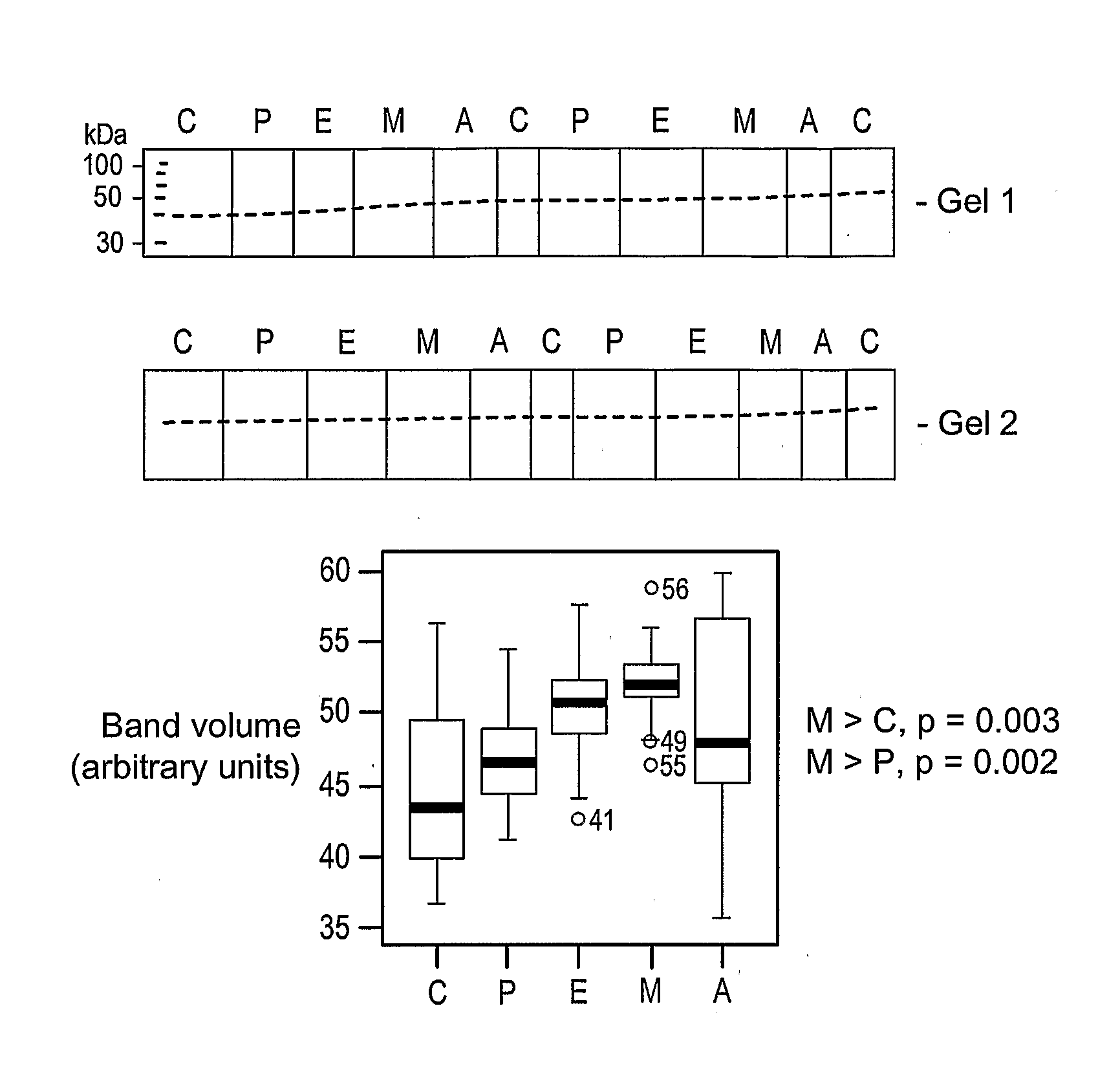
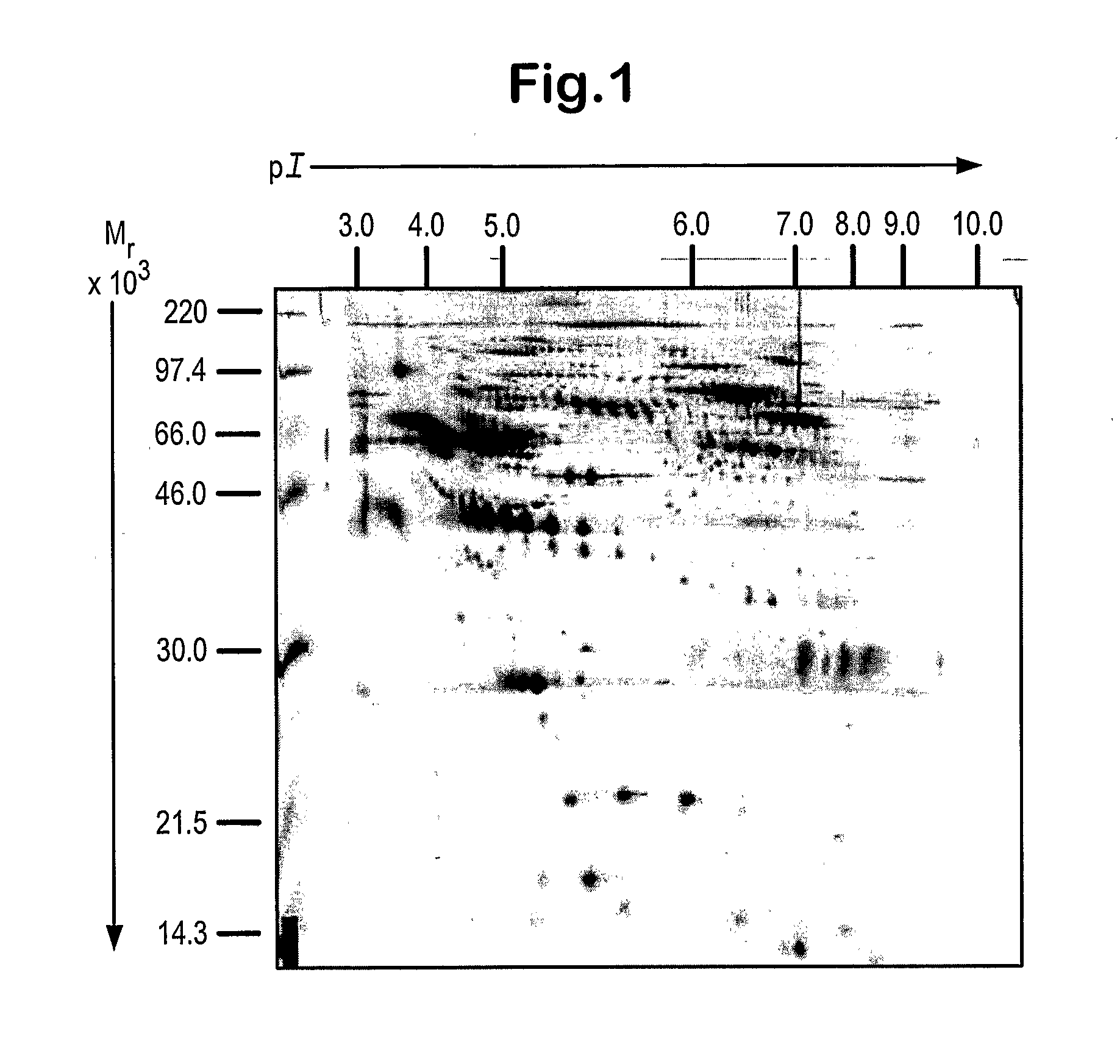
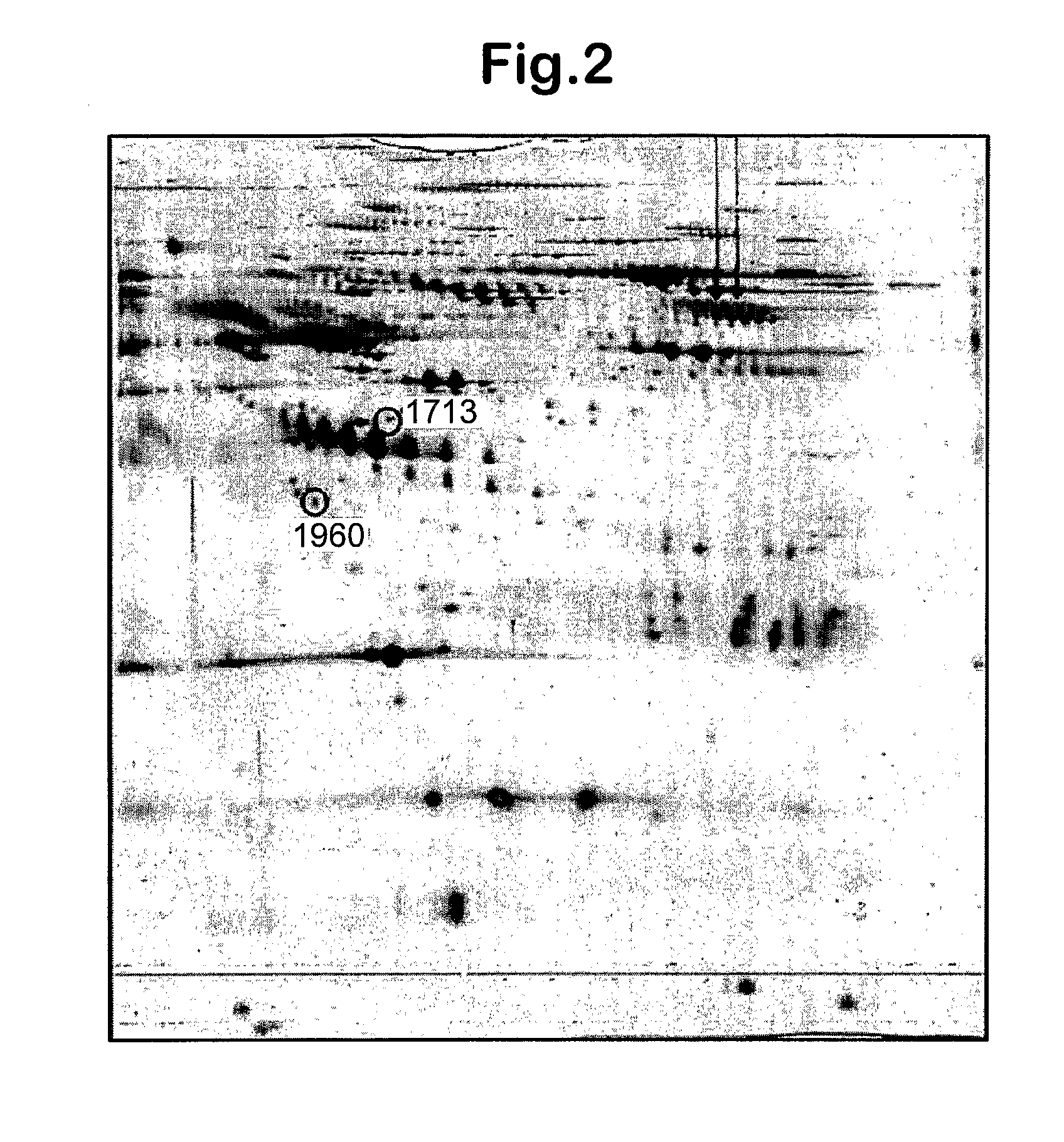
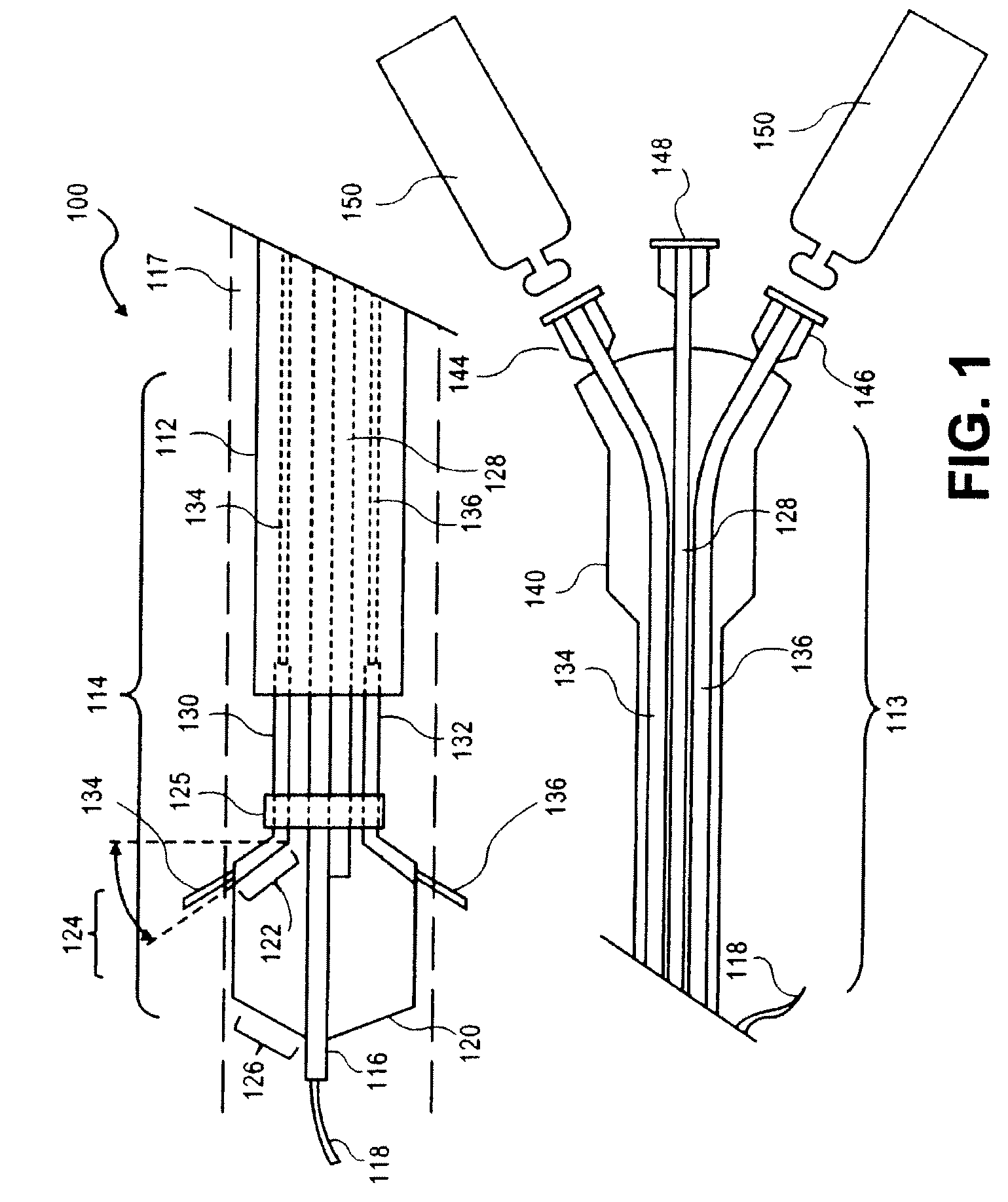
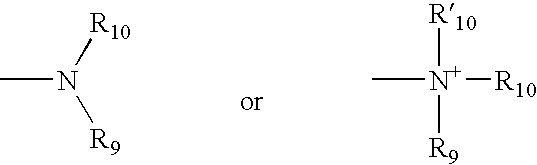Patents
Literature
111 results about "Apolipoproteins A" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
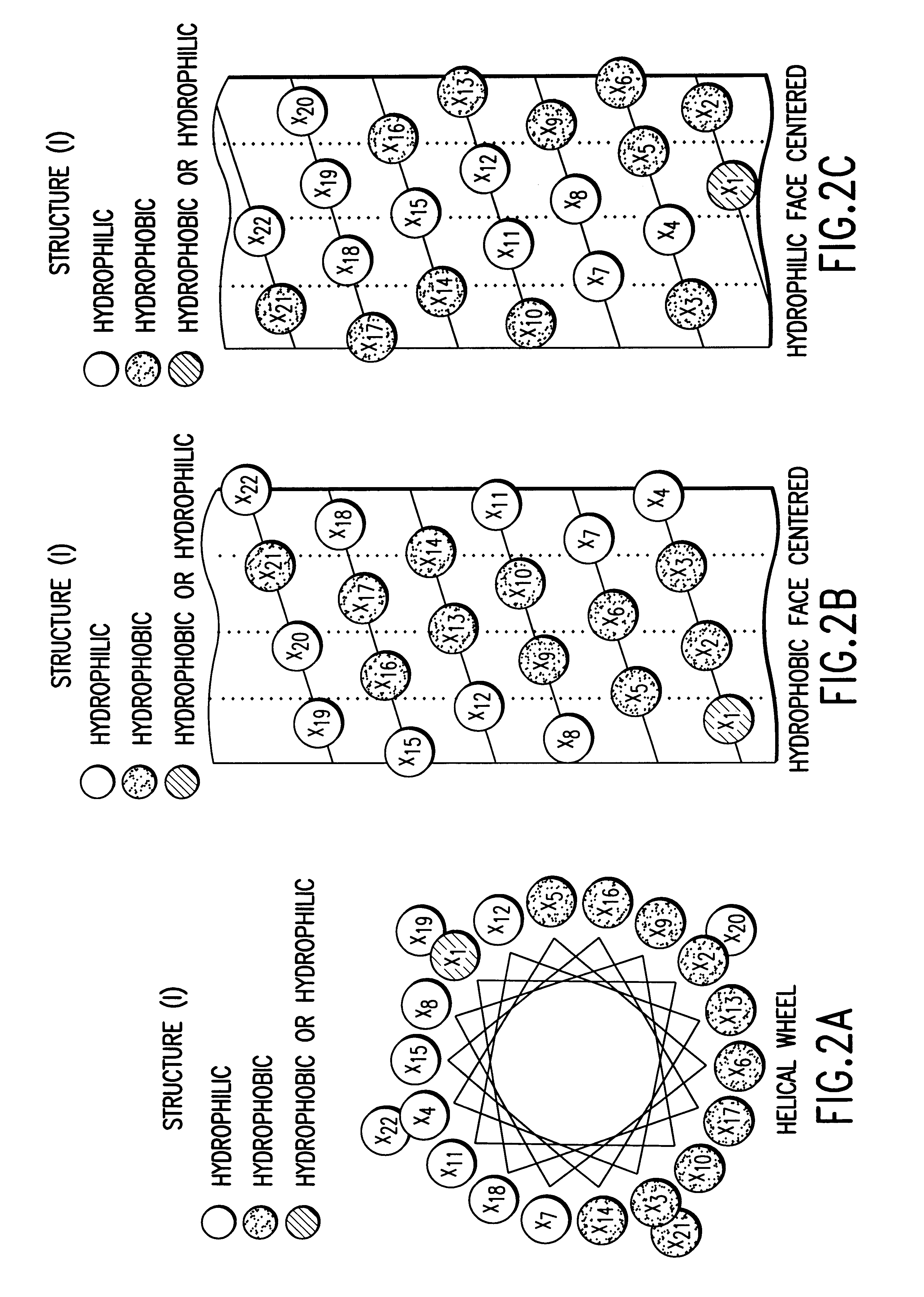
Structural proteins of the alpha-lipoproteins (HIGH DENSITY LIPOPROTEINS), including APOLIPOPROTEIN A-I and APOLIPOPROTEIN A-II. They can modulate the activity of LECITHIN CHOLESTEROL ACYLTRANSFERASE. These apolipoproteins are low in atherosclerotic patients. They are either absent or present in extremely low plasma concentration in TANGIER DISEASE.
Apolipoprotein A-I agonists and their use to treat dyslipidemic disorders
The present invention provides peptides and peptide analogues that mimic the structural and pharmacological properties of human ApoA-I. The peptides and peptide analogues are useful to treat a variety of disorders associated with dyslipidemia.
Owner:DASSEUX JEAN LOUIS +5
Apolipoprotein A-I agonists and their use to treat dyslipidemic disorders
The present invention provides peptides and peptide analogues that mimic the structural and pharmacological properties of human ApoA-I. The peptides and peptide analogues are useful to treat a variety of disorders associated with dyslipidemia.
Owner:JEAN LOUIS DASSEUX +5
Apolipoprotein A-I agonists and their use to treat dyslipidemic disorders
The present invention provides peptides and peptide analogues that mimic the structural and pharmacological properties of human ApoA-I. The peptides and peptide analogues are useful to treat a variety of disorders associated with dyslipidemia.
Owner:DASSEUX JEAN LOUIS +4
Gene therapy approaches to supply apolipoprotein A-I agonists and their use to treat dyslipidemic disorders
InactiveUS6518412B1Improve the level ofIncrease productivityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaDyslipidemiaAmphipathic helix
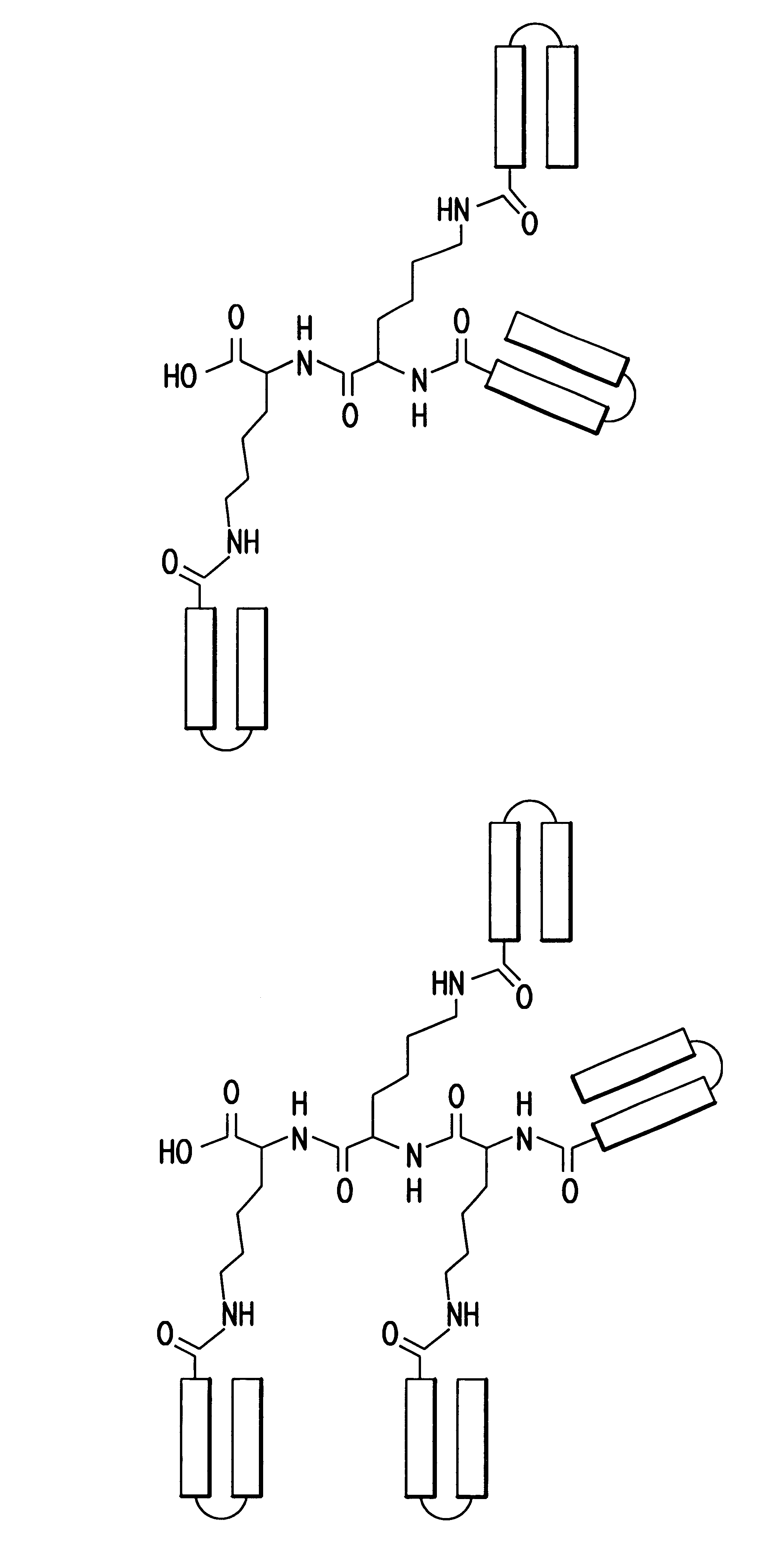
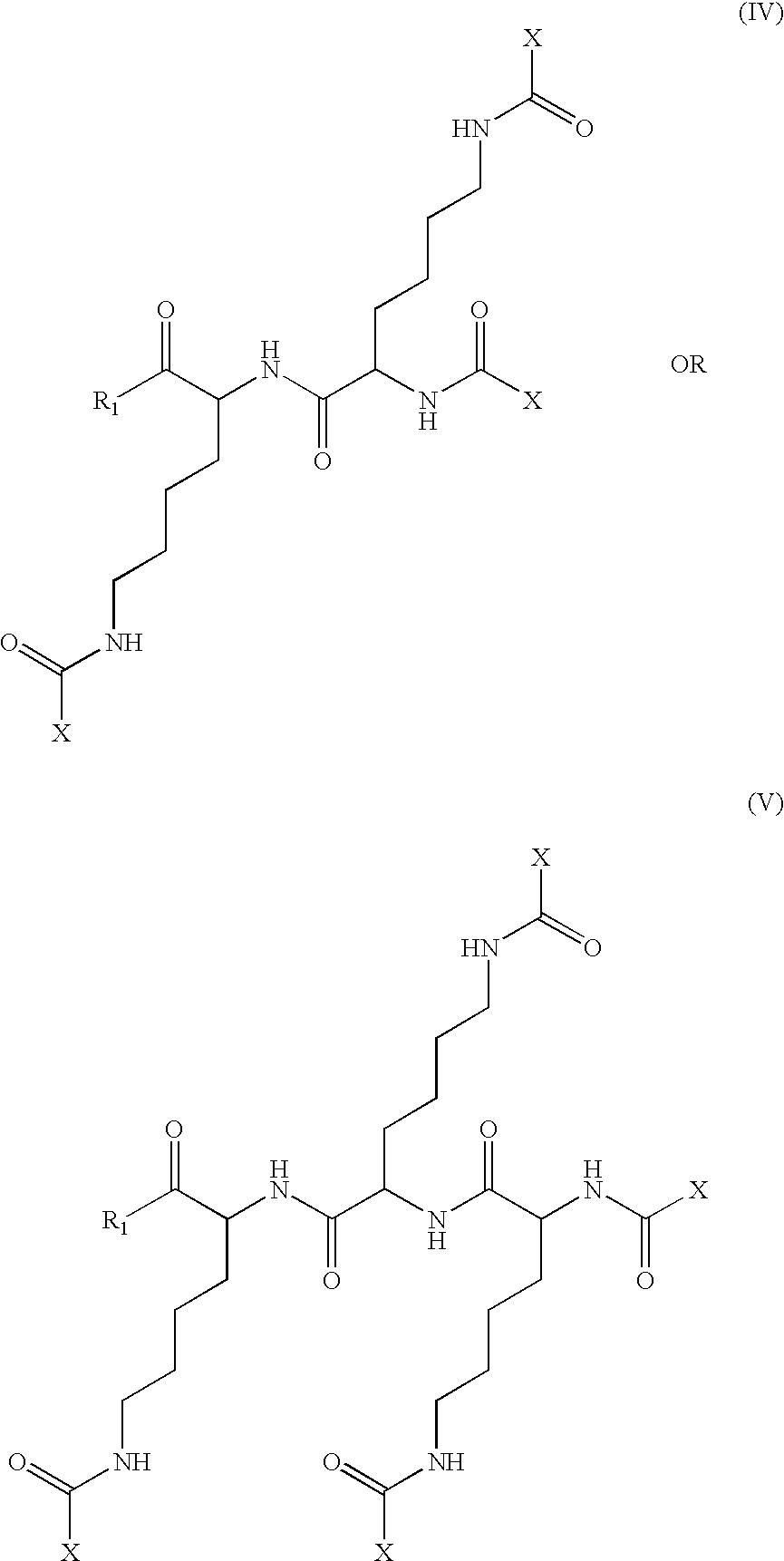
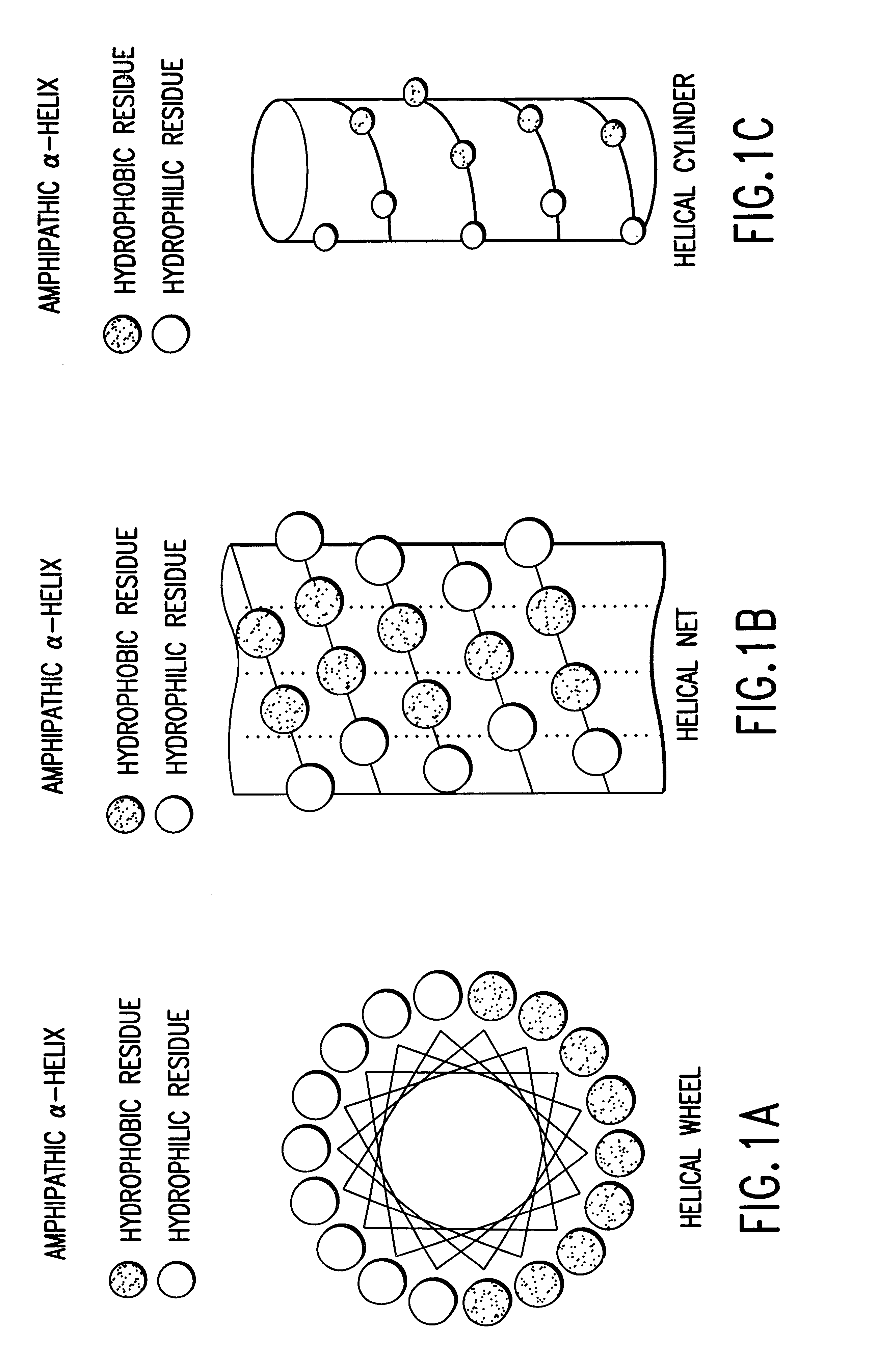
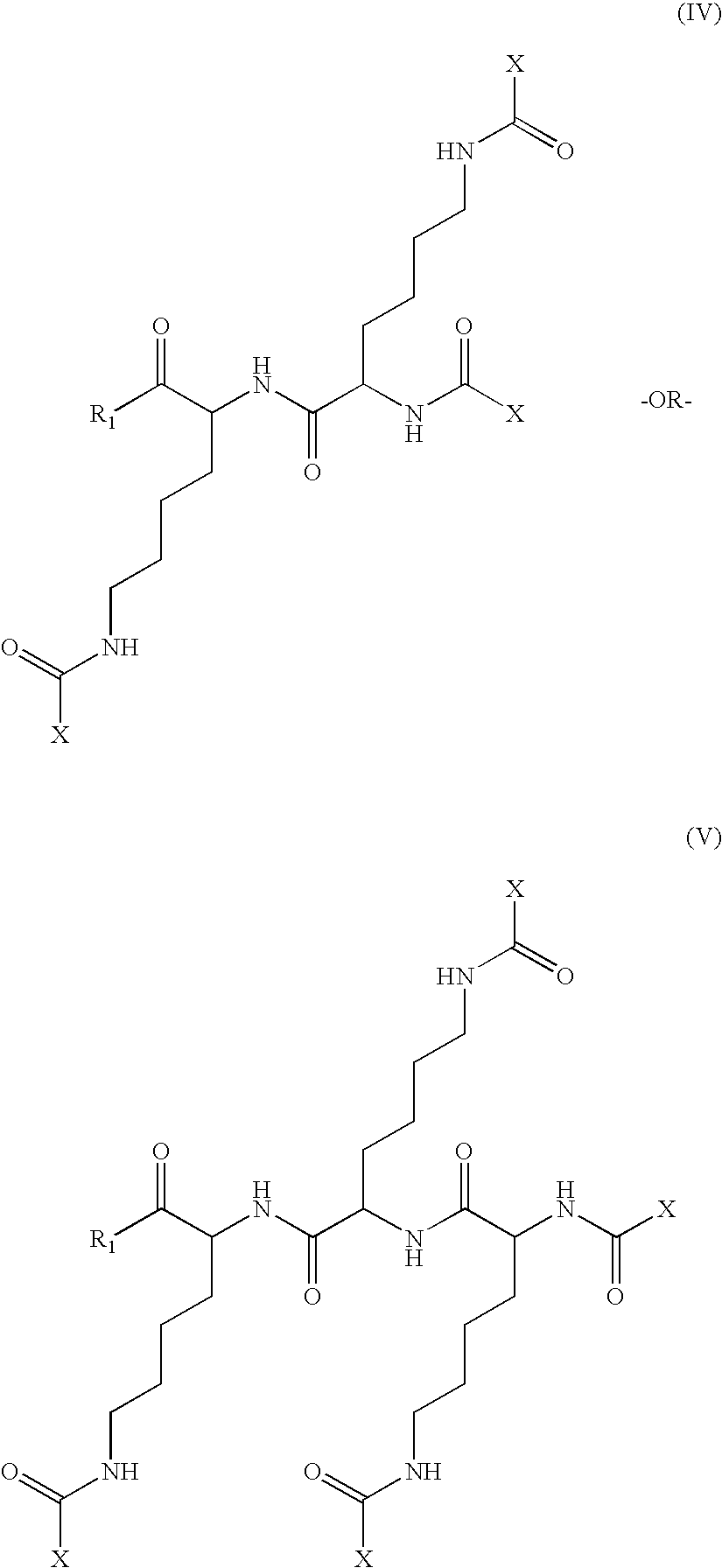
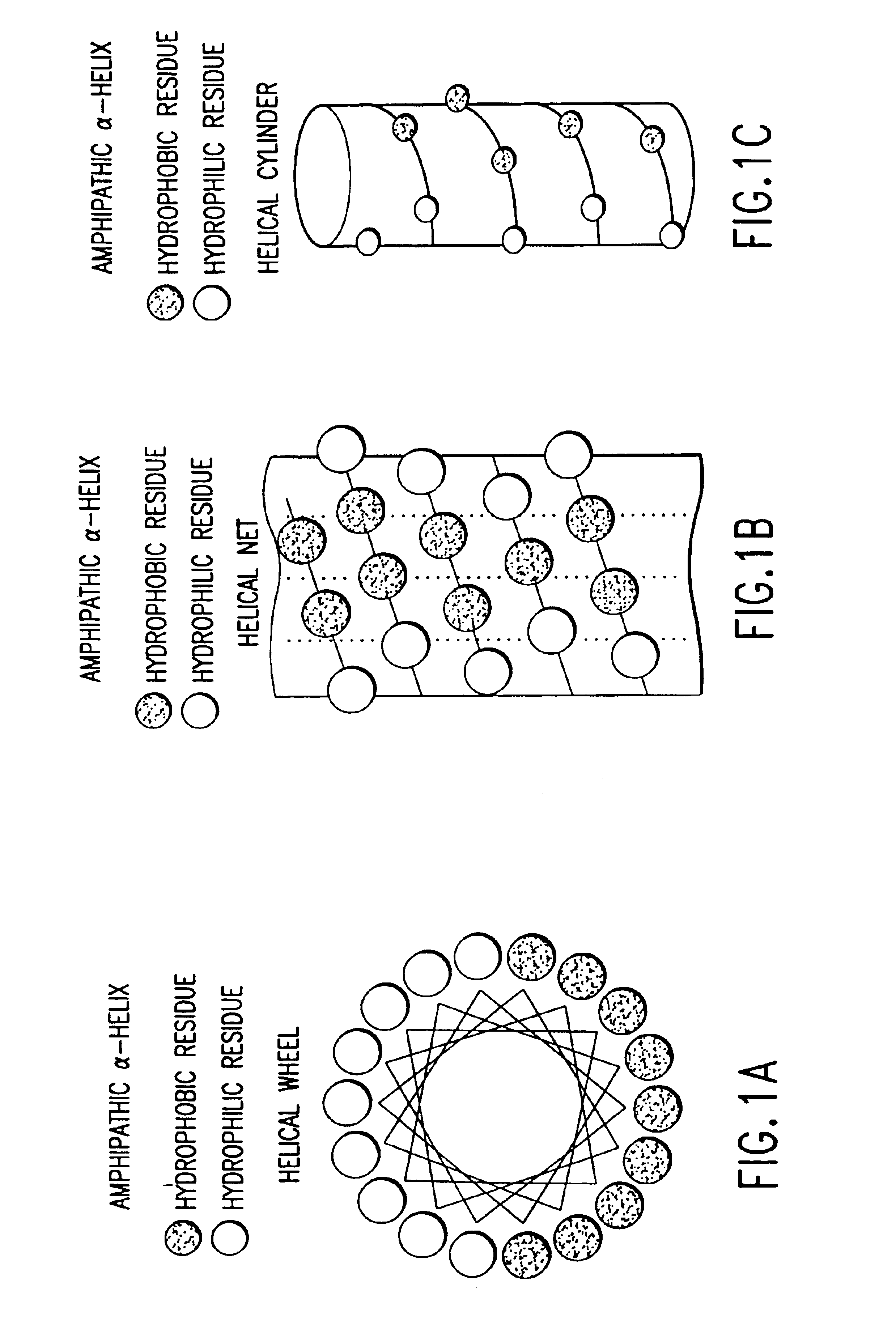
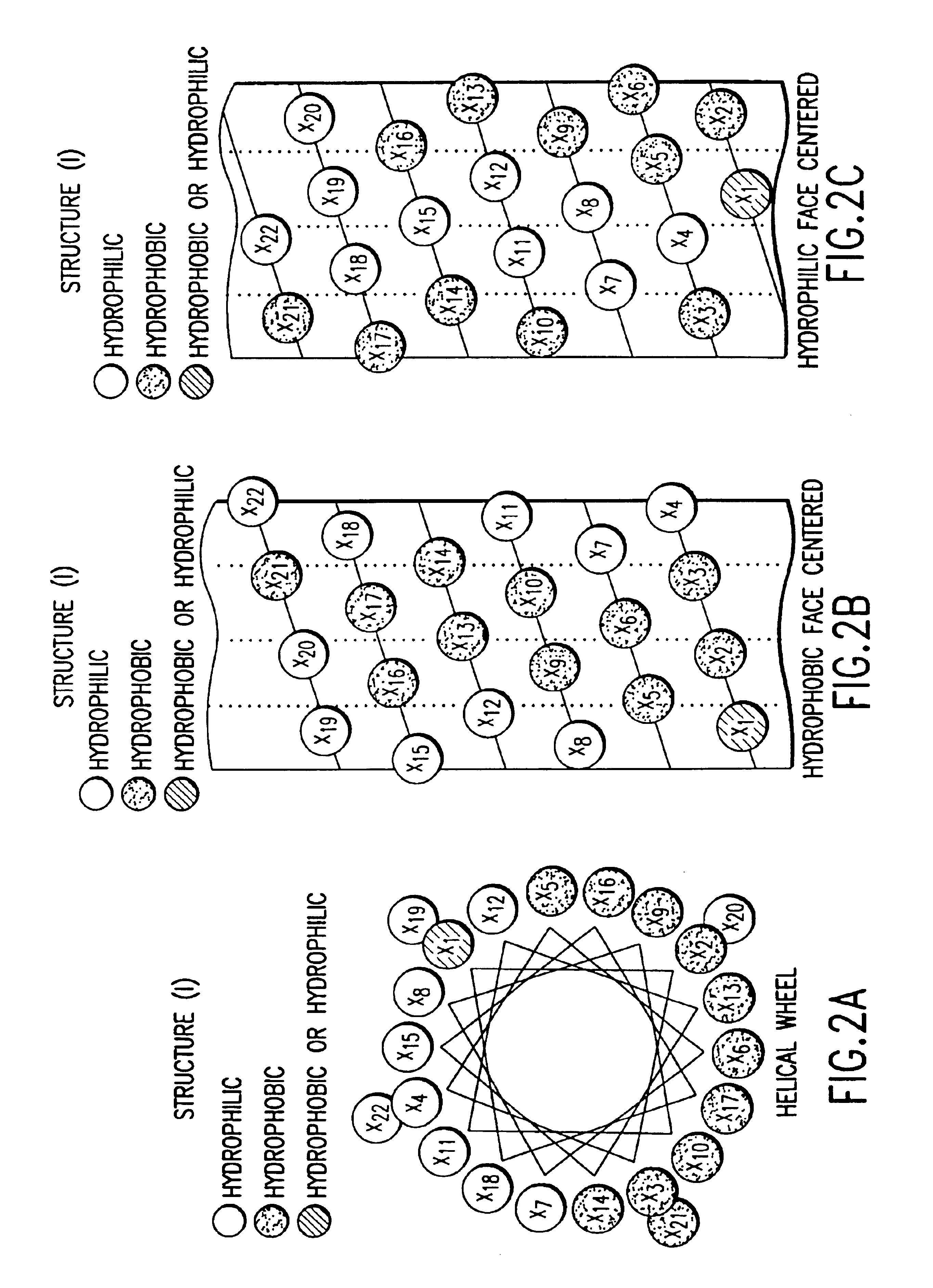
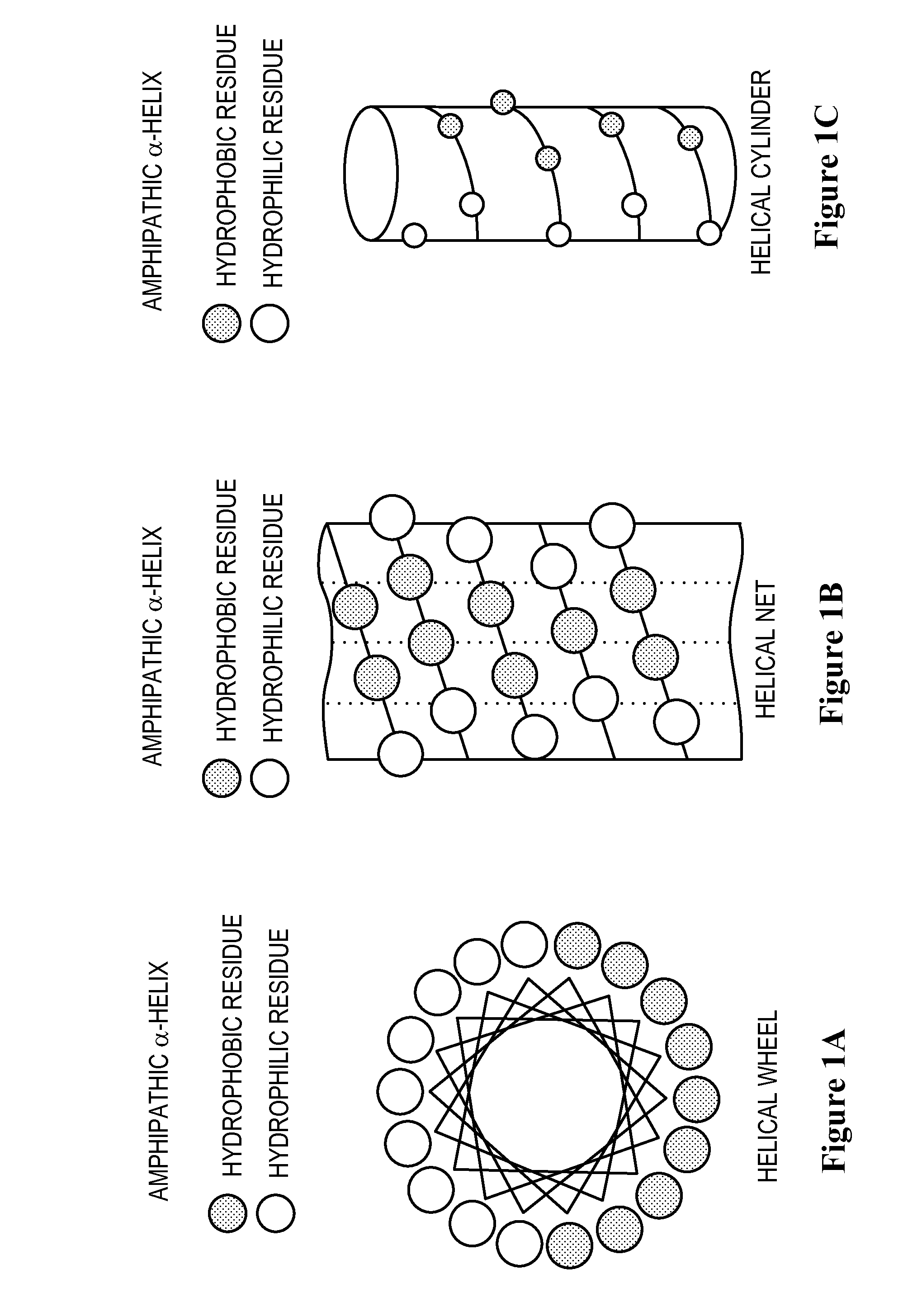
The invention relates to genetic approaches to supply nucleotide sequences encoding modified forms of the native forms of apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-I): mature ApoA-I, preproApoA-I and proApoA-I; including native ApoA-I modified to contain ApoA-I agonists, peptides which mimic the activity of ApoA-I; ApoA-I superagonists, peptides which exceed the activity of native ApoA-I; and modified native ApoA-I having one or more amphipathic helices replaced by the nucleotide sequences of one or more ApoA-I agonists; for the treatment of disorders associated with dyslipoproteinemia, including cardiovascular disease, atherosclerosis, restenosis, hyperlipidemia, and other disorders such as septic shock.
Owner:DASSEUX JEAN LOUIS +5
Apolipoprotein A-I agonist compounds
The present invention provides peptides and peptide analogues that mimic the structural and pharmacological properties of human ApoA-I. The peptides and peptide analogues are useful to treat a variety of disorders associated with dyslipidemia.
Owner:DASSEUX JEAN LOUIS +5
Apolipoprotein A1 mimetics and uses thereof
The present invention provides peptidomimetics derived from Apolipoprotein A-I, which is useful for beneficially influencing lipid parameters and / or plasma cholesterol levels. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions and methods of treatment for elevated levels of plasma cholesterol.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE TUFTS UNIV
Methods of using non-human animal Apolipoprotein A-I protein
The invention provides methods and compositions for treating disorders using non-human animal Apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-I) protein. The invention provides methods and compositions for treating disorders in animals, including humans, associated with dyslipidemia, including hyperlipidemia, hyperlipoproteinemia, hypertriglyceridemia, hypercholesterolemia, HDL deficiency, ApoA-I deficiency, cardiovascular disease, atherosclerosis, restenosis, and other disorders such as septic shock and viral infections.
Owner:PFIZER INC
Apolipoprotein A-I agonists and their use to treat dyslipidemic disorders
The present invention provides peptides and peptide analogues that mimic the structural and pharmacological properties of human ApoA-I. The peptides and peptide analogues are useful to treat a variety of disorders associated with dyslipidemia.
Owner:DASSEUX JEAN LOUIS +4
Gene therapy approaches to supply apolipoprotein A-I agonists and their use to treat dyslipidemic disorders
InactiveUS6844327B2High activityImprove the level ofAntibacterial agentsBiocideDyslipidemiaAmphipathic helix
The invention relates to genetic approaches to supply nucleotide sequences encoding modified forms of the native forms of apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-I): mature ApoA-I, preproApoA-I and proApoA-I; including native ApoA-I modified to contain ApoA-I agonists, peptides which mimic the activity of ApoA-I; ApoA-I superagonists, peptides which exceed the activity of native ApoA-I; and modified native ApoA-I having one or more amphipathic helices replaced by the nucleotide sequences of one or more ApoA-I agonists; for the treatment of disorders associated with dyslipoproteinemia, including cardiovascular disease, atherosclerosis, restenosis, hyperlipidemia, and other disorders such as septic shock.
Owner:DASSEUX JEAN LOUIS +5
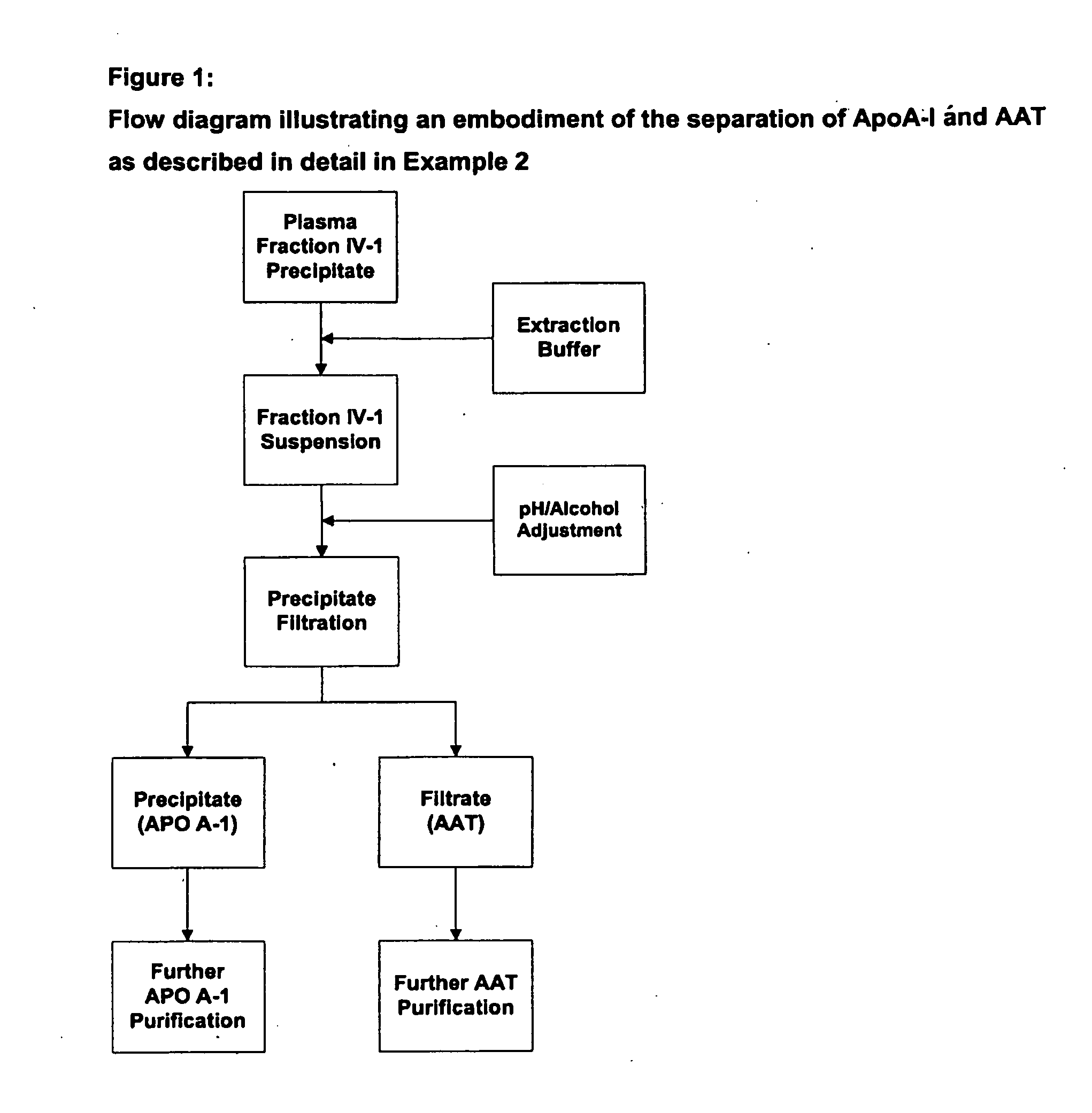
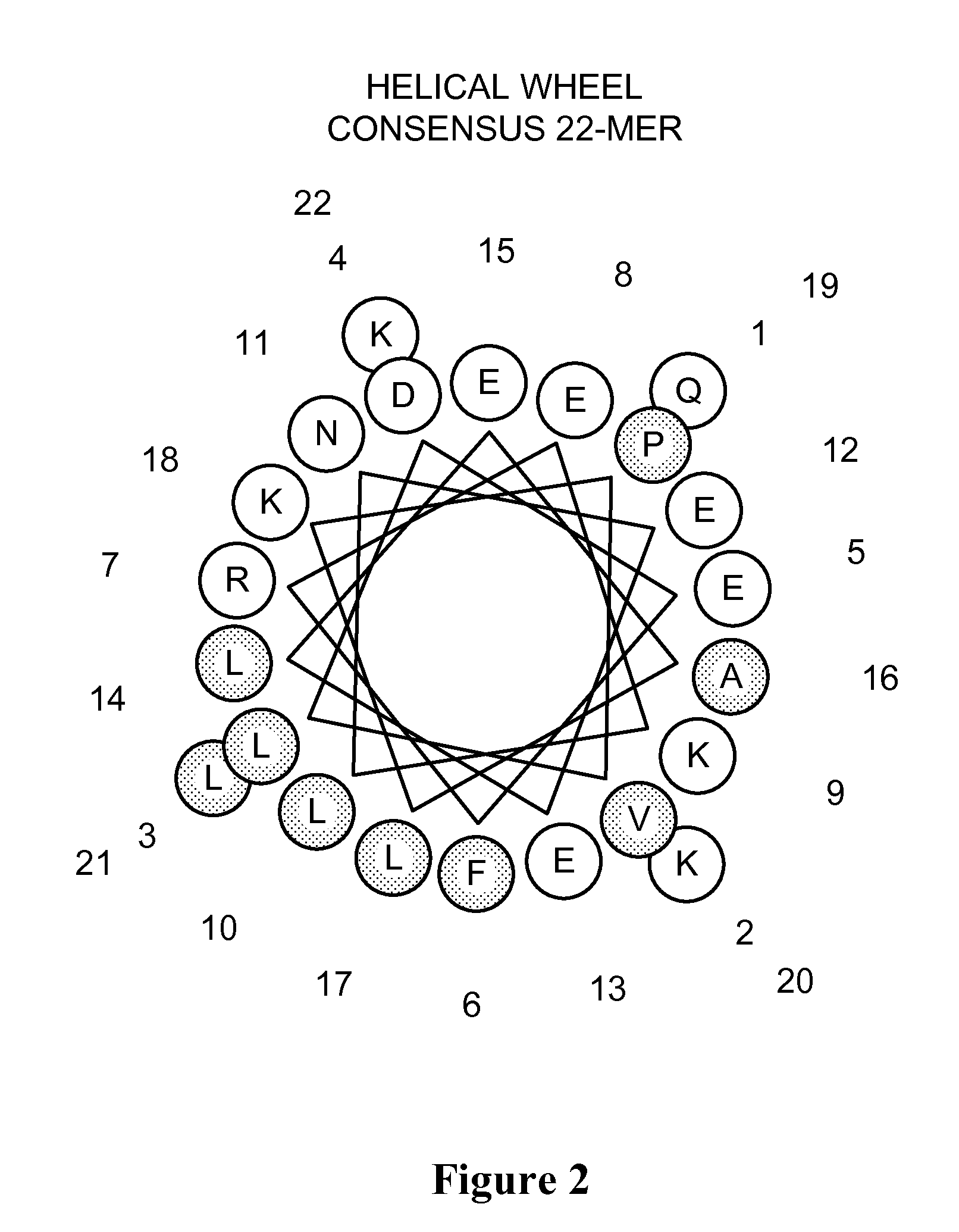
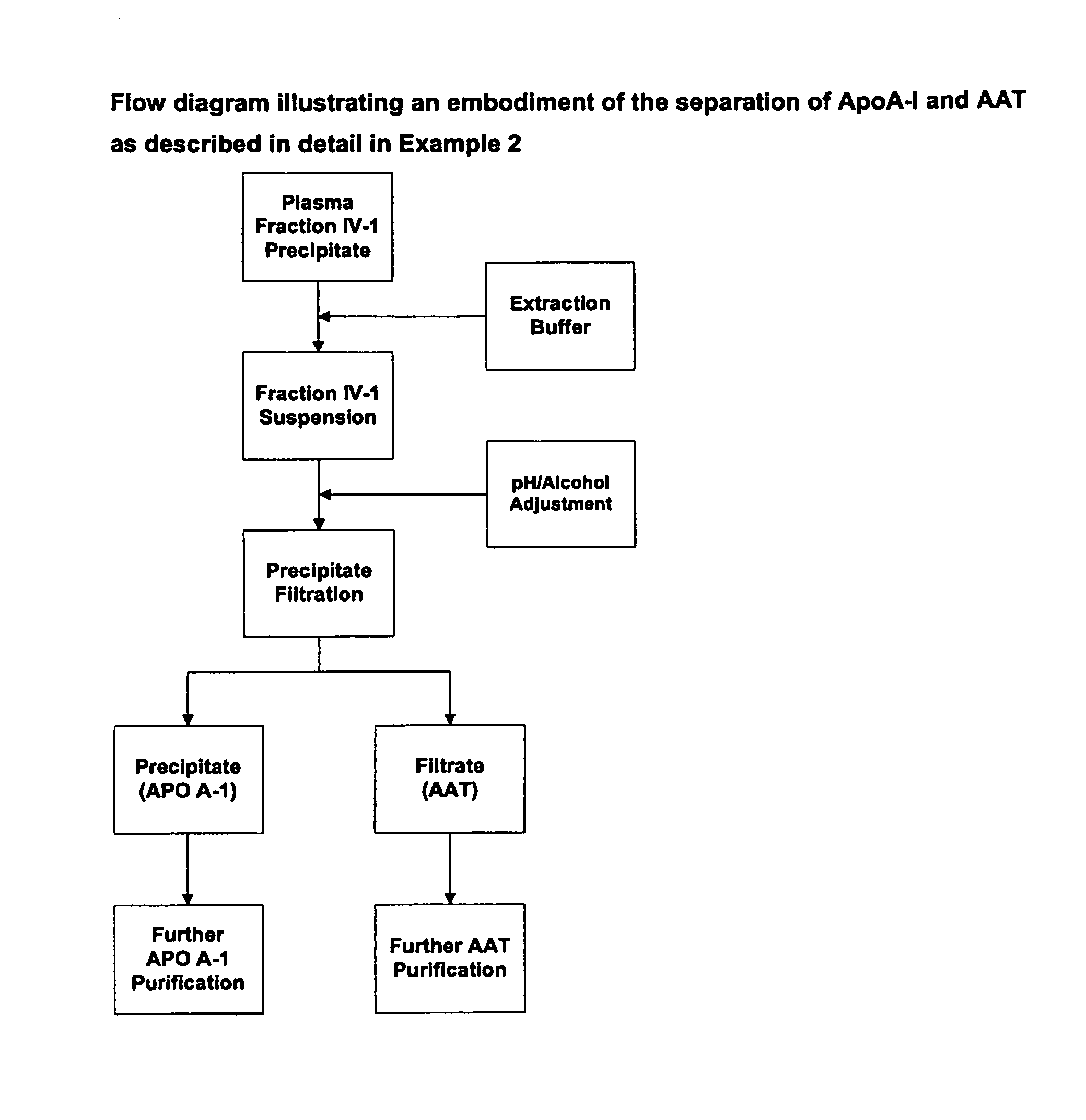
Methods for purification of alpha-1-antitrypsin andapolipoprotein a-1
ActiveUS20110087008A1Minimize deamidationMinimize denaturationApolipeptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsPurification methodsApolipoproteins E
This invention relates to protein separation and purification methods for both alpha-1-antitrypsin (AAT, also known as alpha-1 proteinase inhibitor, API, and A1-PI) and Apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-1) from, for example, a fraction of human blood plasma. In certain embodiments, the invention provides methods for separating AAT from ApoA-1 at the initial stage of purification, so that the same starting material can be used as a source for both proteins. The methods further pertain to providing compositions of AAT and of ApoA-1 suitable for pharmaceutical use and are suitable for large-scale purification.
Owner:CSL BEHRING GMBH
Serum protein marker group for diagnosing MODY (maturity-onset-diabetes of the young) and application thereof
InactiveCN106645757AAccurate diagnosisReliable resultsApolipeptidesHydrolasesFactor iiMass spectrometry
The invention relates to a serum protein marker group for diagnosing MODY (maturity-onset-diabetes of the young) and application thereof. The serum protein marker group comprises five proteins: apolipoprotein C-IV (APOC4), apolipoprotein a (LPA), a complement component C6 (C6), a blood coagulation factor v (F5) and thyroid binding globulin (SERPINA7). ITRAQ (isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation) are used to combine with an MALDI-TOF / MS technology to detect; mass spectrum detection shows that expression levels of the serum apolipoprotein C-IV, the apolipoprotein a, the complement component C6 and the blood coagulation factor v protein in serum of a MODY patient are obviously improved, and an expression level of the thyroid binding globulin in the serum of the MODY patient is obviously reduced. Mass spectrum MRM (multiple-reaction-monitoring) also verifies that the five proteins are abnormal in expression in serums of the MODY patient, type-1 and type-2 diabetics and a healthy control group, and are specific proteins.
Owner:XINJIANG MEDICAL UNIV
Use of biomarkers for the diagnosis and prognosis of lung cancer
InactiveUS20100240546A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningMinichromosome maintenanceSelenium-Binding Proteins
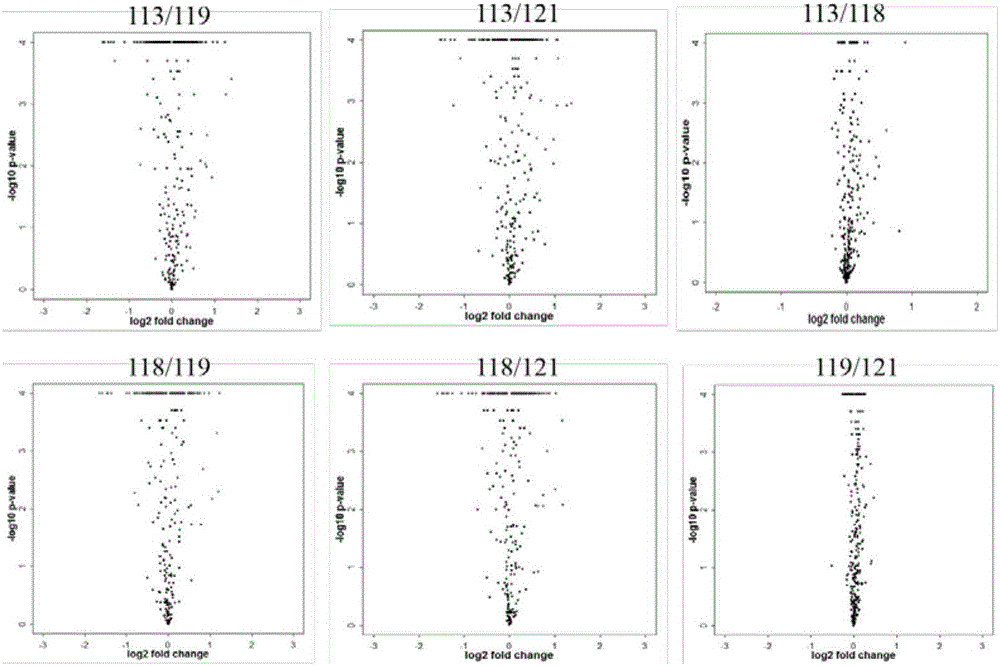
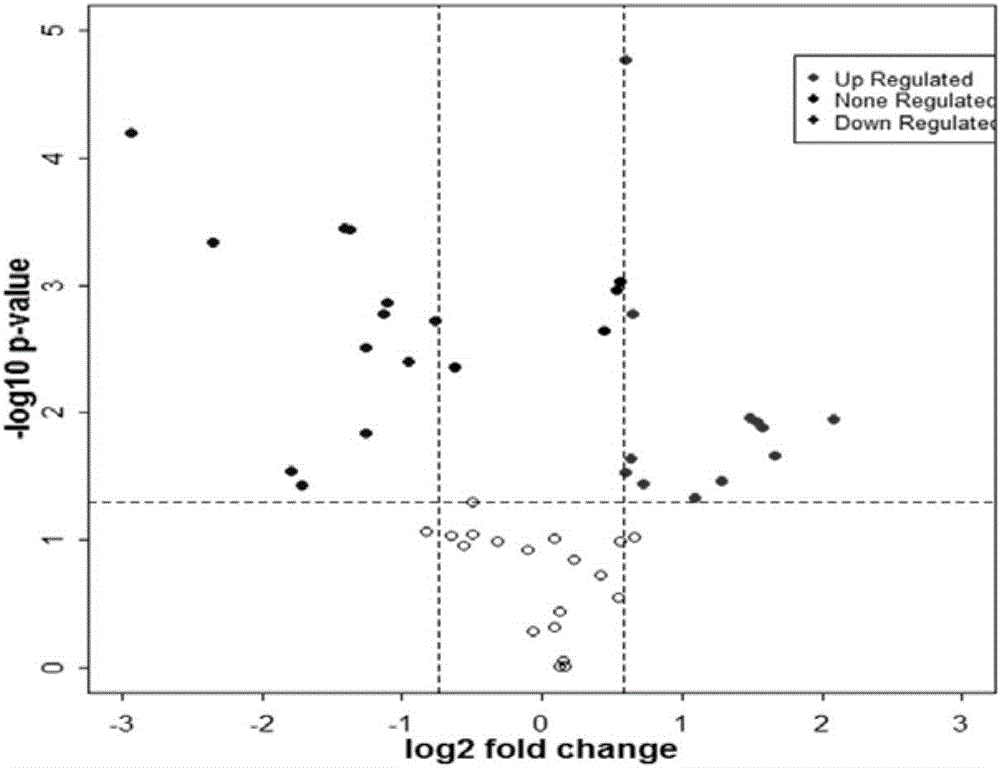
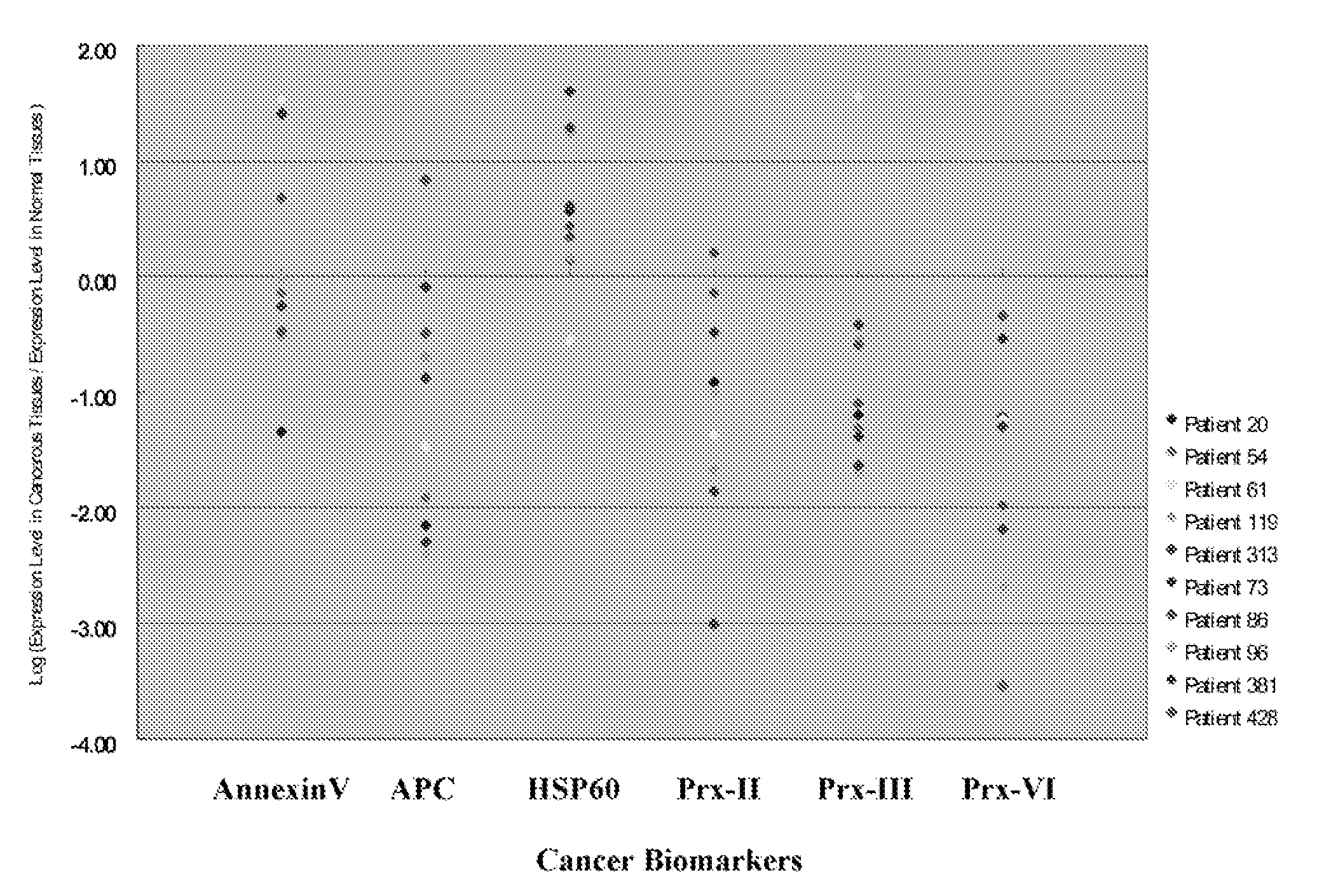
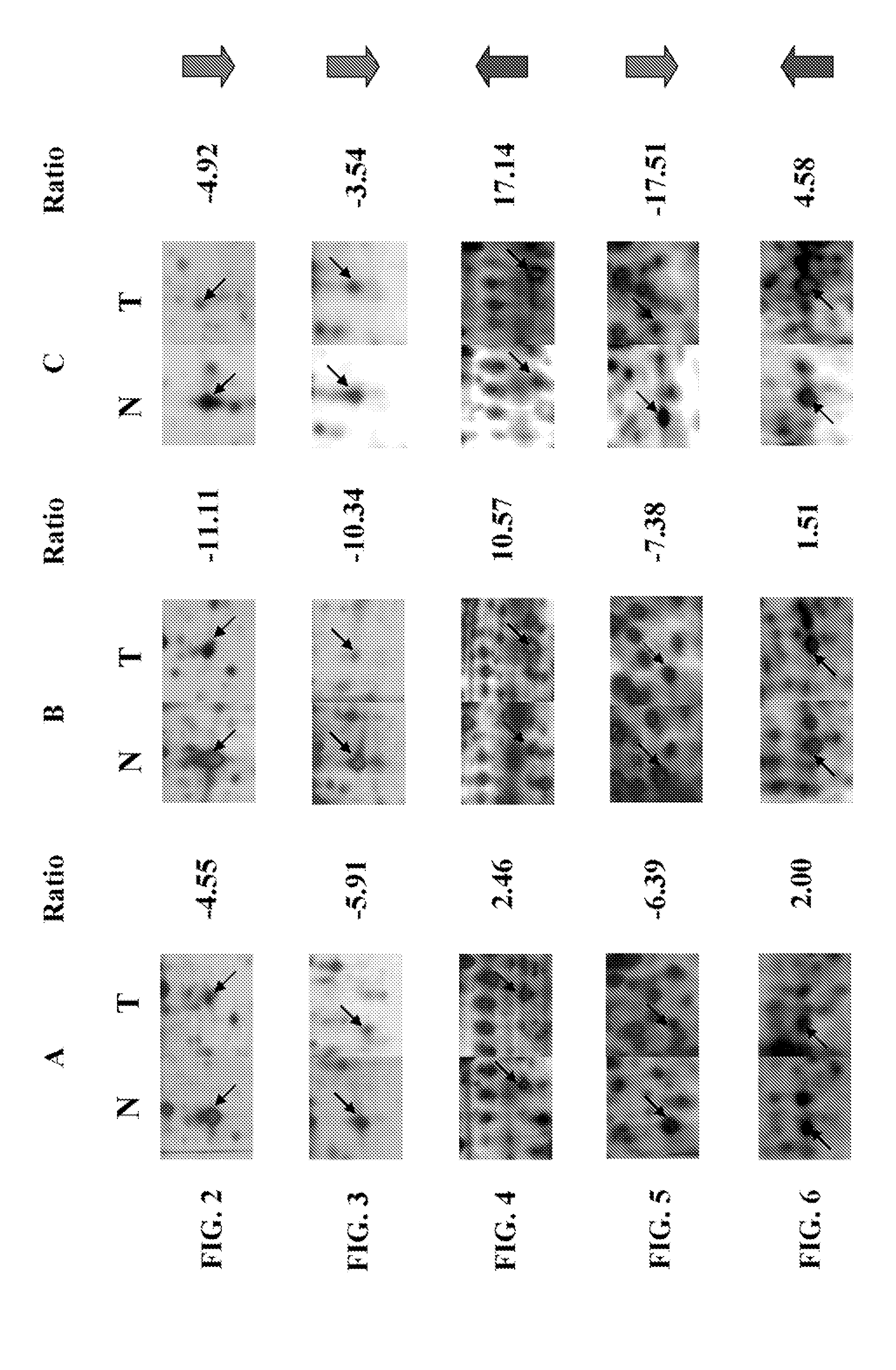
A method for identifying, diagnosing, and monitoring cancerous lung tissues in a subject may include measuring the expression of at least one biomarker in a biological sample in the subject, and comparing the expression against a normal value. When a differential expression of the at least one biomarker between the biological sample and the normal value is more than 1.5-fold, the lung tissue sample is cancerous. The at least one biomarker is selected from the group consisting of peroxiredoxin I, peroxiredoxin II, peroxiredoxin III, peroxiredoxin IV, peroxiredoxin VI, chaperonin, amyloid-P-component, annexin V, dihydropyrimidinase-like 2 protein, glutamate carboxypeptidase, 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate mutase, thymidine phosphorylase, prolyl-4 hydroxylase, selenium binding protein 1, β-mitochondrial ATP synthase H+ transporting F1 complex, laminin-binding protein, minichromosome maintenance deficient protein 5 variant, keratin 9, keratin 10, napsin A aspartic peptidase, M2-type pyruvate kinase, and apolipoprotein A-I.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Methods of using non-human animal Apolipoprotein A-I protein
The invention provides methods and compositions for treating disorders using non-human animal Apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-I) protein. The invention provides methods and compositions for treating disorders in animals, including humans, associated with dyslipidemia, including hyperlipidemia, hyperlipoproteinemia, hypertriglyceridemia, hypercholesterolemia, HDL deficiency, ApoA-I deficiency, cardiovascular disease, atherosclerosis, restenosis, and other disorders such as septic shock and viral infections.
Owner:PFIZER INC
Stable liquid lipid calibrator
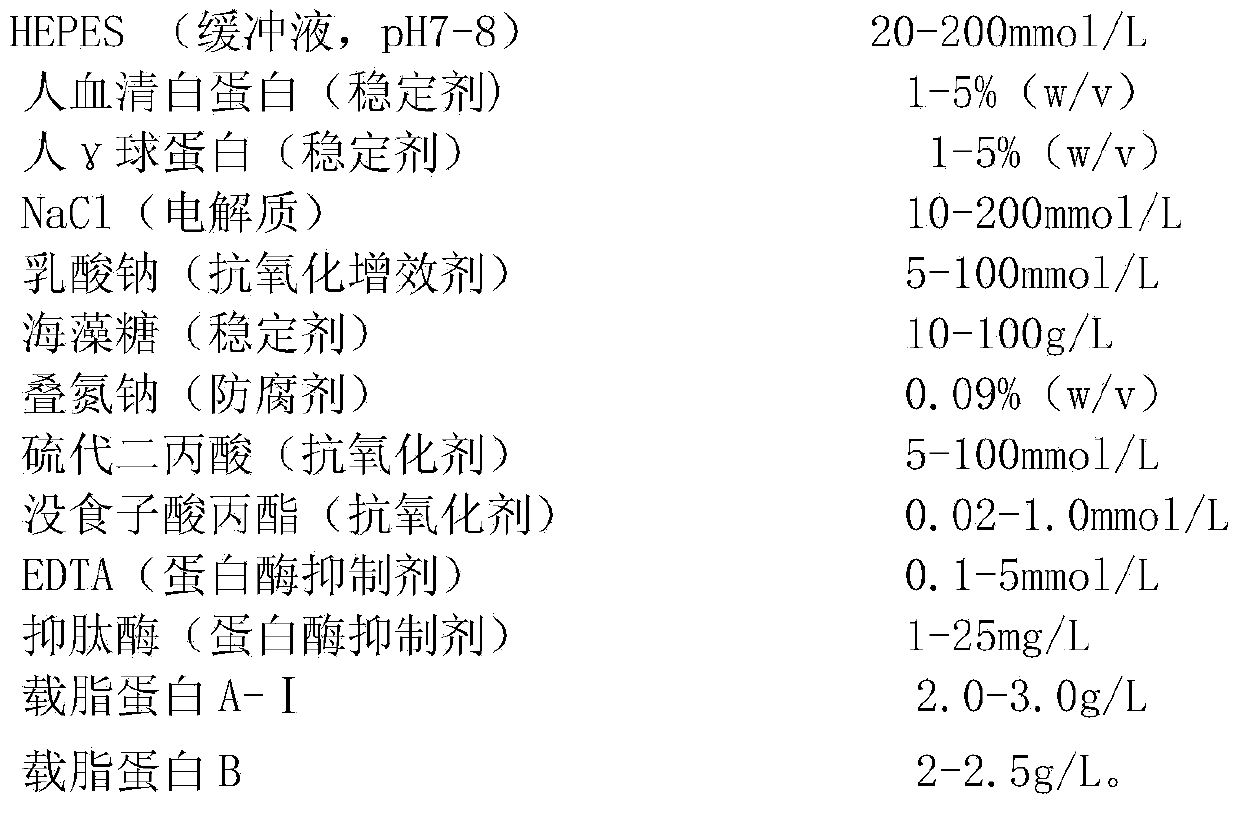
The invention discloses a stable liquid lipid calibrator which comprises 20-200mmol / L of buffer liquid, 2-10% (w / v) of protein stabilizer, 110-200mmol / L of electrolyte NaC, 5-100mmol / L of anti-oxidation synergist, 10-100g / L of sugar stabilizer, 0.09% (w / v) of preservative, 0.02-100mmpl / L of antioxidant, 0.1-5mmol / L of protease inhibitor, 2.0-3.0g / L of apolipoprotein A-I and 2-2.5g / L of apolipoprotein B. By adopting the stable liquid lipid calibrator, the stability of the apolipoprotein A-I and the apolipoprotein B is effectively improved, the apolipoprotein A-I and the apolipoprotein B can be stably frozen at 2-8 DEG C for one year and are relatively convenient and efficient to use and preserve, and the accuracy in measuring the contents of the apolipoprotein A-I and apolipoprotein B in a sample is improved.
Owner:NINGBO RUI BIO TECH
Ophthalmic composition
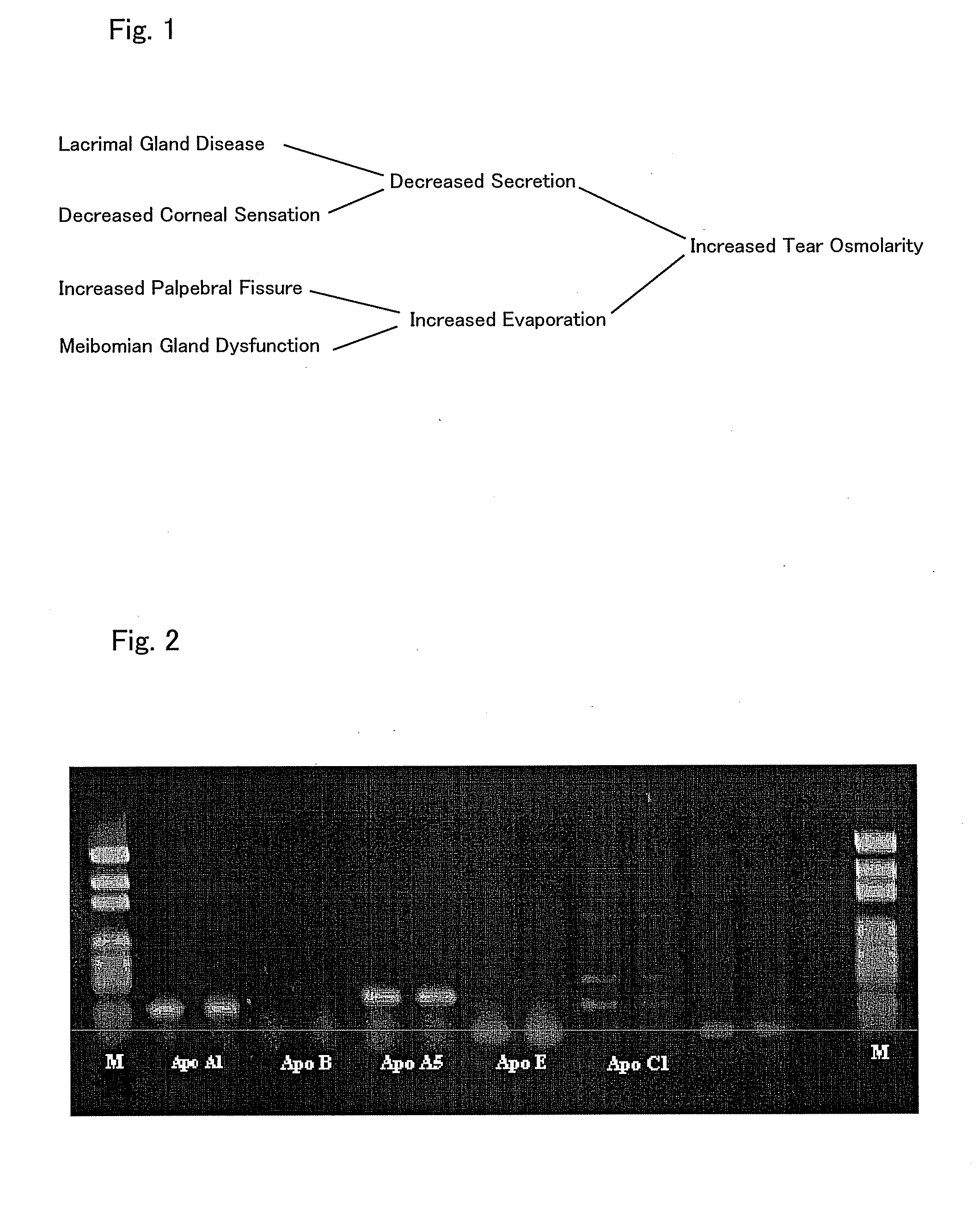
InactiveUS20090238810A1Enhanced barrier functionPreventing and easing a corneal disorderSenses disorderApolipeptidesLipid formationDisease
An ophthalmic composition is provided which is capable of enhancing a barrier function of a lipid layer that constitutes a tear film, for thereby restricting and curing corneal disorders such as dry eye. It is also an object of the invention to provide the ophthalmic composition with anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects for thereby advantageously preventing and easing corneal / conjunctival disorders such as keratoconjunctivitis. In the present invention, apolipoprotein A-1 is included, as an active ingredient, in the ophthalmic composition.
Owner:MENICON CO LTD
Diagnosis Of Neurodegenerative Diseases
InactiveUS20080286263A1Improve trustNervous disorderElectrolysis componentsHemoglobin Beta ChainApolipoprotein C-II
The invention relates to a method of diagnosis of Huntington's Disease in a diagnostic sample of a valid body tissue taken from a human subject, which comprises detecting an altered concentration of a protein in the diagnostic sample, compared with a sample of a control human subject, the protein being selected from: Swiss Prot accession number: Protein name; P10909: Clusterin precursor; P00738: Haptoglobin precursor; P01009: Alpha-1-antitrypsin precursor; P01024: Complement C3 precursor; P01620: 1 g kappa chain V-III region; P01834: 1 g kappa chain C region P01842: 1 g lambda chain C regions; P01857: 1 g gamma-1 chain C region; P01859: Ig gamma-2 chain C region; P01876: 1 g alpha-1 chain C region P02647: Apolipoprotein A-I precursor; P02649: Apolipoprotein E precursor; P02652: Apolipoprotein A-II precursor; P02655: Apolipoprotein C-II precursor; P02656: Apolipoprotein C-II precursor P02671: Fibrinogen alpha / alpha-E chain precursor; P02763: Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein 1 precursor; P02766: Transthyretin precursor; P02768: Serum albumin precursor; P02787: Serotransferrin precursor; P04196: Histidine-rich glycoprotein precursor; P06727: Apolipoprotein A-IV precursor; P19652: Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein 2 precursor; P68871 / P02042: Hemoglobin beta chain / Hemoglobin delta chain; P60709: Beta actin.
Owner:ELECTROPHORETICS LTD
Sustained release of apo a-i mimetic peptides and methods of treatment
InactiveUS20090081299A1Improve concentrationBiocidePowder deliveryReverse cholesterol transportCholesterol
A method including advancing a delivery device through a lumen of a blood vessel to a particular region in the blood vessel; and introducing a composition including a sustained-release carrier and an apolipoprotein A-I (apo A-I) synthetic mimetic peptide into a wall of the blood vessel at the particular region or a perivascular site, wherein the peptide has a property that renders the peptide effective in reverse cholesterol transport. A composition including an apolipoprotein A-I (apo A-I) synthetic peptide, or combination of an apo A-I synthetic mimetic peptide and an Acyl CoA cholesterol: acyltransferase (ACAT) inhibitor in a form suitable for delivery into a blood vessel, the peptide including an amino acid sequence in an order reverse to an order of various apo A-I mimetic peptides, or endogenous apo A-I analogs, or a chimera of helix 1 and helix 9 of endogenous apo A-I.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Therapeutic agents and methods for cardiovascular disease
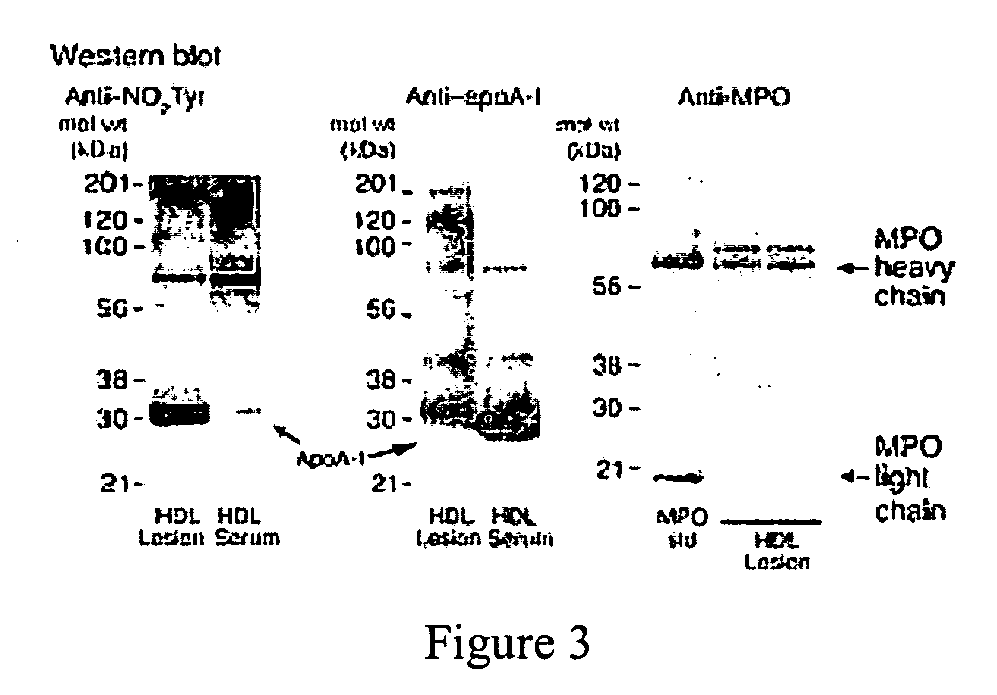
The present invention provides methods and agents for treating subjects who have or are at risk of developing or having cardiovascular disease. Such agents inhibit binding of myeloperoxidase (MPO) to a molecule comprising the MPO binding site of apolipoprotein A-1 (apoA-1) and include a peptide fragment of apoA-1 comprising at least 4 contiguous amino acids in SEQ ID. NO: 2, a modified form of the apo-1 fragment comprising one or more D amino acids, a retro-inverso form of the apoA-1 peptide fragment, an organo-mimetic of the apoA-1 peptide fragment, a peptide-mimetic of the apoA1 peptide fragment, or a nucleic acid encoding the apo A-1 peptide fragment. The present invention also provides methods of identifying or screening test agents for treating subjects having or at risk of having or developing CVD. The method comprises incubating one or more test agents and MPO with a molecule comprising the MPO binding site of apoA-1 under conditions which permit binding of MPO to the MPO binding site and determining whether one or more of the agents inhibit such binding.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
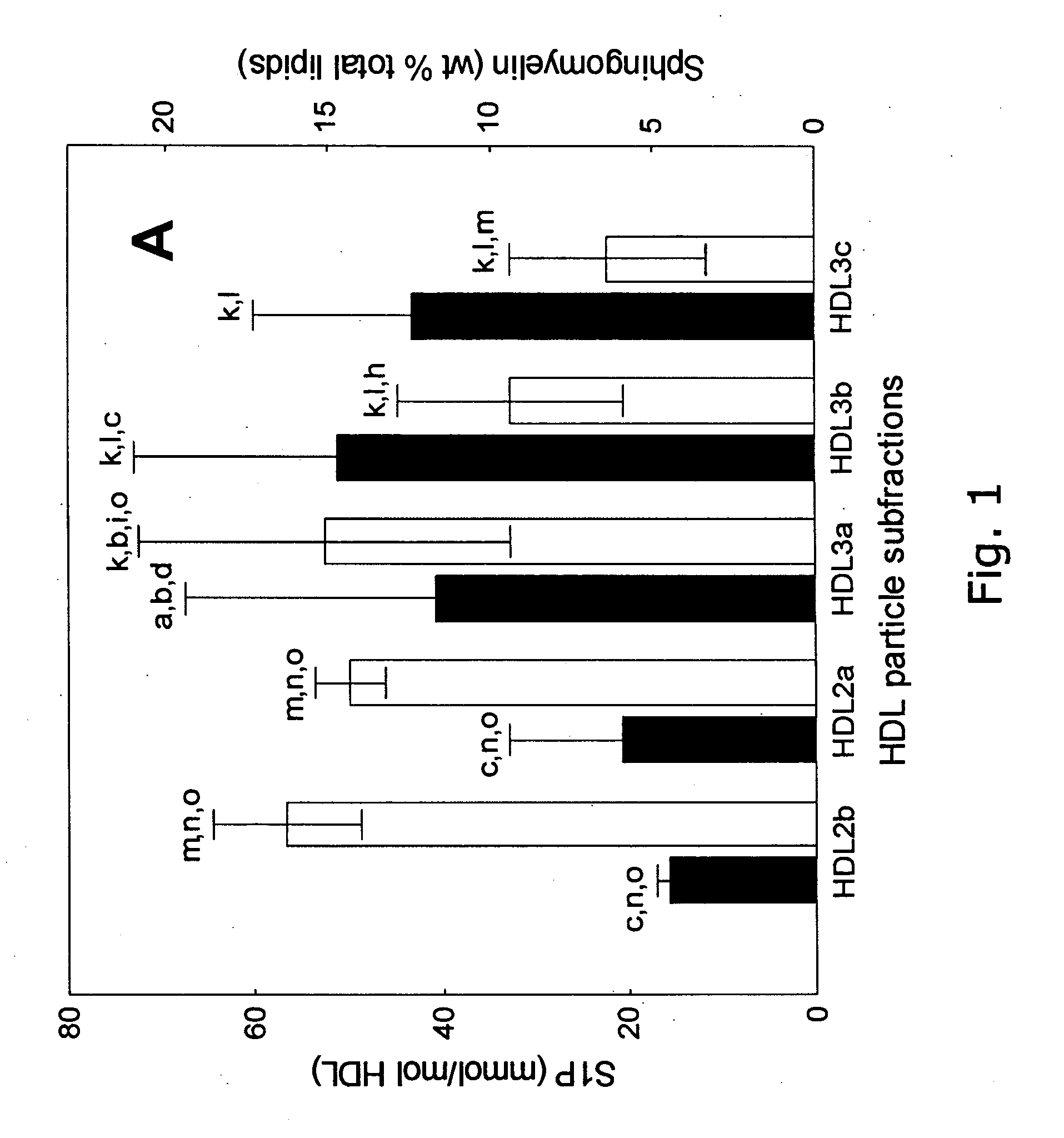
Method for Assessing the Risk of a Cardiovascular Disease and for Diagnosing Dyslipidemia
InactiveUS20100179066A1Intensive attentionIntensive treatmentLibrary screeningDisease diagnosisDyslipidemiaBlood lipids
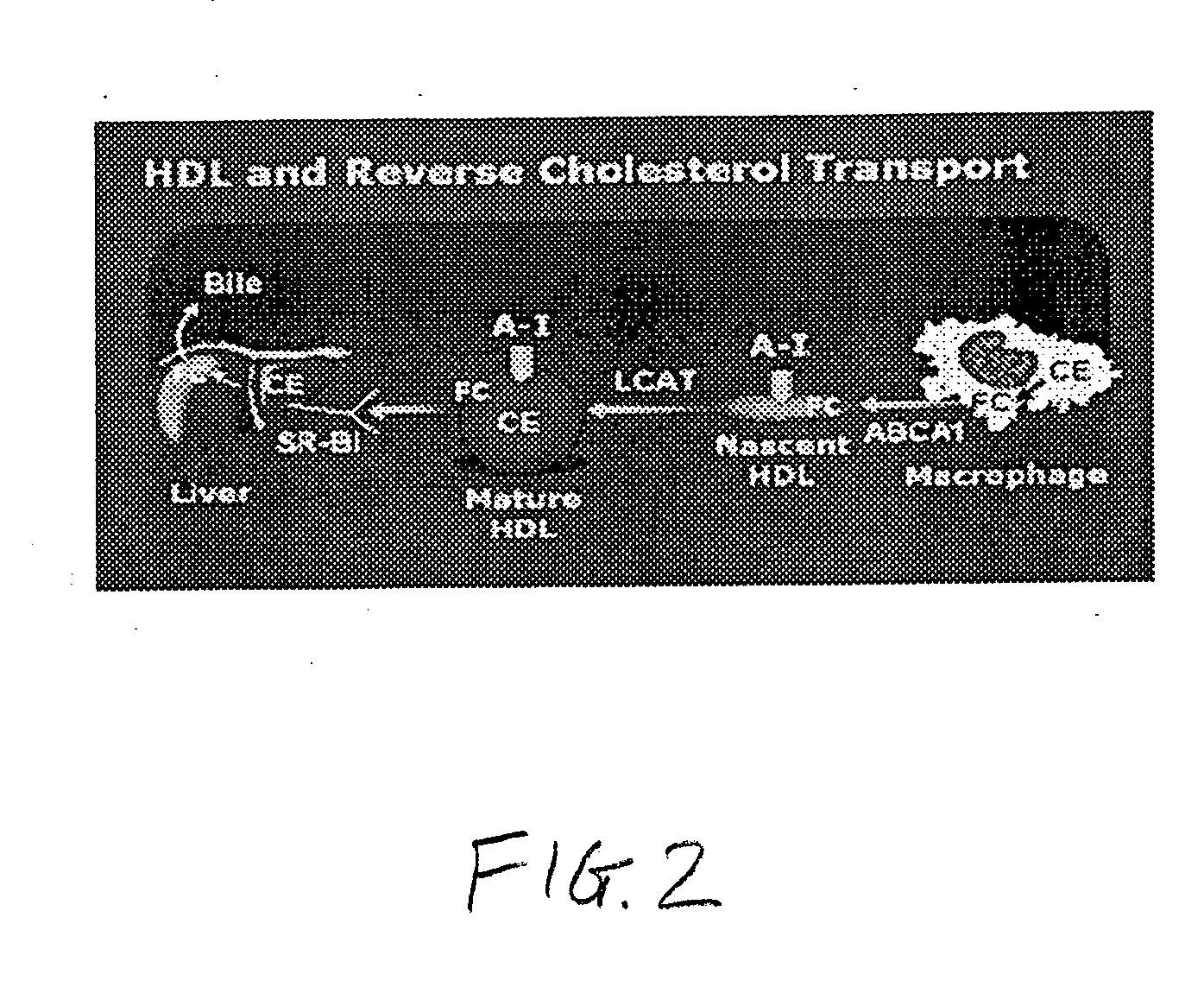
The invention relates to a method for assessing the risk of a cardiovascular disease and / or for diagnosing dyslipidemia in a patient, said method comprising: a) isolating in a blood sample obtained from said patient the high density lipoprotein (HDL) fraction or a subfraction thereof; and b) measuring in said HDL fraction or subfraction thereof the concentration of one or more biomarkers selected from the group consisting of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate (S1P), sphingomyelin (SM) and Apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-1).
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
Method for preparing high-purity apolipoprotein A-I
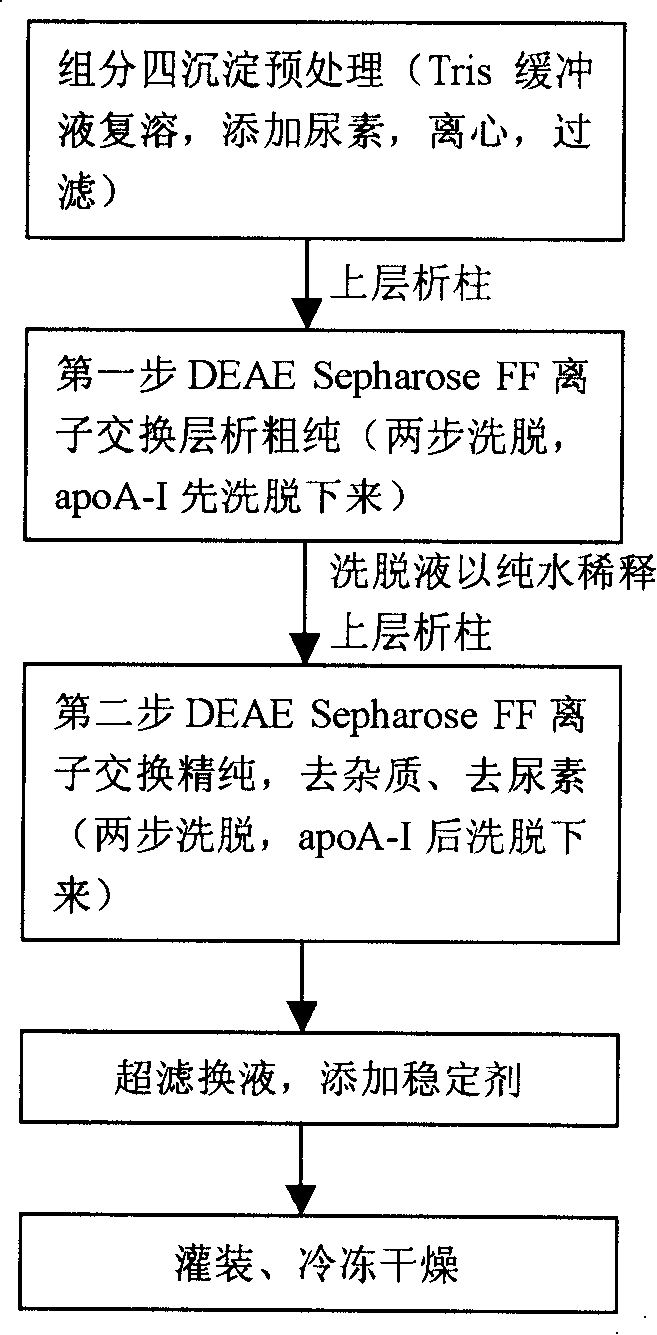
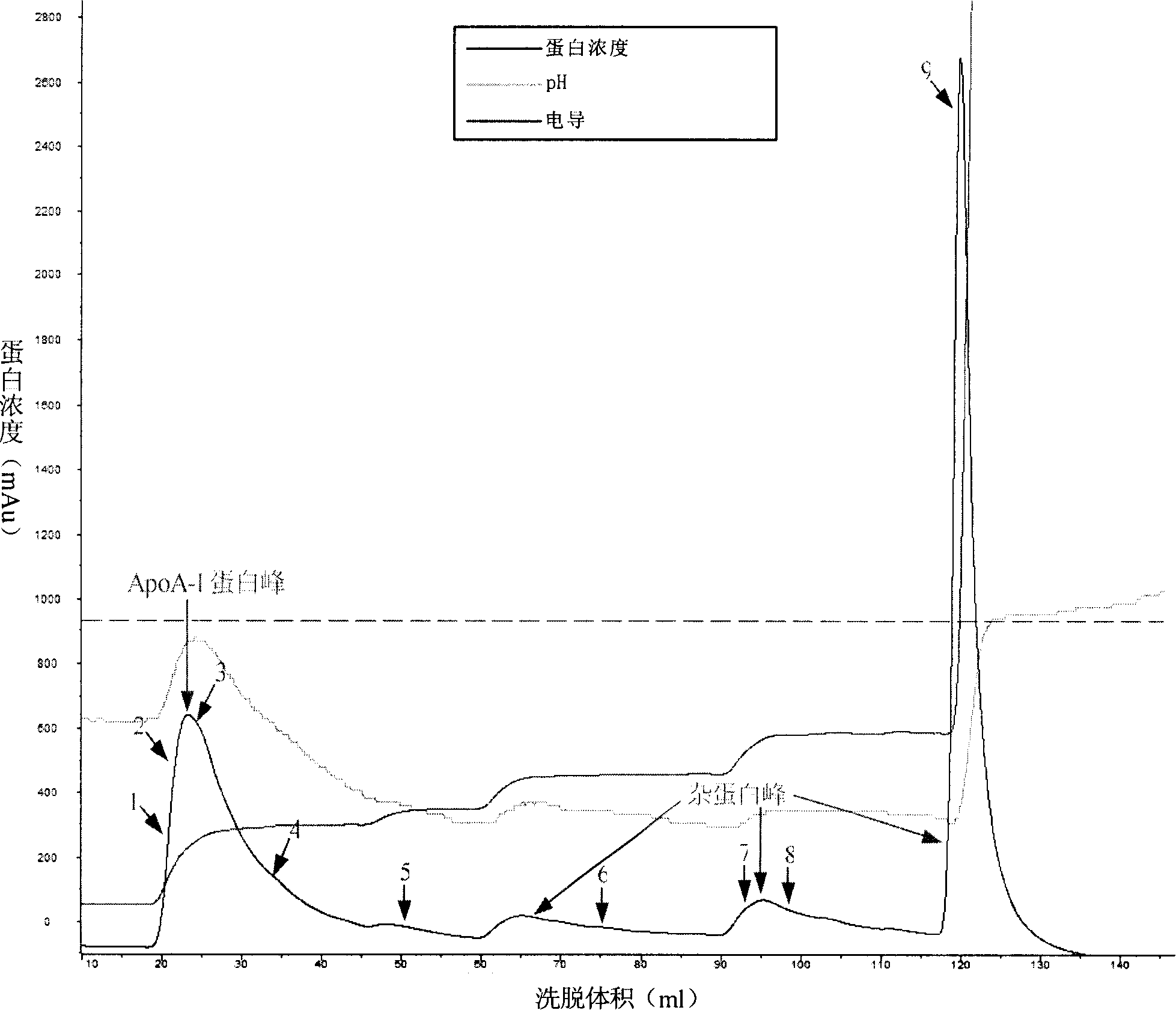
ActiveCN101205250AHigh yieldStrong specificityApolipeptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsBlood plasmaChromatography column
The invention discloses a method for obtaining the apolipoprotein A-I, which comprises the steps that: a. Component 4 obtained through the Cohn cold ethanol method is mixed with the 1-8M urea so as to form the Component 4 pretreatment solution; b. the Component 4 pretreatment solution obtained in Step a flows through an anionic exchange chromatography column before the chromatography column is washed using the buffer containing the 1-8M urea so as to obtain the preliminarily purified apolipoprotein A-I; c. the solution containing the preliminarily purified apolipoprotein A-I obtained in Step b flows through the anionic exchange chromatography column and the chromatography column is washed using the buffer containing the 0-1M urea after the impurities are eluted so as to obtain the purified apolipoprotein A-I. The method delives a high protein extraction yield, has a low cost and is suitable for industrialized production, and simultaneously the method also sufficiently utilzies the plasma resources.
Owner:SHANGHAI RAAS BLOOD PRODUCTS CO LTD
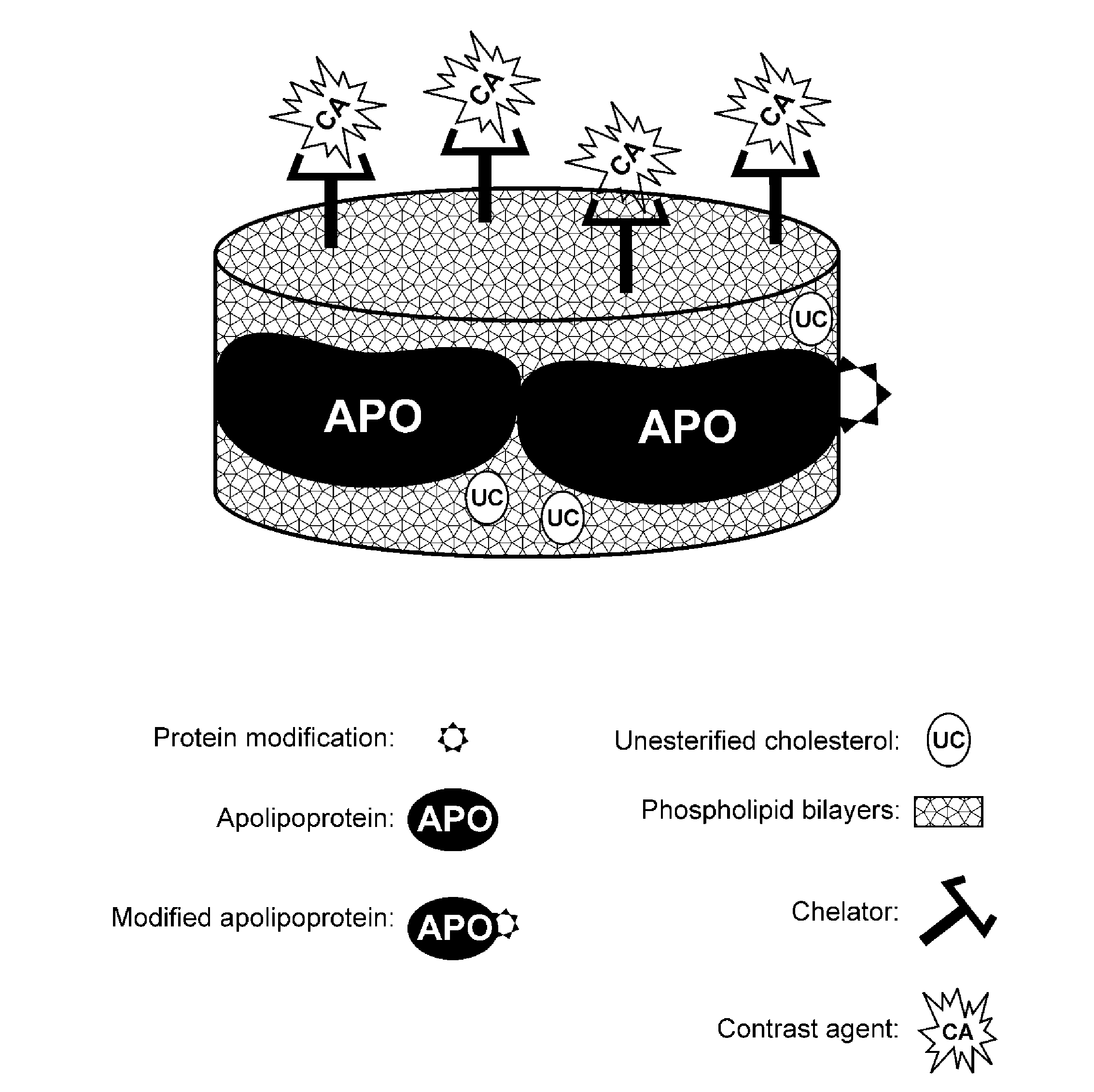
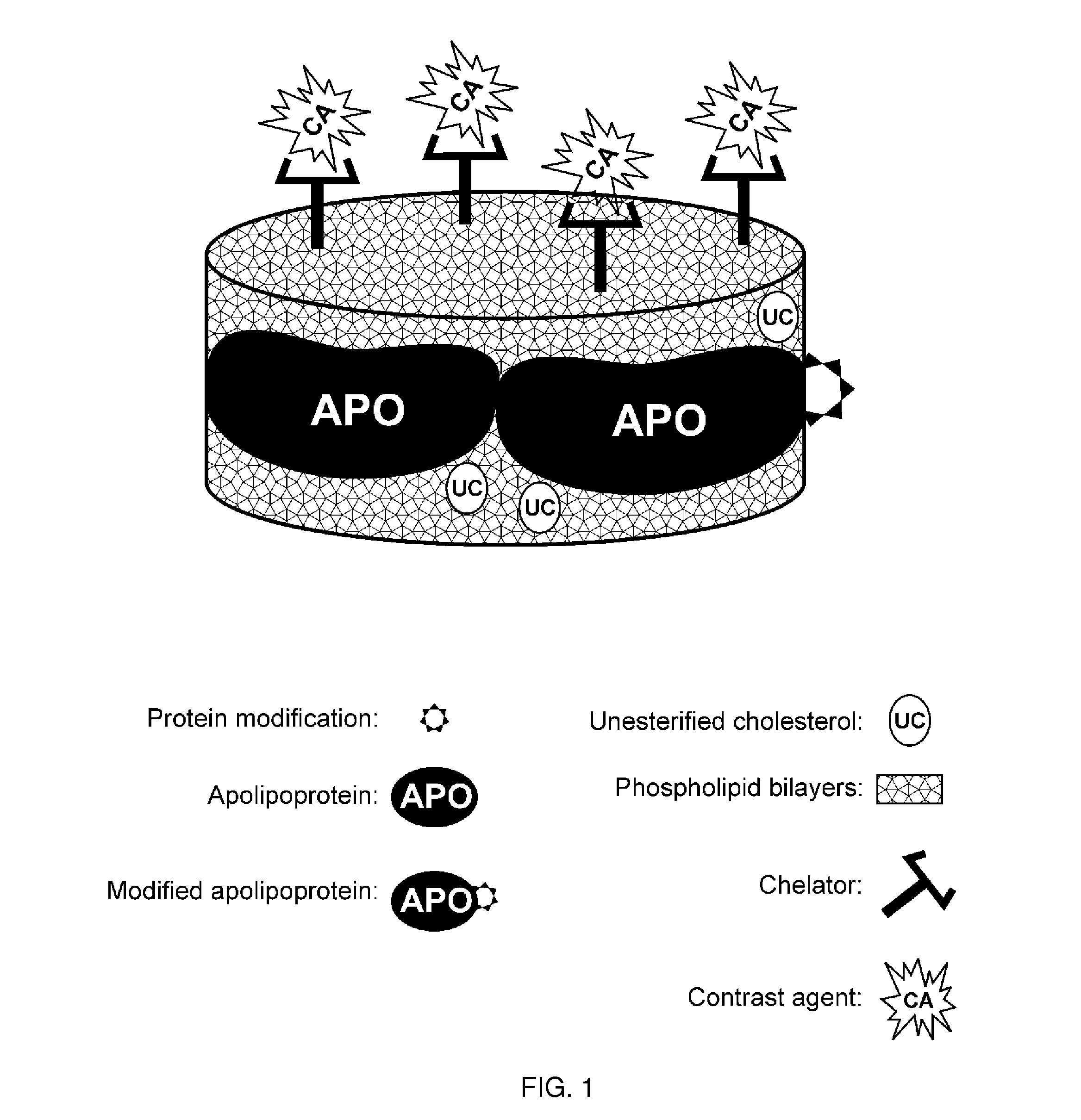
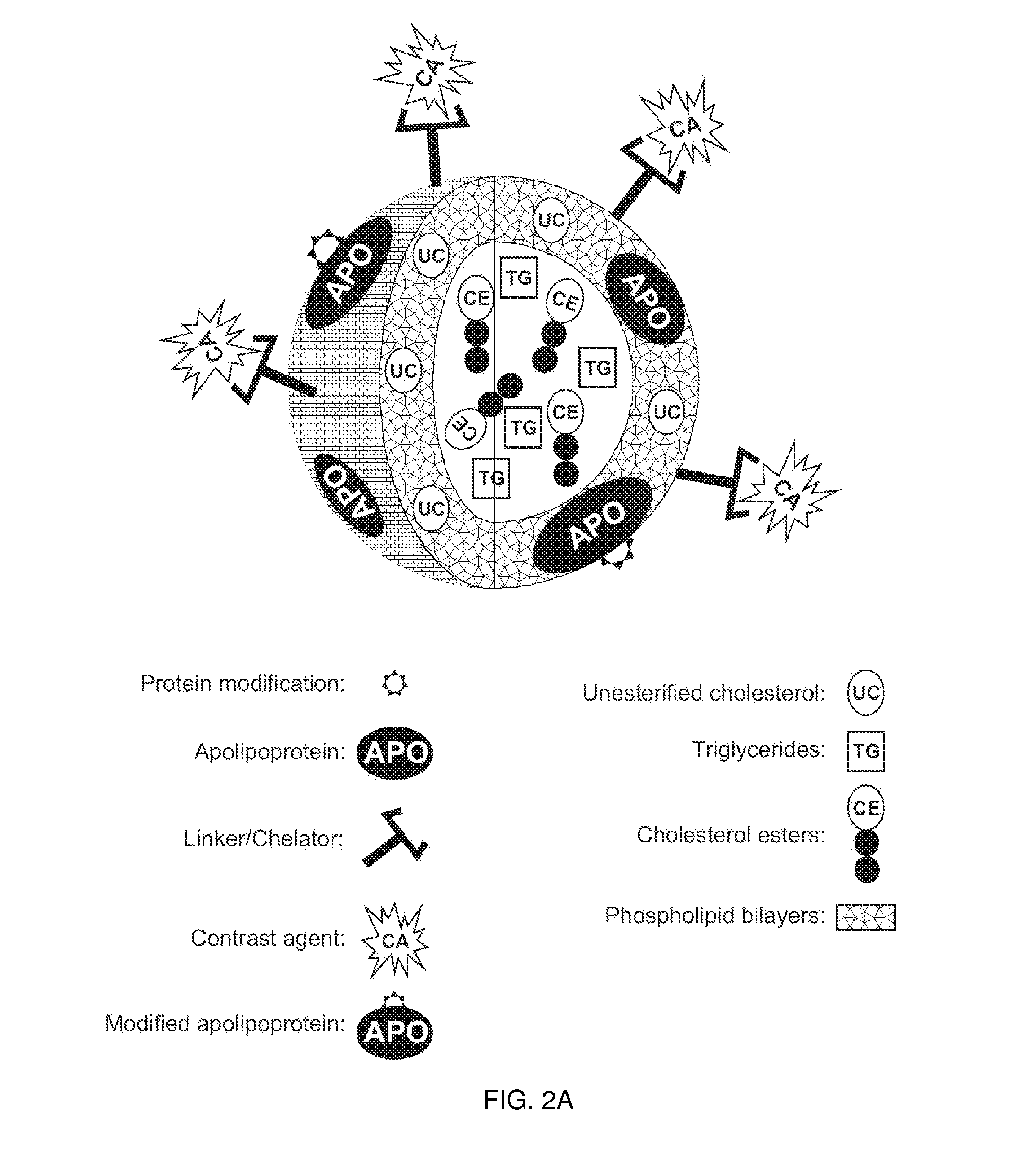
Methods and compositions for targeted imaging
A new approach to targeting imaging agents to macrophage-rich sites of interest is disclosed. Compositions of the invention are rHDL and HDL-like liposomal compositions, protein constituents of which, apolipoproteins A-I and / or A-II or fragments thereof are used not only as structural but also as targeting agents. This is achieved by certain controlled chemical or enzymatic modification of apolipoproteins A-I or A-II or fragments thereof. Such modification converts these apolipoproteins to substrates for macrophage scavenger receptors and results in the improvement of contrast agent-(HDL / modified apolipoprotein)-particle association with macrophages and / or absorption (uptake) by macrophages when compared to that of the contrast agent-(HDL / apolipoprotein)-particle constructed with non-modified naturally occurring apo A-I. The compositions can be used for noninvasive specific in vivo molecular detection and localization of macrophage-rich sites of interest using imaging techniques such as computed tomography (CT), gamma-scintigraphy, positron emission tomography (PET), single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Owner:SIGNABLOK
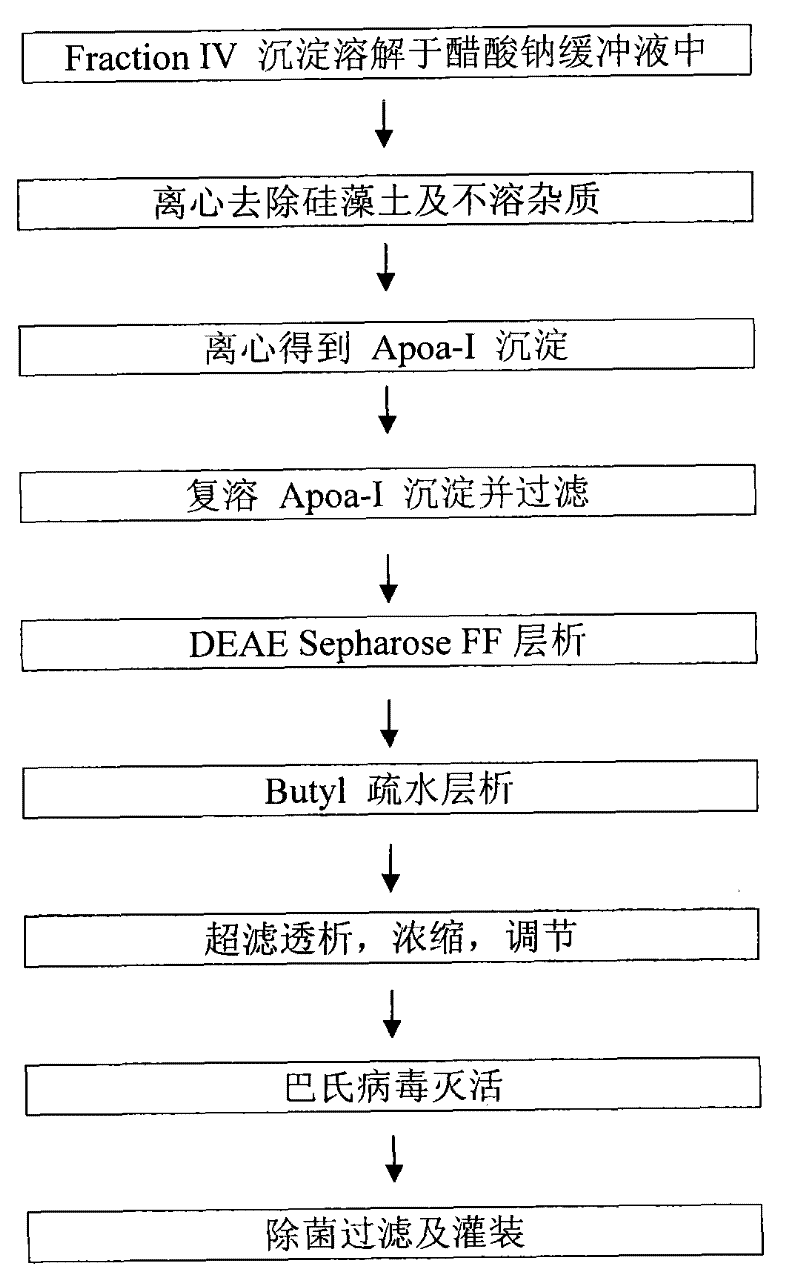
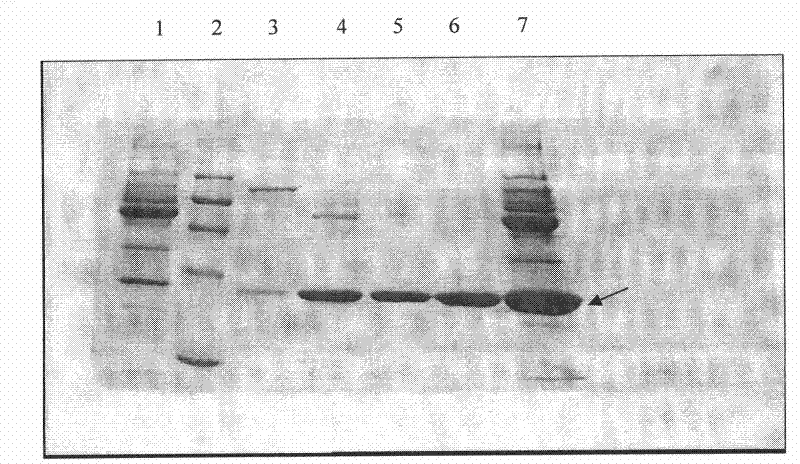
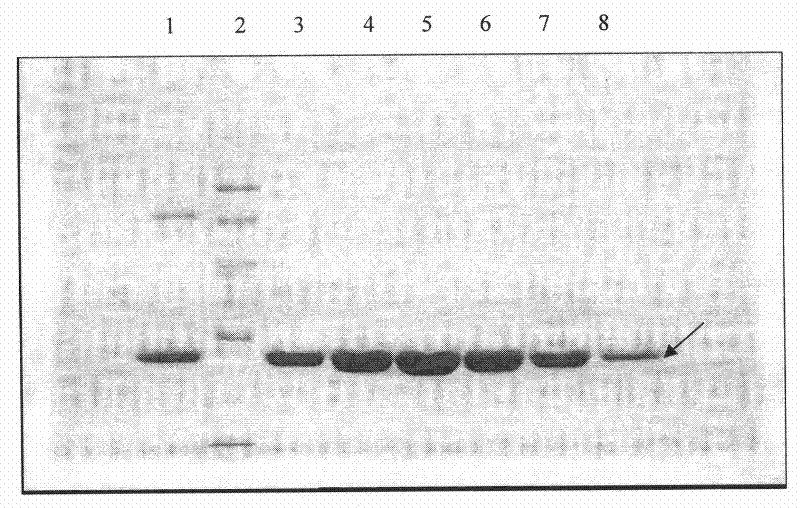
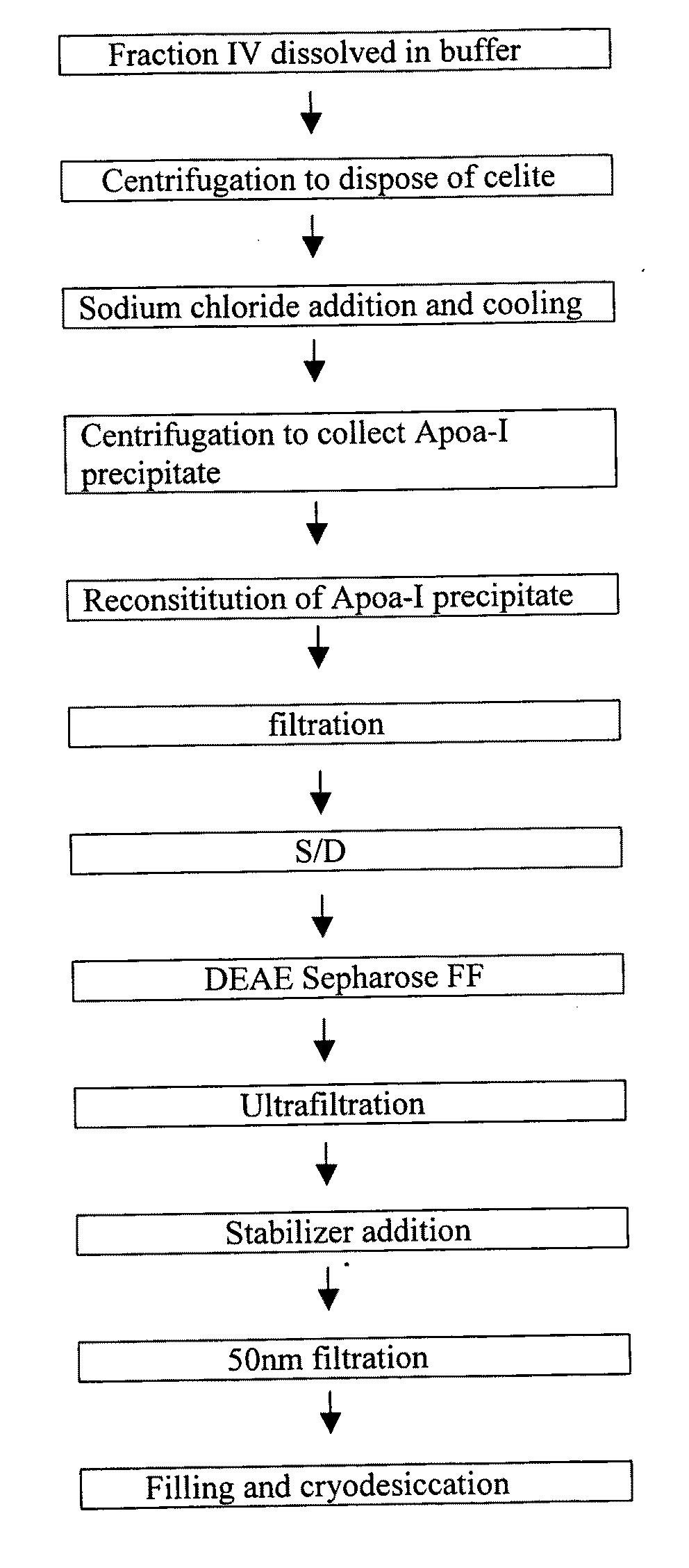
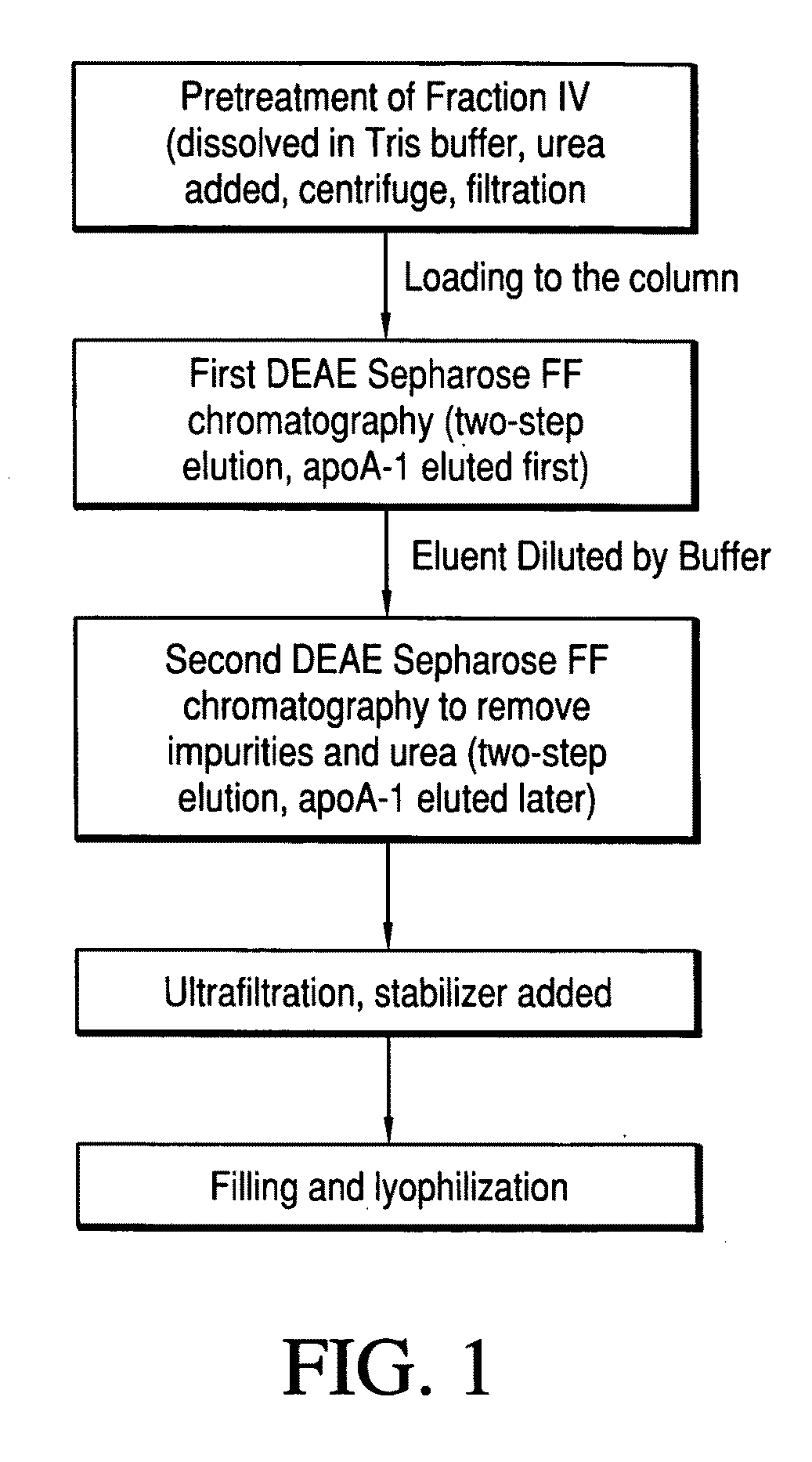
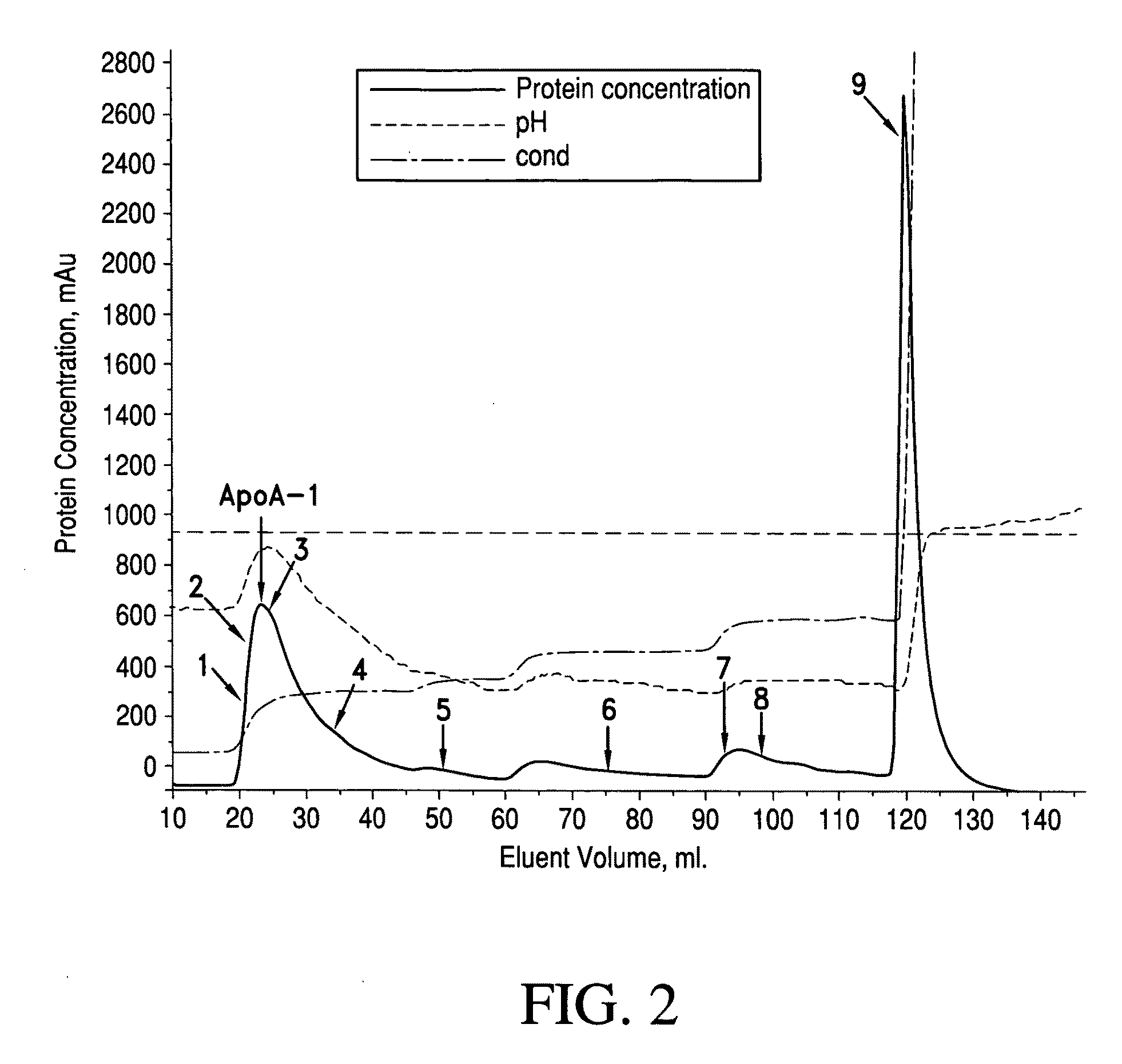
Production process for preparing high-purity ApoA-I (Apolipoprotein A-I) from precipitates of plasma fraction IV
ActiveCN102127165AOperational securityHigh purityApolipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsBlood plasmaImpurity
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-purity ApoA-I (Apolipoprotein A-I) from a plasma fraction IV through purification, comprising the following steps of: dissolving the participates of the plasma fraction IV, centrifuging to remove diatomite and impurities, and collecting a supernate; adding sodium chloride to the supernate so that ApoA-I protein is coagulated and separated out, and centrifuging to obtain an ApoA-I precipitate; redissolving the precipitate and filtrating; and enabling the filtrate to be sequentially subjected to anion column chromatography and hydrophobic column chromatography and separating to obtain a high-purity ApoA-I solution. The ApoA-I prepared by adopting the process disclosed by the invention has high purity capable of reaching more than 95 percent and the ApoA-I yield capable of reaching 70 percent and is safe and convenient to operate, easy to realize process amplification and very suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SHANGHAI RAAS BLOOD PRODUCTS CO LTD
Apolipoprotein a-i mimics
Provided are peptides, compositions thereof, and methods for treating or preventing dyslipidemia, a cardiovascular disease, endothelial dysfunction, a macrovascular disorder, or a microvascular disorder.
Owner:CERENIS THERAPEUTICS HOLDINGS SA
Reagent kit for detecting 2-diabetes serum mark in Chinese people
The invention relates to the reagent box to detect serum of II-type diabetes. Specially, it applies the serum of apolipoprotein A-I and corresponding express-level in patient to modify the box. It also relates to the application in diagnosis and treatment of apolipoprotein A-I.
Owner:THE INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Methods for purification of alpha-1-antitrypsin andapolipoprotein A-1
ActiveUS8436152B2Minimize deamidationMinimize denaturationApolipeptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical drugBlood plasma
This invention relates to protein separation and purification methods for both alpha-1-antitrypsin (AAT, also known as alpha-1 proteinase inhibitor, API, and A1-PI) and Apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-I) from, for example, a fraction of human blood plasma. In certain embodiments, the invention provides methods for separating AAT from ApoA-I at the initial stage of purification, so that the same starting material can be used as a source for both proteins. The methods further pertain to providing compositions of AAT and of ApoA-I suitable for pharmaceutical use and are suitable for large-scale purification.
Owner:CSL BEHRING GMBH
Single-domain antibody aiming at apolipoprotein A1 and application thereof
InactiveCN103833851AEfficient expressionImmunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological testingEscherichia coliSingle-domain antibody
The invention discloses a VHH chain of a single-domain antibody for apolipoprotein A1. The VHH chain comprises a frame region FR and a complementary determining region CDR. The invention discloses amino acid sequences of the frame region FR selected from the following group of FR and the amino acid sequences of the complementary determining region CDR. The invention also discloses two types of single-domain antibodies for the apolipoprotein A1, also discloses two types of DNA molecules for coding the VHH chain of the single-domain antibody for the apolipoprotein A1 mentioned in the invention or the single-domain antibody for the apolipoprotein A1 mentioned in the invention, also discloses a host cell for expressing the single-domain antibody for the apolipoprotein A1, and also discloses the application of the single-domain antibody for the apolipoprotein A in detection of the apolipoprotein A1. Through the gene sequences and the host cell of the single-domain antibody disclosed by the invention, the single-domain antibody can be efficiently expressed in colon bacillus and applied in research and development of an apolipoprotein A1 detection reagent.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Non-invasive treatment of disease using amphipathic compounds
InactiveUS20050176623A1Decreasing extent of atherosclerosisPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsSolventNon invasive
The present invention features a non-invasive system and method for delivering apolipoprotein, amphipathic compounds, and the like into the blood stream using pulmonary delivering. Apolipoprotein, amphipathic compounds, and the like is suspended in a solvent, preferably a saline solution. Next, the soluation is nebulized to form a plurality of droplets sized to reach the periphery of the lung. Once proximate the lung, the apolipoprotein, amphipathic compounds, and the like is dissolved through the lung interface and into the serum. Due to its physical and chemical properties, apolipoprotein A-I is effectively absorbed into the serum through the lung. The present invention can be used for the treatment of cardiovascular disease as well Alzheimer's Disease and other.
Owner:WAGLE NEIL
Method and Compound for the Treatment of Valvular Disease
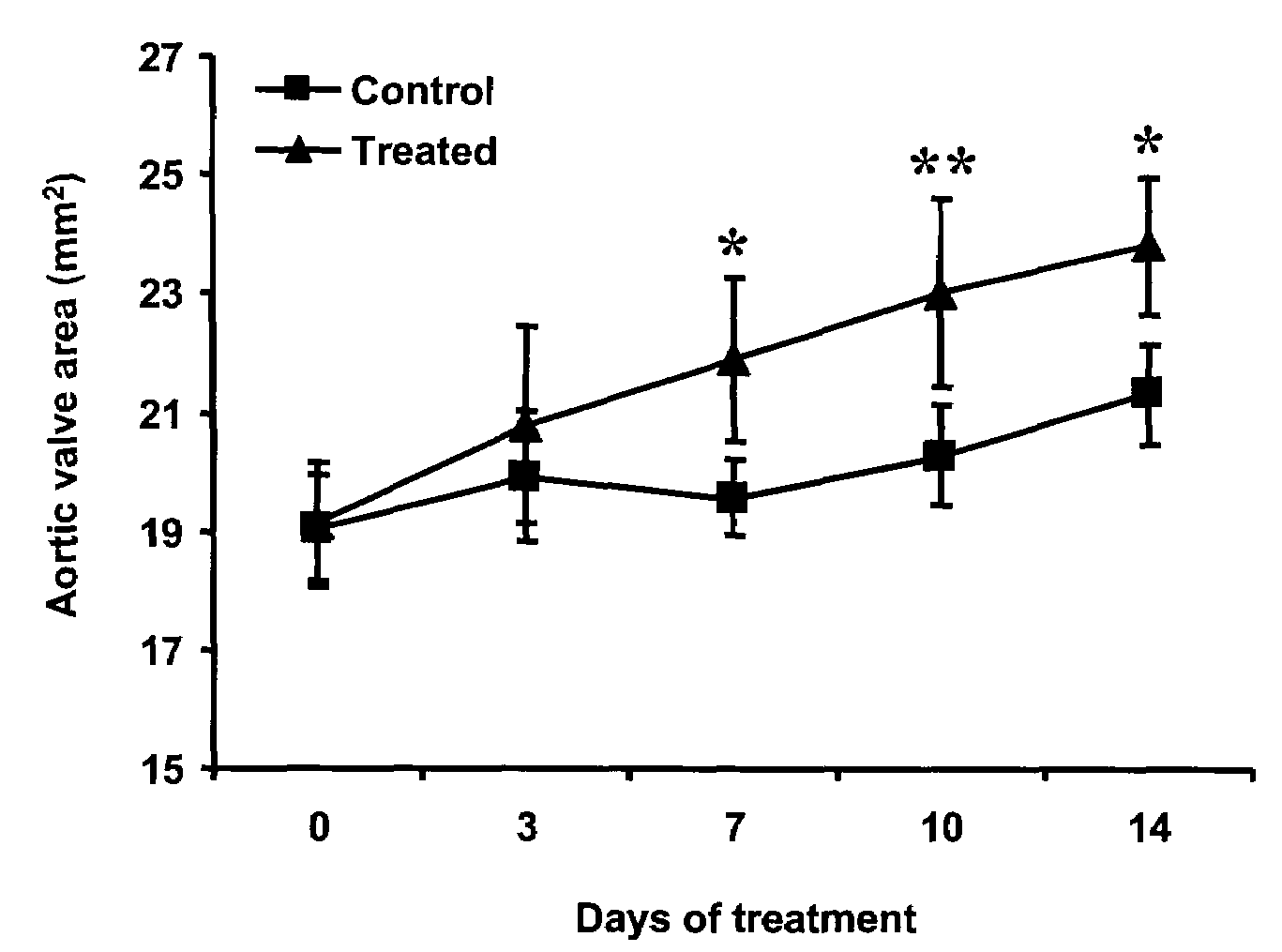
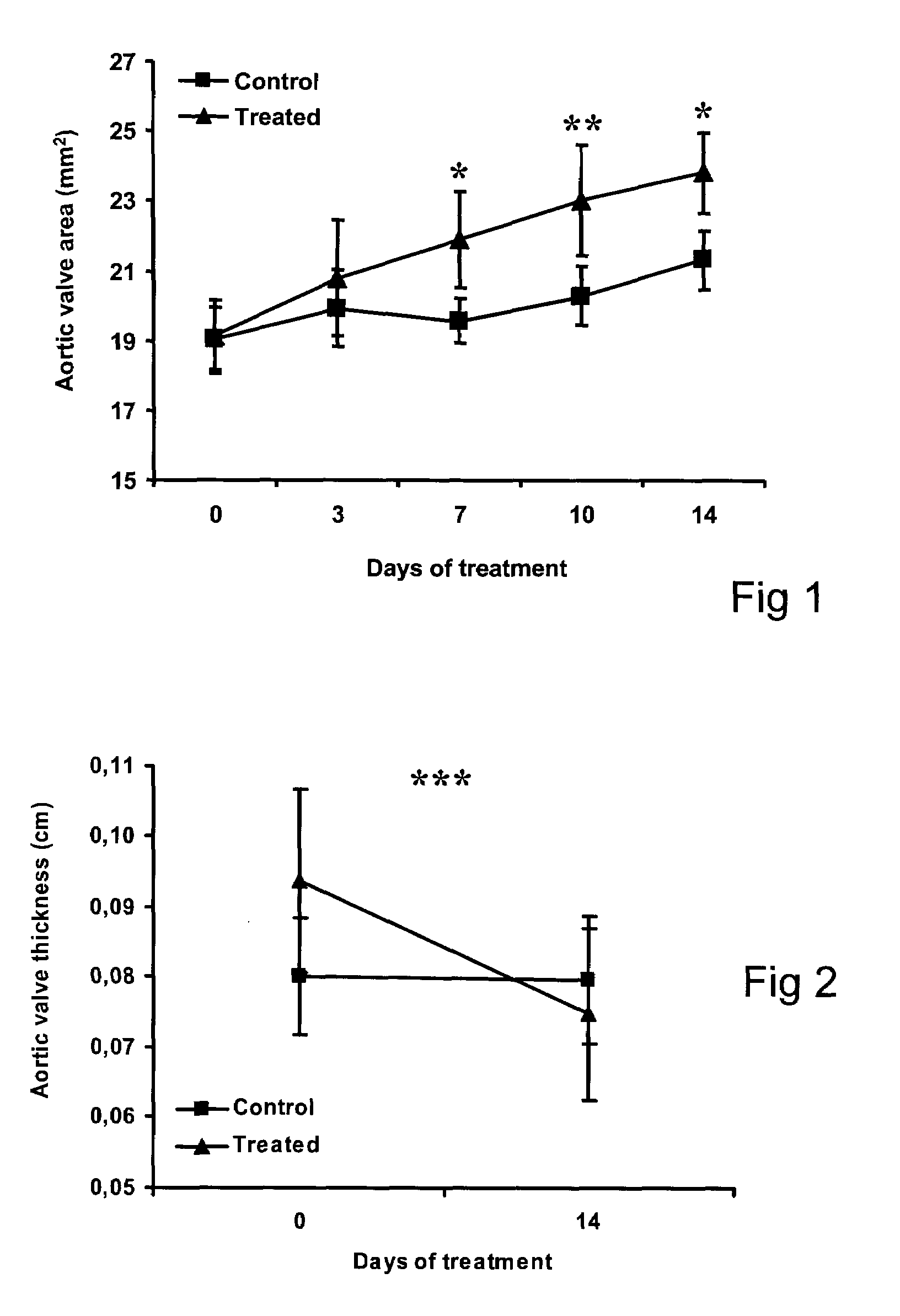
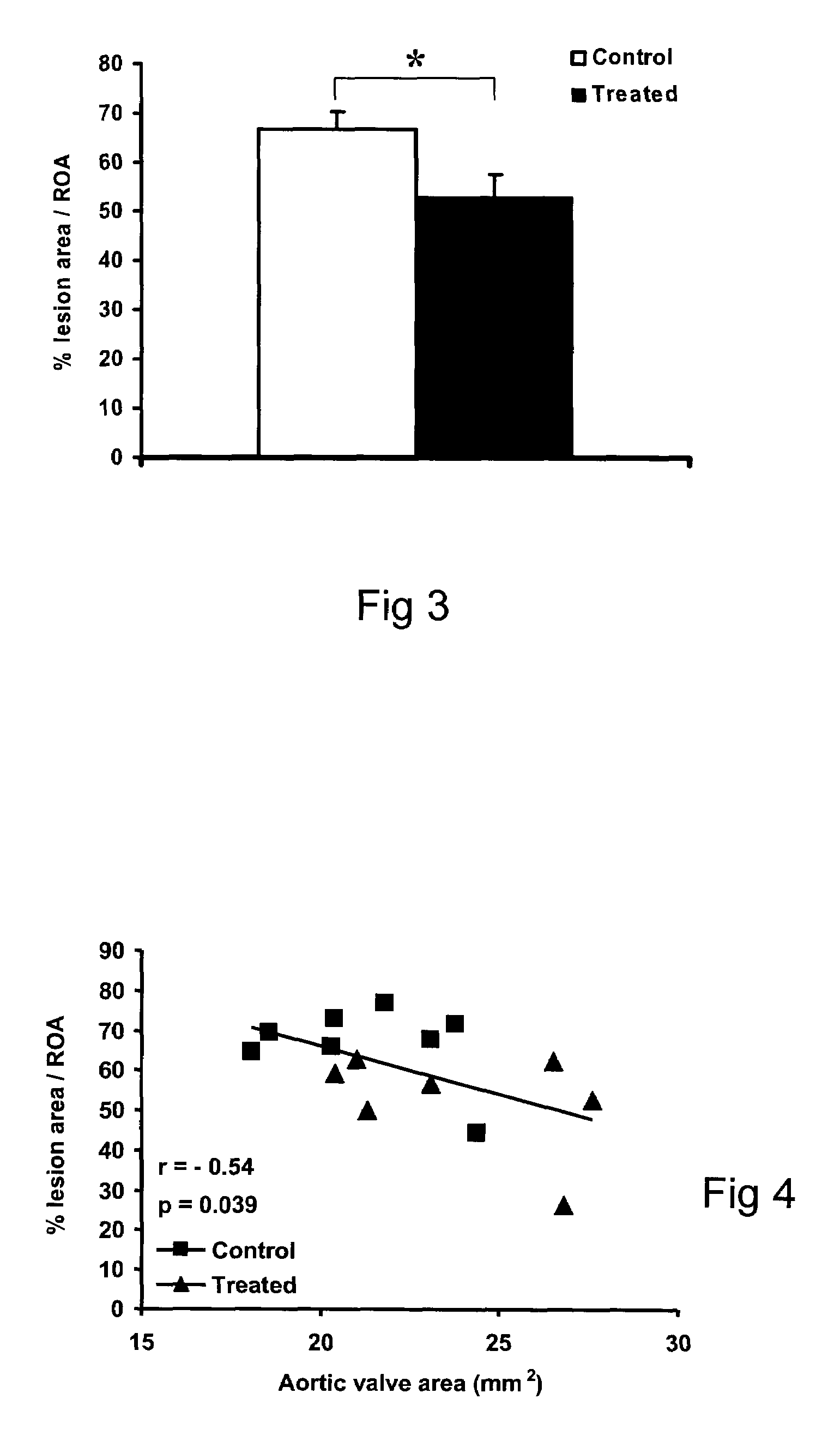
InactiveUS20090186808A1Reduce rateShorten the progressOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineCholesterol
A method for treating valvular stenosis The method involves the administration of a therapeutically effective amount of a reverse lipid (in particular cholesterol) transport agonist to a mammal Most preferred is an Apolipoprotein A-1 mimetic peptide / phospholipid complex, the peptide of which is defined by the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO 1.
Owner:MONTREAL HEART INST
Method of purifying apolipoprotein A-1
ActiveUS20090286960A1Promote absorptionDifficult can be eluted off columnApolipeptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsProtein solutionChromatography column
A first method of purifying apolipoprotein A-1 includes mixing plasma fraction IV with a 1-8 M urea solution to form a pretreatment solution; loading the pretreatment solution to a first anion chromatography column, and then eluting to obtain an apoA-1 protein solution; and loading the apoA-1 protein solution to a second anion chromatography column, and eluting to obtain pure apoA-1 protein. A second method includes dissolving plasma fraction IV in a buffer to produce a pretreatment solution; adding NaCl to the pretreatment solution and cooling it to form apoA-1 precipitate; collecting and reconstituting the apoA-1 precipitate; loading the reconstituted apoA-1 to an anion exchange column; and eluting apoA-1 from the column.
Owner:HOANG KIEU
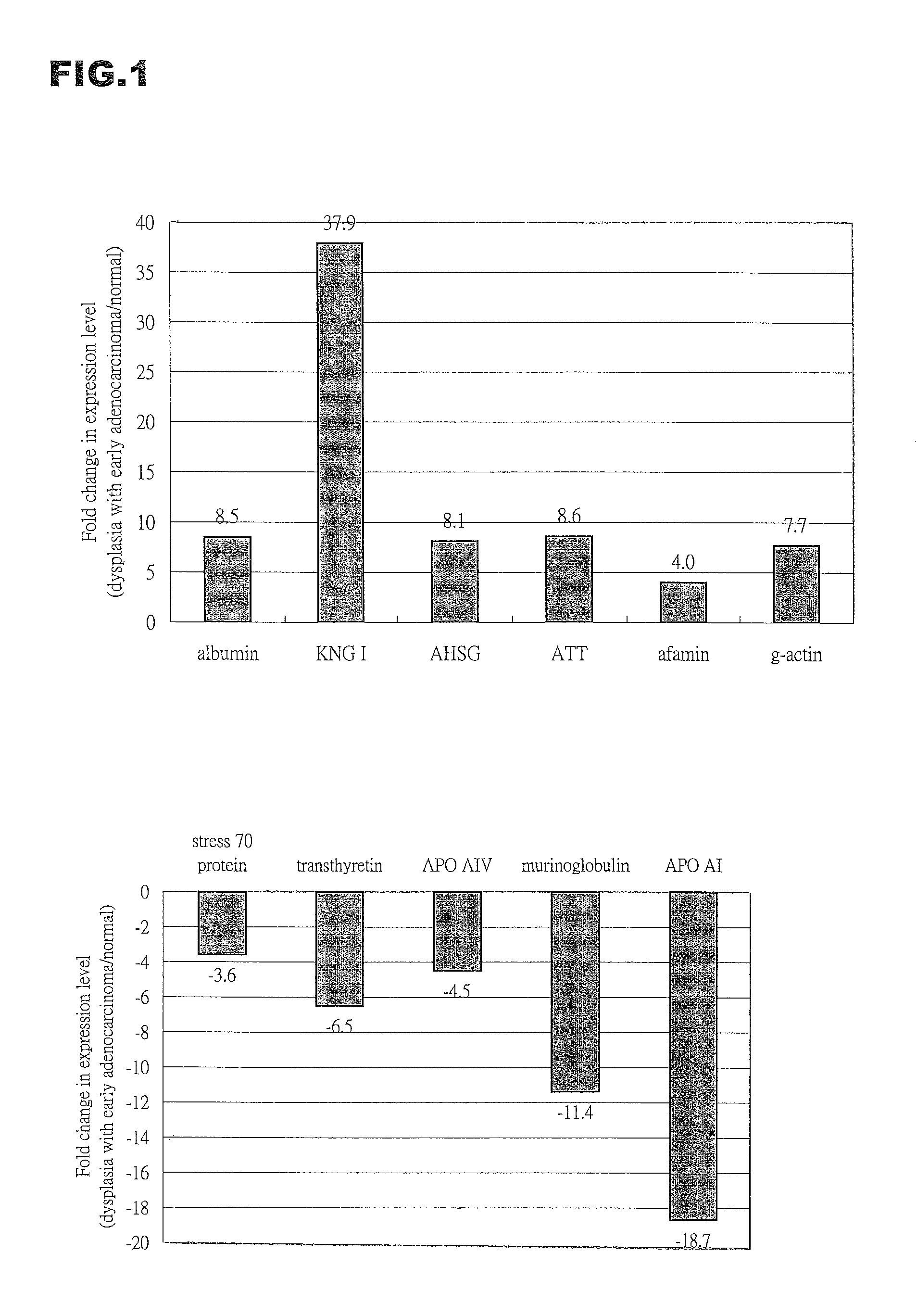
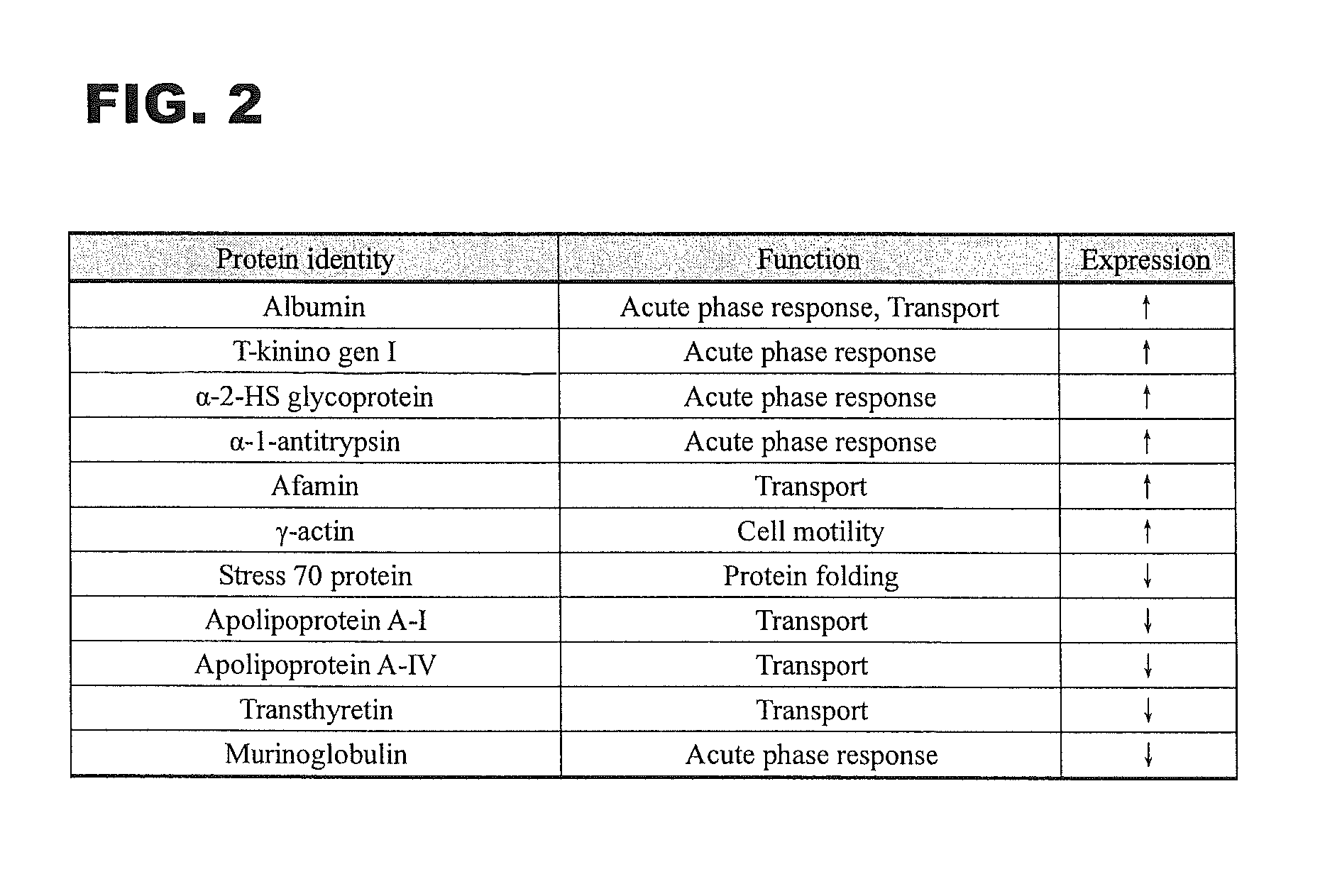
Biomarkers of gastric cancer and use thereof
ActiveUS8709732B2Enhancement of cancer biomarkersEasy accessMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansTryptaseBiomarker (petroleum)
A set of biomarkers indicative of early gastric cancer and method of diagnosing gastric cancer at an early stage by directing the these biomarkers in a blood sample. Detection of over-expression of one or more protein biomarks in the group consisting albumin, T-kininogen I, α-2-HS glycoprotein, α-1-antitrypsin, afamin and γ-actin and / or detection of under-expression of one or more protein biomarks in the group consisting stress 70 protein, apolipoprotein A-I, apolipoprotein A-IV, transthyretin and murinoglobulin is indicative of the presence of gastric cancer.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com