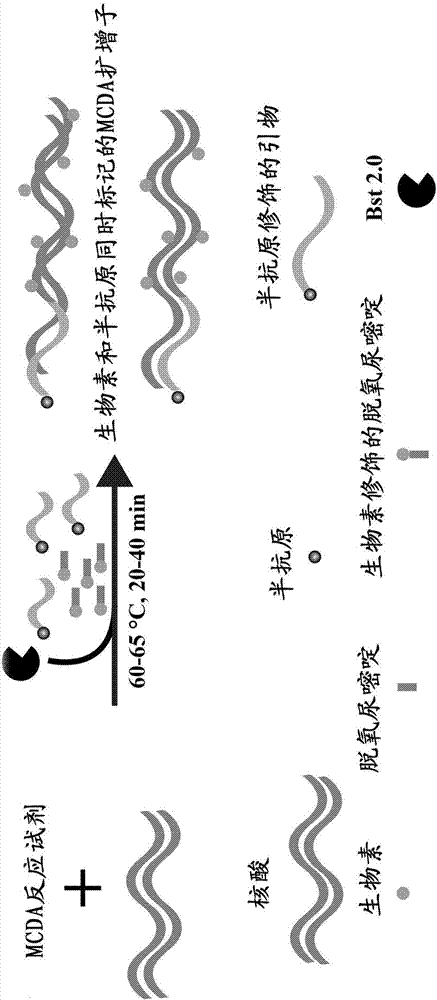
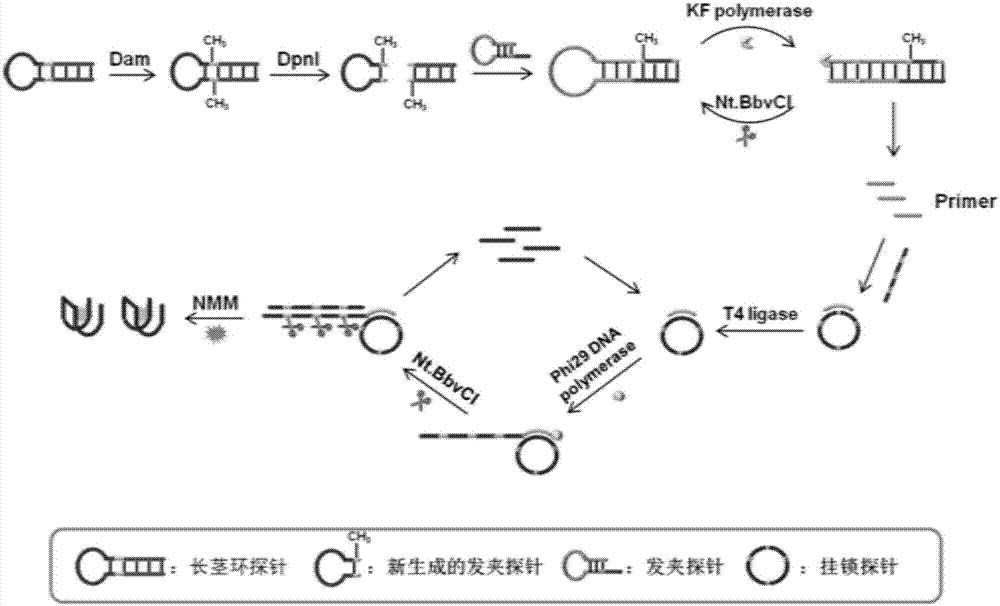
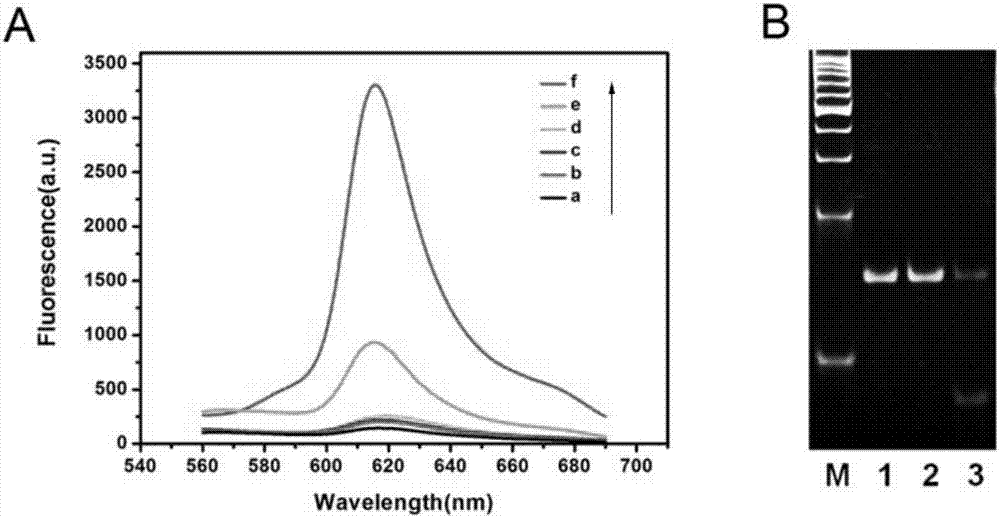
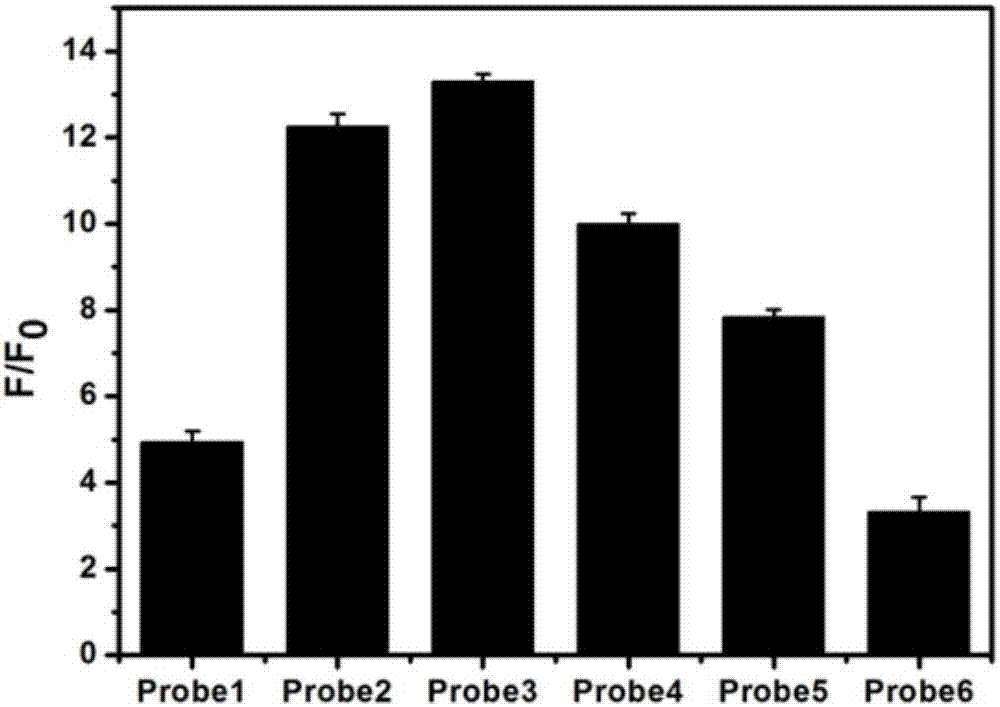
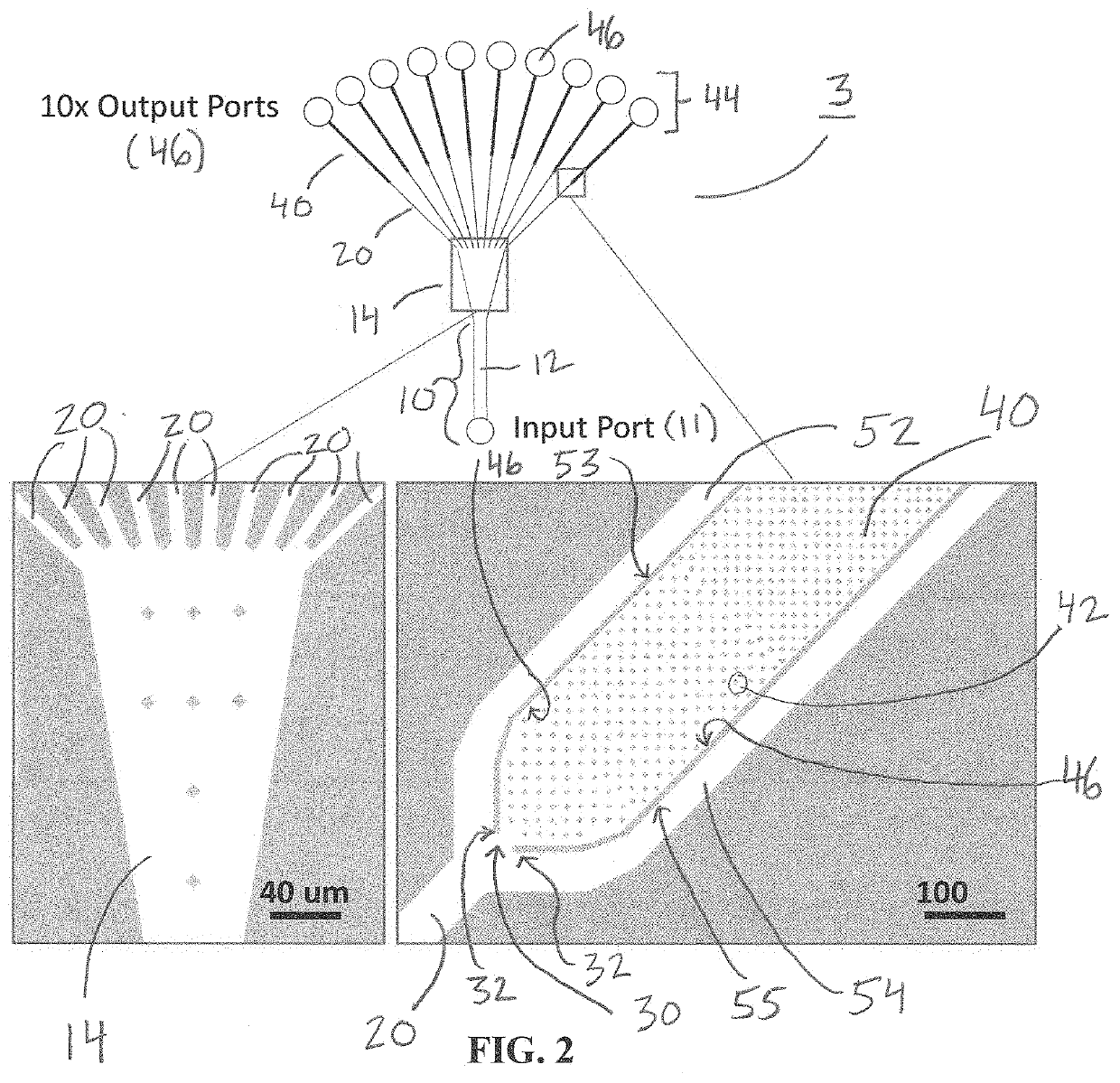
Patents
Literature
58 results about "Multiple displacement amplification" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
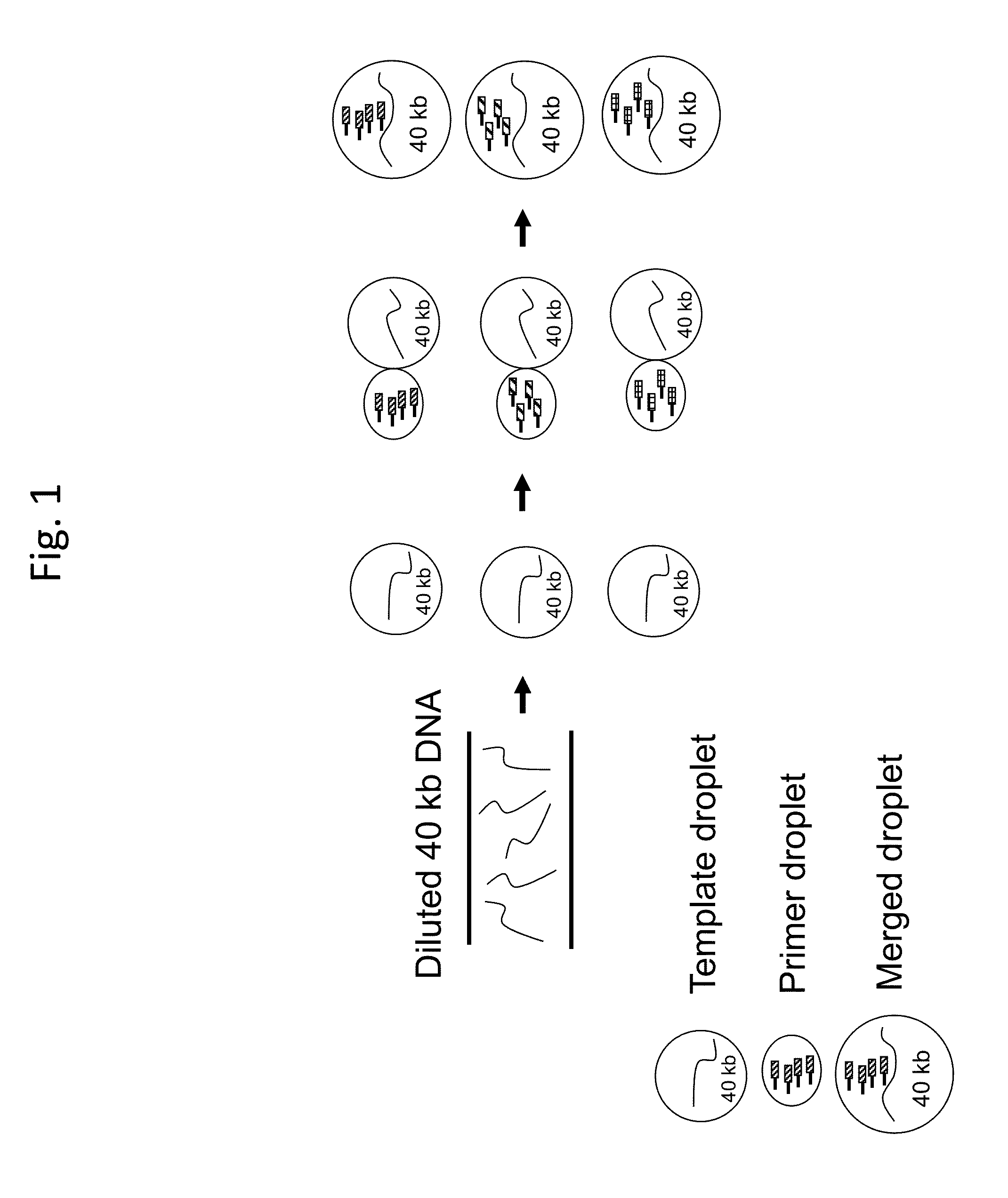
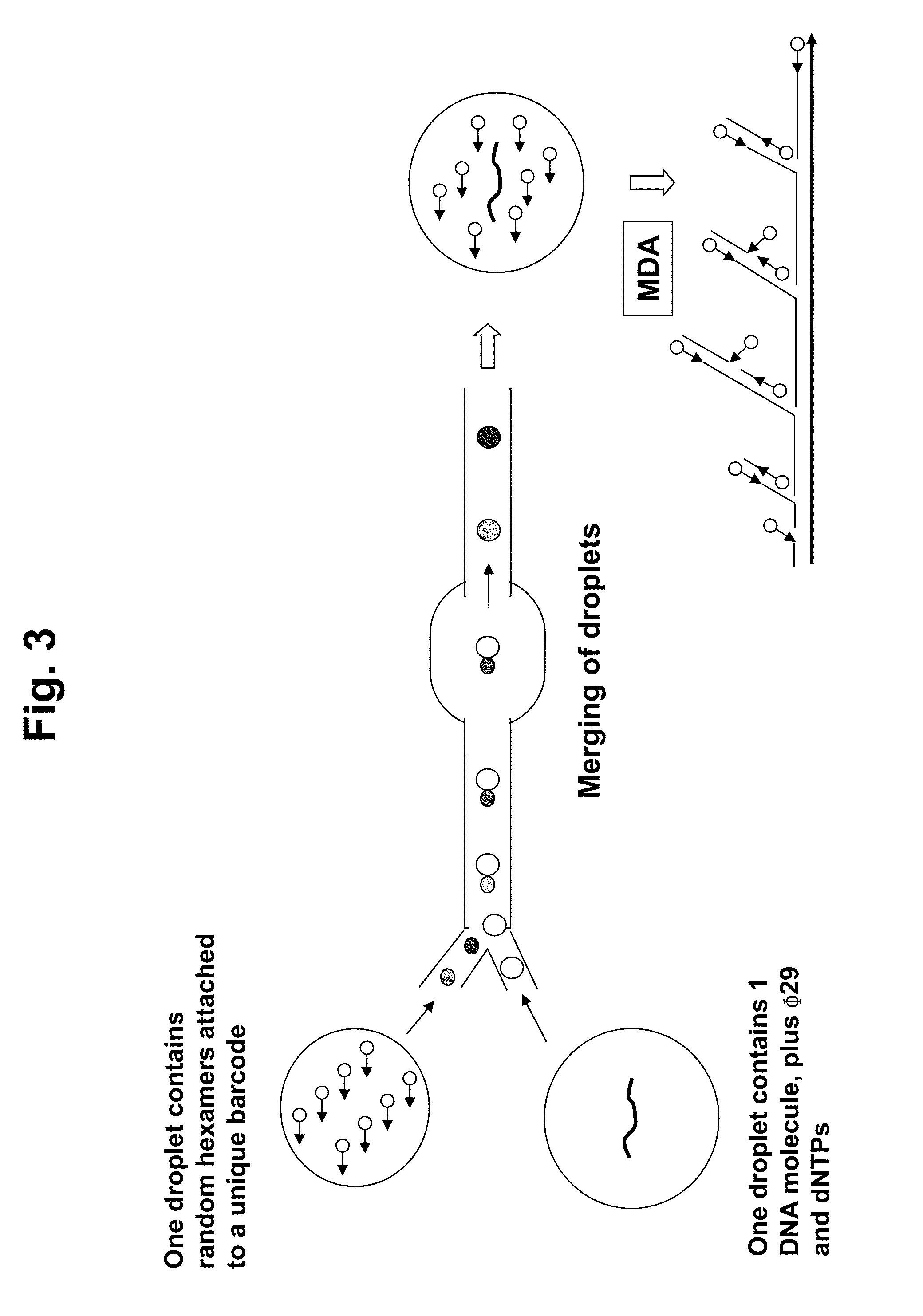
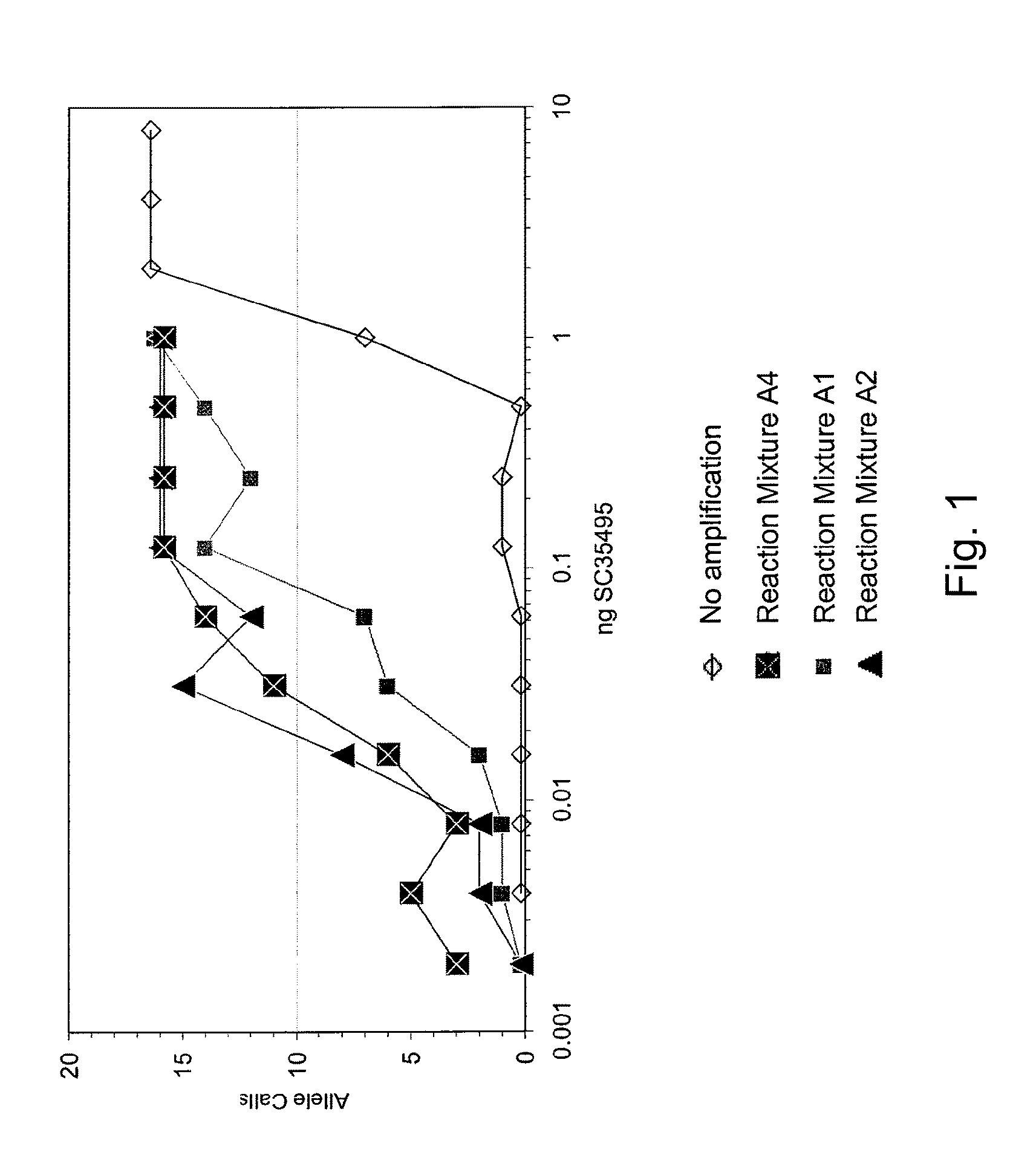
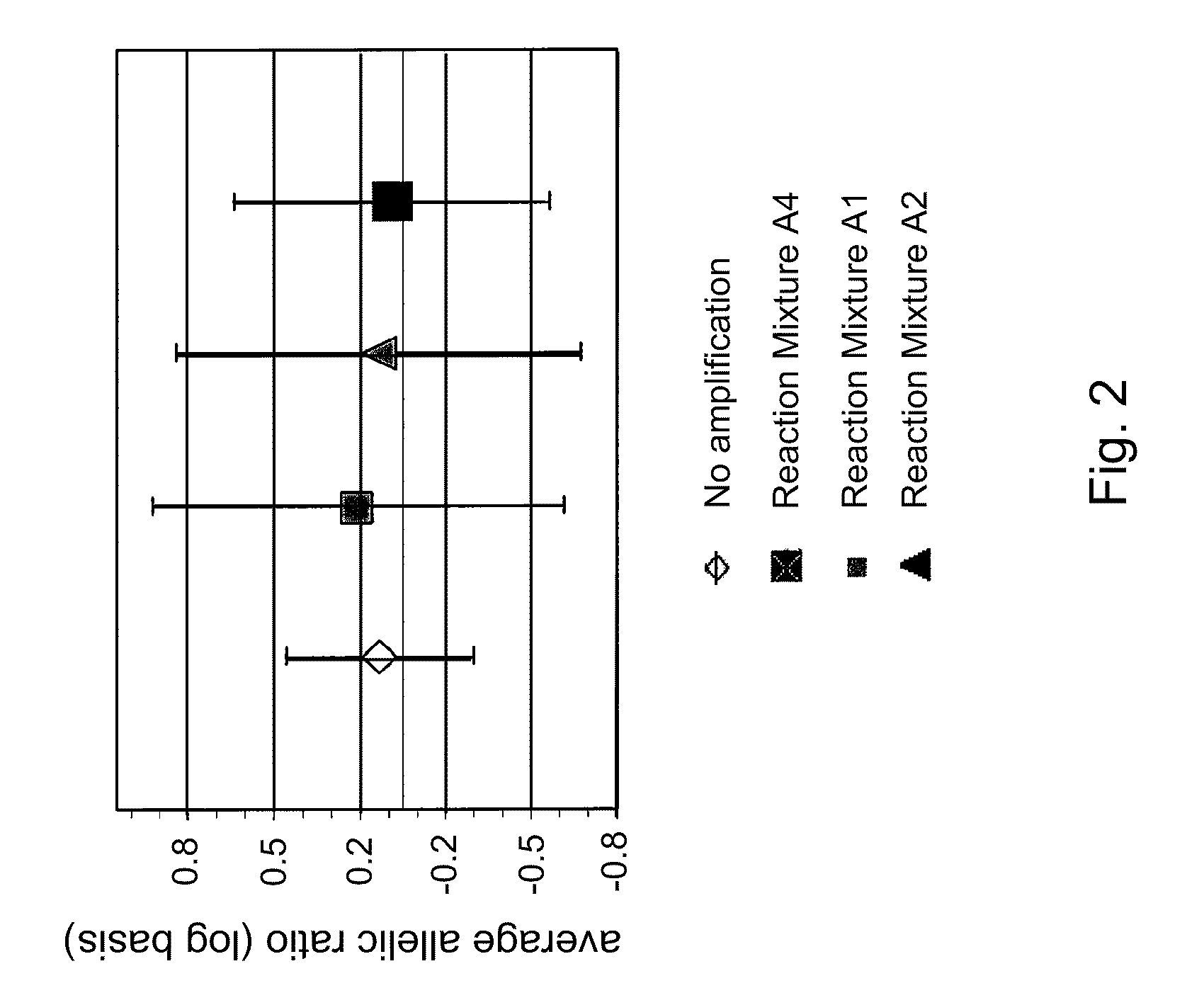
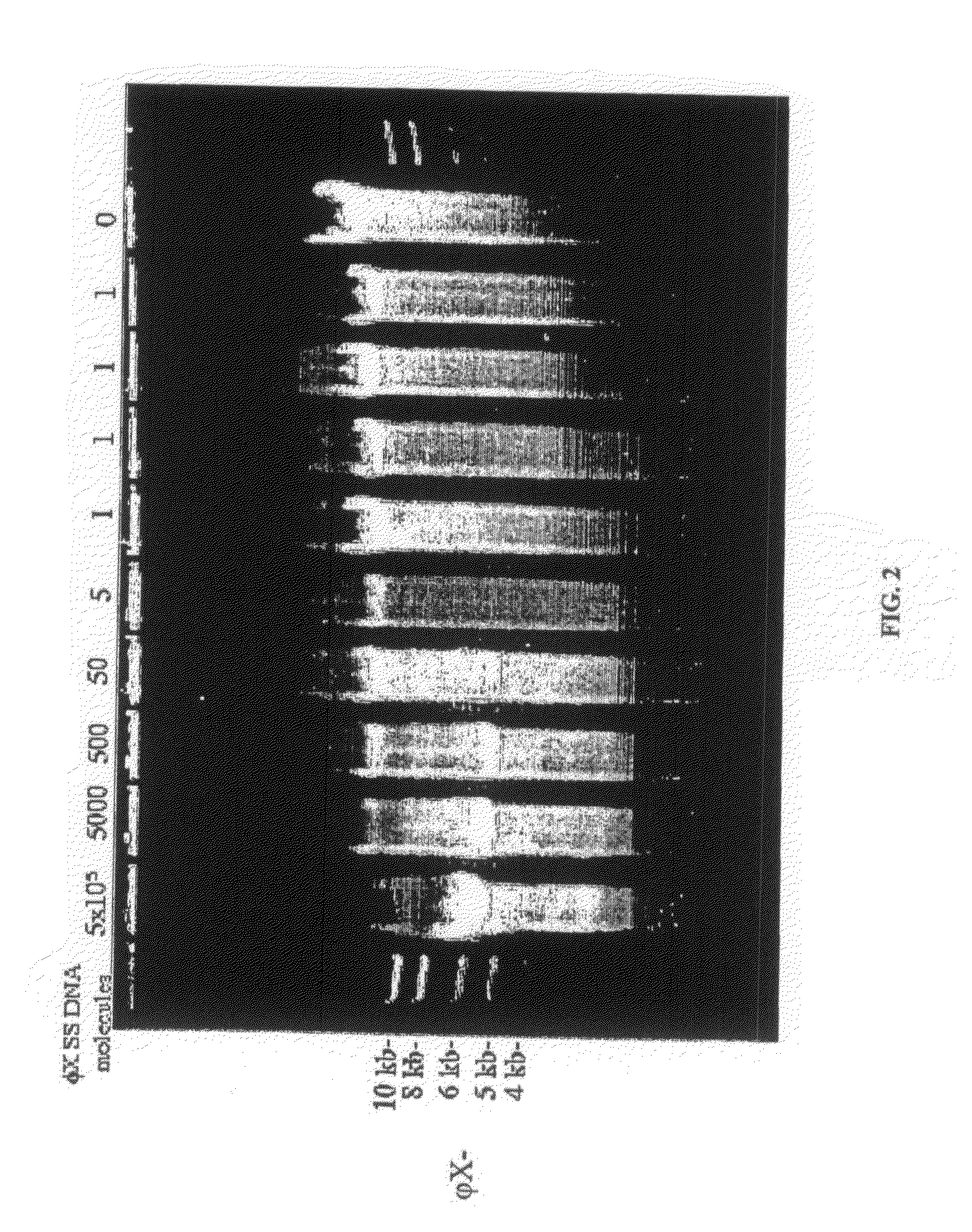
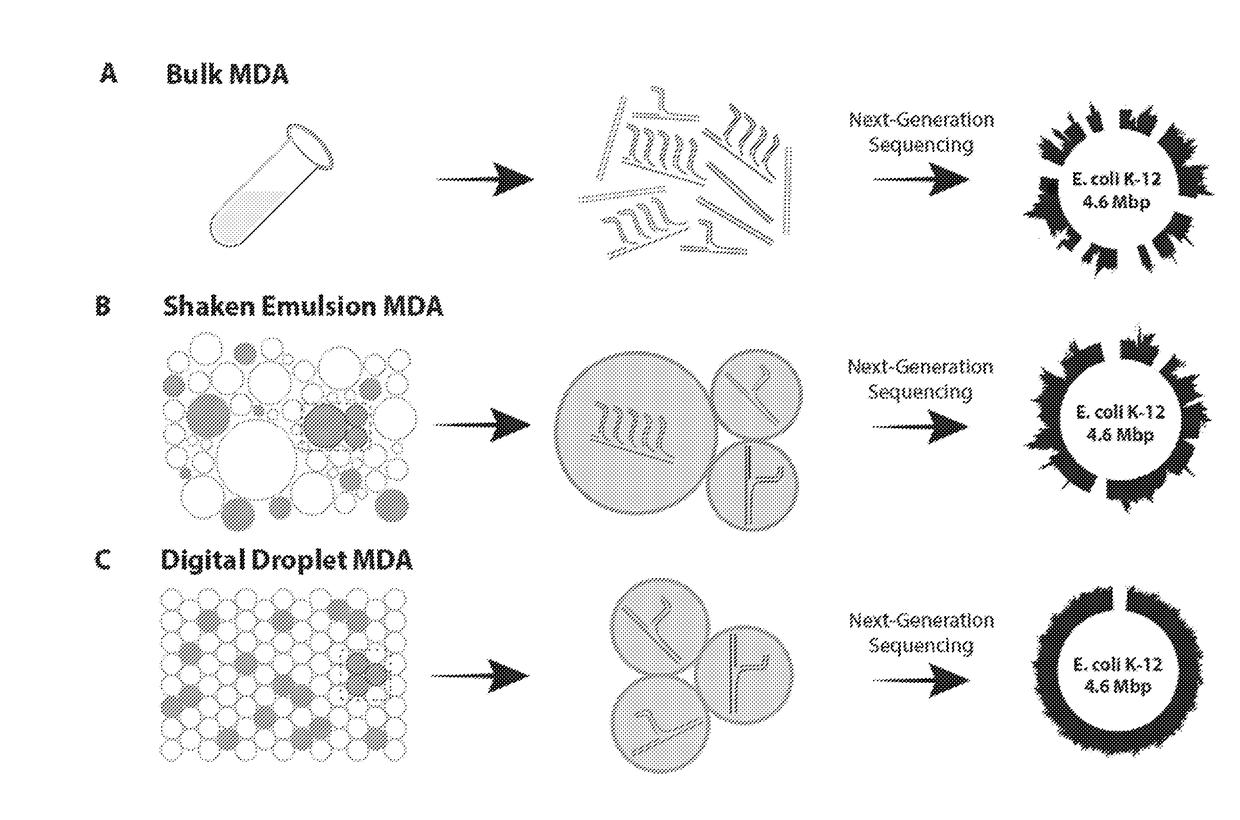
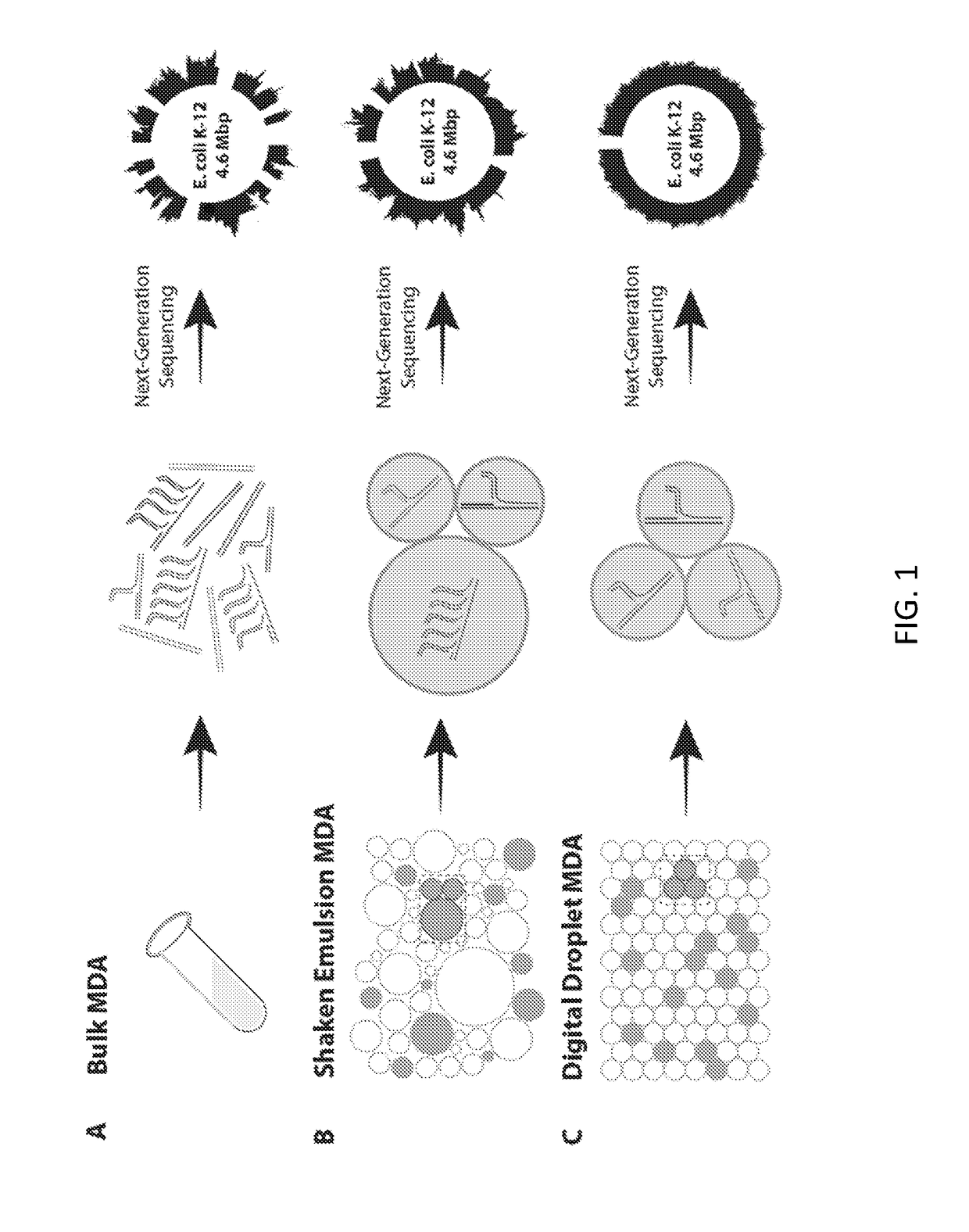
Multiple displacement amplification (MDA) is a non-PCR based DNA amplification technique. This method can rapidly amplify minute amounts of DNA samples to a reasonable quantity for genomic analysis. The reaction starts by annealing random hexamer primers to the template: DNA synthesis is carried out by a high fidelity enzyme, preferentially Φ29 DNA polymerase, at a constant temperature. Compared with conventional PCR amplification techniques, MDA generates larger sized products with a lower error frequency. This method has been actively used in whole genome amplification (WGA) and is a promising method for application to single cell genome sequencing and sequencing-based genetic studies.
Long-Range Barcode Labeling-Sequencing
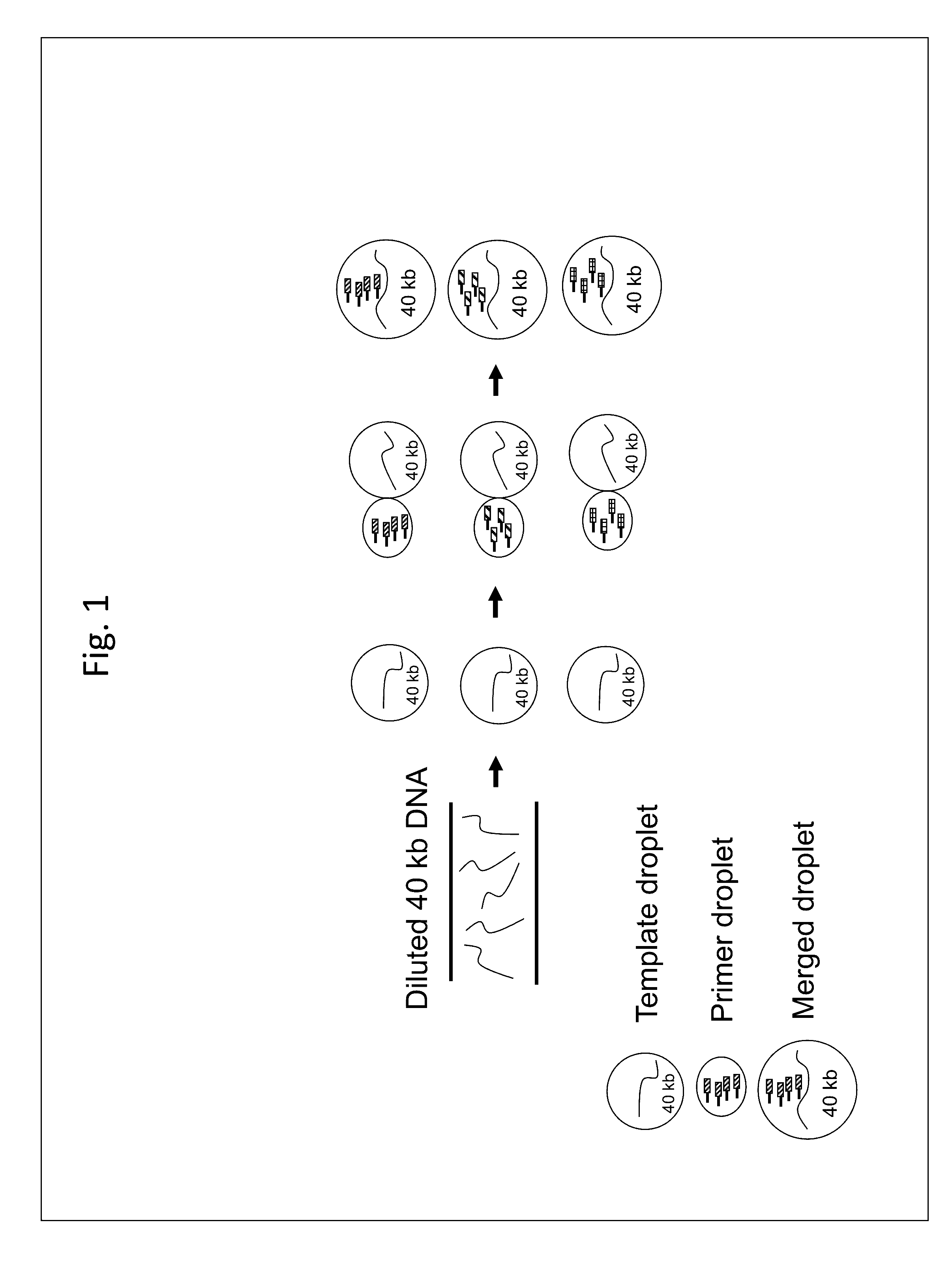
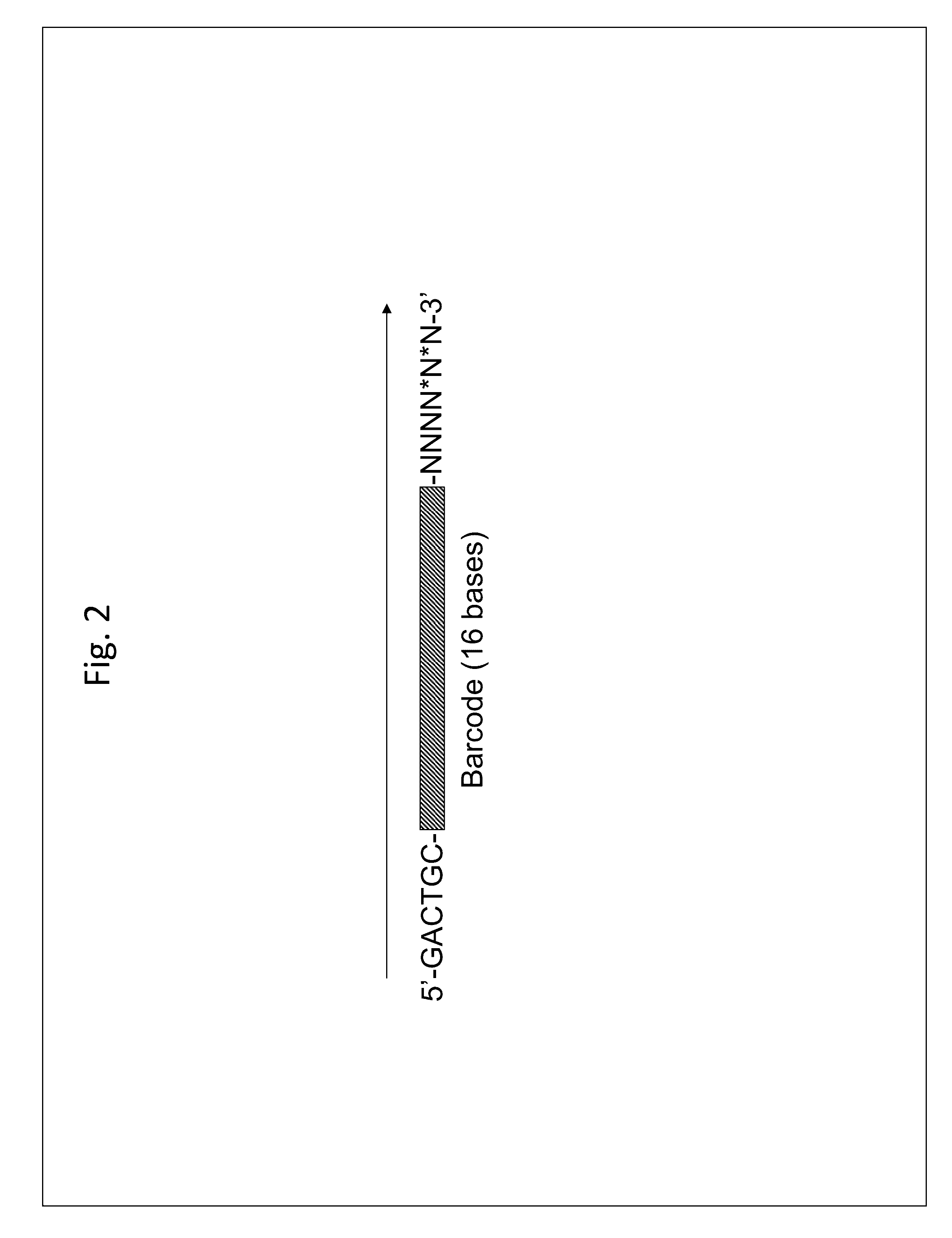
ActiveUS20130130919A1Reduce complexityImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationBarcodeHaplotype
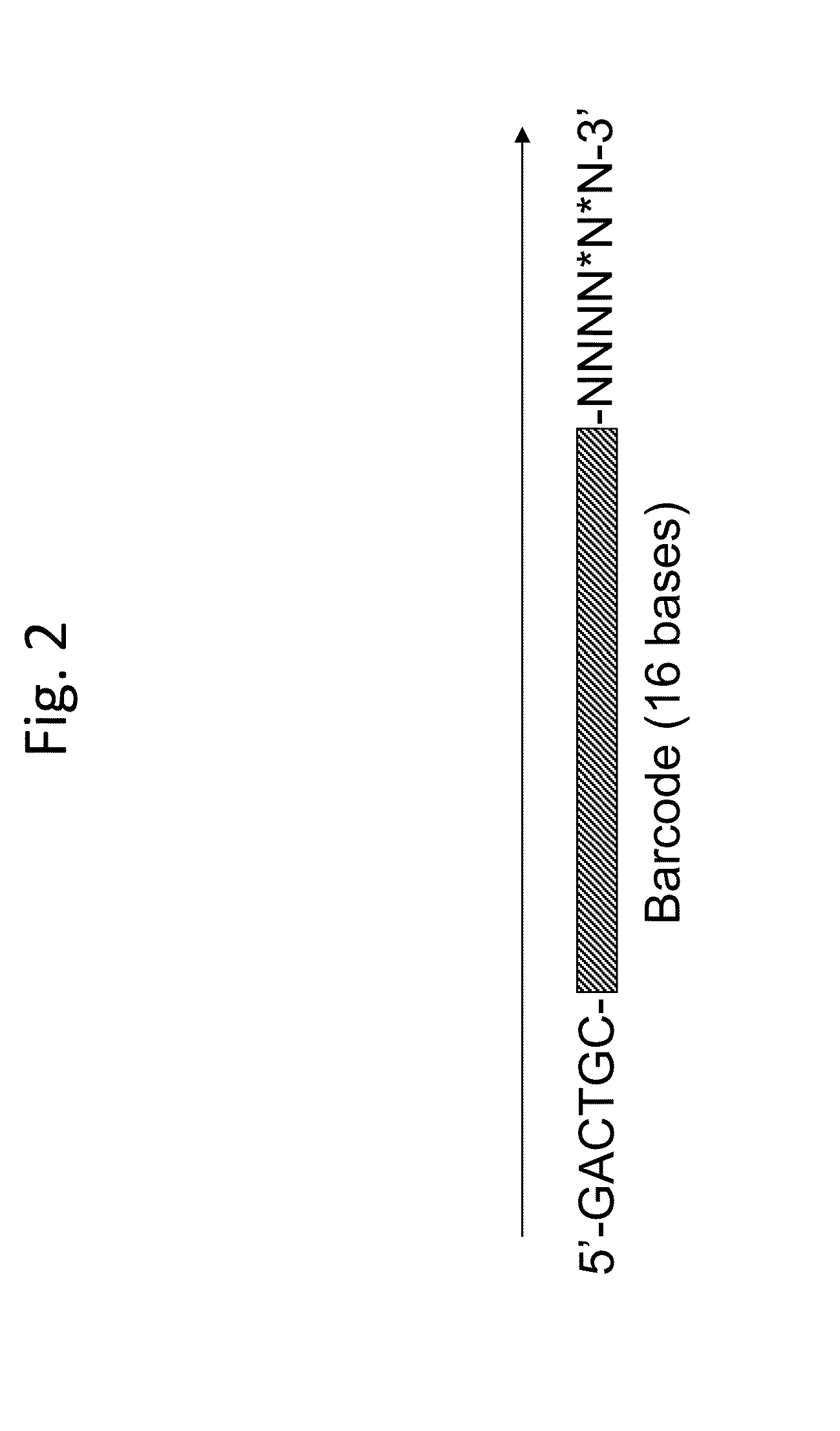
Methods for sequencing single large DNA molecules by clonal multiple displacement amplification using barcoded primers. Sequences are binned based on barcode sequences and sequenced using a microdroplet-based method for sequencing large polynucleotide templates to enable assembly of haplotype-resolved complex genomes and metagenomes.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Multiple displacement amplification
ActiveUS20110118151A1High sensitivityEfficient yieldBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEmulsionHydrophobic polymer
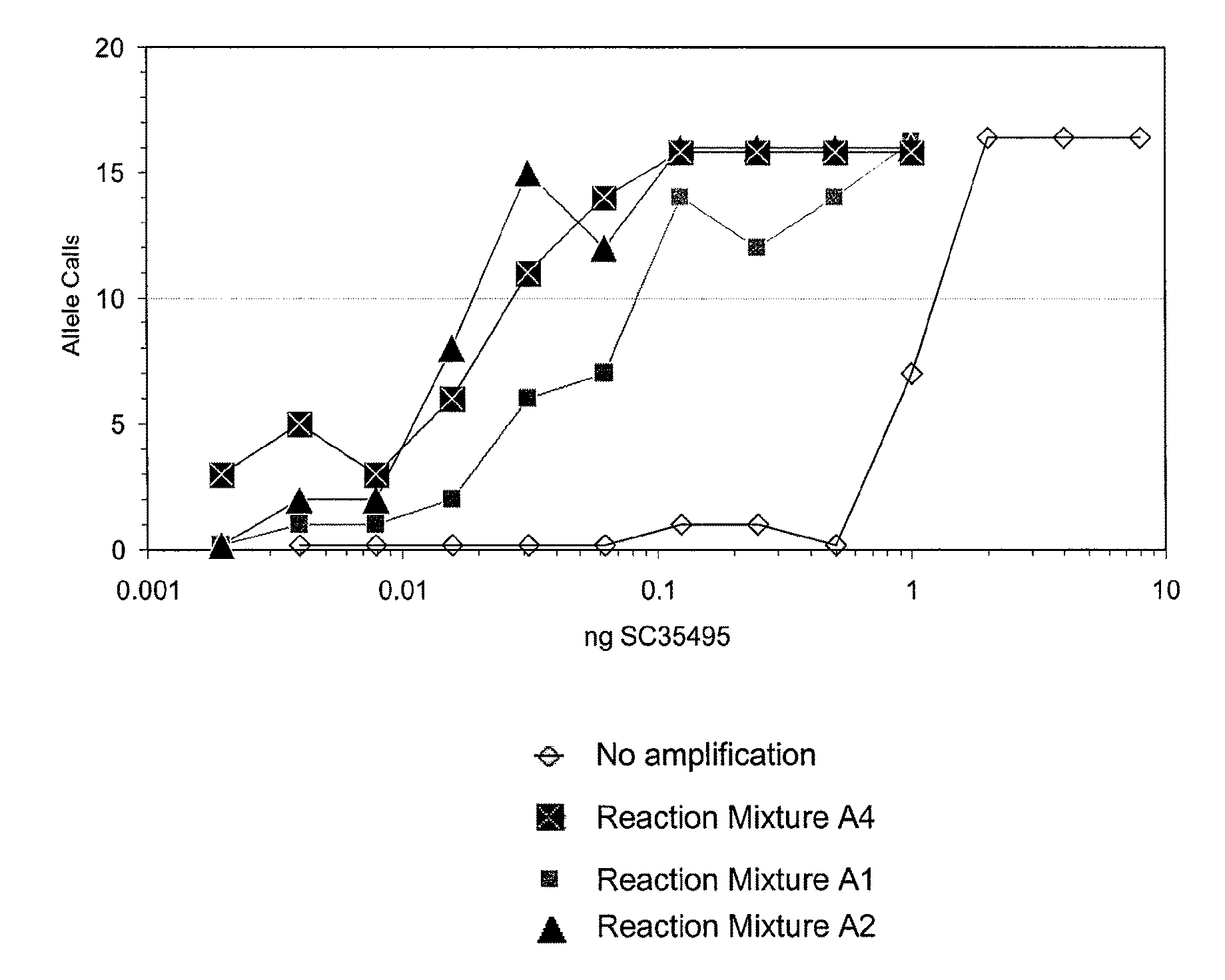
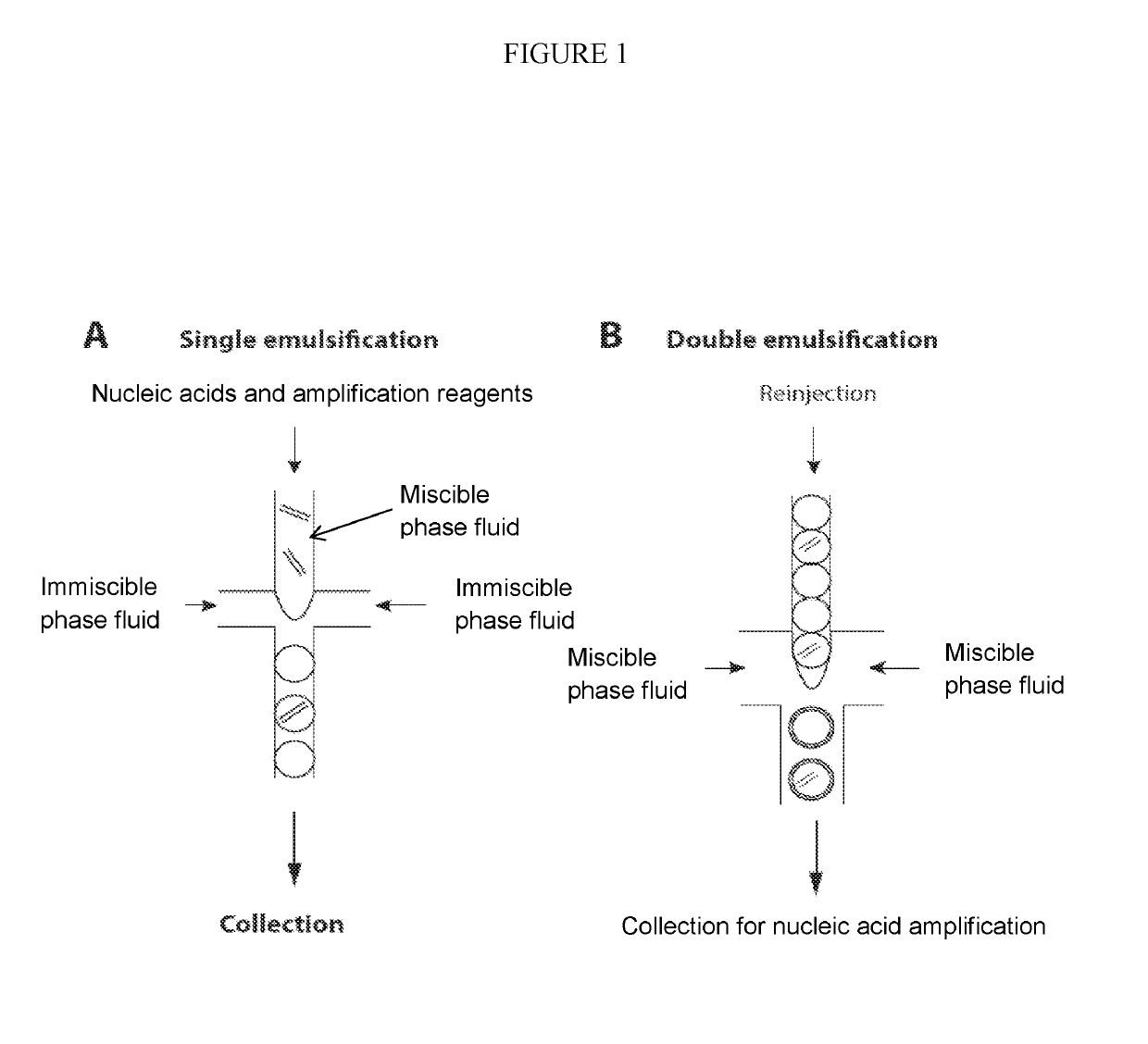
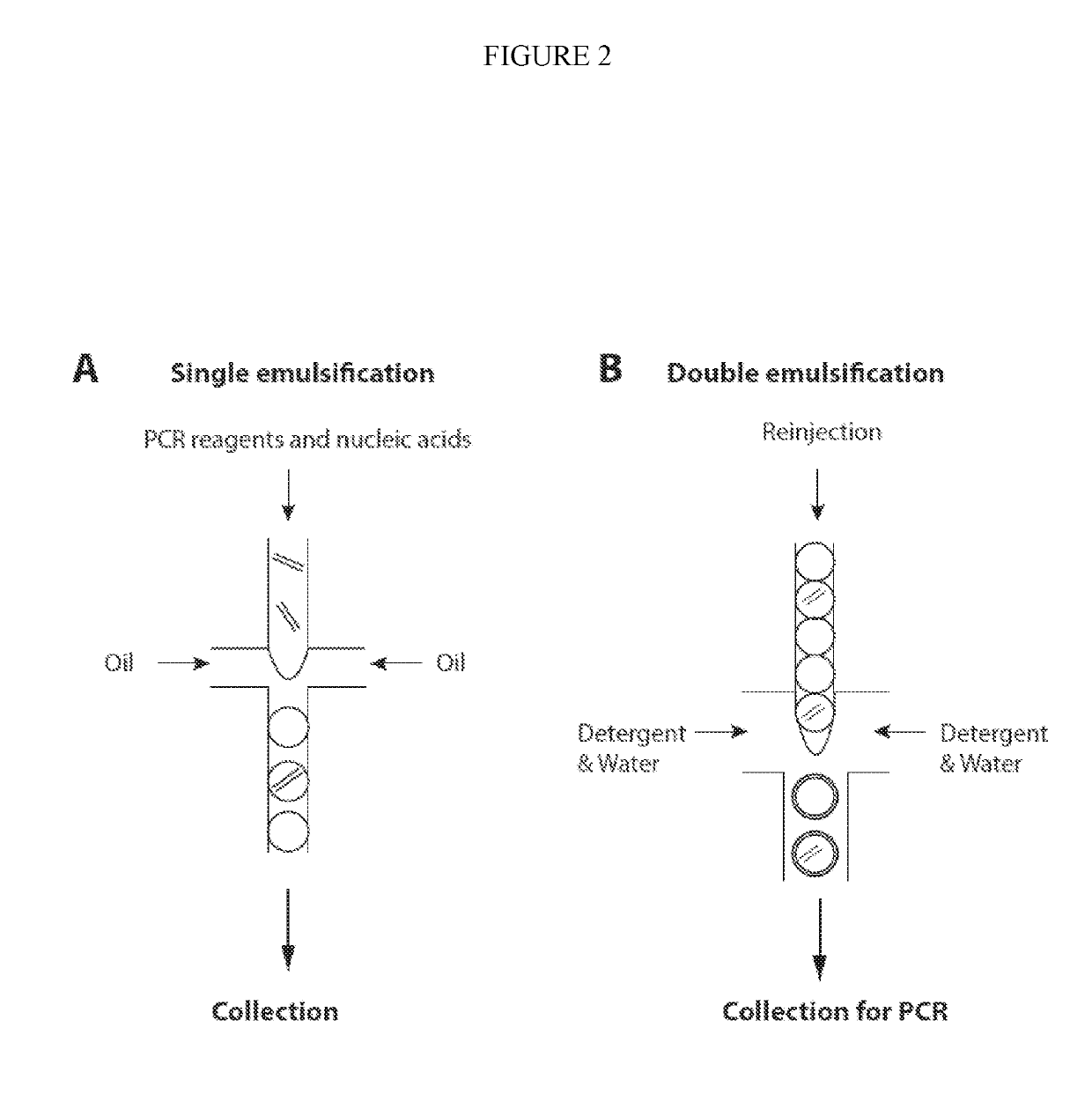
The present invention provides methods kits and systems for performing multiple displacement amplification reactions. In one method a sample of nucleic acid is provided. The nucleic acid is contacted with a reaction mixture which includes a set of oligonucleotide primers, a one or more polymerase enzymes and a detergent. The reaction mixture is then subjected to conditions under which the nucleic acid sequence is amplified to produce an amplified product in a multiple displacement reaction. The method may also be carried out by contacting the nucleic acid with the reaction mixture in the form of an emulsion. A kit is also provided for carrying out either the methods described above. The kit includes one or more polymerases, a plurality of primers and a detergent. The kit may also include a hydrophobic polymer and may include instructions for performing a multiple displacement amplification reaction on a nucleic acid sample.
Owner:IBIS BIOSCI
Amplification and cloning of single DNA molecules using rolling circle amplification
ActiveUS8497069B2Easy to startMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationCell freeAmplification dna
Owner:TELESIS BIO INC
cDNA amplification for expression profiling
ActiveUS20040180372A1Consistent outputQuick buildMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationRNA analysisOligonucleotide
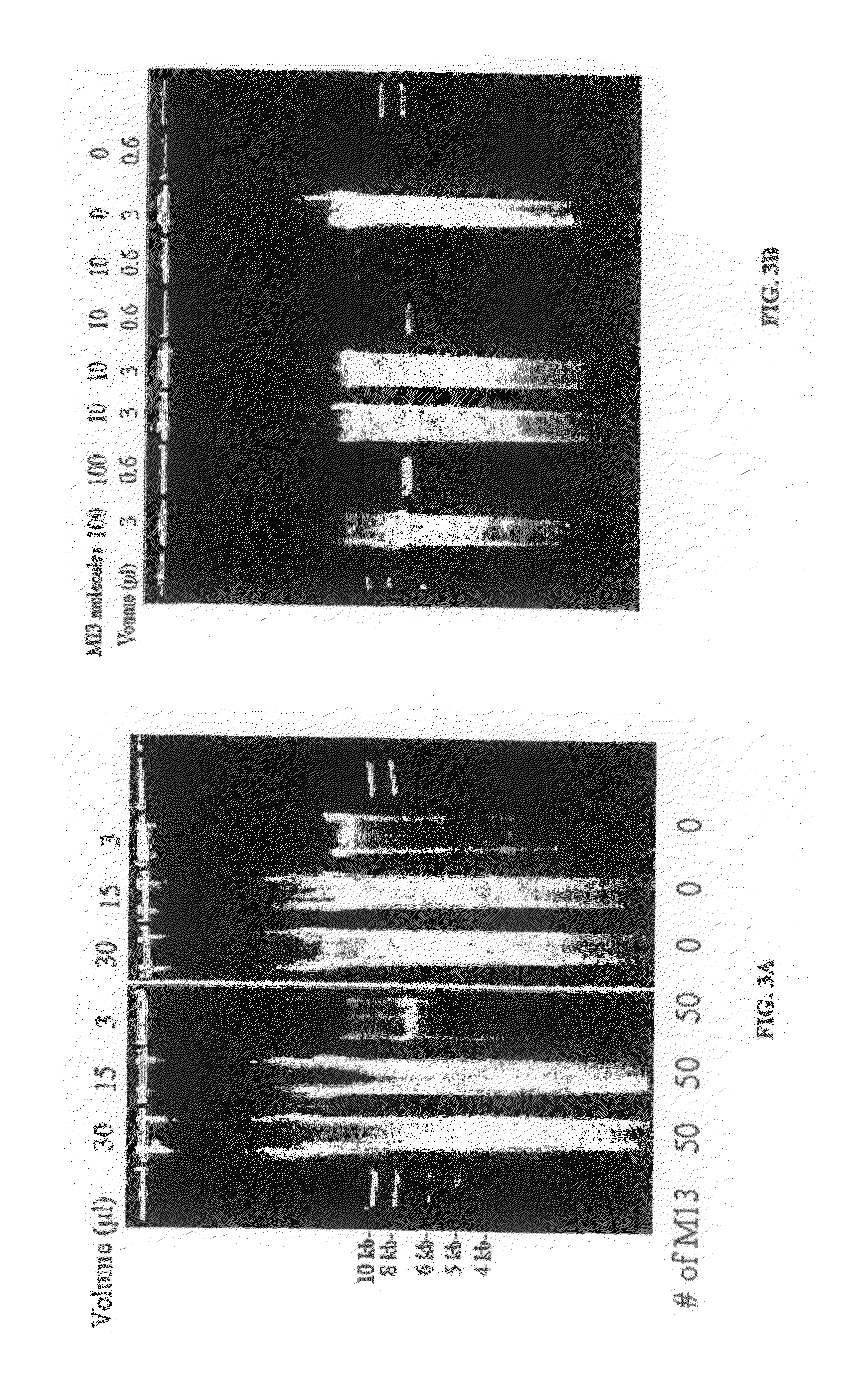
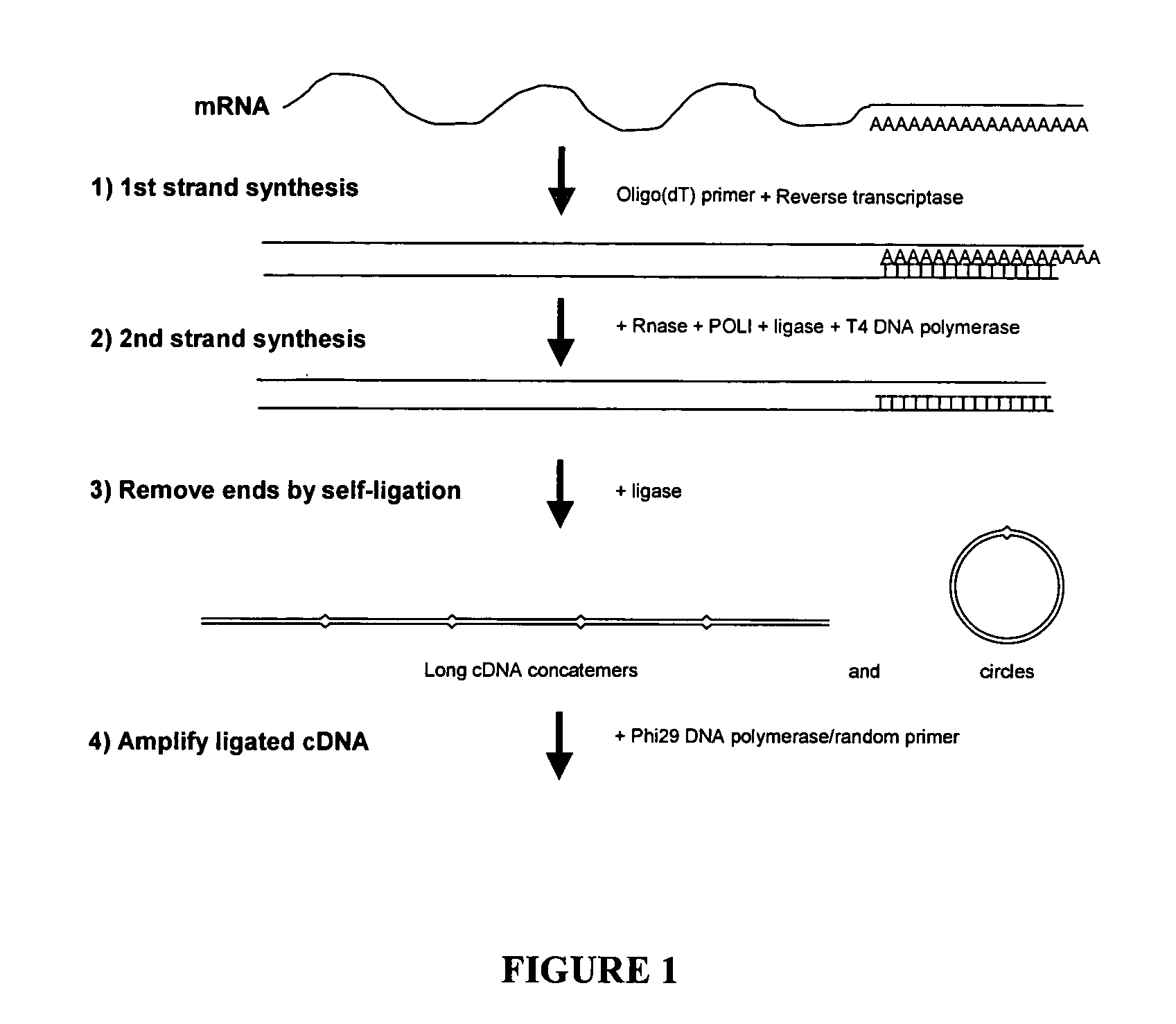
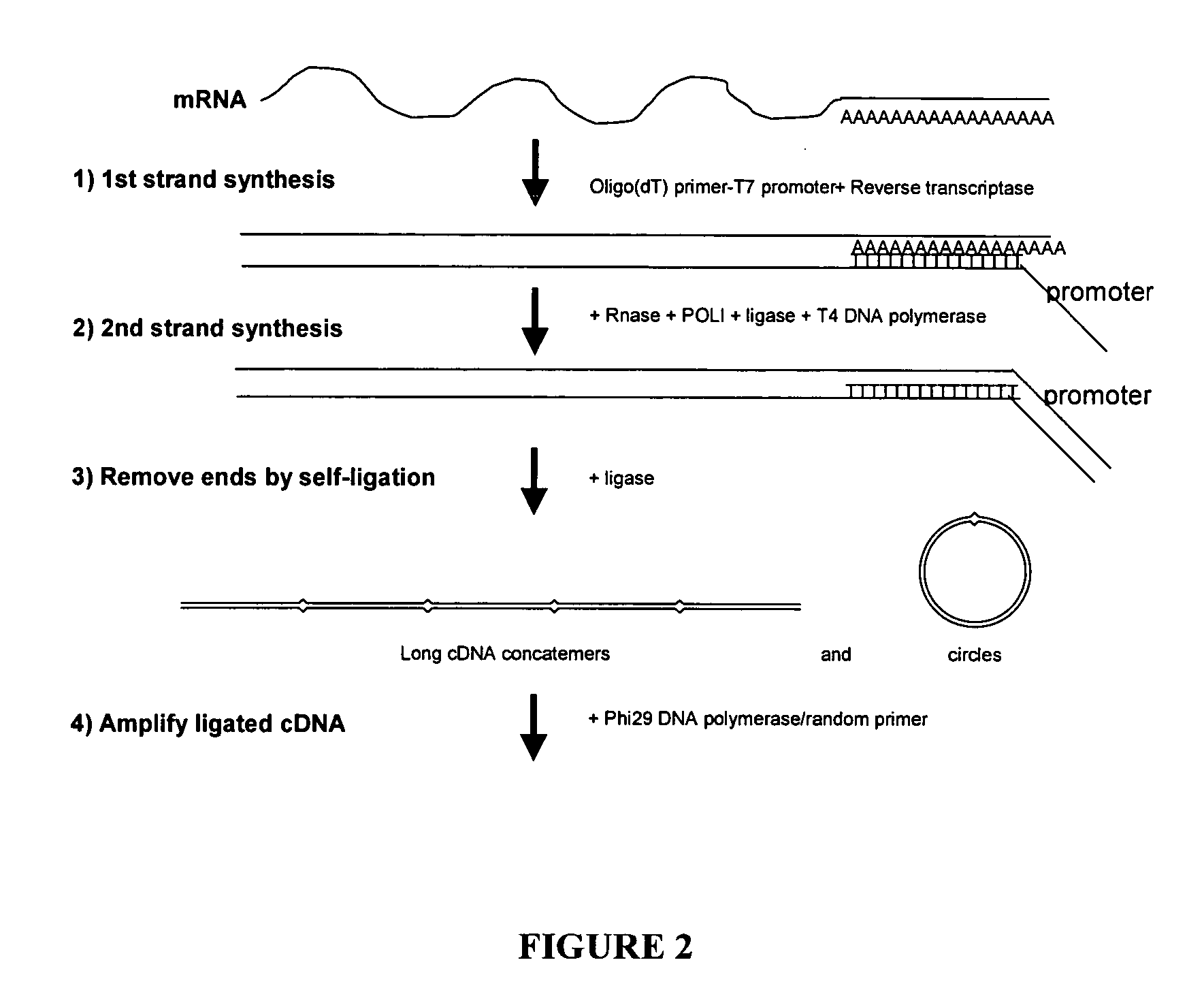
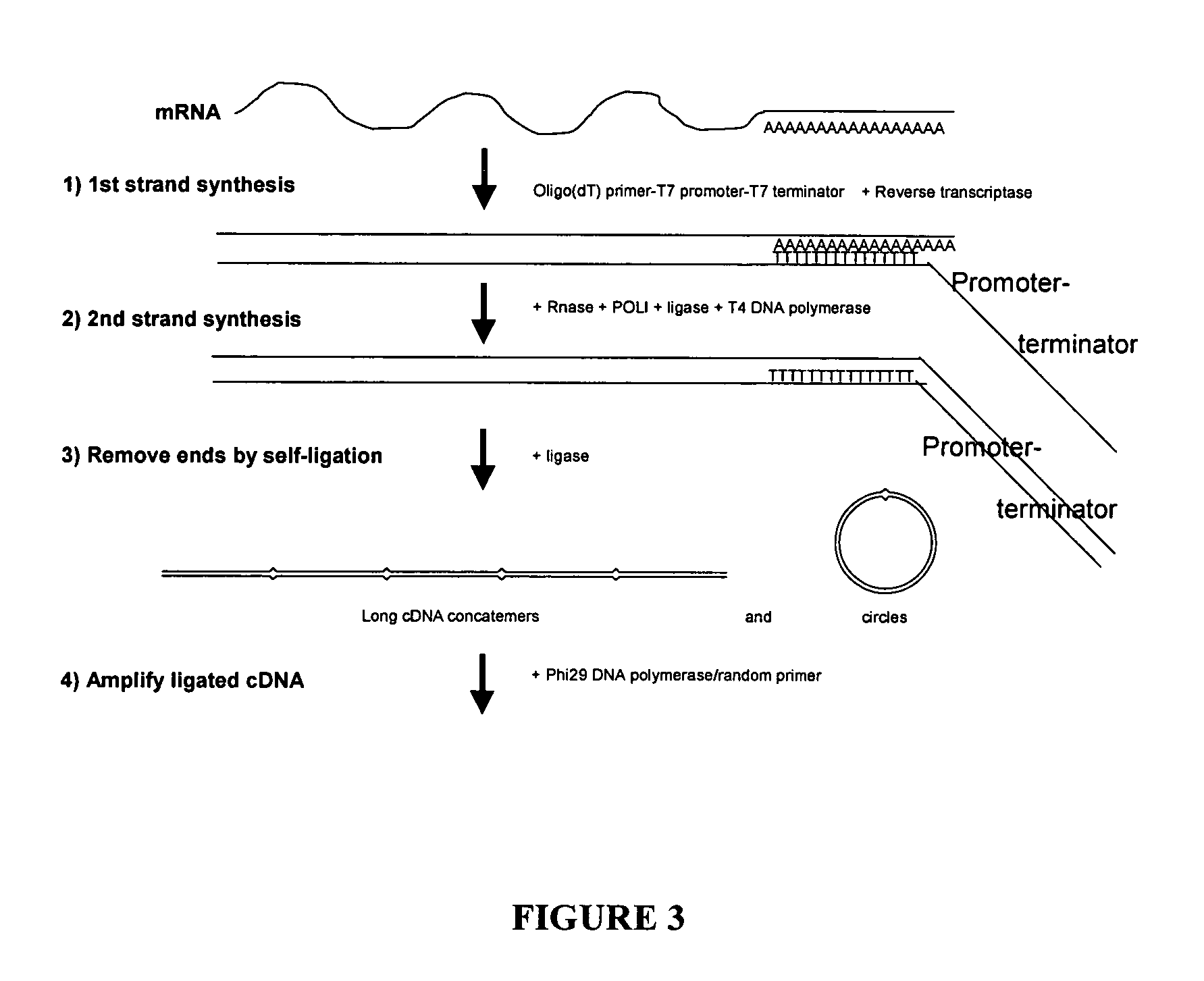
This invention presents a new cDNA amplification method. RNA is first converted to cDNA. The synthesis of cDNA can include a promoter tagged oligonucleotide, and then this cDNA is ligated to form circles (or possibly concatemers). This is then amplified using a Phi29 DNA polymerase based rolling circle and strand displacement amplification. The invention allows for RNA promoter sequences to be attached to the cDNA to facilitate additional amplification through the generation of RNA from the amplified cDNA. The resulting product can then be used to make materials for gene expression studies or other RNA analysis procedures.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
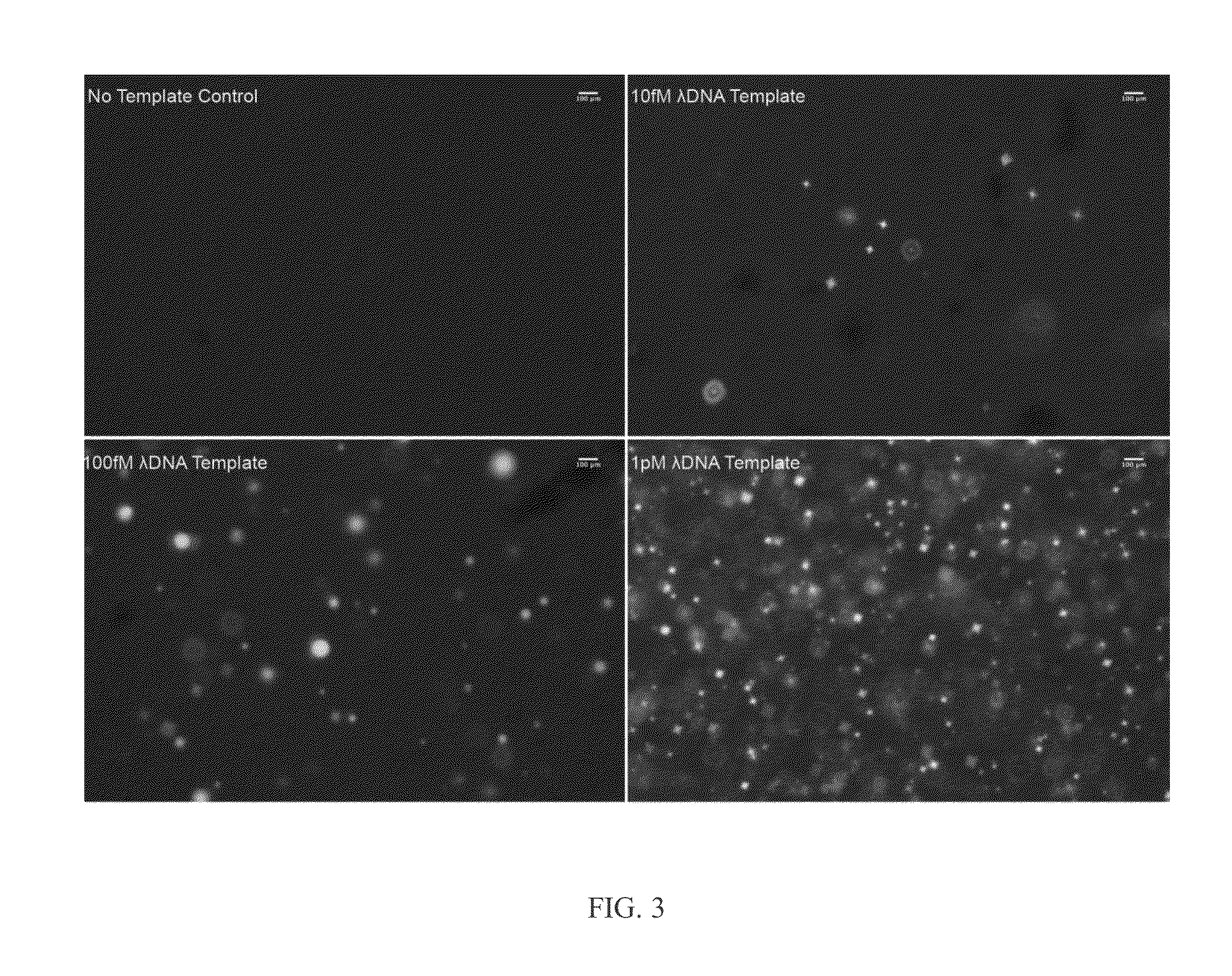
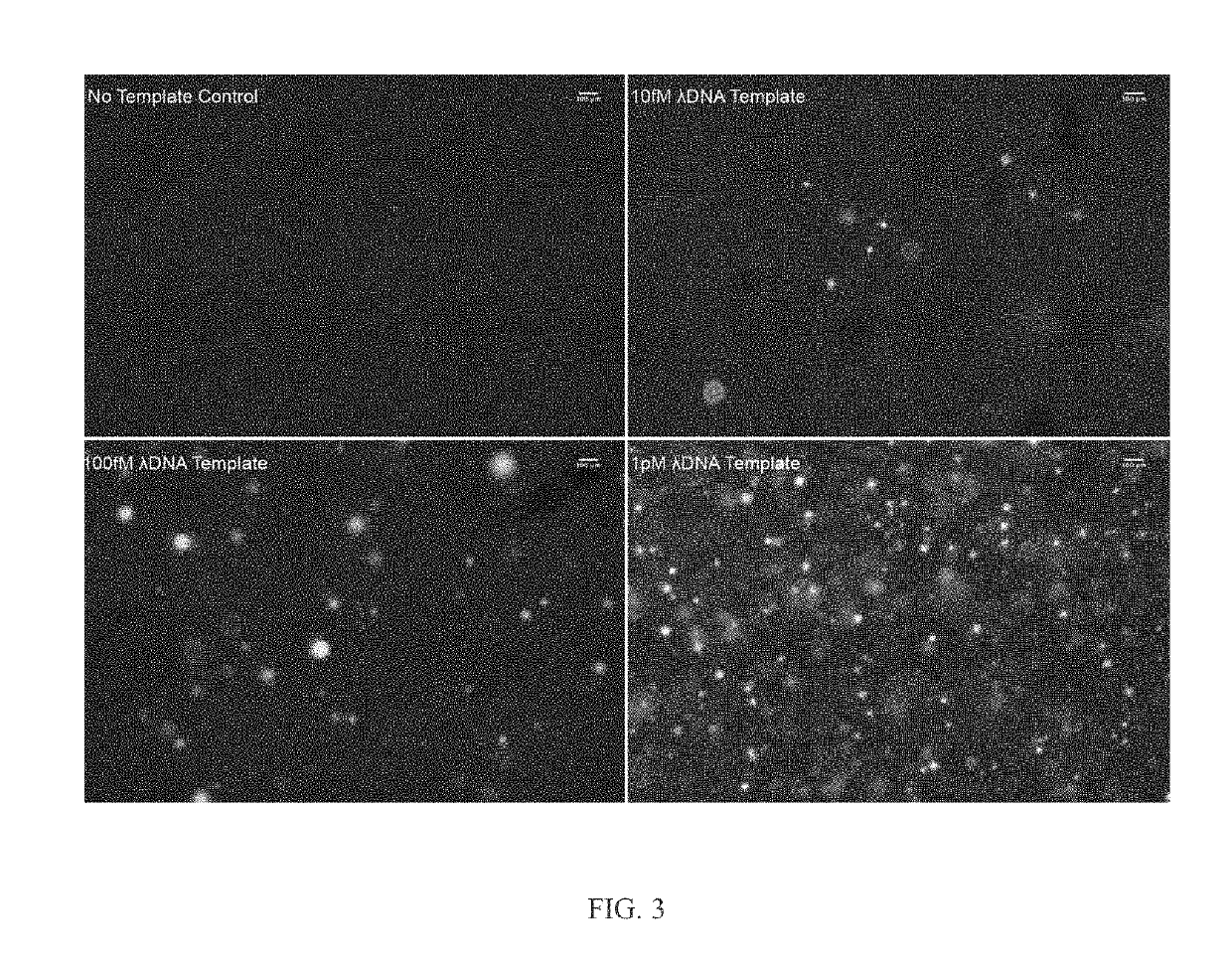
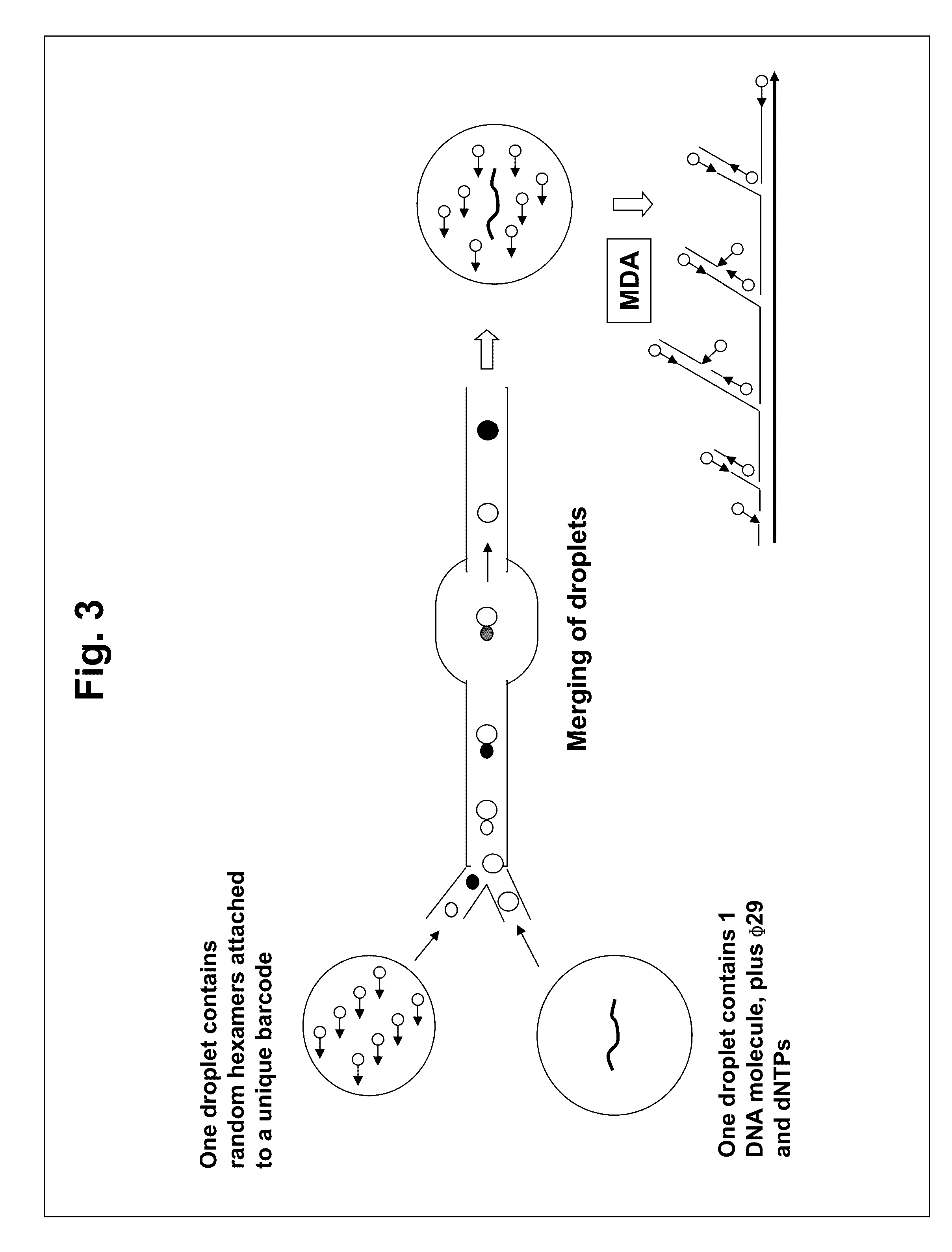
Microdroplet-Based Multiple Displacement Amplification (MDA) Methods and Related Compositions
PendingUS20180237836A1Uniform coverageImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCancer cellGenome
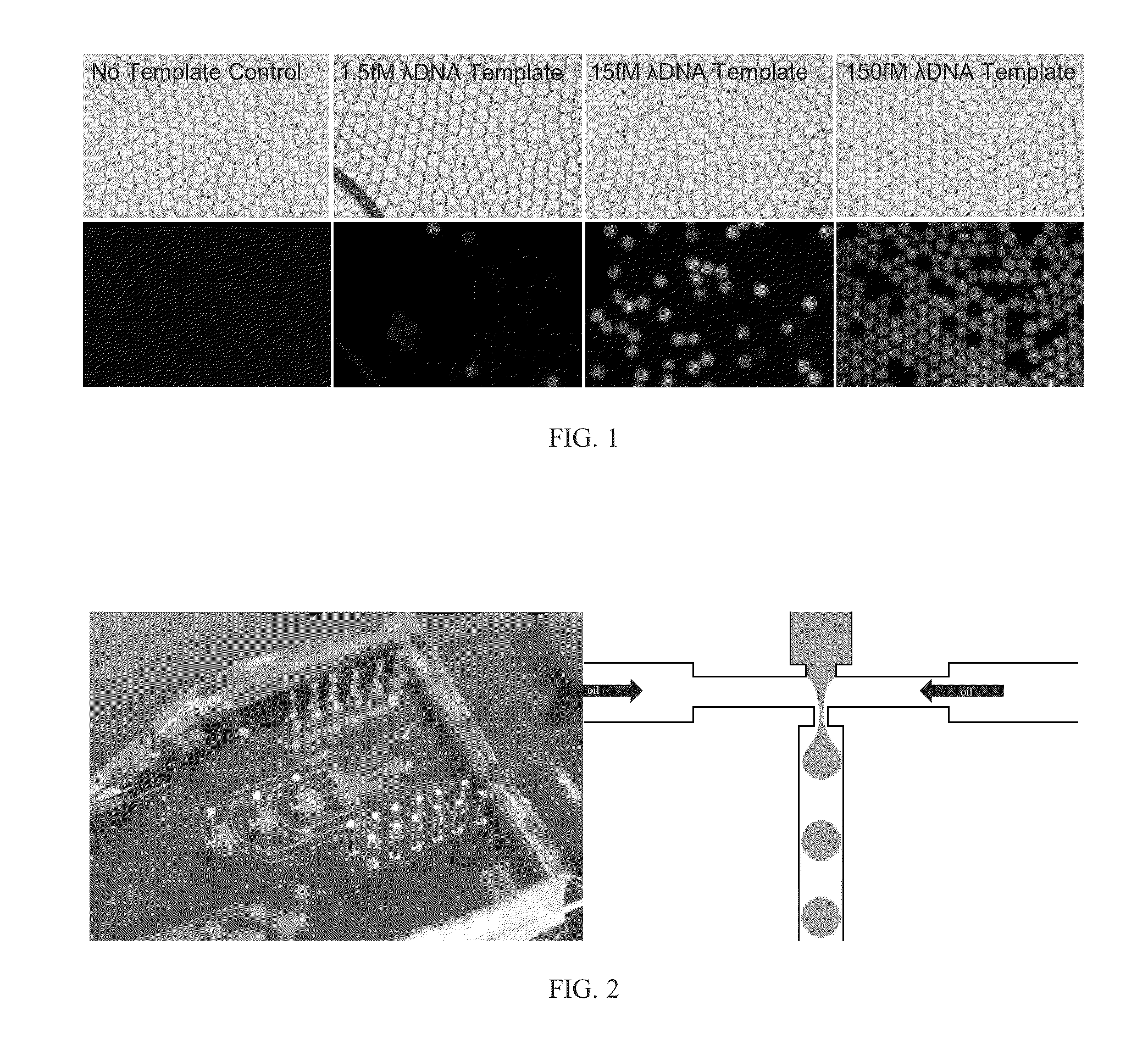
Methods for non-specifically amplifying a nucleic acid template molecule are provided. The methods may be used to amplify nucleic acid template molecule(s) for sequencing, e.g., for sequencing the genomes of uncultivable microbes or sequencing to identify copy number variation in cancer cells. Aspects of the disclosed methods may include non-specifically amplifying a nucleic acid template molecule, including encapsulating in a microdroplet a nucleic acid template molecule obtained from a biological sample, introducing multiple displacement amplification (MDA) reagents and a plurality of MDA primers into the microdroplet, and incubating the microdroplet under conditions effective for the production of MDA amplification products, wherein the incubating is effective to produce MDA amplification products from the nucleic acid template molecule.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method of whole genome amplification with reduced artifact production
ActiveUS7955795B2Reduced and undetectable levelQuality improvementMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPolymerase LNucleic acid sequencing
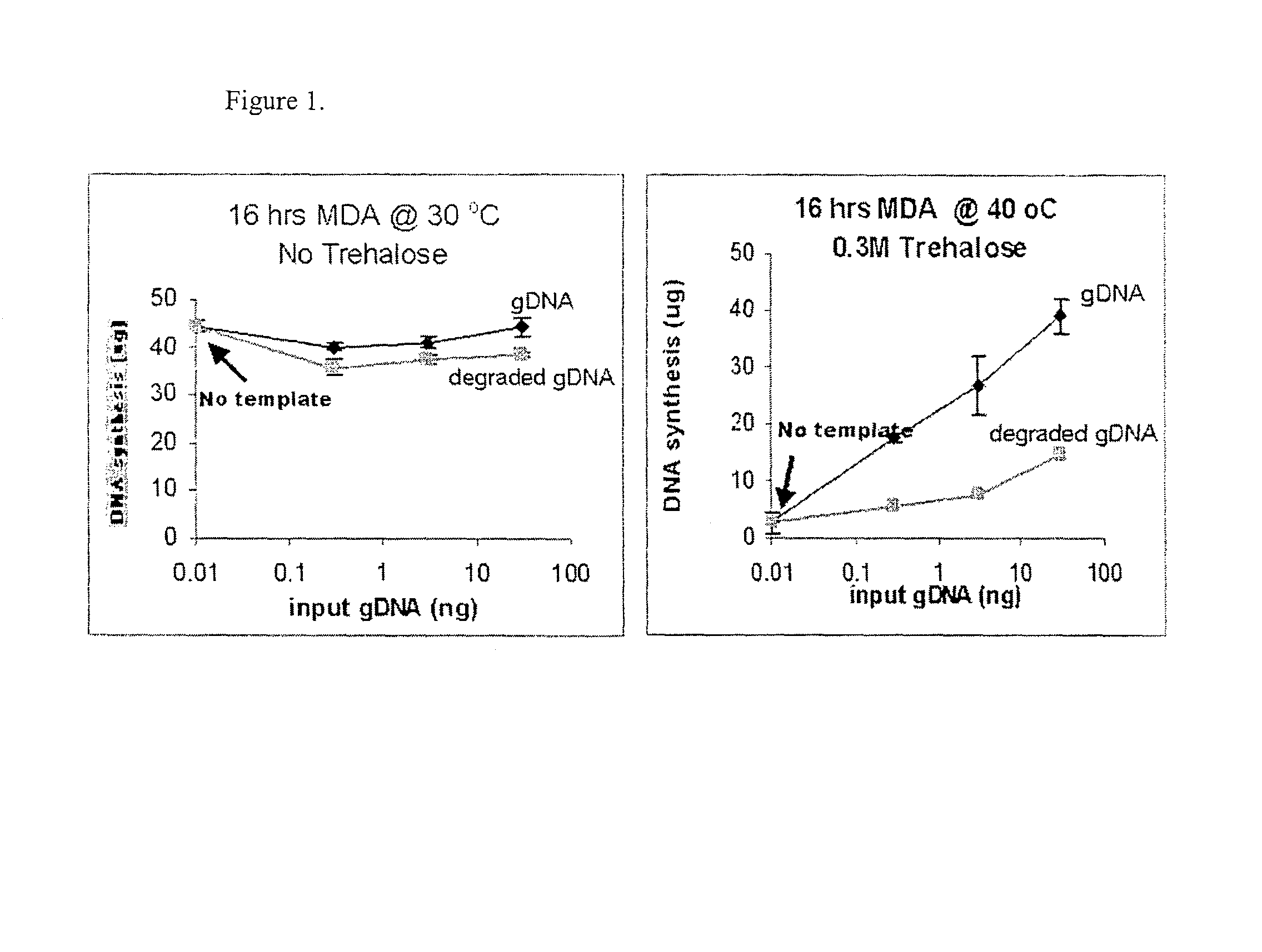
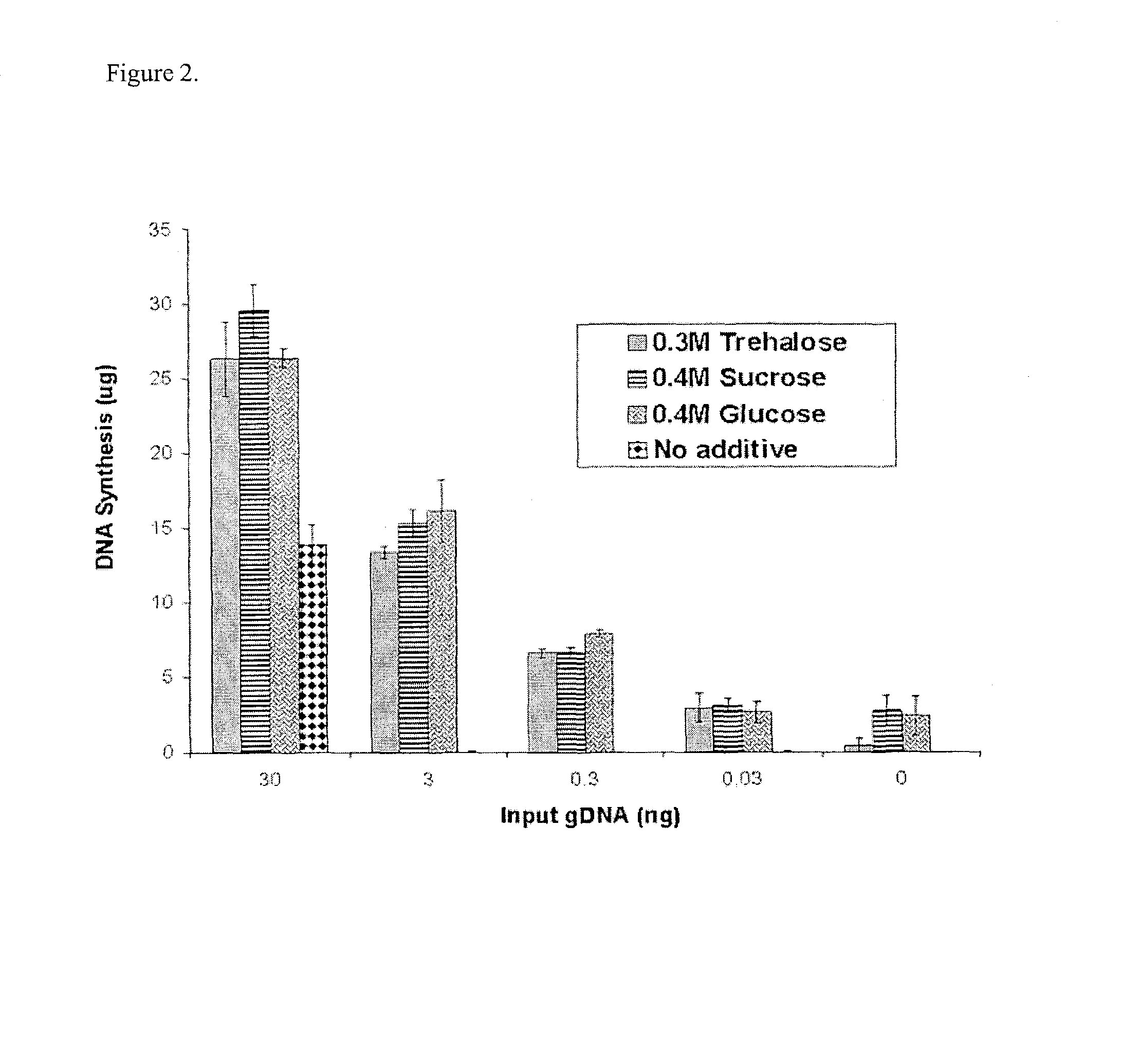
Disclosed are compositions and methods for amplification of nucleic acid sequences of interest with greater efficiency and fidelity. The disclosed method relates to isothermal amplification techniques, such as Multiple Displacement Amplification (MDA), where the generation of DNA artifacts is decreased or eliminated. Generally, this can be accomplished by carrying out the reaction at elevated temperature. In particularly useful embodiments of the method, sugars and / or other additives can be used to stabilized the polymerase at high temperature. It has been discovered that generation of high molecular weight artifacts, in an isothermal amplification procedure, is substantially reduced or eliminated while still allowing the desired amplification of input DNA by carrying out the reaction at a higher temperature and, optionally, in the presence of one or more additives. It also has been discovered that isothermal amplification reactions can produce amplification products of high quality, such as low amplification bias, if performed at a higher temperature and, optionally, in the presence of one or more additives.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Combined multiple-displacement amplification and PCR in an emulsion microdroplet
ActiveUS20190218594A1Easy to identifySequencing is facilitatedHeating or cooling apparatusMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid amplification techniqueVirus
The methods and systems described herein provide an improved emulsion droplet based nucleic acid amplification method, which allows nucleic acids contained in biological systems to be detected, quantitated and / or sorted based on their sequence as detected with nucleic acid amplification techniques, e.g., polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The nucleic acids can be free floating or contained within living or nonliving structures, including particles, viruses, and cells. The nucleic acids can include, e.g., DNA or RNA.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
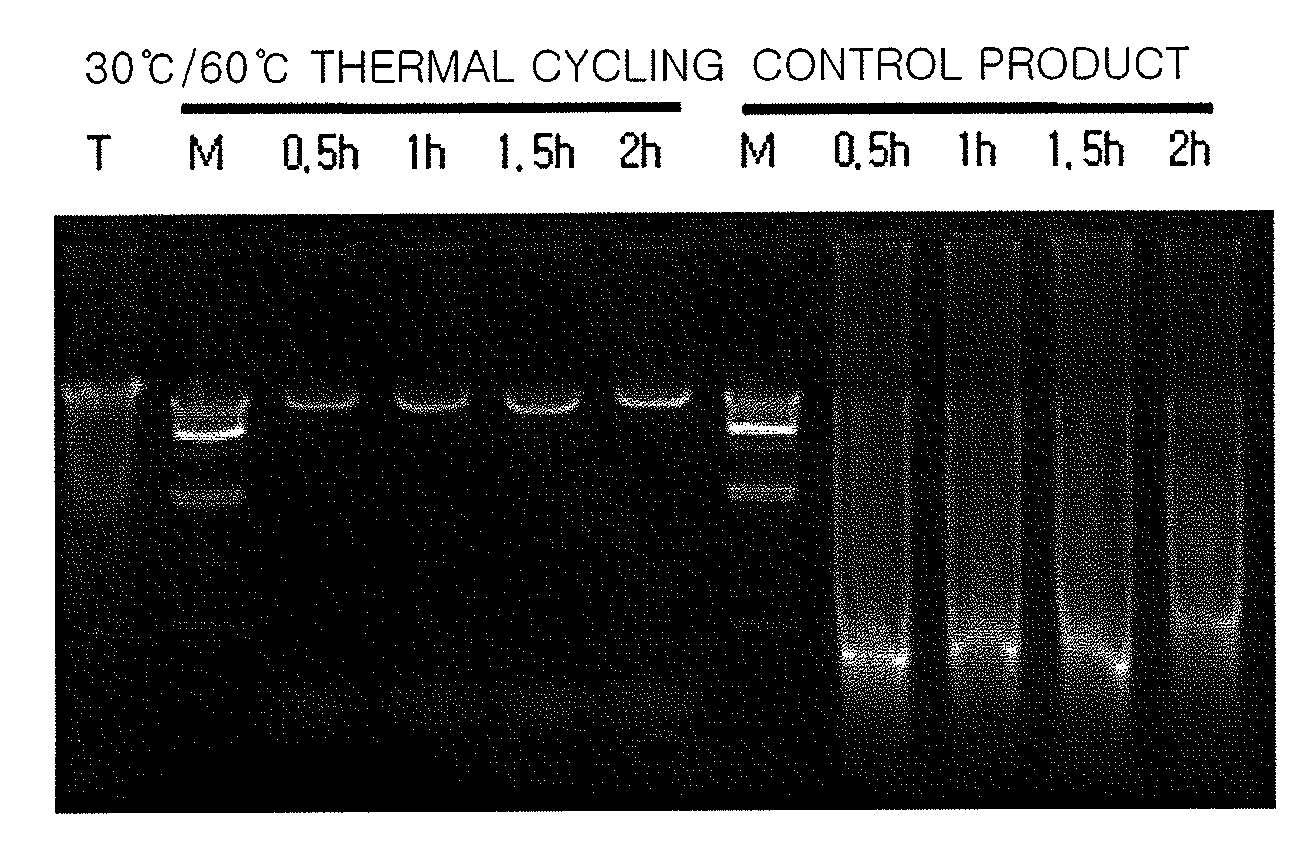
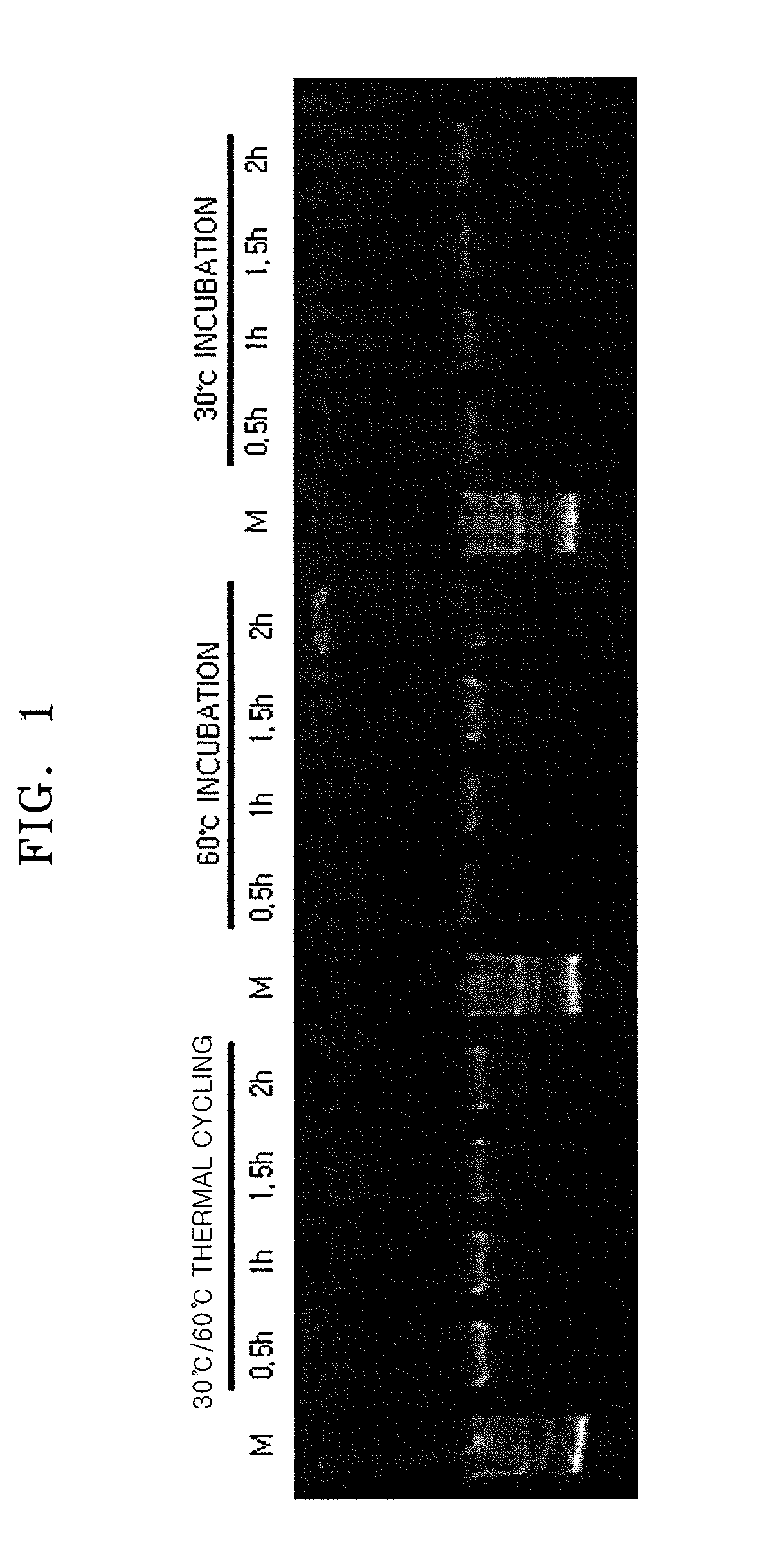
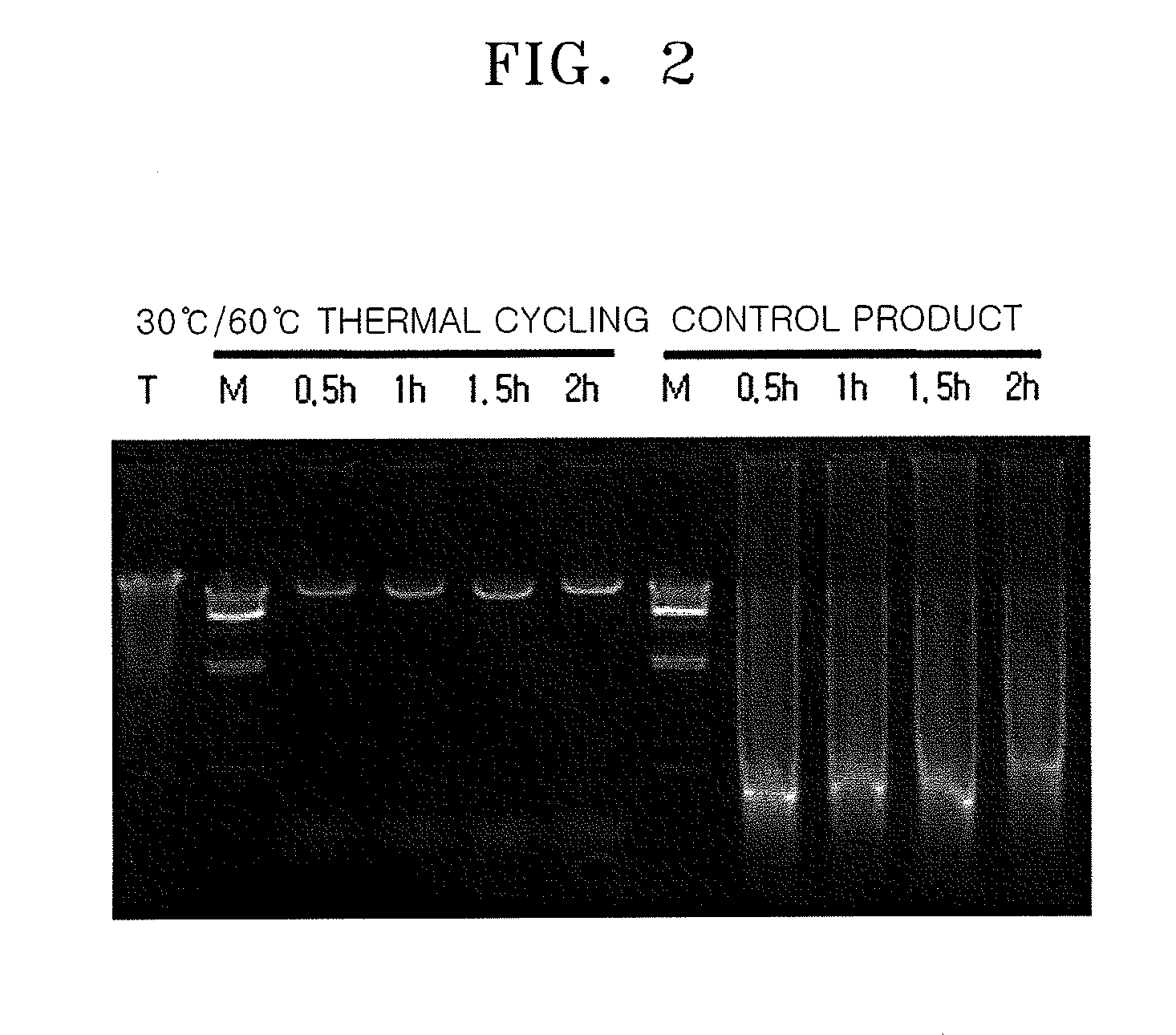
Method of Amplifying Target Nucleic Acid Sequence By Multiple Displacement Amplification Including Thermal Cycling
InactiveUS20100035303A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleic acid sequencingBiology
A method of amplifying a target nucleic acid sequence includes multiple displacement amplification and thermal cycling. According to the method, the target nucleic acid sequence may be effectively amplified.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
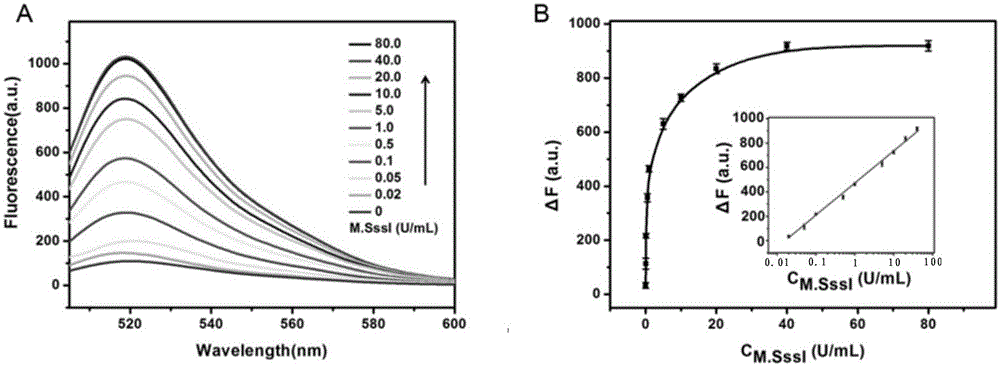
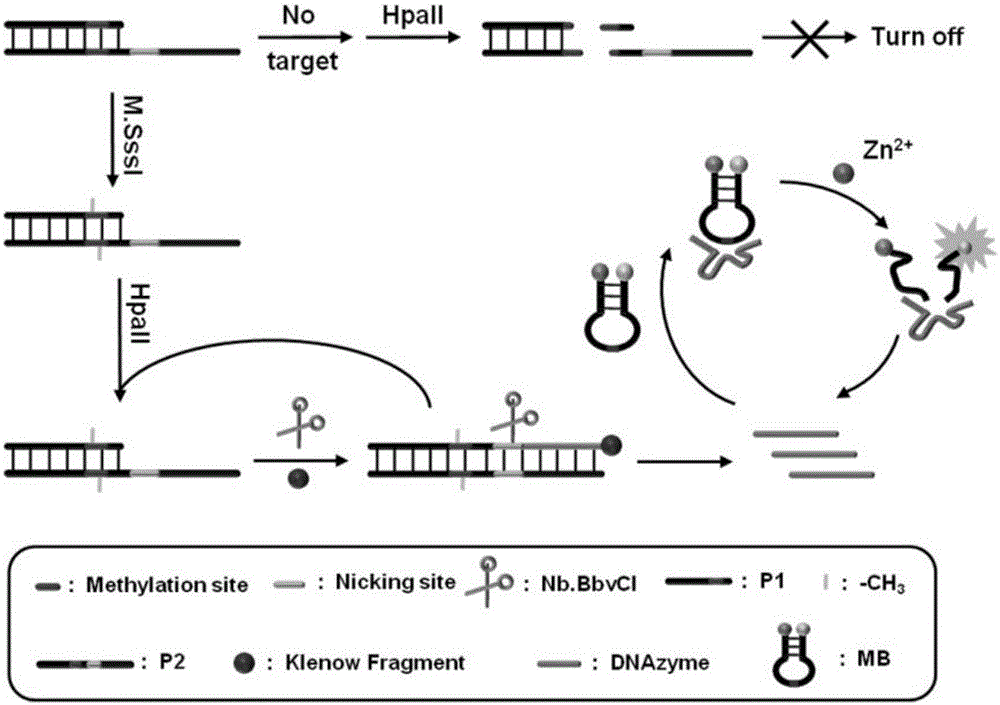
Method for detecting DAN methyltransferase activity based on strand displacement amplification and DNAzyme amplification
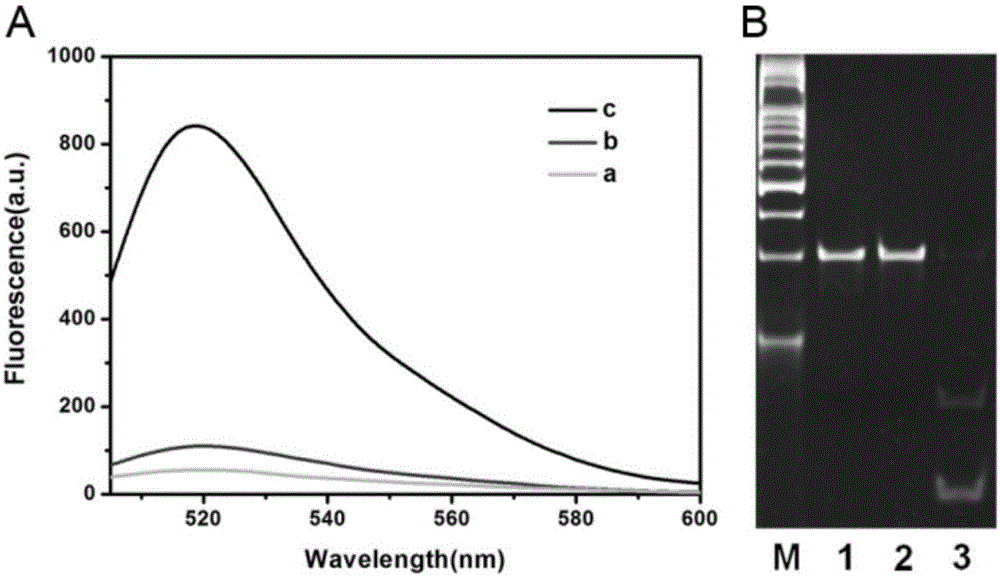
ActiveCN105112540AHighly sensitive detection activityLow detection limitMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisFluorescenceDNA Methyltransferase Inhibitor
The invention relates to a method for detecting DAN methyltransferase activity based on strand displacement amplification and DNAzyme amplification. A three-function double-stranded DNA probe is designed. Methylation happening to the three-function double-stranded DNA probe is specifically recognized through DAN methyltransferase. Remaining non-methylated double-stranded DNA is specifically cut through HpaII restriction enzymes, methylated double-stranded DNA triggers a strand displacement reaction, a large amount of 8-17 DNAzyme is released, the 8-17 DNAzyme catalyzes cutting of a large number of hairpin-line molecular beacon substrates, and remarkable fluorescent enhancement is triggered. The method can sensitively detect the DAN methyltransferase activity, and the detection limit is 0.0082 U / mL. The method has potential application in research of influences of anti-cancer drugs on DAN methyltransferase activity inhibition and screening of DAN methyltransferase inhibitors.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Amplification and separation of nucleic acid sequences using strand displacement amplification and bioelectronic microchip technology
InactiveUS20060110754A1Avoid uncertaintyHigh magnificationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluorescenceCombined use
Described and disclosed are devices, methods, and compositions of matter for the multiplex amplification and analysis of nucleic acid sequences in a sample using novel strand displacement amplification technologies in combination with bioelectronic microchip technology. Specifically, a nucleic acid in a sample is amplified to form amplicons, the amplicons are addressed to specified electronically addressable capture sites of the bioelectronic microchip, the addressed amplicons are captured and labeled, and then the capture sites are analyzed for the presence of label. Samples may be amplified using strand displacement amplification. The invention is also amenable to other amplification methodologies well known by those skilled in the art. The capture and label steps may be by a method of universal capture with sequence specific reporter, or by a method of sequence specific capture with universal reporter. The label may be detected by fluorescence, chemiluminescence, elecrochemiluminescence, or any other technique as are well known by those skilled in the art. This invention further allows for analyzing multiple nucleic acid targets on a single diagnostic platform wherein the nucleic acids may be amplified while either in direct contact with microchip components or in solution above the microchip array.
Owner:NANOGEN INC
AUDG (antarctic thermal sensitive uracil deoxyribonucleic acid glycosylase) mediated multiple cross displacement amplification and biosensing combined nucleic acid testing technique
ActiveCN107164541AEliminate effectiveStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAntigenNano biosensor
The invention discloses a multiple cross isothermal amplification and macromolecular nano biosensing combined target gene testing method. According to the method, a half antigen is marked at a 5' terminal of a cross primer CP1 or CP2 in multiple cross displacement amplification, and antarctic thermal sensitive uracil deoxyribonucleic acid glycosylase and biotinylated deoxyuridine are introduced into an amplification system to test amplification products on the basis of multiple cross displacement amplification combined with macromolecular nano biosensing. According to the method, amplification products of HPV16 type E7 gene or HPV18 type L1 gene can be visually tested by a macromolecular nano biosensor. The method is convenient, fast, sensitive, specific and suitable for testing of various nucleotide fragments.
Owner:ICDC CHINA CDC
Ring mediated cascade amplification strategy used for detecting DNA transmethylase activity in high sensitivity manner
ActiveCN107151694AAvoid non-specific amplificationSensitive detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorescencePolymerase L
The invention discloses a ring mediated cascade amplification strategy used for detecting DNA transmethylase activity in a high sensitivity manner. A long-stem ring probe is designed on the basis of strand displacement amplification and exponential type rolling circle amplification. The probe comprises a methylation locus, a long-stem part and a ring part, wherein the methylation locus is used for identifying DNA transmethylase, the long-stem part is used for guaranteeing the stability of the probe, and the ring part is used for triggering subsequent amplification; the ring part and a small part of stem part are used as the triggering strands for subsequent signal output. The probe is characterized in that the triggering strands are completely sealed in the ring part of the probe by the long-stem part, and non-specific amplification caused by probe leakage is avoided; the long-stem ring probe is methylated by the DNA transmethylase and then cut by restriction endonuclease to produce the triggering strands; under the synergic effect of polymerase and the endonuclease, the produced triggering strands trigger strand displacement amplification to produce a large amount of primers; the produced primers trigger exponential type rolling circle amplification to synthesize a large amount of G-tetraploid sequences, and the sequences interact with dye to obtain enhanced fluorescent signals.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
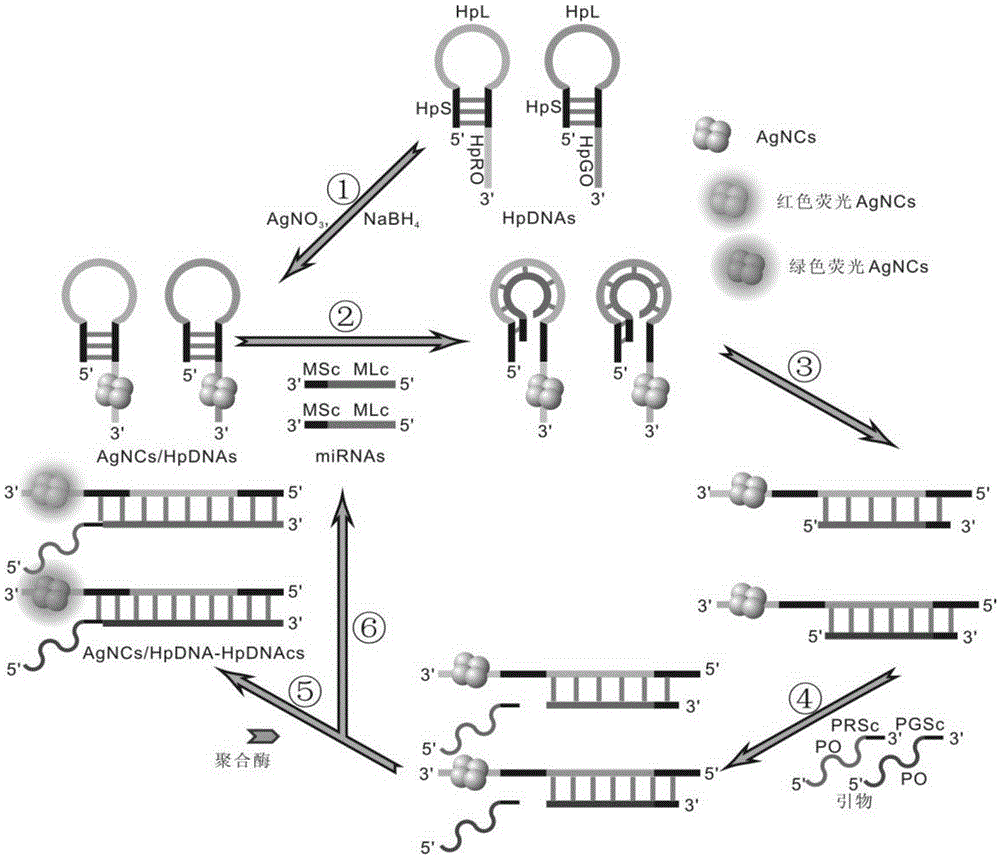
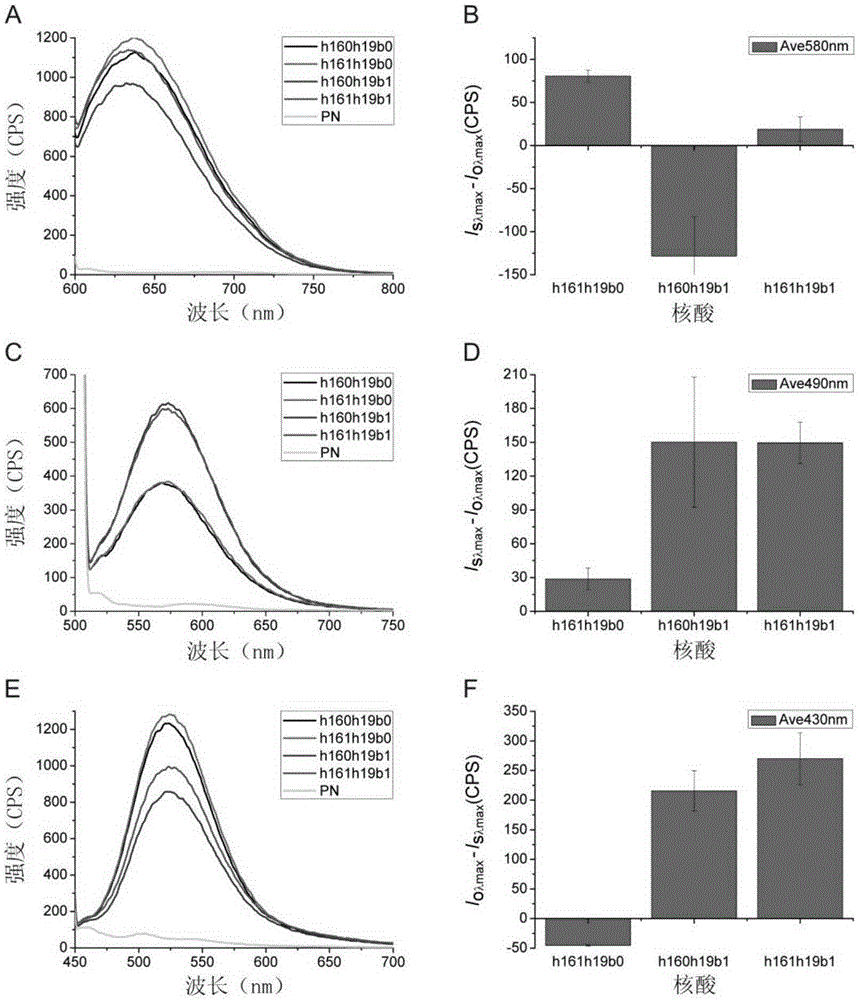
MicroRNA SDA (strand-displacement amplification) detection method based on AgNCs/HpDNA probes
ActiveCN105274226AAchieve high specificity detectionStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceMicroRNA
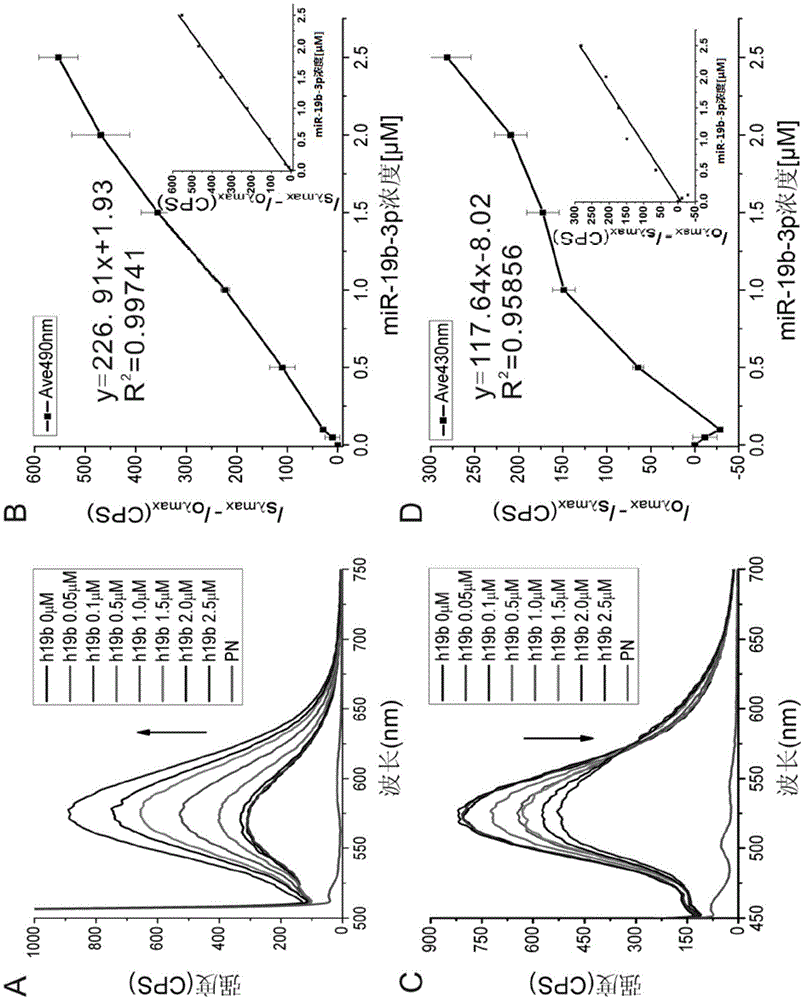
The invention discloses a microRNA SDA (strand-displacement amplification) detection method based on AgNCs / HpDNA probes, particularly discloses a double SDA detection method for miRNA (microRNA) markers of miR-16-5p and miR-19b-3p of gastric cancer plasma, and more particularly discloses a microRNA detection method based on hairpin DNA-templated silver nanoclusters probes combined with isothermal amplification. According to the method, hairpin DNA-templated silver nanoclusters are used as novel molecular beacons, and in a strand-displacement isothermal amplification reaction mediated by G-rich sequences of flap terminals of primers, double detection of the two miRNA markers of the gastric cancer plasma is achieved by the aid of G-rich fluorescence enhancement effect produced by hybridization. The method is high in specificity, short in reaction time, less in raw material consumption and simple and convenient in operation steps and opens up a new direction for establishing a rapid, simple and convenient novel miRNA detection method.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Multiplex PCR detection kit for identifying porcine circovirus
InactiveCN108456747ARapid identificationConvenient for clinical operationMicrobiological testing/measurementGenotypeEpidemiologic survey
The invention discloses a multiplex PCR detection kit for identifying porcine circovirus (PCV). The kit comprises the following three pairs of multiplex PCR detection primers which can quickly distinguish genotype PCV1, genotype PCV2 and genotype PCV3: PCV1-F and PCV1-R, PCV2-F and PCV2-R, and PCV3-F and PCV3-R.The multiplex PCR detection kit disclosed by the invention can be used for detecting the PCV and distinguishing different genotypes, has the characteristics of being quick, simple, convenient, high in specificity and high in sensibility, and can perform large batches of sample detectionat the same time; only one strand displacement amplification is needed, so that the situation whether a sample is infected by PCV1, PCV2 or PCV3, or is jointly infected by two or three of the PCV1, the PCV2 and the PCV3 can be identified; and the multiplex PCR detection kit can provide technical support for epidemic situation surveillance, epidemiologic investigation and comprehensive preventingand controlling of the PCV, and has a favorable application prospect.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY HUBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
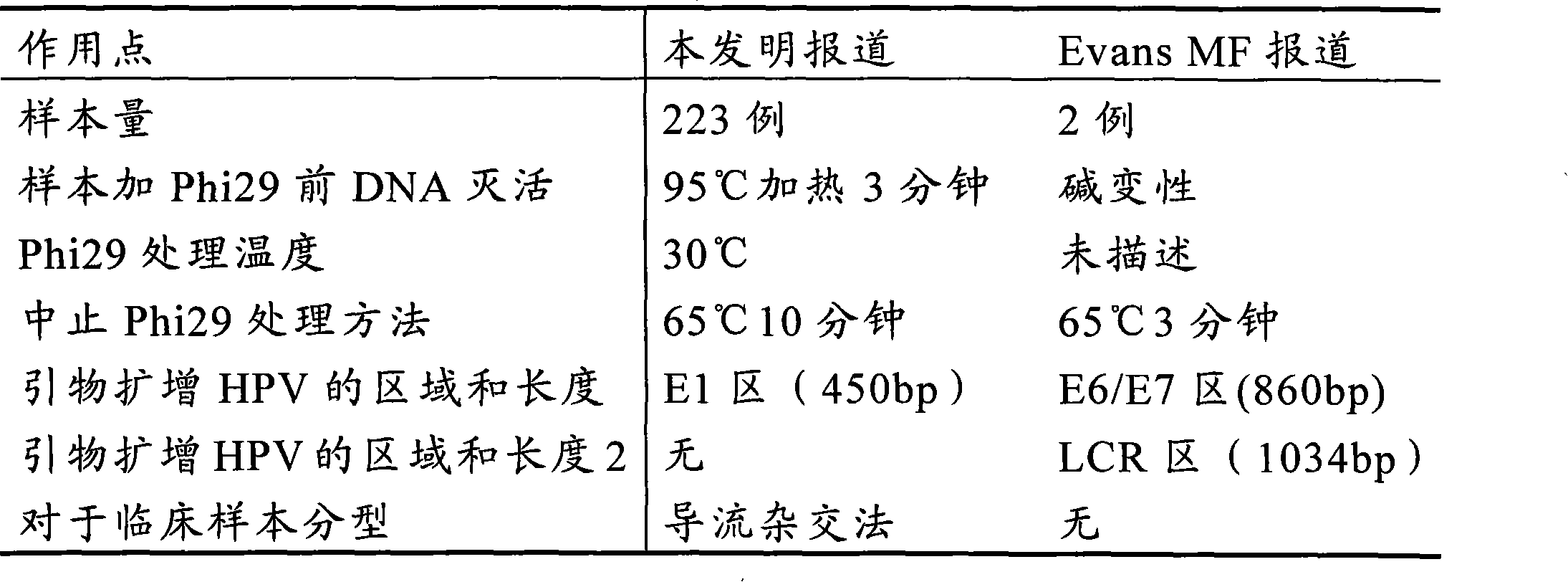
Method for detecting HPV and application of Phi29DNA polymerase in detecting HPV
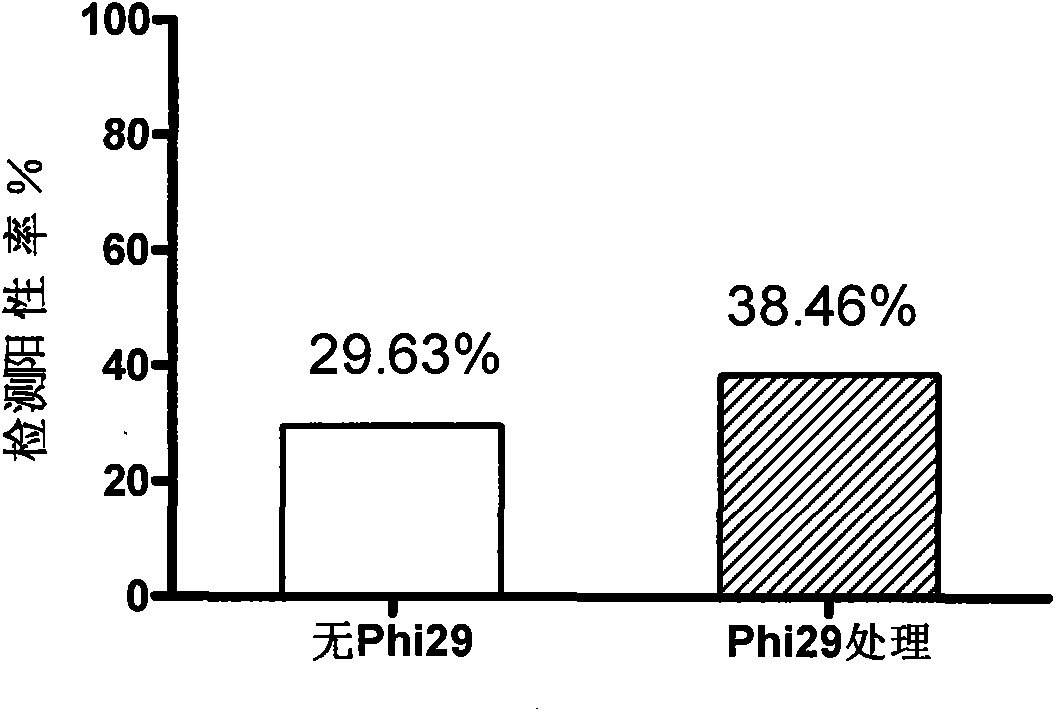
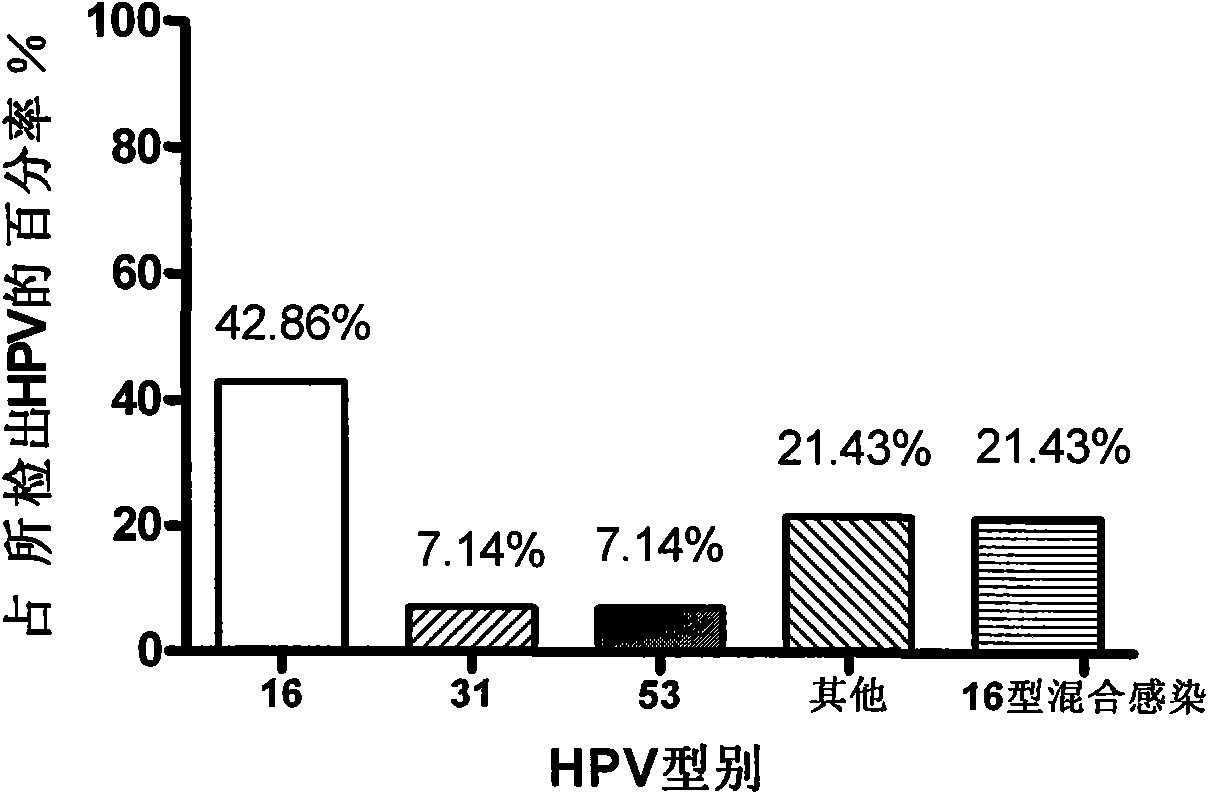
InactiveCN101619364AImprove the detection rateAmplified equalizationMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman papillomavirusPolymerase L
The invention discloses a method for detecting human papillomavirus (HPV) in a sample, which sequentially comprises the following steps: A) extracting DNA in the sample; B) amplifying the extracted DNA in step A); C) amplifying PCR; and D) detecting viruses. The amplifying of the step B) is to carry out multiple displacement amplification on all the genes of the extracted DNA with a Phi29DNA polymerase. The invention also discloses application of the Phi29DNA polymerase in detecting the human papillomavirus. The detection method can obviously improve the detection rate of the HPV. The sample does not need to be purified when the Phi29DNA polymerase is used to amplify the DNA. A gene group is uniformly amplified; the amplifying yield is stable; the operation is simple; the method is independent of a PCR reaction; and no amplified product having specificity is generated.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF IMMUNOLOGY +1
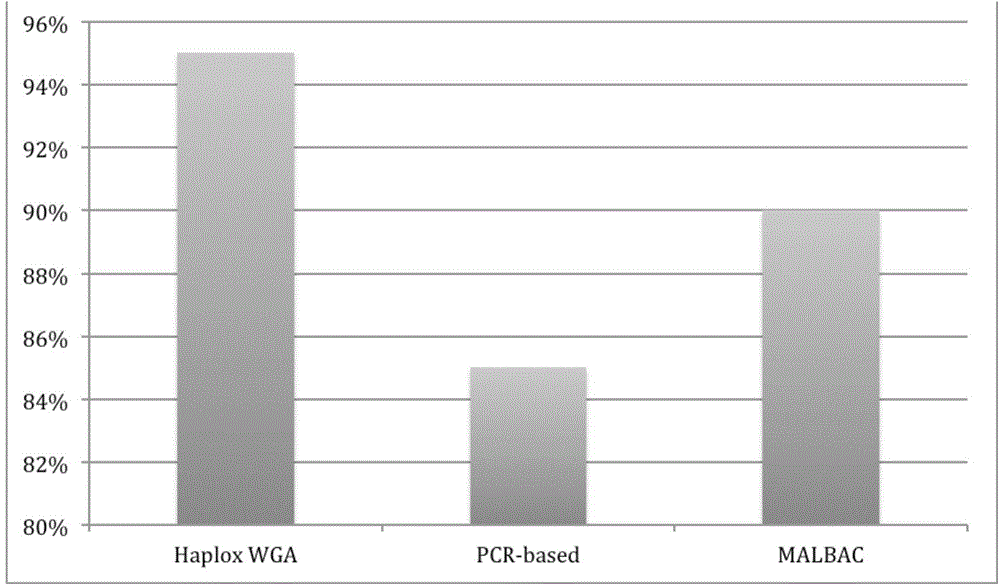
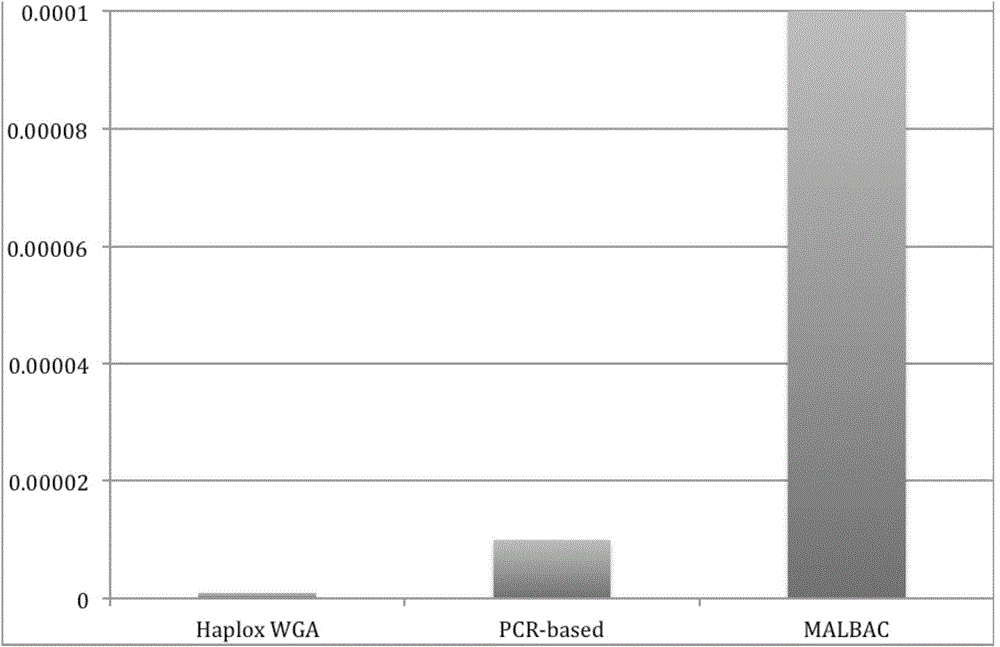
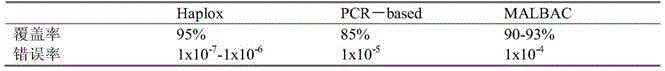
MDA (Multiple Displacement Amplification)-based whole-genome amplification method
InactiveCN104560950AEfficient amplificationOvercoming low coverage issuesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationMicrobiologyGenome amplification
The invention provides an MDA (Multiple Displacement Amplification)-based whole-genome amplification method. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) separating and extracting single cells; (2) extracting DNA of the single cells; (3) carrying out multiple displacement amplification (MDA) by virtue of a Haplox-method single-cell whole-genome amplification kit by taking the DNA of the single cells obtained by the step (2) as a template; and (4) purifying a product obtained by the step (3) to obtain purified DNA.
Owner:SHENZHEN HAPLOX BIOTECH
Long-range barcode labeling-sequencing
ActiveUS9469874B2Reduce complexityImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationBarcodeHaplotype
Methods for sequencing single large DNA molecules by clonal multiple displacement amplification using barcoded primers. Sequences are binned based on barcode sequences and sequenced using a microdroplet-based method for sequencing large polynucleotide templates to enable assembly of haplotype-resolved complex genomes and metagenomes.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
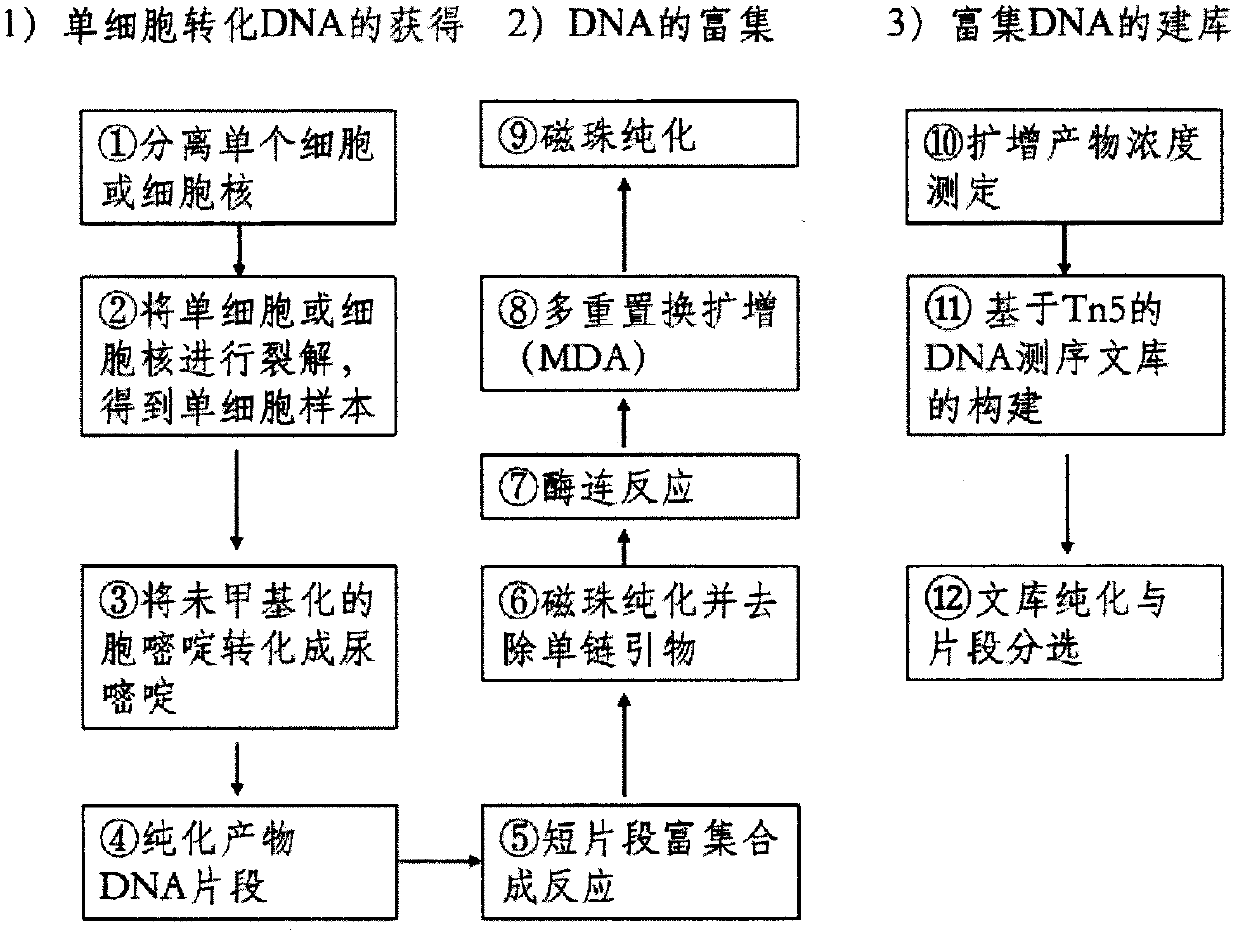
Construction method and application of single-cell methylation sequencing library
InactiveCN107904669AReduce generationMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationSingle strandDouble strand
The invention relates to a construction method and application of a single-cell methylation sequencing library. The invention applies a multiple displacement amplification technology to construction of the single-cell methylation sequencing library, and richness and comparison rate of the sequencing library are obviously enhanced. The construction method comprises the following specific steps: firstly producing small segments containing uracil by utilizing an optimized bisulfate conversion kit, then carrying out amplification extension for multiple times by using a label-free random primer, degrading a free single-stranded small segment primer, then denaturalizing a paired double strand by utilizing high temperature, then connecting single-stranded small segments into a single-stranded long fragment, carrying out multiple displacement amplification by utilizing a label-free random primer segment with a terminal 5' closed, obtaining an amplification end product, and finally carrying outlibrary construction based on Tn5 enzyme on a reaction product.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
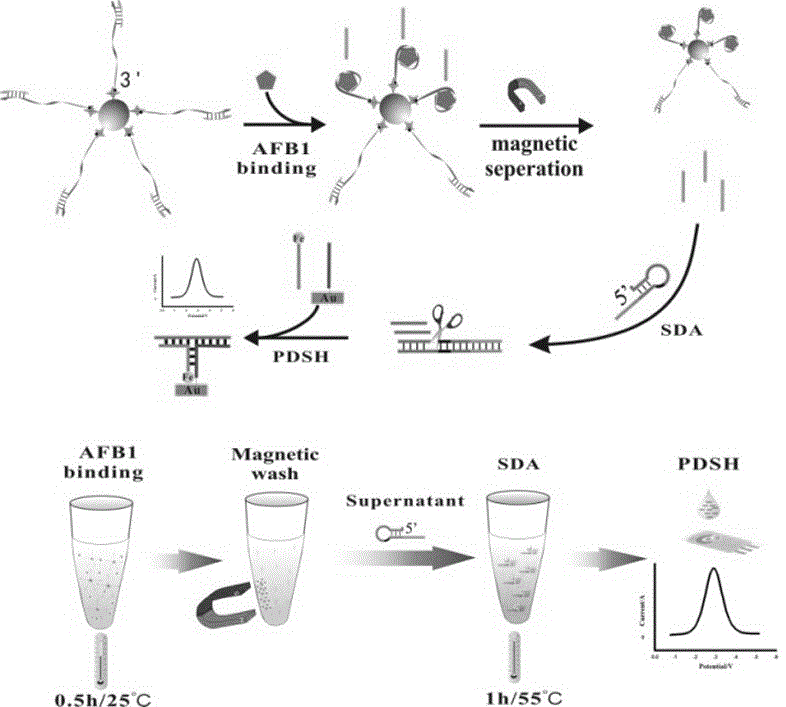
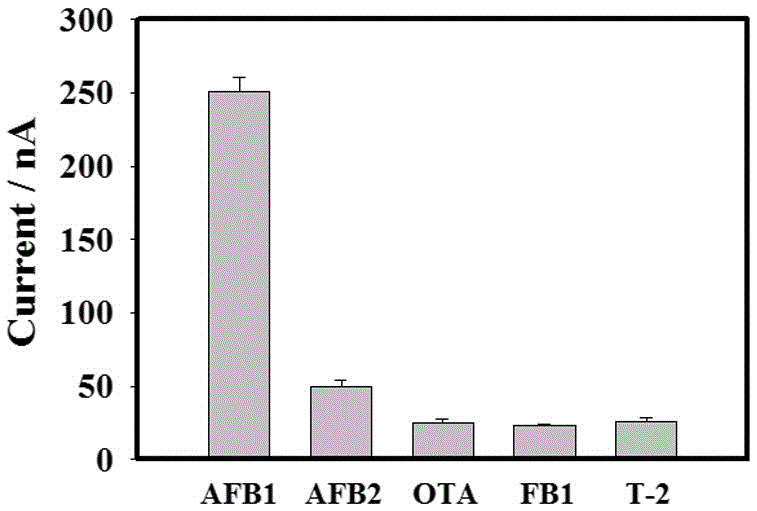
Electrochemical detection method for AFB1 (Aflatoxin B1) based on strand displacement amplification and surface proximity hybridization reaction and application thereof
ActiveCN106680346AReduce testing costsLower synthesis costMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAptamerSorbent
The invention belongs to the technical field of the quality safety detection of agricultural products, and relates to the detection of AFB1 (Aflatoxin B1) in the agricultural products, in particular to an electrochemical detection method for the AFB1 based on a strand displacement amplification and surface proximity hybridization reaction and application thereof. A hybrid complex formed by a biotin-labelled AFB1 aptamer and a Block probe is prefixed on a surface of a magnetic bead; in the presence of a target, the AFB1 and the Block probe are combined with the aptamer in a competitive manner; the replaced Block probe can trigger a strand displacement amplification reaction so as to produce a lot of amplicons; and the amplicons can cooperatively participate in the surface proximity hybridization reaction on a surface of a screen-printed electrode, so as to introduce an electroactive probe to generate a corresponding electrical signal. Compared with specific experiments and conventional ELISA (Enzyme-linked Immuno Sorbent Assay) methods, the electrochemical detection method for the AFB1 disclosed by the invention has the advantages of good specificity, high sensitivity, reliability and accuracy, and is expected to provide a technical selection for large-scale screening of the AFB1 in agricultural products including corn.
Owner:河南省农业科学院农业质量标准与检测技术研究所
Reagent kit for simultaneously detecting multiple deafness genes on single cell level
The invention provides a reagent kit for simultaneously detecting multiple deafness genes on a single cell level. The invention also provides a method for simultaneously detecting various deafness gene sites on a single cell level. By adopting a single-cell whole genome amplification technology, a sample type with little content of DNA such as a single-cell sample is effectively amplified to whole-genome DNA with total amount of micro-gram by virtue of MDA (multiple displacement amplification). The obtained DNA is amplified by virtue of PCR of a specific primer, Sanger sequencing is carried out for an amplified product on a sequencing instrument, and various genetic deafness genes can be effectively detected.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ANNOROAD BIO TECH CO LTD +2
Method for synthesizing DNA nanosphere complementary chains and sequencing method
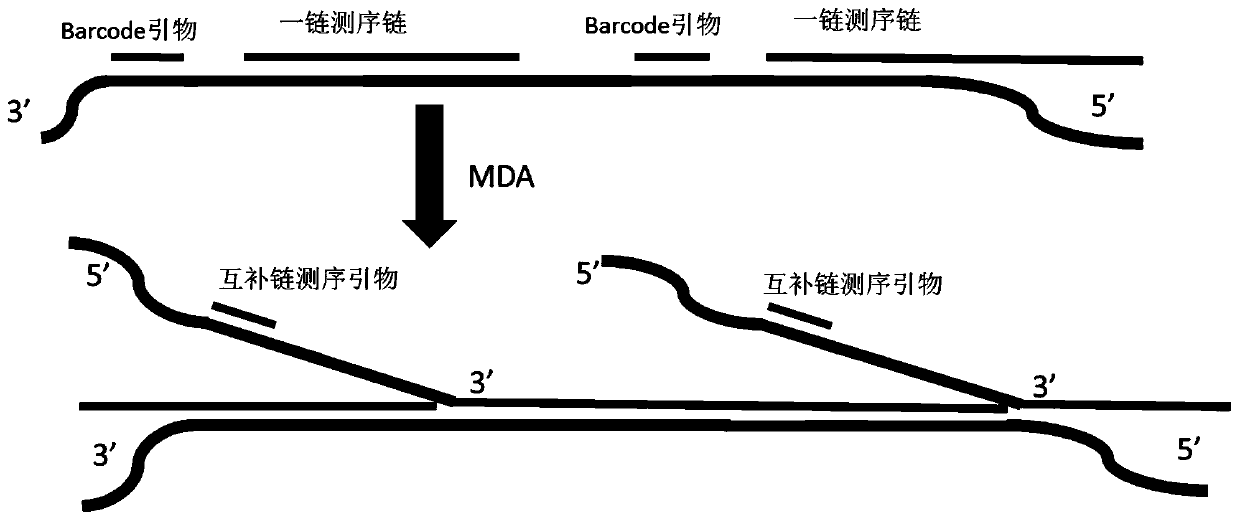
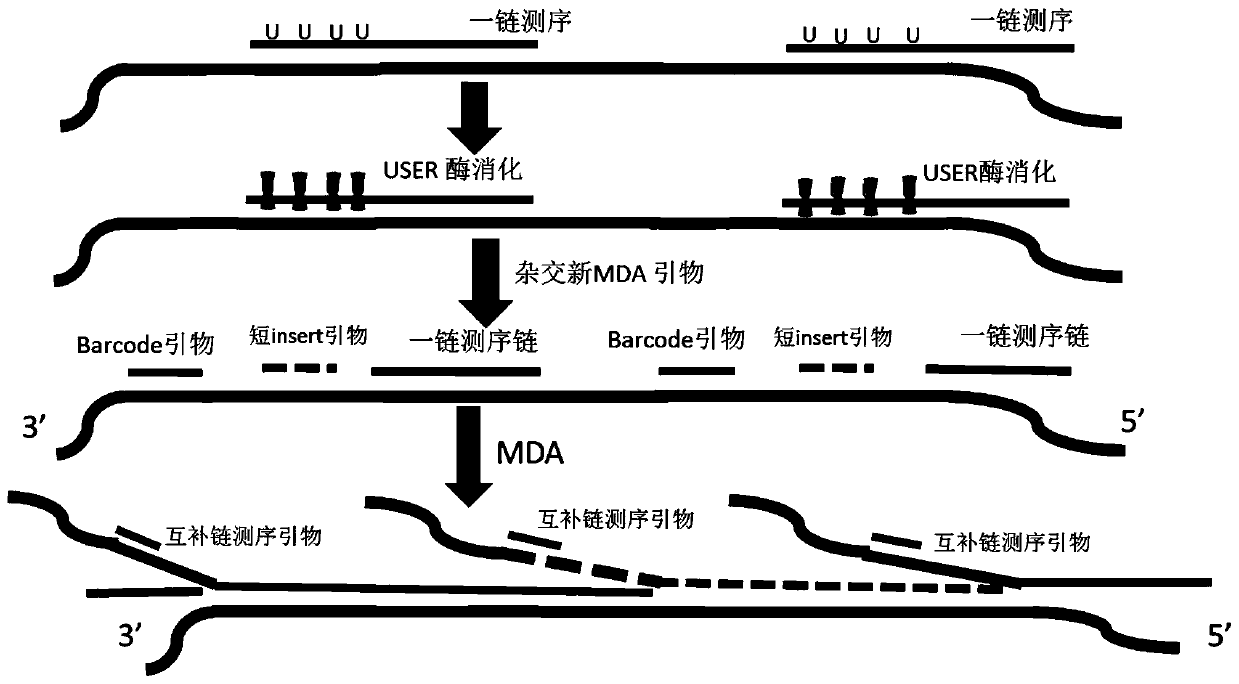
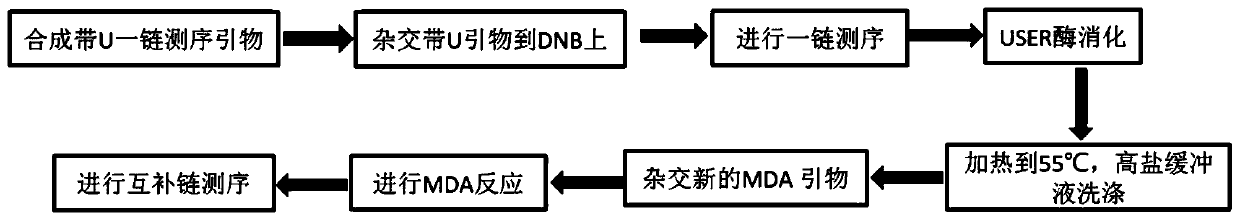
PendingCN111286527AHigh copy numberQuality improvementMicrobiological testing/measurementMultiple displacement amplificationA-DNA
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing DNA nanosphere complementary chains and a sequencing method. The method comprises the following steps: treating a product after one chain sequencingof a DNA nanosphere by using an enzyme, wherein a primer for one chain sequencing is modified, and after enzyme treatment, the modification is destroyed by the enzyme, so that the primer is digested;hybridizing a multiple displacement amplification primer with the product obtained in the previous step, wherein the multiple displacement amplification primer at least comprising a first primer, andthe first primer is completely or partially complementary to a primer binding region of one chain of sequencing; and under the action of polymerase with a chain displacement function, carrying out chain displacement reaction by taking the multiple displacement amplification primer and one chain as primers to generate DNA nanosphere complementary chains. According to the method disclosed by the invention, one chain of occupied primers are removed before MDA, and the position is vacated to carry out MDA primer hybridization, so that the quantity of hybridization primers is increased, and the copy number of DNB is increased.
Owner:MGI TECH CO LTD
Methods for quantitating DNA using digital multiple displacment amplification
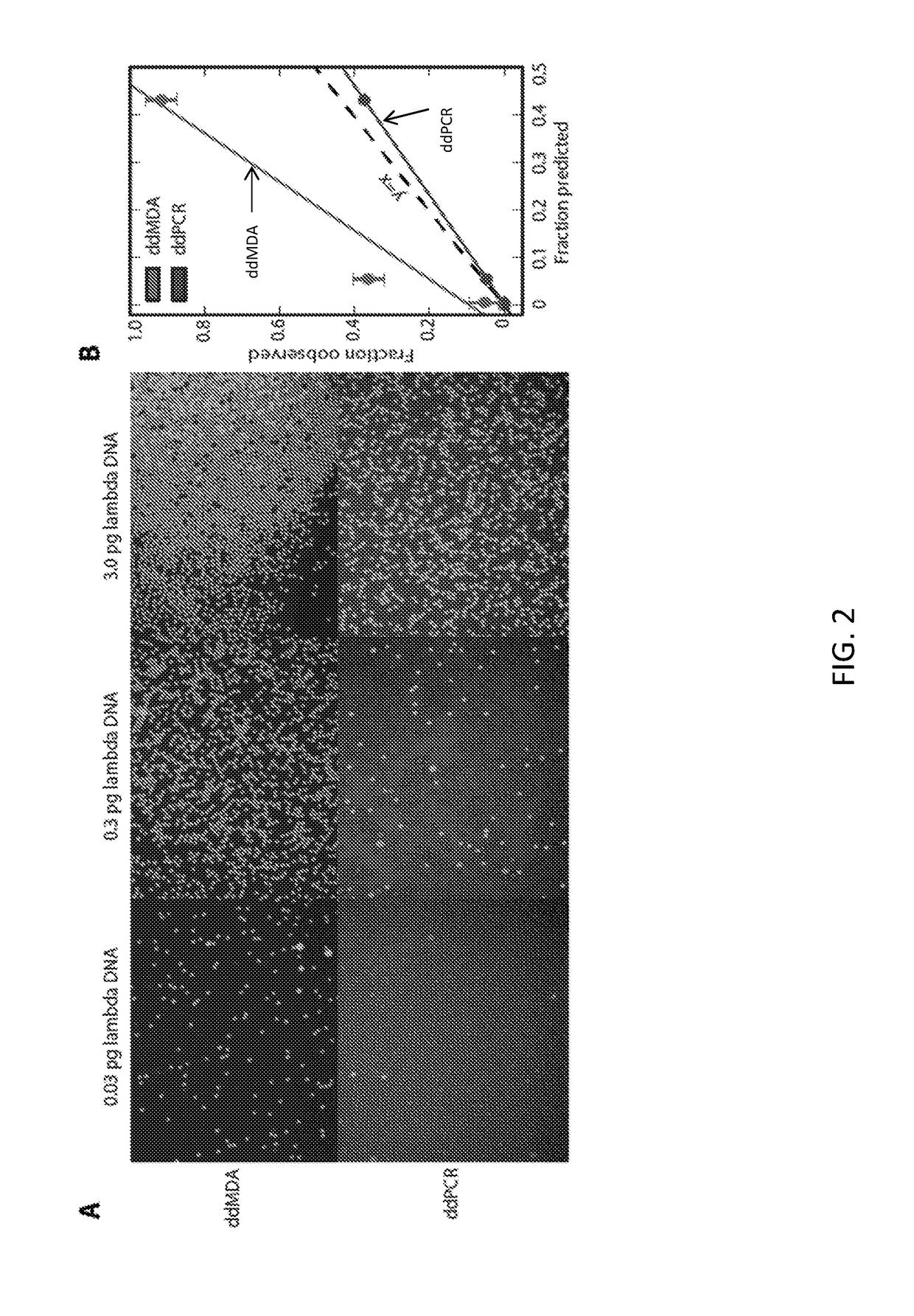
ActiveUS20160068899A1Improve reliabilityImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementDye moleculeDNA
The present invention provides improved methods for detecting contamination in WGA reagents as well as improved methods for quantitating nucleic acids, such as DNA. The present invention relates to novel methods of quantifying nucleic acids involving whole-genome amplification (WGA) reaction components and a dye molecule to detects nucleic acids and partitioning reactions to quantify nucleic acids.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +1
Isothermal amplification detection kit and detection method for Zaire type Ebola virus
InactiveCN104313179ASimple reaction conditionsOptimizing the Reaction TemperatureMicrobiological testing/measurementPositive controlRNA extraction
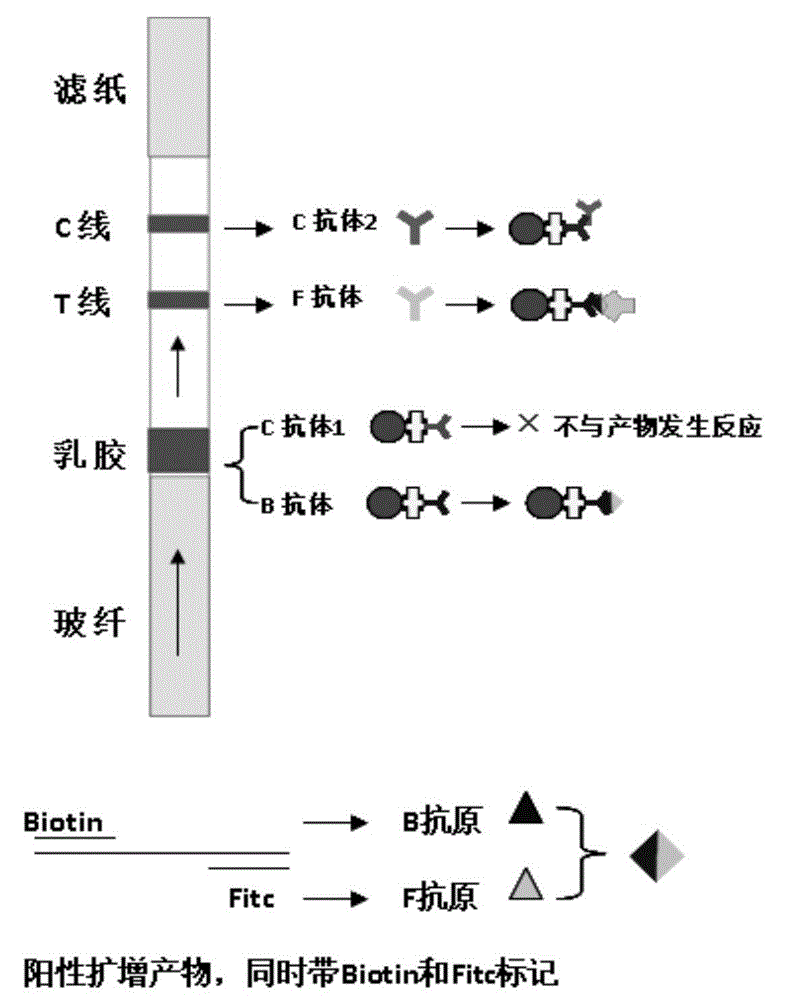
The invention discloses an isothermal amplification detection kit for Zaire type Ebola virus. The isothermal amplification detection kit comprises an RNA extraction agent, an isothermal amplification reaction solution, a positive control and a negative control. The isothermal amplification detection kit has high specificity and sensitivity; from virus RNA reverse transcription to strand displacement amplification, the temperature is constant all the time, isothermal amplification only needs 35min, a detection result of a nucleic acid test strip can be obtained just in 1-2min, the whole detection process from receiving a sample to obtaining the result only needs about 1h, and in addition, the whole reaction process only needs a constant temperature instrument, so that the isothermal amplification detection kit is particularly suitable for field rapid detection.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Whole genome amplification method based on slender reaction cavity
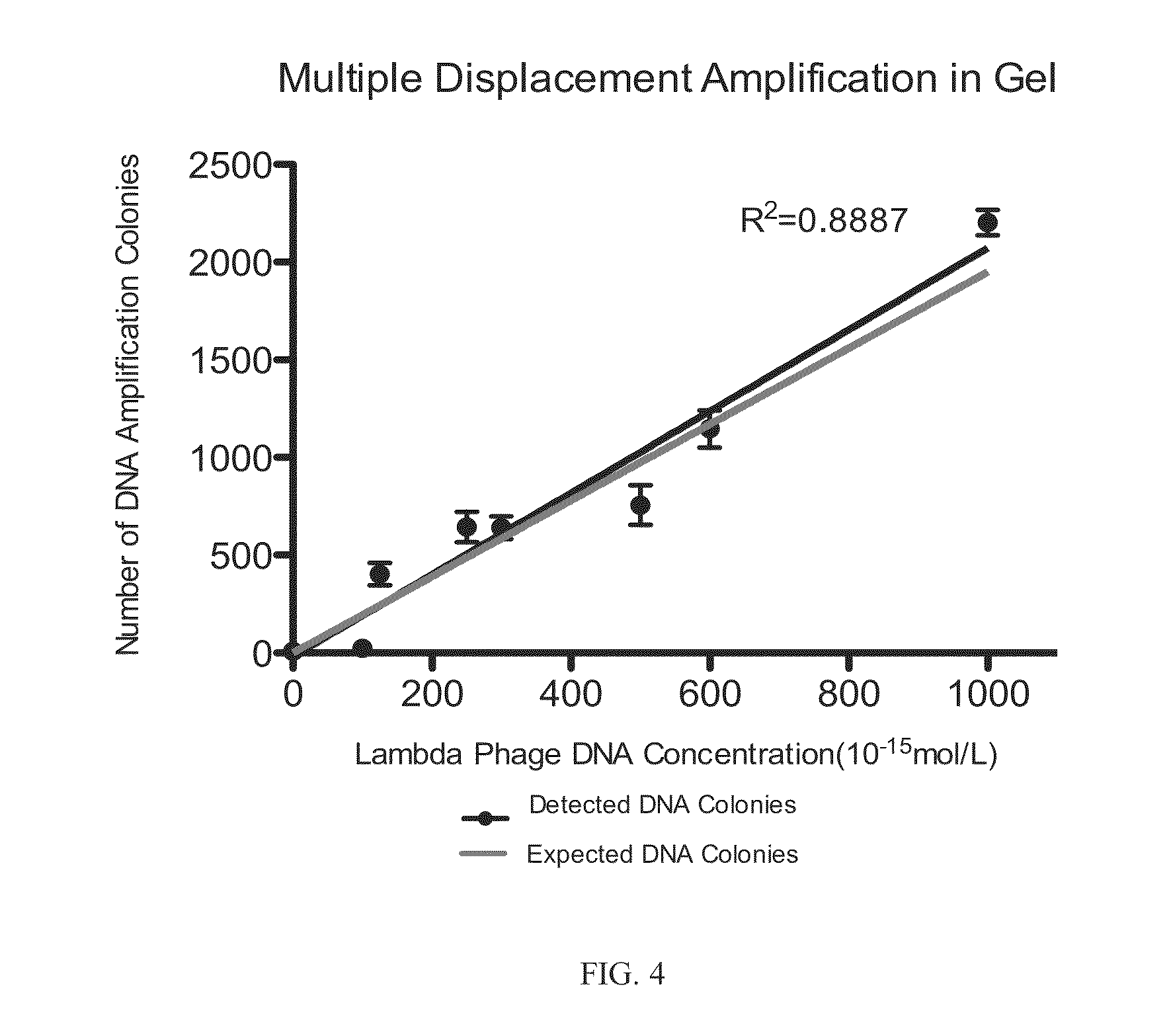
ActiveCN107058291AAlleviate overexpansionMitigation of underexpansionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationReaction systemMutual influence
The invention provides a whole genome amplification method based on a slender reaction cavity; the method is characterized in that a multiple displacement amplification reaction system is injected into the slender reaction cavity so as to finish whole genome amplification for a target genome. The slender reaction cavity isolates the multiple displacement amplification reaction system relatively therein, material exchange and mutual influence of microscopic reaction units are greatly decreased, each microscopic reaction unit performs reacting in relatively independent state, and the uniformity of amplification between fragments of target nucleic acid is greatly improved; in addition, multiple displacement amplification based on the slender reaction cavity has no need for preliminarily preparing a micro-droplet generator or a complex reaction microcavity; trace liquid need not be precisely and complicatedly controlled during system debugging and amplification reaction, the reaction system is simplified, and operation complexity is decreased.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Single cell whole genome amplification via micropillar arrays under flow conditions
ActiveUS20200316598A1Requires preparationMicrobiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresCell trappingA-DNA
The present invention relates to, inter alia, a microfluidic device for performing single cell genomic DNA isolation and amplification under flow. The microfluidic device comprises a solid substrate having one or more microfluidic channel system formed therein. Each microfluidic channel system of the microfluidic device comprises: (a) an intake region comprising a single microchannel; (b) a plurality of cell segregation microchannels; (c) a cell capture site located downstream of each cell segregation microchannel; and (d) a DNA capture array positioned downstream of the cell capture site and comprising a plurality of micropillars. Also disclosed is a whole genome amplification system that includes the microfluidic device of the present disclosure, as well as a method for conducting single cell DNA analysis via on-chip whole genome amplification while under flow, and a method for multiple displacement amplification (MDA) reactions of one or more nucleic acid sequence isolated single cells.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Single cell whole genome sequencing method
InactiveCN111363795AIncrease coverageAvoid heterogeneous amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic sequencingWhole genome sequencing
The present invention provides a single cell whole genome sequencing method and an application of an amplification method in constructing a gene library and conducting single molecule sequencing. Theamplification method comprises step of contacting nucleic acid with nucleic acid polymerase and random primers to carry out multiple displacement amplification of the nucleic acid and strands.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis and special-purpose primers therefor
ActiveCN102787161AShort timePromote enrichmentMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNucleotideMicrobiology
The invention discloses a method for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis and special-purpose primers therefor. The special-purpose primers are a pair of primers for assisting mycobacterium tuberculosis detection. A nucleotide sequence of one of the special-purpose primers is shown in the sequence 1 in the sequence table and a nucleotide sequence of the other of the special-purpose primers is shown in the sequence 2 in the sequence table. An experiment proves that the special-purpose primers are used in a novel multiple displacement amplification (MDA)-polymerase chain reaction (PCR) two-step method and mycobacterium tuberculosis nucleic acids in sputum is enriched by a MDA complete-genome isothermal amplification technology and mycobacterium tuberculosis is detected by a specific primer-PCR combined technology, and thus short detection time, high sensitivity and high accuracy are realized.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
AgNCs/HpDNA probe based microRNA SDA (strand-displacement amplification) detection method
InactiveCN105483212AAchieve high specificity detectionStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorescenceMaterial consumption
The invention discloses an AgNCs / HpDNA probe based microRNA SDA (strand-displacement amplification) detection method. The method includes that silver nanoclusters are synthesized by the aid of a hairpin type DNA template and serve as novel molecular bacons, and single detection of gastric plasm miRNA markers is realized by a hybridization resulted G-rich fluorescence enhancement effect in strand displacement isothermal amplification reaction mediated by a G-rich sequence of a dangling end of a primer. The AgNCs / HpDNA probe based microRNA SDA detection method has the advantages of high specificity, short reaction time, low material consumption and simplicity and convenience in operation and creates a new direction for establishing a quick and simple novel miRNA detection method.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Methods for quantitating DNA using digital multiple displacement amplification
ActiveUS10487354B2Improve throughput and reliabilityReduce impactMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDNADye molecule
The present invention relates to methods of quantifying nucleic acids involving (a) contacting a sample to be tested with whole-genome amplification (WGA) reaction components and a dye molecule to form a reaction sample, wherein the dye molecule detects the nucleic acid; (b) partitioning the reaction sample wherein each partitioned reaction sample corresponds to a single reaction; (c) allowing the reaction to occur in the partitioned reaction sample and (d) determining the number of partitioned reaction samples having the dye molecule, wherein the dye molecule indicates the presence of the nucleic acid; thereby quantifying the nucleic acid in the sample to be tested.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +1
Isothermal amplification detection kit and detection method for chikungunya fever virus
InactiveCN105256058AMeeting requirements for rapid detection of chikungunya virusIncrease concentrationMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesRNA extractionPositive control
The invention discloses an isothermal amplification detection kit and a detection method for chikungunya fever virus. The isothermal amplification detection kit comprises an RNA extraction reagent, isothermal PCR amplification reaction liquid, a positive control and a negative control. The isothermal amplification detection kit is good in specificity and high in sensitivity; the process from virus RNA reverse transcription to strand displacement amplification is finished at a constant temperature, the isothermal amplification can be finished within only 35 minutes, the detection result of a nucleic acid test strip can be acquired within only 2 minutes, the whole detection process from sample acceptation to result acquisition can be finished within only about 1 hour, and furthermore, only one isothermal instrument is required in the whole reaction process; the isothermal amplification detection kit is particularly applicable to the rapid detection of infection medium monitoring of the chikungunya fever virus.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com