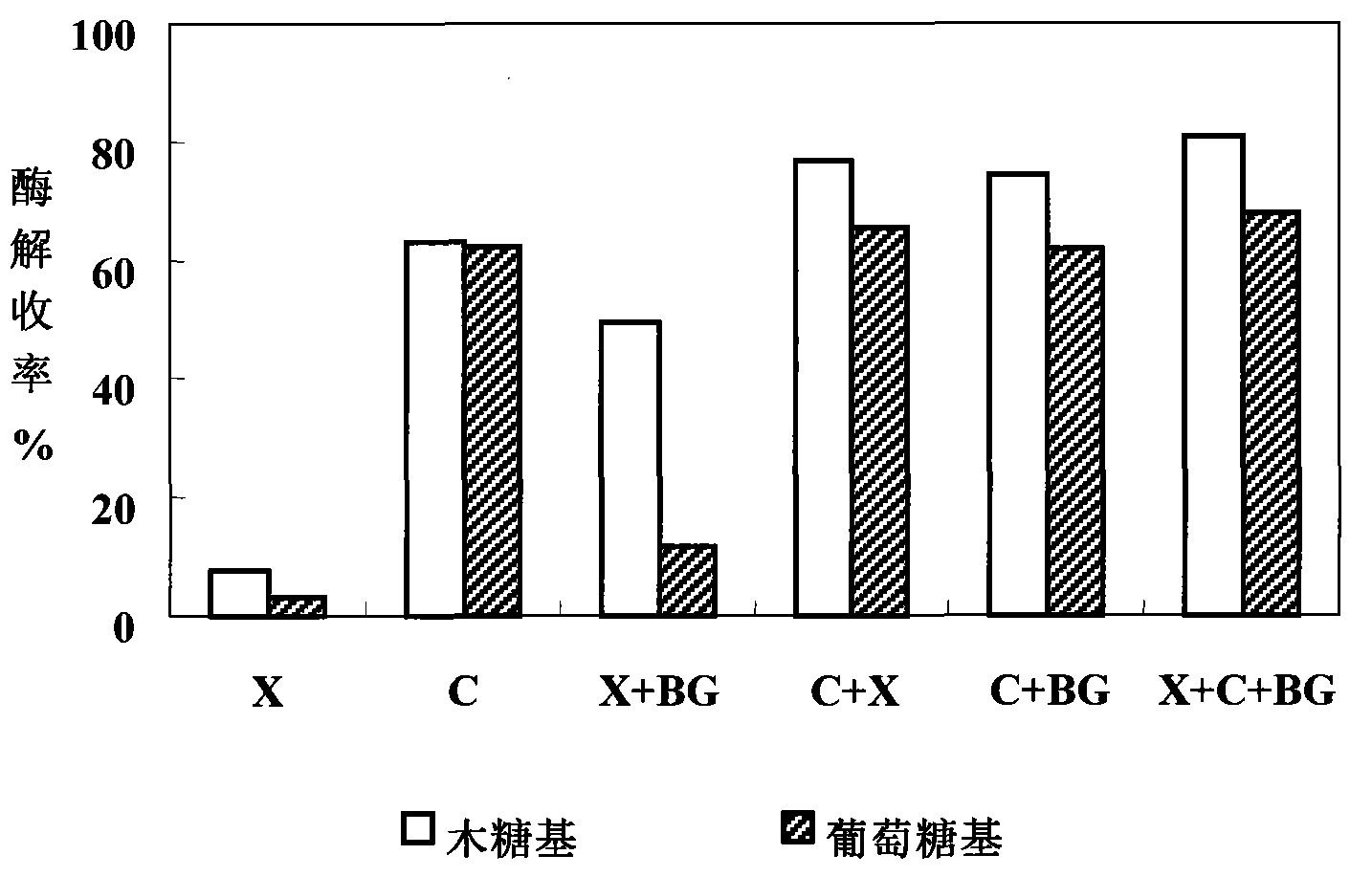
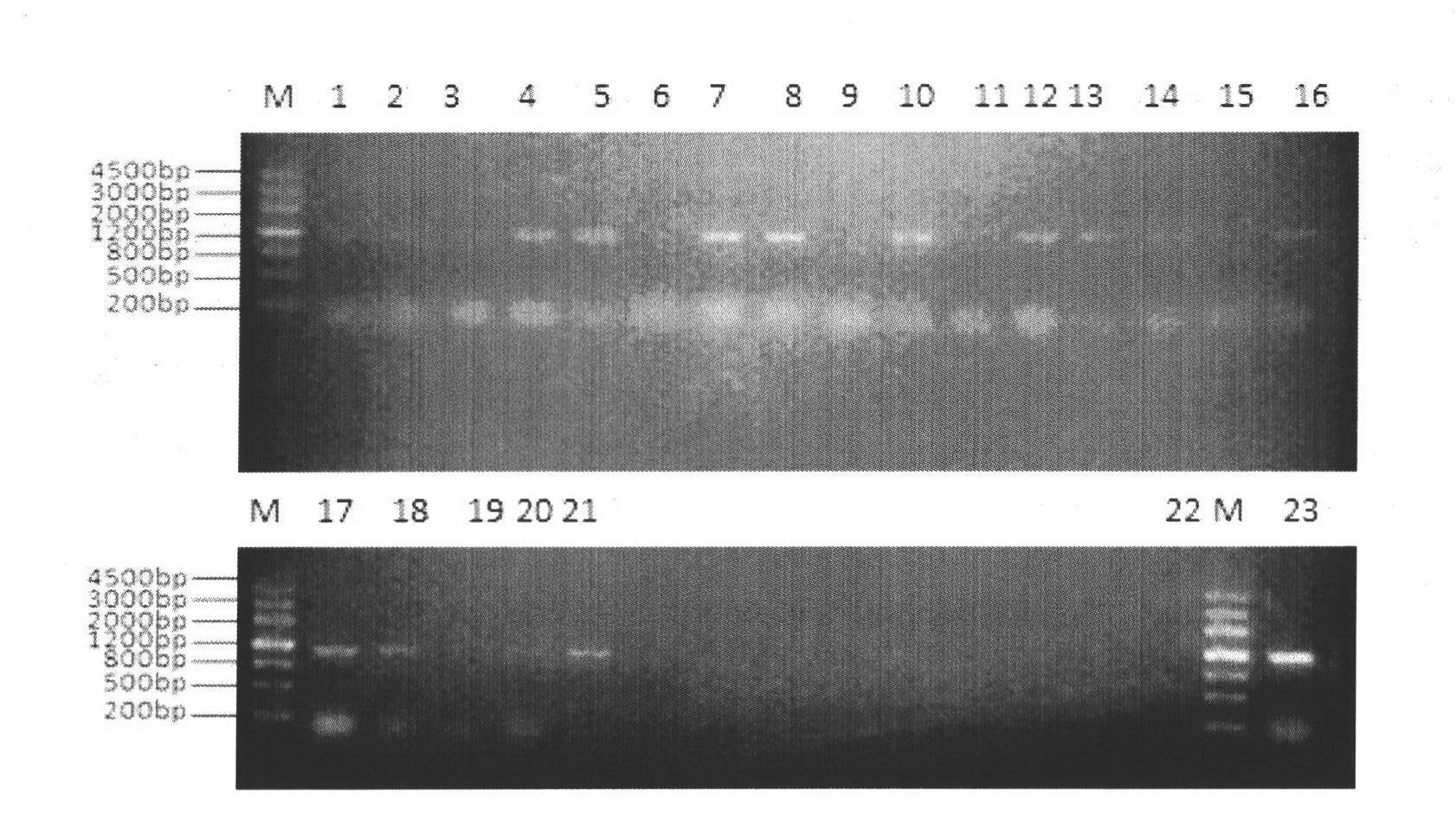
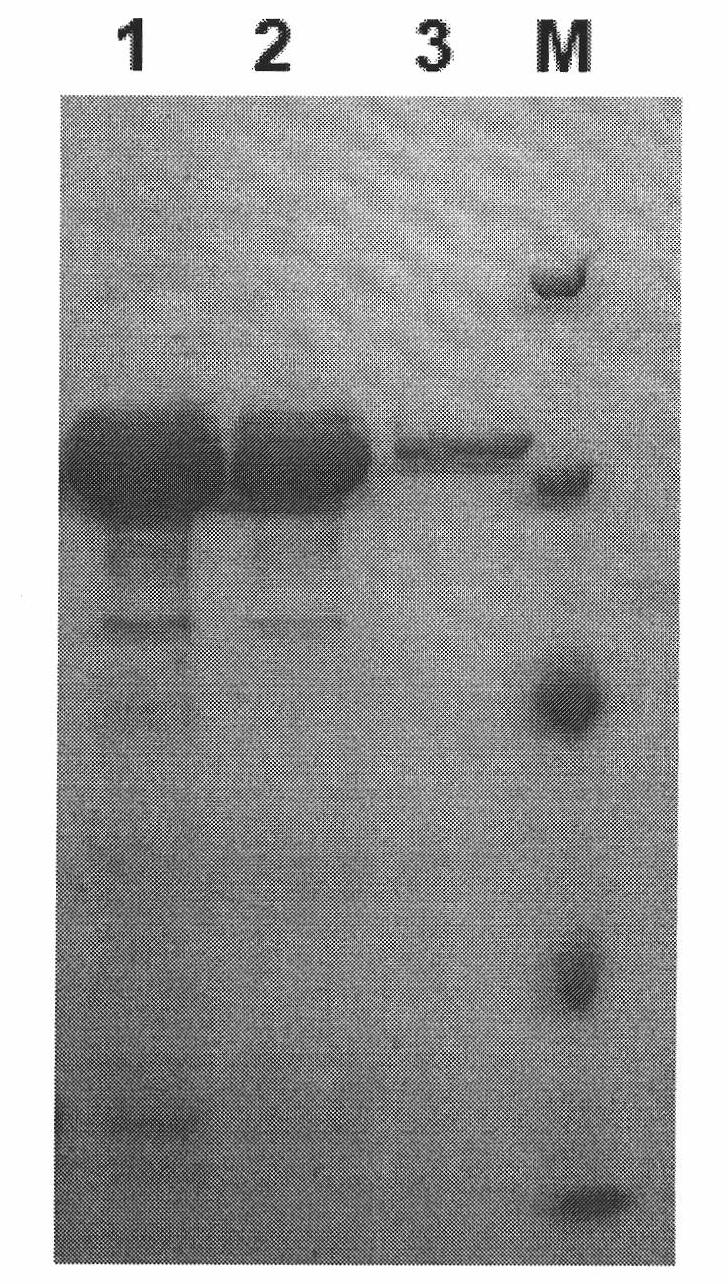
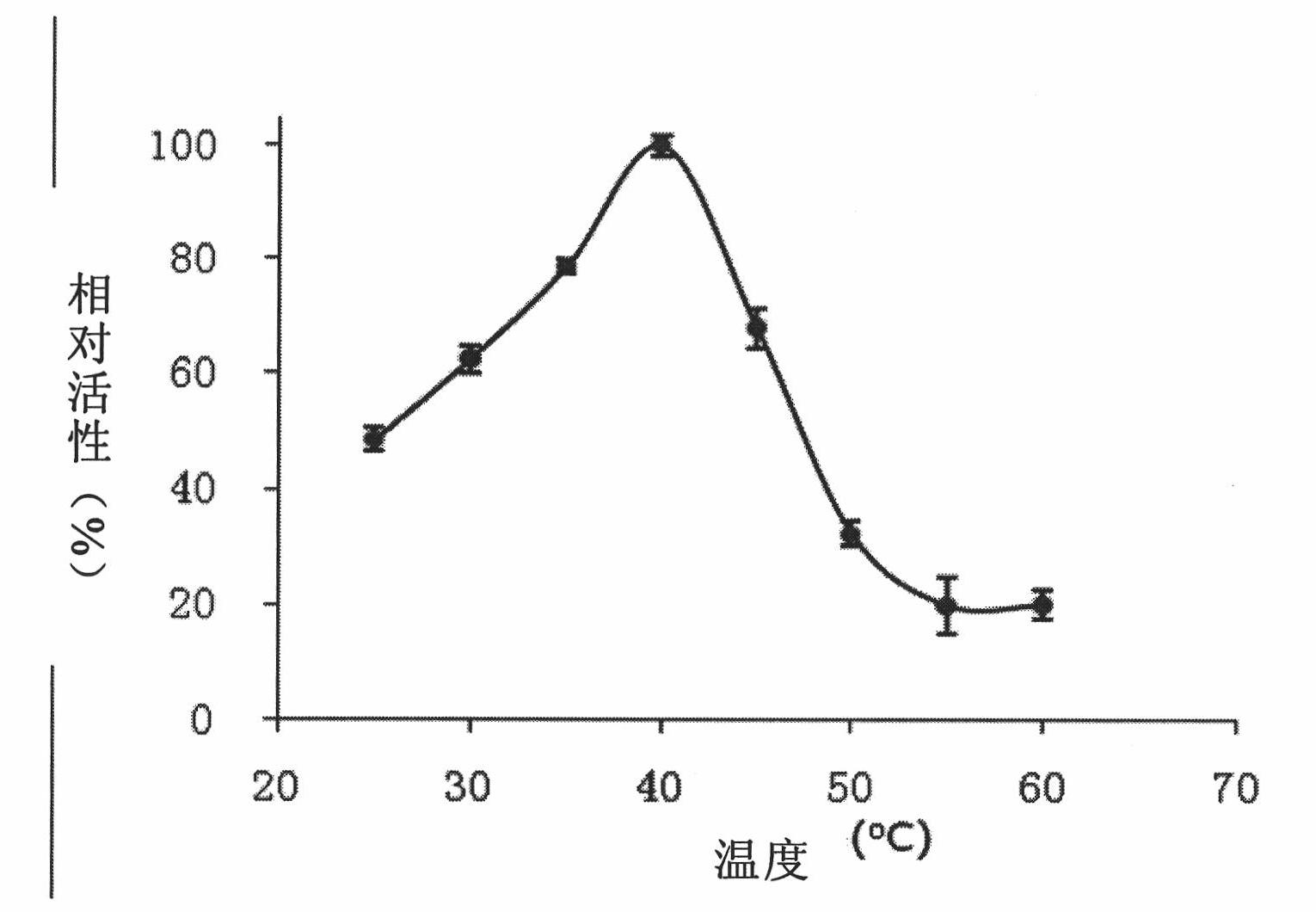
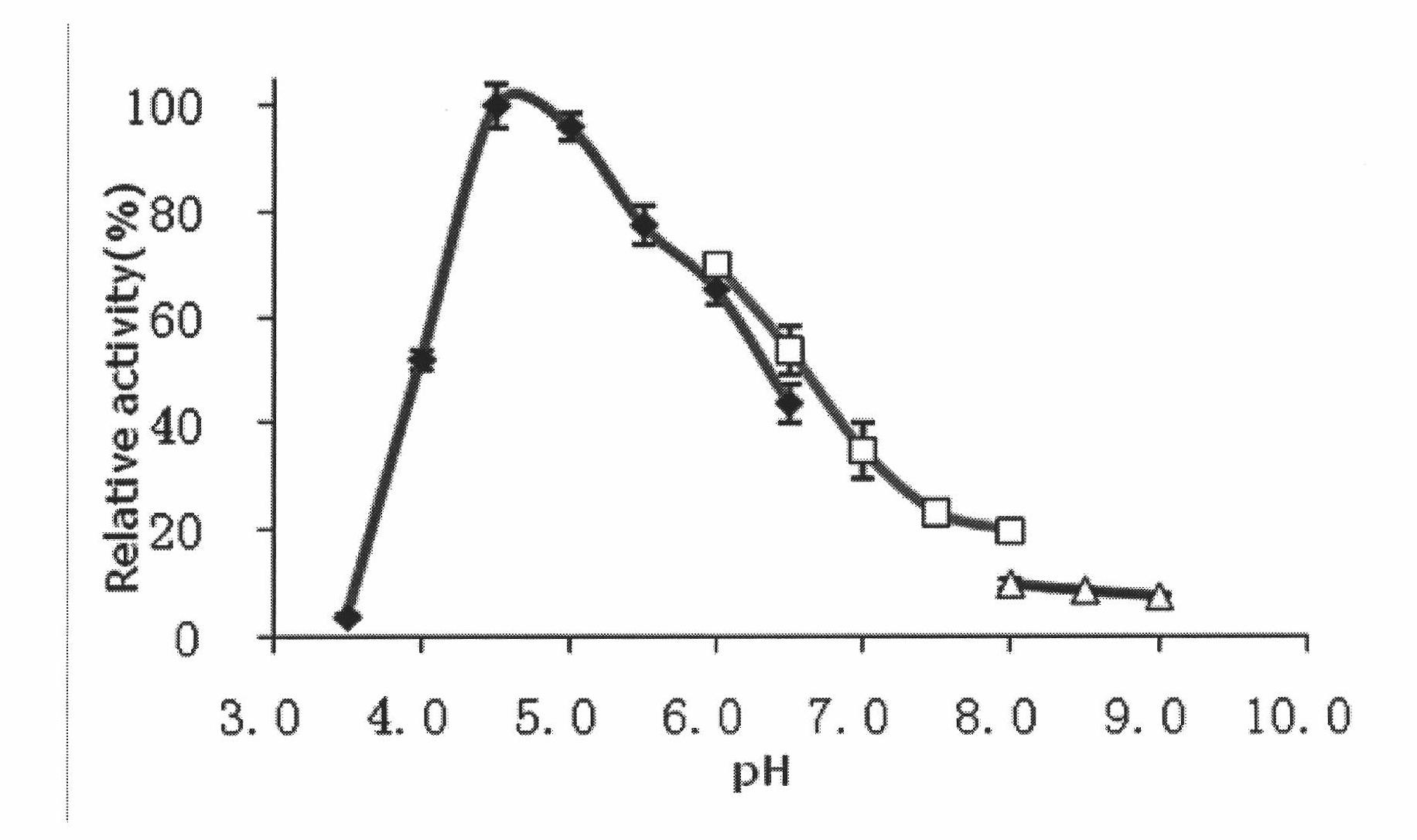
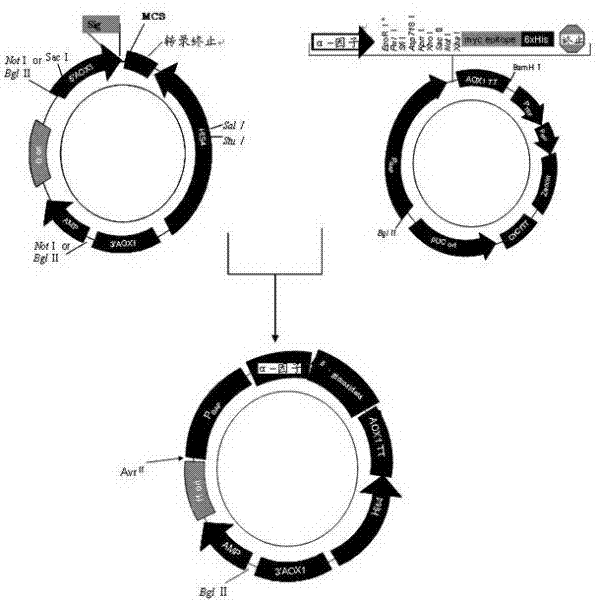
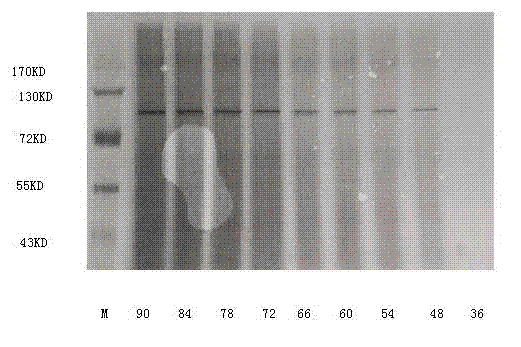
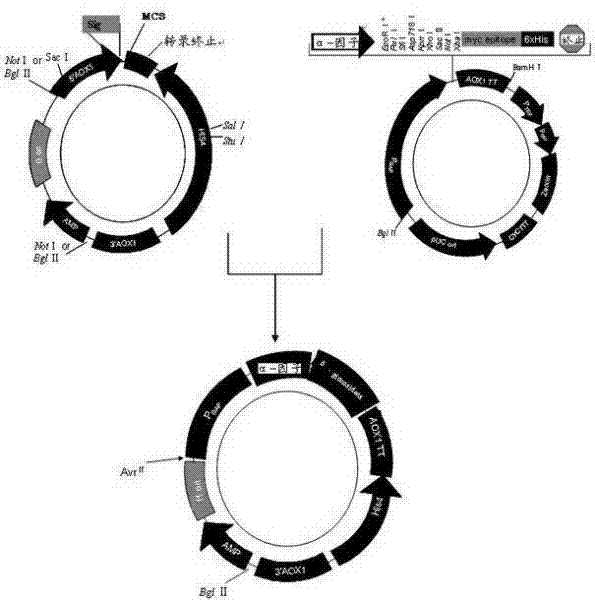
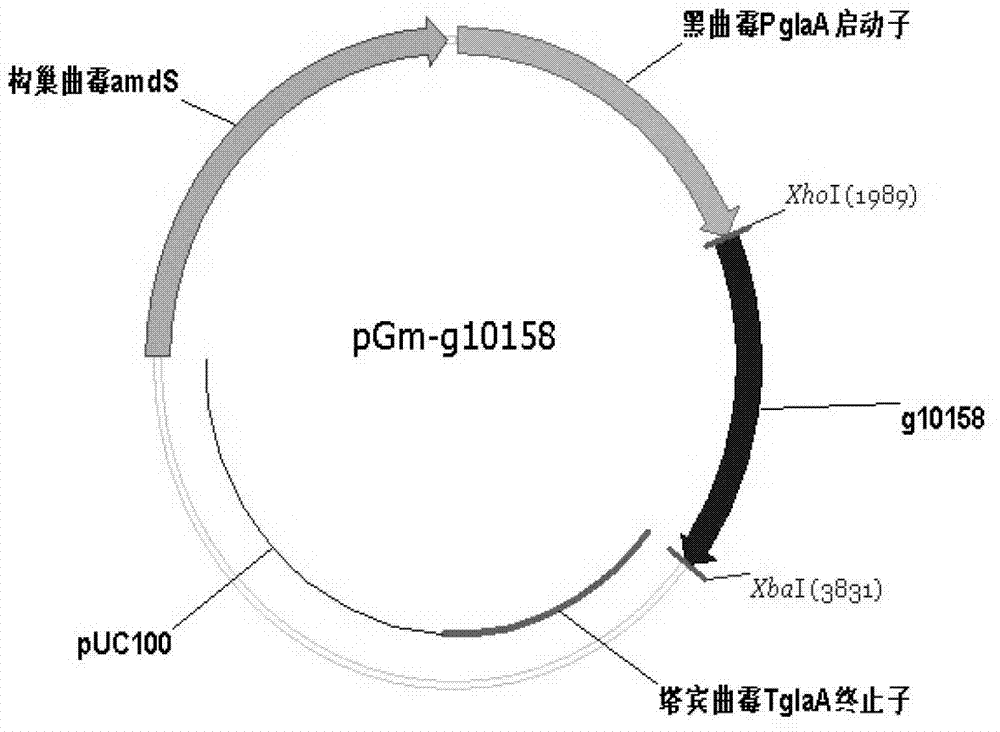
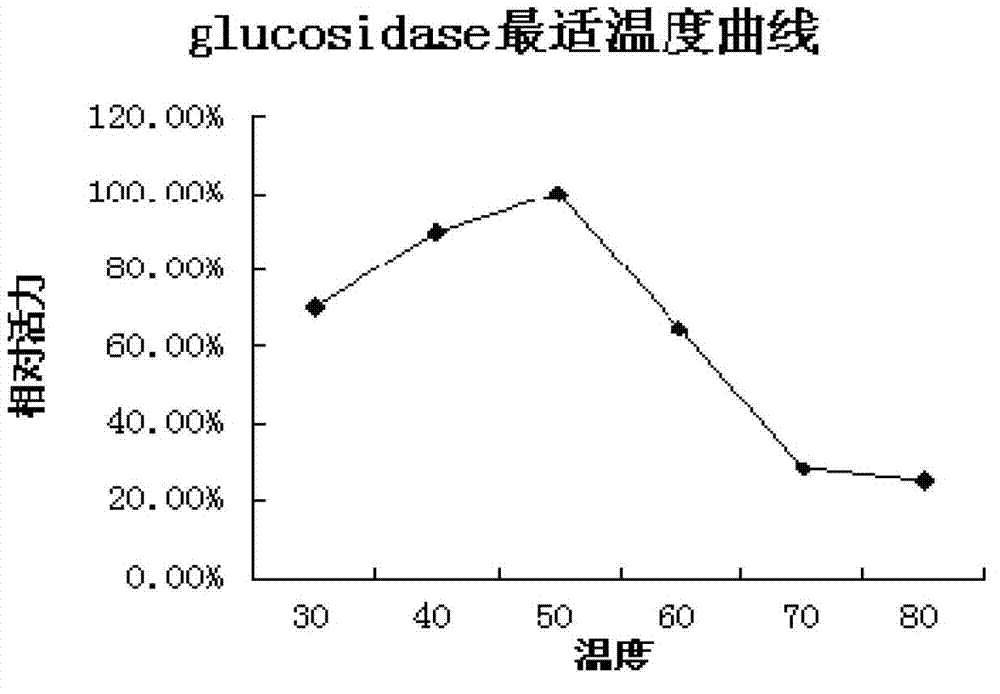
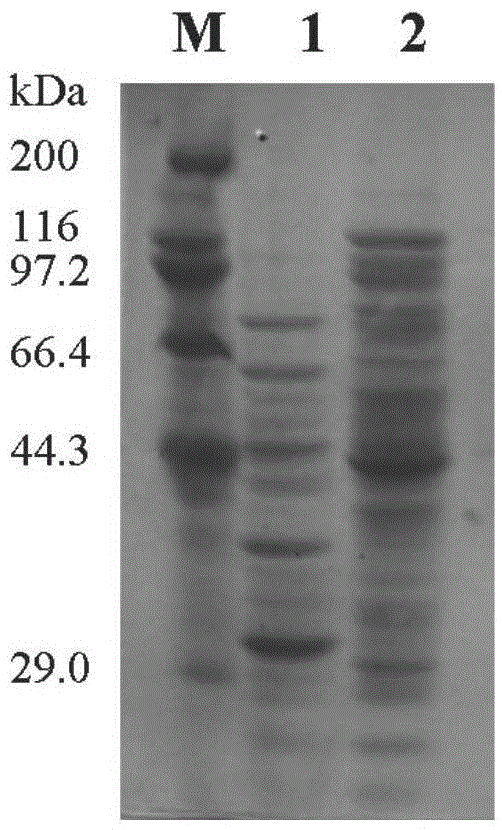
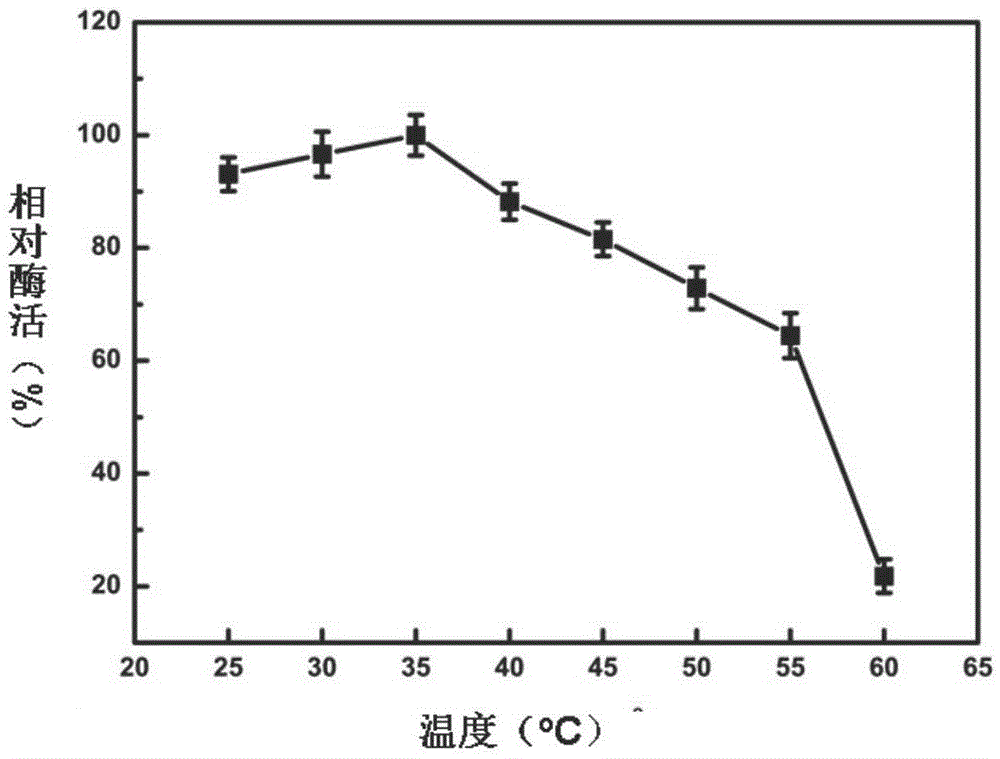
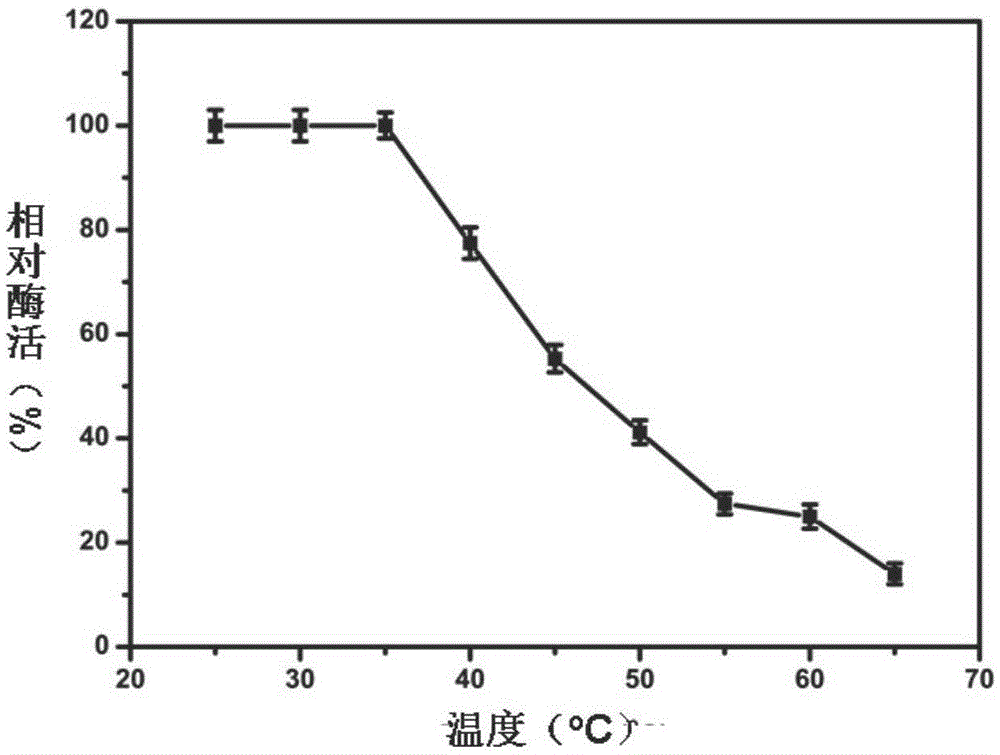
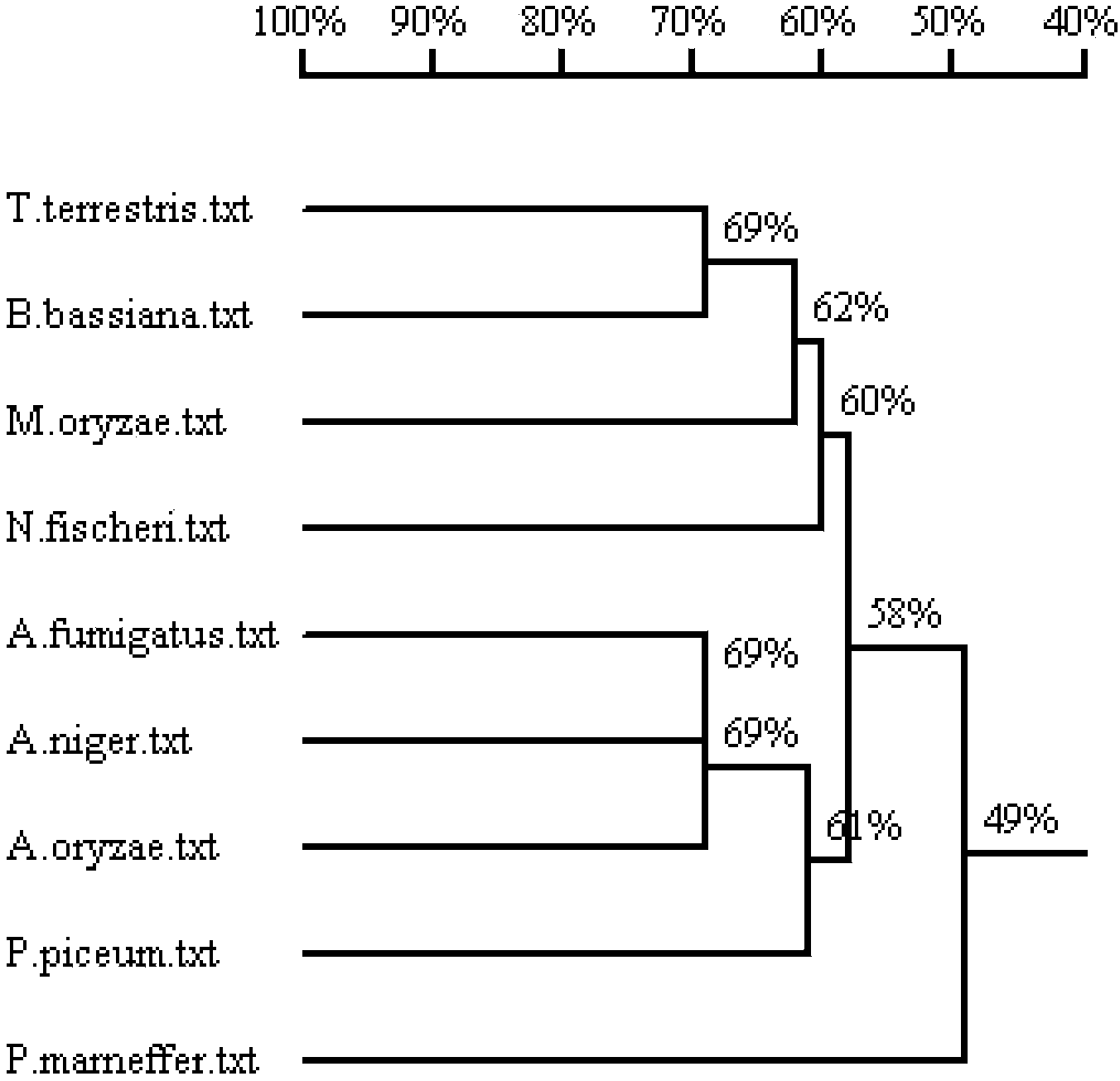
Patents
Literature
149 results about "Beta-glucosidase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
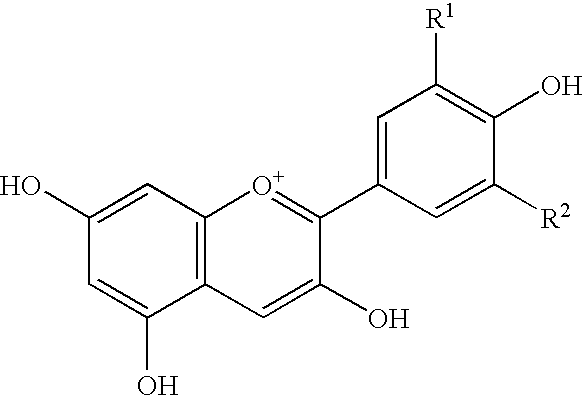
Beta-glucosidase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of the glycosidic bonds to terminal non-reducing residues in beta-D-glucosides and oligosaccharides, with release of glucose. Synonyms, derivatives, and related enzymes include gentiobiase, cellobiase, emulsin, elaterase, aryl-beta-glucosidase, beta-D-glucosidase, beta-glucoside glucohydrolase, arbutinase, amygdalinase, p-nitrophenyl beta-glucosidase, primeverosidase, amygdalase, linamarase, salicilinase, and beta-1,6-glucosidase.
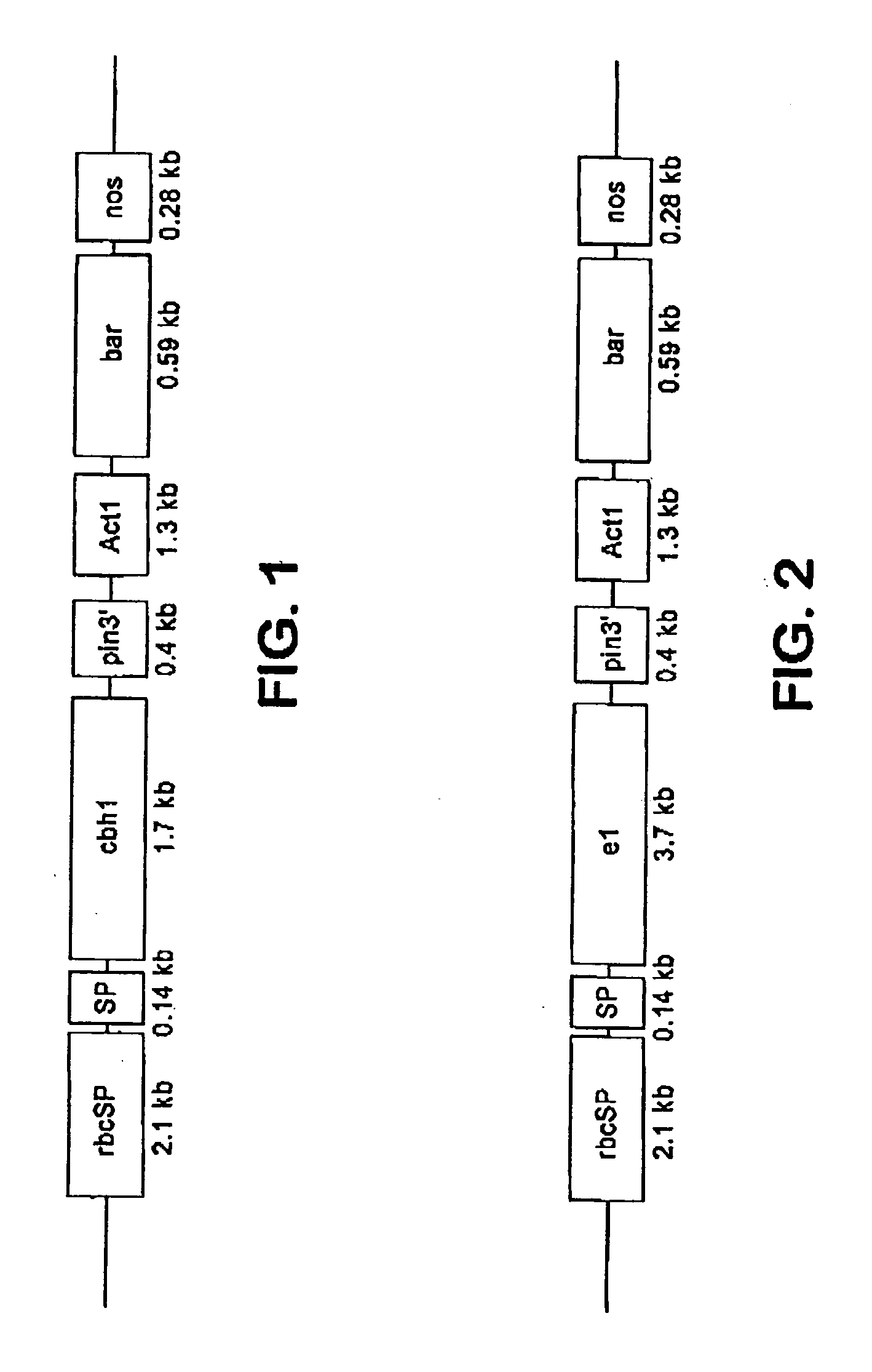
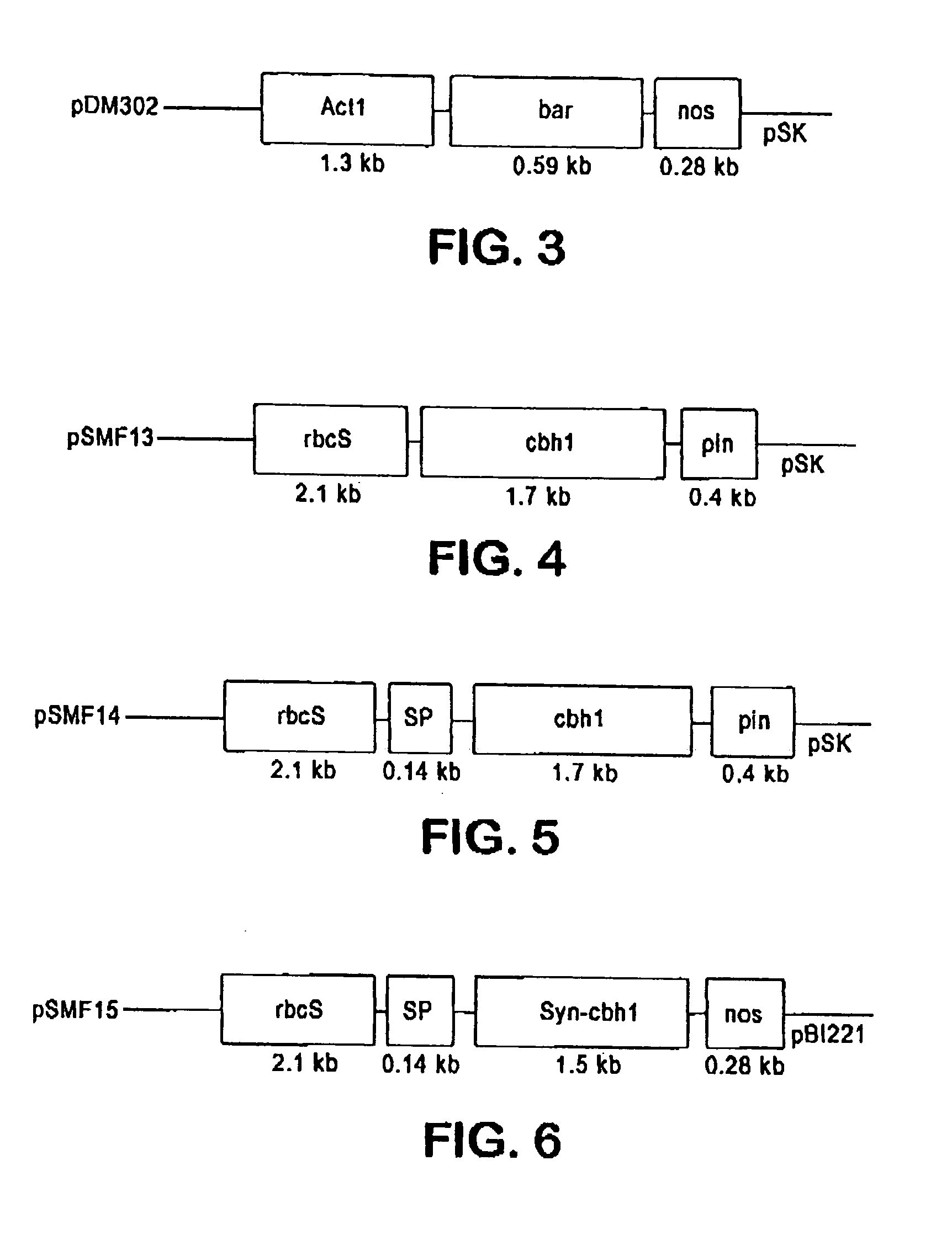
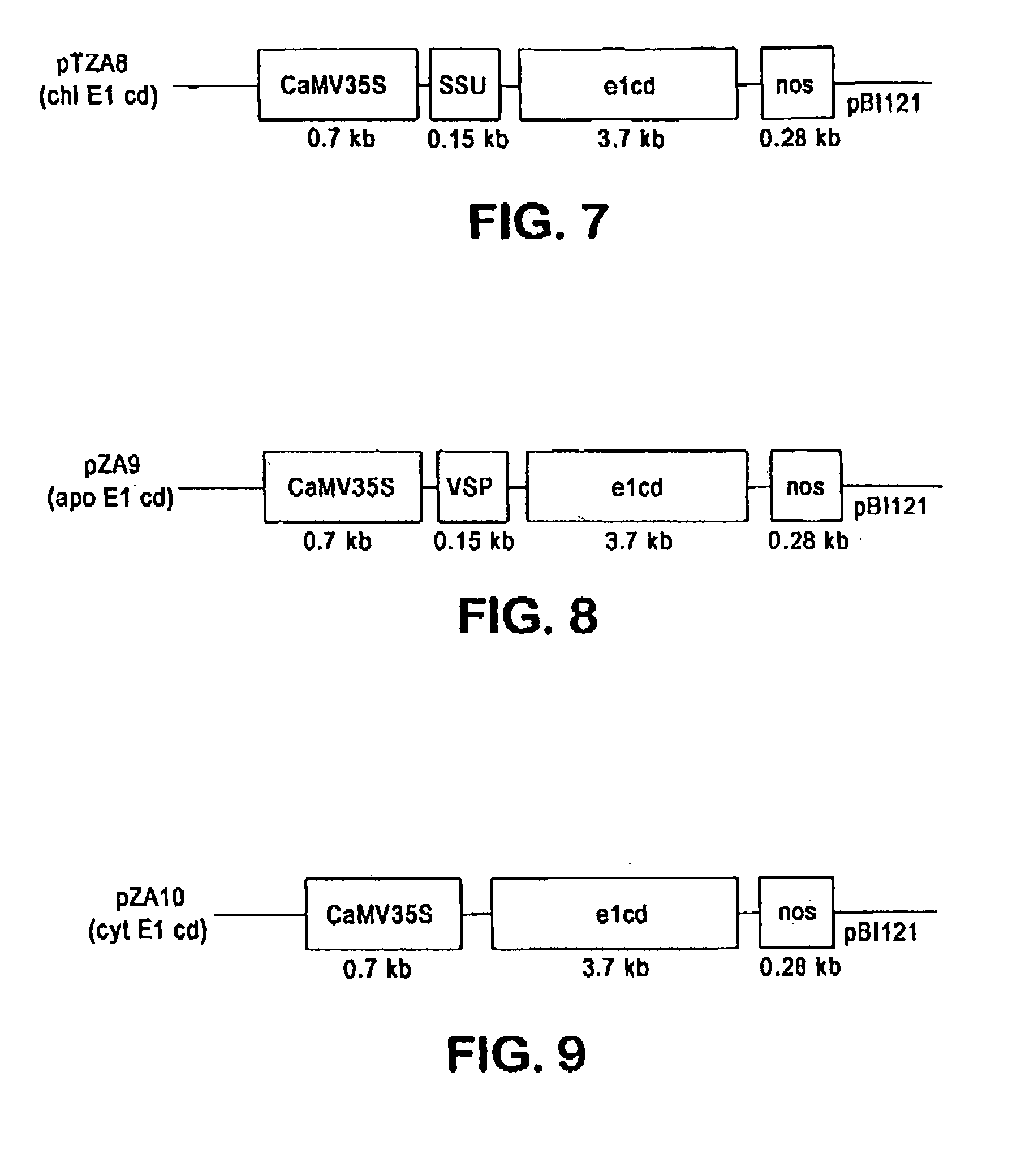
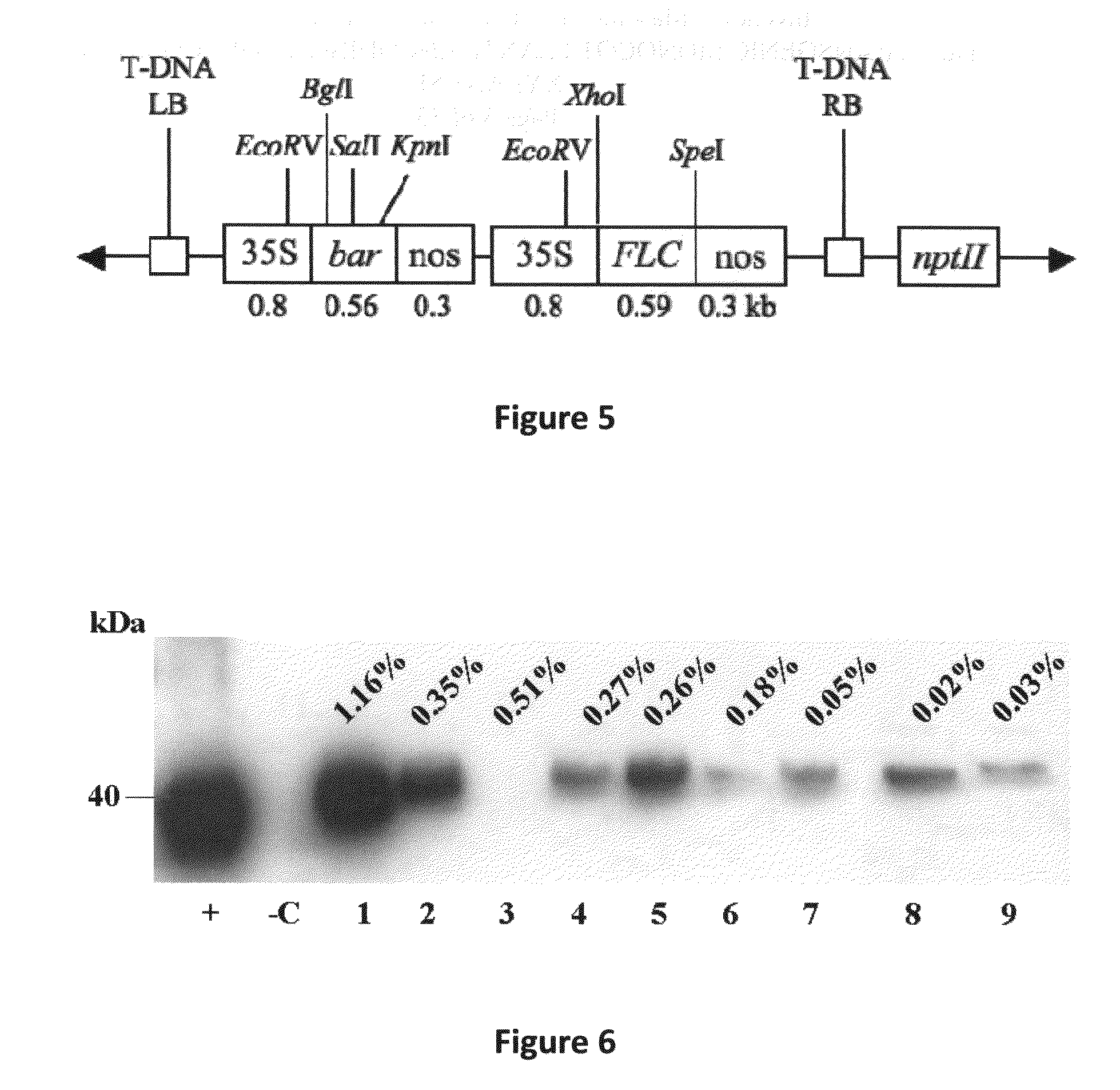
Production of beta-glucosidase, hemicellulase and ligninase in E1 and FLC-cellulase-transgenic plants
InactiveUS20070192900A1Increase biomassReduce the amount of solutionClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesAlgluceraseBeta-glucosidase
The present invention provides transgenic plants expressing one or more cell wall degrading enzymes that can degrade lignocellulose to fermentable sugars. These fermentable sugars can further be fermented to ethanol or other products. The enzymes are directed to the plastids or the apoplasts or the transgenic plant for storage. When the transgenic plants are harvested, the plants are ground to release the enzymes which then are used to degrade the lignocellulose of plant material to produce the fermentable sugars. The transgenic plants express the flowering locus c gene so that flowering is delayed and the plant biomass is increased.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Aspergillusniger strain and application thereof
ActiveCN101899398AIncrease enzyme activityEasy to operateFungiMicroorganism based processesYeastAlglucerase
The invention discloses an aspergillusniger strain for producing beta-glucuroide. Aspergillusniger T2 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on 26th September, 2008 with the preservation number of CGMCC No.2715. The aspergillusniger T2 strain is the aspergillusniger strain which is obtained by performing mutagenesis with ultraviolet rays and nitrous acid and screening by using a Congo red-carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) double-layer flat plate, has high enzymatic activity and is used for producing the beta-glucuroide. The aspergillusniger T2 strain is applied to the production of the beta-glucuroide. The beta-glucuroide produced by performing liquid state fermentation on corn cob, yeast powder and the like serving as raw materials and the aspergillusniger T2 strain serving as the strain has the characteristics of enzymatic activity, simple production method and the like.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Carrier for immobilization as well as preparation method thereof and immobilized beta-glucosaccharase
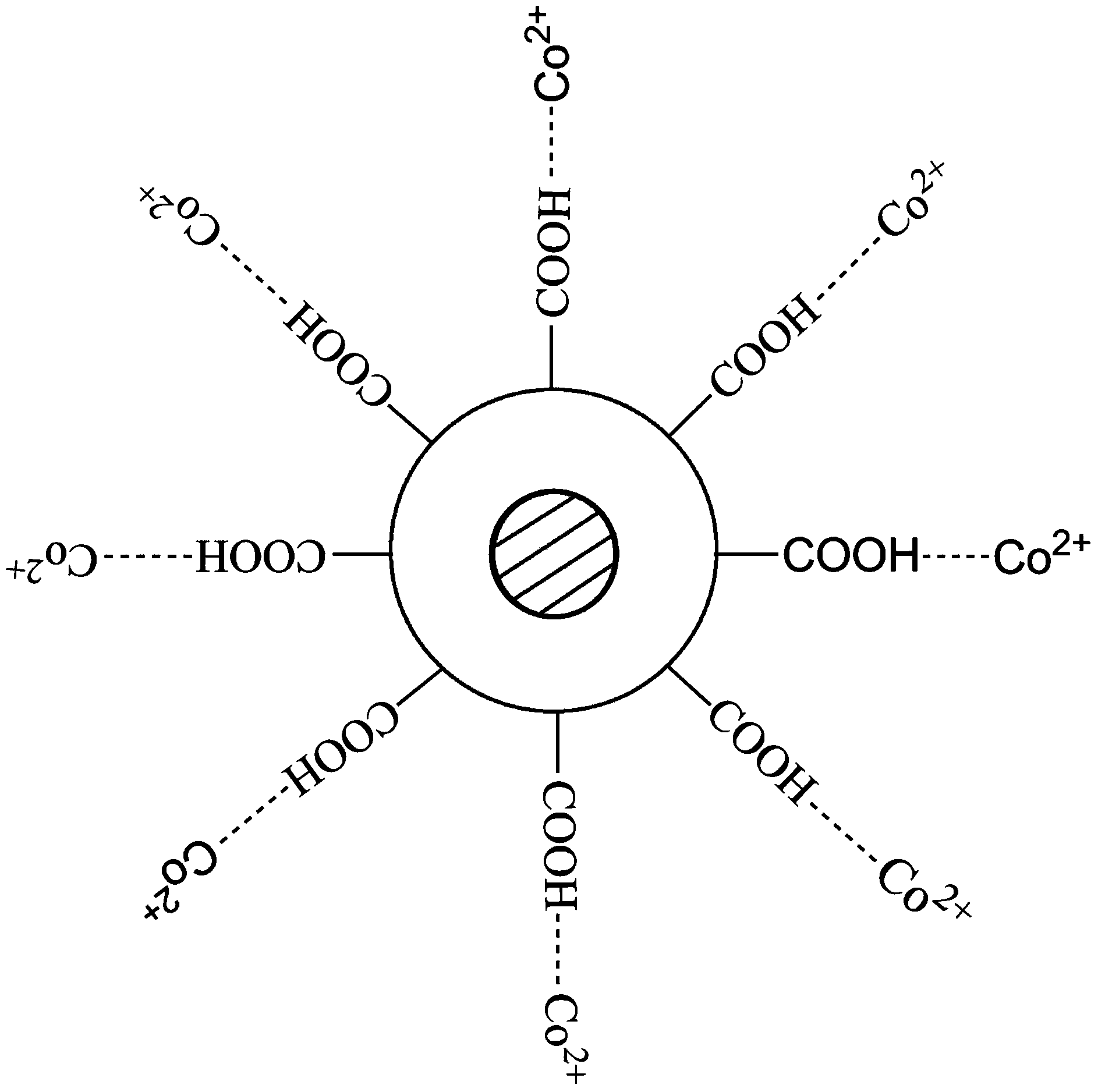
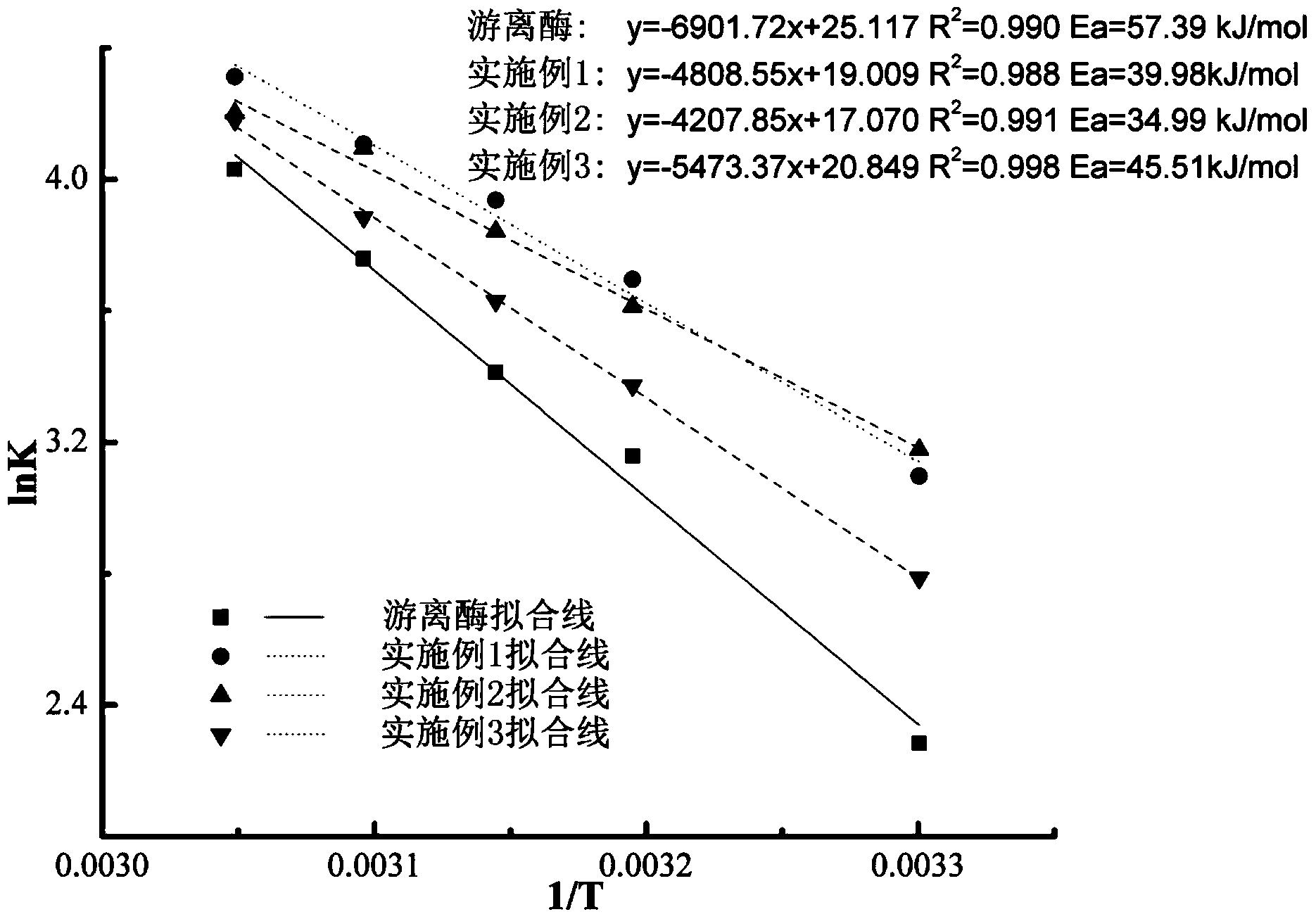
InactiveCN103710333AAchieve targeted immobilizationAvoid key functional domainsOn/in organic carrierOn/in inorganic carrierAlgluceraseBeta-glucosidase
The invention discloses a carrier for immobilization as well as a preparation method thereof and immobilized beta-glucosaccharase. The carrier for the immobilization comprises magnetic nano particles, a carboxyl-rich composite material and transitional metal ions, wherein the carboxyl-rich composite material wraps the surface of the magnetic nano particles to form a carboxyl-rich shell, carboxyl on the surface is complexed with the transitional metal ions, and the transitional metal ions are combined with to-be-immobilized enzyme through a metal ion coordination bond. The preparation method comprises the following steps of (1) preparing the magnetic nano particles; (2) carrying out hydroxyl functional modification for the particles; (3) carrying out epoxy functional modification for the particles; (4) carrying out carboxyl functional modification for the particles; (5) complexing the particles with the transitional metal ions. The functional carrier is combined with beta-glucosaccharase through the metal coordination bond to obtain immobilized beta-glucosaccharase. The biological enzyme is firm in combination, high in enzyme activity, strong in operation stability and suitable for the mass production.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for producing ethanol from lignocellulose biomaterial by use of neu-heat-resistant enzyme
It includes the stages of grinding the lignocellulosic biomass to a size of 15-30 mm, subjecting the product obtained to steam explosion pre-treatment at a temperature of 190-230 DEG C for between 1 and 10 minutes in a reactor (2), collecting the pre-treated material in a cyclone (3) and separating the liquid and solid fractions by filtration in a filter press (9), introducing the solid fraction in a fermentation deposit (10), adding a cellulase at a concentration of 15 UFP per gram of cellulose and 12.6 International Units of beta -glucosidase enzyme dissolved in citrate buffer pH 4.8, inoculating the fermentation deposit (10) with a culture of the heat-tolerant bacteria Kluyveromyces marxianus CECT 10875, obtained by chemical mutagenesis from strain DER-26 of Kluyveromyces marxianus and shaking the mixture for 72 hours at 42 DEG C.
Owner:RES CENT OF ENERGY SOURCE ENVIRONMENT & TECH
Method for preparing beta-glucosidase fixed with magnetic nano-particle
InactiveCN101270352AEasy to operateLow costOn/in organic carrierBeta-glucosidaseMagnetite Nanoparticles
The invention relates to a preparation method for magnetic nanoparticle fixed Beta-glucosaccharase, which comprises the steps that (1) precipitation reaction occurs between chloride solution of Fe<2+> and Fe<3+> and NaOH solution to prepare Fe3O4 particles; (2) chitosan is dissolved in acetum to form homogeneous transparent colloidal solution, and Fe3O4 particles are mixed with the homogeneous transparent colloidal solution, and the mixture is beaten, thus getting magnetic nanoparticles; (3) the magnetic nanoparticles are added to Beta-glucosaccharase solution, thus getting chitosan magnetic nanoparticle immobilized enzyme through absorption and cross linkage of glutaric dialdehyde solution; (4) citric acid buffer solution is added to immobilized Beta-glucosaccharase and free Beta-glucosaccharase solution, respectively, and reaction occurs after the temperature is adjusted; and the enzyme activity is examined. The method is quick, simple, convenient and is low in cost. The product got has the characteristics of uniform shape, large specific area, high coefficient of recovery of enzyme activity and so on.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Method for performing steam explosion of wood fiber raw material, directional enzymatic dissociation and alcoholic fermentation
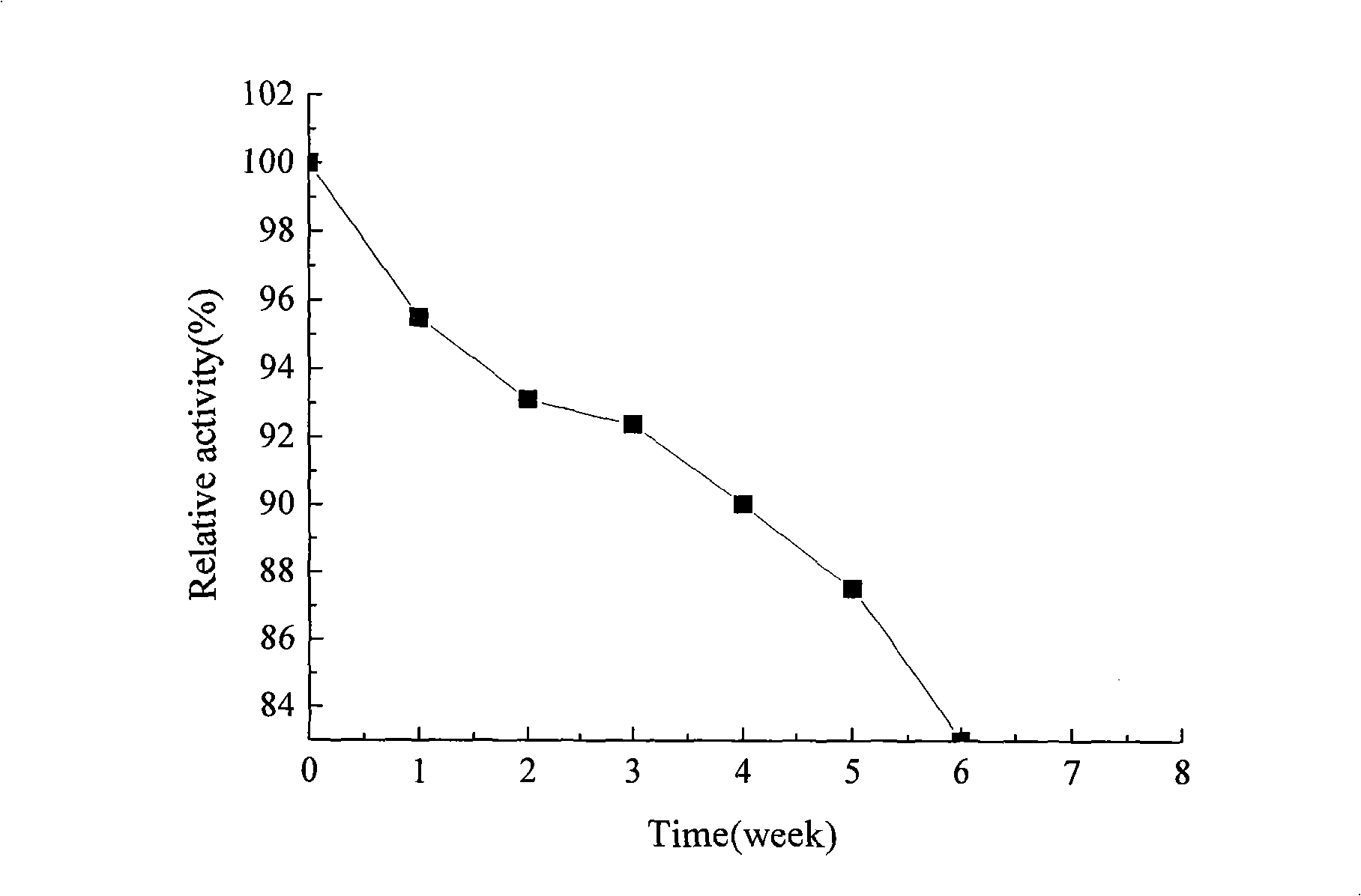
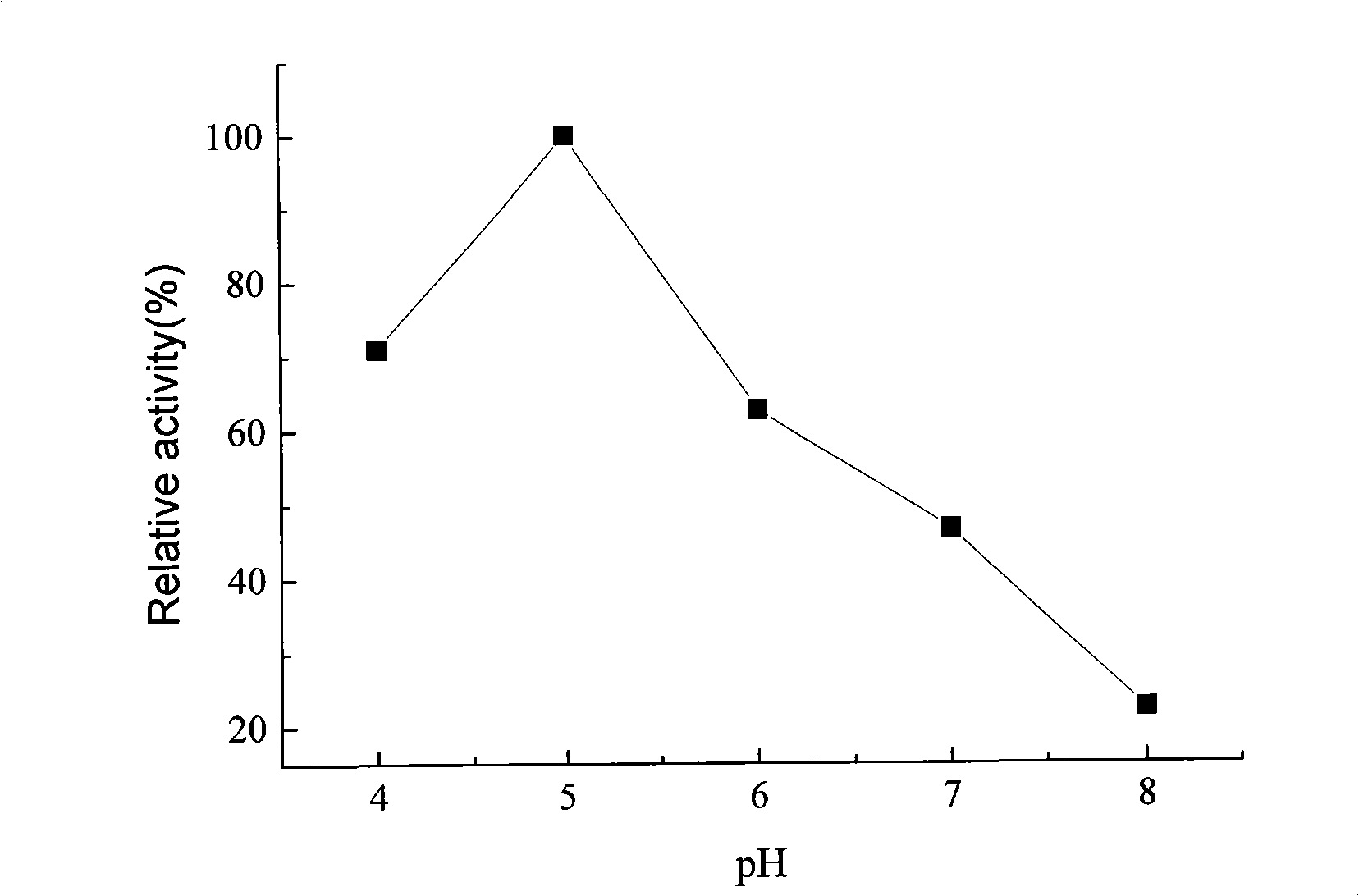
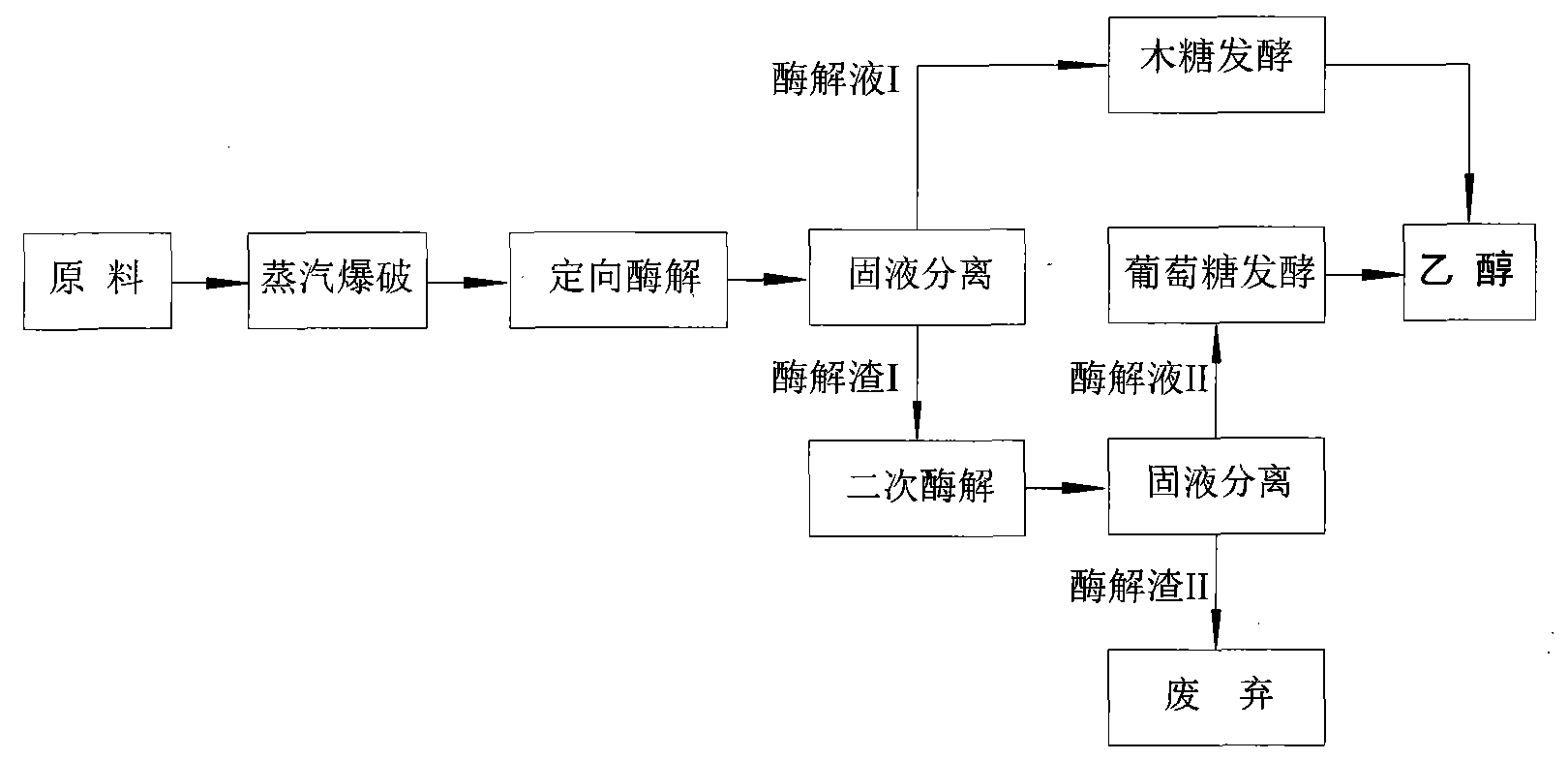
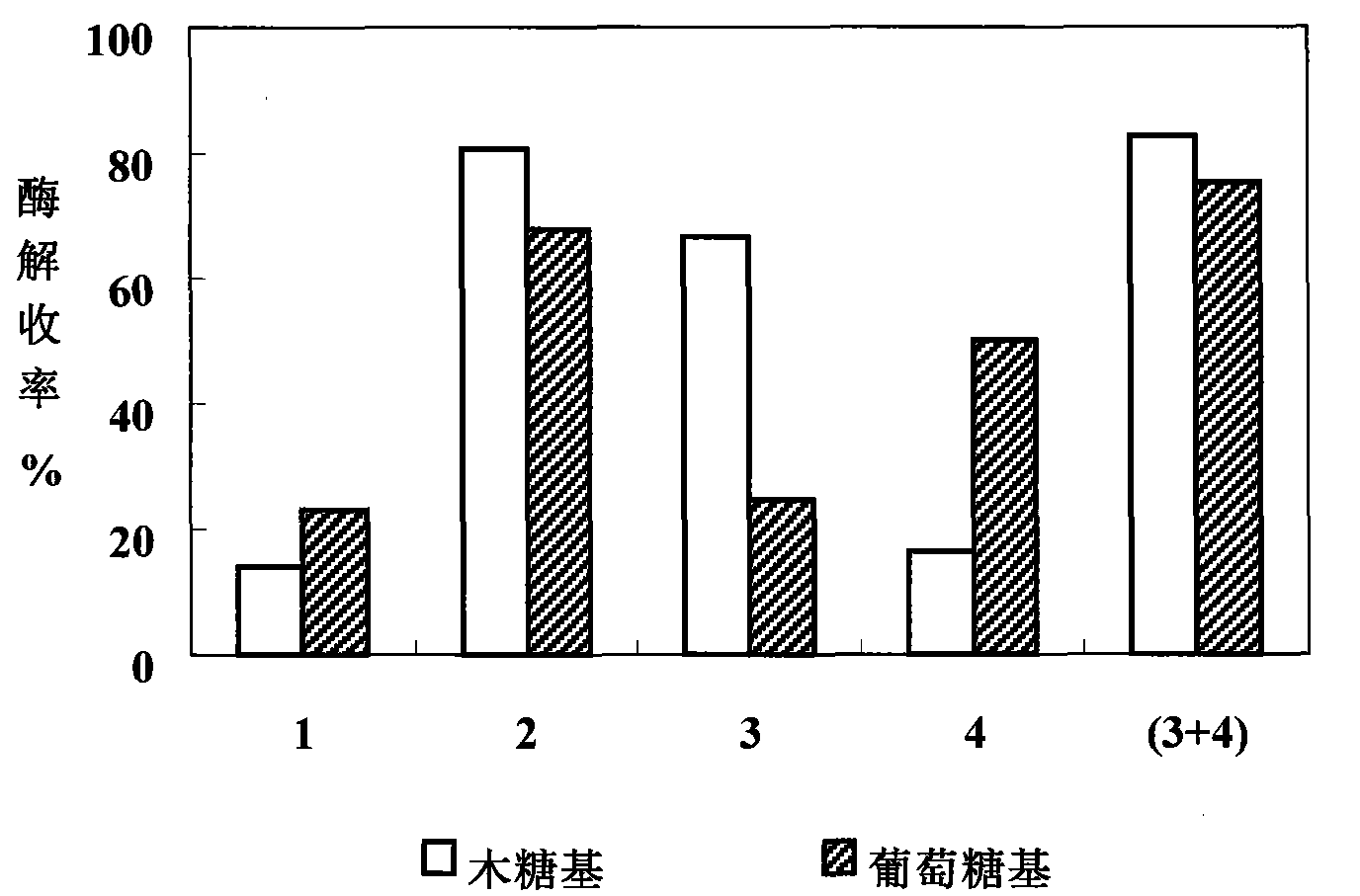
The invention relates to a method for performing steam explosion of wood fiber raw materials, directional enzymatic dissociation and alcoholic fermentation. The method is characterized in that steam explosion, directional enzymolysis of xylan, solid-liquid separation, extensive enzymolysis of cellulose, anaerobic alcoholic fermentation of xylose and anaerobic alcoholic fermentation of glucose areadopted. The new secondary enzymolysis technology is adopted and beta-glucosidase and little cellulose are introduced in xylanase so as to obviously improve the xylan directional enzymolysis and separation effect of raw materials. Therefore, the invention provides a new method for the effective separation of xylose and glucose in the wood fiber raw materials and the efficient alcoholic fermentation and significantly reduces the production cost for the fermentation of the ethanol in wood fiber raw materials.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Nucleic acids and polypeptides useful for diagnosing and treating complications of pregnancy
ActiveUS20060166277A1Diagnosing and effectively treatingSave maternalMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisPregnancyUdp glycosyltransferase
Disclosed herein are methods for diagnosing or treating pregnancy related hypertensive disorders that include the use of a polypeptide or a nucleic acid encoding a polypeptide selected from the following: follistatin related protein, interleukin 8, inhibin A, VEGF-C, angiogenin, beta fertilin, hypothetical protein, leukocyte associated Ig-like receptor secreted protein, erythroid differentiation protein, adipogenesis inhibitory factor, corticotropin releasing factor binding protein, alpha-1 anti-chymotrypsin, insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5, CD33L, cytokine receptor like factor 1, platelet derived endothelial growth factor, lysyl hydroxylase isoform 2, stanniocalcin precursor, secreted frizzled related protein, galectin-3, alpha defensin, ADAM-TS3, cholecystokinin precursor, interferon stimulated T-cell alpha chemoattractant precursor, azurocidin, sperminine oxidase, UDP glycosyltransferase 2 family polypeptide B28, neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor 2, neutral endopeptidase, CDC28 protein kinase regulatory subunit 2, beta glucosidase, lanosterol synthase, calcium / calmodulin-dependent serine protein kinase, estrogen receptor-alternatively spliced transcript H, chemokine (CX3C motif) receptor 1, tyrosinase-related protein 1, hydoxy-delta-5-steroid dehyrogenase, dihydropyramidinase-like-4, and cytochrome P450-family 11.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Transgenic monocot plants encoding beta-glucosidase and xylanase
Plant proteins isolated from monocot plants from transformation of the monocot plant with DNA at least 80% homologous to the bglA gene encoding β-glucosidase from a rumen bacterium which is Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens H17c and targeted to a subcellular compartment. The transformed plant is ground after the β-glucosidase has been accumulated, and the protein is extracted or used directly with the ground plant material to degrade cellobiose, in particular, to produce sugars used in fermentations, particularly to produce ethanol. Also, a gene at least 80% homologous to DNA XYL1 gene encoding a xylanase is also provided in a transformed plant and used to produce sugars.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
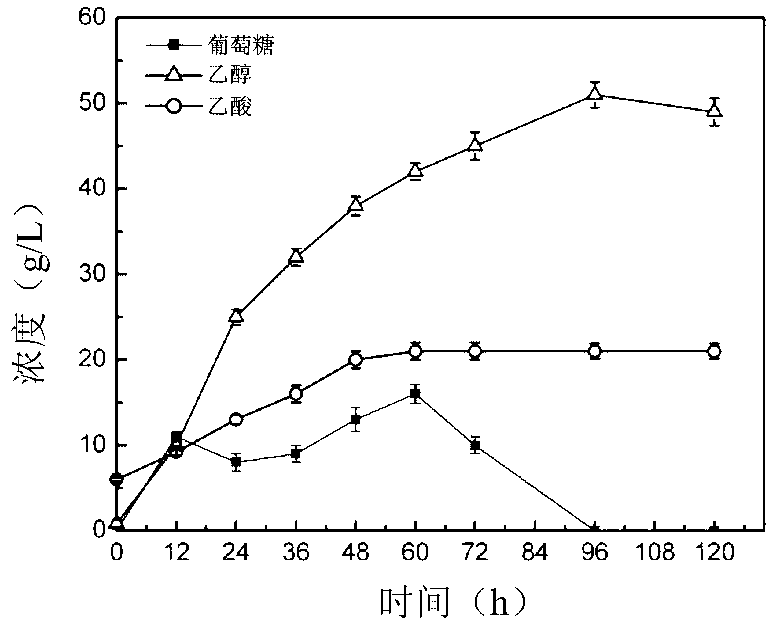
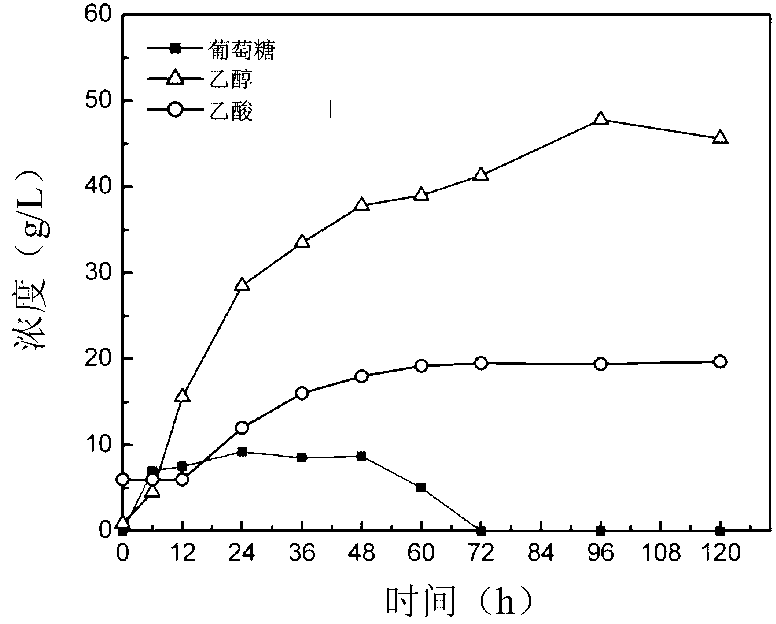
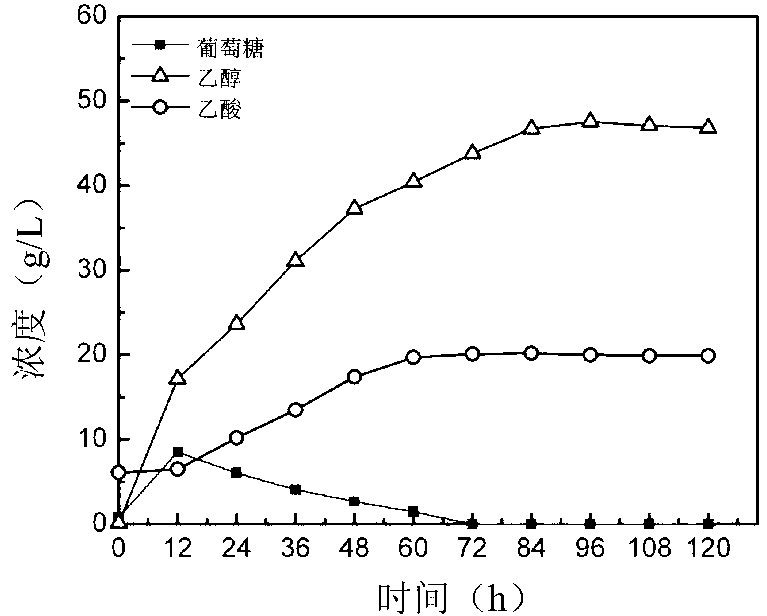
Synchronous saccharification and ethanol fermentation method with lignocelluloses treated by steam explosion method as raw material
InactiveCN103103220AReduce consumptionIncrease ethanol concentrationBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationBeta-glucosidase
The invention provides a synchronous saccharification and ethanol fermentation method with lignocelluloses treated by a steam explosion method as raw material. The method comprises the following steps of taking the lignocelluloses treated by the steam explosion method as raw material and directly as a substrate without detoxification, adding mixed enzyme comprising cellulase and beta-glucosaccharase, simultaneously inoculating (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) Y5 with CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) NO. 2660, adding a nitrogen source, and carrying out ethanol fermentation production. According to the method, the step of detoxification by washing the lignocelluloses (such as maize straw) pre-treated by steam explosion is omitted, and the final fermented product of ethanol of high concentration is obtained. For example, the concentration for steam explosion of the maize straw is 30%, synchronous saccharification and fermentation time is 96 hours, and the ethanol concentration of a reactor of 100ml, a reactor of 3000ml and a fermentation tank of 5L respectively reaches 50g / L, 47.8g / L and 47.5g / L. The production technology is greatly simplified, the equipment investment is lowered, water consumption is reduced, and the production cost is lowered.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Fenugreek seed having reduced bitter taste and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20100055241A1Poor appearanceReduce bitternessCocoaFood preparationAlgluceraseBeta-glucosidase
It is an object of the present invention to obtain fenugreek seeds having reduced bitter taste without causing significant changes in non-bitter components contained in fenugreek seeds.The present invention relates to a method for producing fenugreek seeds having reduced bitter taste, comprising allowing β-glucosidase to act on an eluate in which the components of fenugreek seeds have been eluted and then allowing the fenugreek seeds to absorb the eluate and β-glucosidase, and a food containing such fenugreek seeds.
Owner:HOUSE FOOD IND CO LTD
Recombinant vector and recombinant bacterium of Trichoderma reesei beta-glucosaccharase gene BGL1, and expression of Trichoderma reesei beta-glucosaccharase gene BGL1 in recombinant bacterium
InactiveCN102220369AEfficient productionIncrease productionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPichia pastoris
The invention discloses a recombinant vector and recombinant bacterium of Trichoderma reesei beta-glucosaccharase gene BGL1, and expression of the Trichoderma reesei beta-glucosaccharase gene BGL1 in the recombinant bacterium. The recombinant vector containing the Trichoderma reesei beta-glucosaccharase gene BGL1 is constructed by the following steps: (1) carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification on the Trichoderma reesei beta-glucosaccharase gene BGL1, and connecting to a TA vector; and (2) constructing the Trichoderma reesei beta-glucosaccharase gene to a pichia pastoris expression vector. The recombinant bacterium disclosed by the invention can effectively express the target protein Trichoderma reesei beta-glucosaccharase BGL1. The invention overcomes the defect that a great deal of beta-glucosaccharase can not be purified from Trichoderma reesei in the prior art. Lots of waste lignocellulose exists in the natural world. The method provided by the invention can increase the yield of beta-glucosaccharase, and has very important meanings in enhancing degradation efficiency of cellulose, efficiently producing energy from waste cellulose and solving the problem of energy crisis at present.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Glucosidase/xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme RuGBGX2 as well as coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN102041251AHigh activityReduce complexityMicroorganism based processesEnzymesChemical industryCellulose
The invention relates to a novel beta glucosidase / xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme RuGBGX2 as well as a coding gene and application thereof. The coding sequence of amino acid of the RuGBGX2 contains 18-755th sites of an SEQ ID NO 2 sequence. The RuGBGX2 is sourced from the rumen microorganism of yak from China, a novel coding gene of the beta glucosidase / xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme RuGBGX2 is obtained by function screening and sequencing analysis on a rumen metagenome cosmid library and a subclone library. The beta glucosidase / xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme provided by the invention can be widely applied to the degradation of cellulose and the fields such as cellulose biotransformation, chemical industry, spinning, foods, bioenergy, feed additives, medical industry and the like. By utilizing the difunctional enzyme RuGBGX2 to degrade wood fiber, the varieties of added enzymes can be reduced, and an enzymolysis process can be simplified.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
Method for preparing gardenia blue pigment by utilizing immobilized yeast cells
ActiveCN102559796AKeep it pristineImprove stabilityMicroorganism based processesOn/in organic carrierBeta-glucosidaseIon-exchange resin
The invention relates to a method for preparing gardenia blue pigment by utilizing immobilized yeast cells. The method comprises the following steps of: a) inoculating a yeast strain for producing beta-glucuroide to a culture medium, fermenting to obtain a bacterial liquid, centrifuging the bacterial liquid, embedding a substratum bacterial liquid by using a sodium alginate solution to form a sodium alginate-saccharomycete suspension, and dripping the sodium alginate-saccharomycete suspension into a calcium chloride solution dropwise to form the immobilized yeast cells; b) stirring and mixing a geniposide solution, an amino acid solution and the immobilized yeast cells to obtain a gardenia blue solution; and c) adding the gardenia blue solution into a column which consists of macroporous alkalescent styrene anion exchange resin, eluting by using an ethanol solution, collecting eluent, concentrating the eluent, and spray-drying a concentrated solution to obtain gardenia blue powder. According to the method, a saccharomycete fermentation liquid is immobilized directly without treatment, so that the problems of difficulty in separation of yeast and products, high possibility of loss and the like by the conventional method for performing fermentation by free yeast are solved, and the purity of the gardenia blue is improved.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Preparation of icaritin
The invention relates to a method for preparing icaritin and is characterized in that: the icaritin is prepared by icariin which is subject to the enzymolysis reaction by beta-glycosidase. The method adopts the beta-glycosidase to perform the enzymolysis reaction for the icariin, the beta-glycosidase has complete deglycolysis and high yield, a self-designed method for extracting the icariin from Herba Epimedii is adopted, the whole technical process has simple and convenient operation, the treatment is convenient after the reaction, and the purity of the product fully meets the pharmaceuticalstandard.
Owner:BEIJING SHENOGEN BIOMEDICAL
Enzymolysis treatment method of algae
The invention provides an enzymolysis treatment method of algae. The method comprises the steps of material preparation, pretreatment, enzyme treatment and centrifugating. In the enzyme treatment step, the adopted enzyme is a composite enzyme which comprises proteinase, cellulase and pectinase in a mass ratio of 3:1:2. The proteinase is any one of papain, bromelin, carboxypeptidase and chymopapain. The cellulase is any one of cellobiohydrolase, endoglucanase, beta-glucosaccharase and cellobiase. The pectinase is any one of protopectinase, lyase and polygalacturonase. According to the enzymolysis treatment method of algae, the extraction rate of sodium alginate is 38.0-50.9%, and the extraction rate of alga glycine is 7.5-11.8%.
Owner:SHANDONG HETIANWANG BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Cloning, expression and application of a β-glucosidase gene
ActiveCN102268421AImprove securityThe follow-up processing process is convenientFungiMicroorganism based processesBeta-glucosidaseHigh activity
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and particularly relates to a beta-glucosaccharase which can decompose lactose and has high activity under both high-temperature and low-temperature conditions, and a gene engineering bacterium capable of efficiently expressing secretion-type beta-glucosaccharase. The invention discloses a beta-glucosaccharase having an amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO:2, and constructs a gene engineering bacterium capable of efficiently secreting the beta-glucosaccharase. The gene engineering bacterium is collected in Common Microorganism Center of Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms, and the collection number is CGMCC No.4891. The beta-glucosaccharase produced by the method disclosed by the invention has high activity of galactosidase, and can be applied to dairy industry; and meanwhile, the beta-glucosaccharase has stable activity within wide pH value range and temperature range.
Owner:山西恩泽生物技术有限公司
Beta-glucosidase and application thereof
The invention relates to a beta-glucosidase and an application thereof, wherein the beta-glucosidase comprises: a, enzyme with the sequence of SEQ ID NO:1; and b, enzyme which is derived from the enzyme in step a through substituting, deleting or adding one or a plurality of amino acids and has the activity of the enzyme in the step a. The selected beta-glucosidase provided by the invention has the deoxyglucose and hygromycin resistance and transglycosylation, under the transglycosylation, cellobiose and other oligosaccharides can generate sophorose and other inductors, and enter cells through a constitution permease system on a cell membrane, and the synthesis of cellulose in the cells is initiated. Consequently, the beta-glucosidase can be used for the production of catalytically synthesizing the sophorose to induce the cellulose, and thereby having a greater commercial value.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for producing cellulose by microorganism mixing fermentation
Production cellulase by microbe mixed fermentation is carried out by taking Trichoderma koningii and Rhizopus oryzae as cellulase production bacterium, inoculating spore fluid or secondary seed fluid into solid or liquefied culture medium and controlling culture medium and amount of Trichoderma koningii and Rhizopus oryzae and other culture conditions during mixed bacterium culture. The filter-paper activity, beta-glucosidese activity are increased by 60-100% and 400-500% and fermentation time is shortened. It's benefit to secrete cellulase and improves enzyme system. It's cheap and simple.
Owner:DONGGUAN UNIV OF TECH
Process for producing purified anthocyanin and crystalline anthocyanin
Provided are a process for producing purified anthocyanidin glucoside in which a rhamnose end of anthocyanidin rutinoside is cleaved using rhamnosidase to convert the anthocyanidin rutinoside component into anthocyanidin glucoside, the anthocyanidin glucoside component being then purified and isolated; or a crystalline anthocyanidin glucoside salt obtained by further crystallizing the purified anthocyanidin glucoside and a process for producing the same.Also provided are a process for producing purified anthocyanidin rutinoside in which a glucose end of anthocyanidin glucoside is cleaved using β-glucosidase to degrade and remove the end, the anthocyanidin rutinoside component being then purified and isolated; or a crystalline anthocyanidin rutinoside salt obtained by further crystallizing the purified anthocyanidin rutinoside and a process for producing the same.
Owner:MEIJI SEIKA KAISHA LTD
Beta-glucosaccharase mutant, recombinant expression plasmid thereof and transformed engineering strain
ActiveCN104726435AHigh affinityHigh catalytic efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMutated protein
The invention provides a beta-glucosaccharase gene, mutant plasmid and engineering bacteria. The beta-glucosaccharase gene of which the ethyl alcohol concentration is improved is obtained by a gene site-directed mutation method. After the engineering bacteria are subjected to inducible expression, the beta-glucosaccharase of which the ethyl alcohol concentration is improved is obtained. On the basis of the beta-glucosaccharase which is from uncultured organisms of the sea, a mutant gene is obtained through PCR (polymerase chain reaction) site-specific mutagenesis. Under the condition that the temperature is 35 DEG C, the ethyl alcohol concentration IC50 of obtained mutant protein is increased 1.8 times relative to wild type beta-glucosaccharase protein, the glucose tolerance concentration is increased twice, pH (potential of hydrogen) and temperature stability are improved, and the affinity for a substrate and the catalytic efficiency are also improved. Soybean isoflavone glycoside can be efficiently hydrolyzed by the mutant within a short time so as to prepare aglycone, and the potential application value is high.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Gene encoding beta-glucosidase
InactiveCN101363026AAvoid pollutionSolve the world energy crisisEnzymesGenetic engineeringBeta-glucosidaseNucleotide
The invention provides a gene of coded beta-glucosaccharase, which is called Unbgl1B and is obtained by constructing Metagenome DNA library of uncultured microorganisms of alkality contaminated soil and by the detecting and screening method of the activity of the beta-glucosaccharase of clone library, so as to be one of the following nucleotide sequences: 1) DNA sequences and partial sequence thereof in sequence 1 of a sequence table; 2) DNA sequences having more than 80% of homoeology compared with the DNA sequences defined by the sequence 1 of the sequence table. The DNA in the sequence 1 of a sequence table is DNA sequences of a pGEM-3Zf(+) part of a cloning vector and DNA of exogenetic uncultured microorganisms cloned on the vector, and the exogenetic DNA segment consists of 838 basic groups; the GC content of the gene is 54.3%. The gene is used for producing the beta-glucosaccharase, so as to dissociate cellobiose into single glucose molecule.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Novel glucose-resistant beta-glucosidase gene and application thereof
InactiveCN107828806AHigh productivityGreat application potentialFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliBiotechnology
The invention discloses a novel glucose-resistant beta-glucosidase gene and an application thereof. The novel glucose-resistant beta-glucosidase gene has a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and has an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the novel glucose-resistant beta-glucosidase gene and a recombinant plasmid pET32a-Bgl2238 containing the novel glucose-resistant beta-glucosidase gene; the invention further discloses a recombinant beta-glucosidase and a preparation method thereof; the recombinant beta-glucosidase gene is over-expressed in an escherichia coli prokaryotic expression system, the recombinant beta-glucosidase is subjected to high-efficiency solution expression in an escherichia coli expression system. The invention also discloses an application of the recombinant beta-glucosidase in hydrolysis of polydatin in polygonum cuspidatum; the recombinant beta-glucosidase obtained by the method is indicated to haverelatively high catalytic activity and glucose tolerance activity and have great industrialized production and application prospects.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV
Novel beta-glucosidase, coding gene thereof and applications thereof
The invention related to a novel beta-glucosidase, a coding gene thereof and efficient heterogeneous expression thereof. The invention also relates to a coding-gene-contained expression vector and a coding-gene-contained host cell. The invention also relates to a host cell expressing the coding gene and induction culture conditions thereof. The invention also relates to a method of hydrolyzing a cellobiose which is produced during cellulose degradation by the beta-glucosidase into glucose. The beta-glucosidase has characteristics of good stability and high activity under weak acid conditions, and can be applied for industrial production.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
Method for screening beta-glucosaccharase gene from mildewed sugarcane leaves based on metagenomic technology
PendingCN105462999AHighly solubleEfficient soluble expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymesBiotechnologyBeta-glucosidase
The invention discloses a beta-glucosaccharase gene, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the beta-glucosaccharase gene is shown as the SEQ ID NO.1. The invention further discloses recombinant beta-glucosaccharase, wherein the amino acid sequence of the recombinant beta-glucosaccharase is shown as the SEQ ID NO.2. The invention also discloses a screening method of the recombinant beta-glucosaccharase. The screening method comprises the following steps: extraction of microbial metagenomic DNA from the mildewed sugarcane leaves; establishment of a metagenomic library; screening of the beta-glucosaccharase gene from the metagenomic library, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the beta-glucosaccharase gene is shown as the SEQ ID NO.1; and cloning and expression for the obtained beta-glucosaccharase gene, thus the recombinant beta-glucosaccharase is obtained, wherein the amino acid sequence of the recombinant beta-glucosaccharase is shown as the SEQ ID NO.2. The recombinant beta-glucosaccharase has extremely high activity and is not sensitive to hydrolysis products under the alkaline condition.
Owner:江西省农业科学院农业应用微生物研究所
Beta-glucosaccharase and application thereof
ActiveCN103710326AHigh affinityImprove the efficiency of saccharification and hydrolysisMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyAlglucerase
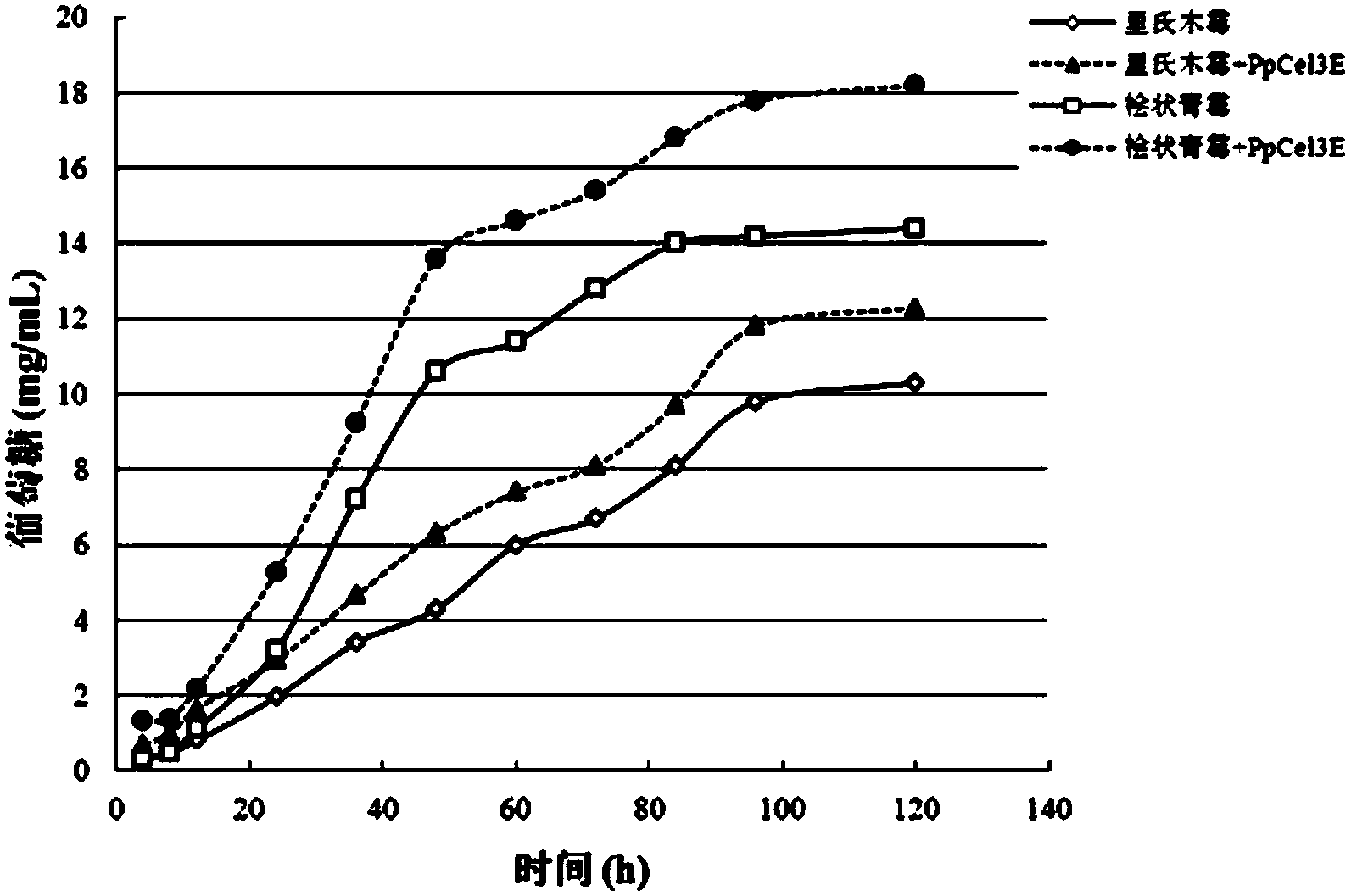
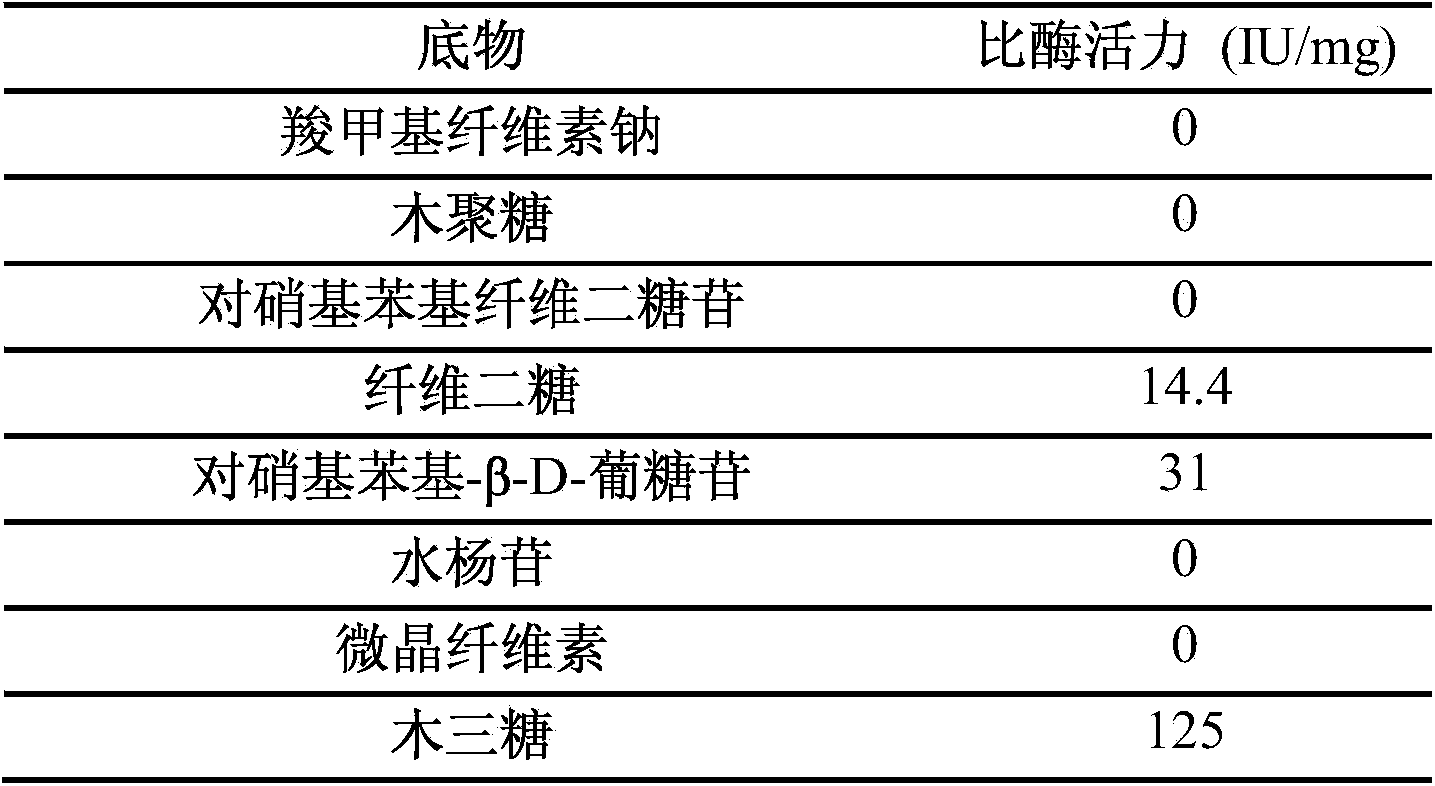
The invention discloses a beta-glucosaccharase and application thereof. The beta-glucosaccharase PpCel3E is separated from a cellulase producing bacterium extracellular crude enzyme solution for the first time. The amino acid sequence of the beta-glucosaccharase is disclosed as SEQ ID NO.1. The nucleotide sequence of the expression gene of the beta-glucosaccharase is disclosed as SEQ ID NO.2. The beta-glucosaccharase PpCel3E has unique actions on inducing cellulase or hemicellulase synthesis and enhancing saccharification and hydrolysis efficiency of cellulase producing fungus extracellular cellulase.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Preparation method of beta-glucosaccharase
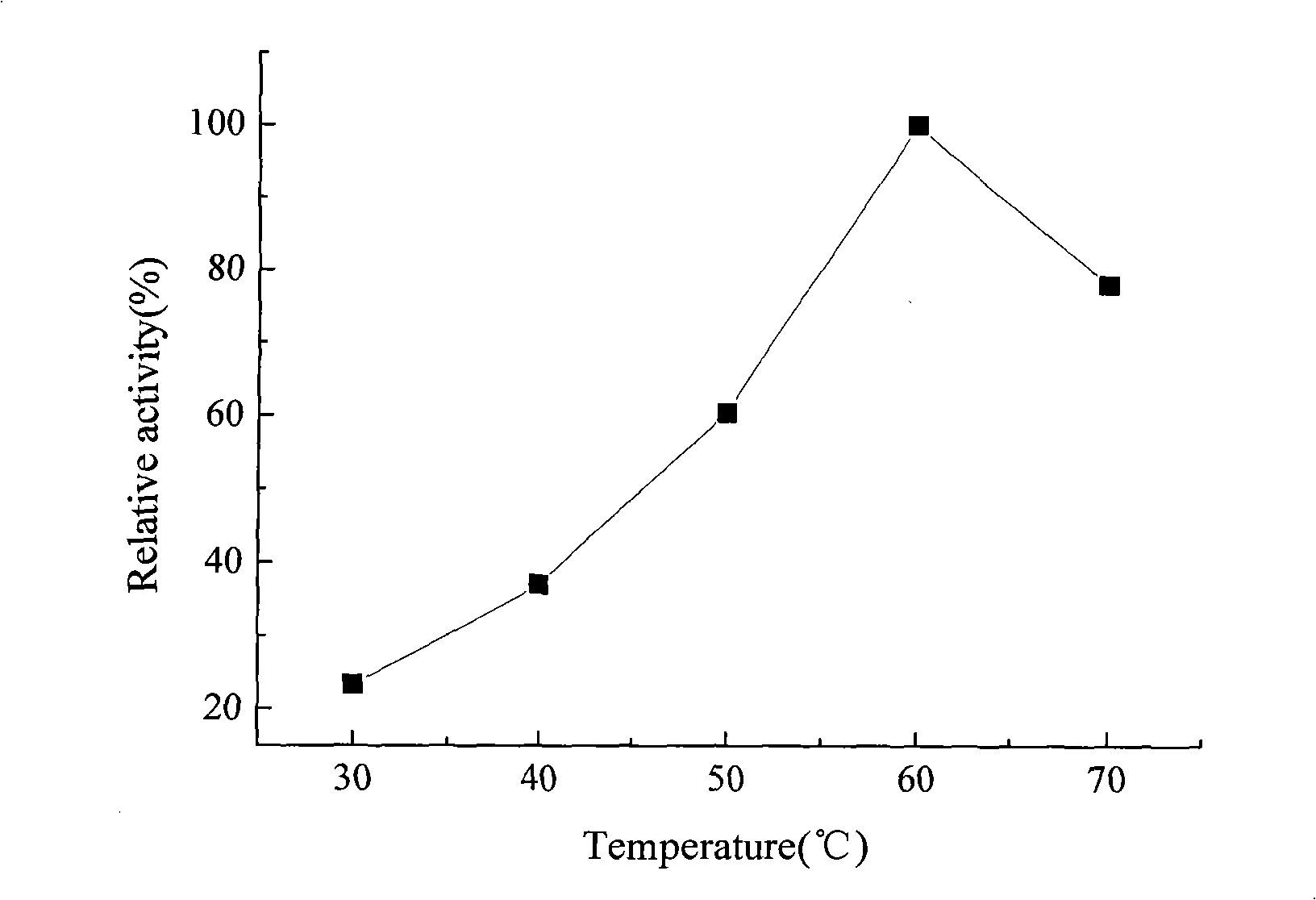
InactiveCN101705213AIncrease enzyme activityLow costMicroorganism based processesAnimal feeding stuffBeta-glucosidaseAspergillus wentii
The invention discloses a preparation method of beta-glucosaccharase. The method includes the following steps: selecting Aspergillus niger as parent strain through screening, inoculating the Aspergillus niger, the inoculum size of which is 106-108cfu / g, to bran, rice bran and ammonia chloride, wherein in a solid culture medium prepared from the bran, the rice bran and the ammonia chloride according to the weight percentage of 90-100 percent: 0-10 percent:1-3 percent, the initial water content of the culture medium is 65-75 percent, and the pH is 5.5-6.5, culturing for 48-80h at the temperature of 25-30 DEG C and detecting the activity of beta-glucosaccharase to reach 300-430U / g. The method adopts solid fermentation, uses cheap and rich subsidiary agricultural products as fermentation substrate, simultaneously optimizes the culture medium and culture conditions and achieves high yield of the beta-glucosaccharase under solid fermentation conditions, thus providing scientific basis to the industrialization development of the beta-glucosaccharase.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
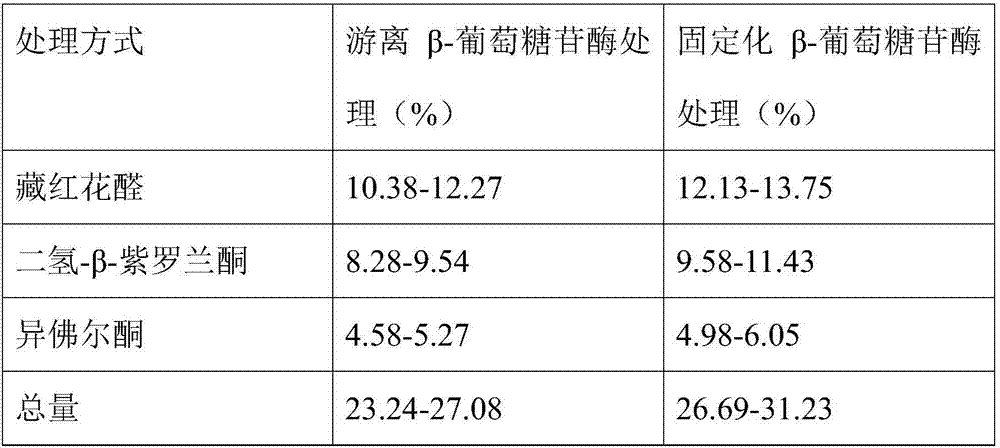
Method for preparing saffron crocus extract for cigarette from immobilized beta-glucosidase
InactiveCN106957880AImprove qualityIncreased sweetness and aromaTobacco preparationOn/in organic carrierAlgluceraseBeta-glucosidase
The invention provides a method for preparing a saffron crocus extract for cigarette from immobilized beta-glucosidase. The method comprises the following steps: (1) taking dry saffron crocus flowers, adding water and performing microwave extraction, thereby acquiring a saffron crocus extracting solution; (2) with sodium alga acid as a carrier, embedding, thereby acquiring sodium alga acid immobilized enzyme; (3) treating the saffron crocus extracting solution with immobilized beta-glucosidase; (4) filtering the extracting solution after enzyme treatment, concentrating the filtered saffron crocus extracting solution at reduced pressure and collecting a concentrated solution, thereby acquiring the saffron crocus extract for cigarette. According to the invention, the saffron crocus extract is treated with immobilized beta-glucosidase, the fragrance precusor substance in saffron crocus is hydrolyzed and the potential aroma constituent in saffron crocus is released, so that the extracting yield of the aromatic substance in saffron crocus is greatly increased, the production cost is lowered and the special cigarette perfume material with richer fragrance and higher quality can be acquired.
Owner:HUBEI CHINA TOBACCO IND
Nucleic acids and polypeptides useful for diagnosing and treating complications of pregnancy
InactiveCN101299962AMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisAlpha defensinInsulin-like growth factor-binding protein
Disclosed herein are methods for diagnosing or treating pregnancy related hypertensive disorders that include the use of a polypeptide or a nucleic acid encoding a polypeptide selected from the following: follistatin related protein, interleukin 8, inhibin A, VEGF-C, angiogenin, beta fertilin, hypothetical protein, leukocyte associated Ig-like receptor secreted protein, erythroid differentiation protein, adipogenesis inhibitory factor, corticotropin releasing factor binding protein, alpha-1- anti-chymotrypsin, insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5, CD33L, cytokine receptor like factor 1, platelet derived endothelial growth factor, lysyl hydroxylase isoform 2, stanniocalcin precursor, secreted frizzled related protein, galectin-3, alpha defensin, ADAM-TS3, cholecystokinin precursor, interferon stimulated T-cell alpha chemoattractant precursor, azurocidin, sperminine oxidase, UDP glycosyltransferase 2 family polypeptide B28, neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor 2, neutral endopeptidase, CDC28 protein kinase regulatory subunit 2, beta glucosidase, lanosterol synthase, calcium / calmodulin-dependent serine protein kinase, estrogen receptor-alternatively spliced transcript H, chemokine (CX3C motif) receptor 1, tyrosinase-related protein 1, hydoxy-delta-5-steroid dehyrogenase, dihydropyramidinase-like-4, and cytochrome P450-family 11.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Thermophilic acid-resisting beta-glucosaccharase producing strain and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a thermophilic acid-resisting beta-glucosaccharase producing strain and a preparation method thereof. The strain (CCTCC M209312) is separated from decayed corn stalks. The screening method comprises the following steps: collecting corn stalks suitable for decaying, cutting, diluting with sterilized water, carrying out induction enrichment culture with cellobiose, carrying out gradient concentration dilution, coating on a screening plate, selecting the colony with larger plaques as the primary screening, and carrying out primary screening for times; and after culturing with a steam-explosion corn stalk powder induction culture medium, measuring the enzyme activity and carrying out second screening, and centrifugating the screened strain fermentation liquid to obtain the supernatant. The supernatant can be used as a liquid enzyme preparation or spray-dried to obtain a solid enzyme preparation, and can adapt to various acid high-heat industrial conditions. The invention screens out a new strain from decayed corn stalks by using biotechnology, and uses steam-explosion stalk powder and other cheap culture media to produce the thermophilic acid-resisting beta-glucosaccharase. The invention is used in the industrial fields of cellulose degradation systems, food, textile, papermaking and the like.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Hyperthermophilic glycosidase mutant and application thereof in preparation of ginsenoside CK
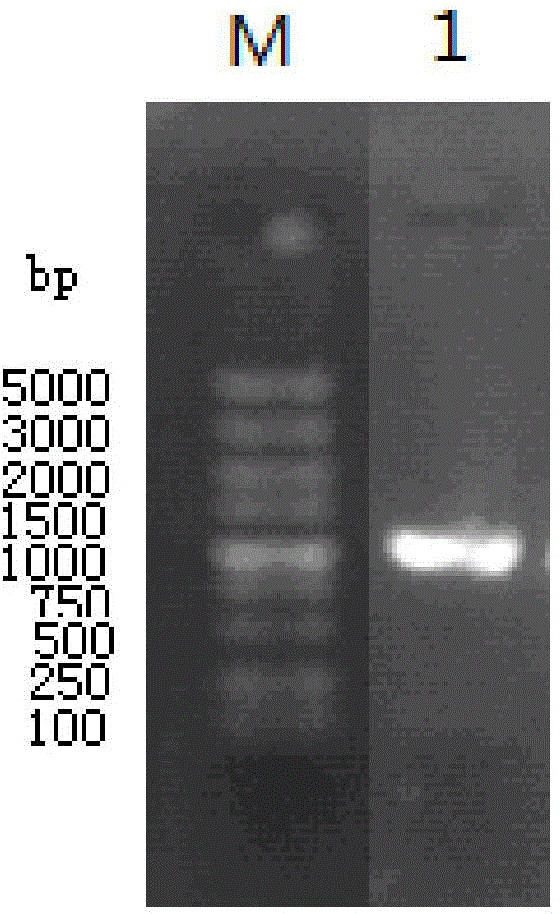
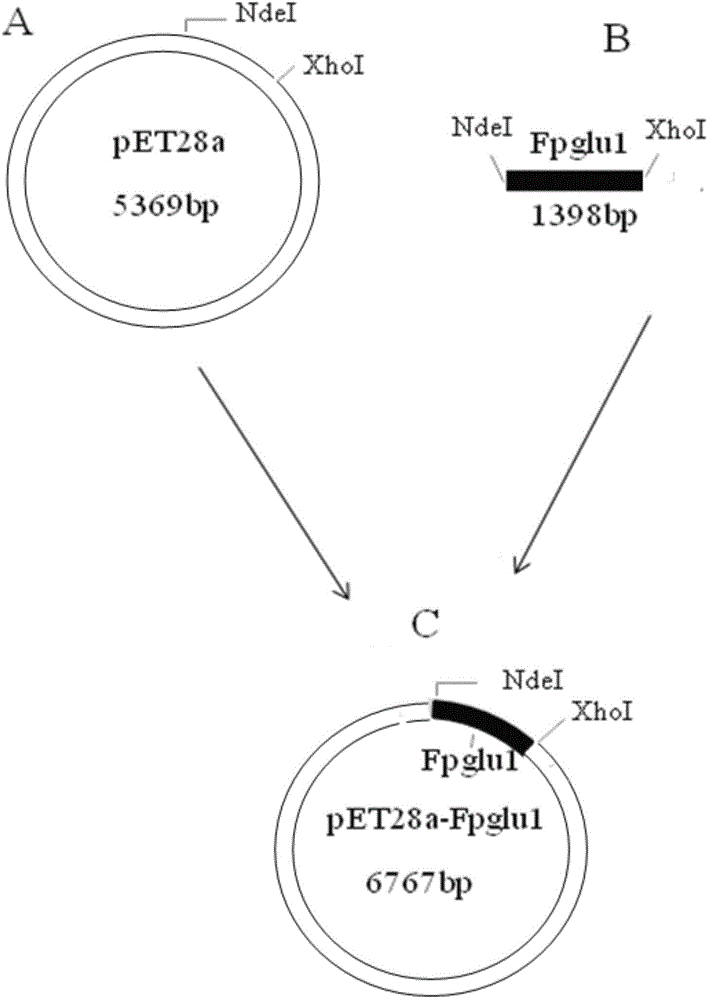
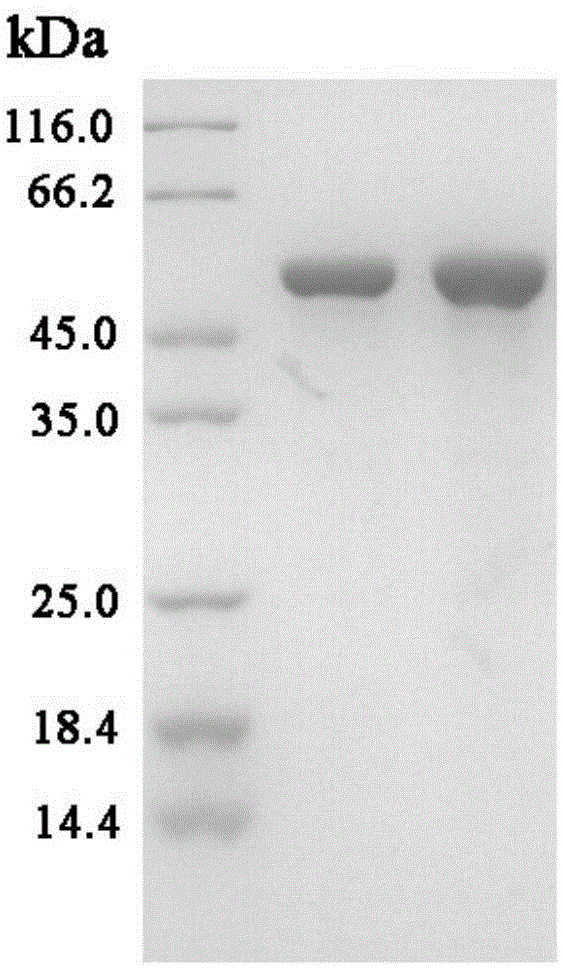
The invention relates to a hyperthermophilic glycosidase mutant and an application thereof in preparation of ginsenoside CK, and belongs to the technical field of biotechnology engineering. An amino acid sequence of the hyperthermophilic glycosidase mutant is as shown in SEQ ID NO:2; and the hyperthermophilic glycosidase mutant is applied to preparation of rare ginsenoside CK. The hyperthermophilic glycosidase mutant has high heat resistance and stability; relatively high catalytic activity can still be kept after heat preservation at 70-80 DEG C for over 300 hours, and thus hyperthermophilic glycosidase mutant has the advantages of low storage and transportation cost, and low requirement standards on a cooling system of a reactor when applied to production; the kinetic reaction is accelerated; meanwhile, the hyperthermophilic glycosidase mutant has beta-glucosaccharase activity; glucosides of main protopanaxadiol type saponins C3 site and C20 site can be hydrolyzed on the basis that the saponin structure is not destroyed; and the hyperthermophilic glycosidase mutant is efficient, specific, few in byproducts, high in yield and the like, so that the Fpglula can be applied to industrial production of a rare ginsenoside Compound K.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com