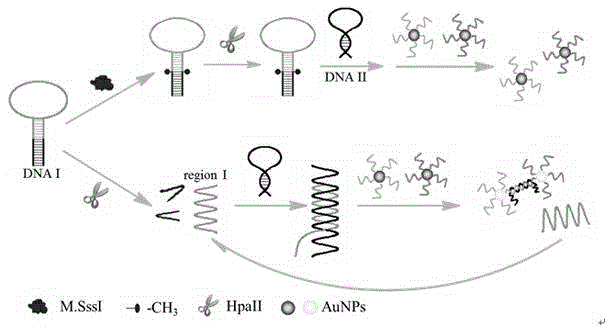
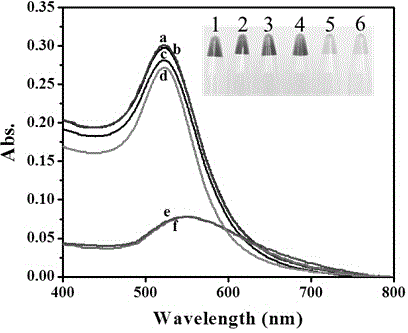
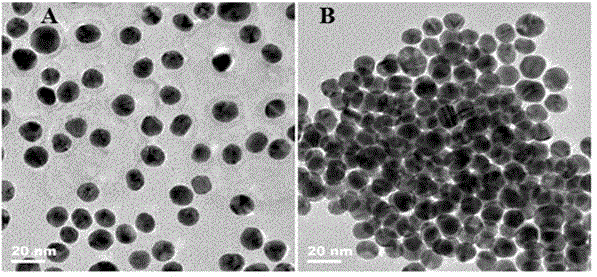
Colorimetric sensing method for detecting activity of DNA transmethylase based on DNA chain substituting circulation amplifying technology
A methyltransferase and cyclic amplification technology, applied in the field of colorimetric sensing, to achieve the effects of high sensitivity, simple and convenient visual detection, and low detection limit
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] (1) Preparation of AuNPs: Add 49 mL of ultrapure water and 1 mL of 2% HAuCl in a round bottom flask 4 ·3H 2 O solution, after heating to make it boil, add 1 mL of trisodium citrate solution with a concentration of 5% by mass, continue to stir and keep boiling for 5 minutes, then let the solution naturally cool to room temperature under stirring, and then prepare a particle size of 13 nm and AuNPs at a concentration of 12 nM, at 4 o C is kept for later use;
[0021] (2) Preparation of AuNPs-labeled probe DNA: Add 5.5 nM activated probe DNA to 3 mL of the AuNPs solution prepared in step (1), shake on a shaker at room temperature for 12 hours, add phosphoric acid to adjust the phosphate radical in the solution The concentration of NaCl was 9 mM. After 30 minutes, the phosphate buffer solution was added, and the phosphate buffer solution was continued to be added six times in the next two days, so that the final concentration of NaCl was 0.3 mM, and aged overnight. Centr...
Embodiment 2
[0026] M.SssI activity detection
[0027] (1) Optimization of DNA I concentration, DNA I:DNA II, SAM concentration, and HpaII concentration
[0028] Figure 4 A is the effect of DNA I concentration on M.SssI activity detection. It can be seen from the figure that as the concentration of DNA I increases, the absorbance of the AuNPs solution decreases first and then reaches a stable trend whether with or without M.SssI. When the DNA I concentration was 40nM, the absorbance difference (ΔA) reached the maximum. Therefore, the optimal concentration of DNA I was chosen to be 40 nM. Figure 4 B is the effect of the ratio of DNA I to DNA II on the detection of M.SssI activity. In the present invention, the efficiency of strand substitution amplification depends to a certain extent on the ratio of DNA I to DNA II (DNA I:DNA II). The concentration of DNA I was fixed at 40 nM, and the DNA I:DNA II was gradually increased from 1:1 to 1:5. When the ratio of DNA I:DNA II was 1:3, the Δ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com