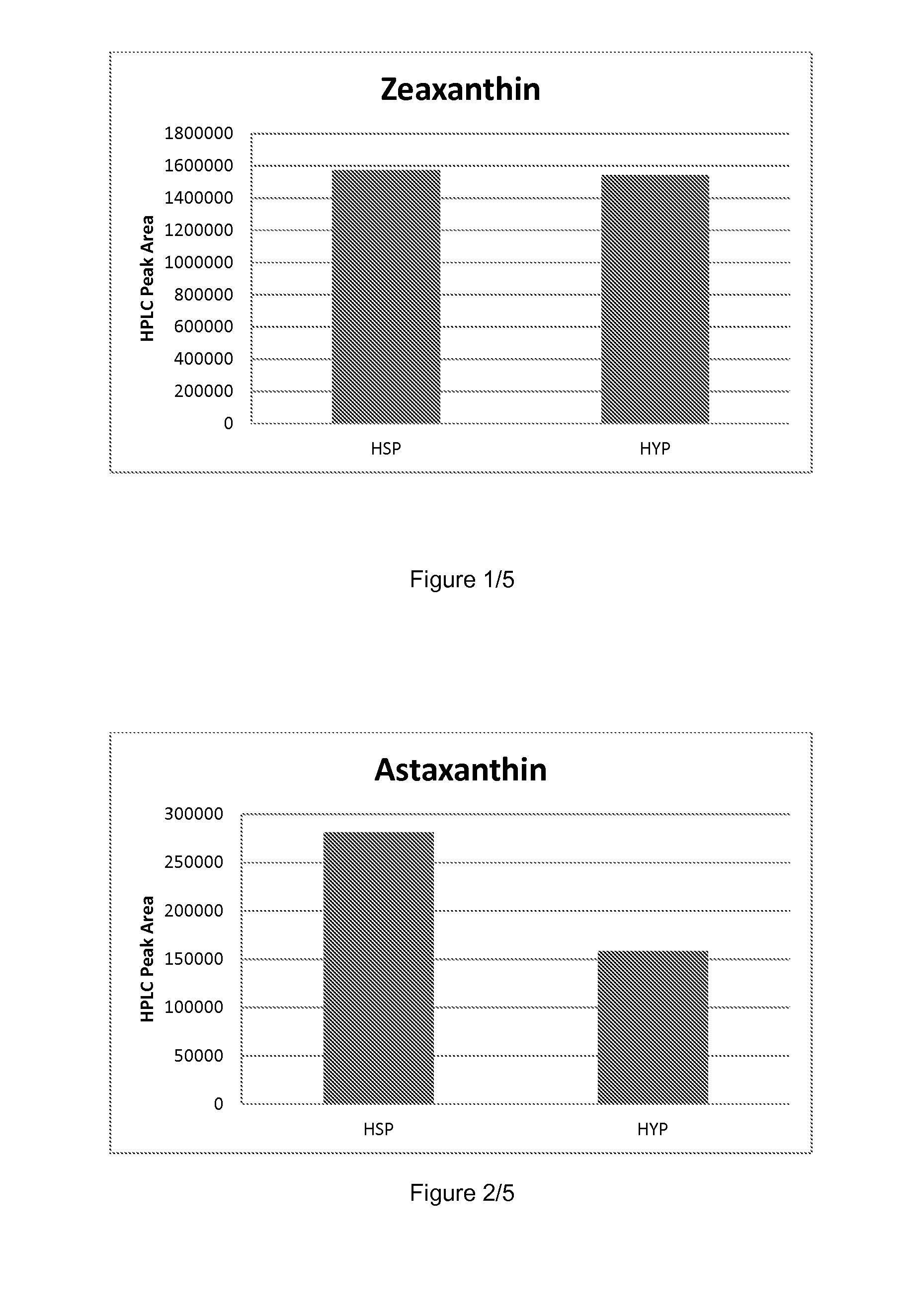
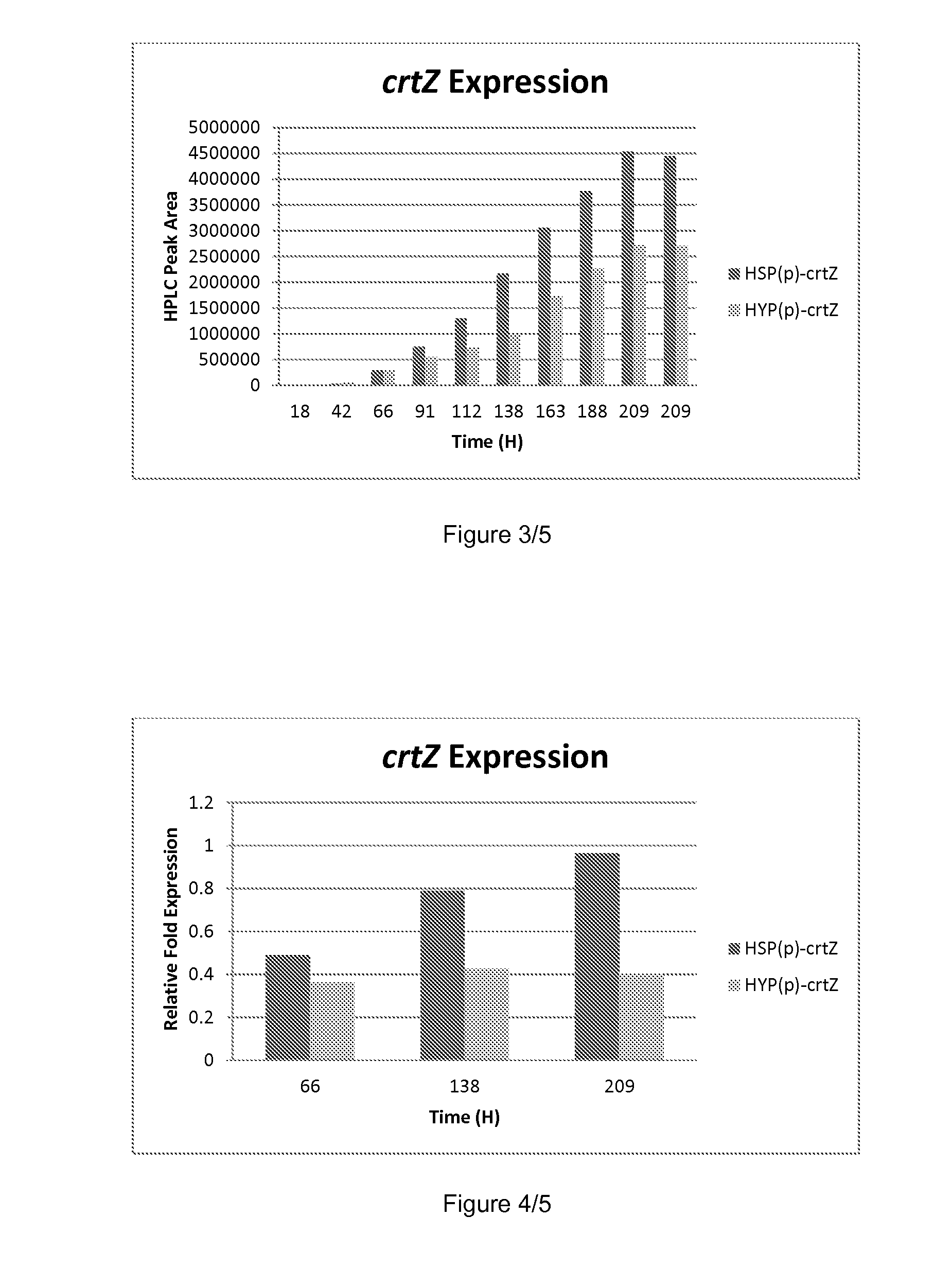
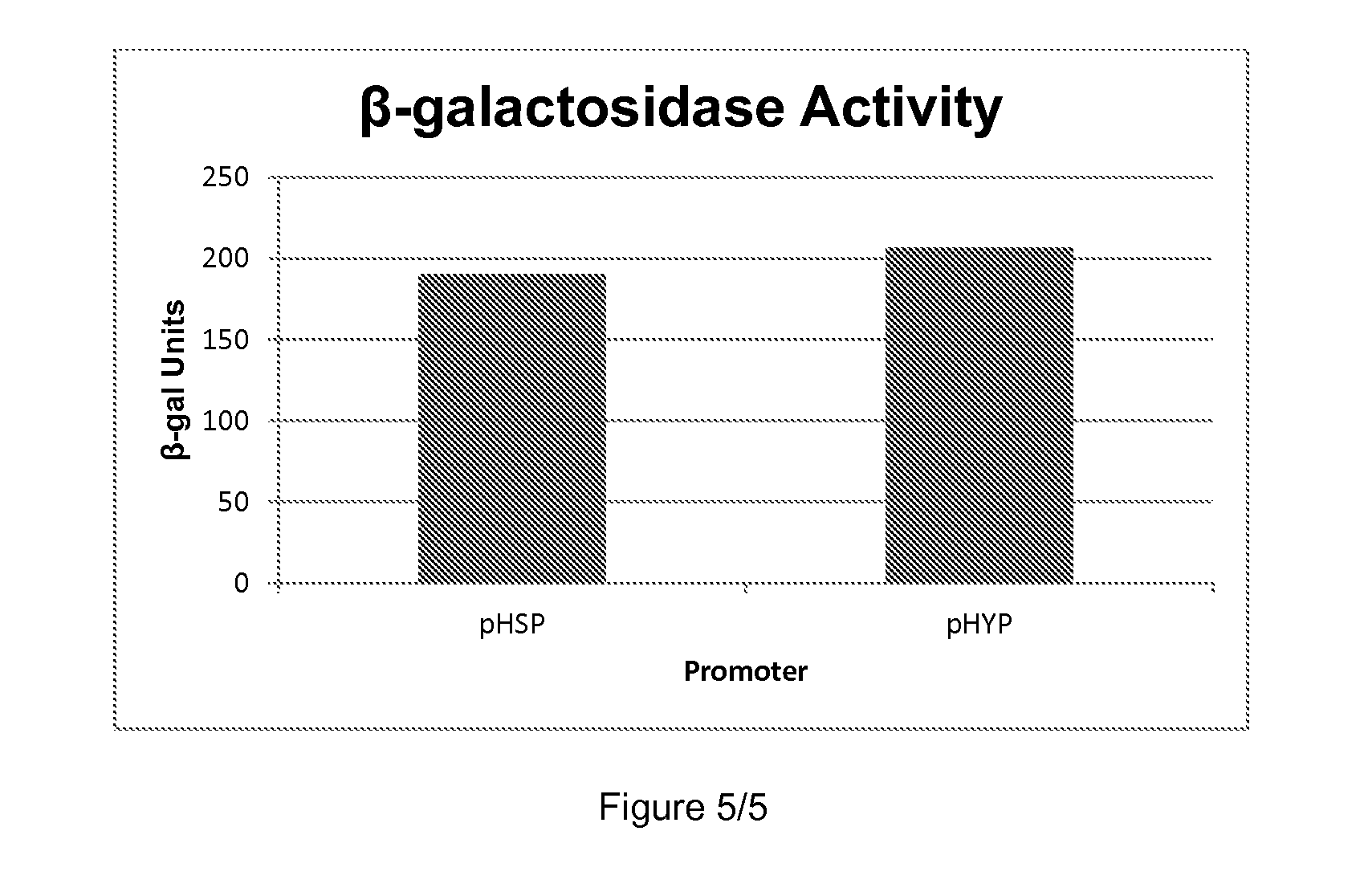
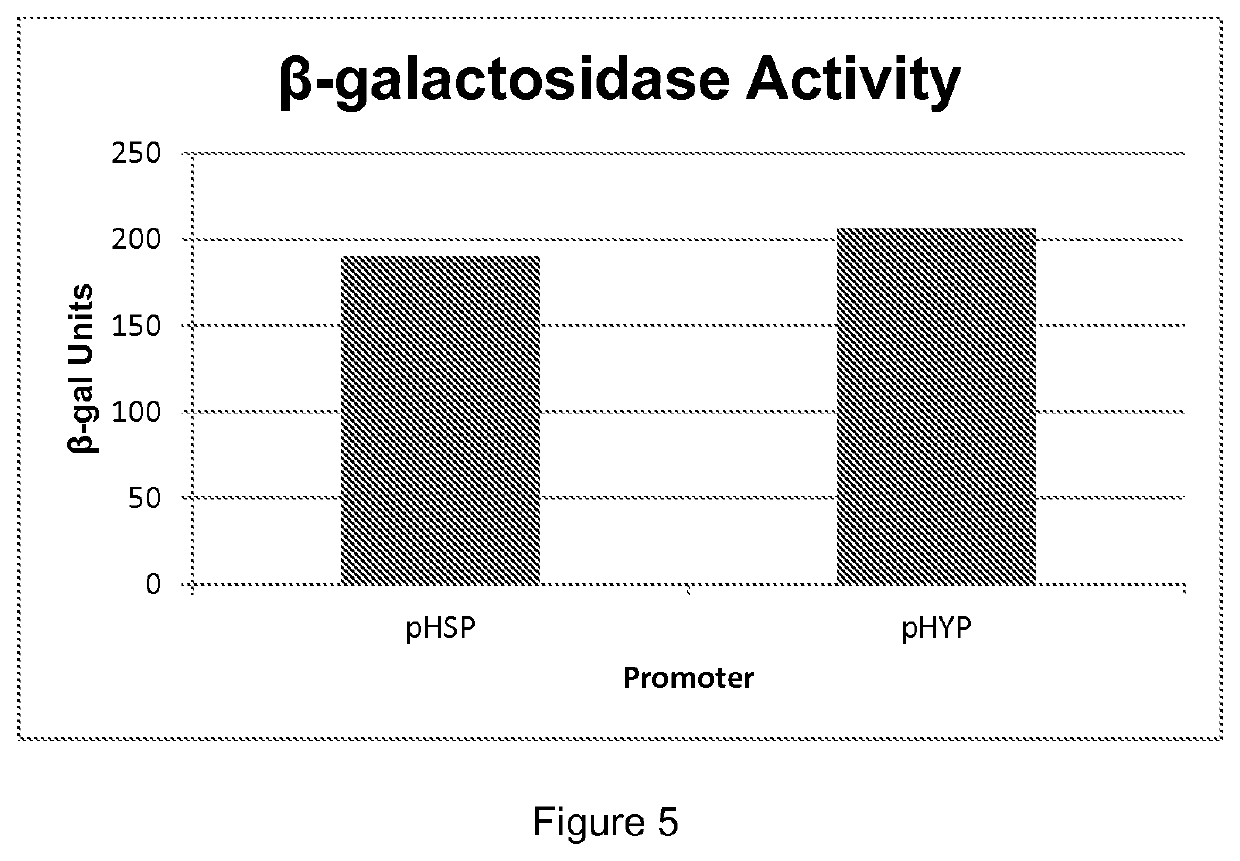
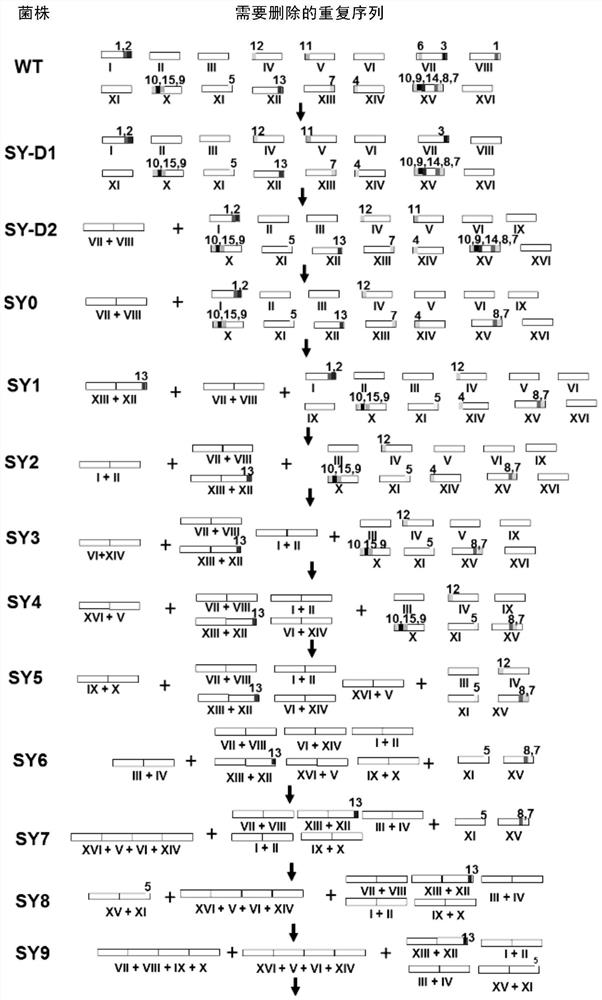
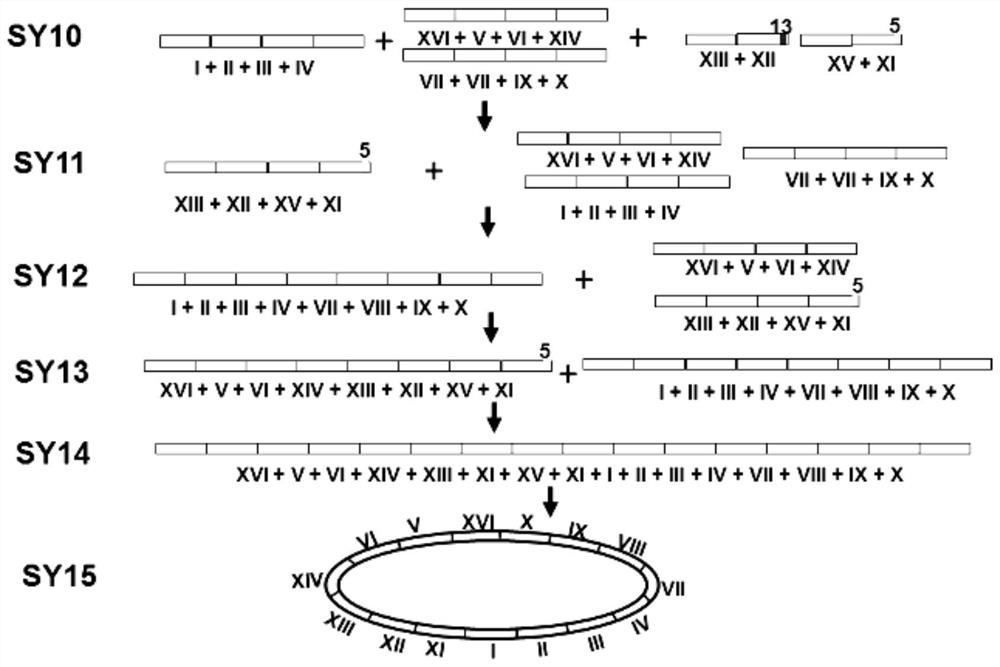
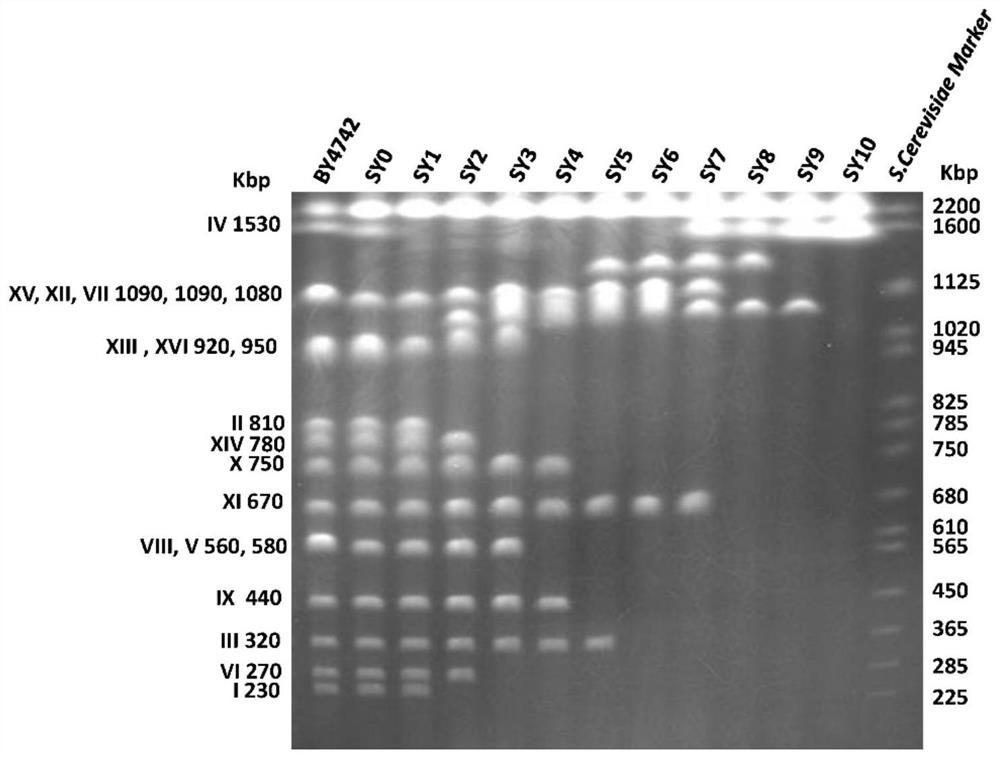
Patents
Literature
38 results about "Heterologous gene expression" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Transcription factors, DNA and methods for introduction of value-added seed traits and stress tolerance
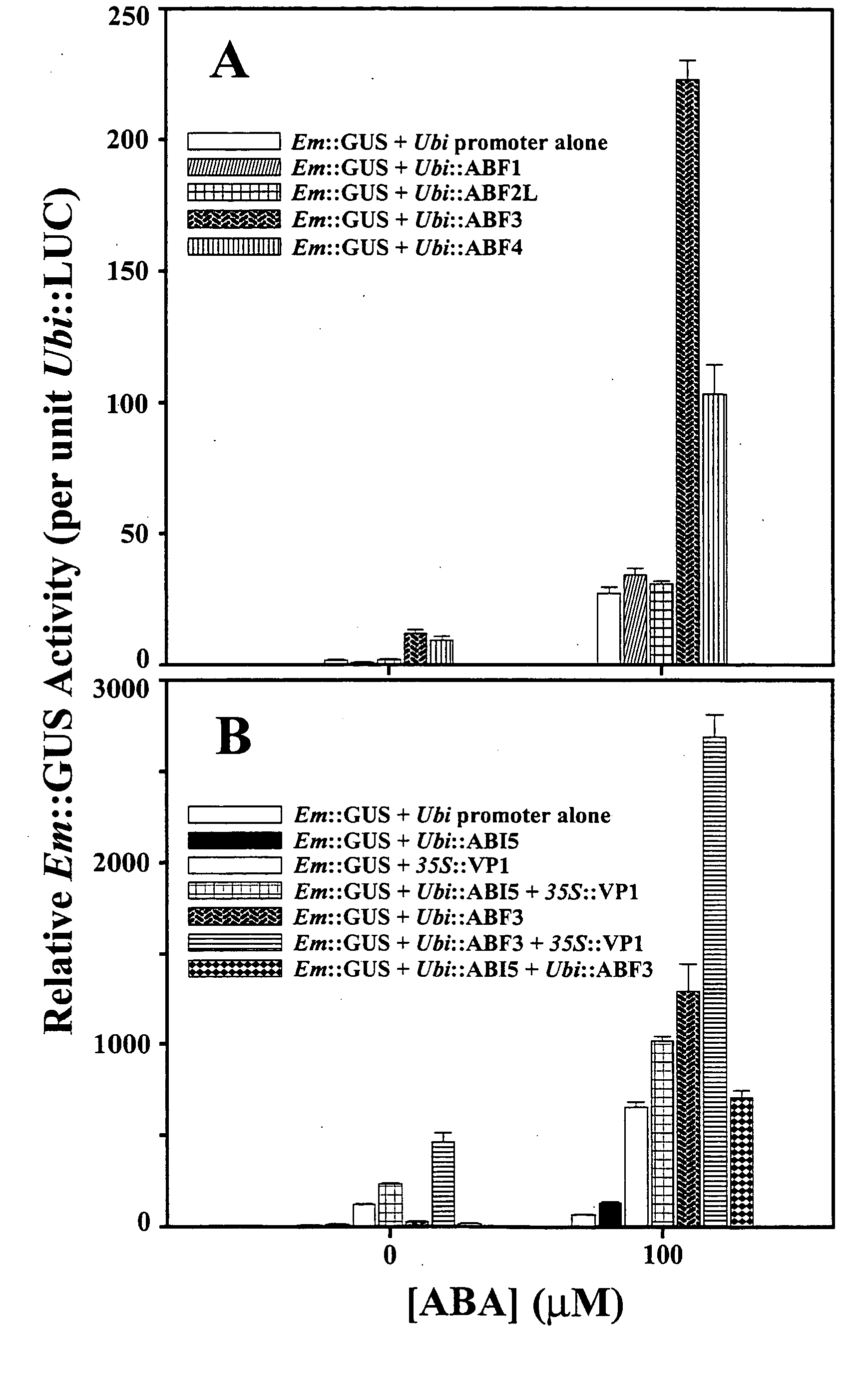
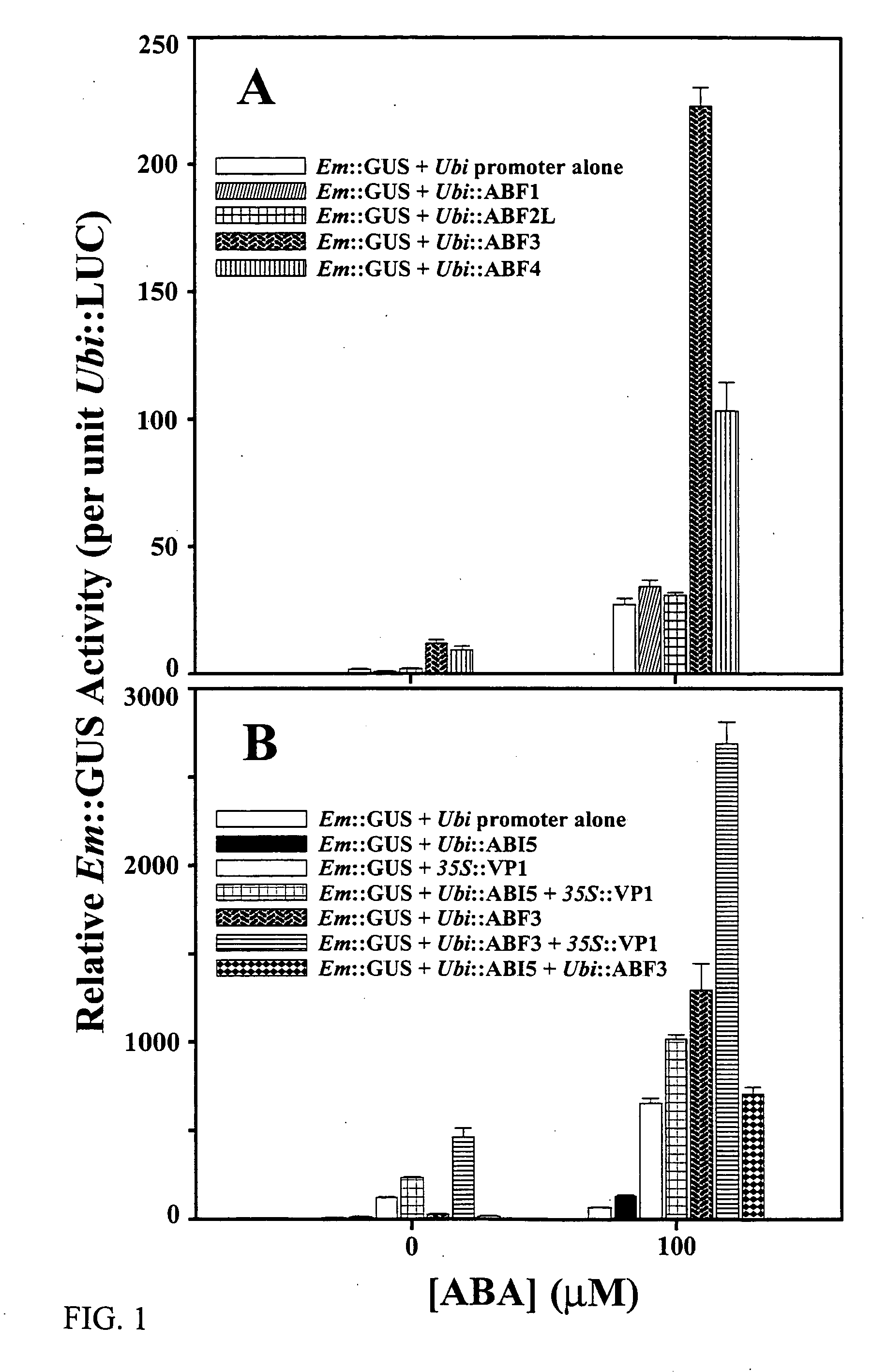
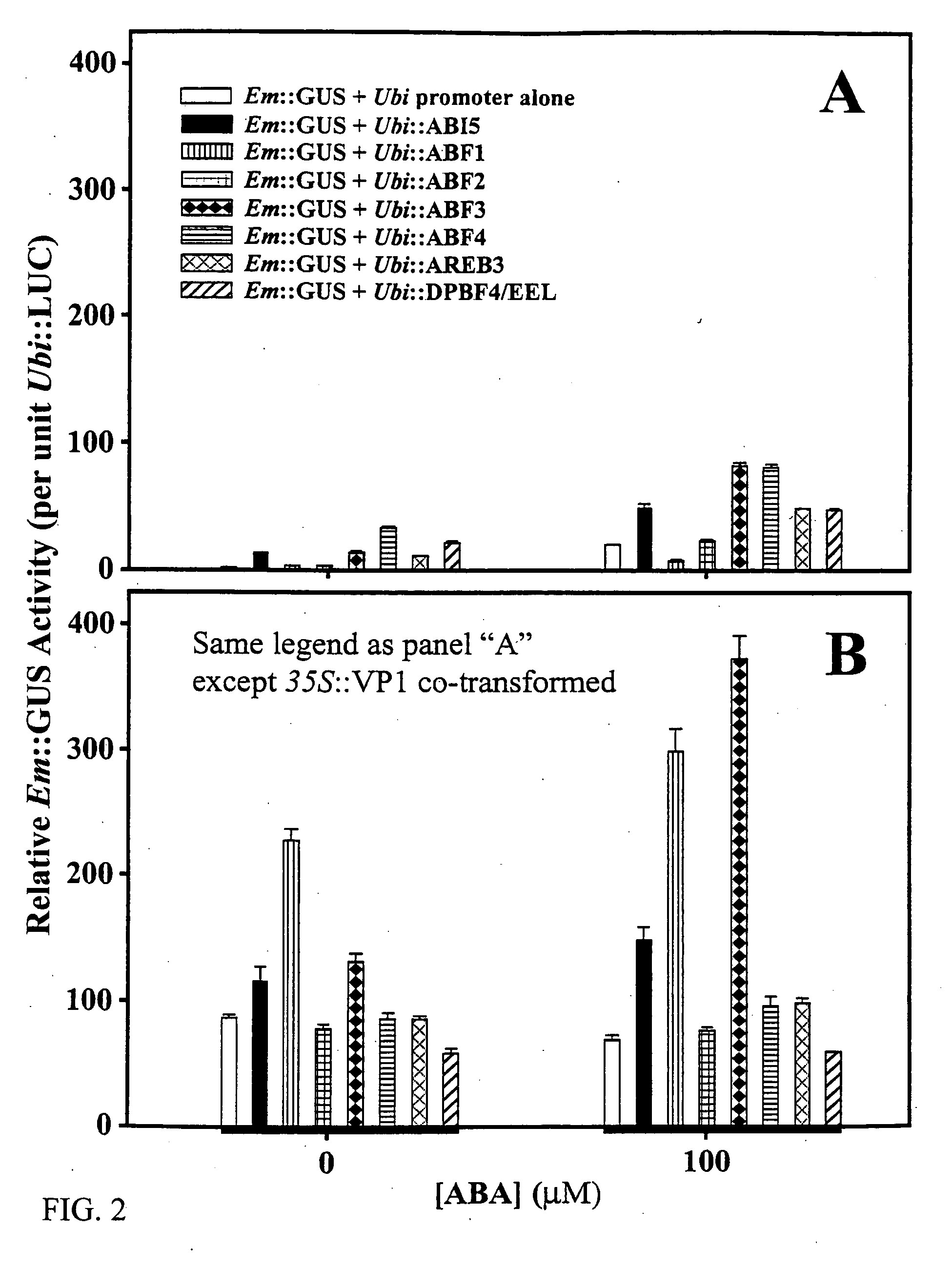
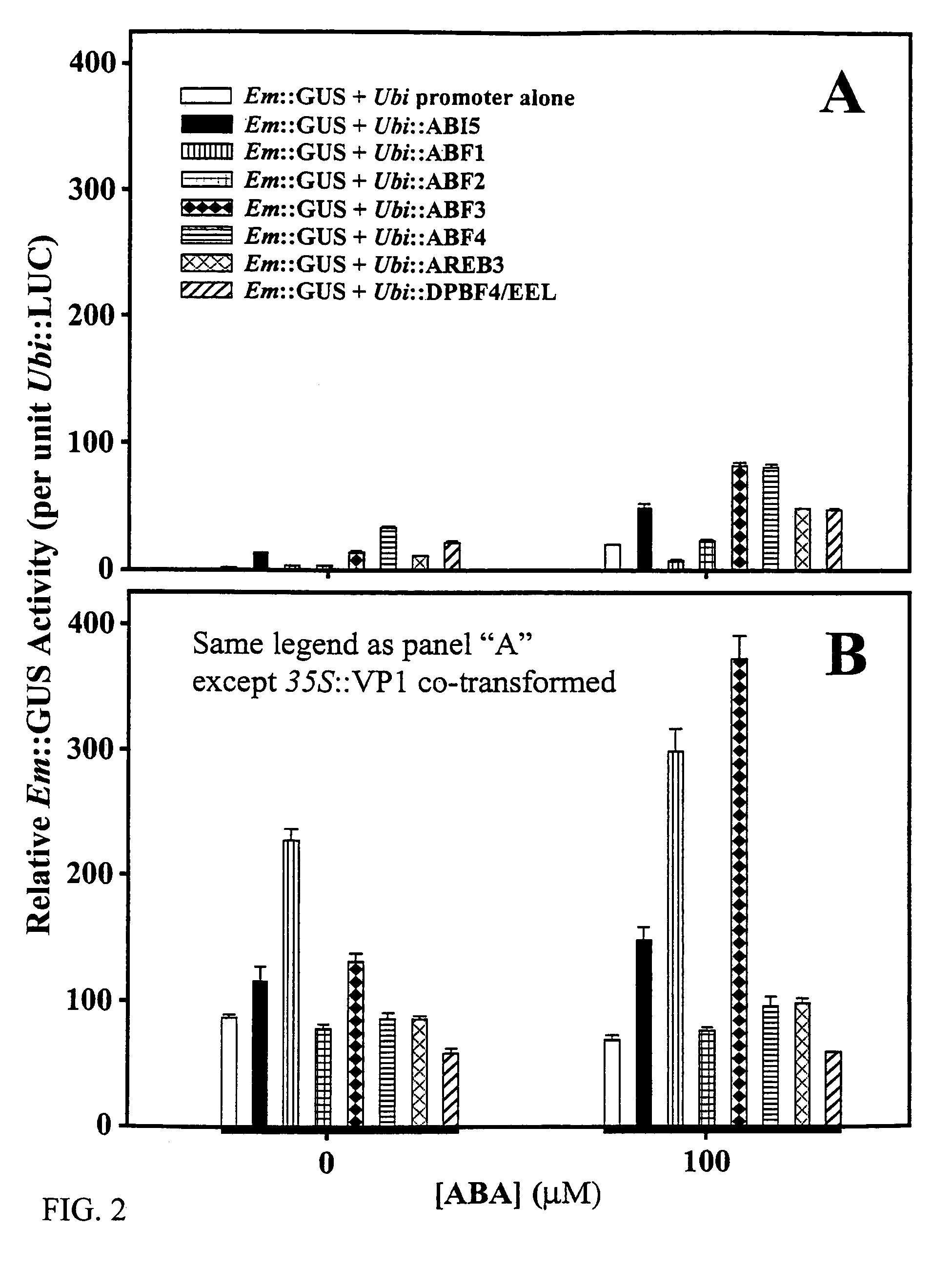
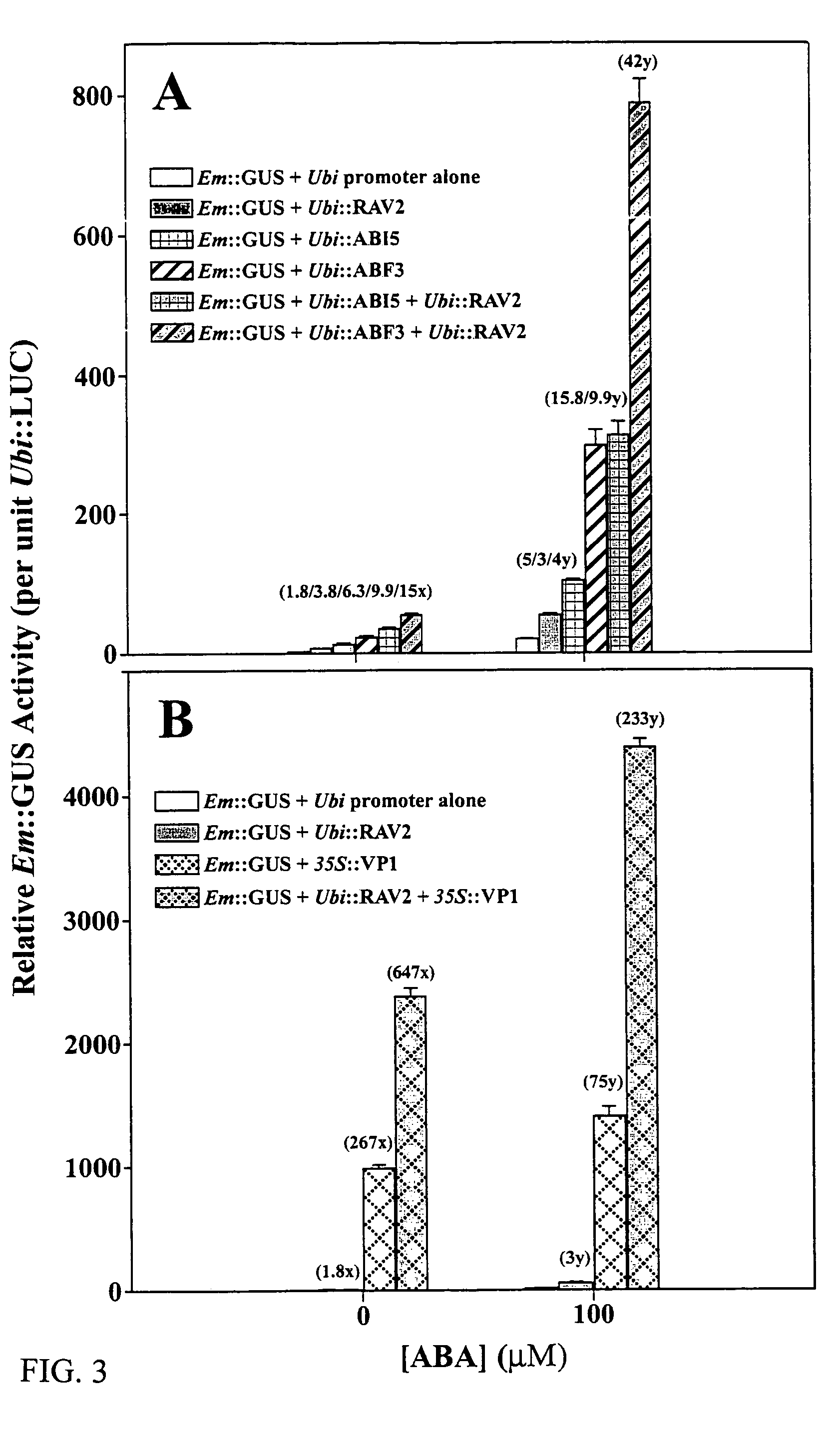
Abscisic acid-inducible gene expression in different plant tissues is enhanced synergistically by the co-expression of a B3-domain transcription factor and various bZIP-domain transcription factors, or a different B3-domain transcription factor. Using these transcription factors in novel formulations, as shown by examples, will confer value-added traits to transgenic plants, including, but not limited to, higher levels of heterologous gene expression, drought and salt tolerance, viability and productivity under stress, and enhanced nutrient reserves and seed properties.
Owner:TEXAS TECH UNIVERSITY
Highly regulable promoter for heterologous gene expression
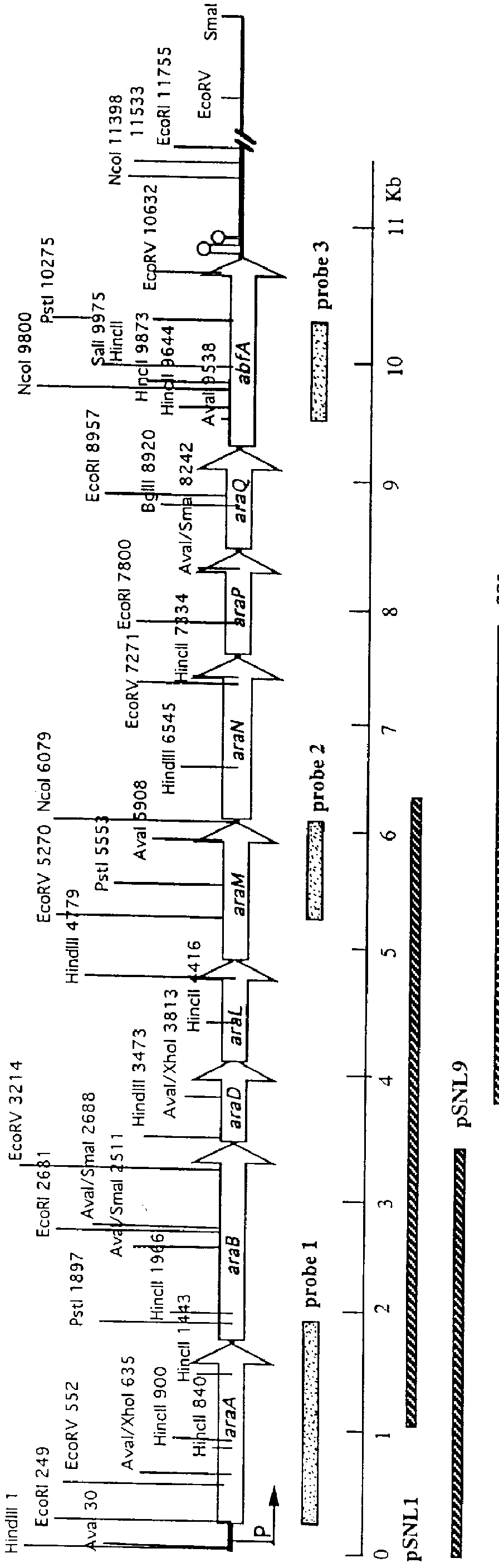
InactiveUS6030807APromote reproductionModulate transcriptional activityBacteriaSugar derivativesL-ArabinoseOperon gene
The invention relates to an operon encoding enzymes involved in the utilization of L-arabinose, to the promoter derived therefrom, and to expression systems utilizing the promoter. The promoter is particularly useful for expression of DNA sequences in prokaryotes because of their inducibility and repressibility of the promoter. The invention also relates to the enzymes of the operon, and antibodies thereto.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Formaldehyde dehydrogenase genes from methylotrophic yeasts
InactiveUS20070298500A1Microbiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesMethyl groupAmmonium sulfate
Owner:RES CORP TECH INC
Eukaryotic gene expression cassette and uses thereof
An expression cassette comprising a herpes simplex virus latency-associated transcript P2 region, a promoter and a heterologous gene operably linked in that order. The expression cassette is incorporated into herpes simplex virus vectors to allow for delivery of heterologous genes to mammalian cells for long-term expression.
Owner:BIOVEX LTD
Flavobacterium heparinum expression system
This invention is directed to Flavobacterium heparinum for use as a host cell organism for the expression of homologous and heterologous genes.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
Transcription factors, DNA and methods for introduction of value-added seed traits and stress tolerance
Abscisic acid-inducible gene expression in different plant tissues is enhanced synergistically by the co-expression of a B3-domain transcription factor and various bZIP-domain transcription factors, or a different B3-domain transcription factor. Using these transcription factors in novel formulations, as shown by examples, will confer value-added traits to transgenic plants, including, but not limited to, higher levels of heterologous gene expression, drought and salt tolerance, viability and productivity under stress, and enhanced nutrient reserves and seed properties.
Owner:TEXAS TECH UNIVERSITY
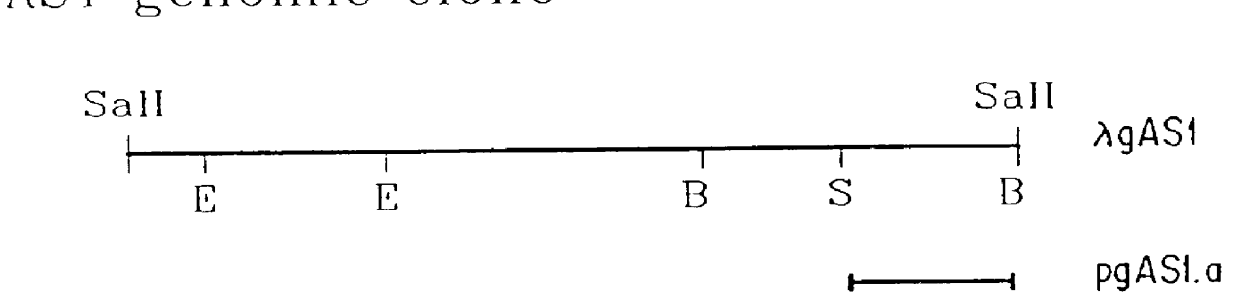
Heterologous gene expression utilizing plant asparagine synthetase promoters
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Novel promoter and application thereof
ActiveCN104789566AIncrease productionIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaHydrolasesMicrobial GeneticBiotechnology
The invention discloses a novel promoter and application thereof, and belongs to the field of microbial genetic engineering. According to a method disclosed by the invention, the related promoter Pd(-35 to -10) HpaII gene is formed by series connection modification on the core area based on the promoter PHpaII; under control and transcription of the novel promoter Pd(-35 to -10) HpaII, the fibrinolytic activity of the recombinant nattokinase is up to 200.8 FU / ml. The method is efficient, safe and capable of effectively improving the expression quantity of nattokinase, and provides a theoretical basis for further study on influence of the promoter on heterologous gene expression.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Process, vectors and engineered cell lines for enhanced large-scale transfection
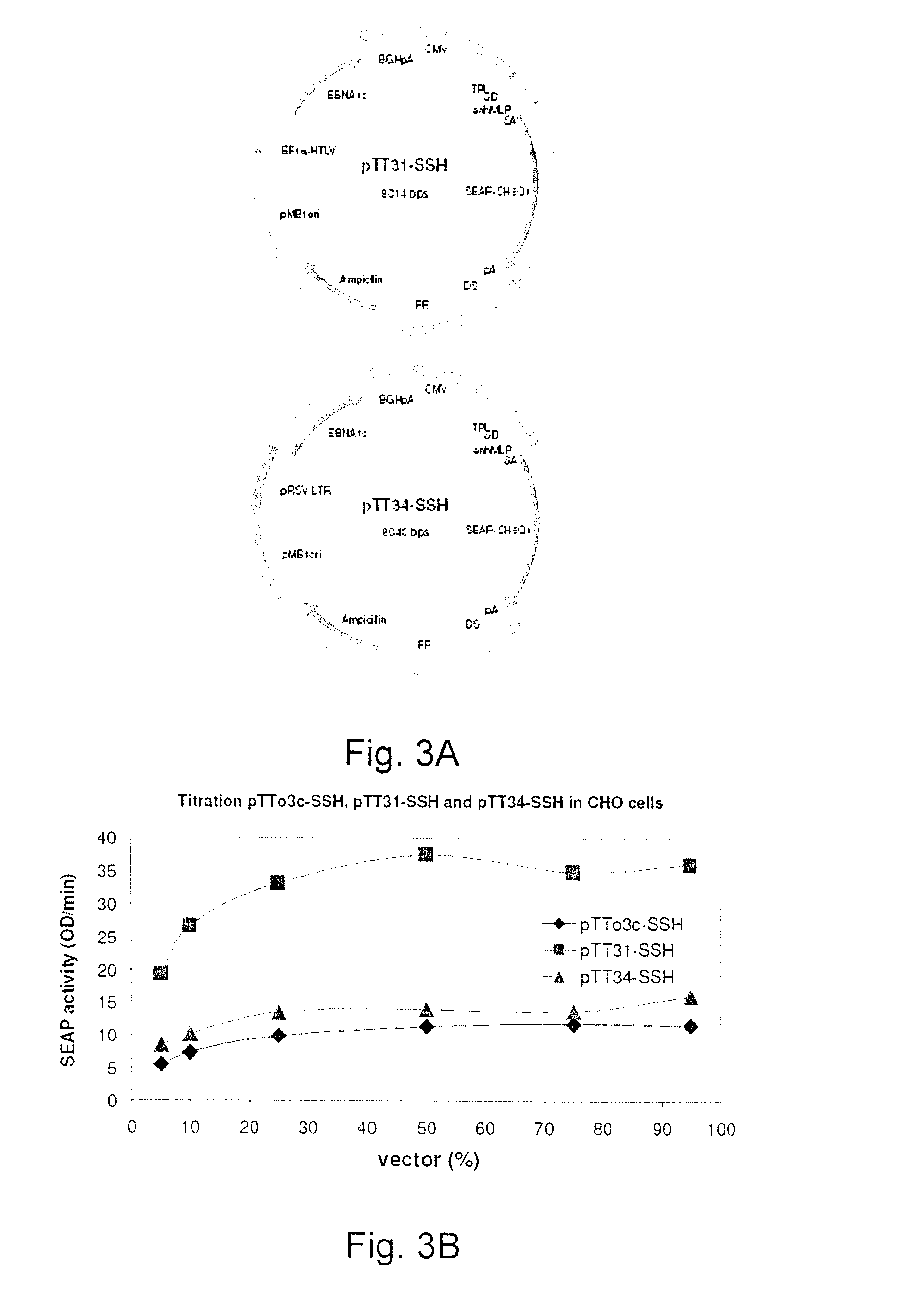
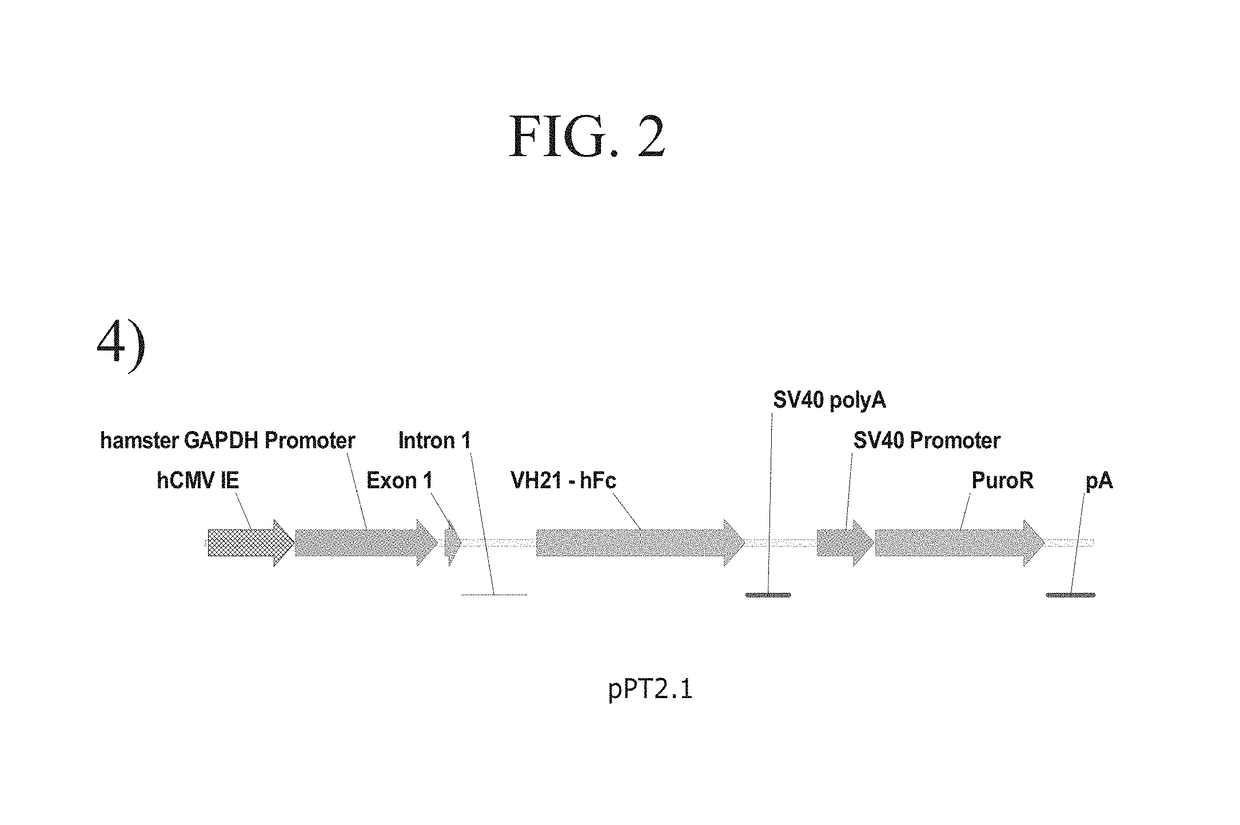
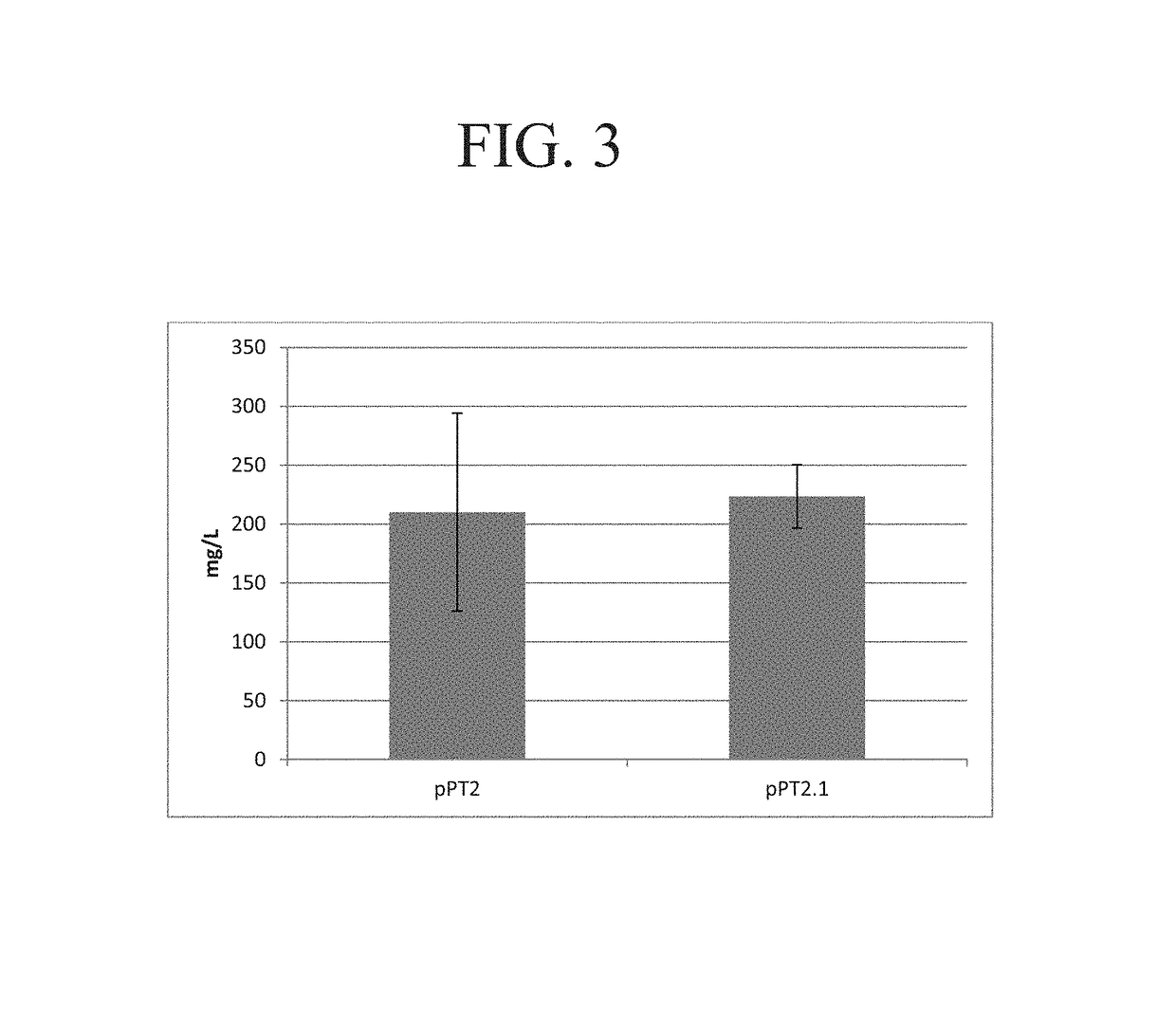
ActiveUS8637315B2Enhanced transfectionHigh expressionAnimal cellsSugar derivativesValproic AcidHamster
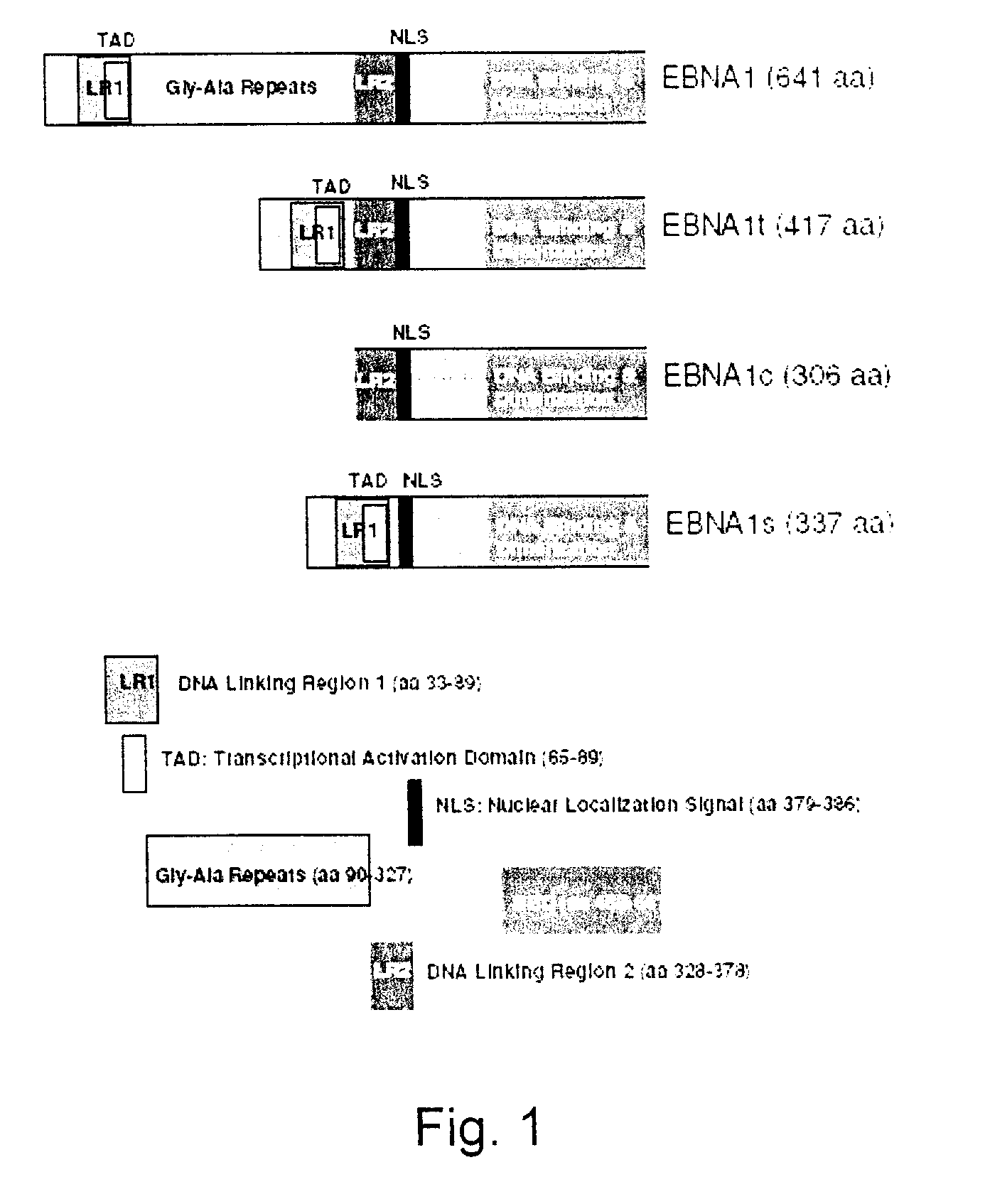
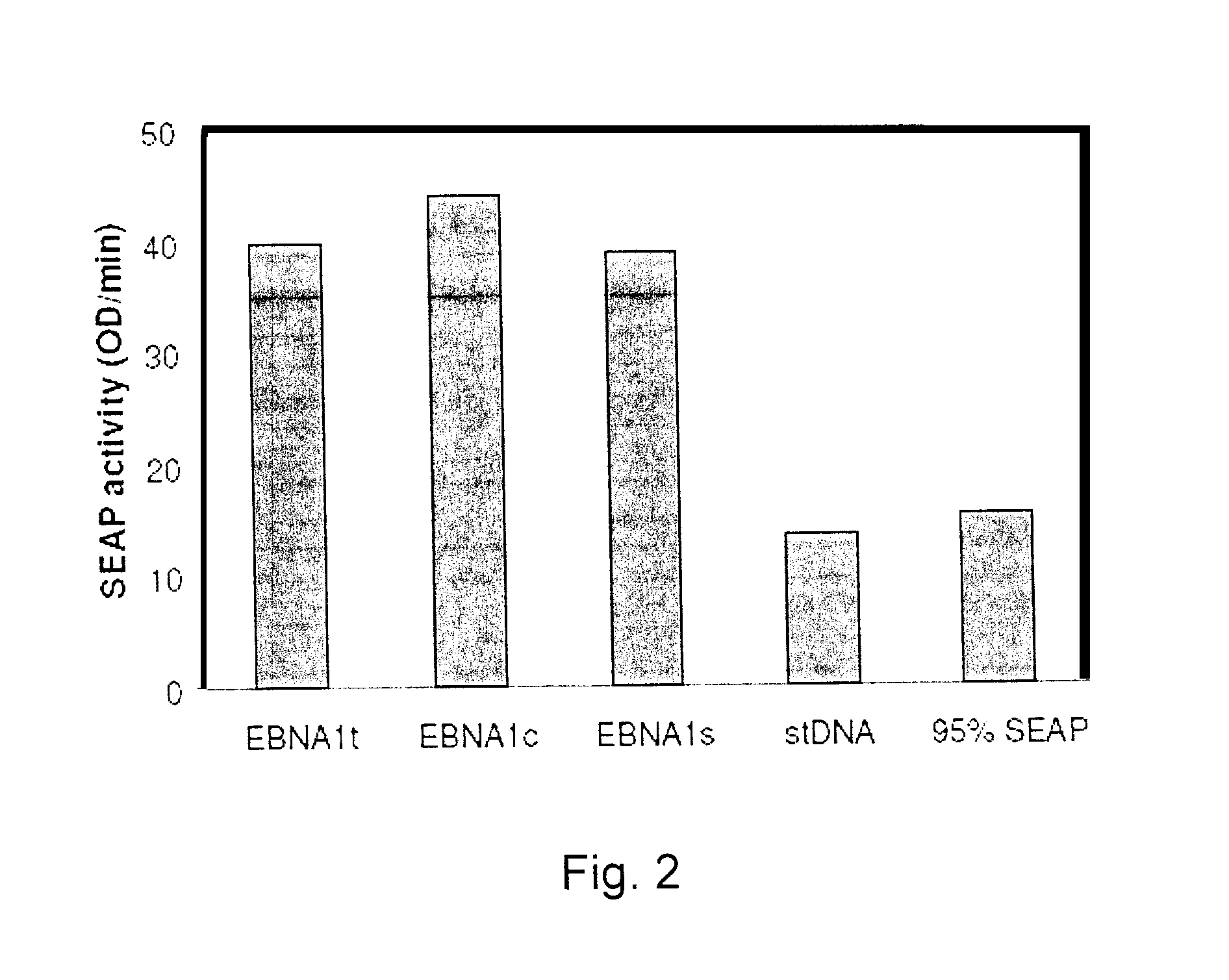
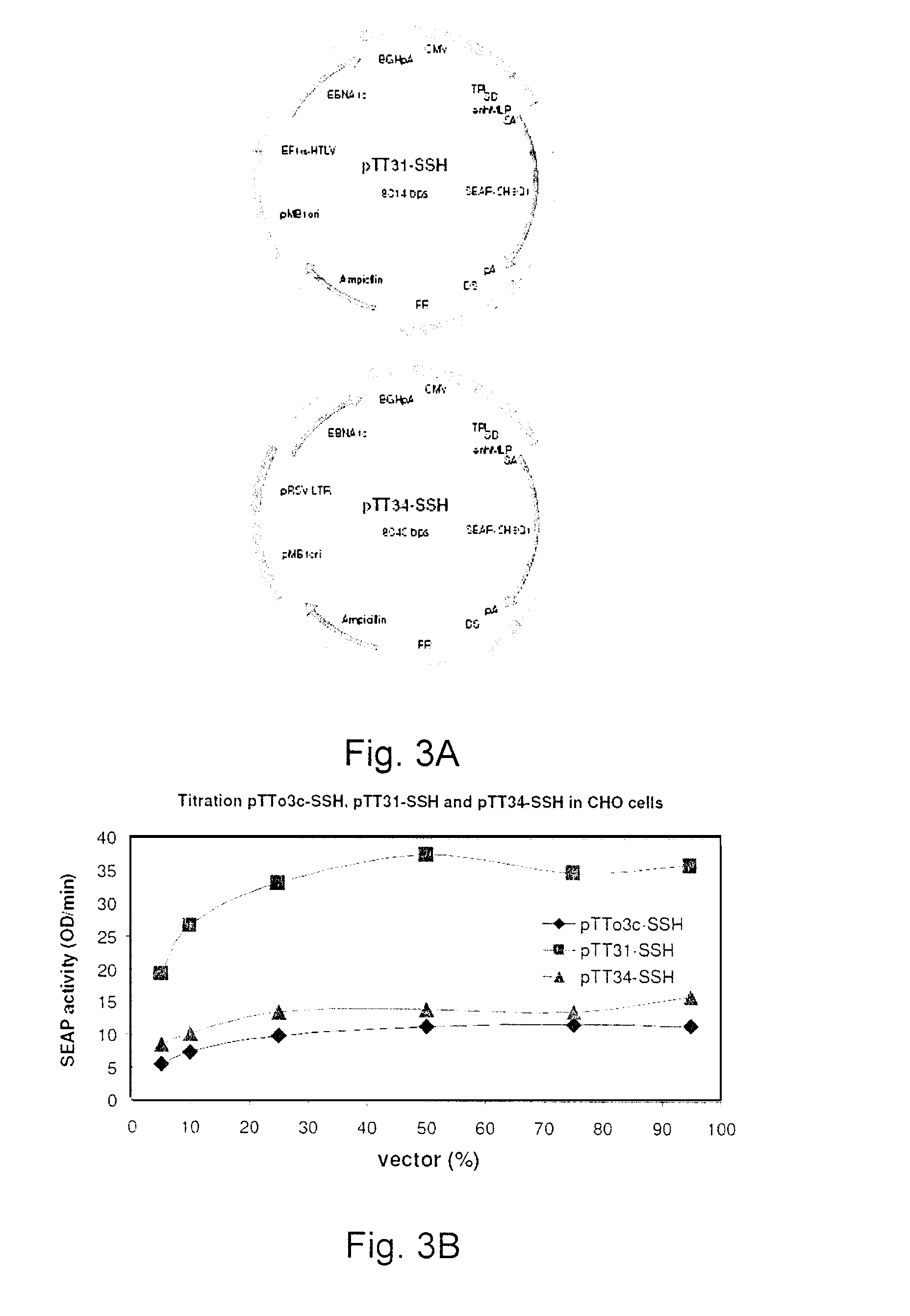
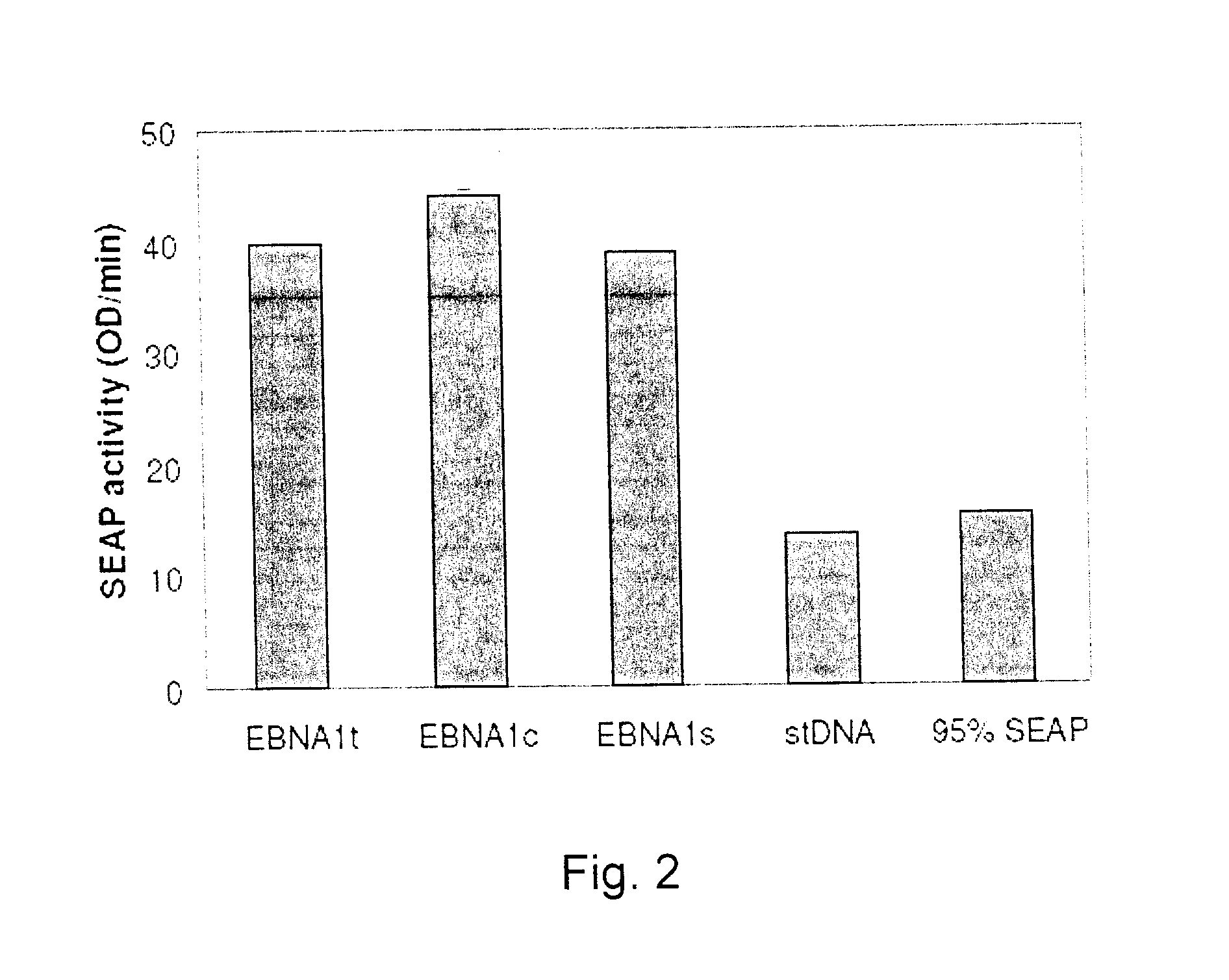
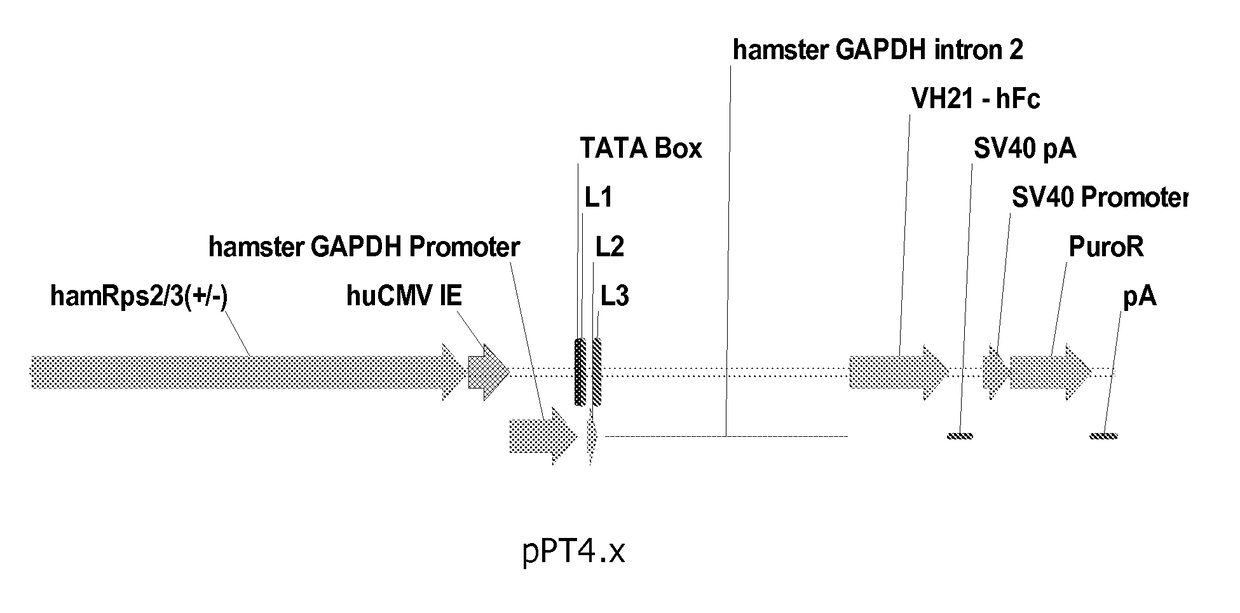
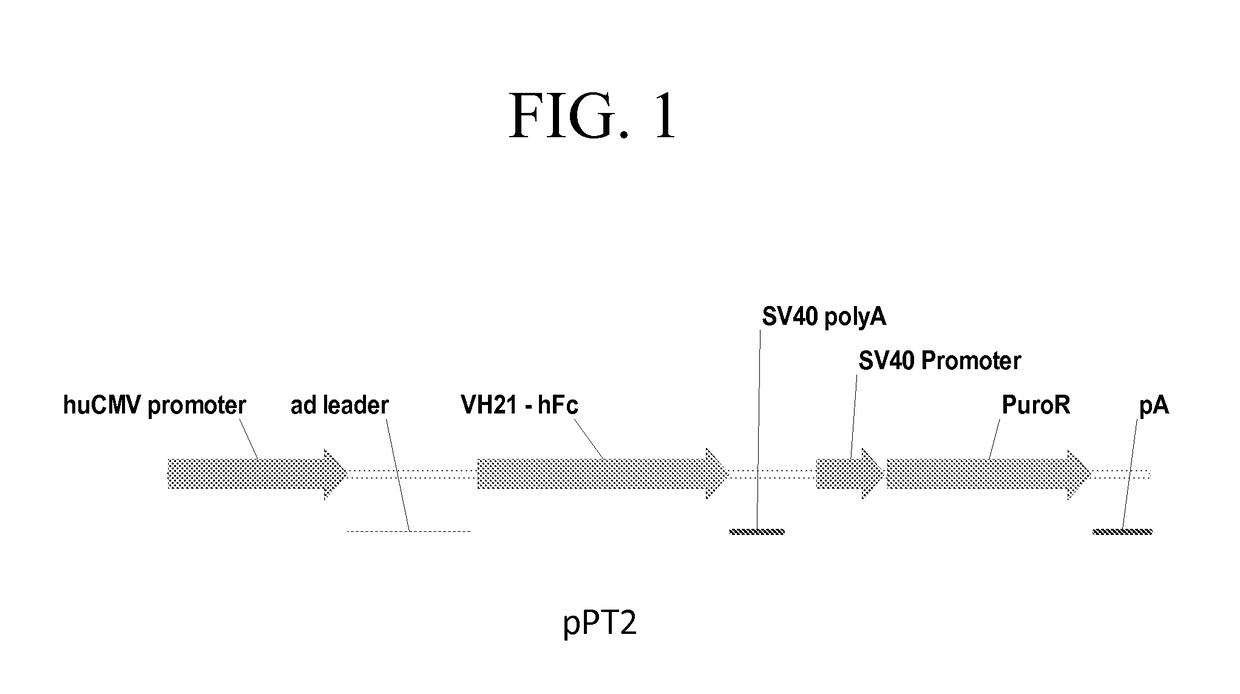
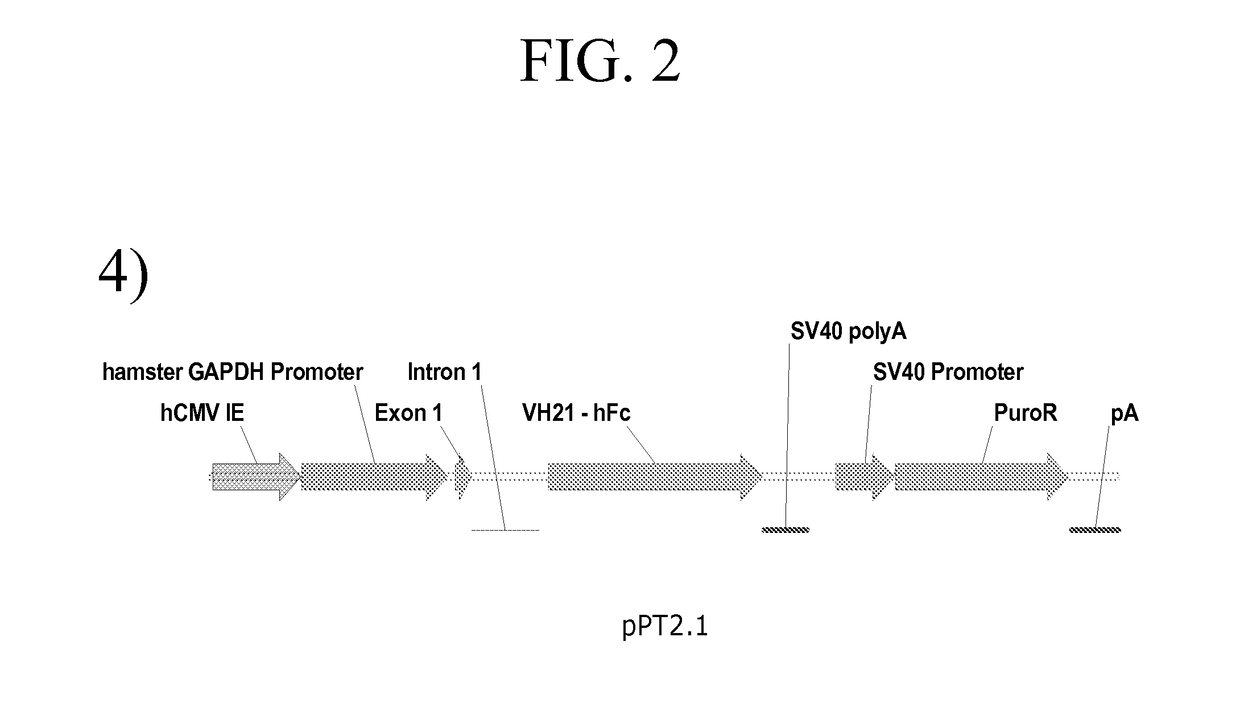
Processes vectors and engineered cell lines for large-scale transfection and protein production in mammalian cells, especially Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells are described in which transfection efficiencies are realized through the use of a single vector system, the use of functional oriP sequences in all plasmids, the use of codon-optimized Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen-1 (EBNA1) constructs the use of a fusion protein between a truncated Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigenen-1c (EBNA1c) protein and a herpes simplex virus protein VP16, the use of a 40 kDa fully deacetylated poly(ethylenimine) as a transfection reagent, the use of co-expression of a fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and / or the use of protein kinase B to potentiate heterologous gene expression enhancement by valproic acid (VPA).
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Truncated glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter
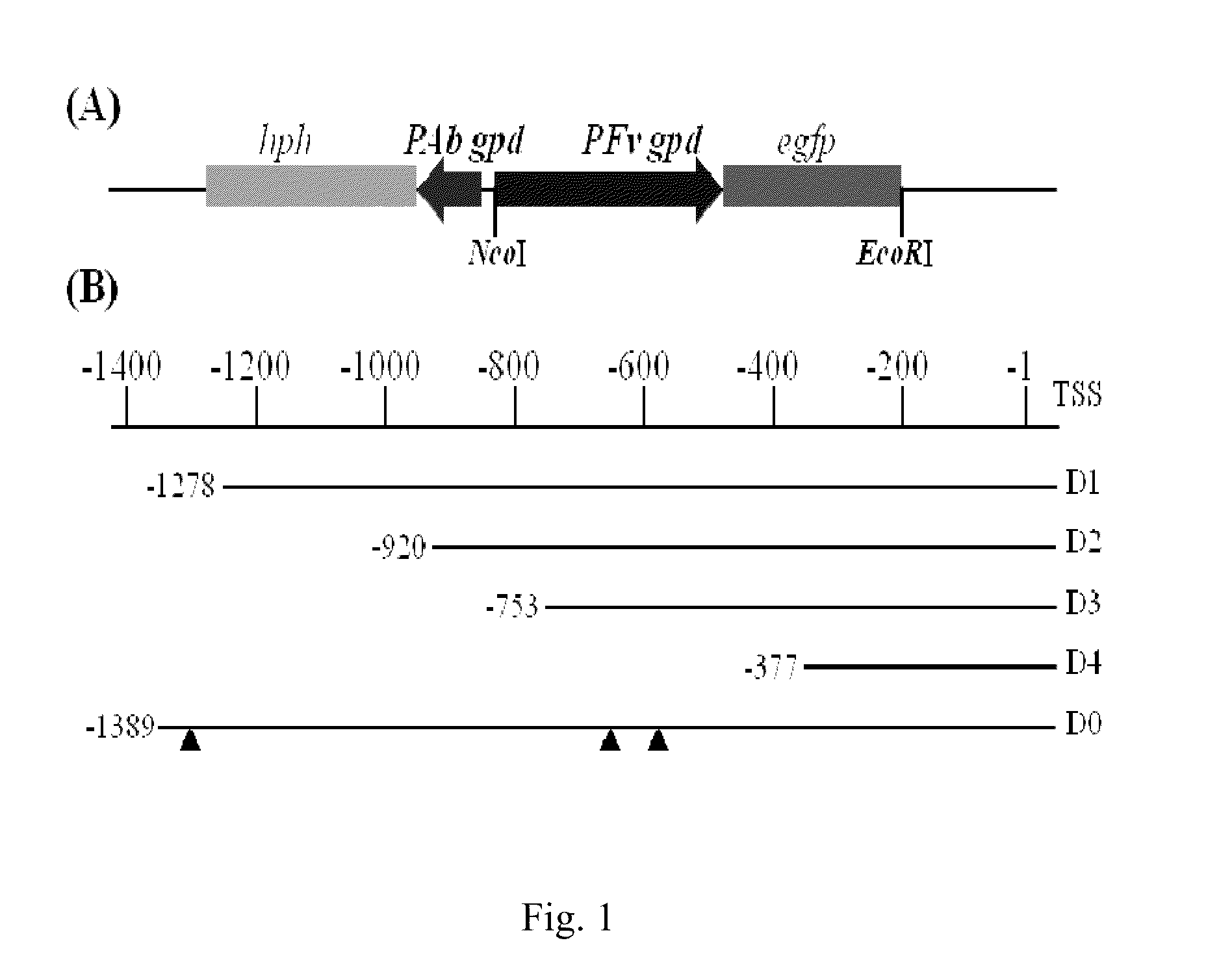
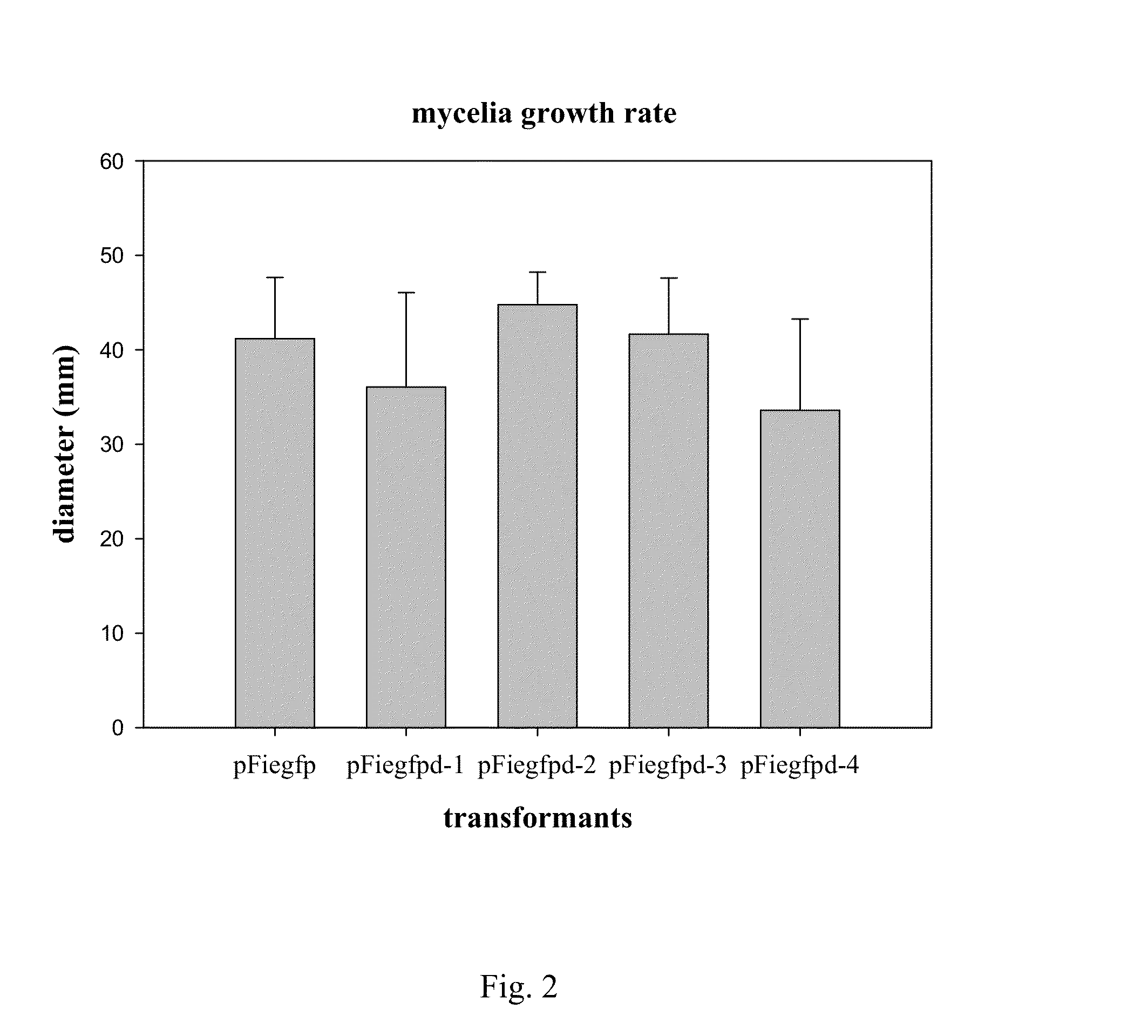
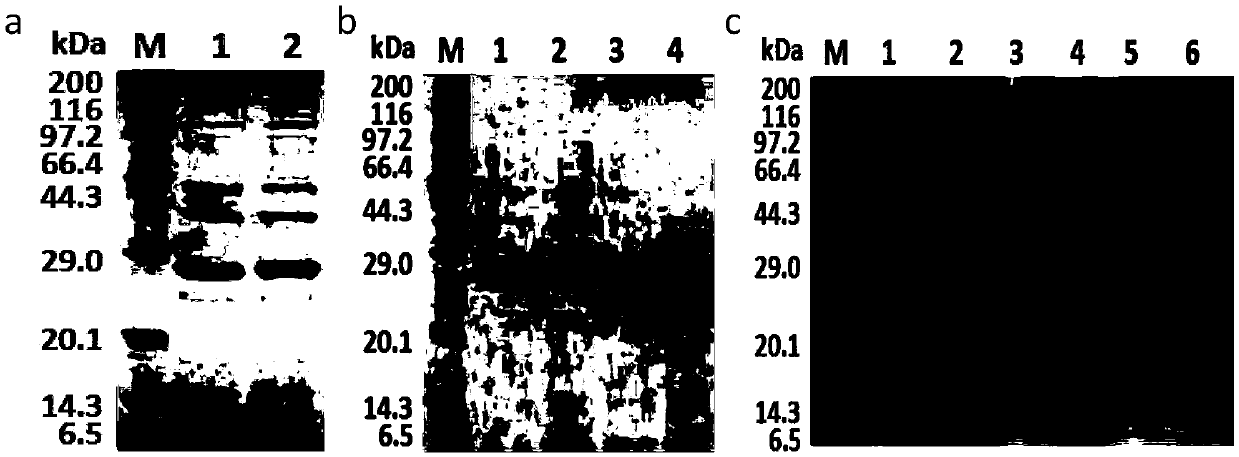
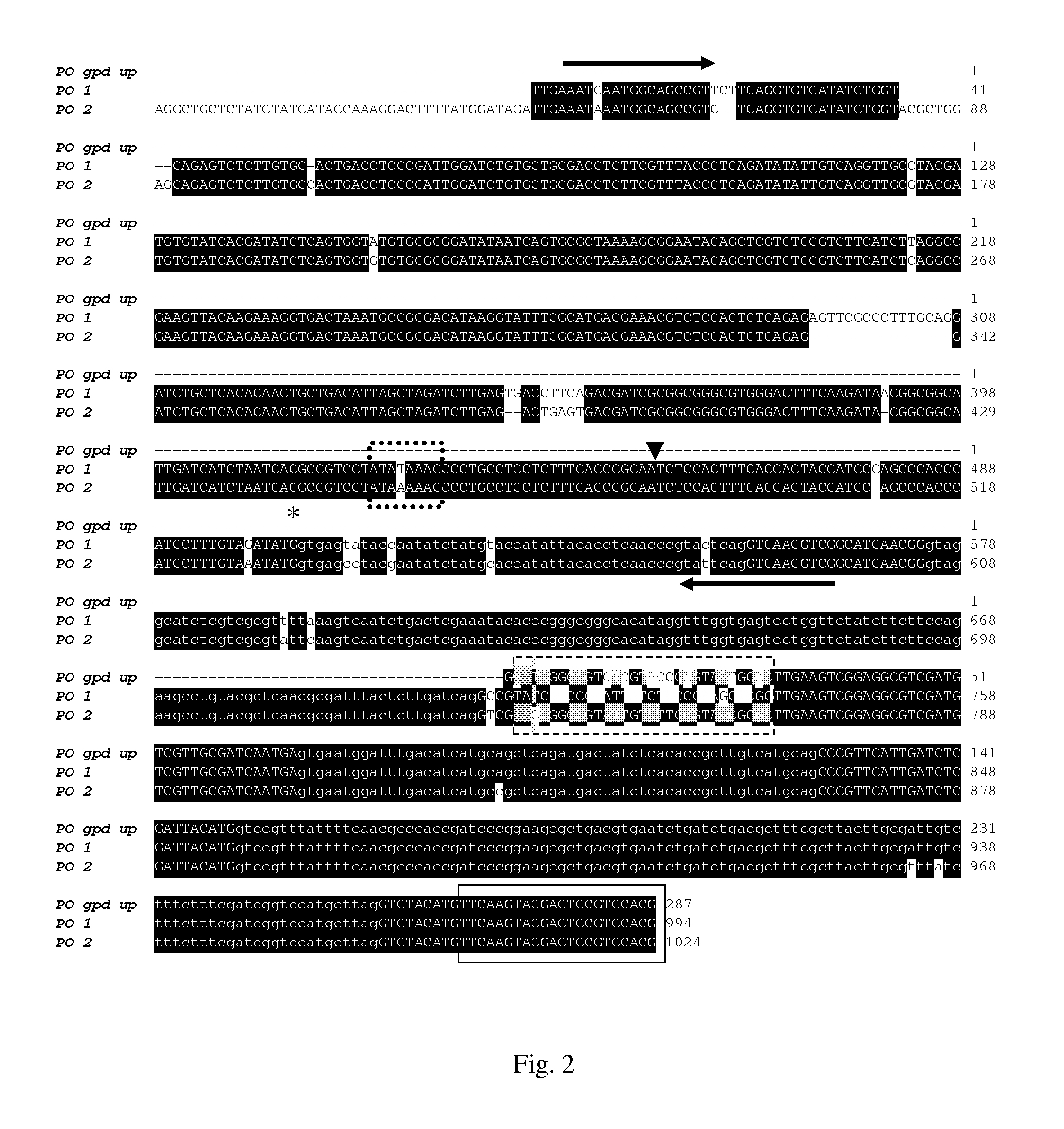
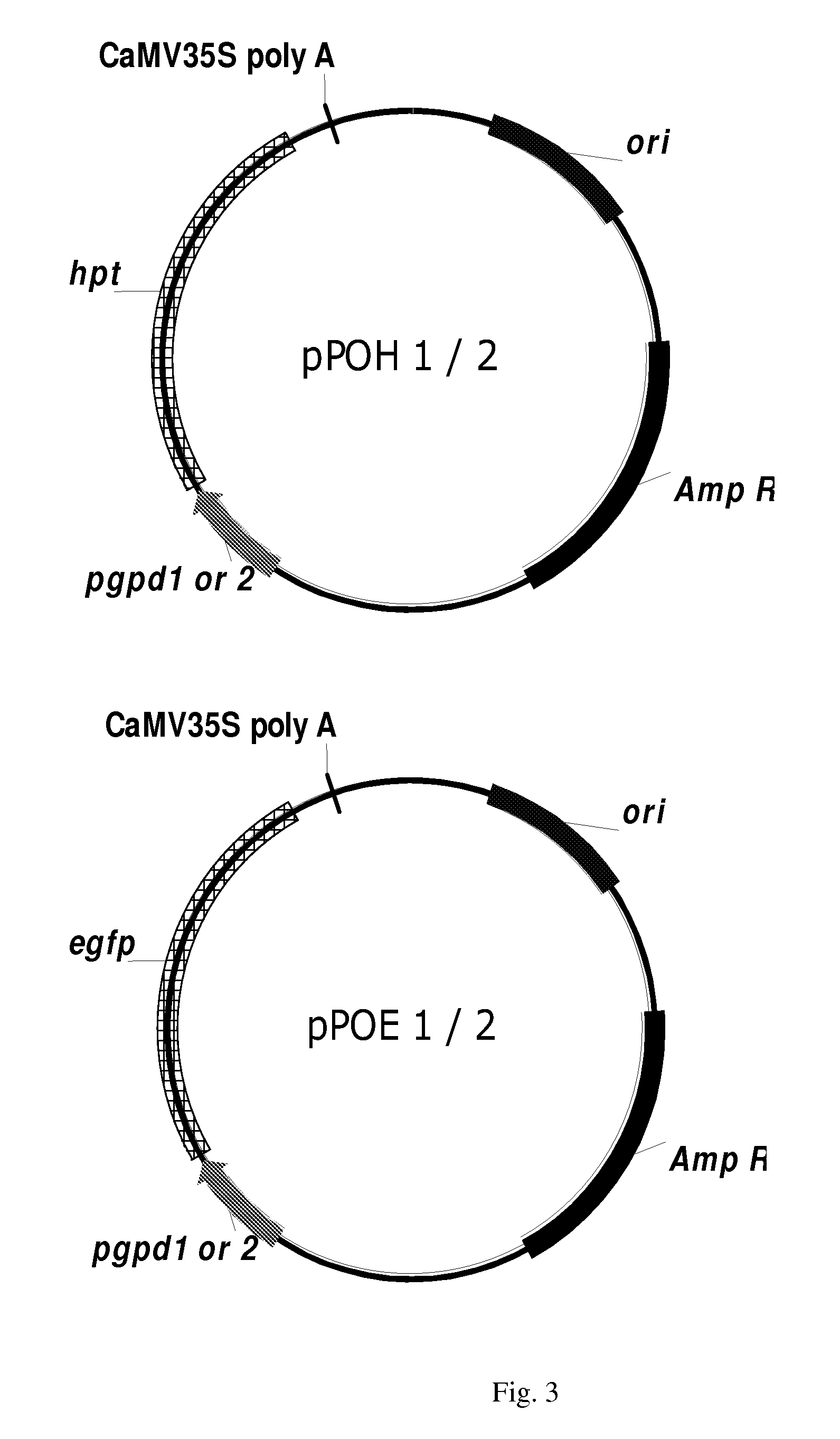
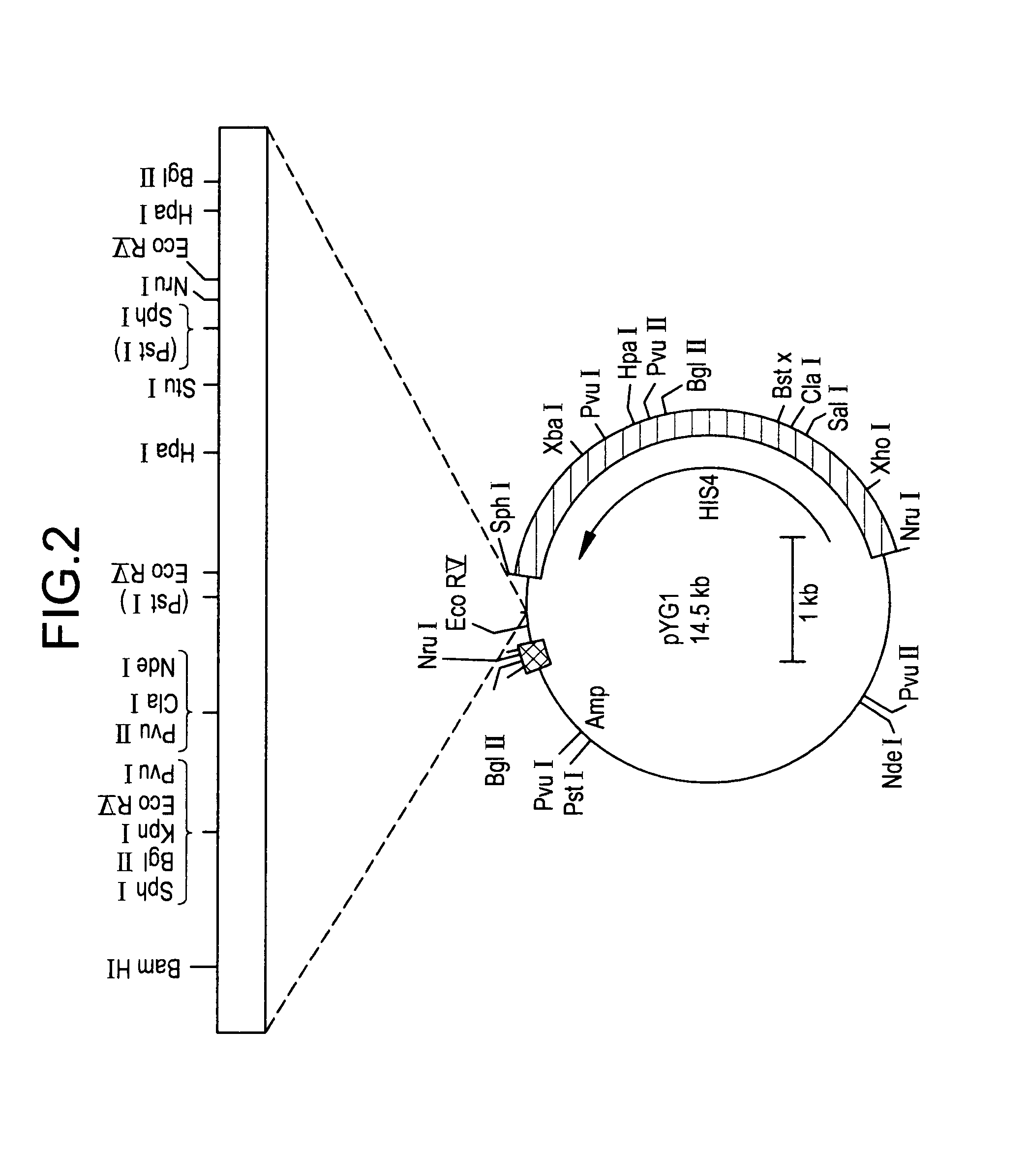
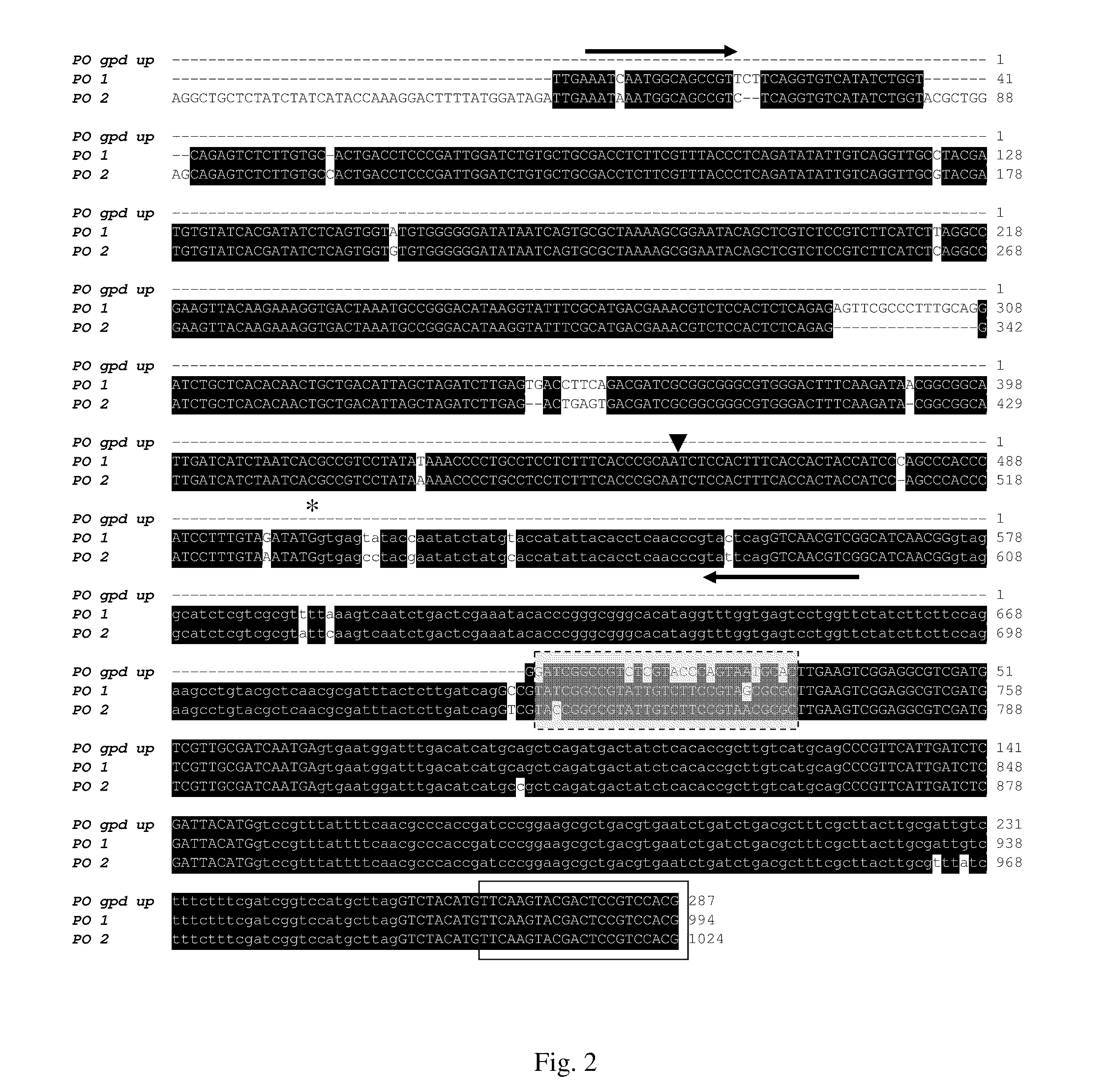
The invention found that partial deletion of the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (gpd) promoter can enhance gene expression (even heterologous gene expression) in basidiomycetous fungi. With the discovery of these gpd promoters, an expression system can be constructed for the expression of a heterologous gene in mushroom. Accordingly, the invention provides a truncated glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter and a construct comprising the promoter of the invention operably linked to a heterologous transcribable polynucleotide molecule and a mushroom comprising the construct.
Owner:MYCOMAGIC BIOTECH
Process, Vectors and Engineered Cell Lines for Enhanced Large-Scale Transfection
ActiveUS20110039339A1Heterologous gene expression can be improvedEnhanced transfectionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVirus peptidesValproic AcidHamster
Processes vectors and engineered cell lines for large-scale transfection and protein production in mammalian cells, especially Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells are described in which transfection efficiencies are realized through the use of a single vector system, the use of functional oriP sequences in all plasmids, the use of codon-optimized Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen-1 (EBNA1) constructs the use of a fusion protein between a truncated Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigenen-1c (EBNA1c) protein and a herpes simplex virus protein VP16, the use of a 40 kDa fully deacetylated poly(ethylenimine) as a transfection reagent, the use of co-expression of a fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and / or the use of protein kinase B to potentiate heterologous gene expression enhancement by valproic acid (VPA).
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
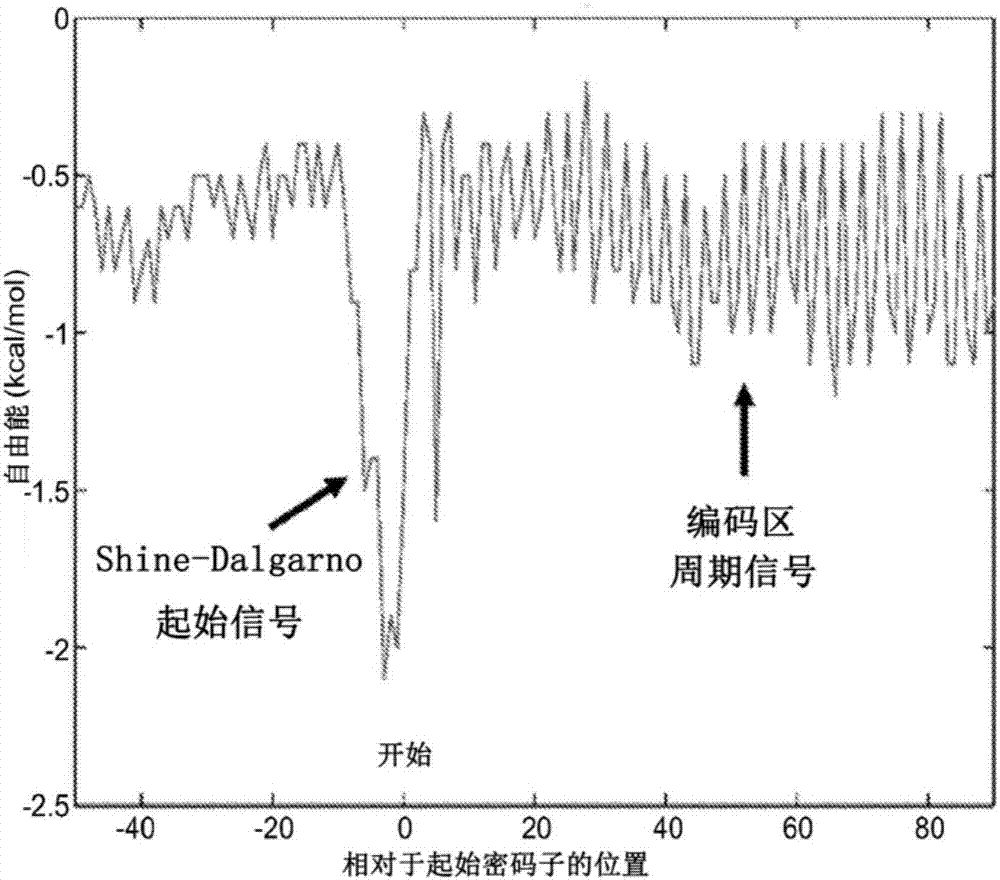
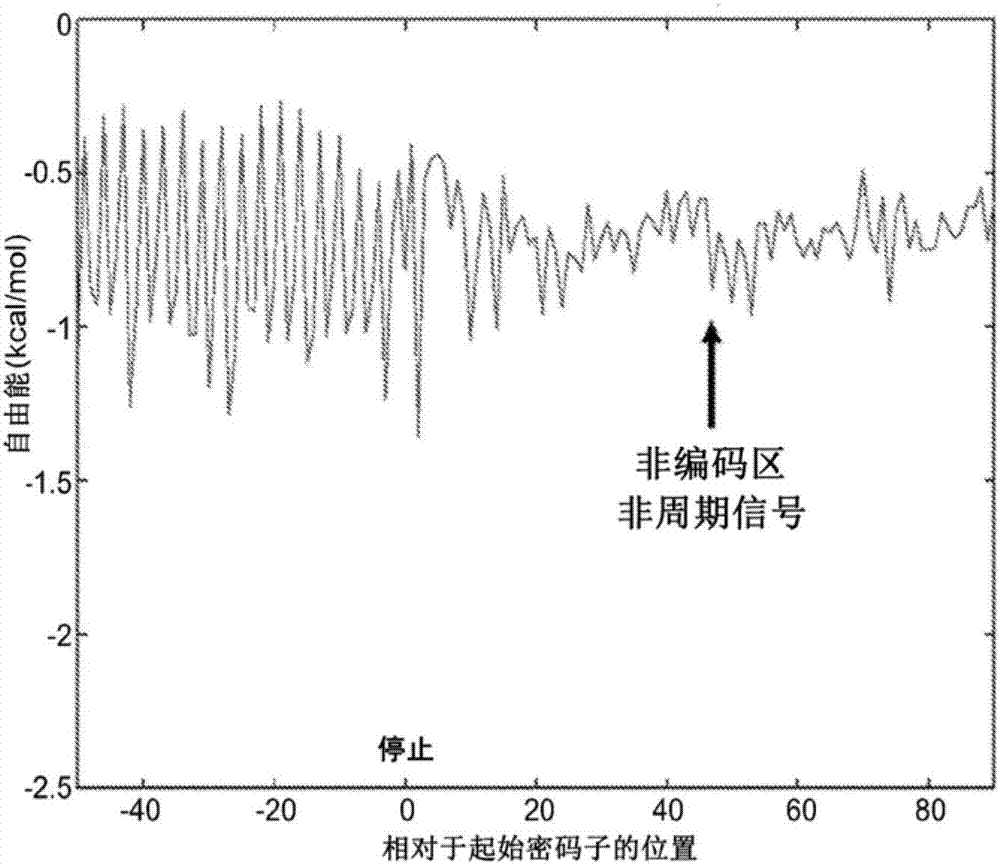
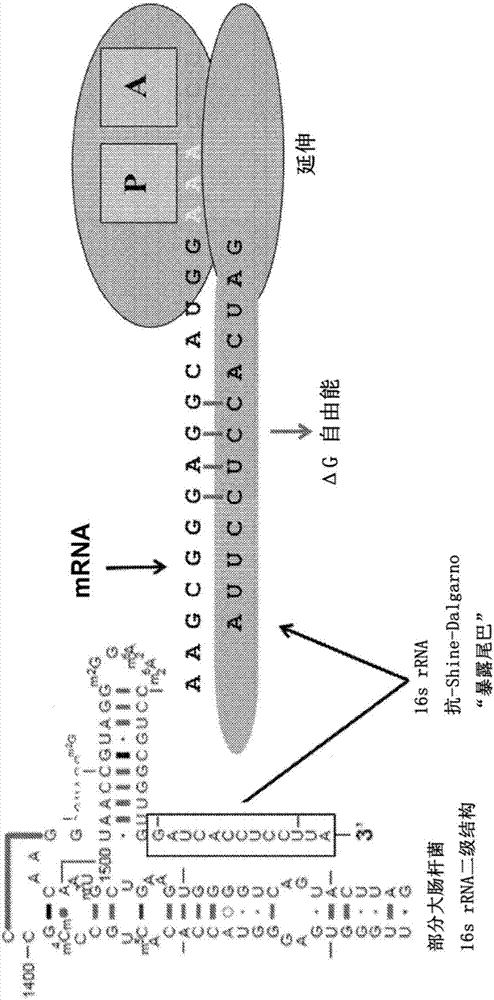
Modeling ribosome dynamics to optimize heterologous protein production
ActiveCN107109496AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsCell AggregationsProtein aggregation
The invention relates to modeling ribosome dynamics to optimize heterologous protein production. The presently disclosed subject matter provides a free-energy based model of translation elongation to predict and optimize heterologous gene expression. The model and software allow for the prediction and optimization of genes for increased or decreased protein yield and for increased or decreased protein aggregation.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Recombinant escherichia coli for producing pentamethylene diamine and application of recombinant escherichia coli
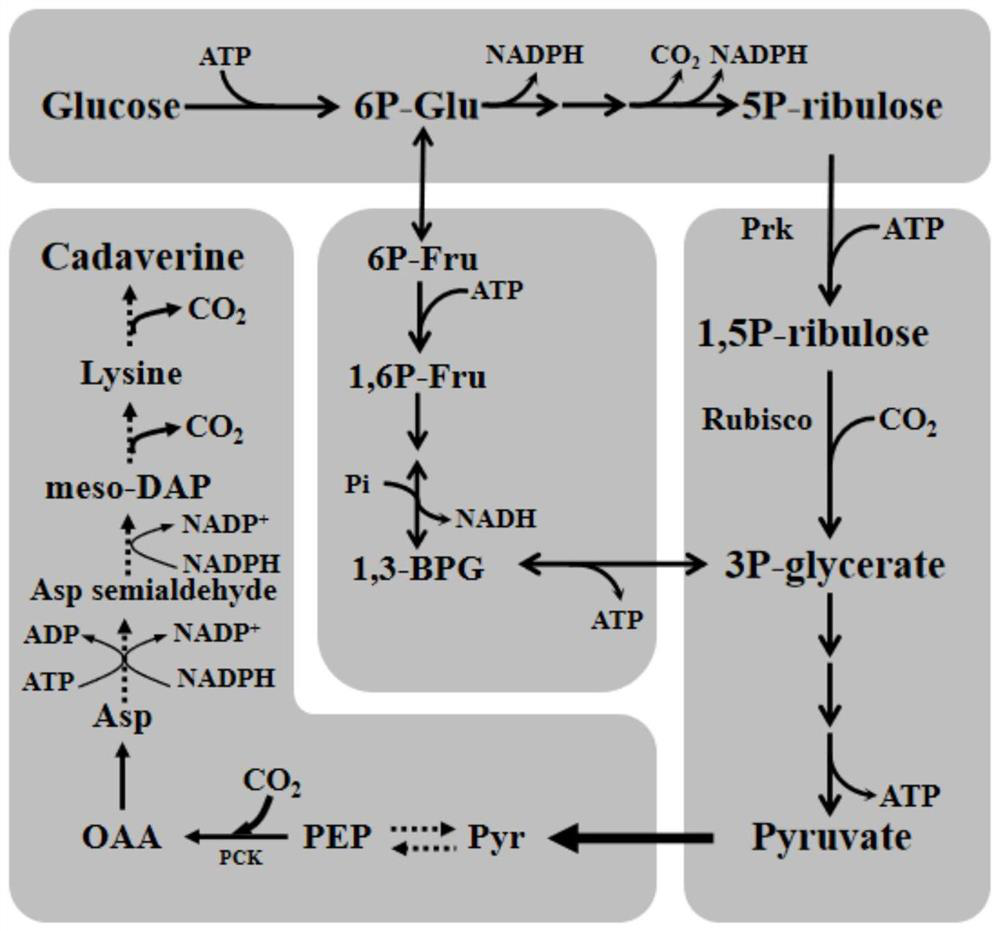
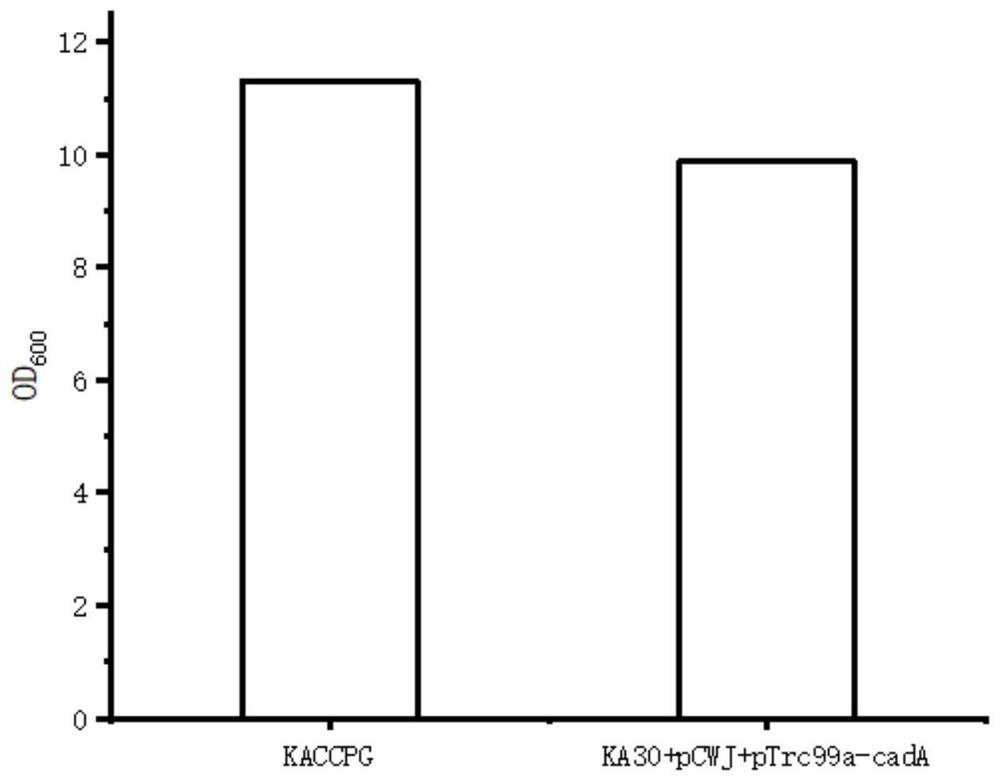
The invention discloses recombinant escherichia coli for producing pentamethylene diamine and application of the recombinant escherichia coli. A ribulose diphosphate carboxylase gene in rhodospirillum, a ribose phosphate kinase gene and a lysine decarboxylase gene in spinach are synthesized from the beginning, PCR copy an escherichia coli molecular chaperone gene to construct a plasmid pTrc99a-cadA-cbbM and a plasmid pCWJ-prkA-GroEL / GroES, the double-plasmid recombinant bacteria grow well in a specific culture medium, and glucose is efficiently utilized. According to the recombinant escherichia coli, inducers arabinose and IPTG are respectively added in different time periods, the heterologous gene expression is stable, the reaction system is simple, the condition is mild, the period is short, few byproducts are produced, the method is clean and pollution-free, the method is a simple, rapid and efficient production way, and the fermentation result shows that the yield of the recombinant escherichia coli KACCPG is obviously improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Strong promoter and application of strong promoter to improving expression of nattokinase
ActiveCN105505931AIncrease productionImprove nattokinase activityBacteriaVector-based foreign material introductionMicroorganismFibrinolysis
The invention discloses a strong promoter and an application of the strong promoter to improving expression of nattokinase, and belongs to the field of microorganism genetic engineering. The genes of the strong promoter in the series of technical schemes are formed in the mode that a promoter PP43 and / or PHpa II are / is subjected to n (n is larger than or equal to 1) times of series connection. Under transcription control of a strong promoter PHpa II-PHpa II-PP43, the fibrinolysis activity of recombined nattokinase is as high as 264.2 FU / m1. A method is efficient and safe, the expression quantity of nattokinase can be effectively increased, and a theoretical foundation is provided for further researching the influence of the promoter to the expression of heterologous genes.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Gylceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter and heterologous gene expression
Owner:MYCOMAGIC BIOTECH
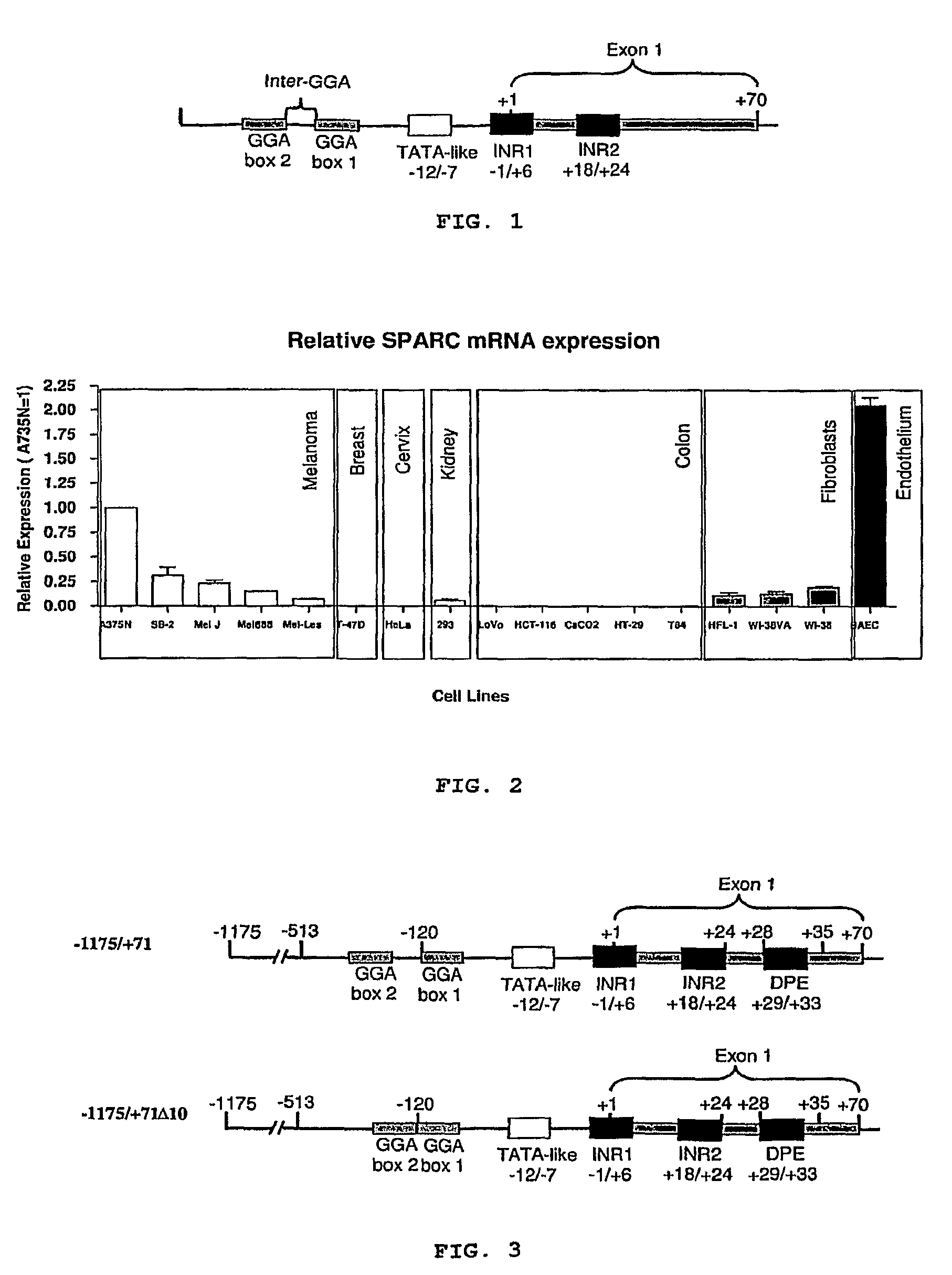
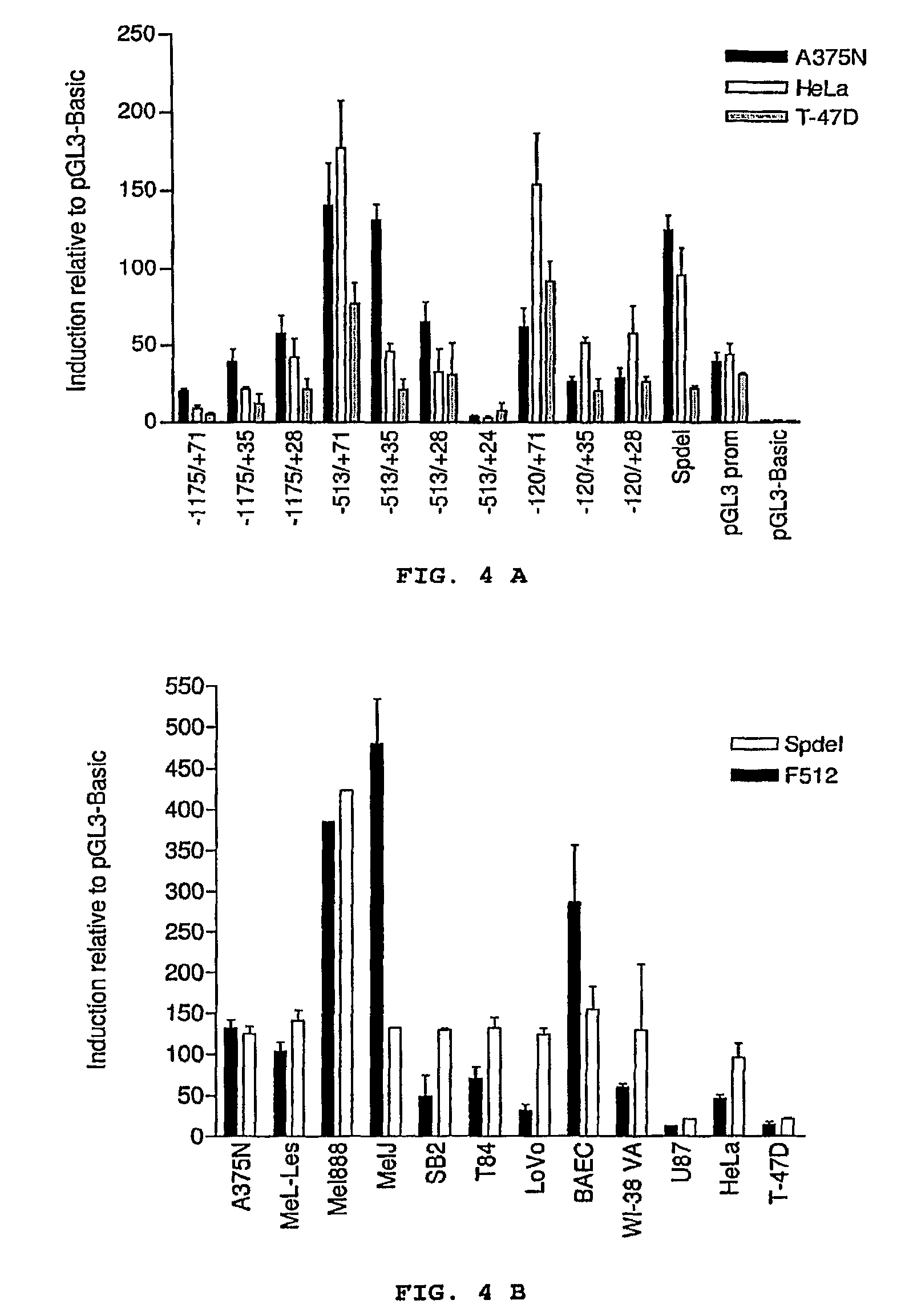
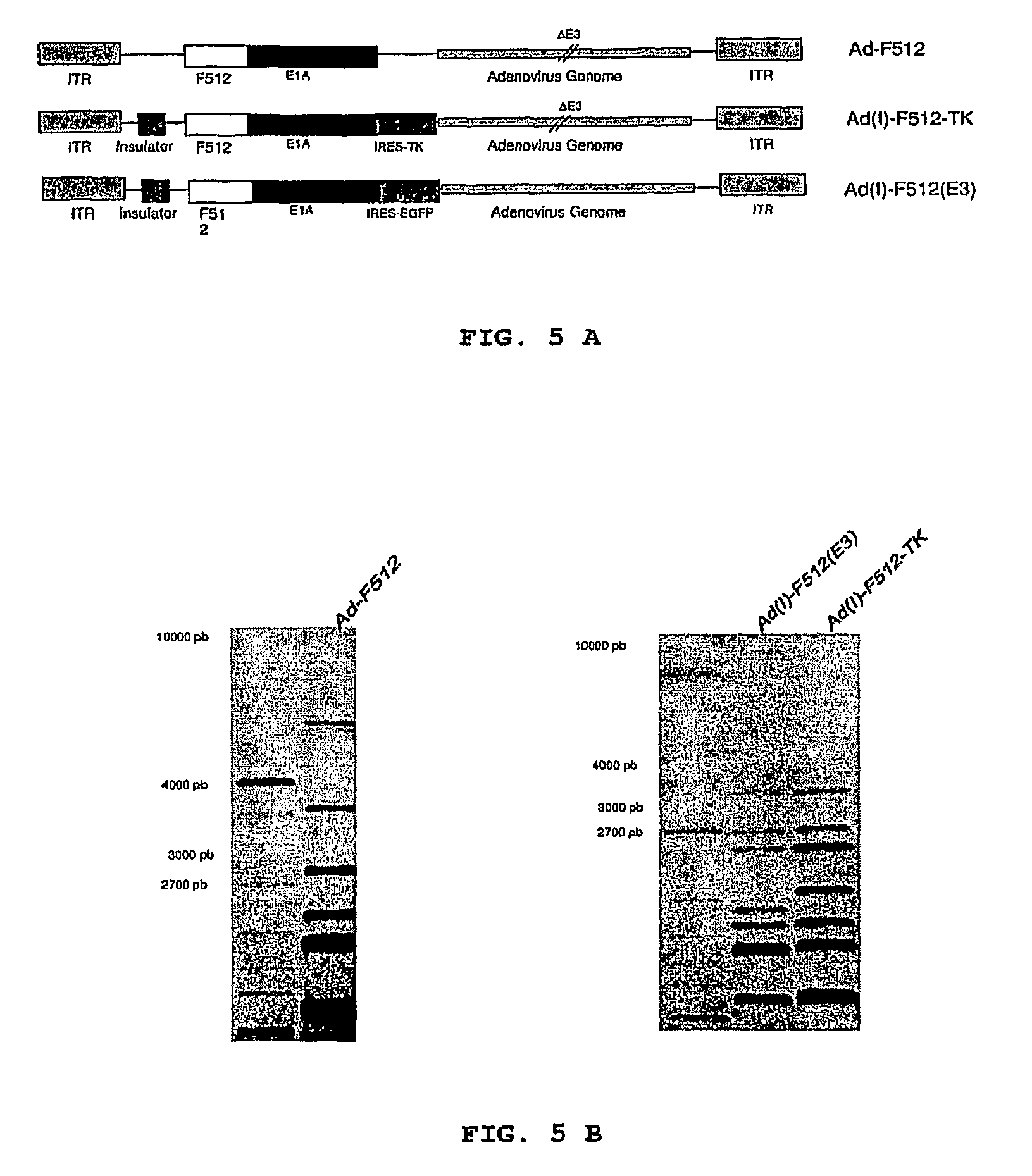
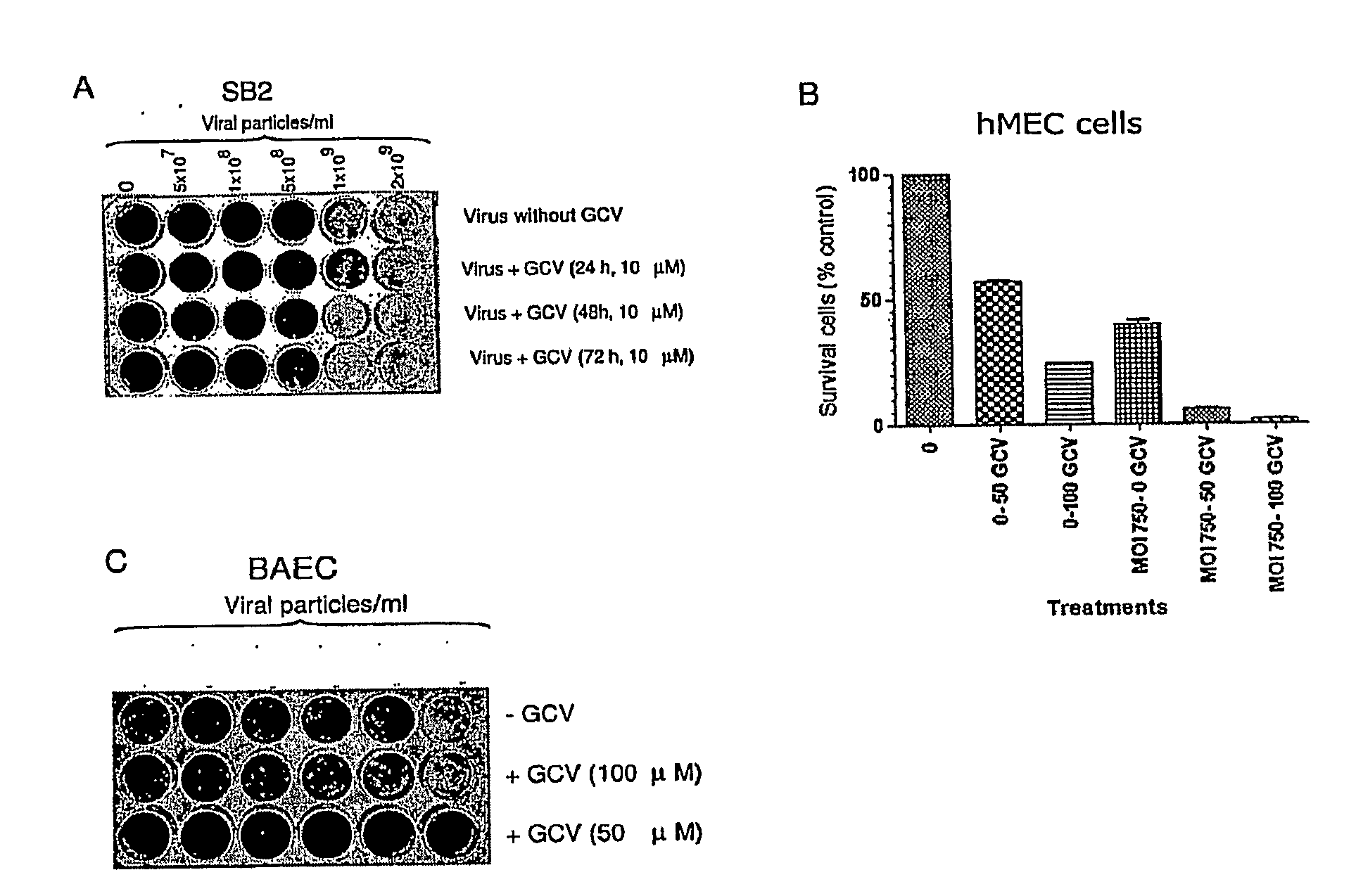
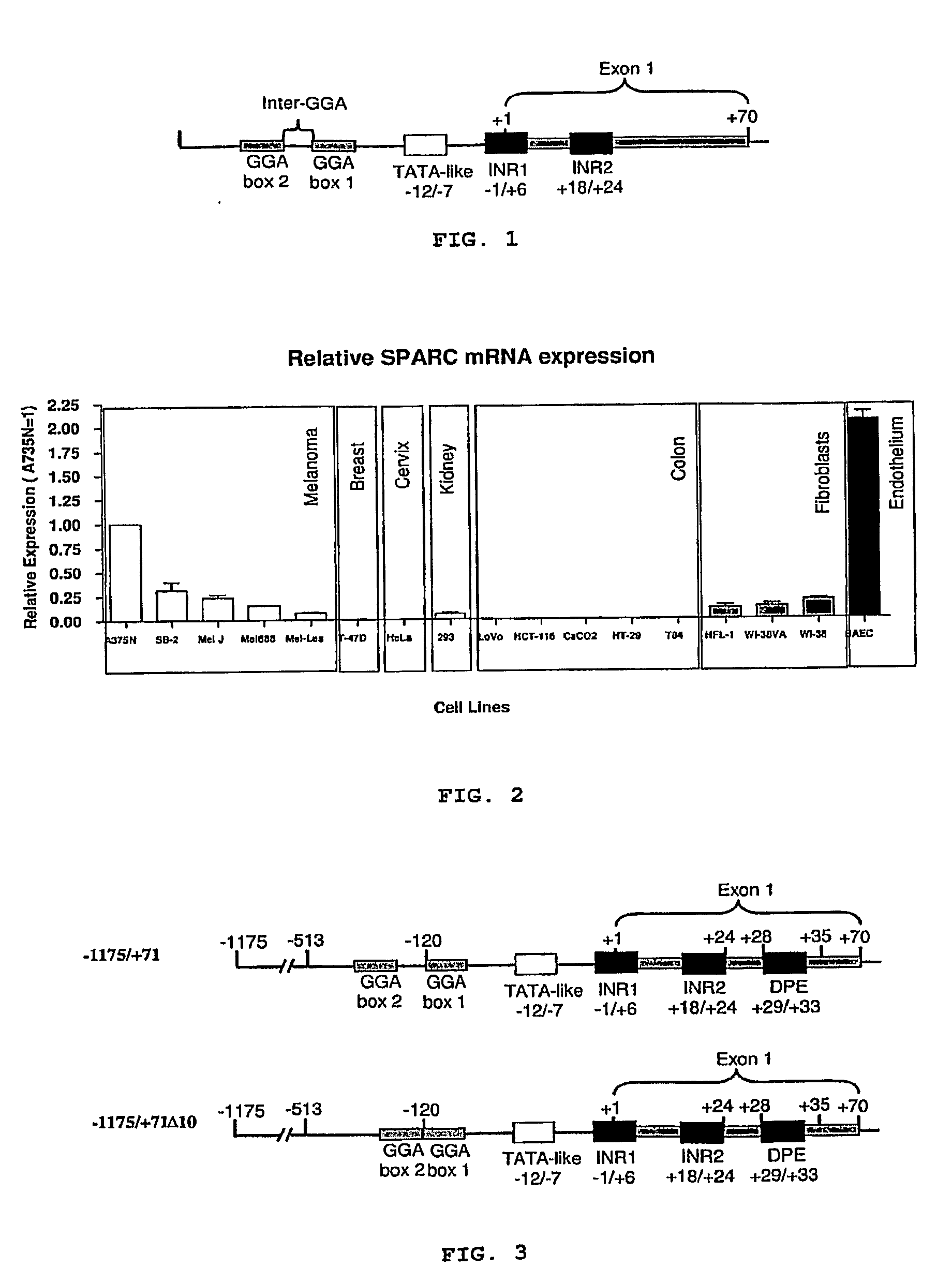
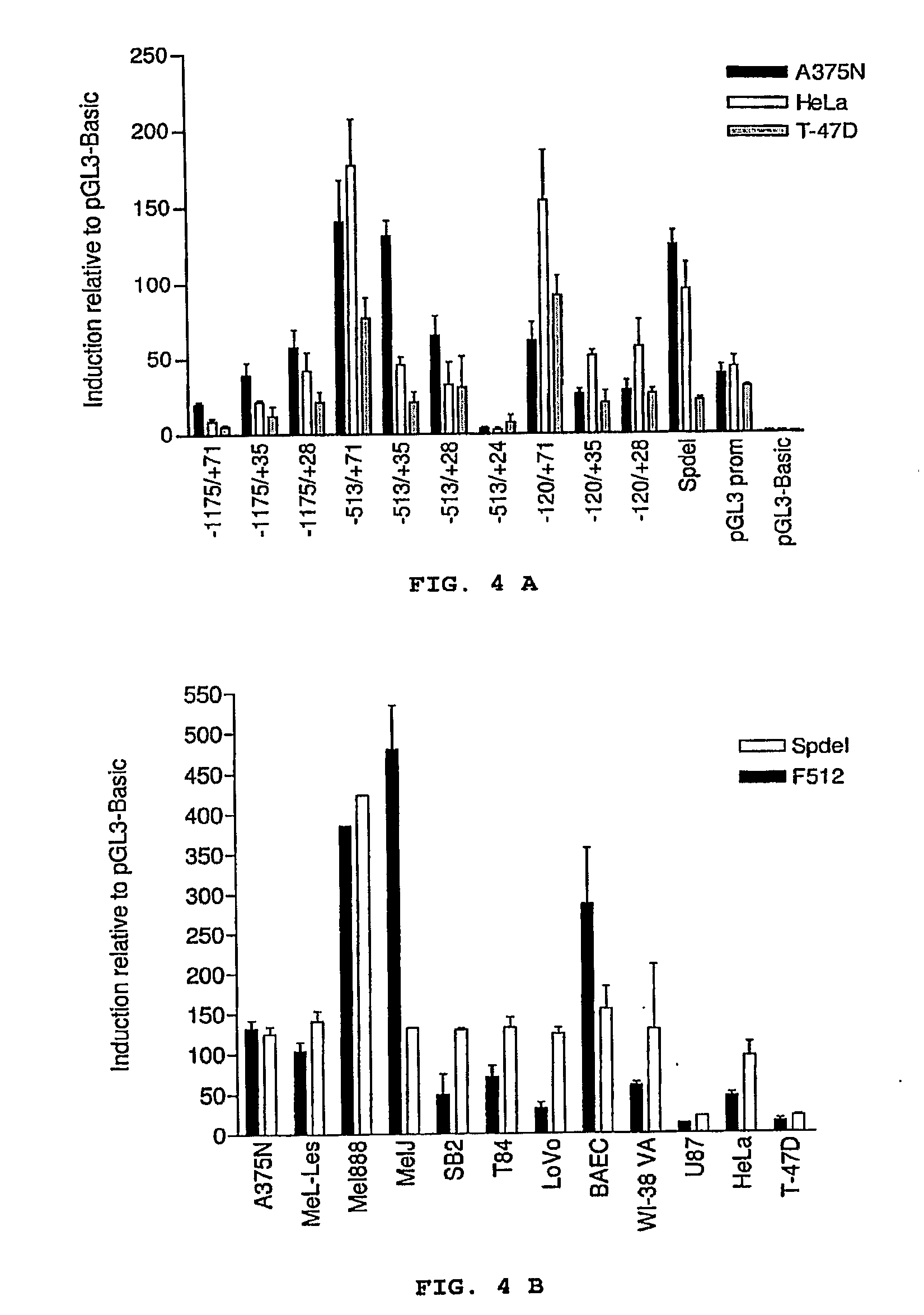
Isolated DNA fragment of the SPARC human promoter and its use for driving the expression of an heterologous gene in tumor cells
ActiveUS8436160B2Tumor rejection antigen precursorsSugar derivativesAbnormal tissue growthViral vector
An isolated DNA sequence corresponding to a region of the SPARC gene human promoter from base pair −513 to base pair +35 capable of driving the expression of a heterologous gene of interest, that can be associated to any other promoter sequence, such as radiation responsive sequence, hypoxia responsive sequence and free-radical responsive sequence. The invention also provides constructs and DNA recombinant expression viral vectors, comprising the isolated sequence of the SPARC gene human promoter and at least one heterologous gene operably linked thereto, wherein the promoter sequence drives the expression of the at least one heterologous gene in tumor cells. Pharmaceutical compositions and a method for treating tumors are also provided.
Owner:CONSEJO NAT DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS Y TECH CONICET +1
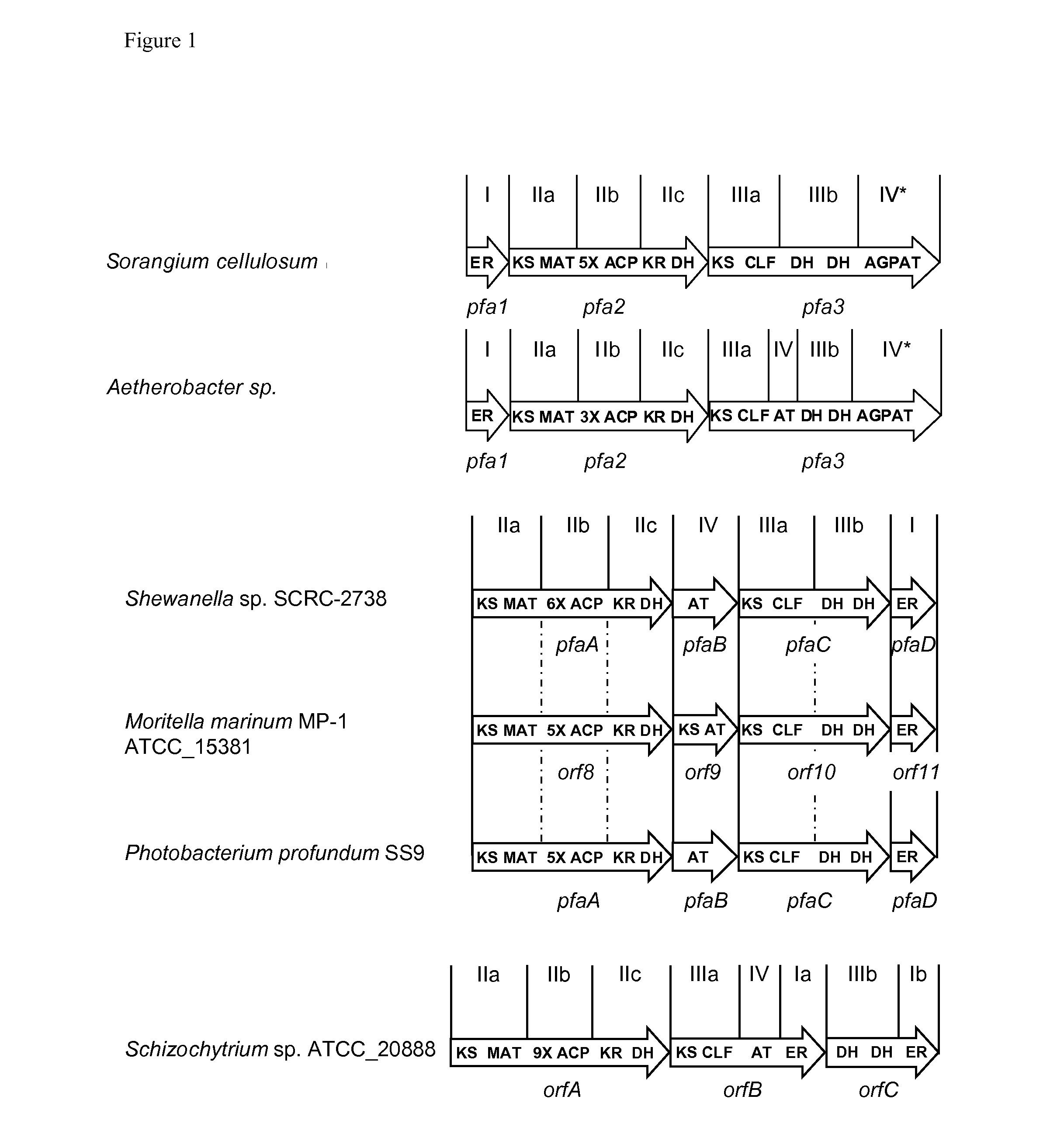
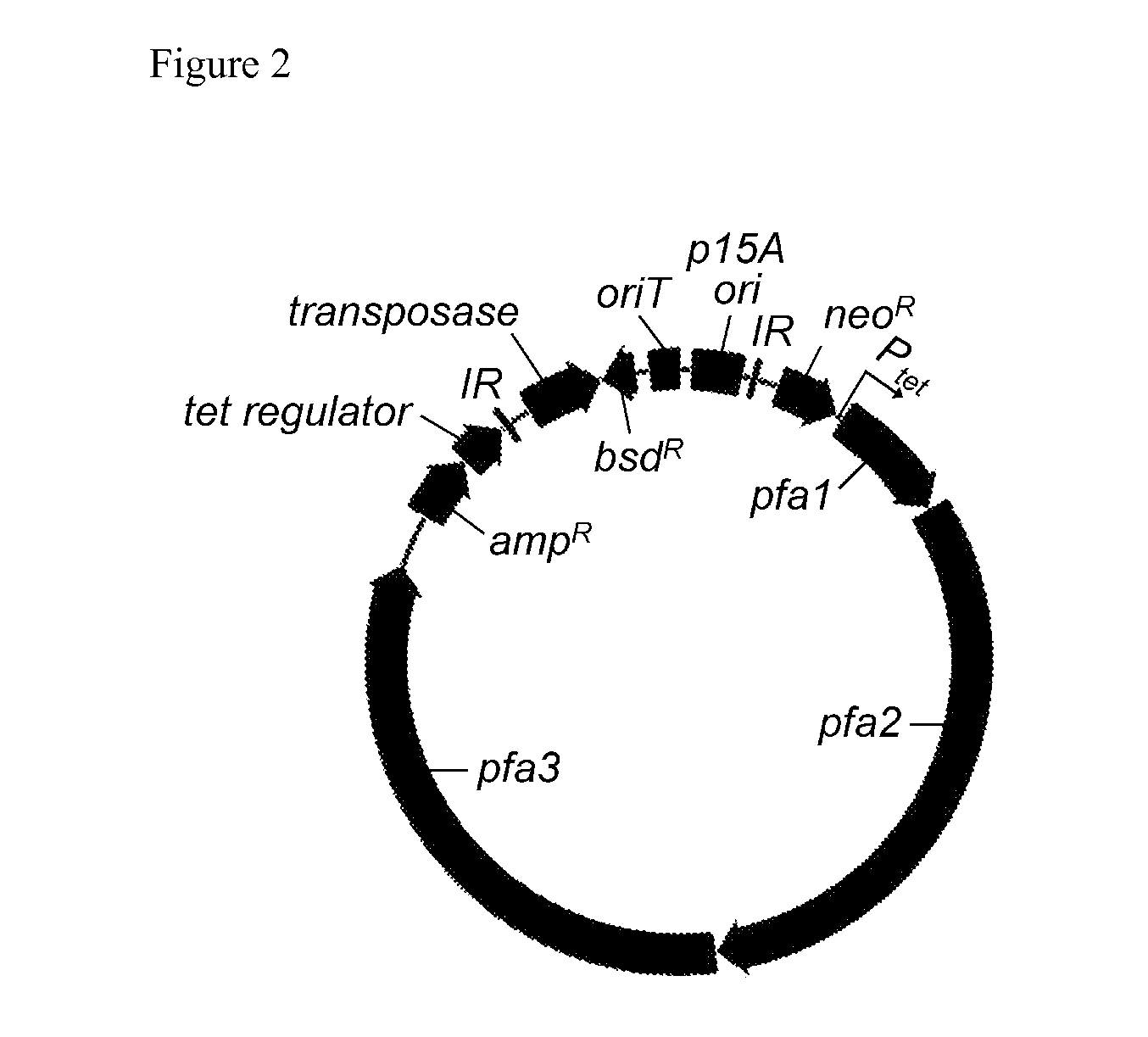
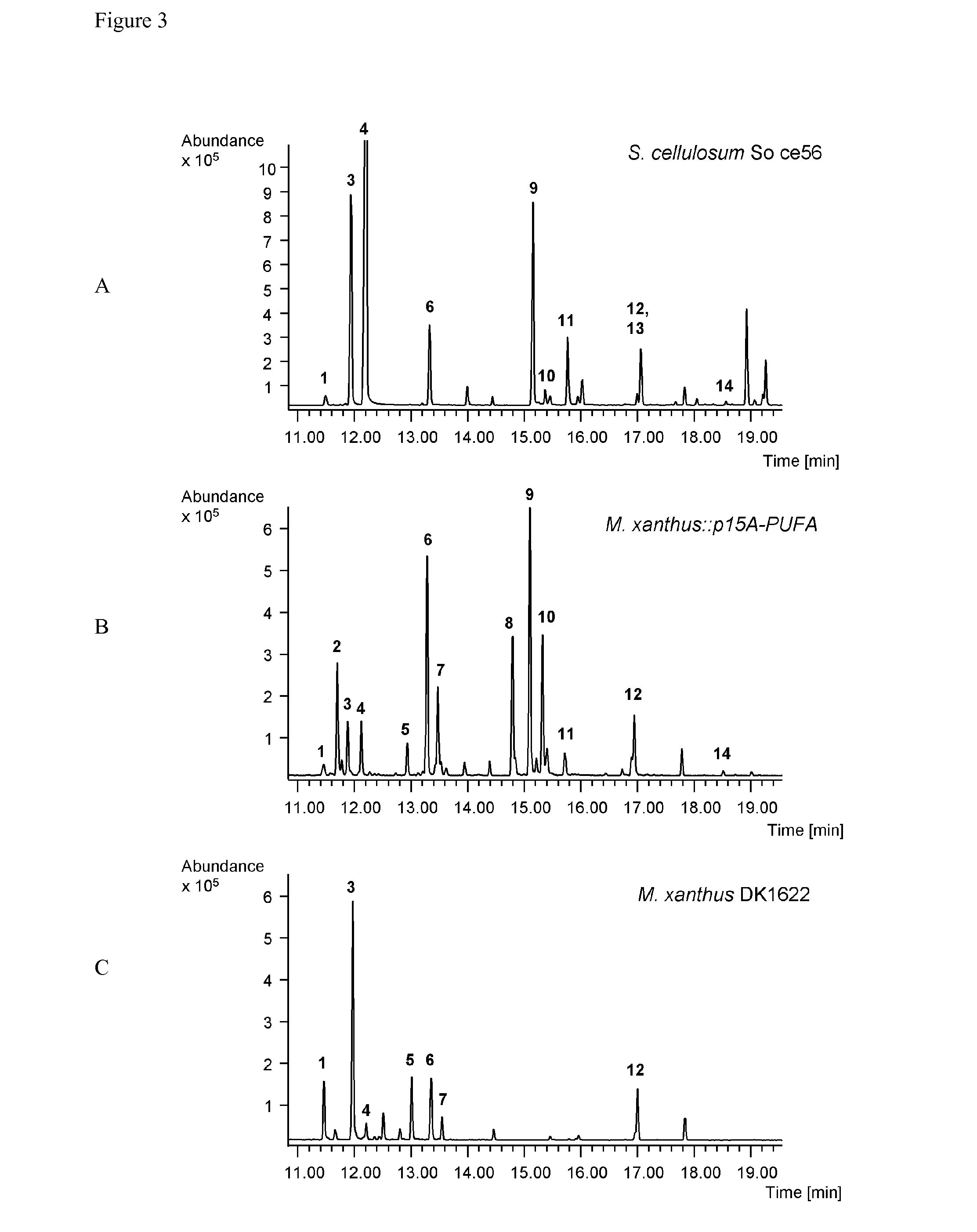
Production of fatty acids by heterologous expression of gene clusters from myxobacteria
The invention relates to a process for producing one or more polyunsaturated fatty acids by means of heterologous gene expression comprising the steps of providing a production organism which comprises a heterologous gene cluster encoding a polyunsaturated fatty acid biosynthetic pathway encompassing a subsequence ER encoding an enoylreductase and a subsequence AT encoding an acyltransferase, growing the production organism in the presence of a fermentable carbon source whereby one or more polyunsaturated fatty acids are produced, and optionally recovering the one or more polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Owner:UNIV DES SAARLANDES
Use of A Plastid-Lipid Associated Protein Promoter (PAP Promoter) For Heterologous Gene Expression
InactiveUS20100021962A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyGenus
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
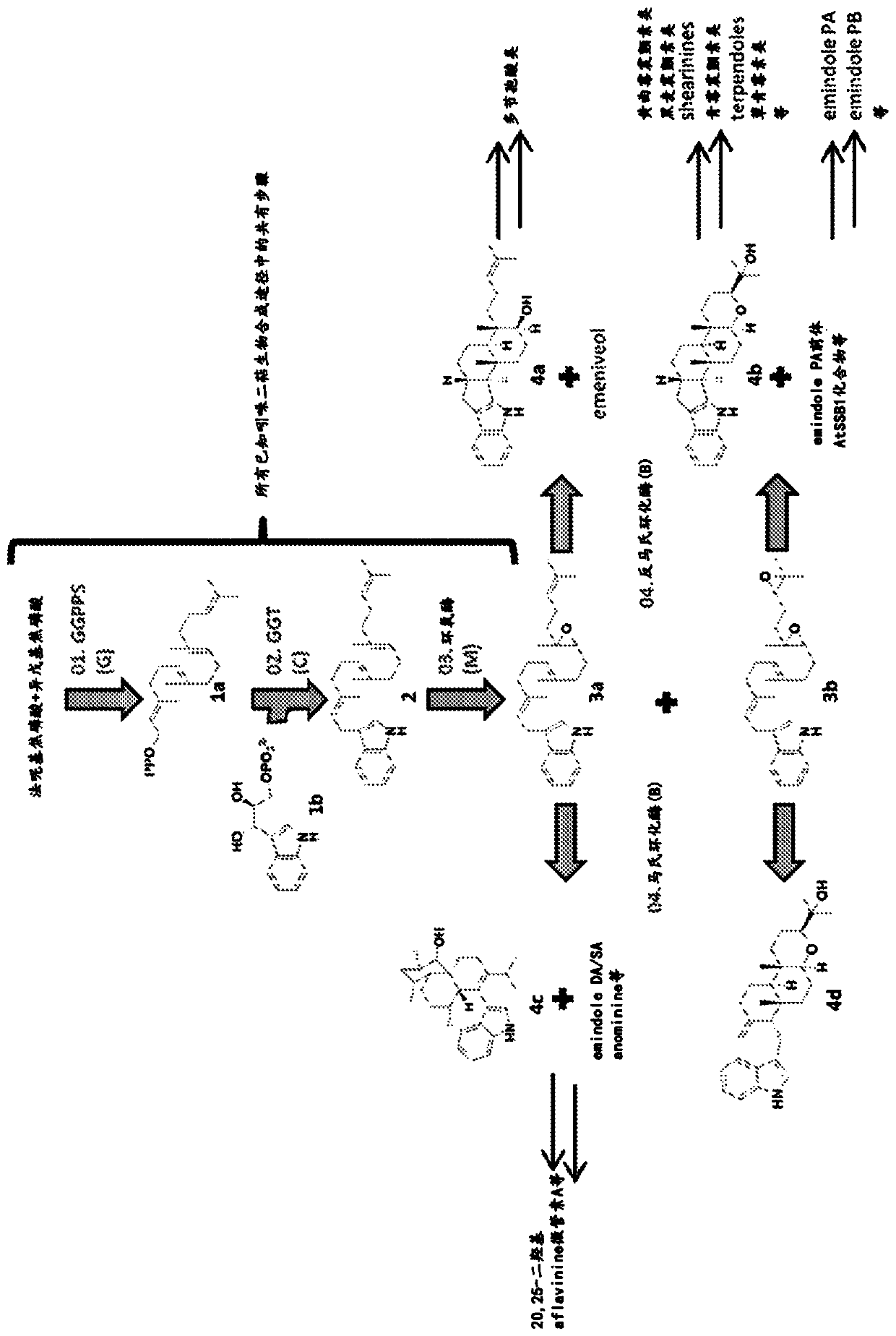
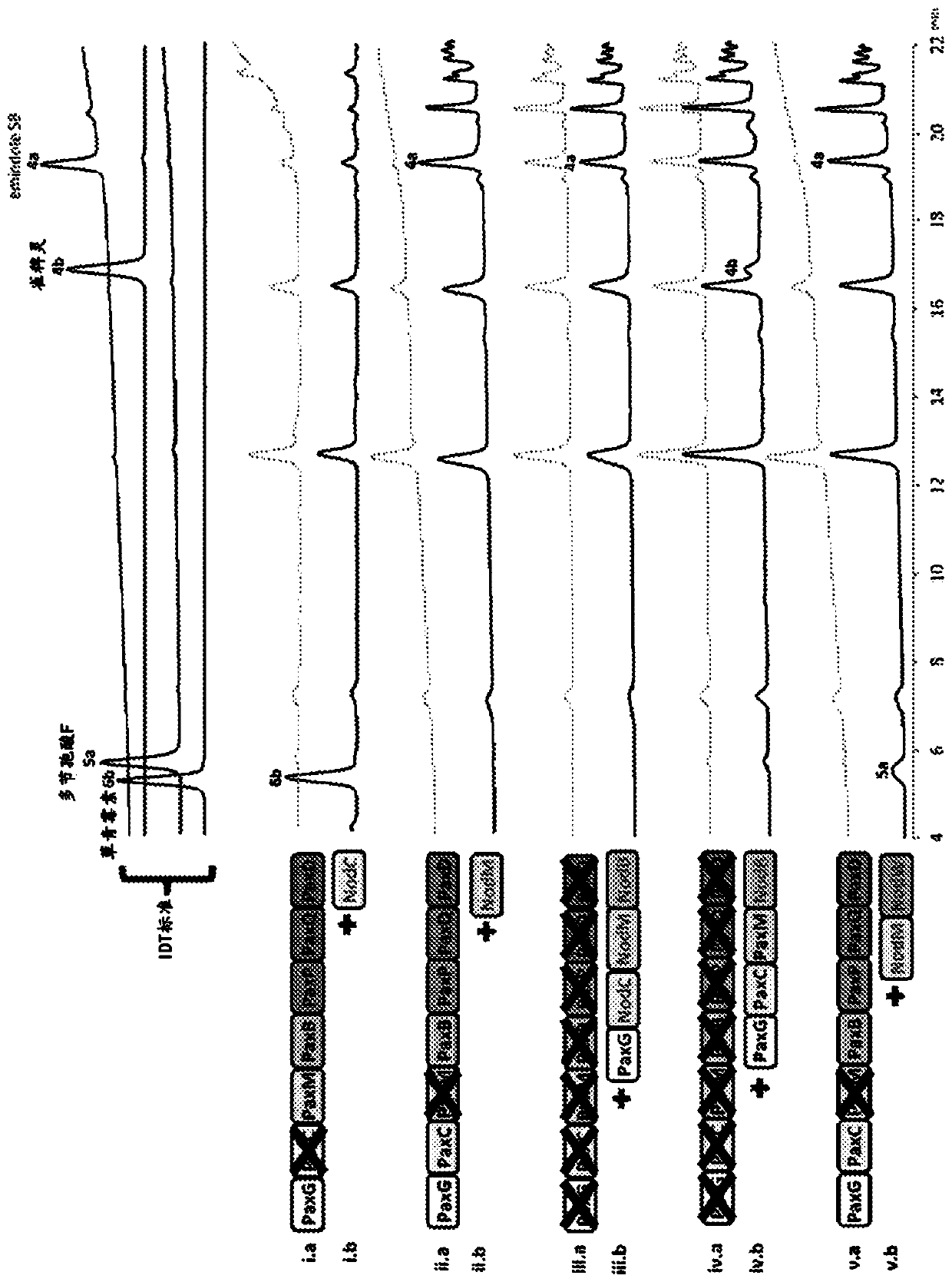
Heterologous biosynthesis of nodulisporic acid
Nodulisporic acids (NAs) comprise a group of indole diterpenes known for their potent insecticidal activities; however, biosynthesis of NAs by its natural producer, Hypoxylon pulicicidum (Nodulisporium sp.) is exceptionally difficult to achieve. The identification of genes responsible for NA production could enable biosynthetic pathway optimization to provide access to NAs for commercial applications. Obtaining useful quantities of NAs using published fermentations methods is challenging, making gene knockout studies an undesirable method to confirm gene function. Alternatively, heterologous gene expression of H. pulicicidum genes in a more robust host species like Penicillium paxilli provides a way to rapidly identify the function of genes that play a role in NA biosynthesis. In this work, we identified the function of four secondary-metabolic genes necessary for the biosynthesis of nodulisporic acid F (NAF) and reconstituted these genes in the genome of P. paxilli to enable heterologous production of NAF in this fungus.
Owner:VICTORIA LINK LTD
Promoter and Regulatory Elements for Improved Expression of Heterologous Genes in Host Cells
ActiveUS20170253889A1Stable and high yieldVectorsOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyHeterologous gene expression
Owner:AMGEN INC
Formaldehyde dehydrogenase genes from methylotrophic yeasts
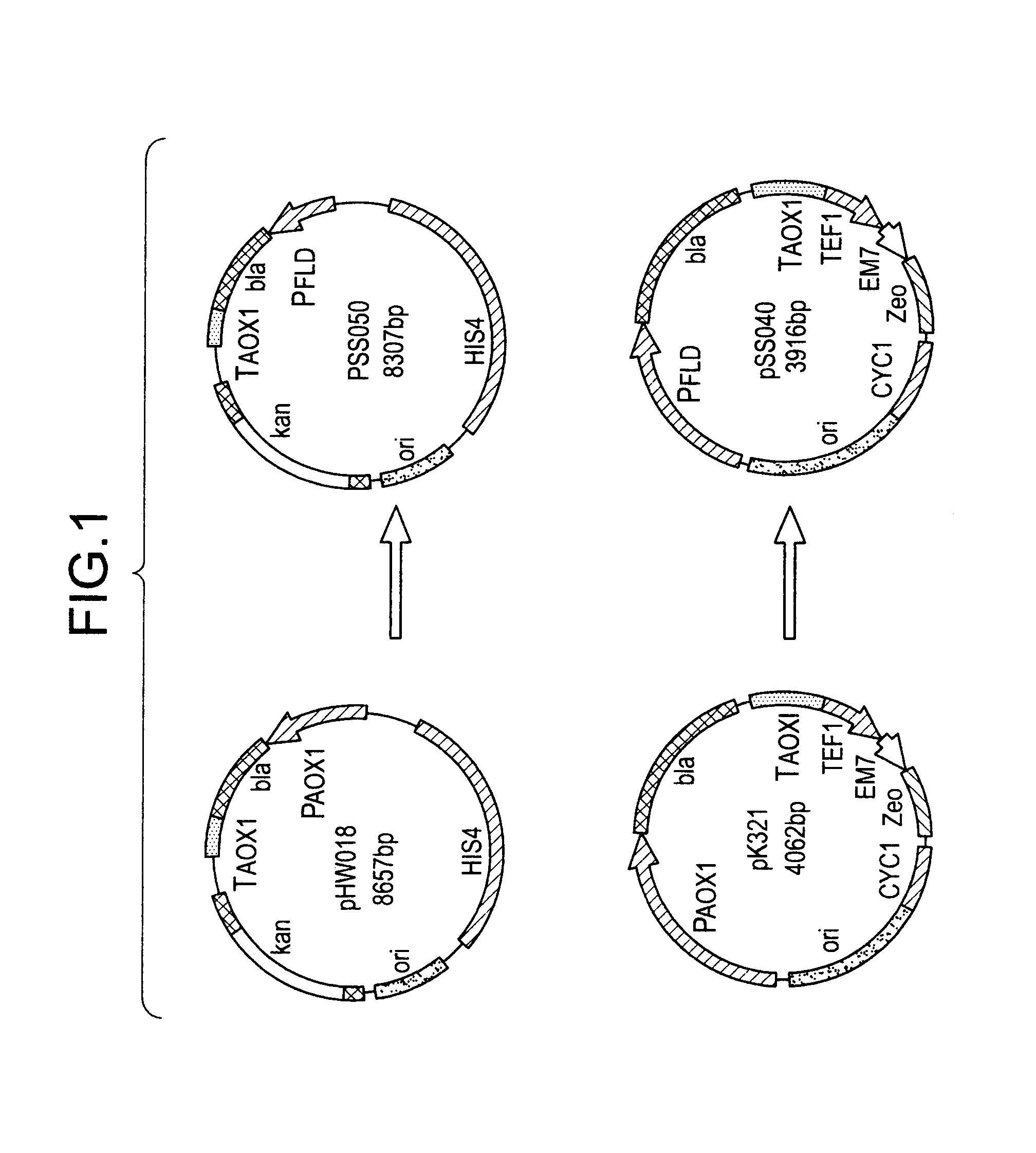
The present invention provides formaldehyde dehydrogenase genes (FLD) from methylotrophic yeasts. The FLD structural genes confer resistance to formaldehyde and are therefore useful as a selectable marker in methylotrophic yeasts. The FLD promoter sequences are strongly and independently induced by either methanol as sole carbon source (with ammonium sulfate as nitrogen source) or methylamine as sole nitrogen source (with glucose as carbon source). Induction under either methanol, methylamine or both provides levels of heterologous gene expression comparable to those obtained with the commonly used alcohol oxidase I gene promoter (PAOX1). The FLD promoter of Pichia pastoris (PFLD1) is an attractive alternative to PAOX1 for expression of foreign genes in P. pastoris, allowing regulation by carbon (methanol) or nitrogen (methylamine) source within the same expression strain. Yeast strains, expression cassettes, expression vectors, and host cells comprising an FLD gene promoter and 3′ termination sequence are also provided.
Owner:RES CORP TECH INC
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter and heterologous gene expression
The invention relates to discovery of an isolated glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter in Pleurotus and a construct comprising the promoter of the invention operably linked to a heterologous transcribable polynucleotide molecule.
Owner:MYCOMAGIC BIOTECH
Isolated DNA fragment of the sparc human promoter and its use for driving the expression of an heterologous gene in tumor cells
ActiveUS20090312401A1Organic active ingredientsTumor rejection antigen precursorsDNA fragmentationFhit gene
An isolated DNA sequence corresponding to a region of the SPARC gene human promoter from base pair −513 to base pair +3 5 capable of driving the expression of a heterologous gene of interest, that can be associated to any other promoter sequence, such as radiation responsive sequence, hypoxia responsive sequence and free-radical responsive sequence. The invention also provides constructs and DNA recombinant expression viral vectors, comprising said isolated sequence of the SPARC gene human promoter and at least one heterologous gene operably linked thereto, wherein said promoter sequence drives the expression of the at least one heterologous gene in tumor cells. Pharmaceutical compositions and a method for treating tumors are also provided.
Owner:CONSEJO NAT DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS Y TECH CONICET +1
Promoter and regulatory elements for improved expression of heterologous genes in host cells
Owner:AMGEN INC
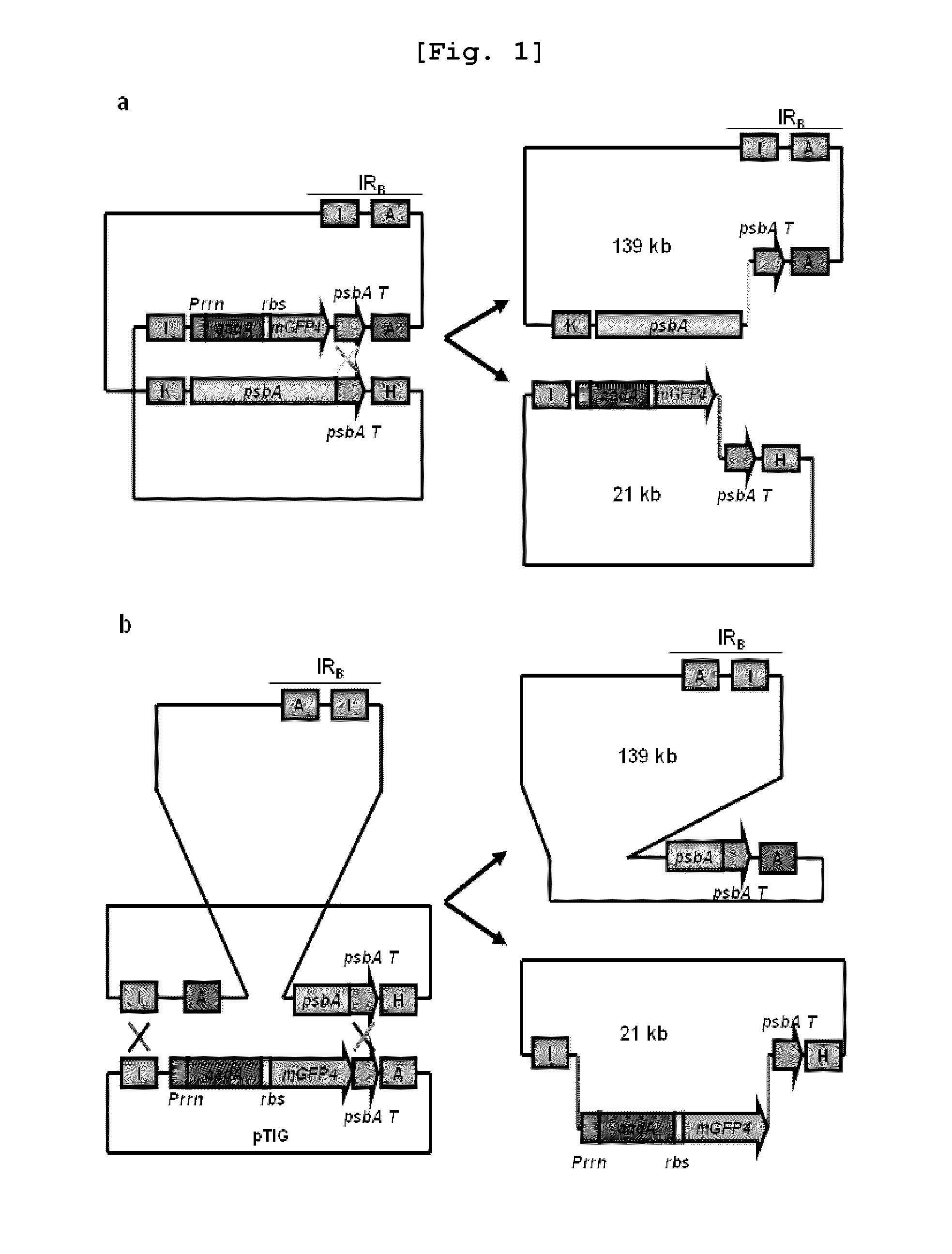
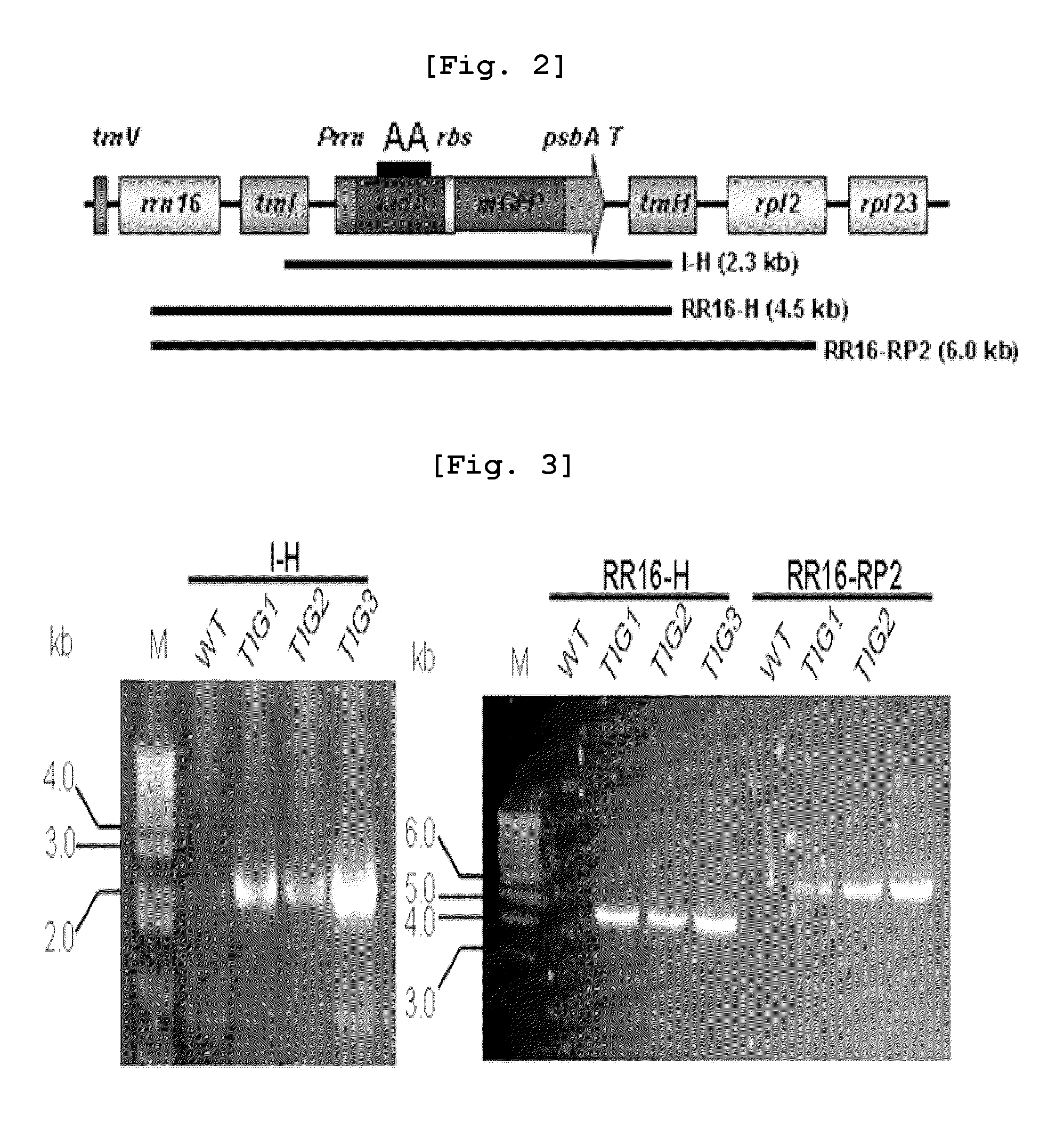
Plastid transformation system to prevent the intramolecular recombination of transgene
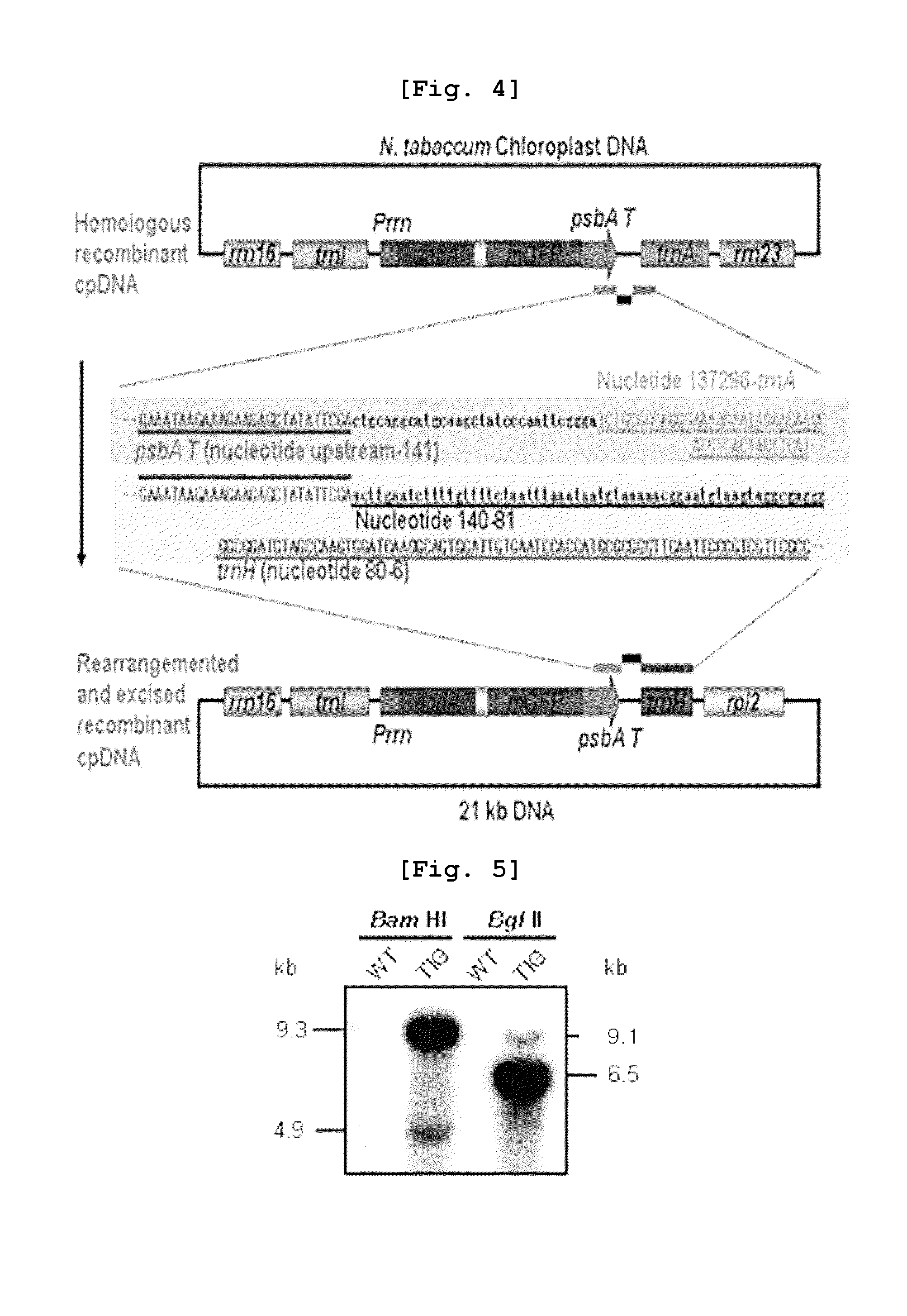
InactiveUS7888562B2Avoid recombinationOther foreign material introduction processesSewer systemsNicotiana tabacumOrganism
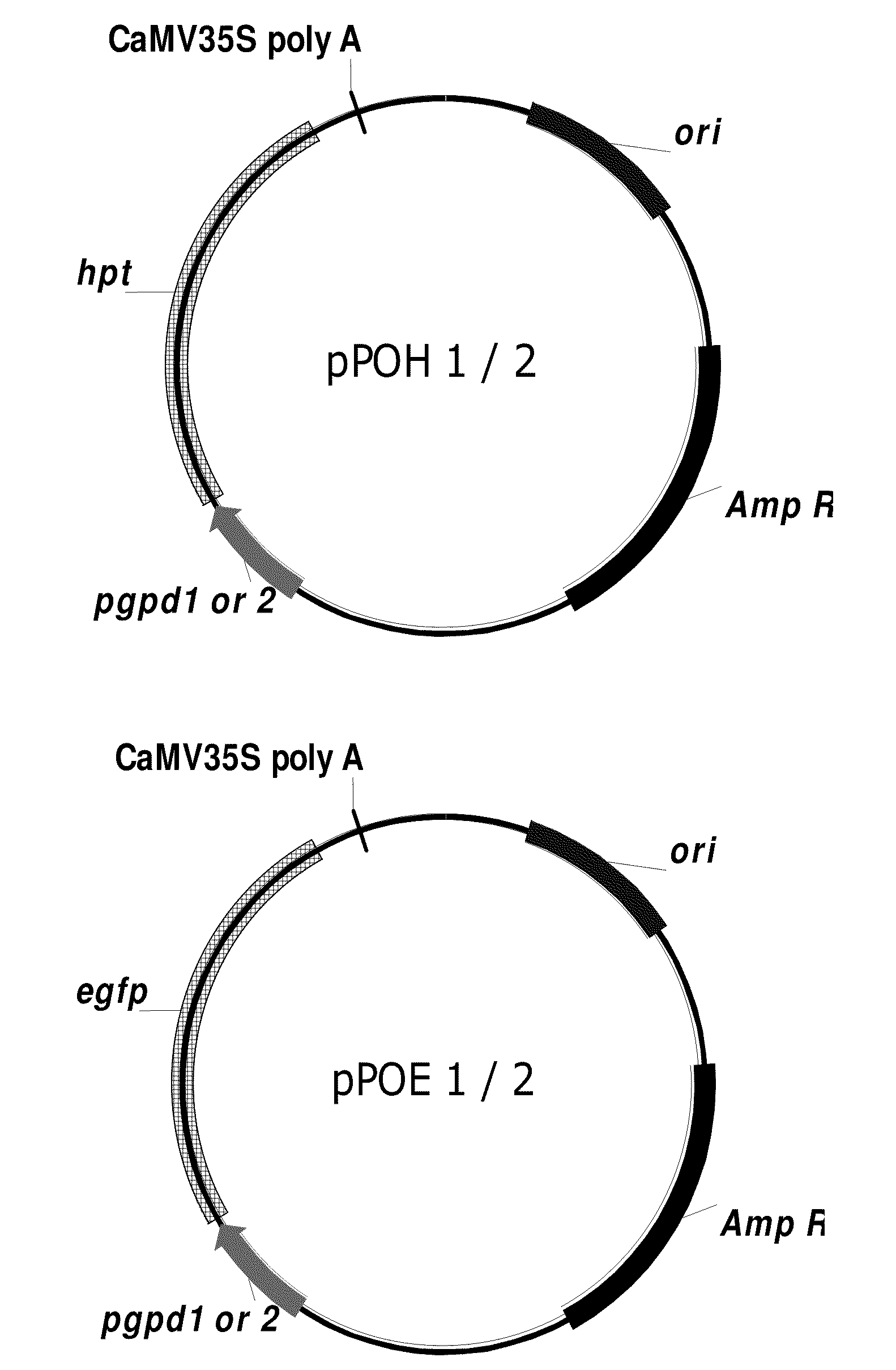
The present invention relates to a plastid transformation system capable of preventing second recombination events of heterologous genes inserted into plastid genomes. More specifically, this invention relates to a plastid transformation vector carrying a promoter and a terminator derived from organisms other than tobacco. The inventive recombinant expression vector for plastid transformation is capable of mass-producing exogenous proteins on a level par with conventional vectors carrying promoter / terminator couples of tobacco origin. At the same time, it is capable of preventing second recombination events within plastids. Thus, the vector of this invention is greatly useful in producing transgenic plants since it can effect a secure introduction of heterologous genes and support normal transformation and heterologous gene expression.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF BIOSCI & BIOTECH
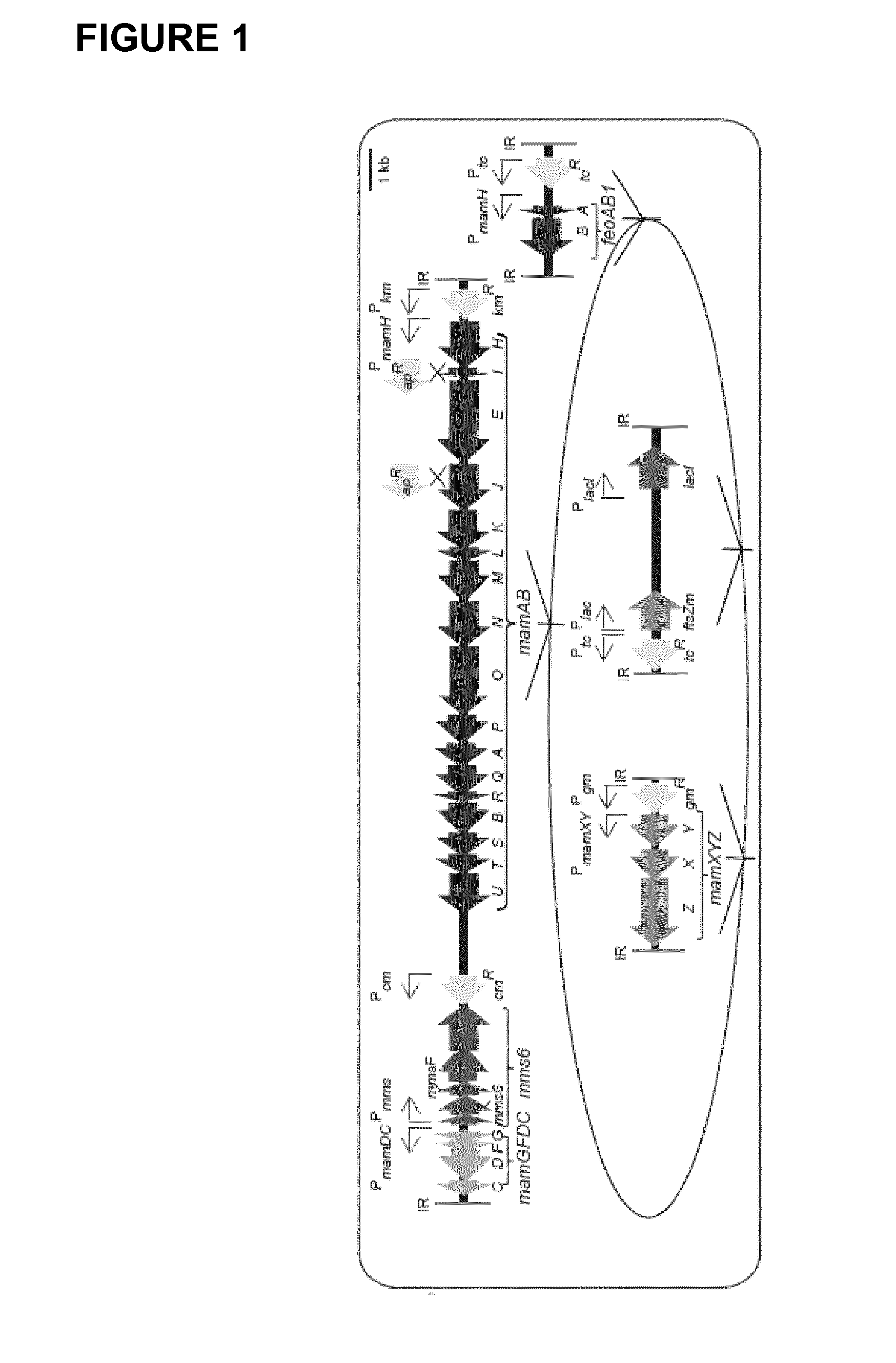
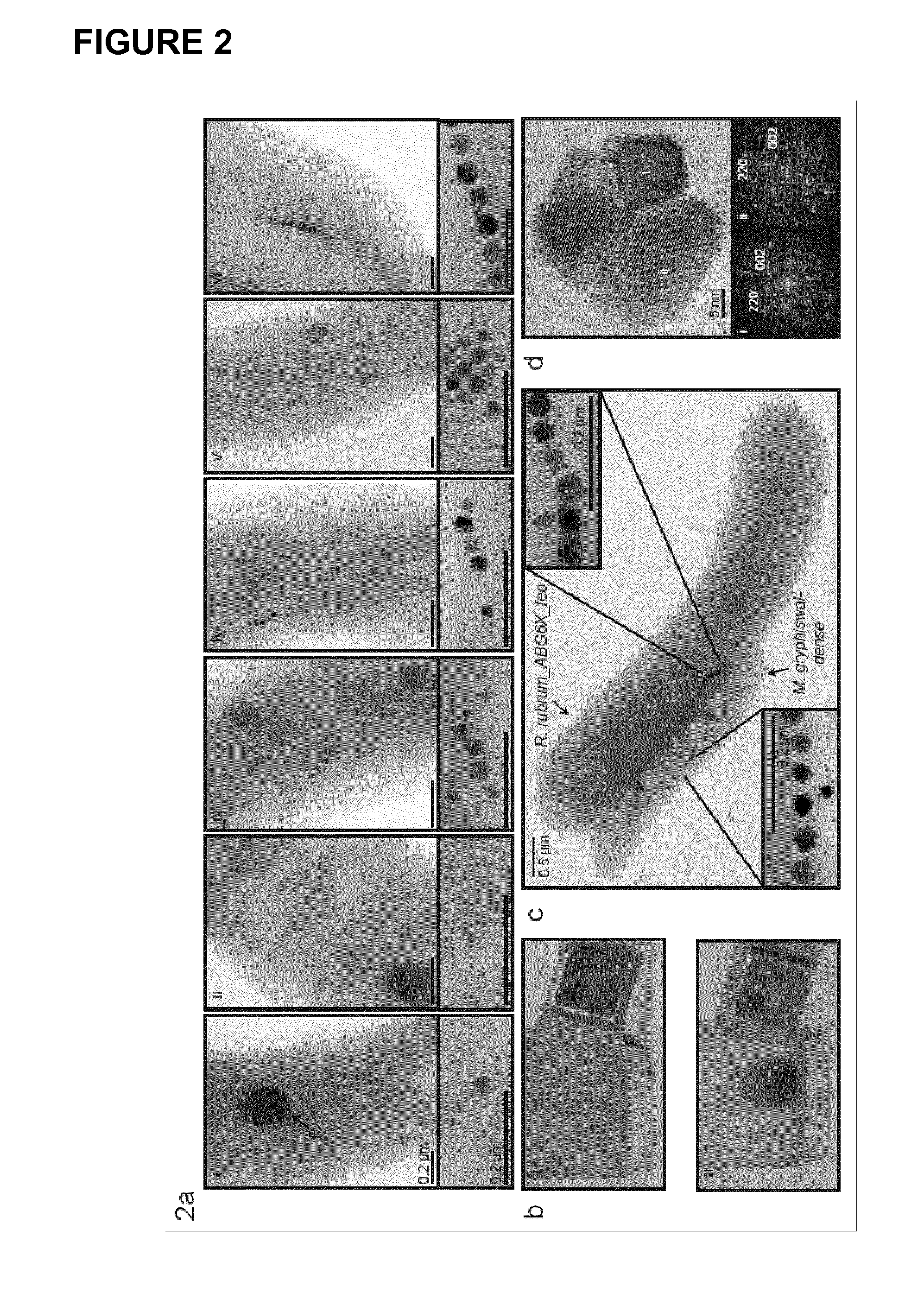
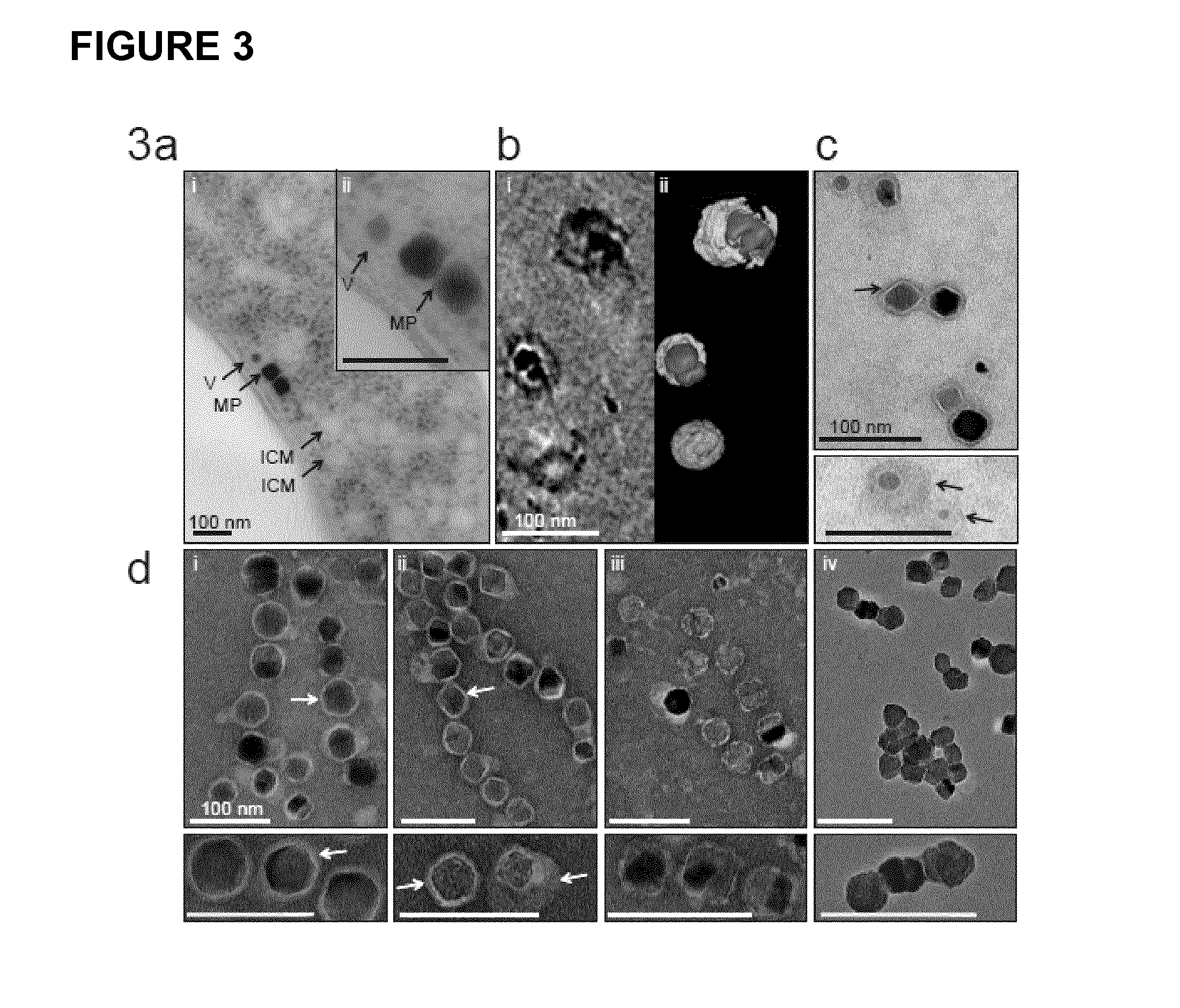
Production of magnetic nanoparticles in recombinant host cells
InactiveUS20160296643A1Bacteria peptidesEmulsion deliveryRhodospirillum rubrumMagnetite Nanoparticles
The present invention relates to a recombinant host cell, comprising in its genome preferably heterologous gene expression cassettes capable of being expressed in the host cell, the gene expression cassettes encoding a nucleic acid sequence encompassing at least 80% of the full-length sequence of the mamAB operon, the mamGDFC operon, and the tmms6 operon of a magnetotactic alphaproteobacterium, respectively, and preferably further comprising gene expression cassettes capable of being expressed in the host cell, the gene expression cassettes encoding a nucleic acid sequence encompassing at least 80% of the full-length sequence of the mamXY operon and / or the feoABI operon of a magnetotactic alphaproteobacterium; wherein the recombinant host cell, upon expression of the gene expression cassettes in their entirety, is capable of producing magnetic nanoparticles. Preferably, the recombinant host cell is derived from Rhodospirillum rubrum. Furthermore, the present invention also relates to a corresponding method for producing such recombinant host cell by means of genetic transposition.
Owner:UNIV OF BAYREUTH
Promoters suitable for heterologous gene expression in yeast
ActiveUS20160333058A1Improve expression rateDepsipeptidesFermentationHeterologous gene expressionYarrowia
The present invention relates to the use of novel promoters for heterologous gene expression, preferably for expression of genes in organisms of the genus Yarrowia, to the genetically modified organisms of the genus Yarrowia, and to a process for producing biosynthetic products by cultivating the genetically modified organisms.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
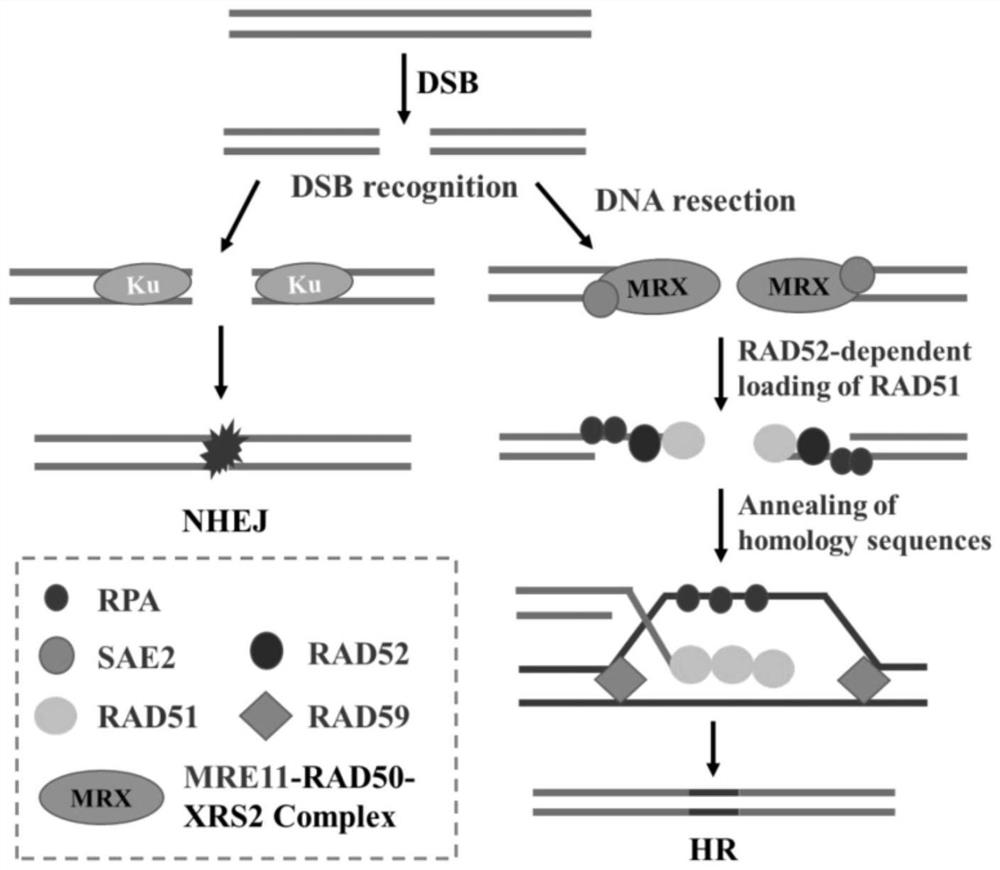
Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetically engineered bacterium for enhancing homologous recombination capability and application thereof
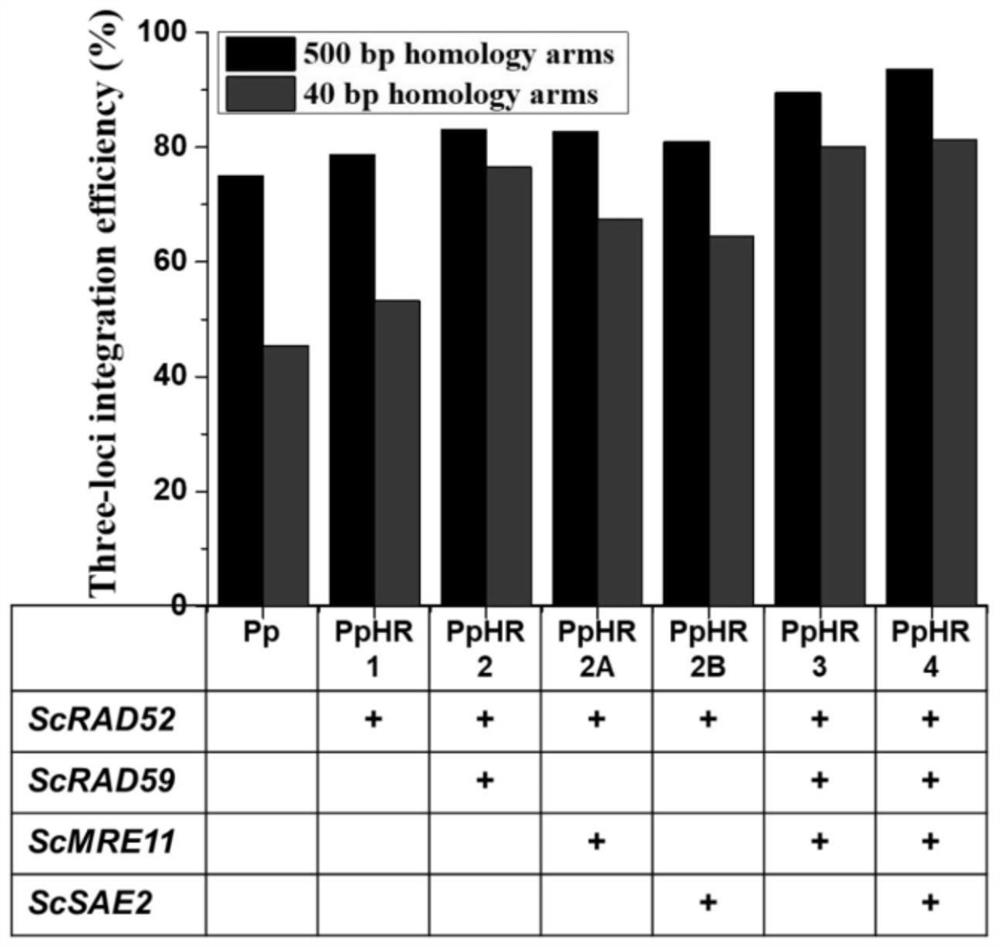
The invention discloses a yeast genetically engineered bacterium for enhancing homologous recombination capability and application thereof, and relates to the field of bioengineering. According to the yeast genetically engineered bacterium, yeast is used as an original strain, the yeast genetically engineered bacterium is constructed by introducing genes, and the introduced genes comprise any one of the following groups: (1) an RAD52 gene, an RAD59 gene and an MRE11 gene; (2) an RAD52 gene and an RAD59 gene; (3) an RAD52 gene and an MRE11 gene; (4) an RAD52 gene and an SAE2 gene; (5) an RAD52 gene; and (6) an RAD52 gene, an RAD59 gene, an MRE11 gene and an SAE2 gene. The yeast genetically engineered bacterium provided by the invention can realize simultaneous integration of single, two and three genes of a heterologous gene expression cassette with about 40bp homologous arms, and the efficiencies are respectively up to 100%, about 98% and about 81%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV HANGZHOU GLOBAL SCI & TECH INNOVATION CENT
Promoters suitable for heterologous gene expression in yeast
The present invention relates to the use of novel promoters for heterologous gene expression, preferably for expression of genes in organisms of the genus Yarrowia, to the genetically modified organisms of the genus Yarrowia, and to a process for producing biosynthetic products by cultivating the genetically modified organisms.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Yeast Engineering Strain Transformed by Chromosomal Fusion
ActiveCN107384968BEasy to distinguishSimplified chromosomeStable introduction of DNAMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyYeast
The invention relates to a yeast engineering strain transformed by chromosomal fusion. The present inventors artificially fused 16 natural chromosomes of yeast to obtain a series of chromosomally fused strains, including 16 linear or circular chromosomes fused into one. The yeast engineering strain of the invention can be used as a host for eukaryotic heterologous gene expression and large-segment DNA cloning.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com