Construction method and fermenting method of antibiotic-resistance-free recombinant bacillus subtilis for expressing glutamate decarboxylase
A technology of Bacillus subtilis and glutamic acid decarboxylase, which is applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of endotoxin production, low enzyme production efficiency, and long culture period, and achieve the effects of simple process, environmental friendliness, and strong protein expression ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Embodiment 1: D-alanine-deficient Bacillus subtilis WB600 ( dal - ) construction
[0033]
[0034] Using the plasmid p7S6 as a template, the primer pair P3 / P4 will lox 71- spc - lox 66 antibiotic resistance gene fragments were amplified and recovered. D-alanine racemase gene on chromosome of Bacillus subtilis WB600 dal The fragments with a length of 800-900 bp on both sides were selected as homologous regions, and the homologous regions at both ends were amplified and recovered with primer pairs P1 / P2 and P5 / P6 respectively. Use the primer pair P1 / P6 to combine the homology arm fragments at both ends with antibiotics lox 71- spc - lox 66 were fused together by PCR technology.
[0035] PCR reaction system: Add the following reagents in order in 0.2mL PCR tube: 1.5μL each of upstream and downstream primers; 5μL Husion HF buffer (5×); 2μL 10mM dNTP mix (2.5mM each); 2μL upstream homology arm; 0.5μL lox 71- spc - lox 66; 2 μL downstream homology ar...
Embodiment 2
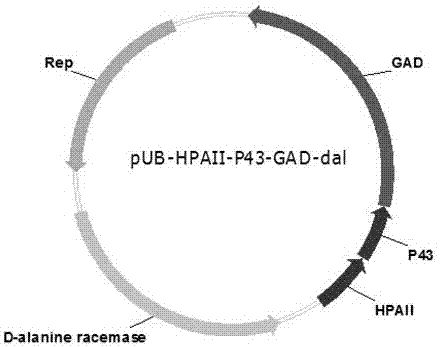
[0040] Embodiment 2: Construction of food-grade safety plasmid pUB-HpaII-P43-gad-dal
[0041]
[0042] Materials and reagents: DNA polymerase PrimeSTAR Max DNA Polymerase (2×) and DL 5000 DNA Marker were purchased from Dalian Bao Biological Engineering Co., Ltd.; SanPrep column type plasmid DNA mini-extraction kit and SanPrep column type DNA gel recovery kit were purchased from From Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.; primers were synthesized by Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.; plasmid pET-22b-gad was synthesized by Shanghai Jierui Bioengineering Co., Ltd.; other common reagents were purchased from Sinopharm Chemicals Reagents Ltd.
[0043] Using P7 and P8 as primers and pET-22b-gad as a template, the gad gene was amplified by PCR,
[0044] reaction system:
[0045] pET-22b-gad 1 μL
[0046] P7 1.25 μL
[0047] P8 1.25 μL
[0048] wxya 2 O 21.5 μL
[0049] PrimeSTAR Max DNA Polymerase (2×) 25μL
[0050] Reaction conditions: pre-denaturation at 98°...
Embodiment 3
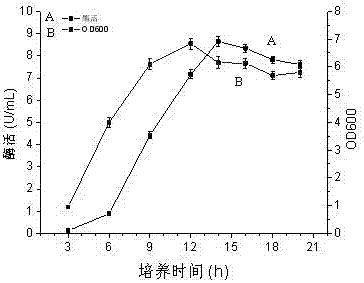
[0067] Example 3 Fermentative expression of glutamic acid decarboxylase by recombinant bacillus subtilis
[0068] Pick a single colony on the plate and inoculate it in 4 mL of LB medium, and incubate at 37°C for 12 h at 200 r / min; add the seed solution to 50 mL of fermentation medium at 37°C at 200 r / min according to the volume fraction of 2%. R / min is cultivated to 21h, the OD600 of measuring fermented liquid and enzyme activity ( image 3 ).
[0069] Media formulations involved:
[0070] LB medium: tryptone 10 g / L; yeast extract 5 g / L; sodium chloride 10 g / L; prepared with deionized water, sterilized at 121°C for 20 min.
[0071] Fermentation medium: soybean peptone 25 g / L; lactose 5 g / L; Na 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O 3g / L; MnSO 4 ·H 2 O0.1g / L; Prepared with deionized water, sterilized at 115°C for 30min.
[0072] Definition of fermentation enzyme activity: under the reaction conditions of 50°C and pH 4.5, the amount of enzyme required to produce 1 μmol of GABA per minute is de...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com