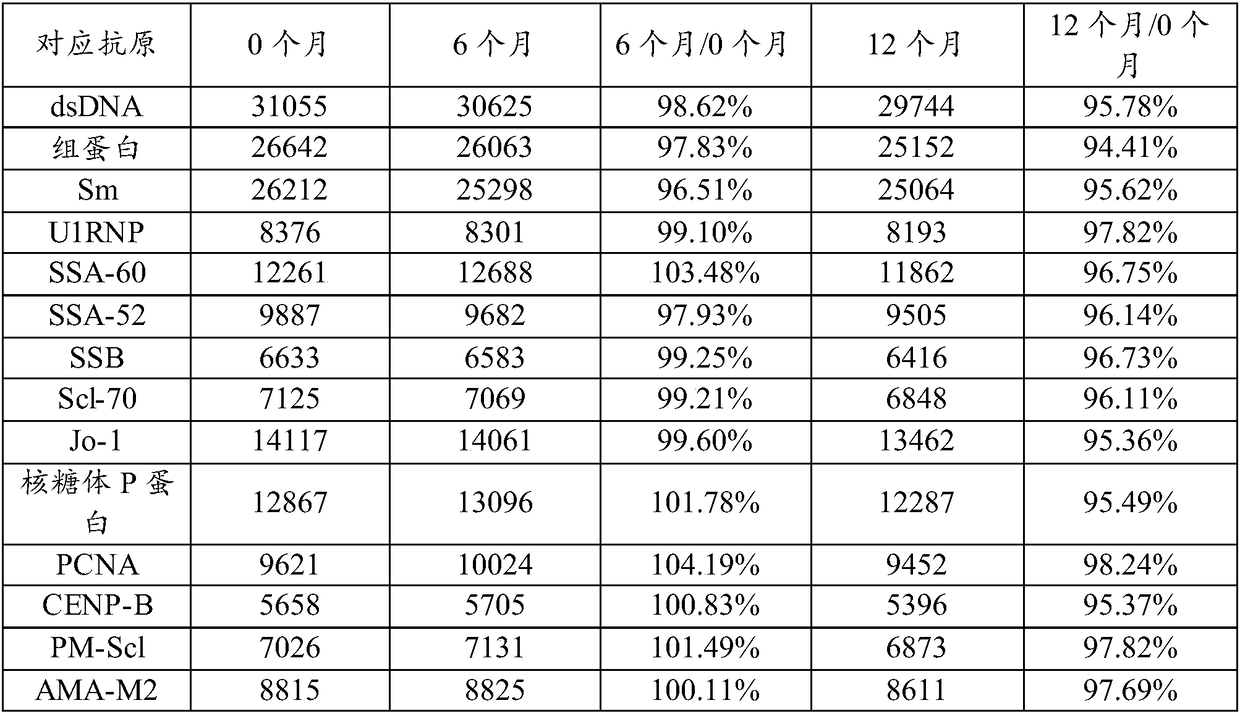
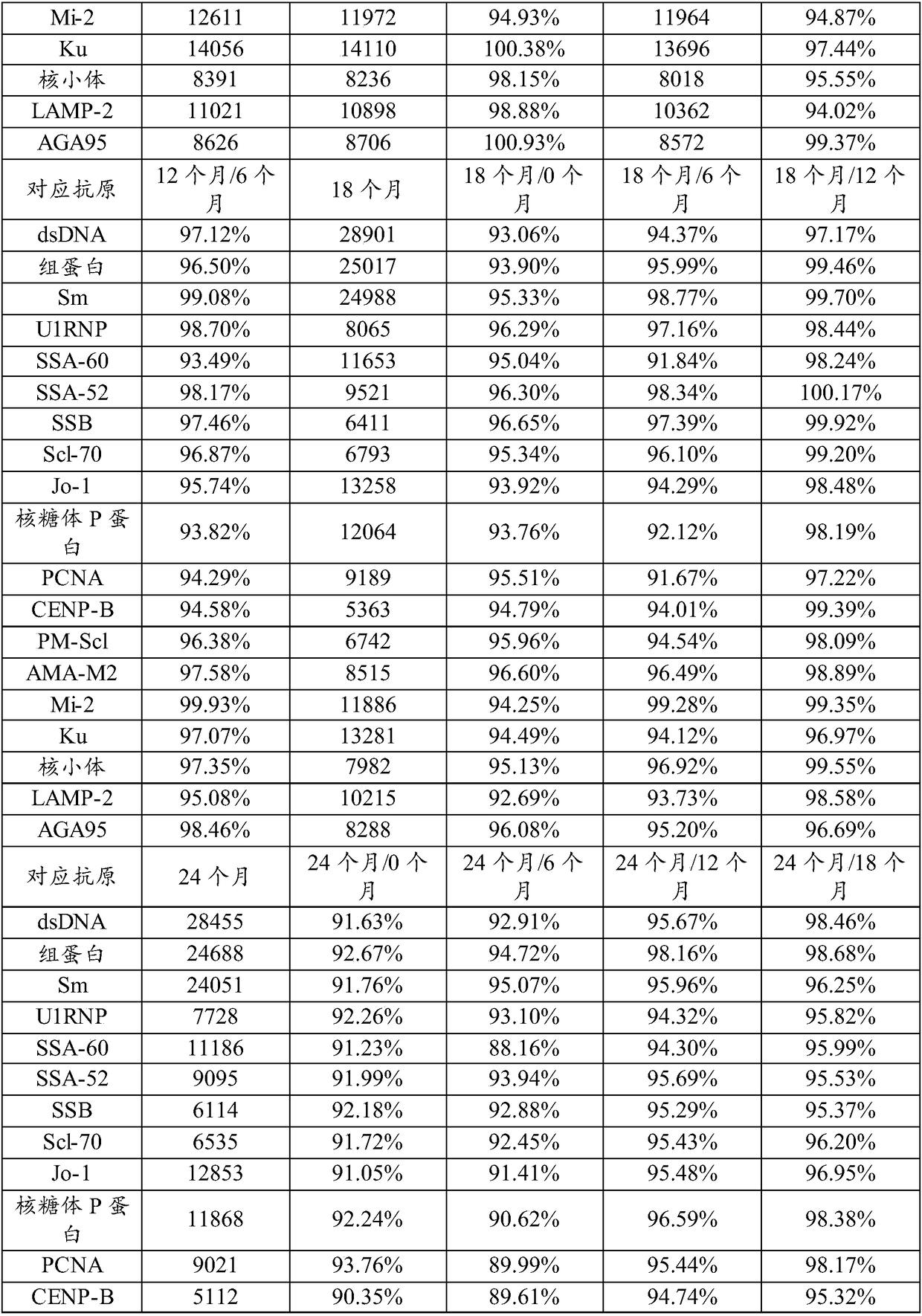
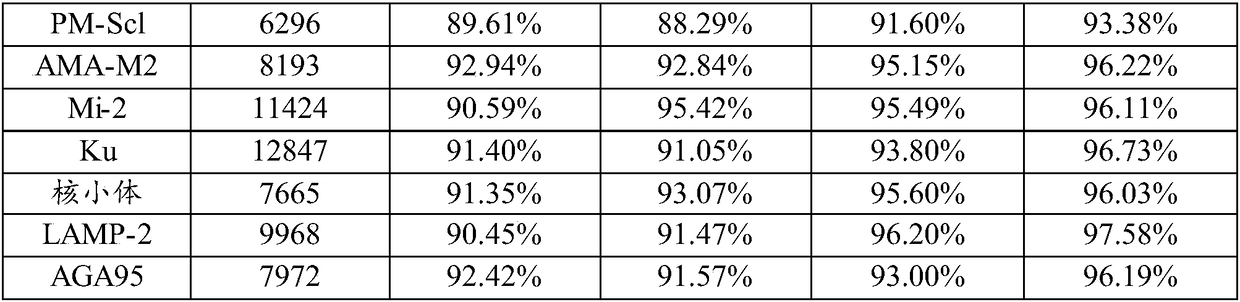
Patents
Literature
75results about "Electrophoretic profiling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Viral identification by generation and detection of protein signatures
InactiveUS20050014134A1Reliable identificationImprove signal-to-noise ratioElectrophoretic profilingVolume/mass flow measurementViral IdentificationBiology
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
Differential protein expression patterns related to disease states
InactiveUS20060068452A1Electrophoretic profilingCharacter and pattern recognitionBiologyProtein expression profile
The present invention is a method for determining protein expression profiles in disease or an altered biological state. The method is based on the use of two-dimensional (2D) gel electrophoresis where the gel images are assigned two different colors. The gels are then compared by an overlay procedure that allows for identification and quantification of unique proteins by determining which colors are detected in the superimposed images and the density of those colors.
Owner:NEOGENOMICS INC
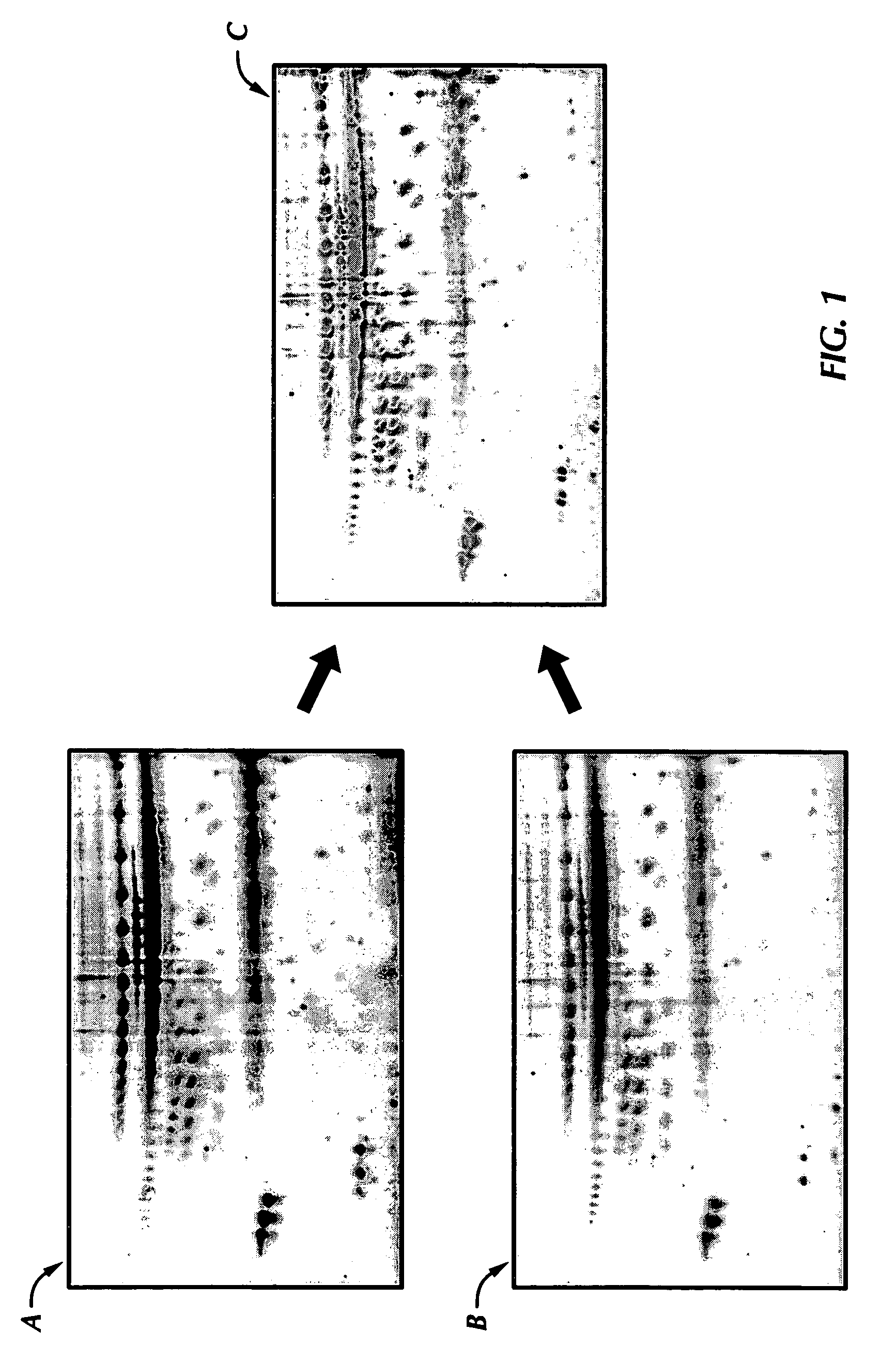
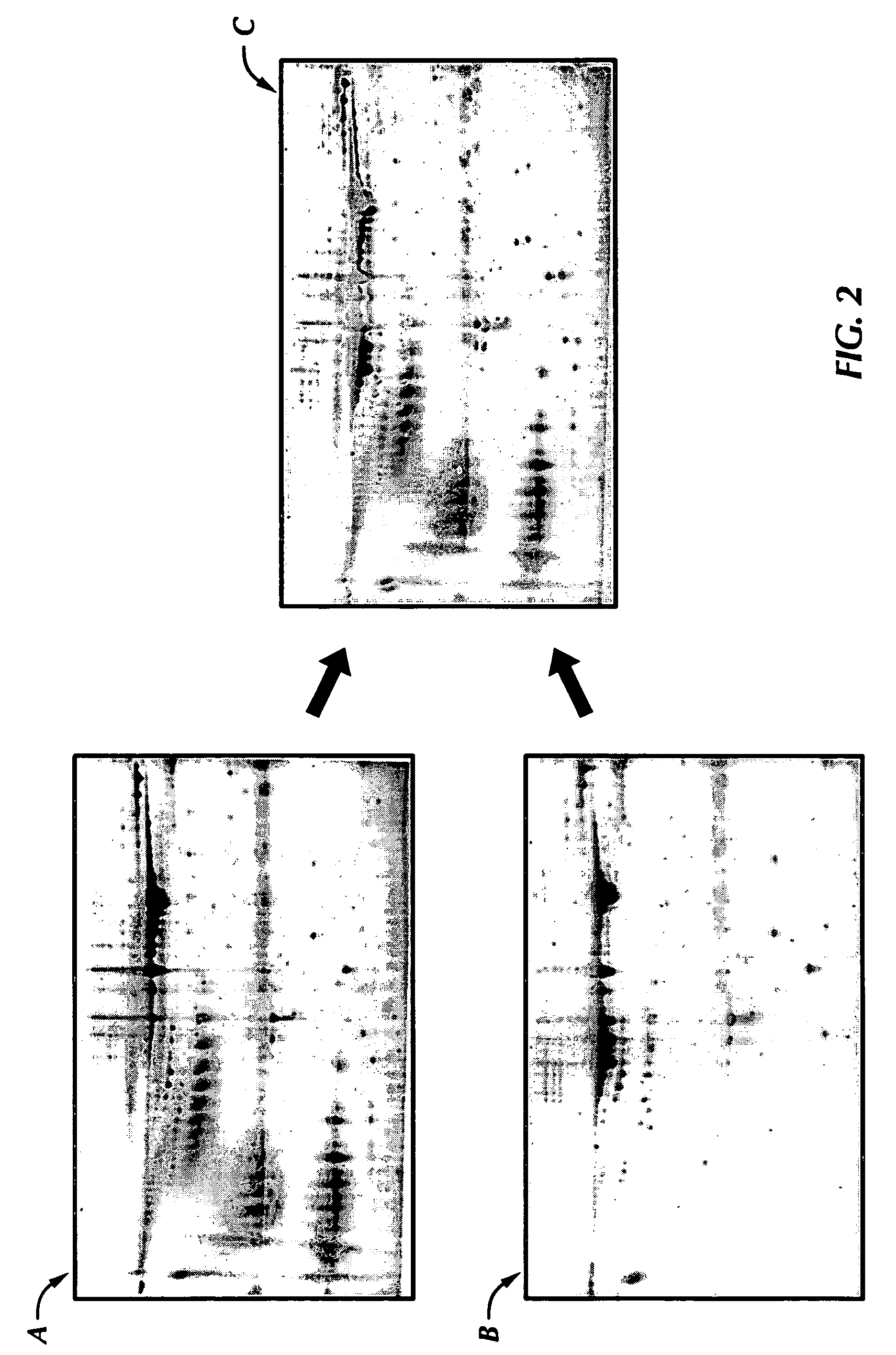
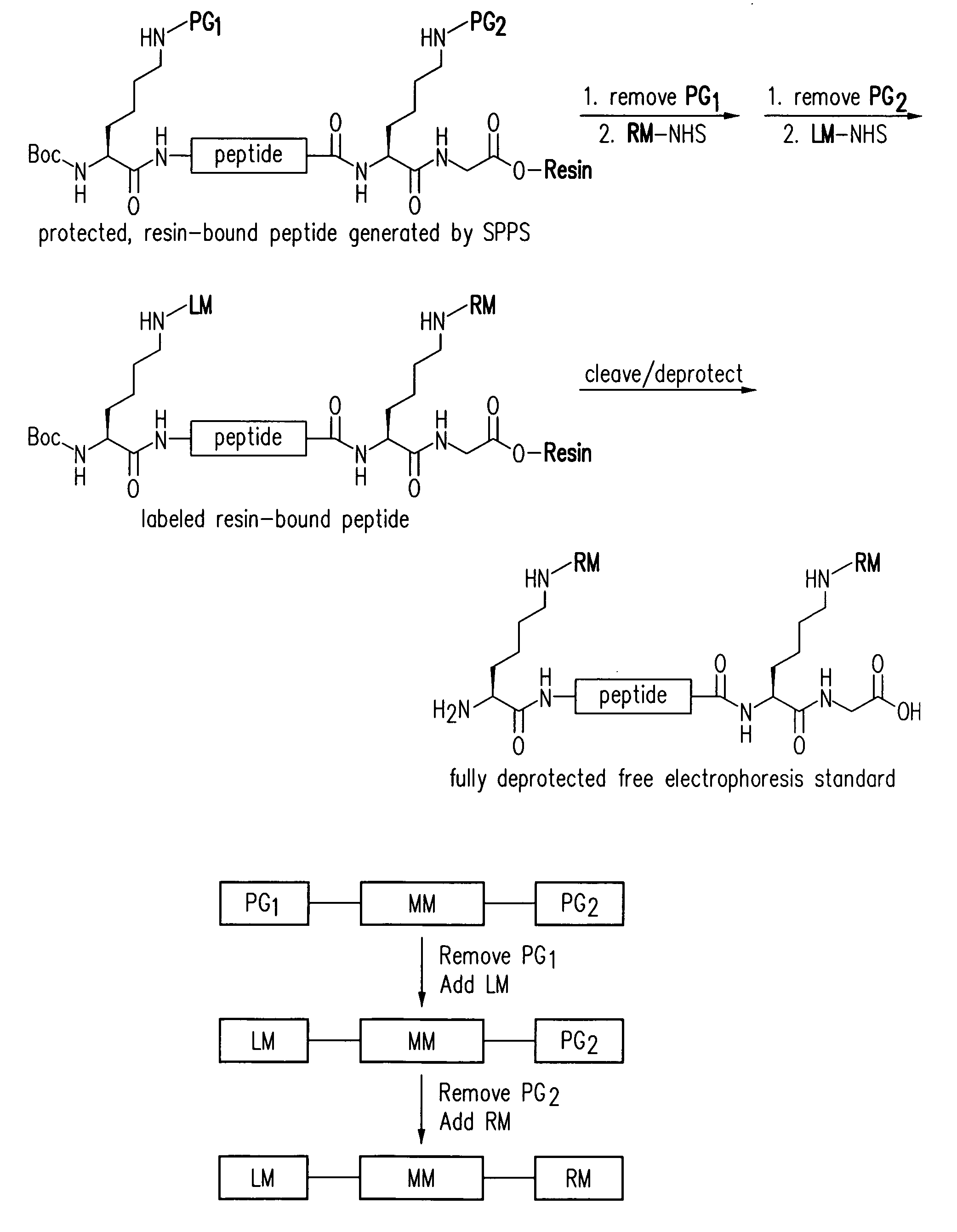
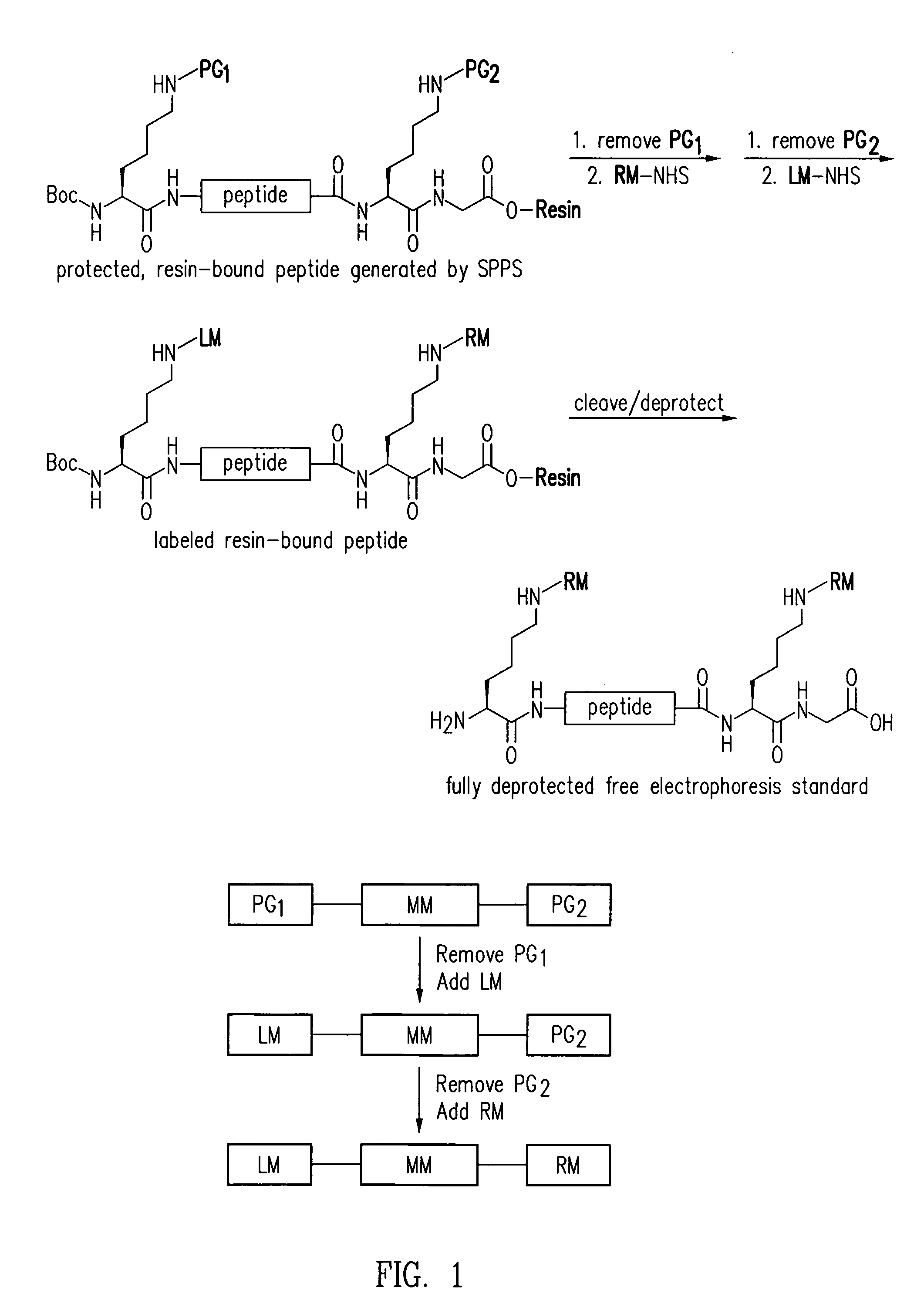
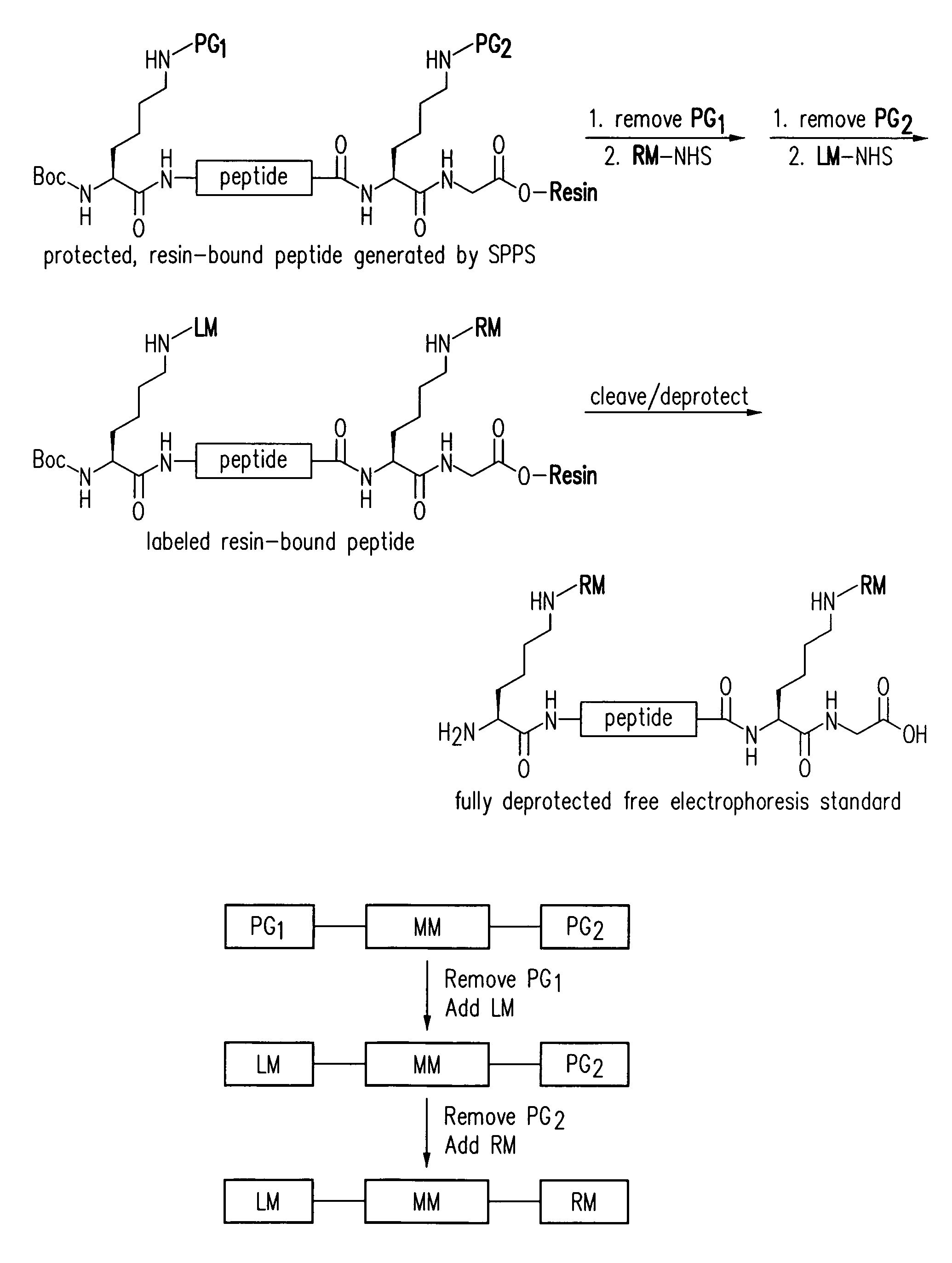
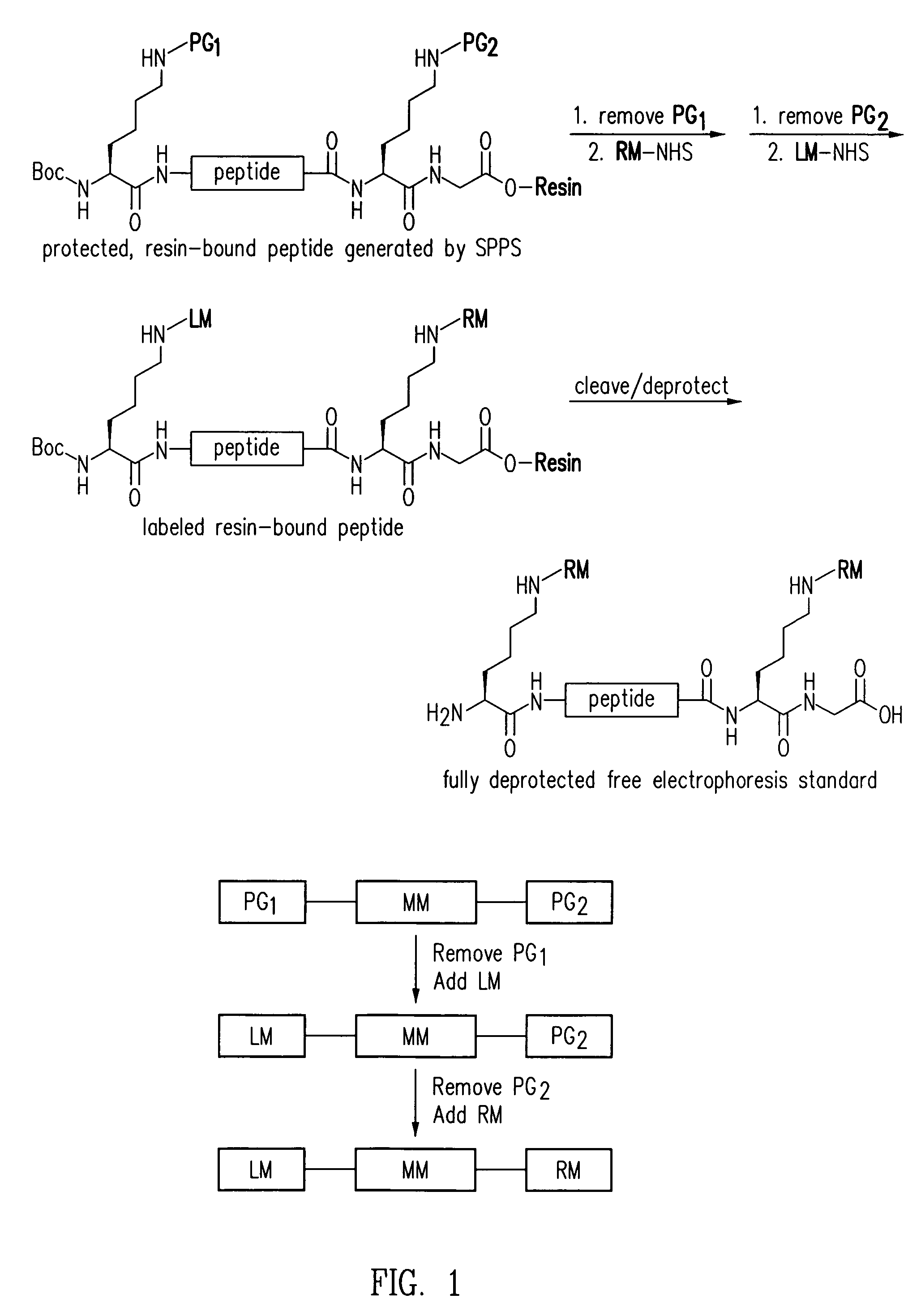
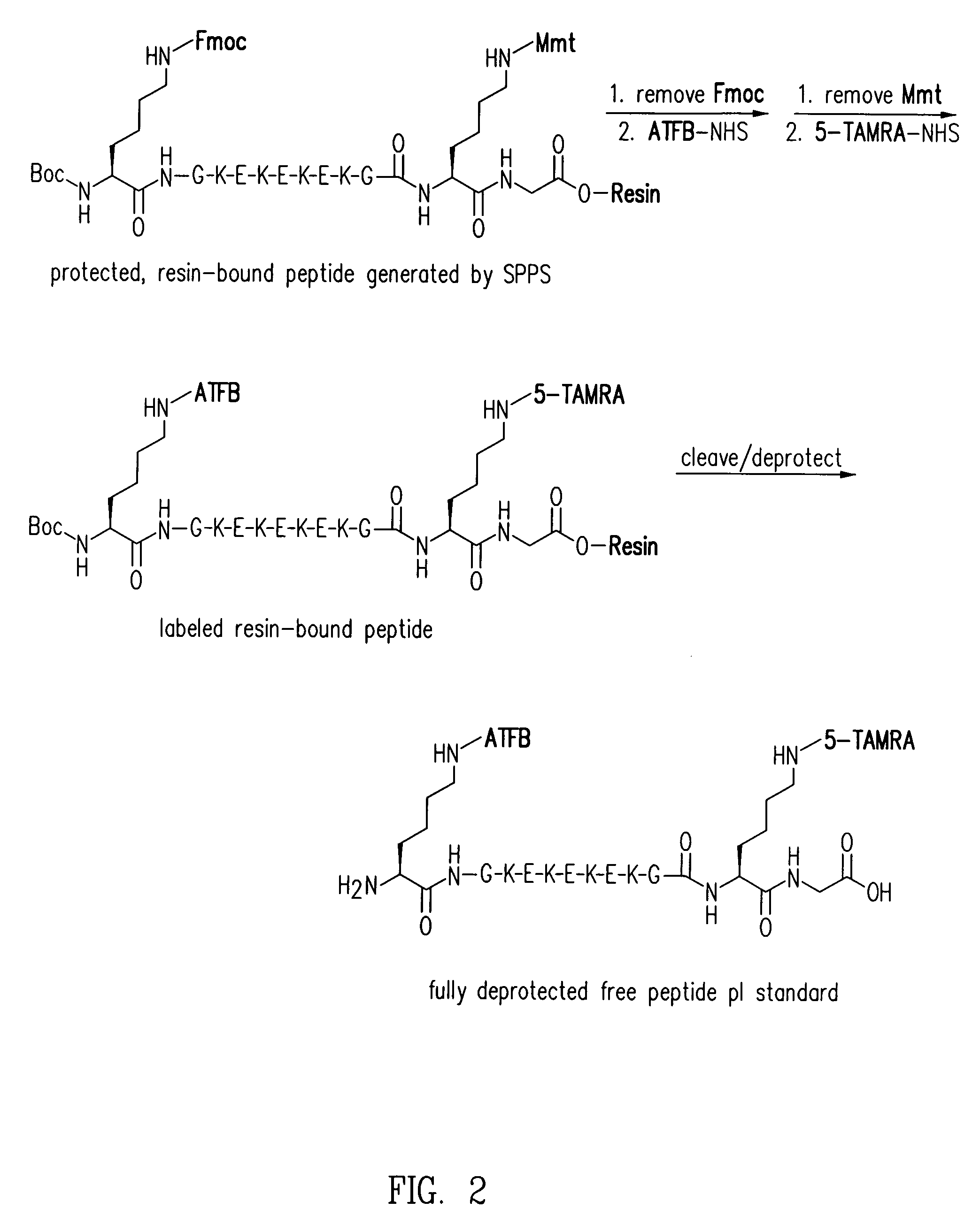
Electrophoresis standards, methods and kits
Electrophoresis Compositions, methods and kits useful for, among other things, detecting, quantifying and / or characterizing analytes are provided. The compositions are useful as electrophoresis standards for determine the isoelectric point and molecular weight of an analyte. The electrophoresis standards generally comprise at least one label moiety and one or more reactive moieties that when activated attach the standard to a substrate.
Owner:PROTEINSIMPLE
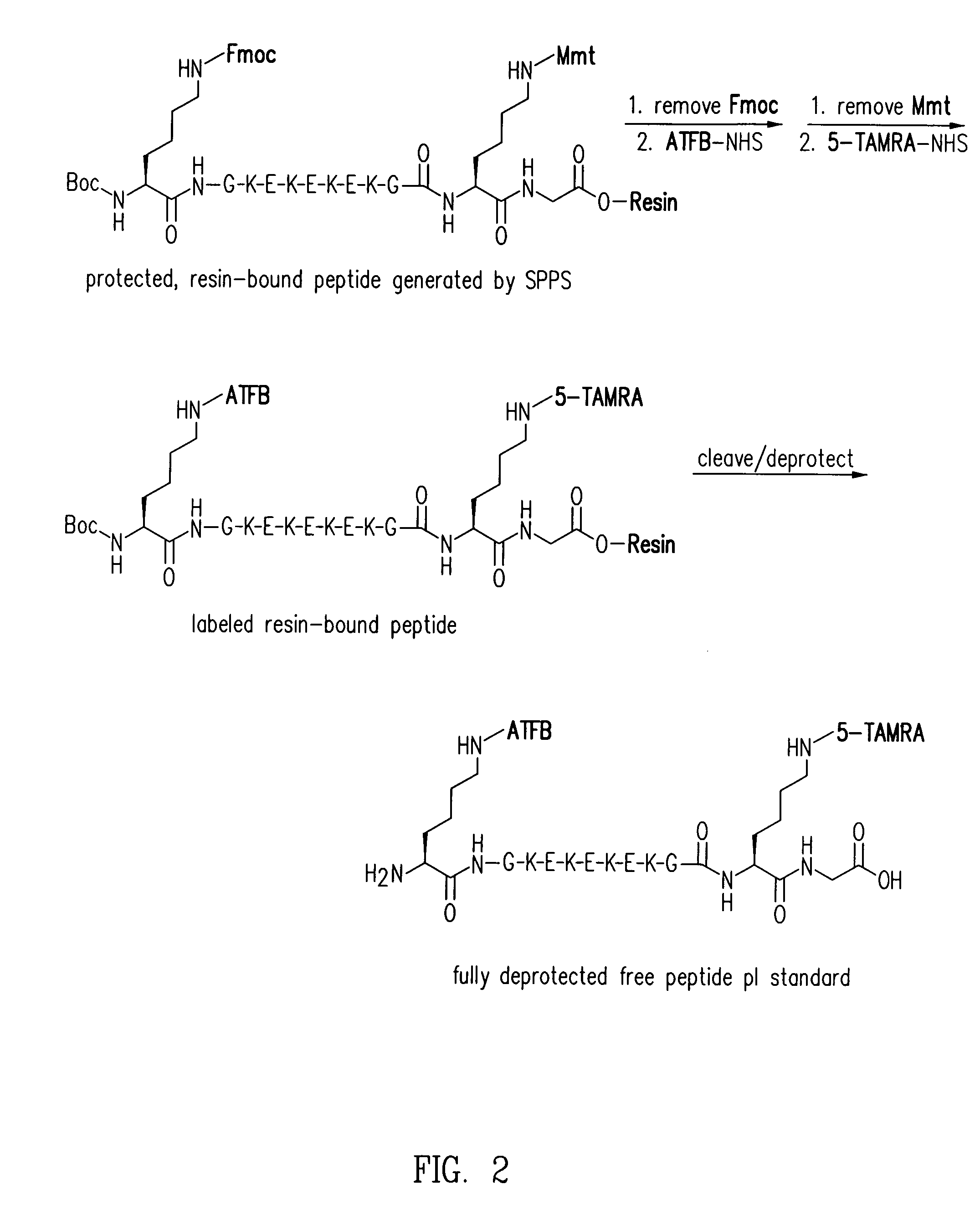
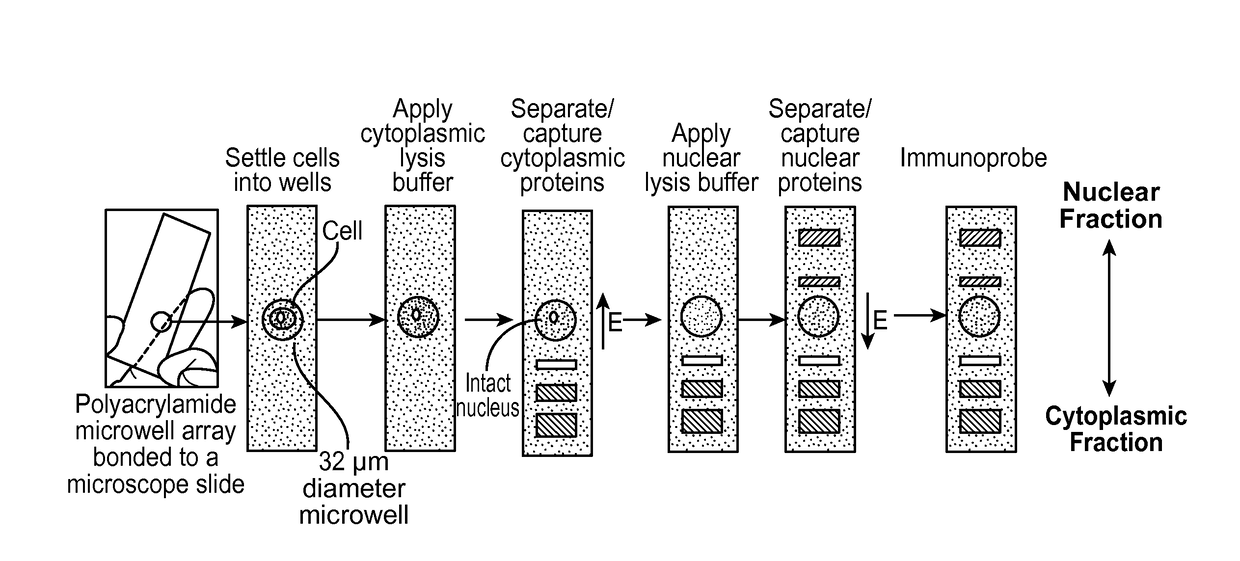
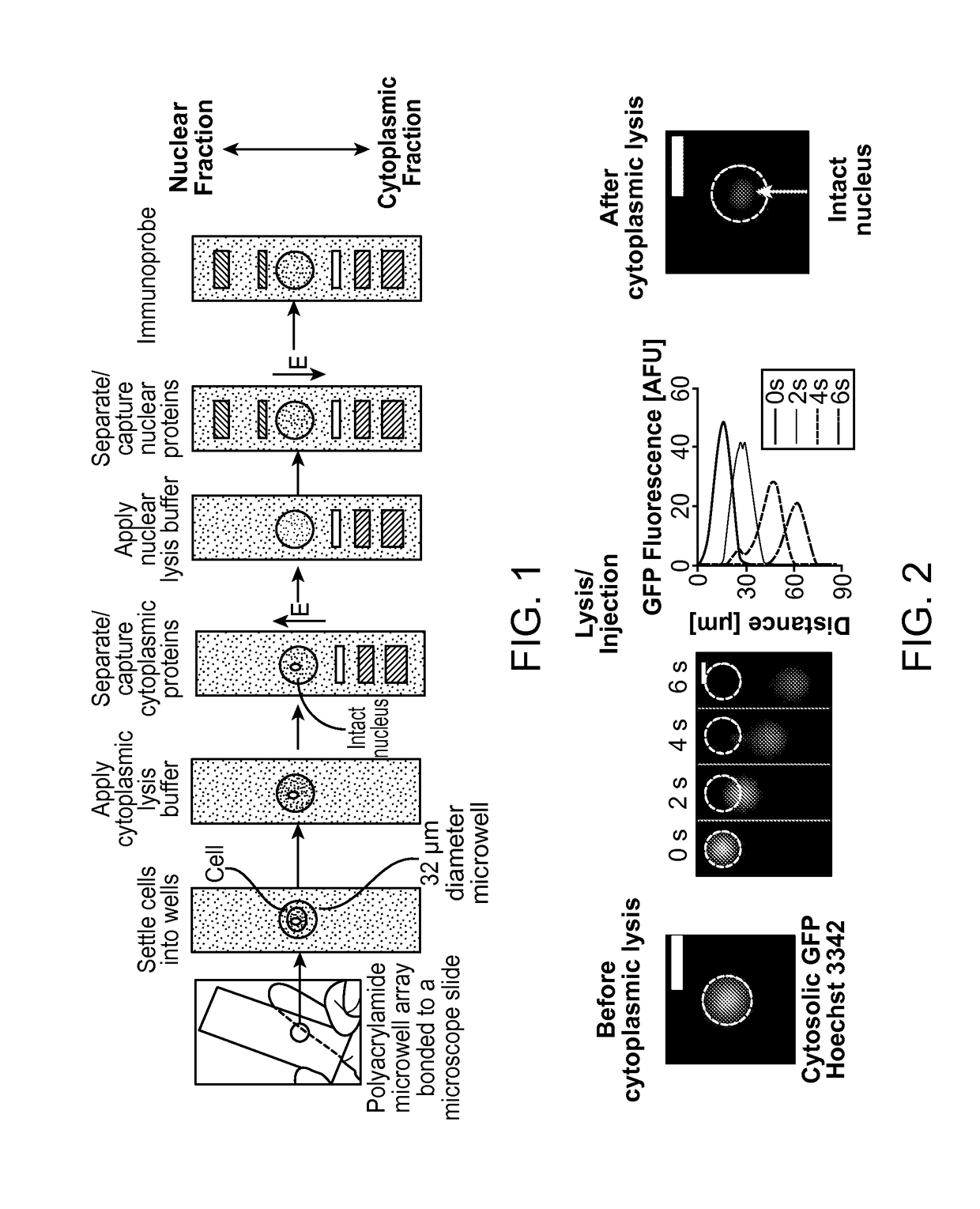
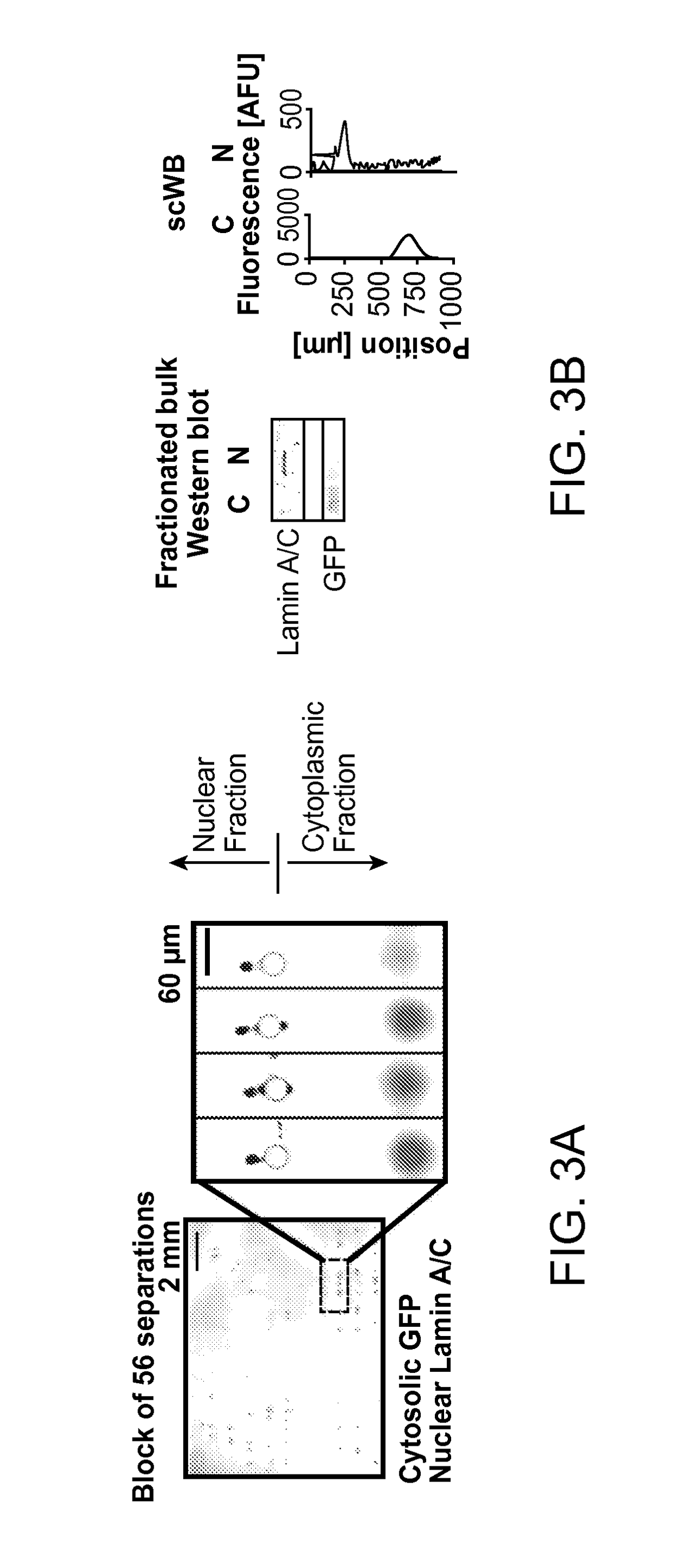
Subcellular Western Blotting of Single Cells
ActiveUS20170242020A1Electrophoretic profilingMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrophoresisAnalytical chemistry
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Multi-directional microfluidic devices comprising a pan-capture binding region and methods of using the same
InactiveUS20120135541A1Facilitate electrostatic bindingLess expensiveAnalysis using chemical indicatorsComponent separationEngineeringElectric field
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method of screening placental proteins responsible for pathophysiology of preeclampsia, and marker for early diagnosis and prediction of preeclampsia
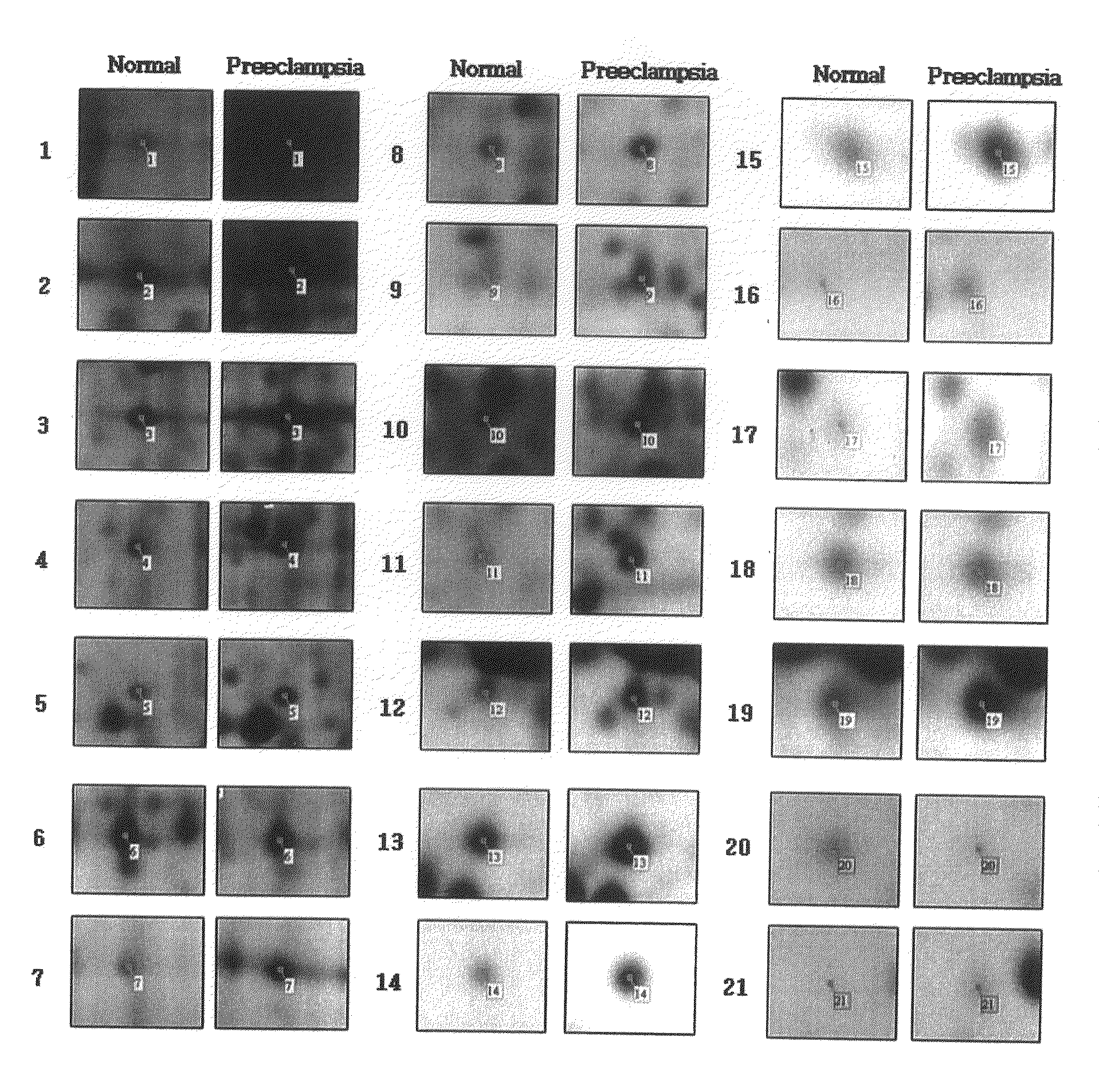
The present invention relates to a method of screening placental proteins responsible for pathophysiology of preeclampsia, and a marker for early diagnosis and prediction of preeclampsia. In accordance with one aspect of the present invention, there is provided a method of screening placental proteins responsible for pathophysiology of preeclampsia by 2D E-proteomics analysis, comprising: isolating placental proteins from a placental tissue; separating the isolated proteins two-dimensionally through 2D electrophoresis; and comparing and analyzing the separated proteins based on scanned gel images and differences in the images between normal placental proteins and preeclamptic placental proteins, wherein the comparison and analysis of the placental proteins based on the scanned gel images and differences in the images are accomplished by selecting proteins with differences of 140% or more between two placentas.
Owner:HAN OU JIN
Method and device for detecting carcinoembryonic antigen content
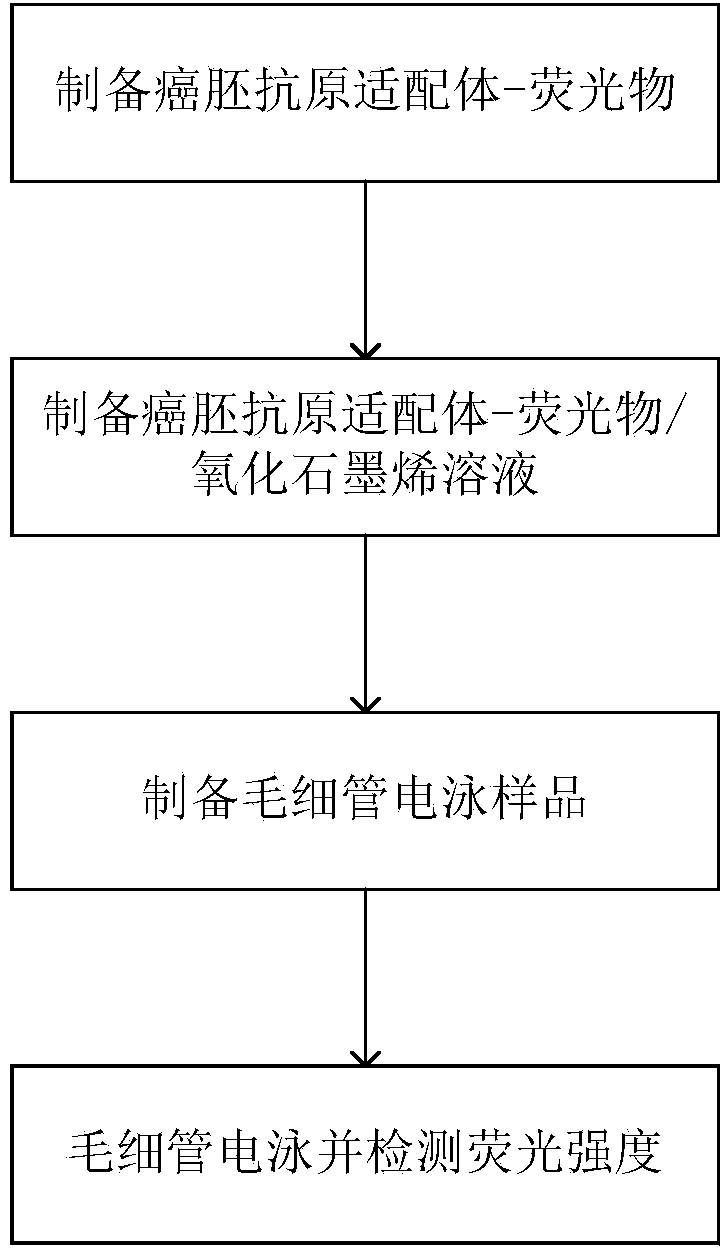
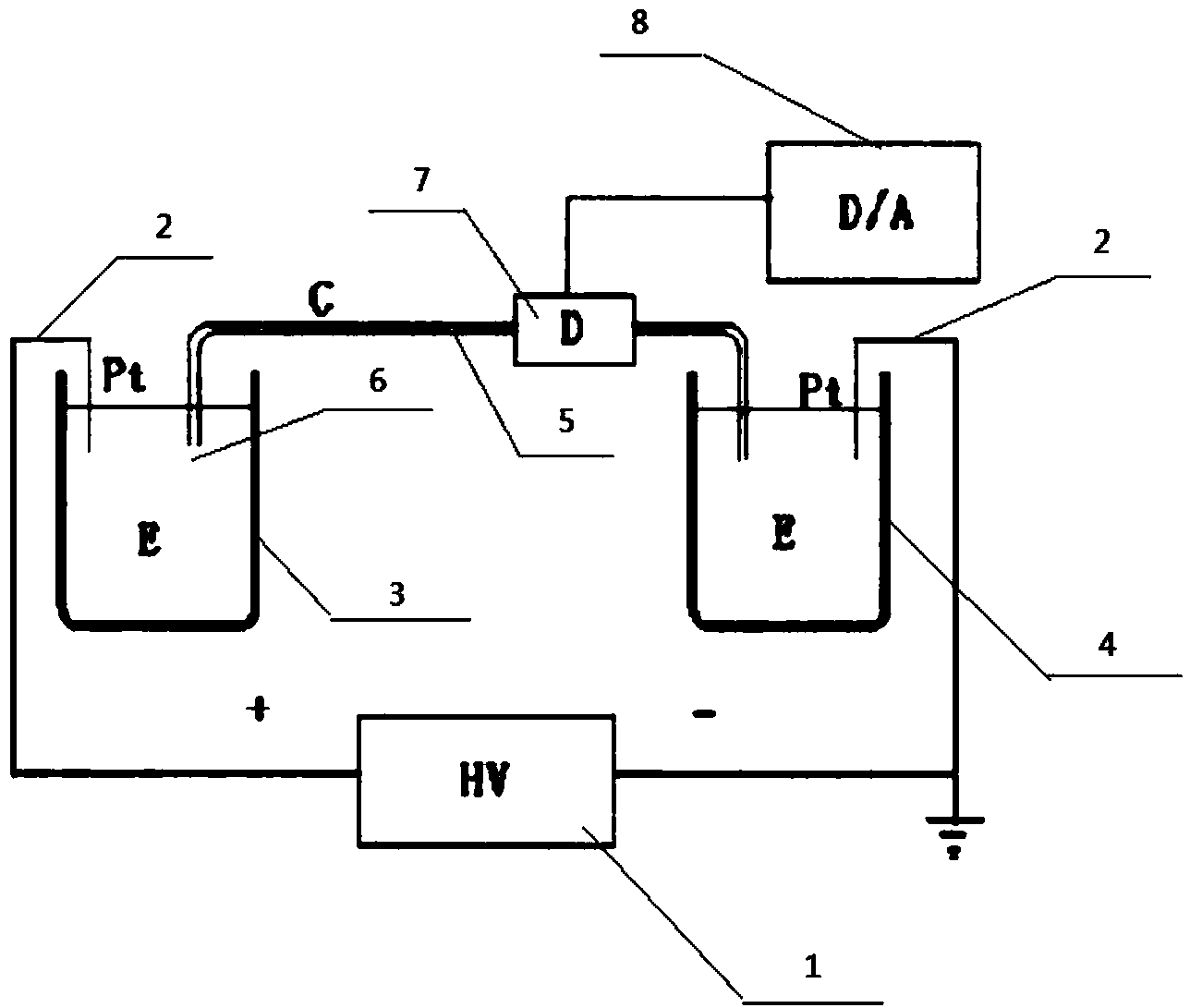
InactiveCN103901197AThe test result is accurateMinimizes the effect of restoring fluorescenceElectrophoretic profilingAptamerCapillary electrophoresis
The invention discloses a method and a device for detecting the carcinoembryonic antigen content. The method comprises the following steps of (1) uniformly mixing a fluorescent substance with a connection agent to obtain a first mixture, and then mixing the first mixture with a carcinoembryonic antigen aptamer solution; (2) uniformly mixing a mixed solution with a graphene oxide solution to cause fluorescence quenching so as to obtain a carcinoembryonic antigen aptamer-phosphor / graphene oxide solution; (3) uniformly mixing a sample to be detected and the carcinoembryonic antigen aptamer-phosphor / graphene oxide solution to cause fluorescence recovery; and (4) performing capillary electrophoresis, performing fluorescent detection at a position meeting the requirement that the distance from the position to a positive electrode is 1 / 2-2 / 3 of the total length of a capillary, and measuring the concentration of a carcinoembryonic antigen. The device comprises a capillary electrophoresis device and a fluorescence inspection device, wherein the total length of the capillary of the capillary electrophoresis device is 50-100cm, and the inner diameter is 50-100 microns; a detection window is arranged in a position meeting the requirement that the distance from the position to a positive electrode buffering solution tank is 1 / 2-2 / 3 of the total length of the capillary; the fluorescence inspection device is arranged at the capillary detection window. The method and the device are high in sensitivity, low in detection limit and high in detection efficiency and can be applied to early screening of cancers.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for screening wheat varieties with low celiac sprue toxicity based on T cell epitopes
InactiveCN103675291AExtraction is fast, effective and comprehensiveHigh detection sensitivityElectrophoretic profilingPreparing sample for investigationStainingScreening method
A method for screening wheat varieties with low celiac sprue toxicity based on T cell epitopes comprises the following steps: separating and extracting wheat gluten protein in two steps, performing SDS-PAGE electrophoresis combined with PageBlue TM staining method to identify the gluten protein, detecting celiac sprue T cell epitopes caused by the gluten protein through immunoblotting and other steps. According to the invention, T cell epitopes-based screening method is adopted to screen out the wheat varieties with low celiac sprue toxicity, so that safe and reliable low gluten food can be supplied for celiac sprue patients from the origin of raw materials, and the safety risk of the celiac sprue patients is reduced.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
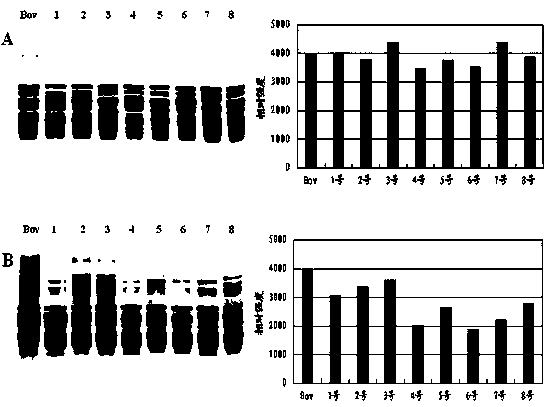
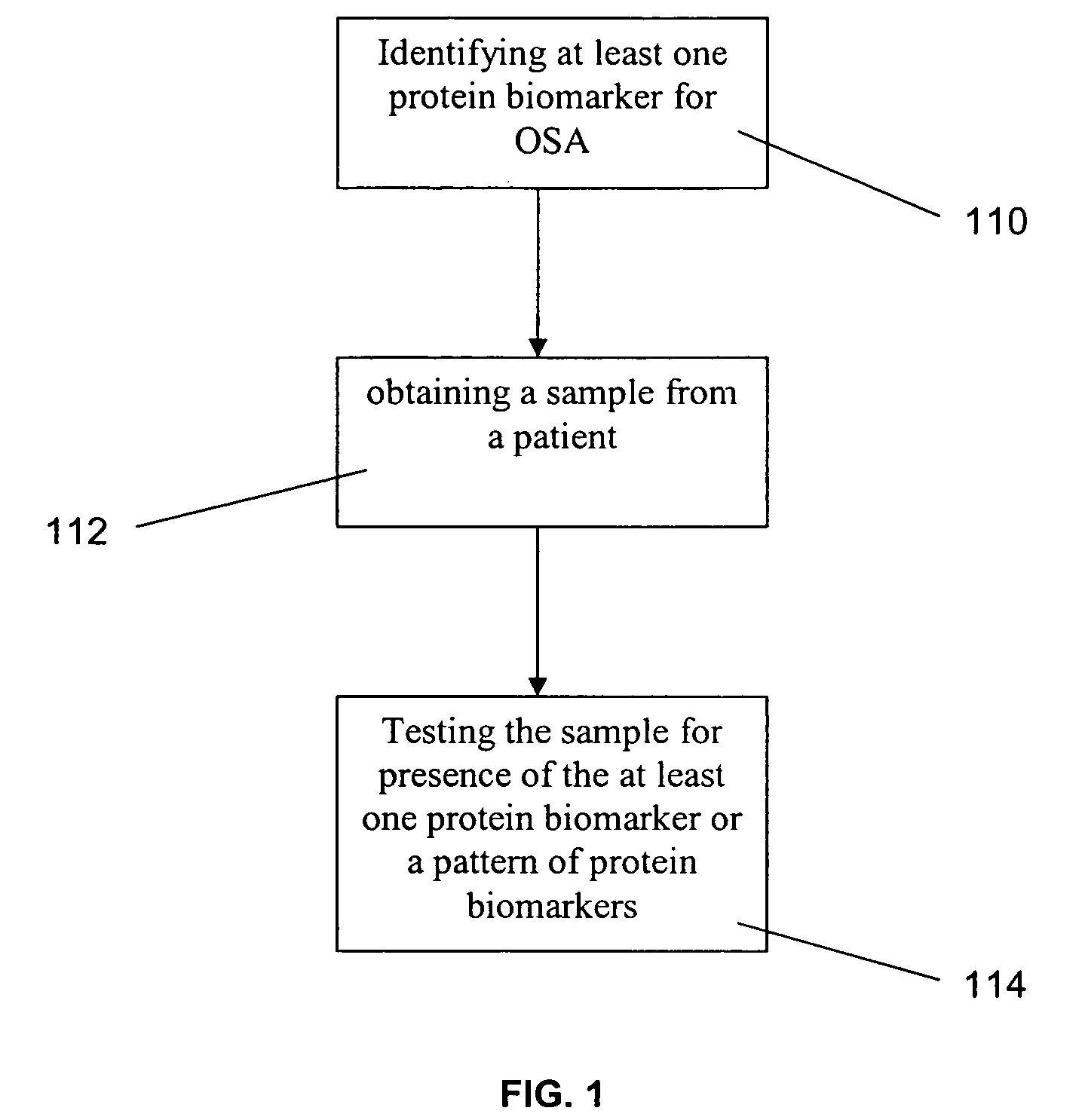
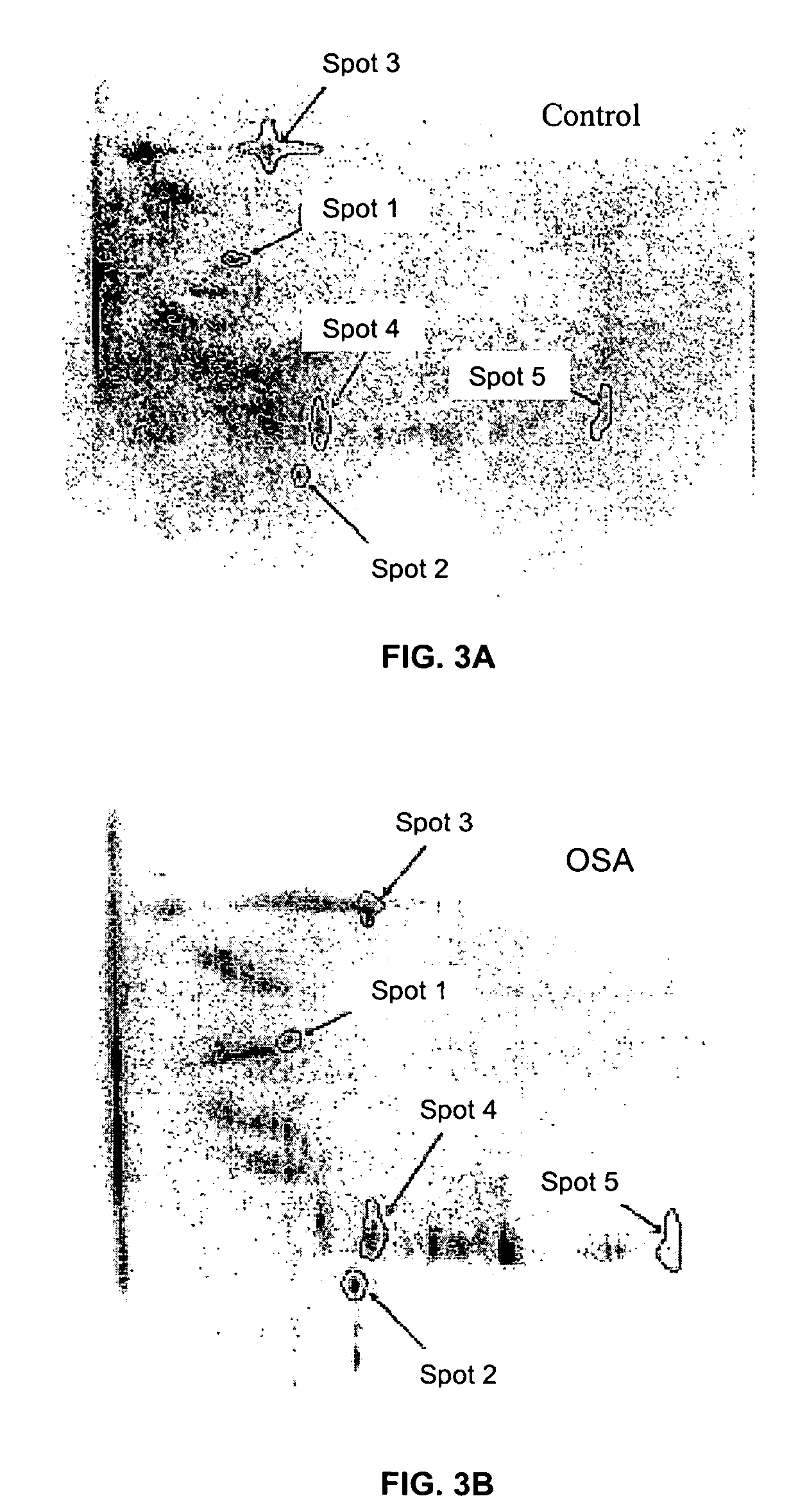
Method for diagnosing obstructive sleep apnea
A method for diagnosing obstructive sleep apnea in a patient comprises identifying at least one protein biomarker for obstructive sleep apnea; obtaining a sample from the patient; and testing the sample for presence of the at least one protein biomarker. The protein biomarkers may include alpha-1 B-glycoprotein; kallikrein, laminin, aldosterone-binding protein and / or urocortin-2 precursor. The presence of the protein biomarkers may be detected using antibodies. These antibodies may be provided in an array for detecting the presence of the at least one protein biomarker or a pattern of protein biomarkers.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
Methods for separation and immuno-detection of biomolecules, and apparatus related thereto
InactiveUS8470541B1Evaluating efficacyOptimize patient therapyElectrophoretic profilingMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansClinical settingsRadioactive agent
Disclosed are methods and apparatus for separation of biomolecules via two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, methods and apparatus for immunoblotting separated biomolecules, and methods for the use of biomolecules processed via the methods and apparatus of the present invention, including use in a clinical setting. The methods and apparatus for separation of biomolecules via two-dimensional gel comprises vertical agarose gel electrophoresis in the first dimension, and the electrophoresis of a novel non-denaturing 3-35% concave gradient polyacrylamide gel in the second dimension. This novel gel can be cast in a modified gel caster that can facilitate the pouring of multiple gels simultaneously. The methods and apparatus for immunblotting are useful with any type of immunoblotting, including Western blot, Northern blot, and Southern blot analyses. These methods and apparatus provide safe, efficient and cost-effective immunoblots, while facilitating the reduction of exposure to toxic or radioactive materials, as well as the disposal of those materials.
Owner:BOSTON HEART DIAGNOSTICS
Differential labeling for quantitative analysis of complex protein mixtures
The present invention relates to a method of simultaneously identifying and determining the levels of expression of cysteine-containing proteins in normal and perturbed cells, a method for proteomic analysis, a process for preparing fusion proteins, and compounds of Formula II and III: (II) Acyl-NH--X-[Epitope Tag Site].sub.A -Y-[Protease Cleavage Site]-Z-Link (III) Acyl-NH--X-alk-O-Ph-CH.sub.2 --Z-Link and reagents related thereto.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
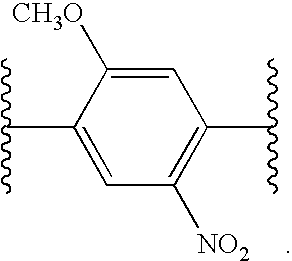
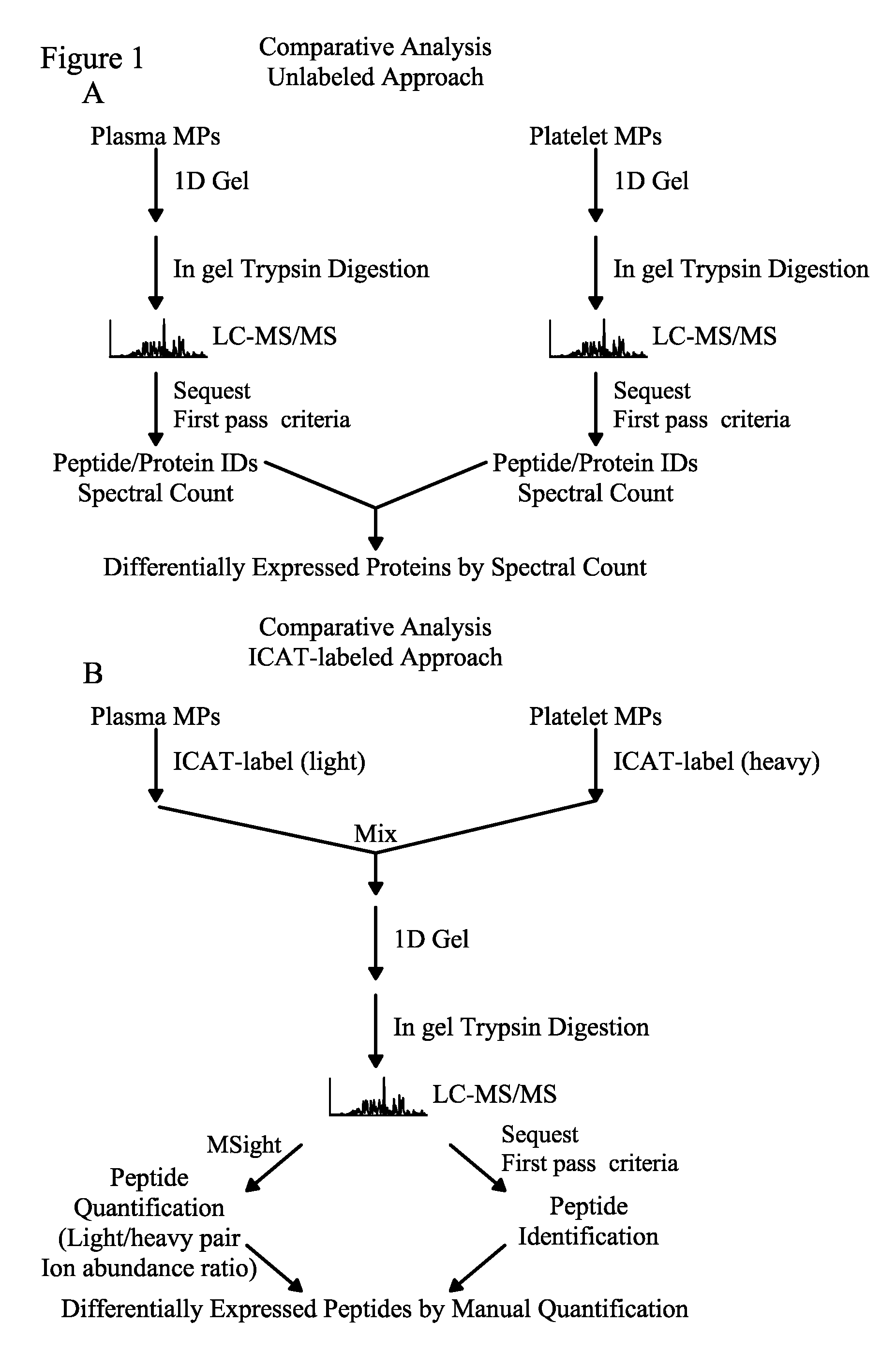
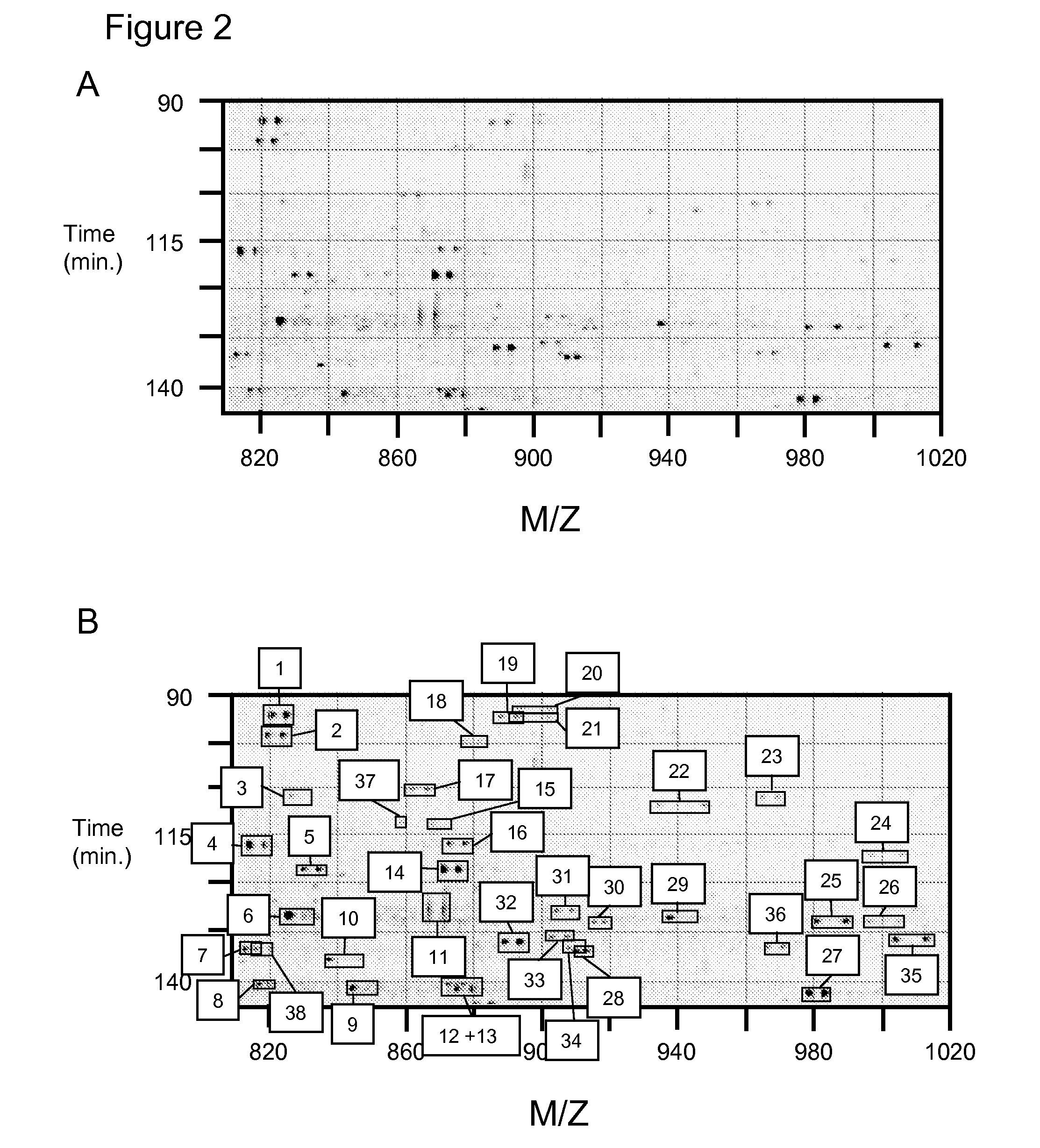
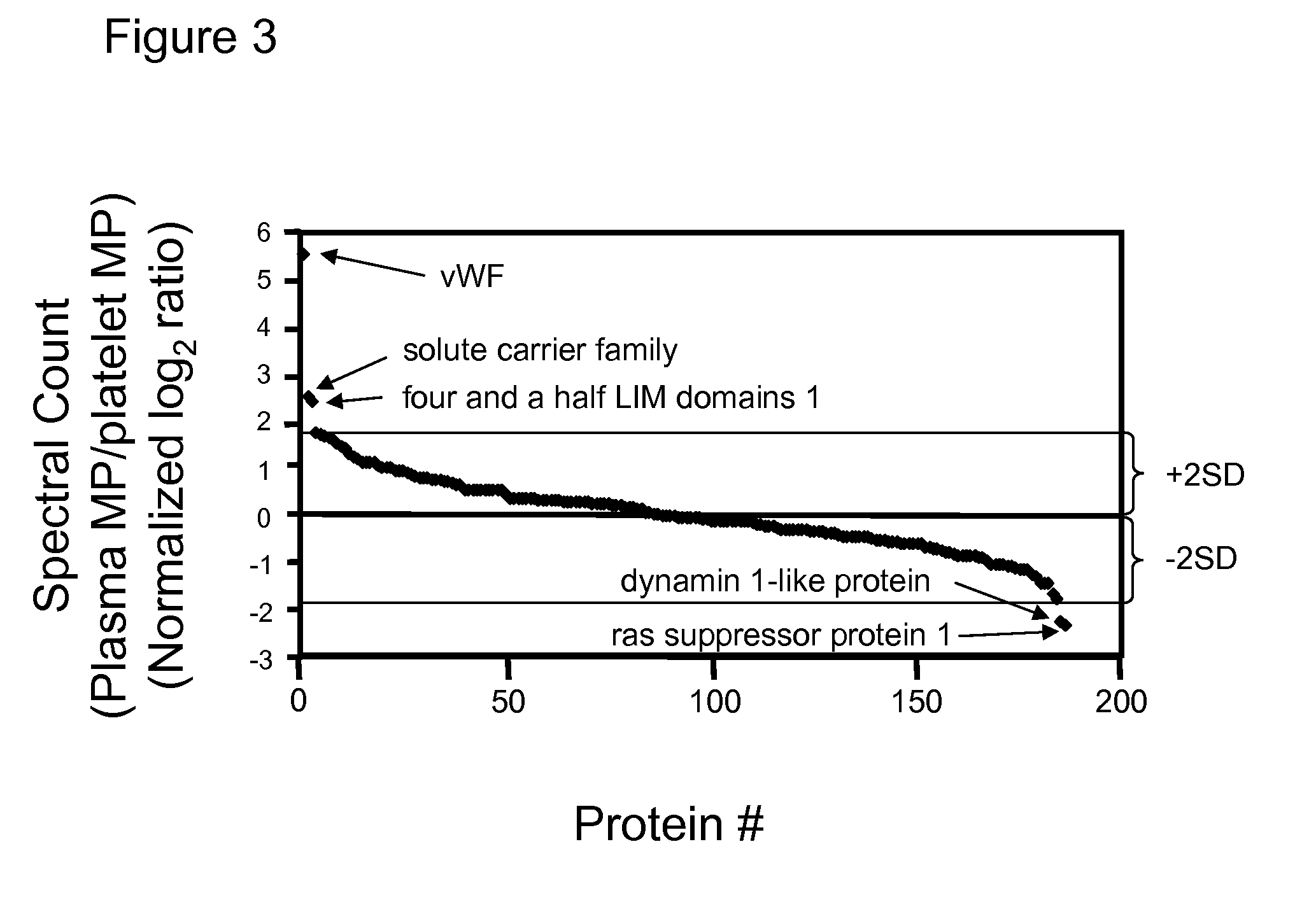
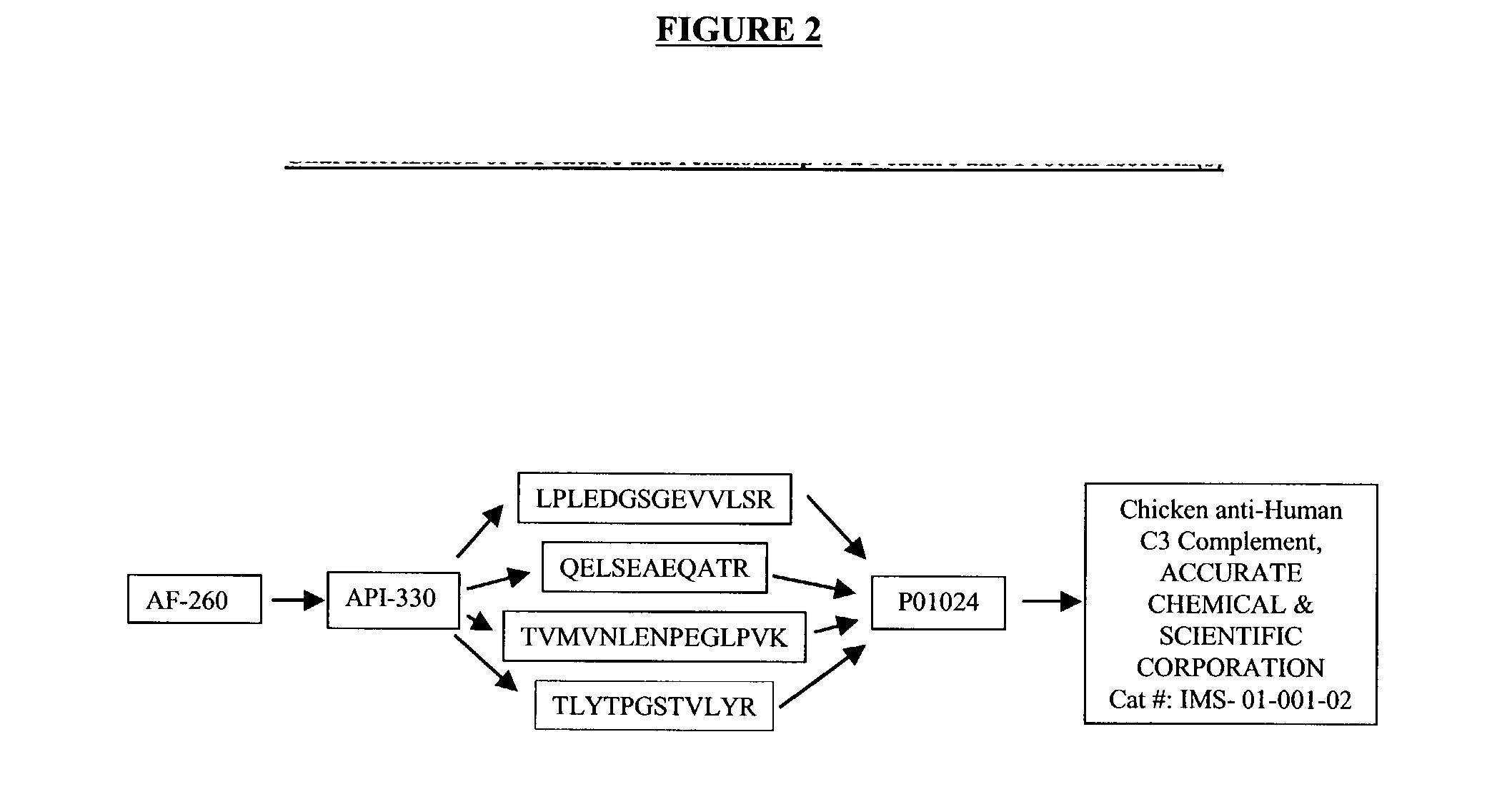
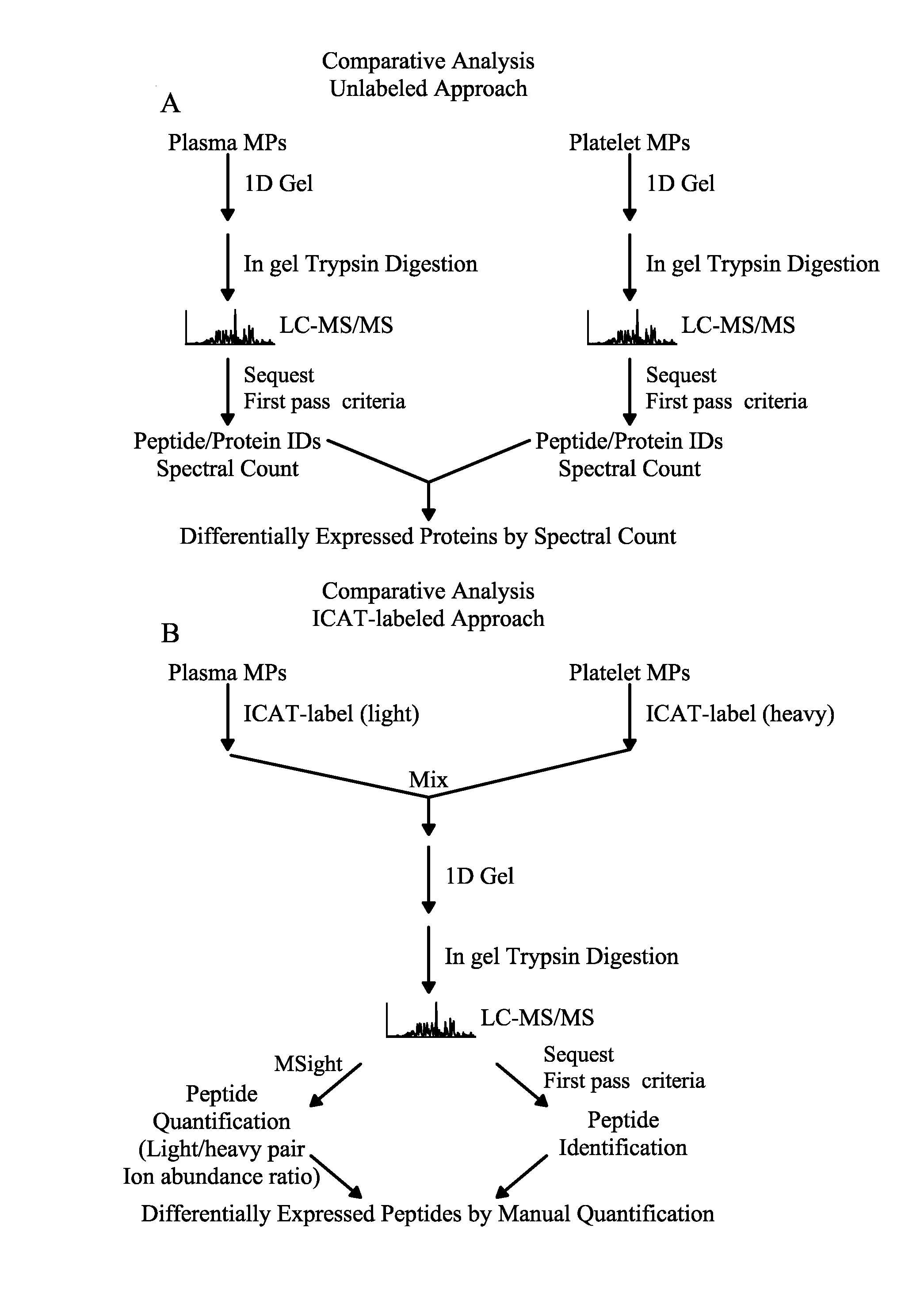
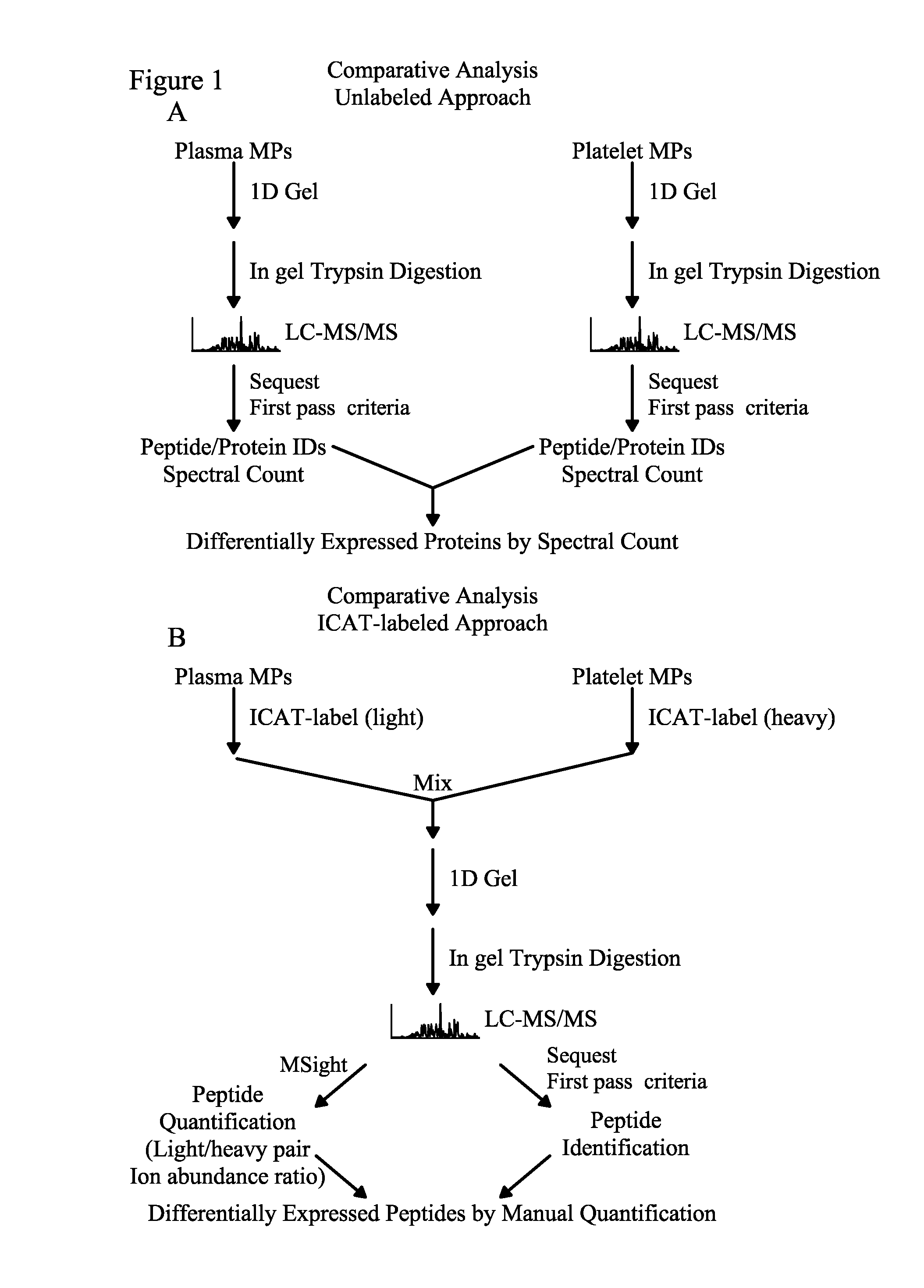
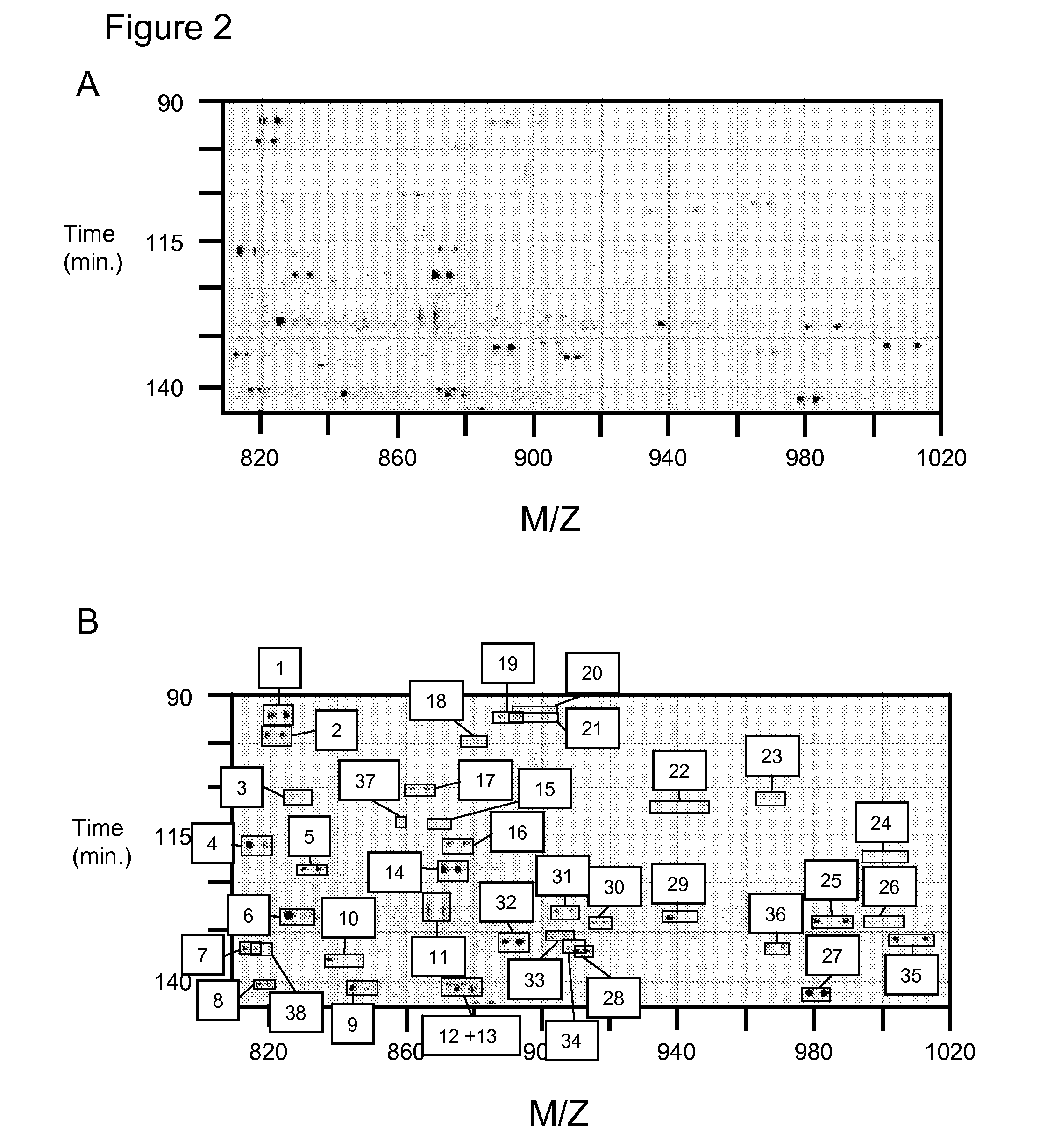
Methods for identifying and analyzing biomarkers from plasma-derived microparticles
Owner:MICROPARTICLE PROTEOMICS LLS
Rapid detection method of fish parvalbumin by capillary electrophoresis
InactiveCN105911127AQuick checkAccurate detectionElectrophoretic profilingMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCapillary electrophoresisAquatic product
The invention discloses a method for detecting fish parvalbumin by capillary electrophoresis. The method comprises the following steps: (1) extracting holoprotein from fish-muscle and dissolving in an equilibrium buffer with pH being 7-8, loading into an anion exchange chromatographic column, eluting with an eluant and collecting a solution corresponding to a flow-through peak so as to obtain a sample; and (2) carrying out capillary zone electrophoresis on the sample to obtain substituting peak area obtained in electrophoretogram into a standard curve regression equation of fish parvalbumin and calculating to obtain concentration of fish parvalbumin in the sample solution. The method of the invention is a method for rapid, qualitative and quantitative detection of aquatic product allergen fish parvalbumin by capillary electrophoresis. The method for qualitative and quantitative analysis of fish parvalbumin has been reported in the literature, and provides new basis for rapid and accurate detection of fish parvalbumin.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
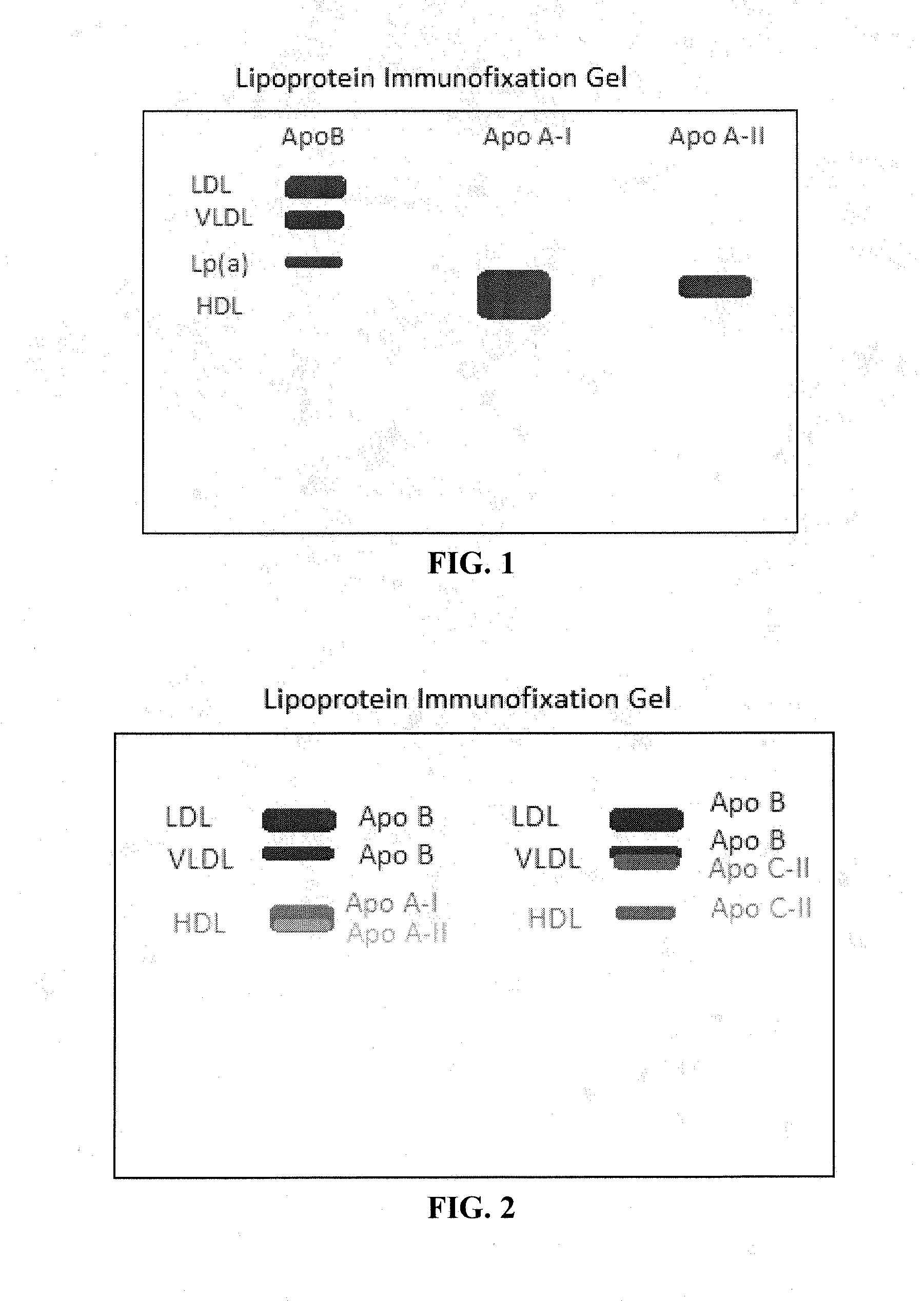
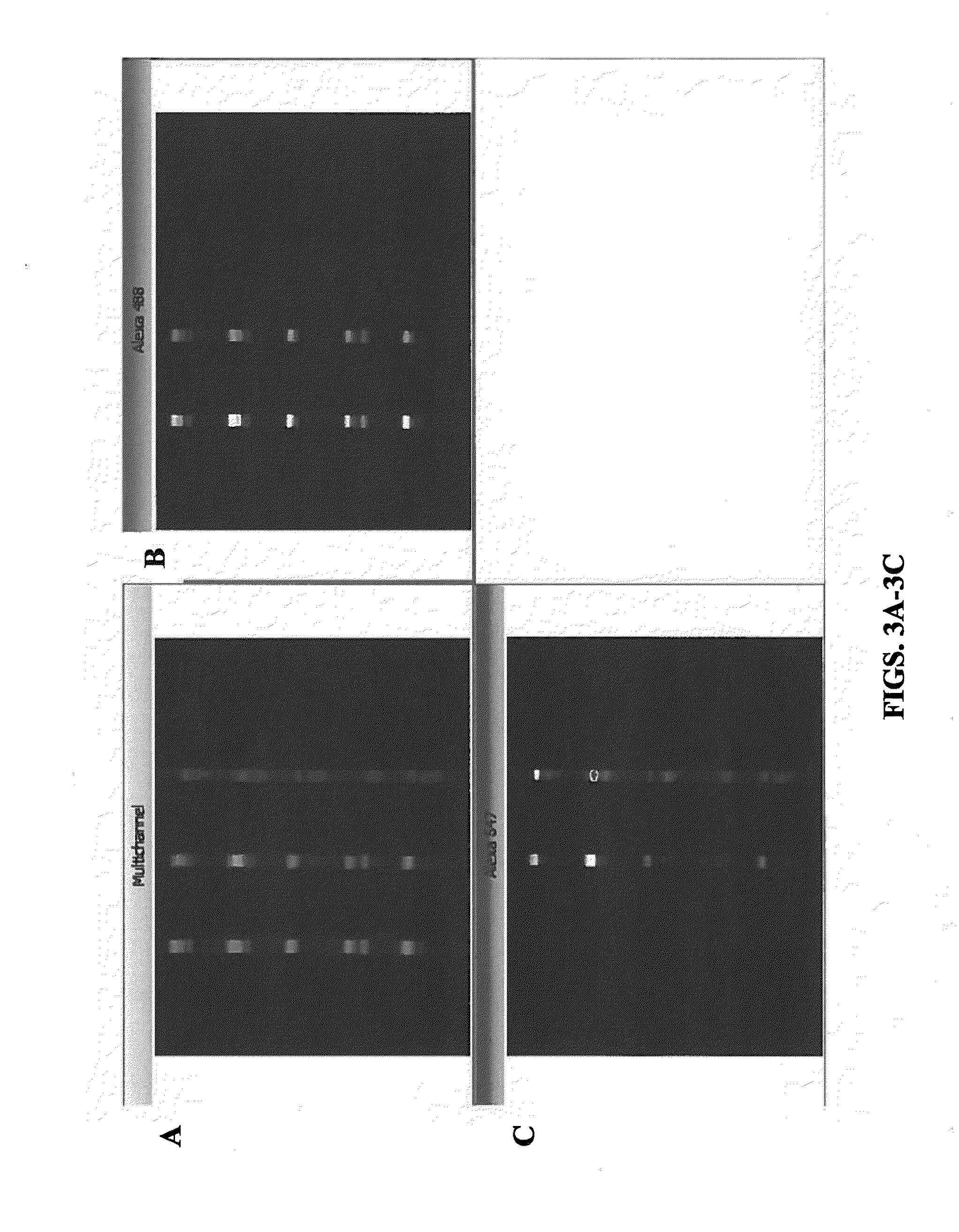
Flourescent in-situ detection of lipid particle apolipoproteins within primary electrophoretic matrix
The present invention relates to, among other things, a gel electrophoresis system for detecting the level of specific Apolipoproteins and / or lipoprotein particles present in intact lipid particles in a biological sample. The system includes a gel substrate to receive a biological sample, at least two lipoprotein-binding complexes. Each complex includes an antibody that binds a lipoprotein particle or a portion thereof, which is bound to a signal producing molecule capable of producing or causing production of a detectable signal. The system also includes a device for detecting the detectable signal. The present invention also relates to methods of assessing the level of specific Apolipoproteins and / or lipoprotein particles present in a biological sample, determining whether a subject is at increased risk for cardiovascular disease, and monitoring the risk for developing cardiovascular disease.
Owner:HELENA LAB
Breeding method of red-grain early-ripe strong-gluten high-quality wheat
InactiveCN106688877AImprove qualityMeeting the demand for high-quality wheatElectrophoretic profilingBiological testingHybrid seedTriticeae
The invention belongs to the technical field of crops breeding, and mainly relates to a breeding method of red-grain early-ripe strong-gluten high-quality wheat. The breeding method comprises the following steps: performing primary hybridization by adopting French wheat variety NSA00-0061 as a female parent and LUYUAN202 as a male parent to obtain hybrid seeds; performing secondary hybridization by adopting the hybrid seeds as the female parent and Jimai 22 as the male parent to obtain generation-F1 seeds; and planting and breeding for the generation-F1 seeds. Since the ripe period of NSA00-0061 is 15 days later than the domestic varieties, the filial generation obtained by virtue of the hybridization of NSA00-0061 and Luyuan202 is still late-maturing; and by virtue of the secondary hybridization, the male parent of the secondary hybridization is Jimai 22, so that the mature period of the obtained generation-F1 seeds is shortened to be consistent with the mature period of the domestic wheat varieties. According to the breeding method, subunit 5+10 in the foreign seed varieties is introduced into a domestic material, and the foreign wheat subunit and the domestic wheat variety subunit are successively polymerized, and the polymerization of various subunits enables the wheat variety to have a high quality of strong gluten.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Methods for separation and immuno-detection of biomolecules, and apparatus related thereto
InactiveUS20130248370A1Safe and efficient and cost-effectiveEfficient and cost-effectiveCellsFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesClinical settingsRadioactive agent
Disclosed are methods and apparatus for separation of biomolecules via two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, methods and apparatus for immunoblotting separated biomolecules, and methods for the use of biomolecules processed via the methods and apparatus of the present invention, including use in a clinical setting. The methods and apparatus for separation of biomolecules via two-dimensional gel comprises vertical agarose gel electrophoresis in the first dimension, and the electrophoresis of a novel non-denaturing 3-35% concave gradient polyacrylamide gel in the second dimension. This novel gel can be cast in a modified gel caster that can facilitate the pouring of multiple gels simultaneously. The methods and apparatus for immunblotting are useful with any type of immunoblotting, including Western blot, Northern blot, and Southern blot analyses. These methods and apparatus provide safe, efficient and cost-effective immunoblots, while facilitating the reduction of exposure to toxic or radioactive materials, as well as the disposal of those materials.
Owner:BOSTON HEART DIAGNOSTICS
Differential labeling for quantitative analysis of complex protein mixtures
InactiveUS20080081343A1Electrophoretic profilingPeptide preparation methodsSubject matterPeptide expression
The disclosed subject matter relates to a method of simultaneously identifying and determining the levels of expression of cysteine-containing proteins in normal and perturbed cells, a method for determining peptide expression levels between a first biological sample and a second biological sample, and a method for quantitative proteomic analysis of two or more peptide populations, and compounds and reagents related thereto.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Composition for enzyme linked immunosorbent assay kit, anti-nuclear antibody spectrum detection kit and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108398551AGuaranteed stabilityImprove stabilityElectrophoretic profilingDisease diagnosisElisa kitAnti-nuclear antibody
The invention relates to the technical field of enzyme linked immune, and discloses a composition for an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay kit, an anti-nuclear antibody spectrum detection kit and a preparation method thereof. The composition comprises sealing liquid and ELISA diluents; the sealing liquid contains casein, saccharose, PBS, mannitol, Tween20, lycine and sodium azide; the ELISA diluents contain PBS, casein, sodium p-hydroxybenzoate, PEG, lycine and Proclin300. By starting from the sealing liquid and the ELISA diluents of the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay kit, the proper ingredients are selected, so that the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay kit can maintain the detection stability for a long time. Meanwhile, the anti-nuclear antibody spectrum detection kit prepared from the composition has higher stability; the guarantee period is 2 years or more.
Owner:SHENZHEN BLOT BIOTECH
Magnetic field assisted dielectrophoresis enrichment method for nanoparticle labeled immunodetection
ActiveCN103869072AHigh sensitivityImprove featuresElectrophoretic profilingAntigenEnrichment methods
The invention discloses a magnetic field assisted dielectrophoresis enrichment method for nanoparticle labeled immunodetection. By utilizing a nanoparticle labeled antibody or antigen, a method for screening and enriching aggregate formed by performing immunoconjugate on a magnetic nanoparticle and sensing nanoparticle labeled antibody or antigen by using magnetic field assisted dielectrophoresis is designed. An alternating electric field is applied between parallel non-uniform electrodes, spatial directional movement of nanoscale particles in the solution is realized, selective enrichment of nanoparticle and magnetic nanoparticle immunoreaction aggregate in a micro area on the surface of a transparent electrode in a complex solution is realized in a specific voltage magnitude and frequency and magnetic field intensity range, and the method is used for sensitivity immunodetection.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
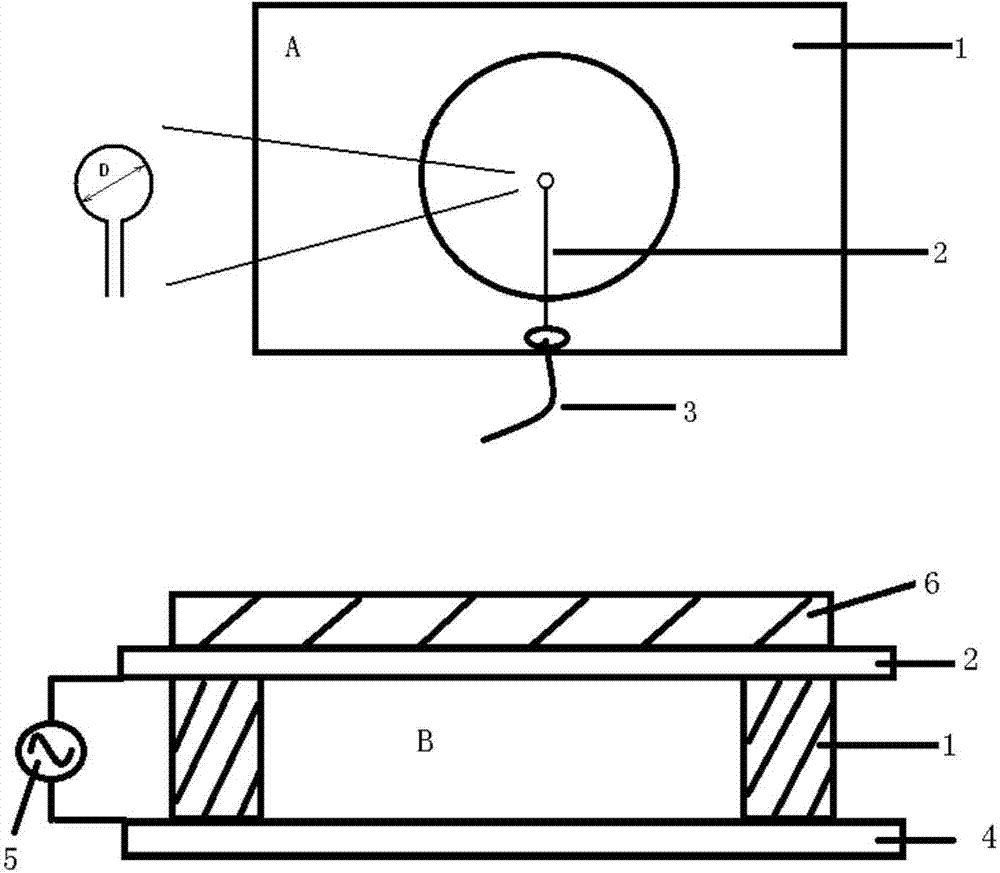
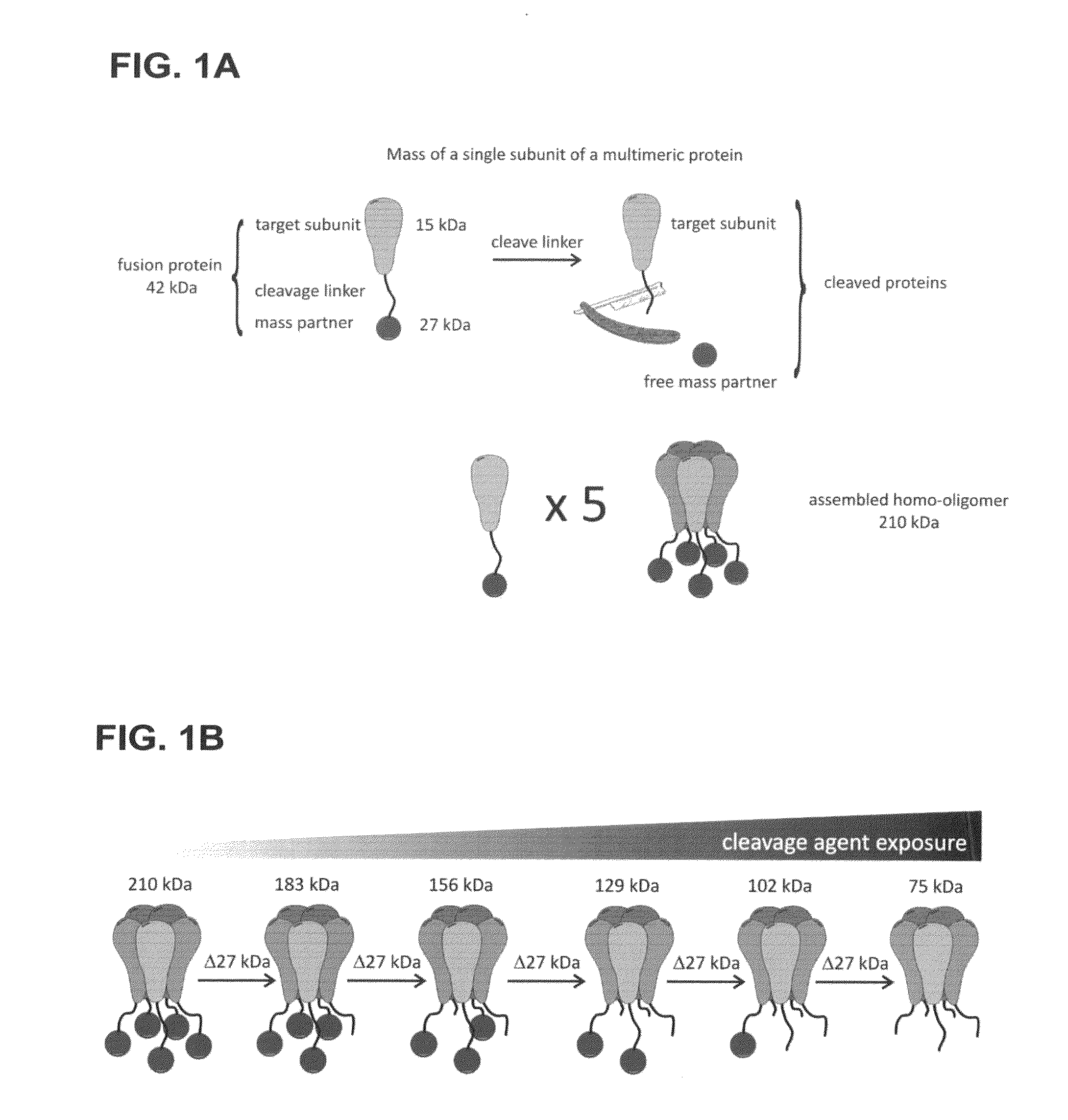
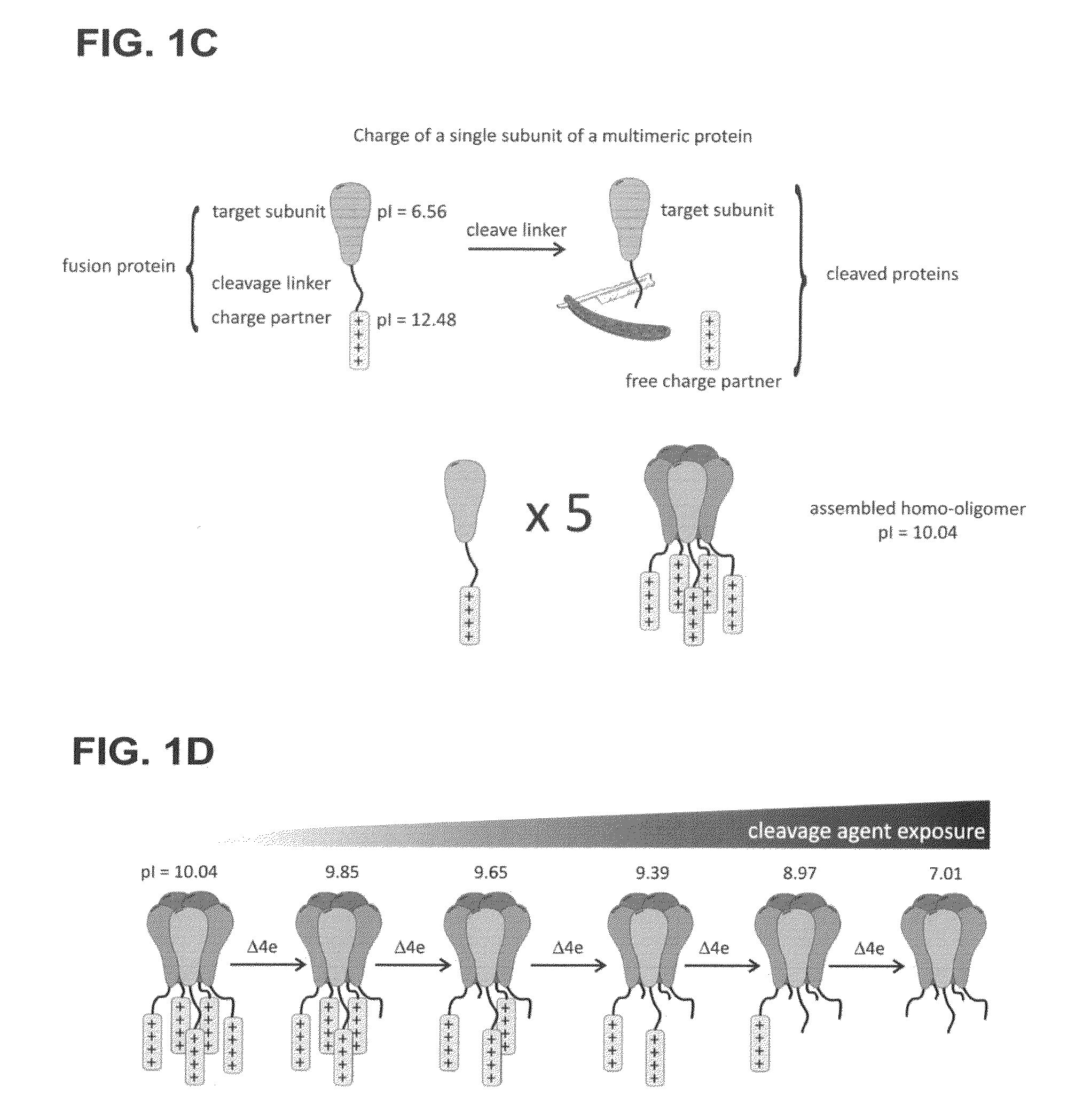
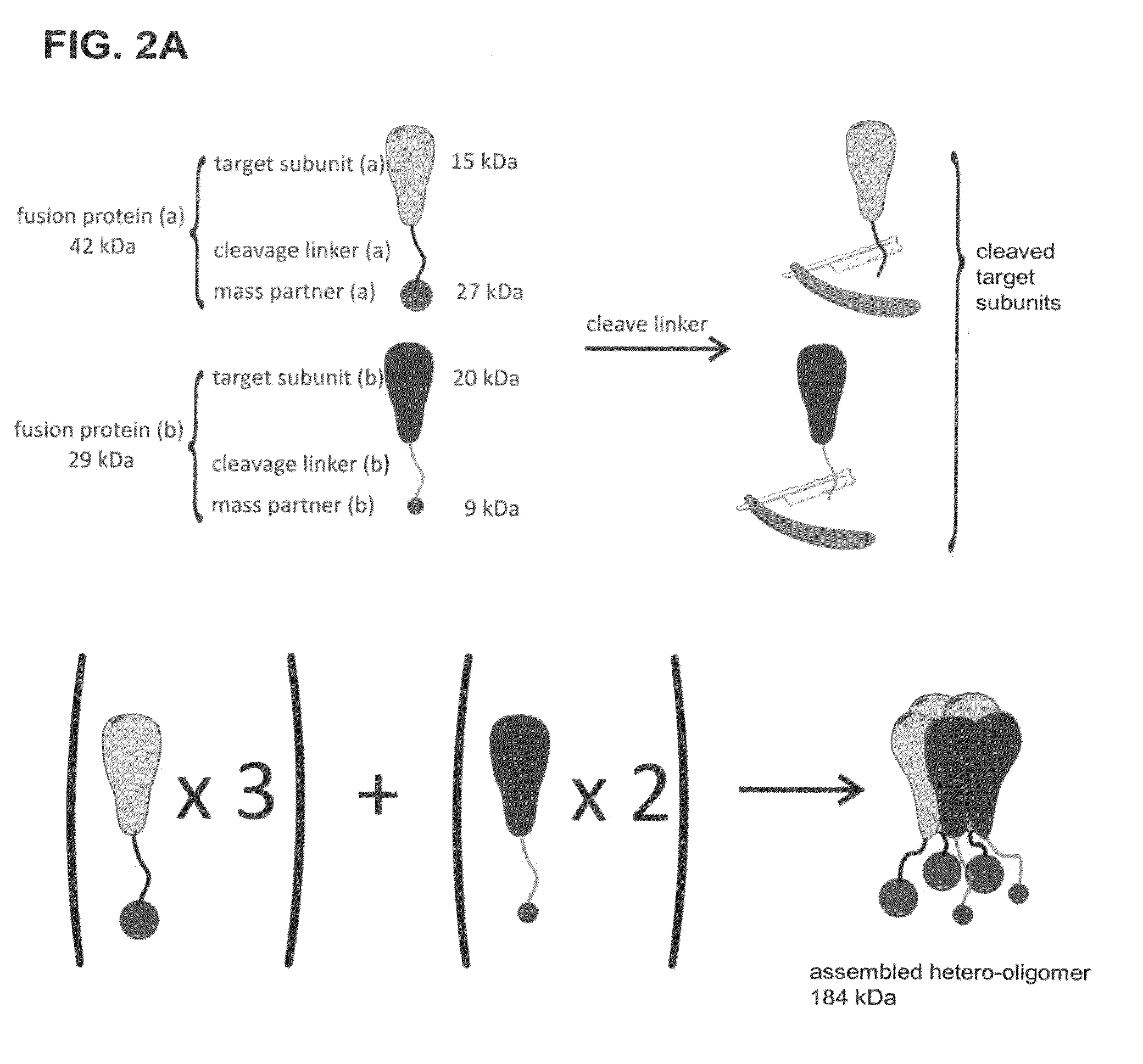
Method of determining the oligomeric state of a protein complex
ActiveUS20120034619A1Electrophoretic profilingMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein subunitProtein-protein complex
A method of counting protein subunits to determine the oligomeric state of an oligomeric protein complex includes tagging and expressing the protein subunits with a mass / charge tag and selectively removing each mass / charge tag. The number of protein subunits of the oligomeric complex corresponds to the number of mass / charge tags removed.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Methods and kits for separation and detection of proteins in biological samples
InactiveUS7709193B2Electrophoretic profilingMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein insertionSkeletal muscle cell
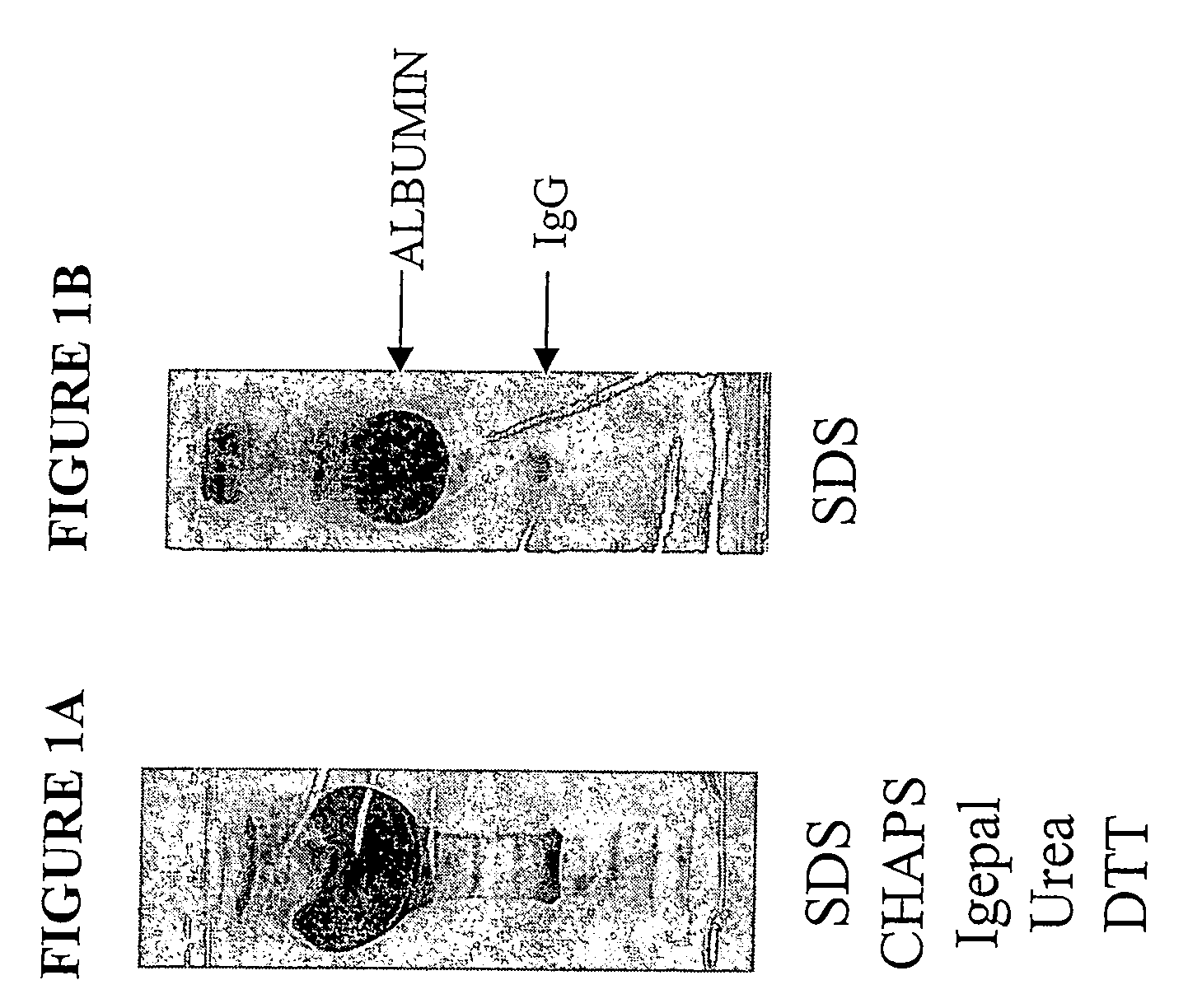
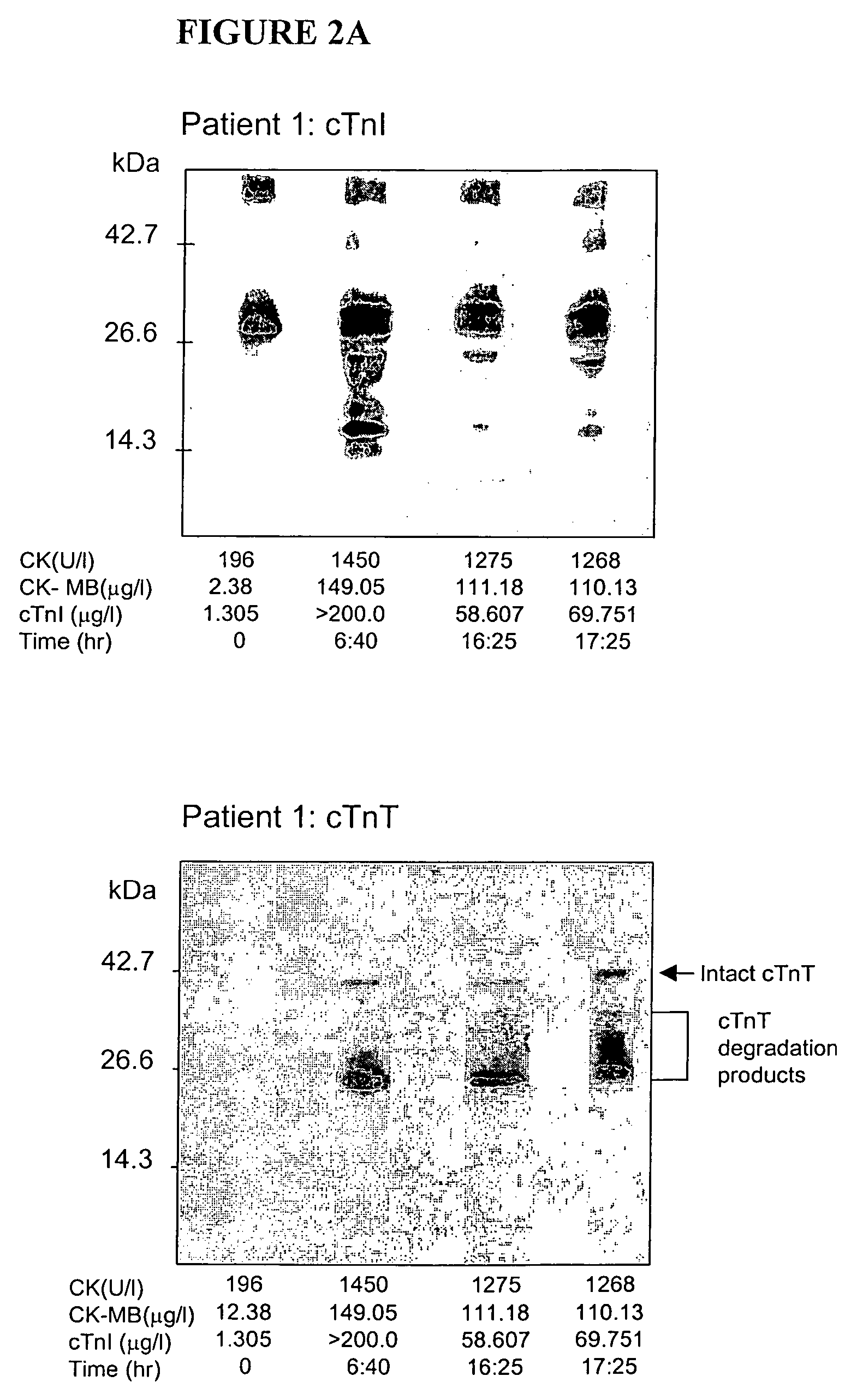
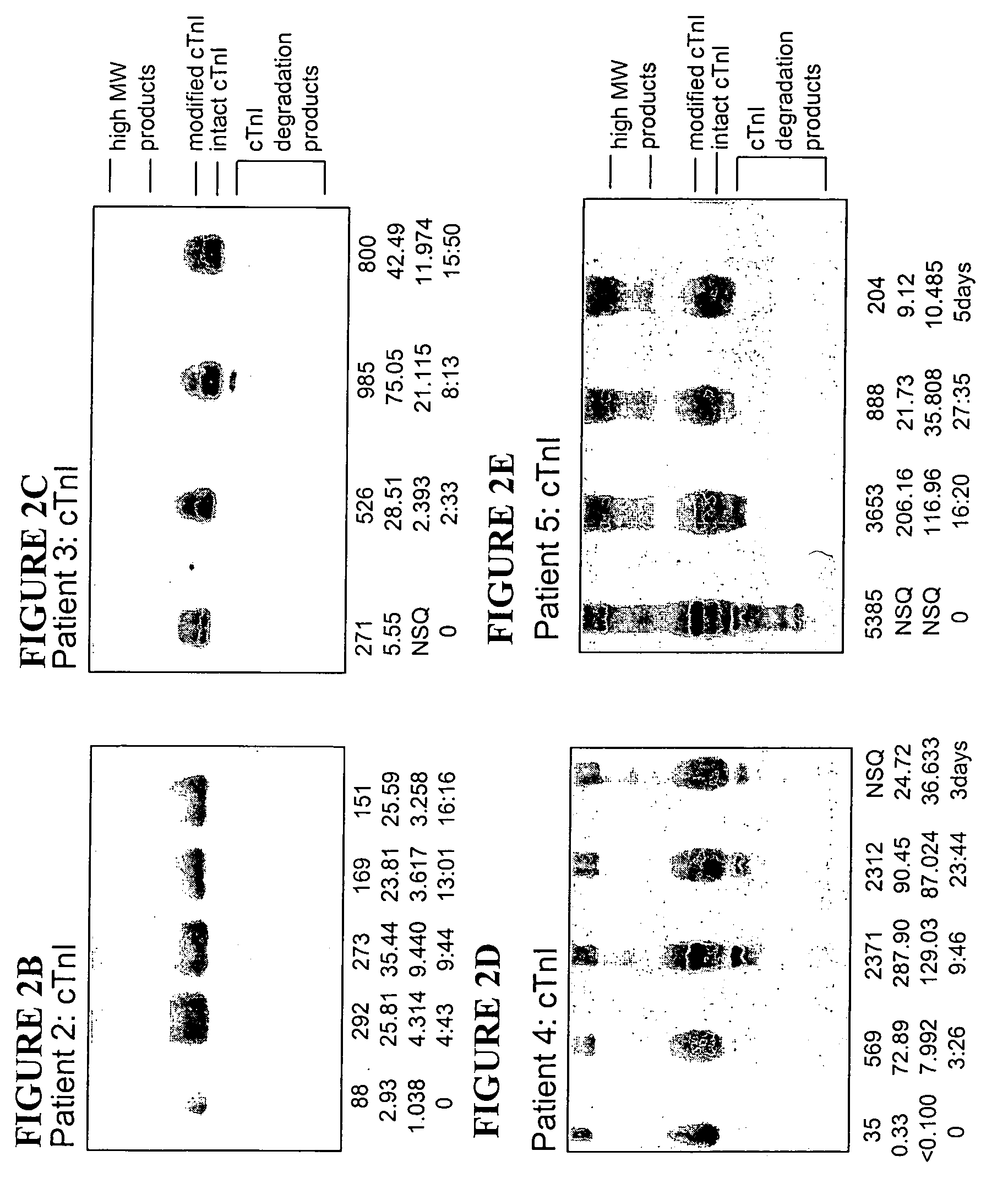
Methods and kits are provided for separating a mixture of proteins in a biological sample. Methods for detecting and profiling proteins in biological samples by the separation method and kits are also provided. These methods are particularly useful in assessing damage to cells such as cardiac and skeletal muscle cells and in the early clinical diagnosis of myocardial damage by detection of myofilament proteins in serum of a subject.
Owner:QUEENS UNIV OF KINGSTON
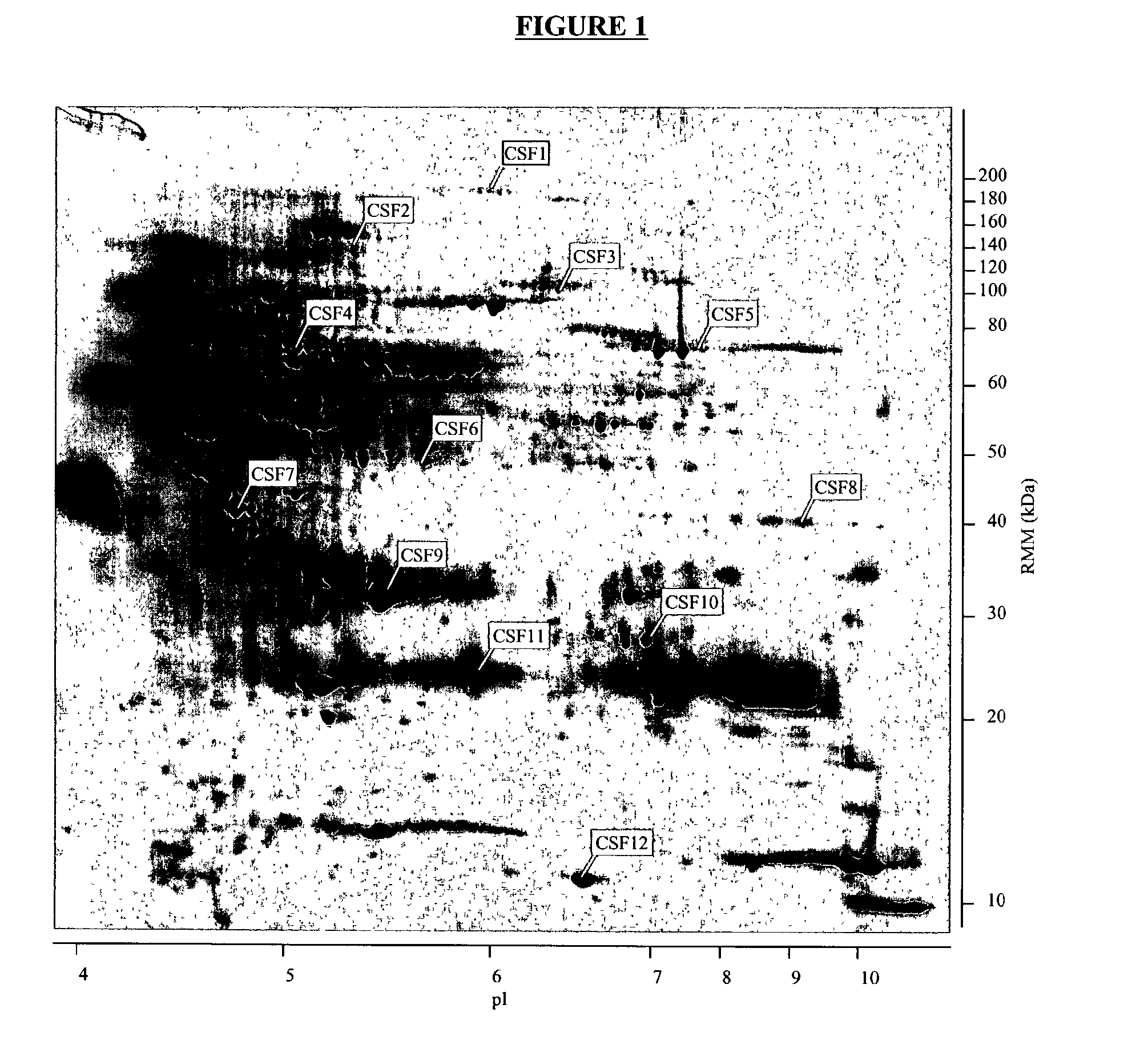
Biomarkers for detection of neonatal sepsis in biological fluid
The present invention concerns the identification and detection of biological fluid biomarkers of neonatal sepsis using global proteomic approaches.
Owner:霍洛吉克公司
Method for identification of proteins from intracellular bacteria
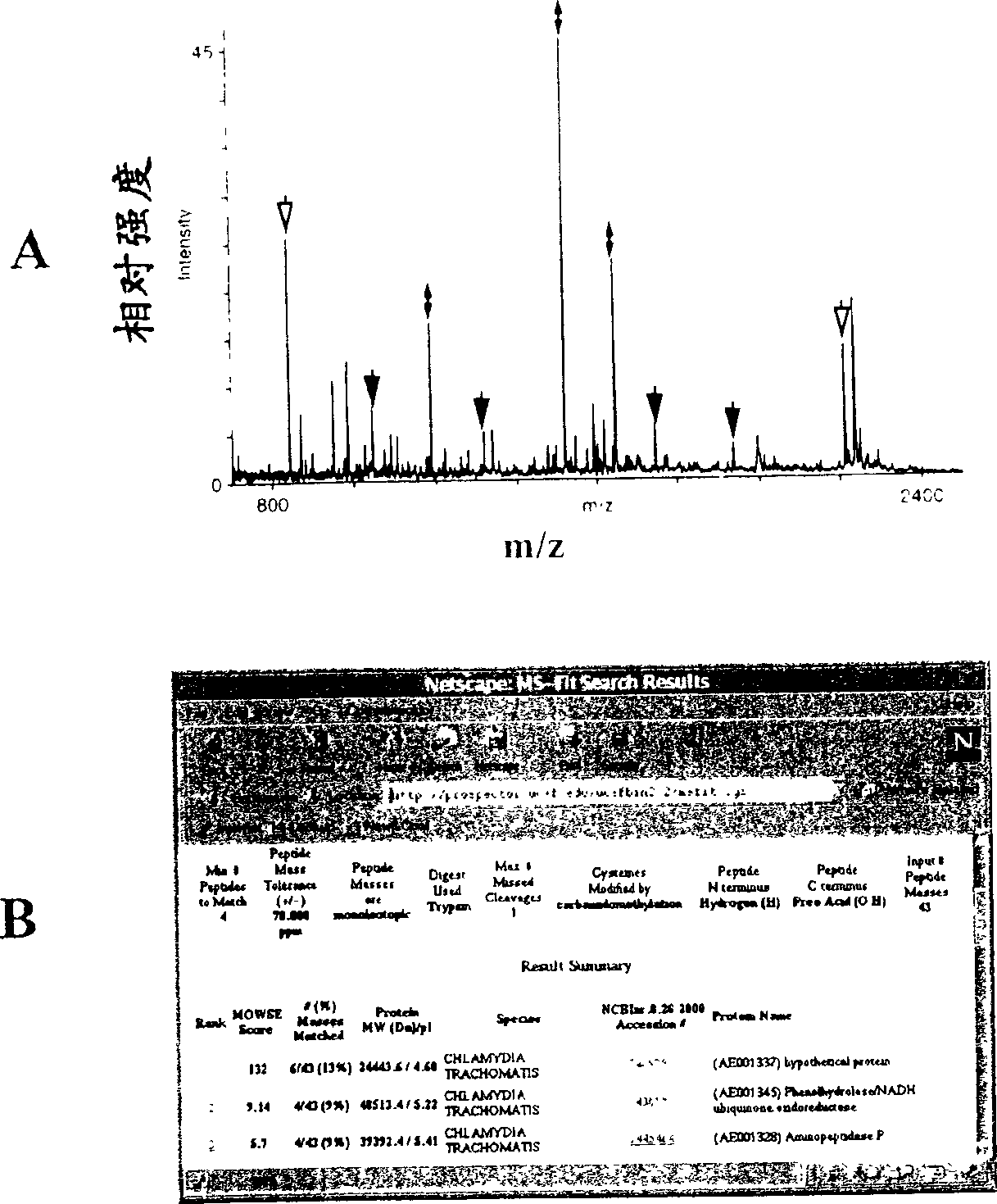
The present invention relates to a novel combination of methods that enables identification of proteins secreted from intracellular bacteria regardless of the secretion pathway. The invention further provides proteins that are identified by these methods. Secreted proteins are known to be suitable candidates for inclusion in immunogenic compositions and / or diagnostic purposes. The invention also provides peptide epitopes (T-cell epitopes) from the identified secreted proteins, as well as nucleic acid compounds that encode the proteins. The invention further comprises various applications of the proteins or fragments thereof, such as pharmaceutical and diagnostic applications.
Owner:阿兰·克里斯蒂安·肖 +1
Protein profiling of hyper acidic plants and high protein extraction compositions thereof
The present invention relates to a method for profiling of protein extract from hyper-acidic aerial parts of plant Scented Geranium (Pelargonium sp.), said method comprising steps of selecting effective extraction medium, with extraction medium consisting of 0.2 M sodium carbonate increasing percentage extract by about 600%, selecting effective medium to determine polypeptide pattern in said extract, with polypeptide pattern medium consisting of Sodium Carbonate ranging between 0.2 to 0.4 M, and 0.2 M Sodium Carbonate along with 50% dimethylsulfoxide, selecting effective media to determine enzyme multimolecular forms in said extract, with enzyme multimolecular forms media consisting of 0.2 M Tris-HCl buffer at pH 7.5, and optionally 50% dimethylsulfoxide; Sodium Carbonate at concentration ranging between 0.2 to 0.4 M and optionally 50% dimethylsulfoxide, and using biochemical and biophysical techniques comprising gel electrophoresis, spectrophotometry, centrifugation, protein estimation in said method to determine quantitative, qualitative, structural and functional facets of the proteins from said extract, and extraction compositions thereof.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Nucleic acid molecules, polypeptides and uses therefor, including diagnosis and treatment of Alzheimer's disease
InactiveUS20050163789A9Electrophoretic profilingMicrobiological testing/measurementDrug developmentBlood plasma
The present invention provides methods and compositions for screening, diagnosis and prognosis of Alzheimer's disease, for monitoring the effectiveness of Alzheimer's disease treatment, and for drug development. Alzheimer's Disease-Associated Features (AFs), detectable by two-dimensional electrophoresis of cerebrospinal fluid, serum or plasma are described. The invention further provides Alzheimer's Disease-Associated Protein Isoforms (APIs) detectable in cerebrospinal fluid, serum or plasma, preparations comprising isolated APIs, antibodies immunospecific for APIs, pharmaceutical compositions, diagnostic and therapeutic methods, and kits comprising or based on the same.
Owner:PFIZER INC +1
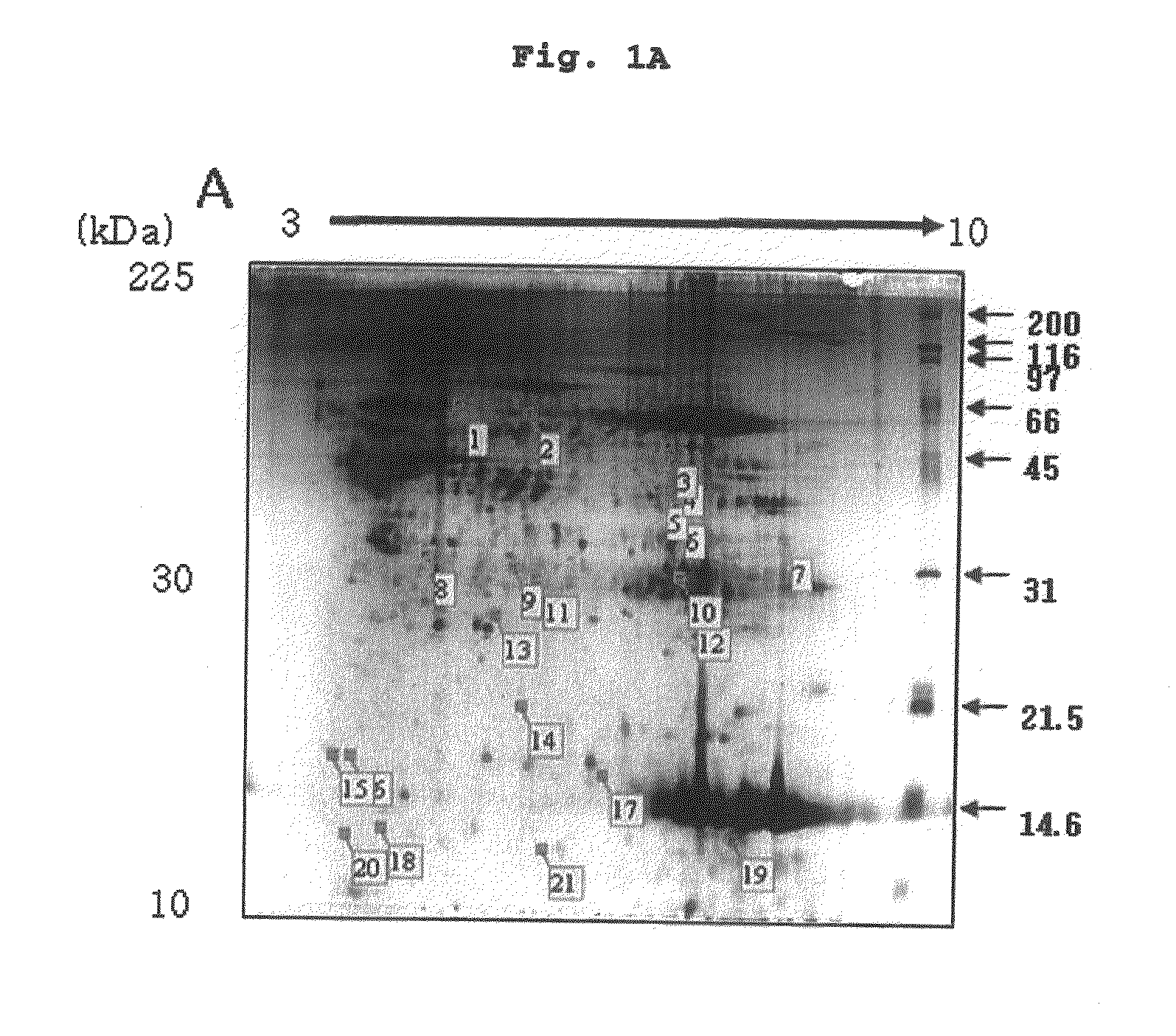
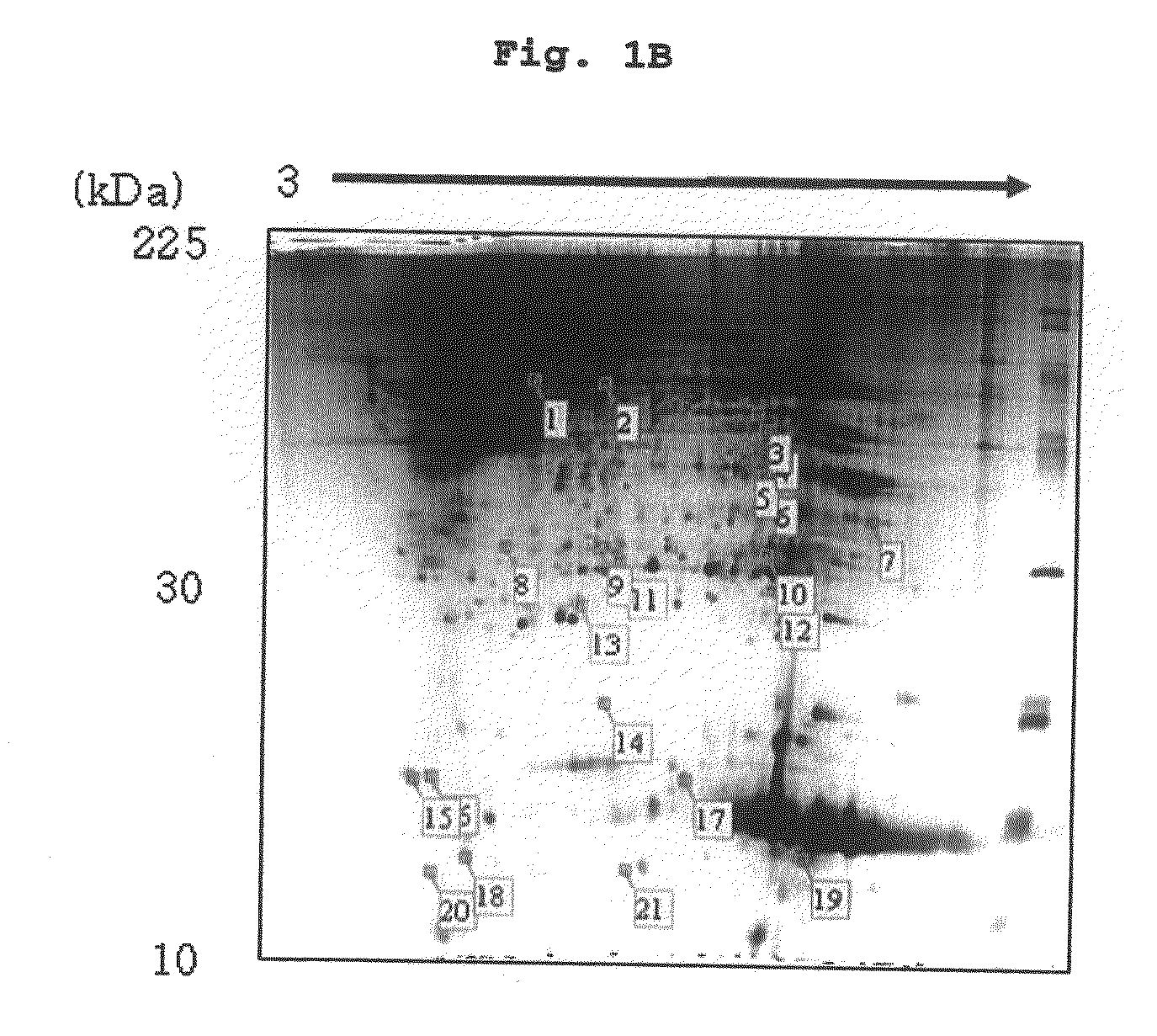
Gel electrophoresis method useful for resolution and characterization of nerve tissue ultra high molecular weight protein aggregates
The instant disclosure describes an electrophoretic procedure capable of resolving and isolating ultra high molecular weight (MW) protein aggregates from nerve tissue. The procedure is based on the use of composite agarose-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (CAPAGE) and resolves proteins and protein aggregates over the range of from approximately 225 kDa to approximately 30,000 kDa. Triton X-100 precipitation is used to obtain a cytoskeleton protein fraction that is subsequently resuspended and subjected to gel electrophoresis. This method demonstrates that a protein aggregate of approximately 30,000 kDa is characteristic of normal murine spinal cord tissue and that the amount of said protein aggregate is increased in spinal cord homogenate obtained from transgenic mice bearing copies of a mutant human gene characteristic of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. This method for separating nerve tissue ultra high MW cytoskeleton protein aggregates can prove useful in a variety of future biophysical and pharmacological studies related to the etiologies of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, diseases based on expansions in tandem DNA repeats, spinal muscular atrophy, Friedreich's ataxia, giant axon neuropathy, juvenile ceroid-lipofuscinosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, diabetic polyneuropathy and Down's syndrome.
Owner:SHAPIRO HOWARD K
Methods for identifying and analyzing biomarkers from plasma-derived microparticles
InactiveUS20080171312A1Peptide/protein ingredientsElectrophoretic profilingPlasma derivedMicroparticle
Owner:MICROPARTICLE PROTEOMICS LLS
Electrophoresis standards, methods and kits
Electrophoresis Compositions, methods and kits useful for, among other things, detecting, quantifying and / or characterizing analytes are provided. The compositions are useful as electrophoresis standards for determine the isoelectric point and molecular weight of an analyte. The electrophoresis standards generally comprise at least one label moiety and one or more reactive moieties that when activated attach the standard to a substrate.
Owner:PROTEINSIMPLE
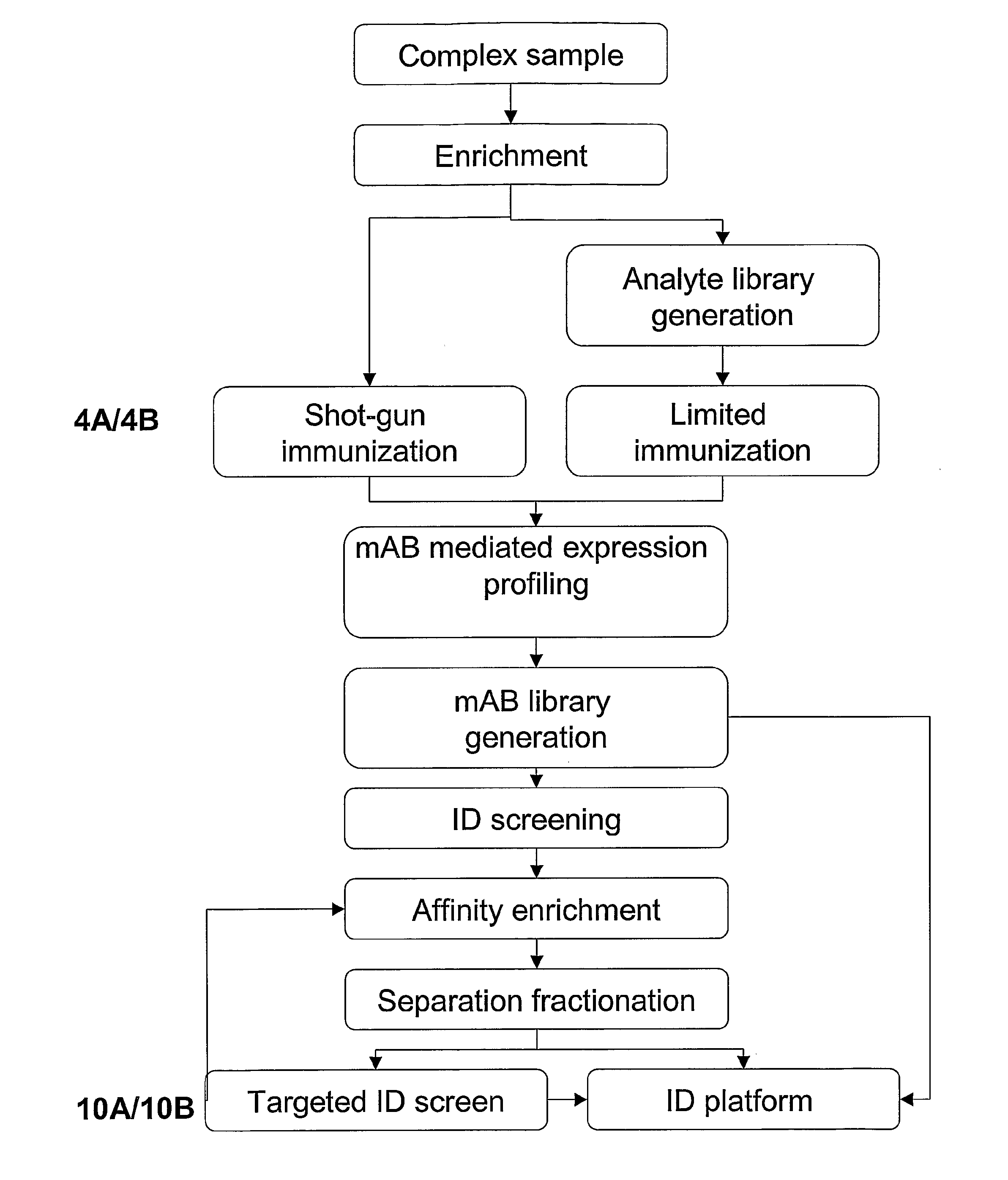
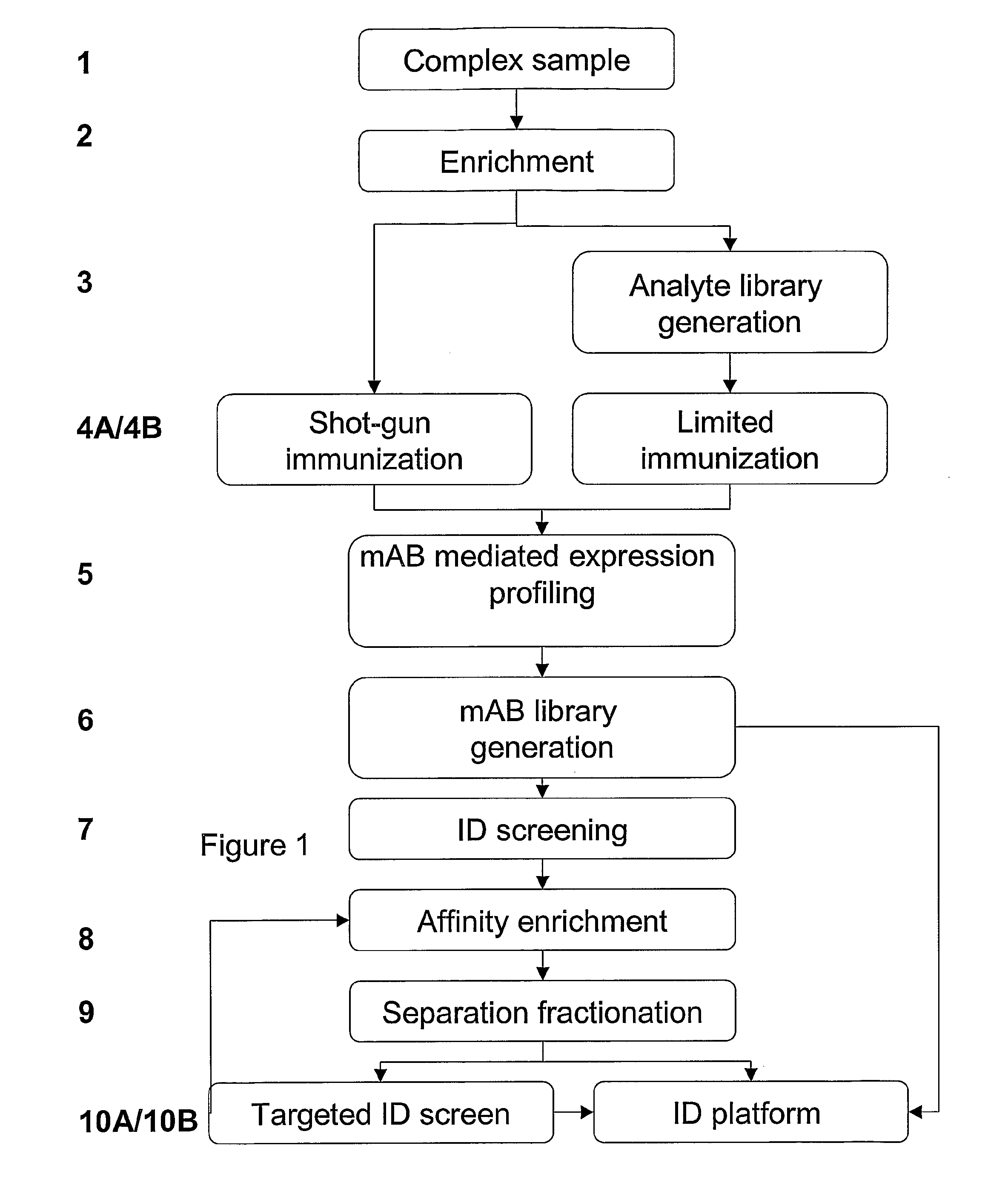
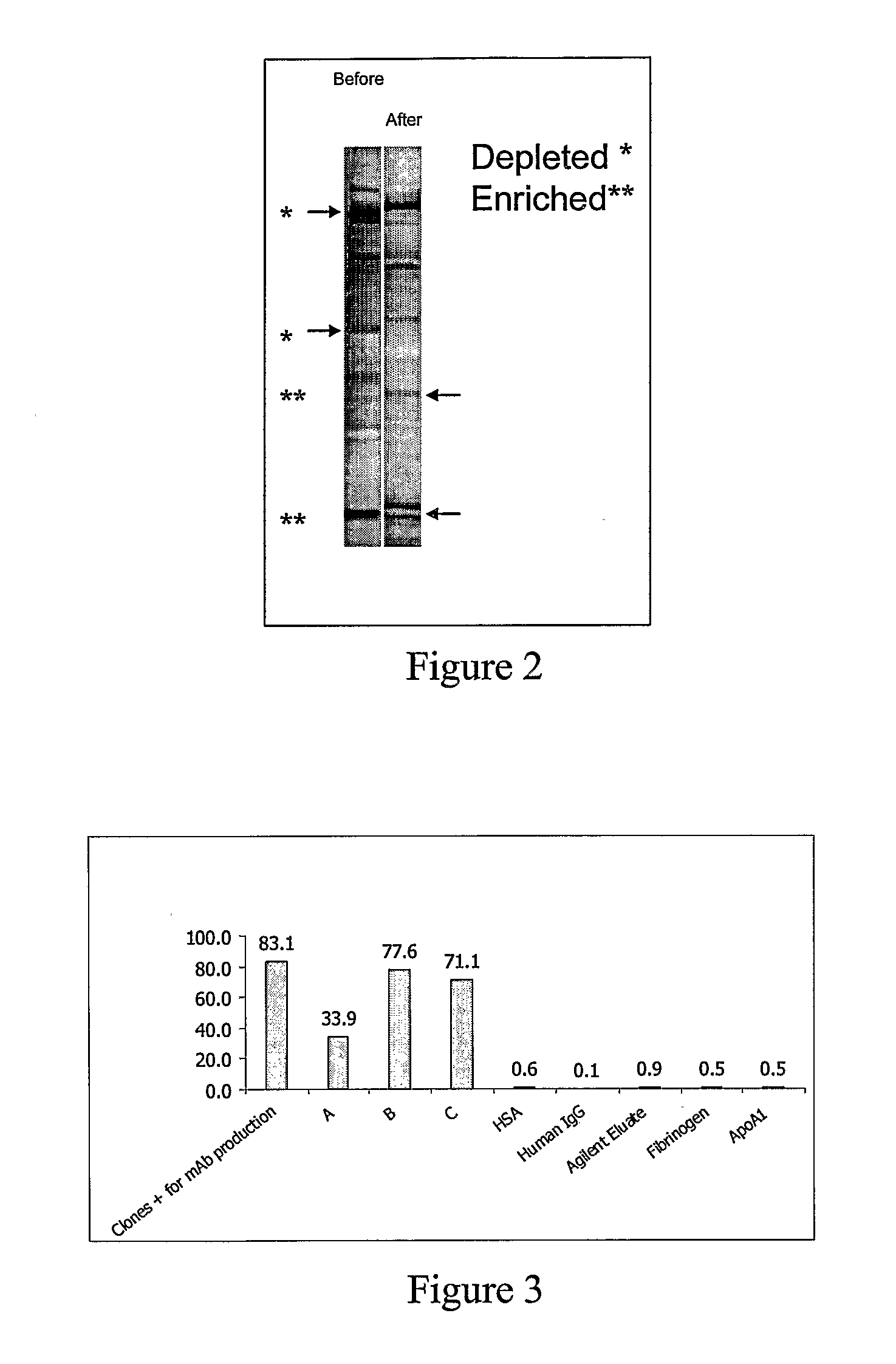
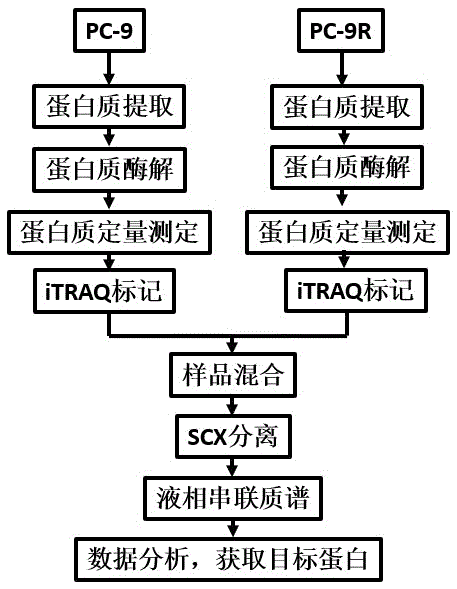
Expression Profiling Platform Technology
InactiveUS20070293437A1Accurate measurementImprove the level ofPeptide/protein ingredientsElectrophoretic profilingPeptideDifferential display
The present invention relates to an efficient mAb panel-based expression profiling technology platform suitable for global and accurate measurement of proteins, peptides and metabolites in complex mixtures. The platform is comprised of new and well established technologies that are coupled in a unique fashion to provide a novel platform technology for (i) the discovery of differentially displayed elements of complex protein, peptide and metabolite mixtures and (ii) the development of robust mAb based assays that detect the differentially expressed elements.
Owner:BIOSYST INT
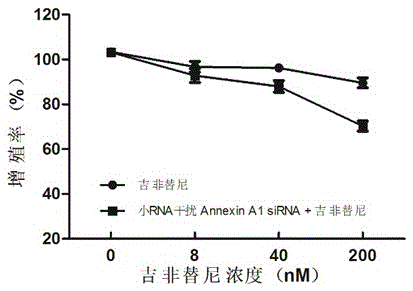
Method for detecting drug-resistant mechanism of gefitinib
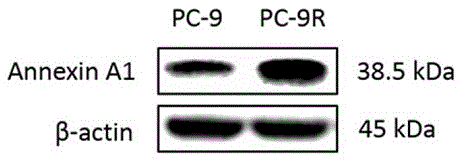
InactiveCN105510603ATo achieve the purpose of reversing the basis of gefitinib resistanceElectrophoretic profilingBiological testingHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsSignalling molecules
The invention discloses a method for detecting a drug-resistant mechanism of gefitinib and belongs to the field of medicines. The method comprises the following steps: (1) performing high throughput screening on protein signaling molecules participating in gefitinib drug resistance by adopting iTRAQ quantification (isotope labeling relative or absolute quantification) proteomics technology; (2) screening to obtain differential expression protein signaling molecules of gefitinib sensitive lung cancer cell lines and gefitinib rug-resistant cell lines by adopting western blot (western immunoblotting test) technical identification; and (3) proving expression of the protein signaling molecules discovered by interference by adopting MTT (MTT cytotoxicity assay). The sensitivity of gefitinib can be improved, so that the expression level change of the newly discovered protein signaling molecules is proved to be a drug-resistant mechanism of gefitinib. The method contributes to detecting new protein signaling molecules participating in gefitinib drug resistance, and tolerance-resistant drugs are designed by virtue of the new detected protein signaling molecules.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF NINGXIA MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com