Production of beta-glucosidase, hemicellulase and ligninase in E1 and FLC-cellulase-transgenic plants
a technology of hemicellulase and ligninase, which is applied in the field of transgenic plants, can solve the problems of harm to plant growth and development, and the heterologous e1 enzyme does not have a direct access, so as to increase the amount of hydrolyzing enzyme and increase the biomass
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
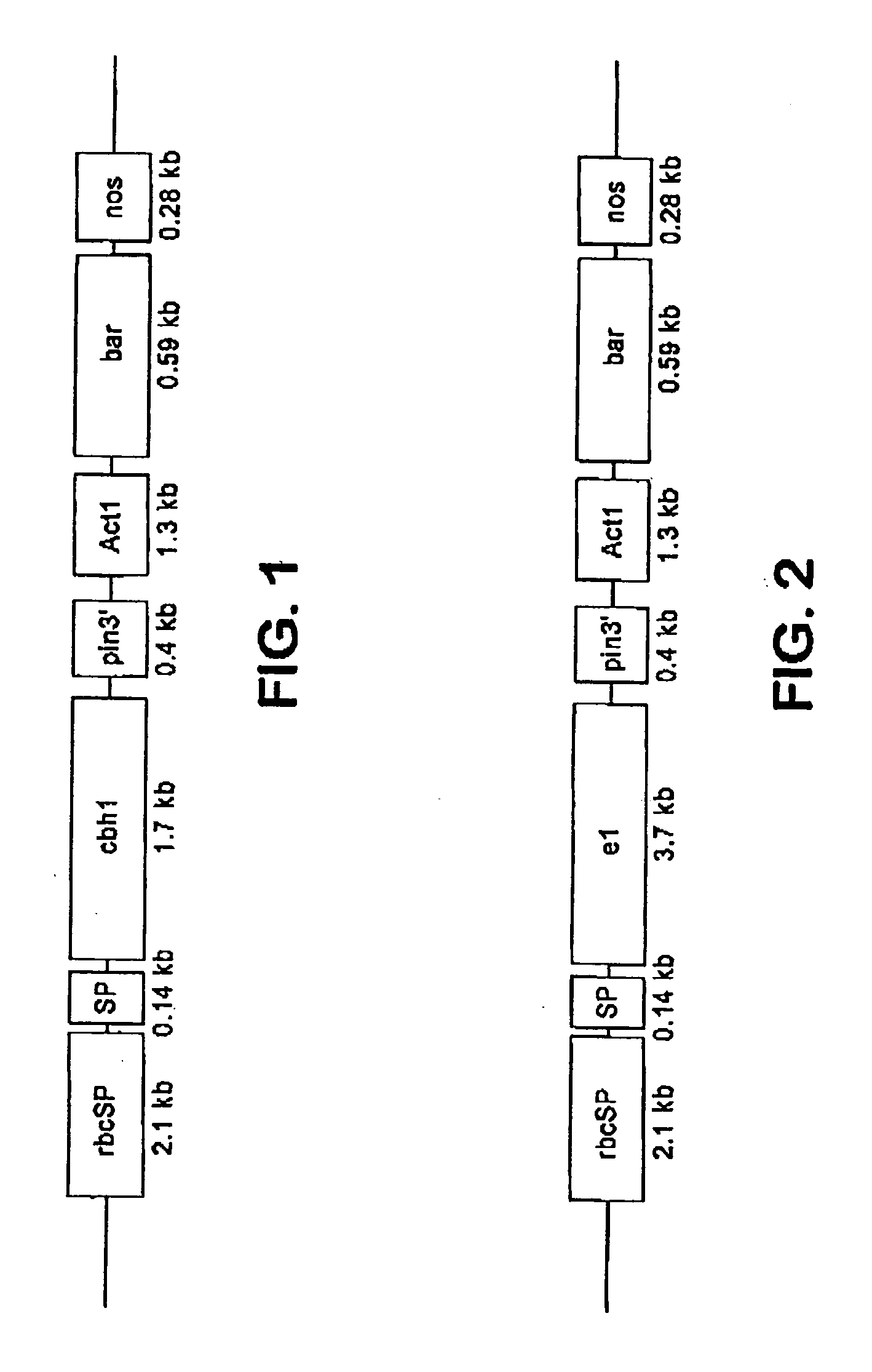
[0114] This example shows the construction of plasmids comprising a heterologous gene expression cassette comprising a DNA encoding a cellulase fusion protein and a heterologous gene expression cassette comprising a DNA encoding the bar gene (Table 1).
TABLE 1ConstructPlasmid features1rbcSP / e1 / pin 3′ / / Act1rbcSP leaf-specificP / bar / nos 3′promoter drivingcellulase cDNA of A. cellulolyticus2rbcSP / cbh1 / pin 3′ / / Act1rbcSP leaf-specificP / bar / nos 3′promoter drivingcellulase cDNA of T. reesi3rbcSP / rbcS SP / e1 / pin 3′ / / Act1The rbcS SP targetsP / bar / nos 3′cellulase of A. cellulolyticusintomaize chloroplasts4rbcSP / rbcS SP / cbh1 / pin 3′ / / The rbcS SP targetsAct1 P / bar / nos 3′cellulase of T. reesiinto maize chloroplasts
Abbreviations:
The term “rbcSP” means the rice rubisco rbcS promoter region. The rbcSP is a leaf-specific promoter that limits transcription of rbcS to the leaves (Schaeffer and Sheen, Plant Cell 3: 997-1012 (1991)). The nucleotide sequence for the rbcS promoter region is set forth in SEQ...
example 2
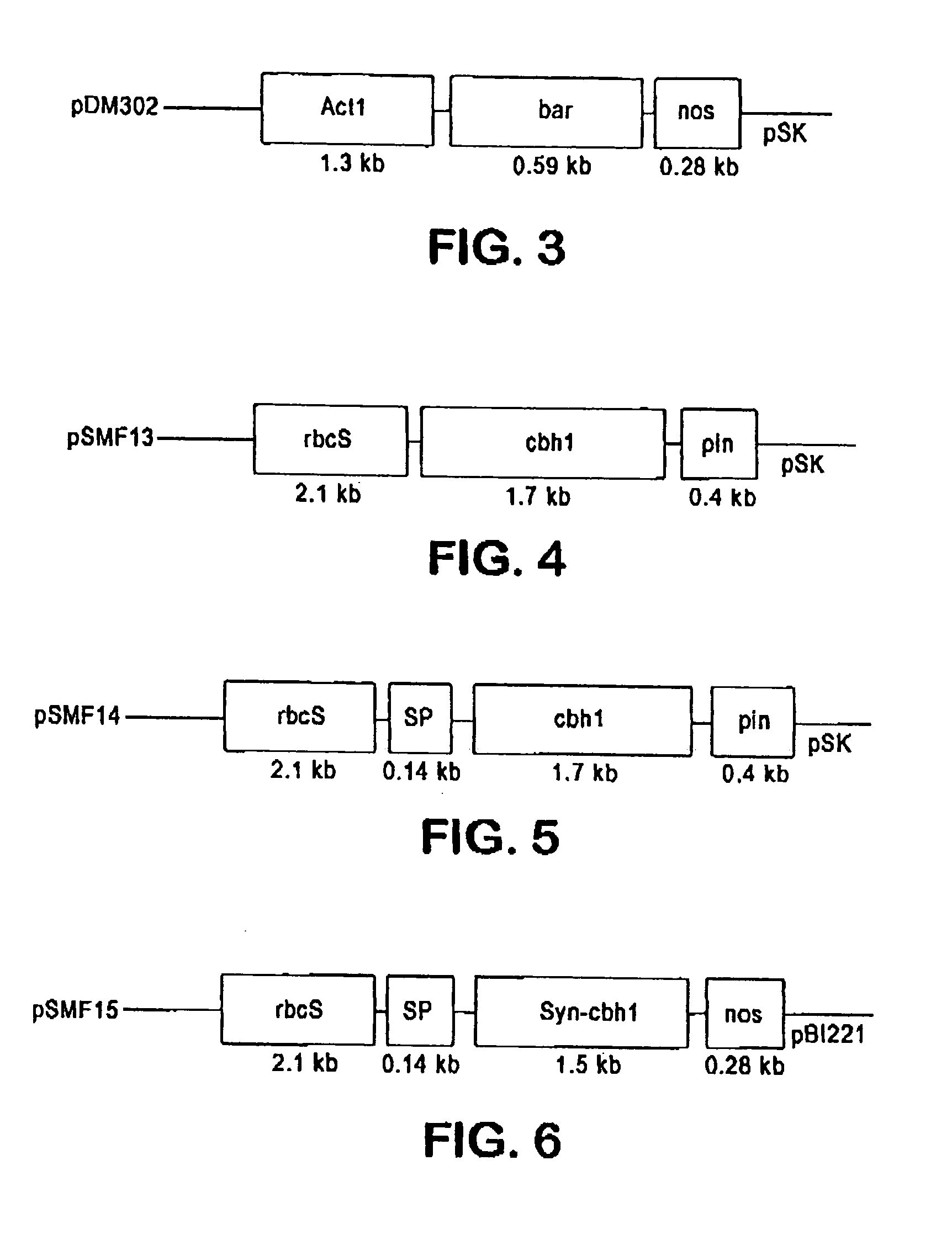
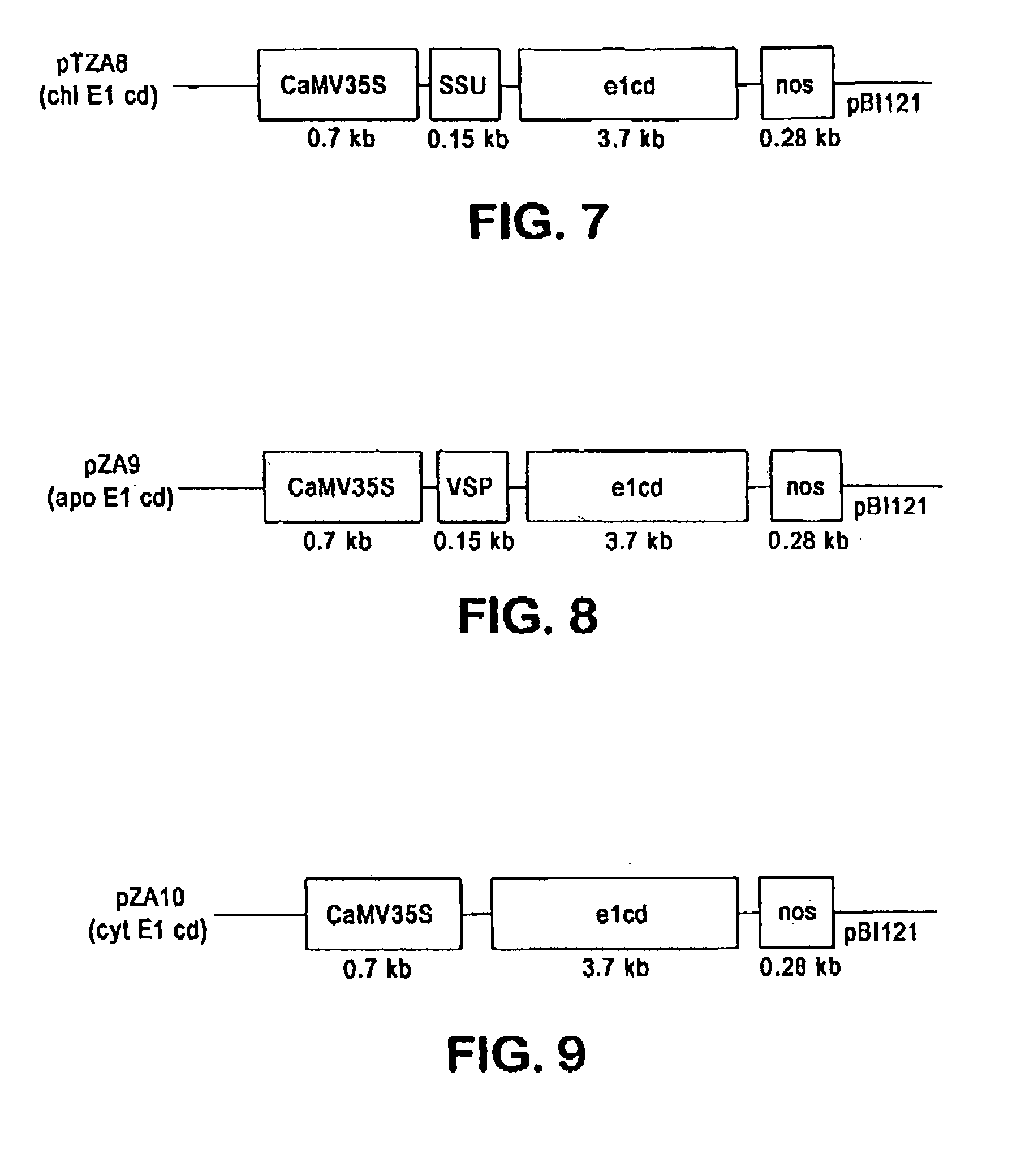
[0131] This example shows the construction of plasmids comprising a heterologous gene expression cassette comprising a DNA encoding a cellulase fusion protein. The plasmid constructs are shown in Table 2.
TABLE 2ConstructPlasmid features1rbcSP / cbh1 / pin 3′rbcSP leaf-specificpromoter drivingcellulase cDNA of T. reesei2rbcSP / rbcS SP / cbh1 / pin 3′The rbcS SP targetscellulase of T. reesiinto maize chloroplasts3rbcSP / rbcS SP / syn-cbh1 / pin 3′The rbcS SP targetsmodified cellulase of T. reeseiinto maizechloroplasts4CaMv35s / SSU / e1 / nos3′The SSU targets thecellulase of A. cellulolyticusintomaize chloroplasts5CaMv35s / VSP / e1 / nos3′The VSP targets thecellulase of A. cellulolyticusintomaize apoplasts6CaMv35s / e1 / nos3′No signal peptide
Abbreviations:
The term “syn-cbh1” refers to a cbh1 gene that has been codon-modified for use in transformation of tobacco plants. It is available from.
The term “CaMV35s” refers to the cauliflower mosaic virus promoter.
example 3
[0148] This example shows the construction of plasmids comprising a heterologous gene expression cassette comprising a DNA encoding a ligninase fusion protein and a heterologous gene expression cassette comprising a DNA encoding the bar gene. The constructs are shown in Table 3.
TABLE 3ConstructPlasmid features1rbcSP / ckg4 / pin 3′ / / Act1rbcSP leaf-specificP / bar / nos 3′promoter driving ckg4cDNA of P. chrysosporium2rbcSP / ckg5 / pin 3′ / / Act1rbcSP leaf-specificP / bar / nos 3′promoter driving ckg5cDNA of P. chrysosporium3rbcSP / rbcS SP / ckg4 / pinThe rbcS SP targets ckg43′ / / Act1 P / bar / nos 3′into maize chloroplasts4rbcSP / rbcS SP / ckg5 / pin 3′ / / The rbcS SP targets ckg5Act1 P / bar / nos 3′into maize chloroplasts
Abbreviations:
The terms “ckg4” and “ckg5” mean the ligninase cDNAs isolated from the basidiomycete Phanerochaete. chrysosporium, SEQ ID NO: 11 and SEQ ID NO: 13, respectively. The codons for the 28 amino acid leader are deleted so that the expressed gene product remains inside the cells.
[0149] The ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical conductance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com