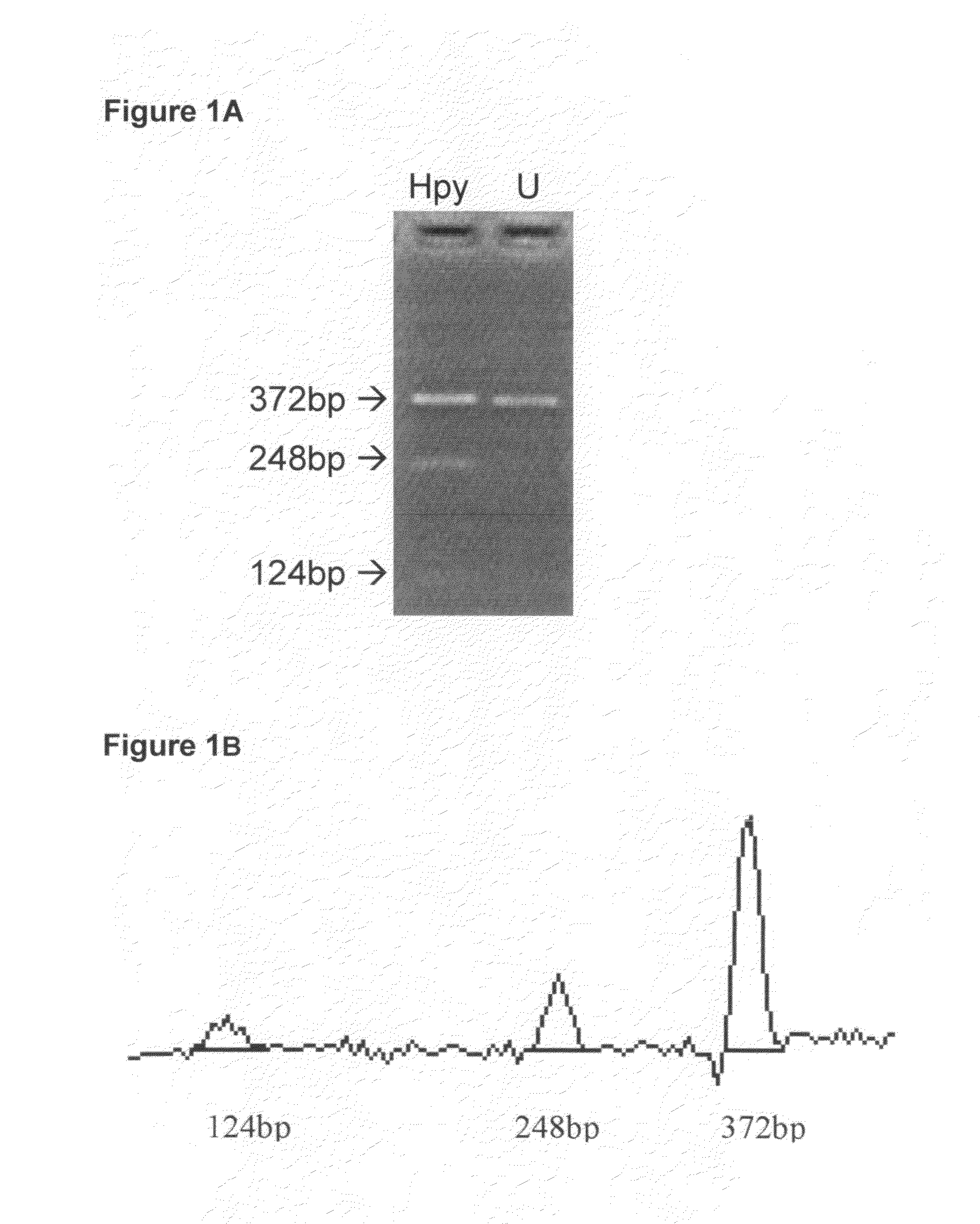
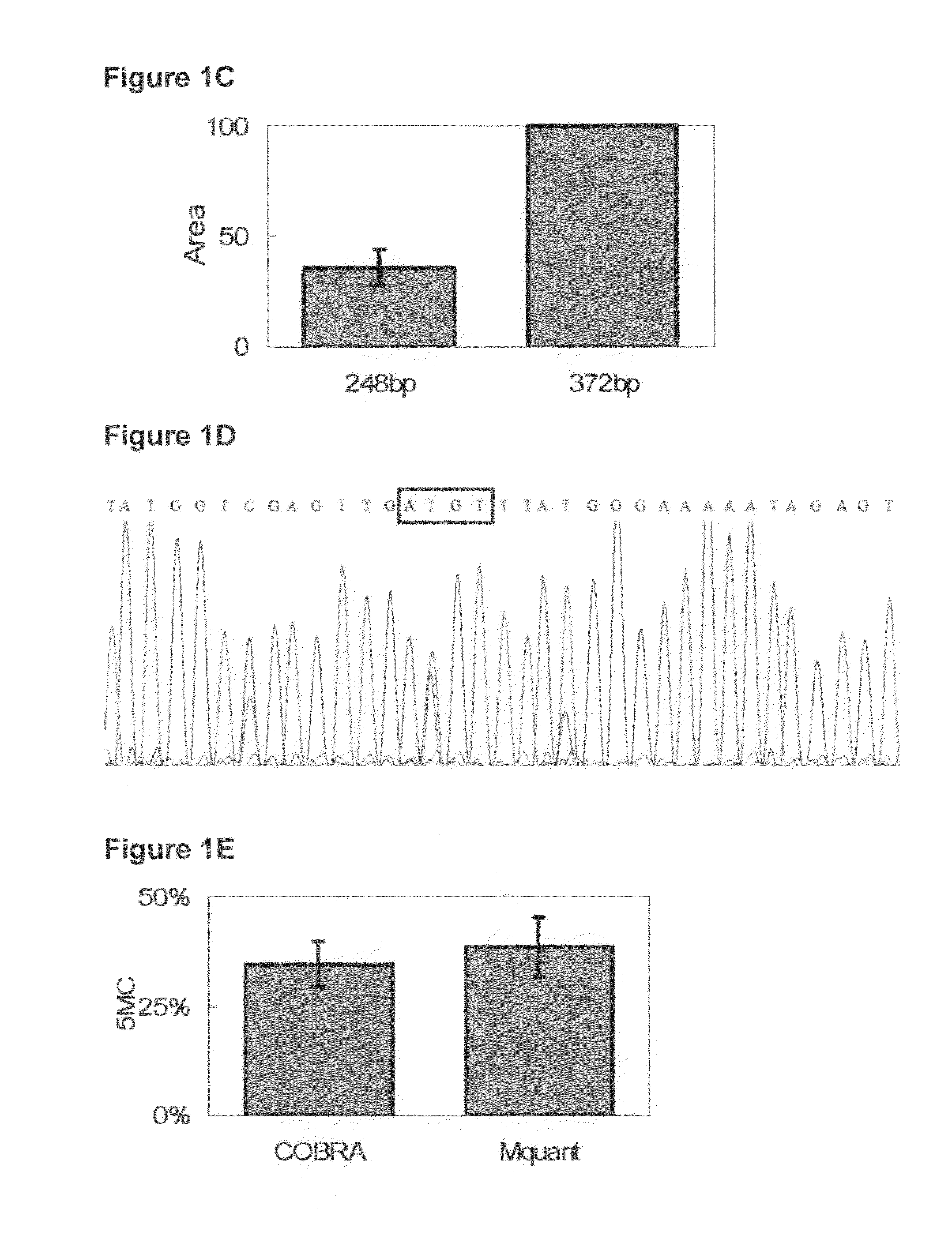
A method for quantifying cytosine methylation at a particular target CpG site in DNA of a cell or organism, by performing bisulfite genomic sequencing, wherein a DNA sample extracted from a cell or organism is treated with sodium bisulfite to convert cytosine to uracil and a selected fragment of this treated DNA is amplified, performing a sequence analysis of the amplificate from an electropherogram wherein the area under a peak is measured in a plurality of peaks at either side of the target CpG site to determine the mean T area (T bar) surrounding the site, subtracting the area of the T at the target CpG site from the mean T area wherein the difference is termed delta T, and calculating the proportional level of methylation as a quotient of delta T / T bar, or as a percent value, is presented.
Owner:COONEY CRAIG A
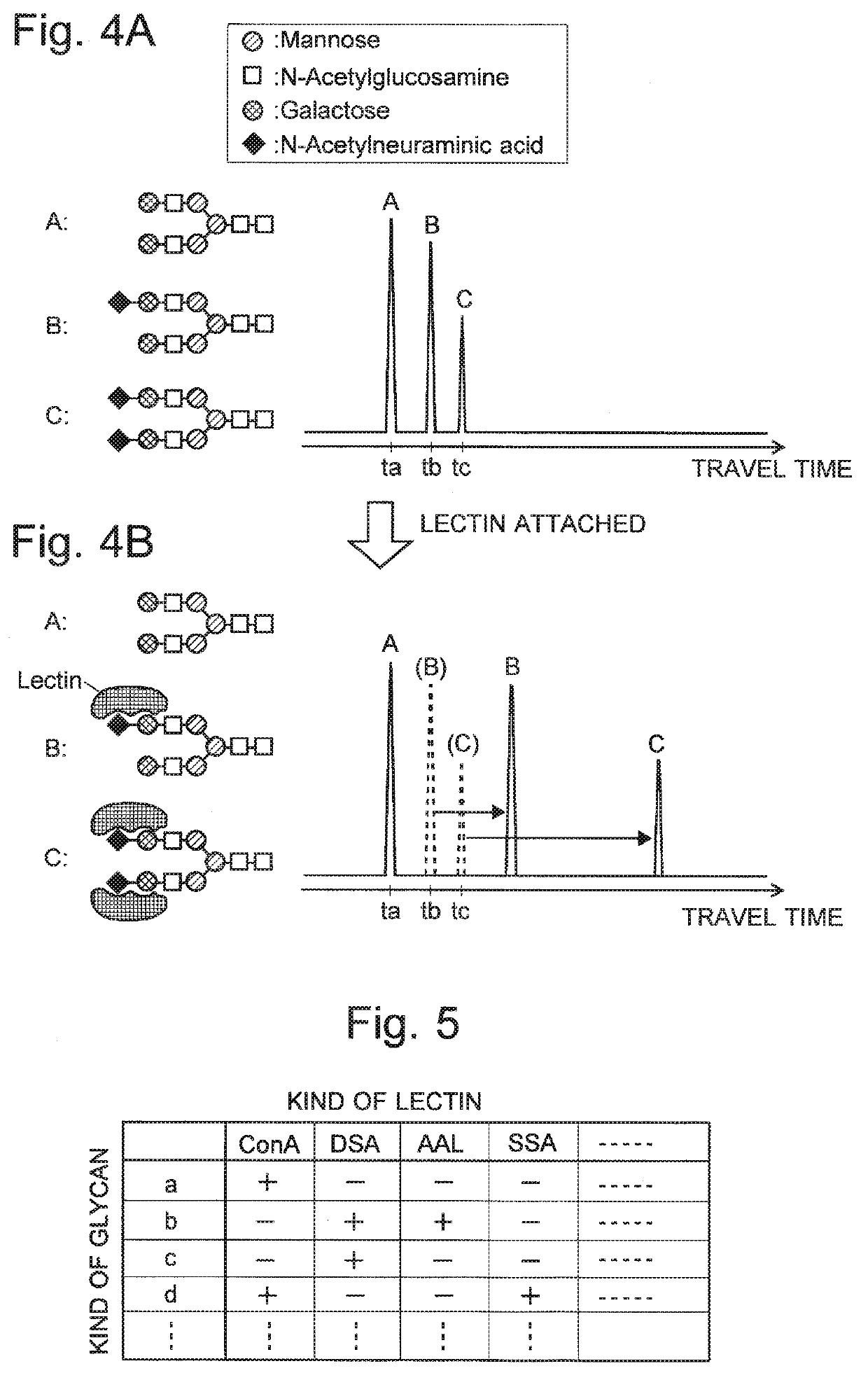
Glycan analysis method, glycan analysis system, program for glycan analysis, and kit for glycan analysis
ActiveUS20190265246A1Shorten the time periodImprove throughputMolecular entity identificationElectrophoretic profilingHigh concentrationMolecular sieve
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Particle based homogeneous assays using capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence detection
InactiveUS7556932B2Sensitive highSimplified electropherogramsElectrolysis componentsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorTarget analysisAnalyte
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
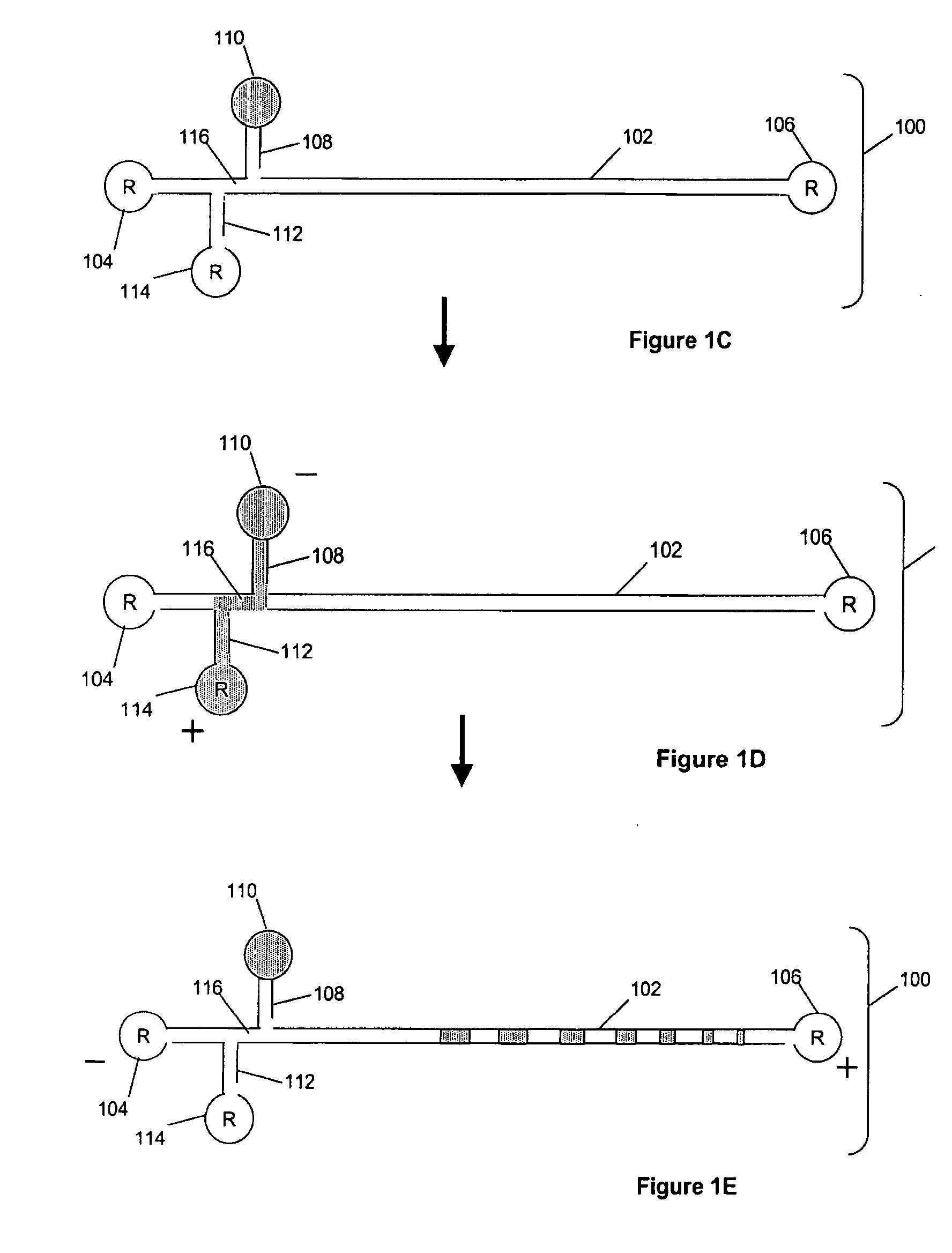
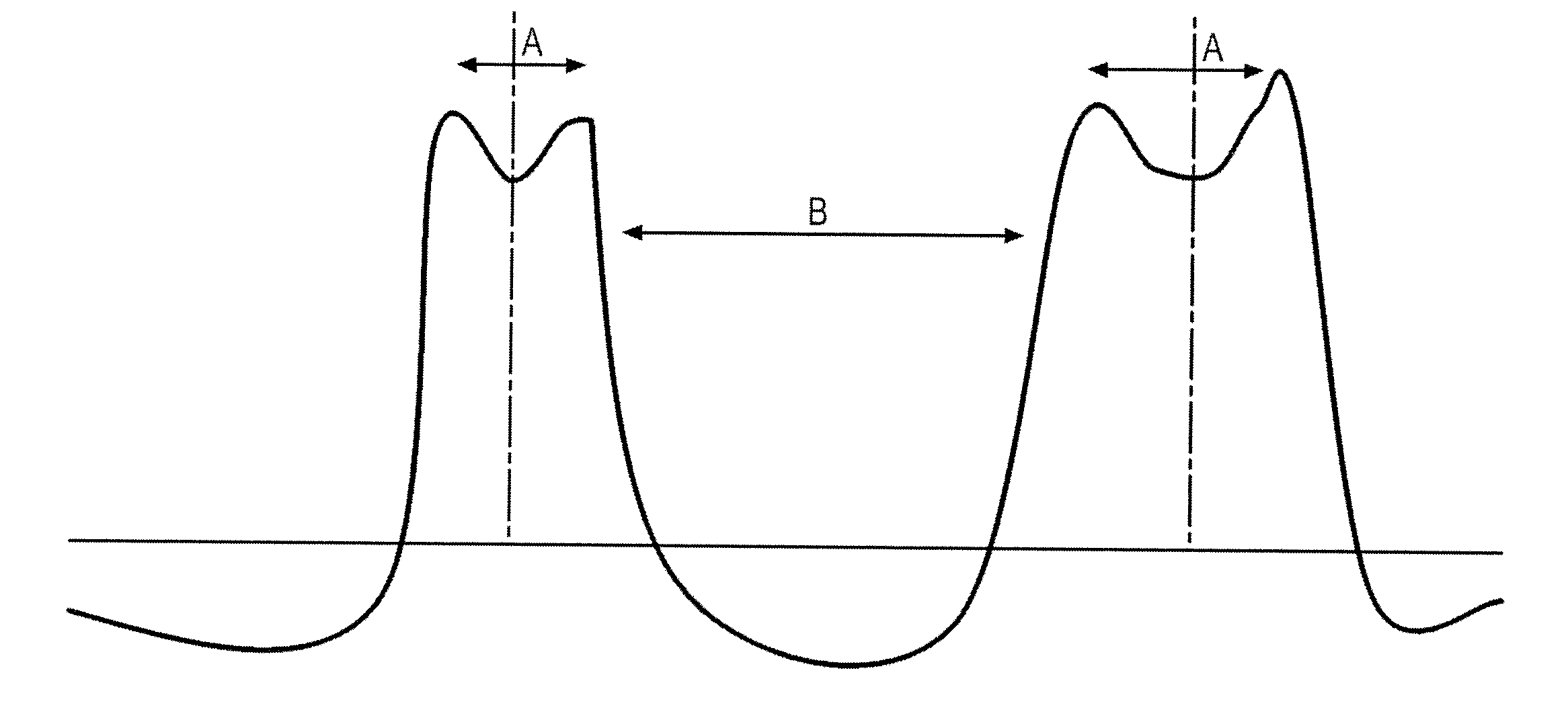
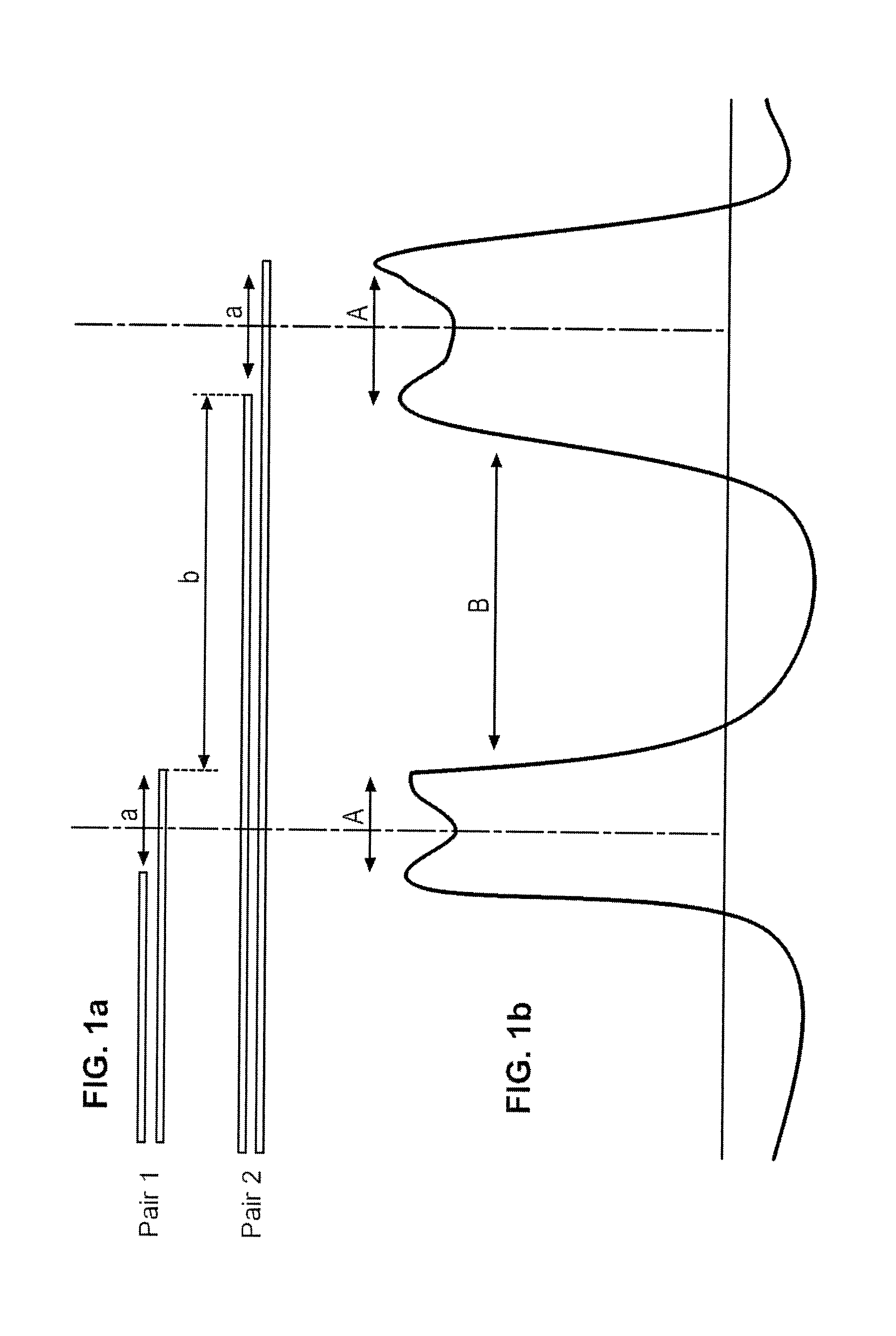
Size marker and method for controlling the resolution of an electropherogram
The invention concerns a size marker for electrophoresis, characterized in that it contains several pairs of molecules the sizes of which are selected to allow the generation of a succession of double-peaks in one same electropherogram, said double-peaks being spaced apart two by two by a distance greater than the distance separating the two peaks of a double-peak. The invention also concerns a method for controlling the resolution of an electropherogram produced with a said marker.
Owner:IDEMIA IDENTITY & SECURITY FRANCE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com