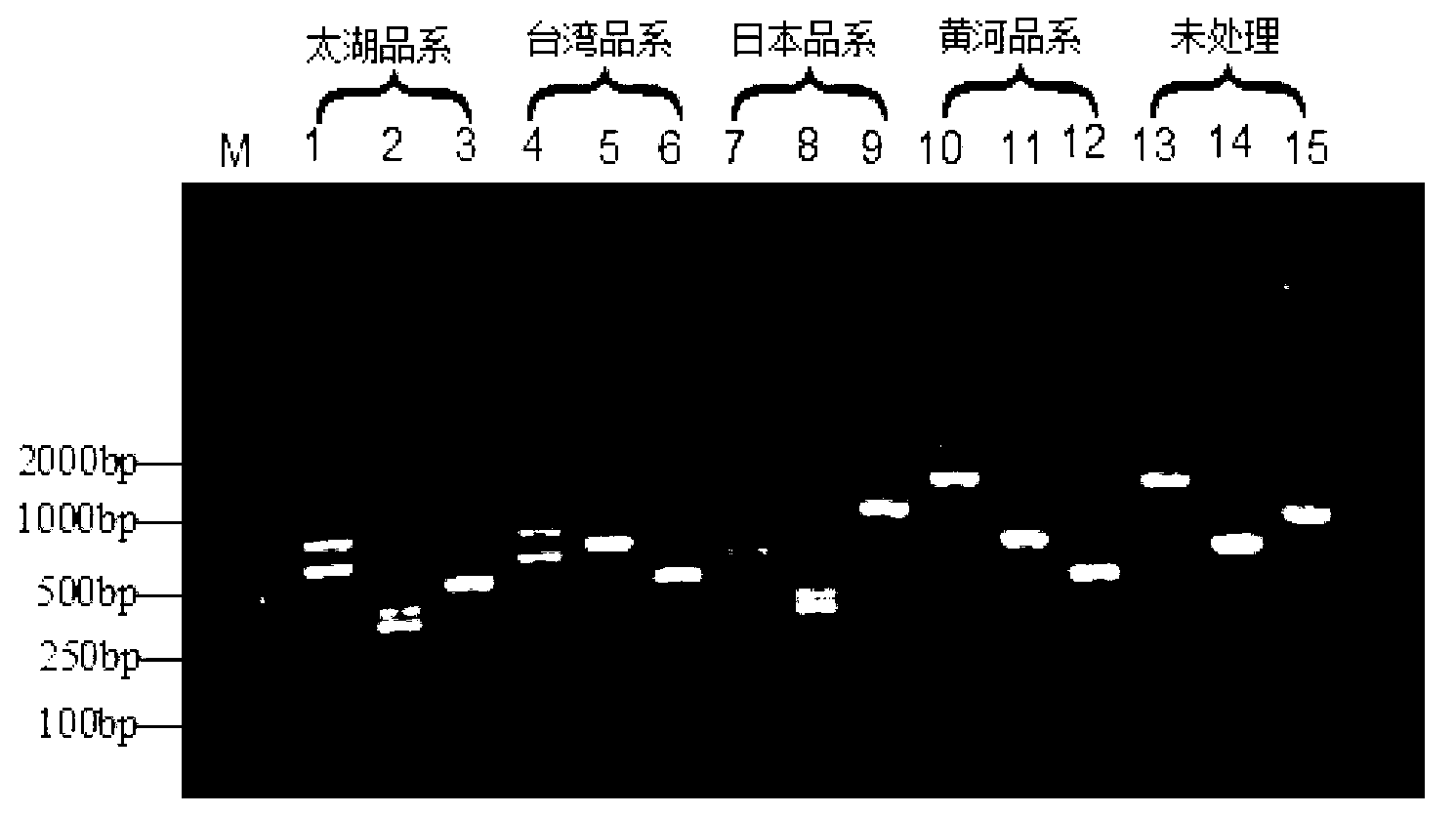
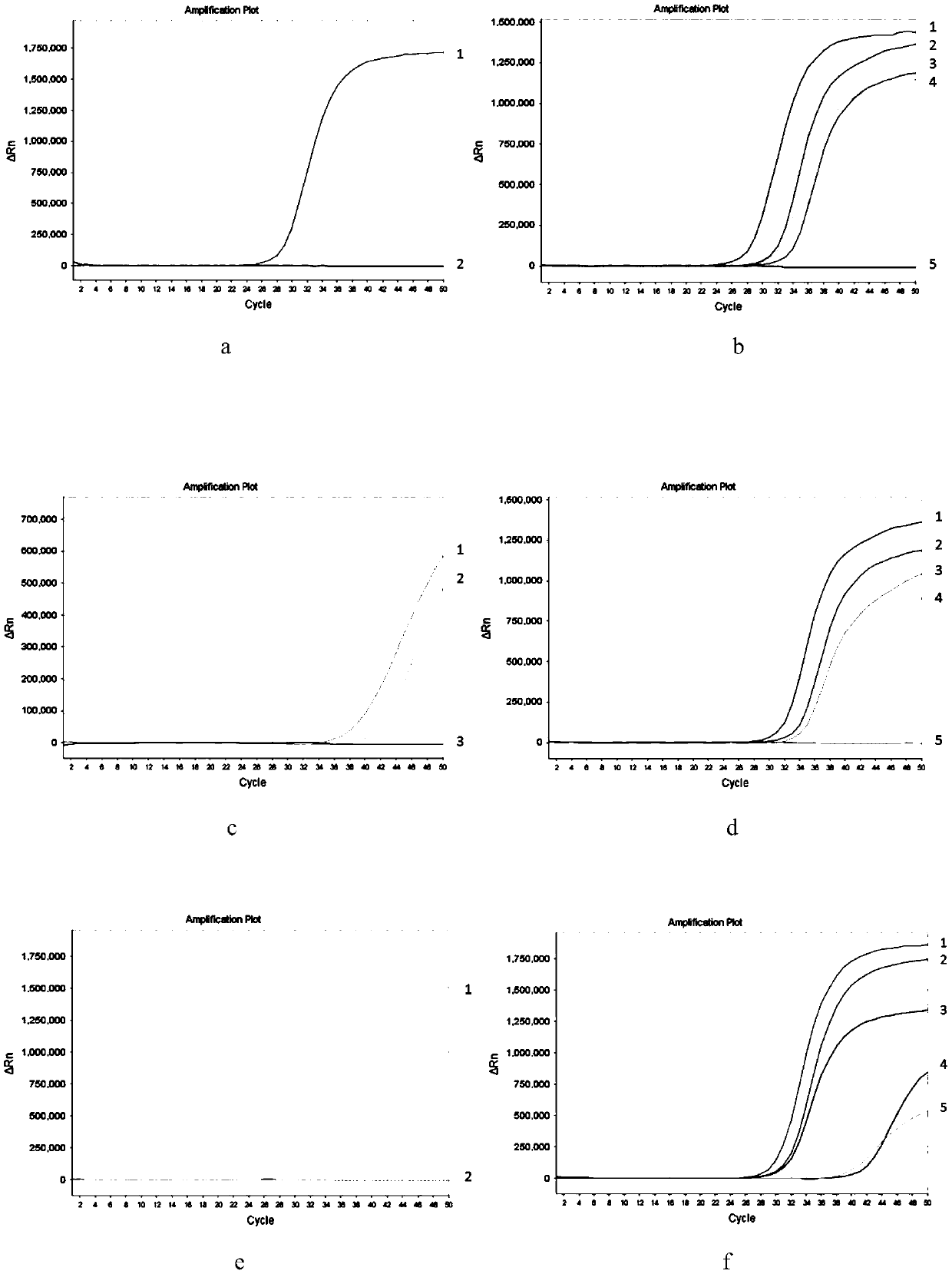
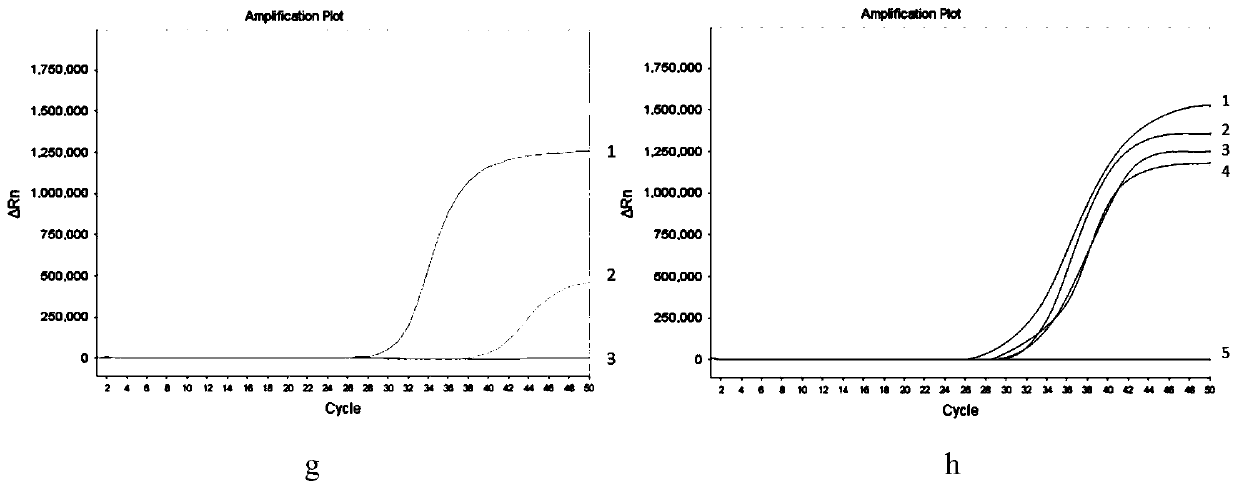
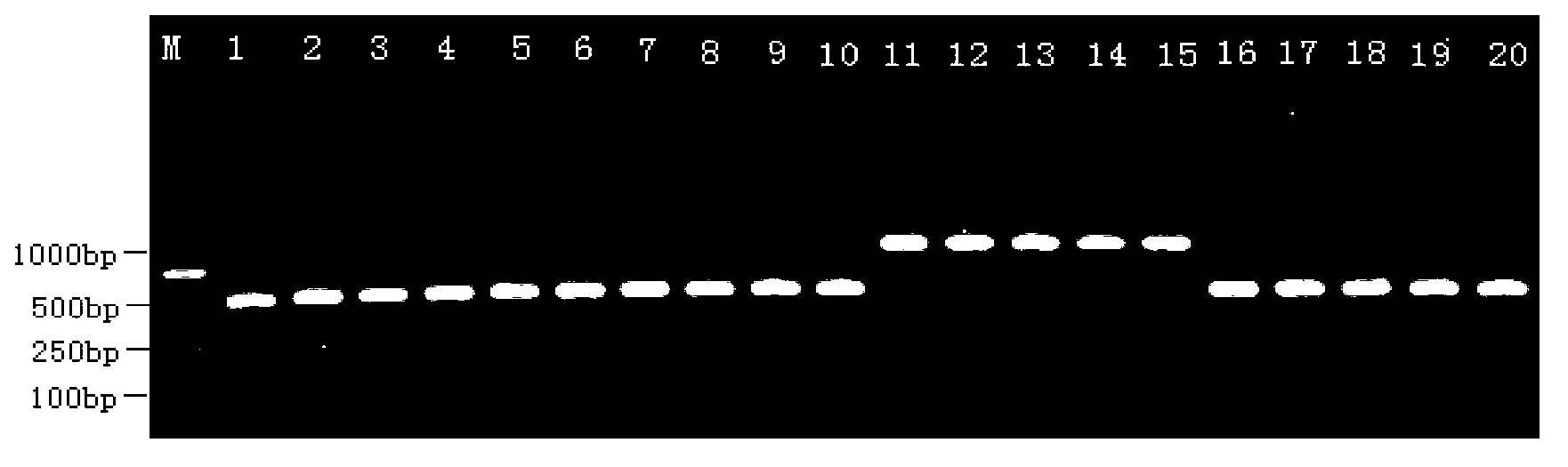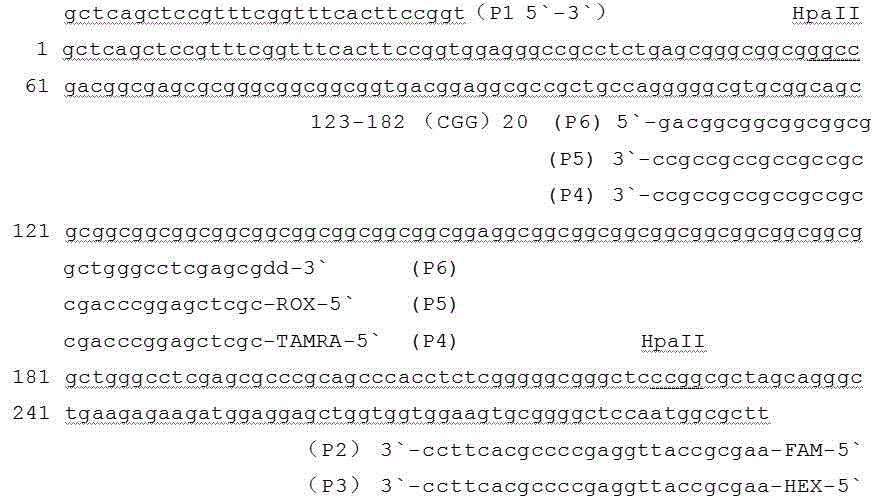Patents
Literature
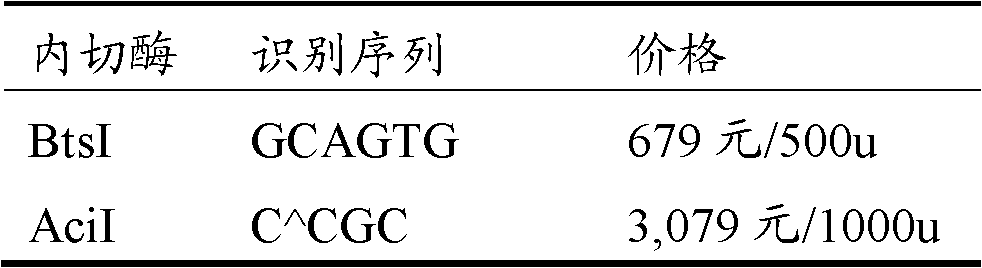
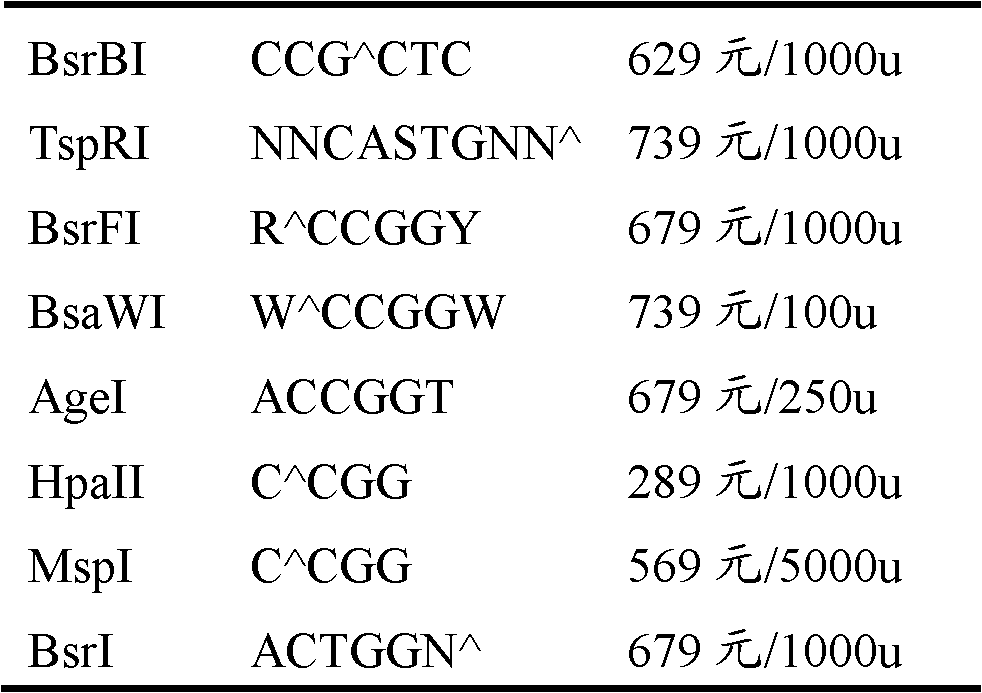
34 results about "HpaII" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
HpaII (IntEnz: EC 3.1.21.4) is a restriction enzyme obtained from the microorganism called Haemophilus parainfluenzae. It is a DNA restriction enzyme, therefore it has the ability to cut the DNA from certain region as demonstrated below. It has the ability to produce cohesive ends, which are rather useful in constructing plasmids.
Method for detecting DAN methyltransferase activity based on strand displacement amplification and DNAzyme amplification
ActiveCN105112540AHighly sensitive detection activityLow detection limitMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisFluorescenceDNA Methyltransferase Inhibitor
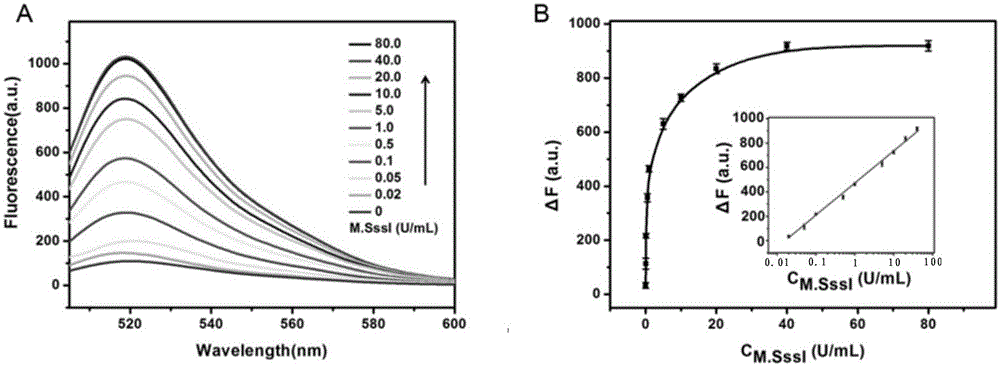
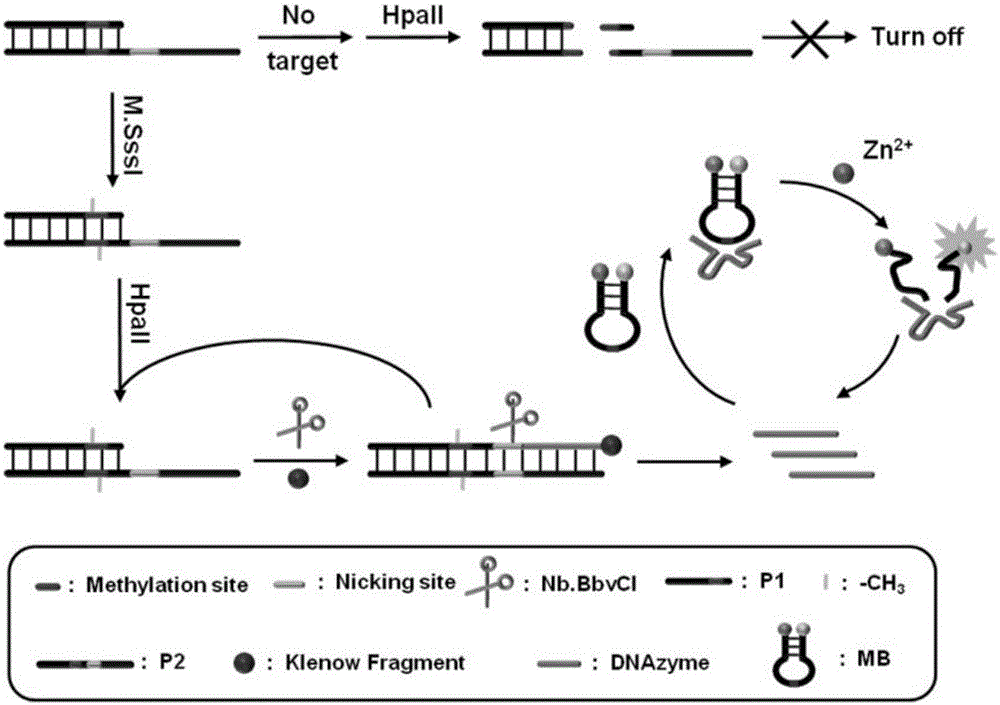
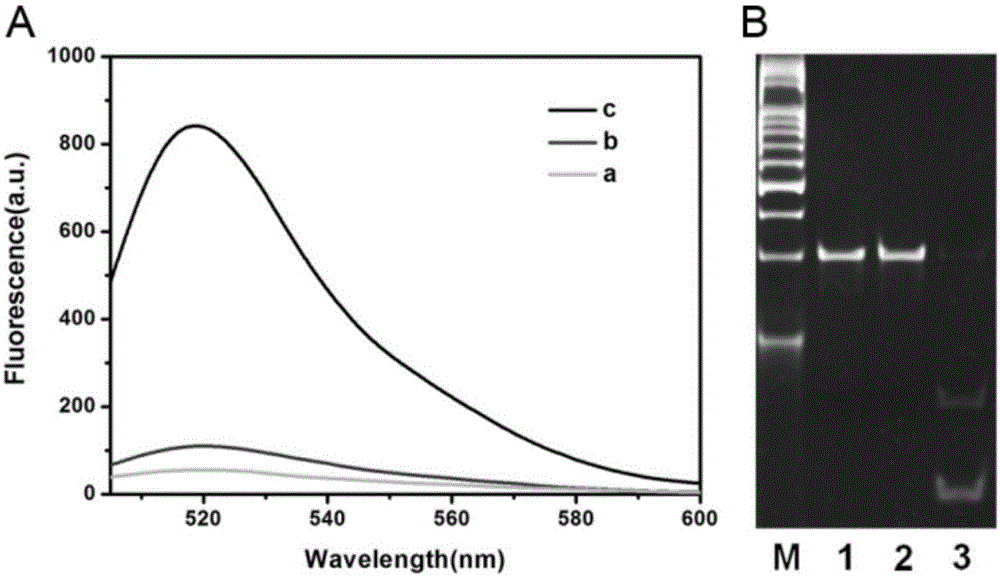
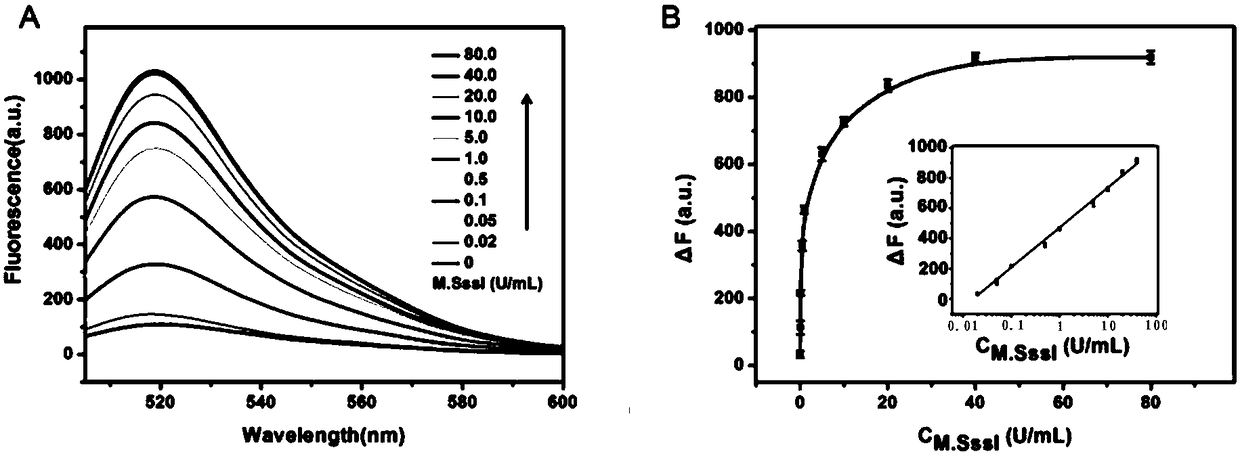
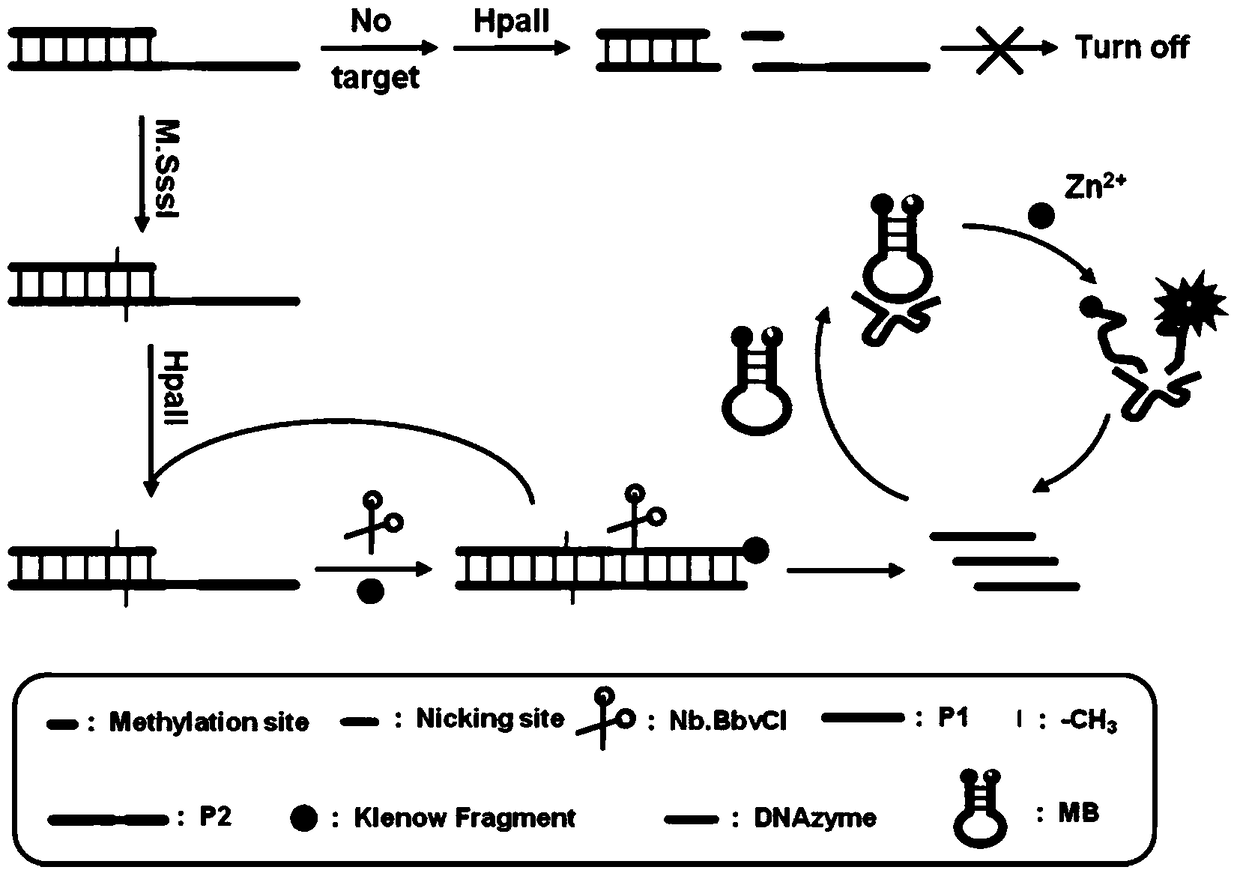
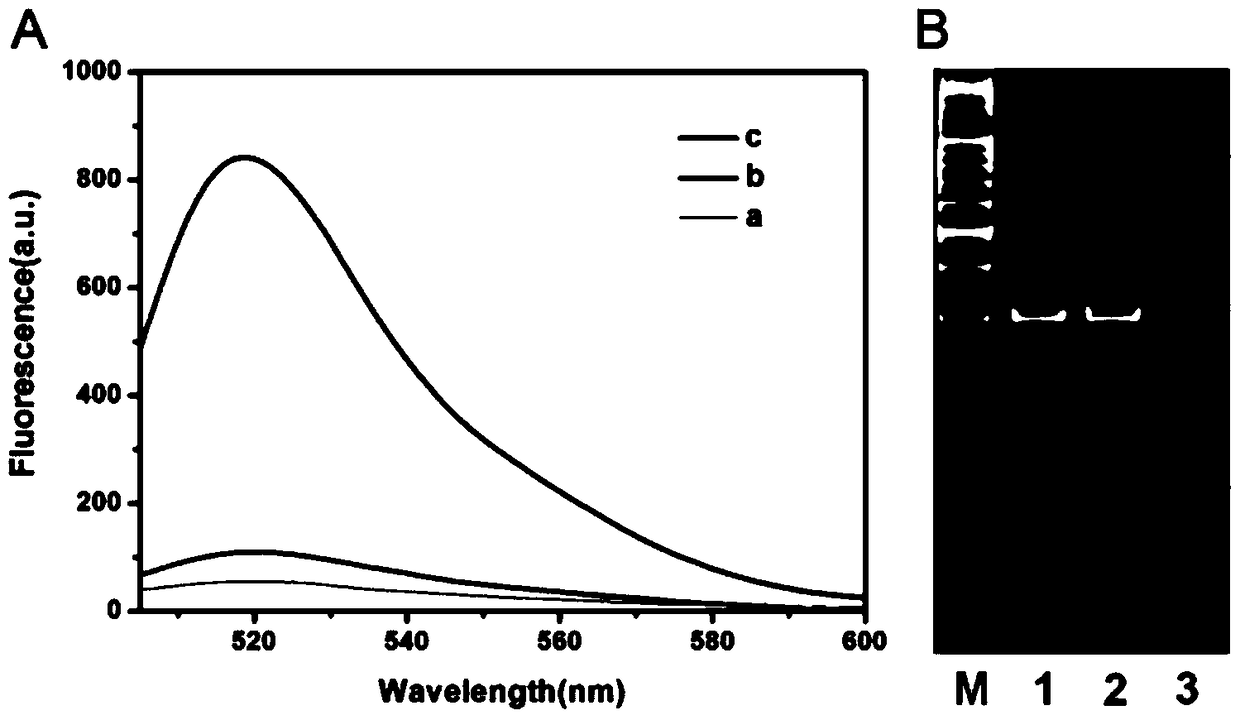
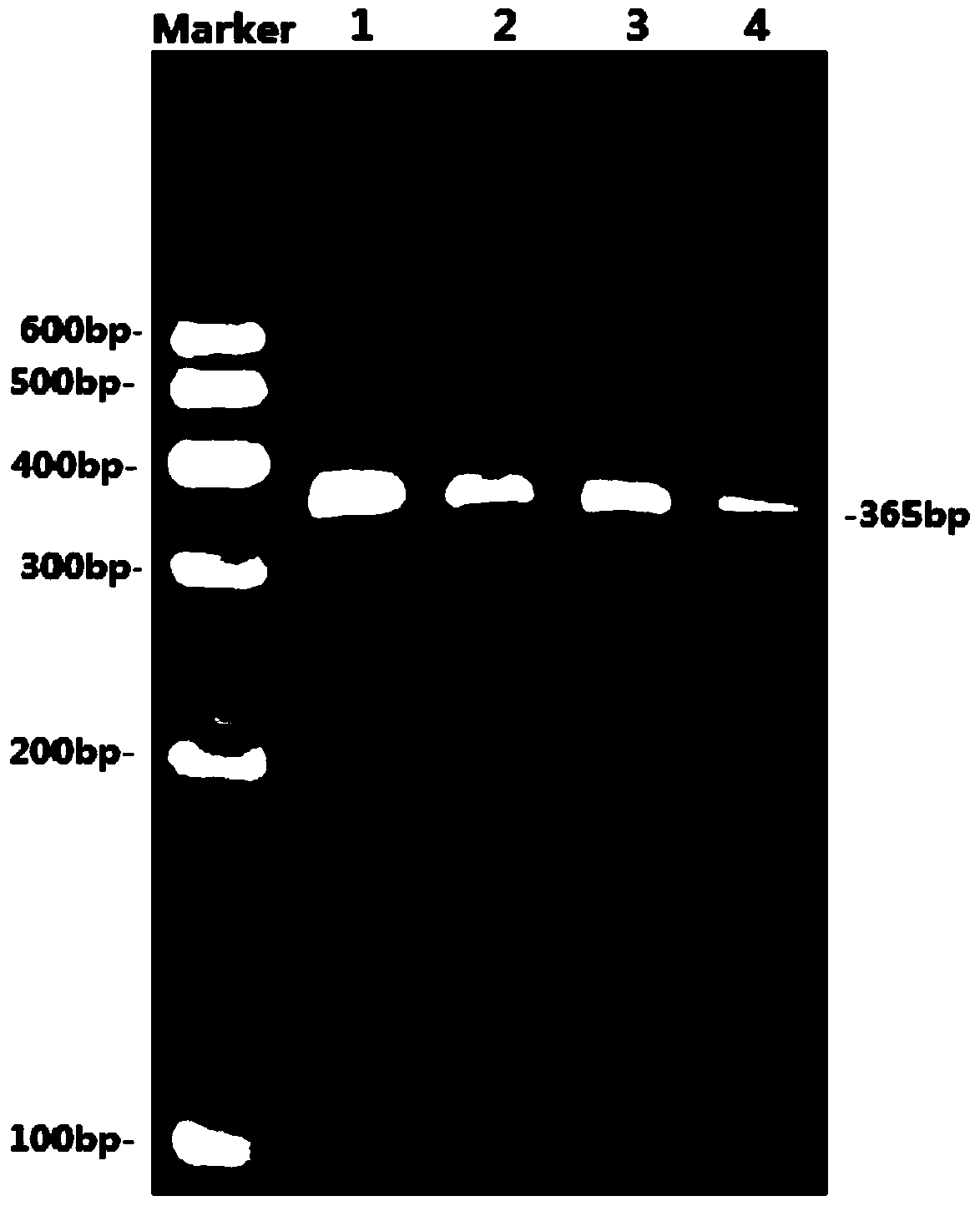
The invention relates to a method for detecting DAN methyltransferase activity based on strand displacement amplification and DNAzyme amplification. A three-function double-stranded DNA probe is designed. Methylation happening to the three-function double-stranded DNA probe is specifically recognized through DAN methyltransferase. Remaining non-methylated double-stranded DNA is specifically cut through HpaII restriction enzymes, methylated double-stranded DNA triggers a strand displacement reaction, a large amount of 8-17 DNAzyme is released, the 8-17 DNAzyme catalyzes cutting of a large number of hairpin-line molecular beacon substrates, and remarkable fluorescent enhancement is triggered. The method can sensitively detect the DAN methyltransferase activity, and the detection limit is 0.0082 U / mL. The method has potential application in research of influences of anti-cancer drugs on DAN methyltransferase activity inhibition and screening of DAN methyltransferase inhibitors.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Construction method and fermenting method of antibiotic-resistance-free recombinant bacillus subtilis for expressing glutamate decarboxylase
InactiveCN106967659AEnhance expressive abilitySimple processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGlutamate decarboxylaseAlanine racemase
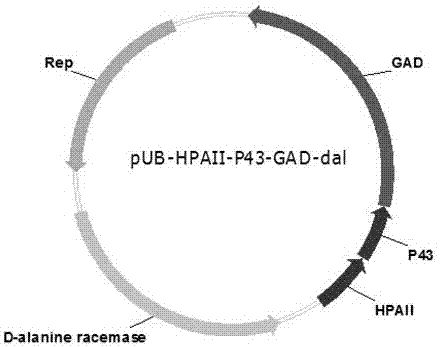
The invention relates to a construction method and a fermenting method of antibiotic-resistance-free recombinant bacillus subtilis for expressing glutamate decarboxylase and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The construction method includes taking bacillus subtilis WB600 as an original strain, and knocking out a D-alanine racemase gene on a chromosome of the bacillus subtilis WB600 so as to obtain D-alanine deficient WB600 (dal); fusing an optimized gad gene with an antibiotic-resistance-free expression vector pUB110 (a antibiotics resistance gene is replaced by the D-alanine racemase gene) through an overlap extension PCR technology to obtain a polymer, transforming the polymer into competence of the bacillus subtilis WB600, and enabling the polymer to recombine in a host so as to obtain a recombinant plasmid Pub-HpaII-P43-gad-dal, which is named as bacillus subtilis SK44.001 with the preservation number being CCTCC NO:M 2016774. The fermentation liquor enzyme activity of the antibiotic-resistance-free recombinant bacillus subtilis can be up to 8.6 U / mL, and accordingly the antibiotic-resistance-free recombinant bacillus subtilis has significant industrial application value.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
SLC39A7 gene as genetic label of pig fat deposition description and application thereof
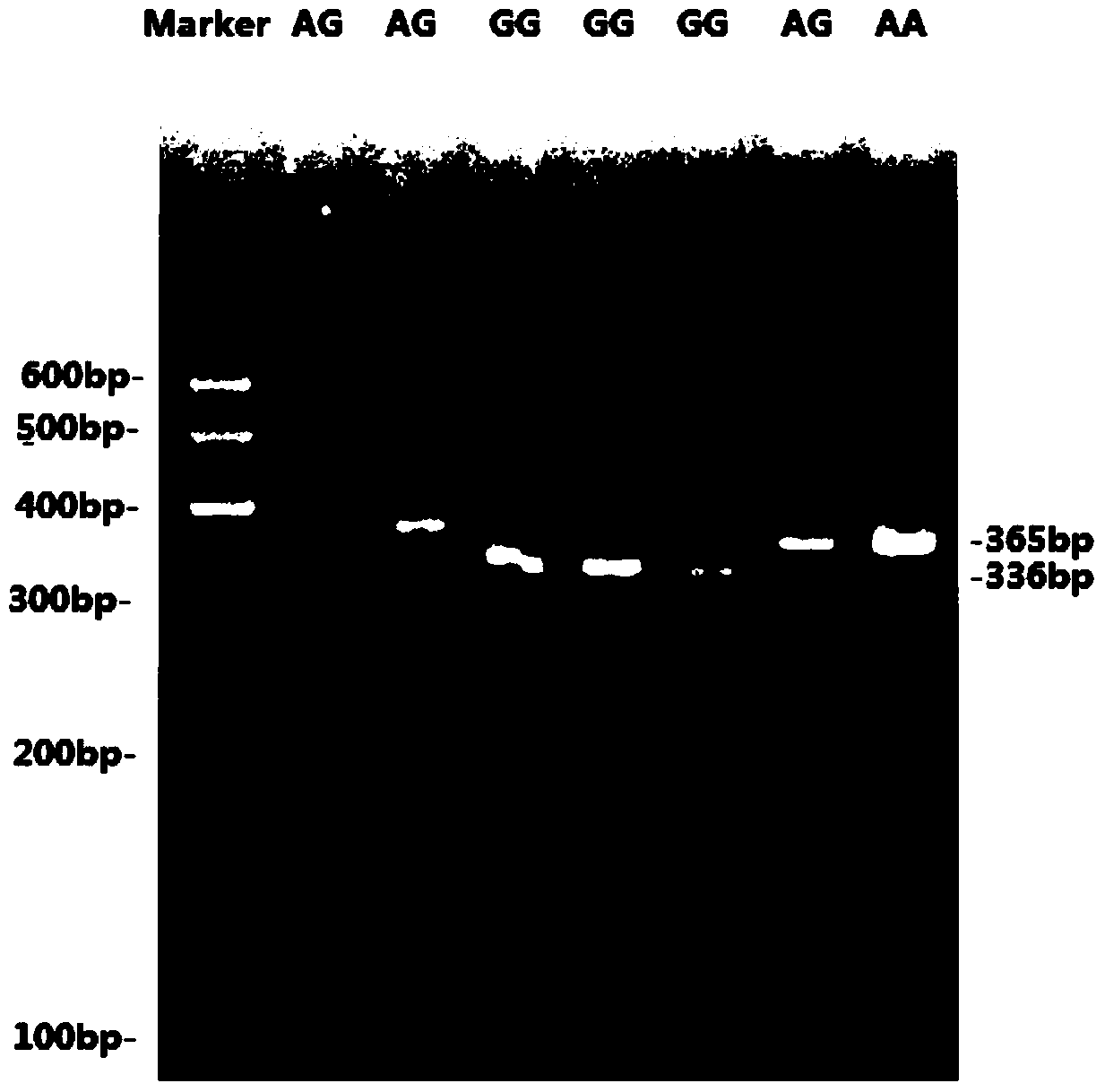
The invention pertains to the technical field of pig genetics and breeding and assistant selection by molecular marker, in particular to a genetic marker for screening SLC39A7 gene of pig fat deposition trait. The genetic marker has a nucleotide sequence as shown in sequence table SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO. 2. A missense mutation of A250-G250 is shown in the place of 250bp in the SEQ ID NO.1, which causes the coded amino acid to be changed from arginine to glycine and causes polymorphism of HpaII-RFLP. The genetic marker of the invention is adopted to do relative analysis of relative fat deposition trait of foreign pig variety and local variety in China. The invention also discloses a detection method of SNP typing of a third exon in SLC39A7 gene and provides the novel genetic marker and the detection method for assistant selection by molecular marker.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for detecting single-nucleotide polymorphism of goat ATBF1 gene and application of goat ATBF1 gene
InactiveCN104878099AEasy to detectAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationElectrophoresisPcr ctpp
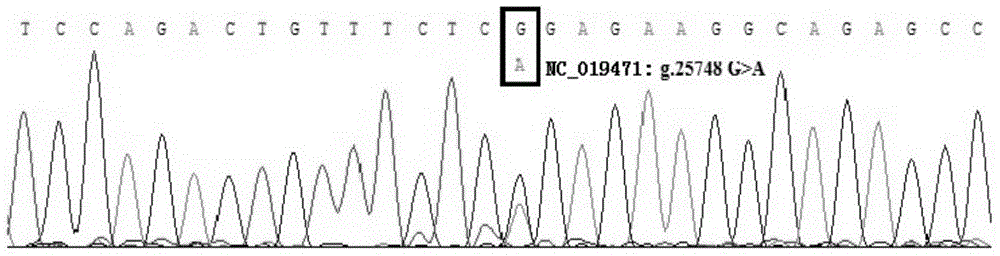
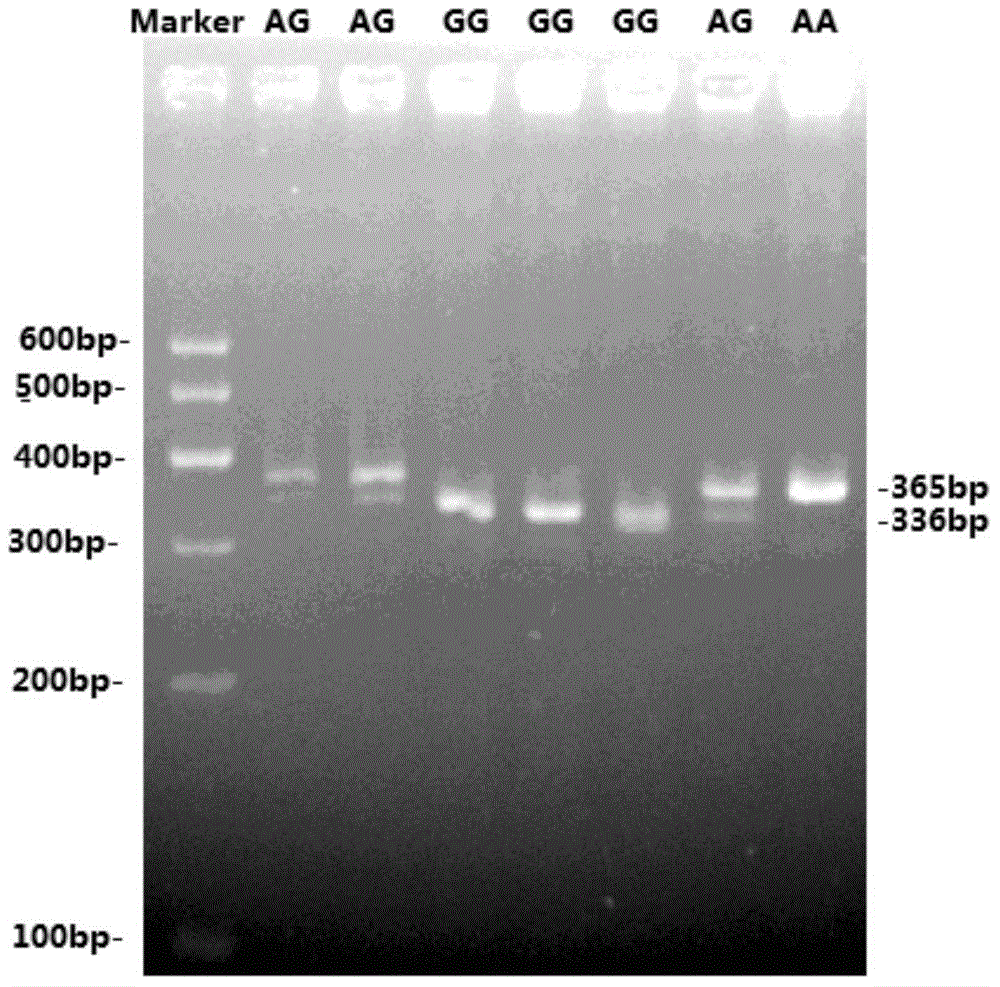
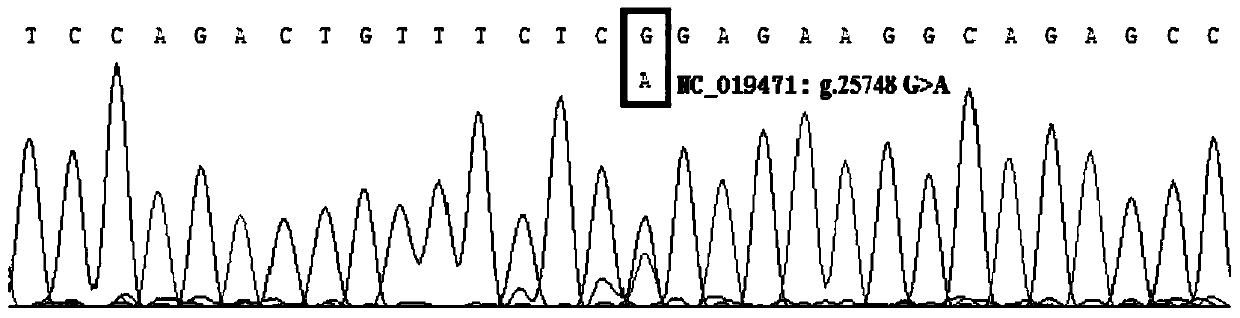
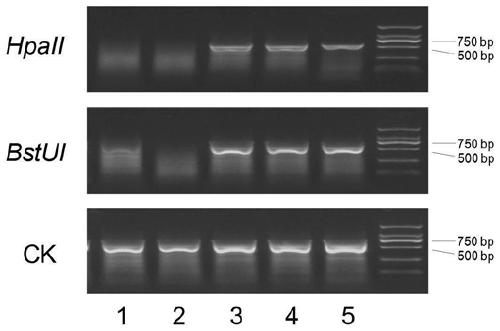
The invention discloses a method for detecting the single-nucleotide polymorphism of a goat ATBF1 gene and the application of the goat ATBF1 gene. According to the method, the goat whole-genome DNA to be tested is taken as a template, the goat ATBF1 gene is amplified by use of the PCR technology, the PCR product is digested by use of a restriction enzyme MspI or HpaII, next, the agarose gel electrophoresis is performed, and the genotype of No.25748nt or No.163517nt SNP of the goat ATBF1 gene is identified according to the electrophoresis result; different genotypes of the No.25748nt and No.163517nt SNPs of the ATBF1 gene have remarkable relevance with the growth and development traits of the goat, and therefore, the ATBF1 gene is advantageous for quickly establishing a good goat genetic resource population.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Novel promoter and application thereof
ActiveCN104789566AIncrease productionIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaHydrolasesMicrobial GeneticBiotechnology
The invention discloses a novel promoter and application thereof, and belongs to the field of microbial genetic engineering. According to a method disclosed by the invention, the related promoter Pd(-35 to -10) HpaII gene is formed by series connection modification on the core area based on the promoter PHpaII; under control and transcription of the novel promoter Pd(-35 to -10) HpaII, the fibrinolytic activity of the recombinant nattokinase is up to 200.8 FU / ml. The method is efficient, safe and capable of effectively improving the expression quantity of nattokinase, and provides a theoretical basis for further study on influence of the promoter on heterologous gene expression.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for protecting efficient recombinant expression of restriction enzymes by virtue of methylase
ActiveCN106480076AAvoid genetic screeningSimplify the recombinant expression processHydrolasesNucleic acid vectorBiologyRestriction endonuclease BstNI
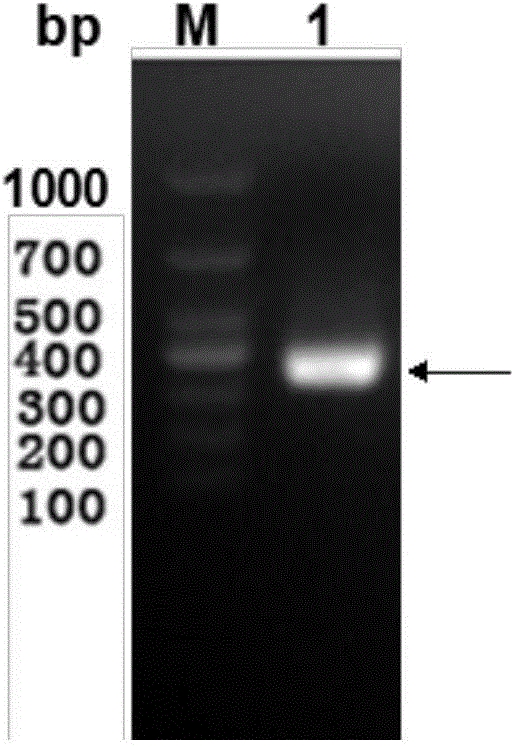
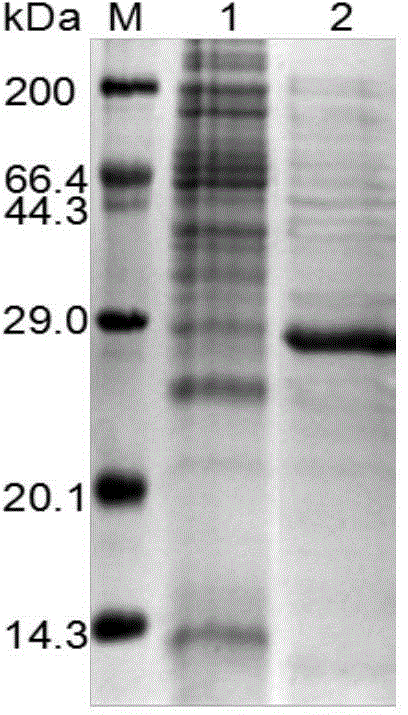
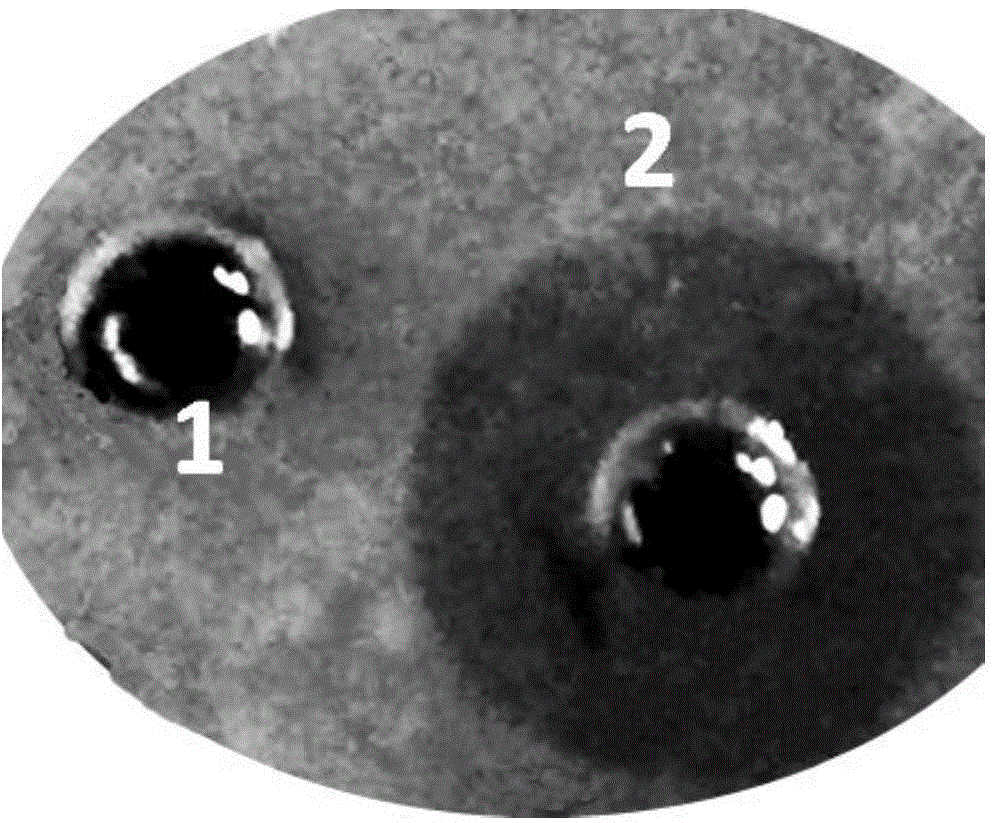
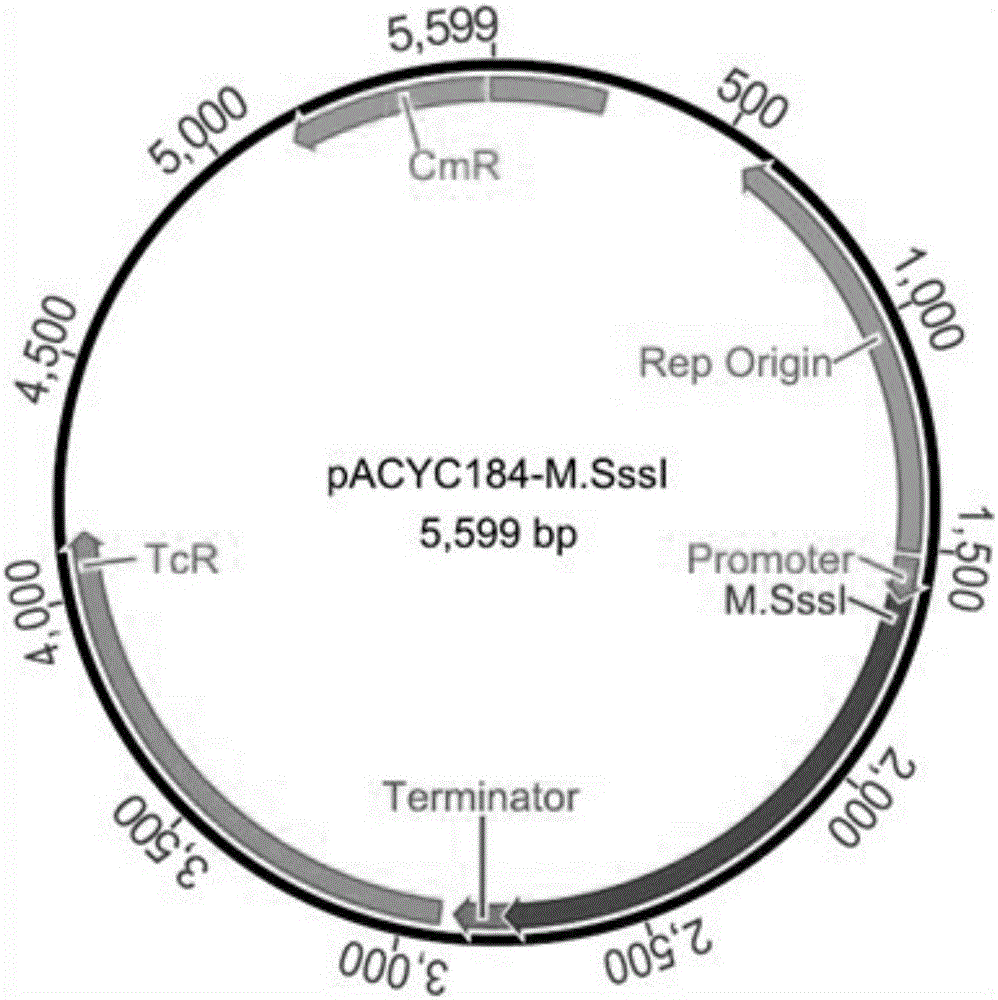
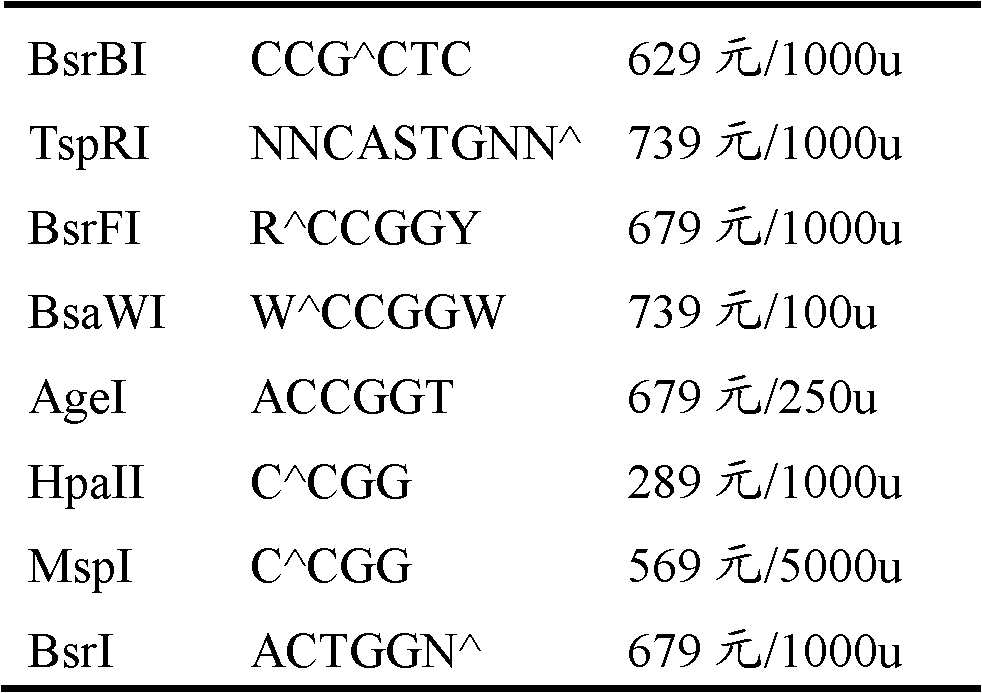
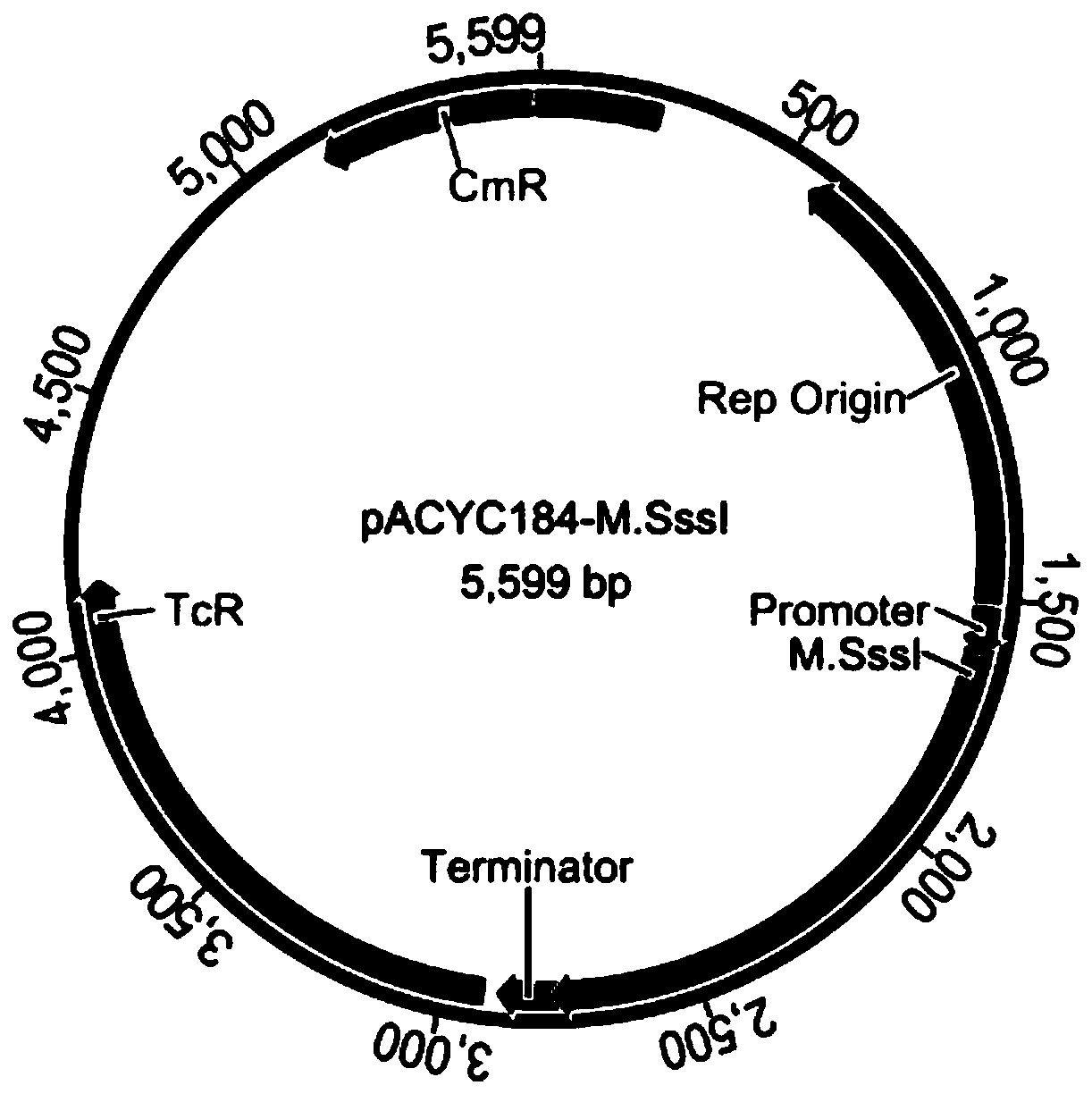
The invention discloses a method for protecting efficient recombinant expression of restriction enzymes by virtue of methylase. The method is characterized in that the methylase is M.Sss I; and the restriction enzymes D are selected from AatII, AciI, AclI, AfeI, AgeI, AscI, AsiSI, AvaI, BceAI, BmgBI, BsaAI, BsaHI, BsiEI, BsiWI, BsmBI, BspDI, BspEI, BsrFI, BssHII, BstBI, BstUI, BtgZI, ClaI, EagI, FauI, FseI, FspI, HaeII, HgaI, HhaI, HinP1I, HpaII, Hpy99I, HpyCH4IV, KasI, MluI, NaeI, NarI, NgoMIV, NotI, NruI, Nt.BsmAI, Nt.CviPII, PaeR7I, PluTI, PmlI, PvuI, RsrII, SacII, SalI, SfoI, SgrAI, SmaI, SnaBI, TliI, TspMI, XhoI, XmaI and ZraI. According to the method provided by the invention, the broad-spectrum protective methylase M.Sss I is directly adopted in a recombinant engineering bacterium construction process, without conducting complex methylase gene screening on a single restriction enzyme, so that the method is broad in application scope and is capable of greatly simplifying a recombinant expression process.
Owner:莫纳(武汉)生物科技有限公司
Colorimetric sensing method for detecting activity of DNA transmethylase based on DNA chain substituting circulation amplifying technology
InactiveCN104694655ASimple and convenient visual detectionHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementMethyltransferaseEndonuclease
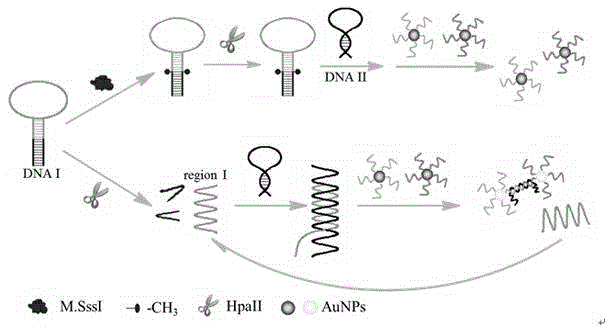
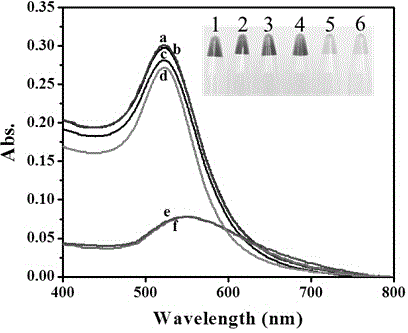
The invention discloses a colorimetric sensing method for detecting activity of DNA transmethylase based on The DNA chain substituting circulation amplifying technology. The method is designed as that the neck to be recognized by CpG transmethylase M.SssI and HpaII restriction enzyme contains hairpin DNA I with the 5'-CCGG-3' sequence; the presence of M.SssI can be determined by determining whether the hairpin DNA I is methylated and whether the hairpin DNA can be cut by HpaII to cause gathering discoloration of AuNPs; the sensitive detection of M.SssI can be achieved by the colorimetric method.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Method and kit for detecting forest tree xylem DNA methylation through MSAP technology
InactiveCN104293893AStable detectionEfficient detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyElectrophoreses
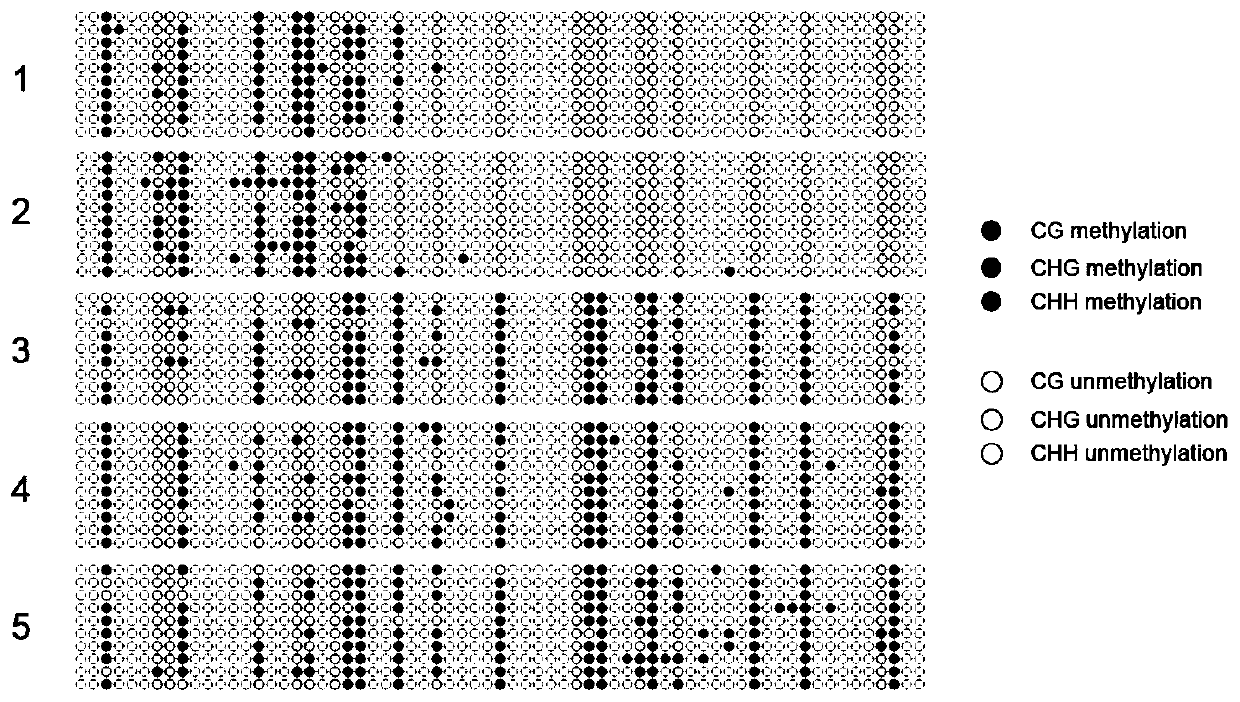
The invention discloses a method and a kit for detecting forest tree xylem DNA methylation through an MSAP technology. The method includes following steps: (S1): extracting forest tree xylem DNA; (S2) performing enzyme digestion to the forest tree xylem DNA with two enzyme sets: EcoRI / HpaII and EcoRI / MspI; (S3) connecting a linker of a restriction enzyme onto a product obtained through the enzyme digestion; (S4) performing PCR pre-amplification to a pre-amplification primer designed with the linker as a template to obtain a PCR pre-amplification product; (S5) diluting the PCR pre-amplification product and performing PCR amplification with addition of a screening primer having selective basic groups; and (S6) carrying out electrophoresis detection to a PCR amplification product and counting and analyzing DNA bands. By means of the technical scheme, a strong technical support is provided for researching of epigenetic variation so that a new candidate marking locus can be provided for targeted forest tree molecular marker assistant breeding.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
PCR detection method for identifying germplasms of four populations of Pelodiscus sinensis, primer group and kit
ActiveCN103276097ATemplate requirements are not highImprove reaction stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGermplasmMicrobiology
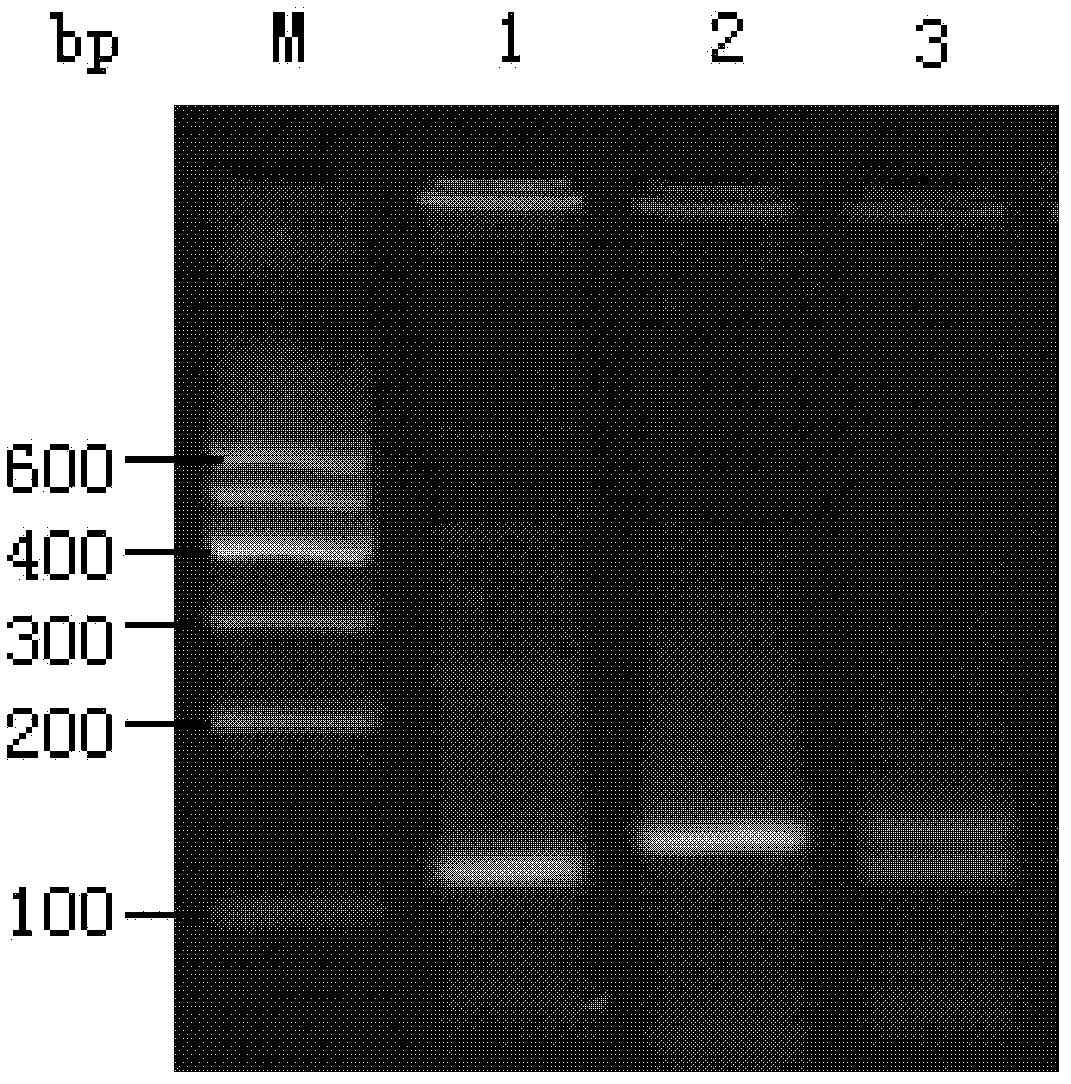
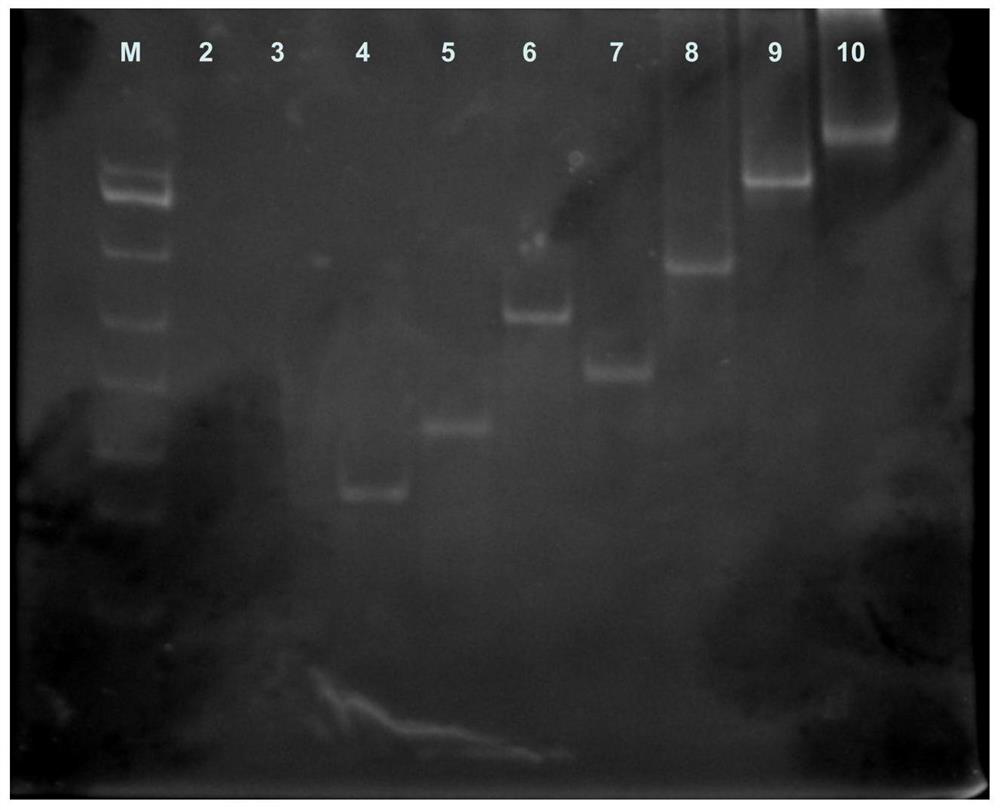
The invention discloses a PCR detection method for identifying germplasms of four populations of Pelodiscus sinensis, a primer group and a kit. The primer group comprises primers of SEQ No.1 / SEQ No.4, SEQ No.2 / SEQ No.5 and SEQ No.3 / SEQ No.6. The kit comprises a 2*TaqPCR premixed liquid, a 5U / mul enzyme BglI and 10*digestion buffer liquid A, a 5U / mul HpaII and 10*digestion buffer liquid B, a 5U / mul ClaI and 10*digestion buffer liquid C, 10mg / ml BSA, a contrast DNA template and a 10pM amplimer. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out PCR amplification of extracted DNA through using the primer group, digesting to obtain a digestion product, carrying out agarose gel electrophoresis, and comparing the obtained electrophoresis result with a standard electrophoretogram to obtain a result. The detection method has the advantages of simplicity, good reaction stability and repeatability, and cost saving.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FISHERIES TECH EXTENSION STATION
Human SGIP1, SCAND3 and MYO1G gene methylation detection kit
PendingCN110669831AGuaranteed accuracyImprove digestion efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementHistiocyteFluorescent pcr
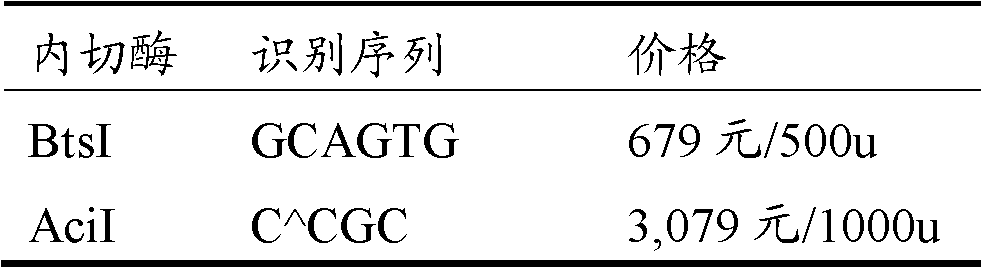
The invention provides a human SGIP1, SCAND3 and MYO1G gene methylation detection kit. The human SGIP1, SCAND3 and MYO1G gene methylation detection kit comprises methylation-sensitive restriction enzymes, a digestion buffer solution and a fluorescent PCR reaction solution, and the methylation-sensitive restriction enzymes are AciI, BstUI and HpaII. The detection kit adopts an enzyme mixture of themethylation-sensitive restriction enzymes being AciI, BstUI and HpaII, the digestion efficiency can be effectively improved, incomplete digestion is avoided, the false positive rate is reduced, the sensitivity is good, and the human SGIP1, SCAND3 and MYO1G gene methylation detection kit is suitable for a variety of sample types such as plasma DNA, tissue DNA and cell DNA.
Owner:SUREXAM BIO TECH
Kit for detecting related gene FMR1 of fragile X chromosome syndrome (FRAX) and application of kit
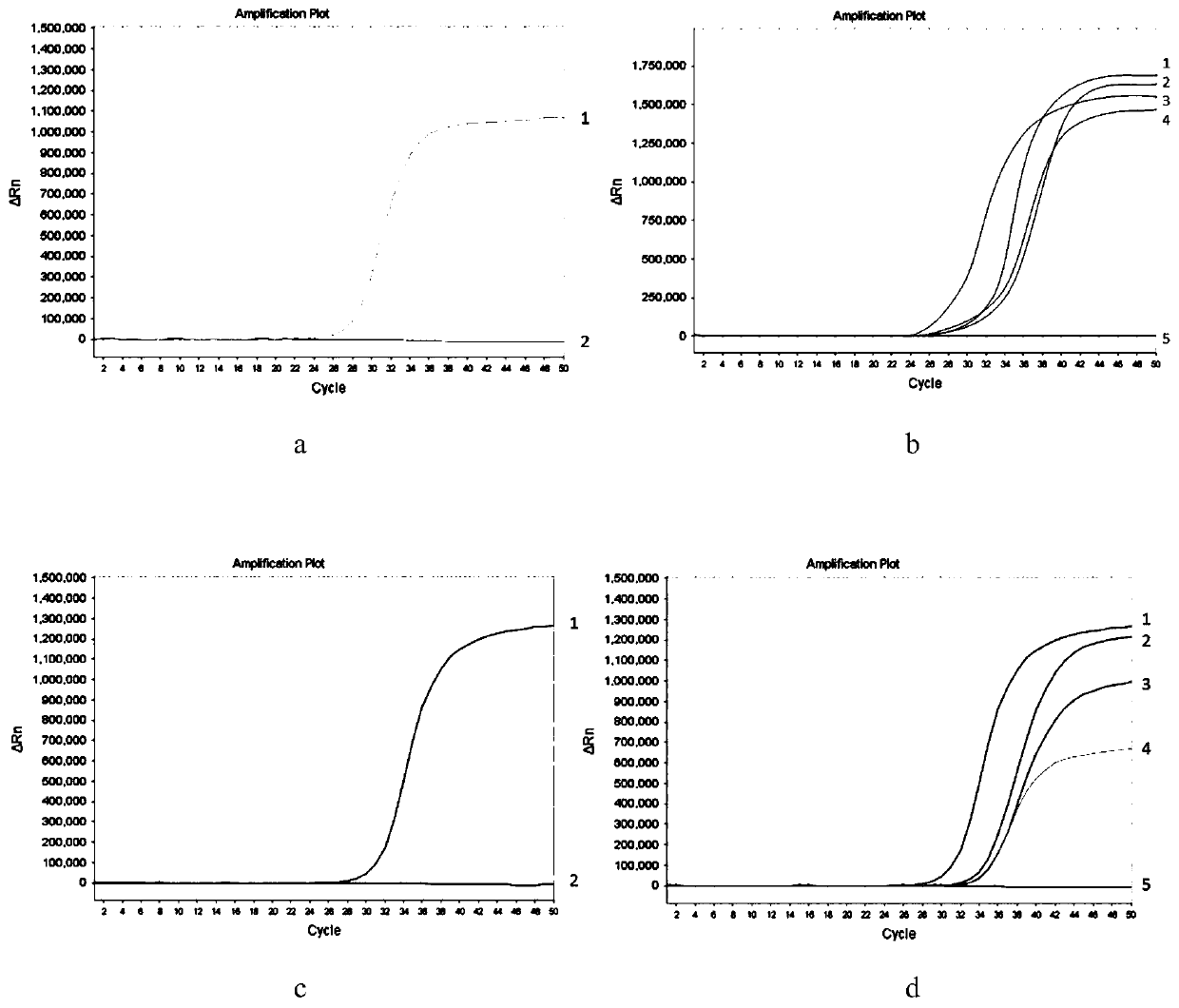
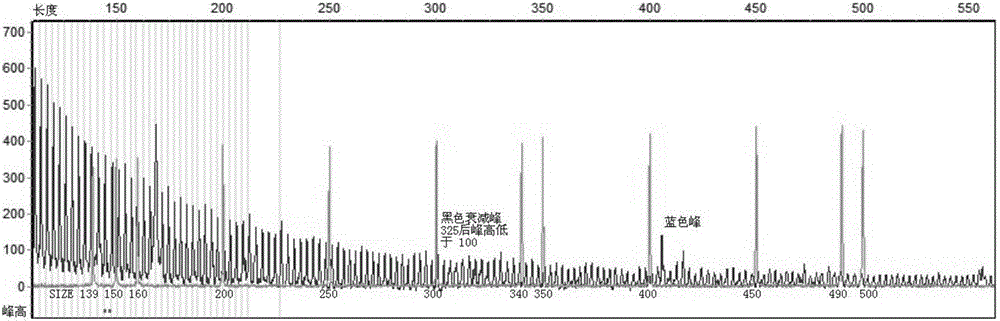
ActiveCN104450911AIngenious designQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme digestionFragile X chromosome
The invention belongs to the technical field of detection of disease-related gene mutation, and in particular discloses a kit for detecting related gene FMR1 mutation of fragile X chromosome syndrome (FRAX). The kit consists of FRAX related gene FMR1 mutation detection probe combinations: namely polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primer groups SEQ ID NO. 1 and 2, SEQ ID NO. 1 and 3, SEQ ID NO. 1, 4 and 6 as well as SEQ ID NO. 1, 5 and 6. The detection steps are the follows: extracting to-be-detected genome DNA; displaying a possible methylation difference by virtue of HpaII enzyme digestion and control preprocessing; carrying out PCR amplification on the preprocessed genome DNA by virtue of a four-color fluorescence PCR primer; carrying out capillary electrophoresis; and according to a capillary electrophoresis curve, analyzing the FMR1 (CGG) n length and methylation situation of FRAX related gene in the genome DNA. The kit disclosed by the invention is fast, accurate, simple and convenient to use, and is suitable for popularization and application.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHROMYSKY MEDICAL RES
Genetic marker using MX1 genes as pig production trait and use thereof
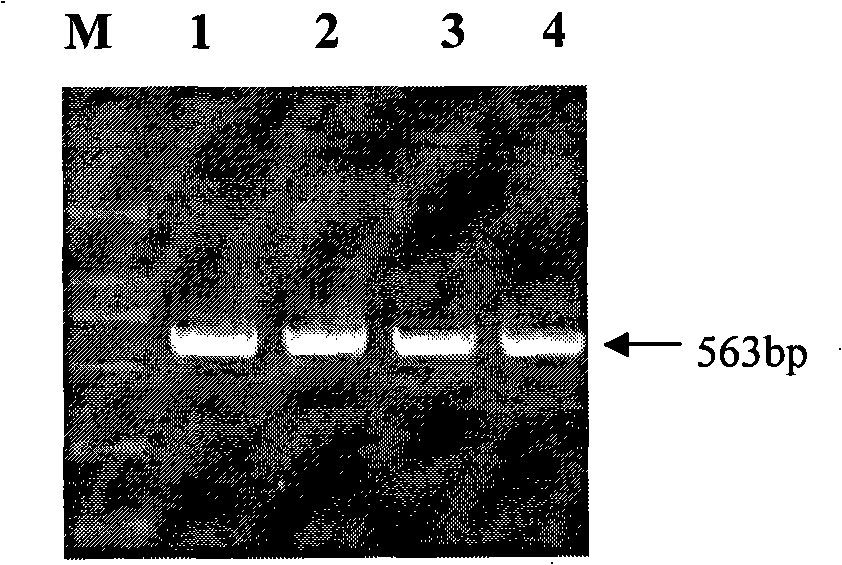
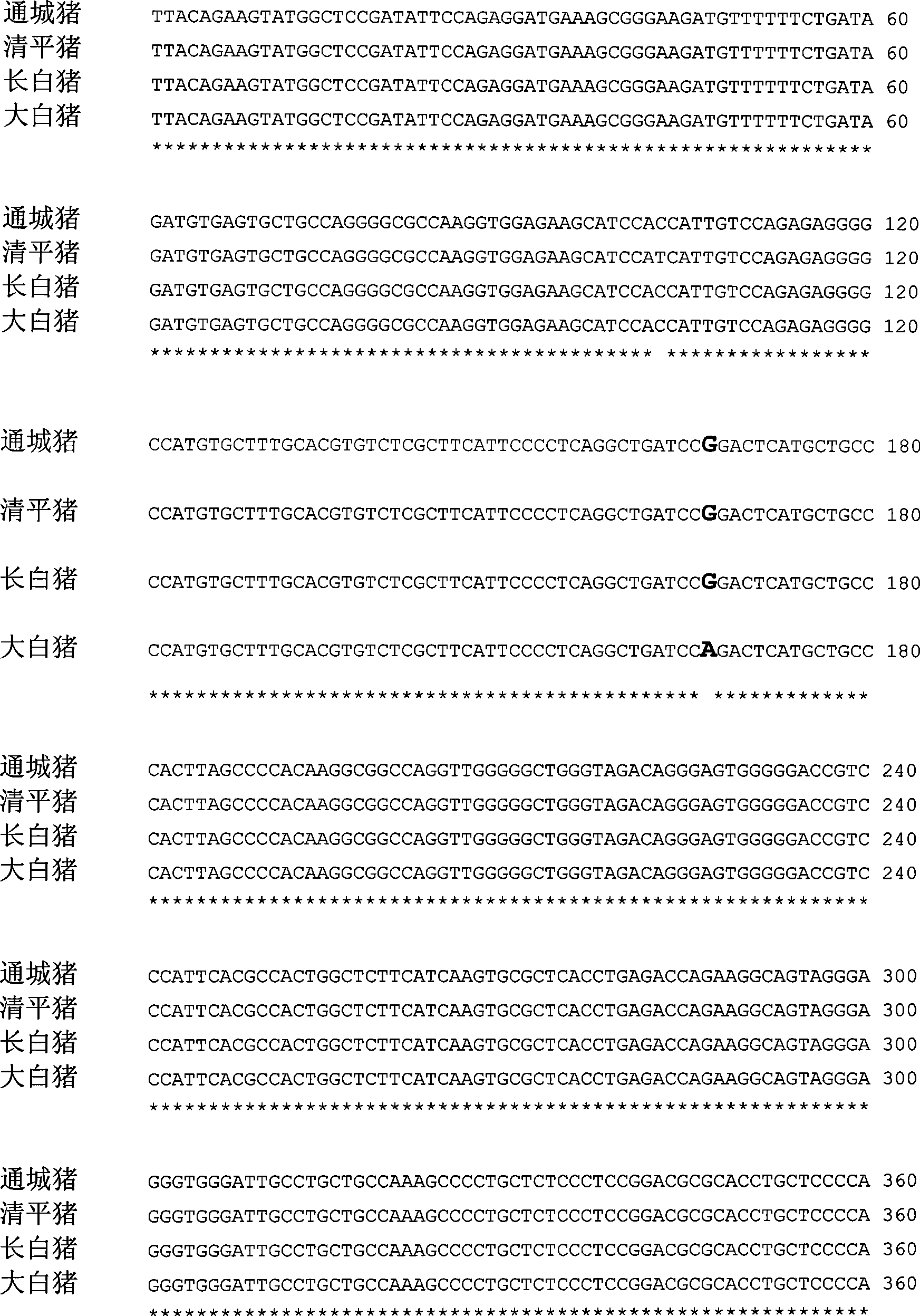
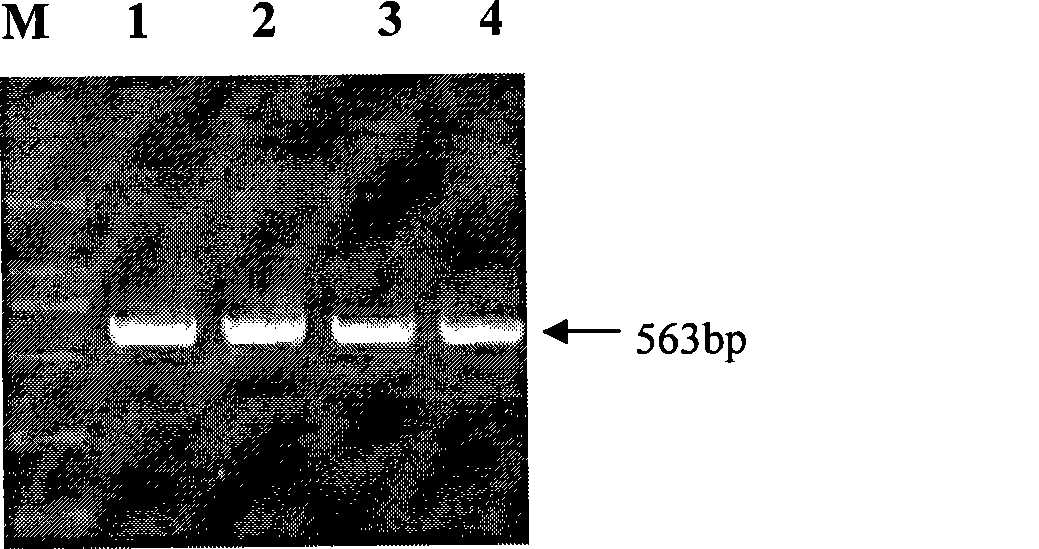
The invention pertains to the technical field of the preparation of a pig genetic marker, more particularly relates to a pig production trait gene MX1 eighth intron mutant site polymorphism detection method and the clone used as the genetic marker of the pig production trait, and the application. Genome DNA is extracted from pig blood, primer PCR amplification is designed, a 563bpDNA sequence is obtained by clone resequencing, and the mutation of A167-G167 is found at the position of 167bp of a sequence list SEQID NO: 1 by sequence comparison analysis, thus causing the polymorphism of HpaII-RFLP. By utilizing the genetic marker, the genotype frequency and the gene frequency of a marker gene and the association analysis of the pig production trait are detected in different swineries, showing that notable association exists between the genetic marker and certain important production trait of the pig. The invention also discloses an SNP typing detection technology of the eighth intron of the pig MX1 gene, thus providing a new marking and detection method for marker auxiliary selection of the pig.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY HUBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Kit for identifying human methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) gene polymorphism rs2274976 by using MspI
InactiveCN102676655ALow costOvercomes the drawback of requiring expensive endonucleasesMicrobiological testing/measurementForward primerGenetics
The invention discloses a kit for identifying human methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) gene polymorphism rs2274976 by using MspI. The kit comprises a forward primer and a reverse primer for amplifying sequences near a human MTHFR gene polymorphism rs2274976 locus, wherein the last base at the 3'end of the forward primer is adjacent to an rs2274976 polymorphic base, and the last second base of the forward primer is a mismatched base C, so that the forward primer and polymorphic G allele form a CCGG structure in an amplification product; and the forward primer is shown as SEQ ID NO:1 or SEQ NO:11, and the reverse primer is shown as SEQ ID NO:2, SEQ ID NO:7 or SEQ NO:12. The kit also comprises restriction enzyme MspI or HpaII, and an instruction book for implementing identification. The kit is easy to operate, low in cost, and wide in application range.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Application of bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein gene in serving as common disease resistance genetic marker of pigs
ActiveCN103173531BImprove disease resistanceEnhance immune responseMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-strand conformation polymorphismEnzyme digestion
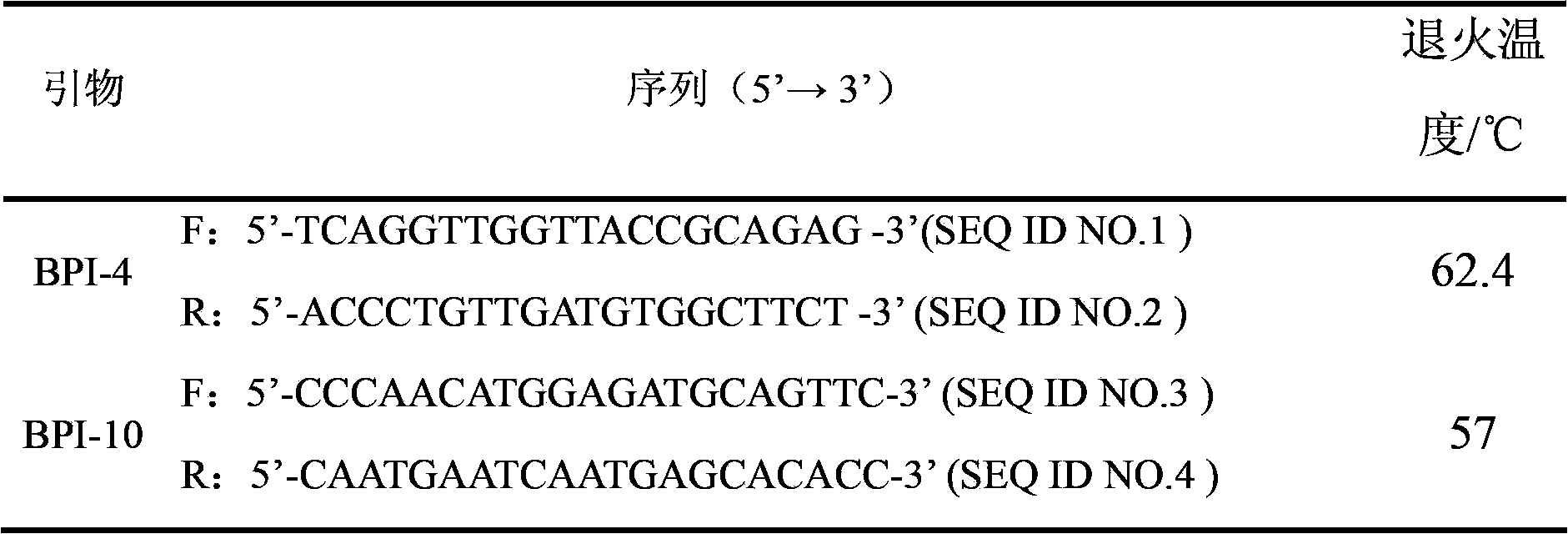
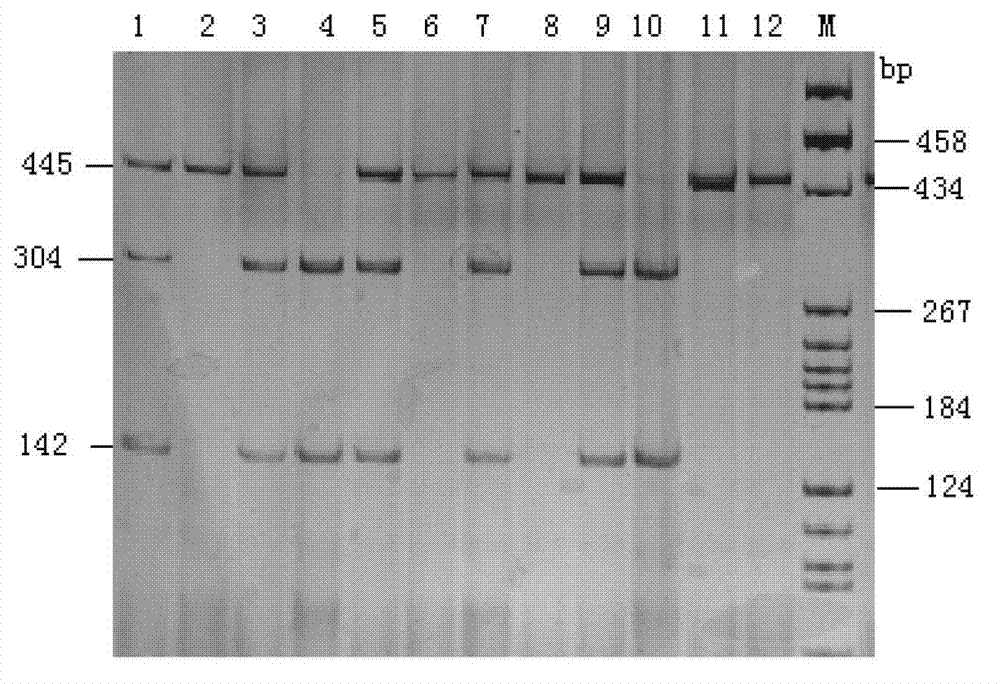
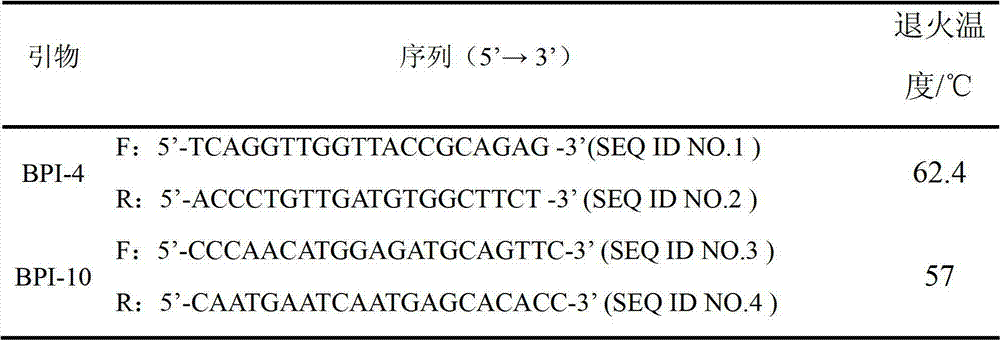
The invention relates to a genetic marker for screening the combined gene model of the fourth and tenth exon variation sites of a common disease resistance BPI (bactericidal / permeability increasing protein) gene of pigs, and belongs to the technical fields of genetic breeding and molecular marker assisted selection of pigs. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of a pig genome of a sample to be tested, and performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on the pig genome; analyzing the PCR product of the exon 4 through SSCP (single strand conformation polymorphism), and performing enzyme digestion on the PCR product of the exon 10 through restriction enzyme HpaII, wherein when the gene model of the pig body to be tested is a CDAB model, the pig body is strong in common disease resistance. According to the application, a molecular genetic marker with higher efficiency and accuracy is provided to molecular marker assisted selection of the pig disease resistance breeding work, and an effective molecular marker breeding means is provided for improving the common disease resistance and immune response capability of piglets. The detection method is simple in operation, low in cost and high in accuracy, can realize automatic direct detection, and takes a magnificent effect in pig breeding.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Application of bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein gene in serving as common disease resistance genetic marker of pigs
ActiveCN103173531AImprove disease resistanceEnhance immune responseMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-strand conformation polymorphismEnzyme digestion
The invention relates to a genetic marker for screening the combined gene model of the fourth and tenth exon variation sites of a common disease resistance BPI (bactericidal / permeability increasing protein) gene of pigs, and belongs to the technical fields of genetic breeding and molecular marker assisted selection of pigs. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of a pig genome of a sample to be tested, and performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on the pig genome; analyzing the PCR product of the exon 4 through SSCP (single strand conformation polymorphism), and performing enzyme digestion on the PCR product of the exon 10 through restriction enzyme HpaII, wherein when the gene model of the pig body to be tested is a CDAB model, the pig body is strong in common disease resistance. According to the application, a molecular genetic marker with higher efficiency and accuracy is provided to molecular marker assisted selection of the pig disease resistance breeding work, and an effective molecular marker breeding means is provided for improving the common disease resistance and immune response capability of piglets. The detection method is simple in operation, low in cost and high in accuracy, can realize automatic direct detection, and takes a magnificent effect in pig breeding.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Cytosine methylation excavation method
InactiveCN106701939AMining simpleEfficient miningMicrobiological testing/measurementCytosineEnzyme digestion
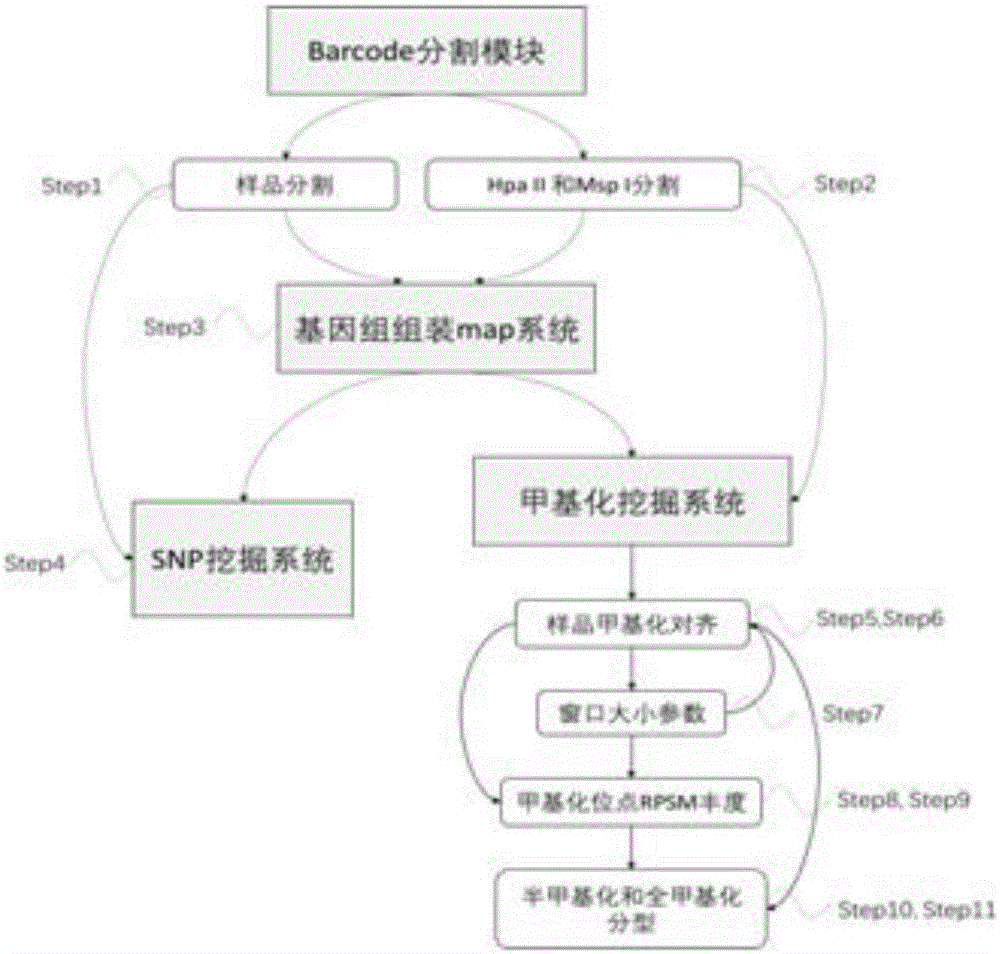
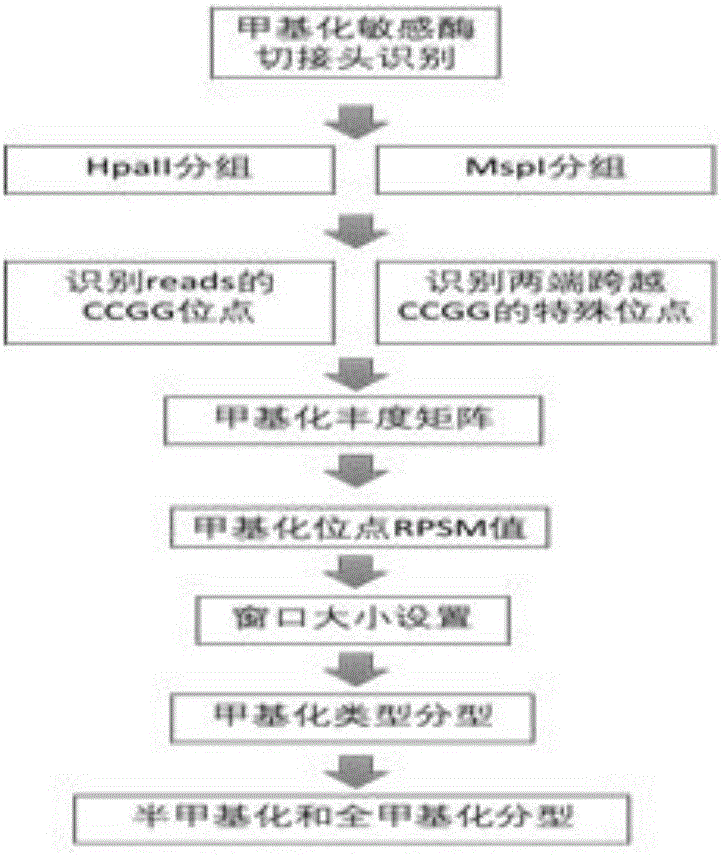
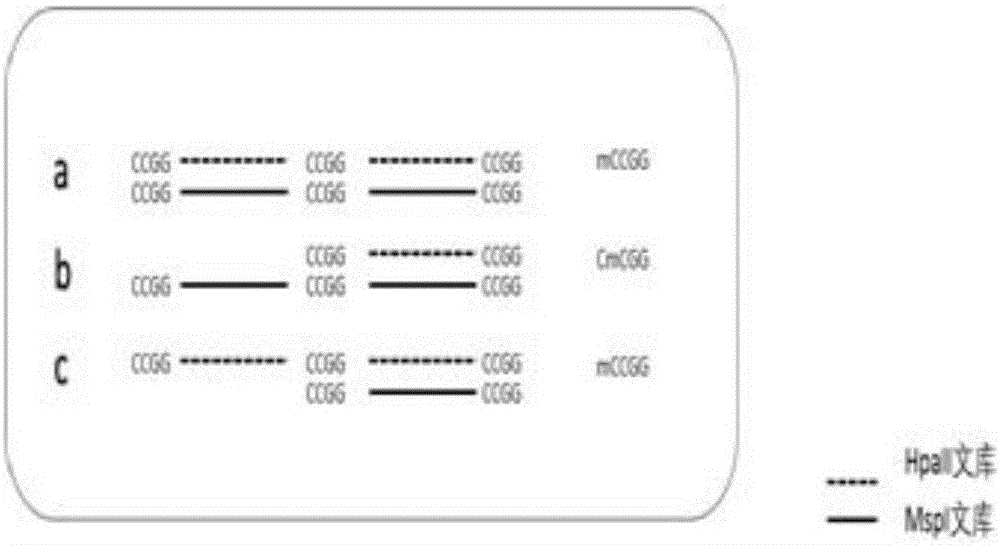
The invention discloses a cytosine methylation excavation method which comprises the following steps: A) acquisition of target data: amplifying gene groups from a same source after an HpaII enzyme digestion and an MspI enzyme digestion are carried out on the gene groups by methylation sensitive enzymes and performing high-throughput sequencing on the gene groups after the enzyme digestions; B) establishment of bases with an AFSM (amplification finite-state machine) technology: establishing DNA libraries of the HpaII enzyme digestion and an MPaI enzyme digestion for a same sample and respectively adding barcode linker sequences; C) interpretation of enzyme digestion sites according to original data of the sequencing; D) output of a bam comparison file by performing map analysis and assembly on the marked original data; E) methylation data excavation of the bam comparison file. The method is a first technology of performing methylation typing on cytosine methylation data after the high-throughput sequencing and the enzyme digestions of the methylation sensitive enzymes and identifying the abundance of methylation sites; a simple and efficient solution with low cost is provided for scientific research personnel to excavate methylation information.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
PCR detection method for identifying germplasms of four populations of Pelodiscus sinensis, primer group and kit
ActiveCN103276097BTemplate requirements are not highImprove reaction stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationElectrophoresesGermplasm
Owner:ZHEJIANG FISHERIES TECH EXTENSION STATION
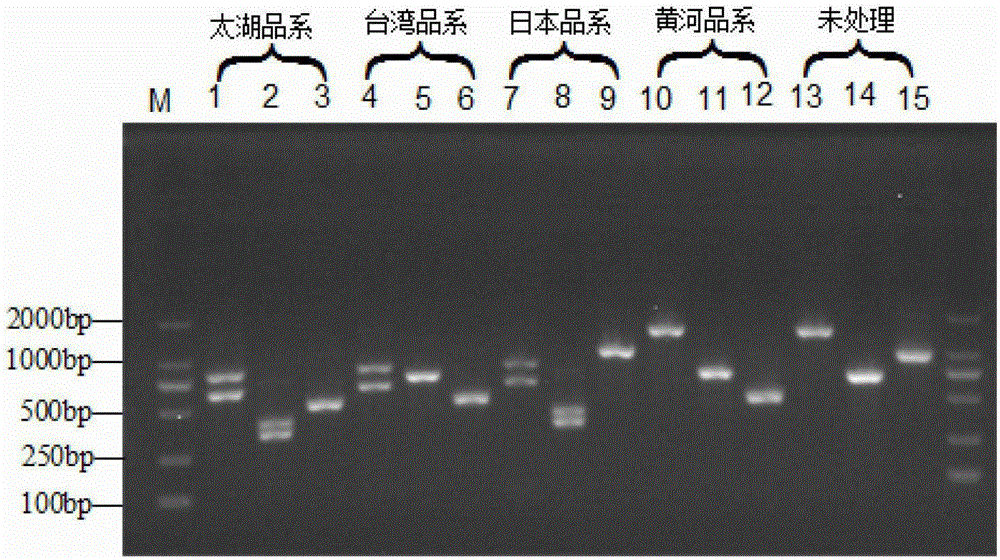
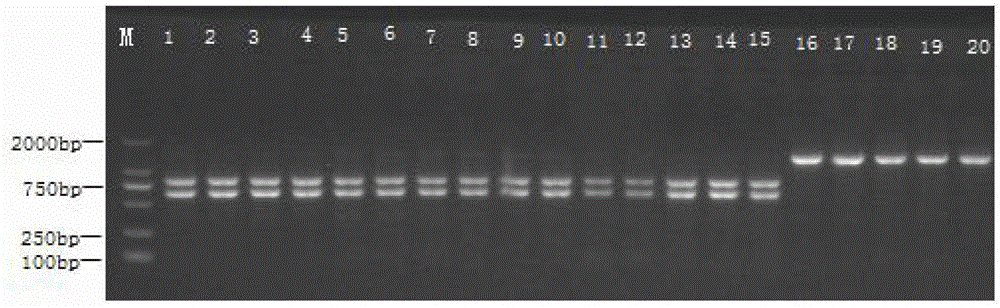
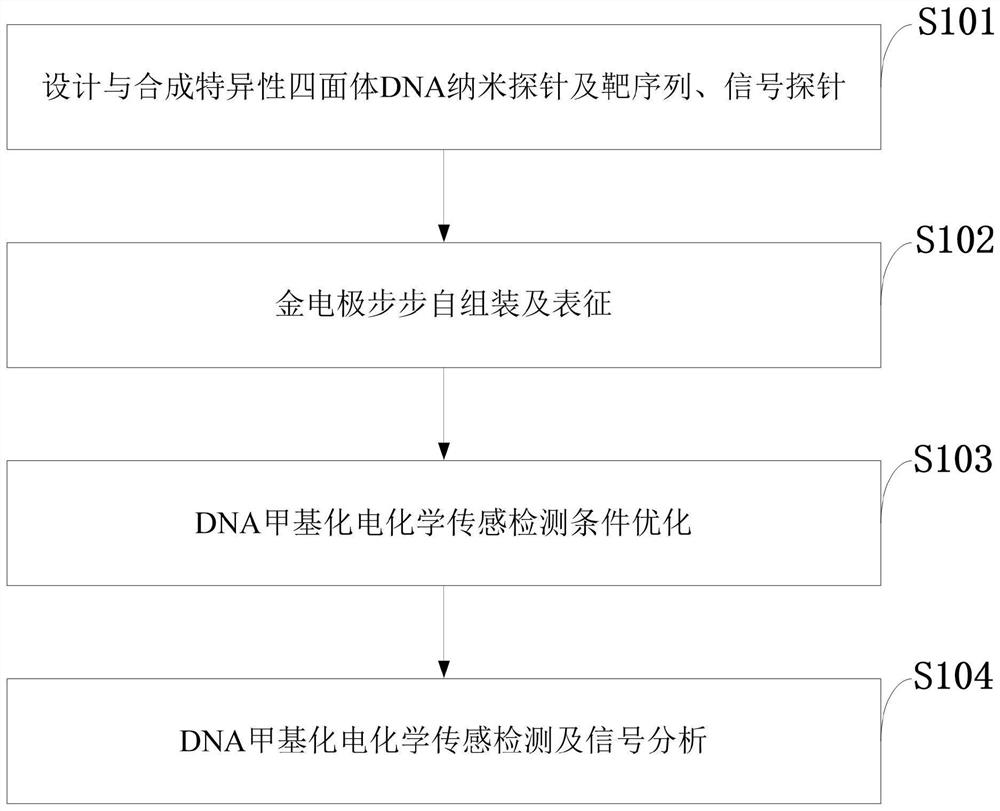
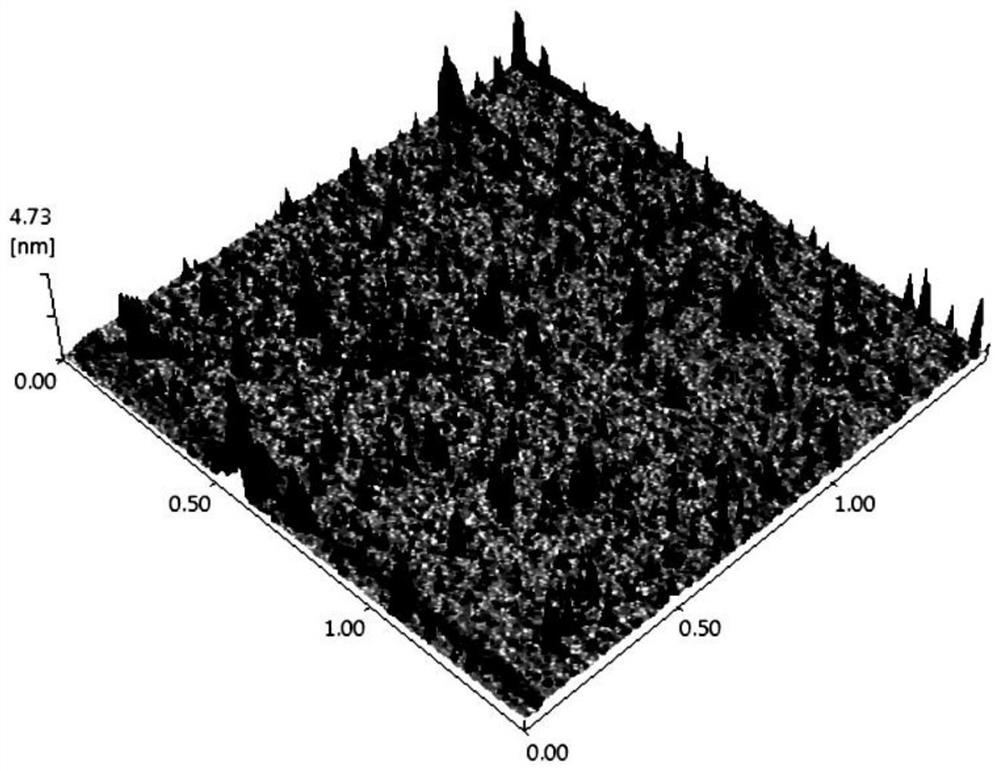
Electrochemical analysis method based on tetrahedral DNA nanoprobe and application
PendingCN113652470AEasy to operateLow priceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEnzyme digestionMethylation analysis
The invention belongs to the technical field of DNA methylation analysis, and discloses an electrochemical analysis method based on a tetrahedral DNA nanoprobe and application, and the electrochemical analysis method comprises a tetrahedral probe structure sequence, different DNA methylation target sequences, a signal amplification sequence and a comparison sequence. According to the present invention, the optimal performance is represented under the conditions of the tetrahedral probe fixation time of 3 h, the target sequence hybridization time of 1 h and the HpaII incision enzyme digestion time of 2 h, the good detection ability is represented within the range of 1 amol / L to 1 pmol / L, the detection limit reaches 0.93 amol / L, and the sensitivity is high; the electrochemical biosensing technology has the unique advantages in the aspect of DNA methylation detection: specific analysis on a methylated DNA target sequence can be completed within a short time, the operation is convenient, the price is low, the sensitivity is high, the specificity is good, the stability is strong, and the electrochemical biosensing technology can be effectively used for DNA methylation detection in complex systems such as serum.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Method for enhancing 2,3-butanediol synthesis by improving intracellular coenzyme level
ActiveCN105154456AReduce the accumulation of acetoinIncrease productivityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus amyloliquefaciensAcetoin reductase
The last step of synthesis of 2,3-butanediol is that acetoin reductase performs catalytic reduction on acetoin, 2,3-butanediol is synthesized, the reaction requires participation of reduced coenzyme NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide hydrogen), and thus the high-low level of intracellular coenzyme NADH is an important factor affecting conversion of acetoin to 2,3-butanediol. In order to further improve the synthesis capability of strain 2,3-butanediol and reduce accumulation of byproduct acetoin, HpaII-fdh fragments are inserted into a gene nox, a fragment nox::HpaII-fdh is obtained and guided into bacillus amyloliquefaciens B10-127, and recombinant bacillus amyloliquefaciens (renamed as N delta F) with the fdh gene inserted into the gene nox on a genome is obtained in a homologous recombination principle. Fermentation performance detection of 2,3-butanediol is performed on original bacteria and recombinant bacteria N delta F. A result proves that by comparison with the original bacteria, the yield of the recombinant bacteria 2,3-butanediol is improved by 18.9%, and the yield of the byproduct acetoin is reduced by 70.8%. Accordingly, by means of the strategy, the yield of 2,3-butanediol can be improved, and accumulation of the byproduct acetoin can be reduced.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
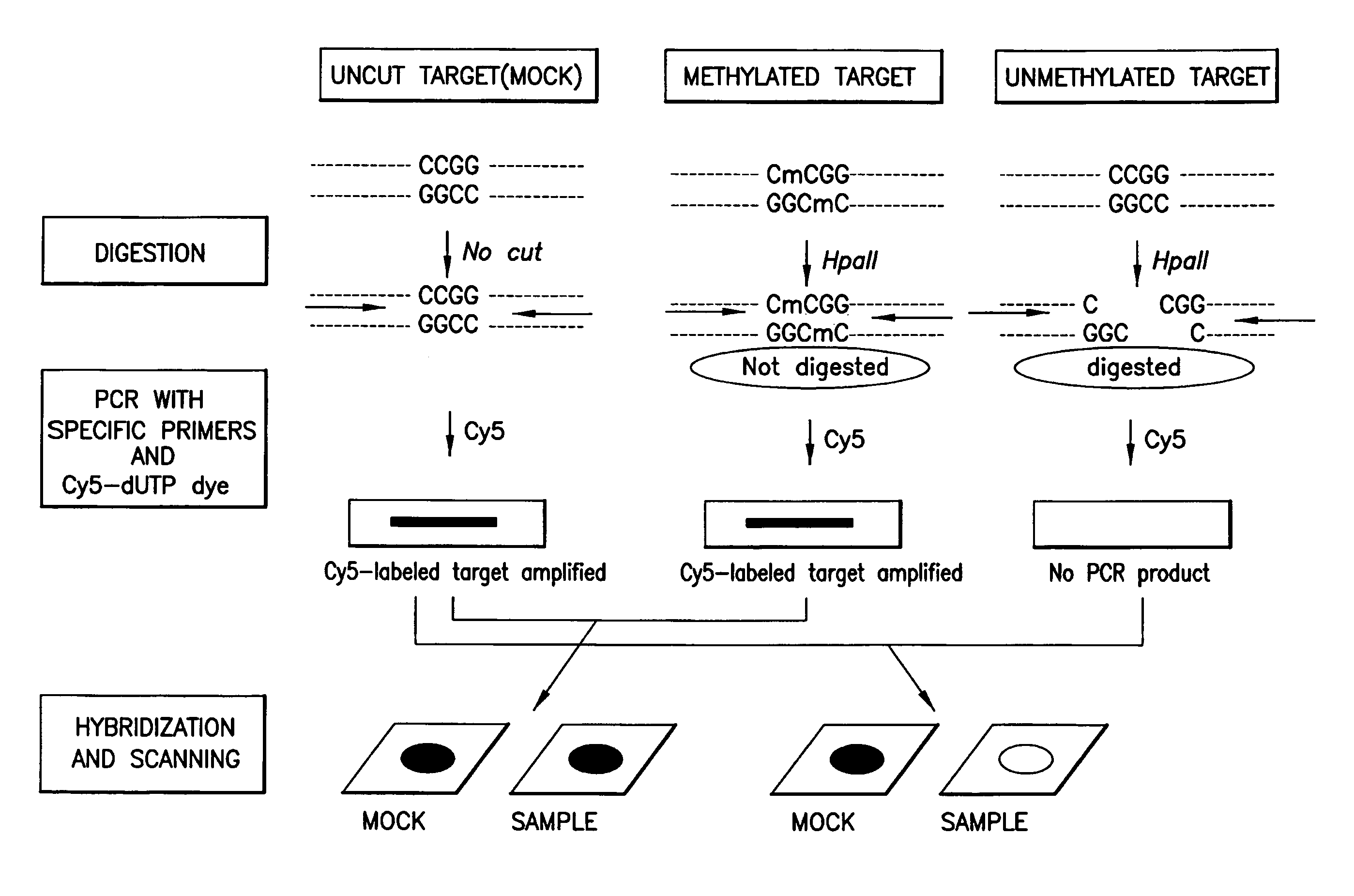
Method for detecting methylation of promoter using restriction enzyme and DNA chip
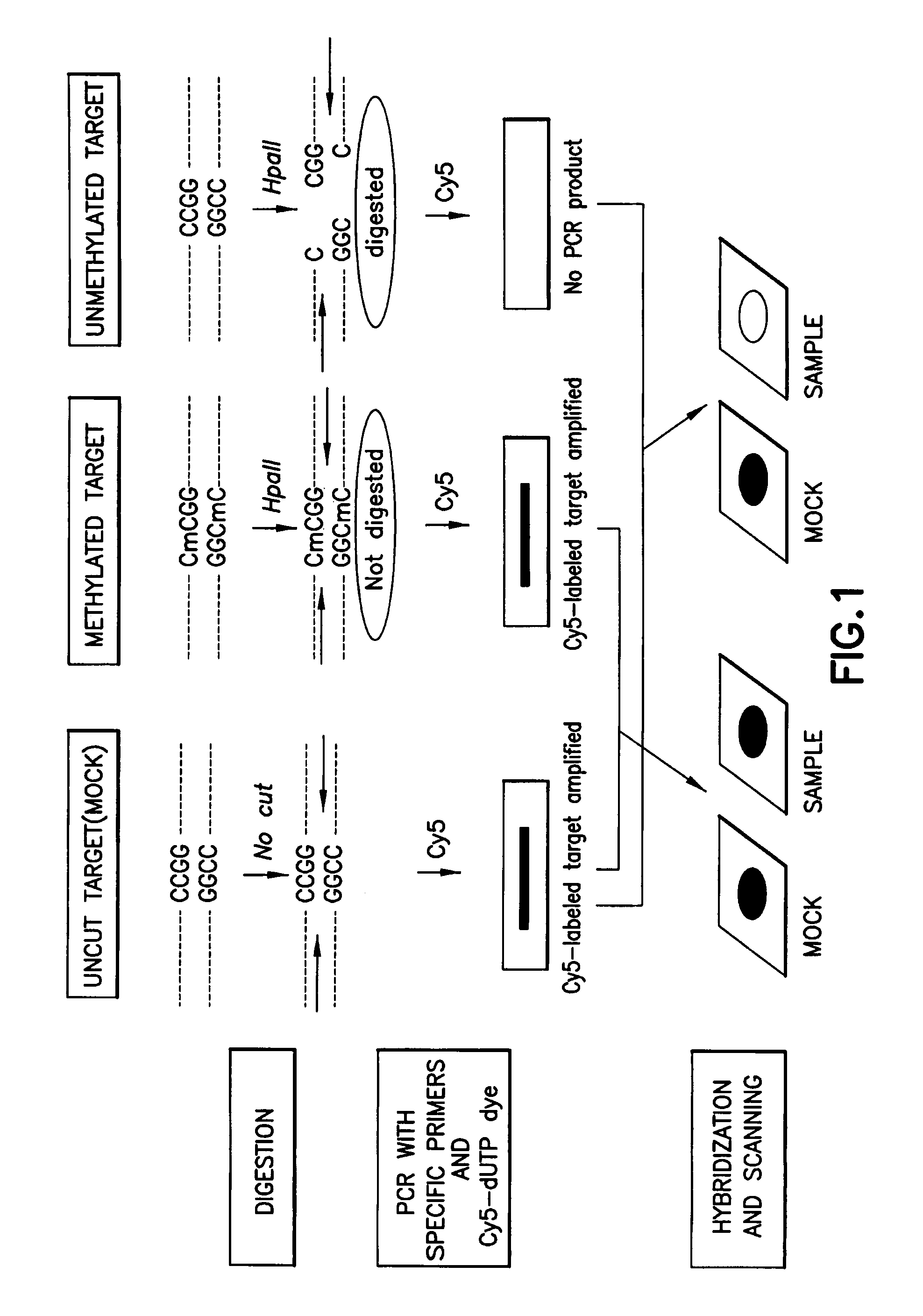
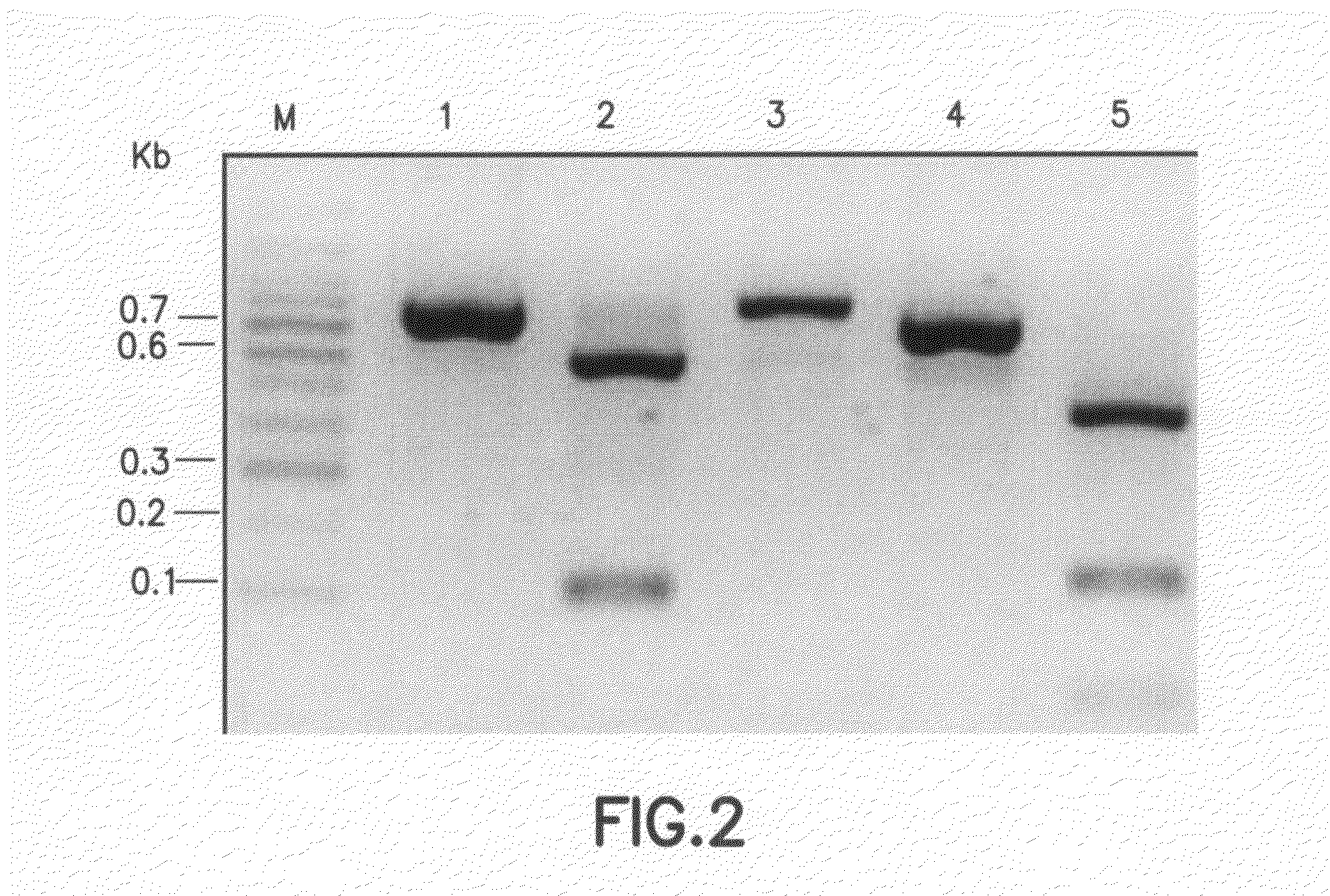
InactiveUS7611841B2Simple and economical mannerRapid and accurate mannerBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsA-DNAPromoter methylation
A method for detecting the methylation of promoters using HpaII, a methylation-sensitive restriction enzyme. In such method, DNAs, derived from clinical samples or subjects to be diagnosed, are cut with HpaII, the cut DNAs are amplified by PCR with primers capable of amplifying CpG islands, and the presence or absence of the PCR amplification products is determined using a DNA chip for methylation detection. Unlike prior approaches, the inventive method allows the methylation of gene promoters to be detected in a simple and economical manner, and thus is useful for the diagnosis of diseases such as cancer that are characterized by methylation of gene promoters.
Owner:GENOMICTREE
A method for enhancing the synthesis of 2,3-butanediol by increasing the level of intracellular coenzyme
ActiveCN105154456BReduce the accumulation of acetoinIncrease productivityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacilliNicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Construction method for forest-tree genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) methylation inheritance linkage maps
InactiveCN106755436AGuaranteed build stabilityEfficient constructionMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme digestionEcoRI
The invention relates to a construction method for forest-tree genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) methylation inheritance linkage maps, and belongs to the technical field of molecular genetics. The construction method includes the steps: 1) extracting genome DNA of xylem tissues; 2) respectively performing dual-enzyme digestion for the genome DNA by the aid of first group of EcoRI and HpaII enzyme and second group of EcoRI and MspI enzyme, connecting connectors on two groups of dual-enzyme digestion products to obtain two groups of enzyme digestion connecting products; sequentially performing pre-amplification and selective amplification by the aid of connecting amplification products, separating selective amplification products by the aid of capillary electrophoresis to obtain population genome methylation marker sites; 4) selecting population methylation polymorphic sites meeting Mendelian inheritance separation from the population genome methylation marker sites to construct the methylation inheritance linkage maps. The construction method is efficient, stable and easy to operate, so that forest-tree population epigenetics research progress can be accelerated.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Genetic marker using MX1 genes as pig production trait and use thereof
The invention pertains to the technical field of the preparation of a pig genetic marker, more particularly relates to a pig production trait gene MX1 eighth intron mutant site polymorphism detection method and the clone used as the genetic marker of the pig production trait, and the application. Genome DNA is extracted from pig blood, primer PCR amplification is designed, a 563bpDNA sequence is obtained by clone resequencing, and the mutation of A167-G167 is found at the position of 167bp of a sequence list SEQID NO: 1 by sequence comparison analysis, thus causing the polymorphism of HpaII-RFLP. By utilizing the genetic marker, the genotype frequency and the gene frequency of a marker gene and the association analysis of the pig production trait are detected in different swineries, showing that notable association exists between the genetic marker and certain important production trait of the pig. The invention also discloses an SNP typing detection technology of the eighth intron ofthe pig MX1 gene, thus providing a new marking and detection method for marker auxiliary selection of the pig.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY HUBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Genetic marker by taking pig miR-27a precursor flanking sequence SNP as trait of litter size of pig and application
InactiveCN101818195BMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationLitterNucleotide sequencing
The invention belongs to the technology field of preparation and application of pig genetic markers, and in particular relates to a genetic marker by taking pig miR-27a precursor flanking genetic fragments as a trait of the litter size of a pig, a preparation method and application thereof. According to the invention, the genetic marker which is related to the character of the litter size of the pig is obtained, wherein the genetic marker comprises the pig miR-27a precursor flanking genetic fragments and is nucleotide sequences expressed by the following sequence lists: SEQ ID NO:1, SEQ ID NO:2, SEQ ID NO:3, SEQ ID NO:4, and SEQ ID NO:5; a base mutation of C461-T461 is generated at 461bp of the following sequence lists: the SEQ ID NO:1, the SEQ ID NO:2, the SEQ ID NO:3, the SEQ ID NO:4, and the SEQ ID NO:5; and the mutation leads to polymorphism of PCR-HpaII-RFLP. In the design, a primer is additionally provided in the miR-27a precursor flanking genetic fragments, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the primer is expressed as SEQ ID NO:6 and SEQ ID NO:7. The invention also discloses the method for preparing the genetic marker and the application of the genetic marker in the pig marker assistant selection.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Increased production of 2,3-butanediol in bacillus amyloliquefaciens by enhancing the regeneration rate of the coenzyme cycle
ActiveCN103602624BReduce accumulationIncrease productivityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesButanedioic acidEnzyme Gene
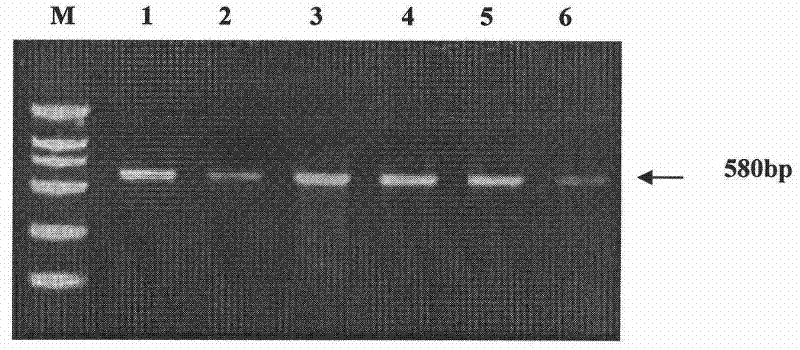
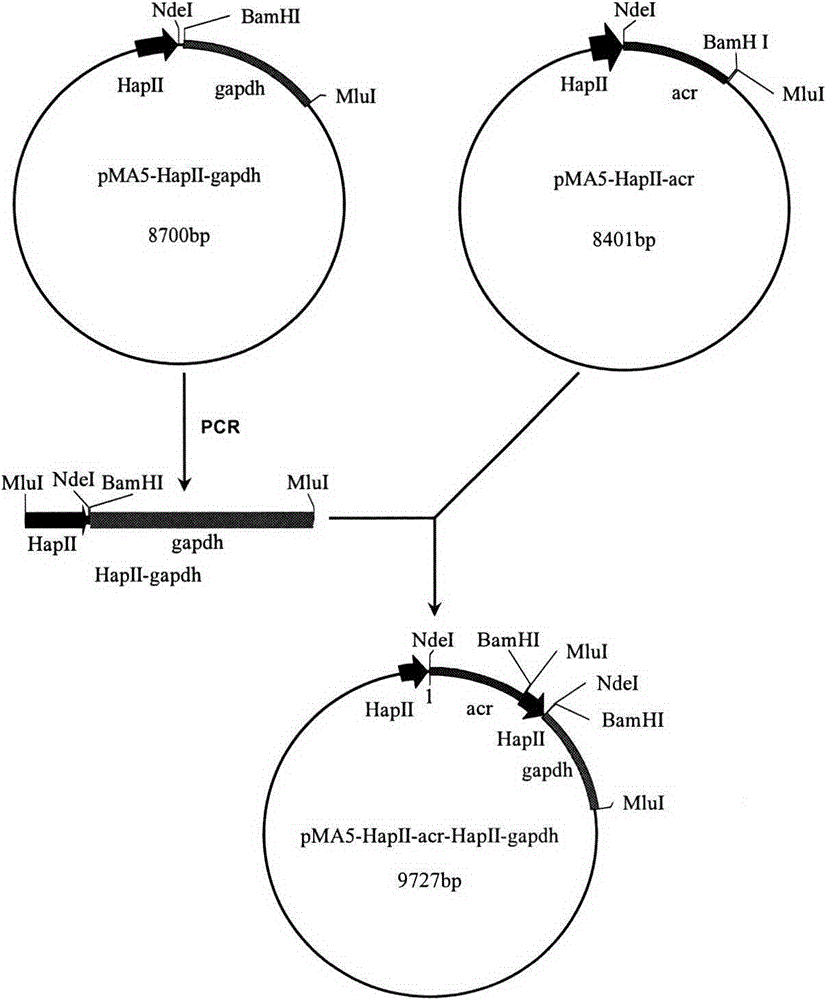
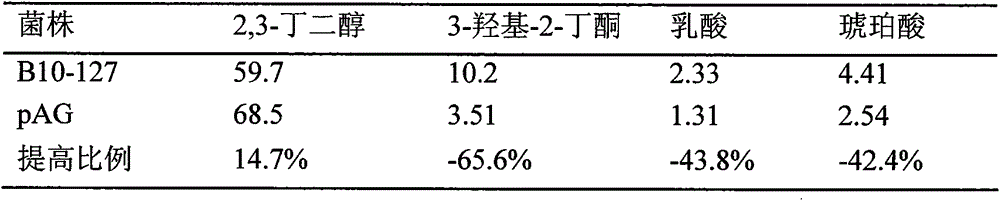
The key enzyme genes, namely 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde dehydrogenase (gapdh) and 3-hydroxyl-2- butanone reductase (acr), which participate in the coenzyme cyclic regeneration process in the synthesis route of 2,3-butylene glycol, are cloned from B. amyloliquefaciens B10-127; then the genes are inoculated to a shuttle expression plasmid pMA5-HpaII so as to successfully establish a shuttle expression plasmid containing gene gapdh and gene acr pMA5-HpaII-acr-HapII-gapdh, and the pMA5-HpaII-acr-HapII-gapdh is transferred to bacillus amyloliquefaciens B10-127 so as to obtain bacillus amyloliquefaciens, which is strengthened in gapdh and acr gene expression, namely pMA5-HpaII-acr-HapII-gapdh / B. amyloliquefaciens. The 2,3-butylene glycol output of the recombinant bacterium is raised by 14.7% compared to that of the original bacterium, the byproduct contents of 3-hydroxyl-2-butone, lactic acid and butanedioic acid are reduced by 65.6%, 43.8% and 42.4, and moreover the fermentation period is shortened. Through the processes of material supplement and fermentation, the 2,3-butylene glycol output can reach 121.3 g / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A method for detecting dna methyltransferase activity based on strand displacement amplification and dnazyme amplification
ActiveCN105112540BHighly sensitive detection activityLow detection limitMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisFluorescenceDNA Methyltransferase Inhibitor
The invention relates to a method for detecting DAN methyltransferase activity based on strand displacement amplification and DNAzyme amplification. A three-function double-stranded DNA probe is designed. Methylation happening to the three-function double-stranded DNA probe is specifically recognized through DAN methyltransferase. Remaining non-methylated double-stranded DNA is specifically cut through HpaII restriction enzymes, methylated double-stranded DNA triggers a strand displacement reaction, a large amount of 8-17 DNAzyme is released, the 8-17 DNAzyme catalyzes cutting of a large number of hairpin-line molecular beacon substrates, and remarkable fluorescent enhancement is triggered. The method can sensitively detect the DAN methyltransferase activity, and the detection limit is 0.0082 U / mL. The method has potential application in research of influences of anti-cancer drugs on DAN methyltransferase activity inhibition and screening of DAN methyltransferase inhibitors.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Detection method and application of goat atbf1 gene single nucleotide polymorphism
InactiveCN104878099BEasy to detectAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyElectrophoreses
The invention discloses a method for detecting the single-nucleotide polymorphism of a goat ATBF1 gene and the application of the goat ATBF1 gene. According to the method, the goat whole-genome DNA to be tested is taken as a template, the goat ATBF1 gene is amplified by use of the PCR technology, the PCR product is digested by use of a restriction enzyme MspI or HpaII, next, the agarose gel electrophoresis is performed, and the genotype of No.25748nt or No.163517nt SNP of the goat ATBF1 gene is identified according to the electrophoresis result; different genotypes of the No.25748nt and No.163517nt SNPs of the ATBF1 gene have remarkable relevance with the growth and development traits of the goat, and therefore, the ATBF1 gene is advantageous for quickly establishing a good goat genetic resource population.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Primer and method for rapidly detecting methylation level of wheat photoperiod gene Ppd-B1 and applications thereof
InactiveCN109943658AProve the results are credibleThe identification result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEnzyme digestionNucleotide
The invention discloses a primer and method for rapidly detecting a methylation level of a wheat photoperiod gene Ppd-B1 and applications thereof. The primer comprises Ppd-B1-HpaII-F1 and Ppd-B1-HpaII-R1, and nucleotide sequences of the primer are respectively as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1 and SEQ ID NO. 2. The method comprises the following steps: extracting wheat material genome DNA by a CTAB method;carrying out enzyme digestion treatment on the wheat material genome DNA; carrying out PCR amplification treatment on a product after the enzyme digestion treatment; detecting an amplified product by1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis, if an amplified fragment with a molecular weight of 586 bp is obtained, indicating that identified material is of a Ppd-B1 hypermethylation type, otherwise indicating that the identified material is of a Ppd-B1 hypomethylation type. The method not only has accurate result, but also greatly reduces reaction cost and reaction time.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Kit for identifying human methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) gene polymorphism rs2274976 by using MspI
InactiveCN102676655BEasy to operateLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementForward primerGenetics
The invention discloses a kit for identifying human methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) gene polymorphism rs2274976 by using MspI. The kit comprises a forward primer and a reverse primer for amplifying sequences near a human MTHFR gene polymorphism rs2274976 locus, wherein the last base at the 3'end of the forward primer is adjacent to an rs2274976 polymorphic base, and the last second base of the forward primer is a mismatched base C, so that the forward primer and polymorphic G allele form a CCGG structure in an amplification product; and the forward primer is shown as SEQ ID NO:1 or SEQ NO:11, and the reverse primer is shown as SEQ ID NO:2, SEQ ID NO:7 or SEQ NO:12. The kit also comprises restriction enzyme MspI or HpaII, and an instruction book for implementing identification. The kit is easy to operate, low in cost, and wide in application range.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
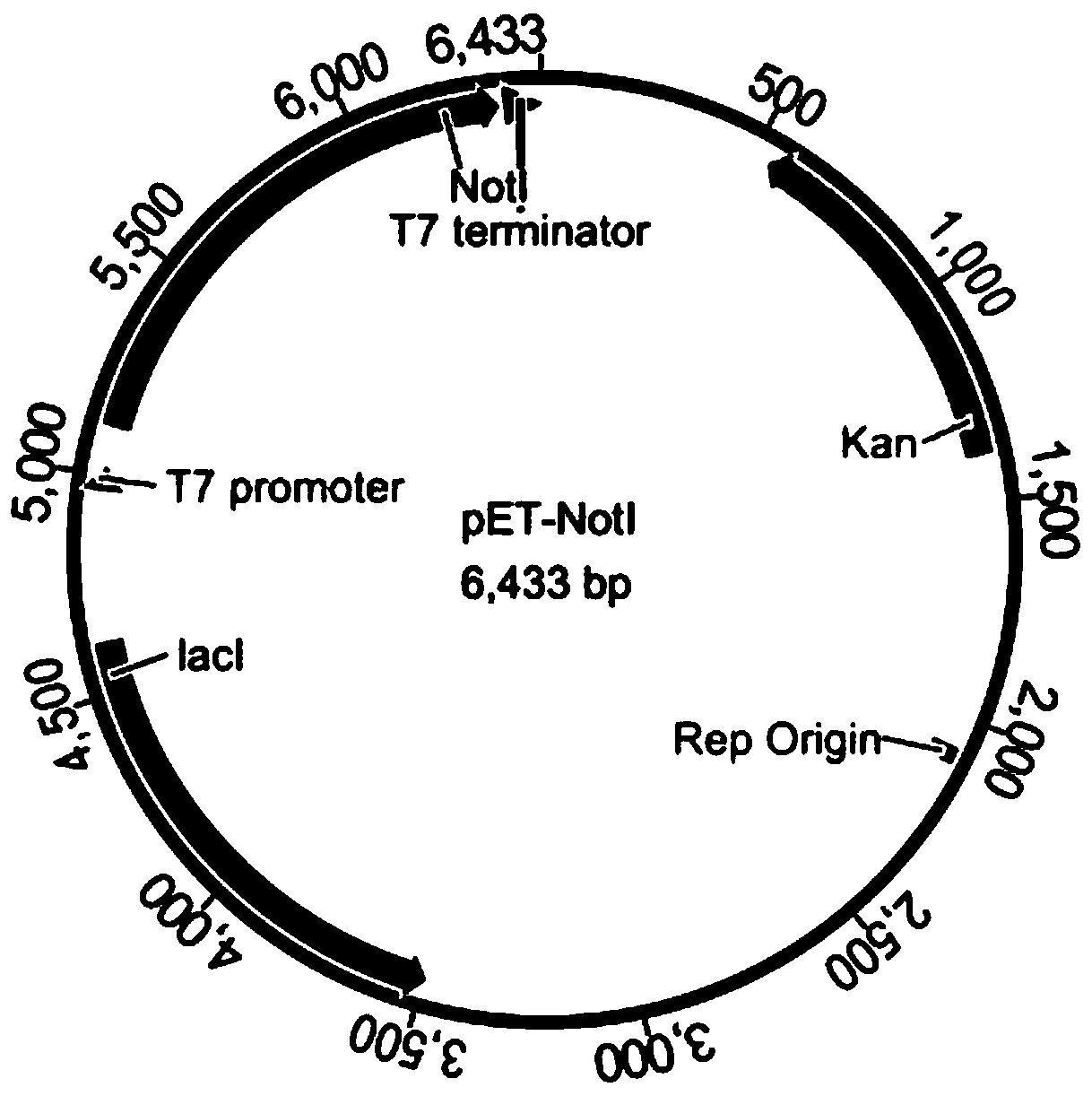
A method for expressing restriction endonucleases efficiently through the protection of methylases
ActiveCN106480076BAvoid genetic screeningSimplify the recombinant expression processHydrolasesNucleic acid vectorGeneticsEndonuclease
Owner:莫纳(武汉)生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com