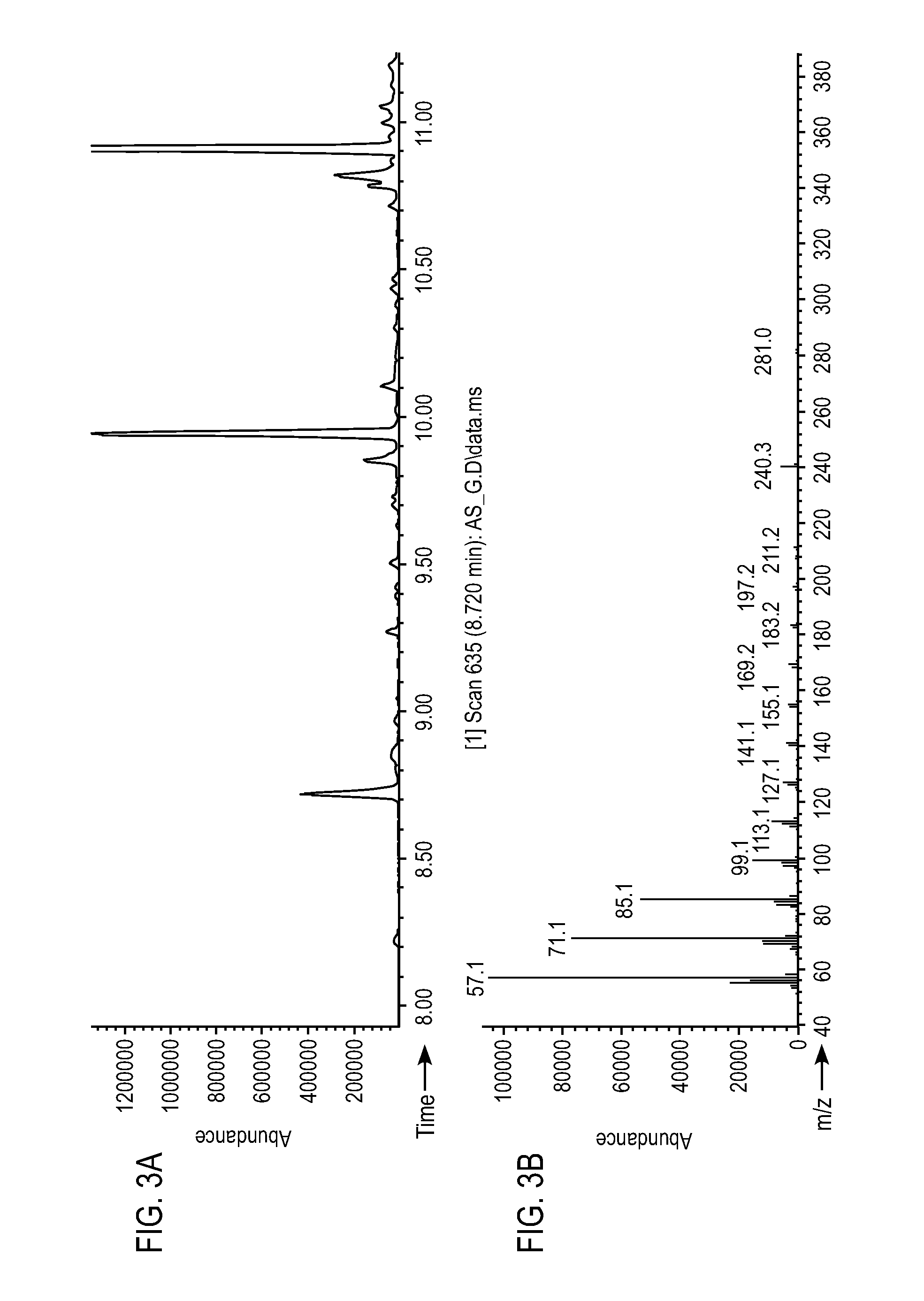
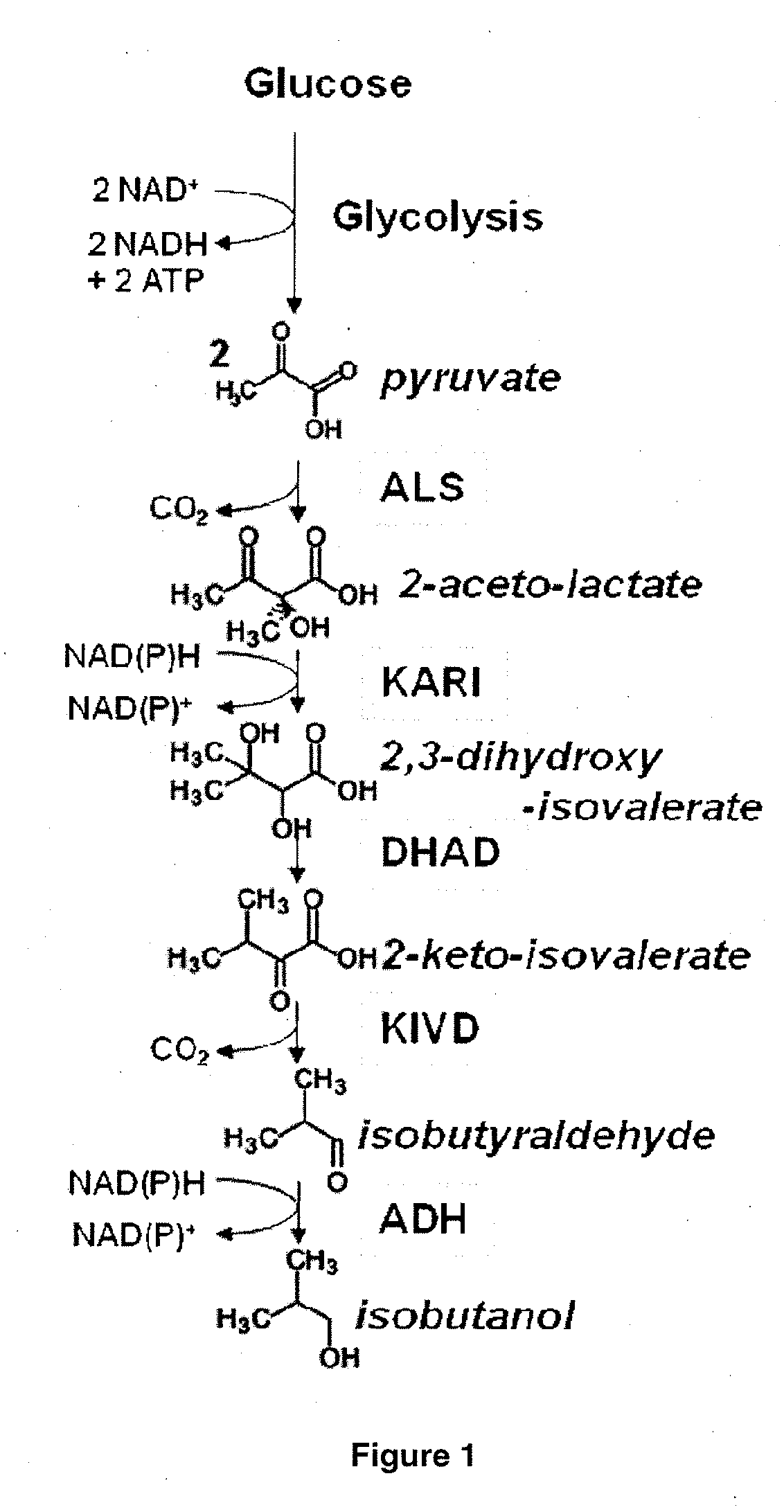
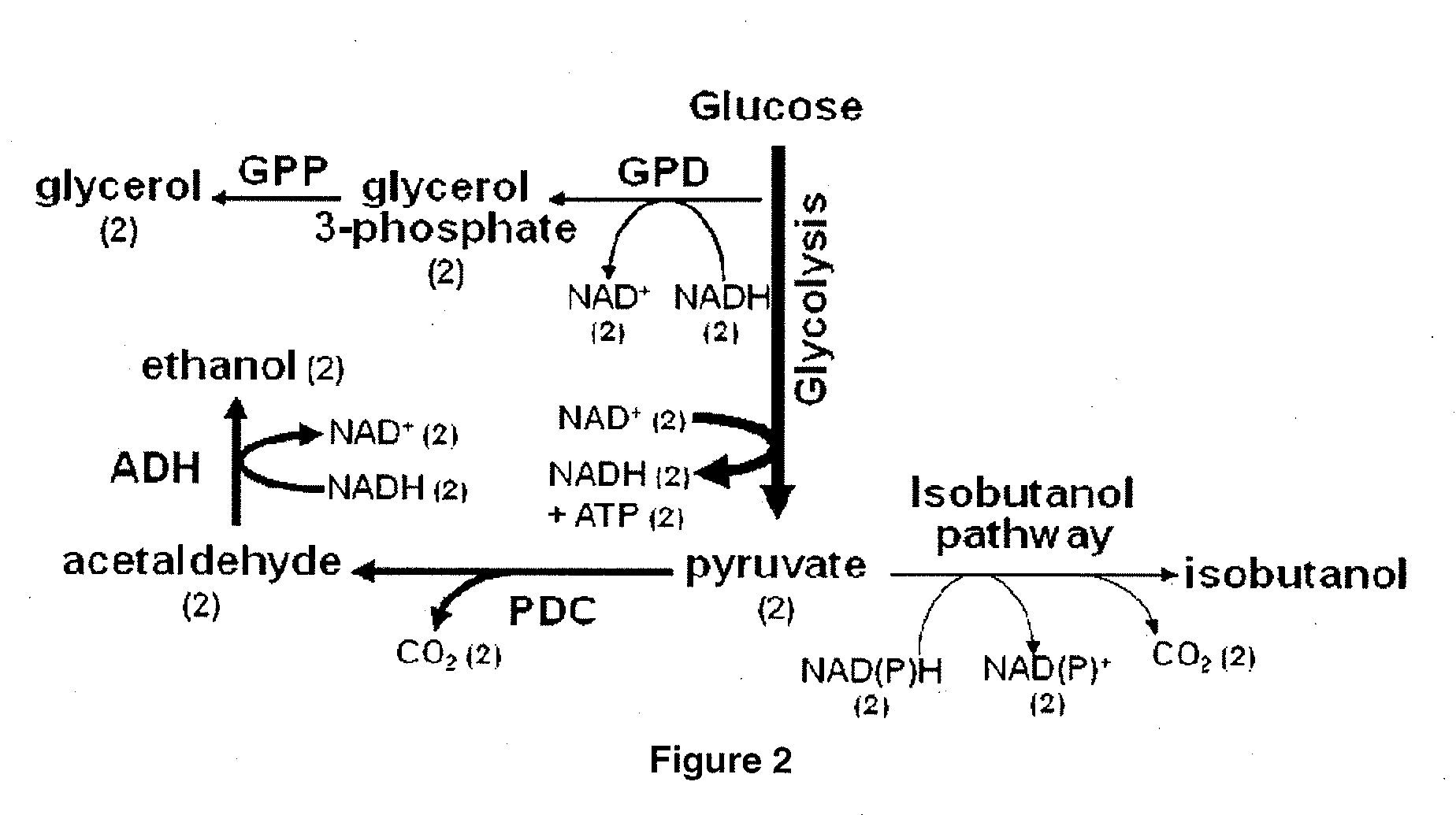
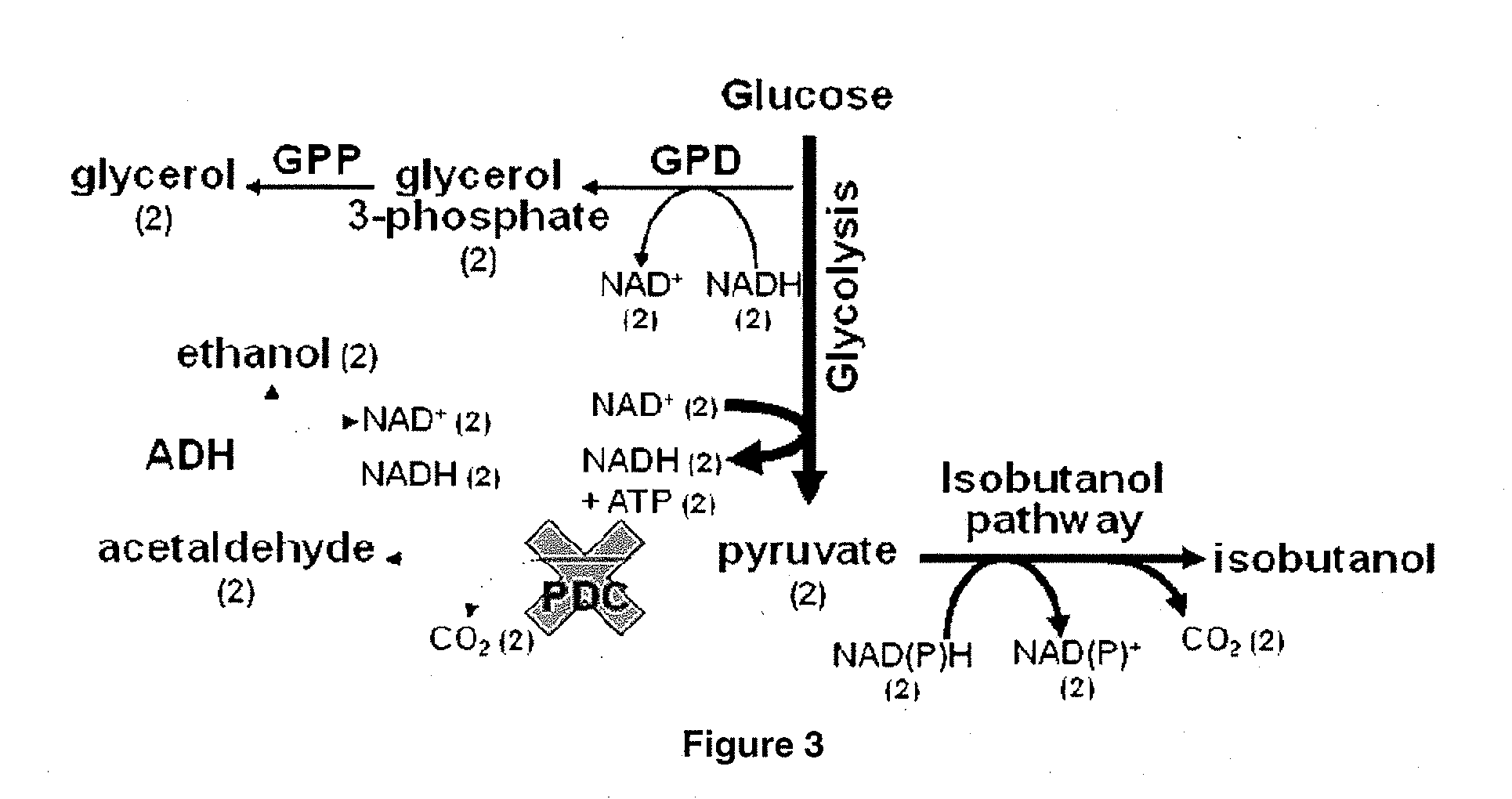
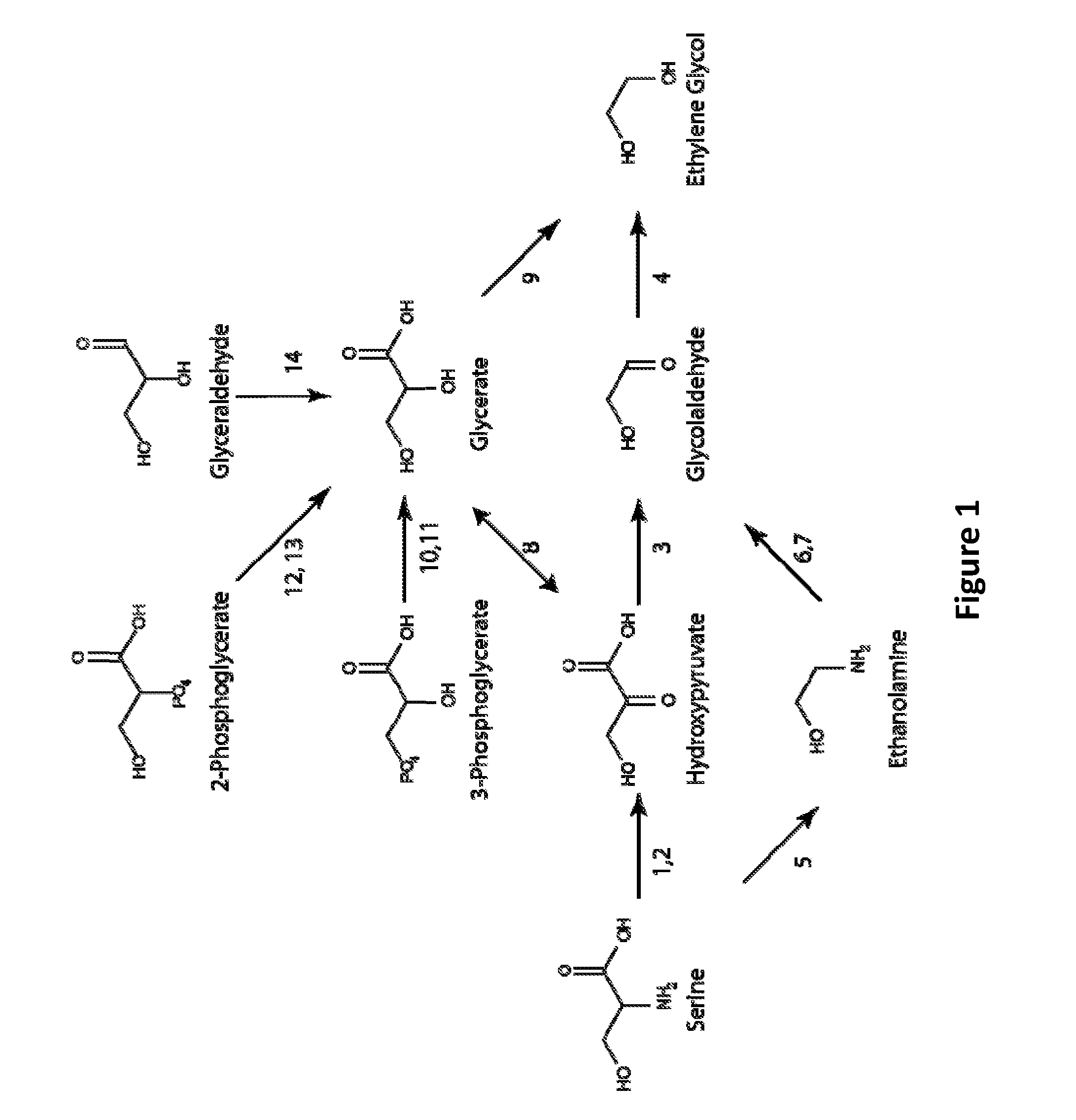
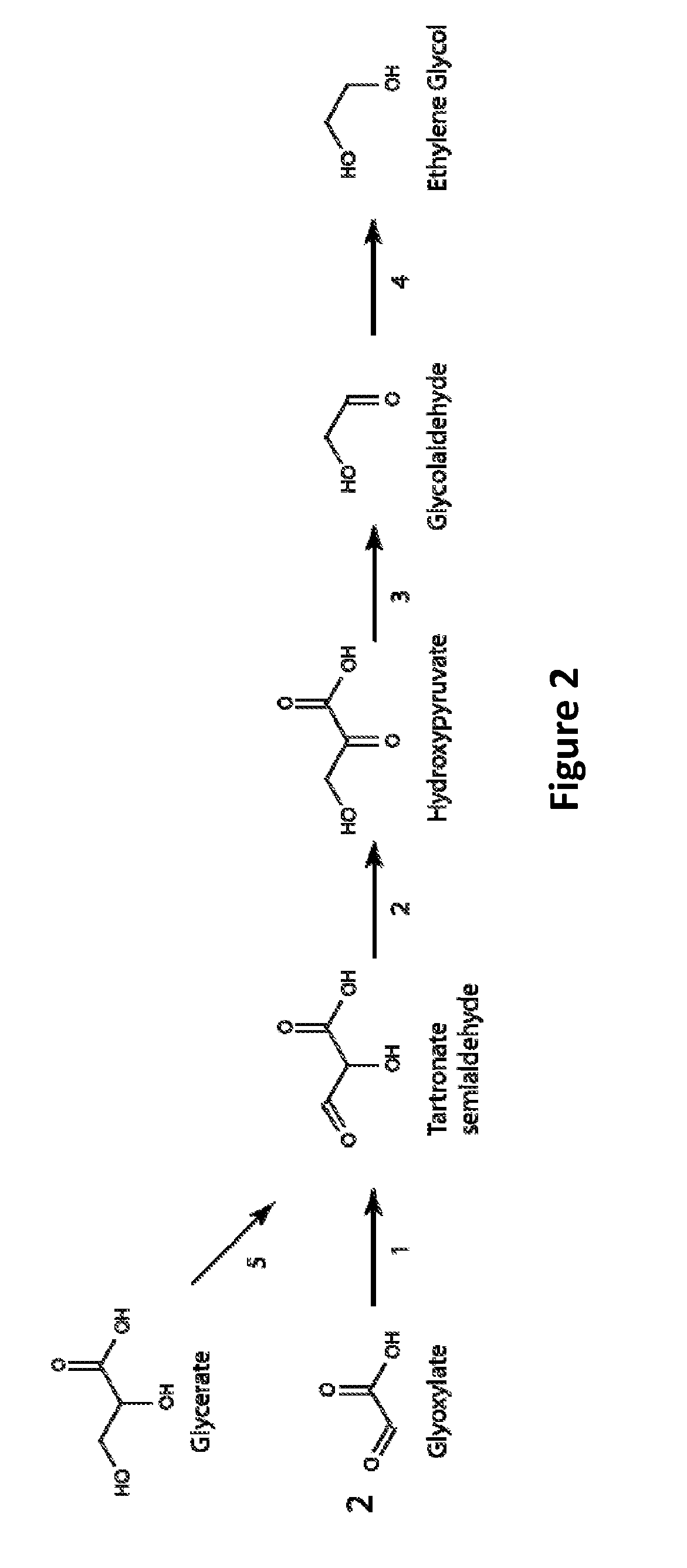
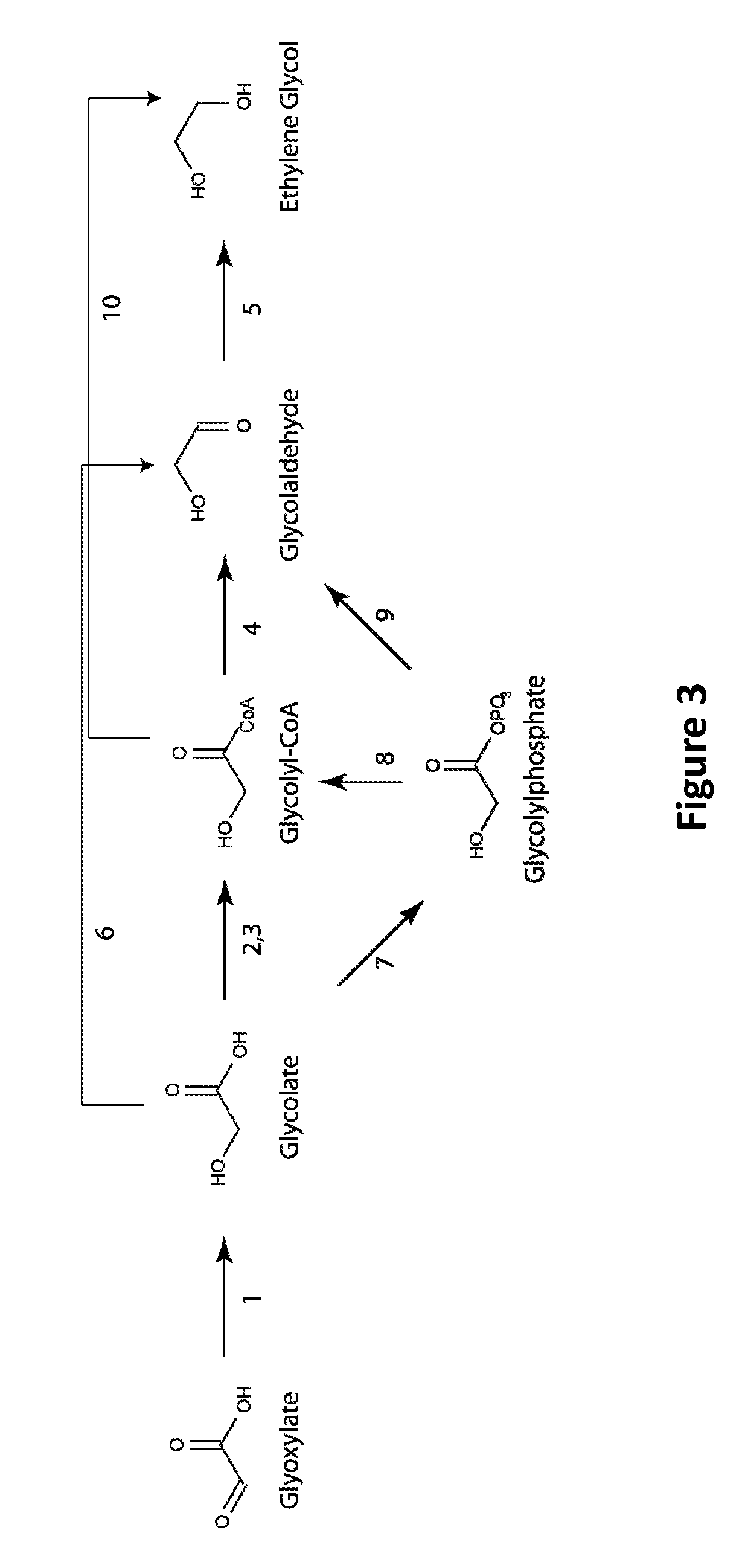
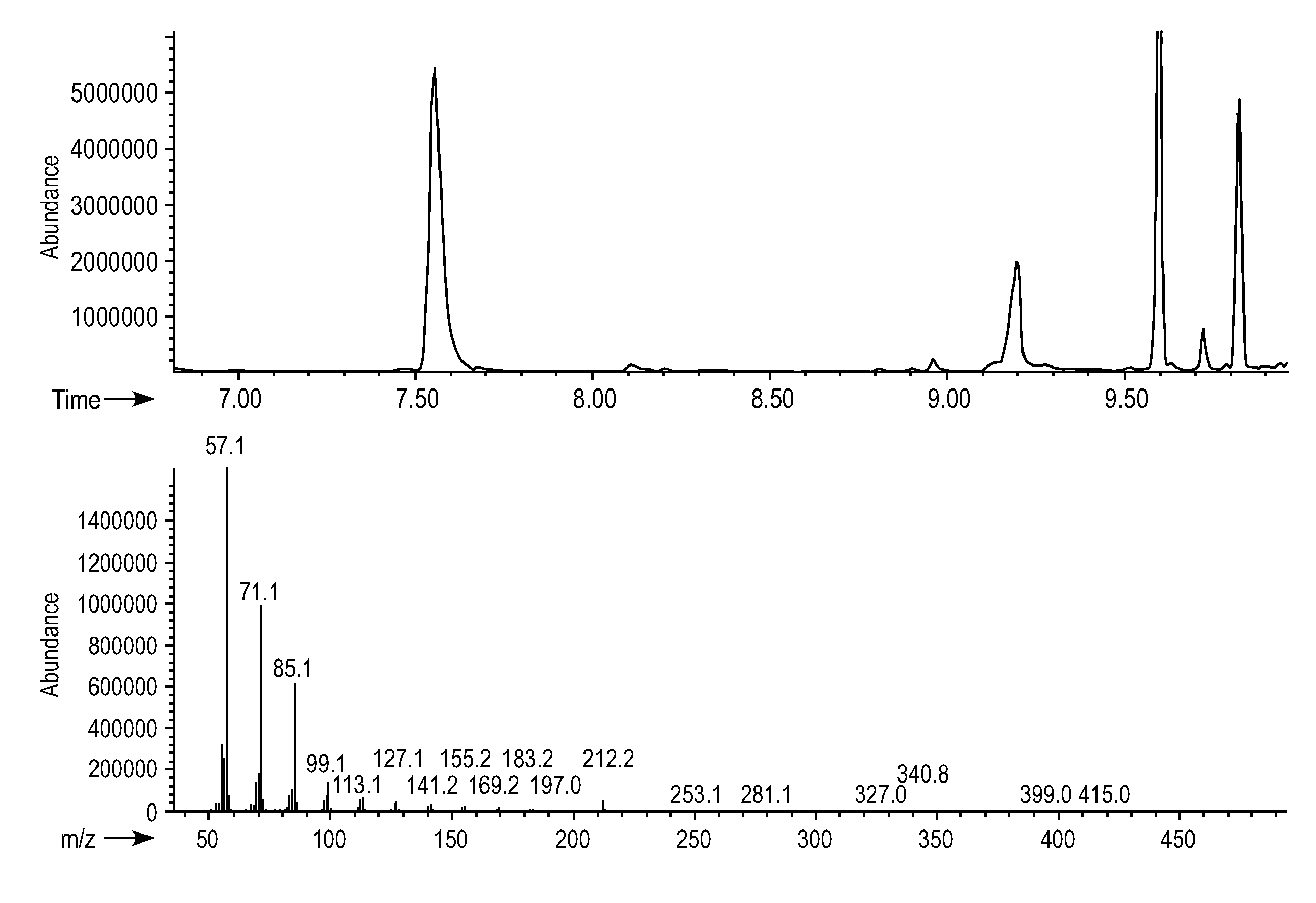
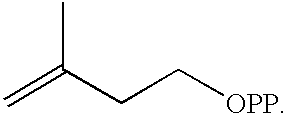
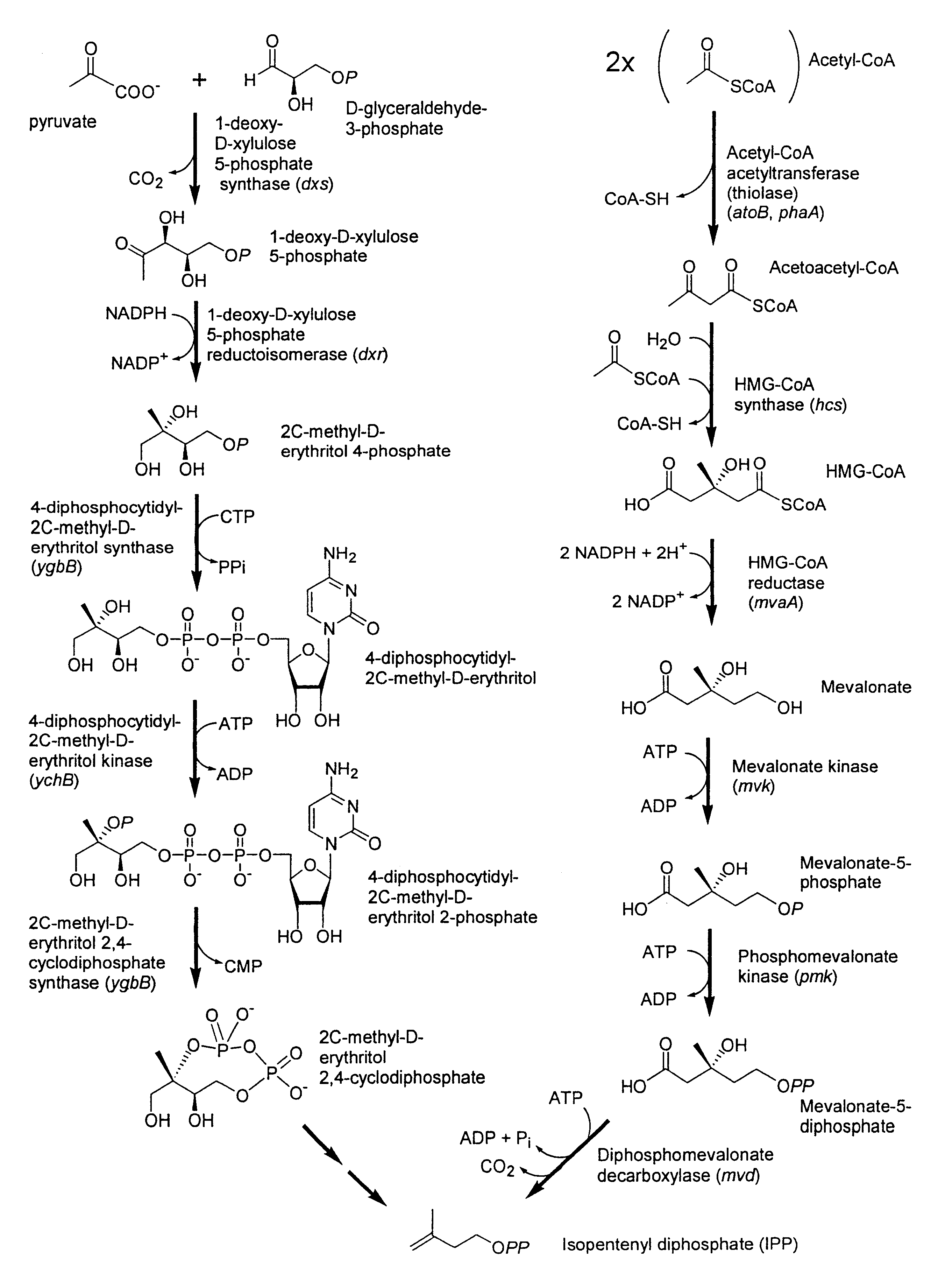
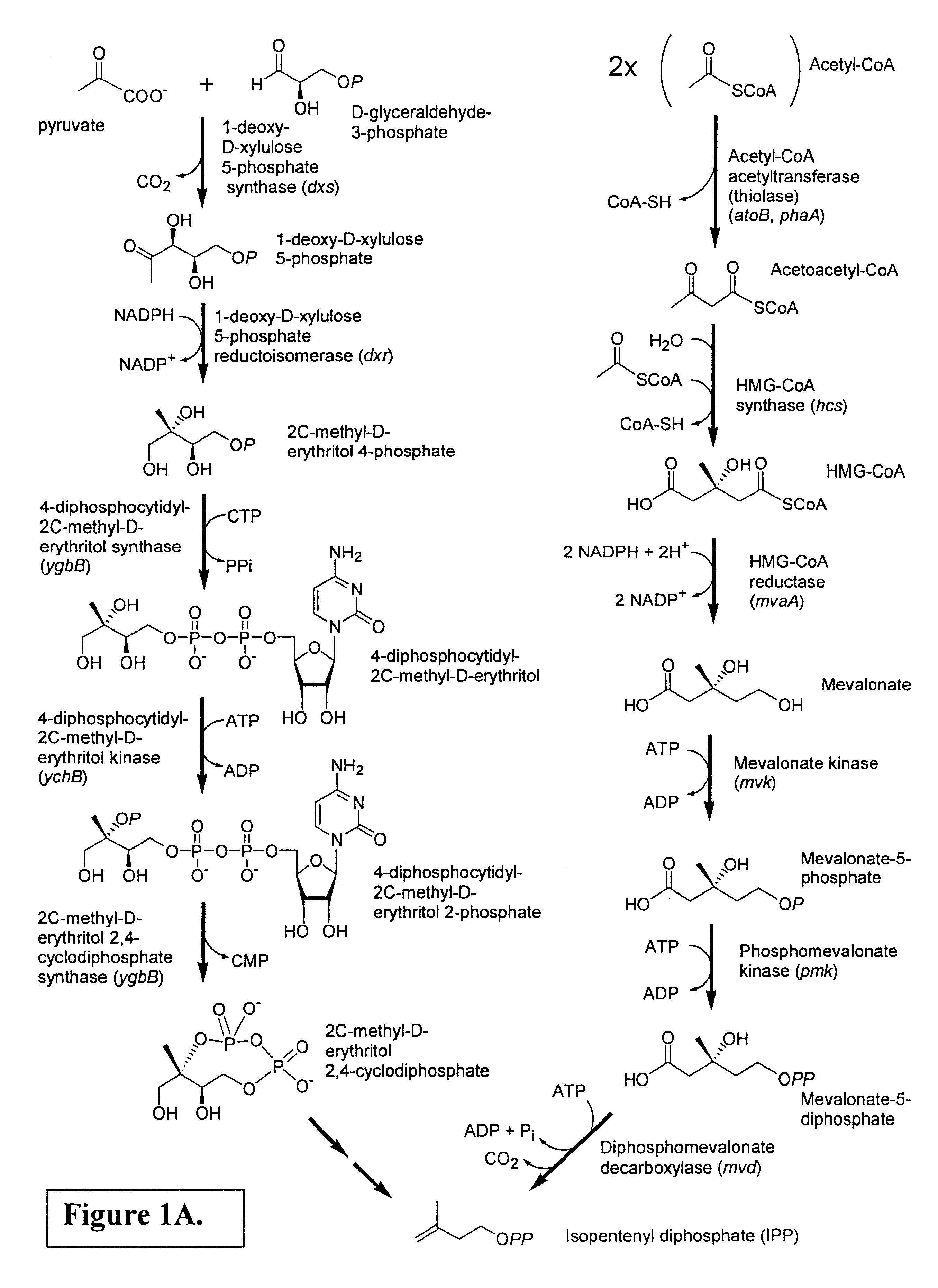
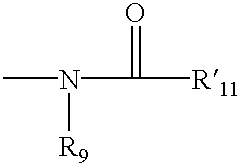
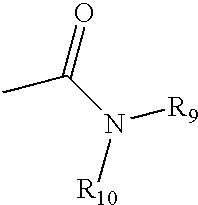
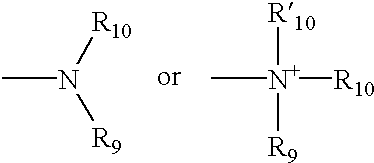Patents
Literature
1662results about "Carbon-carbon lyases" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
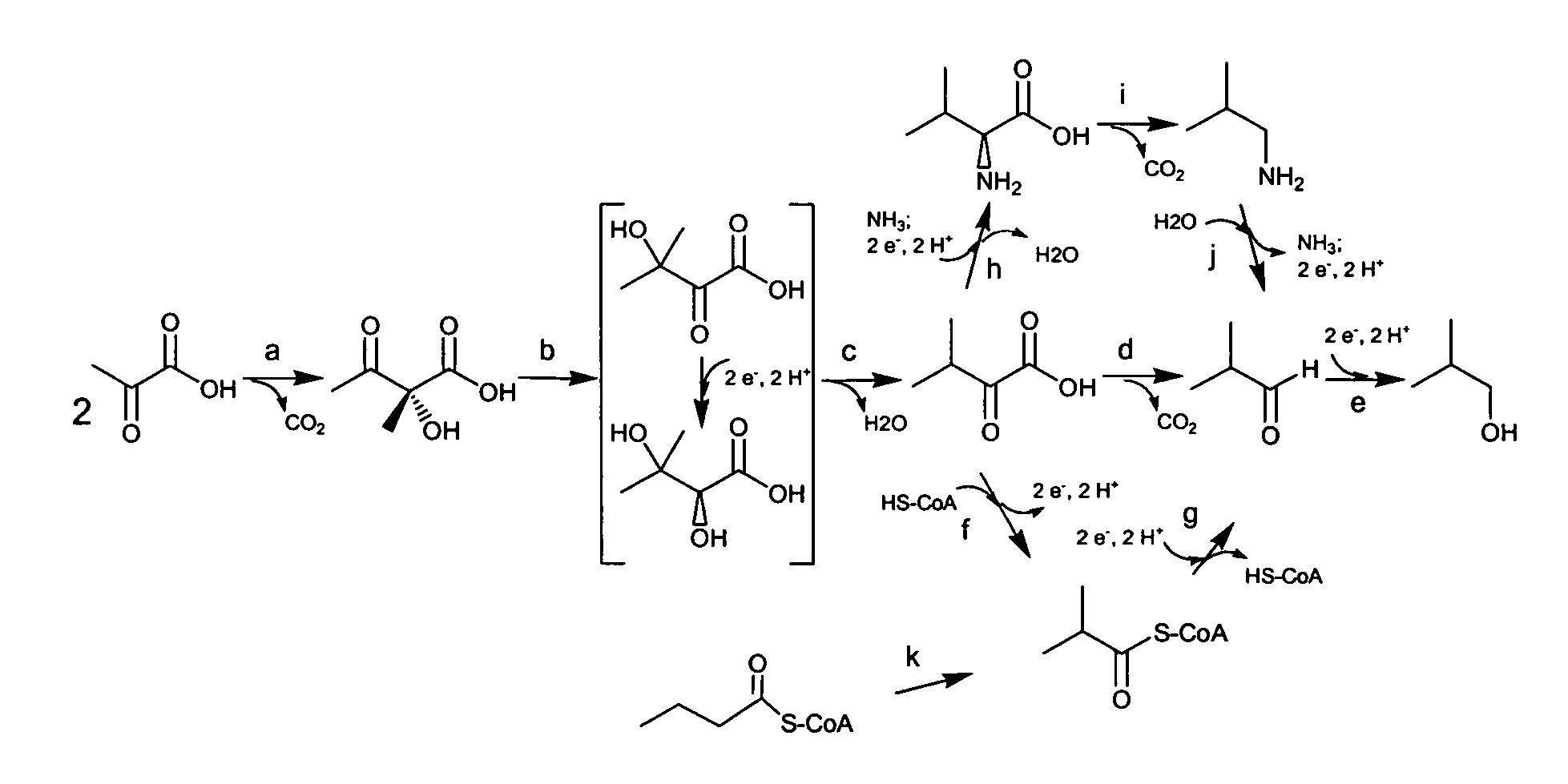
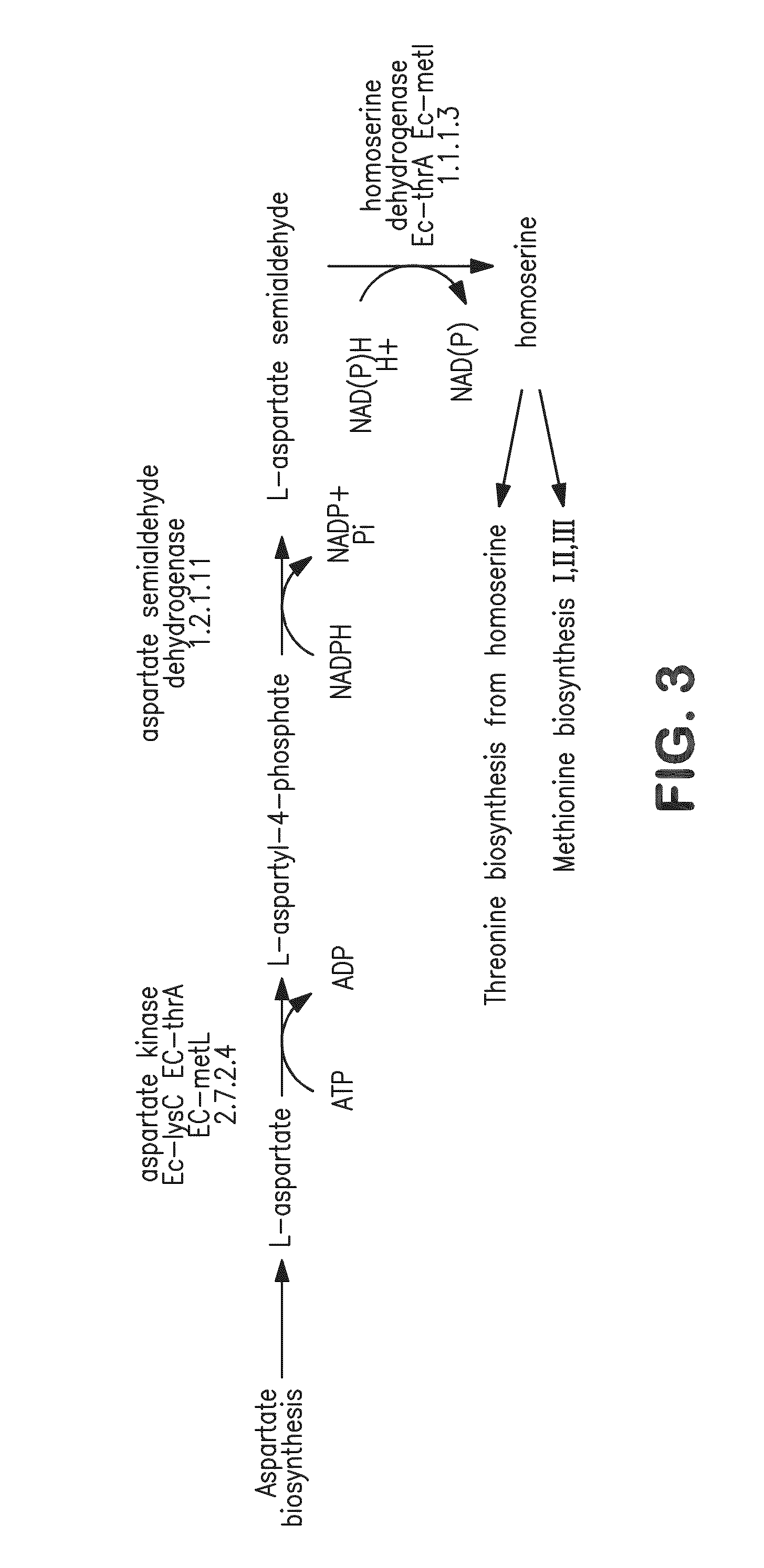
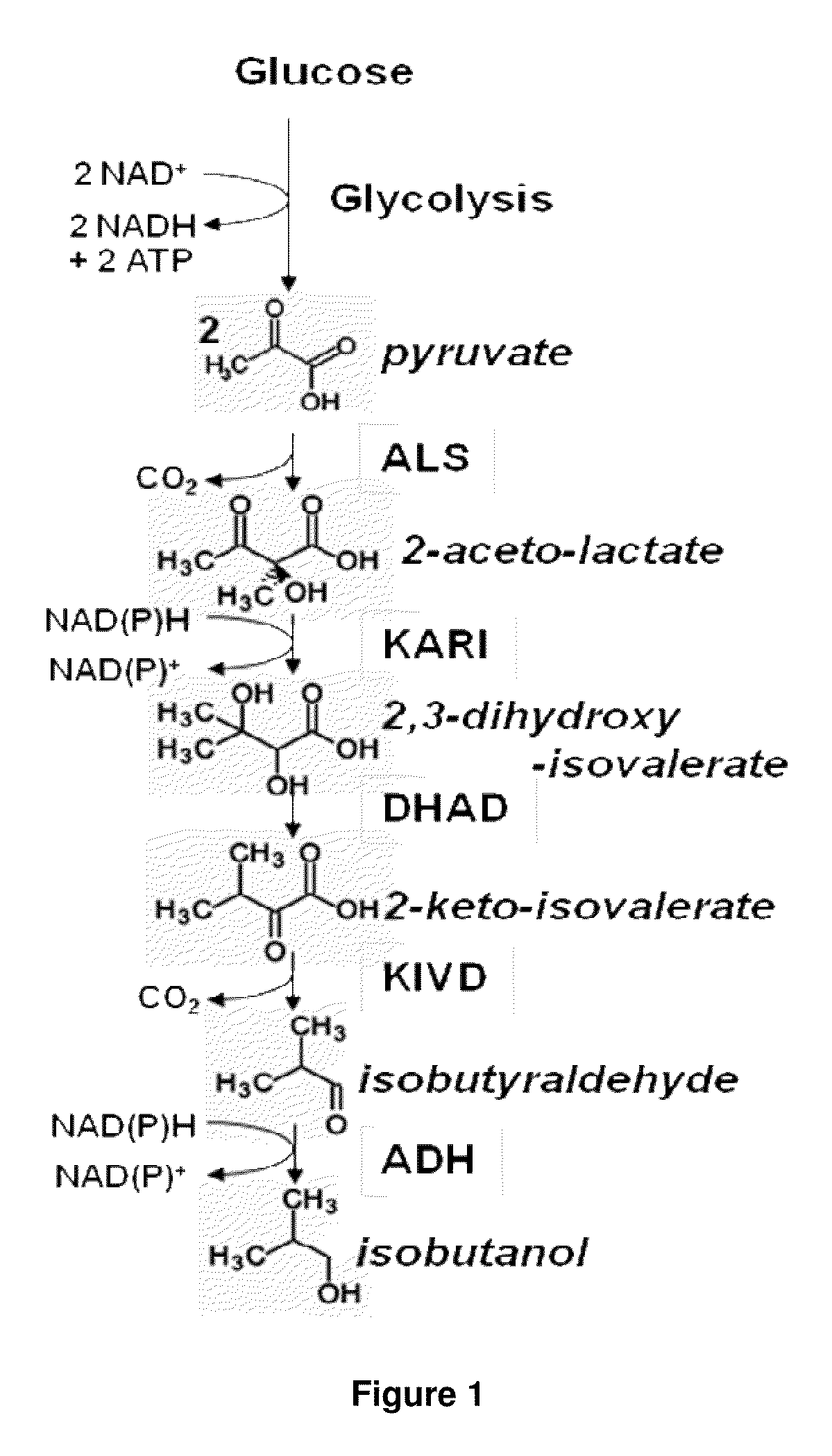
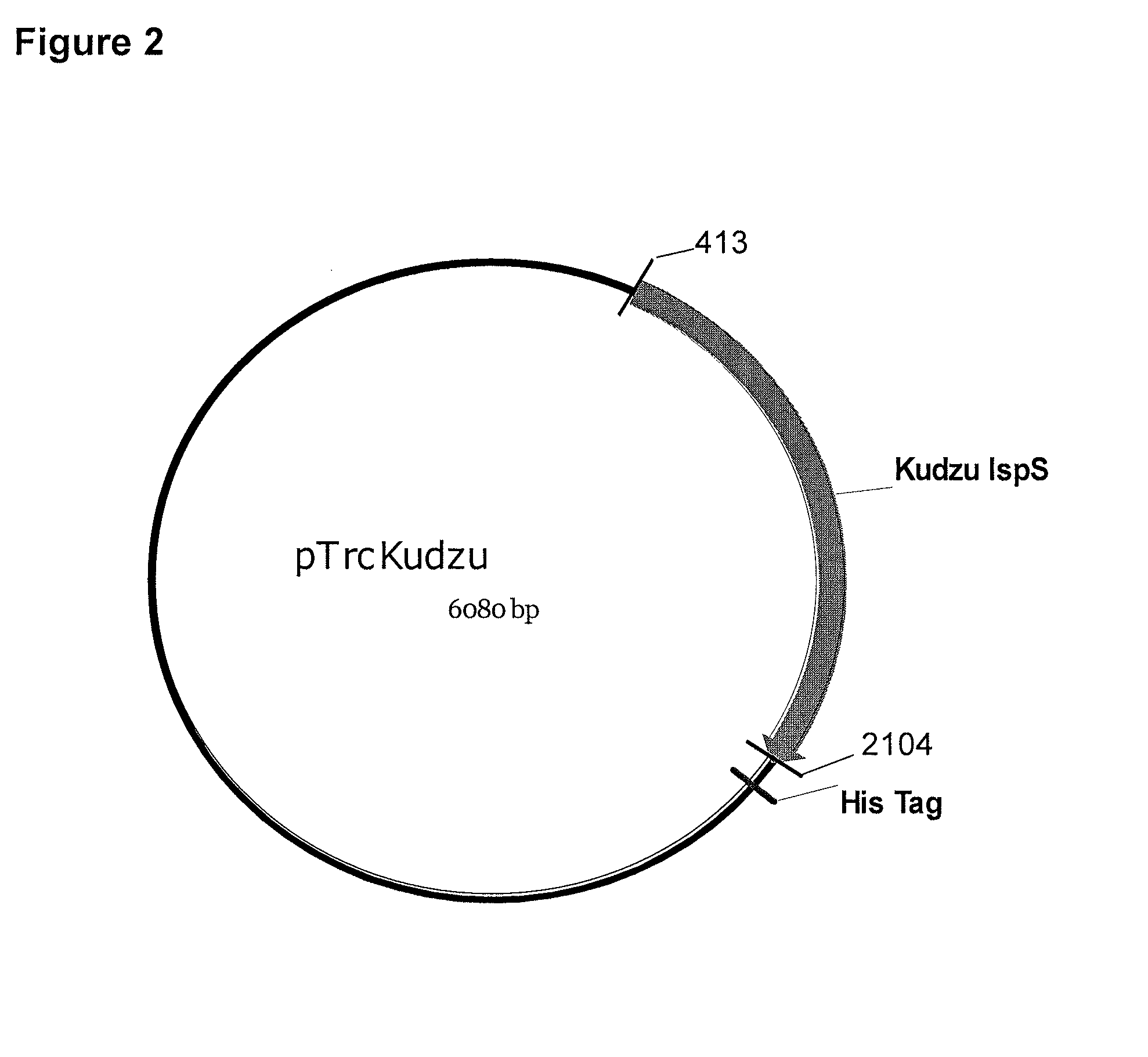
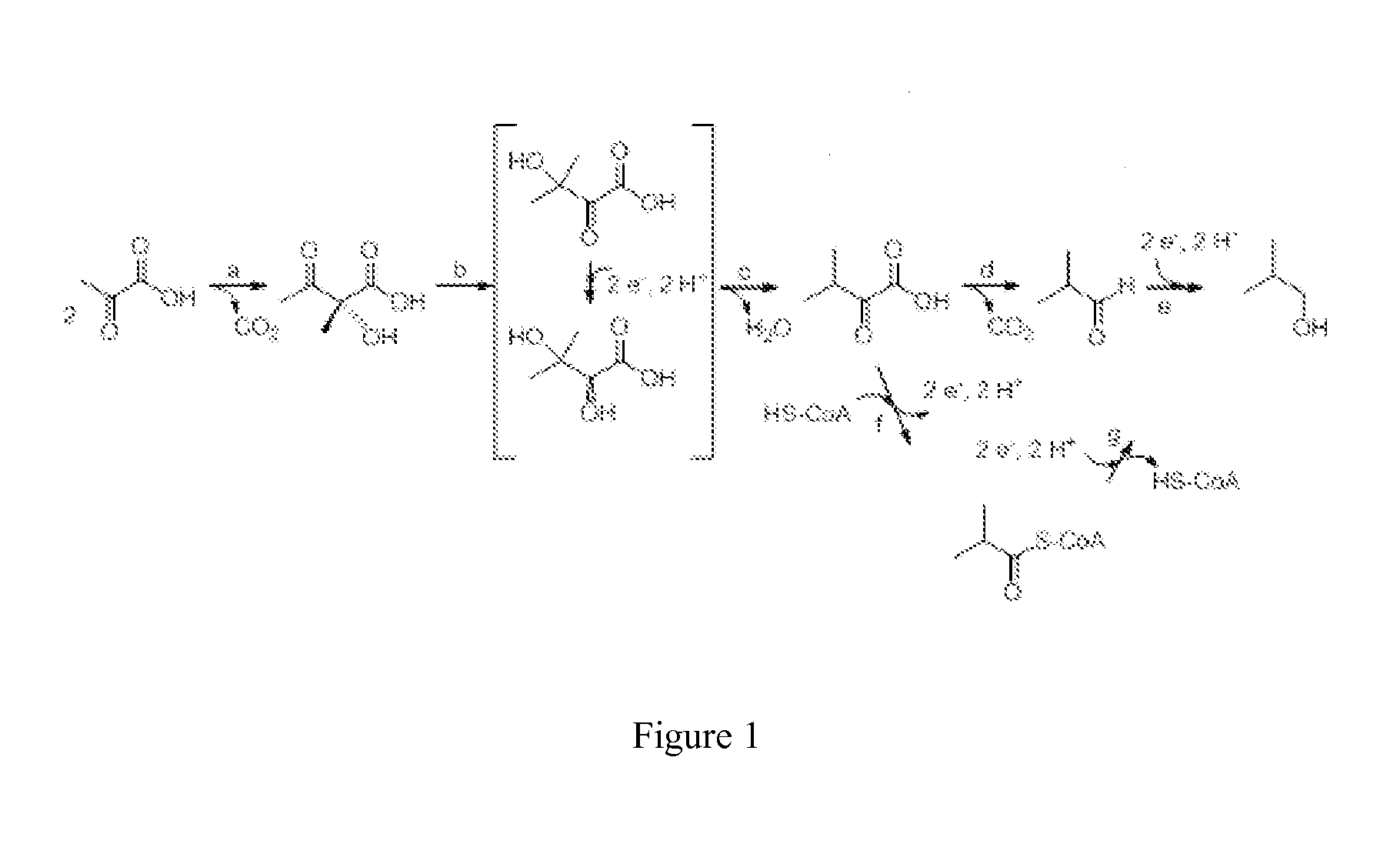
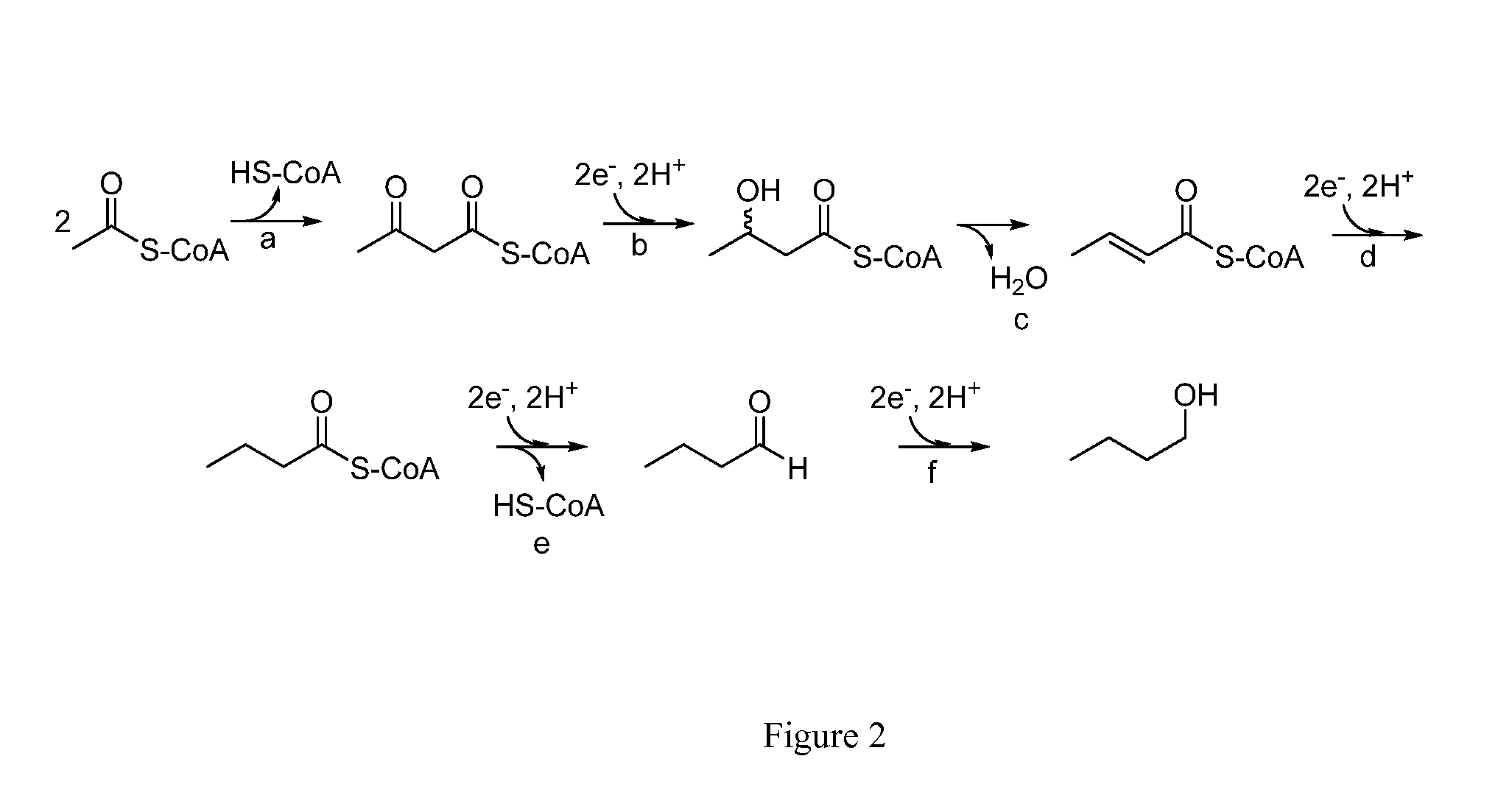
Fermentive production of four carbon alcohols
Owner:GEVO INC
Matrices for drug delivery and methods for making and using the same
In one aspect, biocompatible matrices such as sol-gels encapsulating a reaction center may be administered to a subject for conversion of prodrugs into biologically active agents. In certain embodiments, the biocompatible matrices of the present invention are sol-gels. In one embodiment, the enzyme <SMALLCAPS>L< / SMALLCAPS>-amino acid decarboxylase is encapsulated and implanted in the brain to convert <SMALLCAPS>L< / SMALLCAPS>-dopa to dopamine for treatment of Parkinson's disease.
Owner:MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMA
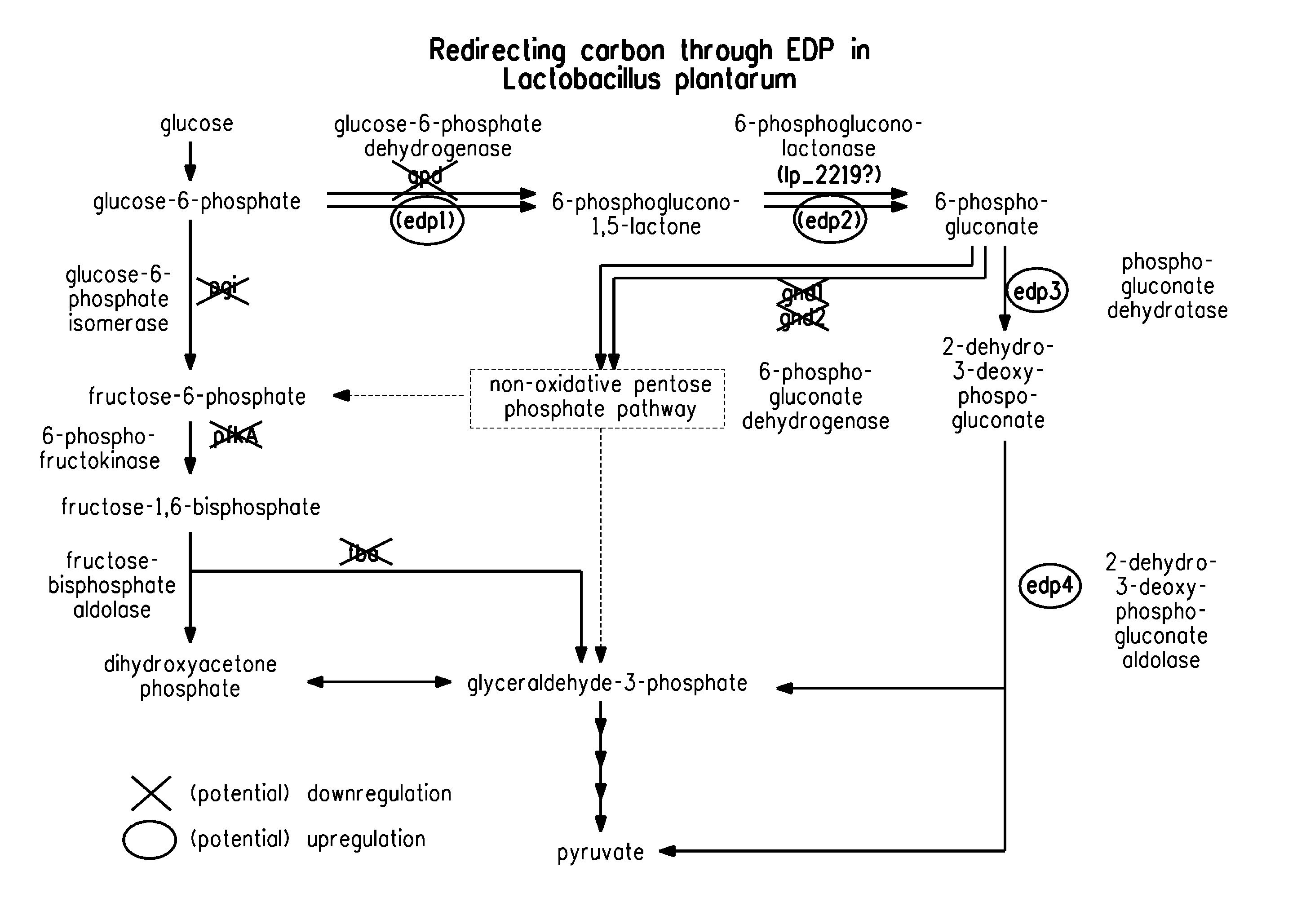
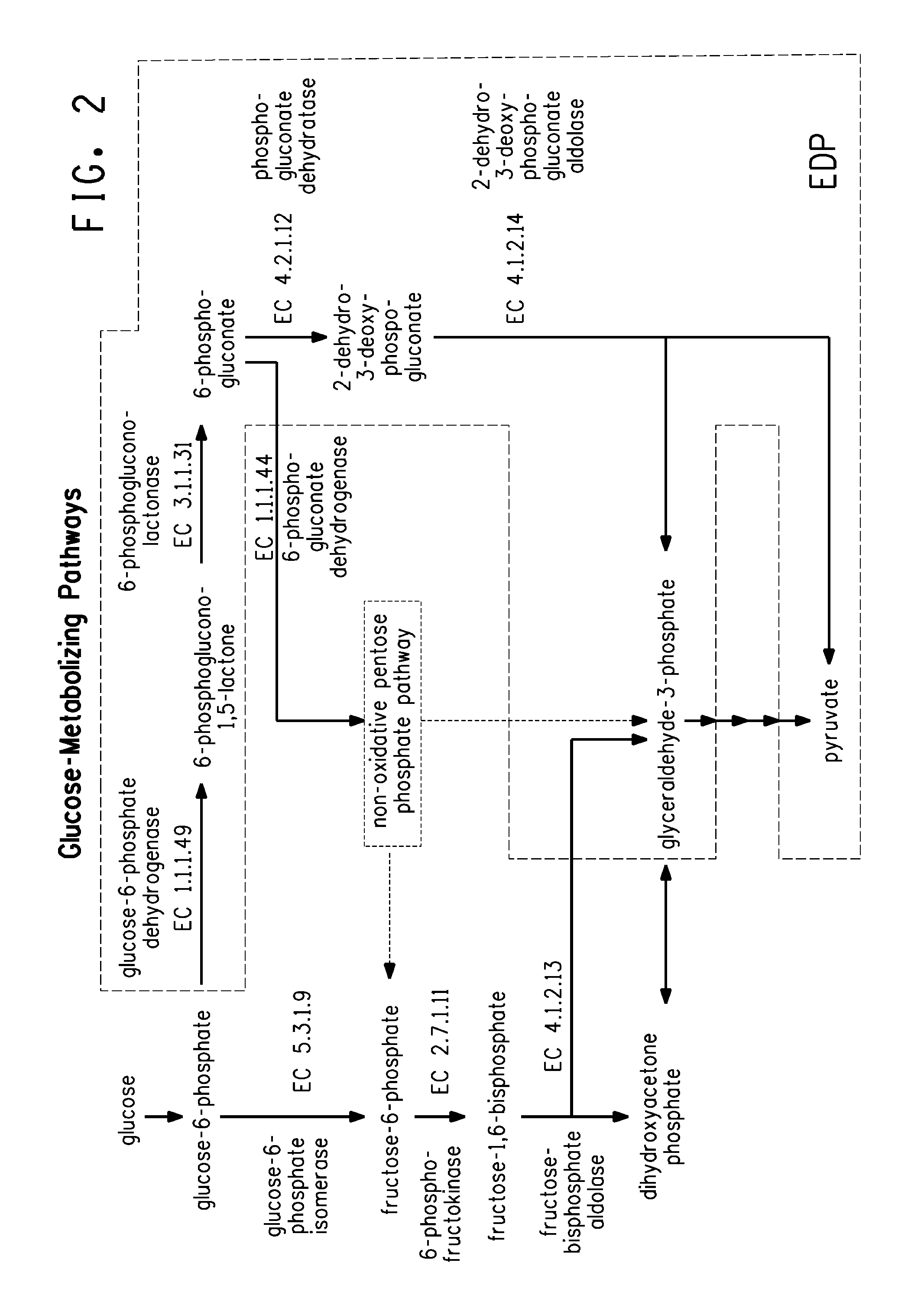
Carbon pathway optimized production hosts for the production of isobutanol
A microbial host cell is provided for the production of isobutanol. Carbon flux in the cell is optimized through the Entner-Doudoroff pathway.
Owner:BUTAMAXTM ADVANCED BIOFUELS
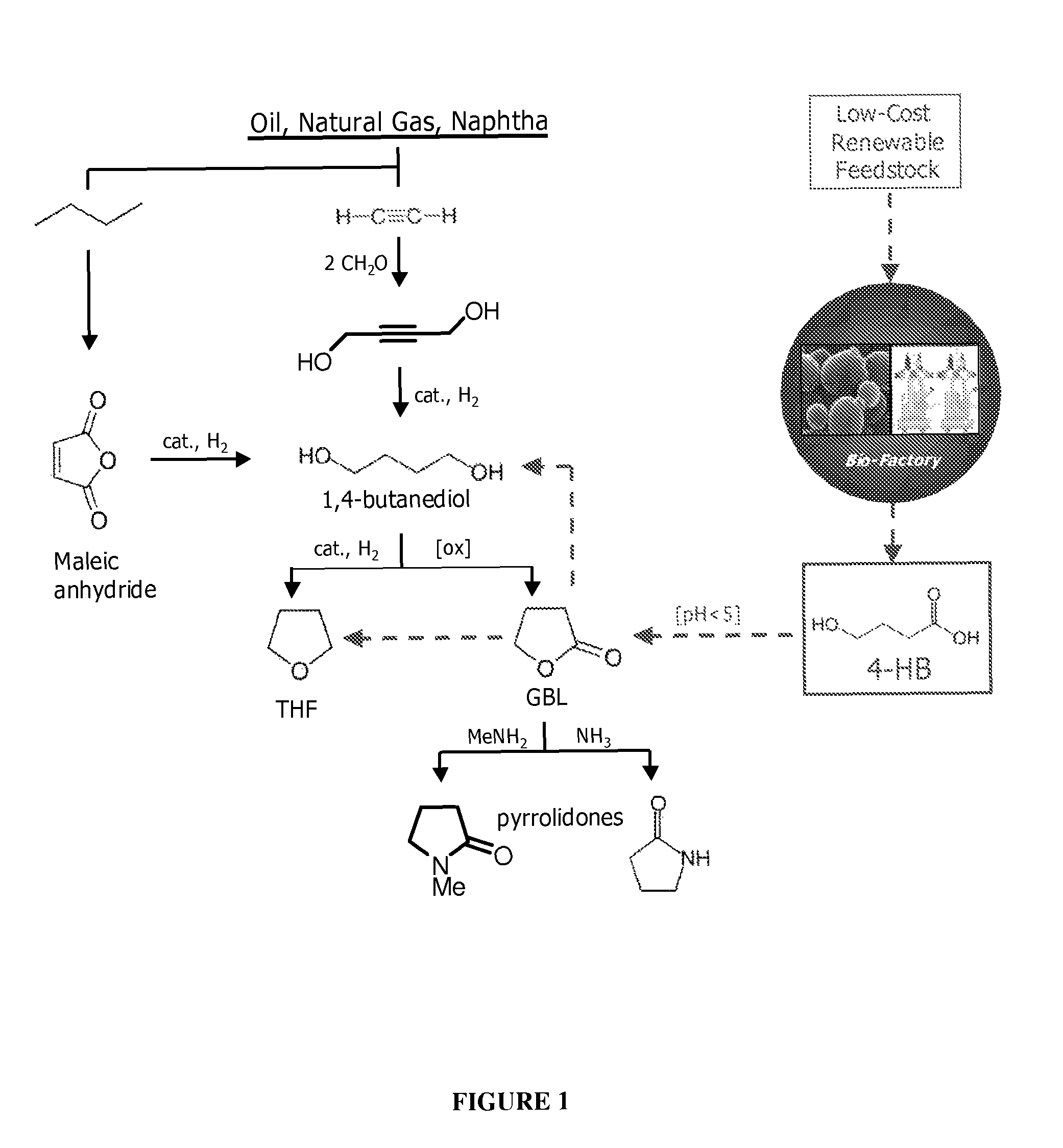
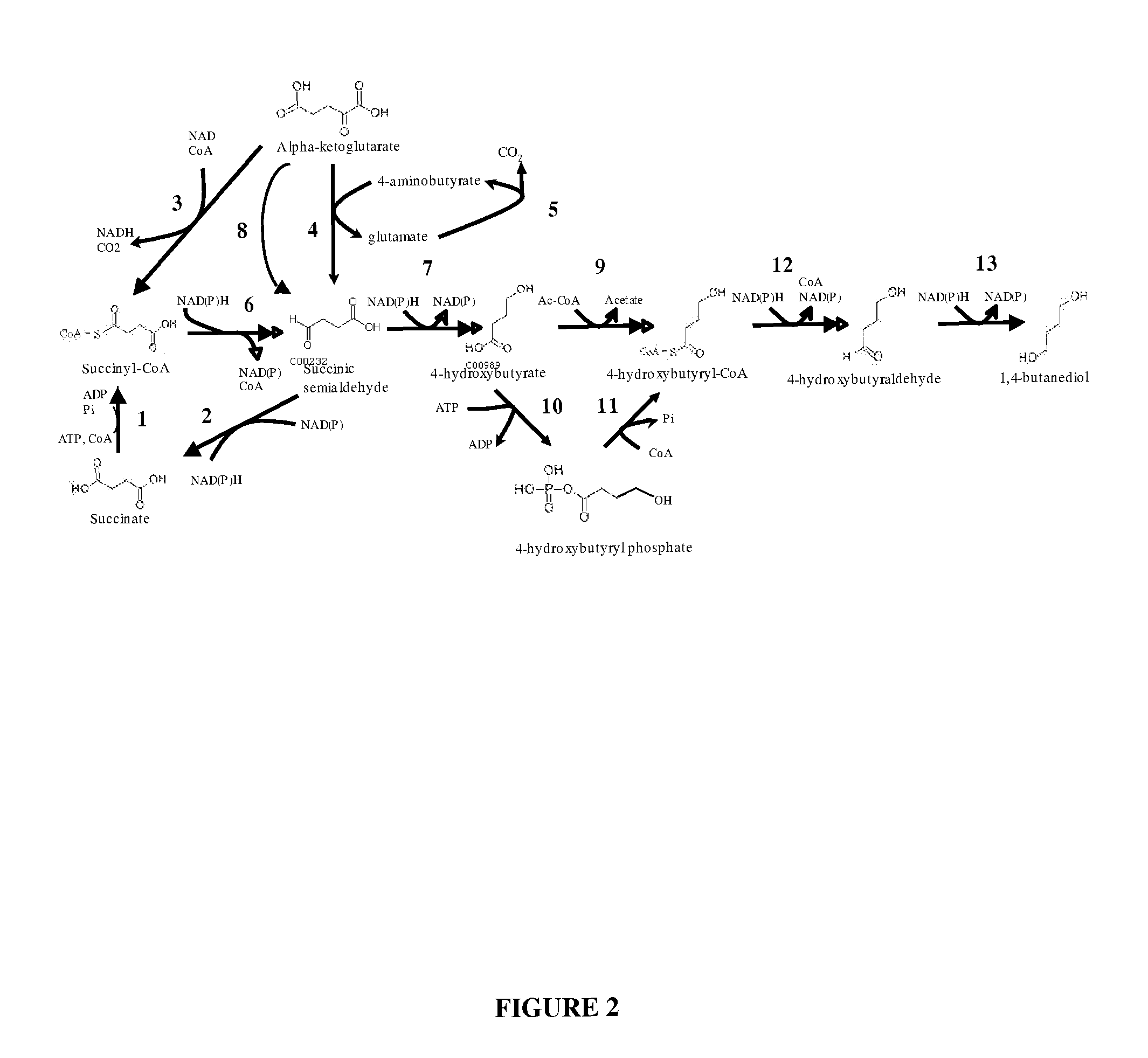
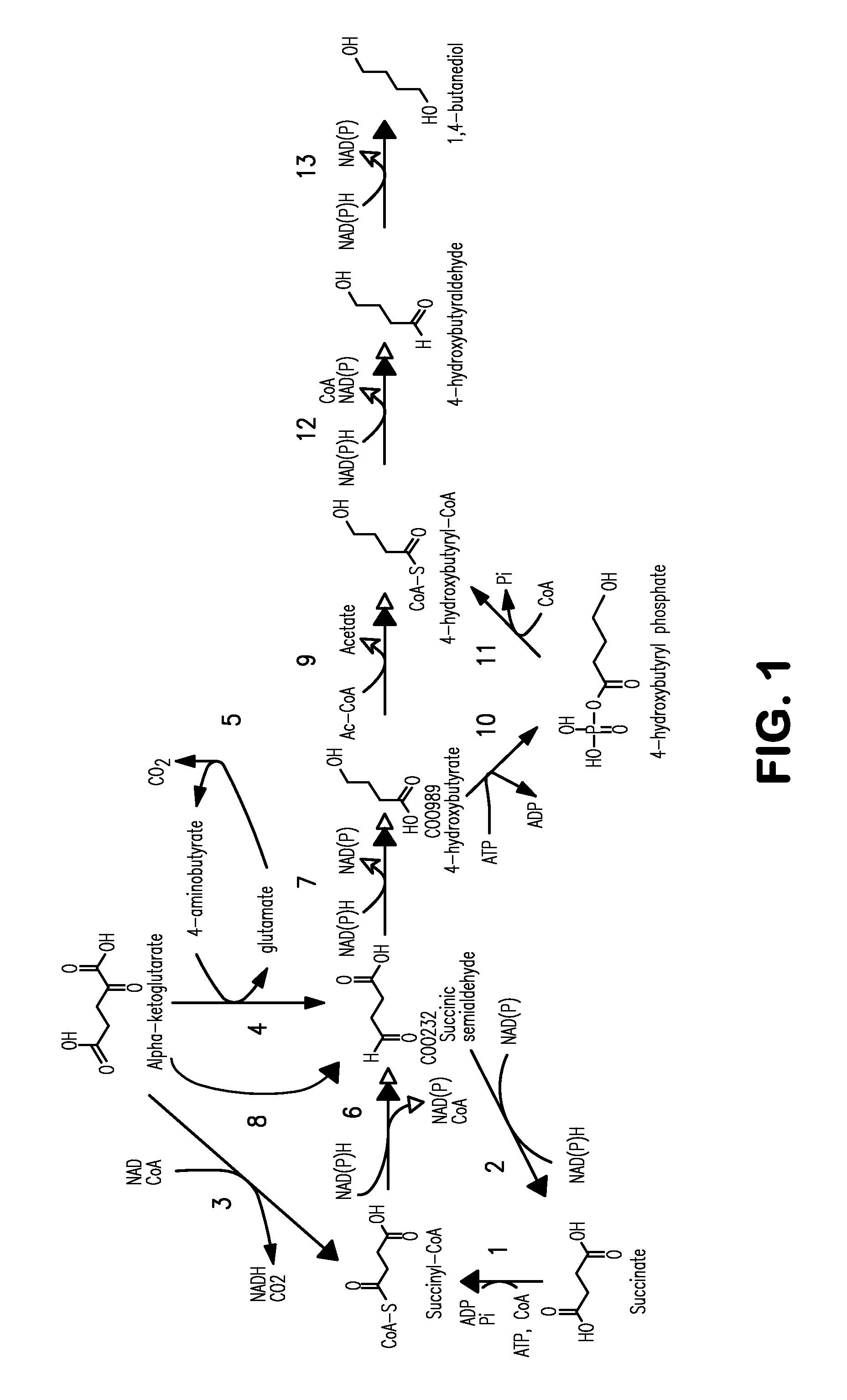
Compositions and methods for the biosynthesis of 1,4-butanediol and its precursors
The invention provides a non-naturally occurring microbial organism having 4-hydroxybutanoic acid (4-HB) and 1,4-butanediol (1,4-BDO) biosynthetic pathways. The pathways include exogenous nucleic acids encoding a) an α-ketoglutarate decarboxylase; b) a 4-hydroxybutanoate dehydrogenase; c) a 4-hydroxybutyryl-CoA:acetyl-CoA transferase or a butyrate kinase and a phosphotransbutyrylase; d) an aldehyde dehydrogenase, and e) an alcohol dehydrogenase, wherein the exogenous nucleic acids are expressed in sufficient amounts to produce 1,4-butanediol (1,4-BDO). Also provide is a method for the production of 1,4-BDO. The method includes culturing the non-naturally occurring microbial organism having 4-HB and 1,4-BDO biosynthetic pathways substantially anaerobic conditions for a sufficient period of time to produce 1,4-BDO.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
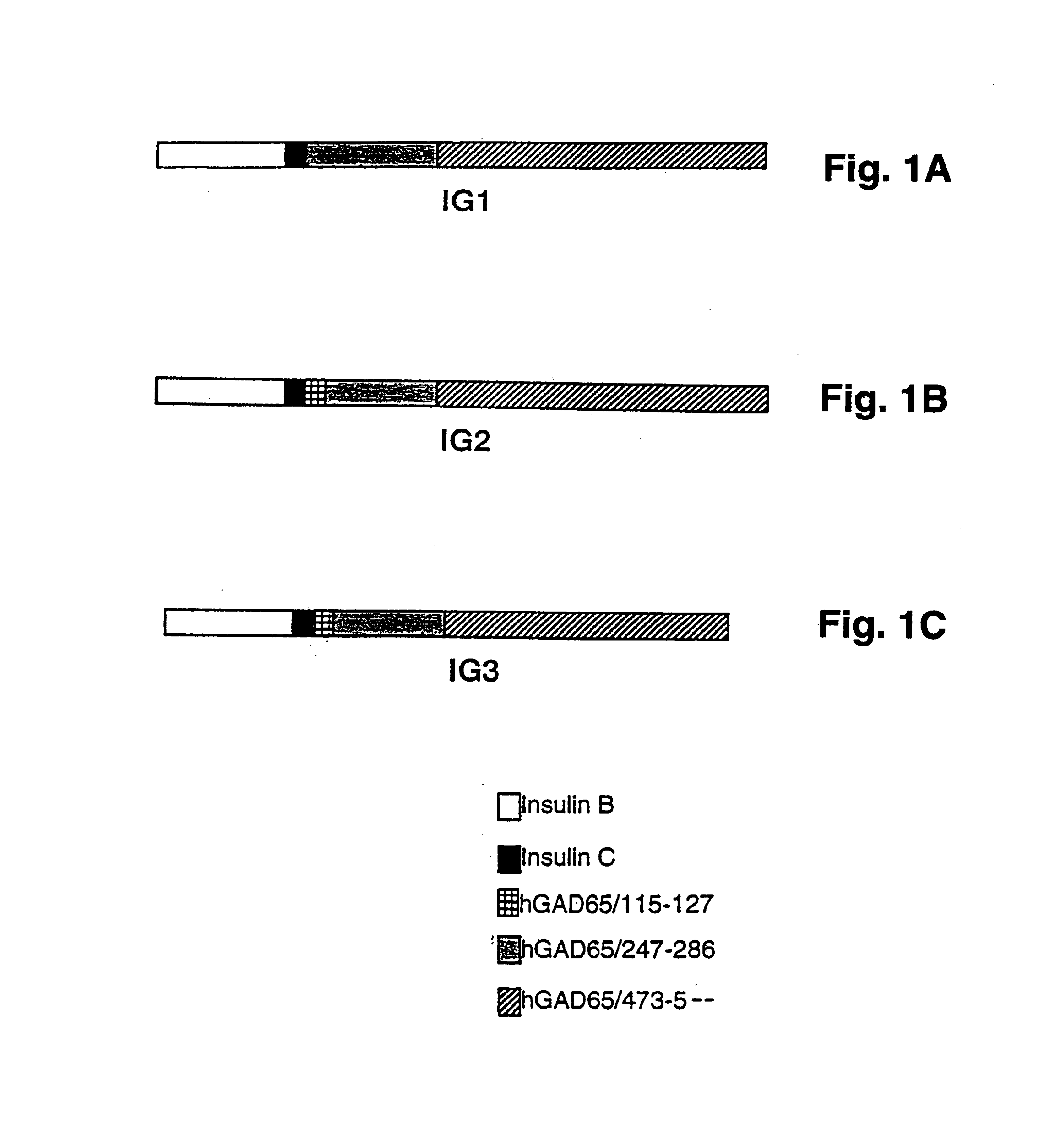
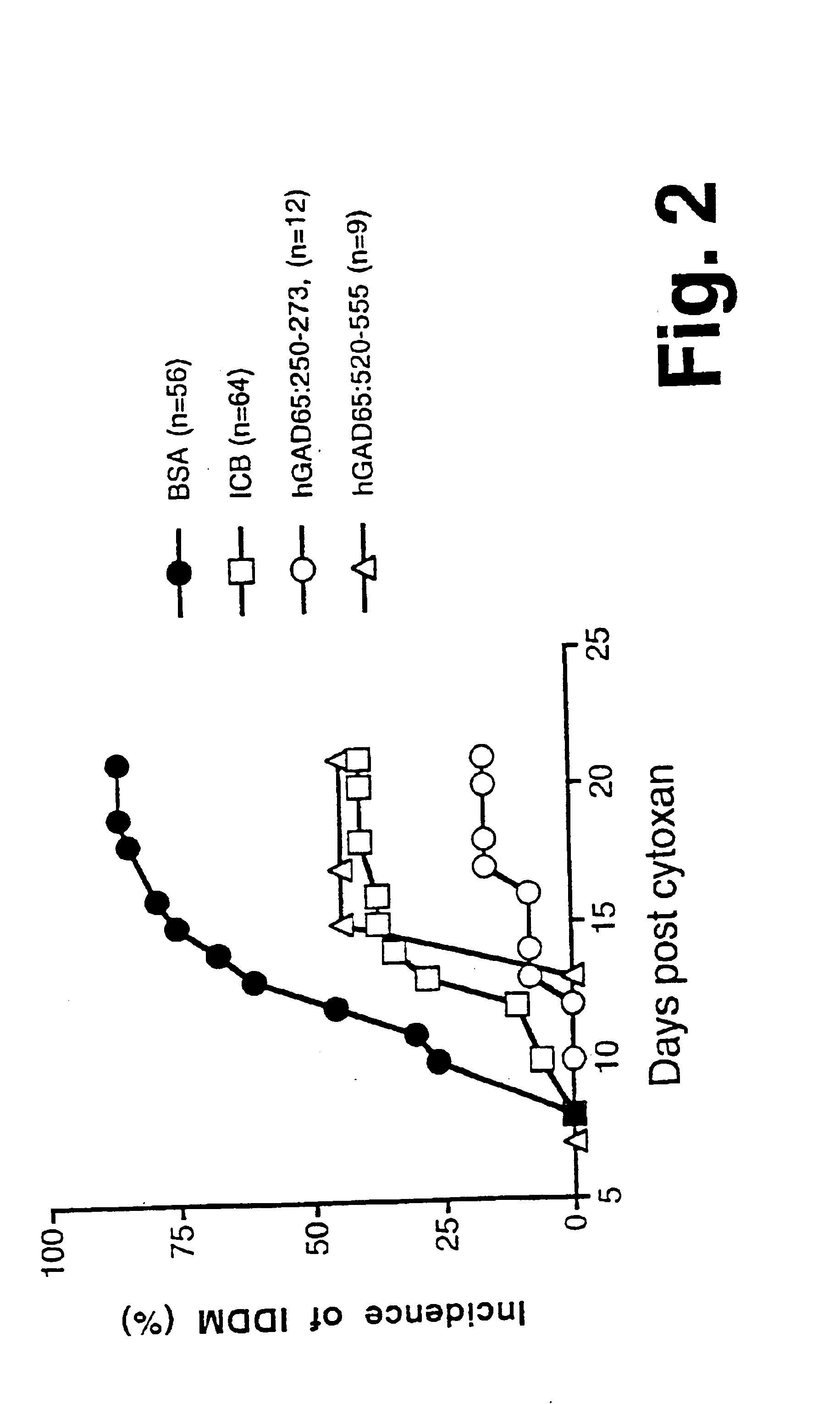
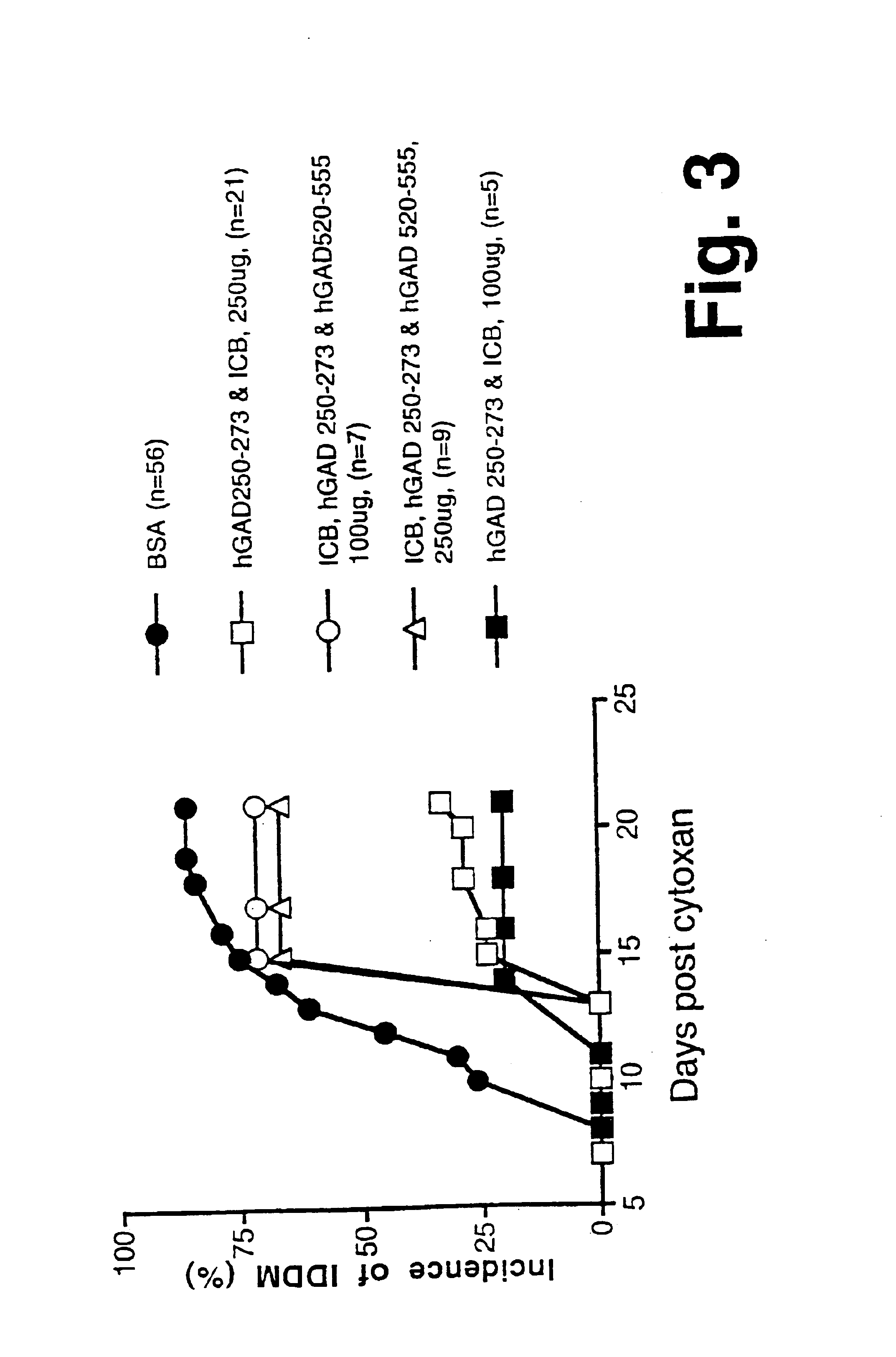
Chimeric proteins for diagnosis and treatment of diabetes
InactiveUS6982323B1Enhance the beneficial effectEasy diagnosisSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunodominant EpitopesPancreas
Novel chimeric fusion proteins comprising immunodominant epitopes of GAD and insulin are provided. Also provided are immunomodulatory methods for the use of such proteins for both the prevention and treatment of Type 1 diabetes mellitus. The chimeric fusion proteins of the invention are useful in predicting risk of onset of Type 1 diabetes, determining prognosis of Type 1 diabetes patients early in disease progression, and in evaluating patients for suitability as recipients of transplants of pancreatic cells or tissues. The administration of the proteins of the invention in accordance with the immunomodulatory methods of the invention results in beneficial effects on disease development and severity in patients suffering from or predicted to be at risk of developing Type 1 diabetes, as well as on the outcome of transplants of pancreatic cells or tissues in Type 1 diabetes patients.
Owner:ALEXION PHARMA INC
Convection-enhanced delivery of AAV vectors
InactiveUS20020141980A1Efficient deliveryEfficient expressionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseConvection-Enhanced Delivery
Methods of delivering viral vectors, particularly recombinant AAV virions, to the CNS are provided. Also provided are methods of treating Parkinson's Disease.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Use of phosphoketolase for producing useful metabolites
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
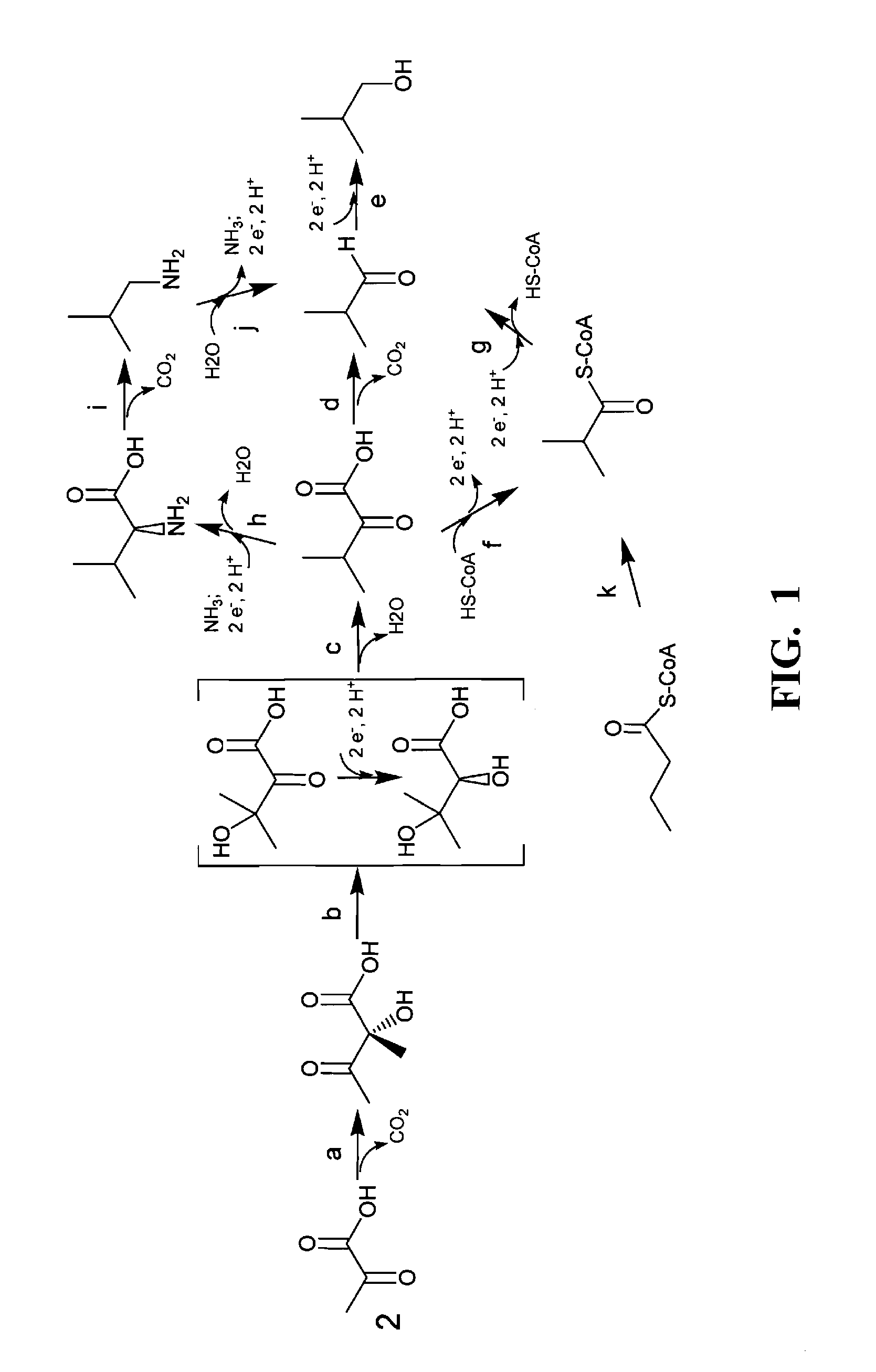
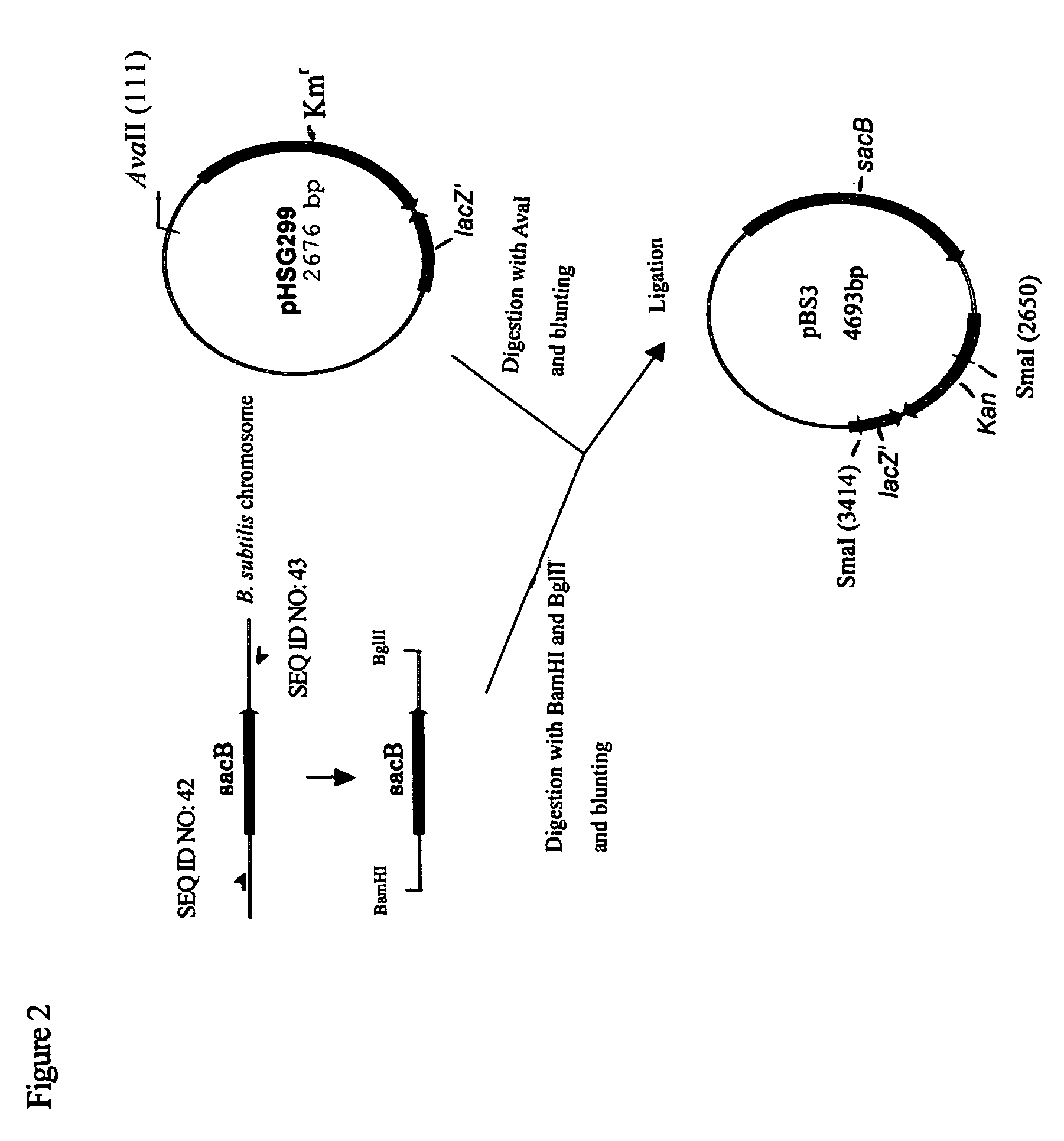
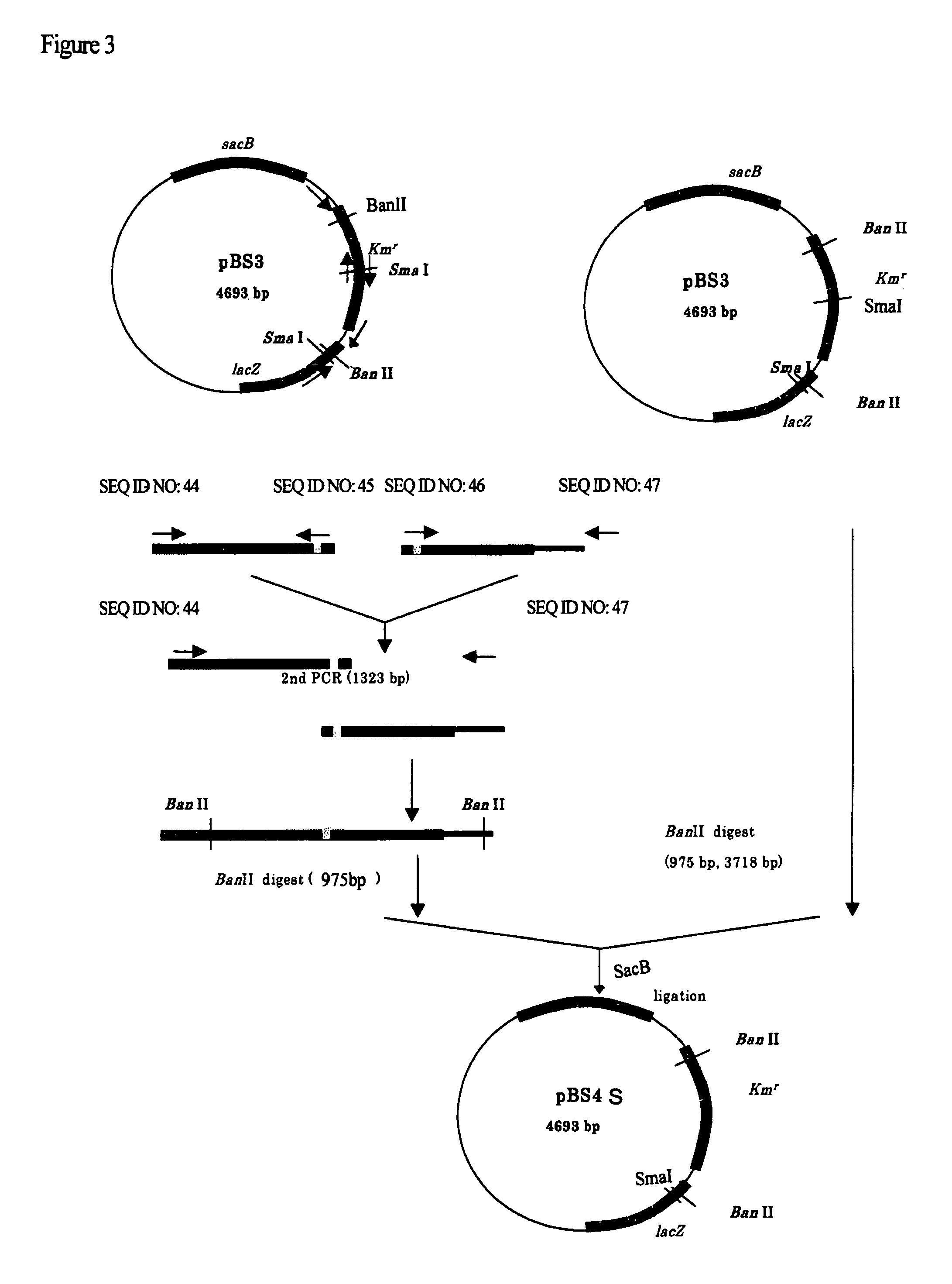
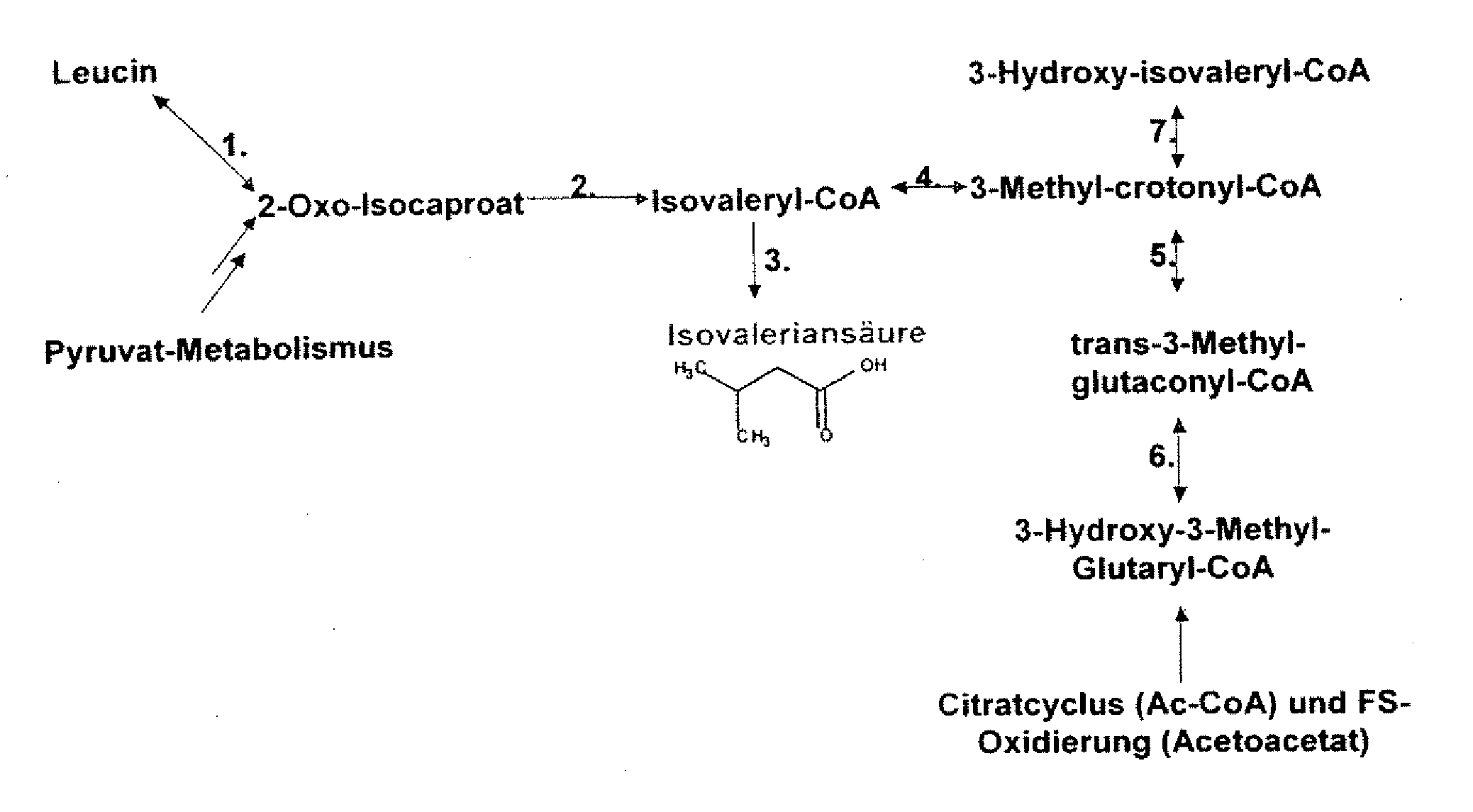
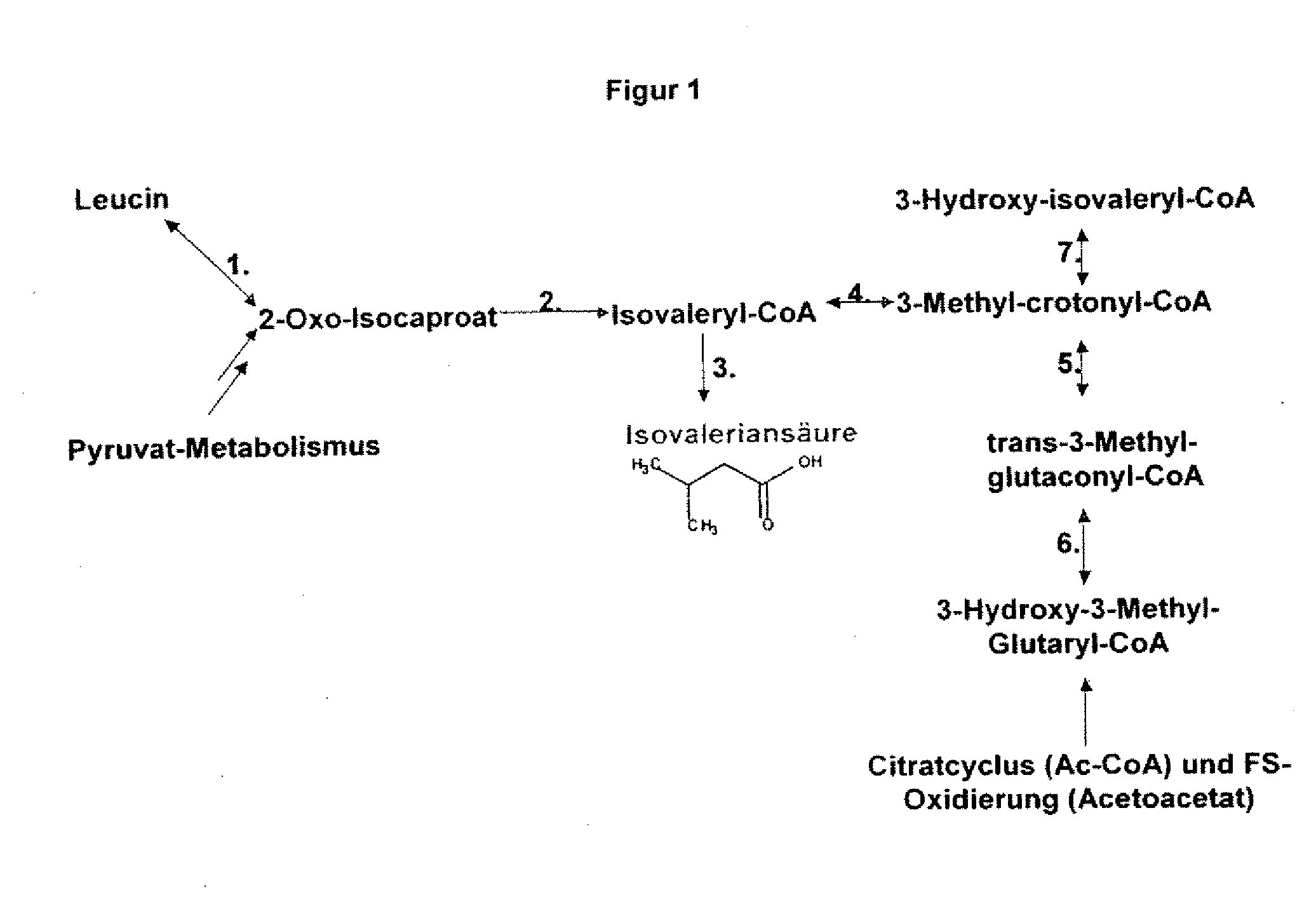
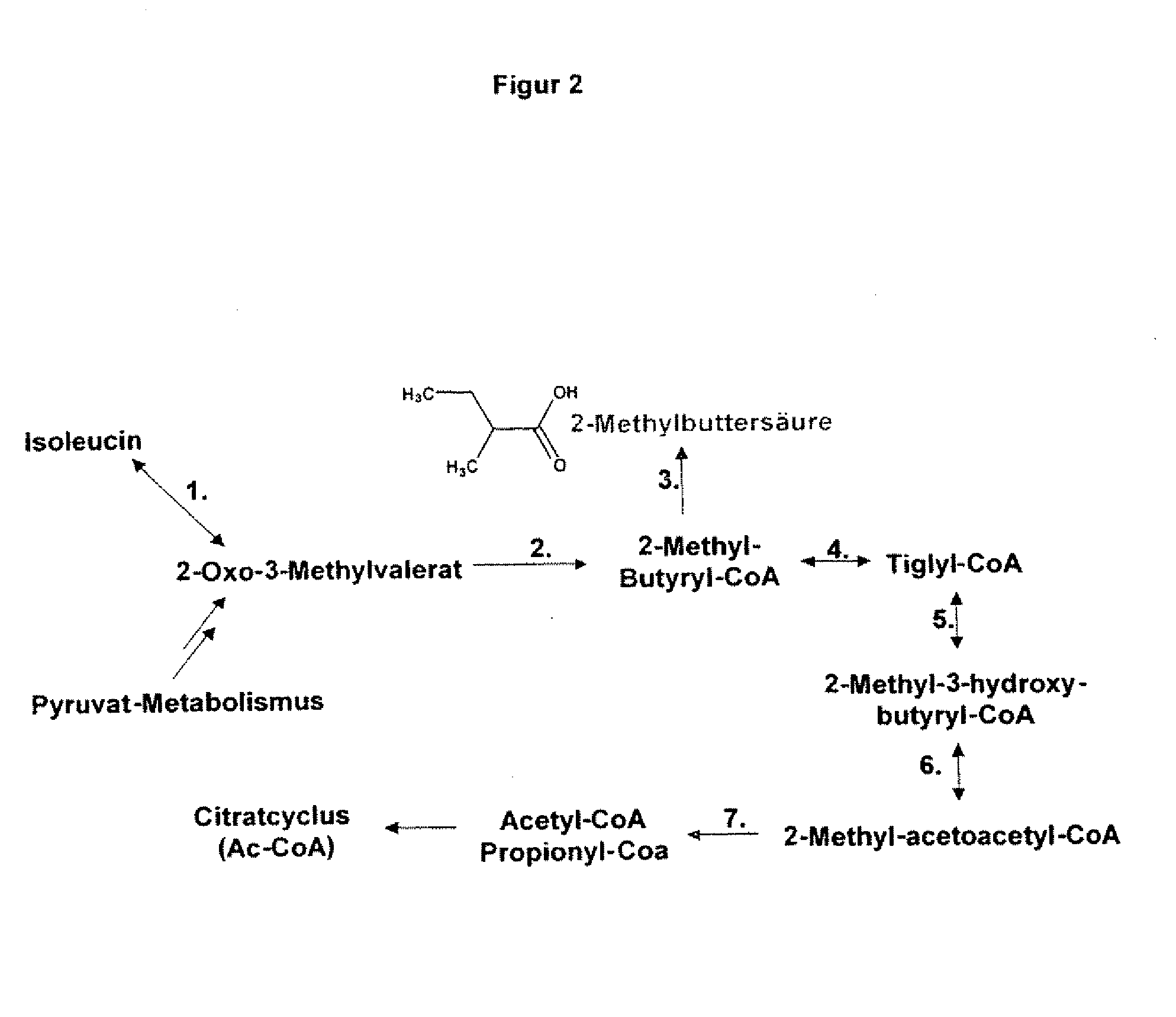
Gene products of bacillus licheniformis which form odorous substances and improved biotechnological production methods based thereon
InactiveUS20070190605A1Reduce formationImprove filtering effectBacteriaHydrolasesBacillus licheniformisPropanoic acid
The present invention relates to 25 hitherto undescribed genes of B. licheniformis and gene products derived therefrom and all sufficiently homologous nucleic acids and proteins thereof. They occur in five different metabolic pathways for the formation of odorous substances. The metabolic pathways in question are for the synthesis of: 1) isovalerian acid (as part of the catabolism of leucine), 2) 2-methylbutyric acid and / or isobutyric acid (as part of the catabolism of valine and / or isoleucine), 3) butanol and / or butyric acid (as part of the metabolism of butyric acid), 4) propyl acid (as part of the metabolism of propionate) and / or 5) cadaverine and / or putrescine (as parts of the catabolism of lysine and / or arginine). The identification of these genes allows biotechnological production methods to be developed that are improved to the extent that, to assist these nucleic acids, the formation of the odorous substances synthesized via these metabolic pathways can be reduced by deactivating the corresponding genes in the micro-organism used for the biotechnological production. In addition, these gene products are thus available for preparing reactions or for methods according to their respective biochemical properties.
Owner:BASF AG
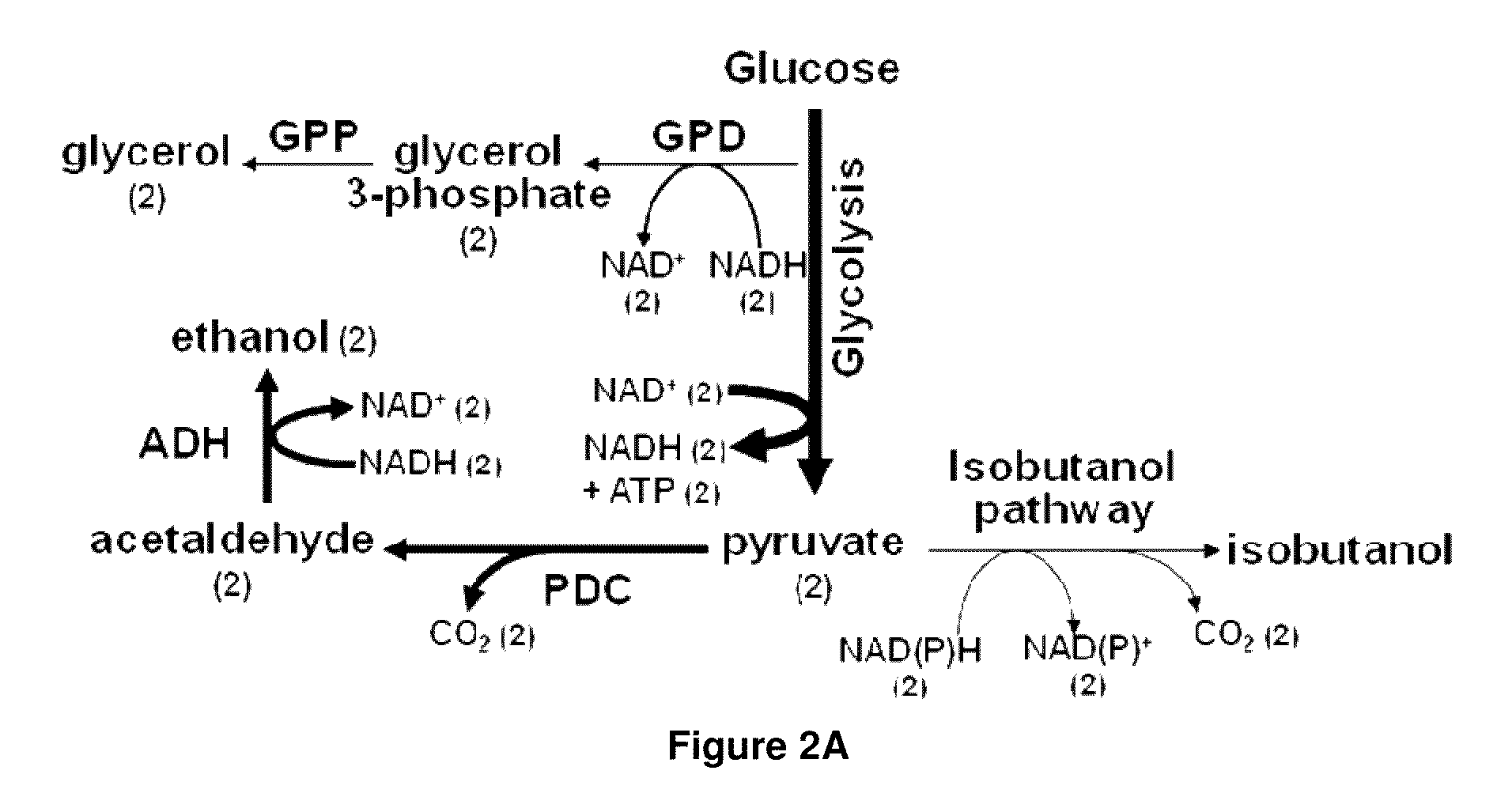
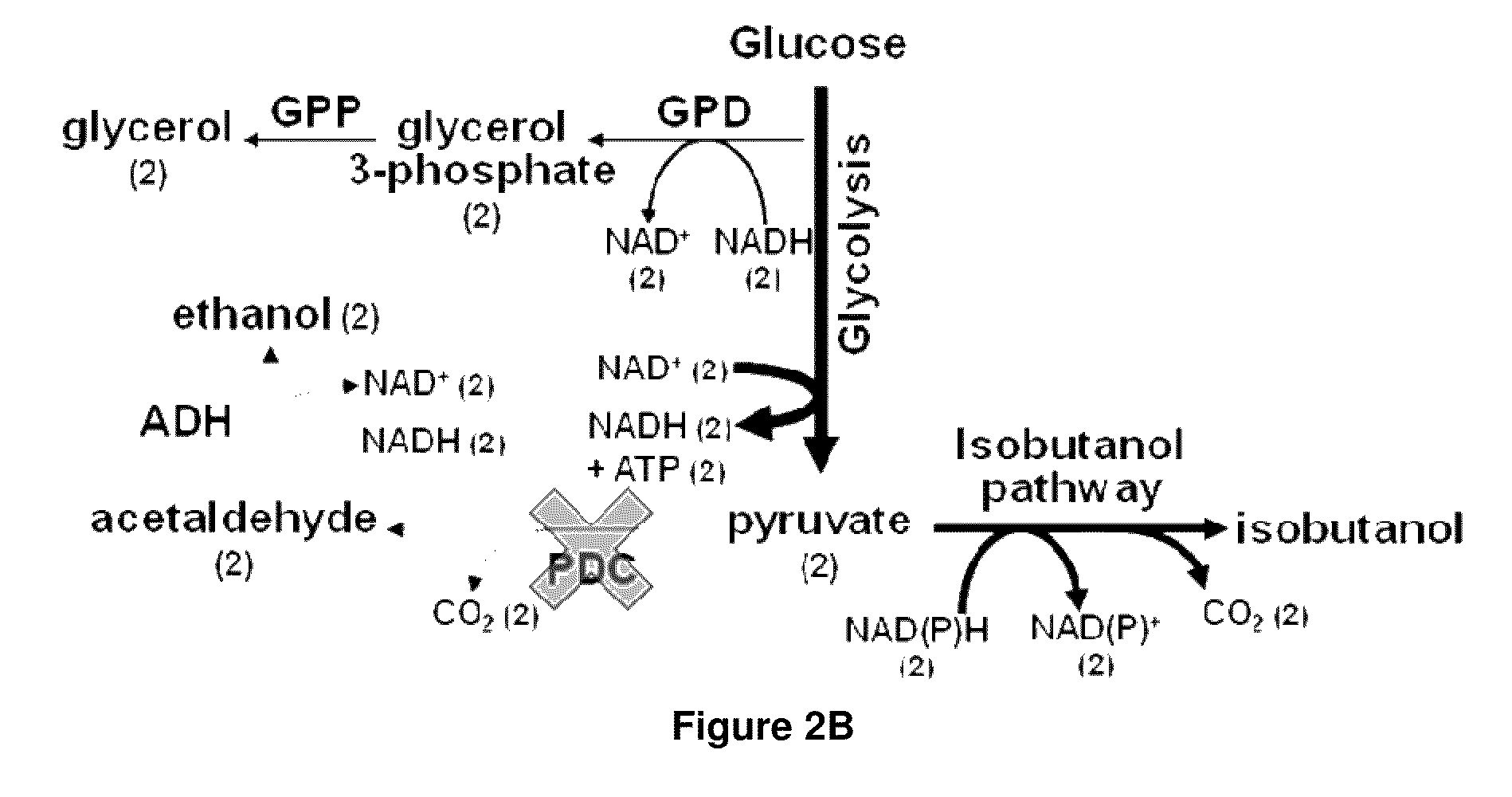
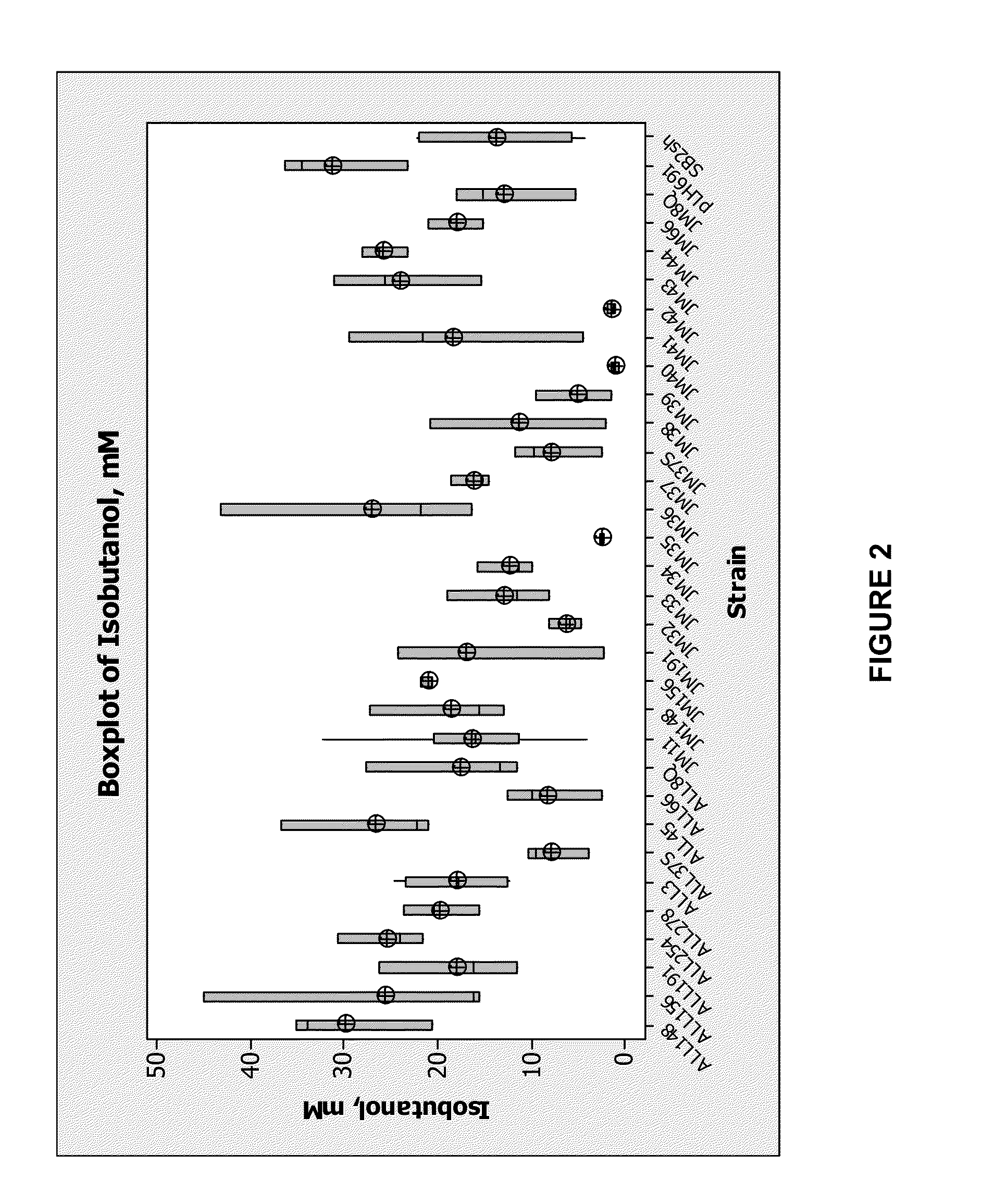
Yeast organism producing isobutanol at a high yield
InactiveUS20090226991A1Reduction of pyruvate decarboxylase activityReduce transcriptionFungiBiofuelsBiotechnologyMicroorganism
There is disclosed a method of producing isobutanol. In an embodiment, the method includes providing a microorganism transformed with an isobutanol producing pathway containing at least one exogenous gene. The microorganism is selected to produce isobutanol from a carbon source at a yield of at least 10 percent theoretical. The method includes cultivating the microorganism in a culture medium containing a feedstock providing the carbon source, until isobutanol is produced. The method includes recovering the isobutanol. In one embodiment, the microorganism is a yeast with a Crabtree-negative phenotype. In another embodiment, the microorganism is a yeast microorganism with a Crabtree-positive phenotype. There is disclosed a microorganism for producing isobutanol. In an embodiment, the microorganism includes an isobutanol producing pathway containing at least one exogenous gene, and is selected to produce a recoverable quantity of isobutanol from a carbon source at a yield of at least 10 percent theoretical.
Owner:GEVO INC
Methods of identifying and creating rubisco large subunit variants with improved rubisco activity, compositions and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20080256666A1Increased Rubisco activityImprove productivitySugar derivativesUnicellular algaeRuBisCO activityAmino acid substitution
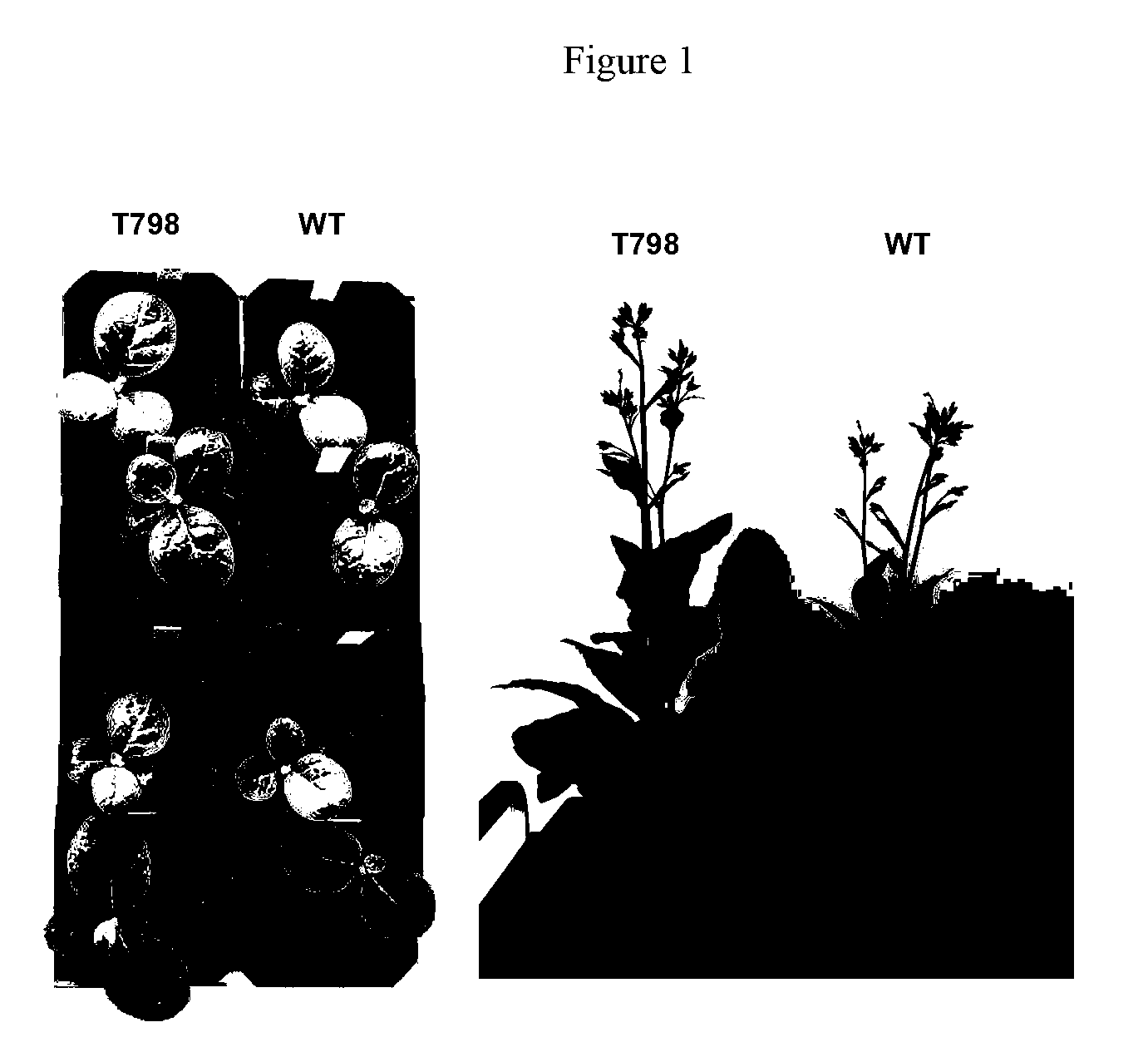
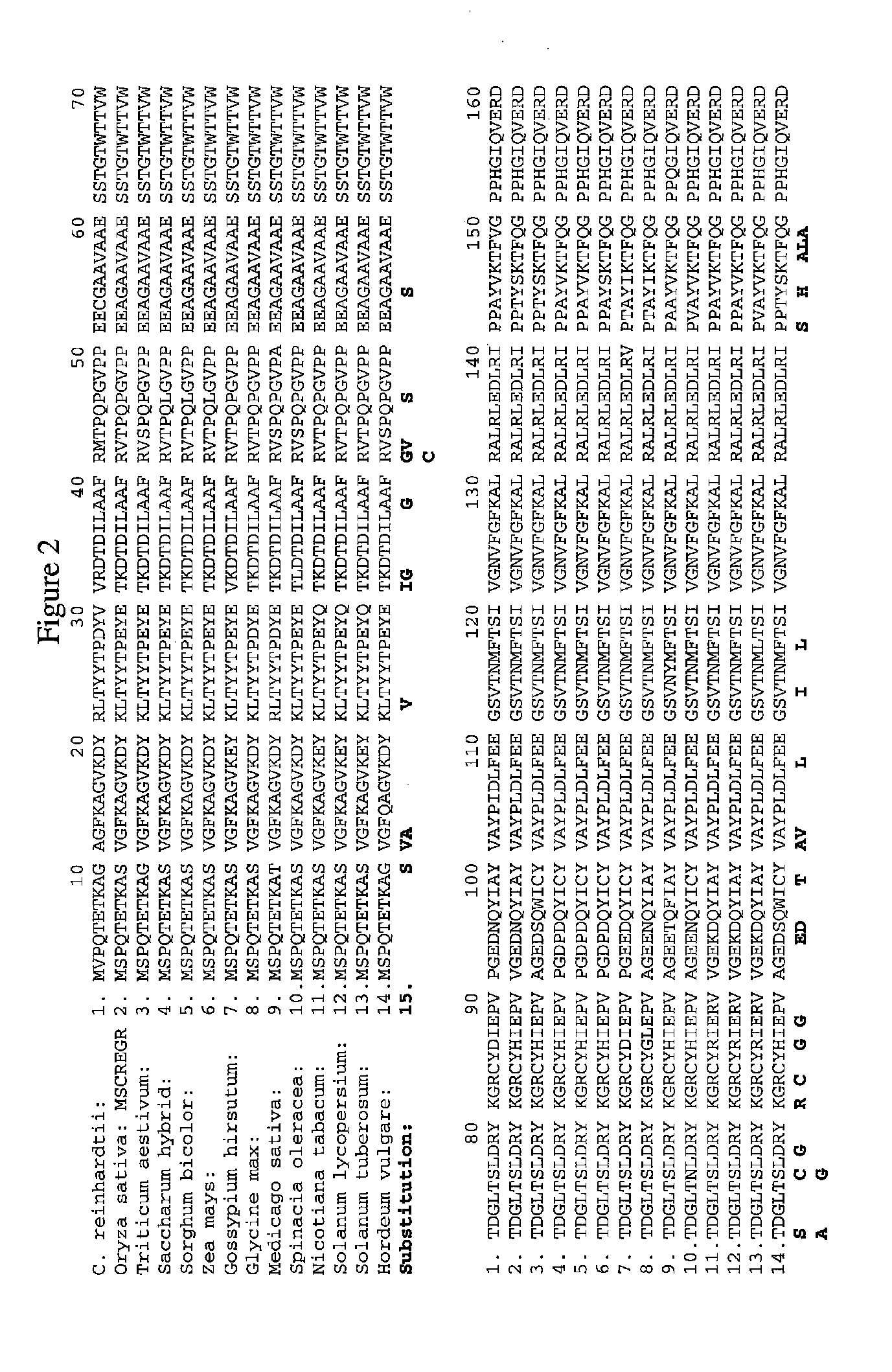
Methods for identifying one or more amino acid substitutions in a Rubisco large subunit polypeptide (variant) that confer increased Rubisco activity in a unicellular photosynthetic organism and transferring those substitutions to a Rubisco large subunit polypeptide of a higher plant cell are described herein. Methods and compositions for modulating plant productivity using the modified Rubisco large subunit polypeptide variants are provided. The Rubisco large subunit sequences are used in a variety of methods including increasing plant productivity in a plant. Transformed plants, plant cell, tissues, seed, and expression vectors are also provided.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Methods and compositions for producing hydrocarbons
Owner:GENOMATICA INC +1
Yeast organism producing isobutanol at a high yield
The present invention provides recombinant mircoorganisms comprising an isobutanol producing metabolic pathway and methods of using said recombinant microorganisms to produce isobutanol. In various aspects of the invention, the recombinant microorganisms may comprise a modification resulting in the reduction of pyruvate decarboxylase and / or glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase activity. In various embodiments described herein, the recombinant microorganisms may be microorganisms of the Saccharomyces clade, Crabtree-negative yeast microorganisms, Crabtree-positive yeast microorganisms, post-WGD (whole genome duplication) yeast microorganisms, pre-WGD (whole genome duplication) yeast microorganisms, and non-fermenting yeast microorganisms.
Owner:GEVO INC
Methods and compositions for producing hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20100221798A1Easy to separateIncrease valueBacteriaOrganic compound preparationBiofuelAlkene
Owner:LS9 INC +1
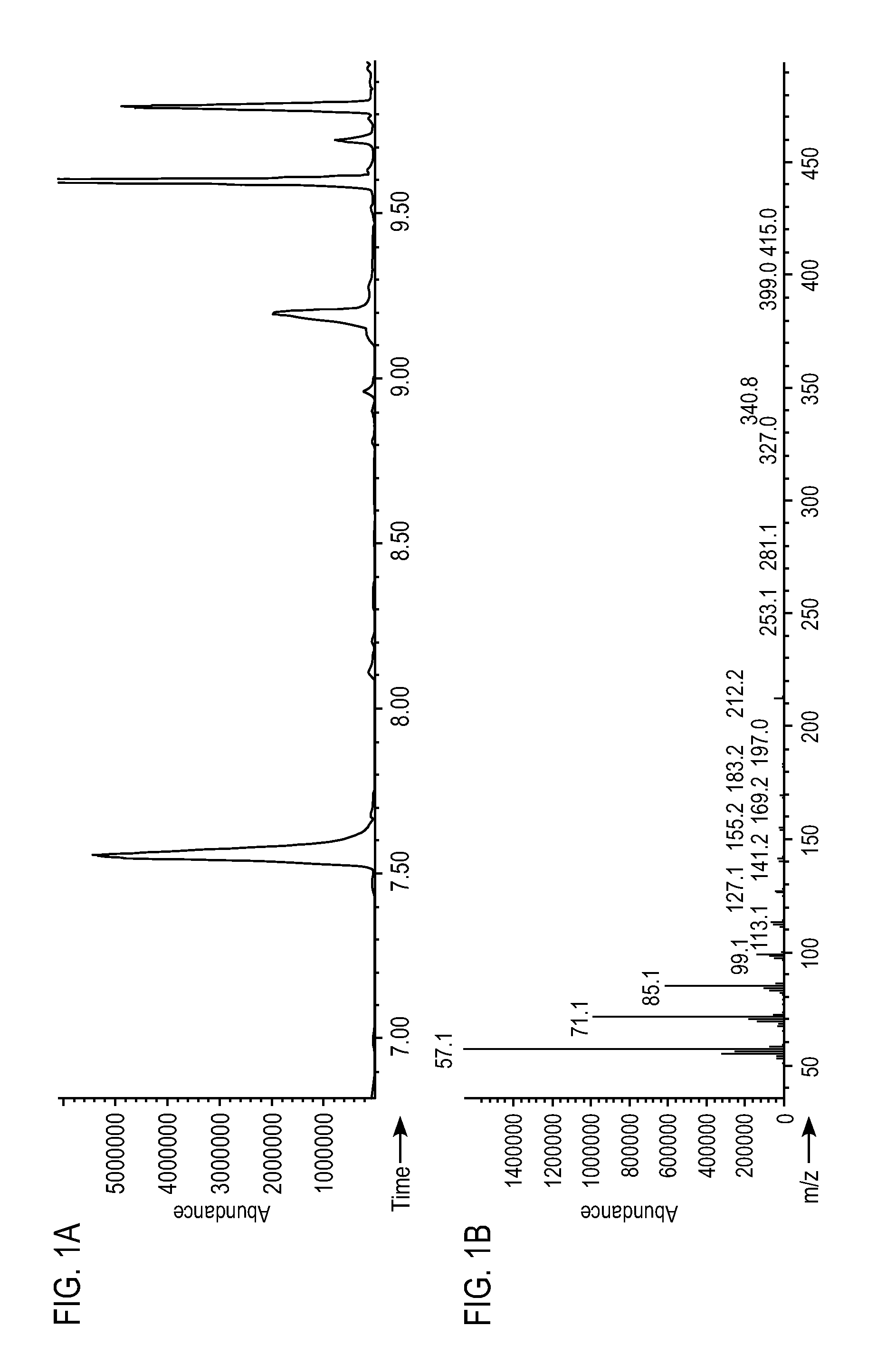
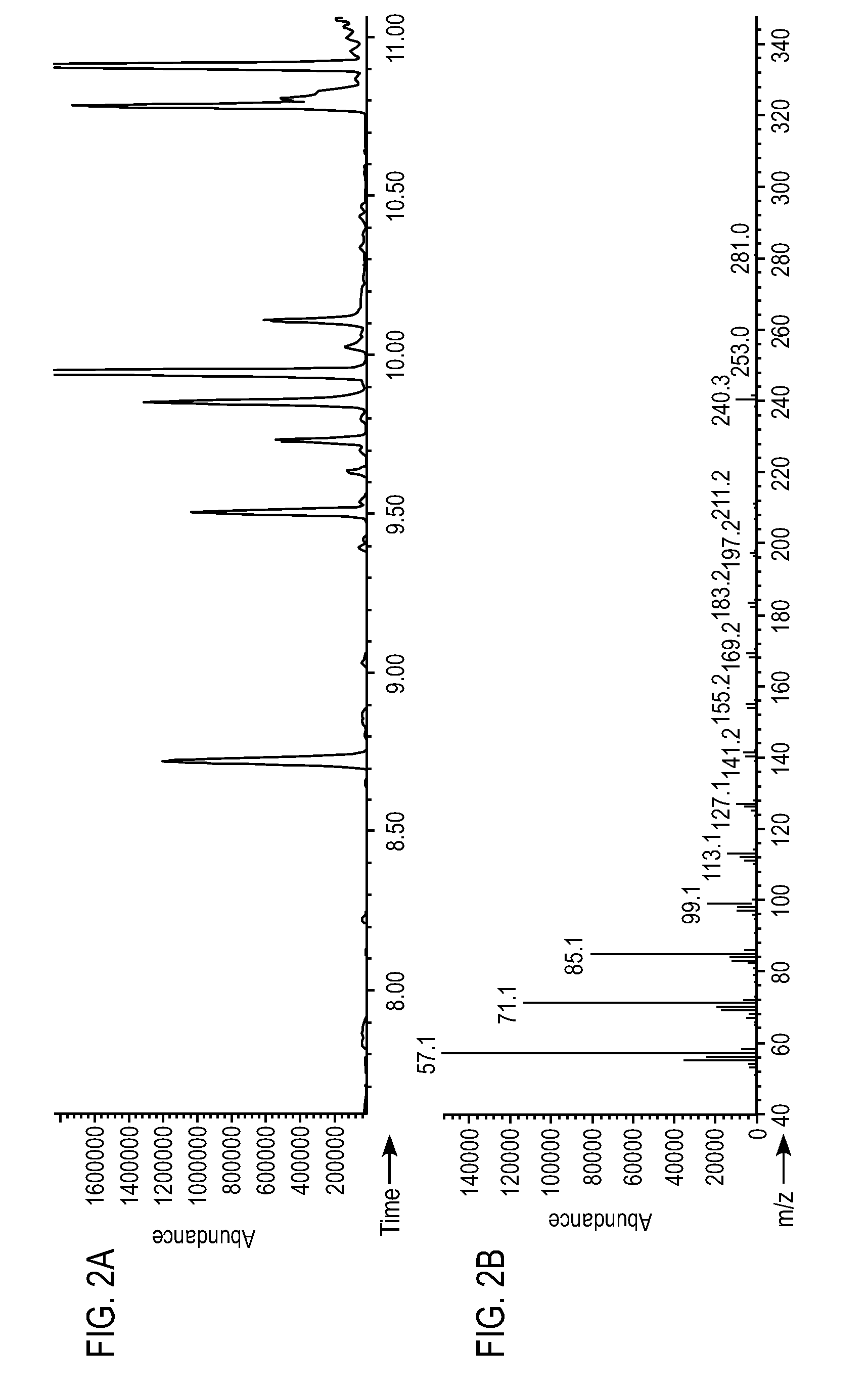
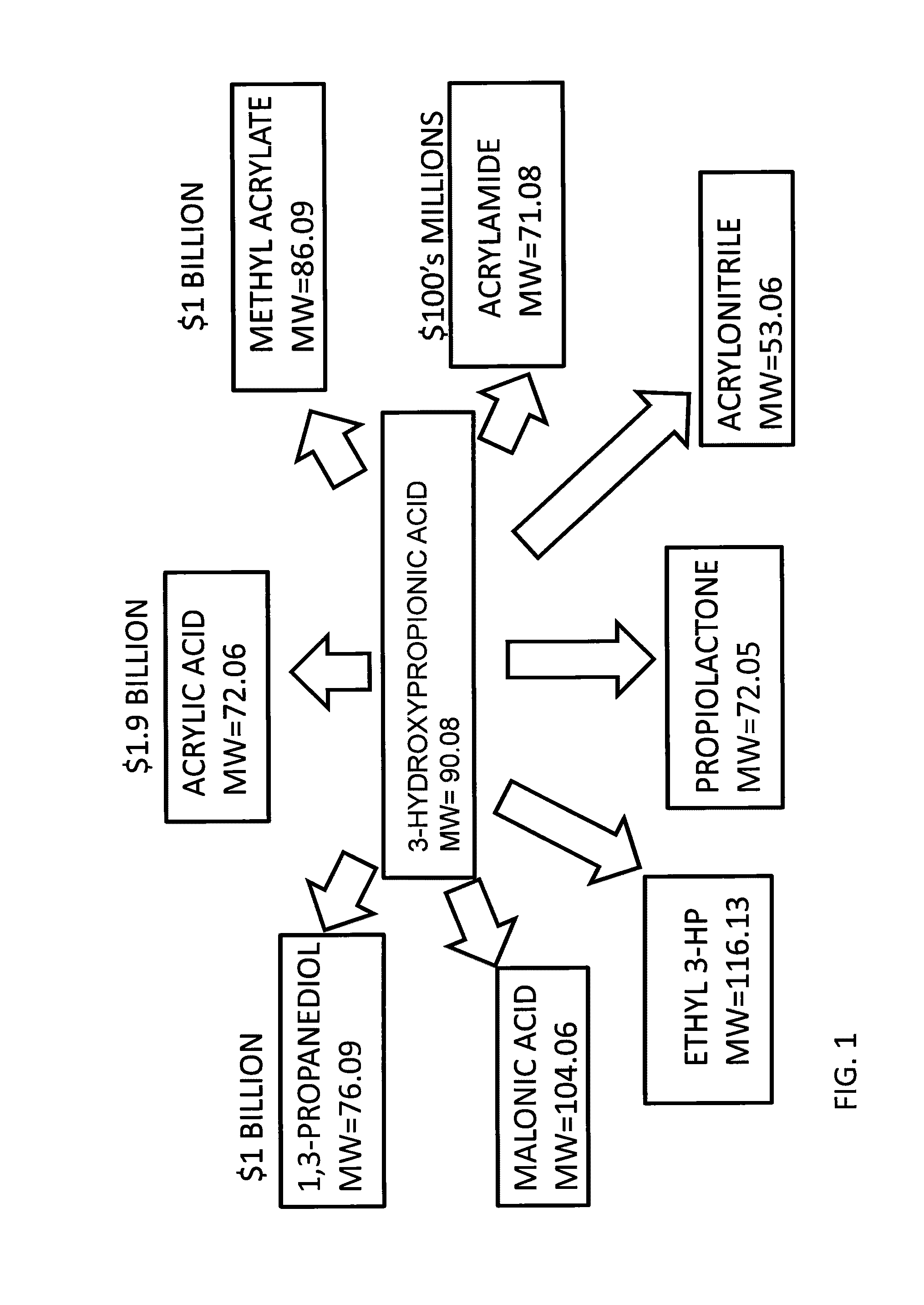
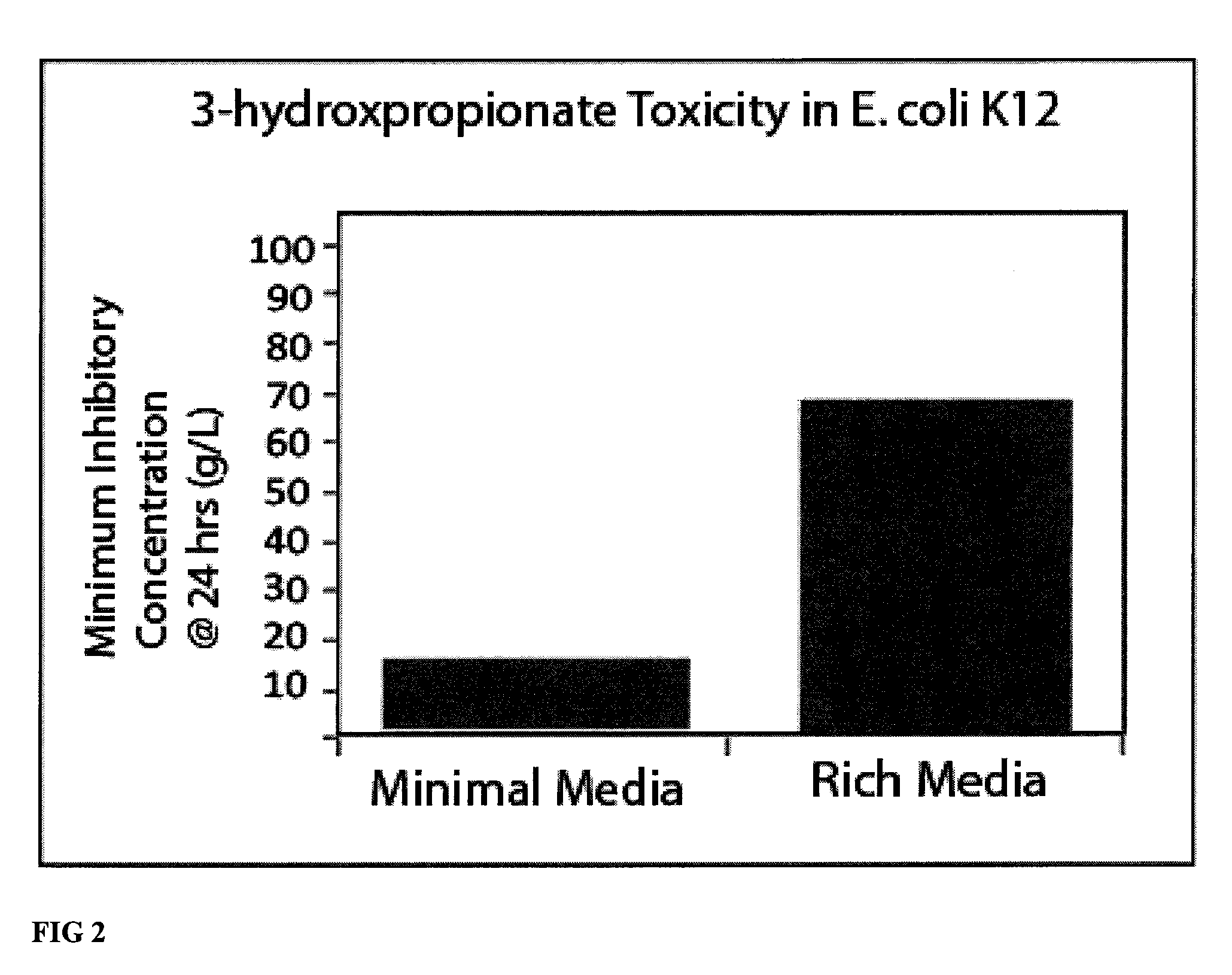
Compositions and methods for 3-hydroxypropionate bio-production from biomass
ActiveUS8048624B1BacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurement3-Hydroxypropionic acidDecarboxylase activity
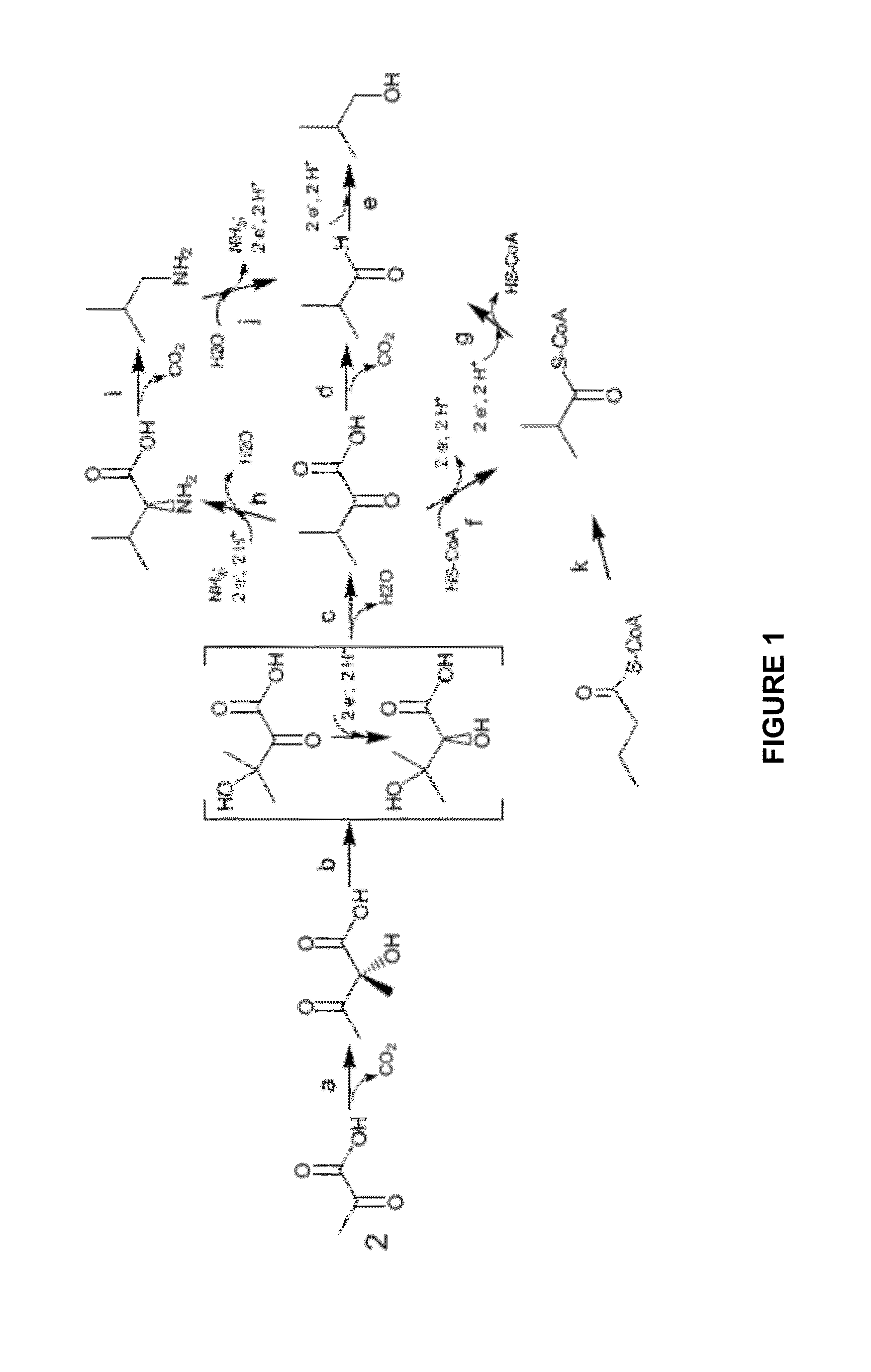
Methods of obtaining mutant nucleic acid sequences that demonstrate elevated oxaloacetate α-decarboxylase activity are provided. Compositions, such as genetically modified microorganisms that comprise such mutant nucleic acid sequences, are described, as are methods to obtain the same.
Owner:OPX BIOTECH
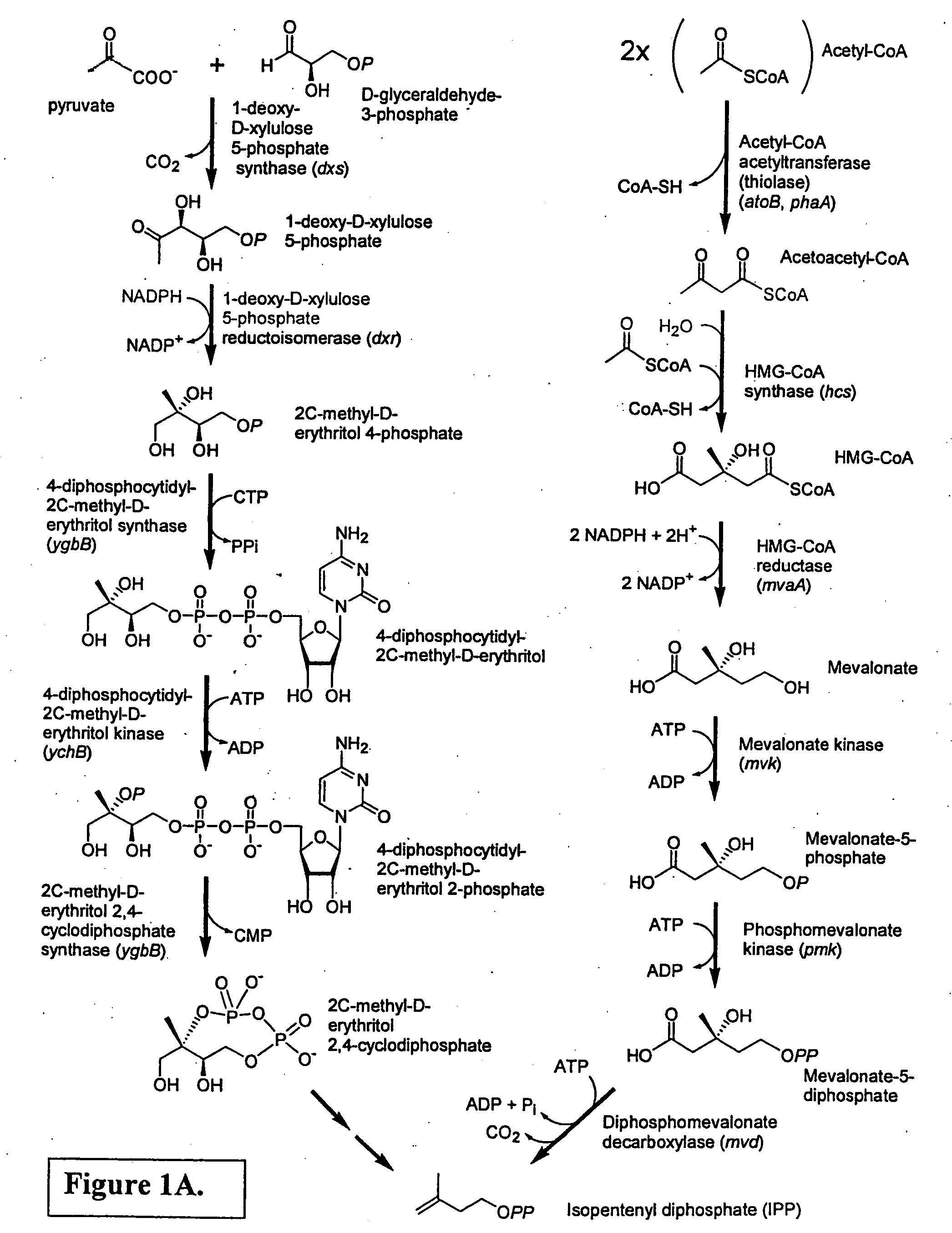
Isoprenoid production
Owner:DSM NUTRITIONAL PROD +1
Compositions and methods for producing isoprene
The invention features methods for producing isoprene from cultured cells. The invention also provides compositions that include these cultured cells.
Owner:DANISCO US INC +1
Acetate supplemention of medium for butanologens
The invention relates to the fields of industrial microbiology and alcohol production. More specifically, the invention relates to improved production of butanol isomers by recombinant microorganisms containing an engineered butanol pathway and disrupted activity of the genes in pathways for the production of by-products during the fermentation when the microorganisms are grown in a fermentation medium containing acetate. In embodiments, recombinant microorganisms have an increased growth rate in a fermentation medium containing acetate as a C2 supplement.
Owner:GEVO INC
Isoprenoid production
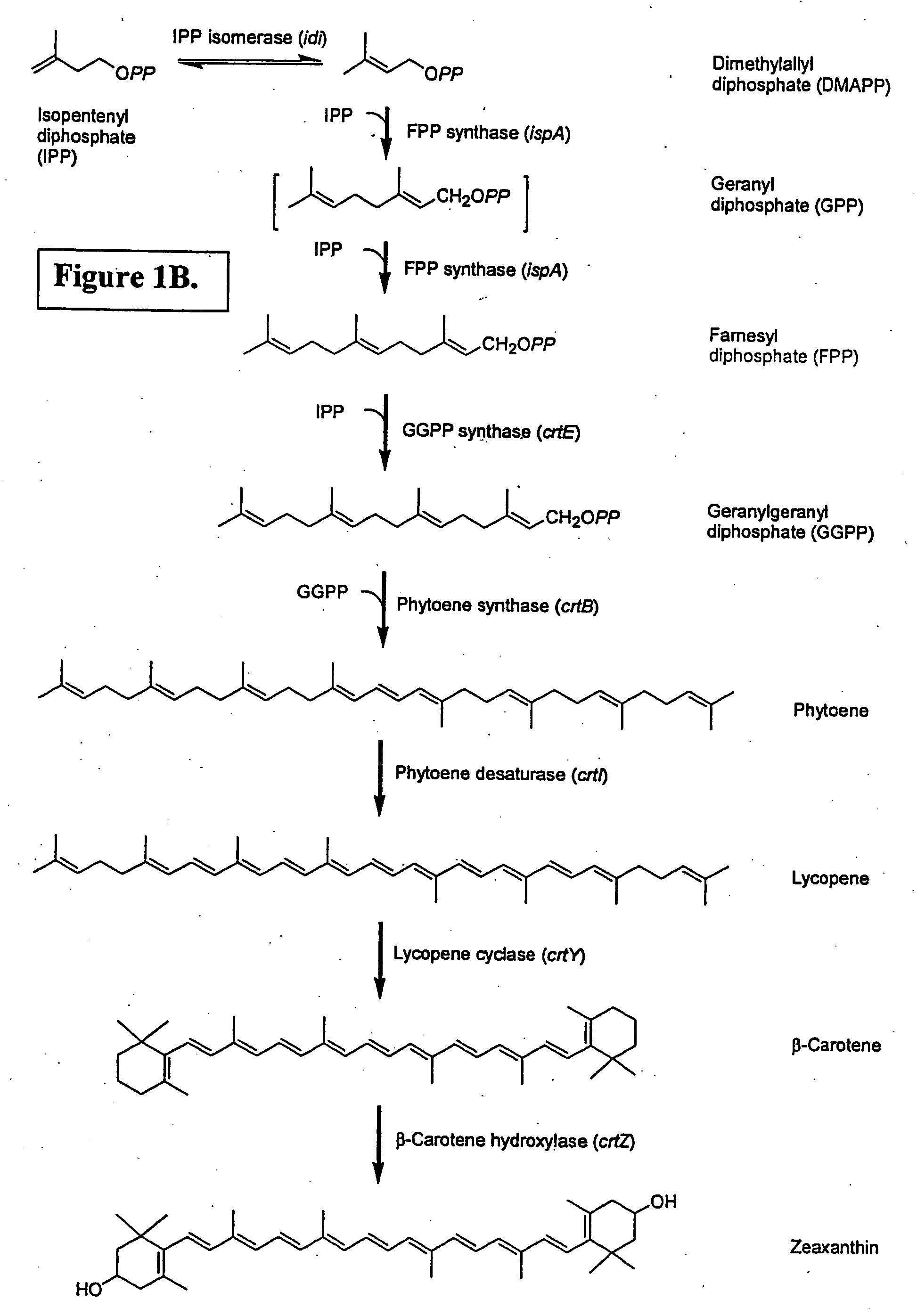
Isolated polynucleotides encoding polypeptides having the activity of enzymes in the mevalonate pathway are provided. These sequences are useful for recombinantly producing isoprenoid compounds, such as carotenoids, in particular zeaxanthin. Expression vectors, cultured cells, and methods of making isoprenoid compounds are also provided.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Polypeptides with Ketol-Acid Reductoisomerase Activity
ActiveUS20140093930A1Reduced and eliminated acetolactate reductase activityReduced and eliminated dehydrogenase activitySugar derivativesMicroorganismsIsobutanolBiochemistry
Polypeptides having ketol-acid reductoisomerase activity are provided. Also disclosed are recombinant host cells comprising isobutanol biosynthetic pathways employing such polypeptides. Methods for producing isobutanol employing host cells comprising the polypeptides having ketol-acid reductoisomerase activity are also disclosed.
Owner:GEVO INC
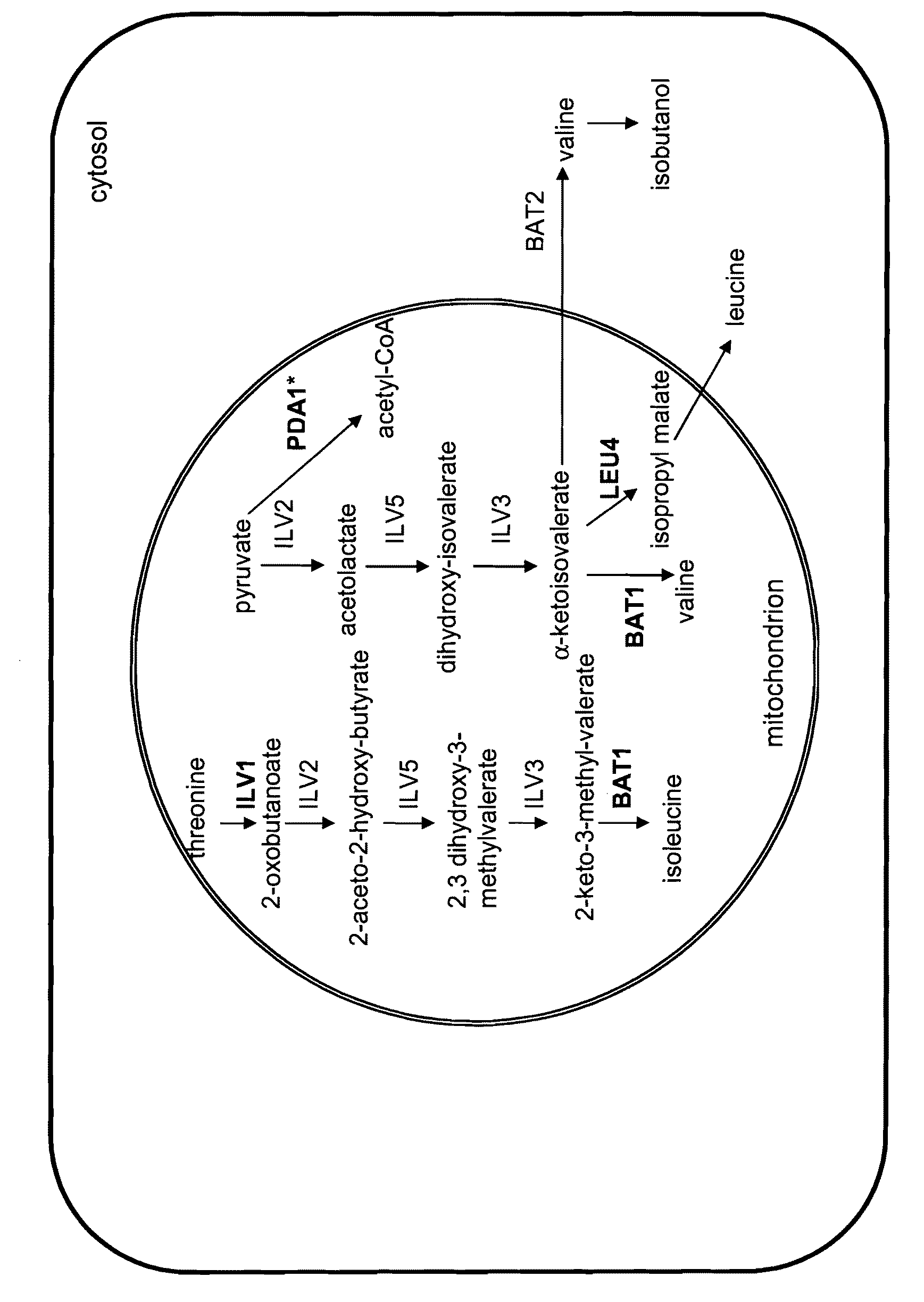
Increased production of isobutanol in yeast with reduced mitochondrial amino acid biosynthesis
ActiveUS8465964B2Reduced activityCarbon-nitrogen lyasesMicroorganismsIsobutanolBranched-chain-amino-acid transaminase
Owner:GEVO INC
Aldolase, aldolase mutant, and method and composition for producing tagatose by using same
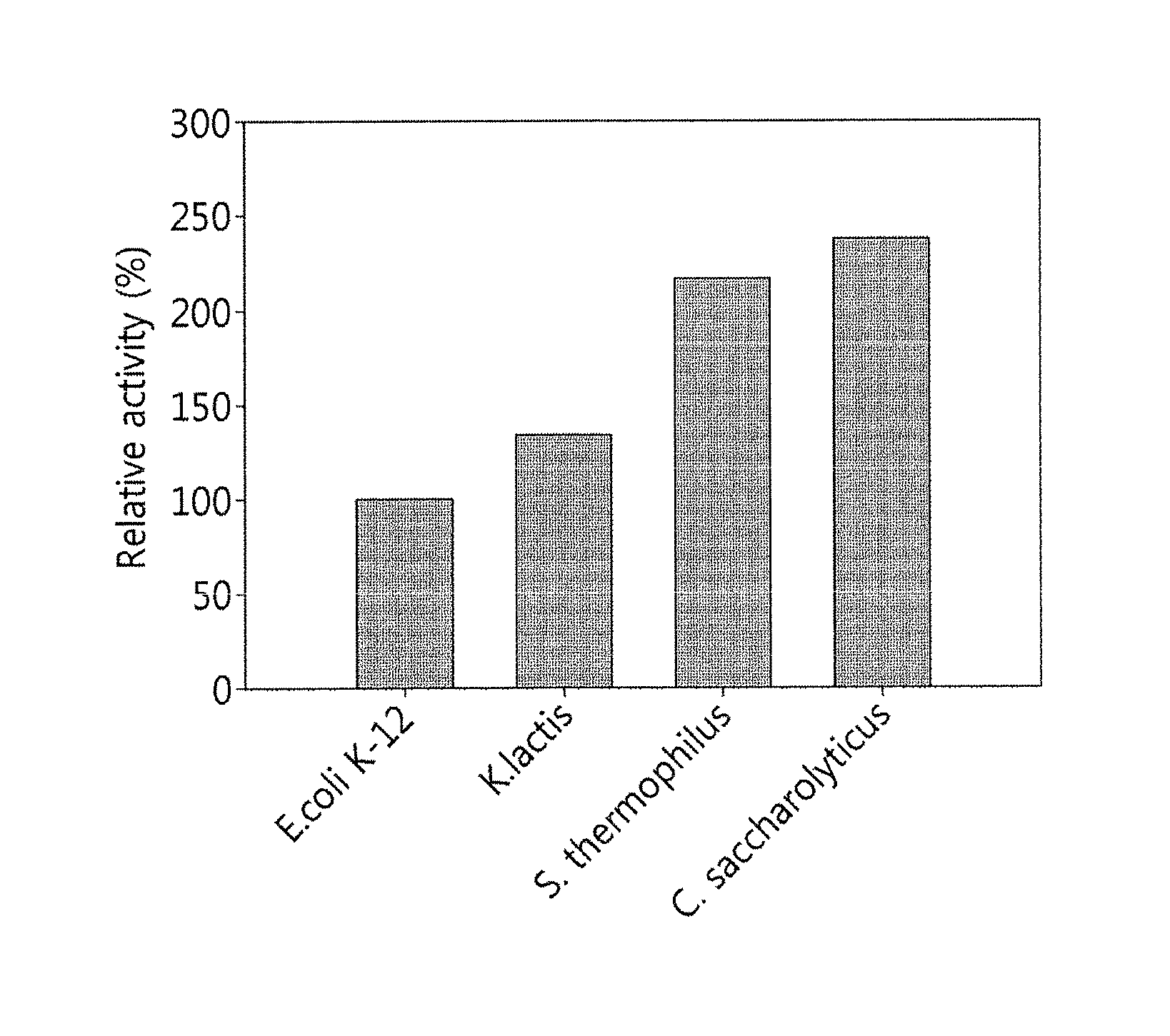
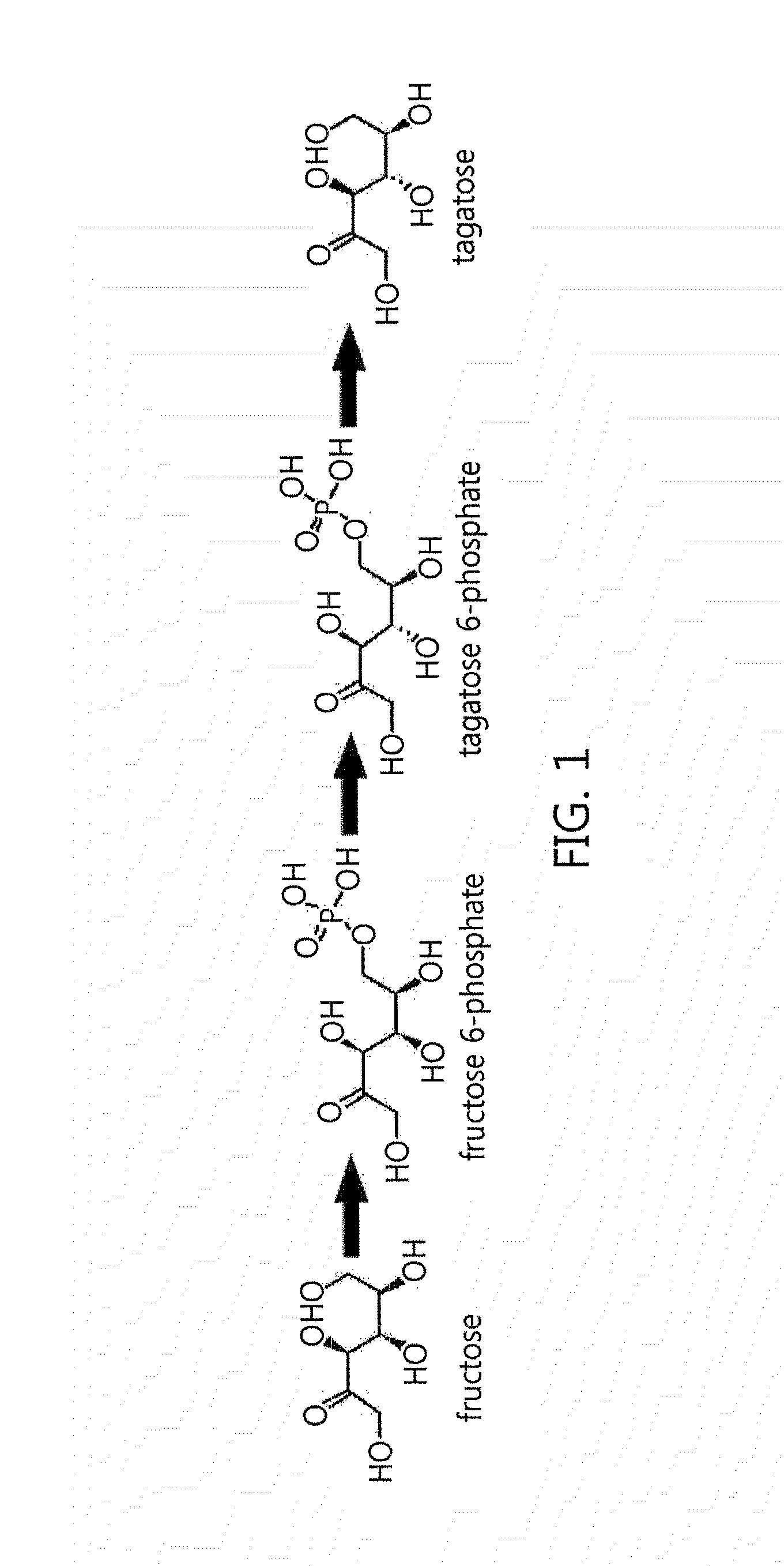
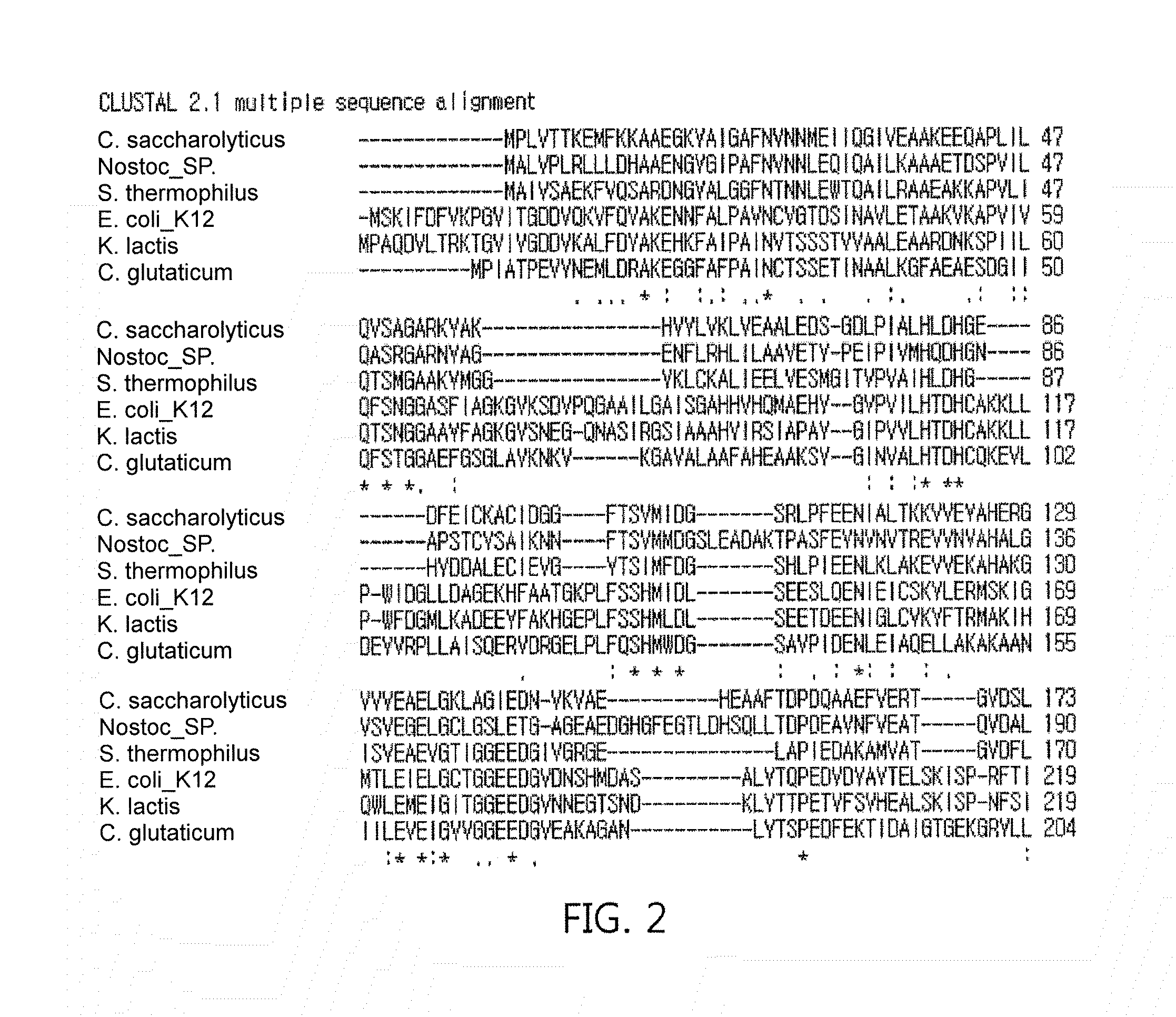
ActiveUS20160186162A1Various environmentalHigh yieldFermentationCarbon-carbon lyasesProduction effectOrganic chemistry
This disclosure relates to aldolase, an aldolase mutant, and a method and a composition for producing tagatose by using the same. The feature of the disclosure is environment-friendly due to the use of an enzyme acquired from microorganisms, requires only a simple process of enzyme immobilization, uses a low-cost substrate in a substrate compared with a conventional method for producing tagatose and has a remarkably high yield, thereby greatly reducing production costs and maximizing production effects.
Owner:SAMSANG CORP
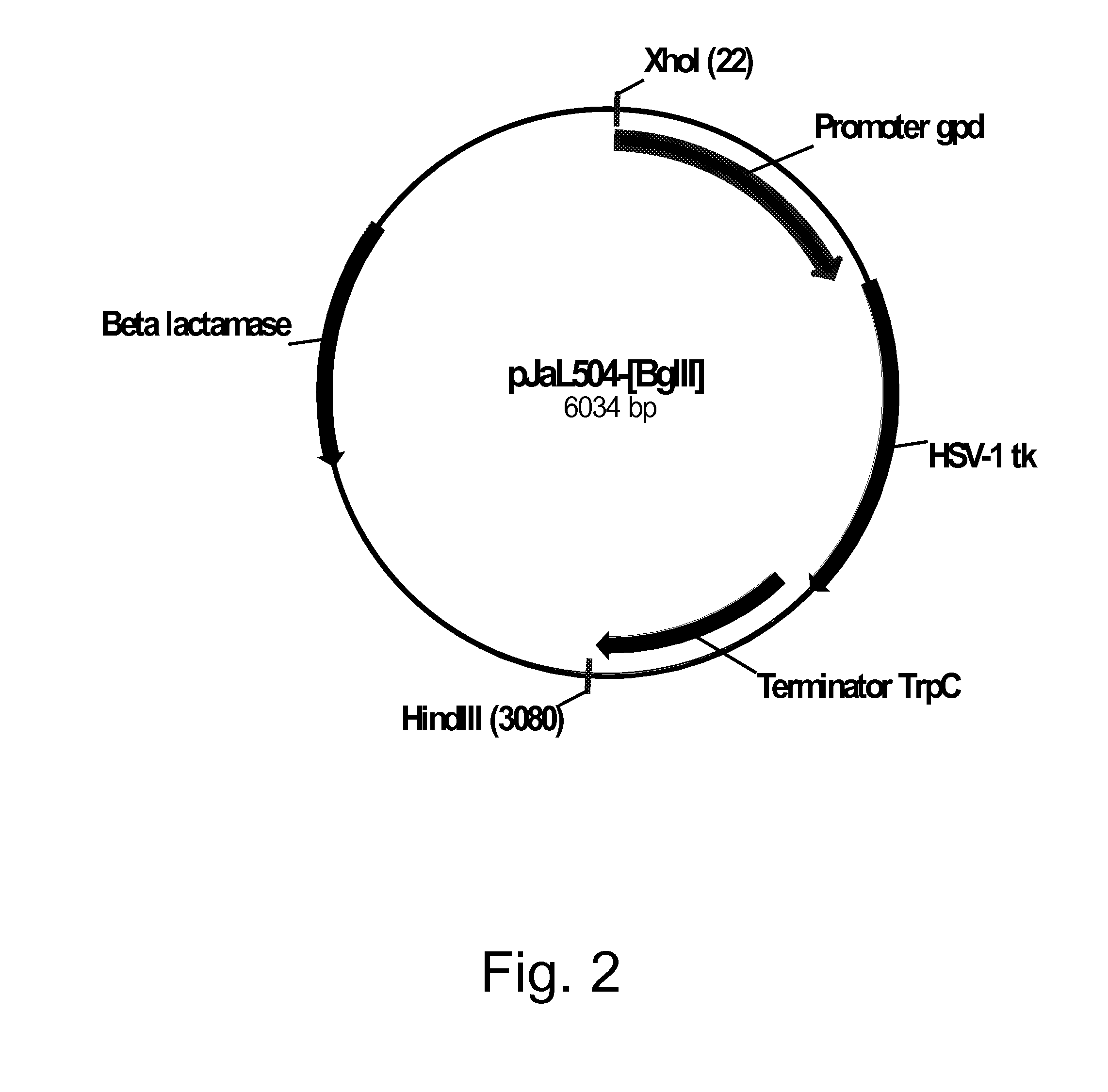
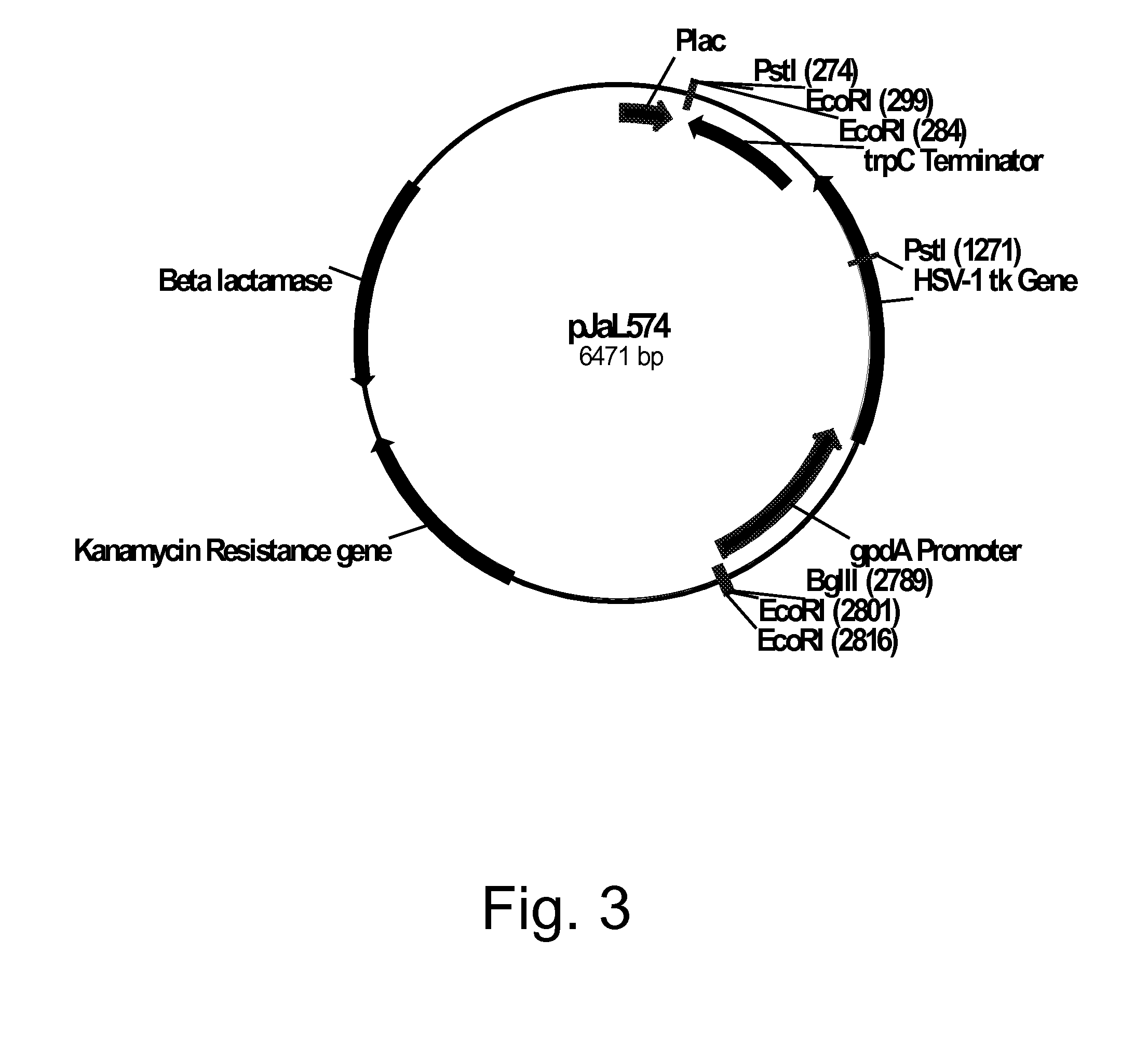
Methods for using positively and negatively selectable genes in a filamentous fungal cell
Owner:NOVOZYMES INC
Methods of treating parkinson's disease using viral vectors
Methods of delivering viral vectors, particularly recombinant AAV virions, to the CNS are provided. Also provided are methods of treating Parkinson's Disease.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Methods of making nylon intermediates from glycerol
ActiveUS20130210090A1Reduce usageRate minimisedBacteriaHydrolases3-Hydroxypropionic acid2,3-Butanediol
Embodiments of the invention relate to the enzymatic conversion of bioderived feedstocks to commercially valuable chemicals. The enzymatic conversions of the embodiments of the invention offer the potential for lower cost routes to these value-added chemicals. Some of the chemicals that are useful include nylon intermediates such as caprolactam, adipic acid, 1,6-hexamethylene diamine; butanediols such as 1,4-butanediol, 1,3-butanediol, and 2,3-butanediol; butanols such as 1-butanol, and 2-butanol; succinic acid, butadiene, isoprene, and 3-hydroxypropanoic acid.
Owner:INV NYLON CHEM AMERICAS LLC
Matrices for drug delivery and methods for making and using the same
In one aspect, biocompatible matrices such as sol-gels encapsulating a reaction center may be administered to a subject for conversion of prodrugs into biologically active agents. In certain embodiments, the biocompatible matrices of the present invention are sol-gels. In one embodiment, the enzyme L-amino acid decarboxylase is encapsulated and implanted in the brain to convert L-dopa to dopamine for treatment of Parkinson's disease.
Owner:BABICH JOHN W +2
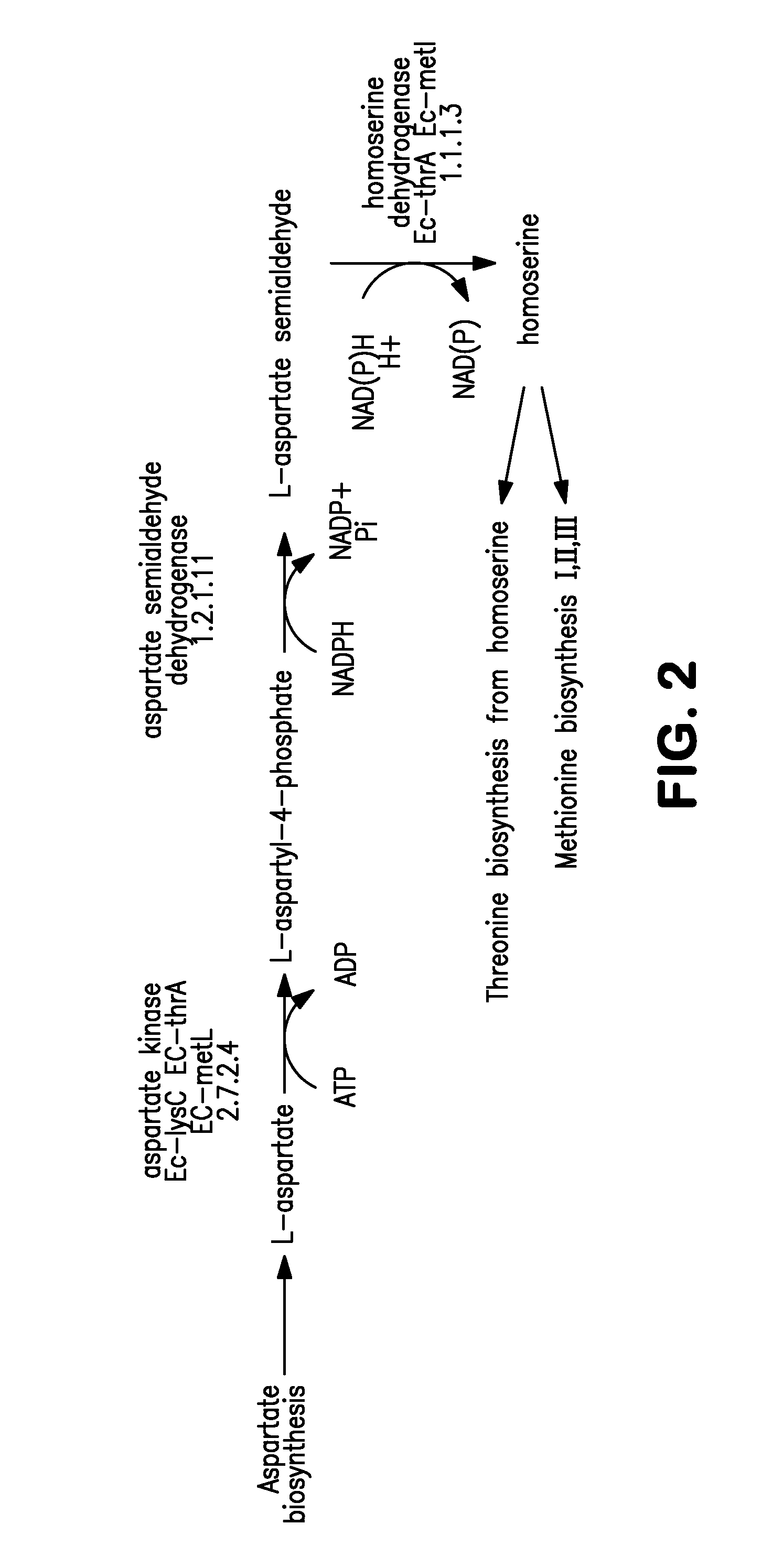
Microorganisms for the production of 1,4-butanediol, 4-hydroxybutanal, 4-hydroxybutyryl-coa, putrescine and related compounds, and methods related thereto
The invention provides non-naturally occurring microbial organisms comprising a 1,4-butanediol (BDO), 4-hydroxybutyryl-CoA, 4-hydroxybutanal or putrescine pathway comprising at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding a BDO, 4-hydroxybutyryl-CoA, 4-hydroxybutanal or putrescine pathway enzyme expressed in a sufficient amount to produce BDO, 4-hydroxybutyryl-CoA, 4-hydroxybutanal or putrescine and further optimized for expression of BDO. The invention additionally provides methods of using such microbial organisms to produce BDO, 4-hydroxybutyryl-CoA, 4-hydroxybutanal or putrescine.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
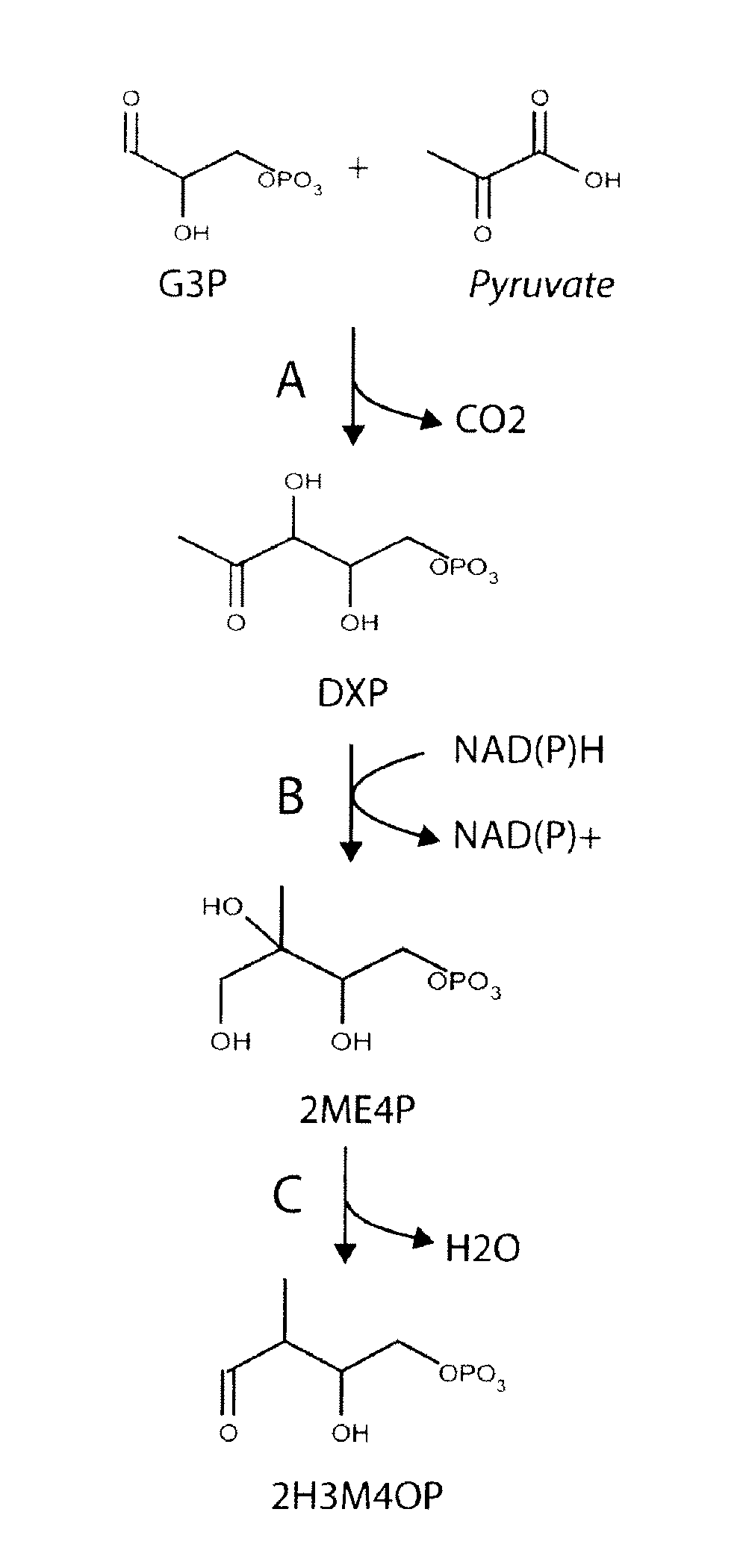
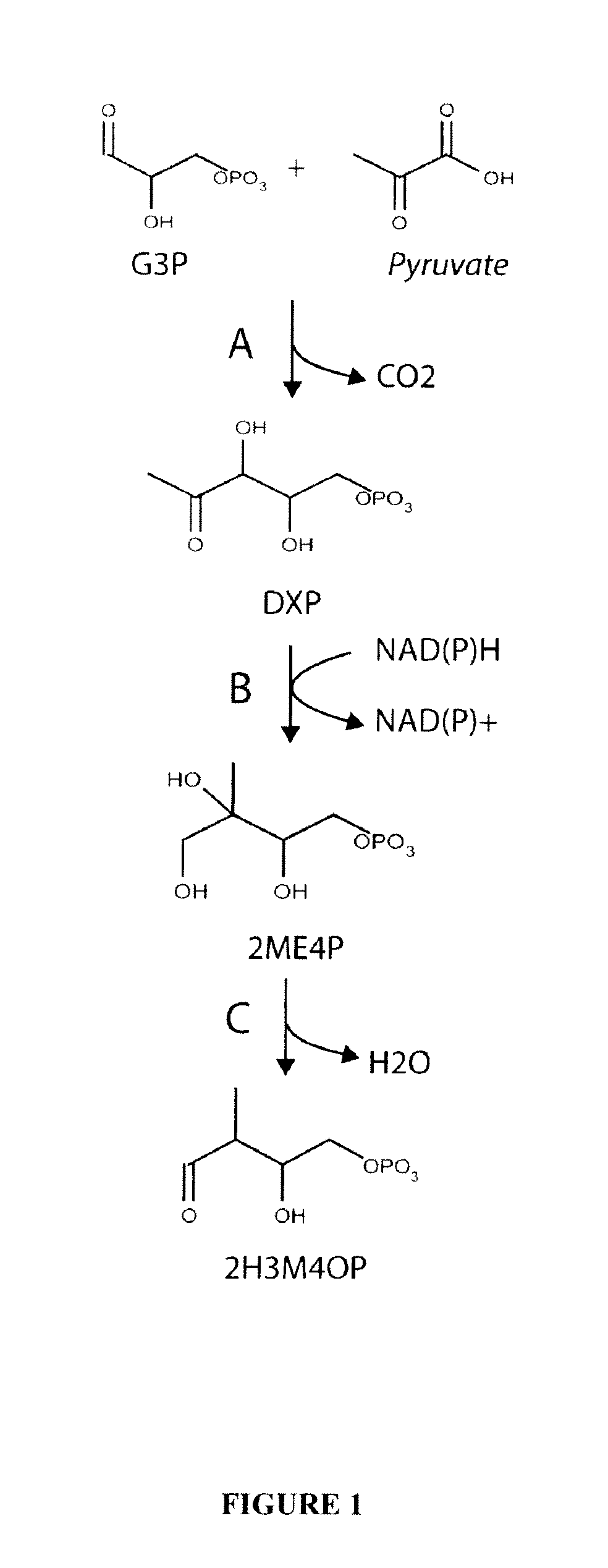
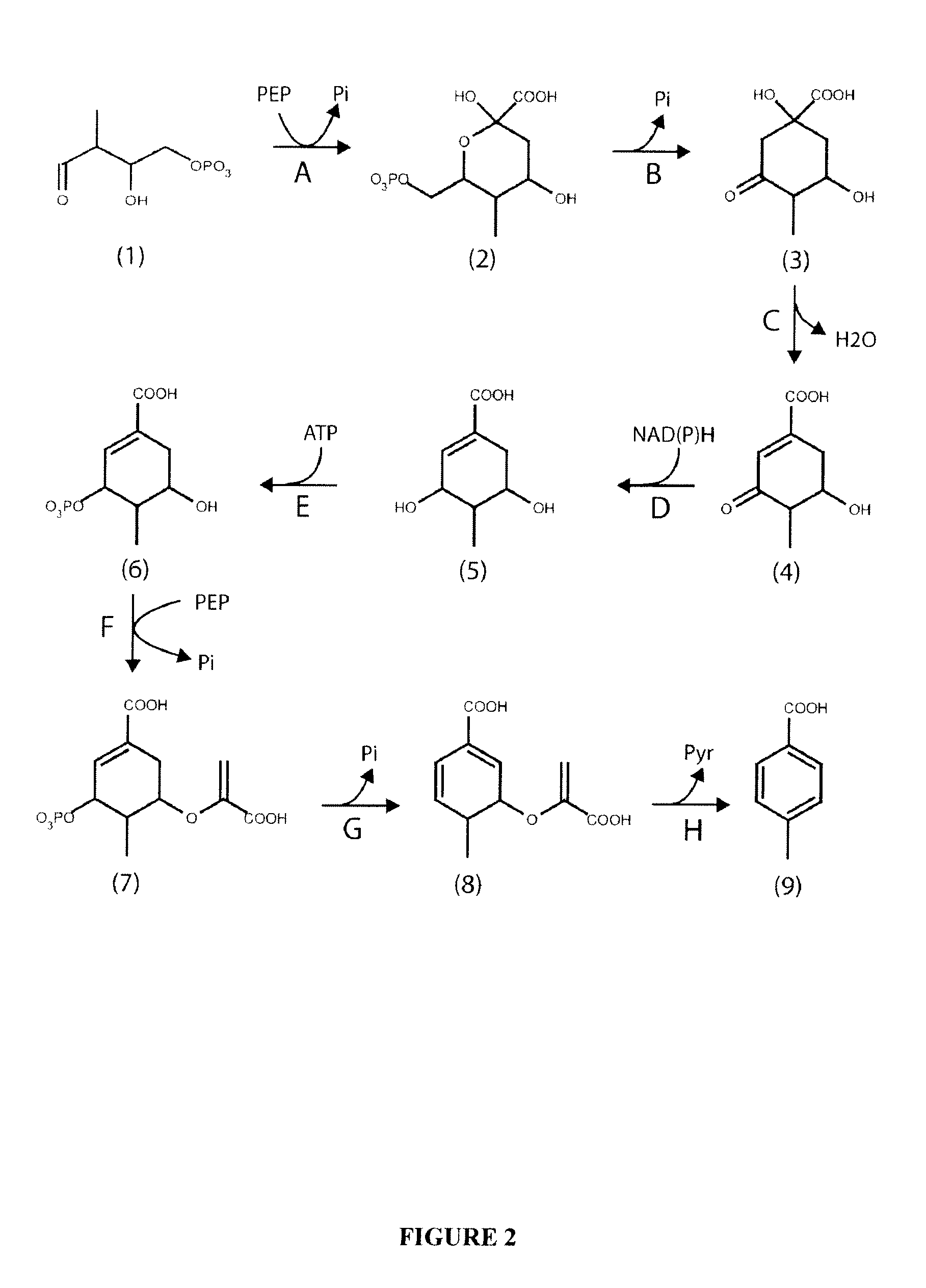
Microorganisms and methods for the biosynthesis of p-toluate and terephthalate
The invention provides non-naturally occurring microbial organisms having a (2-hydroxy-3-methyl-4-oxobutoxy)phosphonate pathway, p-toluate pathway, and / or terephthalate pathway. The invention additionally provides methods of using such organisms to produce (2-hydroxy-3-methyl-4-oxobutoxy)phosphonate pathway, p-toluate pathway or terephthalate pathway.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Biological Conversion of Multi-Carbon Compounds from Methane
Multi-carbon compounds such as ethanol, n-butanol, sec-butanol, isobutanol, tert-butanol, fatty (or aliphatic long chain) alcohols, fatty acid methyl esters, 2,3-butanediol and the like, are important industrial commodity chemicals with a variety of applications. The present invention provides metabolically engineered host microorganisms which metabolize methane (CH4) as their sole carbon source to produce multi-carbon compounds for use in fuels (e.g., bio-fuel, bio-diesel) and bio-based chemicals. Furthermore, use of the metabolically engineered host microorganisms of the invention (which utilize methane as the sole carbon source) mitigate current industry practices and methods of producing multi-carbon compounds from petroleum or petroleum-derived feedstocks, and ameliorate much of the ongoing depletion of arable food source “farmland” currently being diverted to grow bio-fuel feedstocks, and as such, improve the environmental footprint of future bio-fuel, bio-diesel and bio-based chemical compositions.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
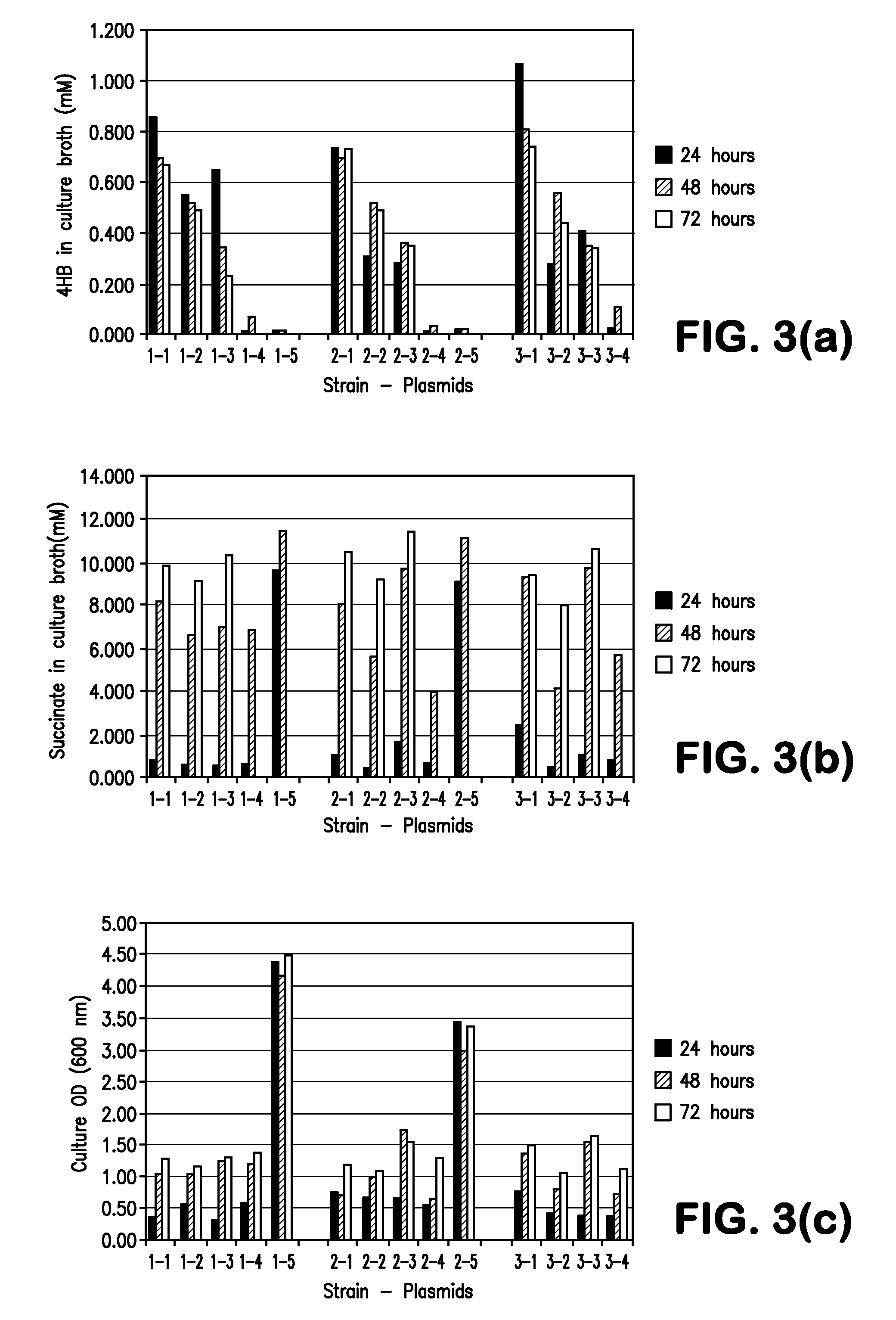
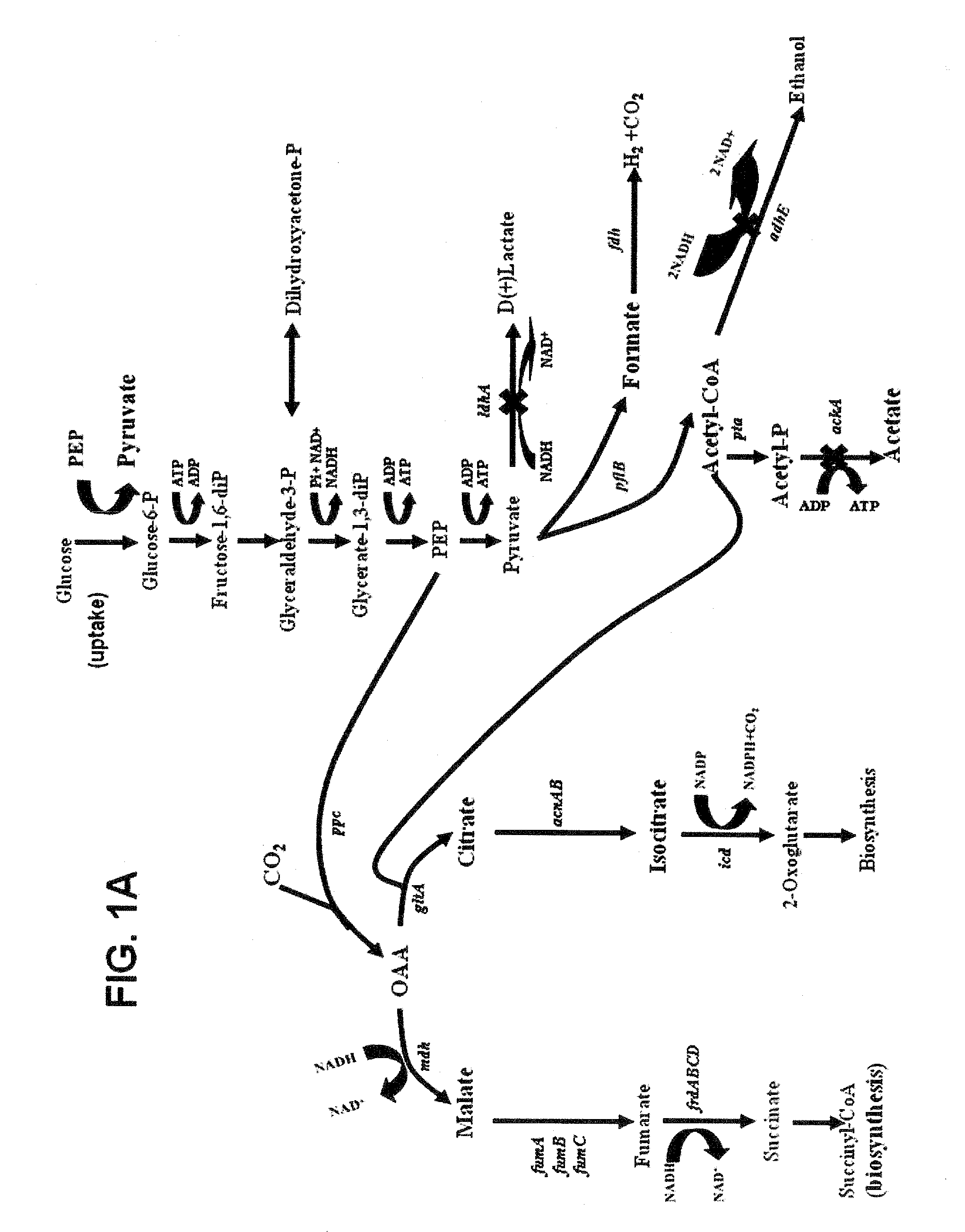
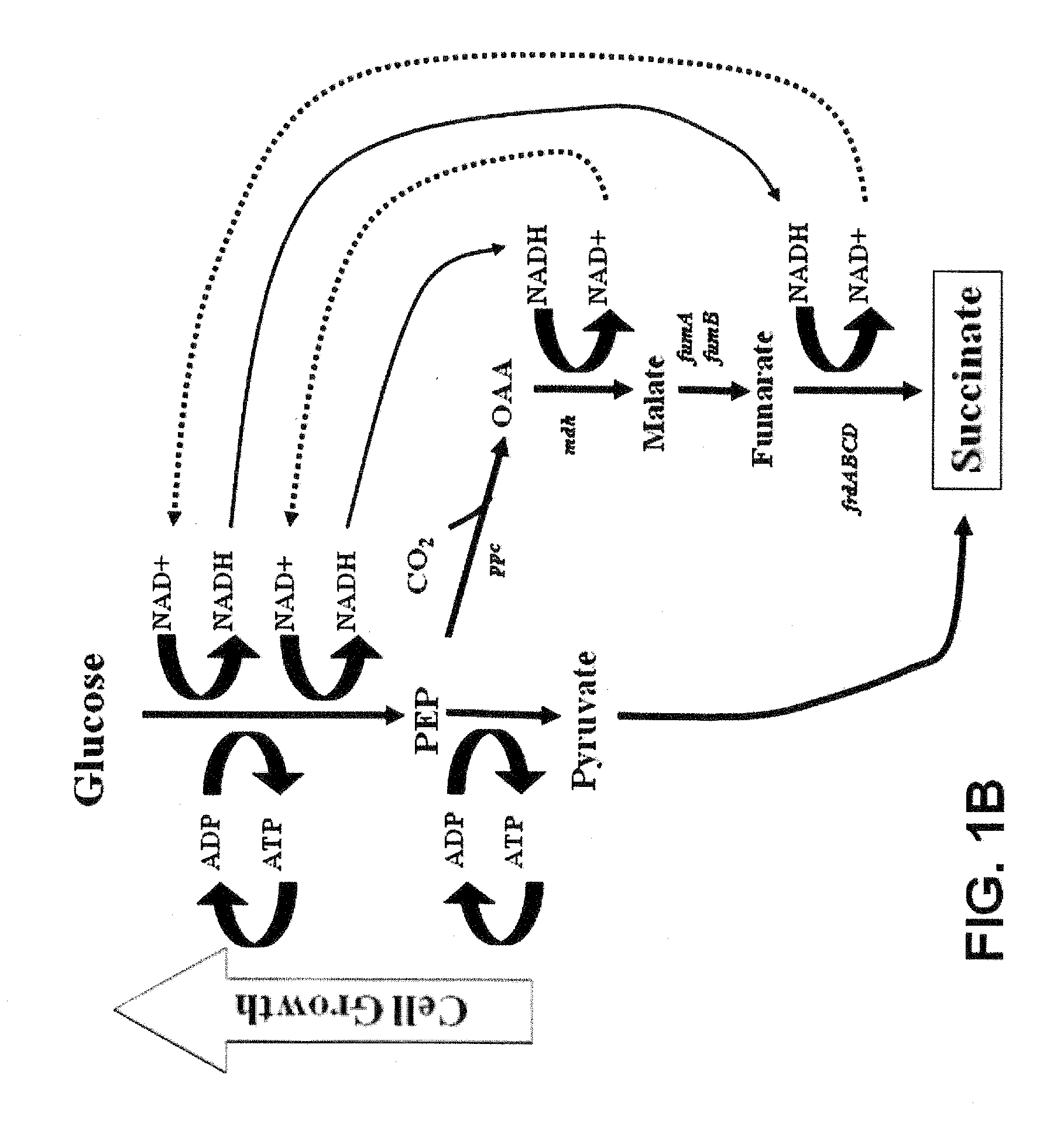
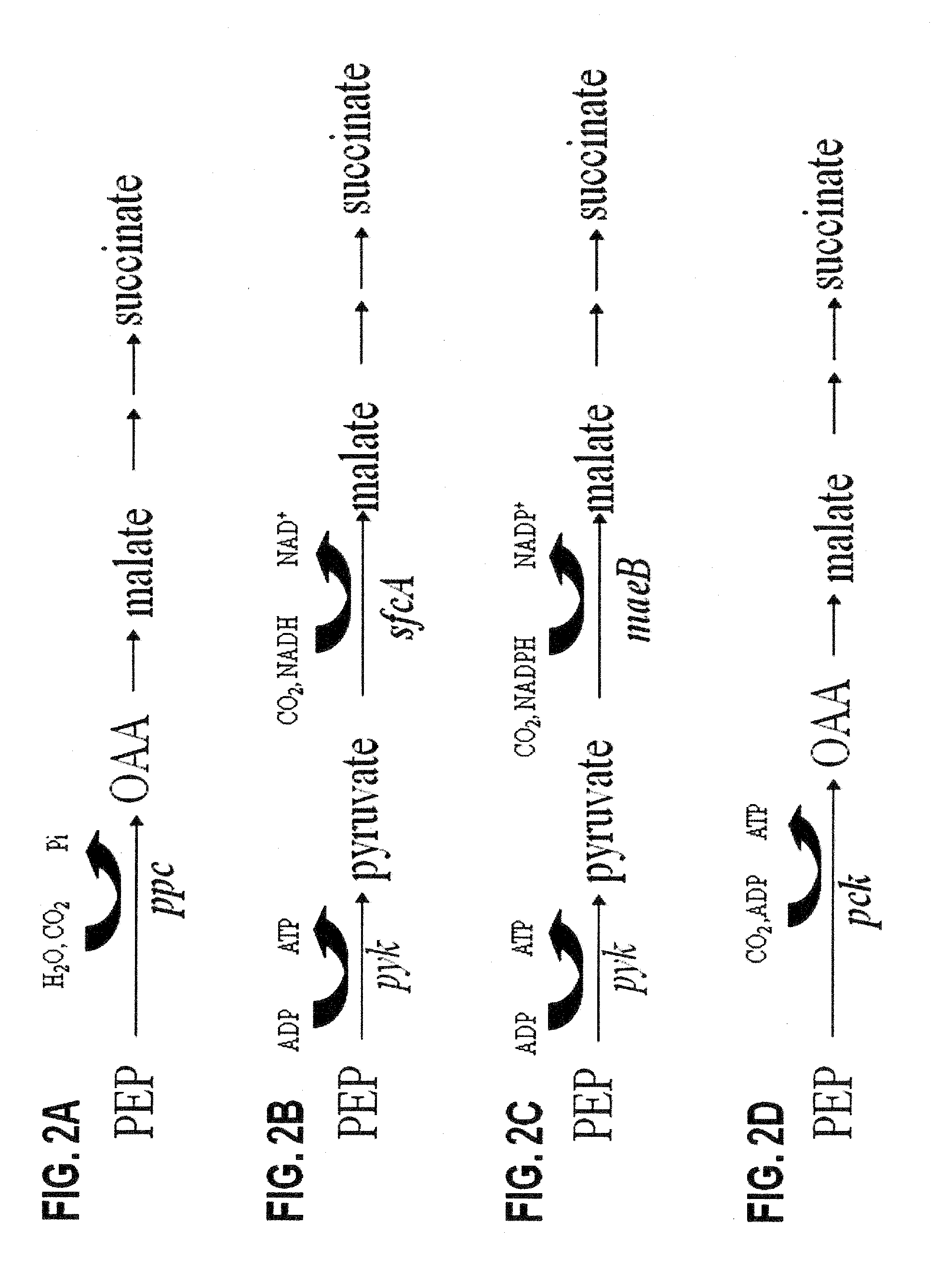
Engineering the pathway for succinate production
InactiveUS20120058530A1Increase overall carbon flowHigh expressionVectorsBacteriaMannheimiaPh control
This invention relates to the biocatalysts for the efficient production of succinic acid and / or other products from renewable biological feedstocks. The biocatalysts have a very high efficiency for the growth-coupled production of succinic acid and / or other products from carbohydrate feed stocks as a result of both genetic manipulations and metabolic evolution. More specifically, certain biocatalysts of the present invention produce succinic acid at high titers and yield in mineral salts media during simple pH-controlled, batch fermentation without the addition of any exogenous genetic material. The genetic manipulations of the present invention are concerned with the energy-conserving strategies coupled with the elimination of alternative routes for NADH oxidation other than the routes for succinic acid production. The biocatalysts contain glucose-repressed gluconeogenic phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase (pck) depressed by genetic modifications and a genetically-inactivated phosphotransferase system. In terms of succinic acid production efficiency, the biocatalysts of the present invention are functionally equivalent to succinate producing rumen bacteria such as Actinobacillus succinogens and Mannheimia succiniproducens with one difference that the biocatalysts are able to achieve this high level of succinic acid production in a minimal salt medium with carbohydrate source as opposed to the requirement for a rich media for succinic acid production by rumen bacteria.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com