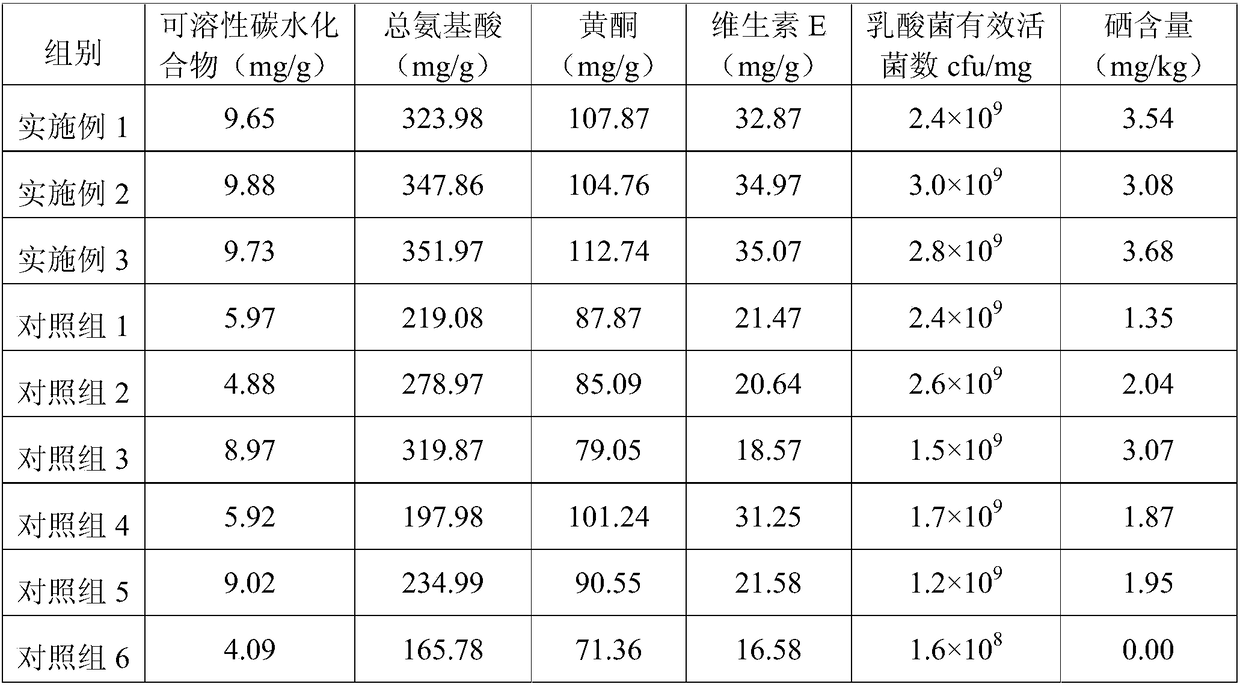
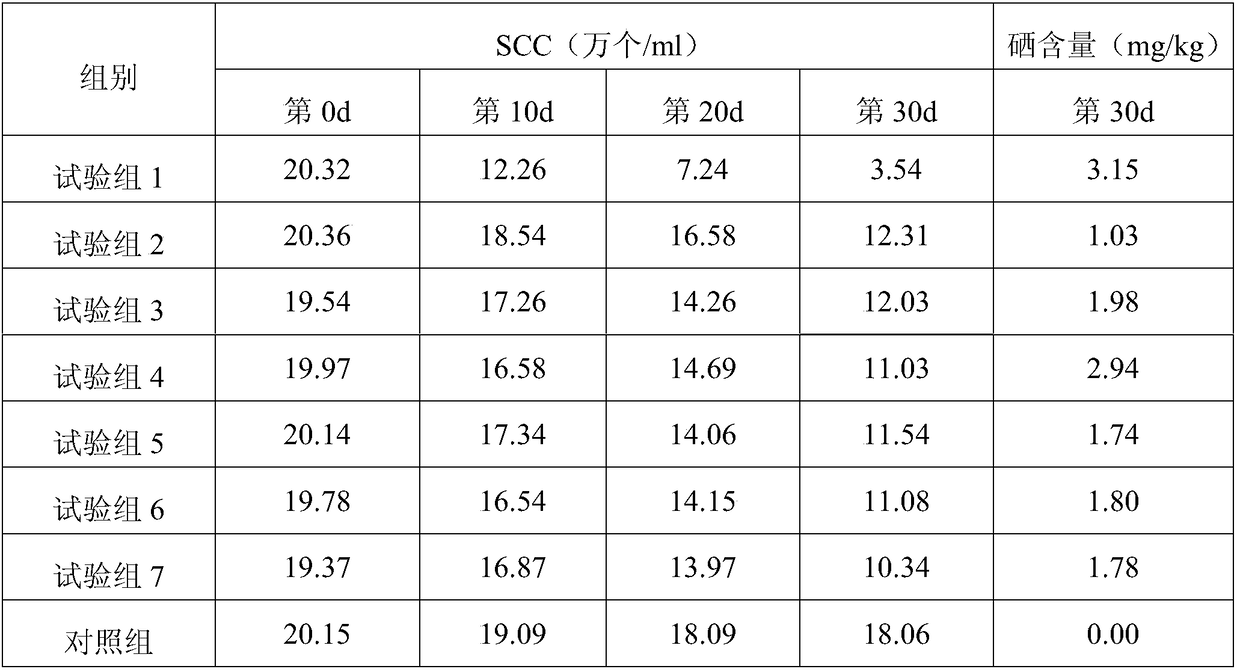
Patents
Literature
103 results about "Carboxypeptidase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
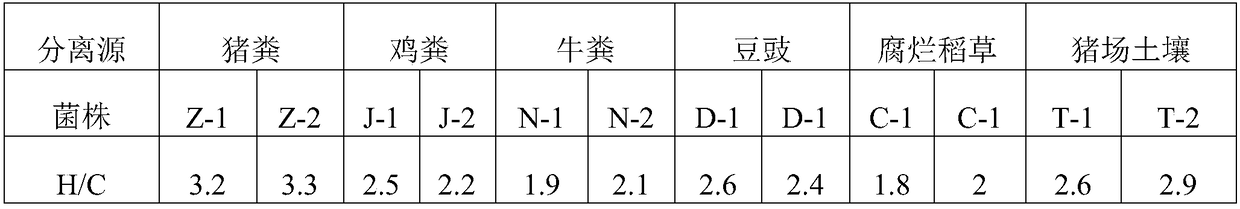
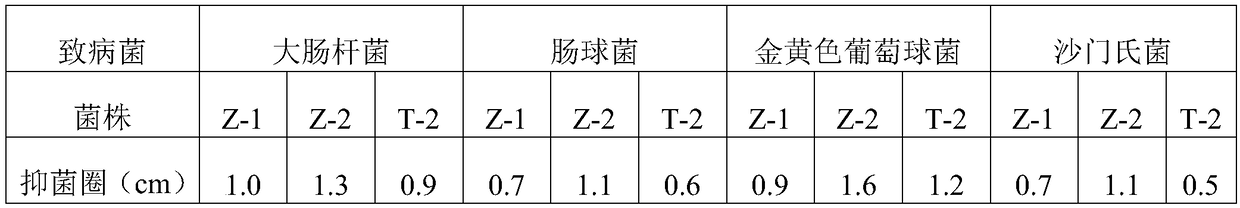
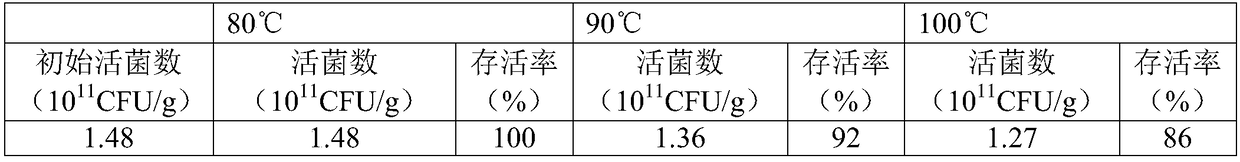
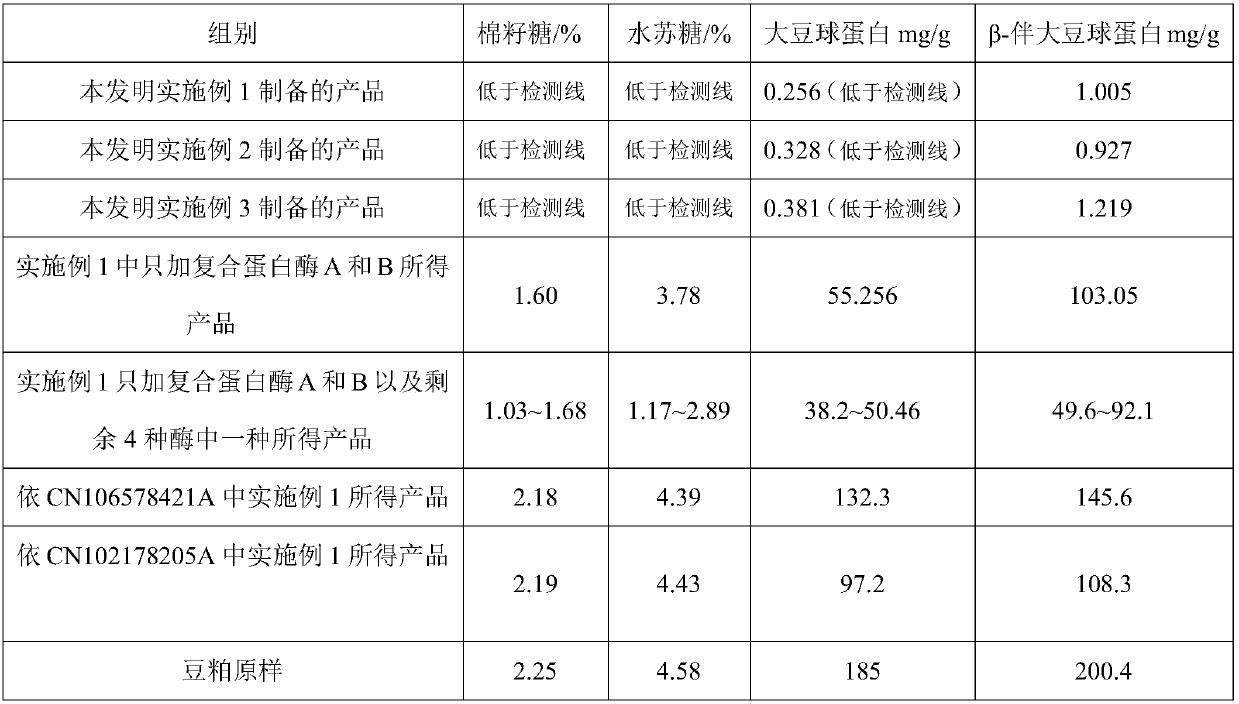
A carboxypeptidase (EC number 3.4.16 - 3.4.18) is a protease enzyme that hydrolyzes (cleaves) a peptide bond at the carboxy-terminal (C-terminal) end of a protein or peptide. This is in contrast to a aminopeptidases, which cleave peptide bonds at the N-terminus of proteins. Humans, animals, bacteria and plants contain several types of carboxypeptidases that have diverse functions ranging from catabolism to protein maturation.
Reagent case for predicting action effect of angiotensin conversion enzyme inhibitor medicament
ActiveCN101063166APredictive validityPredict safetyMicrobiological testing/measurementWild typeBiology
The invention discloses an agent box, which is characterized by the following: utilizing the relation between mononucleotide polymorphism site E112D genetype of important enzyme praline carboxypeptidase gene on vessel or esoderma regulating access and ACEI medical effect; forecasting ACEI medical effect; possessing good ACEI medical effect when genetype as 112EE pure wild-type; possessing bad effect when the genetype as 112ED heterozygous type or 112DD pure saltant; incorporating polymorphism parting oligonucleotide of E112D polymorphism site genetype with praline carboxypeptidase gene to test biological sample and related agent. This invention improves effectiveness and safety of clinic medicine, which provides criterion for new medicine of high blood pressure.
Owner:SHENZHEN AUSA PHARM CO LTD +1
Enzymolysis treatment method of algae
The invention provides an enzymolysis treatment method of algae. The method comprises the steps of material preparation, pretreatment, enzyme treatment and centrifugating. In the enzyme treatment step, the adopted enzyme is a composite enzyme which comprises proteinase, cellulase and pectinase in a mass ratio of 3:1:2. The proteinase is any one of papain, bromelin, carboxypeptidase and chymopapain. The cellulase is any one of cellobiohydrolase, endoglucanase, beta-glucosaccharase and cellobiase. The pectinase is any one of protopectinase, lyase and polygalacturonase. According to the enzymolysis treatment method of algae, the extraction rate of sodium alginate is 38.0-50.9%, and the extraction rate of alga glycine is 7.5-11.8%.
Owner:SHANDONG HETIANWANG BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
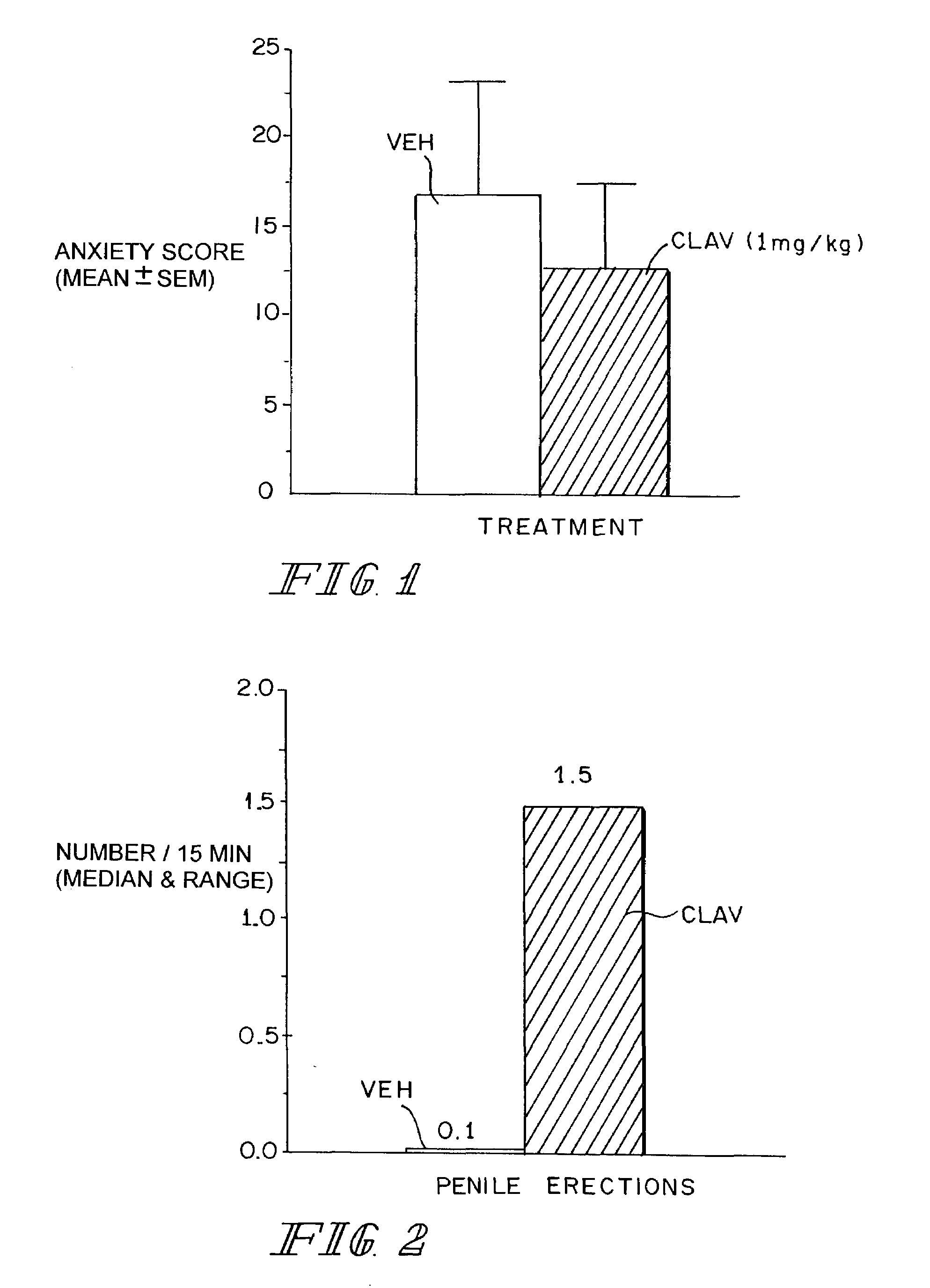
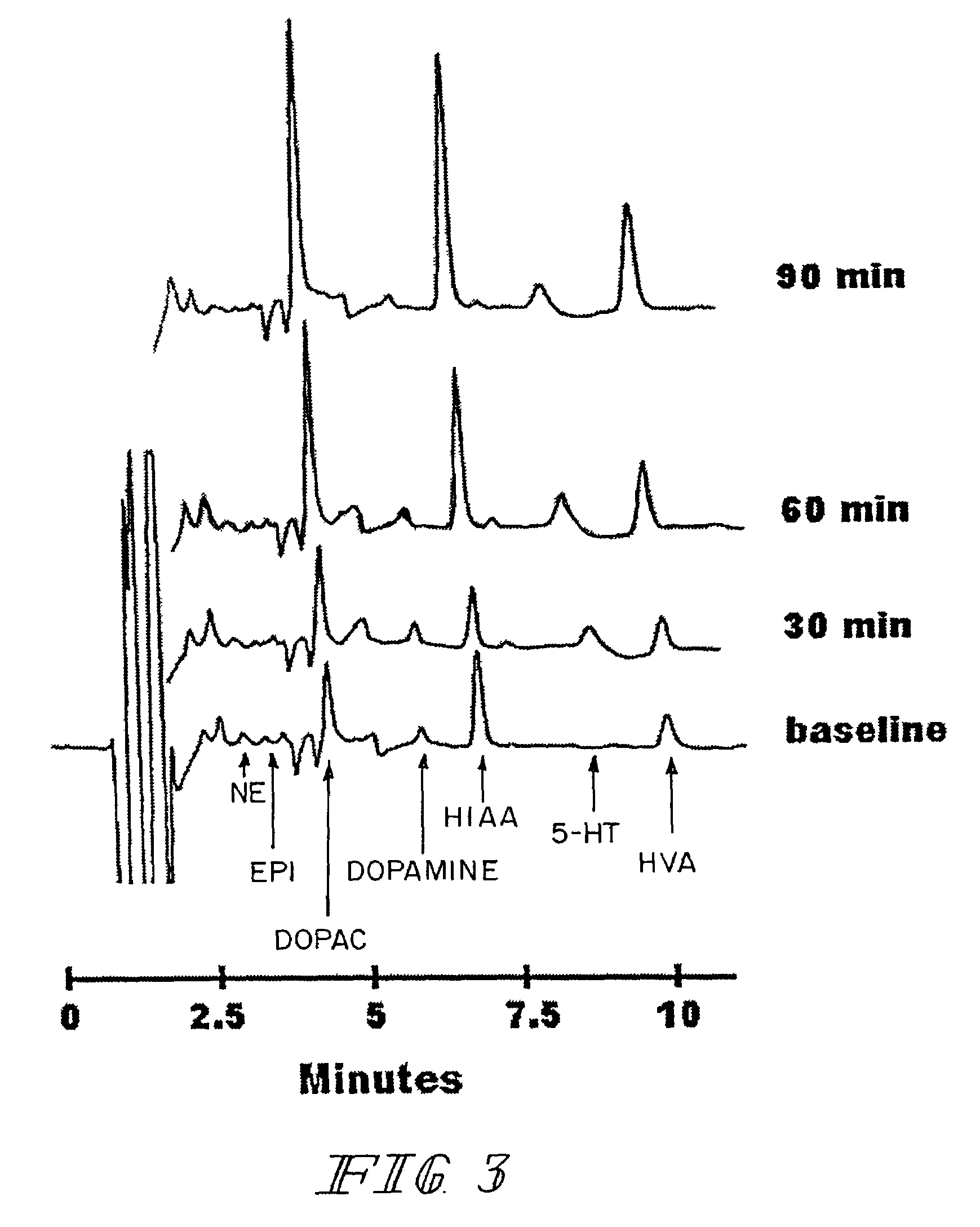
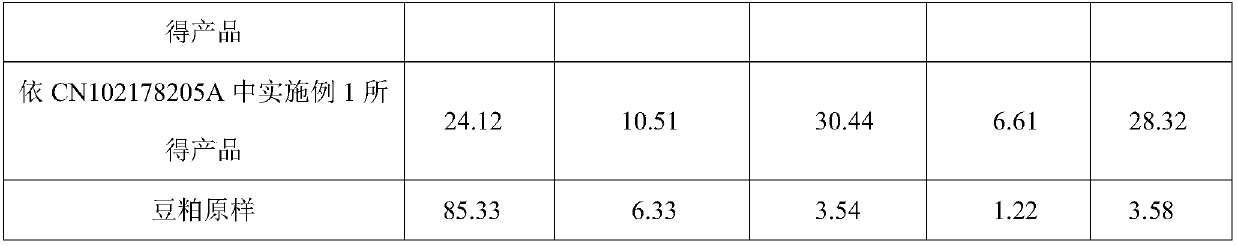
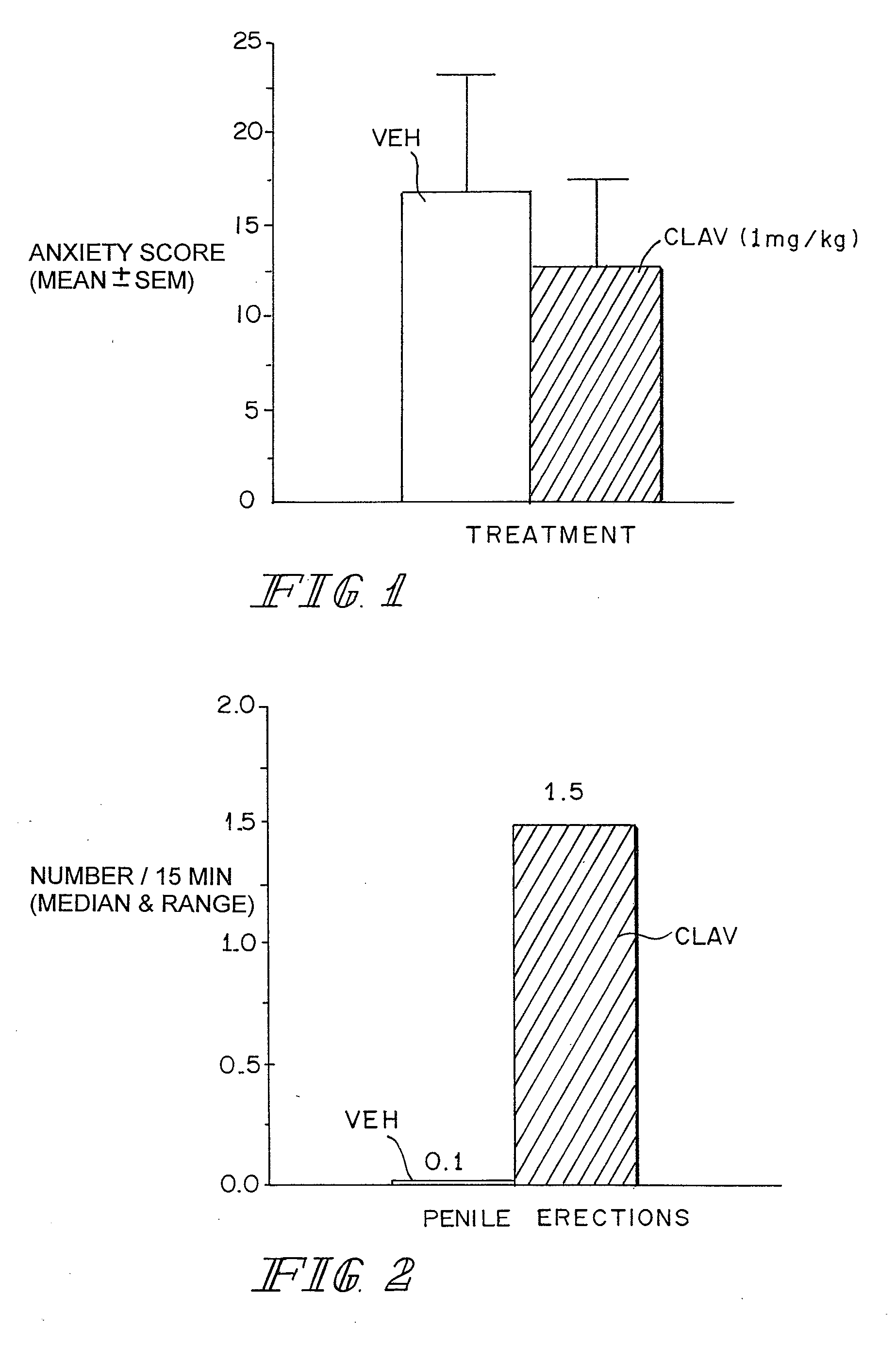
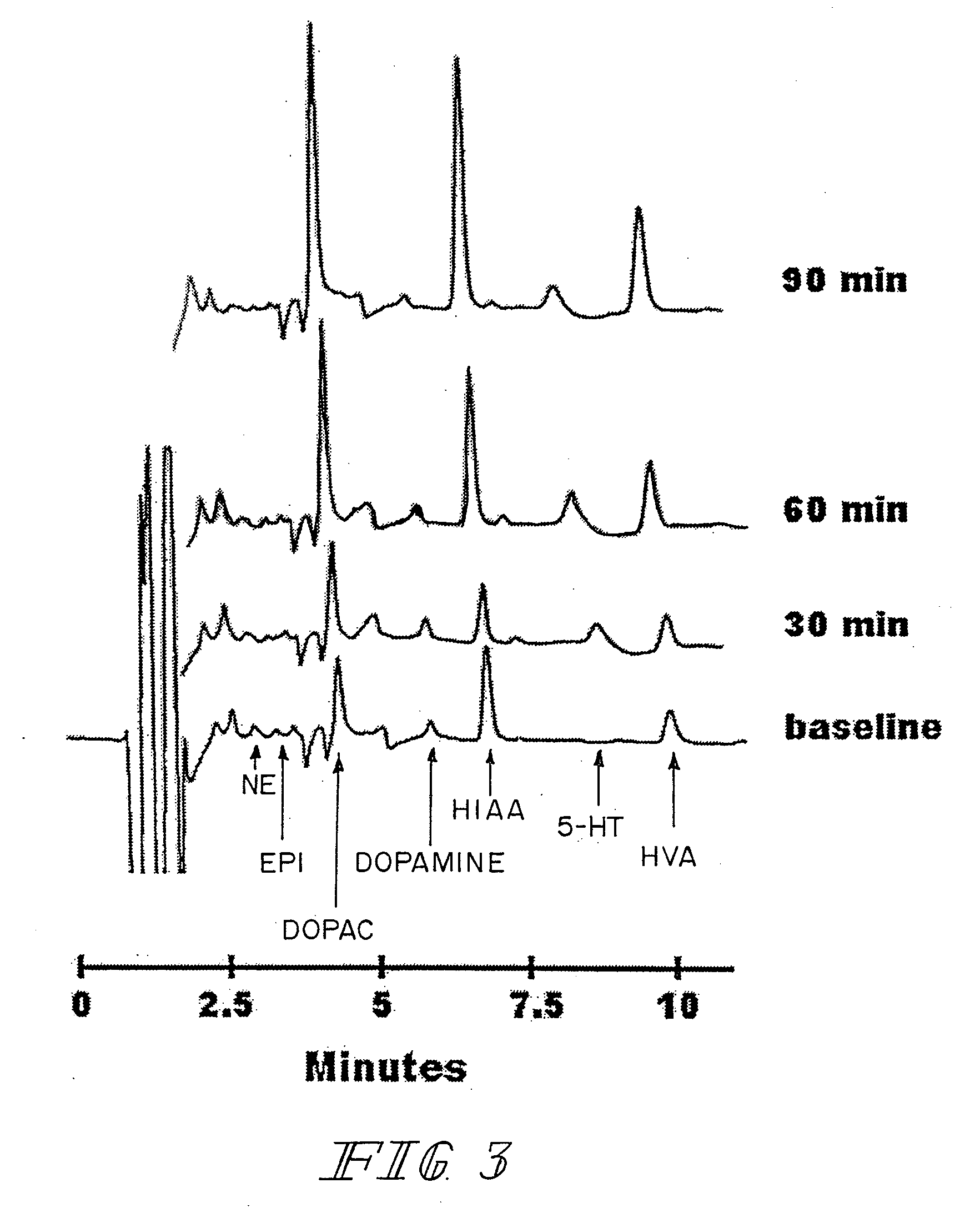
Therapeutic treatment for sexual dysfunction
InactiveUS7166626B2Improve sexual functionNormal and enhanced sexual functionBiocideAnimal repellantsSexual functionPenicillin binding
A method for improving sexual function is described. A mammal suffering from sexual dysfunction or otherwise in need of enhanced sexual function is administered a compound selected from those that are capable of inhibiting the activity of β-lactams, penicillin-binding protein, carboxypeptidase,. Such compounds, including particularly β-lactam ring-containing compounds, can be used to formulate pharmaceutical formulations useful for improving sexual function.
Owner:REVAAX PHARMA LLC
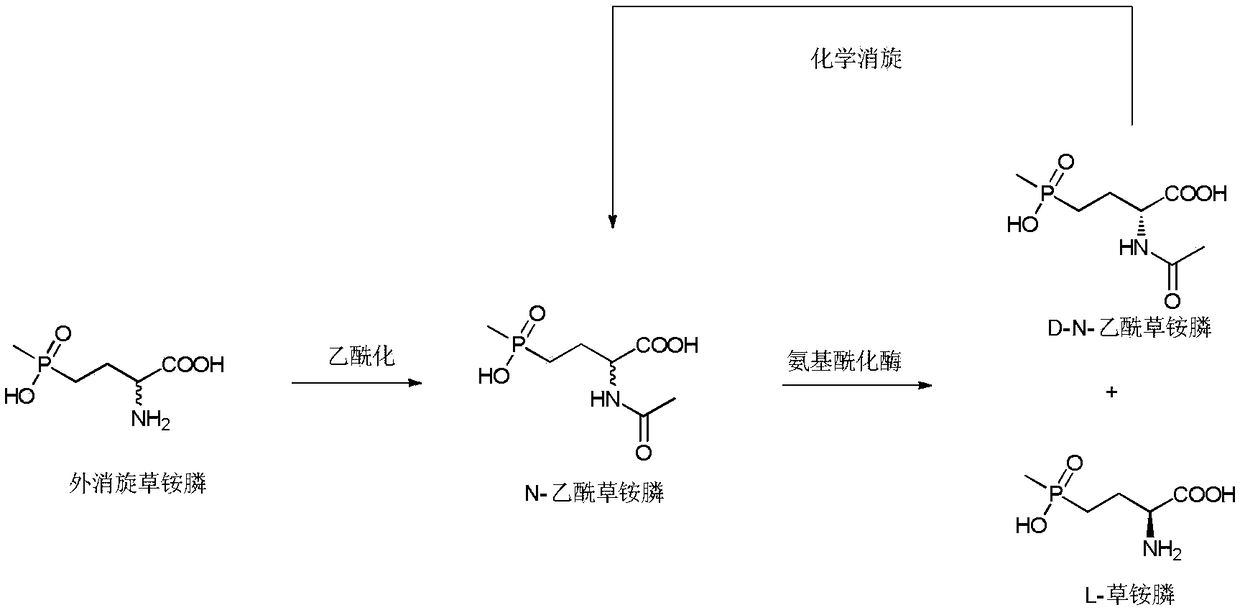
Method of utilizing chemistry-enzyme method to produce L-glufosinate ammonium
The invention discloses a method of utilizing a chemistry-enzyme method to produce L-glufosinate ammonium. According to the method, racemic N-acetyl glufosinate ammonium is taken as the substrate, engineering bacteria containing carboxyl-peptidase genes are subjected to fermentation culture to obtain wet cells, wet cells or pure enzymes, which are obtained by steps of grinding wet cells through ultrasonic waves and extracting grinded wet cells, are taken as the catalyst, a buffer solution with a pH value of 5-10 is taken as the reaction medium, reactions are performed in a water bath with a temperature of 45 DEG C at a rotation speed of 200 rpm, after complete reactions, a reaction solution containing D-N-acetyl glufosinate ammonium and L-glufosinate ammonium is obtained, the reaction solution is separated and purified, and collected D-N-acetyl glufosinate ammonium is subjected to racemization and then split in cycles to obtain L-glufosinate ammonium at the same time. The provided method does not need a coenzyme circulation system or an amino donor with a structure that is similar with the product; the reaction steps are simple, the reaction product is easy to separate, the opticalselectivity is high (ee value is 99%), the separation effect of the ion exchange column is obvious, and L-glufosinate ammonium with higher purity can be obtained more easily (purity is 98%).
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
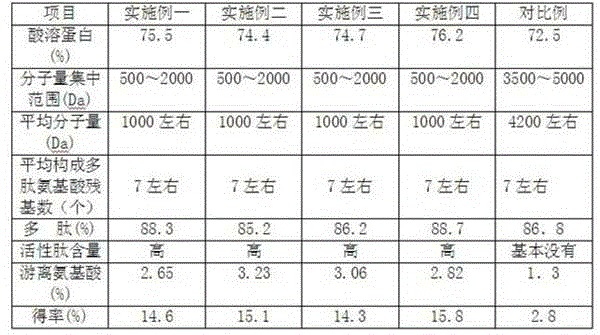
Method for extracting low molecular weight active collagen peptide from pigskin
InactiveCN102911991AHigh activityHigh yieldPeptide preparation methodsFermentationCollagenanOrganic chemistry
The invention relates to the technical field of deep processing of pigskin, particularly relates to a method for extracting pigskin collagen peptide. The method uses fresh pigskin to serve as a raw material, and a pure biology method is used for obtaining the pigskin collagen peptide. The method for extracting low molecular weight active collagen peptide from the pigskin comprises the following steps of: taking the fresh pigskin to serve as the raw material, firstly conducting outer cutting on collagen in the pigskin by adopting aminopeptidase and carboxypeptidase; separating the collagen from other tissue elements in the pigskin, then the pigskin is in a scattered state, and using endo protease to conduct enzymolysis on protein to enable the protein to form micromolecular protein peptides. Different protein peptides are scientifically selected in different stages, processing steps are optimized, production efficiency is improved, yield of the collagen peptide is promoted, and activity of the collagen peptide is improved.
Owner:HUZHOU JIAMEI BIOCHEM PRODS
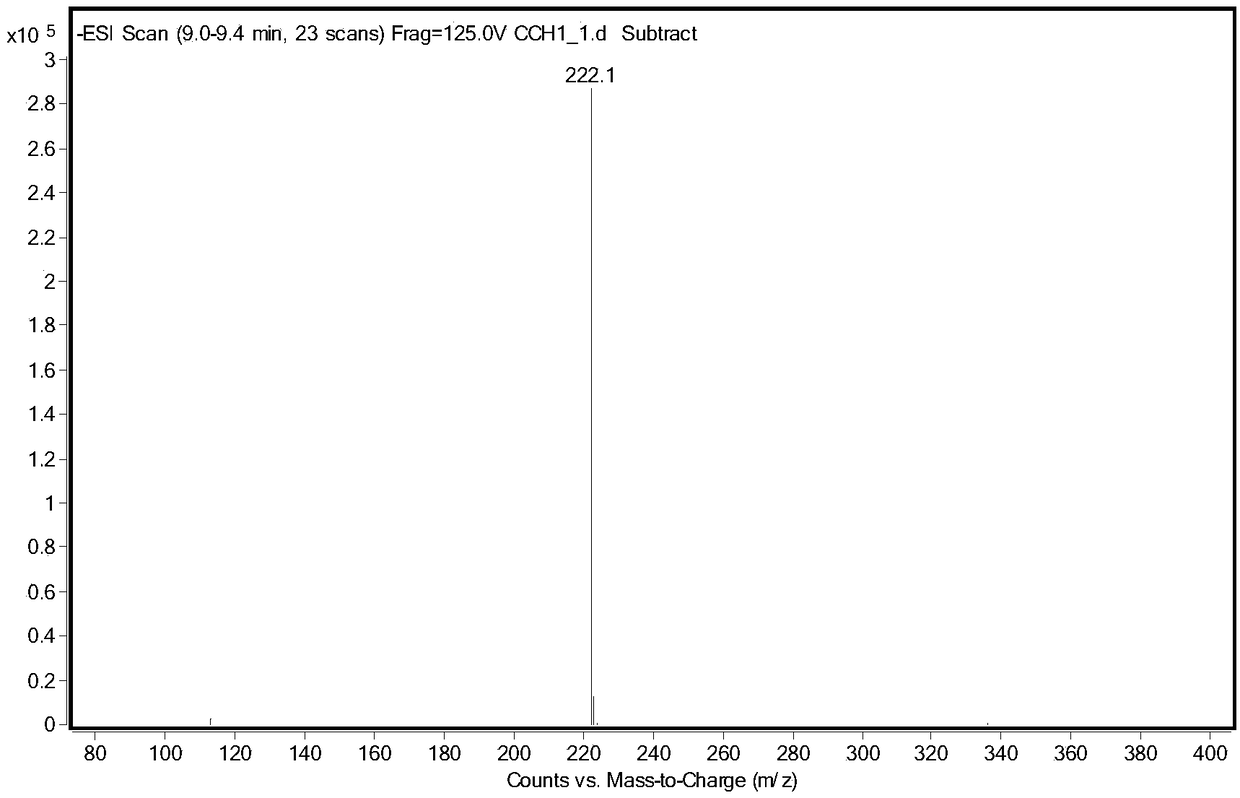
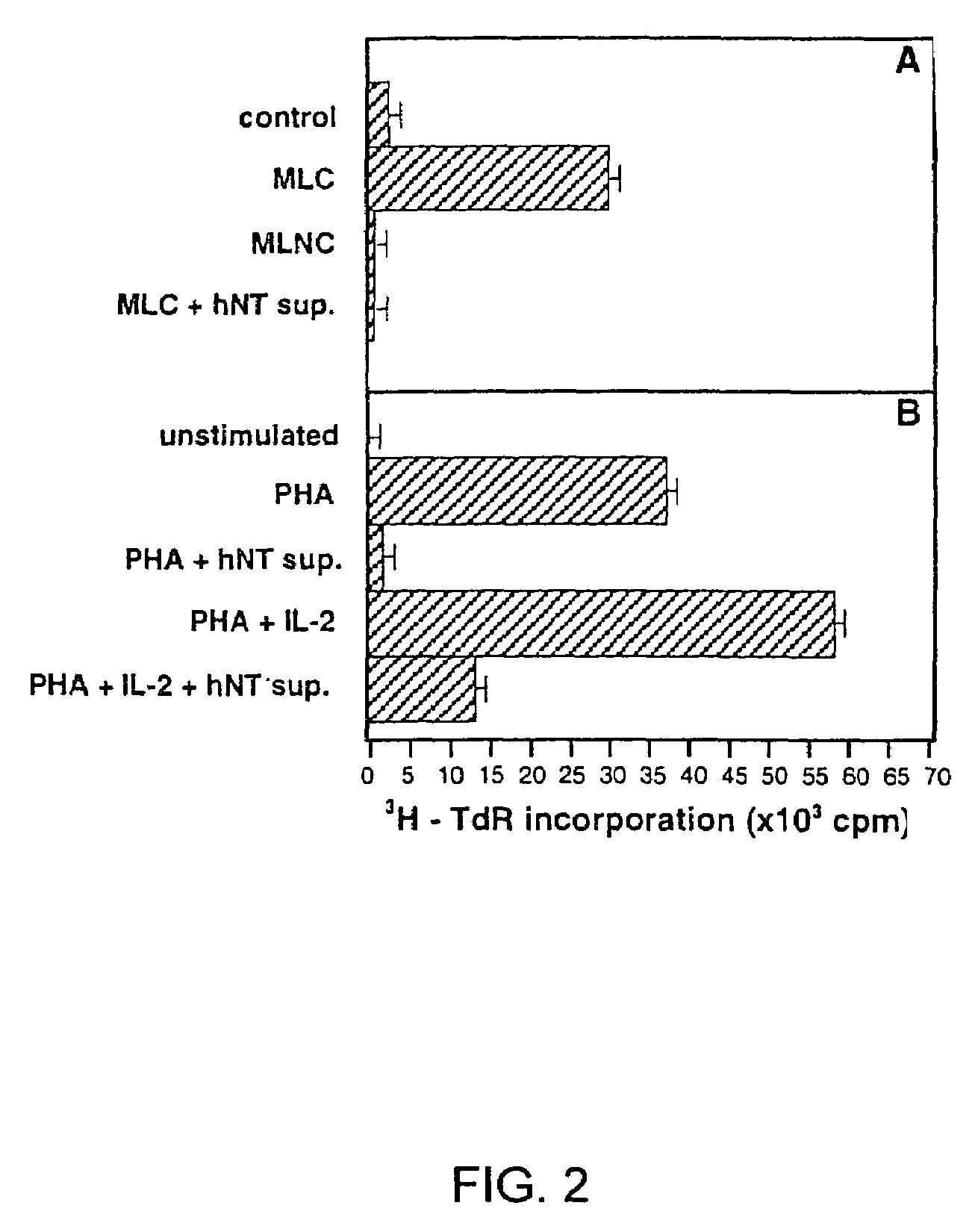
Human immunosuppressive protein
InactiveUS7388076B2Prevent proliferationReduced viabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticEmbryonal Carcinoma CellsPeripheral blood mononuclear cell
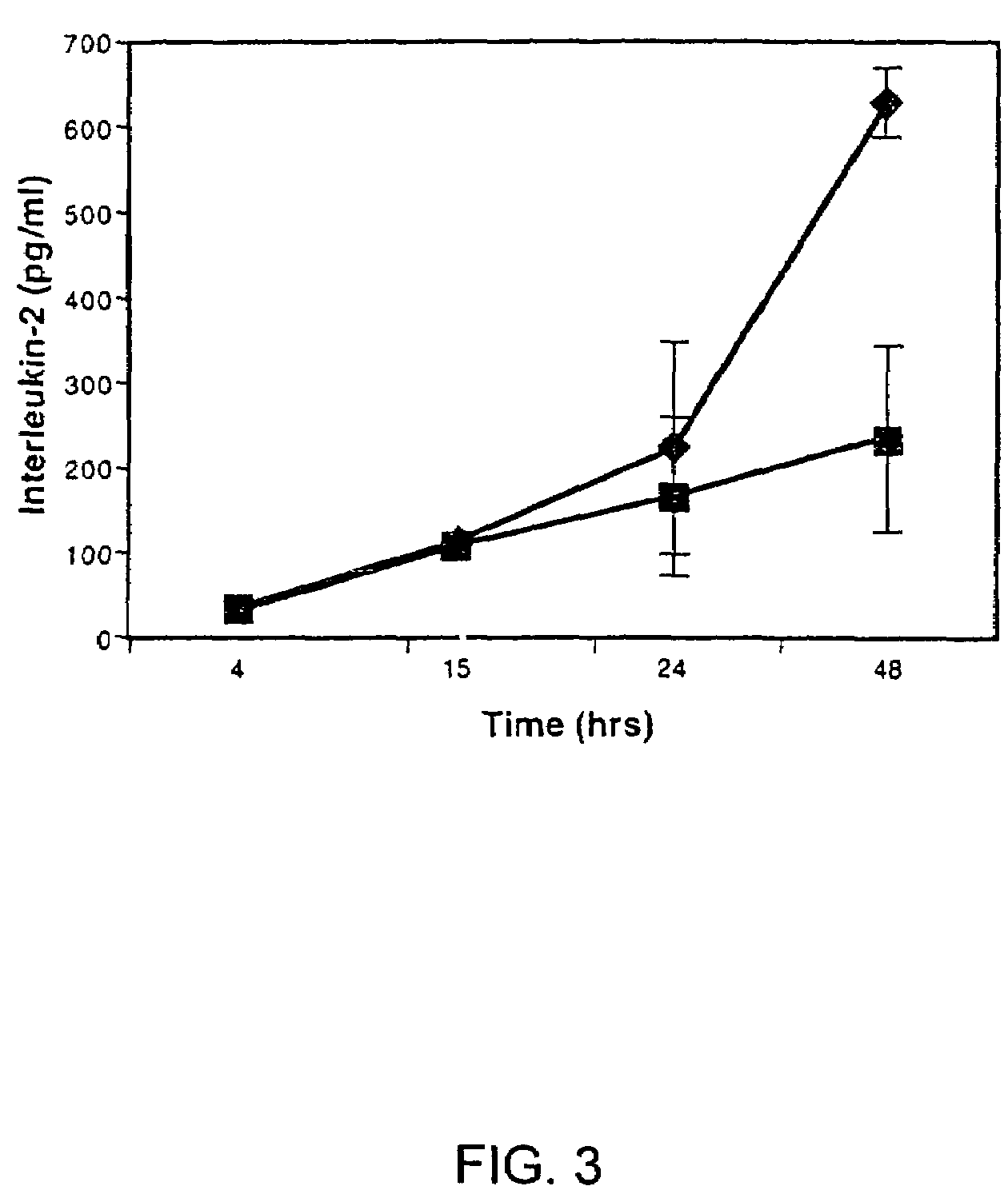
A method for purifying an immunosuppressant protein (HISP) has the steps of obtaining supernatant from hNT cells; exposing the supernatant to preparative polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis to produce 20 isoelectric fractions, including active isoelectric fraction #10; placing the active isoelectric fraction on a Blue Sepharose column to bind albumin; and collecting the free fraction containing the concentrated, isolated HISP. Also disclosed is a method of treating inflammation, using an effective amount of an HISP. The HISP is anionic, has a molecular weight of 40-100 kDa, an isoelectric point of about 4.8 and is obtained from the supernatant of hNT cells, but not from NCCIT embryonal carcinoma cells, T98G glioblastoma cells or THP-1 monocytic leukemia cells. HISP can maintain T cells in a quiescent G0 / G1 state without lowering their viability. HISP loses activity when treated with heat, pH2, pH11, or mixed with trypsin or carboxypeptidase, but not with neuraminidase. HISP can suppress proliferation of responder peripheral blood mononuclear cells in allogeneic mixed lymphocyte cultures; HISP can suppress T-cell proliferation and IL-2 production in response to phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA), ionomycin and concanavalin-A. HISP does not bind to heparin-sepharose CL-B gel; or to albumin-binding resin Blue Sepharose. HISP is concentrated with YM10 ultrafiltration. HISP does not act through the T-cell receptor-CD3 complex or via altered accessory signal cells. A method of treating inflammation comprises administering an effective amount of hNT neuronal cells.
Owner:SOUTH FLORIDA UNIVESITY OF
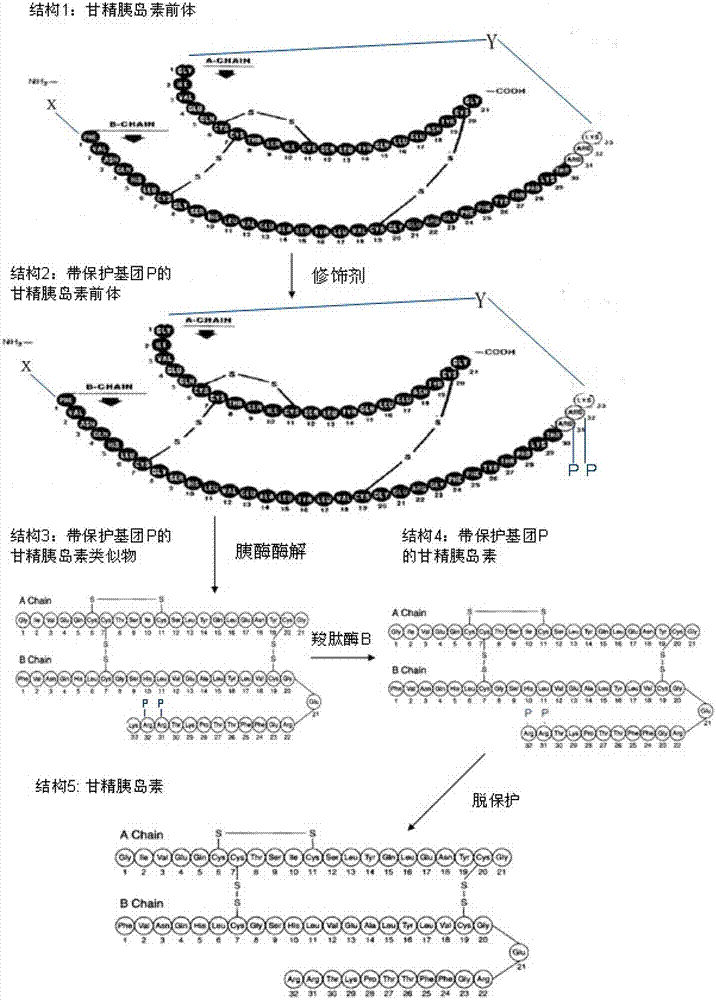
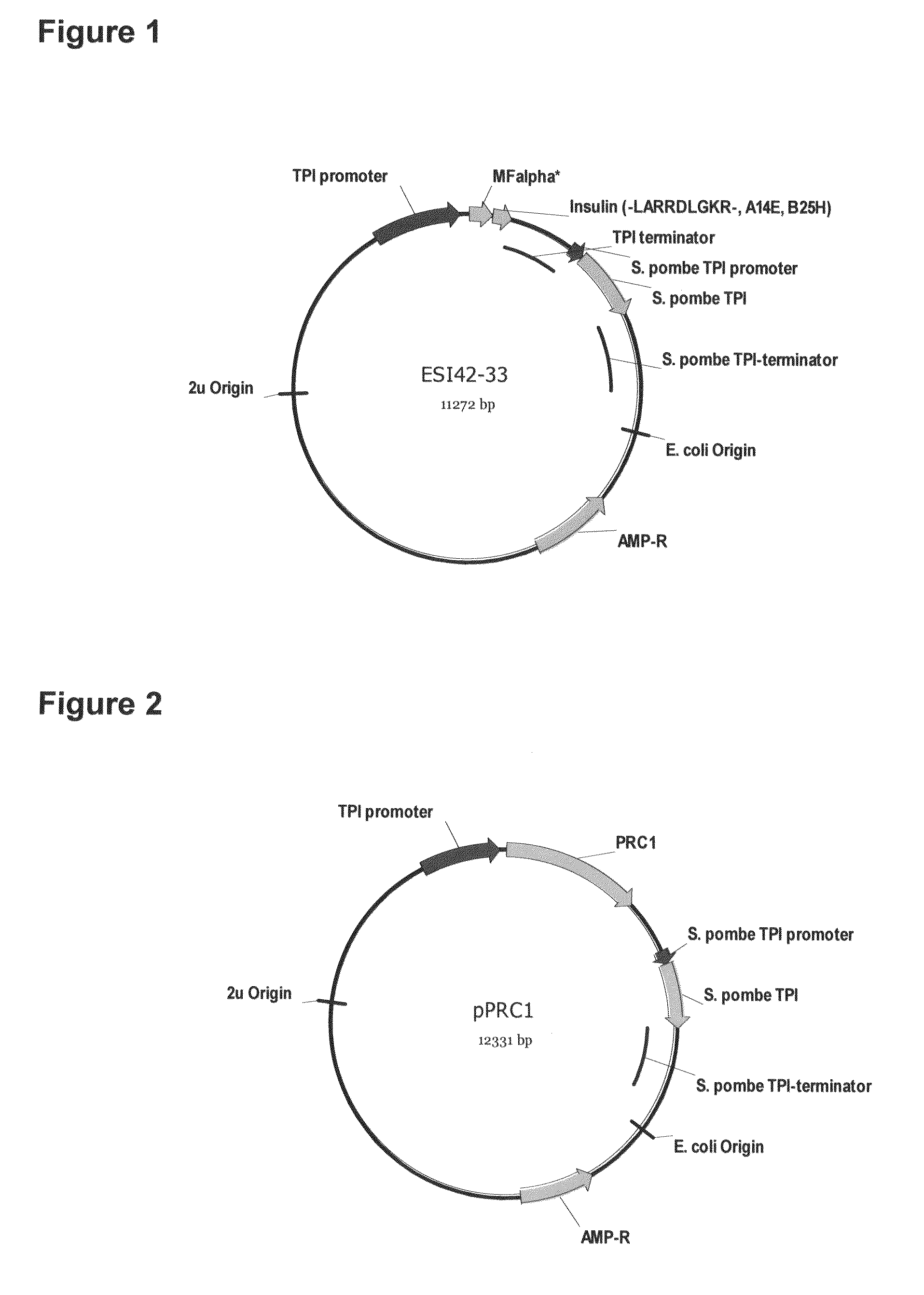
Preparation method of insulin glargine and analogue thereof
The invention discloses a preparation method of insulin glargine and an analogue thereof. The preparation method includes the following steps: (1) a gene engineering method is used for preparing a precursor of the insulin glargine and the analogue of the insulin glargine with a chain B and an end C containing a plurality of basic amino acids; (2) an amino acid side chain protective agent is used for distinguishing arginine or lysine through pancreatic enzyme specificity, and the insulin glargine and the analogue of the insulin glargine are provided with protecting groups and obtained under the effect of the protective agent and pancreatic enzyme; or the specificity is used for acting on clostripain of the arginine (Arg) or endoproteinase lysine (Lys) C of the Lys directly without protection; (3) carboxypeptidase is added optionally to remove unprotected basic amino acids at the tail end of the C; and (4) the glargine and the analogue of the insulin glargine are obtained through deprotection. The preparation method is simple and convenient, high in yield, wide in application range and suitable for introduction of more than two basic amino acids.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAYI BIO LAB CO LTD
Method for the elimination of kunitz and bowman-birk trypsin inhibitors and carboxypeptidase inhibitor from potato proteins
A method for removing protein impurities from extracts of protease inhibitor-containing plant material. Plant materials containing protease inhibitors, such a potato tubers that contain protease inhibitor II, are extracted using an alcohol-free solvent. The proteins present in the extract include impurities other than the protease inhibitor, specifically Kunitz, Bowman-Birk and carboxypeptidase inhibitors. The extract is subjected to heat treatment to denature and precipitate the unstable protein impurities followed by centrifugation to remove the precipitate. Ultrafiltration in the presence of a buffer removes the Bowman-Birk and carboxypeptidase inhibitors. The resulting purified protease inhibitor has applicability in the control of obesity and diabetes.
Owner:KEMIN FOODS L C
Method for the elimination of Kunitz and Bowman-Birk trypsin inhibitors and carboxypeptidase inhibitor from potato proteins
A method for removing protein impurities from extracts of protease inhibitor-containing plant material. Plant materials containing protease inhibitors, such a potato tubers that contain protease inhibitor II, are extracted using an alcohol-free solvent. The proteins present in the extract include impurities other than the protease inhibitor, specifically Kunitz, Bowman-Birk and carboxypeptidase inhibitors. The extract is subjected to heat treatment to denature and precipitate the unstable protein impurities followed by centrifugation to remove the precipitate. Ultrafiltration in the presence of a buffer removes the Bowman-Birk and carboxypeptidase inhibitors. The resulting purified protease inhibitor has applicability in the control of obesity and diabetes.
Owner:KEMIN FOODS L C
Reagent kit for forecasting pregnancy badness come-off generating risks
ActiveCN101063677AImprove waterproof performanceImprove controlMicrobiological testing/measurementSurgeryPregnancyCase fatality rate
This invention provides one agent case by use of blood vessel and endothelium function to adjust its important praline carboxypeptidase gene mononucleotide polymorphism bit E112D gene and conception imperfect rate relationship on the channel to predict the incidence rate, wherein when the gene is of 112EE pure wild type, the incidence rate is low and when gene is of 112ED mixture or 112DD pure burst type the incidence rate is high. This agent case comprises the E112D polymorphism gene parting oligonucleotide and relative agents.
Owner:深圳泰乐德医学检验实验室
Preparation of enzyme preparation with acidic proteinase as main component as well as strain and application of enzyme preparation
ActiveCN111593036AConvenient supplementFit closelyFungiMicroorganism based processesAmylasePectinase
The invention provides preparation of an enzyme preparation with acidic proteinase as a main component as well as a strain and application of the enzyme preparation. The multi-enzyme series acidic proteinase preparation which utilizes the acidic proteinase as the main component, utilizes multiple associated enzymes including pectinase, xylanase, amylase, cellulase, mannase, glucanase, glucosidase,galactosidase, feruloyl esterase, carboxypeptidase and phosphatase and is rich in natural complex enzymes is obtained by culture. Aspergillus niger is named Aspergillus niger BAK200389, and the preservation number of the Aspergillus niger is CGMCC No.19613. According to the used strain, the strain can produce multiple enzymes, and has the characteristics of stable growth, more types of produced enzymes and safety; and enzyme activity is considerable and is daily kept at 90,000-110,000, and the highest enzyme activity can reach about 120,000.
Owner:HANGZHOU BIOCOM BIOLOGICAL TECH
Protein hydrolysates enriched in peptides having a carboxy terminal proline residue
A method of enzymatically producing a protein hydrolysate from a protein substrate is described, wherein a proline-specific endoprotease or a composition containing a proline-specific endoprotease and optionally a subtilisin or a metallo endoprotease, and other enzymes such as carboxypeptidases, is used to produce a protein hydrolysate enriched in peptide fragments having a carboxy terminal proline residue. Such protein hydrolysates may be used as such or to reduce bitterness in foods nutritionally supplemented by protein hydrolysates, as well as to produce hydrolysate containing foodstuffs having low antigenicity.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
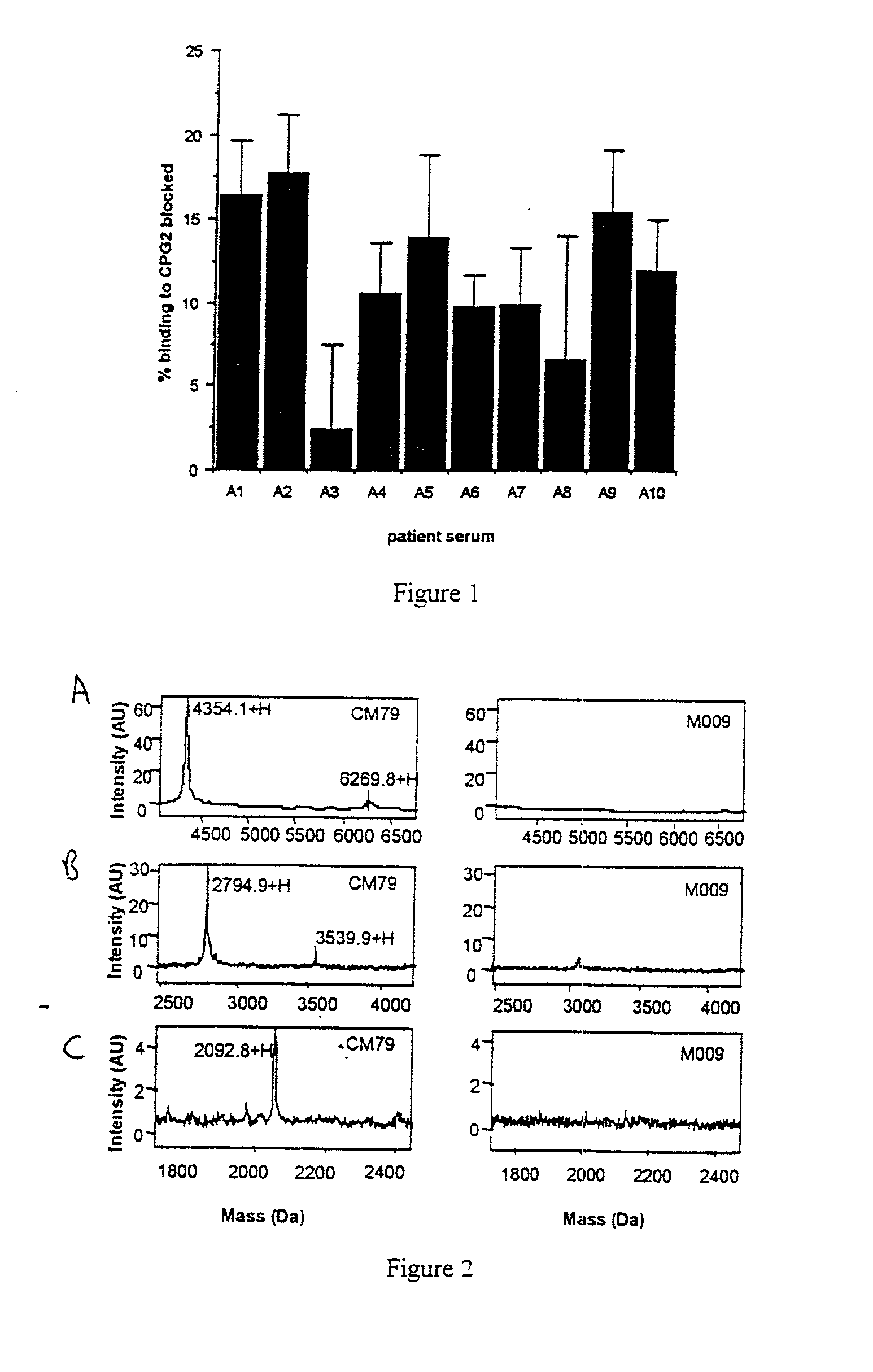
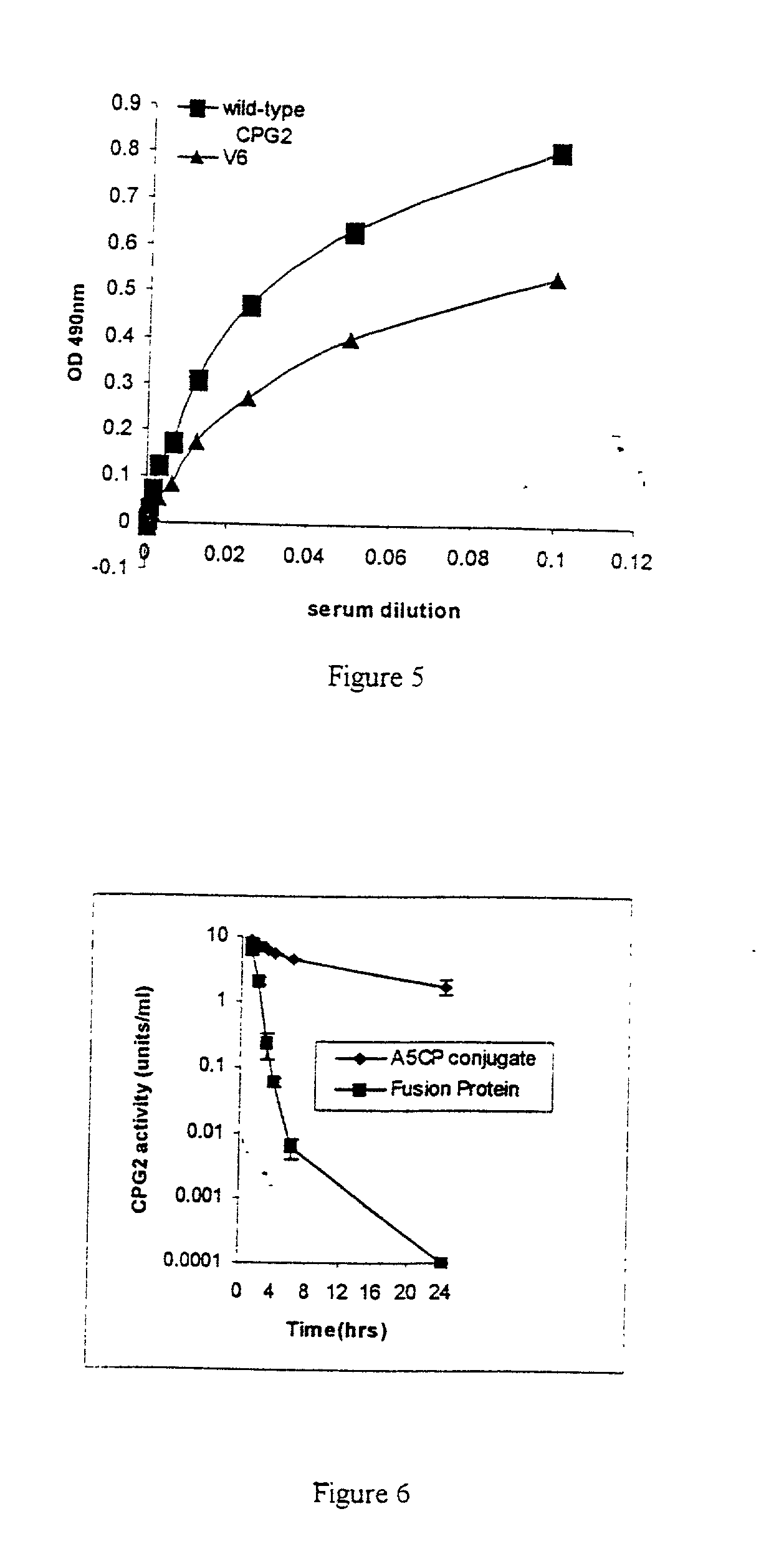
Modifided carboxypeptidase enzymes and their use
The invention relates to improvements relating to cancer therapy based on the identification of a number of regions of CPG2 which contain epitopes which appear to be involved in the production of a host immune response and which may be modified to alter the immunogenicity in patients. Production of fusions of CPG2 with an antibody, where the CPG2 protein has been tagged provides a CPG2 protein which has reduced immunogenicity. By using partially glycosylated enzyme obtainable by P. pastoris expression, the efficacy of antibody-CPG2 fusions is enhanced.
Owner:CANCER RES TECH LTD
Novel fungal proteins and nucleic acids encoding same
Disclosed herein are fungal nucleic acid sequences that encode novel polypeptides. Also disclosed are polypeptides encoded by these nucleic acid sequences, as well as derivatives, variants, mutants, or fragments of the aforementioned polypeptide, polynucleotide, or antibody. The novel leucine aminopeptidase (LAP) and other amino- and carboxypeptidases polypeptides, referred to herein as EXOX nucleic acids and proteins of the invention are useful in a variety of medical, research, and commercial applications.
Owner:AMYRA BIOTECH
Bacillus subtilis and application thereof
ActiveCN109306329AIncreased chance of stickingIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaFood processingMicrobiologyBacillus subtilis
Owner:广州大峰收技术服务有限公司
Method for preparing functional protein polypeptide by using bionic method
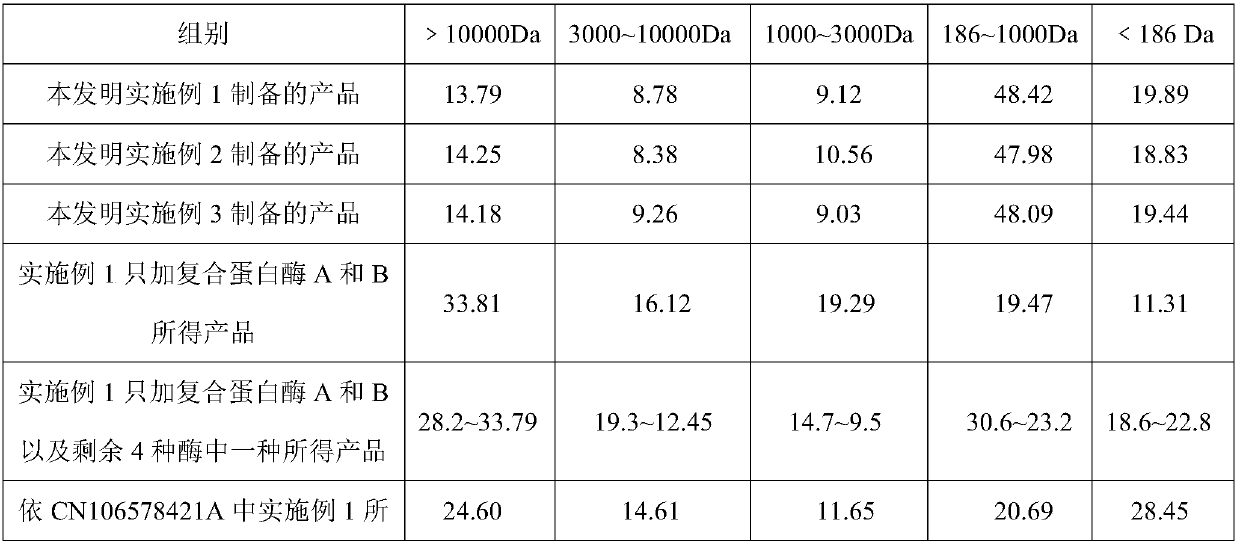
The invention relates to a method for preparing functional protein polypeptide by using a bionic method, which uses natural plant protein as a raw material, utilizes non-animal-derived protease and simulatesan animal digestion process to produce enzymolysis protein polypeptide. The method comprises the following steps of: pre-crushing plant protein raw materials, adding water for preparation, performing primary enzymolysis by adopting non-animal-derived composite protease A, papain and bromelain, adding composite protease B, lysine aminopeptidase and carboxypeptidase for secondary enzymolysisto obtain secondary enzymolysis protein slurry, then homogenizing, spray-drying, and sterilizing to obtain the final product. The method has the advantages of simple process flow, low cost, high content of active micromolecular peptide (the relative molecular weight is between 186 and 1000Da) and free amino acid (186Da) of the prepared product, complete degradation of anti-nutritional factors, invitro digestion absorption rate of more than or equal to 95%, and capability of effectively replacing high-quality animal-derived protein, the growth of young animals isobviously promoted and the method has good social and economic benefits.
Owner:GUANGZHOU WISDOM BIO TECH
Neurotherapeutic treatment for sexual dysfunction
InactiveUS20070093466A1Normal and enhanced sexual functionSufficient blood-brain barrier transport propertyBiocideAnimal repellantsSexual functionPenicillin binding
Owner:REVAAX PHARMA LLC
Processes for preparing 3-substituted 1-(chloromethyl)-1,2-dihydro-3h-[ring fused indol-5-yl-(amine- derived)] compounds and analogues thereof, and to products obtained therefrom
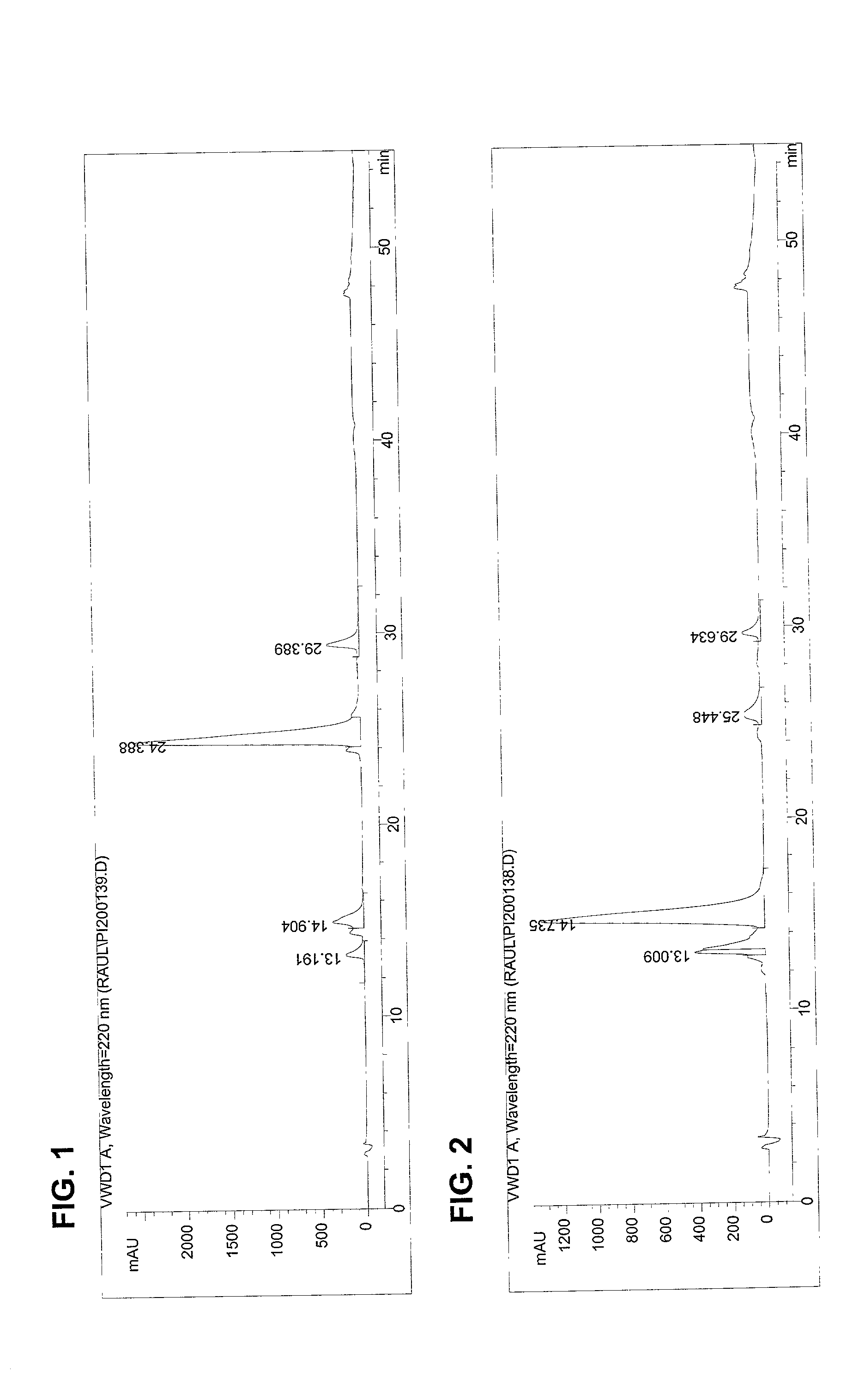
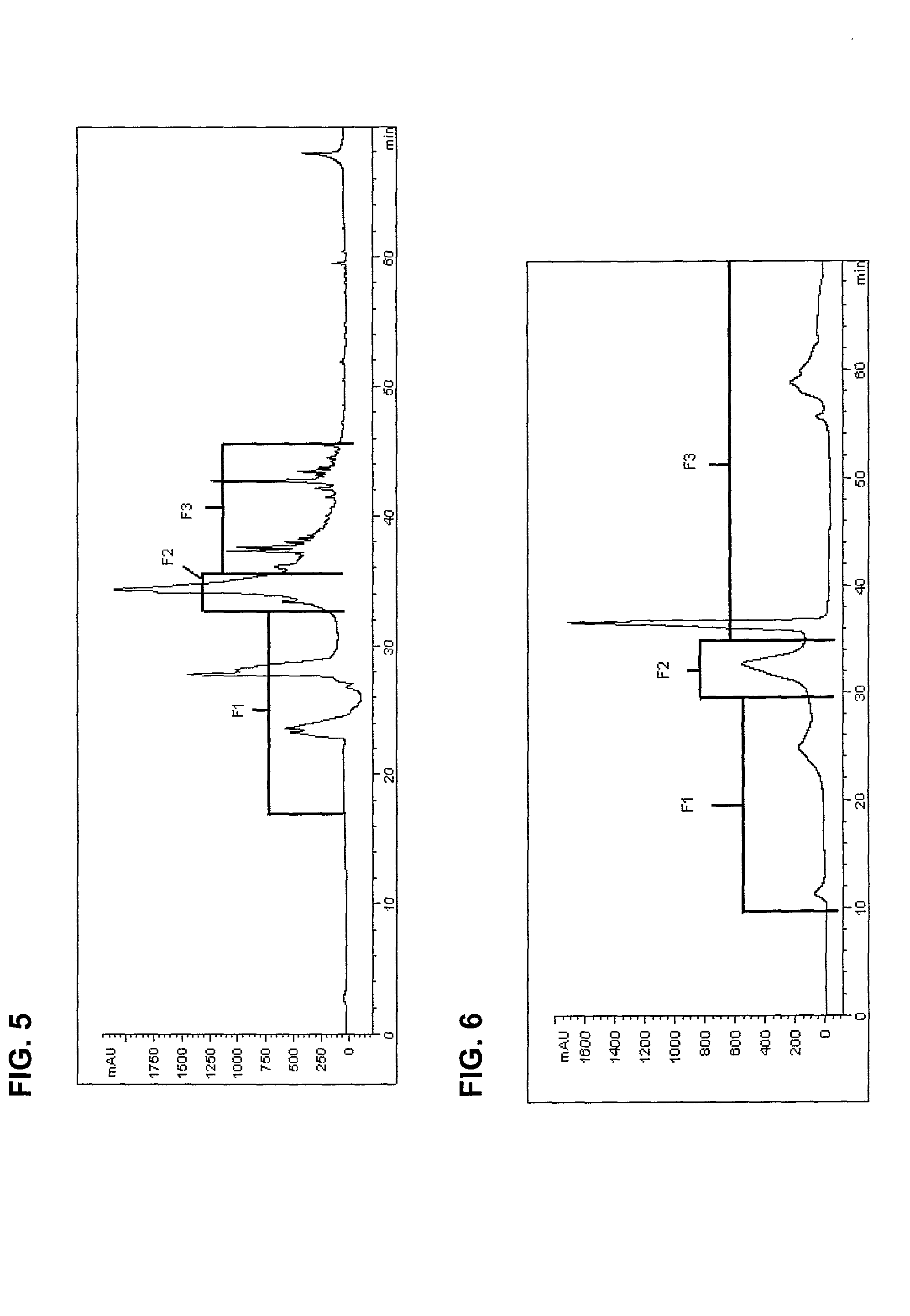
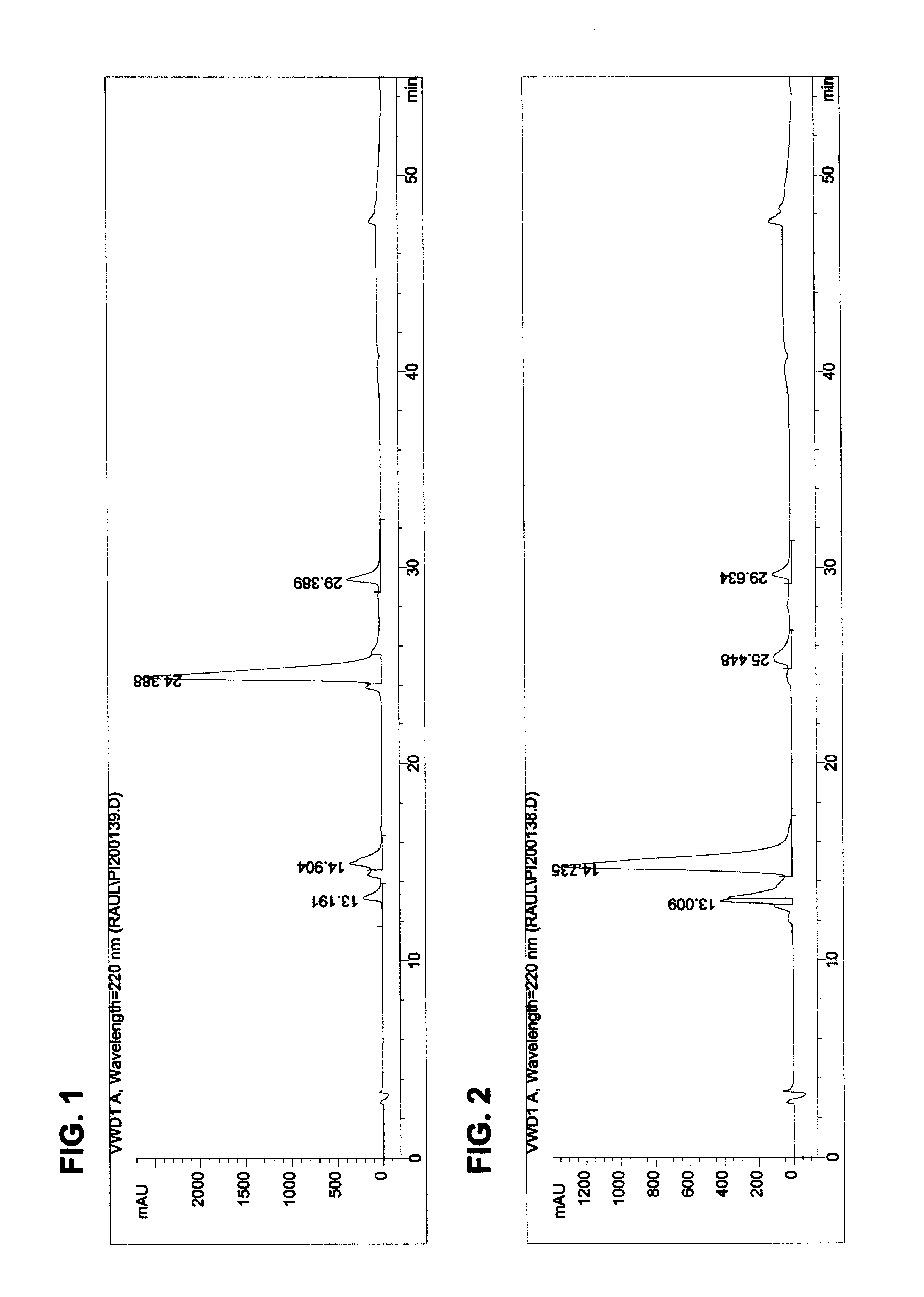
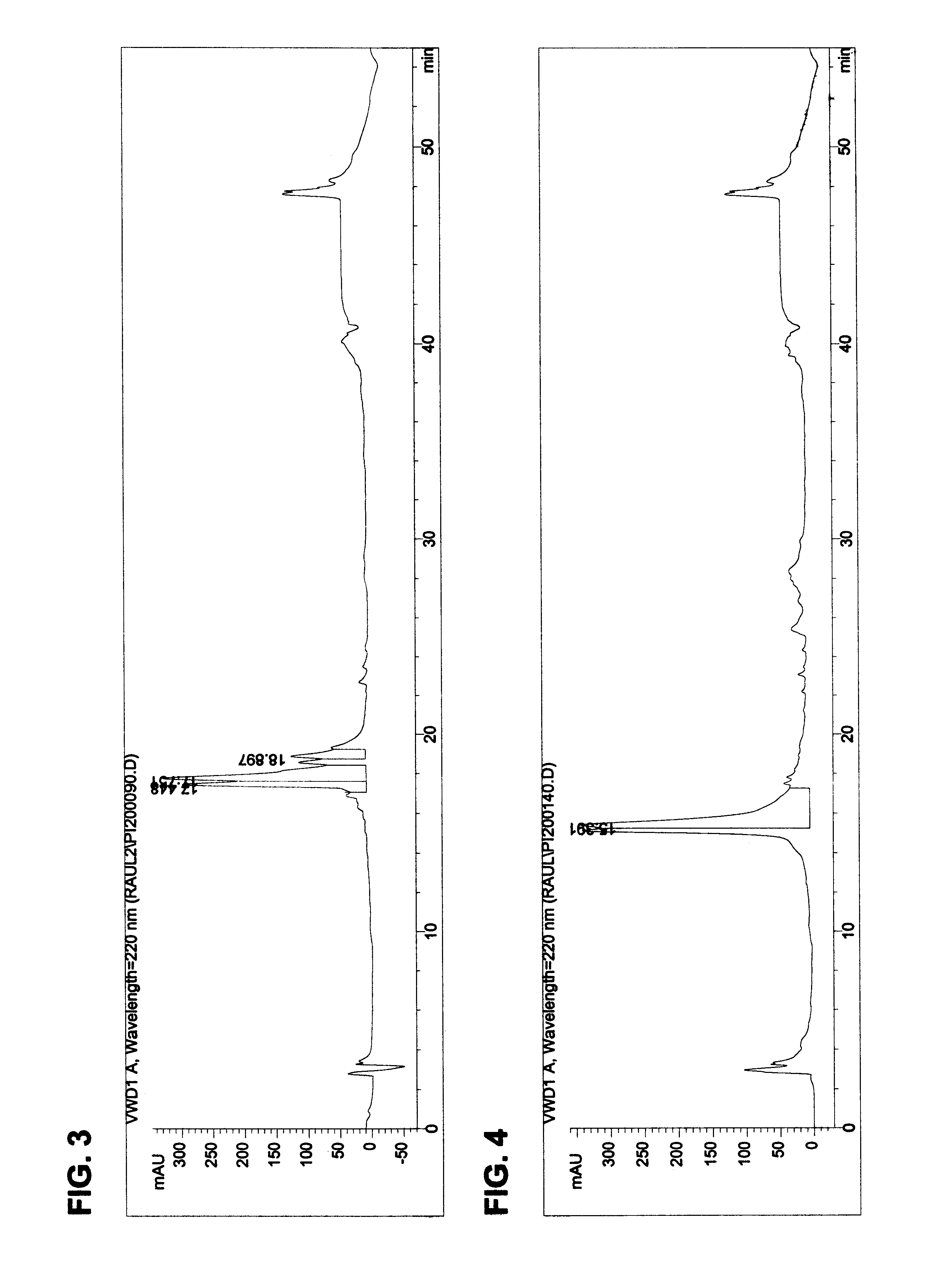
The invention provides processes of preparing 3-substituted 1-(chloromethyl)-1,2-dihydro-3H-[ring fused indol-5-yl(amine-derived)] compounds of formula (I) and its analogues, or a physiologically functional derivative thereof, (I), wherein A and B together may represent a fused optionally substituted benezene, naphthalene, pyridine, furan or a pyrrole ring, where the optional substituents are represented by Y; X is halogen or OSO2R, and W is selected from NO2, NHOH, N(R3)2NHR3, NHCO2R3, N(phthaloyl) or NH2, or W is further selected from the group (a), wherein J is selected from OH or R, and P is a group which is a substrate suitable for a nitroreductase or carboxypeptidase enzyme. The invention is also directed to the use of compounds of formula (I) prepared by the processes of the invention as cytotoxins for cancer therapy and as prodrugs for gene-directed enzyme-prodrug therapy (GDEPT) and antibody-directed enzyme-prodrug therapy (ADEPT).
Owner:AUCKLAND UNISERVICES LTD
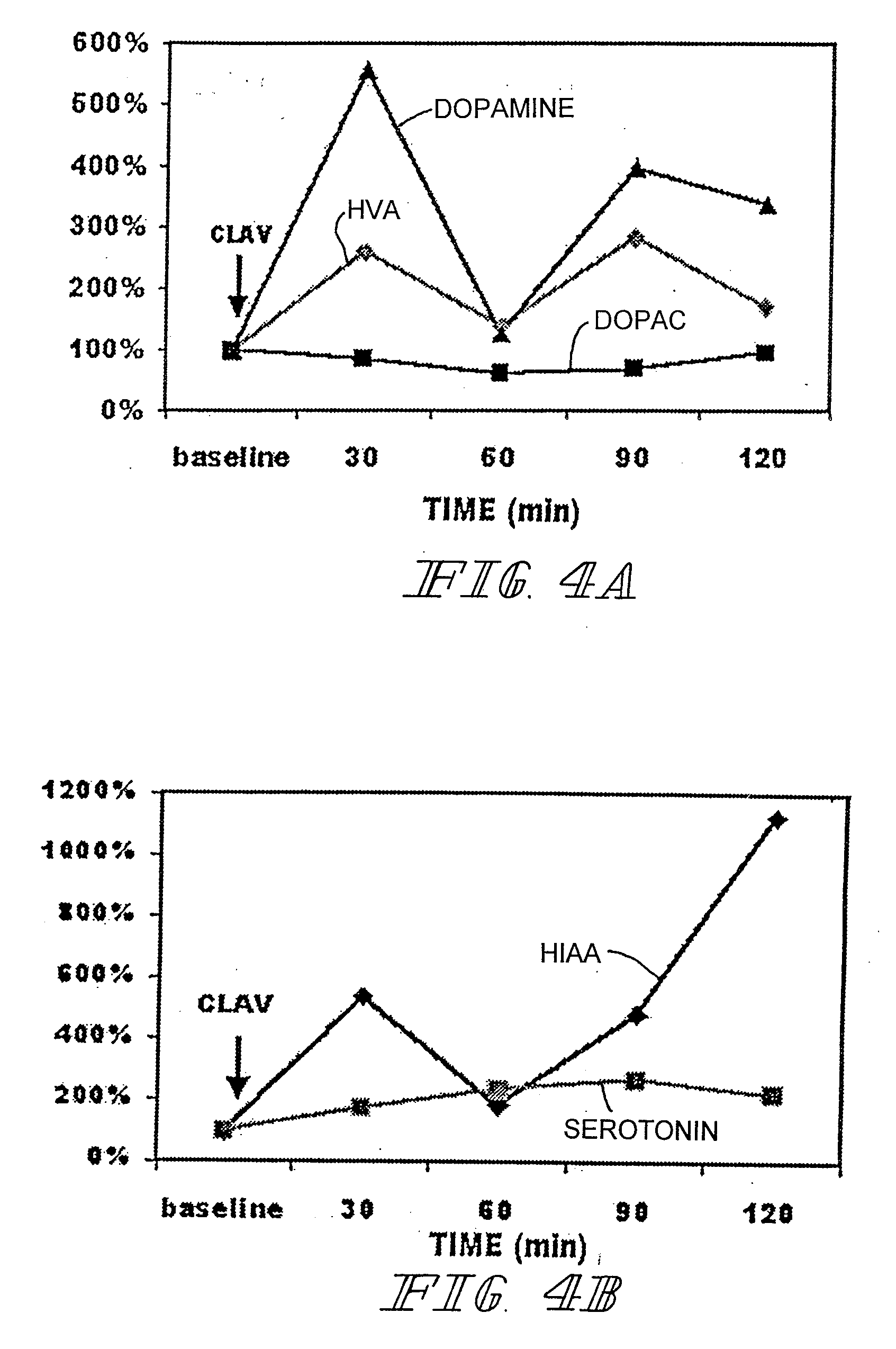
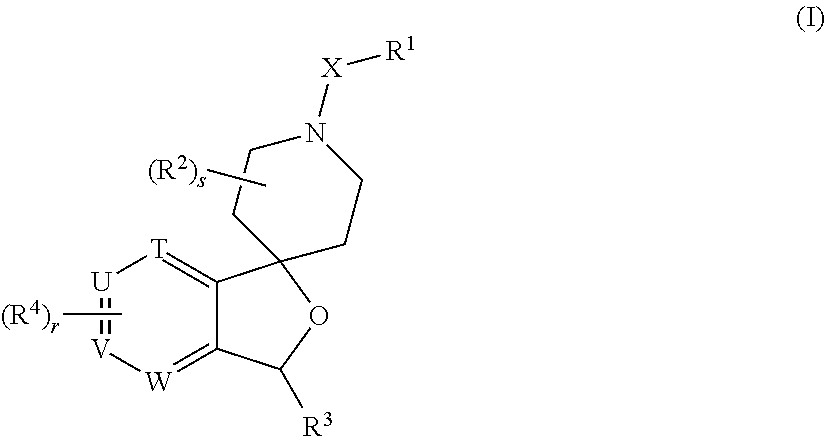
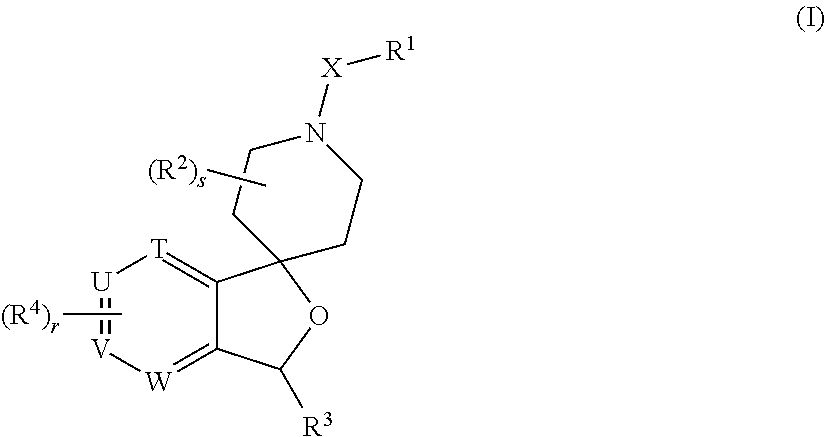
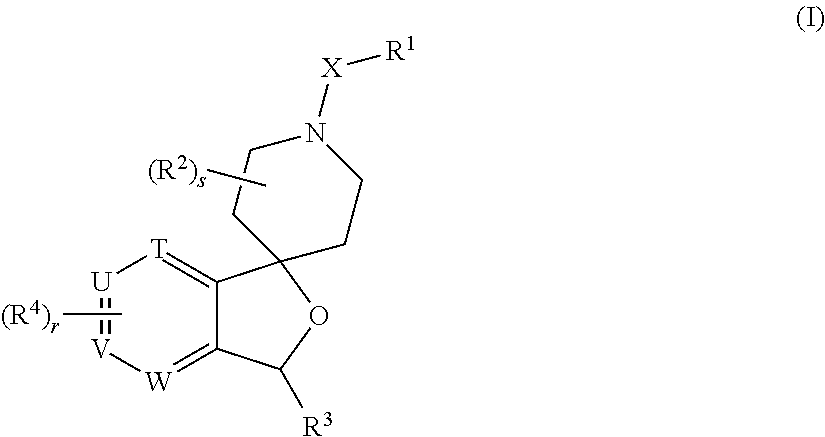
Spiropiperidine prolylcarboxypeptidase inhibitors
Compounds of structural formula (I) are inhibitors of prolylcarboxypeptidase (PrCP). The compounds of the present invention are useful for the prevention and treatment of conditions related to enzymatic activity of PrCP such as abnormal metabolism, including obesity; diabetes; metabolic syndrome; obesity related disorders; and diabetes related disorders.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Complete feed for young stichopus japonicas cultivation
InactiveCN103027202AMeeting nutritional needsPromote growthAnimal feeding stuffIsomaltooligosaccharideRhodotorula
The invention relates to a complete feed for young stichopus japonicas cultivation, which is characterized by consisting of the following components by weight percent: 25% of gulfweed powder, 20% of sargassum thunbergii powder, 25% of kelp powder, 25% of scallop skirt, 2.5% of shrimp powder and 2.5% of soybean flour. The additive comprises the following components with the suitable weights: dried yeast, rhodotorula benthica, VA (Vitamin A), VB1 (Vitamin B1), VB2 (Vitamin B2), VB12 (Vitamin B12), VB6 (Vitamin B6), VE (Vitamin E), VD (Vitamin D), VK (Vitamin K), VC (Vitamin C), glycine, calcium pantothenate, alanine, nicotinic acid, lysine, methionine, arginine, threonine, xylooligosaccharide, isomaltose hypgather, mannan oligosaccharide, beta-glucan, amylase, lipase, protease, carboxypeptidase, cellulose and erepsin. The added amount of the sea mud is 7.5 kg (on a dry weight basis of the sea mud) / 500 g of young stichopus japonicas basal feed. The problem that the high yield of artificial cultivation of young stichopus japonicas is restricted by the stichopus japonicas feed on the market can be solved.
Owner:QINGDAO HENGSHENGYUAN ECOLOGICAL AGRI
Whey protein selenium-enriched biological feed and application thereof
InactiveCN109430526APromote lactationHas the effect of invigorating bloodFood processingAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyWHOLE ANIMAL
The present invention relates to the technical field of feed processing and particularly relates to a whey protein selenium-enriched biological feed and an application thereof. According to the research of the applicant, a lactic acid bacterium source selenium is prepared by chelating lactic acid bacteria with selenium element, can maintain a relatively high activity in animal gastric juice of high acidity, and can protect intestinal tracts of animals. At the same time, milk discharged from animal mammary glands is the highest part of selenium conversion in the whole animal body, therefore, the present application studies to develop the selenium-enriched feed. The feed consists of whey protein powder, bean powder, chequer-shaped indocalamus leaves, safflower carthamus, an enzyme preparation and a lactic acid bacterium source organic selenium solution, wherein the bean powder is composed of soybean powder, black bean powder and broad bean powder; and the enzyme preparation is composed of complex protease and carboxypeptidase. The whey protein selenium-enriched biological feed is reasonable in components, has a good synergistic effect, can effectively protect intestinal and mammary gland functions of animals, and improves conversion rate of selenium in mammals.
Owner:广西壮佳霖农业投资有限公司
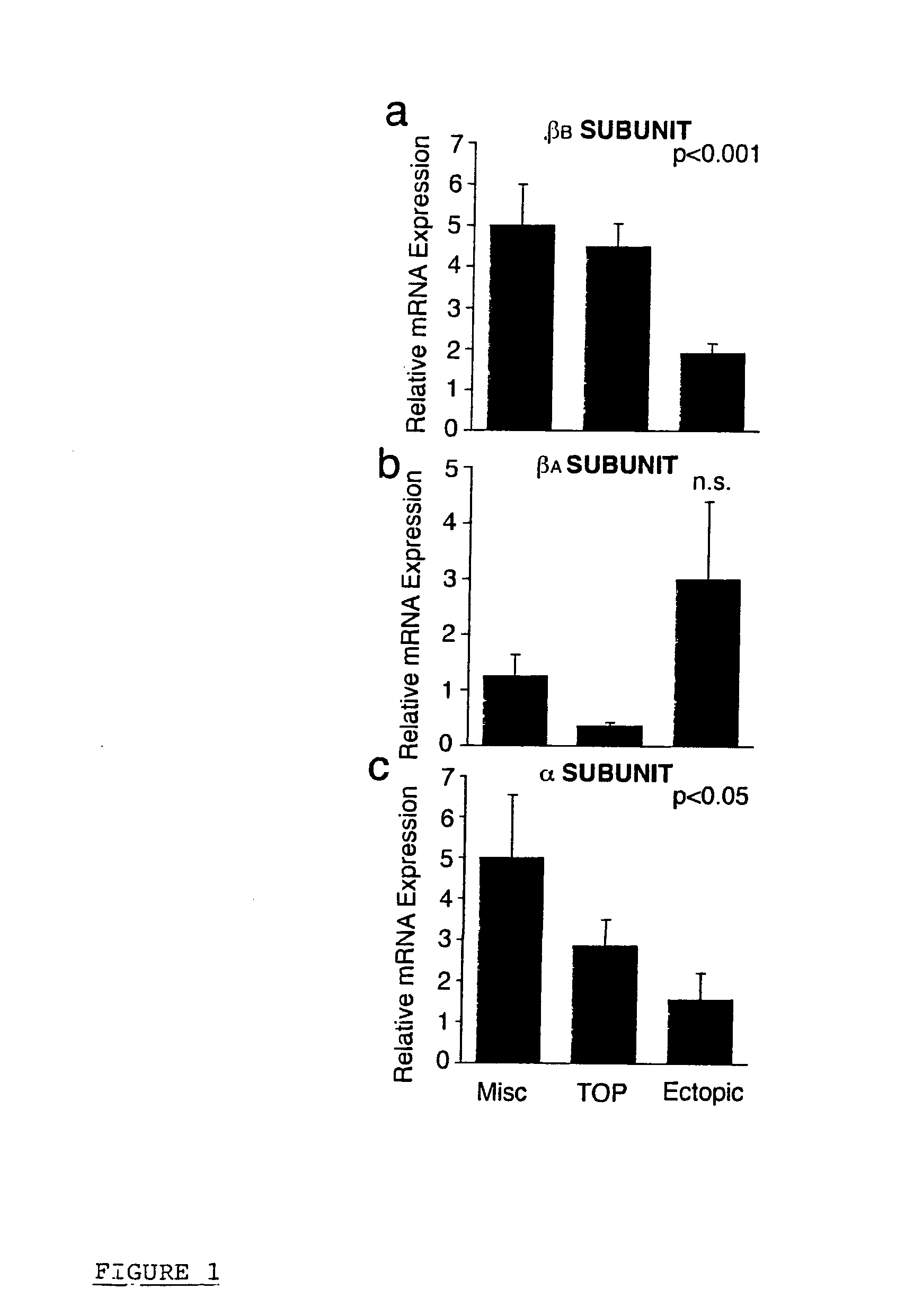
Identification of ectopic pregnancies
InactiveUS20100285974A1Reliable methodRapidly and accurately identifyingMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningACTIVIN BETA-BEctopic pregnancy
The present invention concerns methods of identifying extra-uterine (or ectopic) pregnancies and involves the screening of samples for the presence of certain molecules now known to be markers of extra-uterine pregnancies. The present invention provides a method for identifying an ectopic pregnancy, said method comprising the steps of: (a) providing a sample from a subject; (b) identifying a level of one or more of: (i) inhibin / activin BETA b subunit gene (ii) activin B (iii) cysteine-rich secretory protein 3 (CRISP-3); and / or (iv) carboxypeptidase-B1 (CPB1) (v) SLP1 (vi) elafin (vii) prolactin in the sample, wherein the level of inhibin / activin BETA b subunit gene, activin B, CRISP-3, SLP1, elafin, prolactin and / or CPB1 is associated with, or indicative of, an ectopic pregnancy.
Owner:THE UNIV OF EDINBURGH
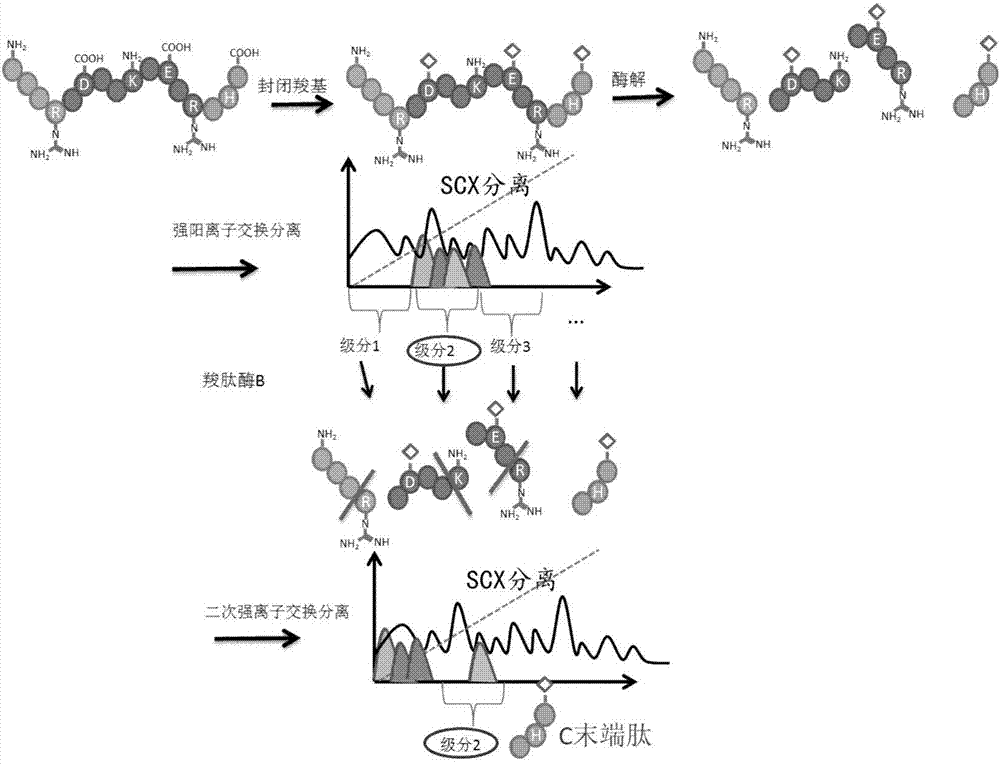
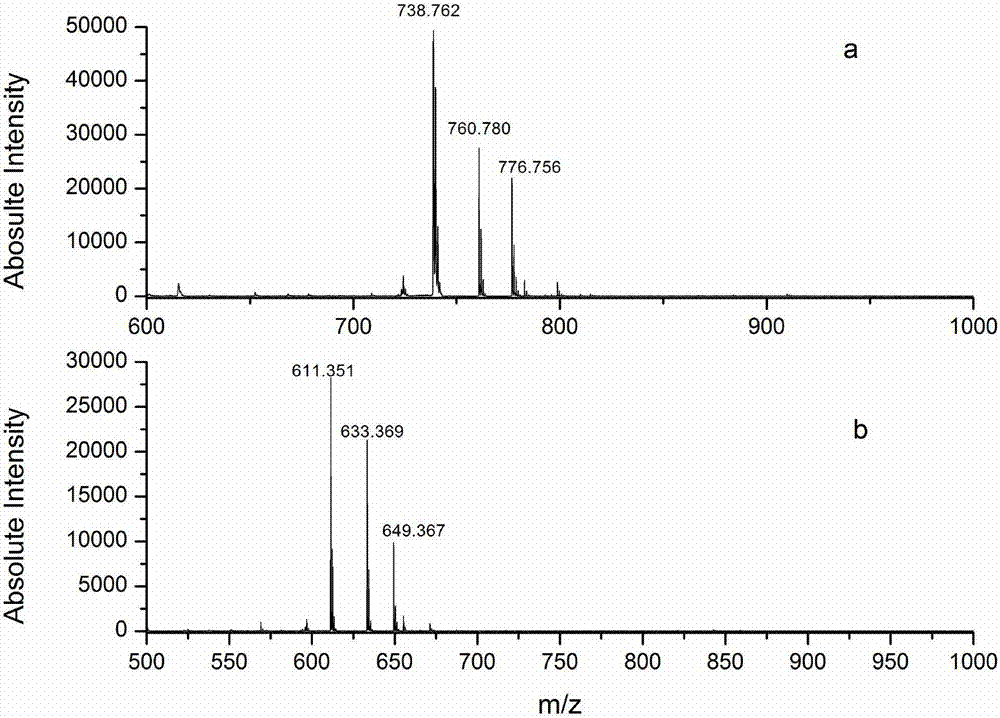
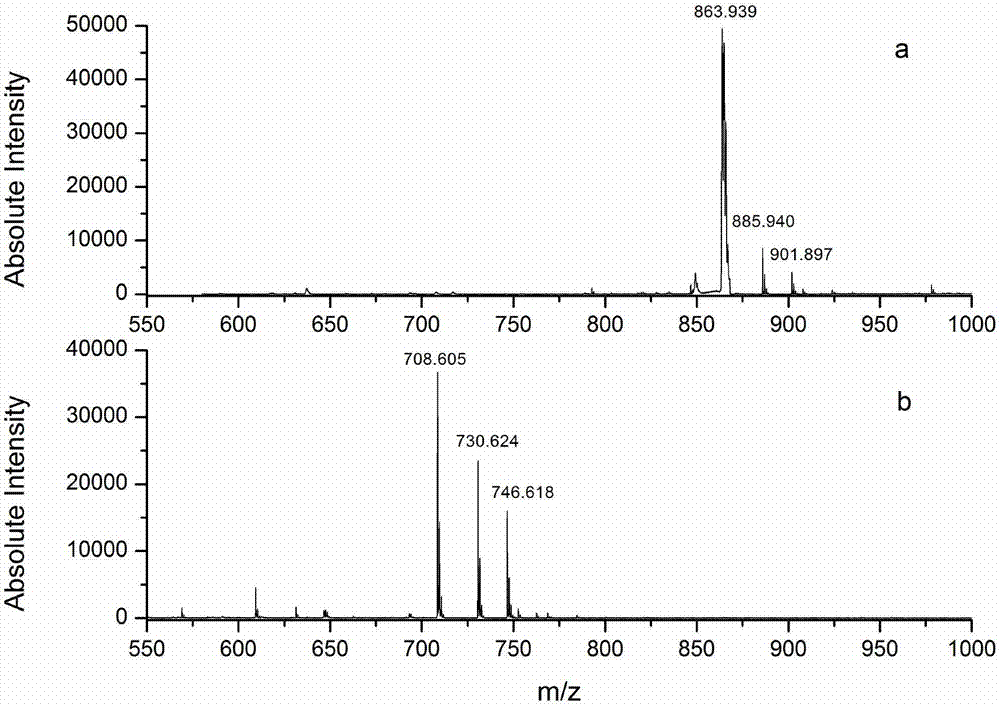
Protein C-terminal enriching method based on carboxypeptidase and strong cation exchange chromatography
InactiveCN107384998AImprove reaction efficiencyHigh selectivityPeptide preparation methodsFermentationChromatographic separationEnzyme digestion
The invention relates to a protein C-terminal enriching method based on a carboxypeptidase and strong cation exchange chromatography. The protein C-terminal enriching method comprises the steps of closing of the protein free carboxyl, enzyme digestion of protein alkaline loci, separation by adopting the ion exchange chromatography and cutting of peptide fragmental carboxyl terminal alkaline amino acid. A protein sample closes the free carboxyl at the tail end and a side chain of C at a protein level firstly, then enzyme digestion is conducted on the protein alkaline loci so as to generate a middle peptide fragment, and the carboxyl terminal is the alkaline amino acid; grading is conducted on an enzyme-digested product by adopting the ion exchange chromatography to obtain a plurality of fractions; and finally cutting is conducted on the alkaline amino acid of the carboxyl terminal of the middle peptide fragment, secondary ion exchange chromatographic separation is conducted on each friction so as to exclude the middle peptide fragment which shifts in the retention time, and thus the C terminal peptide fragment of the protein is obtained. The protein C-terminal enriching method has the advantages that the enzyme digestion efficiency, the removal efficiency and the enriching efficiency are high, multiple enzymes can be adopted to conduct enzyme digestion, and the coverage degree of identification of the C terminal is improved.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of making activated carboxypeptidases
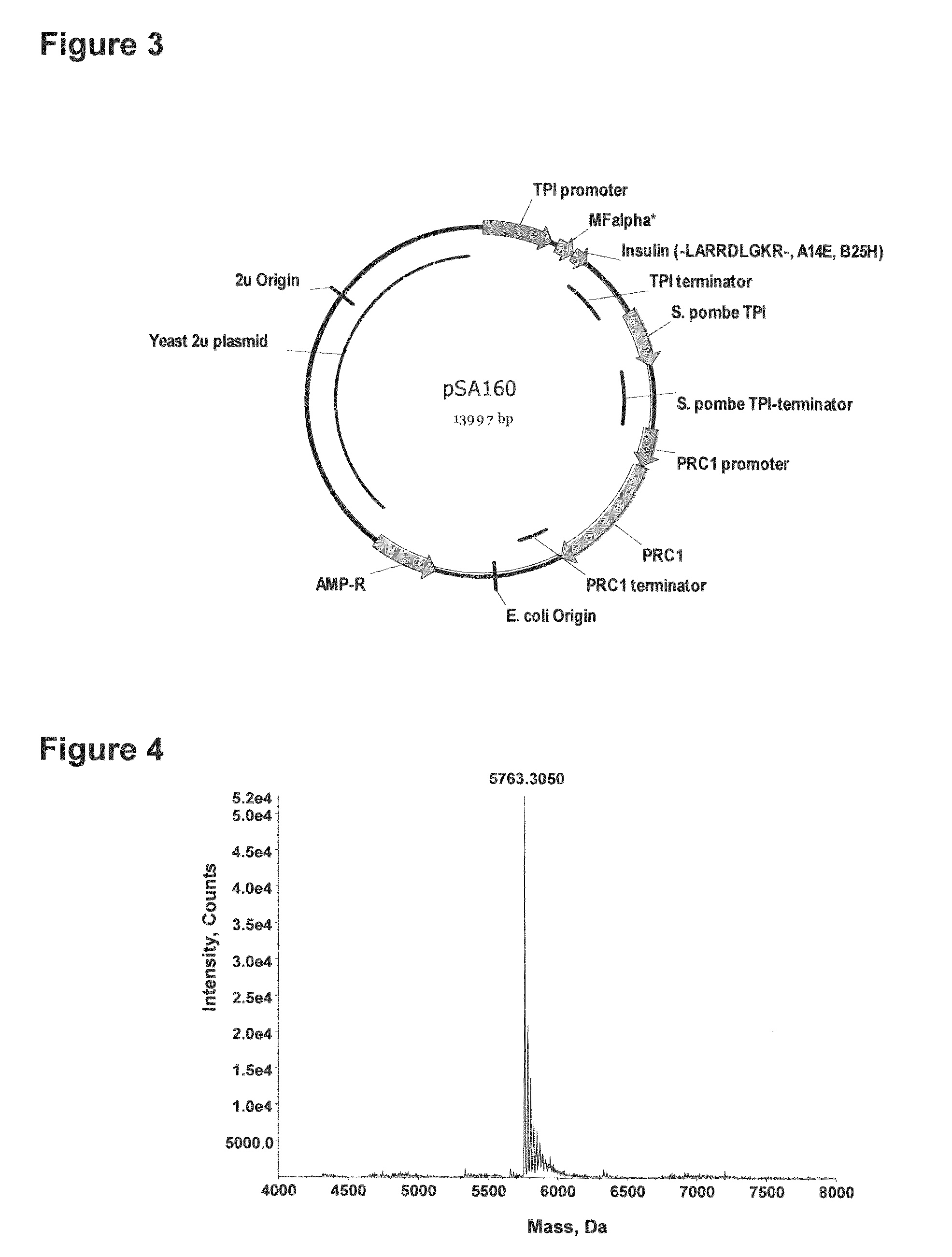
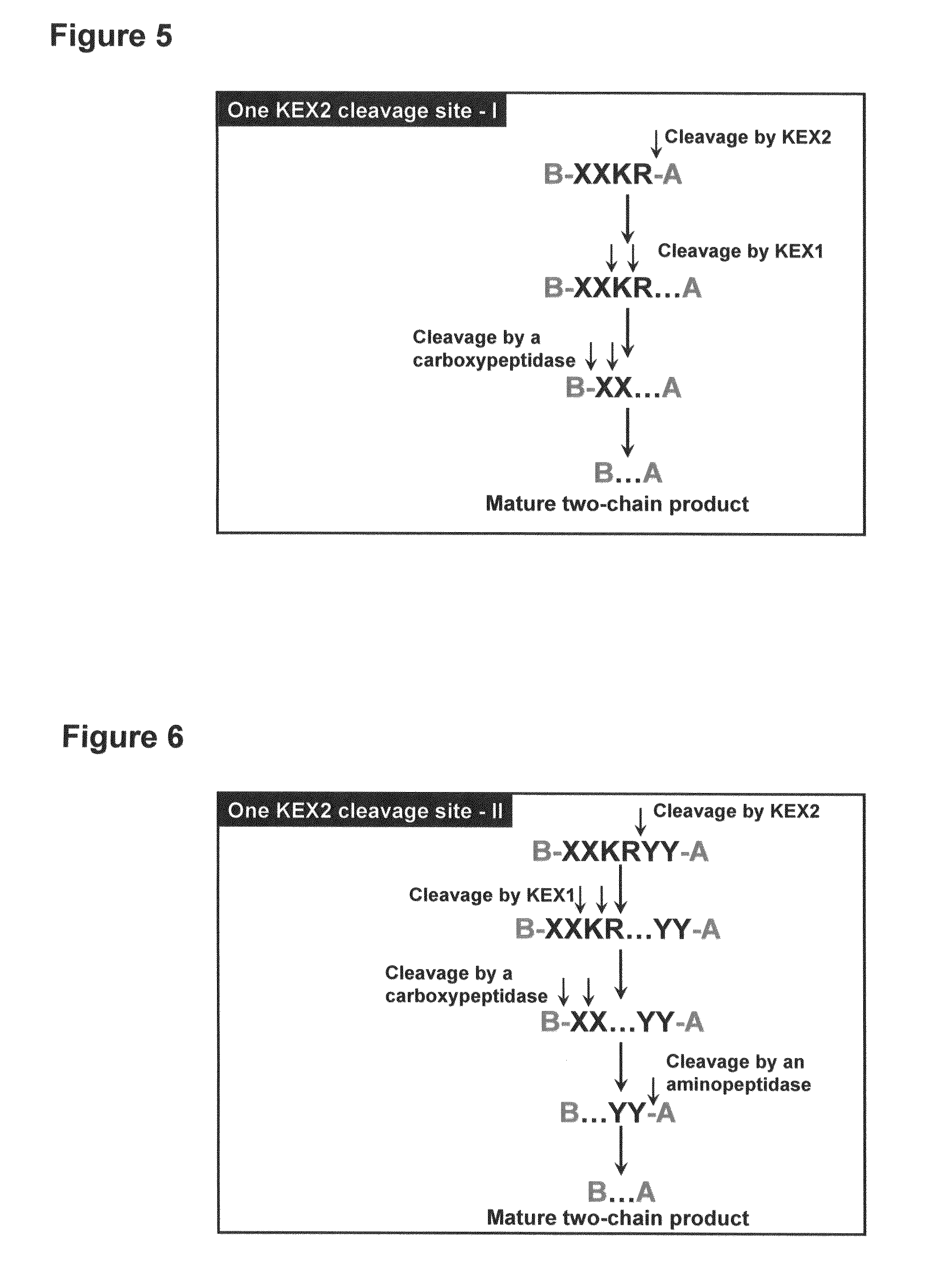
The invention is related to a method for making an activated carboxypeptidase in a fungi cell comprising introducing a DNA sequence encoding a proform of the carboxypeptidase wherein a Kex2 site has been introduced in the prosequence of the carboxypeptidase, culturing the fungi cell under conditions suitable for expression of the procarboxypeptidase and cleaving off the prosequence within the cell to liberate the free active form of the carboxypeptidase. The invention is also related to methods for making mature human insulin and human insulin analogues by use of the activated carboxypeptidase enzyme.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Preparation and application of extremely high temperature resistant non-gelatinization egg liquid
The present invention discloses a preparation technology of extremely high temperature heating resistant egg liquid. Egg liquid is subjected to a moderate enzyme hydrolysis and an appropriate amount of sugar is combined, and mixture is subjected to a Maillard reaction to obtain the sterilized heat resistant egg liquid. The prepared product by the method has excellent high temperature treatment resistant properties. The product improves gelatinization properties and flavor of the egg liquid and the preparation technology is used for the products of drink, baking sauce materials, etc. needing treatments at a temperature higher than 100 DEG C and having relatively high requirements for the flavor. Advantages are as follows: carboxypeptidase is used to conduct the enzymatic hydrolysis, bitterness of enzymatic hydrolysate is inhibited, and neutral protease is combined to speed up an enzyme reaction rate and improve reaction efficiencies. A moderate hydrolysis degree is set by experiments and evaluations, special functions of the egg liquid are preserved, a heat treatment is combined with screening of combined sugar to realize the selective Maillard reaction to promote a formation of the good flavor, and thus the egg liquid product matching heating strength of the drink or baking sauces is obtained, scientific and practical in technology designs, and good in product performances.
Owner:苏州欧福蛋业股份有限公司
Method for preparing whey beer
InactiveCN102181331ARich in nutrientsMeet the concentration requirementsBeer fermentationMicroorganism based processesFermentationAmino acid
The invention discloses a method for preparing whey beer, comprising the following steps of: A, centrifugation; B, whey sterilizing and cooling; C, nanofiltration, namely carrying out circulating nanofiltration on the whey obtained by the step B by adopting a sanitary DurasanDK8038C nanofiltration membrane of the GE (General Electric Co.) company in America until the lactose concentration in the whey is 7-11%; D protease enzymolysis, namely carrying out enzymolysis on the concentrated whey obtained by the step C by adopting 51FP endonuclease-exonuclease mixed protease produced by Danisco company and CPJ carboxypeptidase produced by DSM (Dutch State Mines) company; E, burdening, namely mixing the concentrated and enzymolyzed whey obtained by the step D as well as wort and hop extract in proportion and stirring to be uniform; F feed liquid sterilizing and cooling; G, fermenting, namely adding a fermenting agent into the sterilized feed liquid obtained by the step F to carry out fermentation; H, post fermentation; and I, filtering and filtering. In the invention, a byproduct, namely fresh whey in the cheese manufacturing industry is taken as a raw material, and the whey beer is prepared by adopting a nanofiltration technology and combining with a modern biological engineering technology; the matching ratio of the raw materials is optimized, the technological parameters are improved, and the obtained whey beer has cool bouquet and elegant frankincense; meanwhile, the whey beer is rich in nutrient components such as amino acid, minerals and vitamins and the like and realizes high-efficiency recycling on the whey.
Owner:王玉良
Inhibitors of fibroproliferative disorders and cancer
PendingUS20170190778A1Inhibit TGFβReduce functionPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDiseaseReceptor
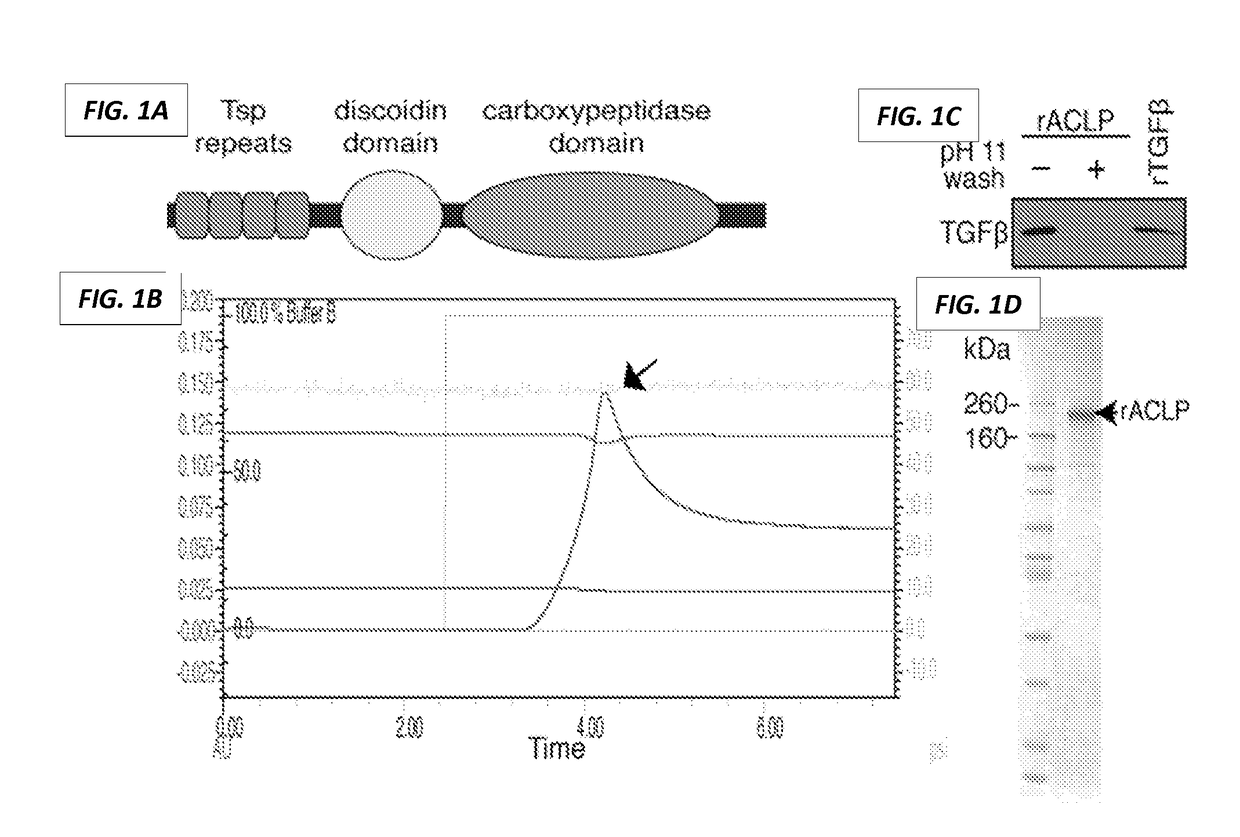
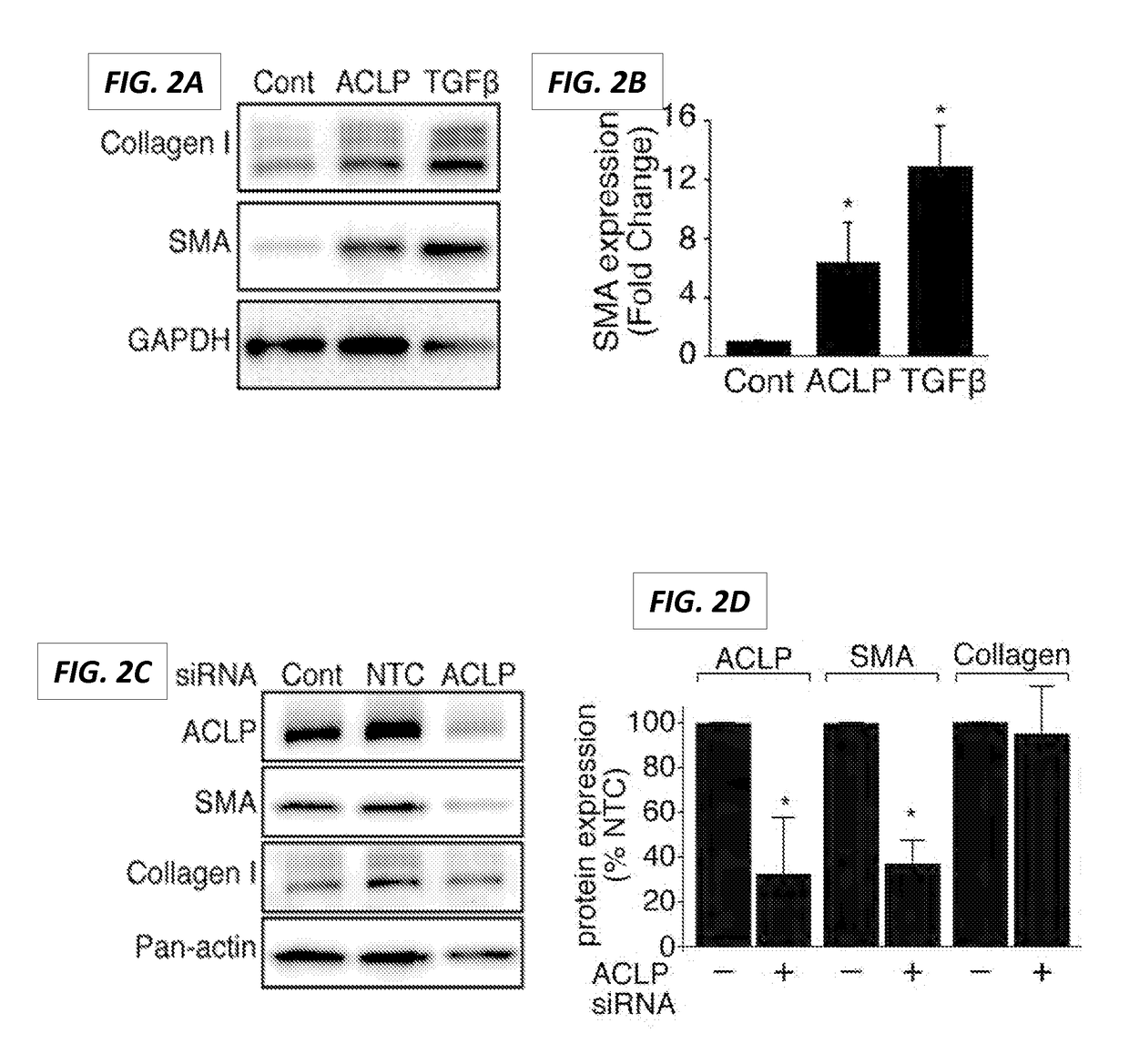
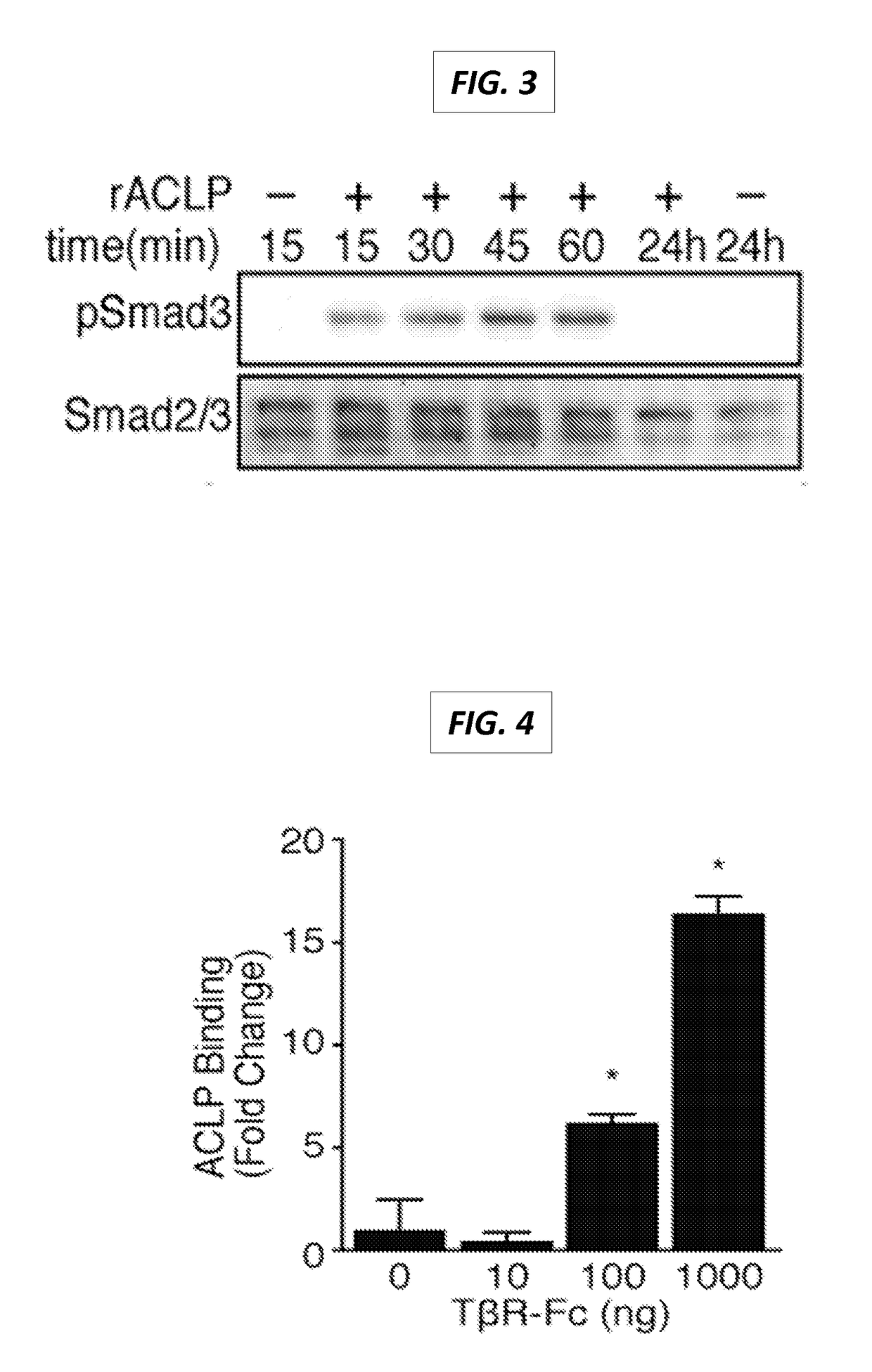
The present invention generally relates to the field of treatment of fibroproliferative diseases and disorders and cancer. Embodiments of the present invention generally relate to compositions, methods and kits comprising an inhibitor of a portion of the N-terminal pro-fibrotic domain (PFD) of Aortic Carboxypeptidase-Like Protein (ACLP), and in some embodiments, in combination with an inhibitor of the discoidin (DS) domain of ACLP, for use in methods for the treatment of fibroproliferative diseases and cancer, and inhibition of ACLP-mediated activation of a member of the TGFβ receptor superfamily.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Processes for preparing 3-substituted 1-(chloromethyl)-1,2-dihydro-3H-[ring fused indol-5-yl-(amine-derived)] compounds and analogues thereof, and to products obtained therefrom
The invention provides processes of preparing 3-substituted 1-(chloromethyl)- 1,2-dihydro-3H-[ring fused indol-5-yl(amine-derived)] compounds of formula (I) and its analogues, or a physiologically functional derivative thereof, (I), wherein A and B together may represent a fused optionally substituted benezene, naphthalene, pyridine, furan or a pyrrole ring, where the optional substituents are represented by Y; X is halogen or OSO2R, and W is selected from NO2, NHOH, N(R3)2NHR3, NHCO2R3, N(phthaloyl) or NH2, or W is further selected from the group (a), wherein J is selected from OH or H, and P is a group which is a substrate suitable for a nitroreductase or carboxypeptidase enzyme. The invention is also directed to the use of compounds of formula (I) prepared by the processes of the invention as cytotoxins for cancer therapy and as prodrugs for gene-directed enzyme-prodrug therapy (GDEPT) and antibody-directed enzyme-prodrug theraphy (ADEPT).
Owner:AUCKLAND UNISERVICES LTD
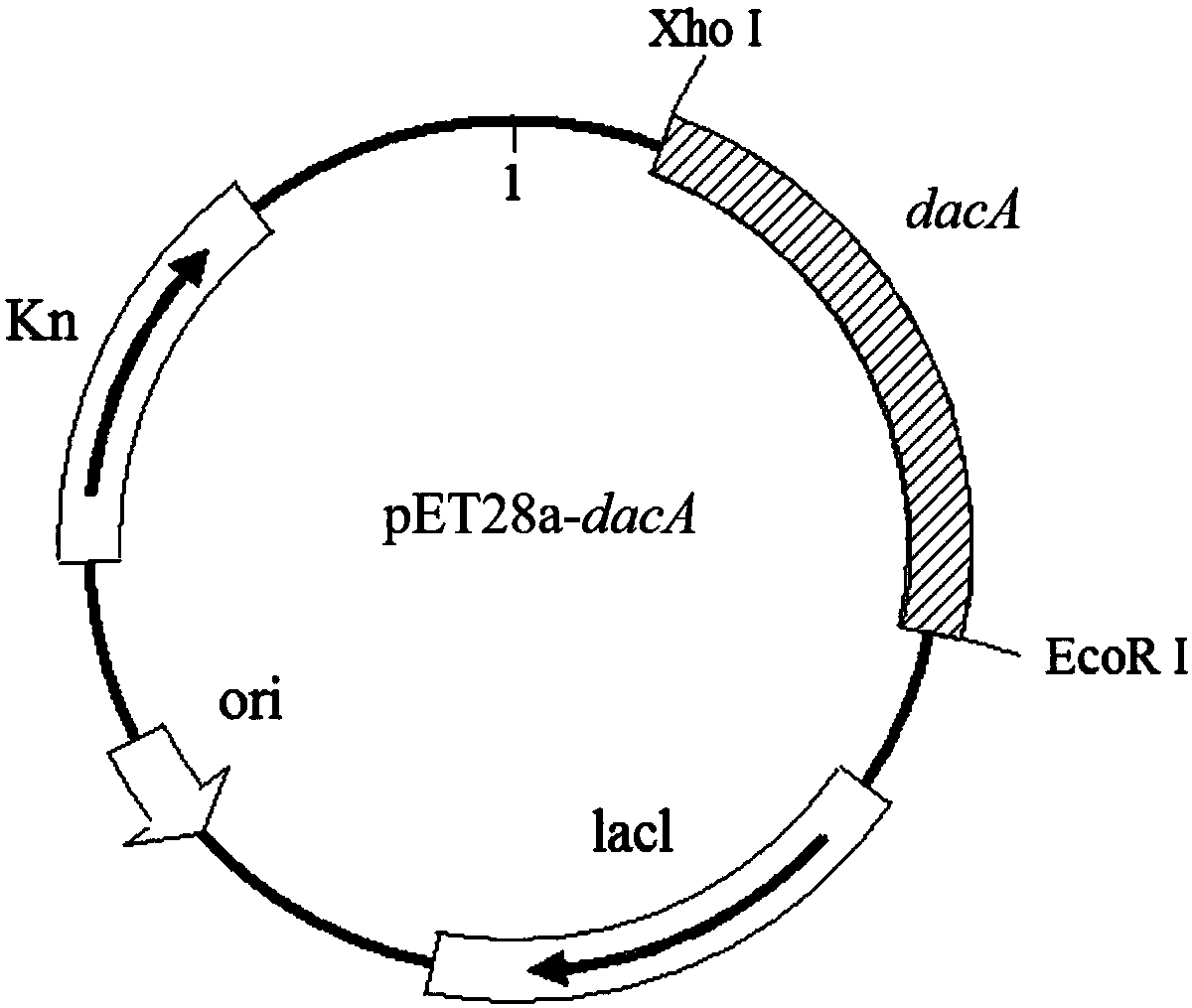
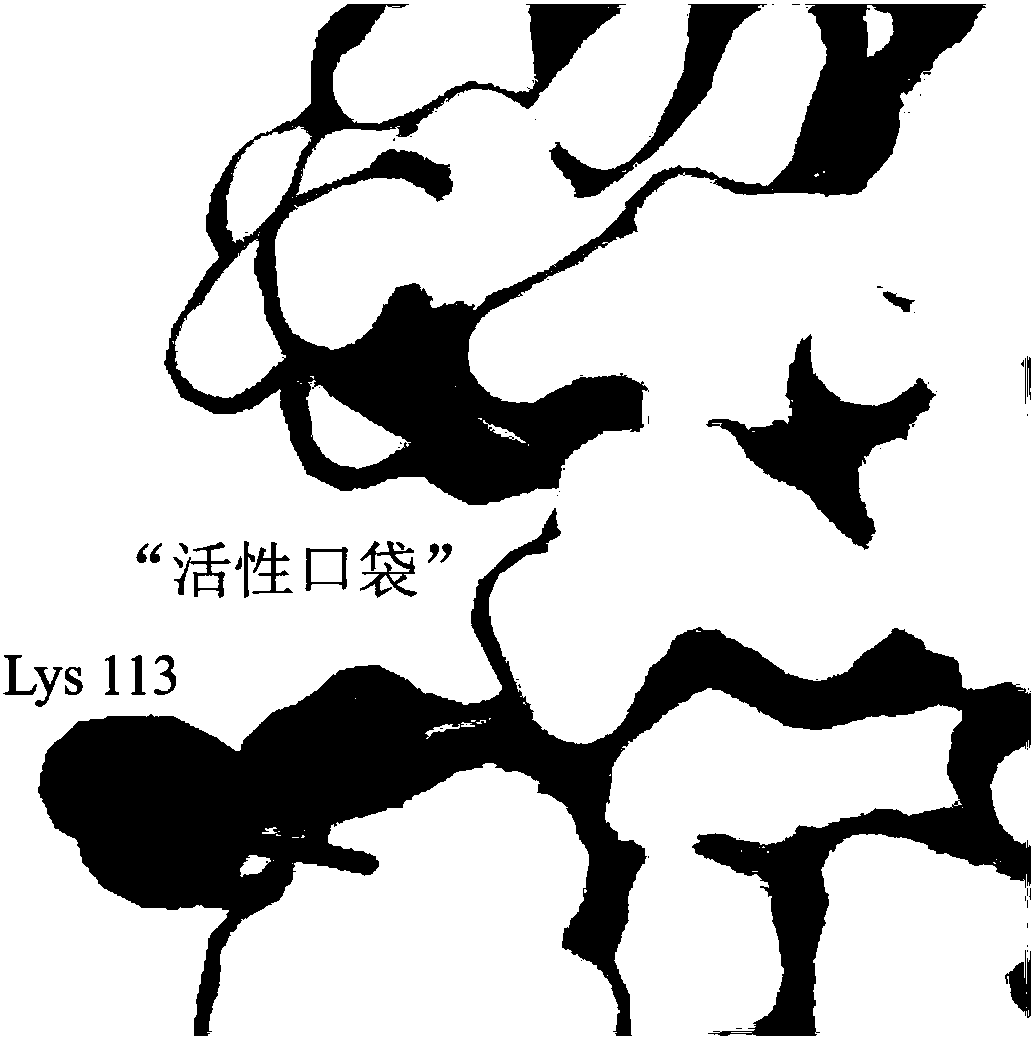
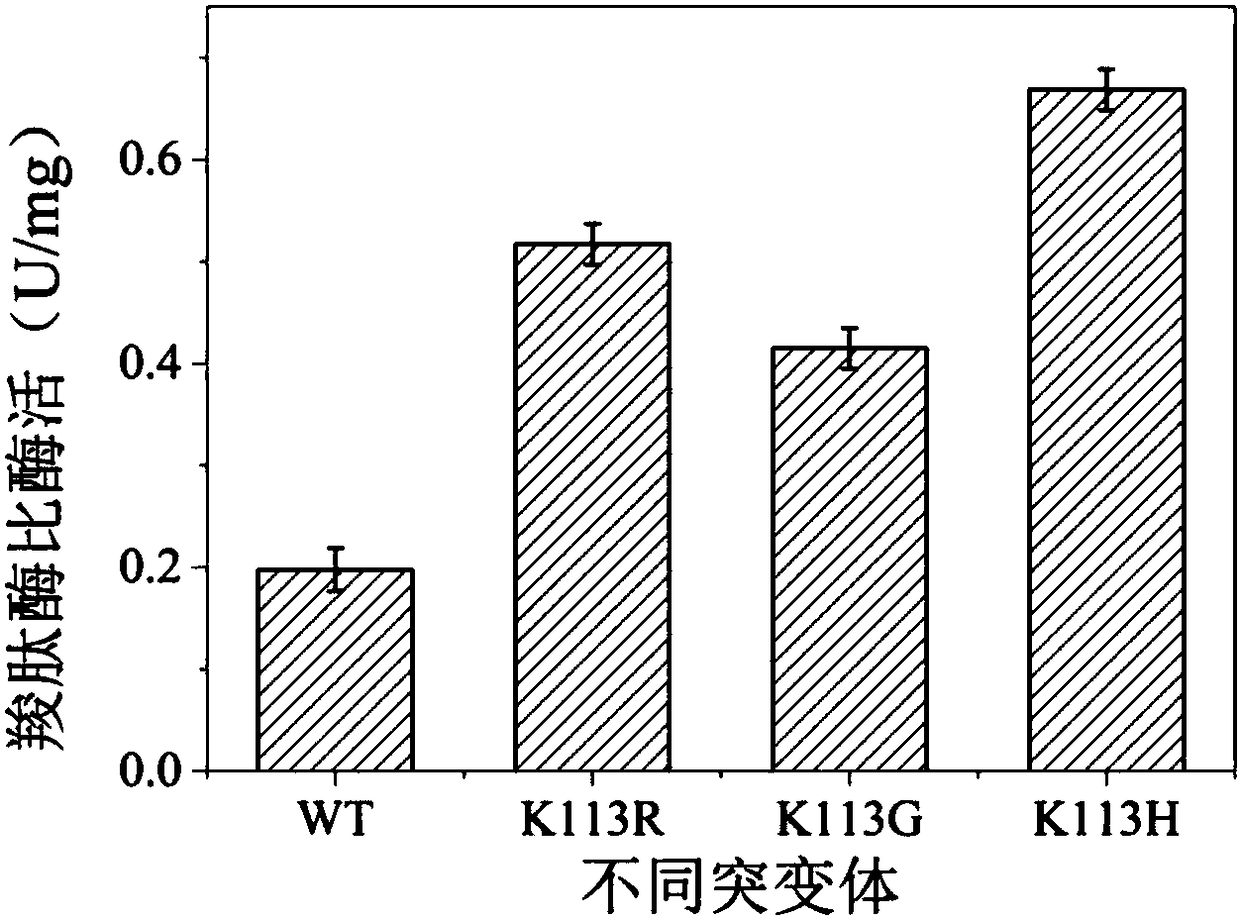
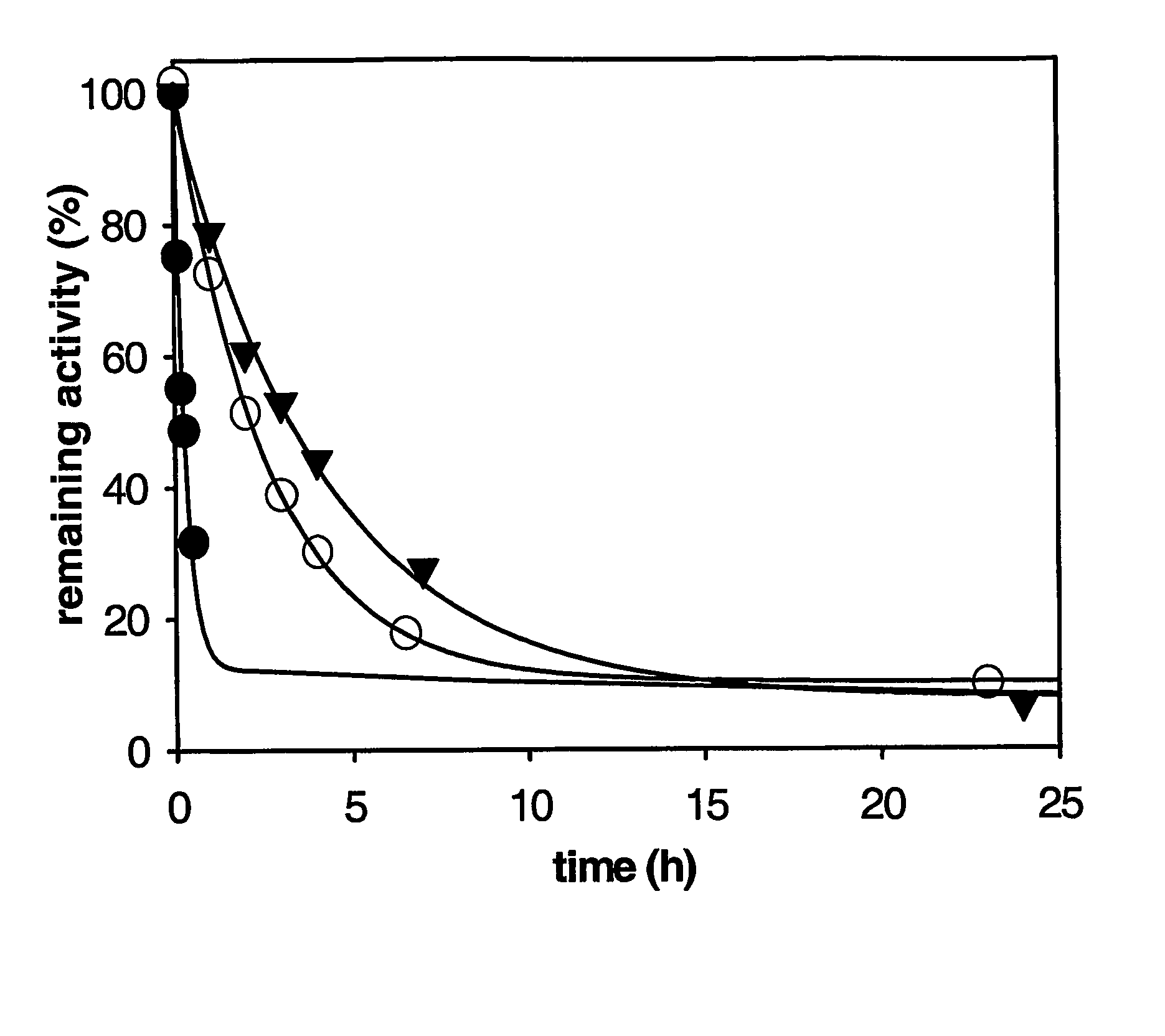
D,D-carboxypeptidase DacA mutant with improved catalysis efficiency and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108410845AIncreased secretory expression levelsShorten retrofit timeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliExocytosis
The invention discloses a D,D-carboxypeptidase DacA mutant with improved catalysis efficiency and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the fields of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. D,D-carboxypeptidase DacA from Escherichia coli BL21 is used as a female parent, key sites and a mutation manner are determined based on enzyme structure analysis, and the DacA mutant with improved catalysis efficiency is obtained through fixed point mutation by using a molecular biological technology. Under the modification condition, the catalysis efficiency constant k<cat> of E.coli D,D-carboxypeptidase DacA mutant K113G is improved at most, from 6543.4s<-1> to 9428.1s<-1>. Due to adoption of the method, the catalysis efficiency of the D,D-carboxypeptidase DacA is improved remarkably, layinga foundation for the application of metabolizing and modifying E.coli to improve exocytosis level and the like. The method has an important guiding significance in property modification of other enzymes.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Carboxypertidase U (Cpu) Mutants
InactiveUS20080175834A1From normal temperature solutionsSugar derivativesCarboxypeptidase UWild type
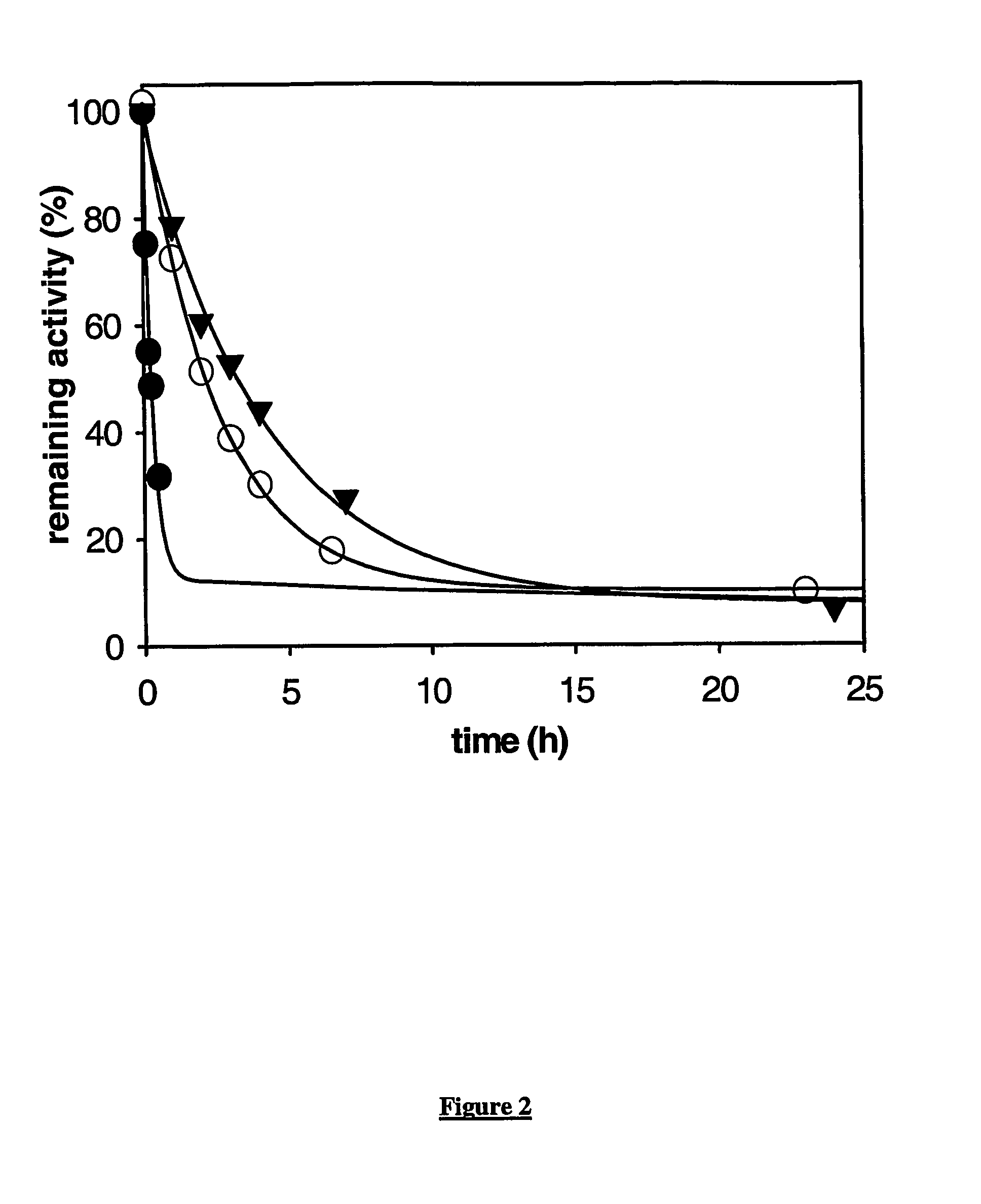
This invention relates to mutant forms of carboxypeptidase U with increased thermal stability relative to wild-type. In addition to the individual thermal stabilizing mutations identified (at positions 166, 204, 219, 230, 251, 315), the inventors have identified a region (S327-H357) that is crucial to the stability of CPU. The invention relates to nucleic acid encoding such mutant forms and the polypeptides encoded thereby. The invention also relates to methods and materials for making CPU mutants with increased thermal stability relative to wild-type and their use, for example to produce crystals of CPU or proCPU for 3-dimensional structure determination, or in therapy.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com










![Processes for preparing 3-substituted 1-(chloromethyl)-1,2-dihydro-3h-[ring fused indol-5-yl-(amine- derived)] compounds and analogues thereof, and to products obtained therefrom Processes for preparing 3-substituted 1-(chloromethyl)-1,2-dihydro-3h-[ring fused indol-5-yl-(amine- derived)] compounds and analogues thereof, and to products obtained therefrom](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/26db9024-a8dc-4272-b048-c1ff85eccab6/US20050148651A1-20050707-C00001.png)
![Processes for preparing 3-substituted 1-(chloromethyl)-1,2-dihydro-3h-[ring fused indol-5-yl-(amine- derived)] compounds and analogues thereof, and to products obtained therefrom Processes for preparing 3-substituted 1-(chloromethyl)-1,2-dihydro-3h-[ring fused indol-5-yl-(amine- derived)] compounds and analogues thereof, and to products obtained therefrom](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/26db9024-a8dc-4272-b048-c1ff85eccab6/US20050148651A1-20050707-C00002.png)
![Processes for preparing 3-substituted 1-(chloromethyl)-1,2-dihydro-3h-[ring fused indol-5-yl-(amine- derived)] compounds and analogues thereof, and to products obtained therefrom Processes for preparing 3-substituted 1-(chloromethyl)-1,2-dihydro-3h-[ring fused indol-5-yl-(amine- derived)] compounds and analogues thereof, and to products obtained therefrom](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/26db9024-a8dc-4272-b048-c1ff85eccab6/US20050148651A1-20050707-C00003.png)


![Processes for preparing 3-substituted 1-(chloromethyl)-1,2-dihydro-3H-[ring fused indol-5-yl-(amine-derived)] compounds and analogues thereof, and to products obtained therefrom Processes for preparing 3-substituted 1-(chloromethyl)-1,2-dihydro-3H-[ring fused indol-5-yl-(amine-derived)] compounds and analogues thereof, and to products obtained therefrom](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/6119a5a3-00db-46ba-a663-a94f6503fc7e/US07235578-20070626-C00001.png)
![Processes for preparing 3-substituted 1-(chloromethyl)-1,2-dihydro-3H-[ring fused indol-5-yl-(amine-derived)] compounds and analogues thereof, and to products obtained therefrom Processes for preparing 3-substituted 1-(chloromethyl)-1,2-dihydro-3H-[ring fused indol-5-yl-(amine-derived)] compounds and analogues thereof, and to products obtained therefrom](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/6119a5a3-00db-46ba-a663-a94f6503fc7e/US07235578-20070626-C00002.png)
![Processes for preparing 3-substituted 1-(chloromethyl)-1,2-dihydro-3H-[ring fused indol-5-yl-(amine-derived)] compounds and analogues thereof, and to products obtained therefrom Processes for preparing 3-substituted 1-(chloromethyl)-1,2-dihydro-3H-[ring fused indol-5-yl-(amine-derived)] compounds and analogues thereof, and to products obtained therefrom](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/6119a5a3-00db-46ba-a663-a94f6503fc7e/US07235578-20070626-C00003.png)