Microfluidic chip for detecting heavy metal ions in water and detection method
A heavy metal ion, microfluidic chip technology, applied in measurement devices, material analysis by electromagnetic means, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as low integration, affect detection accuracy, and complex detection process, so as to reduce production costs and The cost of use, the elimination of preprocessing, and the simple effect of the detection process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
[0058] This embodiment is an embodiment of a microfluidic chip for detecting heavy metal ions in water.
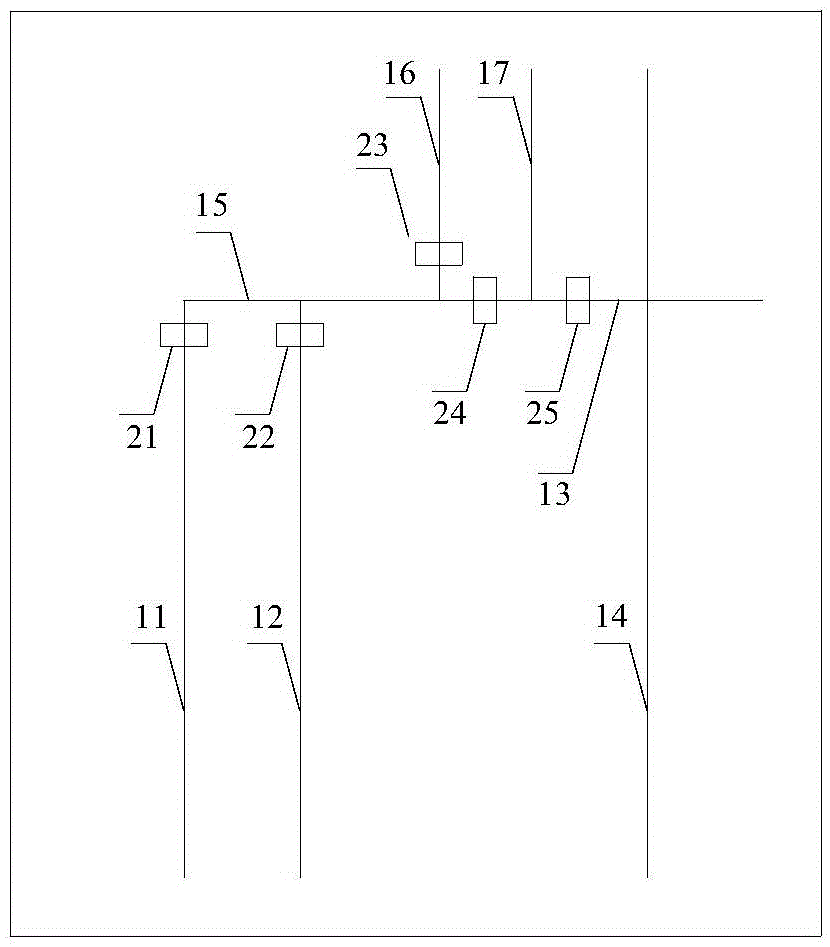
[0059] The structure diagram of the microfluidic chip for detecting heavy metal ions in water in this embodiment is as follows figure 1 shown. The microfluidic chip includes microchannels and microvalves,
[0060] The microchannels include reference microchannels 11, ion imprinting microchannels 12, electrophoresis sampling microchannels 13, electrophoretic separation microchannels 14, connecting microchannels 15, waste liquid discharge microchannels 16 and buffer solution discharge microchannels 17;
[0061] The microvalve includes a reference port outlet microvalve 21, an ion imprint outlet microvalve 22, a waste liquid outlet microvalve 23, a buffer stop microvalve 24 and a sample injection stop microvalve 25;
[0062] The electrophoresis sampling microchannel 13 and the electrophoretic separation microchannel 14 are arranged successively according to the flow directi...
specific Embodiment 2
[0066] This embodiment is an embodiment of a microfluidic chip for detecting heavy metal ions in water.
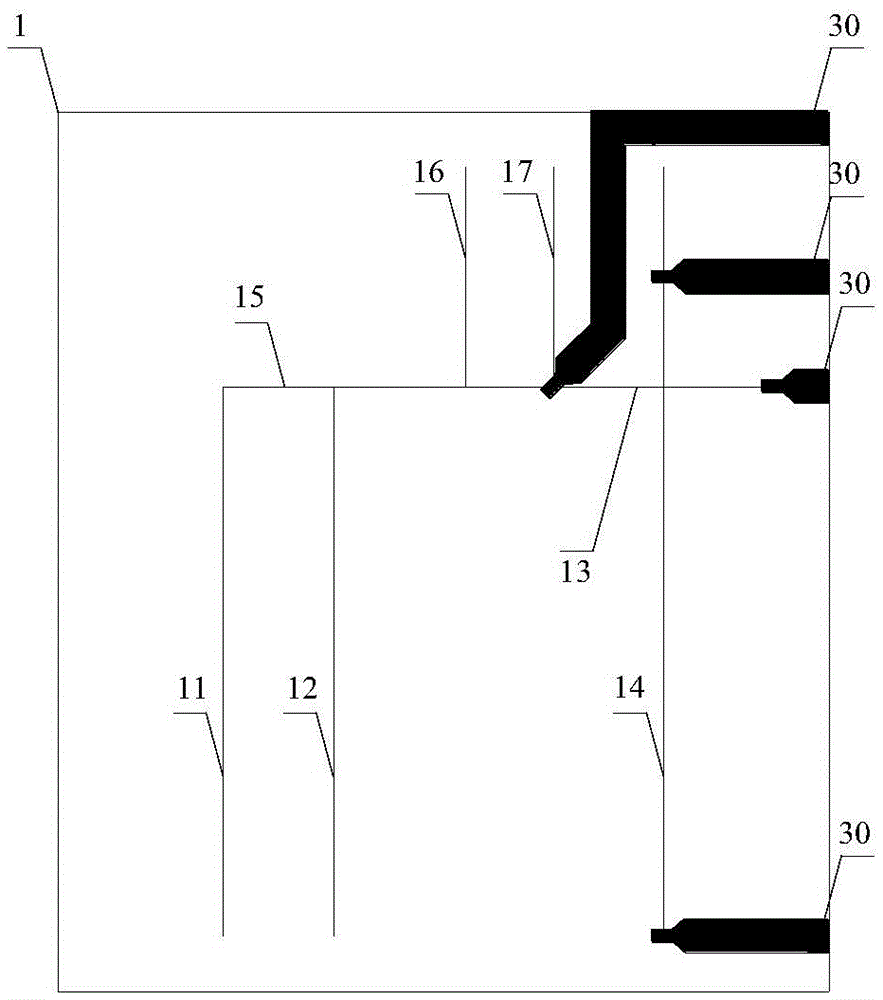
[0067] The microfluidic chip for detecting heavy metal ions in water in this embodiment, on the basis of the specific embodiment 1, further defines the chip, including a substrate layer 1, a thin film layer 2, a microvalve through-hole layer 3 and a gas-liquid connection from bottom to top. Layer 4;
[0068] The schematic diagram of the structure of the substrate layer 1 is as figure 2 As shown, the substrate layer 1 is provided with a reference microchannel 11, an ion imprinting microchannel 12, an electrophoretic sampling microchannel 13, an electrophoretic separation microchannel 14, a connecting microchannel 15, a waste liquid discharge microchannel 16 and a buffer solution discharge microchannel 17 A plurality of electrophoretic electrodes 30 are also provided, and the electrophoretic electrodes 30 are respectively connected with the electrophoretic sampling microch...
specific Embodiment 3
[0077] This embodiment is an embodiment of a microfluidic chip for detecting heavy metal ions in water.
[0078] The microfluidic chip for detecting heavy metal ions in water in this embodiment, on the basis of the above embodiments, further limits the number of ion-imprinted microchannels 12, and each ion-imprinted microchannel contains ion-imprinted polymers capable of adsorbing different heavy metal ions .
[0079] The ion-imprinted microchannel 12 is technically limited to a plurality of ion-imprinted microchannels 12, and it is possible to place imprinted polymers that adsorb different heavy metal ions in different ion-imprinted microchannels 12, thereby achieving the function of detecting multiple heavy metal ions with one device.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com