Biomarkers for detection of neonatal sepsis in biological fluid
A biological and neonatal technology, applied in the field of biomarkers, can solve the problems of increasing the risk of sepsis and increasing the cost of NICU care during hospitalization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
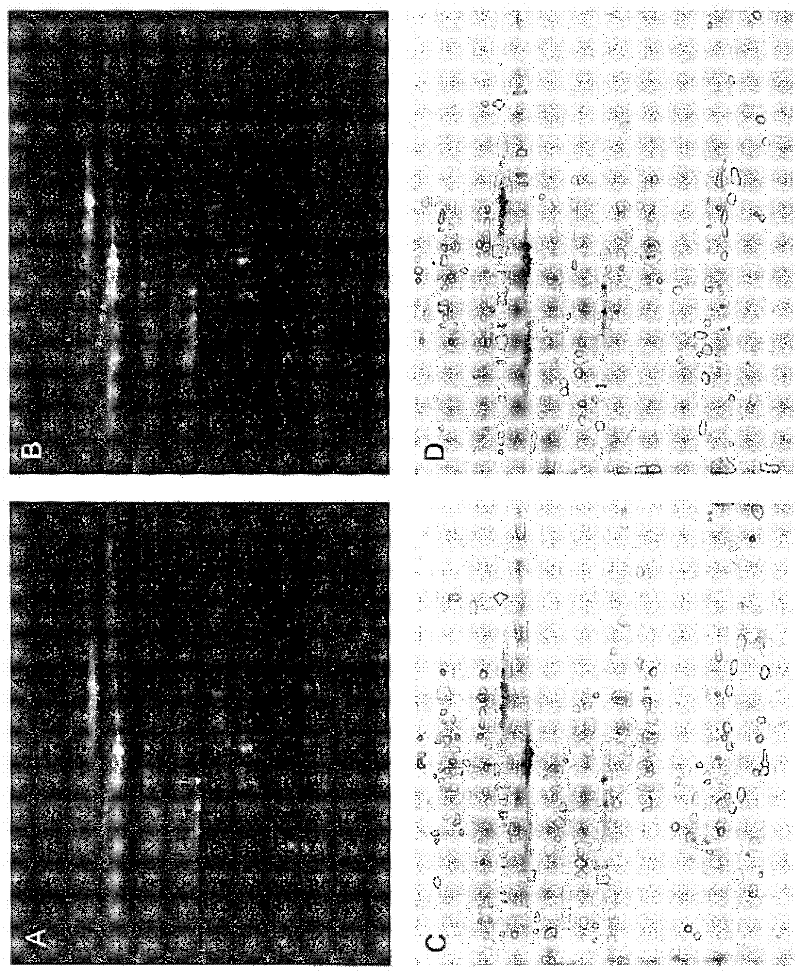
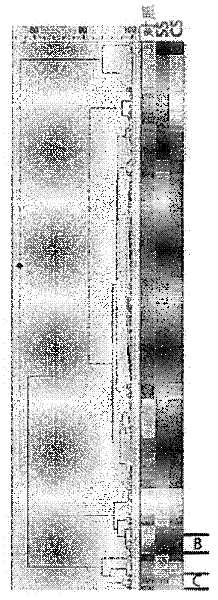
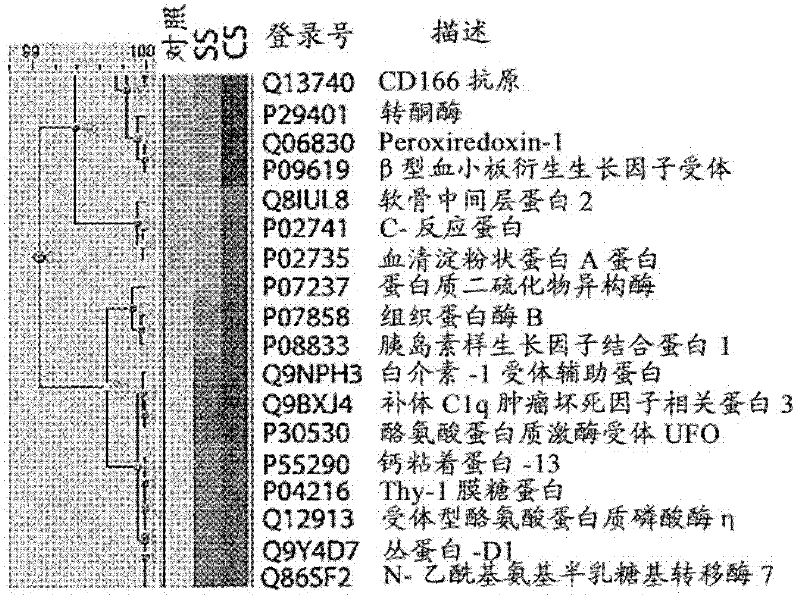
[0087] Example 1: Using a global proteomic approach to identify cord blood biomarkers for neonatal sepsis
[0088] experimental method
[0089] Sample Collection: Cord blood samples from a prospective observational cohort of 82 women in spontaneous preterm labor at 20-34 weeks' gestation were analyzed. Early-onset neonatal sepsis was defined as positive neonatal blood cultures within 72 hours of delivery. Of the 82 subjects, 71 delivered at less than 34 weeks, and 5 neonates had confirmed neonatal sepsis (positive blood cultures in newborns), while 8 neonates had suspected sepsis (positive blood cultures Negative, suggesting clinical symptoms of infection) diagnosis.
[0090] Immunodepletion of umbilical cord serum: Serum samples for 2-DLC experiments were depleted of the 12 most abundant proteins (albumin, IgG, IgA, IgM, α -1 antitrypsin, transferrin, haptoglobin, alpha-1 acid glycoprotein, alpha-2 macroglobulin, fibrinogen, apolipoproteins A-I and A-II). Appropriate fr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com