Modeling ribosome dynamics to optimize heterologous protein production
A protein and ribosome technology, applied in the field of 3' rRNA tail, a kind of protein production, can solve the problems of translocation, poor translation, spacing, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0090] A new biophysical model of translation elongation
[0091] Discovery of periodic free energy signals
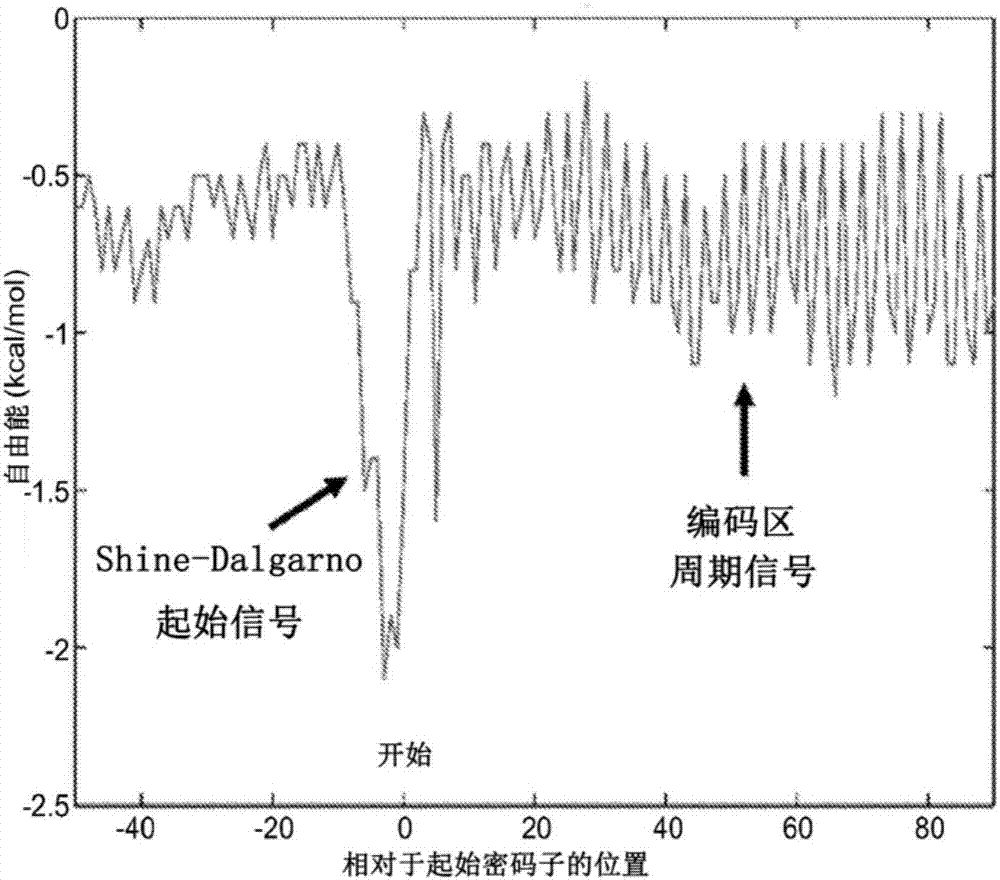
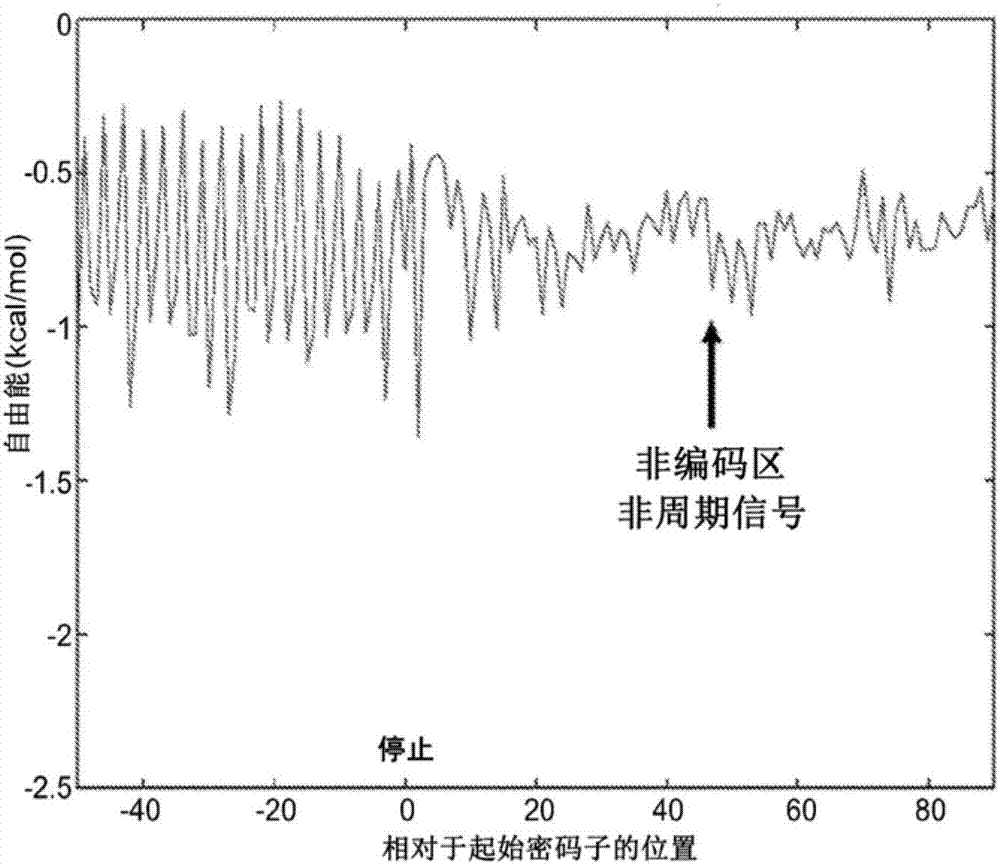
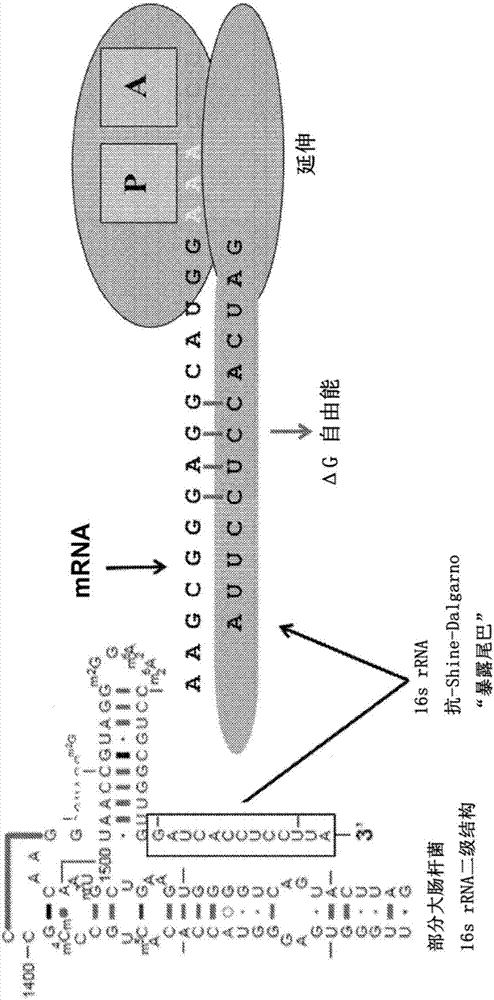
[0092] A periodic free energy signal is observed from the average Watson-Crick binding between the 16S rRNA 3' end "exposed tail" (3'-AUUACCUCCACUAG-5') and mRNA during translation, as figure 1 shown in [45,46]. The most prominent binding energy is at priming, which corresponds to the "exposed tail" of the anti-Shine-Dalgarno (aSD) binding Shine-Dalgarno (SD) sequence. Thereafter, during elongation there is a periodic (sinusoid-like) binding signal corresponding to "in-frame" ribosome translocation (where negative free energy indicates binding) [45, 46, 47]. The Fourier transform of this periodic signal shows prominent peaks with a frequency of 1 / 3 period per nucleotide [46, 48]. This illustrates that the exposed tail binds the mRNA at each codon during elongation. However, after reaching the stop codon, the signal decays rapidly, suggesting that the ribosome h...
Embodiment 2
[0124] Algorithms and Mathematics
[0125] The following examples have been included to provide those of ordinary skill in the art with guidance for practicing representative embodiments of the presently disclosed subject matter. The following specific examples and equations are for illustrative purposes only and should not be construed as limiting the methods of the present invention in any way.
[0126] The ribosome spring model and ribosome translocation were modeled using step-size integrators and a 'probabilistic period' algorithm as described above. This probabilistic periodic algorithm calculates ribosomal translocation and ribosomal "latency" at each codon using the force convolved with the probability of picking up an aminoacyl-tRNA (aa-tRNA). The ribosome displaces every "cycle" with a step function calculated as force multiplied by the step constant δT(dT); a cycle is defined as the state in which the ribosome has not picked up aa-tRNA. Probability cycles are de...
Embodiment 3
[0296] Example Study: Forecasting and Optimization
[0297] The predictive and optimization capabilities of the model were evaluated by expressing five model genes in Escherichia coli: gst (glutathione-S-transferase), pf0132 (α-glucosidase), clju_c11880 (alcohol dehydrogenase) and rt8_0542 ( endoglucanase and exoglucanase). The optimization power of the model was also compared to a codon bias optimization algorithm as described elsewhere herein. Multiple mRNA variants of GST were also designed and expressed to further validate the model's predictions compared to those of codon bias. The codon adaptation index (CAI) of Sharpe et al. [86] was used to measure the codon bias of genes. Measured protein yield (GST activity) was correlated with predicted protein yield by codon adaptation index (CAI) and model index (BNI). The rationale for comparing correlations was to demonstrate that the determinants of protein yield are not limited to codon bias, but encompass convolutions be...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com